Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids. Dr. Coates
|
|
|
- Lynn Griffin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Dr. Coates
2 Learning Objectives I 1. Describe difference in atomic/molecular structure between crystalline/noncrystalline 2. Draw unit cells for FCC, BCC, HCP 3. Derive the relationship between unit cell edge length and atomic radius for FCC, BCC 4. Compute the densities for metals having FCC, BCC given unit cell dimensions 5. Sketch crystallographic directions within unit cells
3 The structure of a material - arrangement of its internal components Subatomic structure Electrons & nuclei within the individual atoms Atomic structure Atoms & molecules within the material Microscopic structure Large groups of atoms aggregated together Macroscopic structure Elements that may be viewed with the naked eye
4 3.2 Fundamental Concepts Crystalline materials Atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances Long-range order Non-crystalline materials (amorphous materials) Do not have long-range order May have short-range order
5 3.2 Fundamental Concepts Atomic hard sphere model Atoms or ions are thought of as being solid spheres having well-defined diameters. Spheres representing nearest-neighbor atoms touch one another.
6 3.2 Fundamental Concepts Lattice A 3-D array of points coinciding with atomic positions
7 In describing crystal structures, it is often convenient to subdivide the structure into small repeat entities called unit cells. 3.3 Unit Cells
8 3.4 Metallic Crystal Structures Atomic bonding is metallic Directional or non-directional? Would number of nearest neighbor atoms be large or small then? How about density of atomic packing? Large or small?
9 3.4 Metallic Crystal Structures Crystal structures of common metals Face-centered cubic crystal structure Body-centered cubic crystal structures Hexagonal close-packed crystal structure
10 Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure
11 Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure Class exercise: Determine the relationship between a and R for an FCC? The lattice parameter a 2 4R a FCC 2R 2 :
12 Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure The total number of atoms per unit cell How many corner atoms? 8 each corner atom is shared by? cells 8 How many face atoms? 6 each face atom is shared by? unit cells 2 total number of atoms per unit cell 1 /8 8 1/ 2 6 4
13 Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure The coordination number (CN) Number of nearest-neighbor or touching atoms CN FCC 12
14 Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure Atomic Packing APF APF Factor (APF): volume of atoms in the unit cell total volume of the unit cell number of atoms in the unit cell volume of an atom total volume of or the unit cell
15 Example 3.1 Calculate the volume of an FCC unit cell in terms of the atomic radius R. The lattice a parameter FCC 2R 2 : Volume of unit cell : V a R 2 16R 2
16 Example 3.2 Show that the APF for the FCC structure is APF number of atoms incell total volume of volume of the unit cell an atom R 4 R a 2R
17 Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure CN of 12 Maximum possible for spheres with same diameter. APF of 0.74 maximum possible for spheres with same diameter.
18
19 Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Crystal Structure
20 Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Crystal Structure The lattice parameter: a 3 2 a 2R BCC 4R 3
21 Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Crystal Structure The total number of atoms per unit cell each corner atom is shared by 8 cells hence, only 1/8 of each corner atom is contained within each cell the center atom is totally contained within the cell total number of atoms per unit cell 1/
22 Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Crystal Structure The coordination number Number of nearest-neighbor or touching atoms CN BCC 8
23 CN of 8 Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Crystal Structure Less than that of the FCC structure. APF of 0.68 Less than that of the FCC structure.
24
25 Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Crystal Structure
26 Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Crystal Structure The total number of atoms per cell six atoms at the corners of the top and bottom planes (basal planes) shared by six unit cells one atom in the center of the top and bottom planes (shared by two unit cells) three atoms in the midplane total number of per cell of HCP atoms 1/ /
27 Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Crystal Structure The short & long unit cell c a 6 - for theideal HCP unit cell dimensions - assuming the atoms are perfect rigid : spheres
28 Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Crystal Structure The coordination number Number of nearest-neighbor or touching atoms CN HCP 12
29 Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Crystal Structure CN of 12 Maximum possible for spheres with same diameter. APF of 0.74 maximum possible for spheres with same diameter.
30 Review:
31 3.5 Density Computations A knowledge of the crystal structure of a metallic solid permits computation of its theoretical density: where n is A is V C N A is na V N C A the atomic the number of the volume of weight, the unit cell is the Avogadro' s number. atoms in each unit cell, and
32 Example 3.4 Copper has an atomic radius of nm, an FCC crystal structure and an atomic weight of 63.5 g/mol. Compute its theoretical density and compare with its measured density.
33 Given : - Cu has an FCC structure A 63.5 g / mol r 0.128nm Theoretical density : na V N C A Example cm g / cm g M easured density 8.94 g 3 / mol / cm 3
34 3.6 Polymorphism and Allotropy Polymorphism Some metals/non-metals have more than one crystal structure Allotropy Elemental solids with more than one crystal structure Carbon as graphite or diamond
35 3.7 Crystal Systems Lattice parameters: a, b, c,, There are seven crystal systems based on unit cell geometry
36
37
38 3.8 Point Coordinates - Miller Indices Coordinates of P : q r s fractional multiples of abc Convention : q, r, s 1 - coordinates are not separated by commas
39 Example 3.5 Locate the point with coordinates ¼ 1 ½.
40 Example 3.6 Specify point coordinates for all atom positions for a BCC unit cell.
41 3.9 Crystallographic Directions A vector of convenient length is positioned such that it passes through the origin of the coordinate system. Any vector may be translated throughout the crystal lattice without alteration, if parallelism is maintained.
