Density What is density? How do you measure density?
|
|
|
- Judith Briggs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Density What is density? How do you measure density?
2 What is density? Density describes how much mass is in a given volume of a material. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. Volume: the amount of space an object occupies (takes up).
3 What is density? Think about the many kinds of matter you come into contact with every day. Wood, cement, aluminum, plastic, foam, steel, etc. Water, soda, cooking oil or hand soap. Air, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, helium. All of these materials have mass and volume. All have their own unique density!
4 What is density? A cube of steel and a cube of aluminum both have the SAME volume. Volume of a cube: L x H x W 1cm X 1cm X 1cm = 1 cm 3
5 What is density? A cube of steel and a cube of aluminum may be the same size, but the steel has a lot more mass than the aluminum.
6 Steel has a high density; 7.8 grams of mass per cubic centimeter.(grams/ cm 3) Aluminum has a lower density; 2.7 grams/ cm 3.
7 Steel has a high density; 7.8 grams of mass per cubic centimeter. Aluminum has a lower density; 2.7 grams/ cm 3. The more matter you place into a defined volume, the denser it becomes.
8 The more matter you place into a defined volume, the denser it becomes. A B Which box has more matter inside of it?
9 Which one is MORE dense? Which box has more red balls inside of it? If each box has the same volume, and each ball has the same mass, which box would have more mass? Why? Which box has more density? Why?
10 For example, New York City is DENSELY populated because there are a lot of people in a small area. 20 people in an elevator is DENSER than 2 people in an elevator.
11 Which has more mass? 100 kilograms of lead or 100kilograms of feathers?
12 Lead and Feathers Although 100kg of feathers may take up much more room than 100 kg of lead, they both still have 100 kg of mass! The lead is heavier for its size, due to the fact that it is denser!!!. Thus, a material such as feathers takes up much more room (volume) than a denser material such as lead, for the same mass. The feathers are less dense than the lead.
13 Calculating Density
14 Use the triangle tool to help with Density word problems M D V
15 Use the triangle tool to help with Density word problems Cover the Measurement Of what you Need to calculate. D = M / V M D V
16 Use the triangle tool to help with Density word problems Cover the Measurement Of what you Need to calculate M = D x V M D V
17 Use the triangle tool to help with Density word problems Cover the Measurement Of what you Need to calculate V = M / D M D V
18 Density Problem Examples 1. A cube 5.0 cm on a side has a mass of 750.0g Find the Density! Volume of a cube L x W x H 5cm x 5 cm x 5 cm = 125 cm3 density = mass / volume mass =750.0g g/ 125 cm3 density = 6.0 g/cm3
19 2.A student determines the density of manganese to be 5.54 g/cm 3. If a sample had a mass of 3.43g what was the volume? V = M / D Mass = Dnsity= 3.43 g/ 5.54 g/cm3 V=.62 cm 3
20 3. The density of a gas is g/cm 3. Find the mass of 280 cm 3 of this gas. M= D x V D = g/cm 3. V= 280 cm x 280 Mass = g
21 Density is a property of materials - independent of shape or quantity. For example, a steel nail and a steel cube have different amounts of matter and therefore different masses. They also have different volumes. However, if you calculate density by dividing mass by volume, the result is the same for both the nail and the cube.
22 Density of Common Materials Solids that are strong, such as steel, typically have high density. High density means there are many atoms per cubic centimeter. Soft materials typically have lower density. Solids with low density, such as cork or foam, are often used as cushioning material. Low density means there are relatively large spaces between atoms.
23 Why does density vary? The density of a material depends on two things: 1. the individual mass of each atom or molecule 2. on how tightly the atoms are packed A diamond is made of carbon atoms and has a density of 3,500 kg/m3. The carbon atoms in diamonds are closely packed.
24 Paraffin wax is mostly carbon, but the density of paraffin is only 870 kg/m3. The density of paraffin is low because the carbon atoms are mixed with hydrogen atoms in long molecules that take up a lot of space.
25 Calculating Density There are several different ways to find the density of an objects. It depends on the shape of the object.
26 Cubes & Rectangular Prisms 1. Find mass Use a balance Units: grams or kg 2. Find volume Use a ruler Measure all 3 sides: length, width, height Units: cm 3, m 3, km 3 Use this equation: 3. Density = mass / volume Units: g/cm 3
27 Cylinders 1. Find mass 2. Find volume Use a ruler Measure the height & diameter Divide the diameter in half to find the radius Units: cm 3, m 3, km 3 Use this equation: 3. Density = mass / volume Units: g/cm 3
28 Irregular Objects 1. Find mass 2. Find volume Displacement method Fill a graduated cylinder with water. Drop the object in without splashing water. Calculate the change in volume! Units: ml, L 3. Density = mass / volume Units: g/ml
CHAPTER 2 HW PRACTICE SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 HW PRACTICE SOLUTIONS SIGNIFICANT FIGURES 1.) How many significant figures are shown in each of the following numbers? a. 0.0320 3 SF c. 503.10 5 SF e. 0.00702 3 SF b. 8000 1 SF d. 91,000,000
CHAPTER 2 HW PRACTICE SOLUTIONS SIGNIFICANT FIGURES 1.) How many significant figures are shown in each of the following numbers? a. 0.0320 3 SF c. 503.10 5 SF e. 0.00702 3 SF b. 8000 1 SF d. 91,000,000
DETERMINING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS & SOLIDS - worksheet
 DETERMINING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS & SOLIDS - worksheet 17 Density, like color, odor, melting point, and boiling point, is a physical property of matter. Therefore, density may be used in identifying matter.
DETERMINING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS & SOLIDS - worksheet 17 Density, like color, odor, melting point, and boiling point, is a physical property of matter. Therefore, density may be used in identifying matter.
