Implant Metrology for Bonded SOI Wafers Using a Surface Photo-Voltage Technique
|
|
|
- Amelia Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Implant Metrology for Bonded SOI Wafers Using a Surface Photo-Voltage Technique Adam Bertuch a, Wesley Smith a, Ken Steeples a, Robert Standley b, Anca Stefanescu b, and Ron Johnson c a QC Solutions Inc., Billerica, Massachusetts 01821, USA b MEMC Electronic Materials Inc., St Peters, Missouri 63376, USA c Innovion, Gresham, Oregon 97230, USA Small signal Surface Photo-voltage (SPV) measurement techniques have been applied to monitor ion implants typical of those used for layer-transfer SOI processes. This SPV wafer mapping technique was investigated for sensitivity to dose, implant uniformity, and repeatability for hydrogen and helium implants into (100) silicon wafers through a 1450Å surface oxide. Introduction With continued CMOS scaling, problems such as active and passive power dissipation, short channel effects and SRAM single event upsets are becoming increasingly intractible. Engineered substrates, in particular SOI wafers, provide an important avenue to managing these problems and enabling further scaling. This is driving the large-scale manufacturing of state-of-the-art, large diameter SOI wafers having very thin top silicon layers with very tightly controlled layer thickness and uniformity. The two dominant methods for producing such SOI wafers, SIMOX and bonded, ion implant-assisted layer transfer, both rely on ion-implantation technology (1). This places increased emphasis on monitoring and process control methods for ion implantation of non-dopant species. This paper presents preliminary results of an implant monitor technology applicable to donor wafers prior to the bond-and-layer-transfer process. The donor wafers in bonded, layer-transfer SOI manufacture are generally subjected to implantation of H + (2) or co-implantation of H + with He + (3) to define a cleave plane. Prior to ion implantation, a thermal oxidation of the donor wafer is usually performed. Subsequent to implantation, the donor wafer is bonded to the handle wafer and layer transfer is effected. Proper dose, uniformity, and damage level are critical parameters for proper transfer of the layer from the donor wafer. Historically, SIMS, Hydrogen Forward Scattering (HFS) or Nuclear Reaction Analysis (NRA) have been used to estimate H + dose. These techniques give depth profile information about the implant, but have rather low dose resolution, and are inherently single point measurements. They are also destructive tests, and require costly and complex measurement apparatus. Presently, non-destructive, in-line, whole-wafer mapping of layer-transfer implants is not widely used. In some cases, other metrology techniques are performed after layer transfer, or at the End of Line (EOL) on completed SOI wafers to indirectly infer and monitor the implant performance. Surface Photo-voltage (SPV) measurement of as-implanted wafers is an established technique to produce high-resolution wafer maps of critical dopant implant parameters, without the need to thermally activate the implanted dopant (4). The small signal SPV technique has proven to be highly sensitive to such critical implant parameters as species, dose, and energy (5,6); sensitivity being defined as is typical, percentage change in
2 metrology device signal divided by percentage change in input variable. Such normalized dose and energy sensitivities have been observed for non-activated dopants with values ranging from 1 to 4. Here, we extend this SPV technique to non-destructive, in-line monitoring of ion implants characteristic of those used for layer-transfer bonded SOI processing. Experimental - SPV Measurement A QC Solutions ICT300 SPV system was used for the measurements in this study. This technique is a low intensity, high modulation frequency, ac-spv measurement. The light source and sensing probe are capacitively coupled to the wafer, approximately 100µm above the wafer surface. The wafer measurements are non-contact and nondestructive allowing product wafers to be measured, as is currently done in epi wafer applications of the system. A blue light photo source was used for the measurements, and all SPV measurement values are reported as dynamic charge (C/m 3 ) from the ICT300 system. This above-bandgap, modulated light is strongly absorbed, creating electron hole pairs in the near-surface, Si space charge region. Drift and diffusion of these photocarriers in the space charge region modulates the surface potential, giving rise to the dynamic charge, Qd. At the modulation frequency used, the induced photo-carriers have sufficient time to recombine, creating a dynamic charge (Qd) that depends on the depletion width and the recombination time in the near surface region. The implanted ions introduce damage that acts as recombination centers, reducing photo-carrier lifetime and thus affecting the SPV-measured dynamic charge (4,5). The wafer samples tested were ~10 ohm cm, p-type, (100) crystalline substrates with 1450Å thermal oxide. The wafers were implanted with either hydrogen or helium through the oxide, at doses typical for thin SOI layer transfer processes (2,3). The implanted wafers were measured with the 1450Å thermal oxide intact, representative of a donor wafer immediately after ion implantation. Samples were prepared in both 200mm and 300mm wafer sizes. Results and Discussion Wafer Map Uniformity In Figure 1 300mm medium resolution wafer maps (>4400 points/wafer) are presented for wafers implanted with 42 kev He +, shown to the left, and with 24 kev H +, shown on the right. Implanted doses of 1-1.5x10 16 /cm 2 were used, typical of the coimplantation method (3). Both wafers were measured through a 1450Å oxide on asimplanted donor wafers and show similar map signatures for the He + and H + implants. These wafer features were observed on all wafers measured from multiple implant lots from this particular implanter, indicating the map is characteristic of the implanter. The dynamic charge statistics for each wafer map are presented in Figure 1; average map value (X), range (R), and standard deviation (S). The dynamic charge value for the He + implant is >1 order of magnitude larger which may be attributed in part to the larger damage component and deeper implant profile for this implant. Map uniformity and wafer features are quite similar between the two implanted species that were investigated. In this study helium and hydrogen were investigated individually, and co-implanted wafers were not evaluated.
