1.2. The Periodic Table. The Development of the Periodic Table SECTION. Key Terms
|
|
|
- Kevin Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECTION. The Periodic Table Key rms periodic law period group The periodic table contains a large amount of useful data. For example, you can use the periodic table to look up chemical symbols, atomic numbers, and average atomic masses of elements. owever, the periodic table can reveal much more about the elements when you have a full understanding of its design. The Development of the Periodic Table During a timespan of about 00 years, between the 00s and the 800s, chemists increased the number of recognized elements to and observed and recorded many of their properties. Chemists began to observe similarities in the chemical nature of groups of elements. English chemist John Newlands (8 898) discovered that elements could be classified into groups that have similar chemical properties. Newlands also discovered that the elements in each group differed in atomic mass (then called atomic weight) by factors of eight. Working independently of each other, German chemist Lothar Meyer (80 89) and Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (8 90) both developed a table of the known elements according to their atomic masses. Because Mendeleev published his table first (89), he is considered to be the father of the periodic table. To develop his table, Mendeleev made a card for each of the known elements. e wrote the symbol, atomic mass, and chemical and physical properties of an element on each card. Mendeleev arranged the cards vertically, according to the atomic masses of the elements. When he came to an element that had chemical and physical characteristics that were similar to the first element in the previous column, he started a new column. e then placed the next element beside the element with similar properties. In a few cases, however, Mendeleev had to reverse the order of the elements to make their chemical properties match those of their neighbouring elements. Later, in 9, British physicist enry Moseley (88 9) developed a method for determining the number of protons in the nucleus of atoms, and thus the atomic number of an element. When the elements were ordered according to atomic number instead of atomic mass, the order agreed with Mendeleev s order. Mendeleev left several gaps in his periodic table, attributing these gaps to elements that had not yet been discovered. The positions of these gaps enabled him to predict the properties of the missing elements. Several of these elements were discovered within the next few years, and the properties that Mendeleev had predicted were shown to be correct. The discovery of these elements gave validity to Mendeleev s work. The first periodic table that Mendeleev published is shown in Figure.0. Figure.0 In Mendeleev s first periodic table, he listed the atomic masses vertically and placed elements with similar properties in horizontal rows. Infer why some of the columns are longer than others. MR Unit Matter, Chemical Trends, and Chemical Bonding
2 Characteristics of the Modern Periodic Table The periodic table that you use today looks very different from Mendeleev s table, but it is based on the same periodic, or repeating, relationships. In fact, chemists now call the concept underlying the organization of the periodic table the periodic law. The Periodic Law When elements are arranged by atomic number, their chemical and physical properties recur periodically. periodic law a statement that describes the repeating nature of the properties of the elements Modern chemists have learned much more about the properties of elements and have filled in all the gaps in Mendeleev s table. As you read in Section., chemists have also learned much more about the structure of atoms in general. This new information can explain the periodic nature of the table. To begin to understand the periodicity, examine the partial periodic table in Figure.. Only the atomic numbers and Lewis diagrams of the elements are shown in the table. The Lewis diagrams clearly show the configuration of the electrons in the valence shell of the atoms of each element. 8 Period 9 Li Na K Group 8 9 Be B C N O F Mg Al Si P S Cl 0 Ca Ga Ge As Se Br 0 8 e Ne Ar Kr Figure. Lewis diagrams are shown in this partial periodic table, so you can quickly and easily analyze the electron configuration in each column of the table Rb Sr In Sn l Xe Cs Ba Tl Pb Rn The atomic number increases as you go from left to right in the table. Because the atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, the number of electrons must also increase to make the net charge on the atom zero. The rows are called periods. The period number is the number of electron shells that are occupied by one or more electrons. As you go across a period, the outer electron shell is being filled. When the shell contains the maximum number of electrons allowed in that shell, the period ends. Because the first shell can contain only two electrons, the first period has only two elements. The second shell can contain up to eight electrons, so the second period has eight elements. The partial periodic table in Figure. omits columns through because, in Period, the valence shells of atoms of some elements have more than eight electrons. The analysis of the electron structure of these elements is very complex, so it is left for more advanced chemistry courses. Figure. was drawn with only valence electrons to highlight another important feature of the elements as they are arranged in the periodic table. The columns are called groups. All elements in a group have the same electron configuration in the valence shell of their atoms. Before chemists knew about valence electrons, they knew that the elements in each group had similar chemical and physical properties. Chemists now know that the configuration of the valence electrons is responsible for these similar properties. period a row in the periodic table group a column in the periodic table Chapter Elements and the Periodic Table MR
3 hydrogen.0 Li lithium Na sodium 9 K potassium Rb rubidium Cs cesium 8 0. Fr maingroup Solid elements.8 Liquid maingroup elements, Common ion Gas Electronegativity.8 charges No stable isotopes.0, (). barium francium radium Be beryllium. Mg magnesium 0.0 Ca calcium 8.0 Sr strontium Ba 88 Ra (). Sc scandium 9. Y yttrium La Lu Ac Lr Atomic number Element Symbol Ti titanium 0. Zr zirconium. f hafnium 0 iron rutherfordium Fe inner transition elements transition elements , +,,,,,,, () Name of element V vanadium. Nb niobium. Ta tantalum 0 dubnium 9.9 +, 8 + () Cr chromium Mo molybdenum W tungsten Rf Db Sg Relative atomic mass (u) seaborgium Mn manganese. Tc technetium.9 Re rhenium 0 bohrium (98) Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals Transition metals Other metals Other nonmetals alogens Noble gases Lanthanoids Actinoids Metalloids Fe iron Ru ruthenium Os osmium 08 hassium Co cobalt. Rh rhodium Ir iridium 09 Legend 9 meitnerium Ni nickel Pd palladium Pt platinum 0., 9.08, darmstadtium Cu copper Ag silver Au gold Bh s Mt Ds Rg , roentgenium Zn zinc Cd cadmium g mercury Cn.. 0, () () () (8) () () (8) B boron. Al aluminum.8 Ga gallium 9.8 In indium 8.8 Tl thallium , C carbon.9 Si silicon.0 Ge germanium 0.0 Sn tin 8.8 Pb lead , 0.*, N nitrogen P phosphorus As arsenic. antimony 8.9 bismuth oxygen sulfur selenium tellurium polonium fluorine chlorine bromine iodine astatine helium neon argon 8 krypton xenon radon copernicum ununtrium ununquadium ununpentium ununhexium ununoctium.9., , + O S Se (09), F Cl Br I At e Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn 8 Uut* Uuq* Uup* Uuh* Uuo* (0) (8) (89) (88) (9) (9) *mporary names () Lanthanoids Actinoids. La lanthanum 89. Ac actinium 8.9 () (). () ,,, Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy o Er Tm Yb Lu cerium praseodymium neodymium promethium samarium europium gadolinium terbium dysprosium holmium erbium thulium ytterbium lutetium () () () () () () () () (8) (9) () +, +, +, +,,,,..... Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr thorium protactinium uranium neptunium plutonium americium curium berkelium californium einsteinium fermium mendelevium nobelium lawrencium Although Group elements are often included in the transition elements, these elements are chemically more similar to the maingroup elements. Any value in parentheses is the mass of the least unstable or best known isotope for elements that do not occur naturally. Figure. The brackets above this table divide the elements into large general categories, while the colours break down the categories according to the chemical properties of the elements. MR Unit Matter, Chemical Trends, and Chemical Bonding