42 Crystallographic Directions Algorithm pt. 2 head z pt. 1: tail y 1. Determine coordinates of vector tail, pt. 1: x 1, y 1, & z 1 ; and vector head, pt. 2: x 2, y 2, & z Tail point coordinates subtracted from head point coordinates. 3. Normalize coordinate differences in terms of lattice parameters a, b, and c: x ex: pt. 1 x 1 = 0, y 1 = 0, z 1 = 0 pt. 2 x 2 = a, y 2 = 0, z 2 = c/2 4. Adjust to smallest integer values 5. Enclose in square brackets, no commas [uvw] => 1, 0, 1/2 => 2, 0, 1 => [ 201 ]
43 z Crystallographic Directions pt. 2 head Example 2: pt. 1 x 1 = a, y 1 = b/2, z 1 = 0 pt. 2 x 2 = -a, y 2 = b, z 2 = c y x pt. 1: tail => -2, 1/2, 1 Multiplying by 2 to eliminate the fraction -4, 1, 2 => [ 412 ] where the overbar represents a negative index
44 3.9 Crystallographic Directions For some crystal systems, can have equivalent directions Nonparallel directions with different indices but with same spacing of atoms along each direction Can be grouped into a family of directions <uvw> Cubic crystals 100, 100, 010, 010, 001, 001 are equivalent Grouped together into the family ex. 100
45 Learning Outcomes met thus far! 1. Describe difference in atomic/molecular structure between crystalline/non-crystalline 2. Draw unit cells for FCC, BCC, HCP 3. Derive the relationship between unit cell edge length and atomic radius for FCC, BCC 4. Compute the densities for metals having FCC, BCC given unit cell dimensions 5. Sketch crystallographic directions within unit cells
46 HCP Crystallographic Directions Hexagonal Crystals a 3 4 parameter Miller-Bravais lattice coordinates are related to the direction indices (i.e., uvw) in the 3 space Bravais lattice as follows. z a 2 a 1 - [ UV W ] u v t w 1 (2U -V ) 3 1 (2 V -U) 3 -( u + v ) W [uvtw ]
47 Computing HCP Miller- Bravais Directional Indices (an alternative way): z We confine ourselves to the bravais parallelpiped in the hexagon: a 1 -a 2 -Z and determine: (u,v w ) Here: [1 1 0] - so now apply the models to create M-B Indices a 2 u 1 2 u ' v ' a 3 a 1 - v 1 2 v ' u ' t u v w w' 0 M-B Indices: [11 20]
48 Drawing HCP Crystallographic Directions (ii) Draw the direction in a hexagonal unit cell. Adapted from p. 72, Callister & Rethwisch 9e. s [1213] [1 2 13] Algorithm a 1 a 2 a 3 z 1. Remove brackets Divide by Projections r q p 4. Construct Vector start at point o proceed a/3 units along a 1 axis to point p 2a/3 units parallel to a 2 axis to point q a/3 units parallel to a 3 axis to point r c units parallel to z axis to point s [1213] direction represented by vector from point o to point s 48
49 3.10 Crystallographic Planes 1. If the plane passes through the selected origin, another parallel plane must be constructed by translation within the unit cell to another corner. 2. The length of the planar intercept for each axis is determined in terms of the lattice parameters a, b and c. 3. The reciprocals of the above numbers are taken. A plane that parallels an axis is considered to have an infinite intercept. 4. The numbers are changed to the set of smallest integers by multiplication or division by a common factor. 5. The integer indices, not separated by commas, are enclosed within parentheses: h k l
50 3.10 Crystallographic Planes Parallel planes are equivalent and have identical indices. Unique to cubic crystals Planes & directions having the same indices are perpendicular to one another
51 Crystallographic Planes z example a b c 1. Intercepts Reciprocals 1/1 1/1 1/ Reduction Miller Indices (110) example a b c 1. Intercepts 1/2 2. Reciprocals 1/½ 1/ 1/ 3. Reduction Miller Indices (100) x x a a c c z b b y y
52 Crystallographic Planes example a b c 1. Intercepts 1/2 1 3/4 2. Reciprocals 1/½ 1/1 1/¾ 2 1 4/3 3. Reduction Miller Indices (634) x a c z b y Family of Planes {hkl} Ex: {100} = (100), (010), (001), (100), (010), (001)
53 Determine the Miller indices for the plane shown in the sketch x y z Intercept in terms of lattice parameters Intercepts Reciprocals Reductions Enclosure a -b c/2-1 1/ N/A (012)
54 Crystallographic Planes (HCP) In hexagonal unit cells the same idea is used z example a 1 a 2 a 3 c 1. Intercepts Reciprocals 1 1/ Reduction a 2 a 3 4. Miller-Bravais Indices (1011) a 1 Adapted from Fig. 3.8(a), Callister 7e.
55
56 Example 3.11 Construct a 0 11 plane within a cubic unit cell.
57 Atomic Arrangements
58 3.10 Crystallographic Planes Equivalent planes Have the same atomic packing Can be grouped into a family of planes Cubic crystals, , 1 1 1, 111, 111 are equivalent Grouped together into the family: 111
59 3.11 Linear and Planar Densities Equivalent directions have identical linear density LD # of atoms centered on direction vector length of direction vector Equivalent planes have identical planar density PD # of atoms centered on a area of plane plane
60 3.11 Linear and Planar Densities LD110 # atomscenteredon direction vector (linear length of direction vector atomicdiameter representsatom) 2 4R 1 2R
61 3.11 Linear and Planar Densities PD110 # of atomscenteredon a plane(planar areaof plane circular arearepresentsatom) 2 2 8R R 2
62
63
64 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structure Close-packed directions Directions with maximum atom-packing density Close-packed planes Planes with maximum atom-packing density Atoms packed together are close-packed if they occupy the minimum volume possible (assuming they are incompressible spheres). They would have the maximum possible packing efficiency, defined as the ratio of volume of atoms to volume of space used.
65 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structures FCC structures APF = 0.74 CN = 12 close-packed planes close-packed directions HCP structures APF = 0.74 CN = 12 close-packed planes close-packed directions
66 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structures
67 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structures Centers of this layer are directly above the bottom A layer
68 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structures
69 Centers of this layer are above the C sites of the bottom A layer
70 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structures FCC structures stacking sequence of the close-packed planes is ABCABC HCP structures stacking sequence of the close-packed planes is ABAB
71 3.12 Close-Packed Crystal Structures FCC structures stacking sequence of the close-packed planes is ABCABC HCP structures stacking sequence of the close-packed planes is ABAB
72 3.13 Single Crystals Single crystal the periodic & repeated arrangement of atoms is perfect or extends throughout the material without interruption. Silicon single crystals in the semiconductor industry.
