Oxide Growth. 1. Introduction
|
|
|
- Christiana McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oxide Growth 1. Introduction Development of high-quality silicon dioxide (SiO2) has helped to establish the dominance of silicon in the production of commercial integrated circuits. Among all the various oxidation methods (thermal oxidation, electrochemical anodization, and plasma enhanced chemical vaporization deposition), only thermal oxidation can provide the highest-quality oxides having the lowest interface trap densities. Silicon dioxide is an excellent insulator and dielectric material. Silicon dioxide is extensively used in semiconductors due to this property. One such example is a MOSFET. 1.1 MOSFET MOSFET is a voltage controlled field effect transistor that has a Metal Oxide Gate electrode which is electrically insulated from the main semiconductor by a very thin layer of insulating material, usually SiO2. The aim of the MOSFET is to be able to control the voltage and current flow between the source and drain. It works as a switch. SiO2 is used to avoid direct charge flow from the gate to the channel and vice-versa. SiO2 layer is used as an electrical isolation between the gate and the channel through which major conduction will take place. SiO2 is used as base insulating layer on which the other layers (Drain, Source, etc.) are grown. The gate potential causes charge build up at the bottom of the SiO2 layer thereby aiding in turning ON of the device. Figure 1. Basic Structure of a MOSFET[9] 1
2 2. Theory 2.1. Thermal oxidation process There are two SiO2 growth methods, dry and wet oxidation, depending on whether dry oxygen or water vapor is used: Dry oxidation: Si + O 2 SiO 2 Wet oxidation: Si + 2H 2 O SiO 2 + 2H 2 (g) The oxidizing ambient may also contain several percent of hydrochloric acid. The chlorine removes metal ions that may occur in the oxide. Dry oxidation is usually used to form thin oxides in a device structure because of its good Si-SiO2 interface characteristics, whereas wet oxidation is used for thicker layers because of its higher growth rate. In this experiment, we will use dry oxidation to form the SiO2 film. SiO2 incorporates silicon consumed from the substrate and oxygen supplied from the ambient. Thus, the oxide grows both down into the wafer and up out of it. Every unit thickness of silicon consumed yields 2.27-unit thickness of oxide [1] Kinetics of growth: Deal-Grove model The kinetics of thermal oxidation of silicon can be studied based on a simple model [1] illustrated in Figure 1. At the initial stage of oxidation, the oxidizing species (oxygen or water vapor) reacts with silicon atoms at the surface. This results in growth of a thin SiO2 layer. Now, in order to oxidize Si, the oxidizing species has to diffuse through the SiO2 layer to the Si-SiO2 interface. The diffusive flux is F 1 = D dc dx D(C 0 C s ), (1) x where C0 is the concentration of the oxidizing species in atmosphere adjacent to the SiO2 surface, Cs is the concentration of the oxidizing species at the Si-SiO2 interface, D is the diffusion coefficient of the oxidizing species, and x is the thickness of the oxide layer. C0 corresponds to the equilibrium bulk concentration of the oxidation species. At 1000 and at a pressure of 1 atm, the concentration C0 is molecules/cm 3 for dry oxygen and molecules/cm 3 for water vapor. 2
3 Figure 1. Deal-Grove model for the thermal oxidation of silicon [1]. The oxidizing species reacts with silicon at the Si-SiO2 interface. Assuming that the reaction rate is proportional to the concentration Cs of the oxidizing species near the interface, the reactive flux is F 2 = kc s, (2) where k is the reaction rate. At a steady-state, F1=F2=F. Combining Eqs. (1) and (2) gives The growth rate of the oxide layer is F = DC 0 x + D/k. (3) dx dt = F C 1 = DC 0/C 1 x + D/k, (4) where C1 is the number of molecules of the oxidizing species required to produce a unit volume of the oxide. There are SiO2 units per cm 3 of silicon dioxide and production of each unit requires one oxygen molecule (O2). Therefore, C1 for oxidation in dry oxygen is cm -3. On the other hand, in wet oxidation, it is necessary to add two water molecules (H2O) to 3
4 produce a single SiO2 unit. Therefore, C1 for oxidation in water vapor is cm -3. Solving the differential equation (4) subject to the initial condition x(0) =0 yields This equation can be rewritten in a more compact form: x 2 + 2D k x = 2DC 0 C 1 t. (5) where x 2 + Ax = Bt, (6) A = 2D k and B = 2DC 0 C 1 (7) The values of A and B for dry oxidation at various temperatures are shown in Table 1. Table 1. Oxidation coefficients for (100) silicon surface. Temperature ( ) A (μm) B(μm 2 /hr)