4 Categories within the Complete Periodic Table So far, you have been examining a partial periodic table. The design of the complete, modern, periodic table makes it possible to divide the elements into categories based on their properties. The complete periodic table in Figure. has brackets and colour codes that highlight different categories of elements. Categorizing Elements According to Their Properties The colours codes in Figure. divide the elements into categories that highlight unique chemical and physical properties. Some of the categories have specific names. Figure. shows a reduced copy of the periodic table in Figure., with labels that show the names of these categories. You will see references to these categories many times throughout your study of chemistry. SuggestedInvestigation Inquiry Investigation A, Developing an Activity Series alkali metals All of the elements in Group, except hydrogen, are called alkali metals. They are very reactive. In fact, all alkali metals react vigorously with water. When rubidium and cesium are added to water, the reaction with water is explosive. other nonmetals This category consists of the nonmetals that are not halogens or noble gases. These nonmetals are neither as reactive as the halogens nor as unreactive as the noble gases. They are the most common elements in the tissues of living organisms. noble gases The Group 8 elements are called the noble gases. They are completely unreactive. They do not undergo any naturally occurring reactions. owever, chemists have made artificial compounds that contain some of the noble gases. alkaline earth metals The elements in Group are called the alkaline earth metals. They are reactive, but less so than the alkali metals. metalloids Metalloids have properties that are between those of the metals and nonmetals. Many are shiny solids but they are poor conductors of electric current and are brittle. halogens The elements in Group are called the halogens. They are reactive nonmetals..0,.0 hydrogen Li lithium Na sodium magnesium aluminum silicon phosphorus sulfur , +,,,,,,, K potassium Rb rubidium Cs cesium 8 0. Fr francium.9. Be beryllium.99. Mg Ca calcium Sr strontium.9 Ba barium () 88 Ra radium () Sc scandium Y yttrium transition metals The transition metals in Groups through are very hard metals with very high melting points. Because of their complex electron configuration, they can form a wide variety of compounds with other elements. La Lu 89 0 Ac Lr Ti titanium Zr zirconium f hafnium Rf () rutherfordium V vanadium 9.. Nb niobium Ta tantalum 0 Db dubnium () Cr chromium 9.9 +, Mo 8 +. molybdenum W tungsten 0 Sg seaborgium Mn manganese Tc technetium Re rhenium 0 bohrium other metals This category includes the maingroup metals that are not alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. These metals are not as reactive as the Group and metals. They are quite common and useful. For example, you may be familiar with many objects that are made from aluminum or tin. Fe iron (98) + Ru ruthenium 8. + Os osmium 08 hassium Co cobalt 0.0. Rh rhodium 90. Ir iridium 09 meitnerium Ni nickel Pd palladium 9 8 Pt platinum 0 darmstadtium Cu copper 0.,.9 Ag silver ,. Au gold Bh s Mt Ds Rg roentgenium Zn zinc Cd cadmium ,.9 g mercury () () () (8) () () (8) Cn B boron Al Ga gallium In indium Tl thallium C carbon Si Ge germanium Sn tin Pb lead N nitrogen P As arsenic antimony bismuth oxygen selenium tellurium polonium fluorine chlorine bromine iodine astatine neon argon 8 krypton xenon radon copernicum ununtrium ununquadium ununpentium ununhexium ununoctium O S Se Uut* Uuq* Uup* Uuh* F Cl Br I At (0) e Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn.00 helium , , ,. 0.* 8,.9.., , (09) 8, () (8) (89) (88) (9) (9) Uuo* Lanthanoids Actinoids. La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy o Er Tm Yb Lu lanthanum cerium praseodymium neodymium samarium promethium europium gadolinium terbium dysprosium holmium erbium thulium ytterbium lutetium 89. Ac 8.9 () () 0.. () ,,, () () () () () () () () (8) (9) () +, +, +, +,,,,..... Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr actinium thorium protactinium uranium plutonium neptunium americium curium berkelium californium einsteinium fermium mendelevium nobelium lawrencium lanthanoids The inner transition elements in Period are called the lanthanoids, because the first element is lanthanum. They are sometimes called the rare earth elements. For many years, chemists had difficulty separating them from one another. owever, techniques were finally developed to purify them. Some rare earth elements are used in the advanced batteries that are being developed for hybrid cars. actinoids The inner transition elements in Period are called the actinoids, because the first element is actinium. These elements have no stable isotopes. As a consequence, they are all radioactive. In fact, all of the elements beyond uranium are not naturally occurring and can only be produced artificially. Figure. Each colour in this periodic table represents a group of elements that have similar and unique properties. Chapter Elements and the Periodic Table MR
5 Categorizing Elements According to More General Properties The colours in the periodic table in Figure. show another way to categorize the elements. These categories are based on the general properties of the elements. The elements shaded in blue are metals. Recall from previous science courses that all metals, except mercury, are solid at room temperature. (Mercury is a liquid.) Metals tend to be shiny, are good conductors of electric current, and are malleable and ductile. The elements shaded in yellow are nonmetals. Some nonmetals are solid at room temperature, some are gases, and one (bromine) is a liquid. Nonmetals are not shiny, do not conduct electric current, and are not malleable or ductile. The elements shaded in green are metalloids. Their properties are between those of metals and nonmetals. In their pure form, many metalloids look like metals, but they are brittle and often poor conductors of electric current. For example, silicon is shiny, but it is brittle and a poor conductor. It is an important semiconductor, used in transistors and integrated circuits in computer chips. Categorizing According to Blocks of Elements in the Periodic Table When you look at the periodic table in Figure., you can imagine cutting it into rectangles or blocks. These blocks are indicated by brackets across the top of the table and are based on the electron configurations of the elements. Maingroup Elements Groups,, and through 8 are the maingroup elements. Varied in their chemical and physical properties, they are the most prevalent elements on Earth. The number of valence electrons, with the exception of the elements in Group, is completely predictable from the group number. The number of valence electrons increases from one to eight going from left to right (skipping Group ) across the maingroup elements. Although Group does not fit into this pattern, it is often included with the maingroup elements because its elements are chemically more similar to the maingroup elements than to any other elements. Transition Elements The centre of the table contains the transition elements, sometimes called the transition metals. These elements make the periodic table 8 columns wide because atoms of some of the elements can have up to 8 electrons in their outer shell. Thus, their electron configurations are more complex than those of the maingroup elements. Inner Transition Elements At the bottom of the table lie two rows called the inner transition elements. These elements fit between columns and. Notice that, in Figure., the square in Group of Period reads La Lu, meaning that all of the elements from lanthanum through lutetium belong there. The square in Group of Period reads Ac Lr, indicating the location of the elements from actinium through lawrencium. Atoms of the inner transition elements can have as many as electrons in some of their valence shells. Learning Check. ow did Mendeleev organize his periodic table? 8. State the periodic law and explain its meaning. 9. Compare and contrast groups and periods. 0. Explain why each period ends with a noble gas.. Describe the basis for the different categories of the elements in the periodic table.. Use a graphic organizer such as a main idea web to distinguish and describe key characteristics of the categories of elements in the periodic table. MR Unit Matter, Chemical Trends, and Chemical Bonding
6 Silver Examples of Some Properties and Uses of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Sulfur Chlorine Silver, a metal, is ductile and can be drawn into a wire and shaped into coils. Sulfur, a nonmetal, is a yellow solid at room temperature. It is used in the processing of rubber and it is an ingredient in gunpowder. Chlorine, a nonmetal, is a greenishyellow gas. It is very toxic and can damage the respiratory tract. 8 e Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd ln Sn l Xe Cs Ba La f Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au g Tl Pb At Rn Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh s Mt Ds Rg Cn Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy o Er Tm Yb Lu Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr Mercury Silicon Bromine Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature. But, like the other metals, it is shiny and can conduct electric current. Silicon, a metalloid, is purified and shaped into ingots, which are sliced into wafers that are less than a millimetre thick. These wafers are used for making solar cells and computer chips. Bromine, a nonmetal, is a volatile, reddishbrown liquid at room temperature. It is used in water purification and in pesticides. Figure. Some properties and uses of metals, metalloids, and nonmetals are summarized here. Chapter Elements and the Periodic Table MR