73 3.14 Polycrystalline Materials Polycrystalline Composed of a collection of many crystals or grains
74
75 3.15 Anisotropy Anisotropy Materials having different properties in different directions Isotropy Materials having same properties in all directions.
76 Anisotropy & Isotropy
77 3.17 Non-crystalline Solids Non-crystalline materials (amorphous materials) Do not have long-range order May have short-range order Rapid cooling through the freezing temperature favors formation of a non-crystalline solid Little time is allowed for the ordering process
78 3.17 Non-crystalline Solids
79 Crystalline Solids Metals Normally form crystalline solids Ceramics Crystalline or amorphous Polymers Non-crystalline or semi-crystalline Increasing Tendency to Form crystalline solids
Chapter-3 MSE-201-R. Prof. Dr. Altan Türkeli
 Chapter-3 MSE-201-R Prof. Dr. Altan Türkeli The Structure of Crystalline Solids FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS Solid materials may be classified according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged
Chapter-3 MSE-201-R Prof. Dr. Altan Türkeli The Structure of Crystalline Solids FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS Solid materials may be classified according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged
MME 2001 MATERIALS SCIENCE
 MME 2001 MATERIALS SCIENCE 1 20.10.2015 crystal structures X tal structure Coord. # Atoms/ unit cell a=f(r) APF % SC 6 1 2R 52 BCC 8 2 4R/ 3 68 FCC 12 4 2R 2 74 HCP 12 6 2R 74 Theoretical Density, knowing
MME 2001 MATERIALS SCIENCE 1 20.10.2015 crystal structures X tal structure Coord. # Atoms/ unit cell a=f(r) APF % SC 6 1 2R 52 BCC 8 2 4R/ 3 68 FCC 12 4 2R 2 74 HCP 12 6 2R 74 Theoretical Density, knowing
Ex: NaCl. Ironically Bonded Solid
 Ex: NaCl. Ironically Bonded Solid Lecture 2 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS 3.2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS SOLIDS AMORPHOUS CRYSTALLINE Atoms in an amorphous Atoms in a crystalline solid solid are arranged
Ex: NaCl. Ironically Bonded Solid Lecture 2 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS 3.2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS SOLIDS AMORPHOUS CRYSTALLINE Atoms in an amorphous Atoms in a crystalline solid solid are arranged
Energy and Packing. typical neighbor bond energy. typical neighbor bond energy. Dense, regular-packed structures tend to have lower energy.
 Energy and Packing Non dense, random packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r Dense, regular packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r
Energy and Packing Non dense, random packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r Dense, regular packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r
9/16/ :30 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 17/9/2015 3 Why study the structure
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 17/9/2015 3 Why study the structure
9/28/2013 9:26 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 2 Why study the structure of crystalline solids? Properties of some materials are directly related to their crystal structure. Significant property differences
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 2 Why study the structure of crystalline solids? Properties of some materials are directly related to their crystal structure. Significant property differences
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحیم. Materials Science. Chapter 3 Structures of Metals & Ceramics
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحیم Materials Science Chapter 3 Structures of Metals & Ceramics 1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure?
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحیم Materials Science Chapter 3 Structures of Metals & Ceramics 1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure?
9/29/2014 8:52 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 12/10/2014 Quiz # 1 will be held on Monday 13/10/2014 at 11:00 am
1 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 12/10/2014 Quiz # 1 will be held on Monday 13/10/2014 at 11:00 am
Crystal structure of the material :- the manner in which atoms, ions, or molecules are spatially.
 Crystal structure A crystalline material :- is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances. Crystal structure of the material :- the manner in which
Crystal structure A crystalline material :- is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances. Crystal structure of the material :- the manner in which
CHAPTER 3. Crystal Structures and Crystal Geometry 3-1
 CHAPTER 3 Crystal Structures and Crystal Geometry 3-1 The Space Lattice and Unit Cells 3-2 Atoms, arranged in repetitive 3-Dimensional pattern, in long range order (LRO) give rise to crystal structure.
CHAPTER 3 Crystal Structures and Crystal Geometry 3-1 The Space Lattice and Unit Cells 3-2 Atoms, arranged in repetitive 3-Dimensional pattern, in long range order (LRO) give rise to crystal structure.
ENGINEERING MATERIALS LECTURE #4
 ENGINEERING MATERIALS LECTURE #4 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Topics to Cover What is the difference in atomic arrangement between crystalline and noncrystalline solids? What features
ENGINEERING MATERIALS LECTURE #4 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Topics to Cover What is the difference in atomic arrangement between crystalline and noncrystalline solids? What features
Packing of atoms in solids
 MME131: Lecture 6 Packing of atoms in solids A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s topics Atomic arrangements in solids Points, directions and planes in unit cell References:
MME131: Lecture 6 Packing of atoms in solids A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s topics Atomic arrangements in solids Points, directions and planes in unit cell References:
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS
 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS crystalline material - a material in which atoms, ions, or molecules are situated in a periodic 3-dimensional array over large atomic distances (all metals, many ceramic materials,
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS crystalline material - a material in which atoms, ions, or molecules are situated in a periodic 3-dimensional array over large atomic distances (all metals, many ceramic materials,
STATE OF SOLIDIFICATION & CRYSTAL STRUCTURE
 STATE OF SOLIDIFICATION & CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Chapter Outline Determination of crystal properties or properties of crystalline materials. Crystal Geometry! Crystal Directions! Linear Density of atoms! Crystal
STATE OF SOLIDIFICATION & CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Chapter Outline Determination of crystal properties or properties of crystalline materials. Crystal Geometry! Crystal Directions! Linear Density of atoms! Crystal
General Objective. To develop the knowledge of crystal structure and their properties.
 CRYSTAL PHYSICS 1 General Objective To develop the knowledge of crystal structure and their properties. 2 Specific Objectives 1. Differentiate crystalline and amorphous solids. 2. To explain nine fundamental
CRYSTAL PHYSICS 1 General Objective To develop the knowledge of crystal structure and their properties. 2 Specific Objectives 1. Differentiate crystalline and amorphous solids. 2. To explain nine fundamental
Energy and Packing. Materials and Packing
 Energy and Packing Non dense, random packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r Dense, regular packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r
Energy and Packing Non dense, random packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r Dense, regular packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r
Chapter Outline. How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids?
 Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
 Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed crystal structures Density computations Crystal structure
Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed crystal structures Density computations Crystal structure
MSE420/514: Session 1. Crystallography & Crystal Structure. (Review) Amaneh Tasooji
 MSE420/514: Session 1 Crystallography & Crystal Structure (Review) Crystal Classes & Lattice Types 4 Lattice Types 7 Crystal Classes SIMPLE CUBIC STRUCTURE (SC) Rare due to poor packing (only Po has this
MSE420/514: Session 1 Crystallography & Crystal Structure (Review) Crystal Classes & Lattice Types 4 Lattice Types 7 Crystal Classes SIMPLE CUBIC STRUCTURE (SC) Rare due to poor packing (only Po has this
Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids
 Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids Crystal Structures Points, Directions, and Planes Linear and Planar Densities X-ray Diffraction How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on
Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids Crystal Structures Points, Directions, and Planes Linear and Planar Densities X-ray Diffraction How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on
Solid State Device Fundamentals
 Solid State Device Fundamentals ENS 345 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 Office 4N101b 1 Solids Three types of solids classified according to atomic
Solid State Device Fundamentals ENS 345 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 Office 4N101b 1 Solids Three types of solids classified according to atomic
How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure?
 제 3 장 : 결정질고체의구조 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure? When do material properties vary with the sample (i.e., part)
제 3 장 : 결정질고체의구조 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure? When do material properties vary with the sample (i.e., part)
Single vs Polycrystals
 WEEK FIVE This week, we will Learn theoretical strength of single crystals Learn metallic crystal structures Learn critical resolved shear stress Slip by dislocation movement Single vs Polycrystals Polycrystals
WEEK FIVE This week, we will Learn theoretical strength of single crystals Learn metallic crystal structures Learn critical resolved shear stress Slip by dislocation movement Single vs Polycrystals Polycrystals
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids?
 Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures Face-centered cubic Body-centered cubic Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures Face-centered cubic Body-centered cubic Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Materials Science and Engineering
 Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering Chap. 3. The Structures of Crystalline Solids How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure?
Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering Chap. 3. The Structures of Crystalline Solids How do atoms assemble into solid structures? How does the density of a material depend on its structure?
Materials Science ME 274. Dr Yehia M. Youssef. Materials Science. Copyright YM Youssef, 4-Oct-10
 ME 274 Dr Yehia M. Youssef 1 The Structure of Crystalline Solids Solid materials may be classified according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another. A crystalline
ME 274 Dr Yehia M. Youssef 1 The Structure of Crystalline Solids Solid materials may be classified according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another. A crystalline
Chapter 3: Atomic and Ionic Arrangements. Chapter 3: Atomic and Ionic Arrangements Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 3: Atomic and Ionic Arrangements 3-1 Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Short-range order versus long-range order Amorphous materials Lattice, basis, unit cells, and crystal structures
Chapter 3: Atomic and Ionic Arrangements 3-1 Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Short-range order versus long-range order Amorphous materials Lattice, basis, unit cells, and crystal structures
Carbon nanostructures. (http://www.mf.mpg.de/de/abteilungen/schuetz/index.php?lang=en&content=researchtopics&type=specific&name=h2storage)
 Carbon nanostructures (http://www.mf.mpg.de/de/abteilungen/schuetz/index.php?lang=en&content=researchtopics&type=specific&name=h2storage) 1 Crystal Structures Crystalline Material: atoms arrange into a
Carbon nanostructures (http://www.mf.mpg.de/de/abteilungen/schuetz/index.php?lang=en&content=researchtopics&type=specific&name=h2storage) 1 Crystal Structures Crystalline Material: atoms arrange into a
Chapter1: Crystal Structure 1
 Chapter1: Crystal Structure 1 University of Technology Laser Engineering & Optoelectronic Department Glass: 3 rd year Optoelectronic Engineering Subject: Solid state physics & material science Ass. Prof.
Chapter1: Crystal Structure 1 University of Technology Laser Engineering & Optoelectronic Department Glass: 3 rd year Optoelectronic Engineering Subject: Solid state physics & material science Ass. Prof.
Metallic crystal structures The atomic bonding is metallic and thus non-directional in nature
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids Hw: 4, 6, 10, 14, 18, 21, 26, 31, 35, 39, 42, 43, 46, 48, 49, 51, 56, 61 Due Wensday 14/10/2009 Quiz1 on Wensday 14/10/2009 Why study the structure of crystalline
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids Hw: 4, 6, 10, 14, 18, 21, 26, 31, 35, 39, 42, 43, 46, 48, 49, 51, 56, 61 Due Wensday 14/10/2009 Quiz1 on Wensday 14/10/2009 Why study the structure of crystalline
Chapter One: The Structure of Metals
 Fourth Edition SI Version Chapter One: The Structure of Metals 2010. Cengage Learning, Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 1.1 Importance of the structure: Structures Processing Properties Applications Classification
Fourth Edition SI Version Chapter One: The Structure of Metals 2010. Cengage Learning, Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 1.1 Importance of the structure: Structures Processing Properties Applications Classification
Point coordinates. Point coordinates for unit cell center are. Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111
 Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Solid State Device Fundamentals
 Solid State Device Fundamentals ENS 345 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 Office 4N101b 1 Interatomic bonding Bonding Forces and Energies Equilibrium
Solid State Device Fundamentals ENS 345 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 Office 4N101b 1 Interatomic bonding Bonding Forces and Energies Equilibrium
Chapter 3: Structures of Metals & Ceramics
 Chapter 3: Structures of Metals & Ceramics School of Mechanical Engineering Professor Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 3-1 Chapter 3: Structures of Metals & Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into
Chapter 3: Structures of Metals & Ceramics School of Mechanical Engineering Professor Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 3-1 Chapter 3: Structures of Metals & Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th ed Donald R. Askeland Pradeep P. Phulé. Chapter 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements
 The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th ed Donald R. Askeland Pradeep P. Phulé Chapter 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements 1 Objectives of Chapter 3 To learn classification of materials based on atomic/ionic
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th ed Donald R. Askeland Pradeep P. Phulé Chapter 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements 1 Objectives of Chapter 3 To learn classification of materials based on atomic/ionic
CRYSTAL LATTICE. Defining lattice: Mathematical construct; ideally infinite arrangement of points in space.