5 Time-dependence of the SiO2 thickness predicted by Eq. (6) is shown in Figure 2. At the early stages of oxidation, the oxide thickness is relatively small so that the timescale of diffusion of oxidizing species through the oxide layer is much smaller than the timescale of the oxidation reaction, i.e. oxidation is reaction-limited. As the oxide layer becomes thicker, the timescale of diffusion through this layer exceeds the reaction timescale at the Si-SiO2 interface, thus the reaction becomes diffusion-limited. Figure 2. Time dependence of the SiO 2 thickness predicted by Eq. (6). The small- and large-time limits are given by Eqs. (10) and (11), respectively. Both the reaction- and diffusion-limited stages of oxidation are predicted by the Deal-Grove model. To see this, write the solution of Eq. (6) as follows: x(t) = A 2 [ 1 + t t c 1]. (8) where is the time corresponding to transition between the two regimes. t c = A2 4B. (9) The reaction- and diffusion-limited regimes correspond to t << tc and t >> tc, respectively. In these cases, Eq. (8) reduces to x At 4t c = B A t = C 0 C 1 kt for t t c and (10) 5
6 x A 2 [( t 2 1 ) 1 + t c 1 2 (t c t ) 1 2 ] A 2 ( t t c ) 1 2 = Bt for t tc (11) I.e., during the reaction-controlled oxide growth, the oxide thickness grows linearly with time, whereas in the diffusion-controlled regime, the thickness grows as the square root of time. In Figure 2, these regimes are shown by the red and blue lines, respectively Oxidation Reactor The basic thermal oxidation reactor is shown in Figure 3. The reactor consists of a resistance-heated furnace, a cylindrical fused-quartz tube containing the silicon wafers held vertically in a slotted quartz boat, and a source of either pure dry oxygen or pure water vapor. The loading end of the furnace tube protrudes into a vertical flow hood where a filtered flow of air is maintained. Flow is a directed as shown by the arrow in Figure 3. The hood reduces dust and particular matter in the air surrounding the wafers and minimizes contamination during wafer loading. The oxidation temperature is generally in the range of 900 C to 1200 C, and the typical gas flow rate is about 1 L/min. The oxidation system uses microprocessors to regulate the gas flow sequence, to control the automatic insertion and removal of silicon wafers, to ramp the temperature up (i.e., to increase the furnace temperature linearly) from a low temperature to the oxidation temperature so that the wafers will not warp due to sudden temperature change, to maintain the oxidation temperature to within ± 1 C, and to ramp the temperature down when oxidation is completed. Filtered air Exhaust Figure 3. Schematic cross section of a resistance-heated oxidation furnace [2]. 6
7 2.4. Oxide quality The simplest method for determining the thickness of an oxide is to compare the color of the wafer with a reference color chart. When an oxide-coated wafer is illuminated with white light perpendicular to the surface, the light penetrates the oxide and is reflected by the underlying silicon wafer. Constructive interference leads to enhancement of a certain wavelength of reflected light, and the color of the wafer corresponds to that wavelength. For example, a wafer with a 500 nm silicon dioxide layer will appear blue green. Clearly, color chart comparisons are subjective and are therefore not the most accurate mechanism for determining oxide thickness. A more accurate measurement can be obtained using techniques such as ellipsometry. Ellipsometry is a very powerful and accurate optical method to measure the thickness of thin films [3], [4], [5]. The technique uses plane polarized monochromatic light to illuminate the oxidized silicon surface at an angle. The film thickness is determined from interference between the light reflected by the SiO2 surface and the light traveling through the SiO2 layer and reflected by the silicon substrate. This light interference is determined by the film thickness and the refractive index of SiO2. This technique requires that the thickness is known to be within approximately 250 nm since the measured quantities are periodic functions of this thickness. Thicknesses down to the very thin (<5nm) regime may be measured. However, inaccuracies in this regime may be present. The technique assumes that the refractive index does not vary with thickness. More complicated methods, such as spectral or multiple wavelength ellipsometry [6], [7] or multiple angle ellipsometry are now being used to improve the accuracy of these measurements to <1nm [7], [8]. 7
8 3. References [1] B.E. Deal and A.S. Grove, "General Relationship for the Thermal Oxidation of Silicon," J. Appl. Phys., 36, 3770 (1965). [2] E.H. Nicollins and J.R. Brews, MOS Physics and Technology. New York: Wily, [3] W. A. Pliskin and E. E. Conrad, IBM J. Res. Devices, 8, (1964). [4] R.J. Archer, J. Electrochem. Soc., 104, 619 (1957). [5] R. M. A. Azzam and N. M. Bashara, Ellipsometry and Polarized Light. Amsterdam, North Holland: Wiley Interscience, [6] H. Reisinger, H. Oppolzer, and W. Honlein, 35, (1992). [7] P.G. Snyder et al, J. Appl. Phys., 60, 3292 (1986). [8] T.S. Chao, C. L. Lee, and T. F. Lei, J. Electrochem. Soc. p. 138 (1991). [9] Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET), University of Cambridge. Available: 8
Instructor: Dr. M. Razaghi. Silicon Oxidation