3 He + 42keV 1.5e16/cm 2 H + 24keV 1e16/cm 2 Contour 1% Lower than Mean Mean Higher than Mean Figure mm wafer Map of He + 42 kev, 1.5E16/cm 2 and H + 24 kev, 1E16/cm 2 with 1450Å surface oxide (contour interval = 1%). The SPV measurement sensitivity to implantation can be understood with reference to Figure 2. The photo source illumination is absorbed within approximately 2 microns of silicon below the oxide, creating photo-carriers in the Si near surface region. For wafers doped with ~10 15 /cm 3 boron, the depletion region extends ~8000Å below the oxide. At 24keV H + implant energy, the implanted hydrogen depth of ~ 3000Å from the surface produces an extensive damage profile lying within this Si depletion region as well as in the surface oxide. This Si damage directly affects the measured dynamic charge in the near-surface region by creating recombination centers that reduce minority carrier lifetimes, and by creating charged defects that affect the space-charge density, and hence minority carrier drift during illumination. For the 42 kev He + implant, the implant depth is slightly deeper at ~3500Å, but the damage density is considerably larger due to the fourfold increase in the ion mass. A higher damage concentration profile from the He+ implant gives and increase in the measured dynamic charge signal compared to the H+ measurement. H + Implant Depth Oxide ~ 1450Å Final SOI Si Surface ~1500A Wd for /cm 3 boron ac photo illumination depth Surface 1450Å 3000Å 8000Å ~2 microns Figure 2. Depth Profile of SOI donor wafer after typical H + implant.
4 Since the SPV technique relies upon light transmission through the SiO 2 -Si interface, the thickness and the transmission factor of the oxide need to be accounted for. The ICT300 software incorporates a recipe-specific light transmission algorithm, which corrects for variation in oxide thickness. The impact on the measurement of the implant damage in the oxide and oxide thickness variations within-wafer were investigated. Wafers with a high H + implant dose, 6.6x10 16 /cm 2, typical of mono-implant layer transfer (2) were prepared. SPV measurements were initially performed with the thermal oxide intact. After initial measurement, the wafer oxide was removed using a 5% HF:DI strip for 5 minutes, followed by a DI rinse and spin dry. The wafer surface after wet processing was hydrogen terminated. Direct comparison of an implanted wafer with the 1450Å oxide in place and after an HF strip is presented in Figure 3. By removing the oxide, the effect of the surface oxide damage on the SPV measurement can be eliminated and the response from the implant/substrate alone evaluated. The comparison before and after HF strip is presented on a single 200mm wafer. The implant map characteristic is similar before and after HF strip with similar range (R) and std deviation (S) for the wafer map summaries. The map average for the HF stripped wafer is shifted to a larger Qd value, which is attributed to altered light transmission into the Si through the SiO 2. For the data presented the light transmission algorithm was not applied to the measurement in order to directly evaluate the magnitude and wafer map statistics. The impact of the oxide on light transmission through the SiO 2 for the oxide thickness and light wavelength in the present case is fairly small, <10%. It is important to note that the measured SPV signal is generated from the implanted Si region, and does not show a dependence on the surface oxide or damage within the SiO 2 region, allowing accurate measurement of the implant without removing the 1450 Å oxide. 1450Å oxide Post HF Strip Contour 2% Lower than Mean Mean Higher than Mean Figure mm SPV wafer maps, H + 24keV, 6.6E16/cm 2, with and without a 1450Å oxide.
5 Dose Sensitivity Figure 4 shows dose sensitivity for He + 42keV and H + 25keV implants into oxidized donor wafers. Implant dose was varied around the reported nominal dose values as reported with a normalized value along the x-axis. The dose ranges investigated are ~1.5x10 16 /cm 2 for the He + implants, typical of the co-implantation method, and ~6x10 16 /cm 2 for H + implants, typical of the mono-implantation method. Average Qd values for full wafer maps were used in the evaluation and were measured through the surface oxide on the as-implanted donor wafers. The measured sensitivity to implanted dose are shown as a normalized Qd sensitivity of ~1.2 for the two cases investigated He + 42keV 1.5e16/cm 2 Dose Sens = H + 25keV 6e16/cm 2 Dose Sens = 1.16 Qd (C/m 3 ) Qd (C/m 3 ) Normalized Dose Normalized Dose Figure 4. Qd response as a function of normalized dose for He + 42 kev 1.5E16/cm 2 and H + 25 kev 6E16/cm 2 with 1450Å surface oxide. Repeatability Measurement repeatability was evaluated for the H + implant with the 1450Å thermal oxide intact. Measurements were collected hourly for the test period of 5 days. The SPV measurements were full wafer maps using the standard wavelength light for the ICT300. Repeatability of the SPV measured technique shows a standard deviation (1-sigma) repeatability of 0.21% for the five day test period. This level of stability within the measurement system, would suggest that a dose variation of 1% can be resolvable using the investigated SPV monitor system with a 2 sigma tolerance level. 422 Qd (Coul/m^3) Avg = Std Dev = 0.21% Qd Figure 5. 5 Day Repeatability H + 24keV, 6.6E16/cm 2