 CRYSTAL LATTICE How to form a crystal? 1. Define the structure of the lattice 2. Define the lattice constant 3. Define the basis Defining lattice: Mathematical construct; ideally infinite arrangement of
CRYSTAL LATTICE How to form a crystal? 1. Define the structure of the lattice 2. Define the lattice constant 3. Define the basis Defining lattice: Mathematical construct; ideally infinite arrangement of
Structure of silica glasses (Chapter 12)
 Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
Density Computations
 CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS Fundamental Concepts 3.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Unit Cells Metallic Crystal Structures 3.2 If the atomic radius
CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS Fundamental Concepts 3.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Unit Cells Metallic Crystal Structures 3.2 If the atomic radius
Chapter 1. Crystal Structure
 Chapter 1. Crystal Structure Crystalline solids: The atoms, molecules or ions pack together in an ordered arrangement Amorphous solids: No ordered structure to the particles of the solid. No well defined
Chapter 1. Crystal Structure Crystalline solids: The atoms, molecules or ions pack together in an ordered arrangement Amorphous solids: No ordered structure to the particles of the solid. No well defined
ASE324: Aerospace Materials Laboratory
 ASE324: Aerospace Materials Laboratory Instructor: Rui Huang Dept of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin Fall 2003 Lecture 3 September 4, 2003 Iron and Steels
ASE324: Aerospace Materials Laboratory Instructor: Rui Huang Dept of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin Fall 2003 Lecture 3 September 4, 2003 Iron and Steels
Two marks questions and answers. 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples
 UNIT V CRYSTAL PHYSICS PART-A Two marks questions and answers 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples Crystalline solids (or) Crystals are those in which the constituent
UNIT V CRYSTAL PHYSICS PART-A Two marks questions and answers 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples Crystalline solids (or) Crystals are those in which the constituent
Point coordinates. x z
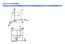 Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
CHAPTER. The Structure of Crystalline Solids
 CHAPTER 4 The Structure of Crystalline Solids 1 Chapter 4: The Structure of Crystalline Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are common crystal structures for metals and ceramics? What features of a metal
CHAPTER 4 The Structure of Crystalline Solids 1 Chapter 4: The Structure of Crystalline Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are common crystal structures for metals and ceramics? What features of a metal
Problems. 104 CHAPTER 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements
 104 CHAPTER 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements Repeat distance The distance from one lattice point to the adjacent lattice point along a direction. Short-range order The regular and predictable arrangement
104 CHAPTER 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements Repeat distance The distance from one lattice point to the adjacent lattice point along a direction. Short-range order The regular and predictable arrangement
Physics of Materials: Symmetry and Bravais Lattice To understand Crystal Plane/Face. Dr. Anurag Srivastava
 Physics of Materials: Symmetry and Bravais Lattice To understand Crystal Plane/Face Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Physics
Physics of Materials: Symmetry and Bravais Lattice To understand Crystal Plane/Face Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Physics
Example: Compute the wavelength of a 1 [kg] block moving at 1000 [m/s].
![Example: Compute the wavelength of a 1 [kg] block moving at 1000 [m/s]. Example: Compute the wavelength of a 1 [kg] block moving at 1000 [m/s].](/thumbs/95/123245062.jpg) Example: Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n = 1 to level n = 2. Also calculate the wavelength of light that must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state
Example: Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n = 1 to level n = 2. Also calculate the wavelength of light that must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state
Chapter 8: Molecules and Materials
 Chapter 8: Molecules and Materials Condensed Phases - Solids Bonding in Solids Metals Insulators Semiconductors Intermolecular Forces Condensed Phases - Liquids Carbon There are three forms of the element
Chapter 8: Molecules and Materials Condensed Phases - Solids Bonding in Solids Metals Insulators Semiconductors Intermolecular Forces Condensed Phases - Liquids Carbon There are three forms of the element
CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES & PROPERTIES
 CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on metals) How does the density of a material depend on its structure? When
CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on metals) How does the density of a material depend on its structure? When
ENERGY AND PACKING. Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES MATERIALS AND PACKING METALLIC CRYSTALS ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... 1. How do s assemble into solid structures? (For now, focus on metals) ENERGY AND PACKING non dense, random packing bond energy Energy bond
Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... 1. How do s assemble into solid structures? (For now, focus on metals) ENERGY AND PACKING non dense, random packing bond energy Energy bond
METALLIC CRYSTALS. tend to be densely packed. have several reasons for dense packing: have the simplest crystal structures.