 SILICON OXIDATION Silicon Oxidation Many different kinds of thin films are used to fabricate discrete devices and integrated circuits. Including: Thermal oxides Dielectric layers Polycrystalline silicon
SILICON OXIDATION Silicon Oxidation Many different kinds of thin films are used to fabricate discrete devices and integrated circuits. Including: Thermal oxides Dielectric layers Polycrystalline silicon
Kinetics of Silicon Oxidation in a Rapid Thermal Processor
 Kinetics of Silicon Oxidation in a Rapid Thermal Processor Asad M. Haider, Ph.D. Texas Instruments Dallas, Texas USA Presentation at the National Center of Physics International Spring Week 2010 Islamabad
Kinetics of Silicon Oxidation in a Rapid Thermal Processor Asad M. Haider, Ph.D. Texas Instruments Dallas, Texas USA Presentation at the National Center of Physics International Spring Week 2010 Islamabad
Processing of Semiconducting Materials Prof. Pallab Banerjee Department of Material Science Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Processing of Semiconducting Materials Prof. Pallab Banerjee Department of Material Science Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 35 Oxidation I (Refer Slide Time: 00:24) Today s topic of
Processing of Semiconducting Materials Prof. Pallab Banerjee Department of Material Science Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 35 Oxidation I (Refer Slide Time: 00:24) Today s topic of
CHAPTER 4: Oxidation. Chapter 4 1. Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are:
 Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO 2 (glass) Major factor in making
 Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO (glass) Major factor in making Silicon the main semiconductor Grown at high temperature in
Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO (glass) Major factor in making Silicon the main semiconductor Grown at high temperature in
MICROCHIP MANUFACTURING by S. Wolf
 MICROCHIP MANUFACTURING by S. Wolf Chapter 13: THERMAL- OXIDATION of SILICON 2004 by LATTICE PRESS Chapter 13: THERMAL-OXIDATION of SILICON n CHAPTER CONTENTS Applications of Thermal Silicon-Dioxide Physical
MICROCHIP MANUFACTURING by S. Wolf Chapter 13: THERMAL- OXIDATION of SILICON 2004 by LATTICE PRESS Chapter 13: THERMAL-OXIDATION of SILICON n CHAPTER CONTENTS Applications of Thermal Silicon-Dioxide Physical
the surface of a wafer, usually silicone. In this process, an oxidizing agent diffuses into the wafer
 Analysis of Oxide Thickness Measurement Techniques of SiO2: Nanometrics Nanospec Reflectometer and Color Chart Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Analysis of Oxide Thickness Measurement Techniques of SiO2: Nanometrics Nanospec Reflectometer and Color Chart Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
ELEC 7364 Lecture Notes Summer Si Oxidation. by STELLA W. PANG. from The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
 ELEC 7364 Lecture Notes Summer 2008 Si Oxidation by STELLA W. PANG from The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA Visiting Professor at The University of Hong Kong The University of Michigan Visiting
ELEC 7364 Lecture Notes Summer 2008 Si Oxidation by STELLA W. PANG from The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA Visiting Professor at The University of Hong Kong The University of Michigan Visiting
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation. Jaeger Chapter 3. EE143 - Ali Javey
 Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
More on oxidation. Oxidation systems Measuring oxide thickness Substrate orientation Thin oxides Oxide quality Si/SiO2 interface Hafnium oxide
 More on oxidation Oxidation systems Measuring oxide thickness Substrate orientation Thin oxides Oxide quality Si/SiO2 interface Hafnium oxide EE 432/532 oxide measurements, etc 1 Oxidation systems silicon
More on oxidation Oxidation systems Measuring oxide thickness Substrate orientation Thin oxides Oxide quality Si/SiO2 interface Hafnium oxide EE 432/532 oxide measurements, etc 1 Oxidation systems silicon
Chapter 4. UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication. Oxidation
 Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation. Jaeger Chapter 3
 Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
Section 4: Thermal Oxidation Jaeger Chapter 3 Properties of O Thermal O is amorphous. Weight Density =.0 gm/cm 3 Molecular Density =.3E molecules/cm 3 O Crystalline O [Quartz] =.65 gm/cm 3 (1) Excellent
HOMEWORK 4 and 5. March 15, Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook:
 HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
Semiconductor Technology
 Semiconductor Technology from A to Z Oxidation www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Oxidation 1 1.1 Overview..................................... 1 1.1.1 Application...............................
Semiconductor Technology from A to Z Oxidation www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Oxidation 1 1.1 Overview..................................... 1 1.1.1 Application...............................