6 Summary The small signal SPV measurement technique presented is a capable high-resolution full wafer map technique for monitoring SOI implants, as implanted through a thick surface oxide. Standard hydrogen and helium layer transfer implants were evaluated for sensitivity to dose with a normalized sensitivity of approximately 1.2 for the investigated cases. A demonstrated repeatability of much less than 0.5% 1-sigma was observed for a multi-day period on hydrogen implanted wafers. This non-destructive technique produces high-resolution wafer maps of as-implanted, oxidized donor wafers. The H + and He + implants can be monitored non-destructively on standard, oxidized donor wafers without altering the SOI manufacturing process flow, allowing in-line SPC control of this critical step within the SOI layer transfer manufacturing process. References 1. G.K. Celler and Sorin Cristoloveanu, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4955 (2003) 2. M. Bruel, Electron. Lett. 37, 1201 (1995) 3. A. Agarwal, T.E. Haynes, V.C. Venezia, O.W. Holland and D.J. Eaglesham, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1086 (1998) 4. Tsidilkovski, E., Crocker, K., Steeples, K. Ion Implant Process Monitoring with a Dynamic Surface Photo-charge Technique. Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference, (2004). 5. K. Steeples, E. Tsidilkovski, Photoelectric Measurment Method for Implanted Silicon: A Phenomenological Approach, CP866, Ion Implantation Technology, (2006). 6. R.S. Nakmanson, Solid State Electronics 18, (1975)
Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology
 Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology Background The following contains a brief description of isolation technologies used for radiation hardened integrated circuits. The technologies mentioned are junction
Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology Background The following contains a brief description of isolation technologies used for radiation hardened integrated circuits. The technologies mentioned are junction
PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS
 Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Isolation Technology. Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
HOMEWORK 4 and 5. March 15, Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook:
 HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
CMOS Technology. Flow varies with process types & company. Start with substrate selection. N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI
 CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
M. Hasumi, J. Takenezawa, Y. Kanda, T. Nagao and T. Sameshima
 Proceedings of 6th Thin Film Materials & Devices Meeting November 2-3, 2009, Kyoto, Japan http://www.tfmd.jp/ Characterization of SiO x /Si Interface Properties by Photo Induced Carrier Microwave Absorption
Proceedings of 6th Thin Film Materials & Devices Meeting November 2-3, 2009, Kyoto, Japan http://www.tfmd.jp/ Characterization of SiO x /Si Interface Properties by Photo Induced Carrier Microwave Absorption
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST
 Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Development of Silicon Pad and Strip Detector in High Energy Physics
 XXI DAE-BRNS High Energy Physics Symposium 2014, IIT Guwahati Development of Silicon Pad and Strip Detector in High Energy Physics Manoj Jadhav Department of Physics I.I.T. Bombay 2 Manoj Jadhav, IIT Bombay.
XXI DAE-BRNS High Energy Physics Symposium 2014, IIT Guwahati Development of Silicon Pad and Strip Detector in High Energy Physics Manoj Jadhav Department of Physics I.I.T. Bombay 2 Manoj Jadhav, IIT Bombay.
Doping and Oxidation
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
EE 143 FINAL EXAM NAME C. Nguyen May 10, Signature:
 INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
A Nano-thick SOI Fabrication Method
 A Nano-thick SOI Fabrication Method C.-H. Huang 1, J.T. Cheng 1, Y.-K. Hsu 1, C.-L. Chang 1, H.-W. Wang 1, S.-L. Lee 1,2, and T.-H. Lee 1,2 1 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering National Central University,
A Nano-thick SOI Fabrication Method C.-H. Huang 1, J.T. Cheng 1, Y.-K. Hsu 1, C.-L. Chang 1, H.-W. Wang 1, S.-L. Lee 1,2, and T.-H. Lee 1,2 1 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering National Central University,
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
Czochralski Crystal Growth
 Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells With Two Different Metals. Toshiyuki Sameshima*, Kazuya Kogure, and Masahiko Hasumi
 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells With Two Different Metals Toshiyuki Sameshima*, Kazuya Kogure, and Masahiko Hasumi Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo 184-8588,
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells With Two Different Metals Toshiyuki Sameshima*, Kazuya Kogure, and Masahiko Hasumi Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo 184-8588,
An advantage of thin-film silicon solar cells is that they can be deposited on glass substrates and flexible substrates.
 ET3034TUx - 5.2.1 - Thin film silicon PV technology 1 Last week we have discussed the dominant PV technology in the current market, the PV technology based on c-si wafers. Now we will discuss a different
ET3034TUx - 5.2.1 - Thin film silicon PV technology 1 Last week we have discussed the dominant PV technology in the current market, the PV technology based on c-si wafers. Now we will discuss a different
Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Semiconductor Technology
 Semiconductor Technology from A to Z Oxidation www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Oxidation 1 1.1 Overview..................................... 1 1.1.1 Application...............................
Semiconductor Technology from A to Z Oxidation www.halbleiter.org Contents Contents List of Figures List of Tables II III 1 Oxidation 1 1.1 Overview..................................... 1 1.1.1 Application...............................
