Development of EAF Dust Recycling and Melting Technology Using the Coal-based FASTMELT Process
|
|
|
- Eugene Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Development of Recycling and Melting Technology Using the -based FASTMELT Process By M. Tateishi, H. Fujimoto, T. Harada, H. Sugitatsu Kobe Steel, Ltd. Editor s note: this article was adapted from a paper presented at the SEAISI Conference in May INTRODUCTION The accumulation of EAF dust and its disposal have become a serious issue worldwide. EAF dust contains valuable metal resources such as iron, zinc, lead and other elements. Effective recovery of these metals would contribute to the development of a sustainable society. Kobe Steel, Ltd. and Midrex Technologies, Inc. have developed and commercially applied the FASTMET Process for both direct reduced iron () production and steel mill waste recycling. Since 2003, Kobe Steel has carried out a process development project, including three years beginning in 2005, of pilot plant operations at Kakogawa Works in Japan. This project, titled Development of Valuable Metal Recovery Technology by Using a Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF), was subsidized by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). The purpose of the process development project was to: Produce from EAF dust using the coal-based FASTMET Process. Effectively recover valuable metal resources such as zinc in the flue gas. Melt the into hot metal using the coal-based FASTMELT Process to increase added value of recovery metal. As a result of the study and pilot plant operations, the follow ing points are discussed in this article: The FASTMET Process offers a solution to EAF dust recovery. The FASTMELT Process enables the production of hot metal from iron ore or steel mill by-products. CHARACTERISTICS OF EAF DUST AND THE CONVENTIONAL RECYCLING METHOD Table I shows the chemical composition of electric arc furnace (EAF) dust, which we acquired from EAF steelmakers. Table II shows the chemical composition of blast furnace (BF) wet dust and basic oxygen furnace (BOF) dust as a comparison. The main component of all the dust is iron oxide. EAF dust is especially high in zinc since it contains very fine particles smaller than one micron, making it difficult to agglomerate. In Japan, EAF dust is designated as a special management industrial waste. Moreover, because EAF dust includes dioxin, plants in Japan that recover zinc from EAF dust are designated as special facilities under the Law Concerning Special Measures Against Dioxins. Total Fe Zn Pb C CaO SiO 2 S Cl Group 1 31~33 17~ ~4 4~ ~4 Group 2 21~25 26~29 1~3 3~6 2~4 3~5 0.4~0.6 5~7 Table I - Chemical Composition (mass %) BF and BOF Dust Total Fe C Zn C1 F S Na 2 O K 2 O CaO SiO 2 BF Wet Dust BOF Dust Table II - BF and BOF Dust Chemical Composition (mass %) PAGE 9
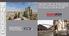
2 Location By-product RHF Dia. (m) Start-Up (Tons/Year) Nippon Steel Hirohata, No , Apr - 00 Kobe Steel Kakogawa 14, Apr - 01 Nippon Steel Hirohata, No , Feb - 05 Nippon Steel Hirohata, No , Dec - 08 Table III - FASTMET Commercial Plants Conventional Method of Recycling Steel Mill Dust The Waelz Kiln process is a well-established technology that uses a rotary kiln to treat steel mill dust. Dust containing zinc oxide and a carbon source, such as coke, are charged into the rotary kiln and heated by combustion heat. Compared to the FASTMET Process, the rotary kiln has lower productivity because of a lower operating temperature and less contact between dust and coal. The temperature in the kiln is generally below 1,200 C to prevent kiln rings from forming. Kiln rings are accretions of material that build up on the inside of the kiln shell. Contact between dust and coal is not as good as in FASTMET because in the kiln process, coal is added separately from the dust; whereas, FASTMET uses a pellet with coal and dust combined. Because of its lower operating temperature and inferior dust and coal contact, the Waelz Process achieves lower iron metallization and less dezincification than FASTMET. Therefore, the iron product cannot be used as a metallic in blast furnaces, basic oxygen furnaces and electric arc furnaces, and it must be disposed of in special landfills. Such disposal is becoming more difficult and expensive. Also, there is a growing trend toward zero emissions of steel mill waste and EAF dust. The FASTMET Process as a New Method of Recycling FASTMET is an improved method of treating EAF dust. Several plants using the FASTMET Process to recycle steel mill waste have started up in Japan since 2000, and they have achieved high operating rates and good productivity. Several other plants are under construction. Table III shows the three operating commercial plants in Japan that use the FASTMET Process. Comparison of the RHF Process and Rotary Kiln Process The characteristics of the FASTMET Process, versus the rotary kiln process, are as follows: FASTMET operates at higher temperatures, over 1,300 C. FASTMET achieves higher metallization and dezincification because of the higher temperatures and higher uniformity of the mixed EAF dust and carbon source before they are fed into the RHF. FASTMET can be used as a metallic in BFs, BOFs and EAFs because of the higher metallization and recovery of zinc in the. Fines generation is lower because the agglomerated raw materials (iron ore and coal) do not roll, but are stationary on the rotary hearth. The zinc content of the recovered flue dust is higher because the amount of dust generated is lower and the dust can be separated in the flue gas system. The amount of dioxin in the is lower because the dioxin in the EAF dust is broken down under high temperatures. The amount of dioxin in the flue gas is lower, because the hot flue gas from the RHF is cooled rapidly in the flue gas system to prevent de novo formation. The PROCESS DEVELOPMENT PROJECT Themes The KSL project for METI includes an RHF and melter. The RHF was designed to produce from EAF dust, with the melter generating hot metal from the using oxygen and a carbon source. In order for the FASTMET/FASTMELT Process to treat EAF dust, the following technical themes were undertaken: Produce agglomerated mixed material in the form of briquettes. Produce higher strength from the briquettes. Recover a higher amount of zinc in the form of zinc oxide in the flue gas. Prevent erosion, corrosion and adhesion in the flue gas system. (Some of the elements in EAF dust, especially zinc, are ten times higher than that of other steel mill waste.) Confirm that the amount of dioxin in the flue gas is lower. Confirm that the produced can be melted into hot metal using the FASTMELT Process. The project was carried out at Kobe Steel's Kakogawa Works. A photo of the FASTMET pilot plant, known as the Kakogawa Pilot Plant (KPP) is shown in Figure 1. Project Schedule The project was begun in 2003 and demonstration operation at Kakogawa Works was carried out until The total period from start to finish was about five years. Figure 1 - Kakogawa Works FASTMET Pilot Plant PAGE 10
