Part 1. References: Gray: Chapter 6 OGN: Chapter 19 and (24.1)
|
|
|
- Suzan Bradley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part 1 References: Gray: Chapter 6 OGN: Chapter 19 and (24.1)
2 Aspects of Chemical Bonds Bonding in Chem 1a Atomic Structure Explain Atomic Line Spectra, Galaxies, etc. Shapes of Orbitals in Atoms for Bonding Ionization Energies and Trends in Chemical Reactivity (e.g., Li + vs Li) Which Molecules are Likely to Exist and Their Shapes and Reactivities (Ozone, Glo. Warm.) Magnetic and Bonding Properties of Molecules (Magnetic Tapes, Disks, etc.) Special Properties of Resonance Stabilization Directionality of Covalent Chemical Bonds Bonding in Solids
3 A Simple Cubic Lattice
4 A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice 6 Face Atoms 8 Corner Atoms
5 FCC Lattice of Metals and Insulators Metals Are Closed Packed Atomic Spheres Insulators Arise from Binary Compounds with Holes Filled in FCC Lattice
6 A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice
7 Two Face-Centered Cubic Lattices Replicate the Original Lattice
8 Two Face-Centered Cubic Lattices Offset the Lattice by 1/2 An Edge-Edge Distance
9 Two Face-Centered Cubic Lattices Start to Interpenetrate the Two Lattices
10 Two Face-Centered Cubic Lattices Two Interpenetrating FCC Lattices
11 A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice Chop Off Top and Bottom Atoms to View Original Unit Cell Volume
12 Rock Salt: Two Interpenetrating FCC Structures Every Atom Has Six Nearest Neighbors of the Opposite Atom Type with a Locally Octahedral Geometry
13 Rock Salt: Two Interpenetrating FCC Structures One Can Not See Through the Cube in this View
14 Rock Salt: Two Interpenetrating FCC Structures
15 A Simple Cubic Lattice Again
16 A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice 6 Face Atoms 8 Corner Atoms
17 One Octahedral Hole in a Face-Centered Cubic Lattice There is a Hole at Center of Unit Cell
18 Fill The Unique Octahedral Hole at Center
19 Two of The Octahedral Holes at Edge Midpoints
20 Showing Coordination Around Edge Octahedral Holes
21 Showing Coordination Around Edge Octahedral Holes
22 Forming Rock Salt: Fill All of the Octahedral Holes Fill All of The Octahedral Holes at Edge Midpoints and the Unique Hole in the Center of the Unit Cell
23 Rock Salt Structure Two Interpenetrating FCC Lattices or Fill All Octahedral Holes in One FCC Lattice
24 Tetrahedral Holes in A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice Each Corner (with 3 Face Atoms) Defines One Tetrahedral Hole; Favored by sp 3 Hybrids
25 Filling 1/2 T d Holes in a FCC Lattice Note: Face Atoms Not Shown For Clarity
26 Filling 1/2 T d Holes in a FCC Lattice When Atoms Are All Identical, Have Diamond (Si) Structure
27 Filling 1/2 T d Holes in a FCC Lattice When T d Atoms are Different than FCC Atoms, Have Zinc Blende (GaAs, InP, etc.) Structure
28 A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice Face Atom Corner Atom How Do We Determine Stoichiometry? Consider Face and Corner Atoms Separately
29 Face Atoms in a FCC Lattice Face Atoms Are Shared Between 2 Unit Cells So Each Face Atom Counts as 1/2 for Each Unit Cell 6 Face Atoms per Unit Cell * 1/2 = 3 Atoms/Unit Cell
30 Corner Atoms in a FCC Lattice Corner Atoms Are Shared Between 8 Unit Cells So Each Face Atom Counts as 1/8 for Each Unit Cell 8 Corner Atoms in a Unit Cell * 1/8 = 1 Atom/Unit Cell
31 A Face-Centered Cubic Lattice Corner Atom (8 * 1/8 = 1) Face Atom (6 * 1/2 = 3) 3 Face Equivalents and 1 Corner Equivalent = 4 Total Atoms/Unit Cell From the FCC Lattice
32 Octahedral Holes in FCC Lattice: Rock Salt Edge Hole Central Hole Now We Will Consider the Contribution of Holes /Unit Cell
33 Octahedral Holes in FCC Lattice: Rock Salt Edge Hole (12) Central Hole (1) What About Edge Atoms? (12 Total Edge Atoms)
34 Edge Atoms in a FCC Lattice Edge Atoms Are Shared Between 4 Unit Cells So Each Edge Atom Counts as 1/4 for Each Unit Cell 12 Edge Atoms per cell * 1/4 = 3 Edge Atoms/Unit Cell
35 Face Atoms (6 * 1/2 = 3) Stoichiometry of Rock Salt Corner Atoms (8 * 1/8=1) Edge Hole (12*1/4 = 3) Central Hole (1 * 1 = 1) 4 Total Lattice Atoms: 4 Lattice Holes 1:1 Stoichiometry (NaCl)
36 Stoichiometry of Zinc Blende Face Atoms (6 * 1/2 = 3) Corner Atoms (8 * 1/8 = 1) T d Holes (4 * 1 = 4) 4 Lattice Atoms: 4 Tetrahedral Holes 1:1 Stoichiometry (GaAs, InP, CdS, ZnS)
37 Body Centered Cubic Lattice 1 Extra Atom at Center of Unit Cell; 1:1 Also
38 ZnS (Smallest Cation/Anion) CsCl (Biggest Cation/Anion) NaCl (Intermediate Cation/Anion)
39 END Part 1 References: Gray: Chapter 6 OGN: Chapter 19 and (24.1)
ENGINEERING MATERIALS LECTURE #4
 ENGINEERING MATERIALS LECTURE #4 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Topics to Cover What is the difference in atomic arrangement between crystalline and noncrystalline solids? What features
ENGINEERING MATERIALS LECTURE #4 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Topics to Cover What is the difference in atomic arrangement between crystalline and noncrystalline solids? What features
Chem 241. Lecture 19. UMass Amherst Biochemistry... Teaching Initiative
 Chem 241 Lecture 19 UMass Amherst Biochemistry... Teaching Initiative Announcement March 26 Second Exam Recap Water Redox Comp/Disproportionation Latimer Diagram Frost Diagram Pourbaix Diagram... 2 Ellingham
Chem 241 Lecture 19 UMass Amherst Biochemistry... Teaching Initiative Announcement March 26 Second Exam Recap Water Redox Comp/Disproportionation Latimer Diagram Frost Diagram Pourbaix Diagram... 2 Ellingham
SOLID-STATE STRUCTURE.. FUNDAMENTALS
 SOLID-STATE STRUCTURE.. FUNDAMENTALS Metallic Elements & Sphere Packing, Unit Celis, Coordination Number, Ionic Structures Stoichiometry PRELAB ASSIGNMENT Properties of Shapes & Patterns following question
SOLID-STATE STRUCTURE.. FUNDAMENTALS Metallic Elements & Sphere Packing, Unit Celis, Coordination Number, Ionic Structures Stoichiometry PRELAB ASSIGNMENT Properties of Shapes & Patterns following question