3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005
 3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005 1) This is an open book, take-home quiz. You are not to consult with other class members or anyone else. You may discuss the
3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005 1) This is an open book, take-home quiz. You are not to consult with other class members or anyone else. You may discuss the
Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Accelerate dopant ions to very
 Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Accelerate dopant ions to very high voltages (10-600 KeV) Use analyzer to selection charge/mass
Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Accelerate dopant ions to very high voltages (10-600 KeV) Use analyzer to selection charge/mass
Introduction to Lithography
 Introduction to Lithography G. D. Hutcheson, et al., Scientific American, 290, 76 (2004). Moore s Law Intel Co-Founder Gordon E. Moore Cramming More Components Onto Integrated Circuits Author: Gordon E.
Introduction to Lithography G. D. Hutcheson, et al., Scientific American, 290, 76 (2004). Moore s Law Intel Co-Founder Gordon E. Moore Cramming More Components Onto Integrated Circuits Author: Gordon E.
Process Integration. MEMS Release Techniques Sacrificial Layer Removal Substrate Undercut
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
the surface of a wafer, usually silicone. In this process, an oxidizing agent diffuses into the wafer
 Analysis of Oxide Thickness Measurement Techniques of SiO2: Nanometrics Nanospec Reflectometer and Color Chart Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Analysis of Oxide Thickness Measurement Techniques of SiO2: Nanometrics Nanospec Reflectometer and Color Chart Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Extended Abstracts of the Sixth International Workshop on Junction Technology
 IWJT-2006 Extended Abstracts of the Sixth International Workshop on Junction Technology May.15-16, 2006, Shanghai, China Editors: Yu-Long Jiang, Guo-Ping Ru, Xin-Ping Qu, and Bing-Zong Li IEEE Press IEEE
IWJT-2006 Extended Abstracts of the Sixth International Workshop on Junction Technology May.15-16, 2006, Shanghai, China Editors: Yu-Long Jiang, Guo-Ping Ru, Xin-Ping Qu, and Bing-Zong Li IEEE Press IEEE
MEMS Surface Fabrication
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING MEMS Surface Fabrication Dr. Lynn Fuller webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee Electrical and Microelectronic Engineering Rochester Institute
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING MEMS Surface Fabrication Dr. Lynn Fuller webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee Electrical and Microelectronic Engineering Rochester Institute
MOSFET. n+ poly Si. p- substrate
 EE143 Midterm #1 Solutions Fall 2005 (maximum score is 97) Problem 1 Processing Modules and Simple Process Sequence (25 points total) The following schematic cross-section shows a MOSFET together with
EE143 Midterm #1 Solutions Fall 2005 (maximum score is 97) Problem 1 Processing Modules and Simple Process Sequence (25 points total) The following schematic cross-section shows a MOSFET together with
Electrical Properties of Ultra Shallow p Junction on n type Si Wafer Using Decaborane Ion Implantation
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 686 2002 Materials Research Society Electrical Properties of Ultra Shallow p Junction on n type Si Wafer Using Decaborane Ion Implantation Jae-Hoon Song, Duck-Kyun Choi
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 686 2002 Materials Research Society Electrical Properties of Ultra Shallow p Junction on n type Si Wafer Using Decaborane Ion Implantation Jae-Hoon Song, Duck-Kyun Choi
Transmission Mode Photocathodes Covering the Spectral Range
 Transmission Mode Photocathodes Covering the Spectral Range 6/19/2002 New Developments in Photodetection 3 rd Beaune Conference June 17-21, 2002 Arlynn Smith, Keith Passmore, Roger Sillmon, Rudy Benz ITT
Transmission Mode Photocathodes Covering the Spectral Range 6/19/2002 New Developments in Photodetection 3 rd Beaune Conference June 17-21, 2002 Arlynn Smith, Keith Passmore, Roger Sillmon, Rudy Benz ITT
Chapter 2 Problems. The CMOS technology we need to realize is shown below, from Figure 1-34 in the text. S P + N P + N WELL P +
 Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Characteristics of HfO 2 pmosfet with Ultrashallow Junction Prepared by Plasma Doping and Laser Annealing
 Characteristics of HfO 2 pmosfet with Ultrashallow Junction Prepared by Plasma Doping and Laser Annealing Sungkweon Baek, Sungho Heo, and Hyunsang Hwang Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering Kwangju
Characteristics of HfO 2 pmosfet with Ultrashallow Junction Prepared by Plasma Doping and Laser Annealing Sungkweon Baek, Sungho Heo, and Hyunsang Hwang Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering Kwangju
Junction formation in Ge by coimplant. and pre-heating techniques
 Junction formation in Ge by coimplant. and pre-heating techniques Takashi Kuroi Nissin Ion Equipment Co., Ltd. 0 Content Introduction Purpose and Motivation Experimental Acceptor impurity implanted Germanium
Junction formation in Ge by coimplant. and pre-heating techniques Takashi Kuroi Nissin Ion Equipment Co., Ltd. 0 Content Introduction Purpose and Motivation Experimental Acceptor impurity implanted Germanium
EE 143 MICROFABRICATION TECHNOLOGY FALL 2014 C. Nguyen PROBLEM SET #9
 Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
GRAIN BOUNDARY RECOMBINATION PROCESSES AND CARRIER TRANSPORT IN POLYCRYSTALLINE SEMICONDUCTORS UNDER OPTICAL ILLUMINATION
 CHAPTER V GRAIN BOUNDARY RECOMBINATION PROCESSES AND CARRIER TRANSPORT IN POLYCRYSTALLINE SEMICONDUCTORS UNDER OPTICAL ILLUMINATION 5.1 INTRODUCTION P olycrystalline semiconductors are potential candidates
CHAPTER V GRAIN BOUNDARY RECOMBINATION PROCESSES AND CARRIER TRANSPORT IN POLYCRYSTALLINE SEMICONDUCTORS UNDER OPTICAL ILLUMINATION 5.1 INTRODUCTION P olycrystalline semiconductors are potential candidates
Advances in Optical Densitometry for Low Dose Measurements
 Advances in Optical Densitometry for Low Dose Measurements Ray Kuzbyt, Ron Eddy Core Systems Inc. Sunnyvale, CA, USA Nicholas R. White * Consultant Manchester, MA, USA Raymond Callahan Varian Semiconductor
Advances in Optical Densitometry for Low Dose Measurements Ray Kuzbyt, Ron Eddy Core Systems Inc. Sunnyvale, CA, USA Nicholas R. White * Consultant Manchester, MA, USA Raymond Callahan Varian Semiconductor
Process Integration. NMOS Generic NMOS Process Flow. CMOS - The MOSIS Process Flow
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