 METALLIC CRYSTALS tend to be densely packed. have several reasons for dense packing: -Typically, only one element is present, so all atomic radii are the same. -Metallic bonding is not directional. -Nearest
METALLIC CRYSTALS tend to be densely packed. have several reasons for dense packing: -Typically, only one element is present, so all atomic radii are the same. -Metallic bonding is not directional. -Nearest
Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices
 Outline: Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices Review (example with square lattice) Lattice: square,
Outline: Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices Review (example with square lattice) Lattice: square,
UNIT V -CRYSTAL STRUCTURE
 UNIT V -CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Solids are of two types: Amorphous and crystalline. In amorphous solids, there is no order in the arrangement of their constituent atoms (molecules). Hence no definite structure
UNIT V -CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Solids are of two types: Amorphous and crystalline. In amorphous solids, there is no order in the arrangement of their constituent atoms (molecules). Hence no definite structure
CH445/545 Winter 2008
 CH445/545 Winter 2008 Assignment # 1 - due 01/18/08 60 total points SHOW ALL WORKING FOR FULL CREDIT, ANSWERS WITHOUT WORKING WILL BE PENALIZED! 1. Text Ch. 1 # 2 "Calculate the size of the largest sphere
CH445/545 Winter 2008 Assignment # 1 - due 01/18/08 60 total points SHOW ALL WORKING FOR FULL CREDIT, ANSWERS WITHOUT WORKING WILL BE PENALIZED! 1. Text Ch. 1 # 2 "Calculate the size of the largest sphere
LAB II CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND CRYSTAL GROWTH PART 1: CRYSTAL GROWTH. I. Introduction
 LAB II CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND CRYSTAL GROWTH This lab will be divided into two parts. In the first part, you will be growing crystals from a seed crystal in a very visual demonstration of heterogeneous
LAB II CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND CRYSTAL GROWTH This lab will be divided into two parts. In the first part, you will be growing crystals from a seed crystal in a very visual demonstration of heterogeneous
3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (112 ) (c) (102 ) (d) (13 1) Solution
 3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (11 ) (c) (10 ) (d) (13 1) The planes called for are plotted in the cubic unit cells shown below. 3.41 Determine the Miller indices
3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (11 ) (c) (10 ) (d) (13 1) The planes called for are plotted in the cubic unit cells shown below. 3.41 Determine the Miller indices
Solids. The difference between crystalline and non-crystalline materials is in the extent of ordering
 Chapter 3 The Structure t of Crystalline Solids The difference between crystalline and non-crystalline materials is in the extent of ordering Both materials have the same composition but one is ordered
Chapter 3 The Structure t of Crystalline Solids The difference between crystalline and non-crystalline materials is in the extent of ordering Both materials have the same composition but one is ordered
A New Technique to Determine the Coordination Number of BCC, FCC and HCP Structures of Metallic Crystal Lattices using Graphs
 A New Technique to Determine the Coordination Number of BCC, FCC and HCP Structures of Metallic Crystal Lattices using Graphs Sucharita Chakrabarti Department of Applied Science and Humanities (Mathematics)
A New Technique to Determine the Coordination Number of BCC, FCC and HCP Structures of Metallic Crystal Lattices using Graphs Sucharita Chakrabarti Department of Applied Science and Humanities (Mathematics)
CHAPTER 2. Structural Issues of Semiconductors
 CHAPTER 2 Structural Issues of Semiconductors OUTLINE 1.0 Energy & Packing 2.0 Materials & Packing 3.0 Crystal Structures 4.0 Theoretical Density, r 5.0.Polymorphism and Allotropy 6.0 Close - Packed Crystal
CHAPTER 2 Structural Issues of Semiconductors OUTLINE 1.0 Energy & Packing 2.0 Materials & Packing 3.0 Crystal Structures 4.0 Theoretical Density, r 5.0.Polymorphism and Allotropy 6.0 Close - Packed Crystal
MSE 170 Midterm review
 MSE 170 Midterm review Exam date: 11/2/2008 Mon, lecture time Place: Here! Close book, notes and no collaborations A sheet of letter-sized paper with double-sided notes is allowed Material on the exam
MSE 170 Midterm review Exam date: 11/2/2008 Mon, lecture time Place: Here! Close book, notes and no collaborations A sheet of letter-sized paper with double-sided notes is allowed Material on the exam
EP 364 SOLID STATE PHYSICS. Prof. Dr. Beşire Gönül. Course Coordinator
 EP 364 SOLID STATE PHYSICS Course Coordinator Prof. Dr. Beşire Gönül INTRODUCTION AIM OF SOLID STATE PHYSICS WHAT IS SOLID STATE PHYSICS AND WHY DO IT? CONTENT REFERENCES EP364 SOLID STATE PHYSICS INTRODUCTION
EP 364 SOLID STATE PHYSICS Course Coordinator Prof. Dr. Beşire Gönül INTRODUCTION AIM OF SOLID STATE PHYSICS WHAT IS SOLID STATE PHYSICS AND WHY DO IT? CONTENT REFERENCES EP364 SOLID STATE PHYSICS INTRODUCTION
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms
 Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Introduction Basic concepts Characteristics of dislocations Slip systems Slip in single crystals Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials Plastically
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Introduction Basic concepts Characteristics of dislocations Slip systems Slip in single crystals Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials Plastically
Materials Science. Imperfections in Solids CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS. Types of Imperfections
 In the Name of God Materials Science CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
In the Name of God Materials Science CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR000 Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives 1. Describe both vacancy and self interstitial defects. Calculate the equilibrium number
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR000 Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives 1. Describe both vacancy and self interstitial defects. Calculate the equilibrium number
much research (in physics, chemistry, material science, etc.) have been done to understand the difference in materials properties.
 1.1: Introduction Material science and engineering Classify common features of structure and properties of different materials in a well-known manner (chemical or biological): * bonding in solids are classified
1.1: Introduction Material science and engineering Classify common features of structure and properties of different materials in a well-known manner (chemical or biological): * bonding in solids are classified
Topic 2-1: Lattice and Basis Kittel Pages: 2-9
 Topic 2-1: Lattice and Basis Kittel Pages: 2-9 Summary: We begin our introduction of crystal structure by defining a few terms. The first is translational symmetry which explains the periodicity of a crystal.
Topic 2-1: Lattice and Basis Kittel Pages: 2-9 Summary: We begin our introduction of crystal structure by defining a few terms. The first is translational symmetry which explains the periodicity of a crystal.
Materials Science. Why?
