Influence of compound deoxidation of steel with Al, Zr, rare earth metals, and Ti on properties of heavy castings
|
|
|
- Gervais Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN ( ) Volume 12 Issue 1/ /1 Influence of compound deoxidation of steel with Al, Zr, rare earth metals, and Ti on properties of heavy castings J. Senberger a*, J. Cech b, A. Zadera a a Department of Foundry, Institute of Engineering Technology, Brno University of Technology, Brno, Czech Republic b Joint-stock company of ŽĎAS a.s., Zdar nad Sazavou, Czech Republic *Corresponding author. address: senberger@fme.vutbr.cz Received ; accepted in revised form Abstract Heavy steel castings deoxidized with aluminium are sometimes brittle intercrystalline failed during their service along primary grain boundaries what is initiated by aluminium nitrides and so called conchoidal fractures are formed. The tendency to forming the conchoidal fractures depends in particular on cooling rate (the casting modulus), aluminium and nitrogen contents in steel. During deoxidation, when manufacturing heavy castings, the elements with high affinity to nitrogen, zirconium or titanium, are added to steel that would decrease nitrogen activity by the bond on stable nitrides. The formation of stable nitrides should reduce the tendency of steel to the formation of conchoidal fractures. Deoxidation was thermodynamically analyzed at presence of the mentioned elements. For particular conditions a probable course of deoxidation was estimated at test castings. The deoxidation course was checked by microanalysis of deoxidation products (inclusions). For service and experimental castings the anticipated composition of inclusions was compared. It has been proved that in heavy castings with high aluminium contents in steel under studied conditions neither the addition of zirconium nor of titanium nor of rare earth metals will prevent the formation of conchoidal fractures. Keywords: Steel casting; Deoxidation; Conchoidal fractures 1. Introduction Mechanical properties of the material in steel castings are influenced in particular by the presence of foundry defects, by morphology of inclusions, and reoxidation products. In heavy castings the effect of the mentioned factors is the more important the higher modulus have the castings or their parts. In some cases the mechanical values of heavy castings are decreasing under values prescribed by the standard. The standards take into account the decrease of mechanical values. And therefore the standardized values are valid most frequently for wall thicknesses up to 100 mm. For values determined by the static tensile test at heavy castings (the casting modulus of ca 10 cm and more) it is possible to observe the decrease of values that depend on deformation of the test bar, i.e. of ductility, contraction, and of breaking strength and breaking stress too. The yield value isn t changed with the casting thickness or it is changed slightly only [1]. Similar dependences were found out at heavy castings with the modulus higher than 30 cm [2]. In this case the mechanical values were influenced by the change of chemical composition of the steel caused by segregation of elements, particularly of carbon. Dynamically stressed castings can be failed by low cycle fatigue. A failure of a casting as a machine part during its service belongs to the most severe casting failures with huge financial losses for casting manufacturers. In such a case the crack is initiated by a ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Volume 12, Issue 1/2012,
2 foundry defect of a supercritical size. The size of a foundry defects depends on steel properties. The most frequent foundry defects are shrinkage porosities and inclusion clusters, in particular continuous separations of inclusions in interdendritic spaces in some casting places that may have a connection with segregation of elements. Steel toughness can be also decreased by separation, precipitation of particles along the primary grain boundaries during steel cooling. Embrittlement is often caused by separation of aluminium nitride as it was observed already in 60 th and 70 th of last century [3, 4]. Steel embrittlement can be also caused by other reasons as e.g. by separation of metallic phases along the grain boundaries or separation of inclusions in a form of the IV th type. All those phenomena are connected with the last phase of steel production, in particular with steel deoxidation. Therefore the metallurgists sometimes try to replace aluminium with other element or to choose a combined deoxidation with more elements. A combination of an element with high affinity to oxygen with an element that will bind nitrogen is often chosen. Such measurements would prevent the formation of conchoidal fractures. But deoxidation with aluminium is very well checked up in practice. Unsuitable replacement of deoxidizing aluminium with other element or a combination of elements can cause serious problems in casting manufacture. Equilibrium oxygen and nitrogen activities with concentrations of elements used for deoxidation and denitration can be determined by thermodynamic calculation. Thermodynamic calculation serves only for estimation which element will bond oxygen and which one will bond nitrogen. The main problem in calculation is difficult determination of activities of products that are formed during reaction. Therefore it is presumed in calculation that compounds (oxides or nitrides) forming during reactions can be considered pure matters (oxides and nitrides of one element). Then in such a case when choosing a standard state of a pure matter for those products their activity can be considered a unit one. The composition of deoxidation products is then checked by their microanalysis and applicability of the given calculations is estimated. Another problem of the thermodynamic calculation consists in a fact that a part of deoxidation and denitration elements determined from a sample spectrochemically is bound on compounds (oxides, nitrides). Determination of concentrations or activities of elements dissolved in steel is unfeasible in technical practice. 2. Thermodynamic analysis of the course of compound deoxidation with Al, Zr, Ce, and Ti Aluminium is most often used for steel deoxidation. In case of heavy castings aluminium can be partly or quite replaced with an element or elements with high affinity to oxygen and possibly to nitrogen too. Aluminium remains in some foundries a basic deoxidation element for manufacture of heavy castings and it is further on complemented with an element with high affinity to nitrogen. As this element has a higher affinity to nitrogen than aluminium, its bond on nitrogen is expected what should prevent the formation of aluminium nitrides. For combined deoxidation with aluminium and other element the use of Zr, Ce, or Ti can be considered. But the use of these elements causes in some cases an important drop of plastic properties and toughness. Combined deoxidation with aluminium and calcium can be further on used that seems to be very suitable for heavy castings. This deoxidation was already researched in details in the past and its favourable effects are known. The course of following reactions [5] in the melt is oftenest expected when deoxidizing with aluminium, zirconium, titanium, and cerium. 2 [ Al ] 3 [ O ] = Al O 2 3 [ Zr ] 2[ O] = ZrO2 [ Ti ] 2[ O] = TiO2 2 [ Ce] 3[ O] = Ce 2 O3 + G = , 25T (1) + G = , 93T (2) + G = , 22T (3) + G = , 68T (4) For the reaction of aluminium, zirconium, and titanium with nitrogen in molten steel the reactions are expected as follows: [ Al ] [ N] = AlN [ Zr ] [ N] = ZrN [ Ti ] [ N] = TiN + G = , 34T (5) + G = , 55T (6) + G = , 40T (7) According to equations (5) up to (7) it is possible to determine the nitrogen equilibrium activity in steel with given concentration of the deoxidation element, i.e. it can be evaluated if it is possible to expect a decrease of nitrogen activity connected with formation of nitrides of the chosen element for the given concentration of nitrogen and the chosen element. Chemical composition and morphology of inclusions in dependence on a type of the deoxidation or denitration element were studied on test castings with a thermal modulus of ca 10 cm. The material of studied castings was steel containing 0.20 % C; % Al and up to % N. On the one hand only aluminium, and on the other further on aluminium in combination with one of chosen elements (Zr, Ti, or Ce) were used for deoxidation of castings. For thermodynamic calculation the aluminium content was chosen in two levels, and namely % and % Al. Equilibrium oxygen activities for equilibrium between oxygen and aluminium under different temperatures and aluminium concentrations were calculated for the above mentioned chemical composition and aluminium concentrations. For oxygen activities determined in such a way the activities of deoxidation elements Zr, Ti, and Ce were further on calculated (Table 1.). Then it is possible to find out from these results which activities of the chosen deoxidation elements will ensure under given temperature the same oxygen activity (the deoxidation degree) as the chosen aluminium concentration. The calculation was done for steel temperature of 1600 C and further on for calculated steel temperature in the mould cavity after pouring the experimental castings and liquidus temperature. Results are given in Table 1. In calculations the activities tantamount to concentrations were considered in Table 1. If the activities of deoxidation additives are low, then it can be assumed that they equal to concentrations. In contrary case it is 100 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Volume 12, Issue 1/2012,