3 Briquette Machine Day Bins Mixer CBQ Pulverizer Combustion Air Air Preheater Container Burners Offgas Cooler Rotary Hearth Furnace Bag Filter ID Fan Stack Figure 2 - Kakogawa Pilot Plant Flowsheet PILOT PLANT TESTS USING EAF DUST Process Flowsheet and Equipment Figure 2 shows the process flowsheet for the FASTMET pilot plant and Table IV provides details of the feedstock and equipment. The Rotary Hearth Furnace has the capacity to process approximately 20,000 tons of dust per year. EAF dust, pulverized coal for the reductant and a binder are mixed together. Then the mixture is agglomerated into cold briquettes (CBQ). The CBQ, fed into the RHF, are heated rapidly to temperatures of 1,200 C -1,400 C. The iron oxide in the CBQ is reduced to metallic iron. Zinc, lead and other volatile substances are vaporized and reoxidized in the flue gas. The product goes into the container and is cooled with nitrogen. The vaporized substances in the flue gas are collected in a bag filter and the zinc is recovered as zinc oxide. The sensible heat of the flue gas is recovered by combustion air using a heat exchanger. Item Feedstock RHF Description Iron ore, Bituminous, Non-coking Table IV - Feedstock and Equipment Details 11.5 meter OD Capacity: 20,000 t/y Feed Offgas Temperature: max. 1,400 C Characteristics of and The chemical compositions of the EAF dust and coal used in the project are shown in Table V. EAF dust was classified into two groups. Group I contained higher total iron (Total Fe) and lower zinc. Total Fe Zn Pb C CaO SiO 2 S Cl Group 1 31~33 17~ ~4 4~ ~4 Group 2 21~25 26~29 1~3 3~6 2~4 3~5 0.4~0.6 5~7 C H N O S Table V - Chemical Compositions of and PAGE 11
4 IN OUT and other Total Zinc oxide Gas and other Total Table VI - Mass Balance of RHF Using 263 t 63 t 326 t 144 t 79 t 103 t 326 t Test Results Table VI shows the mass balance for the project. The amount of EAF dust treated was 263 tons, which produced 145 tons of and 79 tons of crude zinc oxide. The remaining output was vapor and other constituents. Figure 3 shows the material flow and photos of the raw materials, cold briquettes and. Table VII shows the chemical composition of the and the baghouse dust under the test conditions. The metallization averaged 73 to 88 percent. The residual zinc content in the was 1-4 percent, giving a dezincification degree of percent. The baghouse dust had percent zinc as zinc oxide, with less than one percent iron. The dezincification degree is calculated using the following formula: De-zinc (%) = {1 (ZnO in / T.Fe in ) / (ZnO in dry ball / T.Fe in dry ball)} x 100 Most of the zinc in the EAF dust was vaporized and then re-oxidized in the flue gas., etc. Cold Briquette in RHF Vapor in flue Zinc as Zinc Oxide EAF Dust Cold Briquette Figure 3 - Material Flow and Photos and Baghouse Dust (Mass %) Total Fe Metallic Fe Zn Pb C CaO SiO 2 S Group I Group II Average Met (%) De-Zn Degree (%) De-Pb Ratio (%) (Mass %) Total Fe Zn Pb C CaO SiO 2 S Cl Crude Group I Zinc Oxide Group II Table VII - Chemical Composition of and Baghouse Dust PAGE 12
5 Dezincification Degree (%) Retention Time (1): Longer Retention Time (2): Shorter Temperature of RHF Figure 4 - Relationship of Temperature of RHF and Dezincification NO x (ppm) SO x (ppm) Dust (g/nm 3 ) Dioxin (ng-teq/nm 3 ) <40 <50 <0.015 <0.1 Table VIII - Emissions Data of RHF at KPP Figure 4 shows the relationship between the temperature in the RHF and dezincification degree. As the temperature in the RHF increases, the dezincification degree also rises. In addition, the dezincification degree increases with longer retention time. Table VIII shows the emissions data of the RHF at KPP. Samples were taken at the outlet point of the bag filter. The NOx content in the flue gas was controlled to less than 40 ppm (12 percent O 2 ) and the dioxin content was lower than 0.1 ng-teq/nm 3. DEVELOPMENT OF THE COAL-BASED FASTMELT PROCESS Development Features of FASTMELT KSL and Midrex Technologies, Inc. offer the FASTMELT process, using an Electric Ironmaking Furnace (EIF) to melt hot and produce hot metal. Figure 5 shows the features considered in the development of the coal-based melter, which is a cylindrical stationary furnace operating at low pressure. The ultimate goal is continuous operation of the coal-based melter. /HBI, etc. Oxygen (1) Suitable method of oxygen blowing, such as lance height (4) Method of melting, especially charging speed depending on various brands of Metal (2) Suitable method of adding carbon into the hot metal (3) Method of discharging slag from the stationary furnace under normal pressure N 2 Continuous Operation Figure 5 - -based Melter Features PAGE 13
6 Material Bins (,, Lime, etc.) Oxygen Cooling Chamber Scrubber ID-Fan Flare Stack Combustion Air Melter Figure 6 - Process Flowsheet of the -based Melter Cylindrical Stationary Furnace Method Tapping: Drilling Dimension: I.D. 2m x 2.6m Capacity: 16,000 t/y Hot Metal Feed Material Metallization Total Fe Metallic Fe C Iron Ore Carbon Steel Stainless Steel Table IX - Profile of -based Melter Table X - Typical Chemical Composition of (mass %) Process Flowsheet and Facility Figure 6 shows the process flow and Table IX provides details of the equipment for the coal-based melter., coal and other materials are charged into the melting furnace from the top by gravity. Oxygen is blown into the furnace from the top using lances, and input energy is obtained from the oxidation of carbon. The flue gas passes through a cooling chamber that cools the flue gas down to less than 500 C using atomized water. This is followed by a wet scrubber to remove dust. The flue gas then goes to an induced draft fan and then to a flare stack. Combustibles in the flue gas are completely burned before discharge to the atmosphere. The capacity of the facility is 16,000 tons of hot metal per year. Test Results A typical chemical composition of the produced using various feed material is shown in Table X. Figures 7 and 8 show typical operations data during Temperature of Hot Metal ( C) 6.0 1,650 2nd Blowing 3rd Blowing 5.5 [C] 1, temperature 4.5 1, nd Tapping 3rd Tapping 1, :46 14:00 14:15 14:29 14:44 14:58 15:12 15:27 15:41 15:56 Figure 7 - Transition of Metal Temperature and Carbon Content Carbon in Metal (%) PAGE 14