Density. How tightly the atoms are packed together in an object
 Density How tightly the atoms are packed together in an object Mass vs Weight Mass is the amount of matter in an object. (it doesn t change) Weight is determined based on the amount of gravity pulling
Density How tightly the atoms are packed together in an object Mass vs Weight Mass is the amount of matter in an object. (it doesn t change) Weight is determined based on the amount of gravity pulling
NOTE: If substances have the SAME VOLUME, they can have DIFFERENT MASSES.
 Grade 8 SCIENCE Chapter 8 questions Page 306 1. When particles are CLOSER TOGETHER, DENSITY is GREATER. 2. Particles in SOLIDS have FEWER SPACES between them. The ATTRACTIVE FORCES between the particles
Grade 8 SCIENCE Chapter 8 questions Page 306 1. When particles are CLOSER TOGETHER, DENSITY is GREATER. 2. Particles in SOLIDS have FEWER SPACES between them. The ATTRACTIVE FORCES between the particles
Directions: Complete the following prior to class. Be prepared to show your work on the board.
 Worksheet L4X Student s Name Directions: Complete the following prior to class. Be prepared to show your work on the board. 1) Convert 30 ml to oz, qt, L, gal. 2) Convert 16 oz to kg, lb, tons, g. Page
Worksheet L4X Student s Name Directions: Complete the following prior to class. Be prepared to show your work on the board. 1) Convert 30 ml to oz, qt, L, gal. 2) Convert 16 oz to kg, lb, tons, g. Page
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET
 SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET PART 1 - Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. 1.) 0.02 2.) 0.020 3.) 501 4.) 501.0 5.) 5,000 6.) 5,000. 7.) 6,051.00 8.) 0.0005 9.) 0.1020
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET PART 1 - Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. 1.) 0.02 2.) 0.020 3.) 501 4.) 501.0 5.) 5,000 6.) 5,000. 7.) 6,051.00 8.) 0.0005 9.) 0.1020
Determining the Density of Unknown Substances
 Determining the Density of Unknown Substances Introduction: Most of the elements on the periodic table are metals and solids. These elements have observable properties that make it possible to identify
Determining the Density of Unknown Substances Introduction: Most of the elements on the periodic table are metals and solids. These elements have observable properties that make it possible to identify
Experiment #3. Density
 Experiment #3. Density Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background Density is the mass per unit volume of a
Experiment #3. Density Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background Density is the mass per unit volume of a
Copyright 2014 Science Doodles
 Copyright 2014 Science Doodles If a scientist comes across an unknown element, could she use density to identify the element? A. Yes, because each element has a specific density. B. No, because density
Copyright 2014 Science Doodles If a scientist comes across an unknown element, could she use density to identify the element? A. Yes, because each element has a specific density. B. No, because density
LESSON hat is density? 24
 LESSON hat is density? 24 Rocks are heavy. A small box of rocks has a large. Yet a box of the same size containing corks has a small. How can objects that are the same size have different es? Scientists
LESSON hat is density? 24 Rocks are heavy. A small box of rocks has a large. Yet a box of the same size containing corks has a small. How can objects that are the same size have different es? Scientists
T. Trimpe Lesson 1: Length
 T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
Density. The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the topic of density by determining the densities of some materials.
 Density Goals The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the topic of density by determining the densities of some materials. Introduction There is a lesson in the old bromide: Which is heavier,
Density Goals The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the topic of density by determining the densities of some materials. Introduction There is a lesson in the old bromide: Which is heavier,
Lab 0.4: Density and Thickness of Aluminum Foil
 Name Block Lab 0.4: Density and Thickness of Aluminum Foil Student will be able to: Correctly use measuring instruments with accuracy Correctly apply the principles of significant figures in measurements
Name Block Lab 0.4: Density and Thickness of Aluminum Foil Student will be able to: Correctly use measuring instruments with accuracy Correctly apply the principles of significant figures in measurements
DENSITY of Solids and Liquids
 Regents Earth Science Name: Date: Lab # DENSITY of Solids and Liquids Introduction: Density is the term used to describe the relationship between the mass of an object and its volume. Under given conditions
Regents Earth Science Name: Date: Lab # DENSITY of Solids and Liquids Introduction: Density is the term used to describe the relationship between the mass of an object and its volume. Under given conditions
Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity.
 Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity. Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density and specific gravity of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background
Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity. Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density and specific gravity of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background
Density (d) is a property of a substance equal to the ratio of its mass (m) to its volume (V): d = m V
 Experiment 2 Name: DEN 14 Si TY In this experiment, you will learn about density and practice the proper way to report measurements and calculated quantities. Properties Properties of a substance can be
Experiment 2 Name: DEN 14 Si TY In this experiment, you will learn about density and practice the proper way to report measurements and calculated quantities. Properties Properties of a substance can be
D =? D = M = 10 g = 5 g/cm 3 M = 10 g V 2 cm 3 V = 2 cm 3 5 g/cm 3
 Using the formula for density, answer the following calculation problems. M D = (g/ml or g/cm 3 ) Density = Mass D = M M = (g) Volume V D V V = (ml or cm 3 ) For all of your problems, please complete them
Using the formula for density, answer the following calculation problems. M D = (g/ml or g/cm 3 ) Density = Mass D = M M = (g) Volume V D V V = (ml or cm 3 ) For all of your problems, please complete them
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use.