3 necessary to convert the activities into concentrations with use of interactive coefficients. In case of thermodynamic calculation under different temperatures it is necessary to consider the dependence of interactive coefficients on temperature. Table 1. Equilibrium Henry activities of Zr, Ti and Ce after deoxidation of steel with Al of C = 0.2 % content Al content [weight %] T=1873 K T=1813 K T=1793K a Zr a Ti a Ce a Zr a Ti a Ce a Zr a Ti a Ce As follows from results given in Table 1. the lower concentrations of zirconium and cerium are sufficient for achieving the same oxygen activity in the melt as in case of deoxidation with aluminium. Further on it is evident from the results that temperature hasn t large influence on the change of calculated equilibrium activities of Zr and Ce. Only titanium shows important changes of equilibrium activity. Table 2 gives chemical composition of metal determined from samples taken from thermal axis of experimental castings. Table 2. Content of C and elements used for deoxidation in weight % C Al Zr C Al Ti C Al Ce min max Table 3. Equilibrium concentrations of Al, Ti, and Zr [%] in steel with content of C = 0.2 % and % and 0.018% N under liquidus temperature nitrogen activity equilibrium concentration nitrogen activity equilibrium concentration Al Ti Zr By comparison of real zirconium concentrations in the experimental casting deoxidized with aluminium and zirconium (Table 2.) and calculated equilibrium activity of zirconium (Table 1.) the formation of zirconium based oxides can be expected in the experimental casting. With zirconium concentration higher than ca % under the given conditions (Al content in the range of weight %) zirconium has higher affinity to oxygen than aluminium. Under lower temperatures the presumption is valid too. Thus the oxides (deoxidation products) above all zirconium based ones would be present in the casting. In the casting deoxidized with aluminium and titanium the titanium affinity to oxygen under the given conditions is always lower than the aluminium affinity. With decreasing temperature the titanium affinity to oxygen in comparison with aluminium is further on decreasing. It is expected that in the melt with Ti addition the oxygen will be bound to aluminium and titanium will not occur in oxides. In case of the aluminium and cerium deoxidized casting the affinity of cerium to oxygen under the given conditions is higher than that one of aluminium, and namely under all considered temperatures. Thus it can be expected that oxides containing mainly cerium would occur in the casting. The above mentioned estimation takes into account the concentrations of aluminium dissolved in the solution instead of the activity. Concentration of deoxidation elements in the solution will be in reality lower as their part will be bound on oxygen. At the same time it cannot be expected that so low oxygen activities will be achieved as that ones determined during thermodynamic calculation. It can be expected in real conditions that deviations between calculated and real oxygen activities will be growing with increasing affinity of the deoxidation element to oxygen. Speaking in other ways, if e.g. cerium is added after deoxidation with aluminium, the decrease of oxygen activity can be expected partly only. For the reaction of the mentioned elements with nitrogen the equilibriums for liquidus temperature were calculated. For the calculation the nitrogen concentration was chosen in two levels, and namely and % N. Calculation results are given in Table 3. It results from comparison of calculated equilibrium concentrations of elements with the affinity to nitrogen given in Table 3. and real concentrations of these elements in experimental castings that concentrations of denitration elements in steel are lower than they would be under the considered conditions. Thus the formation of nitrides in liquid steel cannot be expected in practice. Nitrogen will be separated in a form of nitrides after casting solidification only. ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Volume 12, Issue 1/2012,
4 3. Analysis of inclusions in experimental castings Inclusions were analyzed on samples taken from experimental castings in a cubic form of an edge of 500 mm equipped with a runner of 400 mm diameter. The casting material was steel deoxidized with aluminium in a ladle and next above mentioned deoxidation elements were added in the mould cavity only. Metallographic samples were made from the material taken from bars for tensile tests after their breakage. The material for making the test bars was taken on the one hand from thermal axis ca 50 mm from the casting bottom, and on the other from thermal axis ca 400 mm from the casting bottom Deoxidation with aluminium In steel castings of common weight after deoxidation with aluminium the oxygen is bound to angular inclusions of the III rd type with stoichiometric ratio Al:O ~ 2:3. Composition of inclusions corresponds to aluminium oxide. Sulphur is bound to manganese sulphides of the II nd and III rd type. Chemical composition corresponds to manganese monosulphide (MnS). In heavy castings after deoxidation with aluminium the oxygen is bound to globular aluminium oxides with a MnS envelope. MnS in a form of inclusions the II nd type is separated only in places with strong segregation of sulphur, e.g. under the riser in the thermal axis. Oxides on the metallographic sample given on Figure 1. look like an Ib type. With 2000 x magnification (Figure 2.) it is possible to observe a dark centre of the Al 2 O 3 oxide with the addition of up to 10 at. % of Mg or Ca. The envelope contains MnS often with the additive of Ca or Mg Deoxidation with aluminium In casting with high excess of deoxidation elements the inclusions of the IV th type occur that are a cause of an important decrease of mechanical properties in particular in steels with higher carbon content. In the experimental casting, where the deoxidation with the aid of Al only was used, the inclusions of the IV th type were not observed. In the casting deoxidized with Al + Zr a mass occurrence of inclusions of the IV th type was observed as shown on Figure 3. Both oxygen, and nitrogen too, are bound to aluminium. Figure 4. gives an example of an inclusion consisting of three phases. The dark phase is composed of aluminium oxide with Mg addition, the grey phase represents the Mn sulphide with Ca, Mg, and Zr addition, and the white phase contains zirconium oxide above all. Before zirconium addition the steel was deoxidized with aluminium. After zirconium addition the aluminium oxides were reduced with zirconium partly only up to its consumption for the reaction. Therefore a part of aluminium oxides was retained. Zr and Al oxides in the next cooling and solidification phase served as crystal nuclei for separation of manganese sulphides. Aluminium oxides in some cases contained even more than 10 at. % of Mg. Besides manganese the sulphides contained calcium too. In some sulphides the content of calcium was higher than that one of manganese. In the studied sample calcium reacted primarily with sulphur and magnesium primarily with oxygen. Phases containing zirconium and nitrogen were not found. Fig. 3. Inclusions of the IV th type (100 x) Fig. 1. Aluminium oxides with the MnS envelope (100 x) Fig. 4. Complex inclusions after deoxidation with Al+Zr (750 x) Fig. 2. Aluminium oxides with the MnS envelope (2,000 x) 102 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Volume 12, Issue 1/2012,