ET3034TUx High efficiency concepts of c- Si wafer based solar cells
 ET3034TUx - 4.4 - High efficiency concepts of c- Si wafer based solar cells In the previous block we have discussed various technological aspects on crystalline silicon wafer based PV technology. In this
ET3034TUx - 4.4 - High efficiency concepts of c- Si wafer based solar cells In the previous block we have discussed various technological aspects on crystalline silicon wafer based PV technology. In this
Microelettronica. Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication. 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica
 Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells
 61 Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Victor Prajapati. Department ofmicroelectronic Engineering, 82 Lomb Memorial Dr., Rochester, NY 14623. Email: Victor.Prajapati@gmail.com Abstract Fully processed CMOS Si
61 Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Victor Prajapati. Department ofmicroelectronic Engineering, 82 Lomb Memorial Dr., Rochester, NY 14623. Email: Victor.Prajapati@gmail.com Abstract Fully processed CMOS Si
9/4/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
1. Introduction. What is implantation? Advantages
 Ion implantation Contents 1. Introduction 2. Ion range 3. implantation profiles 4. ion channeling 5. ion implantation-induced damage 6. annealing behavior of the damage 7. process consideration 8. comparison
Ion implantation Contents 1. Introduction 2. Ion range 3. implantation profiles 4. ion channeling 5. ion implantation-induced damage 6. annealing behavior of the damage 7. process consideration 8. comparison
Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Steven Levitan Fall 2008 1 The Manufacturing Process For a great tour through the IC manufacturing
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Steven Levitan Fall 2008 1 The Manufacturing Process For a great tour through the IC manufacturing
ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline:
 ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline: Fabrication of p-n junctions Contact Potential Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the necessary steps to fabricate
ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline: Fabrication of p-n junctions Contact Potential Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the necessary steps to fabricate
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003
 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon
 Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Two-dimensional Computer Modeling of Single Junction a-si:h Solar Cells
 Two-dimensional Computer Modeling of Single Junction a-si:h Solar Cells Changwoo Lee, Harry Efstathiadis, James E. Raynolds, Pradeep Haldar Energy and Environmental Applications Center (E2TAC) College
Two-dimensional Computer Modeling of Single Junction a-si:h Solar Cells Changwoo Lee, Harry Efstathiadis, James E. Raynolds, Pradeep Haldar Energy and Environmental Applications Center (E2TAC) College
VLSI Technology. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam
 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
UT Austin, ECE Department VLSI Design 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout Rules
 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
Electrical properties of multiple-layer structures formed by implantation of nitrogen or oxygen and annealed under high pressure
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 033506 2006 Electrical properties of multiple-layer structures formed by implantation of nitrogen or oxygen and annealed under high pressure Irina V. Antonova a Institute
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 033506 2006 Electrical properties of multiple-layer structures formed by implantation of nitrogen or oxygen and annealed under high pressure Irina V. Antonova a Institute
A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process
 Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
Activation Behavior of Boron and Phosphorus Atoms Implanted in Polycrystalline Silicon Films by Heat Treatment at 250 C
 Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 3, 2005, pp. 1186 1191 #2005 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Activation Behavior of Boron and Phosphorus Atoms Implanted in Polycrystalline Silicon
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 3, 2005, pp. 1186 1191 #2005 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Activation Behavior of Boron and Phosphorus Atoms Implanted in Polycrystalline Silicon
Boron Back Surface Field Using Spin-On Dopants by Rapid Thermal Processing
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 44, No. 6, June 2004, pp. 1581 1586 Boron Back Surface Field Using Spin-On Dopants by Rapid Thermal Processing Ji Youn Lee Photovoltaics R&D Center, Sung Jin
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 44, No. 6, June 2004, pp. 1581 1586 Boron Back Surface Field Using Spin-On Dopants by Rapid Thermal Processing Ji Youn Lee Photovoltaics R&D Center, Sung Jin
R Sensor resistance (Ω) ρ Specific resistivity of bulk Silicon (Ω cm) d Diameter of measuring point (cm)
 4 Silicon Temperature Sensors 4.1 Introduction The KTY temperature sensor developed by Infineon Technologies is based on the principle of the Spreading Resistance. The expression Spreading Resistance derives
4 Silicon Temperature Sensors 4.1 Introduction The KTY temperature sensor developed by Infineon Technologies is based on the principle of the Spreading Resistance. The expression Spreading Resistance derives
CHAPTER 4: Oxidation. Chapter 4 1. Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are:
 Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology
 Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Quarterly Report EPRI Agreement W
 Quarterly Report EPRI Agreement W08069-07 PI: S.J. Pearton, University of Florida (Co-investigators F. Ren, C.R. Abernathy, R.K. Singh, P.H. Holloway, T.J. Anderson, M. Berding, A. Sher, S. Krishnimurthy,
Quarterly Report EPRI Agreement W08069-07 PI: S.J. Pearton, University of Florida (Co-investigators F. Ren, C.R. Abernathy, R.K. Singh, P.H. Holloway, T.J. Anderson, M. Berding, A. Sher, S. Krishnimurthy,
CMOS Fabrication. Dr. Bassam Jamil. Adopted from slides of the textbook
 CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
Challenges and Future Directions of Laser Fuse Processing in Memory Repair
 Challenges and Future Directions of Laser Fuse Processing in Memory Repair Bo Gu, * T. Coughlin, B. Maxwell, J. Griffiths, J. Lee, J. Cordingley, S. Johnson, E. Karagiannis, J. Ehrmann GSI Lumonics, Inc.