7 Last Page the testwork. The charging rate was adjusted to control the temperature of the hot metal. The carbon content in the hot metal was kept above 4.7 percent. Technical factors affecting the melting process were investigated during the numerous test runs. The following results were achieved: development of suitable methods of oxygen blowing and lance height, adding coal, smooth tapping of hot metal iron using the coal-based melter. FASTMELT Plant The complete process flowsheet for a FASTMELT Plant is shown in Figure 9. is produced in the RHF and fed hot to the melter to make hot metal. CONCLUSION Trials conducted at the Kobe Steel Kakogawa Pilot Plant with the support of METI provided the following results for the FASTMELT Process treating EAF dust and iron oxide: Development of an agglomerating technology to mix EAF dust and coal. Development of technology to achieve dezincification of over 95 percent, higher metallization and higher strength than the rotary kiln process. As a result, the can be used as a metallic feedstock for steelmaking, rather than being disposed of. RHF operations using EAF dust were undertaken without plugging, erosion and corrosion problems in the flue gas system. This is a challenge because EAF dust often contains ten times the amount of zinc as ordinary steel mill waste. Baghouse dust from the flue gas contained a higher zinc content than the rotary kiln product and less than one percent iron. NOx, SOx and dioxin emission levels were lower than for the kiln process. Dioxin emissions were less than 0.1 ng-teq/nm 3. The FASTMELT process produced hot metal from iron ore fines and coal. The basic characteristics for melting various types of using oxygen and carbon were confirmed. Discharging slag from the stationary furnace under normal pressure was carried out smoothly. The cycle of melting to produce hot metal and tapping were repeated successfully. The coal-based FASTMET Process provides a viable method to recover valuable metals using a rotary hearth furnace. Based on the results gained from the pilot plant, we were able to develop both the basic concept and engineering for the FASTMET Process. Taking an extra step using the FASTMELT Process, we successfully produced hot metal from the. Based on these & Charging Rates (kg/h) Iron Ore Charging Rate Pellets/ Briquettes 2nd Blowing Charging Rate RHF Figure 9 - FASTMELT Plant Flowsheet 2nd Tapping Figure 8 - Transition of and Charging Rates Recycled Gas Hot 3rd Blowing Offgas, etc. results, Kobe Steel is promoting commercial plants using the FASTMET Process to make and the FASTMELT Process to make hot metal. When EAF dust is used as the raw material, both processes can be used not only to recycle EAF dust, but also to effectively collect difficult-to-recover zinc, which can be subsequently recovered. In this way, these two innovative direct reduction processes can reduce the burden on the environment and contribute to the development of a sustainable society. O 2 3rd Tapping N 2 -based Melter PAGE 15
Introduction. 1. MIDREX R process
 Kobe Steel, along with MIDREX Technologies, is the world leader in direct reduction (DR) technologies. Kobe Steel has developed a coal based DR process which utilizes non-coking coal as a reductant instead
Kobe Steel, along with MIDREX Technologies, is the world leader in direct reduction (DR) technologies. Kobe Steel has developed a coal based DR process which utilizes non-coking coal as a reductant instead
EAF DUST TREATMENT FOR HIGH METAL RECOVERY MICHIO NAKAYAMA *
 EAF DUST TREATMENT FOR HIGH METAL RECOVERY BY MICHIO NAKAYAMA * SYNOPSYS: Electric arc furnaces (EAF) generate much dust during operation, which contains very high percentages of zinc, lead, and iron,
EAF DUST TREATMENT FOR HIGH METAL RECOVERY BY MICHIO NAKAYAMA * SYNOPSYS: Electric arc furnaces (EAF) generate much dust during operation, which contains very high percentages of zinc, lead, and iron,
NEW EAF DUST TREATMENT PROCESS : ESRF MICHIO NAKAYAMA *
 NEW EAF DUST TREATMENT PROCESS : ESRF BY MICHIO NAKAYAMA * SYNOPSYS: Electric arc furnaces (EAF) generate much dust during operation, which contains very high percentages of zinc, lead, and iron, as well
NEW EAF DUST TREATMENT PROCESS : ESRF BY MICHIO NAKAYAMA * SYNOPSYS: Electric arc furnaces (EAF) generate much dust during operation, which contains very high percentages of zinc, lead, and iron, as well
By-Products from EAF Dust Recycling and Their Valorisation. Vlad POPOVICI
 By-Products from EAF Dust Recycling and Their Valorisation Bredero Shaw, Canada 5 th Global Slag Conference, Brussels, 23-24 November 2009 Agenda Electric Arc Furnace Dust Global Production EAF Dust Recycling
By-Products from EAF Dust Recycling and Their Valorisation Bredero Shaw, Canada 5 th Global Slag Conference, Brussels, 23-24 November 2009 Agenda Electric Arc Furnace Dust Global Production EAF Dust Recycling
KOBELCO Pelletizing System - Contributing to Outstanding Ironmaking Operations
 KOBELCO Pelletizing System - Contributing to Outstanding Ironmaking Operations Kobe Steel, Ltd. (KSL) March 3 rd, 2015 Kobe Steel, Ltd. retains copyrights and all other proprietary rights related to this
KOBELCO Pelletizing System - Contributing to Outstanding Ironmaking Operations Kobe Steel, Ltd. (KSL) March 3 rd, 2015 Kobe Steel, Ltd. retains copyrights and all other proprietary rights related to this
ADVANCED SOLUTIONS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES IN EAF MELTSHOP MICHIO NAKAYAMA *
 ADVANCED SOLUTIONS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES IN EAF MELTSHOP BY MICHIO NAKAYAMA * SYNOPSYS: Steel scrap, which is used as raw material for electric arc furnaces (EAF), is an essential industrial waste.
ADVANCED SOLUTIONS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES IN EAF MELTSHOP BY MICHIO NAKAYAMA * SYNOPSYS: Steel scrap, which is used as raw material for electric arc furnaces (EAF), is an essential industrial waste.
Not All RHFs Are Created Equal A Rotary Hearth Furnace Primer. Proven Commercial Success in RHF Technology
 Not All RHFs Are Created Equal A Rotary Hearth Furnace Primer Proven Commercial Success in RHF Technology Successful Iron Nuggets Production at ITmk3 Pilot Plant Construction of Mesabi Nugget Plant to
Not All RHFs Are Created Equal A Rotary Hearth Furnace Primer Proven Commercial Success in RHF Technology Successful Iron Nuggets Production at ITmk3 Pilot Plant Construction of Mesabi Nugget Plant to
Dust Recycling System by the Rotary Hearth Furnace
 UDC 669. 054. 83 : 66. 041. 49 Dust Recycling System by the Rotary Hearth Furnace Hiroshi ODA* 1 Tetsuharu IBARAKI* 1 Youichi ABE* 2 Abstract Dust recycling technology by the rotary hearth furnace has
UDC 669. 054. 83 : 66. 041. 49 Dust Recycling System by the Rotary Hearth Furnace Hiroshi ODA* 1 Tetsuharu IBARAKI* 1 Youichi ABE* 2 Abstract Dust recycling technology by the rotary hearth furnace has
Application of CFB (Circulating Fluidized Bed) to Sewage Sludge Incinerator
 Application of CFB (Circulating Fluidized Bed) to Sewage Sludge Incinerator Akira Nakamura*, Toshihiko Iwasaki**, Takashi Noto*, Hisanao Hashimoto***, Nobuyuki Sugiyama**** and Masahiro Hattori***** *
Application of CFB (Circulating Fluidized Bed) to Sewage Sludge Incinerator Akira Nakamura*, Toshihiko Iwasaki**, Takashi Noto*, Hisanao Hashimoto***, Nobuyuki Sugiyama**** and Masahiro Hattori***** *
THE MOST ADVANCED POWER SAVING TECHNOLOGY IN EAF INTRODUCTION TO ECOARC
 THE MOST ADVANCED POWER SAVING TECHNOLOGY IN EAF INTRODUCTION TO ECOARC T. Nagai, Y. Sato, H. Kato, M. Fujimoto and T. Sugasawa JP Steel Plantech Co., Yokohama, Japan Contact data T. Nagai, JP Steel Plantech
THE MOST ADVANCED POWER SAVING TECHNOLOGY IN EAF INTRODUCTION TO ECOARC T. Nagai, Y. Sato, H. Kato, M. Fujimoto and T. Sugasawa JP Steel Plantech Co., Yokohama, Japan Contact data T. Nagai, JP Steel Plantech