 This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
Measurement and Density - Experiment 1
 Measurement and Density - Experiment 1 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to acquaint you with some common metric units of length, volume, and mass. You will also measure the density of an unknown
Measurement and Density - Experiment 1 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to acquaint you with some common metric units of length, volume, and mass. You will also measure the density of an unknown
v = 5.00cm x 3.00cm x 2.00cm 2. What is the volume of a marble that has a mass of 3.0 g and a density of 2.7 g/ml? Formula (density) Substitution
 Name: STUDY GUIDE: MEASUREMENT, DENSITY, MASS, VOLUME, AND DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS (2016) 1. A solid block is 5.00 cm high, 3.00 cm wide, and 2.00 cm long. It has a mass of 129 g. What is the density? Formula
Name: STUDY GUIDE: MEASUREMENT, DENSITY, MASS, VOLUME, AND DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS (2016) 1. A solid block is 5.00 cm high, 3.00 cm wide, and 2.00 cm long. It has a mass of 129 g. What is the density? Formula
Lab Section. Experiment 2 Density. Introduction
 Experiment 2 Density Introduction Density (given the symbol d or ρ depending upon which book you read) is an intrinsic property of materials. The term intrinsic means that it is independent upon the amount
Experiment 2 Density Introduction Density (given the symbol d or ρ depending upon which book you read) is an intrinsic property of materials. The term intrinsic means that it is independent upon the amount
Topic 1 Review Questions Set 1
 Topic 1 Review Questions Set 1 Base your answers to questions 1-5 on your knowledge of Earth Science, the Earth Science Reference Tables, and the diagrams below. The diagrams represent three samples of
Topic 1 Review Questions Set 1 Base your answers to questions 1-5 on your knowledge of Earth Science, the Earth Science Reference Tables, and the diagrams below. The diagrams represent three samples of
Quest Chapter 18. If you don t already know, check out the materials online, or read #4.
 1 (part 1 of 2) In everyday use, the word dense is often used interchangeably with the word hard. In physics, density and hardness have completely different meanings. Which object is the densest? 1. lead
1 (part 1 of 2) In everyday use, the word dense is often used interchangeably with the word hard. In physics, density and hardness have completely different meanings. Which object is the densest? 1. lead
ES 106 Laboratory # 1 PROPERTIES OF WATER
 ES 106 Laboratory # 1 PROPERTIES OF WATER 1-1 Introduction What are the physical and chemical properties of water that make it so unique and necessary for living things? When you look at water, taste and
ES 106 Laboratory # 1 PROPERTIES OF WATER 1-1 Introduction What are the physical and chemical properties of water that make it so unique and necessary for living things? When you look at water, taste and
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example,
 SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example, density, thermal or electrical conductivity, solubility,
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example, density, thermal or electrical conductivity, solubility,
Density Measurements Background
 Density Measurements Background The density (ρ) of a substance or an object is defined by its mass (m) divided by its volume (V):!"#$%&' =!"##!"#$%&!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! =!! The units used
Density Measurements Background The density (ρ) of a substance or an object is defined by its mass (m) divided by its volume (V):!"#$%&' =!"##!"#$%&!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! =!! The units used
T. Trimpe Lesson 1: Length
 T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
Practice with Properties of Matter. Practice with Physical and Chemical Changes. Practice with Mixtures and Pure Substances
 Chapter 1 Practice Problems Practice with Properties of Matter Indicate whether each of the following statements describes a physical or a chemical property. a) the normal color of elemental bromine is
Chapter 1 Practice Problems Practice with Properties of Matter Indicate whether each of the following statements describes a physical or a chemical property. a) the normal color of elemental bromine is
Science 8. Unit 1. Booklet
 Science 8 Unit 1 Mixture and Flow of Matter Booklet Name: Class: 1 TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT The Particle Model Goal Demonstrate your understanding of the particle model and changes of state. BLM 1-1 Answer
Science 8 Unit 1 Mixture and Flow of Matter Booklet Name: Class: 1 TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT The Particle Model Goal Demonstrate your understanding of the particle model and changes of state. BLM 1-1 Answer
Unit-2. Properties of Matter. Solutions 2.1 Matter & Density page V 1 =4.3.6=72 cm 3. Volume of the removed triangular prism (V 2 )
 2.1 & Density page - 61 1. A solid object is given in the figure. Volume of the rectangular prism (V 1 ) V 1 =4.3.6=72 cm 3 Volume of the removed triangular prism (V 2 ) V 2 =((2.3)/2).6=18 cm 3 What is
2.1 & Density page - 61 1. A solid object is given in the figure. Volume of the rectangular prism (V 1 ) V 1 =4.3.6=72 cm 3 Volume of the removed triangular prism (V 2 ) V 2 =((2.3)/2).6=18 cm 3 What is
SOLIDS: Mass, Volume and Density Measurements
 CHEM 1411 Lab Solids: Mass, Volume, and Density 23 SOLIDS: Mass, Volume and Density Measurements A. Overview Review Sections 1.4-1.6 in your textbook (Chemistry: The Central Science, 9th Ed., Brown, LeMay,
CHEM 1411 Lab Solids: Mass, Volume, and Density 23 SOLIDS: Mass, Volume and Density Measurements A. Overview Review Sections 1.4-1.6 in your textbook (Chemistry: The Central Science, 9th Ed., Brown, LeMay,
Chemistry: The Central Science, 12e (Brown et al.) Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement. 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Chemistry: The Central Science, 12e (Brown et al.) Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) In the following list, only is not an example of matter. A) planets B)
Chemistry: The Central Science, 12e (Brown et al.) Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) In the following list, only is not an example of matter. A) planets B)
Seawater TA Initials: for finished Activity. 1 & 2 Or lose 10% of credit!