Crystal Structures of Interest
 rystal Structures of Interest Elemental solids: Face-centered cubic (fcc) Hexagonal close-packed (hcp) ody-centered cubic (bcc) Diamond cubic (dc) inary compounds Fcc-based (u 3 u,nal, ß-ZnS) Hcp-based
rystal Structures of Interest Elemental solids: Face-centered cubic (fcc) Hexagonal close-packed (hcp) ody-centered cubic (bcc) Diamond cubic (dc) inary compounds Fcc-based (u 3 u,nal, ß-ZnS) Hcp-based
Energy and Packing. Materials and Packing
 Energy and Packing Non dense, random packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r Dense, regular packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r
Energy and Packing Non dense, random packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r Dense, regular packing Energy typical neighbor bond length typical neighbor bond energy r
Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
 Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed crystal structures Density computations Crystal structure
Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed crystal structures Density computations Crystal structure
Chapter 16. Liquids and Solids. Chapter 16 Slide 1 of 87
 Chapter 16 Liquids and Solids Chapter 16 Slide 1 of 87 Chapter Preview Intramolecular forces determine such molecular properties as molecular geometries and dipole moments. Intermolecular forces determine
Chapter 16 Liquids and Solids Chapter 16 Slide 1 of 87 Chapter Preview Intramolecular forces determine such molecular properties as molecular geometries and dipole moments. Intermolecular forces determine
Ceramic Science 4RO3. Lecture 2. Tannaz Javadi. September 16, 2013
 Ceramic Science 4RO3 Lecture 2 September 16, 2013 Tannaz Javadi Rule 5: In an Ionic structure the chemical environment (cations) that is surrounding an anion should be at least uniform and similar. Although
Ceramic Science 4RO3 Lecture 2 September 16, 2013 Tannaz Javadi Rule 5: In an Ionic structure the chemical environment (cations) that is surrounding an anion should be at least uniform and similar. Although
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics
 Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Review of structures for ceramics How are impurities accommodated in the ceramic lattice? In what ways are ceramic phase diagrams similar
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Review of structures for ceramics How are impurities accommodated in the ceramic lattice? In what ways are ceramic phase diagrams similar
Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS)
 Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What are anistropic substances. 2. Why are amorphous solids isotropic in nature?. Why glass is regarded as an amorphous solid? 4.
Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What are anistropic substances. 2. Why are amorphous solids isotropic in nature?. Why glass is regarded as an amorphous solid? 4.
Unit 1 The Solid State
 Points to Remember Amorphous and Crystalline Solids Unit 1 The Solid State Amorphous- short range order, Irregular shape eg-glass Crystalline Solids- long range order, regular shape eg : NaCl Molecular
Points to Remember Amorphous and Crystalline Solids Unit 1 The Solid State Amorphous- short range order, Irregular shape eg-glass Crystalline Solids- long range order, regular shape eg : NaCl Molecular
Semiconductors. Types of Solids. Figure 10.30: Energy-level diagrams for (a) an n-type semiconductor and (b) a ptype semiconductor.
 Figure 102: Partial representation of the molecular orbital energies in (a) diamond and (b) a typical metal Figure 1024: The p orbitals (a) perpendicular to the plane of the carbon ring system in graphite
Figure 102: Partial representation of the molecular orbital energies in (a) diamond and (b) a typical metal Figure 1024: The p orbitals (a) perpendicular to the plane of the carbon ring system in graphite
STATE OF SOLIDIFICATION & CRYSTAL STRUCTURE
 STATE OF SOLIDIFICATION & CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Chapter Outline Determination of crystal properties or properties of crystalline materials. Crystal Geometry! Crystal Directions! Linear Density of atoms! Crystal
STATE OF SOLIDIFICATION & CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Chapter Outline Determination of crystal properties or properties of crystalline materials. Crystal Geometry! Crystal Directions! Linear Density of atoms! Crystal
Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids
 Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids Crystal Structures Points, Directions, and Planes Linear and Planar Densities X-ray Diffraction How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on
Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids Crystal Structures Points, Directions, and Planes Linear and Planar Densities X-ray Diffraction How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on
Metallic crystal structures The atomic bonding is metallic and thus non-directional in nature
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids Hw: 4, 6, 10, 14, 18, 21, 26, 31, 35, 39, 42, 43, 46, 48, 49, 51, 56, 61 Due Wensday 14/10/2009 Quiz1 on Wensday 14/10/2009 Why study the structure of crystalline
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids Hw: 4, 6, 10, 14, 18, 21, 26, 31, 35, 39, 42, 43, 46, 48, 49, 51, 56, 61 Due Wensday 14/10/2009 Quiz1 on Wensday 14/10/2009 Why study the structure of crystalline
Crystal Structure. Andrew R. Barron Carissa Smith. 1 Introduction. 2 Crystallography
 OpenStax-CNX module: m16927 1 Crystal Structure Andrew R. Barron Carissa Smith This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Introduction In any
OpenStax-CNX module: m16927 1 Crystal Structure Andrew R. Barron Carissa Smith This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Introduction In any
Free Electron Model What kind of interactions hold metal atoms together? How does this explain high electrical and thermal conductivity?