Challenges and limiting factors for the Recycling of steel scrap in Europe
 Challenges and limiting factors for the Recycling of steel scrap in Europe International Workshop on Technospheric Mining 2 nd October 2015 Philip Bundschuh Table of Content Scrap availability trading
Challenges and limiting factors for the Recycling of steel scrap in Europe International Workshop on Technospheric Mining 2 nd October 2015 Philip Bundschuh Table of Content Scrap availability trading
OXYFINES TM TECHNOLOGY FOR THE RE-MELTING OF FINES, DUST AND SLUDGE
 OXYFINES TM TECHNOLOGY FOR THE RE-MELTING OF FINES, DUST AND SLUDGE J. von Schéele Linde AG, Gas Division; SE-18181 Lidingö, Sweden. E-mail: joachim.von.scheele@linde-gas.com ABSTRACT OXYFINES TM is an
OXYFINES TM TECHNOLOGY FOR THE RE-MELTING OF FINES, DUST AND SLUDGE J. von Schéele Linde AG, Gas Division; SE-18181 Lidingö, Sweden. E-mail: joachim.von.scheele@linde-gas.com ABSTRACT OXYFINES TM is an
The HIsarna Ironmaking Process
 Presentation title, change View >> Header & Footer The HIsarna Ironmaking Process Together we make the difference 1 Content 1. Introduction 2. The benefits of HIsarna 3. The pilot plant 4. Further development
Presentation title, change View >> Header & Footer The HIsarna Ironmaking Process Together we make the difference 1 Content 1. Introduction 2. The benefits of HIsarna 3. The pilot plant 4. Further development
Development of Technology for Advanced Utilization of Hydrogen from By-product Gas of Steelmaking Process
 Technical Review UDC 669. 1. 054. 8 Development of Technology for Advanced Utilization of Hydrogen from By-product Gas of Steelmaking Process Ken-ichiro FUJIMOTO* Kimihito SUZUKI 1. Introduction Huge volumes
Technical Review UDC 669. 1. 054. 8 Development of Technology for Advanced Utilization of Hydrogen from By-product Gas of Steelmaking Process Ken-ichiro FUJIMOTO* Kimihito SUZUKI 1. Introduction Huge volumes
Treatment of lead and zinc slags in hollow electrode DC-EAF
 Treatment of lead and zinc slags in hollow electrode DC-EAF E. Hecker, B. Friedrich, J. Böhlke IME Process Metallurgy and Metal Aachen University, Germany Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Friedrich Motivation for
Treatment of lead and zinc slags in hollow electrode DC-EAF E. Hecker, B. Friedrich, J. Böhlke IME Process Metallurgy and Metal Aachen University, Germany Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Friedrich Motivation for
FINEX - AN OLD VISION OF THE IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY BECOMES REALITY*
 FINEX - AN OLD VISION OF THE IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY BECOMES REALITY* Shibu John 1 Christian Boehm 2 Wolfgang Sterrer 3 Norbert Rein 4 Yi Sang-ho 5 Shin Sungkee 6 Abstract Rising energy demand and steadily
FINEX - AN OLD VISION OF THE IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY BECOMES REALITY* Shibu John 1 Christian Boehm 2 Wolfgang Sterrer 3 Norbert Rein 4 Yi Sang-ho 5 Shin Sungkee 6 Abstract Rising energy demand and steadily
DRI Direct Reduced Iron
 DRI Direct Reduced Iron What is DRI? Sponge iron/dri has gained great prominence in world as a substitute of steel scrap (partially) in steel making in electric arc furnace and in induction furnace. Direct
DRI Direct Reduced Iron What is DRI? Sponge iron/dri has gained great prominence in world as a substitute of steel scrap (partially) in steel making in electric arc furnace and in induction furnace. Direct
Lecture 17 Alternative Charge Materials in EAF
 Lecture 17 Alternative Charge Materials in EAF Contents: Introduction Types of metallic charge materials Carbon content in DRI Charging methods Key words: Sponge iron, DRI, electric arc furnace, UHP furnaces
Lecture 17 Alternative Charge Materials in EAF Contents: Introduction Types of metallic charge materials Carbon content in DRI Charging methods Key words: Sponge iron, DRI, electric arc furnace, UHP furnaces
Development status of the EAGLE Gasification Pilot Plant
 Development status of the EAGLE Gasification Pilot Plant Gasification Technologies 2002 San Francisco, California, USA October 27-30, 2002 Masaki Tajima Energy and Environment Technology Development Dept.
Development status of the EAGLE Gasification Pilot Plant Gasification Technologies 2002 San Francisco, California, USA October 27-30, 2002 Masaki Tajima Energy and Environment Technology Development Dept.
Johannes Schenk. Hans-Bodo Lüngen. Chair of Ferrous Metallurgy, Montanuniversitaet Leoben, Austria. Steel Institute VDEh, Germany
 EVALUATION OF THE CAPABILITIES OF DIRECT AND SMELTING REDUCTION PROCESSES TO ENHANCE THE ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND TO REDUCE THE CO 2 EMISSION OF THE STEEL PRODUCTION IN EUROPE Johannes Schenk Chair of Ferrous
EVALUATION OF THE CAPABILITIES OF DIRECT AND SMELTING REDUCTION PROCESSES TO ENHANCE THE ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND TO REDUCE THE CO 2 EMISSION OF THE STEEL PRODUCTION IN EUROPE Johannes Schenk Chair of Ferrous
TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
 THE SEARCH FOR A NEW IRONMAKING PROCESS TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT WiK Wei Kao Lu Professor Emeritus Materials Science and Engineering g McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada GCEP Industry
THE SEARCH FOR A NEW IRONMAKING PROCESS TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT WiK Wei Kao Lu Professor Emeritus Materials Science and Engineering g McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada GCEP Industry
CEMENT MANUFACTURING PROCESS
 CEMENT MANUFACTURING PROCESS Definition: Defined as a product material obtained by calcination of calcareous (a material containing lime) and argillaceous (a material which contain silica) materials. According
CEMENT MANUFACTURING PROCESS Definition: Defined as a product material obtained by calcination of calcareous (a material containing lime) and argillaceous (a material which contain silica) materials. According
PILOT PLANT PRODUCTION OF FERRONICKEL FROM NICKEL OXIDE ORES AND DUSTS IN A DC ARC FURNACE. Abstract
 PILOT PLANT PRODUCTION OF FERRONICKEL FROM NICKEL OXIDE ORES AND DUSTS IN A DC ARC FURNACE I.J Kotzé (Pyrometallurgy Division, Mintek, South Africa) E-mail for correspondence: isabelk@mintek.co.za Abstract
PILOT PLANT PRODUCTION OF FERRONICKEL FROM NICKEL OXIDE ORES AND DUSTS IN A DC ARC FURNACE I.J Kotzé (Pyrometallurgy Division, Mintek, South Africa) E-mail for correspondence: isabelk@mintek.co.za Abstract
Energy Saving & Breakthrough Technologies. Dr Ladislav Horvath Zhang Jiagang, Jiangsu, China, August 1, 2013
 Energy Saving & Breakthrough Technologies Dr Ladislav Horvath Zhang Jiagang, Jiangsu, China, August 1, 2013 Disclaimer text For presentations to the general public: This document is protected by copyright.
Energy Saving & Breakthrough Technologies Dr Ladislav Horvath Zhang Jiagang, Jiangsu, China, August 1, 2013 Disclaimer text For presentations to the general public: This document is protected by copyright.