Microelettronica. Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication. 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica
 Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelectronics. Integrated circuits. Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, Expected decrease in line width
 Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Doping and Oxidation
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Oxidation of Silicon
 OpenStax-CNX module: m24908 1 Oxidation of Silicon Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 note: This module was developed
OpenStax-CNX module: m24908 1 Oxidation of Silicon Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 note: This module was developed
Why silicon? Silicon oxide
 Oxidation Layering. Oxidation layering produces a thin layer of silicon dioxide, or oxide, on the substrate by exposing the wafer to a mixture of highpurity oxygen or water at ca. 1000 C (1800 F). Why
Oxidation Layering. Oxidation layering produces a thin layer of silicon dioxide, or oxide, on the substrate by exposing the wafer to a mixture of highpurity oxygen or water at ca. 1000 C (1800 F). Why
Lecture 4. Oxidation (applies to Si and SiC only) Reading: Chapter 4
 Lecture 4 Oxidation (applies to Si and SiC only) Reading: Chapter 4 Introduction discussion: Oxidation: Si (and SiC) Only The ability to grow a high quality thermal oxide has propelled Si into the forefront
Lecture 4 Oxidation (applies to Si and SiC only) Reading: Chapter 4 Introduction discussion: Oxidation: Si (and SiC) Only The ability to grow a high quality thermal oxide has propelled Si into the forefront
THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts
 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. Oxide Thickness µm 0. µm 0 nm nm Thermally Grown Oxides
THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. Oxide Thickness µm 0. µm 0 nm nm Thermally Grown Oxides
NON-PLANAR SILICON OXIDATION: AN EXTENSION OF THE DEAL-GROVE MODEL BRIAN D. LEMME. B.S., University of Nebraska-Lincoln, 2000 A REPORT
 NON-PLANAR SILICON OXIDATION: AN EXTENSION OF THE DEAL-GROVE MODEL by BRIAN D. LEMME B.S., University of Nebraska-Lincoln, 2000 A REPORT submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
NON-PLANAR SILICON OXIDATION: AN EXTENSION OF THE DEAL-GROVE MODEL by BRIAN D. LEMME B.S., University of Nebraska-Lincoln, 2000 A REPORT submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
EE THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6. Basic Concepts
 EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
Figure 2.3 (cont., p. 60) (e) Block diagram of Pentium 4 processor with 42 million transistors (2000). [Courtesy Intel Corporation.
 Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
ME 141B: The MEMS Class Introduction to MEMS and MEMS Design. Sumita Pennathur UCSB
 ME 141B: The MEMS Class Introduction to MEMS and MEMS Design Sumita Pennathur UCSB Outline today Introduction to thin films Oxidation Deal-grove model CVD Epitaxy Electrodeposition 10/6/10 2/45 Creating
ME 141B: The MEMS Class Introduction to MEMS and MEMS Design Sumita Pennathur UCSB Outline today Introduction to thin films Oxidation Deal-grove model CVD Epitaxy Electrodeposition 10/6/10 2/45 Creating
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 9/13/2007 Fabrication Technology Lecture 1 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world)
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 9/13/2007 Fabrication Technology Lecture 1 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world)
EFFECT OF CRYSTALORIENTATIONIN OXIDATION PROCESS OF VLSI FABRICATION
 International Journal of Research in Engineering, Technology and Science, Volume VII, Special Issue, Feb 2017 www.ijrets.com, editor@ijrets.com, ISSN 2454-1915 EFFECT OF CRYSTALORIENTATIONIN OXIDATION
International Journal of Research in Engineering, Technology and Science, Volume VII, Special Issue, Feb 2017 www.ijrets.com, editor@ijrets.com, ISSN 2454-1915 EFFECT OF CRYSTALORIENTATIONIN OXIDATION
ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline:
 ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline: Fabrication of p-n junctions Contact Potential Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the necessary steps to fabricate
ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline: Fabrication of p-n junctions Contact Potential Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the necessary steps to fabricate
M. Hasumi, J. Takenezawa, Y. Kanda, T. Nagao and T. Sameshima
 Proceedings of 6th Thin Film Materials & Devices Meeting November 2-3, 2009, Kyoto, Japan http://www.tfmd.jp/ Characterization of SiO x /Si Interface Properties by Photo Induced Carrier Microwave Absorption
Proceedings of 6th Thin Film Materials & Devices Meeting November 2-3, 2009, Kyoto, Japan http://www.tfmd.jp/ Characterization of SiO x /Si Interface Properties by Photo Induced Carrier Microwave Absorption
A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in
 Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
Czochralski Crystal Growth
 Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology
 Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Nano structural properties of Al 2 O 3 /SiO 2 /Si in Integrated electronic Systems
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol. 3, No.3, pp 1681-1685, July-Sept 2011 Nano structural properties of Al 2 O 3 /SiO 2 /Si in Integrated electronic Systems
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol. 3, No.3, pp 1681-1685, July-Sept 2011 Nano structural properties of Al 2 O 3 /SiO 2 /Si in Integrated electronic Systems
Silicon Oxides: SiO 2
 Silicon Oxides: SiO 2 Uses: diffusion masks surface passivation gate insulator (MOSFET) isolation, insulation Formation: grown / native thermal: highest quality anodization deposited: C V D, evaporate,
Silicon Oxides: SiO 2 Uses: diffusion masks surface passivation gate insulator (MOSFET) isolation, insulation Formation: grown / native thermal: highest quality anodization deposited: C V D, evaporate,
Microelectronic Device Instructional Laboratory. Table of Contents
 Introduction Process Overview Microelectronic Device Instructional Laboratory Introduction Description Flowchart MOSFET Development Process Description Process Steps Cleaning Solvent Cleaning Photo Lithography
Introduction Process Overview Microelectronic Device Instructional Laboratory Introduction Description Flowchart MOSFET Development Process Description Process Steps Cleaning Solvent Cleaning Photo Lithography
Lect. 2: Basics of Si Technology
 Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes
 Chapter 5 Thermal Processes 1 Topics Introduction Hardware Oxidation Diffusion Annealing Post-Implantation Alloying Reflow High Temp CVD Epi Poly Silicon Nitride RTP RTA RTP Future Trends 2 Definition
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes 1 Topics Introduction Hardware Oxidation Diffusion Annealing Post-Implantation Alloying Reflow High Temp CVD Epi Poly Silicon Nitride RTP RTA RTP Future Trends 2 Definition
EE40 Lec 22. IC Fabrication Technology. Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009
 Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor.