 Electrical Good conductors of heat & electricity Create semiconductors Oxides are basic ionic solids Aqueous cations (positive charge, Lewis acids) Reactivity increases downwards in family Free Electron
Electrical Good conductors of heat & electricity Create semiconductors Oxides are basic ionic solids Aqueous cations (positive charge, Lewis acids) Reactivity increases downwards in family Free Electron
Two marks questions and answers. 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples
 UNIT V CRYSTAL PHYSICS PART-A Two marks questions and answers 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples Crystalline solids (or) Crystals are those in which the constituent
UNIT V CRYSTAL PHYSICS PART-A Two marks questions and answers 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples Crystalline solids (or) Crystals are those in which the constituent
1.10 Close packed structures cubic and hexagonal close packing
 1.9 Description of crystal structures The most common way for describing crystal structure is to refer the structure to the unit cell. The structure is given by the size and shape of the cell and the position
1.9 Description of crystal structures The most common way for describing crystal structure is to refer the structure to the unit cell. The structure is given by the size and shape of the cell and the position
Free Electron Model What kind of interactions hold metal atoms together? How does this explain high electrical and thermal conductivity?
 Electrical Good conductors of heat & electricity Create semiconductors Oxides are basic ionic solids Aqueous cations (positive charge, Lewis acids) Reactivity increases downwards in family Mechanical Lustrous
Electrical Good conductors of heat & electricity Create semiconductors Oxides are basic ionic solids Aqueous cations (positive charge, Lewis acids) Reactivity increases downwards in family Mechanical Lustrous
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids?
 Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures Face-centered cubic Body-centered cubic Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures Face-centered cubic Body-centered cubic Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Alloys and Solid Solutions
 Alloys and Solid Solutions Chemistry 123 Spring 2008 Dr. Woodward Solutions Solid Solution 14 Carat Gold Liquid Solution Vodka Gaseous Solution Air Solution = A homogeneous mixture 1 Alloys An alloy is
Alloys and Solid Solutions Chemistry 123 Spring 2008 Dr. Woodward Solutions Solid Solution 14 Carat Gold Liquid Solution Vodka Gaseous Solution Air Solution = A homogeneous mixture 1 Alloys An alloy is
UNIT V -CRYSTAL STRUCTURE
 UNIT V -CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Solids are of two types: Amorphous and crystalline. In amorphous solids, there is no order in the arrangement of their constituent atoms (molecules). Hence no definite structure
UNIT V -CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Solids are of two types: Amorphous and crystalline. In amorphous solids, there is no order in the arrangement of their constituent atoms (molecules). Hence no definite structure
(C) Na 2. (B) NaWO 3 WO 3
 EXERCISE-01 CHECK YOUR GRASP SELECT THE CORRECT ALTERNATIVE (ONLY ONE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. A solid has a structure in which W atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, O atom at the centre of
EXERCISE-01 CHECK YOUR GRASP SELECT THE CORRECT ALTERNATIVE (ONLY ONE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. A solid has a structure in which W atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, O atom at the centre of
Donald Neamen 물리전자 / 김삼동 1-1
 An Introduction to Semiconductor Devices Donald Neamen Images and illustrations from supplements of An Introduction to Semiconductor Devices, 4 th Ed., Mc Graw Hill were used for this lecture materials.
An Introduction to Semiconductor Devices Donald Neamen Images and illustrations from supplements of An Introduction to Semiconductor Devices, 4 th Ed., Mc Graw Hill were used for this lecture materials.
CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES & PROPERTIES
 CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on metals) How does the density of a material depend on its structure? When
CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on metals) How does the density of a material depend on its structure? When
Chem 253, UC, Berkeley. Chem 253, UC, Berkeley
 1 2 Theorem: For any family of lattice planes separated by distance d, there are reciprocal lattice vectors perpendicular to the planes, the shortest being 2 /d. Orientation of plane is determined by a
1 2 Theorem: For any family of lattice planes separated by distance d, there are reciprocal lattice vectors perpendicular to the planes, the shortest being 2 /d. Orientation of plane is determined by a
ENERGY AND PACKING. Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES MATERIALS AND PACKING METALLIC CRYSTALS ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... 1. How do s assemble into solid structures? (For now, focus on metals) ENERGY AND PACKING non dense, random packing bond energy Energy bond
Chapter 3 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... 1. How do s assemble into solid structures? (For now, focus on metals) ENERGY AND PACKING non dense, random packing bond energy Energy bond
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives I 1. Describe difference in atomic/molecular structure between crystalline/noncrystalline
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives I 1. Describe difference in atomic/molecular structure between crystalline/noncrystalline
Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices
 Outline: Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices Review (example with square lattice) Lattice: square,
Outline: Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices Review (example with square lattice) Lattice: square,
Packing of atoms in solids
 MME131: Lecture 6 Packing of atoms in solids A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s topics Atomic arrangements in solids Points, directions and planes in unit cell References:
MME131: Lecture 6 Packing of atoms in solids A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s topics Atomic arrangements in solids Points, directions and planes in unit cell References:
Impurities in Solids. Crystal Electro- Element R% Structure negativity Valence
 4-4 Impurities in Solids 4.4 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the three possible solid solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following
4-4 Impurities in Solids 4.4 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the three possible solid solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following
Problem 1: (a) Describe the ß-ZnS structure and show how it is related to the FCC structure.