HIGHVELD STEEL PROSPECTUS IRON MAKING PLANT 1
 HIGHVELD STEEL PROSPECTUS IRON MAKING PLANT 1 January 2018 IRON MAKING PLANT 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Highveld Steel and Vanadium was founded in 1960 with the objective of building a unique plant with the ability
HIGHVELD STEEL PROSPECTUS IRON MAKING PLANT 1 January 2018 IRON MAKING PLANT 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Highveld Steel and Vanadium was founded in 1960 with the objective of building a unique plant with the ability
Laboratory Investigations of the Electrical Resistivity of Cokes and Smelting Charge for Optimizing Operation in Large Ferrochrome Furnaces
 Southern African Pyrometallurgy 2006, Edited by R.T. Jones, South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Johannesburg, 5-8 March 2006 Laboratory Investigations of the Electrical Resistivity of Cokes
Southern African Pyrometallurgy 2006, Edited by R.T. Jones, South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Johannesburg, 5-8 March 2006 Laboratory Investigations of the Electrical Resistivity of Cokes
Productive recycling of basic oxygen furnace sludge in integrated steel plant
 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 64, September 2005, pp 702-706 Productive recycling of basic oxygen furnace sludge in integrated steel plant Raj Kumar Agrawal 1 and Piyush Kant Pandey
Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 64, September 2005, pp 702-706 Productive recycling of basic oxygen furnace sludge in integrated steel plant Raj Kumar Agrawal 1 and Piyush Kant Pandey
4th Slag Valorisation Symposium, April Conditioning of Lead and Zinc Slags in Pilot Scale SAF for further Utilization
 4th Slag Valorisation Symposium, 15-17 April 2015 Conditioning of Lead and Zinc Slags in Pilot Scale SAF for further Utilization Frank Kaußen, Jörn Böhlke, Christoph Kemper, Bernd Friedrich IME Process
4th Slag Valorisation Symposium, 15-17 April 2015 Conditioning of Lead and Zinc Slags in Pilot Scale SAF for further Utilization Frank Kaußen, Jörn Böhlke, Christoph Kemper, Bernd Friedrich IME Process
Steel Industry Technology Roadmap. Barriers and Pathways for Yield Improvements. by Energetics, Inc. for the American Iron and Steel Institute
 Steel Industry Technology Roadmap Barriers and Pathways for Yield Improvements by Energetics, Inc. for the American Iron and Steel Institute October 7, 2003 Table of Contents Executive Summary...ii 1 Modeling,
Steel Industry Technology Roadmap Barriers and Pathways for Yield Improvements by Energetics, Inc. for the American Iron and Steel Institute October 7, 2003 Table of Contents Executive Summary...ii 1 Modeling,
THE VALUE OF ENERGY & RESOURCE TOWARDS AN EFFICIENT FUTURE STEELMAKING
 THE VALUE OF ENERGY & RESOURCE TOWARDS AN EFFICIENT FUTURE STEELMAKING Dr. Alexander Fleischanderl primetals.com The Value of Energy and Resource Content 1. Introduction a. Economy Facts & Figures b. Scrap
THE VALUE OF ENERGY & RESOURCE TOWARDS AN EFFICIENT FUTURE STEELMAKING Dr. Alexander Fleischanderl primetals.com The Value of Energy and Resource Content 1. Introduction a. Economy Facts & Figures b. Scrap
Hamm MW Pyrolysis Plant. Integrated Pyrolysis into Power Plant Plant capacity 100,000 t/a Pre-processed Waste Materials
 Integrated Pyrolysis into Power Plant Plant capacity 100,000 t/a Pre-processed Waste Materials Schematic Flow sheet Integrated Pyrolysis for Power Plants Pyrolysis of high calorific solid recovered fuels
Integrated Pyrolysis into Power Plant Plant capacity 100,000 t/a Pre-processed Waste Materials Schematic Flow sheet Integrated Pyrolysis for Power Plants Pyrolysis of high calorific solid recovered fuels
Proposal for Energy Efficiency Improvement. 1. Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) for steelmaking 2. Reheating Furnace (RHF) for rolling
 Proposal for Energy Efficiency Improvement 1. Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) for steelmaking 2. Reheating Furnace (RHF) for rolling (1) Operational skill (2) Equipment improvement (3) Advanced technology November
Proposal for Energy Efficiency Improvement 1. Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) for steelmaking 2. Reheating Furnace (RHF) for rolling (1) Operational skill (2) Equipment improvement (3) Advanced technology November
Technical and economic aspects of production and use of DRI in integrated steel works
 Technical and economic aspects of production and use of DRI in integrated steel works The use of surplus energy from integrated steel works for the on-site production and use of DRI in blast furnaces and
Technical and economic aspects of production and use of DRI in integrated steel works The use of surplus energy from integrated steel works for the on-site production and use of DRI in blast furnaces and
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF THE STEEL MAKING INDUSTRY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY RESEARCH Int. J. Energy Res., 22, 1049 1054 (1998) ENERGY ANALYSIS OF THE STEEL MAKING INDUSTRY MOUSA S. MOHSEN* AND BILAL A. AKASH Department of Mechanical & Industrial
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY RESEARCH Int. J. Energy Res., 22, 1049 1054 (1998) ENERGY ANALYSIS OF THE STEEL MAKING INDUSTRY MOUSA S. MOHSEN* AND BILAL A. AKASH Department of Mechanical & Industrial
CO2 Capture in the Steel Industry Review of the Current State of Art
 CO2 Capture in the Steel Industry Review of the Current State of Art Stanley Santos IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme Cheltenham, UK Industry CCS Workshop Vienna, Austria 28 th April 2014 IEAGHG Activities
CO2 Capture in the Steel Industry Review of the Current State of Art Stanley Santos IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme Cheltenham, UK Industry CCS Workshop Vienna, Austria 28 th April 2014 IEAGHG Activities
GASIFICATION AND THE MIDREX DIRECT REDUCTION PROCESS
 GASIFICATION AND THE MIDREX DIRECT REDUCTION PROCESS By: Rob Cheeley Senior Sales Engineer Midrex Direct Reduction Corporation 201 S. College Street, Suite 2100 Charlotte, NC 28244 Phone: 704-378-3343
GASIFICATION AND THE MIDREX DIRECT REDUCTION PROCESS By: Rob Cheeley Senior Sales Engineer Midrex Direct Reduction Corporation 201 S. College Street, Suite 2100 Charlotte, NC 28244 Phone: 704-378-3343
ZincOx Resources plc. Corporate Overview
 ZincOx Resources plc Corporate Overview May 2012 Where there s Muck there s Brass Disclaimer This document is for informational purposes only and must not be used or relied upon for the purposes of making
ZincOx Resources plc Corporate Overview May 2012 Where there s Muck there s Brass Disclaimer This document is for informational purposes only and must not be used or relied upon for the purposes of making
Pelletizing technologies for iron ore
 Pelletizing technologies for iron ore The Outokumpu partnership As one of the world s leading developers and suppliers of technology, Outokumpu Technology designs and delivers plants, processes and equipment
Pelletizing technologies for iron ore The Outokumpu partnership As one of the world s leading developers and suppliers of technology, Outokumpu Technology designs and delivers plants, processes and equipment
Brimacombe Lecture. Research on Sustainable Steelmaking
 Brimacombe Lecture Research on Sustainable Steelmaking R. J. Fruehan Center for Iron and Steelmaking Research Materials Science and Engineering Department Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh PA Tel:
Brimacombe Lecture Research on Sustainable Steelmaking R. J. Fruehan Center for Iron and Steelmaking Research Materials Science and Engineering Department Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh PA Tel:
EAF Technology and process
 EAF Technology and process In the last 100 years,the EAF technology has evolved to meet the demands of higher productivity, improved quality of product and flexibility of metallic inputs. The product mix
EAF Technology and process In the last 100 years,the EAF technology has evolved to meet the demands of higher productivity, improved quality of product and flexibility of metallic inputs. The product mix
Guidelines for Selecting Pellet Plant Technology I. Cameron, M. Huerta, J. Bolen M. Okrutny, K. O Leary
 Guidelines for Selecting Pellet Plant Technology I. Cameron, M. Huerta, J. Bolen M. Okrutny, K. O Leary AusIMM, Iron Ore Conference, Perth WA 13 15 July 2015 Introduction 2 The availability of lump ore
Guidelines for Selecting Pellet Plant Technology I. Cameron, M. Huerta, J. Bolen M. Okrutny, K. O Leary AusIMM, Iron Ore Conference, Perth WA 13 15 July 2015 Introduction 2 The availability of lump ore
Researches on the production of self-reducing briquettes from waste containing iron and carbon
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Researches on the production of self-reducing briquettes from waste containing iron and carbon To cite this article: E Ardelean et al
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Researches on the production of self-reducing briquettes from waste containing iron and carbon To cite this article: E Ardelean et al
Study of the Compressive Strength of Concrete with Various Proportions of Steel Mill Scale as Fine Aggregate
 Study of the Compressive Strength of Concrete with Various Proportions of Steel Mill Scale as Fine Aggregate Akhinesh K 1, Jithu G Francis 1, Junaid K T 1, Jishnulal K 1, Jeril Netto Joseph 1, Remya Neelancherry
Study of the Compressive Strength of Concrete with Various Proportions of Steel Mill Scale as Fine Aggregate Akhinesh K 1, Jithu G Francis 1, Junaid K T 1, Jishnulal K 1, Jeril Netto Joseph 1, Remya Neelancherry
CO2 Capture in the Steel Industry Review of the Current State of Art
 CO2 Capture in the Steel Industry Review of the Current State of Art Stanley Santos IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme Cheltenham, UK Industry CCS Workshop Vienna, Austria 28 th April 2014 IEAGHG Activities
CO2 Capture in the Steel Industry Review of the Current State of Art Stanley Santos IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme Cheltenham, UK Industry CCS Workshop Vienna, Austria 28 th April 2014 IEAGHG Activities
WASTE TO WEALTH. Utilisation of High Oxide bearing Sludge/Dust as Coolant in BOF
 WASTE TO WEALTH Utilisation of High Oxide bearing Sludge/Dust as Coolant in BOF By: Vinod Arora and Pawan Verma All the past years, the need was not felt strongly for Reduce, Reuse, Recycle or Recover
WASTE TO WEALTH Utilisation of High Oxide bearing Sludge/Dust as Coolant in BOF By: Vinod Arora and Pawan Verma All the past years, the need was not felt strongly for Reduce, Reuse, Recycle or Recover
High-Carbon DRI: the feeding material to improve performances and decrease
 Alessandro Martinis- EVP Danieli Centro Metallics 12-14 Sept, Linz, Austria High-Carbon DRI: the feeding material to improve performances and decrease CO2 emissions in both BF and EAF THE STATE OF ART
Alessandro Martinis- EVP Danieli Centro Metallics 12-14 Sept, Linz, Austria High-Carbon DRI: the feeding material to improve performances and decrease CO2 emissions in both BF and EAF THE STATE OF ART
Industrial Process & Pilot Plant
 Industrial Process & Pilot Plant Vienna, June 2008 3 Process Steps in 3 Sections Cooling Pelleting Mixing Sludge Ash Residues Thermal Treatment Energy Recycling Flue Gas Cleaning P-Half- Product Fertilizer
Industrial Process & Pilot Plant Vienna, June 2008 3 Process Steps in 3 Sections Cooling Pelleting Mixing Sludge Ash Residues Thermal Treatment Energy Recycling Flue Gas Cleaning P-Half- Product Fertilizer
Summary of findings from HYBRIT Pre-Feasibility Study
 Fe₂O₃ A joint venture between SSAB, LKAB and Vattenfall H₂O Summary of findings from HYBRIT Pre-Feasibility Study 2016 2017 This work was funded by the Swedish Energy Agency, SSAB, LKAB, and Vattenfall
Fe₂O₃ A joint venture between SSAB, LKAB and Vattenfall H₂O Summary of findings from HYBRIT Pre-Feasibility Study 2016 2017 This work was funded by the Swedish Energy Agency, SSAB, LKAB, and Vattenfall
Polyurethane. Polyurethane Recycling and Recovery. Options for Polyurethane Recycling and Recovery
 Options for Polyurethane Recycling and Recovery Polyurethane Repair and Reuse Mechanical Recycling Chemical Recycling Feedstock Mechanical Energy Recovery Long-life products, such as building panels can
Options for Polyurethane Recycling and Recovery Polyurethane Repair and Reuse Mechanical Recycling Chemical Recycling Feedstock Mechanical Energy Recovery Long-life products, such as building panels can
Although the BF-BOF route of iron and steelmaking accounts for
 Indian Sponge Iron Industry An Overview Although the BF-BOF route of iron and steelmaking accounts for about 65 percent of global production of crude steel, the process requires various treatment of raw
Indian Sponge Iron Industry An Overview Although the BF-BOF route of iron and steelmaking accounts for about 65 percent of global production of crude steel, the process requires various treatment of raw
The World Leader in Direct Reduction
 The World Leader in Direct Reduction G l o b a l P l a n t S u p p ly T e c h n o l o g y D e v e l o p m e n t A f t e r m a r k e t Contents 3 Global plant supply 7 Technology development 11 Aftermarket
The World Leader in Direct Reduction G l o b a l P l a n t S u p p ly T e c h n o l o g y D e v e l o p m e n t A f t e r m a r k e t Contents 3 Global plant supply 7 Technology development 11 Aftermarket
< > The Experience of ArcelorMittal Lázaro Cardenas Flat Carbon. By R. Lule 1), F.Lopez 2), J. Espinoza 3) R. Torres 4) & R.D.
 3 table of contents THE PRODUCTION OF STEELS APPLYING 100% DRI FOR NITROGEN REMOVAL The Experience of ArcelorMittal Lázaro Cardenas Flat Carbon By R. Lule 1), F.Lopez 2), J. Espinoza 3) R. Torres 4) &
3 table of contents THE PRODUCTION OF STEELS APPLYING 100% DRI FOR NITROGEN REMOVAL The Experience of ArcelorMittal Lázaro Cardenas Flat Carbon By R. Lule 1), F.Lopez 2), J. Espinoza 3) R. Torres 4) &
Recent Developments in Iron and Steel Making Industry
 Journal of Engineering Innovation And Research Volume: 1, Issue: 1 Recent Developments in Iron and Steel Making Industry R.N.Dash*, Chinmay Das Although iron was produced more than 3000 years ago, innovations
Journal of Engineering Innovation And Research Volume: 1, Issue: 1 Recent Developments in Iron and Steel Making Industry R.N.Dash*, Chinmay Das Although iron was produced more than 3000 years ago, innovations
DRI Production Using Coke Oven Gas (COG): Results of the MIDREX Thermal Reactor System TM (TRS ) Testing and Future Commercial Application
 DRI Production Using Coke Oven Gas (COG): Results of the MIDREX Thermal Reactor System TM (TRS ) Testing and Future Commercial Application Gary Metius a, Henry Gaines b, Michael F. Riley c, Lawrence E.