 Name: Section/ TA: Seawater TA Initials: for finished Activity. 1 & 2 Or lose 10% of credit! Seawater is an unusual substance. It is pure water mixed with various salts, trace elements, and gases. The
Name: Section/ TA: Seawater TA Initials: for finished Activity. 1 & 2 Or lose 10% of credit! Seawater is an unusual substance. It is pure water mixed with various salts, trace elements, and gases. The
Density of Matter. Fast Track GRASP Math Packet. Photo by Ben Stephenson (Wikimedia Commons) Version 1.0 Released 12/4/2018
 Density of Matter Fast Track GRASP Math Packet Photo by Ben Stephenson (Wikimedia Commons) Version 1.0 Released 12/4/2018 This Fast Track GRASP Math Packet was made possible through support from the New
Density of Matter Fast Track GRASP Math Packet Photo by Ben Stephenson (Wikimedia Commons) Version 1.0 Released 12/4/2018 This Fast Track GRASP Math Packet was made possible through support from the New
Density of Matter. Fast Track GRASP Math Packet. Photo by Ben Stephenson (Wikimedia Commons) Version 1.2 Released 1/16/2019
 Density of Matter Fast Track GRASP Math Packet Photo by Ben Stephenson (Wikimedia Commons) Version 1.2 Released 1/16/2019 This Fast Track GRASP Math Packet was made possible through support from the New
Density of Matter Fast Track GRASP Math Packet Photo by Ben Stephenson (Wikimedia Commons) Version 1.2 Released 1/16/2019 This Fast Track GRASP Math Packet was made possible through support from the New
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter.
 1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
DETERMINING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS & SOLIDS
 DETERMINING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS & SOLIDS Density, like color, odor, melting point, and boiling point, is a physical property of matter. Therefore, density may be used in identifying matter. Density
DETERMINING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS & SOLIDS Density, like color, odor, melting point, and boiling point, is a physical property of matter. Therefore, density may be used in identifying matter. Density
2.3 Density and Density Calculations
 2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
M. It is expressed in units such a g/cc,
 Experiment 2 Density Part I: Density of a solid Density is defined as mass per unit volume, D = V M. It is expressed in units such a g/cc, g/ml, lb/ft 3, etc. Determination of mass is done by weighing
Experiment 2 Density Part I: Density of a solid Density is defined as mass per unit volume, D = V M. It is expressed in units such a g/cc, g/ml, lb/ft 3, etc. Determination of mass is done by weighing
Creation Settings. can be separated into two or more pure substances by distillation. can be separated into two or more substances by chromatography.
 Page 1 of 10 TEST BANK (ACCT3321_201_1220) > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to
Page 1 of 10 TEST BANK (ACCT3321_201_1220) > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to
atoms = 1.66 x g/amu
 CHAPTER 2 Q1- How many grams are there in a one amu of a material? A1- In order to determine the number of grams in one amu of material, appropriate manipulation of the amu/atom, g/mol, and atom/mol relationships
CHAPTER 2 Q1- How many grams are there in a one amu of a material? A1- In order to determine the number of grams in one amu of material, appropriate manipulation of the amu/atom, g/mol, and atom/mol relationships
Name # Date Period! FINDING&VOLUME&AND&DENSITY& !!! !!!!!!!
 Name # Date Period FINDING&VOLUME&AND&DENSITY& TherectangularshapedboxinFigure1isfilledwithdrysand.Findthe volumeanddensityofthesand. 1.Firstfindthevolumeofthebox.Thisisalsothevolumeofthesand. Usethediagramtofindthedimensionsofthebox.
Name # Date Period FINDING&VOLUME&AND&DENSITY& TherectangularshapedboxinFigure1isfilledwithdrysand.Findthe volumeanddensityofthesand. 1.Firstfindthevolumeofthebox.Thisisalsothevolumeofthesand. Usethediagramtofindthedimensionsofthebox.
Introduction to Density
 Introduction to Density INTRODUCTION Which is heavier, a pound of aluminum or a pound of lead? The answer, of course, is neither, but many people confuse the words "heavy" and "dense". "Heavy" refers to
Introduction to Density INTRODUCTION Which is heavier, a pound of aluminum or a pound of lead? The answer, of course, is neither, but many people confuse the words "heavy" and "dense". "Heavy" refers to
Item 36 has not been slated for public release in 2011.
 S Use the power-plant diagrams and information below to answer questions 35 37. Power Plants 35. Which describes a chemical change and a physical change that take place during the production of electricity
S Use the power-plant diagrams and information below to answer questions 35 37. Power Plants 35. Which describes a chemical change and a physical change that take place during the production of electricity
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Density.
 1.4 ensity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International Examinations(IE) General Physics 1.4 ensity Question Paper Time llowed: 20 minutes Score:
1.4 ensity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International Examinations(IE) General Physics 1.4 ensity Question Paper Time llowed: 20 minutes Score:
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS
 ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
, as well as some other materials. Use boiling point elevation to determine the percentages of each by mass.
 Remarks: - Use appropriate units. Note: SI units are always acceptable. - If you take apart the test, write your team number on every page in the space provided. - Sometimes, the answers won t make sense.
Remarks: - Use appropriate units. Note: SI units are always acceptable. - If you take apart the test, write your team number on every page in the space provided. - Sometimes, the answers won t make sense.
Standard Test Procedures Manual
 STP 205-5 Standard Test Procedures Manual 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test 1.2. Application of Test This method describes the procedure for determining the relationship between the moisture content and
STP 205-5 Standard Test Procedures Manual 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test 1.2. Application of Test This method describes the procedure for determining the relationship between the moisture content and
This pyramid is cut by the plane shown. The plane is parallel to the base of the square pyramid. What is the shape of the crosssection?