5 3.3. Deoxidation with aluminium and titanium Titanium content in steel was insufficient for formation of titanium oxides. It can be expected that titanium will be mostly bound to nitrogen in a form of TiN. Oxygen will be bound to aluminium and sulphur to manganese. Figure 5. shows globular aluminium oxides with sulphide envelopes again. Separation of inclusions is similar as after deoxidation with aluminium. On Figure 6. the grey phase corresponds to Mn sulphide with Ca addition. The dark phase is formed by aluminium oxide with Mg addition. The sharp angular inclusion corresponds to TiN. Calcium is primarily bound to sulphur and magnesium to oxygen in the given sample. Titanium bonds nitrogen and forms many nitrides. Morphology of titanium nitride corresponds to the phase separated from the solid solution. Fig. 7. Complex oxisulphides of rare earth metals (1,000 x) Fig. 8. Needles of aluminium nitride (5,000 x) Fig. 5. Globular inclusions after deoxidation with Al+Ti (100 x) Fig. 6. A complex inclusion after deoxidation with Al+Ti (5,000 x) 3.4. Deoxidation with aluminium and rare earth metals Rare earth metals were added in the mould cavity by means of misch metal containing of ca 60 % Ce. The addition of rare earth metals was sufficient for reduction of all oxides present in steel. The excess of rare earth metals participated in the bond with sulphur. After the addition of rare earth metals in the mould cavity the sulphur content importantly decreased. Nitrides of rare earth metals were not observed on samples. Figure 7. shows typical complex oxides of rare earth metals with Ca addition. Similarly as after the addition of zirconium the needles containing aluminium and nitrogen occurred on the sample (Figure 8.). 4. Interpretation of results of measurement By subjective evaluation of fracture surfaces it has been found out that during the tensile test the casting deoxidized with aluminium only was failed largely by brittle intercrystalline fracture along primary grain boundaries (conchoidal fracture) and partly by transcrystalline cleavage fracture. In case of other three castings the fracture surfaces or their predominant part showed the conchoidal fracture. The occurrence of conchoidal fractures in castings with Zr and Ti additions was higher than in melts deoxidized with aluminium only. According to thermodynamic calculation the deoxidation ability of zirconium is considerably higher than that one of aluminium. Provided that steel after deoxidation with Al contains 50 ppm of total oxygen, ca % weight % of Zr is consumed for its total reduction to ZrO 2 in theory. The added zirconium addition of ca up to was consumed from a great part for deoxidation of aluminium oxide. Nitrogen and zirconium compounds were not found on studied fracture surfaces. Zirconium solubility in steel is almost zero under indoor temperature. Zirconium that isn t used for the bond with oxygen or nitrogen is separated under lower temperatures as crystals of pure Zr or Zr with Ti addition. Under the studied conditions the nitrogen addition as a denitration element was ineffective. According to thermodynamic calculation under the given conditions the titanium cannot participate in steel deoxidation. Then the all titanium remains available for the reaction with nitrogen in austenite. But the used titanium addition is insufficient for bonding of nitrogen in liquid steel under solidification ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Volume 12, Issue 1/2012,
6 temperature. Titanium nitrides in the casting with titanium addition were common ones and morphologically they correspond to the phase separated from the solid solution. Titanium nitrides were also found in castings without the Ti addition what could witness the high affinity of titanium with nitrogen in austenite. The addition of cerium was sufficient for reduction of aluminium oxides from previous deoxidation with aluminium. Besides cerium it is necessary to expect the presence of other elements from the group of rare earth metals. The misch metal contained ca 60 % of Ce. After the reaction of cerium with oxygen the reaction of cerium with sulphur took place. For the reaction of Ce with nitrogen no proofs were found out. After zirconium and cerium additions in castings a considerable amount of needles containing aluminium and nitrogen was observed on samples. Acknowledgements The contribution has been worked out with the support of the Ministry of Industry and Commerce in the framework of the project, evident No FR-TI1/070 Research and optimization of production technology of heavy steel castings. References [1] J. Senberger, A. Zadera, J. Cech, Influence of deoxidation on properties of steel cast in heavy castings. In 48 th Foundry Days, Brno 11 th 12 th October ISBN [2] J. Senberger, A. Zadera, Z. Carbol, J. Pluhacek, V. Krutis, M. Kovac. Segregation in heavy castings and its influence on material properties. In Theory and practice of steel manufacture and treatment p ISBN [3] P. Fremund. Rack-candy fractures. Slevarenstvi, vol. 10, No. 6 (1962) p ISSN [4] STRÁNSKÝ. K.; FORET, R. Effect of aluminium on the properties of steel for castings. Slevarenstvi, vol. 25, No. 5 (1977) p [5] Z. Buzek, Basic thermodynamic data about metallurgical reactions and interactions of elements in systems important for metallurgical theory and practice Hutnicke aktuality, No. 1-2 (1979). 104 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Volume 12, Issue 1/2012,
Checking the metallurgy with the aid of inclusion analysis
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 11 Issue 1/2011 118 122 25/1
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 11 Issue 1/2011 118 122 25/1
Cracks in high-manganese cast steel
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 9 Issue 4/2009 17 22 4/4 Cracks in high-manganese cast
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 9 Issue 4/2009 17 22 4/4 Cracks in high-manganese cast
Effects in Ductile Iron
 Summary of Element Effects in Ductile Iron Rick Gundlach Element Materials Technology Wixom Insert Company Logo Here DIS Annual Meeting, June 7, 2012 Muskegon, Michigan Types of Alloying Elements Substitutional
Summary of Element Effects in Ductile Iron Rick Gundlach Element Materials Technology Wixom Insert Company Logo Here DIS Annual Meeting, June 7, 2012 Muskegon, Michigan Types of Alloying Elements Substitutional
Rare earth metals influence on morphology of non-metallic inclusions and mechanism of GP240GH and G17CrMo5-5cast steel cracking
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 9 Issue 4/2009 45 52 8/4 Rare earth metals influence
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 9 Issue 4/2009 45 52 8/4 Rare earth metals influence
Controlled Precipitation Gaseous Cavities in Aluminium Castings
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 15 Issue 4/2015 124 128 23/4 Controlled Precipitation
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 15 Issue 4/2015 124 128 23/4 Controlled Precipitation
A STUDY OF CASTING CHARACTERISTICS FOR DIE-CAST ALUMINUM ALLOY
 ME8109: Casting And Solidification of Material A STUDY OF CASTING CHARACTERISTICS FOR DIE-CAST ALUMINUM ALLOY Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering Graduate Program in Mechanical Engineering
ME8109: Casting And Solidification of Material A STUDY OF CASTING CHARACTERISTICS FOR DIE-CAST ALUMINUM ALLOY Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering Graduate Program in Mechanical Engineering
Influence of Remelting AlSi9Cu3 Alloy with Higher Iron Content on Mechanical Properties
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 18 Issue 3/2018 25 30 4/3 Influence
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 18 Issue 3/2018 25 30 4/3 Influence
MICROSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF HOT TEARS IN A WCB STEEL VALVE BODY
 STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA TECHNICAL SERVICE REPORT #l05 MICROSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF HOT TEARS IN A WCB STEEL VALVE BODY Published by the STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA Mr. Malcolm Blair Technical
STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA TECHNICAL SERVICE REPORT #l05 MICROSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF HOT TEARS IN A WCB STEEL VALVE BODY Published by the STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA Mr. Malcolm Blair Technical
Manufacturing Process - I Dr. D. K. Dwivedi Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Manufacturing Process - I Dr. D. K. Dwivedi Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 3 Lecture - 14 Reaction in Weld Region & Welding Defects
Manufacturing Process - I Dr. D. K. Dwivedi Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 3 Lecture - 14 Reaction in Weld Region & Welding Defects
Quality Prediction of Cast Ingots
 Quality Prediction of Cast Ingots I. Hahn, M. Schneider* J. Terhaar, J. Jarolimeck, R. Sauermann** *MAGMA Giessereitechnologie GmbH, Aachen, Germany **Saarschmiede GmbH Freiformschmiede, Völklingen, Germany
Quality Prediction of Cast Ingots I. Hahn, M. Schneider* J. Terhaar, J. Jarolimeck, R. Sauermann** *MAGMA Giessereitechnologie GmbH, Aachen, Germany **Saarschmiede GmbH Freiformschmiede, Völklingen, Germany
EFFECT OF YTTRIUM ADDITION ON MICROSTRUCTURE OF ALLOY Ti-47Al, PREPARED BY PLASMA MELTING AND VACUUM INDUCTION MELTING
 EFFECT OF YTTRIUM ADDITION ON MICROSTRUCTURE OF ALLOY Ti-47Al, PREPARED BY PLASMA MELTING AND VACUUM INDUCTION MELTING Tomáš ČEGAN, Miroslav KURSA VŠB-TU Ostrava, 17. listopadu 15, 708 33, Ostrava-Poruba,
EFFECT OF YTTRIUM ADDITION ON MICROSTRUCTURE OF ALLOY Ti-47Al, PREPARED BY PLASMA MELTING AND VACUUM INDUCTION MELTING Tomáš ČEGAN, Miroslav KURSA VŠB-TU Ostrava, 17. listopadu 15, 708 33, Ostrava-Poruba,
ME 415 Failure Analysis and Prevention Failure of the Fortnight #4 H-1 Engine LOX Dome Failure. Evrim ERSU (ee51) Due Date: Thursday, March 29!!