7 Alternative Forms of the Periodic Table The commonly used periodic table, as shown in Figure., is convenient for many purposes. owever, it is only one of several possible designs. Some chemists have proposed the designs in Figure. for a table of the elements to highlight certain properties of the elements. SUPERACTINOIDS La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy o Er Tm Yb Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No TRANSITION METALS LANTANOIDS & ACTINOIDS Sc 9 Y Lu Ti Zr f V Nb Ta Cr Mo W Mn Tc Re Fe Ru Os Co Rh Ir Ni Pd Pt Cu Ag Au Zn Cd g Lr Rf Db Sg Bh s Mt Ds Rg Cn 0 8 e.0.00 B C Si Ge Sn Pb N Al Ga In Tl 9 8 P As O S Se F Cl Br I At Uut Uuq Uup Uuh Uus Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Uuo e Li Na K Rb Cs Fr Uue Be Mg Ca Sr Ba Ra Ubn In this circular table, hydrogen is at the centre, and each circumference contains one period. Each group is in the shape of a piece of pie. The transition elements form an arm extending out from the circle. The inner transition elements form another arm extending out from the transition elements. This design emphasizes that the increase in atomic number is continuous. The circle highlights the repeating nature of the properties of the elements. This pyramidal periodic table is separated into four blocks, based on the electron configurations of the elements. You will learn more about electron configurations if you take more advanced chemistry courses. Notice, however, that the inner transition elements form the top of the pyramid, with the transition elements just below them. The base of the pyramid consists of the maingroup elements. Each group forms a horizontal row. Figure. These are just a few of the alternative periodic tables that some chemists have suggested. 8 MR Unit Matter, Chemical Trends, and Chemical Bonding
8 This student has constructed a unique and edible version of the periodic table. In this periodic spiral, hydrogen is in the centre. As you go around the spiral clockwise, the atomic number increases. The maingroup elements, the alkali and alkaline earth metals, the inner transition metals, and the transition metals all form separate clusters. The noble gases form a line by themselves. Zinc, cadmium, and mercury are also in a line by themselves because they have some characteristics of maingroup elements and some characteristics of transition metals. This periodic spiral comes with interactive software that contains a wealth of information about the elements. Identify the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, actinoids, and lanthanoids in this periodic table. Chapter Elements and the Periodic Table MR 9
9 Section. REVIEW Section Summary Mendeleev developed the periodic table by first listing the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. Then, when the chemical properties of an element resembled those of a previous element in the list, he put this element alongside the previous element. With a little adjusting, Mendeleev developed a table of elements with increasing mass in the columns and similar properties in the rows. Elements are categorized as maingroup, transition, and inner transition elements, based on their electron configurations. Elements are categorized as metals, metalloids, and nonmetals, based on their chemical properties. Several groups of elements are given specific names due to their uniquely similar properties. Group elements are called the alkali metals, Group elements are called the alkaline earth metals, Group elements are called the halogens, and Group 8 elements are called the noble gases. Many alternative forms of the periodic table have been developed to highlight specific properties of the elements. Review Questions. K/U When Mendeleev was working on his periodic table, he listed the elements according to their mass. e discovered that he had to reverse the order of a few of the elements to make them fit the pattern of chemical properties. Why were these elements out of order?. K/U Explain why some elements were missing in Mendeleev s periodic table.. K/U What characteristic is the same for all the maingroup elements in a given period? What characteristic is the same for all the maingroup elements in a group?. T/I Sodium metal is usually stored in oil. Find sodium in the periodic table. Based on its position in the periodic table, why do you think that sodium must be stored in oil?. A The platter shown here is made from copper. Why could silicon not be used to make objects such as this? 9. T/I If the inner transition elements were inserted into the periodic table between Groups and in Periods and, how many columns wide would the table be? Explain your answer. 0. K/U Name three different categories into which the Group elements could be classified.. K/U Why are the lanthanoids sometimes called rare earth elements?. A Strontium is sometimes called a bone seeker because, when ingested, it is deposited in bones and remains there for long periods of time. Find strontium in the periodic table. Offer a possible explanation for why strontium is called a bone seeker.. T/I Examine each of the following pairs of elements. State which element is the most reactive, and explain how you made your choice. a. Na or Mg b. Br or Kr c. or e. K/U The photograph below shows what happened when a sample of a pure element was dropped in water. Name two elements that could have caused this reaction.. K/U Name two characteristics that distinguish maingroup elements from transition or inner transition elements.. K/U Which category metals, metalloids, or nonmetals includes elements that are gases at room temperature? 8. T/I List the following elements in order, from best to worst conductor of electric current: silicon, copper, iodine.. A Living tissues are made up of just a few elements. In what category are most of these elements found?. C Create a chart that summarizes the different types of periodic tables presented in this chapter and include the benefits of each model. 0 MR Unit Matter, Chemical Trends, and Chemical Bonding
This resource contains three different versions of the periodic table, including a blank one for colouring!
 Teaching notes This resource contains three different versions of the periodic table, including a blank one for colouring! It also contains tables of the Group 0, 1 and 7 elements with a few columns for
Teaching notes This resource contains three different versions of the periodic table, including a blank one for colouring! It also contains tables of the Group 0, 1 and 7 elements with a few columns for
AIM: SWBAT determine the location of metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the periodic table. What is another name for a column in the periodic table?
 th Grade Science Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Name Date: UNIT 1 LESSON 1 Do Now AIM: SWBAT determine the location of metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the periodic table Directions: Answer the following
th Grade Science Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Name Date: UNIT 1 LESSON 1 Do Now AIM: SWBAT determine the location of metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the periodic table Directions: Answer the following
Periodic Table of the Elements Current View MCHS Periodic Table of the Elements
 Periodic Table of the Elements Current View MCHS Periodic Table of the Elements 1 18 1 H hydrogen 1.0 2 13 14 15 16 17 2 He helium 4.0 3 Li lithium 7.0 4 Be beryllium 9.0 5 B boron 10.8 6 C carbon 12.0
Periodic Table of the Elements Current View MCHS Periodic Table of the Elements 1 18 1 H hydrogen 1.0 2 13 14 15 16 17 2 He helium 4.0 3 Li lithium 7.0 4 Be beryllium 9.0 5 B boron 10.8 6 C carbon 12.0
Ch 12 End of Chapter - Study Questions
 Ch 12 End of Chapter - Study Questions Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All atoms of actinides a. are radioactive. b. have
Ch 12 End of Chapter - Study Questions Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All atoms of actinides a. are radioactive. b. have
Periodic Table of the Elements
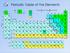 Period ydrogen.0 Name Symbol gas liquid solid Li Be Lithium Beryllium synthetic Sodium Magnesium.0. 9 0 Potassium lcium Scandium Titanium 9. 0. Group.0.9 8 9 0 Rubidium Strontium Yttrium Zirconium 8. 8.
Period ydrogen.0 Name Symbol gas liquid solid Li Be Lithium Beryllium synthetic Sodium Magnesium.0. 9 0 Potassium lcium Scandium Titanium 9. 0. Group.0.9 8 9 0 Rubidium Strontium Yttrium Zirconium 8. 8.