 Note: I ve finished correcting mistakes from some of the later exams but not the earlier ones. If you see a mistake, plz msg me on AIM:huangnankun or huangnankun@berkeley.edu, I ll update this document
Note: I ve finished correcting mistakes from some of the later exams but not the earlier ones. If you see a mistake, plz msg me on AIM:huangnankun or huangnankun@berkeley.edu, I ll update this document
Point Defects in Metals
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Point Defects in Metals 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for lead at its melting temperature of 327 C (600 K). Assume an energy
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Point Defects in Metals 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for lead at its melting temperature of 327 C (600 K). Assume an energy
Chapter 12: Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solids
 1. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point? A) Br 2 B) Cl 2 C) F 2 D) I 2 3. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point?
1. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point? A) Br 2 B) Cl 2 C) F 2 D) I 2 3. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point?
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
Mat E 272 Lectures 22-23: Introduction to Ceramic Materials
 Mat E 272 Lectures 22-23: Introduction to Ceramic Materials November 26 & 28, 2001 Introduction: The primary emphasis of this class has previously been on the structure and properties of pure metals and
Mat E 272 Lectures 22-23: Introduction to Ceramic Materials November 26 & 28, 2001 Introduction: The primary emphasis of this class has previously been on the structure and properties of pure metals and
Chemistry 145 Exam number 4 name 11/19/98 # Faraday s constant is 96,500 c/mole of electrons.
 Chemistry 145 Exam number 4 name 11/19/98 # Faraday s constant is 96,500 c/mole of electrons. A.(16) An electrochemical cell is prepared with a strip of manganese metal dipping in to a 1.0 M MnSO 4 solution
Chemistry 145 Exam number 4 name 11/19/98 # Faraday s constant is 96,500 c/mole of electrons. A.(16) An electrochemical cell is prepared with a strip of manganese metal dipping in to a 1.0 M MnSO 4 solution
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Design of Yb 3+ optical bandwidths by crystallographic modification of disordered
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Design of Yb 3+ optical bandwidths by crystallographic modification of disordered
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS ev /atom = exp. kt ( =
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
C h a p t e r 4 : D e f e c t s i n C r y s t a l s
 C h a p t e r 4 : D e f e c t s i n C r y s t a l s...perfection's a gift of The gods, few can boast they possess it - and most Of you, my dears, don't. - Ovid, The Art of Love Chapter 4: Defects in Crystals...
C h a p t e r 4 : D e f e c t s i n C r y s t a l s...perfection's a gift of The gods, few can boast they possess it - and most Of you, my dears, don't. - Ovid, The Art of Love Chapter 4: Defects in Crystals...
(a) 7.27 m (b) m (c) 5.38 m (d) 5380 m (e) m
 1. The density of liquid cesium at 30 C is 1.87 g/ml. Because of its wide liquid range (28 to 678 C), cesium could be used as a barometer fluid at high temperatures. What height of cesium will be supported
1. The density of liquid cesium at 30 C is 1.87 g/ml. Because of its wide liquid range (28 to 678 C), cesium could be used as a barometer fluid at high temperatures. What height of cesium will be supported
Density Computations
 CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS Fundamental Concepts 3.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Unit Cells Metallic Crystal Structures 3.2 If the atomic radius
CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS Fundamental Concepts 3.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Unit Cells Metallic Crystal Structures 3.2 If the atomic radius
Alloys GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS 621 SUBSTITUTIONAL SOLID SOLUTIONS HUME-ROTHERY RULES 624
 ch22.qxd 9/22/4 5:29 PM Page 619 22 Alloys GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS 621 SUBSTITUTIONAL SOLID SOLUTIONS HUME-ROTHERY RULES 624 ORDER-DISORDER TRANSFORMATION 627 Elementary theory of order 629 PHASE DIAGRAMS
ch22.qxd 9/22/4 5:29 PM Page 619 22 Alloys GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS 621 SUBSTITUTIONAL SOLID SOLUTIONS HUME-ROTHERY RULES 624 ORDER-DISORDER TRANSFORMATION 627 Elementary theory of order 629 PHASE DIAGRAMS
Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities)
 Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities) 1 Structural Imperfections A perfect crystal has the lowest internal energy E Above absolute zero
Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities) 1 Structural Imperfections A perfect crystal has the lowest internal energy E Above absolute zero
CHAPTER 2. Structural Issues of Semiconductors
 CHAPTER 2 Structural Issues of Semiconductors OUTLINE 1.0 Energy & Packing 2.0 Materials & Packing 3.0 Crystal Structures 4.0 Theoretical Density, r 5.0.Polymorphism and Allotropy 6.0 Close - Packed Crystal
CHAPTER 2 Structural Issues of Semiconductors OUTLINE 1.0 Energy & Packing 2.0 Materials & Packing 3.0 Crystal Structures 4.0 Theoretical Density, r 5.0.Polymorphism and Allotropy 6.0 Close - Packed Crystal
Basic Solid State Chemistry, 2 nd ed. West, A. R.