 ME 415 Failure Analysis and Prevention Failure of the Fortnight #4 H-1 Engine LOX Dome Failure Evrim ERSU (ee51) Due Date: Thursday, March 29!! Space travel and exploration has always been one of humanity's
ME 415 Failure Analysis and Prevention Failure of the Fortnight #4 H-1 Engine LOX Dome Failure Evrim ERSU (ee51) Due Date: Thursday, March 29!! Space travel and exploration has always been one of humanity's
Numerical modelling of the surface cracking tendency in solidifying ceramic materials
 Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics X 99 Numerical modelling of the surface cracking tendency in solidifying ceramic materials J. Dobrovská1, F. Kavička2, K. Stránský2 & B. Sekanina2 1 Faculty of Metallurgy
Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics X 99 Numerical modelling of the surface cracking tendency in solidifying ceramic materials J. Dobrovská1, F. Kavička2, K. Stránský2 & B. Sekanina2 1 Faculty of Metallurgy
The Study of a Drop of Plasticity Behavior of the As-Cast Low Carbon Steels in γ α Transformation Region
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol. 15 No.2 pp. 25-29, 2005 The Study of a Drop of Plasticity Behavior of the As-Cast Low Carbon Steels in γ α Transformation Region Antonín Ševčík 1 and Jarmila
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol. 15 No.2 pp. 25-29, 2005 The Study of a Drop of Plasticity Behavior of the As-Cast Low Carbon Steels in γ α Transformation Region Antonín Ševčík 1 and Jarmila
An establish attempt of reasons of machining splinter formation in AC47000 alloy high pressure die castings
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 8 Issue 3/2008 167 172 32/3 An
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 8 Issue 3/2008 167 172 32/3 An
Deoxidation Process Change to Prevent Under-Riser Cracking Caused by Aluminum Nitrides on Heavy Sections
 Deoxidation Process Change to Prevent Under-Riser Cracking Caused by Aluminum Nitrides on Heavy Sections M.C.M. Terrazas, Mario & Kulkarni, Shrirang. Metallurgy & Melt Acerlan Matrix Metals San Juan del
Deoxidation Process Change to Prevent Under-Riser Cracking Caused by Aluminum Nitrides on Heavy Sections M.C.M. Terrazas, Mario & Kulkarni, Shrirang. Metallurgy & Melt Acerlan Matrix Metals San Juan del
Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2008 Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2008 Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
TROUBLESHOOTING CRACKS IN STEEL CASTINGS. By Rodman Duncan Casteel Technical Service
 TROUBLESHOOTING CRACKS IN STEEL CASTINGS By Rodman Duncan Casteel Technical Service rod@casteeltec.com 360 468-3588 This presentation is given to the members of Steel Founder s Society of America in order
TROUBLESHOOTING CRACKS IN STEEL CASTINGS By Rodman Duncan Casteel Technical Service rod@casteeltec.com 360 468-3588 This presentation is given to the members of Steel Founder s Society of America in order
The influence of remelting on the properties of AlSi6Cu4 alloy modified by antimony
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 12 Issue 1/2012 81 86 16/1 The influence of remelting
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 12 Issue 1/2012 81 86 16/1 The influence of remelting
Microstructure and mechanical properties of synthetic nodular cast iron
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Issue Special1/2010 93-98 16/1 Microstructure and
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Issue Special1/2010 93-98 16/1 Microstructure and
Study of pinholes genesis in iron castings
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 11 Issue 1/2011 21 26 4/1 Study
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 11 Issue 1/2011 21 26 4/1 Study
Solidification and Crystallisation 5. Formation of and control of granular structure
 MME 345 Lecture 08 Solidification and Crystallisation 5. Formation of and control of granular structure Ref: [1] A. Ohno, The Solidification of Metals, Chijin Shokan Co. Ltd., 1976 [2] P. Beeley, Foundry
MME 345 Lecture 08 Solidification and Crystallisation 5. Formation of and control of granular structure Ref: [1] A. Ohno, The Solidification of Metals, Chijin Shokan Co. Ltd., 1976 [2] P. Beeley, Foundry
COMPUTER SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH OF CAST PISTON POROSITY
 Tome V (year 2007), Fascicole 2, (ISSN 1584 2665) COMPUTER SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH OF CAST PISTON POROSITY D. KAKAS, L. KOVACEVIC, P. TEREK UNIVERSITY OF NOVI SAD, FACULTY OF TECHNICAL SCIENCES,
Tome V (year 2007), Fascicole 2, (ISSN 1584 2665) COMPUTER SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH OF CAST PISTON POROSITY D. KAKAS, L. KOVACEVIC, P. TEREK UNIVERSITY OF NOVI SAD, FACULTY OF TECHNICAL SCIENCES,
Lecture 25: Principles of degassing
 Lecture 25: Principles of degassing Contents Introduction Principles Side reactions General considerations Fluid flow in degassing Material balance in de gassing Key words: Degassing, gases in steel, ladle
Lecture 25: Principles of degassing Contents Introduction Principles Side reactions General considerations Fluid flow in degassing Material balance in de gassing Key words: Degassing, gases in steel, ladle
STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NICKEL ALLOYS
 STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NICKEL ALLOYS Martin POHLUDKA a, Jitka MALCHARCZIKOVÁ a, Vít MICHENKA b, Miroslav KURSA a, Tomáš ČEGAN a, Ivo SZURMAN a a VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, 17.
STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NICKEL ALLOYS Martin POHLUDKA a, Jitka MALCHARCZIKOVÁ a, Vít MICHENKA b, Miroslav KURSA a, Tomáš ČEGAN a, Ivo SZURMAN a a VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, 17.