DRI Production Using Coke Oven Gas (COG): Results of the MIDREX Thermal Reactor System TM (TRS ) Testing and Future Commercial Application Gary Metius a, Henry Gaines b, Michael F. Riley c, Lawrence E.
COMPETITIVE STEEL PRODUCTION
 ENZO RUSCIO EVP DANIELI COMPETITIVE STEEL PRODUCTION 19TH MIDDLE EAST IRON & STEEL CONFERENCE 14-16 DECEMBER 2015 ATLANTIS, THE PALM DUBAI, U.A.E RAW MATERIAL FLEXIBILITY: KEY TO SUCCESS RAW MATERIALS
ENZO RUSCIO EVP DANIELI COMPETITIVE STEEL PRODUCTION 19TH MIDDLE EAST IRON & STEEL CONFERENCE 14-16 DECEMBER 2015 ATLANTIS, THE PALM DUBAI, U.A.E RAW MATERIAL FLEXIBILITY: KEY TO SUCCESS RAW MATERIALS
Long Life Copper Stave for Blast Furnace Developed by Nippon Steel & Sumikin Engineering
 Technical Report Long Life Copper Stave for Blast Furnace Developed by Nippon Steel & Sumikin Engineering Makoto GOTO Plant & Machinery Division Steel Plant Engineering Department I Iron Making - Engineering
Technical Report Long Life Copper Stave for Blast Furnace Developed by Nippon Steel & Sumikin Engineering Makoto GOTO Plant & Machinery Division Steel Plant Engineering Department I Iron Making - Engineering
Effective Utilization of Fly-Ash
 24 th Jan, 2013 in Mongolia under the framework of NAMAs Effective Utilization of Fly-Ash from Power Plant for Cement Production YOSHIYUKI UENOYAMA General Manager Green-Innovation Business Promotion Department
24 th Jan, 2013 in Mongolia under the framework of NAMAs Effective Utilization of Fly-Ash from Power Plant for Cement Production YOSHIYUKI UENOYAMA General Manager Green-Innovation Business Promotion Department
Manufacture of Iron & Steel. Prepared By: John Cawley
 Manufacture of Iron & Steel Prepared By: John Cawley Presentation Objectives Identify the basic steps in the production of steel. Identify the properties and uses of iron ore and pig iron. Differentiate
Manufacture of Iron & Steel Prepared By: John Cawley Presentation Objectives Identify the basic steps in the production of steel. Identify the properties and uses of iron ore and pig iron. Differentiate
Examples in Material Flow Analysis
 China Steel Technical Report, No. 27, pp.1-5, (2014) Kuo-Chung Liu 1 Examples in Material Flow Analysis KUO-CHUNG LIU Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs China Steel Corporation The inputs and outputs
China Steel Technical Report, No. 27, pp.1-5, (2014) Kuo-Chung Liu 1 Examples in Material Flow Analysis KUO-CHUNG LIU Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs China Steel Corporation The inputs and outputs
Ilmenite Pellet Production and use at TiZir
 Ilmenite Pellet Production and use at TiZir Arne Hildal and Stian Seim www.tizir.co.uk Tyssedal ilmenite upgrading facility - History 1908 Start production of hydro electrical power in Tyssedal 1916-81
Ilmenite Pellet Production and use at TiZir Arne Hildal and Stian Seim www.tizir.co.uk Tyssedal ilmenite upgrading facility - History 1908 Start production of hydro electrical power in Tyssedal 1916-81
Circular Pelletizing Technology
 Metal Bulletin s World DRI and Pellet Congress 29 th 30 th, Abu Dhabi Circular Pelletizing Technology A smart combination Christoph Aichinger, Siemens VAI We didn t invent Pelletizing. We just made it
Metal Bulletin s World DRI and Pellet Congress 29 th 30 th, Abu Dhabi Circular Pelletizing Technology A smart combination Christoph Aichinger, Siemens VAI We didn t invent Pelletizing. We just made it
ESS Smelting Technology Enabling FeNi Smelting from Limonite
 ESS Smelting Technology Enabling FeNi Smelting from Limonite L.J. Erasmus 1 and L.J. Fourie 2 1 LJE Consulting, PO Box 2661, Pinegowrie, 2123, RSA, e-mail: lourens.erasmus@telkomsa.net 2 Envirosteel Pty
ESS Smelting Technology Enabling FeNi Smelting from Limonite L.J. Erasmus 1 and L.J. Fourie 2 1 LJE Consulting, PO Box 2661, Pinegowrie, 2123, RSA, e-mail: lourens.erasmus@telkomsa.net 2 Envirosteel Pty
Contribution of Waste to Energy Technology to Global Warming
 Contribution of Waste to Energy Technology to Global Warming MASAO TAKUMA* 1 YUUJI KAIHARA* 2 AKIHIRO YAMADA* 2 Based on the additional new energy measures in the Guideline of Measures to prevent Global
Contribution of Waste to Energy Technology to Global Warming MASAO TAKUMA* 1 YUUJI KAIHARA* 2 AKIHIRO YAMADA* 2 Based on the additional new energy measures in the Guideline of Measures to prevent Global
ENERGY MANAGEMENT IN STEELWORKS BY USING ISO14404 AND COOPERATION WITH THE ASEAN STEEL INDUSTRY
 ENERGY MANAGEMENT IN STEELWORKS BY USING ISO14404 AND COOPERATION WITH THE ASEAN STEEL INDUSTRY BY SHIRO WATAKABE*, MICHIO NAKAYAMA** and HIROMI KAWAMATA*** SYNOPSIS: As attentions towards the climate
ENERGY MANAGEMENT IN STEELWORKS BY USING ISO14404 AND COOPERATION WITH THE ASEAN STEEL INDUSTRY BY SHIRO WATAKABE*, MICHIO NAKAYAMA** and HIROMI KAWAMATA*** SYNOPSIS: As attentions towards the climate
Dr. Joseph J Poveromo, Raw Materials & Ironmaking Global Consulting DR Pellet Quality & MENA Applications
 Dr. Joseph J Poveromo, Raw Materials & Ironmaking Global Consulting joe.poveromo@rawmaterialsiron.com DR Pellet Quality & MENA Applications Chemistry Considerations direct reduction processes: chemical
Dr. Joseph J Poveromo, Raw Materials & Ironmaking Global Consulting joe.poveromo@rawmaterialsiron.com DR Pellet Quality & MENA Applications Chemistry Considerations direct reduction processes: chemical
Draw a ring around the correct word in the box to complete the sentence.