 Basic Solid State Chemistry, 2 nd ed. West, A. R. Chapter 1 Crystal Structures Many of the properties and applications of crystalline inorganic materials revolve around a small number of structure types
Basic Solid State Chemistry, 2 nd ed. West, A. R. Chapter 1 Crystal Structures Many of the properties and applications of crystalline inorganic materials revolve around a small number of structure types
Symmetry in crystalline solids.
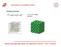 Symmetry in crystalline solids. Translation symmetry n 1,n 2,n 3 are integer numbers 1 Unitary or primitive cells 2D 3D Red, green and cyano depict all primitive (unitary) cells, whereas blue cell is not
Symmetry in crystalline solids. Translation symmetry n 1,n 2,n 3 are integer numbers 1 Unitary or primitive cells 2D 3D Red, green and cyano depict all primitive (unitary) cells, whereas blue cell is not
Structure of silica glasses (Chapter 12)
 Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
ALE 20. Crystalline Solids, Unit Cells, Liquids and the Uniqueness of Water
 Name Chem 162, Section: Group Number: ALE 20. Crystalline Solids, Unit Cells, Liquids and the Uniqueness of Water (Reference: pp. 463 473 of Sec. 12.6 Silberberg 5 th edition) How are the particles within
Name Chem 162, Section: Group Number: ALE 20. Crystalline Solids, Unit Cells, Liquids and the Uniqueness of Water (Reference: pp. 463 473 of Sec. 12.6 Silberberg 5 th edition) How are the particles within
Magnetic semiconductors
 Magnetic semiconductors Classical magnetic semiconductors Diluted magnetic semiconductors Ferromagnetic semiconductors New materials, nanostructures, interfaces Magnetic semiconductors Classical magnetic
Magnetic semiconductors Classical magnetic semiconductors Diluted magnetic semiconductors Ferromagnetic semiconductors New materials, nanostructures, interfaces Magnetic semiconductors Classical magnetic
Experiment 3 * Thermochromism in the Ionic Conductor, Cu 2 HgI 4
 Experiment 3 * Thermochromism in the Ionic Conductor, Cu 2 HgI 4 *This lab taken from Teaching General Chemistry; A Materials Science Companion, Eds. Ellis, A.B.; Geselbracht, M.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Lisensky,
Experiment 3 * Thermochromism in the Ionic Conductor, Cu 2 HgI 4 *This lab taken from Teaching General Chemistry; A Materials Science Companion, Eds. Ellis, A.B.; Geselbracht, M.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Lisensky,
Analytical Methods for Materials
 Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 13 Crystallography and Crystal Structures continued Chapter 6 in Waseda Excerpt from ASM Metals Handbook. Suggested Reading 337 Notation for crystal structures 1.
Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 13 Crystallography and Crystal Structures continued Chapter 6 in Waseda Excerpt from ASM Metals Handbook. Suggested Reading 337 Notation for crystal structures 1.
Review of Metallic Structure
 Phase Diagrams Understanding the Basics F.C. Campbell, editor Copyright 2012 ASM International All rights reserved www.asminternational.org Appendix A Review of Metallic Structure The word metal, derived
Phase Diagrams Understanding the Basics F.C. Campbell, editor Copyright 2012 ASM International All rights reserved www.asminternational.org Appendix A Review of Metallic Structure The word metal, derived
TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III
 Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Understanding Cation-Disordered Cathode Materials Based on Percolation Theory and Ligand Field Theory
 2016 ECS Prime meeting (10/5/2016, 8:40 9:00 am) Understanding Cation-Disordered Cathode Materials Based on Percolation Theory and gand Field Theory Jinhyuk Lee, Dong-Hwa Seo, Alexander Urban, Gerbrand
2016 ECS Prime meeting (10/5/2016, 8:40 9:00 am) Understanding Cation-Disordered Cathode Materials Based on Percolation Theory and gand Field Theory Jinhyuk Lee, Dong-Hwa Seo, Alexander Urban, Gerbrand
Carbon nanostructures. (http://www.mf.mpg.de/de/abteilungen/schuetz/index.php?lang=en&content=researchtopics&type=specific&name=h2storage)
 Carbon nanostructures (http://www.mf.mpg.de/de/abteilungen/schuetz/index.php?lang=en&content=researchtopics&type=specific&name=h2storage) 1 Crystal Structures Crystalline Material: atoms arrange into a
Carbon nanostructures (http://www.mf.mpg.de/de/abteilungen/schuetz/index.php?lang=en&content=researchtopics&type=specific&name=h2storage) 1 Crystal Structures Crystalline Material: atoms arrange into a
CRYSTAL LATTICE. Defining lattice: Mathematical construct; ideally infinite arrangement of points in space.