 Materials Science and Engineering, 2012 Compiled by Greg Heness & Mike Cortie Chapter 3 Crystalline Structure - Perfection, pp. 40-101 Materials Science A knowledge of this material is needed for diverse
Materials Science and Engineering, 2012 Compiled by Greg Heness & Mike Cortie Chapter 3 Crystalline Structure - Perfection, pp. 40-101 Materials Science A knowledge of this material is needed for diverse
Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews. Cindy Smith
 Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews Cindy Smith Motivation Review: Outline Crystal lattices (fcc, bcc, hcp) Fcc vs. hcp stacking sequences Cubic {hkl} naming Hcp {hkil} naming Twinning
Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews Cindy Smith Motivation Review: Outline Crystal lattices (fcc, bcc, hcp) Fcc vs. hcp stacking sequences Cubic {hkl} naming Hcp {hkil} naming Twinning
Materials and their structures
 Materials and their structures 2.1 Introduction: The ability of materials to undergo forming by different techniques is dependent on their structure and properties. Behavior of materials depends on their
Materials and their structures 2.1 Introduction: The ability of materials to undergo forming by different techniques is dependent on their structure and properties. Behavior of materials depends on their
Chapter 3 Basic Crystallography and Electron Diffraction from Crystals. Lecture 9. Chapter 3 CHEM Fall, L. Ma
 Chapter 3 Basic Crystallography and Electron Diffraction from Crystals Lecture 9 Outline The geometry of electron diffraction Crystallography Kinetic Theory of Electron diffraction Diffraction from crystals
Chapter 3 Basic Crystallography and Electron Diffraction from Crystals Lecture 9 Outline The geometry of electron diffraction Crystallography Kinetic Theory of Electron diffraction Diffraction from crystals
The structures of pure metals are crystalline (crystal lattice) with regular arrangement of metal atoms that are identical perfect spheres.
 HW#3 Louisiana Tech University, Chemistry 481. POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) Exercise on Chapter 3. Metals and Alloys. Why? Metals What is the structure of a metallic solid? What is
HW#3 Louisiana Tech University, Chemistry 481. POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) Exercise on Chapter 3. Metals and Alloys. Why? Metals What is the structure of a metallic solid? What is
Stacking Oranges. Packing atoms together Long Range Order. What controls the nearest number of atoms? Hard Sphere Model. Hard Sphere Model.
 { Stacking atoms together Crystal Structure Stacking Oranges Packing atoms together Long Range Order Crystalline materials... atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays typical of: -metals -many ceramics -some
{ Stacking atoms together Crystal Structure Stacking Oranges Packing atoms together Long Range Order Crystalline materials... atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays typical of: -metals -many ceramics -some
How can we describe a crystal?
 How can we describe a crystal? Examples of common structures: (1) The Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Structure (LiH, MgO, MnO, AgBr, PbS, KCl, KBr) The NaCl structure is FCC The basis consists of one Na atom and
How can we describe a crystal? Examples of common structures: (1) The Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Structure (LiH, MgO, MnO, AgBr, PbS, KCl, KBr) The NaCl structure is FCC The basis consists of one Na atom and
Chapter 12 The Solid State The Structure of Metals and Alloys
 Chapter 12 The Solid State The Structure of Metals and Alloys The Solid State Crystalline solid a solid made of an ordered array of atoms, ion, or molecules Amorphous solids a solid that lacks long-range
Chapter 12 The Solid State The Structure of Metals and Alloys The Solid State Crystalline solid a solid made of an ordered array of atoms, ion, or molecules Amorphous solids a solid that lacks long-range
E45 Midterm 01 Fall 2007! By the 0.2% offset method (shown on plot), YS = 500 MPa
 1.!Mechanical Properties (20 points) Refer to the following stress-strain plot derived from a standard uniaxial tensile test of a high performance titanium alloy to answer the following questions. Show
1.!Mechanical Properties (20 points) Refer to the following stress-strain plot derived from a standard uniaxial tensile test of a high performance titanium alloy to answer the following questions. Show
These metal centres interact through metallic bonding
 The structures of simple solids The majority of inorganic compounds exist as solids and comprise ordered arrays of atoms, ions, or molecules. Some of the simplest solids are the metals, the structures
The structures of simple solids The majority of inorganic compounds exist as solids and comprise ordered arrays of atoms, ions, or molecules. Some of the simplest solids are the metals, the structures
Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids
 Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects exist in solids? How do defects affect material properties? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects exist in solids? How do defects affect material properties? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Dr. Coates An edge dislocation moves in response to an applied shear stress dislocation motion 7.1 Introduction
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Dr. Coates An edge dislocation moves in response to an applied shear stress dislocation motion 7.1 Introduction
Crystallography. Duration: three weeks (8 to 9 hours) One problem set. Outline: 1- Bravais Lattice and Primitive
 Crystallography Duration: three weeks (8 to 9 hours) One problem set Outline: 1- Bravais Lattice and Primitive 2- Cubic lattices, Simple, Body-centered and Face-centered 3- Primitive Unit Cell, Wigner-Seitz
Crystallography Duration: three weeks (8 to 9 hours) One problem set Outline: 1- Bravais Lattice and Primitive 2- Cubic lattices, Simple, Body-centered and Face-centered 3- Primitive Unit Cell, Wigner-Seitz
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS
 MODULE ONE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Metallic crystal structures; BCC, FCC and HCP Coordination number and Atomic Packing Factor (APF) Crystal imperfections:
MODULE ONE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Metallic crystal structures; BCC, FCC and HCP Coordination number and Atomic Packing Factor (APF) Crystal imperfections:
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS ev /atom = exp. kt ( =
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
How do you expect the packing factor to vary with coordination number?
 DATA SHEETS: Crystal Structures and Metallography Date: Lab Partners: Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Structure: CN: Atoms touch along: Number of atoms per unit cell: Determination of PF: Face Centered Cubic
DATA SHEETS: Crystal Structures and Metallography Date: Lab Partners: Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Structure: CN: Atoms touch along: Number of atoms per unit cell: Determination of PF: Face Centered Cubic
Atomic Densities. Linear Density Number of atoms per length whose centers lie on the direction vector for a specific crystallographic direction.
 Atomic Densities Linear Density Number of atoms per length whose centers lie on the direction vector for a specific crystallographic direction. Planar Density Number of atoms per unit area that are centered
Atomic Densities Linear Density Number of atoms per length whose centers lie on the direction vector for a specific crystallographic direction. Planar Density Number of atoms per unit area that are centered
Impurities in Solids. Crystal Electro- Element R% Structure negativity Valence
 4-4 Impurities in Solids 4.4 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the three possible solid solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following
4-4 Impurities in Solids 4.4 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the three possible solid solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following
Chem 241. Lecture 19. UMass Amherst Biochemistry... Teaching Initiative
 Chem 241 Lecture 19 UMass Amherst Biochemistry... Teaching Initiative Announcement March 26 Second Exam Recap Water Redox Comp/Disproportionation Latimer Diagram Frost Diagram Pourbaix Diagram... 2 Ellingham
Chem 241 Lecture 19 UMass Amherst Biochemistry... Teaching Initiative Announcement March 26 Second Exam Recap Water Redox Comp/Disproportionation Latimer Diagram Frost Diagram Pourbaix Diagram... 2 Ellingham
Order in materials. Making Solid Stuff. Primary Bonds Summary. How do they arrange themselves? Results from atomic bonding. What are they?