Chapter 5-The Periodic Table
 Chapter 5-The Periodic Table Organizing the elements --> Placement of elements in a table links the atomic structure of the elements and their properties Search for order --> In 1750 there were only 17
Chapter 5-The Periodic Table Organizing the elements --> Placement of elements in a table links the atomic structure of the elements and their properties Search for order --> In 1750 there were only 17
Chemistry Data Booklet Access 3 and Intermediate 1
 Chemistry Data Booklet Access 3 and Intermediate 1 For use in National Qualification Courses leading to the 2007 examinations and beyond. Published date: January 2007 Publication code: BB3572 ISBN: 978
Chemistry Data Booklet Access 3 and Intermediate 1 For use in National Qualification Courses leading to the 2007 examinations and beyond. Published date: January 2007 Publication code: BB3572 ISBN: 978
Chemistry The Periodic Table: How the Elements are Organized
 Chemistry 1010 The Periodic Table: How the Elements are Organized Review Name some elements that you remember from the previous lecture, and what you remember about them. gold and copper are the only metals
Chemistry 1010 The Periodic Table: How the Elements are Organized Review Name some elements that you remember from the previous lecture, and what you remember about them. gold and copper are the only metals
Families on the Periodic Table
 Families on the Periodic Table Elements on the periodic table can be grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families
Families on the Periodic Table Elements on the periodic table can be grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families
Chemistry I. Final Examination Reference Materials
 Chemistry I Final Examination Reference Materials DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BOOKLET Chemistry I: final Exam REFERENCE 2013 April 13 Miscellaneous 1 mole = 6.02 x 10 23 representative particles 1 mole = 22.4
Chemistry I Final Examination Reference Materials DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BOOKLET Chemistry I: final Exam REFERENCE 2013 April 13 Miscellaneous 1 mole = 6.02 x 10 23 representative particles 1 mole = 22.4
Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Section 2 3E, 5B, 6e Main Ideas The periods of the periodic table are determined by electron configuration. 3E describe the connection between chemistry and future careers; 5B use the Periodic Table to
Section 2 3E, 5B, 6e Main Ideas The periods of the periodic table are determined by electron configuration. 3E describe the connection between chemistry and future careers; 5B use the Periodic Table to
Basic Electricity. Learning Objec=ves. Defini=on 9/27/11
 Basic Electricity EAS 199A Lecture Notes Learning Objec=ves Successful comple=on of this module will enable students to Link the basic model of an atom to the flow of electricity Apply the defini=ons of
Basic Electricity EAS 199A Lecture Notes Learning Objec=ves Successful comple=on of this module will enable students to Link the basic model of an atom to the flow of electricity Apply the defini=ons of
Basic Electricity. EAS 199A Lecture Notes
 Basic Electricity EAS 199A Lecture Notes Learning Objec:ves Successful comple:on of this module will enable students to Link the basic model of an atom to the flow of electricity Apply the defini:ons of
Basic Electricity EAS 199A Lecture Notes Learning Objec:ves Successful comple:on of this module will enable students to Link the basic model of an atom to the flow of electricity Apply the defini:ons of
Name: Date: Period: 7. Lithium can be found in Mount Palomar's 200-inch telescopic mirror. Draw the Bohr model for lithium.
 ......... Name: Date: Period: 7. Lithium can be found in Mount Palomar's 200-inch telescopic mirror. Draw the Bohr model for lithium.................. 8. Sulfur dioxide is often used at water treatment
......... Name: Date: Period: 7. Lithium can be found in Mount Palomar's 200-inch telescopic mirror. Draw the Bohr model for lithium.................. 8. Sulfur dioxide is often used at water treatment
Types of Matter. Chapter 1 Section 3. Pure Substances vs. Mixtures
 Types of Matter E = element C = compound M = mixture Pure Substances vs. Mixtures Types of Pure S. Elements Compounds Compounds vs. Mixtures About 2/3 of the space for notes Each term needs 2 to 3 lines
Types of Matter E = element C = compound M = mixture Pure Substances vs. Mixtures Types of Pure S. Elements Compounds Compounds vs. Mixtures About 2/3 of the space for notes Each term needs 2 to 3 lines
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level CANDIDATE NAME CENTRE NUMBER CANDIDATE NUMBER * 0501 706038* SCIENCE 5124/03 Paper 3 Chemistry October/November
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level CANDIDATE NAME CENTRE NUMBER CANDIDATE NUMBER * 0501 706038* SCIENCE 5124/03 Paper 3 Chemistry October/November
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS. PAPER 3 OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION hour 15 minutes
 Centre Number www remepapers.com Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS CHEMISTRY 0620/3 PAPER 3 OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION 2002 1 hour
Centre Number www remepapers.com Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS CHEMISTRY 0620/3 PAPER 3 OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION 2002 1 hour
Candidate Number. In addition to this paper you will require: a calculator. Number
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY CHM2 Unit 2 Foundation Physical
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY CHM2 Unit 2 Foundation Physical
Elements. The periodic table organizes elements by their chemical properties. Main Idea. Key Terms group period nonmetal family metal metalloid
 Section 3 5B, 5C s The periodic table organizes elements by their chemical properties. Some elements are metals. Some elements are nonmetals or metalloids. Elements Key Terms group period nonmetal family
Section 3 5B, 5C s The periodic table organizes elements by their chemical properties. Some elements are metals. Some elements are nonmetals or metalloids. Elements Key Terms group period nonmetal family
PHYSICAL SCIENCE ( ) Section C2 Winter Quiz #2 March 29, 2006
 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 98-01-06 (98-00-03) Section C Winter 006 Quiz # March 9, 006 Name ID Number MULTIPLE CHOICE: [ MARKS EACH] (Circle the letter of the one alternative that best completes the statement or
PHYSICAL SCIENCE 98-01-06 (98-00-03) Section C Winter 006 Quiz # March 9, 006 Name ID Number MULTIPLE CHOICE: [ MARKS EACH] (Circle the letter of the one alternative that best completes the statement or
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education *2399434482* EMISTRY 0620/43 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2016 1 hour 15 minutes andidates answer
ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education *2399434482* EMISTRY 0620/43 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2016 1 hour 15 minutes andidates answer
The content assessed by the examination papers and the type of questions is unchanged.
 Location Entry Codes As part of CIE s continual commitment to maintaining best practice in assessment, CIE uses different variants of some question papers for our most popular assessments with large and
Location Entry Codes As part of CIE s continual commitment to maintaining best practice in assessment, CIE uses different variants of some question papers for our most popular assessments with large and
Groups of Elements 3B 5B 6B 7B 2 C. 10 Na. 36 Rb. 54 Cs. 86 Fr. 57 Ac. 71 Th. Nitrogen group. Alkali metals. Alkaline earth metals.
 Groups of Elements * * Li He C N O 8 F 9 Ne 0 B Be H Al Si P S Cl Ar 8 K 9 Ca 0 Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni 8 Cu 9 Zn 0 Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr 8 Y 9 Zr 0 Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd 8 In 9 Sn 0 Sb Te I Xe Cs Ba
Groups of Elements * * Li He C N O 8 F 9 Ne 0 B Be H Al Si P S Cl Ar 8 K 9 Ca 0 Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni 8 Cu 9 Zn 0 Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr 8 Y 9 Zr 0 Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd 8 In 9 Sn 0 Sb Te I Xe Cs Ba
ACTIVITY SHEETS ACTIVITY SHEET 1. THE UNIVERSE ACTIVITY SHEET 2. PLANET EARTH ACTIVITY SHEET 3. LIVING THINGS ACTIVITY SHEET 4.