 CRYSTAL LATTICE How to form a crystal? 1. Define the structure of the lattice 2. Define the lattice constant 3. Define the basis Defining lattice: Mathematical construct; ideally infinite arrangement of
CRYSTAL LATTICE How to form a crystal? 1. Define the structure of the lattice 2. Define the lattice constant 3. Define the basis Defining lattice: Mathematical construct; ideally infinite arrangement of
Non-crystalline Materials
 Noncrystalline (or amorphous) solids by definition means atoms are stacked in irregular, random patterns. The general term for non-crystallline solids with compositions comparable to those of crystalline
Noncrystalline (or amorphous) solids by definition means atoms are stacked in irregular, random patterns. The general term for non-crystallline solids with compositions comparable to those of crystalline
Fine Structure and Magnetism of the Cubic Oxide Compound Ni 0.3 Zn 0.7 O
 ISSN 163-7834, Physics of the Solid State, 11, Vol. 53, No. 7, pp. 136 1366. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 11. Original Russian Text S.F. Dubinin, V.I. Maksimov, V.D. Parkhomenko, V.I. Sokolov, A.N. Baranov,
ISSN 163-7834, Physics of the Solid State, 11, Vol. 53, No. 7, pp. 136 1366. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 11. Original Russian Text S.F. Dubinin, V.I. Maksimov, V.D. Parkhomenko, V.I. Sokolov, A.N. Baranov,
Interatomic bonding, elastic properties, and ideal strength of transition metal aluminides: A case study for Al 3 V,Ti
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 71, 024101 (2005) Interatomic bonding, elastic properties, and ideal strength of transition metal aluminides: A case study for Al 3 V,Ti M. Jahnátek, 1 M. Krajčí, 1,2 and J. Hafner 2
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 71, 024101 (2005) Interatomic bonding, elastic properties, and ideal strength of transition metal aluminides: A case study for Al 3 V,Ti M. Jahnátek, 1 M. Krajčí, 1,2 and J. Hafner 2
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS
 MODULE ONE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Metallic crystal structures; BCC, FCC and HCP Coordination number and Atomic Packing Factor (APF) Crystal imperfections:
MODULE ONE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Metallic crystal structures; BCC, FCC and HCP Coordination number and Atomic Packing Factor (APF) Crystal imperfections:
Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic. Ceramics. Ceramics exhibit ionic, covalent bonding or a combination of the two (like in Al 2 O 3 )
 What are Ceramics? CERAMIC MATERIALS Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic and crystalline materials that are typically produced using clays and other minerals from the earth or chemically processed powders
What are Ceramics? CERAMIC MATERIALS Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic and crystalline materials that are typically produced using clays and other minerals from the earth or chemically processed powders
Primitive cells, Wigner-Seitz cells, and 2D lattices. 4P70, Solid State Physics Chris Wiebe
 Primitive cells, Wigner-Seitz cells, and 2D lattices 4P70, Solid State Physics Chris Wiebe Choice of primitive cells! Which unit cell is a good choice?! A, B, and C are primitive unit cells. Why?! D, E,
Primitive cells, Wigner-Seitz cells, and 2D lattices 4P70, Solid State Physics Chris Wiebe Choice of primitive cells! Which unit cell is a good choice?! A, B, and C are primitive unit cells. Why?! D, E,
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number:
 Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering
 01 Askeland Chap 9/27/05 1:48 PM Page 1 1 Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering 1 4 Steel is often coated with a thin layer of zinc if it is to be used outside. What characteristics do you
01 Askeland Chap 9/27/05 1:48 PM Page 1 1 Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering 1 4 Steel is often coated with a thin layer of zinc if it is to be used outside. What characteristics do you
Materials and their structures
 Materials and their structures 2.1 Introduction: The ability of materials to undergo forming by different techniques is dependent on their structure and properties. Behavior of materials depends on their
Materials and their structures 2.1 Introduction: The ability of materials to undergo forming by different techniques is dependent on their structure and properties. Behavior of materials depends on their
Chapter 1 - Introduction
 Chapter 1 - Introduction What is materials science? Why should we know about it? Materials drive our society Stone Age Bronze Age Iron Age Now? Silicon Age? Polymer Age? Chapter 1-1 Chapter 1-2 Hardness
Chapter 1 - Introduction What is materials science? Why should we know about it? Materials drive our society Stone Age Bronze Age Iron Age Now? Silicon Age? Polymer Age? Chapter 1-1 Chapter 1-2 Hardness
CHAPTER 3 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Law
 CHAPTER 3 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Law . Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals in the Periodic Table Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Metals, Metalloids, and
CHAPTER 3 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Law . Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals in the Periodic Table Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Metals, Metalloids, and
It is instructive however for you to do a simple structure by hand. Rocksalt Structure. Quite common in nature. KCl, NaCl, MgO
 Today the structure determinations etc are all computer -assisted It is instructive however for you to do a simple structure by hand Rocksalt Structure Quite common in nature KCl, NaCl, MgO 9-1 Typical
Today the structure determinations etc are all computer -assisted It is instructive however for you to do a simple structure by hand Rocksalt Structure Quite common in nature KCl, NaCl, MgO 9-1 Typical
Topics Relevant to CdTe Thin Film Solar Cells
 Topics Relevant to CdTe Thin Film Solar Cells March 13, 2012 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy (PHYS 4400) and Fundamentals
Topics Relevant to CdTe Thin Film Solar Cells March 13, 2012 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy (PHYS 4400) and Fundamentals
Ionic Conductivity and Solid Electrolytes II: Materials and Applications
 Ionic Conductivity and Solid Electrolytes II: Materials and Applications Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Lecture #27 June 4, 2003 References A. Manthiram & J. Kim Low Temperature Synthesis of Insertion
Ionic Conductivity and Solid Electrolytes II: Materials and Applications Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Lecture #27 June 4, 2003 References A. Manthiram & J. Kim Low Temperature Synthesis of Insertion
Point Defects LATTICE VACANCIES 585. DIFFUSION 588 Metals 591. COLOR CENTERS 592 F centers 592 Other centers in alkali halides 593 PROBLEMS 595
 ch20.qxd 9/22/04 5:27 PM Page 583 20 Point Defects LATTICE VACANCIES 585 DIFFUSION 588 Metals 591 COLOR CENTERS 592 F centers 592 Other centers in alkali halides 593 PROBLEMS 595 1. Frenkel defects 595
ch20.qxd 9/22/04 5:27 PM Page 583 20 Point Defects LATTICE VACANCIES 585 DIFFUSION 588 Metals 591 COLOR CENTERS 592 F centers 592 Other centers in alkali halides 593 PROBLEMS 595 1. Frenkel defects 595
Chemical Activation of Low Calcium Fly Ash Part 1: Identification of Suitable Activators and their Dosage
 Chemical Activation of Low Calcium Fly Ash Part 1: Identification of Suitable Activators and their Dosage P. Arjunan 1, M. R. Silsbee 2, and D. M. Roy 2, 1 Custom Building Products, 6515, Salt Lake Ave,
Chemical Activation of Low Calcium Fly Ash Part 1: Identification of Suitable Activators and their Dosage P. Arjunan 1, M. R. Silsbee 2, and D. M. Roy 2, 1 Custom Building Products, 6515, Salt Lake Ave,
Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews. Cindy Smith
 Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews Cindy Smith Motivation Review: Outline Crystal lattices (fcc, bcc, hcp) Fcc vs. hcp stacking sequences Cubic {hkl} naming Hcp {hkil} naming Twinning
Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews Cindy Smith Motivation Review: Outline Crystal lattices (fcc, bcc, hcp) Fcc vs. hcp stacking sequences Cubic {hkl} naming Hcp {hkil} naming Twinning
The First principle calculation of bulk modulus and Young's modulus for amorphous carbon material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The First principle calculation of bulk modulus and Young's modulus for amorphous carbon material To cite this article: A M Ito et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The First principle calculation of bulk modulus and Young's modulus for amorphous carbon material To cite this article: A M Ito et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf.