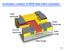 Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor. Gate electrode Drain electrode Source electrode Gate oxide Gate length Page 1 Step 0 The positively doped silicon wafer is first coated with an insulating
Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor. Gate electrode Drain electrode Source electrode Gate oxide Gate length Page 1 Step 0 The positively doped silicon wafer is first coated with an insulating
Silicon Wafers: Basic unit Silicon Wafers Basic processing unit 100, 150, 200, 300, 450 mm disk, mm thick Current industrial standard 300 mm
 Silicon Wafers: Basic unit Silicon Wafers Basic processing unit 100, 150, 200, 300, 450 mm disk, 0.5-0.8 mm thick Current industrial standard 300 mm (12 inches) Most research labs 100, 150 mm wafers (ours
Silicon Wafers: Basic unit Silicon Wafers Basic processing unit 100, 150, 200, 300, 450 mm disk, 0.5-0.8 mm thick Current industrial standard 300 mm (12 inches) Most research labs 100, 150 mm wafers (ours
Fabrication Technology
 Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS. CHAPTER 3 Conventional Si Processing
 3. Conventional licon Processing Micromachining, Microfabrication. EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 3 Conventional Processing Why silicon? Abundant, cheap, easy to process. licon planar Integrated
3. Conventional licon Processing Micromachining, Microfabrication. EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 3 Conventional Processing Why silicon? Abundant, cheap, easy to process. licon planar Integrated
University of Texas Arlington Department of Electrical Engineering. Nanotechnology Microelectromechanical Systems Ph.D. Diagnostic Examination
 University of Texas Arlington Department of Electrical Engineering Nanotechnology Microelectromechanical Systems Ph.D. Diagnostic Examination Fall 2012 November 17, 2012 Question # 1 2 3 To be filled by
University of Texas Arlington Department of Electrical Engineering Nanotechnology Microelectromechanical Systems Ph.D. Diagnostic Examination Fall 2012 November 17, 2012 Question # 1 2 3 To be filled by
KGC SCIENTIFIC Making of a Chip
 KGC SCIENTIFIC www.kgcscientific.com Making of a Chip FROM THE SAND TO THE PACKAGE, A DIAGRAM TO UNDERSTAND HOW CPU IS MADE? Sand CPU CHAIN ANALYSIS OF SEMICONDUCTOR Material for manufacturing process
KGC SCIENTIFIC www.kgcscientific.com Making of a Chip FROM THE SAND TO THE PACKAGE, A DIAGRAM TO UNDERSTAND HOW CPU IS MADE? Sand CPU CHAIN ANALYSIS OF SEMICONDUCTOR Material for manufacturing process
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003
 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE
 Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
Chemical Vapour Deposition: CVD Reference: Jaeger Chapter 6 & Ruska: Chapter 8 CVD - Chemical Vapour Deposition React chemicals to create a thin film
 Chemical Vapour Deposition: CVD Reference: Jaeger Chapter 6 & Ruska: Chapter 8 CVD - Chemical Vapour Deposition React chemicals to create a thin film layer at the surface Typically gas phase reactions
Chemical Vapour Deposition: CVD Reference: Jaeger Chapter 6 & Ruska: Chapter 8 CVD - Chemical Vapour Deposition React chemicals to create a thin film layer at the surface Typically gas phase reactions
4. Thermal Oxidation. a) Equipment Atmospheric Furnace
 4. Thermal Oxidation a) Equipment Atmospheric Furnace Oxidation requires precise control of: temperature, T ambient gas, G time spent at any given T & G, t Vito Logiudice 34 4. Thermal Oxidation b) Mechanism
4. Thermal Oxidation a) Equipment Atmospheric Furnace Oxidation requires precise control of: temperature, T ambient gas, G time spent at any given T & G, t Vito Logiudice 34 4. Thermal Oxidation b) Mechanism
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Zheng Yang
 Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Zheng Yang ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu Page 1 Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow UV light Mask oxygen Silicon dioxide photoresist exposed photoresist oxide
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Zheng Yang ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu Page 1 Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow UV light Mask oxygen Silicon dioxide photoresist exposed photoresist oxide
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
 Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Steven Glenn July 8, 2009 Thin Films Lab 4 ABSTRACT The objective of this lab was to explore lab and the Applied Materials P5000 from a different point of view.
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Steven Glenn July 8, 2009 Thin Films Lab 4 ABSTRACT The objective of this lab was to explore lab and the Applied Materials P5000 from a different point of view.