HEAT TREATMENT OF REACTOR VESSEL STEEL AISI 321
 HEAT TREATMENT OF REACTOR VESSEL STEEL AISI 321 Pavel PODANÝ a, Petr MARTÍNEK a, Petr NACHÁZEL a, Martin BALCAR b a COMTES FHT a.s., Dobřany, Czech Republic, EU, comtes@comtesfht.cz b ŽDAS a.s., Žďár nad
HEAT TREATMENT OF REACTOR VESSEL STEEL AISI 321 Pavel PODANÝ a, Petr MARTÍNEK a, Petr NACHÁZEL a, Martin BALCAR b a COMTES FHT a.s., Dobřany, Czech Republic, EU, comtes@comtesfht.cz b ŽDAS a.s., Žďár nad
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ALUMINIUM ALLOYS Aluminium and its alloys offer an extremely wide range of capability and applicability, with a unique combination of advantages that make the material of choice
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ALUMINIUM ALLOYS Aluminium and its alloys offer an extremely wide range of capability and applicability, with a unique combination of advantages that make the material of choice
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER-1 1.0 INTRODUCTION Contents 1.0 Introduction 1 1.1 Aluminium alloys 2 1.2 Aluminium alloy classification 2 1.2.1 Aluminium alloys (Wrought) 3 1.2.2 Heat treatable alloys (Wrought). 3 1.2.3 Aluminum
1 CHAPTER-1 1.0 INTRODUCTION Contents 1.0 Introduction 1 1.1 Aluminium alloys 2 1.2 Aluminium alloy classification 2 1.2.1 Aluminium alloys (Wrought) 3 1.2.2 Heat treatable alloys (Wrought). 3 1.2.3 Aluminum
Materials engineering. Iron and steel making
 Materials engineering Iron and steel making Metals: rarely exist in pure state mostly in ores Ore: Metallic and other compounds, mostly oxides Metallic content: Iron ores: 30-70% Fe Copper ores: 0.1-0.8
Materials engineering Iron and steel making Metals: rarely exist in pure state mostly in ores Ore: Metallic and other compounds, mostly oxides Metallic content: Iron ores: 30-70% Fe Copper ores: 0.1-0.8
PRODUCTION AND HEAT TREATMENT OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FORGINGS
 PRODUCTION AND HEAT TREATMENT OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FORGINGS Ing. Martin BALCAR, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Libor SOCHOR 1), Ing. Jaroslav NOVÁK 1), Ing. Ludvík MARTÍNEK, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Pavel FILA 1), Ing. Josef
PRODUCTION AND HEAT TREATMENT OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FORGINGS Ing. Martin BALCAR, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Libor SOCHOR 1), Ing. Jaroslav NOVÁK 1), Ing. Ludvík MARTÍNEK, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Pavel FILA 1), Ing. Josef
Effect of Atmosphere in a Foundry Mould on Casting Surface Quality
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/v10266-012-0003-3 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 12 Issue 1/2012 13 18
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/v10266-012-0003-3 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 12 Issue 1/2012 13 18
Segregation of Admixing Elements in The Boundary Layer of the Main Inlet of a Ductile Iron Casting
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 13 Special Issue 2/2013 10 17
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 13 Special Issue 2/2013 10 17
Effect of Temperature on Chromite-Based Moulding Sands Bonded with Sodium Silicate
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 16 Issue 4/2016 147 152 27/4
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 16 Issue 4/2016 147 152 27/4
OPTIMIZATION OF PROPERTIES AND STRUCTURE WITH ADDITION OF TITANIUM IN HADFIELD STEELS Mohammad Bagher Limooei (1), Shabnam Hosseini (1)
 Abstract OPTIMIZATION OF PROPERTIES AND STRUCTURE WITH ADDITION OF TITANIUM IN HADFIELD STEELS Mohammad Bagher Limooei (1), Shabnam Hosseini (1) 1- Islamic Azad University, Ayatollah Amoli Branch sh_hosseini@yahoo.com,
Abstract OPTIMIZATION OF PROPERTIES AND STRUCTURE WITH ADDITION OF TITANIUM IN HADFIELD STEELS Mohammad Bagher Limooei (1), Shabnam Hosseini (1) 1- Islamic Azad University, Ayatollah Amoli Branch sh_hosseini@yahoo.com,
is detrimental to hot workability and subsequent surface quality. It is used in certain steels to improve resistance to atmospheric corrosion.
 Glossary of Terms Alloying Elements ALUMINIUM - Al is used to deoxidise steel and control grain size. Grain size control is effected by forming a fine dispersion with nitrogen and oxygen which restricts
Glossary of Terms Alloying Elements ALUMINIUM - Al is used to deoxidise steel and control grain size. Grain size control is effected by forming a fine dispersion with nitrogen and oxygen which restricts
Analysis of Cast Iron Using Shimadzu PDA-7000
 Analysis of Cast Iron Using Shimadzu PDA-7000 C112-0510M The analysis of low and high alloy cast iron by optical emission spectrometry is presented. Cast iron alloys are classified by their mechanical
Analysis of Cast Iron Using Shimadzu PDA-7000 C112-0510M The analysis of low and high alloy cast iron by optical emission spectrometry is presented. Cast iron alloys are classified by their mechanical
Lecture 11: Metallic Alloys
 Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 11: Metallic Alloys TRIP Steels A phase change can do work; a good example of this is how viruses infect
Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 11: Metallic Alloys TRIP Steels A phase change can do work; a good example of this is how viruses infect
Studies of Gas Atmosphere Near the Metalmould Interface During Casting and Solidification of Ductile Iron
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 12 Issue 4/2012 166 170 28/4
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 12 Issue 4/2012 166 170 28/4
Method to Improve Inoculant Efficiency
 Method to Improve Inoculant Efficiency R. L. (Rod) Naro, ASI International, Ltd., Cleveland, Ohio Since the early 1960 s, ferrosilicon producers have made significant progress in the development of improved
Method to Improve Inoculant Efficiency R. L. (Rod) Naro, ASI International, Ltd., Cleveland, Ohio Since the early 1960 s, ferrosilicon producers have made significant progress in the development of improved
Determination of the cast structure parameter on the basis of micro-segregation analysis
 Determination of the cast structure parameter on the basis of micro-segregation analysis J. Dobrovská 1, F. Kavička 2, K. Stránský 2 and V. Dobrovská 1 1 Faculty of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering,
Determination of the cast structure parameter on the basis of micro-segregation analysis J. Dobrovská 1, F. Kavička 2, K. Stránský 2 and V. Dobrovská 1 1 Faculty of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering,
Fundamentals of Casting
 Fundamentals of Casting Chapter 11 11.1 Introduction Products go through a series of processes before they are produced Design Material selection Process selection Manufacture Inspection and evaluation
Fundamentals of Casting Chapter 11 11.1 Introduction Products go through a series of processes before they are produced Design Material selection Process selection Manufacture Inspection and evaluation
The Stand of Horizontal Continuous Casting of Al and its Alloys
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 13 Issue 3/2013 113 118 23/3
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 13 Issue 3/2013 113 118 23/3
Wide Ranging Influence of Mischmetal on Properties of GP240GH Cast Steel
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/v10266-012-0112-z Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 12 Issue 4/2012 85 94
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/v10266-012-0112-z Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 12 Issue 4/2012 85 94
SiMo Ductile Iron Crystallization Process
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-331) Volume 17 Issue 1/217 147 152 27/1 SiMo
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-331) Volume 17 Issue 1/217 147 152 27/1 SiMo
INOCULATION OF GREY AND DUCTILE IRON
 INOCULATION OF GREY AND DUCTILE IRON S.O. OLSEN and T. SKALAND Elkem, Norway ABSTRACT The objective of the present paper is to review some major aspects related to cast iron inoculation. The paper describes
INOCULATION OF GREY AND DUCTILE IRON S.O. OLSEN and T. SKALAND Elkem, Norway ABSTRACT The objective of the present paper is to review some major aspects related to cast iron inoculation. The paper describes
Understanding Contamination From Feeding Aids In Cast Steel
 Understanding Contamination From Feeding Aids In Cast Steel Riser sleeves and hot-toppings can improve the overall quality and cost of steel castings, but they may impact the chemistry of the metal. Tests
Understanding Contamination From Feeding Aids In Cast Steel Riser sleeves and hot-toppings can improve the overall quality and cost of steel castings, but they may impact the chemistry of the metal. Tests
Interactions at the mould modifying coating molten nickel alloy interface
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 11 Issue 3/2011 5 10 1/3 Interactions
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 11 Issue 3/2011 5 10 1/3 Interactions
Compensation for Boron in Pearlitic Ductile Iron
 Compensation for Boron in Pearlitic Ductile Iron Project Proposal presented to the Ductile Iron Society Richard B. Gundlach Gundlach Consulting Services and Element Materials Technology August 31, 2017
Compensation for Boron in Pearlitic Ductile Iron Project Proposal presented to the Ductile Iron Society Richard B. Gundlach Gundlach Consulting Services and Element Materials Technology August 31, 2017
Cast Iron Foundry Practices 3. Metallurgy of grey irons
 MME 345, Lecture 36 Cast Iron Foundry Practices 3. Metallurgy of grey irons Ref: Heine, Loper and Rosenthal. Principles of Metal Casting, Tata McGraw-Hill, 19670 Topics to discuss today 1. Graphite morphology
MME 345, Lecture 36 Cast Iron Foundry Practices 3. Metallurgy of grey irons Ref: Heine, Loper and Rosenthal. Principles of Metal Casting, Tata McGraw-Hill, 19670 Topics to discuss today 1. Graphite morphology
Electronics materials - Stress and its effect on materials
 Electronics materials - Stress and its effect on materials Introduction You will have already seen in Mechanical properties of metals that stress on materials results in strain first elastic strain and
Electronics materials - Stress and its effect on materials Introduction You will have already seen in Mechanical properties of metals that stress on materials results in strain first elastic strain and
The Need For Protecting The Weld And Rationale
 The Need For Protecting The Weld And Rationale This chapter presents the need of protecting the weld and rationale behind variations in cleanliness of the weld developed by different welding processes.