Atomic Radii of Some Representative Elements (in Picometers)
 Atomic Radii of Some Representative Elements (in Picometers) Group 3A, Group 13 B, Al, Ga, In, and Tl; Valence-shell electron configuration: ns 2 np 1 Group 3A elements show increasing metallic character
Atomic Radii of Some Representative Elements (in Picometers) Group 3A, Group 13 B, Al, Ga, In, and Tl; Valence-shell electron configuration: ns 2 np 1 Group 3A elements show increasing metallic character
GEOLOGY 284: MINERALOGY
 Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University FALL 2014 GEOLOGY 284: MINERALOGY Ore Deposits and Economic Minerals An ore is anything that can be mined from the Earth at a profit,
Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University FALL 2014 GEOLOGY 284: MINERALOGY Ore Deposits and Economic Minerals An ore is anything that can be mined from the Earth at a profit,
Synthesis and characterization of Aln 2 O 4 indates, A ˆ Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE LETTERS 17 (1998) 619±623 Synthesis and characterization of Aln 2 O 4 indates, A ˆ Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba S. ESTHER DALI, V. V. S. S. SAI SUNDAR, M. JAYACHANDRAN, M. J. CHOCKALINGAM
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE LETTERS 17 (1998) 619±623 Synthesis and characterization of Aln 2 O 4 indates, A ˆ Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba S. ESTHER DALI, V. V. S. S. SAI SUNDAR, M. JAYACHANDRAN, M. J. CHOCKALINGAM
Electricity and Chemistry
 Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
XRD AND XAFS STUDIES OF CARBON SUPPORTED Pt-Ru ELECTROCATALYST IN A POLYMER-ELECTROLYTE-FUEL-CELL
 Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 4, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 47. 56 XRD AND XAFS STUDIES OF CARBON SUPPORTED Pt-Ru ELECTROCATALYST IN A POLYMER-ELECTROLYTE-FUEL-CELL
Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 4, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 47. 56 XRD AND XAFS STUDIES OF CARBON SUPPORTED Pt-Ru ELECTROCATALYST IN A POLYMER-ELECTROLYTE-FUEL-CELL
7.3 Bonding in Metals > Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding. 7.3 Bonding in Metals. 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
 Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU What
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU What
Chapter 20 CHEMISTRY. Metallurgy and the Chemistry of Metals. Dr. Ibrahim Suleiman
 CHEMISTRY Chapter 20 Metallurgy and the Chemistry of Metals Dr. Ibrahim Suleiman GENERAL PROPERTIES AND STRUCTURE OF METALS opaque good conductors of heat and electricity high malleability and ductility
CHEMISTRY Chapter 20 Metallurgy and the Chemistry of Metals Dr. Ibrahim Suleiman GENERAL PROPERTIES AND STRUCTURE OF METALS opaque good conductors of heat and electricity high malleability and ductility
Magnetic and Structural Properties of Fe Mn Al Alloys Produced by Mechanical Alloying
 Hyperfine Interactions 148/149: 295 305, 2003. 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 295 Magnetic and Structural Properties of Fe Mn Al Alloys Produced by Mechanical Alloying G.
Hyperfine Interactions 148/149: 295 305, 2003. 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 295 Magnetic and Structural Properties of Fe Mn Al Alloys Produced by Mechanical Alloying G.
Cu/Ag Eutectic System
 Eutectic Systems The simplest kind of system with two solid phases is called a eutectic system. A eutectic system contains two solid phases at low temperature. These phases may have different crystal structures,
Eutectic Systems The simplest kind of system with two solid phases is called a eutectic system. A eutectic system contains two solid phases at low temperature. These phases may have different crystal structures,
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter.