Lecture Day 2 Deposition
 Deposition Lecture Day 2 Deposition PVD - Physical Vapor Deposition E-beam Evaporation Thermal Evaporation (wire feed vs boat) Sputtering CVD - Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD LPCVD MVD ALD MBE Plating
Deposition Lecture Day 2 Deposition PVD - Physical Vapor Deposition E-beam Evaporation Thermal Evaporation (wire feed vs boat) Sputtering CVD - Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD LPCVD MVD ALD MBE Plating
Module 1 and 2 Report
 Module 1 and 2 Report Interdisciplinary Microelectronics Processing Lab Group D Jaimie Stevens, Erich P. Meinig, Adam Longoria, Emily Makoutz, Ben Timmer Date: February 10, 2015 Abstract This report details
Module 1 and 2 Report Interdisciplinary Microelectronics Processing Lab Group D Jaimie Stevens, Erich P. Meinig, Adam Longoria, Emily Makoutz, Ben Timmer Date: February 10, 2015 Abstract This report details
Oxidation induced precipitation in Al implanted epitaxial silicon
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 88, NUMBER 7 1 OCTOBER 2000 Oxidation induced precipitation in Al implanted epitaxial silicon A. La Ferla, G. Galvagno, P. K. Giri, G. Franzò, and E. Rimini Dipartimento
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 88, NUMBER 7 1 OCTOBER 2000 Oxidation induced precipitation in Al implanted epitaxial silicon A. La Ferla, G. Galvagno, P. K. Giri, G. Franzò, and E. Rimini Dipartimento
Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells
 Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication
 Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
Microstructure of Electronic Materials. Amorphous materials. Single-Crystal Material. Professor N Cheung, U.C. Berkeley
 Microstructure of Electronic Materials Amorphous materials Single-Crystal Material 1 The Si Atom The Si Crystal diamond structure High-performance semiconductor devices require defect-free crystals 2 Crystallographic
Microstructure of Electronic Materials Amorphous materials Single-Crystal Material 1 The Si Atom The Si Crystal diamond structure High-performance semiconductor devices require defect-free crystals 2 Crystallographic
Passivation of SiO 2 /Si Interfaces Using High-Pressure-H 2 O-Vapor Heating
 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 39 (2000) pp. 2492 2496 Part, No. 5A, May 2000 c 2000 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Passivation of O 2 / Interfaces Using High-Pressure-H 2 O-Vapor Heating Keiji SAKAMOTO
Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 39 (2000) pp. 2492 2496 Part, No. 5A, May 2000 c 2000 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Passivation of O 2 / Interfaces Using High-Pressure-H 2 O-Vapor Heating Keiji SAKAMOTO
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology
 Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 10 Oxidation 2001 2000 by Prentice Hall Diffusion Area of Wafer Fabrication Wafer fabrication (front-end)
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 2001 by Prentice Hall Chapter 10 Oxidation 2001 2000 by Prentice Hall Diffusion Area of Wafer Fabrication Wafer fabrication (front-end)
Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University
![Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University](/thumbs/75/72824557.jpg) 2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
Thermal Evaporation. Theory
 Thermal Evaporation Theory 1. Introduction Procedures for depositing films are a very important set of processes since all of the layers above the surface of the wafer must be deposited. We can classify
Thermal Evaporation Theory 1. Introduction Procedures for depositing films are a very important set of processes since all of the layers above the surface of the wafer must be deposited. We can classify
Oxidation SMT Yau - 1
 Oxidation Yau - 1 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe an oxide film for semiconductor manufacturing, including its atomic structure, how it is used
Oxidation Yau - 1 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe an oxide film for semiconductor manufacturing, including its atomic structure, how it is used
Visualization and Control of Particulate Contamination Phenomena in a Plasma Enhanced CVD Reactor
 Visualization and Control of Particulate Contamination Phenomena in a Plasma Enhanced CVD Reactor Manabu Shimada, 1 Kikuo Okuyama, 1 Yutaka Hayashi, 1 Heru Setyawan, 2 and Nobuki Kashihara 2 1 Department
Visualization and Control of Particulate Contamination Phenomena in a Plasma Enhanced CVD Reactor Manabu Shimada, 1 Kikuo Okuyama, 1 Yutaka Hayashi, 1 Heru Setyawan, 2 and Nobuki Kashihara 2 1 Department
A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process
 Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
Silicon Manufacturing
 Silicon Manufacturing Group Members Young Soon Song Nghia Nguyen Kei Wong Eyad Fanous Hanna Kim Steven Hsu th Fundamental Processing Steps 1.Silicon Manufacturing a) Czochralski method. b) Wafer Manufacturing
Silicon Manufacturing Group Members Young Soon Song Nghia Nguyen Kei Wong Eyad Fanous Hanna Kim Steven Hsu th Fundamental Processing Steps 1.Silicon Manufacturing a) Czochralski method. b) Wafer Manufacturing
EE 143 FINAL EXAM NAME C. Nguyen May 10, Signature:
 INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF TANTALUM NITRIDE FILMS BY PLASMA ASSISTED ATOMIC LAYER DEPOSITION AS CU DIFFUSION BARRIER
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 766 2003 Materials Research Society E3.22.1 DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF TANTALUM NITRIDE FILMS BY PLASMA ASSISTED ATOMIC LAYER DEPOSITION AS CU DIFFUSION BARRIER Kyoung-Il