 ACTIVITY SHEETS ACTIVITY SHEET 1. THE UNIVERSE ACTIVITY SHEET 2. PLANET EARTH ACTIVITY SHEET 3. LIVING THINGS ACTIVITY SHEET 4. INVERTEBRATES ACTIVITY SHEET 5. VERTEBRATES ACTIVITY SHEET 6. THE PLANT AND
ACTIVITY SHEETS ACTIVITY SHEET 1. THE UNIVERSE ACTIVITY SHEET 2. PLANET EARTH ACTIVITY SHEET 3. LIVING THINGS ACTIVITY SHEET 4. INVERTEBRATES ACTIVITY SHEET 5. VERTEBRATES ACTIVITY SHEET 6. THE PLANT AND
New GCSE 4462/02 SCIENCE A HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4462/02 SCIENCE A HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. WEDNESDAY, 18 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4462/02 SCIENCE A HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. WEDNESDAY, 18 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
An Organized Table Worksheet Due Thursday Name: Date: Period:
 An Organized Table Worksheet Due Thursday Name: Date: Period: The Periodic Table of Elements In 1871, the first periodic table was developed by Dmitrii Mendeleev. Mendeleev is known as the father of the
An Organized Table Worksheet Due Thursday Name: Date: Period: The Periodic Table of Elements In 1871, the first periodic table was developed by Dmitrii Mendeleev. Mendeleev is known as the father of the
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Centre Number Candidate Number Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Centre Number Candidate Number Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Pearson Edexcel GCSE Chemistry/Science Unit C1: Chemistry in Our World
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Chemistry/Science Unit C1: Chemistry in Our World Candidate Number Thursday 19 May 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator,
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Chemistry/Science Unit C1: Chemistry in Our World Candidate Number Thursday 19 May 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator,
Major Challenges in Minor Metals
 Major Challenges in Minor Metals 21 March 2011 Dr. Heinz Schimmelbusch Chief Executive Officer AMG Advanced Metallurgical Group N.V. Cautionary Note 2 THIS DOCUMENT IS STRICTLY CONFIDENTIAL AND IS BEING
Major Challenges in Minor Metals 21 March 2011 Dr. Heinz Schimmelbusch Chief Executive Officer AMG Advanced Metallurgical Group N.V. Cautionary Note 2 THIS DOCUMENT IS STRICTLY CONFIDENTIAL AND IS BEING
Part 1. Preparation and Color of Solutions. Experiment 1 (2 session lab) Electrons and Solution Color. Pre-lab Report, page 29
 Experiment 1 (2 session lab) Electrons and Solution Color Pre-lab Report, page 29 Session 1 One hour discussion (E2) Two hour lab (E1) Aim to complete Parts 1, 2, and 3 of E1. Part 1. Preparation and Color
Experiment 1 (2 session lab) Electrons and Solution Color Pre-lab Report, page 29 Session 1 One hour discussion (E2) Two hour lab (E1) Aim to complete Parts 1, 2, and 3 of E1. Part 1. Preparation and Color
High Purity Acids Trace Elemental Analysis. Detect as low as 1 to 100 ppt
 High Purity Acids Trace Elemental Analysis Detect as low as 1 to 100 ppt High purity acids If you are looking for acids, look no further. Whether you are analyzing environmental samples, etching glass,
High Purity Acids Trace Elemental Analysis Detect as low as 1 to 100 ppt High purity acids If you are looking for acids, look no further. Whether you are analyzing environmental samples, etching glass,
Chemistry/Science Unit C1: Chemistry in our World
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Chemistry/Science Unit C1: Chemistry in our World Candidate Number Thursday 1 March 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator,
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Chemistry/Science Unit C1: Chemistry in our World Candidate Number Thursday 1 March 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator,
GCE A level 1095/01 CHEMISTRY CH5
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1095/01 CHEMISTRY CH5 P.M. TUESDAY, 17 June 2014 1 hour 45 minutes For Examiner s use only ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1095/01 CHEMISTRY CH5 P.M. TUESDAY, 17 June 2014 1 hour 45 minutes For Examiner s use only ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination
Skill-Builders. Grades 4 5. Science & Technology. Writer Sasha Rancourt-Thomas. Editorial Director Susan A. Blair. Project Editor Holly Moirs
 Daily Skill-Builders Science & Technology Grades 4 5 Writer Sasha Rancourt-Thomas Editorial Director Susan A. Blair Project Editor Holly Moirs Cover Designer Roman Laszok Interior Designer Mark Sayer Production
Daily Skill-Builders Science & Technology Grades 4 5 Writer Sasha Rancourt-Thomas Editorial Director Susan A. Blair Project Editor Holly Moirs Cover Designer Roman Laszok Interior Designer Mark Sayer Production
particles/mole
 Chemistry Reference Tables Name Value Avogadro s number 6.0 10 particles/mole 0.081 L atm mole K Gas constant (R) 6. L mmhg mole K 8.1 L kpa mole K Standard pressure Standard temperature Volume of 1 mole
Chemistry Reference Tables Name Value Avogadro s number 6.0 10 particles/mole 0.081 L atm mole K Gas constant (R) 6. L mmhg mole K 8.1 L kpa mole K Standard pressure Standard temperature Volume of 1 mole
THE PERIODIC TABLE. Chapter 15
 THE PERIODIC TABLE Chapter 15 MENDELEEV 1869 The first version of the periodic table was published by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass This
THE PERIODIC TABLE Chapter 15 MENDELEEV 1869 The first version of the periodic table was published by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass This
Where do we start? ocreate the Universe oform the Earth and elements omove the elements into their correct positions obuild the atmosphere and oceans
 Where do we start? ocreate the Universe oform the Earth and elements omove the elements into their correct positions obuild the atmosphere and oceans 1 The BIG BANG The Universe was created 13.8 billion
Where do we start? ocreate the Universe oform the Earth and elements omove the elements into their correct positions obuild the atmosphere and oceans 1 The BIG BANG The Universe was created 13.8 billion
GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B WEDNESDAY 23 JANUARY 2008 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION B624/01
 F GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION B624/01 GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B Unit 2 Modules B4 C4 P4 (Foundation Tier) WEDNESDAY 23 JANUARY 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour *CUP/T42452* Candidates
F GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION B624/01 GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B Unit 2 Modules B4 C4 P4 (Foundation Tier) WEDNESDAY 23 JANUARY 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour *CUP/T42452* Candidates
Tree Essential Elements Manual
 Tree Essential Elements Manual (art 1) ( element genesis, organization & essentiality ) by Dr. Kim D. Coder rofessor of Tree Biology & Health Care Warnell School of Forestry & atural Resources University
Tree Essential Elements Manual (art 1) ( element genesis, organization & essentiality ) by Dr. Kim D. Coder rofessor of Tree Biology & Health Care Warnell School of Forestry & atural Resources University
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge rdinary Level *0083225865* EMISTRY 5070/22 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2016 1 hour 30 minutes andidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are
ambridge International Examinations ambridge rdinary Level *0083225865* EMISTRY 5070/22 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2016 1 hour 30 minutes andidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are
4. Where do the names of the elements come from? Some were named as substances before they were known to be elements. sulfur 16
 4. Where do the names of the elements come from? Some were named as substances before they were known to be elements. silver 47 sulfur 16 copper 29 Some are named from the natural substance that they are
4. Where do the names of the elements come from? Some were named as substances before they were known to be elements. silver 47 sulfur 16 copper 29 Some are named from the natural substance that they are
Fall 2007 October 18,2007
 1 26.9815 Chemistry 121 Exam 1 Fall 2007 October 18,2007 Oregon State University Dr. Richard Nafshun Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" note card,
1 26.9815 Chemistry 121 Exam 1 Fall 2007 October 18,2007 Oregon State University Dr. Richard Nafshun Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" note card,
Essential Elements Of Tree Health
 Essential Elements Of Tree Health by Dr. Kim D. Coder, rofessor of Tree Biology & Health Care Warnell School of Forestry & atural Resources University of Georgia June 2013 H 1 Li Be B C O F 3 4 5 6 7 8
Essential Elements Of Tree Health by Dr. Kim D. Coder, rofessor of Tree Biology & Health Care Warnell School of Forestry & atural Resources University of Georgia June 2013 H 1 Li Be B C O F 3 4 5 6 7 8
SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "PMI-MASTER Pro" Spark - mode Fe 000
 SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "PMI-MASTER Pro" Spark - mode Fe 100 Fe 200 *** Fe 250 *** Fe 300 Fe 400 Fe 500 Fe 000 Fe low alloy steel cast iron Cr hard / Ni resist stainless steel tool
SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "PMI-MASTER Pro" Spark - mode Fe 100 Fe 200 *** Fe 250 *** Fe 300 Fe 400 Fe 500 Fe 000 Fe low alloy steel cast iron Cr hard / Ni resist stainless steel tool
WHERE SHOULD ALUMINUM GO IN THE PERIODIC TABLE?.pdf
 Laval University From the SelectedWorks of Fathi Habashi November, 2008 WHERE SHOULD ALUMINUM GO IN THE PERIODIC TABLE?.pdf Fathi Habashi Available at: https://works.bepress.com/fathi_habashi/175/ WHERE
Laval University From the SelectedWorks of Fathi Habashi November, 2008 WHERE SHOULD ALUMINUM GO IN THE PERIODIC TABLE?.pdf Fathi Habashi Available at: https://works.bepress.com/fathi_habashi/175/ WHERE
Fabrication and Evaluation of SFR Cladding Tubes
 International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles 2013, Paris, France Fabrication and Evaluation of SFR Cladding Tubes Sung Ho Kim, J.H. Baek, J.H. Kim, C.B. Lee Next Generation Fuel Development
International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles 2013, Paris, France Fabrication and Evaluation of SFR Cladding Tubes Sung Ho Kim, J.H. Baek, J.H. Kim, C.B. Lee Next Generation Fuel Development
METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK
 METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK FOURTH EDITION Robert B. Ross Ross Materials Technology Ltd, East Kilbride, Glasgow Volume I SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS
METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK FOURTH EDITION Robert B. Ross Ross Materials Technology Ltd, East Kilbride, Glasgow Volume I SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS
Chemistry CHEM2 Unit 2 Chemistry In Action Thursday 11 June pm to 3.15 pm For this paper you must have: Time allowed Instructions all
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initial General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2009 Question 1 2 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initial General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2009 Question 1 2 Mark
Thursday 13 June 2013 Morning
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION F Thursday 13 June 2013 Morning GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B B721/01 Additional Science modules B3, C3, P3 (Foundation Tier) *B722270613* Candidates answer on the
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION F Thursday 13 June 2013 Morning GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B B721/01 Additional Science modules B3, C3, P3 (Foundation Tier) *B722270613* Candidates answer on the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education EMISTRY 0620/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) May/June 2016 *2847144730* dditional Materials: RE TESE
ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education EMISTRY 0620/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) May/June 2016 *2847144730* dditional Materials: RE TESE
GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B MONDAY 21 JANUARY 2008 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION B623/01
 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION B623/01 GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B Unit 1 Modules B3 C3 P3 (Foundation Tier) MONDAY 21 JANUARY 2008 F Afternoon Time: 1 hour *CUP/T45737* Candidates
GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION B623/01 GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B Unit 1 Modules B3 C3 P3 (Foundation Tier) MONDAY 21 JANUARY 2008 F Afternoon Time: 1 hour *CUP/T45737* Candidates
STUDENT NAME DATE ID. Integrated Physics and Chemistry 10 th Grade (IPC)
 STUDENT NAME DATE ID Integrated Physics and Chemistry 10 th Grade (IPC) Administered October 2005 FORMULA CHART for Science Assessment Density = heat gained or ( ) = mass in change in specific lost by
STUDENT NAME DATE ID Integrated Physics and Chemistry 10 th Grade (IPC) Administered October 2005 FORMULA CHART for Science Assessment Density = heat gained or ( ) = mass in change in specific lost by
Physical Science Chapter 19. Elements and Their Properties Quick Notes
 Physical Science Chapter 19 Elements and Their Properties Quick Notes 1 19:1 A.Metals conduct heat and electricity, reflect light (luster); are malleable ( ) Can be hammered or rolled into sheets are ductile
Physical Science Chapter 19 Elements and Their Properties Quick Notes 1 19:1 A.Metals conduct heat and electricity, reflect light (luster); are malleable ( ) Can be hammered or rolled into sheets are ductile
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *0022143872* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education EMISTRY 0620/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) May/June 2016 dditional Materials: Multiple
*0022143872* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education EMISTRY 0620/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) May/June 2016 dditional Materials: Multiple
Chapter: The Periodic Table
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Periodic Table Section 1: Introduction to the Periodic Table Section 2: Representative Elements Section 3: Transition Elements 1 Introduction to the Periodic Table Development
Table of Contents Chapter: The Periodic Table Section 1: Introduction to the Periodic Table Section 2: Representative Elements Section 3: Transition Elements 1 Introduction to the Periodic Table Development
Thursday 26 January 2012 Morning
 THIS IS A LEGACY SPECIFICATION H Thursday 26 January 2012 Morning GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B B623/02 Unit 1 Modules B3 C3 P3 (Higher Tier) *B620760112* Candidates answer on the Question
THIS IS A LEGACY SPECIFICATION H Thursday 26 January 2012 Morning GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE B B623/02 Unit 1 Modules B3 C3 P3 (Higher Tier) *B620760112* Candidates answer on the Question
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8700818334* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Core) May/June 2017 2 hours Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8700818334* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Core) May/June 2017 2 hours Candidates answer
Classifying Living Things
 APPENDIX A Classifying Living Things Over 2000 years ago, the Greek philosopher Aristotle developed a system of classification that grouped organisms according to whether they were plant or animal. Scientists
APPENDIX A Classifying Living Things Over 2000 years ago, the Greek philosopher Aristotle developed a system of classification that grouped organisms according to whether they were plant or animal. Scientists
THE PERIODIC TABLE AND THE METALLURGIST
 Laval University From the SelectedWorks of Fathi Habashi June, 2008 THE PERIODIC TABLE AND THE METALLURGIST Fathi Habashi Available at: https://works.bepress.com/fathi_habashi/79/ Metall-Forschung The
Laval University From the SelectedWorks of Fathi Habashi June, 2008 THE PERIODIC TABLE AND THE METALLURGIST Fathi Habashi Available at: https://works.bepress.com/fathi_habashi/79/ Metall-Forschung The
CHEMISTRY. Written examination DATA BOOK. Instructions
 Victorian ertificate of Education Year EMISTY Written examination DATA BK Instructions This data book is provided for your reference. A question and answer book is provided with this data book. Students
Victorian ertificate of Education Year EMISTY Written examination DATA BK Instructions This data book is provided for your reference. A question and answer book is provided with this data book. Students
Douglas G. Brookins. Eh-pH Diagrams. for. Geochemistry. With 98 Figures and 61 Tables. Springer -Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo
 Douglas G. Brookins Eh-pH Diagrams for Geochemistry With 98 Figures and 61 Tables Springer -Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Dr. Douglas G. Brookins Department of Geology University
Douglas G. Brookins Eh-pH Diagrams for Geochemistry With 98 Figures and 61 Tables Springer -Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Dr. Douglas G. Brookins Department of Geology University
Chapter 11 The Periodic Table
 Chapter 11 The Periodic Table Lesson 1 Using the Periodic Table Textbook pages 391 397 Lesson 2 Metals Textbook pages 401 402 Lesson 3 Nonmetals and Metalloids Textbook pages 409 410 & 413-414 1 Chapter
Chapter 11 The Periodic Table Lesson 1 Using the Periodic Table Textbook pages 391 397 Lesson 2 Metals Textbook pages 401 402 Lesson 3 Nonmetals and Metalloids Textbook pages 409 410 & 413-414 1 Chapter
PC IV Grenzflächen WS 2011/12
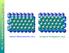 kubisch flächenzentriert (fcc) hexagonal dichtgepackt (hcp) kubisch flächenzentriert fcc hexagonal dichtgepackt hcp kubisch raumzentriert bcc Kubische Kristalle kubisch raumzentriert kubisch flächenzentriert
kubisch flächenzentriert (fcc) hexagonal dichtgepackt (hcp) kubisch flächenzentriert fcc hexagonal dichtgepackt hcp kubisch raumzentriert bcc Kubische Kristalle kubisch raumzentriert kubisch flächenzentriert
Dr Nick Voulvoulis. Presentation at the Industrial Waste & Wastewater Treatment & Valorisation conference May 2015, Athens, Greece