 1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geology 211. Crystal Form, Zones, Crystal Habit. Crystal Forms
 Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geology 211 Tulane University Mineralogy Crystal Form, Zones, Crystal Habit This page last updated on 27-Aug-2002 Crystal Forms As stated at the end of the last lecture, the next
Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geology 211 Tulane University Mineralogy Crystal Form, Zones, Crystal Habit This page last updated on 27-Aug-2002 Crystal Forms As stated at the end of the last lecture, the next
MICROWAVES AS AN ENERGY SOURCE FOR PRODUCING MAGNESIA - ALUMINA SPINEL
 MICROWAVES AS AN ENERGY SOURCE FOR PRODUCING MAGNESIA - ALUMINA SPINEL JUAN A. AGUILAR MARIO GONZALEZ IDALIA GOMEZ Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica y Eléctrica Apartado
MICROWAVES AS AN ENERGY SOURCE FOR PRODUCING MAGNESIA - ALUMINA SPINEL JUAN A. AGUILAR MARIO GONZALEZ IDALIA GOMEZ Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica y Eléctrica Apartado
Crystal structure, electronic structure, chemical bonding and defects in metal-ion battery materials
 Crystal structure, electronic structure, chemical bonding and defects in metal-ion battery materials Artem Abakumov Center for Electrochemical Energy Storage, Skoltech Li-ion batteries Li x C 6 graphite
Crystal structure, electronic structure, chemical bonding and defects in metal-ion battery materials Artem Abakumov Center for Electrochemical Energy Storage, Skoltech Li-ion batteries Li x C 6 graphite
Design of Conducting Metal-Organic Framework: Orbital- Level Matching in MIL-140A Derivatives
 Supporting Information Design of Conducting Metal-Organic Framework: Orbital- Level Matching in MIL-140A Derivatives Tokutaro Komatsu,*, Jared M. Taylor,,, and Hiroshi Kitagawa,,,# Division of Chemistry,
Supporting Information Design of Conducting Metal-Organic Framework: Orbital- Level Matching in MIL-140A Derivatives Tokutaro Komatsu,*, Jared M. Taylor,,, and Hiroshi Kitagawa,,,# Division of Chemistry,
Etching of CVD diamond surfaces
 Etching of CVD diamond surfaces By: Maria D. Stoikou MPhys (Hons.) Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, Heriot-Watt University, School of Engineering and Physical Sciences August 2010 The
Etching of CVD diamond surfaces By: Maria D. Stoikou MPhys (Hons.) Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, Heriot-Watt University, School of Engineering and Physical Sciences August 2010 The
INTRODUCTION:- 1.Classification of magnetic material Diamagnetic
 INTRODUCTION:- Ferrites are ferromagnetic material containing predominantly oxides iron along with other oxides of barium, strontium, manganese, nickel, zinc, lithium and cadmium.ferrites are ideally suited
INTRODUCTION:- Ferrites are ferromagnetic material containing predominantly oxides iron along with other oxides of barium, strontium, manganese, nickel, zinc, lithium and cadmium.ferrites are ideally suited
Laboratory Testing of Three Above Ground Paint Systems for Canadian Applications
 Laboratory Testing of Three Above Ground Paint Systems for Canadian Applications Amal Al-Borno, Mick Brown Charter Coating Service (2000) Ltd. #6, 4604 13 th Street N.E. Calgary, AB, Canada T2E 6P1 Robert
Laboratory Testing of Three Above Ground Paint Systems for Canadian Applications Amal Al-Borno, Mick Brown Charter Coating Service (2000) Ltd. #6, 4604 13 th Street N.E. Calgary, AB, Canada T2E 6P1 Robert
Supplementary material for Ab initio structure modeling of complex thin-film oxides: thermodynamical stability of TiC/thin-film
 Supplementary material for Ab initio structure modeling of complex thin-film oxides: thermodynamical stability of TiC/thin-film alumina (Rohrer et al 2009 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22 015004) J Rohrer
Supplementary material for Ab initio structure modeling of complex thin-film oxides: thermodynamical stability of TiC/thin-film alumina (Rohrer et al 2009 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22 015004) J Rohrer
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Dislocations and Plastic Deformation
 Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Edge and screw are the two fundamental dislocation types. In an edge dislocation, localized lattice distortion exists along the end of an extra half-plane of atoms,
Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Edge and screw are the two fundamental dislocation types. In an edge dislocation, localized lattice distortion exists along the end of an extra half-plane of atoms,
a. 50% fine pearlite, 12.5% bainite, 37.5% martensite. 590 C for 5 seconds, 350 C for 50 seconds, cool to room temperature.
 Final Exam Wednesday, March 21, noon to 3:00 pm (160 points total) 1. TTT Diagrams A U.S. steel producer has four quench baths, used to quench plates of eutectoid steel to 700 C, 590 C, 350 C, and 22 C
Final Exam Wednesday, March 21, noon to 3:00 pm (160 points total) 1. TTT Diagrams A U.S. steel producer has four quench baths, used to quench plates of eutectoid steel to 700 C, 590 C, 350 C, and 22 C
Diffraction: Powder Method
 Diffraction: Powder Method Diffraction Methods Diffraction can occur whenever Bragg s law λ = d sin θ is satisfied. With monochromatic x-rays and arbitrary setting of a single crystal in a beam generally
Diffraction: Powder Method Diffraction Methods Diffraction can occur whenever Bragg s law λ = d sin θ is satisfied. With monochromatic x-rays and arbitrary setting of a single crystal in a beam generally
Engineering Materials Department of Physics K L University
 Engineering Materials Department of Physics K L University 1 Crystallography Bonding in solids Many of the physical properties of materials are predicated on a knowledge of the inter-atomic forces that
Engineering Materials Department of Physics K L University 1 Crystallography Bonding in solids Many of the physical properties of materials are predicated on a knowledge of the inter-atomic forces that
X-ray diffraction and structure analysis Introduction
 Teknillisen fysiikan ohjelmatyö X-ray diffraction and structure analysis Introduction Oleg Heczko 120 100 80 118 12-5 125 Ni-Mn-Ga (298K) SQRT(Intensity) 60 40 20 015 200 123 12-7 20-10 20,10 20-8 040
Teknillisen fysiikan ohjelmatyö X-ray diffraction and structure analysis Introduction Oleg Heczko 120 100 80 118 12-5 125 Ni-Mn-Ga (298K) SQRT(Intensity) 60 40 20 015 200 123 12-7 20-10 20,10 20-8 040