The Need For Protecting The Weld And Rationale This chapter presents the need of protecting the weld and rationale behind variations in cleanliness of the weld developed by different welding processes.
B Moulding plant. A Clay-bonded sand
 124 Assistance for decisions: Burnt-on sand 125 Assistance for decisions: Burnt-on sand A Clay-bonded sand B Moulding plant Examine lustrous carbon production Measure active carbon in moulding sand, examine
124 Assistance for decisions: Burnt-on sand 125 Assistance for decisions: Burnt-on sand A Clay-bonded sand B Moulding plant Examine lustrous carbon production Measure active carbon in moulding sand, examine
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND MICROSTRUCTURE OF IN713LC NICKEL SUPERALLOY CASTINGS
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND MICROSTRUCTURE OF IN713LC NICKEL SUPERALLOY CASTINGS Jiří ZÝKA 1, Irena ANDRŠOVÁ 1, Božena PODHORNÁ 1, Karel HRBÁČEK 2 1 UJP PRAHA a.s., Nad Kamínkou 1345, Prague, Czech republic,
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND MICROSTRUCTURE OF IN713LC NICKEL SUPERALLOY CASTINGS Jiří ZÝKA 1, Irena ANDRŠOVÁ 1, Božena PODHORNÁ 1, Karel HRBÁČEK 2 1 UJP PRAHA a.s., Nad Kamínkou 1345, Prague, Czech republic,
Schematic representation of the development of microstructure. during the equilibrium solidification of a 35 wt% Ni-65 wt% Cu alloy
 Schematic representation of the development of microstructure during the equilibrium solidification of a 35 wt% Ni-65 wt% Cu alloy At 1300 ºC (point a) the alloy is in the liquid condition This continues
Schematic representation of the development of microstructure during the equilibrium solidification of a 35 wt% Ni-65 wt% Cu alloy At 1300 ºC (point a) the alloy is in the liquid condition This continues
An investigation of the effect of five different inoculants on the metal expansion penetration in grey cast iron
 1 An investigation of the effect of five different inoculants on the metal expansion penetration in grey cast iron Izudin Dugic and Ingvar L Svensson Division of Component Technology Jönköping University,
1 An investigation of the effect of five different inoculants on the metal expansion penetration in grey cast iron Izudin Dugic and Ingvar L Svensson Division of Component Technology Jönköping University,
Behaviour of oxygen in cast irons
 Archives of Materials Science and Engineering Volume 33 Issue 2 October 2008 Pages 111-116 International Scientific Journal published monthly by the World Academy of Materials and Manufacturing Engineering
Archives of Materials Science and Engineering Volume 33 Issue 2 October 2008 Pages 111-116 International Scientific Journal published monthly by the World Academy of Materials and Manufacturing Engineering
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 7, July-01 1 EFFECT OF MAGNESIUM ENHANCEMENT ON MECHANICAL PROPERTY AND WEAR BEHAVIOUR OF LM6 ALUMINUM ALLOY R. S. Rana and Rajesh
International Journal Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 7, July-01 1 EFFECT OF MAGNESIUM ENHANCEMENT ON MECHANICAL PROPERTY AND WEAR BEHAVIOUR OF LM6 ALUMINUM ALLOY R. S. Rana and Rajesh
Characterization of Coatings on Grey Cast Iron Fabricated by Hot-dipping in Pure Al, AlSi11 and AlTi5 Alloys
 A R C H I V E S o f F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 14 Issue 1/2014 85 90 20/1 Characterization
A R C H I V E S o f F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 14 Issue 1/2014 85 90 20/1 Characterization
Menghani, Jyoti1; Bhushan, Bharat1; Singh, Balraj1; Suthat, Deepak1; Shah, Dimple1 SVNIT Surat,India
 Menghani, Jyoti1; Bhushan, Bharat1; Singh, Balraj1; Suthat, Deepak1; Shah, Dimple1 SVNIT Surat,India Aluminum, magnesium alloys and plastics have received growing attentions as light-weight materials for
Menghani, Jyoti1; Bhushan, Bharat1; Singh, Balraj1; Suthat, Deepak1; Shah, Dimple1 SVNIT Surat,India Aluminum, magnesium alloys and plastics have received growing attentions as light-weight materials for
Influence of hydrogen in weld joints
 Influence of hydrogen in weld joints This chapter presents influence of hydrogen in weld joints on the soundness and performance of weld joints. Further, different types of fluxes, their stability and
Influence of hydrogen in weld joints This chapter presents influence of hydrogen in weld joints on the soundness and performance of weld joints. Further, different types of fluxes, their stability and
9. Welding Defects 109
 9. Welding Defects 9. Welding Defects 109 Figures 9.1 to 9.4 give a rough survey about the classification of welding defects to DIN 8524. This standard does not classify existing welding defects according
9. Welding Defects 9. Welding Defects 109 Figures 9.1 to 9.4 give a rough survey about the classification of welding defects to DIN 8524. This standard does not classify existing welding defects according
Oxidation of Chromium
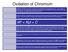 Oxidation of Chromium Oxidation of chromium is very simple as it usually forms a single oxide Cr 2 O 3, It is a p-type of oxide with Cr 3+ ions diffusing outward. Since the defect concentration is so low
Oxidation of Chromium Oxidation of chromium is very simple as it usually forms a single oxide Cr 2 O 3, It is a p-type of oxide with Cr 3+ ions diffusing outward. Since the defect concentration is so low
Lecture 36 CHEMICAL REACTION IN WELDS II
 Lecture 36 CHEMICAL REACTION IN WELDS II This chapter presents influence of hydrogen in weld joints on the soundness and performance of weld joints. Further, different types of fluxes, their stability
Lecture 36 CHEMICAL REACTION IN WELDS II This chapter presents influence of hydrogen in weld joints on the soundness and performance of weld joints. Further, different types of fluxes, their stability
Sulphur Problem. AkMB Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka. Today s Topics
 10 Sulphur Problem AkMB Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Introduction Behaviour of sulphur in metal and slag Oxidation of sulphur in the furnace Oxidation of sulphur in the
10 Sulphur Problem AkMB Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Introduction Behaviour of sulphur in metal and slag Oxidation of sulphur in the furnace Oxidation of sulphur in the
Analysis of Nonmetallic Inclusions Distribution and Microstructure in Centrifugally Cast Steel Pipes Boris Katavić 1,a, Zoran Odanović 2,b
 Analysis of Nonmetallic Inclusions Distribution and Microstructure in Centrifugally Cast Steel Pipes Boris Katavić 1,a, Zoran Odanović 2,b 1 Institute Goša, Milana Rakića 35, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia 2 IMS
Analysis of Nonmetallic Inclusions Distribution and Microstructure in Centrifugally Cast Steel Pipes Boris Katavić 1,a, Zoran Odanović 2,b 1 Institute Goša, Milana Rakića 35, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia 2 IMS
+ Improvement of the hot deformation characteristics of stainless steels. "Why do we Need to Measure Trace Elements in Steel?"