Challenges and Future Directions of Laser Fuse Processing in Memory Repair Bo Gu, * T. Coughlin, B. Maxwell, J. Griffiths, J. Lee, J. Cordingley, S. Johnson, E. Karagiannis, J. Ehrmann GSI Lumonics, Inc.
Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells
 Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
University of Texas Arlington Department of Electrical Engineering. Nanotechnology Microelectromechanical Systems Ph.D. Diagnostic Examination
 University of Texas Arlington Department of Electrical Engineering Nanotechnology Microelectromechanical Systems Ph.D. Diagnostic Examination Fall 2012 November 17, 2012 Question # 1 2 3 To be filled by
University of Texas Arlington Department of Electrical Engineering Nanotechnology Microelectromechanical Systems Ph.D. Diagnostic Examination Fall 2012 November 17, 2012 Question # 1 2 3 To be filled by
Design & Fabrication of a High-Voltage Photovoltaic Cell. Jennifer Felder
 SLAC-TN-12-021 Design & Fabrication of a High-Voltage Photovoltaic Cell Jennifer Felder Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) North Carolina State University SLAC National
SLAC-TN-12-021 Design & Fabrication of a High-Voltage Photovoltaic Cell Jennifer Felder Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) North Carolina State University SLAC National
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
MATTHEW A. WICKHAM 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology ABSTRACT
 ION IMPLANTATION TO ADJUST NMOS THRESHOLD VOLTAGES MATTHEW A. WICKHAM 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT NMOS processes require a variety
ION IMPLANTATION TO ADJUST NMOS THRESHOLD VOLTAGES MATTHEW A. WICKHAM 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT NMOS processes require a variety
More on oxidation. Oxidation systems Measuring oxide thickness Substrate orientation Thin oxides Oxide quality Si/SiO2 interface Hafnium oxide
 More on oxidation Oxidation systems Measuring oxide thickness Substrate orientation Thin oxides Oxide quality Si/SiO2 interface Hafnium oxide EE 432/532 oxide measurements, etc 1 Oxidation systems silicon
More on oxidation Oxidation systems Measuring oxide thickness Substrate orientation Thin oxides Oxide quality Si/SiO2 interface Hafnium oxide EE 432/532 oxide measurements, etc 1 Oxidation systems silicon
High Temperature Oxygen Out-Diffusion from the Interfacial SiOx Bond Layer in Direct Silicon Bonded (DSB) Substrates
 High Temperature Oxygen Out-Diffusion from the Interfacial SiOx Bond Layer in Direct Silicon Bonded (DSB) Substrates Jim Sullivan, Harry R. Kirk, Sien Kang, Philip J. Ong, and Francois J. Henley Silicon
High Temperature Oxygen Out-Diffusion from the Interfacial SiOx Bond Layer in Direct Silicon Bonded (DSB) Substrates Jim Sullivan, Harry R. Kirk, Sien Kang, Philip J. Ong, and Francois J. Henley Silicon
Bulk MEMS Fabrication Details Dr. Lynn Fuller, Casey Gonta, Patsy Cadareanu
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Bulk MEMS Fabrication Details Dr. Lynn Fuller, Casey Gonta, Patsy Cadareanu Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester,
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Bulk MEMS Fabrication Details Dr. Lynn Fuller, Casey Gonta, Patsy Cadareanu Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester,
Process Flow in Cross Sections
 Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Formation and Annihilation of Hydrogen-Related Donor States in Proton-Implanted and Subsequently Plasma-Hydrogenated N-Type Float-Zone Silicon
 Formation and Annihilation of Hydrogen-Related Donor States in Proton-Implanted and Subsequently Plasma-Hydrogenated N-Type Float-Zone Silicon Reinhart Job, University of Hagen, Germany Franz-Josef Niedernostheide,
Formation and Annihilation of Hydrogen-Related Donor States in Proton-Implanted and Subsequently Plasma-Hydrogenated N-Type Float-Zone Silicon Reinhart Job, University of Hagen, Germany Franz-Josef Niedernostheide,
Epi Replacement and up to 30% Process Simplification in a CMOS Foundry Environment Using the BILLI Structure
 Epi Replacement and up to 30% Process Simplification in a CMOS Foundry Environment Using the BILLI Structure Martin Teague, Susan Johns, Rob Haase, Paul Jones & Peter Lister Newport Waferfab Limited, Cardiff
Epi Replacement and up to 30% Process Simplification in a CMOS Foundry Environment Using the BILLI Structure Martin Teague, Susan Johns, Rob Haase, Paul Jones & Peter Lister Newport Waferfab Limited, Cardiff
Microelectronics. Integrated circuits. Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, Expected decrease in line width
 Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
CMOS FABRICATION. n WELL PROCESS
 CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
EE 143 MICROFABRICATION TECHNOLOGY FALL 2014 C. Nguyen PROBLEM SET #9
 Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROBLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROBLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Implant dopants by accelerating individual atoms (ions) Ionize gas sources (single +,
 Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Implant dopants by accelerating individual atoms (ions) Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Use analyzer to selection charge/mass
Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Implant dopants by accelerating individual atoms (ions) Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Use analyzer to selection charge/mass
ON-INSULATOR (SOI) 5.2 FABRICATION OF SURFACE ETCHED FEATURES 5.1 SILICON-ON. on-silicon dioxide. Figure 5.1 Silicon-on-silicon dioxide
 課程編號 :941: U0460 科目名稱 : 矽光子學授課教師 : 黃鼎偉時間地點 : 一 678 明達館 303 5.1 SILICON-ON ON-INSULATOR (SOI) 5.2 FABRICATION OF SURFACE ETCHED FEATURES SOI: a generic term used to describe structures which consist of
課程編號 :941: U0460 科目名稱 : 矽光子學授課教師 : 黃鼎偉時間地點 : 一 678 明達館 303 5.1 SILICON-ON ON-INSULATOR (SOI) 5.2 FABRICATION OF SURFACE ETCHED FEATURES SOI: a generic term used to describe structures which consist of
EE CMOS TECHNOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text
 1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
Amorphous silicon / crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cell
 Workshop on "Physics for Renewable Energy" October 17-29, 2005 301/1679-9 "Amorphous Silicon / Cyrstalline Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cell" E. Centurioni CNR/IMM AREA Science Park - Bologna Italy Amorphous
Workshop on "Physics for Renewable Energy" October 17-29, 2005 301/1679-9 "Amorphous Silicon / Cyrstalline Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cell" E. Centurioni CNR/IMM AREA Science Park - Bologna Italy Amorphous
Future technologies for the electrical isolation of III-V semiconductor devices. Final report on grant no. GR/N32969 (including GR/S52797/01)
 Future technologies for the electrical isolation of III-V semiconductor devices Final report on grant no. GR/N32969 (including GR/S52797/01) Introduction This report, which summarises the work done by
Future technologies for the electrical isolation of III-V semiconductor devices Final report on grant no. GR/N32969 (including GR/S52797/01) Introduction This report, which summarises the work done by
Photoresist Coat, Expose and Develop Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Photoresist Coat, Expose and Develop Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Photoresist Coat, Expose and Develop Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
Enhancement of Phosphorus Activation in Vacancy. Engineered thin Silicon-on-Insulator Substrates
 Enhancement of Phosphorus Activation in Vacancy Engineered thin Silicon-on-Insulator Substrates A J Smith*, R M Gwilliam and V Stolojan Ion Beam Centre, Advanced Technology Institute, University of Surrey,
Enhancement of Phosphorus Activation in Vacancy Engineered thin Silicon-on-Insulator Substrates A J Smith*, R M Gwilliam and V Stolojan Ion Beam Centre, Advanced Technology Institute, University of Surrey,
Implant And Annealing Process Integration Issues To Reduce Device Variability For <10nm p+ & n+ Ultra-Shallow junctions
 Implant And Annealing Process Integration Issues To Reduce Device Variability For
Implant And Annealing Process Integration Issues To Reduce Device Variability For
566 Zheng Zhong-Shan et al Vol Device and experiment First, standard SIMOX (separation-by-implantedoxygen) wafers were formed through implanting
 Vol 14 No 3, March 2005 cfl 2005 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2005/14(03)/0565-06 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Effect of the technology of implanting nitrogen into buried oxide on the radiation
Vol 14 No 3, March 2005 cfl 2005 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2005/14(03)/0565-06 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Effect of the technology of implanting nitrogen into buried oxide on the radiation
Oxidation of Silicon
 OpenStax-CNX module: m24908 1 Oxidation of Silicon Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 note: This module was developed
OpenStax-CNX module: m24908 1 Oxidation of Silicon Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 note: This module was developed
Synchrotron X-Ray Topography Measurements on 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layer
 Synchrotron X-Ray Topography Measurements on 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layer Isaho KAMATA, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) Kamata@criepi.denken.or.jp Silicon carbide has excellent
Synchrotron X-Ray Topography Measurements on 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layer Isaho KAMATA, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) Kamata@criepi.denken.or.jp Silicon carbide has excellent
CMOS Manufacturing process. Design rule set
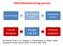 CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
REAR SURFACE PASSIVATION OF INTERDIGITATED BACK CONTACT SILICON HETEROJUNCTION SOLAR CELL AND 2D SIMULATION STUDY
 REAR SURFACE PASSIVATION OF INTERDIGITATED BACK CONTACT SILICON HETEROJUNCTION SOLAR CELL AND 2D SIMULATION STUDY Meijun Lu 1,2, Ujjwal Das 1, Stuart Bowden 1, and Robert Birkmire 1,2 1 Institute of Energy
REAR SURFACE PASSIVATION OF INTERDIGITATED BACK CONTACT SILICON HETEROJUNCTION SOLAR CELL AND 2D SIMULATION STUDY Meijun Lu 1,2, Ujjwal Das 1, Stuart Bowden 1, and Robert Birkmire 1,2 1 Institute of Energy
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
Manufacturing Process
 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. May 5 th 2014