 Geometry EOC (GSE) Quiz Equations and Measurement - (MGSE9-12.G.GMD.4) Identify Shapes, (MGSE9-12.G.MG.1) Describe Objects, (MGSE9-12.G.MG.2) Density Concepts, (MGSE9-12.G.MG.3) Geometric Methods 1) Student
Geometry EOC (GSE) Quiz Equations and Measurement - (MGSE9-12.G.GMD.4) Identify Shapes, (MGSE9-12.G.MG.1) Describe Objects, (MGSE9-12.G.MG.2) Density Concepts, (MGSE9-12.G.MG.3) Geometric Methods 1) Student
Geometric formulas for volume include: Where r is the radius of the cylinder and h is the height. Volume of a rectangular prism = LxWxH
 Supplement Density The density of an object is defined as its mass per unit of volume. The formula below may be used to calculate the density of an object: Density = mass/volume Volume may be measured
Supplement Density The density of an object is defined as its mass per unit of volume. The formula below may be used to calculate the density of an object: Density = mass/volume Volume may be measured
PHARMACOPOEIAL DISCUSSION GROUP BULK AND TAPPED DENSITY OF SOLIDS
 PHARMACOPOEIAL DISCUSSION GROUP BULK AND TAPPED DENSITY OF SOLIDS It is understood that sign-off covers the technical content of the draft and each party will adapt it as necessary to conform to the usual
PHARMACOPOEIAL DISCUSSION GROUP BULK AND TAPPED DENSITY OF SOLIDS It is understood that sign-off covers the technical content of the draft and each party will adapt it as necessary to conform to the usual
(b) Fertilizers help to increase agricultural production. chemical property physical property
 Score 1. [Chang7 1.P.011.] Do the following statements describe chemical or physical properties? (a) Oxygen gas supports combustion. chemical property physical property (b) Fertilizers help to increase
Score 1. [Chang7 1.P.011.] Do the following statements describe chemical or physical properties? (a) Oxygen gas supports combustion. chemical property physical property (b) Fertilizers help to increase
KATEDRA MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ A CHEMIE. 123MAEN basic materials properties
 KATEDRA MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ A CHEMIE 123MAEN basic materials properties Porosity very important quantity - especially for insulating materials. Determination on the basis of bulk and matrix density
KATEDRA MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ A CHEMIE 123MAEN basic materials properties Porosity very important quantity - especially for insulating materials. Determination on the basis of bulk and matrix density
To become bigger or make bigger the amount or size of something.
 Increase Decrease (Reduce) State of Matter Property Density Energy Temperature To become bigger or make bigger the amount or size of something. To become smaller or make smaller the amount or size of something.
Increase Decrease (Reduce) State of Matter Property Density Energy Temperature To become bigger or make bigger the amount or size of something. To become smaller or make smaller the amount or size of something.
N = N A ρ Pb A Pb. = ln N Q v kt. 지난문제. Below are shown three different crystallographic planes for a unit cell of some hypothetical metal.
 지난문제. Below are shown three different crystallographic planes for a unit cell of some hypothetical metal. The circles represent atoms: (a) To what crystal system does the unit cell belong? (b) What would
지난문제. Below are shown three different crystallographic planes for a unit cell of some hypothetical metal. The circles represent atoms: (a) To what crystal system does the unit cell belong? (b) What would
Practice Problems; Chapter#1
 Practice Problems; Chapter#1 #1. Determine the density of an object that has a mass of 149.8 g and displaces 12.1 ml of water when placed in a graduated cylinder. A) 8.08 g/ml B) 1.38 g/ml C) 12.4 g/ml
Practice Problems; Chapter#1 #1. Determine the density of an object that has a mass of 149.8 g and displaces 12.1 ml of water when placed in a graduated cylinder. A) 8.08 g/ml B) 1.38 g/ml C) 12.4 g/ml
European Pharmacopoeia
 i PHARMACOPOEIAL DISCUSSION GROUP REV 1 - CORR 1 G02 Bulk density and tapped density of powders It is understood that sign-off covers the technical content of the draft and each party will adapt it as
i PHARMACOPOEIAL DISCUSSION GROUP REV 1 - CORR 1 G02 Bulk density and tapped density of powders It is understood that sign-off covers the technical content of the draft and each party will adapt it as
DENSITY OF MATTER. To experimentally determine the densities of given solids and liquids.
 DENSITY OF MATTER PURPOSE: To experimentally determine the densities of iven solids and liquids. EQUIPMENT: Triple-beam balance, vernier caliper, raduated, lass block, metal, metal sphere, wooden sphere,
DENSITY OF MATTER PURPOSE: To experimentally determine the densities of iven solids and liquids. EQUIPMENT: Triple-beam balance, vernier caliper, raduated, lass block, metal, metal sphere, wooden sphere,
Practice Problems; Chapter#1
 Practice Problems; Chapter#1 #1. Determine the density of an object that has a mass of 149.8 g and displaces 12.1 ml of water when placed in a graduated cylinder. A) 8.08 g/ml B) 1.38 g/ml C) 12.4 g/ml
Practice Problems; Chapter#1 #1. Determine the density of an object that has a mass of 149.8 g and displaces 12.1 ml of water when placed in a graduated cylinder. A) 8.08 g/ml B) 1.38 g/ml C) 12.4 g/ml
Bulk Density Protocol
 Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the bulk density of each horizon in a soil profile Overview In the field, students collect three soil samples from each horizon in a soil profile using a container
Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the bulk density of each horizon in a soil profile Overview In the field, students collect three soil samples from each horizon in a soil profile using a container
Density Answers to the End of module questions
 IDS 101 Density Answers to the End of module questions 1. You are experimenting with the mysterious substance X. You carefully measure the mass of a uniform 2 ml sample of pure substance X. You slice it
IDS 101 Density Answers to the End of module questions 1. You are experimenting with the mysterious substance X. You carefully measure the mass of a uniform 2 ml sample of pure substance X. You slice it
The Planet s Lungs: Planting Giant Sequoias to Combat Carbon Dioxide
 The Planet s Lungs: Planting Giant Sequoias to Combat Carbon Dioxide By Matthew Auman Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing. This is not controversial. Global warming has been cited
The Planet s Lungs: Planting Giant Sequoias to Combat Carbon Dioxide By Matthew Auman Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing. This is not controversial. Global warming has been cited
* Whenever you have x number of something per y number of something else, the x goes on top and the y goes on bottom.