 JOURNAL DE PHYSIQUE IV Colloque C7, supplcment au Journal de Physique 111, Volume 5, novembre 1995 "Why do we Need to Measure Trace Elements in Steel?" J.J. Dufrane Q-C/R&D Division Manager, Fabrique de
JOURNAL DE PHYSIQUE IV Colloque C7, supplcment au Journal de Physique 111, Volume 5, novembre 1995 "Why do we Need to Measure Trace Elements in Steel?" J.J. Dufrane Q-C/R&D Division Manager, Fabrique de
International Conference on Material Science and Application (ICMSA 2015)
 International Conference on Material Science and Application (ICMSA 2015) Effect of Magnesium Addition on the Inclusions Composition in the Cast Microstructure of HSLA Steel Yan LIU 1, a,*, Kai WANG 2,
International Conference on Material Science and Application (ICMSA 2015) Effect of Magnesium Addition on the Inclusions Composition in the Cast Microstructure of HSLA Steel Yan LIU 1, a,*, Kai WANG 2,
Lecture 29 DESIGN OF WELDED JOINTS VII
 Lecture 29 DESIGN OF WELDED JOINTS VII This chapter presents the influence of various welding related parameters on fatigue behavior of weld joints. Attempts have been made to explain how (residual stress,
Lecture 29 DESIGN OF WELDED JOINTS VII This chapter presents the influence of various welding related parameters on fatigue behavior of weld joints. Attempts have been made to explain how (residual stress,
Learning Objectives. Chapter Outline. Solidification of Metals. Solidification of Metals
 Learning Objectives Study the principles of solidification as they apply to pure metals. Examine the mechanisms by which solidification occurs. - Chapter Outline Importance of Solidification Nucleation
Learning Objectives Study the principles of solidification as they apply to pure metals. Examine the mechanisms by which solidification occurs. - Chapter Outline Importance of Solidification Nucleation
Sintering of HDH Ti powder
 Sintering of HDH Ti powder Kováčik Jaroslav 1, Emmer Štefan 2 11 1 Keywords: powder metallurgy, sintering, titanium, HDH powder Abstract Titanium powders prepared by hydro-dehydration process (HDH powder)
Sintering of HDH Ti powder Kováčik Jaroslav 1, Emmer Štefan 2 11 1 Keywords: powder metallurgy, sintering, titanium, HDH powder Abstract Titanium powders prepared by hydro-dehydration process (HDH powder)
Strontium As a Structure Modifier for Non-binary Al Si Alloy
 Strontium As a Structure Modifier for Non-binary Al Si Alloy Barbora Bryksí Stunová 1 1 CTU in Prague, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Manufacturing Technology, Technická 4, 166 07 Prague,
Strontium As a Structure Modifier for Non-binary Al Si Alloy Barbora Bryksí Stunová 1 1 CTU in Prague, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Manufacturing Technology, Technická 4, 166 07 Prague,
Metals, Refining Processes and Materials Recycling, 17. listopadu 15/2172, Ostrava - Poruba, Czech Republic,
 MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF Ni 3 Al BASED ALLOYS WITH STOICHIOMETRIC AND HYPO-STOICHIOMETRIC COMPOSITION Jitka MALCHARCZIKOVÁ a, Miroslav KURSA b a VŠB-TU Ostrava, Faculty of Metallurgy and Materials
MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF Ni 3 Al BASED ALLOYS WITH STOICHIOMETRIC AND HYPO-STOICHIOMETRIC COMPOSITION Jitka MALCHARCZIKOVÁ a, Miroslav KURSA b a VŠB-TU Ostrava, Faculty of Metallurgy and Materials
Steels Processing, Structure, and Performance, Second Edition Copyright 2015 ASM International G. Krauss All rights reserved asminternational.
 Steels Processing, Structure, and Performance, Second Edition Copyright 2015 ASM International G. Krauss All rights reserved asminternational.org Contents Preface to the Second Edition of Steels: Processing,
Steels Processing, Structure, and Performance, Second Edition Copyright 2015 ASM International G. Krauss All rights reserved asminternational.org Contents Preface to the Second Edition of Steels: Processing,
Prediction of mechanical properties of Al alloys with change of cooling rate
 November 2012 Overseas Foundry Prediction of mechanical properties of Al alloys with change of cooling rate Quan-Zhi Dong 1, Young-Sim Choi 2, Jun-Ho Hong 2 and *Ho-Young Hwang 2 (1. Dept. of Virtual Engineering,
November 2012 Overseas Foundry Prediction of mechanical properties of Al alloys with change of cooling rate Quan-Zhi Dong 1, Young-Sim Choi 2, Jun-Ho Hong 2 and *Ho-Young Hwang 2 (1. Dept. of Virtual Engineering,
Defects caused by air bubbles during casting filling process: A review
 Defects caused by air bubbles during casting filling process: A review Alok Ranjan Pradhan, Sarojrani Pattnaik and Mihir Kumar Sutar* Mechanical Engineering Department, Veer Surendra Sai University of
Defects caused by air bubbles during casting filling process: A review Alok Ranjan Pradhan, Sarojrani Pattnaik and Mihir Kumar Sutar* Mechanical Engineering Department, Veer Surendra Sai University of
Steel Making. Modern Long Product Manufacturing. Process Flow Chart
 Rolling Process Metallurgical Aspects Material Specifications and Chemistries Standard Mill Practices Miscellaneous Tables & Data Elastic Section Modulus Plastic Section Modulus Moment of Inertia SI Conversion
Rolling Process Metallurgical Aspects Material Specifications and Chemistries Standard Mill Practices Miscellaneous Tables & Data Elastic Section Modulus Plastic Section Modulus Moment of Inertia SI Conversion
SOLIDIFICATION, PHASE DIAGRAM & STEELS
 MODULE TWO SOLIDIFICATION, PHASE DIAGRAM & STEELS 4. SOLIDIFICATION Introduction Mechanism of solidification - crystallization and development of cast structure - nucleation and grain growth - dendritic
MODULE TWO SOLIDIFICATION, PHASE DIAGRAM & STEELS 4. SOLIDIFICATION Introduction Mechanism of solidification - crystallization and development of cast structure - nucleation and grain growth - dendritic
The excellent performance of austempered ductile iron
 Design and control of chemical compositions for high-performance austempered ductile iron *Gong Wenbang 1, Chen Guodong 1, Luo Li 1, Hao Jing 2 and Zhang Zhonghe 3 (1. Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan 430073,
Design and control of chemical compositions for high-performance austempered ductile iron *Gong Wenbang 1, Chen Guodong 1, Luo Li 1, Hao Jing 2 and Zhang Zhonghe 3 (1. Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan 430073,
Failure Analysis for the Economizer Tube of the Waste Heat Boiler
 China Steel Technical Report, No. 22, pp. 53 58, (2009) Tsung-Feng Wu 53 Failure Analysis for the Economizer Tube of the Waste Heat Boiler TSUNG-FENG WU New Materials Research and Development Department
China Steel Technical Report, No. 22, pp. 53 58, (2009) Tsung-Feng Wu 53 Failure Analysis for the Economizer Tube of the Waste Heat Boiler TSUNG-FENG WU New Materials Research and Development Department
Microsegregation in Nodular Cast Iron with Carbides
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/v10266-012-0120-z Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 12 Issue 4/2012 127 134
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/v10266-012-0120-z Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 12 Issue 4/2012 127 134
Effect of Charge Materials on Slag Formation in Ductile Iron Melts
 Effect of Charge Materials on Slag Formation in Ductile Iron Melts C. Labrecque, M. Gagné and E. Planque Rio Tinto Iron & Titanium Inc. Sorel-Tracy, Quebec, Canada ABSTRACT The formation of an oxide slag
Effect of Charge Materials on Slag Formation in Ductile Iron Melts C. Labrecque, M. Gagné and E. Planque Rio Tinto Iron & Titanium Inc. Sorel-Tracy, Quebec, Canada ABSTRACT The formation of an oxide slag
FATIGUE LIFE IMPROVEMENT OF METAL SHEETS MADE OF 34CRNIMO6 STEEL. Jan Džugan, Zbyšek Nový, Martina Donátová, Jaromír Dlouhý, Pavel Konopík
 FATIGUE LIFE IMPROVEMENT OF METAL SHEETS MADE OF 34CRNIMO6 STEEL Jan Džugan, Zbyšek Nový, Martina Donátová, Jaromír Dlouhý, Pavel Konopík COMTES FHT Inc., Průmyslová 995, 334 41 Dobřany, Czech Republic,
FATIGUE LIFE IMPROVEMENT OF METAL SHEETS MADE OF 34CRNIMO6 STEEL Jan Džugan, Zbyšek Nový, Martina Donátová, Jaromír Dlouhý, Pavel Konopík COMTES FHT Inc., Průmyslová 995, 334 41 Dobřany, Czech Republic,