 Centre for Environmental Policy Environmental Quality Research Mining in the context of sustainable management of natural capital: the importance of waste recycling and reuse Presentation at the Industrial
Centre for Environmental Policy Environmental Quality Research Mining in the context of sustainable management of natural capital: the importance of waste recycling and reuse Presentation at the Industrial
FRIB Project History
 EAST LANSING, Mich. Michigan State University announced the signing of a cooperative agreement with the U.S. Department of Energy concerning the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams on June 6. The agreement,
EAST LANSING, Mich. Michigan State University announced the signing of a cooperative agreement with the U.S. Department of Energy concerning the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams on June 6. The agreement,
2016 CHEMISTRY ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX. Question Booklet 1
 1 2016 CHEMISTRY External Examination 2016 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX QUESTION BOOKLET 1 14 pages, 4 questions RE-MARKED Wednesday 16 November:
1 2016 CHEMISTRY External Examination 2016 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX QUESTION BOOKLET 1 14 pages, 4 questions RE-MARKED Wednesday 16 November:
Thursday 17 January 2013 Afternoon
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION F Thursday 17 January 2013 Afternoon GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE SCIENCE B B712/01 Science modules B2, C2, P2 (Foundation Tier) *B734510113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION F Thursday 17 January 2013 Afternoon GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE SCIENCE B B712/01 Science modules B2, C2, P2 (Foundation Tier) *B734510113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Thursday 17 January 2013 Afternoon
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Thursday 17 January 2013 Afternoon GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE SCIENCE B B712/02 Science modules B2, C2, P2 (Higher Tier) *B734520113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Thursday 17 January 2013 Afternoon GCSE GATEWAY SCIENCE SCIENCE B B712/02 Science modules B2, C2, P2 (Higher Tier) *B734520113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A
Periodic Table of the Elements. Alphabetical Listing of the Elements
 CIECE 1 Data Pages Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 1 Page 11 Page 12 Table of Contents Periodic Table of the Elements ph cale Alphabetical Listing of the Elements ames,
CIECE 1 Data Pages Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 1 Page 11 Page 12 Table of Contents Periodic Table of the Elements ph cale Alphabetical Listing of the Elements ames,
Skyline High School Reference Tables for Chemistry DATA BOOK. Physical Constants and Conversions Factors. Name Symbol Value or Conversion Factor Units
 Absolute Zero (temperature) Angstrom unit (length) Atomic mass unit Avogadro s number of particles Charge of an electron Electron volt Heat in calories or joules Molarity (concentration) Mole conversion:
Absolute Zero (temperature) Angstrom unit (length) Atomic mass unit Avogadro s number of particles Charge of an electron Electron volt Heat in calories or joules Molarity (concentration) Mole conversion:
UNIFORM EXAMINATIONS Secondary Cycle Two
 UNIFORM EXAMINATIONS Secondary Cycle Two Information Document - June 2018 - July 2018 - January 2019 Science and Technology 555-410 Applied Science and Technology 557-410 Secondary IV Gouvernement du Québec
UNIFORM EXAMINATIONS Secondary Cycle Two Information Document - June 2018 - July 2018 - January 2019 Science and Technology 555-410 Applied Science and Technology 557-410 Secondary IV Gouvernement du Québec
6.022 x mol C mol J g 1 K 1. One litre (1.00 L) 1000 ml or 1000 cm L
 hemistry Subject ode: M315114 2014 External Examination Information Sheet hemical Data and onstants QUANTITY Standard atmospheric pressure Absolute zero temperature (zero kelvin) Standard temperature &
hemistry Subject ode: M315114 2014 External Examination Information Sheet hemical Data and onstants QUANTITY Standard atmospheric pressure Absolute zero temperature (zero kelvin) Standard temperature &
Table of Contents. Quality Management LIMS System... Customer Services...
 2013 Price List Inside Front Inside Back 26 Table of Contents Quality Management LIMS System... Customer Services... MINING SERVICES... Metallurgical Sample Receiving... Sample Pickup... Sample Submittal...
2013 Price List Inside Front Inside Back 26 Table of Contents Quality Management LIMS System... Customer Services... MINING SERVICES... Metallurgical Sample Receiving... Sample Pickup... Sample Submittal...
G r a d e 1 1 C h e m i s t r y ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice examination
 G r a d e 1 1 C h e m i s t r y ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice examination G r a d e 1 1 C h e m i s t r y ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Examination IInstructions the final examination will be weighted as follows
G r a d e 1 1 C h e m i s t r y ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice examination G r a d e 1 1 C h e m i s t r y ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Examination IInstructions the final examination will be weighted as follows
Evidence of Performance regarding the requirements for float glass according to EN 572
 Evidence of Performance regarding the requirements for float glass according to EN 572 Test Report 605 32401 Client Noval Glass Industrial Group (China) Co., Ltd. Noval Glass Industiral Zone Qingdao, 523965
Evidence of Performance regarding the requirements for float glass according to EN 572 Test Report 605 32401 Client Noval Glass Industrial Group (China) Co., Ltd. Noval Glass Industiral Zone Qingdao, 523965
Name: Date: Per: Directions
 Name: Date: Per: Element superhero or villain project Assignment: Personify one element on the periodic table. Your element s physical features and personality must relate with the real physical and chemical
Name: Date: Per: Element superhero or villain project Assignment: Personify one element on the periodic table. Your element s physical features and personality must relate with the real physical and chemical
systematic table of elements
 systematic table of elements increasing num mber of electrons increasin ng atomar mass Be B C N O F Ne hydrogen (1 electron) helium (2 electrons) lithium (3 electrons) beryllium (4 electrons) boron (5
systematic table of elements increasing num mber of electrons increasin ng atomar mass Be B C N O F Ne hydrogen (1 electron) helium (2 electrons) lithium (3 electrons) beryllium (4 electrons) boron (5
H Hydrogen Key. Li Lithium Be Beryllium Mg Magnesium Pa Protactinium
 Periodic Table of the Elements Chemistry Reference Sheet California Standards Test 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 1A 1 H Hydrogen 1.01 3 Li Lithium 6.94 11 Na Sodium 22.99 19 2 2A 4 Be Beryllium 9.01 12 Mg Magnesium
Periodic Table of the Elements Chemistry Reference Sheet California Standards Test 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 1A 1 H Hydrogen 1.01 3 Li Lithium 6.94 11 Na Sodium 22.99 19 2 2A 4 Be Beryllium 9.01 12 Mg Magnesium
CHAPTER 19 Elements and their Properties
 CHAPTER 19 Elements and their Properties Elements and their Properties PSc.2.1 Understand types, properties, and structure of matter. PSc.2.1.1 Classify matter as: homogeneous or heterogeneous; pure substance
CHAPTER 19 Elements and their Properties Elements and their Properties PSc.2.1 Understand types, properties, and structure of matter. PSc.2.1.1 Classify matter as: homogeneous or heterogeneous; pure substance
UK Baseline Geochemistry: A Key Environmental Yardstick
 UK Baseline Geochemistry: A Key Environmental Yardstick Geochemical Baselines and Medical Geology Team Content Geochemical baselines G-BASE project Applications how the data have been used and what can
UK Baseline Geochemistry: A Key Environmental Yardstick Geochemical Baselines and Medical Geology Team Content Geochemical baselines G-BASE project Applications how the data have been used and what can
Joint ICTP/IAEA School on Physics and Technology of Fast Reactors Systems November 2009
 2055-39 Joint ICTP/IAEA School on Physics and Technology of Fast Reactors Systems 9-20 November 2009 Principles of Design of Radiation Resistant Materials for Fast Reactor Fuel Assembly: SCOPE M. Vijayalakshmi
2055-39 Joint ICTP/IAEA School on Physics and Technology of Fast Reactors Systems 9-20 November 2009 Principles of Design of Radiation Resistant Materials for Fast Reactor Fuel Assembly: SCOPE M. Vijayalakshmi
Chapter: The d and f Block Elements
 Chapter: The d and f Block Elements Introduction to d block elements Question 1 In Tc ( Z = 43) and Tb( Z = 65) which one is inner transition metal and which one is transition metal and why? The outer
Chapter: The d and f Block Elements Introduction to d block elements Question 1 In Tc ( Z = 43) and Tb( Z = 65) which one is inner transition metal and which one is transition metal and why? The outer
MBH. Introduction. Element & Symbol Pack Sizes. Catalogue No. 26 X 1-Ag 26 X 10-Ag. Concentrations Available. Suppliers. France U.K.