 Quick Reviews of Basic Math That You ll Need for the Exam Rule #1: When you have finished a problem, the most important thing to ask yourself is does this answer make sense? A. Multiplication & Division
Quick Reviews of Basic Math That You ll Need for the Exam Rule #1: When you have finished a problem, the most important thing to ask yourself is does this answer make sense? A. Multiplication & Division
1.4 Density. Question Paper. Subject Physics (0625) Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) General Physics A* A B C D E U
 1.4 ensity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic General Physics Sub-Topic 1.4 ensity ooklet Question Paper Time llowed: 33 minutes Score:
1.4 ensity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic General Physics Sub-Topic 1.4 ensity ooklet Question Paper Time llowed: 33 minutes Score:
(3) The compound boron nitride (BN) has a high melting point (2967 ºC), high density, and is very hard. What is the best classification of this solid?
 Solids and Liquids Name: Period: (1) Identify the type of solid formed by each compound. (a) Ag (b) CO 2 (c) SiO 2 (d) wax (e) MgCl 2 (f) Fe (g) graphite (h) SO 2 (i) CaCO 3 (j) I 2 (k) rubber (l) SiC
Solids and Liquids Name: Period: (1) Identify the type of solid formed by each compound. (a) Ag (b) CO 2 (c) SiO 2 (d) wax (e) MgCl 2 (f) Fe (g) graphite (h) SO 2 (i) CaCO 3 (j) I 2 (k) rubber (l) SiC
CAMI Education links: Maths Literacy NQF Level 3
 - 1 - CONTENT 1.1 Use numbers correctly when working with problems in the workplace MATHS LITERACY NQF Level 3 LEARNING OUTCOME Use numbers to count, order and estimate Use positive and negative numbers
- 1 - CONTENT 1.1 Use numbers correctly when working with problems in the workplace MATHS LITERACY NQF Level 3 LEARNING OUTCOME Use numbers to count, order and estimate Use positive and negative numbers
Experiment: Measurements
 Experiment: Measurements I. INTRODUCTION Measurements are essential to experimental sciences such as chemistry, physics, biology, and geology. The measurements are usually made using the metric system
Experiment: Measurements I. INTRODUCTION Measurements are essential to experimental sciences such as chemistry, physics, biology, and geology. The measurements are usually made using the metric system
Iÿtÿÿeÿ/ÿrh Jÿtcket. Tÿlchÿwÿeÿ
 o 0 Iÿtÿÿeÿ/ÿrh Jÿtcket Tÿlchÿwÿeÿ Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Classify each of the pictures below by placing the correct label in the blanks below: A= Element D-- Mixture of compounds B= Compound
o 0 Iÿtÿÿeÿ/ÿrh Jÿtcket Tÿlchÿwÿeÿ Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Classify each of the pictures below by placing the correct label in the blanks below: A= Element D-- Mixture of compounds B= Compound
Standard Test Procedures Manual
 STP 208-3 Standard Test Procedures Manual 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the procedure for determining the relationship between the moisture content and density for soil cement
STP 208-3 Standard Test Procedures Manual 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the procedure for determining the relationship between the moisture content and density for soil cement
Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3
 Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
Basic Measuring and Calculations. Formulas, Workings Hints and Tips
 Basic Measuring and Calculations Formulas, Workings Hints and Tips Start by writing down the formula When working out mathematics Ensure you show all working out (Marks will be awarded for working out)
Basic Measuring and Calculations Formulas, Workings Hints and Tips Start by writing down the formula When working out mathematics Ensure you show all working out (Marks will be awarded for working out)
Part II. [24 pts] Problems [6 pts] How many ml of soda are there in a bottle that contains 16 liq oz?
![Part II. [24 pts] Problems [6 pts] How many ml of soda are there in a bottle that contains 16 liq oz? Part II. [24 pts] Problems [6 pts] How many ml of soda are there in a bottle that contains 16 liq oz?](/thumbs/96/129255969.jpg) CHM 1030 Examination 1A January 30, 2002 SOME GENERAL INFORMATION 1 in = 2.54 cm 1 mile = 5280 ft 16 oz = 1 lb = 453.6 g 32 liq oz = 1 qt = 0.25 gal = 0.946 L speed of light (c) = 2.998 10 8 m/s 1 cal
CHM 1030 Examination 1A January 30, 2002 SOME GENERAL INFORMATION 1 in = 2.54 cm 1 mile = 5280 ft 16 oz = 1 lb = 453.6 g 32 liq oz = 1 qt = 0.25 gal = 0.946 L speed of light (c) = 2.998 10 8 m/s 1 cal
The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel.