 Making Solid Stuff Primary Bonds Summary What are they? Results from atomic bonding So the atoms bond together! Order in materials No long range order to atoms Gases little or no interaction between components
Making Solid Stuff Primary Bonds Summary What are they? Results from atomic bonding So the atoms bond together! Order in materials No long range order to atoms Gases little or no interaction between components
Engineering Materials Department of Physics K L University
 Engineering Materials Department of Physics K L University 1 Crystallography Bonding in solids Many of the physical properties of materials are predicated on a knowledge of the inter-atomic forces that
Engineering Materials Department of Physics K L University 1 Crystallography Bonding in solids Many of the physical properties of materials are predicated on a knowledge of the inter-atomic forces that
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
 Solid State-1 1) Ionic solids are characterised by 1) Good conductivity in solid state 2) High vapour pressure 3) Low melting point 4) Solubility in polar solvents 2) Three metals X, Y and Z are crystallised
Solid State-1 1) Ionic solids are characterised by 1) Good conductivity in solid state 2) High vapour pressure 3) Low melting point 4) Solubility in polar solvents 2) Three metals X, Y and Z are crystallised
Review of Metallic Structure
 Phase Diagrams Understanding the Basics F.C. Campbell, editor Copyright 2012 ASM International All rights reserved www.asminternational.org Appendix A Review of Metallic Structure The word metal, derived
Phase Diagrams Understanding the Basics F.C. Campbell, editor Copyright 2012 ASM International All rights reserved www.asminternational.org Appendix A Review of Metallic Structure The word metal, derived
Basic Solid State Chemistry, 2 nd ed. West, A. R.
 Basic Solid State Chemistry, 2 nd ed. West, A. R. Chapter 1 Crystal Structures Many of the properties and applications of crystalline inorganic materials revolve around a small number of structure types
Basic Solid State Chemistry, 2 nd ed. West, A. R. Chapter 1 Crystal Structures Many of the properties and applications of crystalline inorganic materials revolve around a small number of structure types
Atomic Densities. Linear Density. Planar Density. Linear Density. Outline: Planar Density
 Atomic Densities Outline: Atomic Densities - Linear Density - Planar Density Single- vs poly- crystalline materials X-ray Diffraction Example Polymorphism and Allotropy Linear Density Number of atoms per
Atomic Densities Outline: Atomic Densities - Linear Density - Planar Density Single- vs poly- crystalline materials X-ray Diffraction Example Polymorphism and Allotropy Linear Density Number of atoms per
Lecture # 11. Line defects (1D) / Dislocations
 Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC References: 1-
Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC References: 1-
Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects
 Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects Coordination Close packed structures Cubic close packing Hexagonal close packing Metallic structures Ionic structures with interstitial sites Important
Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects Coordination Close packed structures Cubic close packing Hexagonal close packing Metallic structures Ionic structures with interstitial sites Important
Now, let s examine how atoms are affected as liquids transform into solids.
 Now, let s examine how atoms are affected as liquids transform into solids. 1 Before we deal with PROPERTIES of materials, it s beneficial to remember where we have come from, and where we are going. Later,
Now, let s examine how atoms are affected as liquids transform into solids. 1 Before we deal with PROPERTIES of materials, it s beneficial to remember where we have come from, and where we are going. Later,
Structure-Property Correlation [1] Structure-processing-properties-performance relation
![Structure-Property Correlation [1] Structure-processing-properties-performance relation Structure-Property Correlation [1] Structure-processing-properties-performance relation](/thumbs/86/94718537.jpg) MME 297: Lecture 04 Structure-Property Correlation [1] Structure-processing-properties-performance relation Dr. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Topics to discuss today...
MME 297: Lecture 04 Structure-Property Correlation [1] Structure-processing-properties-performance relation Dr. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Topics to discuss today...
Primitive cells, Wigner-Seitz cells, and 2D lattices. 4P70, Solid State Physics Chris Wiebe
 Primitive cells, Wigner-Seitz cells, and 2D lattices 4P70, Solid State Physics Chris Wiebe Choice of primitive cells! Which unit cell is a good choice?! A, B, and C are primitive unit cells. Why?! D, E,
Primitive cells, Wigner-Seitz cells, and 2D lattices 4P70, Solid State Physics Chris Wiebe Choice of primitive cells! Which unit cell is a good choice?! A, B, and C are primitive unit cells. Why?! D, E,
Solid State Physics 460- Lecture 2a Structure of Crystals (Kittel Ch. 1)
 Solid State Physics 460- Lecture 2a Structure of Crystals (Kittel Ch. 1) See many great sites like ob s rock shop with pictures and crystallography info: http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/xtal/index.html
Solid State Physics 460- Lecture 2a Structure of Crystals (Kittel Ch. 1) See many great sites like ob s rock shop with pictures and crystallography info: http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/xtal/index.html
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT. Sub-topics. Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface
 IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
1.10 Close packed structures cubic and hexagonal close packing
 1.9 Description of crystal structures The most common way for describing crystal structure is to refer the structure to the unit cell. The structure is given by the size and shape of the cell and the position
1.9 Description of crystal structures The most common way for describing crystal structure is to refer the structure to the unit cell. The structure is given by the size and shape of the cell and the position
Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS)
 Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What are anistropic substances. 2. Why are amorphous solids isotropic in nature?. Why glass is regarded as an amorphous solid? 4.
Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What are anistropic substances. 2. Why are amorphous solids isotropic in nature?. Why glass is regarded as an amorphous solid? 4.