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 766 2003 Materials Research Society E3.22.1 DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF TANTALUM NITRIDE FILMS BY PLASMA ASSISTED ATOMIC LAYER DEPOSITION AS CU DIFFUSION BARRIER Kyoung-Il
2007 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits
 Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits ~ December 20-22, 2007 Tayih Landis Hotel, Tainan, Taiwan Volume I Aluminium Incorporation in Lanthanum Oxide
Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits ~ December 20-22, 2007 Tayih Landis Hotel, Tainan, Taiwan Volume I Aluminium Incorporation in Lanthanum Oxide
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 4. Basic Integrated Circuit Processing
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 4 Basic Integrated Circuit Processing Lecture Outline Details of the physical structure of devices will be very important in developing models for electrical behavior
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 4 Basic Integrated Circuit Processing Lecture Outline Details of the physical structure of devices will be very important in developing models for electrical behavior
The Relation of Temperature Distribution on Silicon Wafer with Furnace Temperature and Gas Flow During Thermal Dry Oxidation Process
 The Relation of Temperature Distribution on Silicon Wafer with Furnace Temperature and Gas Flow During Thermal Dry Oxidation Process A.H. Azman 1, a *, S. Norhafiezah 2, b, RM Ayub 3, c, M. K. Md Arshad
The Relation of Temperature Distribution on Silicon Wafer with Furnace Temperature and Gas Flow During Thermal Dry Oxidation Process A.H. Azman 1, a *, S. Norhafiezah 2, b, RM Ayub 3, c, M. K. Md Arshad
High Performance Optical Coatings Deposited Using Closed Field Magnetron Sputtering
 High Performance Optical Coatings Deposited Using Closed Field Magnetron Sputtering D.R. Gibson, I.T. Brinkley, and J.L. Martin Applied Multilayers LLC, 1801 SE Commerce Avenue, Battle Ground, WA 98604
High Performance Optical Coatings Deposited Using Closed Field Magnetron Sputtering D.R. Gibson, I.T. Brinkley, and J.L. Martin Applied Multilayers LLC, 1801 SE Commerce Avenue, Battle Ground, WA 98604
1. Introduction. What is implantation? Advantages
 Ion implantation Contents 1. Introduction 2. Ion range 3. implantation profiles 4. ion channeling 5. ion implantation-induced damage 6. annealing behavior of the damage 7. process consideration 8. comparison
Ion implantation Contents 1. Introduction 2. Ion range 3. implantation profiles 4. ion channeling 5. ion implantation-induced damage 6. annealing behavior of the damage 7. process consideration 8. comparison
Process Flow in Cross Sections
 Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. Andy Neureuther
 EECS 40 Spring 2003 Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. ndy Neureuther How are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other films Pattern transfer by lithography
EECS 40 Spring 2003 Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. ndy Neureuther How are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other films Pattern transfer by lithography
VLSI Technology. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam
 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
FABRICATION of MOSFETs
 FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
Morphology of Thin Aluminum Film Grown by DC Magnetron Sputtering onto SiO 2 on Si(100) Substrate
 Morphology of Thin Aluminum Film Grown by DC Magnetron Sputtering onto SiO 2 on Si(1) Substrate Fan Wu Microelectronics Center, Medtronic Inc., Tempe, AZ 85261 James E. Morris Department of Electrical
Morphology of Thin Aluminum Film Grown by DC Magnetron Sputtering onto SiO 2 on Si(1) Substrate Fan Wu Microelectronics Center, Medtronic Inc., Tempe, AZ 85261 James E. Morris Department of Electrical
Wafer Cleaning and Oxide Growth Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Wafer Cleaning and Oxide Growth Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/~lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Wafer Cleaning and Oxide Growth Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/~lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
Electrical Characteristics of Rare Earth (La, Ce, Pr and Tm) Oxides/Silicates Gate Dielectric
 Electrical Characteristics of Rare Earth (La, Ce, Pr and Tm) Oxides/Silicates Gate Dielectric K. Matano 1, K. Funamizu 1, M. Kouda 1, K. Kakushima 2, P. Ahmet 1, K. Tsutsui 2, A. Nishiyama 2, N. Sugii
Electrical Characteristics of Rare Earth (La, Ce, Pr and Tm) Oxides/Silicates Gate Dielectric K. Matano 1, K. Funamizu 1, M. Kouda 1, K. Kakushima 2, P. Ahmet 1, K. Tsutsui 2, A. Nishiyama 2, N. Sugii
5.8 Diaphragm Uniaxial Optical Accelerometer
 5.8 Diaphragm Uniaxial Optical Accelerometer Optical accelerometers are based on the BESOI (Bond and Etch back Silicon On Insulator) wafers, supplied by Shin-Etsu with (100) orientation, 4 diameter and
5.8 Diaphragm Uniaxial Optical Accelerometer Optical accelerometers are based on the BESOI (Bond and Etch back Silicon On Insulator) wafers, supplied by Shin-Etsu with (100) orientation, 4 diameter and
Review of CMOS Processing Technology
 - Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
- Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
CHAPTER 8: Diffusion. Chapter 8
 1 CHAPTER 8: Diffusion Diffusion and ion implantation are the two key processes to introduce a controlled amount of dopants into semiconductors and to alter the conductivity type. Figure 8.1 compares these
1 CHAPTER 8: Diffusion Diffusion and ion implantation are the two key processes to introduce a controlled amount of dopants into semiconductors and to alter the conductivity type. Figure 8.1 compares these
Edinburgh Microfabrication Facility, University of Edinburgh.