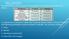 BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
Flowers: natural deployable structures. DEployaBlE structures
 DEployaBlE structures Flowers: natural deployable structures angle width Supported by This resource is designed as an introduction to deployable structures using flowers as an example from the natural
DEployaBlE structures Flowers: natural deployable structures angle width Supported by This resource is designed as an introduction to deployable structures using flowers as an example from the natural
1) An object weighs 75.7 kg. What is this weight in lbs? [1 lb = grams]
![1) An object weighs 75.7 kg. What is this weight in lbs? [1 lb = grams] 1) An object weighs 75.7 kg. What is this weight in lbs? [1 lb = grams]](/thumbs/89/98796796.jpg) CHEMISTRY 51 SPRING 2016 NAME: Exam 1 Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1) An object weighs 75.7 kg. What is this weight in lbs? [1 lb = 453.6 grams] a) 34.3 pounds b) 167 pounds c) 343 pounds d) 16.7 pounds
CHEMISTRY 51 SPRING 2016 NAME: Exam 1 Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1) An object weighs 75.7 kg. What is this weight in lbs? [1 lb = 453.6 grams] a) 34.3 pounds b) 167 pounds c) 343 pounds d) 16.7 pounds
Refer to the Appendices at the back of your lab manual to review laboratory techniques, significant figures and statistical treatment of data.
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT A: Volume of a Solid Cylinder PRELABORATORY ASSIGNMENT: Refer to the Appendices at the back of your lab manual to review laboratory techniques, sinificant fiures and statistical treatment
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT A: Volume of a Solid Cylinder PRELABORATORY ASSIGNMENT: Refer to the Appendices at the back of your lab manual to review laboratory techniques, sinificant fiures and statistical treatment
Chapter 4.1. Estimating Manure Inventory. learning objectives
 Estimating Manure Inventory learning objectives Briefly explain the importance of determining manure weight or volume. Estimate the weight of solid manure in a pile. Estimate the volume of liquid manure
Estimating Manure Inventory learning objectives Briefly explain the importance of determining manure weight or volume. Estimate the weight of solid manure in a pile. Estimate the volume of liquid manure
CHAPTER 1. Conversions. General Plan for Converting Measurements. State the relationship between the unit given and the unit sought as an equality.
 CHAPTER 1 Conversions One of the aims of chemistry is to describe changes to tell what changed, how it changed, and what it changed into. Another aim of chemistry is to look at matter and its changes and
CHAPTER 1 Conversions One of the aims of chemistry is to describe changes to tell what changed, how it changed, and what it changed into. Another aim of chemistry is to look at matter and its changes and
METALLIC CRYSTALS. tend to be densely packed. have several reasons for dense packing: have the simplest crystal structures.
 METALLIC CRYSTALS tend to be densely packed. have several reasons for dense packing: -Typically, only one element is present, so all atomic radii are the same. -Metallic bonding is not directional. -Nearest
METALLIC CRYSTALS tend to be densely packed. have several reasons for dense packing: -Typically, only one element is present, so all atomic radii are the same. -Metallic bonding is not directional. -Nearest
InstrumentationTools.com
 Author: Instrumentation Tools Categories: Formulas Displacer Level Measurement Calculations Displacer Level Measurement Calculations Problem 1 :- A steel displacer of volume 0.25 cubic feet is 50% immersed
Author: Instrumentation Tools Categories: Formulas Displacer Level Measurement Calculations Displacer Level Measurement Calculations Problem 1 :- A steel displacer of volume 0.25 cubic feet is 50% immersed
ENERGY AND PACKING. Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES MATERIALS AND PACKING METALLIC CRYSTALS ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... 1. How do s assemble into solid structures? (For now, focus on metals) ENERGY AND PACKING non dense, random packing bond energy Energy bond
Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... 1. How do s assemble into solid structures? (For now, focus on metals) ENERGY AND PACKING non dense, random packing bond energy Energy bond
Name Class Date. mass of lithium 534 g Li molar mass of lithium 6.94 g/mol Li Unknown:
 Skills Worksheet Math Skills Converting Mass to Amount After you study each sample problem and solution, work out the practice problems on a separate sheet of paper. Write your answers in the spaces provided.
Skills Worksheet Math Skills Converting Mass to Amount After you study each sample problem and solution, work out the practice problems on a separate sheet of paper. Write your answers in the spaces provided.
To convert from grams to kilograms: 1 kilogram = 1,000 grams
 Tips for Making Measurements When you design a structure, it s useful to collect and record quantitative data as evidence for your evaluation. You can use the tips below for making quantitative measurements.
Tips for Making Measurements When you design a structure, it s useful to collect and record quantitative data as evidence for your evaluation. You can use the tips below for making quantitative measurements.
Plasticity and Deformation Processes. Plastic deformation exercises
 Plasticity and Deformation Processes Plastic deformation exercises An aluminum rectangular prism, with sides 60x80x00 cm long and that are oriented parallel to the the x, y, z axes, is subjected to normal
Plasticity and Deformation Processes Plastic deformation exercises An aluminum rectangular prism, with sides 60x80x00 cm long and that are oriented parallel to the the x, y, z axes, is subjected to normal
Solids SECTION Critical Thinking
 SECTION 10.3 Solids A gas has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. A liquid has a definite volume, but not a definite shape. A solid, the third state, has a definite volume and a definite shape.
SECTION 10.3 Solids A gas has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. A liquid has a definite volume, but not a definite shape. A solid, the third state, has a definite volume and a definite shape.
1 Elements. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Look at the illustration and identify one source of iron that comes to Earth from somewhere else.
 CHAPTER 4 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
CHAPTER 4 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
A H M 531 C The Civil Engineering Center
 Objectives: Measuring the strength of a concrete mix designed at the lab. The strengths to be measured are: Compressive strength. Tensile strength. Flexural strength. Standards: Compressive strength: G.S.
Objectives: Measuring the strength of a concrete mix designed at the lab. The strengths to be measured are: Compressive strength. Tensile strength. Flexural strength. Standards: Compressive strength: G.S.
Overview. Learning Objectives: This module provides step-by-step instructions in how to do the Bulk Density Protocol.