 Introduction This catalogue is complementary to the catalogue of solid reference materials. It provides an extensive listing of solutions for ICP-AES, ICP-MS and AAS spectroscopy, as well as glassware
Introduction This catalogue is complementary to the catalogue of solid reference materials. It provides an extensive listing of solutions for ICP-AES, ICP-MS and AAS spectroscopy, as well as glassware
UNIFORM EXAMINATIONS Secondary Cycle Two
 UNIFORM EXAMINATIONS Secondary Cycle Two Information Document - June 2015 - August 2015 - January 2016 Science and Technology 555-410 Applied Science and Technology 557-410 Secondary IV Gouvernement du
UNIFORM EXAMINATIONS Secondary Cycle Two Information Document - June 2015 - August 2015 - January 2016 Science and Technology 555-410 Applied Science and Technology 557-410 Secondary IV Gouvernement du
AAS - Atomic Absorption Mono Element ppm Standard Solutions (Spectro ECON)
 CL01.0105 CL01.0106 CL01.0107 CL01.0126 CL01.0127 CL01.0135 CL01.0136 CL01.0137 CL01.0138 CL01.0205 CL01.0206 CL01.0207 CL01.0216 Aluminium standard solution (Spectro ECON) 8.948 g AlCl3.6H2O / l H2O Solution
CL01.0105 CL01.0106 CL01.0107 CL01.0126 CL01.0127 CL01.0135 CL01.0136 CL01.0137 CL01.0138 CL01.0205 CL01.0206 CL01.0207 CL01.0216 Aluminium standard solution (Spectro ECON) 8.948 g AlCl3.6H2O / l H2O Solution
Market Update for Rare Earths USGS Congressional Briefing Series December 13, 2013
 Market Update for Rare Earths 2013 USGS Congressional Briefing Series December 13, 2013 Joseph Gambogi Rare Earth Commodity Specialist USGS National Minerals Information Center U.S. Department of the Interior
Market Update for Rare Earths 2013 USGS Congressional Briefing Series December 13, 2013 Joseph Gambogi Rare Earth Commodity Specialist USGS National Minerals Information Center U.S. Department of the Interior
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY LANTHANIDES
 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY Topic: 5 LANTHANIDES LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. What are the general characteristics of Lanthanides.. Ans: F BLOCK ELEMENTS The elements in which the differentiating electron enters the
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY Topic: 5 LANTHANIDES LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. What are the general characteristics of Lanthanides.. Ans: F BLOCK ELEMENTS The elements in which the differentiating electron enters the
BLACK STURGEON LAKES WATER QUALITY MONITORING
 BLACK STURGEON LAKES WATER QUALITY MONITORING 2017 REPORT Prepared by: Ryan Haines, B.Sc. Biologist and Project Management Kenora Resource Consultants Inc. Site 155, Compartment 14, RR #1 Kenora, ON P9N
BLACK STURGEON LAKES WATER QUALITY MONITORING 2017 REPORT Prepared by: Ryan Haines, B.Sc. Biologist and Project Management Kenora Resource Consultants Inc. Site 155, Compartment 14, RR #1 Kenora, ON P9N
Class Work 11/25/13. SWBAT to classify an element as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid based on its properties and location on the periodic table.
 Unit 4 NAME Class Work 11/25/13 4.5 Organization of the Periodic Table SPARK: 1. What are valence electrons? 2. What is the Bohr Model for calcium? 3. Draw the Lewis Dot diagram for Neon ObjecOve SWBAT
Unit 4 NAME Class Work 11/25/13 4.5 Organization of the Periodic Table SPARK: 1. What are valence electrons? 2. What is the Bohr Model for calcium? 3. Draw the Lewis Dot diagram for Neon ObjecOve SWBAT
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *8071151377* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education EMISTRY 0620/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2015 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice
*8071151377* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education EMISTRY 0620/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2015 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice
TOP INORGANIC STANDARDS
 The Experts in Custom-made Inorganic and Organic Standards TOP INORGANIC STANDARDS ISO GUIDE 34 ISO/IEC 17025 ISO/IEC 17043 ISO 9001 is the world leader in Certified Reference Materials production (Custom
The Experts in Custom-made Inorganic and Organic Standards TOP INORGANIC STANDARDS ISO GUIDE 34 ISO/IEC 17025 ISO/IEC 17043 ISO 9001 is the world leader in Certified Reference Materials production (Custom
Core Analysis with the Tracer
 BRUKER ELEMENTAL Core Analysis with the Tracer Prepared by: Lee Drake, Senior Application Scientist January 23, 2014 BRUKER ELEMENTAL Key Points OBJECTIVE 3 EXPLORATION 3 DECISION MAKING 3 RECLAMATION
BRUKER ELEMENTAL Core Analysis with the Tracer Prepared by: Lee Drake, Senior Application Scientist January 23, 2014 BRUKER ELEMENTAL Key Points OBJECTIVE 3 EXPLORATION 3 DECISION MAKING 3 RECLAMATION
Chem. 451 (Spring, 2005) Final Exam (100 pts)
 hem. 451 (Spring, 2005) Final Exam (100 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------, Student lid #: ----------------------, May 7, 2005 LAST, First ircle the alphabet segment of
hem. 451 (Spring, 2005) Final Exam (100 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------, Student lid #: ----------------------, May 7, 2005 LAST, First ircle the alphabet segment of
Soft clean eraser Soft pencil (type B or HB is recommended)
 *6370193137* ambridge International Examinations ambridge rdinary Level EMISTRY 5070/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2015 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft pencil
*6370193137* ambridge International Examinations ambridge rdinary Level EMISTRY 5070/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2015 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft pencil
Thin film deposition for next generation DRAM structures
 Thin film deposition for next generation DRAM structures ISPR 2017 13.09.2017 J. Torgersen, F. Berto, F. Prinz, W. Cai NTNU Trondheim/ Stanford University NTNU 10/16/2017 40000 students 50 faculties Nobel
Thin film deposition for next generation DRAM structures ISPR 2017 13.09.2017 J. Torgersen, F. Berto, F. Prinz, W. Cai NTNU Trondheim/ Stanford University NTNU 10/16/2017 40000 students 50 faculties Nobel
WG 5: Radionuclide Transfer to wildlife
 EMRAS II WG 5: Radionuclide Transfer to wildlife EMRAS II Jan 2011 EMRAS II Jan 2011 Objectives This document is primarily intended to provide IAEA Member States with generic transfer parameter values
EMRAS II WG 5: Radionuclide Transfer to wildlife EMRAS II Jan 2011 EMRAS II Jan 2011 Objectives This document is primarily intended to provide IAEA Member States with generic transfer parameter values
SILLIKER, Inc. Southern California Laboratory 6360 Gateway Drive, Cypress, CA Tel. 209/ Fax. 714/
 6360 Gateway Drive, 90630 95073 Page 1 of 8 CI-516 Cistanche 361439388 ICP MS Full Mineral Screen EPA 3050/6020 USP730 BRN Aluminum 2.2 ppm (w/w) Antimony Arsenic 0.06 ppm (w/w) Barium 0.09 ppm (w/w) Beryllium
6360 Gateway Drive, 90630 95073 Page 1 of 8 CI-516 Cistanche 361439388 ICP MS Full Mineral Screen EPA 3050/6020 USP730 BRN Aluminum 2.2 ppm (w/w) Antimony Arsenic 0.06 ppm (w/w) Barium 0.09 ppm (w/w) Beryllium

 VETRI E MATERIALI CERAMICI
VETRI E MATERIALI CERAMICI