 405 CONTROL OF OXIDE GROWTH BY REAL-TIME SIMULATION E. Cameron, J. Robertson, R. Holwill Edinburgh Microfabrication Facility, University of Edinburgh. SUMMARY As critical device features are reduced in
405 CONTROL OF OXIDE GROWTH BY REAL-TIME SIMULATION E. Cameron, J. Robertson, R. Holwill Edinburgh Microfabrication Facility, University of Edinburgh. SUMMARY As critical device features are reduced in
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II?? - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II?? - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow
This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes.
 IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
FABRICATION ENGINEERING MICRO- NANOSCALE ATTHE AND. Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL. of Minnesota. University OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 AND FABRICATION ENGINEERING ATTHE MICRO- NANOSCALE Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL University of Minnesota New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Preface xiii prrt i OVERVIEW AND MATERIALS
AND FABRICATION ENGINEERING ATTHE MICRO- NANOSCALE Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL University of Minnesota New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Preface xiii prrt i OVERVIEW AND MATERIALS
Simultaneous Reflection and Transmission Measurements of Scandium Oxide Thin Films in the Extreme Ultraviolet
 Simultaneous Reflection and Transmission Measurements of Scandium Oxide Thin Films in the Extreme Ultraviolet Introduction Guillermo Acosta, Dr. David Allred, Dr, Steven Turley Brigham Young University
Simultaneous Reflection and Transmission Measurements of Scandium Oxide Thin Films in the Extreme Ultraviolet Introduction Guillermo Acosta, Dr. David Allred, Dr, Steven Turley Brigham Young University
Metallization deposition and etching. Material mainly taken from Campbell, UCCS
 Metallization deposition and etching Material mainly taken from Campbell, UCCS Application Metallization is back-end processing Metals used are aluminum and copper Mainly involves deposition and etching,
Metallization deposition and etching Material mainly taken from Campbell, UCCS Application Metallization is back-end processing Metals used are aluminum and copper Mainly involves deposition and etching,
Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
X-Ray Reflectivity Study of Hafnium Silicate Thin Films Prepared by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
 X-Ray Reflectivity Study of Hafnium Silicate Thin Films Prepared by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition Hideyuki YAMAZAKI, Advanced LSI Technology Laboratory, Toshiba Corporation hideyuki.yamazaki@toshiba.co.jp
X-Ray Reflectivity Study of Hafnium Silicate Thin Films Prepared by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition Hideyuki YAMAZAKI, Advanced LSI Technology Laboratory, Toshiba Corporation hideyuki.yamazaki@toshiba.co.jp
RETARDATION IN THE OXIDATION RATE OF NANOCRYSTALLINE SILICON QUANTUM DOTS
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 638 2 Materials Research Society RETARDATION IN THE OXIDATION RATE OF NANOCRYSTALLINE SILICON QUANTUM DOTS J. OMACHI, R. NAKAMURA, K. NISHIGUCHI and S. ODA Research Center
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 638 2 Materials Research Society RETARDATION IN THE OXIDATION RATE OF NANOCRYSTALLINE SILICON QUANTUM DOTS J. OMACHI, R. NAKAMURA, K. NISHIGUCHI and S. ODA Research Center
Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology
 Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology Background The following contains a brief description of isolation technologies used for radiation hardened integrated circuits. The technologies mentioned are junction
Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology Background The following contains a brief description of isolation technologies used for radiation hardened integrated circuits. The technologies mentioned are junction
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells
 12 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells As we already discussed in Chapter 6, most semiconductor materials have a crystalline lattice structure. As a starting point for our discussion on crystalline silicon
12 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells As we already discussed in Chapter 6, most semiconductor materials have a crystalline lattice structure. As a starting point for our discussion on crystalline silicon
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
 NSC89-2215-E-009-104 89 08 01 90 07 31 Fabrication and Characterization of Low-Temperature Polysilicon Thin Film Transistors with Novel Self-Aligned Sub-Gate Structures NSC89-2215-E009-104 (FID) self-aligned
NSC89-2215-E-009-104 89 08 01 90 07 31 Fabrication and Characterization of Low-Temperature Polysilicon Thin Film Transistors with Novel Self-Aligned Sub-Gate Structures NSC89-2215-E009-104 (FID) self-aligned
Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits
 Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits OUTLINE History Basic Processes Implant; Oxidation; Photolithography; Masks Layout and Process Flow Device Cross Section Evolution Lecture 38, 12/05/05 Reading This
Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits OUTLINE History Basic Processes Implant; Oxidation; Photolithography; Masks Layout and Process Flow Device Cross Section Evolution Lecture 38, 12/05/05 Reading This
Complexity of IC Metallization. Early 21 st Century IC Technology
 EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Lecture # 25 Microfabrication Handout of This Lecture. Today: how are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other
EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Lecture # 25 Microfabrication Handout of This Lecture. Today: how are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part 2
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