 Overview This module provides step-by-step instructions in how to do the Bulk Density Protocol. Learning Objectives: After completing this module, you will be able to: Explain why bulk density is worth
Overview This module provides step-by-step instructions in how to do the Bulk Density Protocol. Learning Objectives: After completing this module, you will be able to: Explain why bulk density is worth
NOTES Minerals.notebook. May 03, ,000. Inorganic. Solid. chemical 3,000. Oxygen. Naturally. elements. Earth's. Crystalline. crust.
 Minerals Mineral Characteristics 1. occurring 2. 3. 4. structure 5. Definite composition Naturally Mineral Characteristics 1. occurring Inorganic 2. Solid 3. Crystalline 4. structure chemical 5. Definite
Minerals Mineral Characteristics 1. occurring 2. 3. 4. structure 5. Definite composition Naturally Mineral Characteristics 1. occurring Inorganic 2. Solid 3. Crystalline 4. structure chemical 5. Definite
Name Class Date. How Much Lumber? Directions: Read the entire lab before doing the procedure and answering the questions.
 Inquiry Lab Outdoors Chapter 11 How Much Lumber? Directions: Read the entire lab before doing the procedure and answering the questions. Problem How can you calculate the amount of lumber in a tree? Background
Inquiry Lab Outdoors Chapter 11 How Much Lumber? Directions: Read the entire lab before doing the procedure and answering the questions. Problem How can you calculate the amount of lumber in a tree? Background
TEST I REVIEW. 1. All of the following are properties of antimony. Which one is not a
 TEST I REVIEW I Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are properties of antimony. Which one is not a physical property? a.
TEST I REVIEW I Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are properties of antimony. Which one is not a physical property? a.
NATURAL GAS Formation of a Clean Source of Energy
 NATURAL GAS Formation of a Clean Source of Energy LESSON SUMMARY This lesson explores how natural gas was formed by identifying states of matter, density, and how density factors into changes in states.
NATURAL GAS Formation of a Clean Source of Energy LESSON SUMMARY This lesson explores how natural gas was formed by identifying states of matter, density, and how density factors into changes in states.
Q11. Helium condenses into the liquid phase at approximately 4 K. What temperature in degrees Fahrenheit, does this correspond to?
 Old-Exam-Questions-Ch.18 T081 Q9. The volume of 1.00 kg water is 958.38 mm 3 at a temperature of 10.0 C and 999.73 mm 3 at temperature of 100.0 C. Calculate coefficient of volume expansion for water in
Old-Exam-Questions-Ch.18 T081 Q9. The volume of 1.00 kg water is 958.38 mm 3 at a temperature of 10.0 C and 999.73 mm 3 at temperature of 100.0 C. Calculate coefficient of volume expansion for water in
Preparing for Technical Training: Essential Skills for Water/Wastewater Operators. Practice Tests
 Practice Tests COURSE OUTLINE: Module # Name Practice Test included Module 1: Basic Math Refresher Module 2: Fractions, Decimals and Percents Module 3: Measurement Conversions Module 4: Linear, Area and
Practice Tests COURSE OUTLINE: Module # Name Practice Test included Module 1: Basic Math Refresher Module 2: Fractions, Decimals and Percents Module 3: Measurement Conversions Module 4: Linear, Area and
Unit I PART I. MATH TOOLS FOR CHEMISTRY I. The Metric System The metric system is the scientific system of units of measurement
 CHEMISTRY 100 LECTURE Unit I PART I. MATH TOOLS FOR CHEMISTRY I. The Metric System The metric system is the scientific system of units of measurement Length Volume Mass METRIC BASIC UNITS LENGTH MASS VOLUME
CHEMISTRY 100 LECTURE Unit I PART I. MATH TOOLS FOR CHEMISTRY I. The Metric System The metric system is the scientific system of units of measurement Length Volume Mass METRIC BASIC UNITS LENGTH MASS VOLUME
WALLBOARD TOOL CO., Inc. Catalog #34 Supplement
 WALLBOARD TOOL CO., Inc. Catalog #34 Supplement Tempered aluminum backing for added strength Ergonomically designed for less user fatigue Blue steel blade 19-038 8 x 3 (203 x 76mm) 19-040 10 x 3 (254 x
WALLBOARD TOOL CO., Inc. Catalog #34 Supplement Tempered aluminum backing for added strength Ergonomically designed for less user fatigue Blue steel blade 19-038 8 x 3 (203 x 76mm) 19-040 10 x 3 (254 x
Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill
 Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill Lesson Overview: Students use the dimensions of the cargo hold of a ship s hull to calculate the volume of material that can be contained. Students will then use the
Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill Lesson Overview: Students use the dimensions of the cargo hold of a ship s hull to calculate the volume of material that can be contained. Students will then use the
EMG 807 Post-test. 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of
 EMG 807 Post-test 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of a. Energy that we use. b. Power that we use. c. Force that we use. a. i only
EMG 807 Post-test 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of a. Energy that we use. b. Power that we use. c. Force that we use. a. i only
(a) Which two measuring instruments should the student use in her investigation? (2)
 1 The photograph shows a water barrel with a tap. The barrel is used to store rainwater. barrel tap A student investigates the water depth in the barrel. She measures the depth and then opens the tap.
1 The photograph shows a water barrel with a tap. The barrel is used to store rainwater. barrel tap A student investigates the water depth in the barrel. She measures the depth and then opens the tap.
Solids, liquids and gases
 Solids, liquids and gases Everything is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Normally, atoms join together to form groups called molecules. Molecules are always moving, even in things that look like
Solids, liquids and gases Everything is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Normally, atoms join together to form groups called molecules. Molecules are always moving, even in things that look like