Engineering Materials
 Engineering Materials Lecture 2 MEL120: Manufacturing Practices 1 Selection of Material A particular material is selected is on the basis of following considerations 1. Properties of material 1. Properties
Engineering Materials Lecture 2 MEL120: Manufacturing Practices 1 Selection of Material A particular material is selected is on the basis of following considerations 1. Properties of material 1. Properties
Relation between Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Al-Si Alloys Produced by Low- Pressure Casting
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 14 Special Issue 1/2014 97-102
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 14 Special Issue 1/2014 97-102
Modeling of the Formation of AlN Precipitates During Solidification of Steel
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.478/afe-013-001 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (99-944) Volume 13 Issue 1/013 63 68 Modeling of
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.478/afe-013-001 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (99-944) Volume 13 Issue 1/013 63 68 Modeling of
Tutorial 2 : Crystalline Solid, Solidification, Crystal Defect and Diffusion
 Tutorial 1 : Introduction and Atomic Bonding 1. Explain the difference between ionic and metallic bonding between atoms in engineering materials. 2. Show that the atomic packing factor for Face Centred
Tutorial 1 : Introduction and Atomic Bonding 1. Explain the difference between ionic and metallic bonding between atoms in engineering materials. 2. Show that the atomic packing factor for Face Centred
Specification Aluminium Die-Casting Alloy, high silicon content Aluminium Die-Casting Alloy, high silicon content
 Specification 2012-10 Class: Aluminium and Al-alloys Class No.:21 Aluminium Die-Casting Alloy, high silicon content JED 853 Previous Edition Part name (for databases) 2011-11 Aluminium Die-Casting Alloy,
Specification 2012-10 Class: Aluminium and Al-alloys Class No.:21 Aluminium Die-Casting Alloy, high silicon content JED 853 Previous Edition Part name (for databases) 2011-11 Aluminium Die-Casting Alloy,
The Effect of a Thin-Wall Casting Mould Cavity Filling Conditions on the Casting Surface Quality
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G DOI: 10.1515/afe-2016-0113 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 16
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G DOI: 10.1515/afe-2016-0113 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 16
REFINING STEELS PRODUCED IN ELECTRIC ARC FURNACE
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, Vol. 75, Iss. 2, 2013 ISSN 1454-2331 REFINING STEELS PRODUCED IN ELECTRIC ARC FURNACE Valentin MINCU 1, Nicolae CONSTANTIN 2 Characteristics and properties of cast and forged
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, Vol. 75, Iss. 2, 2013 ISSN 1454-2331 REFINING STEELS PRODUCED IN ELECTRIC ARC FURNACE Valentin MINCU 1, Nicolae CONSTANTIN 2 Characteristics and properties of cast and forged
Crystallization of Low-alloyed Construction Cast Steel Modified with V and Ti
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/afe-2013-0067 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 13 Issue 3/2013 92 96 Crystallization
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.2478/afe-2013-0067 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 13 Issue 3/2013 92 96 Crystallization
Steel Properties. History of Steel
 History of Steel Steel Properties Cast Iron Cast iron preceded wrought iron. It is brittle, has high carbon content with low tensile strength. It has excellent casting properties. It was mainly used to
History of Steel Steel Properties Cast Iron Cast iron preceded wrought iron. It is brittle, has high carbon content with low tensile strength. It has excellent casting properties. It was mainly used to
Simulation of Stress Distribution in a Thick- Walled Bushing Produced by Die-Casting
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.1515/afe-2017-0143 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 17 Issue 4/2017 127 132 Simulation
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING DOI: 10.1515/afe-2017-0143 Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (2299-2944) Volume 17 Issue 4/2017 127 132 Simulation
HORIZONTAL CONTINUOUS CASTING OF Al AND Al-Si ALLOY IN SEMI-INDUSTRIAL CONDITIONS. Tomasz WRÓBEL, Jan SZAJNAR
 HORIZONTAL CONTINUOUS CASTING OF Al AND Al-Si ALLOY IN SEMI-INDUSTRIAL CONDITIONS Tomasz WRÓBEL, Jan SZAJNAR Silesian University of Technology, Foundry Department, Towarowa 7, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland, tomasz.wrobel@polsl.pl
HORIZONTAL CONTINUOUS CASTING OF Al AND Al-Si ALLOY IN SEMI-INDUSTRIAL CONDITIONS Tomasz WRÓBEL, Jan SZAJNAR Silesian University of Technology, Foundry Department, Towarowa 7, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland, tomasz.wrobel@polsl.pl
The effect of Friction Stir Processing on the fatigue life of MIG-Laser hybrid welded joints as compared to conventional FSW 6082-T6 aluminium joints
 Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics IX 183 The effect of Friction Stir Processing on the fatigue life of MIG-Laser hybrid welded joints as compared to conventional FSW 6082-T6 aluminium joints A. Els-Botes,
Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics IX 183 The effect of Friction Stir Processing on the fatigue life of MIG-Laser hybrid welded joints as compared to conventional FSW 6082-T6 aluminium joints A. Els-Botes,
STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA TECHNICAL SERVICE REPORT #124 ANALYSIS OF DEFECTS OF THE BORED SURFACE OF SIX 1025 CARBON STEEL CASTINGS
 STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA TECHNICAL SERVICE REPORT #124 ANALYSIS OF DEFECTS OF THE BORED SURFACE OF SIX 1025 CARBON STEEL CASTINGS Published by the STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA Malcolm Blair
STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA TECHNICAL SERVICE REPORT #124 ANALYSIS OF DEFECTS OF THE BORED SURFACE OF SIX 1025 CARBON STEEL CASTINGS Published by the STEEL FOUNDERS' SOCIETY OF AMERICA Malcolm Blair
Application of Ni-Mg-Ce Master Alloy Scrap for Inoculation of Copper-Nickel Alloys
 International Conference with Elements of School for Young Scientists on Recycling and Utilization of Technogenic Formations (2017) Conference Paper Application of Ni-Mg-Ce Master Alloy Scrap for Inoculation
International Conference with Elements of School for Young Scientists on Recycling and Utilization of Technogenic Formations (2017) Conference Paper Application of Ni-Mg-Ce Master Alloy Scrap for Inoculation
STATISTICAL DESCRIPTION OF LARGEST PORE SIZE IN MODIFIED AL-SI ALLOYS
 24 STATISTICAL DESCRIPTION OF LARGEST PORE SIZE IN MODIFIED AL-SI ALLOYS Stanislava Fintová 1, Radomila Konečná 1, Gianni Nicoletto 2 Received 8 th May 2009; accepted in revised form 8 th June 2009 Abstract
24 STATISTICAL DESCRIPTION OF LARGEST PORE SIZE IN MODIFIED AL-SI ALLOYS Stanislava Fintová 1, Radomila Konečná 1, Gianni Nicoletto 2 Received 8 th May 2009; accepted in revised form 8 th June 2009 Abstract
Using Automated Inclusion Analysis for Casting Process Improvements
 Missouri University of Science and Technology Scholars' Mine Materials Science and Engineering Faculty Research & Creative Works Materials Science and Engineering 12-1-28 Using Automated Inclusion Analysis
Missouri University of Science and Technology Scholars' Mine Materials Science and Engineering Faculty Research & Creative Works Materials Science and Engineering 12-1-28 Using Automated Inclusion Analysis
Some Peculiarities in Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron
 ISSN 1392 1320 MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 11, No. 4. 2005 Some Peculiarities in Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron Jan KOHOUT 1, Stanislav VĚCHET 2 1 Department
ISSN 1392 1320 MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 11, No. 4. 2005 Some Peculiarities in Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron Jan KOHOUT 1, Stanislav VĚCHET 2 1 Department