 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. May 5 th 2014 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Basic MEMS Processes Front-End Processes Back-End Processes 2 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. Wafers Deposition Lithography Etch Chips 1- Si Substrate
Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. May 5 th 2014 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Basic MEMS Processes Front-End Processes Back-End Processes 2 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. Wafers Deposition Lithography Etch Chips 1- Si Substrate
CMOS VLSI Design. Introduction. All materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN. Introduction
 CMOS VLSI Design Introduction ll materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN Introduction Chapter previews the entire field, subsequent chapters elaborate on specific
CMOS VLSI Design Introduction ll materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN Introduction Chapter previews the entire field, subsequent chapters elaborate on specific
Kerf! Microns. Driving Forces Impact of kerf is substantial in terms of silicon usage 50 % of total thickness for 100 mm wafers
 2nd. Annual c-si PVMC Workshop at Intersolar NA, San Francisco, CA, July 2013 1 Microns Kerf! Driving Forces Impact of kerf is substantial in terms of silicon usage 50 % of total thickness for 100 mm wafers
2nd. Annual c-si PVMC Workshop at Intersolar NA, San Francisco, CA, July 2013 1 Microns Kerf! Driving Forces Impact of kerf is substantial in terms of silicon usage 50 % of total thickness for 100 mm wafers
Ferroelectric Oxide Single-Crystalline Layers by Wafer Bonding and Hydrogen/Helium Implantation
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 748 2003 Materials Research Society U11.8.1 Ferroelectric Oxide Single-Crystalline Layers by Wafer Bonding and Hydrogen/Helium Implantation Ionut Radu, Izabela Szafraniak,
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 748 2003 Materials Research Society U11.8.1 Ferroelectric Oxide Single-Crystalline Layers by Wafer Bonding and Hydrogen/Helium Implantation Ionut Radu, Izabela Szafraniak,
2. High Efficiency Crystalline Si Solar Cells
 2 High Efficiency Crystalline Si Solar Cells Students: Karthick Murukesan, Sandeep S S, Meenakshi Bhaisare, Bandana Singha, Kalaivani S and Ketan Warikoo Faculty members: Anil Kottantharayil, B M Arora,
2 High Efficiency Crystalline Si Solar Cells Students: Karthick Murukesan, Sandeep S S, Meenakshi Bhaisare, Bandana Singha, Kalaivani S and Ketan Warikoo Faculty members: Anil Kottantharayil, B M Arora,
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Future Directions. Stuart Bowden BAPVC January Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 12,
 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Future Directions Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 2011 Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 12, 2011 1 Stuart Bowden Co-Director of Solar Power Labs at ASU Work relevant to BAPVC: Pilot
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Future Directions Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 2011 Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 12, 2011 1 Stuart Bowden Co-Director of Solar Power Labs at ASU Work relevant to BAPVC: Pilot
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes
 Chapter 5 Thermal Processes 1 Topics Introduction Hardware Oxidation Diffusion Annealing Post-Implantation Alloying Reflow High Temp CVD Epi Poly Silicon Nitride RTP RTA RTP Future Trends 2 Definition
Chapter 5 Thermal Processes 1 Topics Introduction Hardware Oxidation Diffusion Annealing Post-Implantation Alloying Reflow High Temp CVD Epi Poly Silicon Nitride RTP RTA RTP Future Trends 2 Definition
Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University
![Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University](/thumbs/75/72824557.jpg) 2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
Iron in crystalline silicon solar cells: fundamental properties, detection techniques, and gettering
 Iron in crystalline silicon solar cells: fundamental properties, detection techniques, and gettering Daniel Macdonald, AnYao Liu, and Sieu Pheng Phang Research School of Engineering The Australian National
Iron in crystalline silicon solar cells: fundamental properties, detection techniques, and gettering Daniel Macdonald, AnYao Liu, and Sieu Pheng Phang Research School of Engineering The Australian National
THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts
 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. Oxide Thickness µm 0. µm 0 nm nm Thermally Grown Oxides
THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. Oxide Thickness µm 0. µm 0 nm nm Thermally Grown Oxides
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in
 Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
SEMICONDUCTORS R. A. SMITH CAMBRIDGE AT THE UNIVERSITY PRESS. M.A., PH.D. Head of the Physics Department Royal Radar Establishment Malvern J 959
 SEMICONDUCTORS BY R. A. SMITH M.A., PH.D. Head of the Physics Department Royal Radar Establishment Malvern CAMBRIDGE AT THE UNIVERSITY PRESS J 959 CONTENTS Chapter 1. The Elementary Properties of Semiconductors
SEMICONDUCTORS BY R. A. SMITH M.A., PH.D. Head of the Physics Department Royal Radar Establishment Malvern CAMBRIDGE AT THE UNIVERSITY PRESS J 959 CONTENTS Chapter 1. The Elementary Properties of Semiconductors