 Q. Iron is the main structural metal used in the world. (a) The diagram represents the particles in iron, Fe. Draw a ring around the correct word in the box to complete the sentence. Iron is described
Q. Iron is the main structural metal used in the world. (a) The diagram represents the particles in iron, Fe. Draw a ring around the correct word in the box to complete the sentence. Iron is described
Problems and Prospects of Halogen Element Contained Dust Treatment in Recycling
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 12 (2003) pp. 2422 to 2426 Special Issue on New Systems and Processes in Recycling and High Performance Waste Treatments #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals OVERVIEW
Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 12 (2003) pp. 2422 to 2426 Special Issue on New Systems and Processes in Recycling and High Performance Waste Treatments #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals OVERVIEW
Metallurgical Gas Cleaning System Design for Emissions Control and Energy Efficiency
 Metallurgical Gas Cleaning System Design for Emissions Control and Energy Efficiency Paykan Safe and Matt Russell WorleyParsons GCT 111 Ferguson Court Suite 103 Irving, TX, USA 75062 ABSTRACT Metallurgical
Metallurgical Gas Cleaning System Design for Emissions Control and Energy Efficiency Paykan Safe and Matt Russell WorleyParsons GCT 111 Ferguson Court Suite 103 Irving, TX, USA 75062 ABSTRACT Metallurgical
Electric Furnace Off-Gas Cleaning Systems Installation at PT Inco ABSTRACT
 Electric Furnace Off-Gas Cleaning Systems Installation at PT Inco Paykan Safe and Matt Russell WorleyParsons Gas Cleaning, Irving, Texas USA ABSTRACT PT Inco is a ferronickel smelter in Soroako, Sulawesi,
Electric Furnace Off-Gas Cleaning Systems Installation at PT Inco Paykan Safe and Matt Russell WorleyParsons Gas Cleaning, Irving, Texas USA ABSTRACT PT Inco is a ferronickel smelter in Soroako, Sulawesi,
Introduction: Thermal treatment
 Thermal Treatment 2 Introduction: Thermal treatment Technologies using high temperatures to treat waste (or RDF) Commonly involves thermal combustion (oxidation) Reduces waste to ash (MSW c. 30% of input)
Thermal Treatment 2 Introduction: Thermal treatment Technologies using high temperatures to treat waste (or RDF) Commonly involves thermal combustion (oxidation) Reduces waste to ash (MSW c. 30% of input)
REDUCTION OF CHROMITE FINES IN SOLID STATE USING A MIXTURE OF GASES CONTAINING NATURAL GAS, HYDROGEN AND NITROGEN
 REDUCTION OF CHROMITE FINES IN SOLID STATE USING A MIXTURE OF GASES CONTAINING NATURAL GAS, HYDROGEN AND NITROGEN C. N. Harman Director (Technical), Facor Alloys Ltd., Shreeramnagar-535 101(A.P.), India;
REDUCTION OF CHROMITE FINES IN SOLID STATE USING A MIXTURE OF GASES CONTAINING NATURAL GAS, HYDROGEN AND NITROGEN C. N. Harman Director (Technical), Facor Alloys Ltd., Shreeramnagar-535 101(A.P.), India;
ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT AIR DIVISION INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETION OF MANUFACTURING OR PROCESSING OPERATION ADEM FORM 105
 ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT AIR DIVISION INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETION OF MANUFACTURING OR PROCESSING OPERATION ADEM FORM 105 All applicable portions of this form should be completed by
ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT AIR DIVISION INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETION OF MANUFACTURING OR PROCESSING OPERATION ADEM FORM 105 All applicable portions of this form should be completed by
Energy consumption, waste heat utilisation and pollution control in ferro alloy industry
 Energy consumption, waste heat utilisation and pollution control in ferro alloy industry UMASHANKAR AGRAWAL Ferro Alloy Industry forms the backbone of the Iron Et Steel Industry in the World. Since energy
Energy consumption, waste heat utilisation and pollution control in ferro alloy industry UMASHANKAR AGRAWAL Ferro Alloy Industry forms the backbone of the Iron Et Steel Industry in the World. Since energy
TOTAL WATER MANAGEMENT IN THE STEEL INDUSTRY. By N. Ramachandran, Ion Exchange (India) Ltd
 TOTAL WATER MANAGEMENT IN THE STEEL INDUSTRY By N. Ramachandran, Ion Exchange (India) Ltd Large quantities of water are required to produce steel and steel products - typically 180-200 m 3 of water per
TOTAL WATER MANAGEMENT IN THE STEEL INDUSTRY By N. Ramachandran, Ion Exchange (India) Ltd Large quantities of water are required to produce steel and steel products - typically 180-200 m 3 of water per
Advanced Master Course Process Technology of Metals
 Institut für Eisenhüttenkunde Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen Advanced Master Course Process Technology of Metals (Part: Ferrous Process Metallurgy) Prof. Dr.-Ing. D. Senk 16-04-2010
Institut für Eisenhüttenkunde Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen Advanced Master Course Process Technology of Metals (Part: Ferrous Process Metallurgy) Prof. Dr.-Ing. D. Senk 16-04-2010
AIR QUALITY MANAGEMENT at URBAN REGIONAL and GLOBAL SCALES 4 International and IUAPPA Regional Conference,10-13 September 2012 Istanbul-Turkey
 AIR QUALITY MANAGEMENT at URBAN REGIONAL and GLOBAL SCALES 4 International and IUAPPA Regional Conference,10-13 September 2012 Istanbul-Turkey WHERE Monitoring sites Rural site Plaine of Aosta Aosta urban
AIR QUALITY MANAGEMENT at URBAN REGIONAL and GLOBAL SCALES 4 International and IUAPPA Regional Conference,10-13 September 2012 Istanbul-Turkey WHERE Monitoring sites Rural site Plaine of Aosta Aosta urban
Sintering of Indian Iron Ores - Technical Considerations
 Sintering of Indian Iron Ores - Technical Considerations Chandan Barman Ray, Bhaskar Roy, Tushar Kanti Mandal & Subhas Das* M. N. Dastur & Company (P) Ltd, Consulting Engineers P-17 Mission Row Extension
Sintering of Indian Iron Ores - Technical Considerations Chandan Barman Ray, Bhaskar Roy, Tushar Kanti Mandal & Subhas Das* M. N. Dastur & Company (P) Ltd, Consulting Engineers P-17 Mission Row Extension
Kazushige KUROSAWA*, Zhibao ZHANG**, and Zhengbing WANG** [Delivered Products & Systems] 1. Introduction. 2. Overview of Nanjing
![Kazushige KUROSAWA*, Zhibao ZHANG**, and Zhengbing WANG** [Delivered Products & Systems] 1. Introduction. 2. Overview of Nanjing Kazushige KUROSAWA*, Zhibao ZHANG**, and Zhengbing WANG** [Delivered Products & Systems] 1. Introduction. 2. Overview of Nanjing](/thumbs/76/73638000.jpg) [Delivered Products & Systems] Report on Delivery and Operational Condition of Grate-type (Stoker-type) Incinerator with Advanced Flue Gas Treatment System in China -Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province- Kazushige
[Delivered Products & Systems] Report on Delivery and Operational Condition of Grate-type (Stoker-type) Incinerator with Advanced Flue Gas Treatment System in China -Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province- Kazushige
WM2008 Conference, February 24-28, 2008, Phoenix, AZ Abstract #8216. Thermal Pretreatment For TRU Waste Sorting
 ABSTRACT Thermal Pretreatment For TRU Waste Sorting T. Sasaki, Y. Aoyama, Y. Miyamoto, and H. Yamaguchi Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4-33, Muramatsu, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki 319-1194 Japan Japan Atomic Energy
ABSTRACT Thermal Pretreatment For TRU Waste Sorting T. Sasaki, Y. Aoyama, Y. Miyamoto, and H. Yamaguchi Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4-33, Muramatsu, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki 319-1194 Japan Japan Atomic Energy
42. Sim Distribution Example
 HSC 8 - Sim Distribution 42. Sim Distribution Example Magnetite Oxidation Example 14022-ORC-J 1 (22) Pelletized magnetite (Fe3O4) ore can be oxidized to hematite (Fe2O3) in a shaft furnace. The typical
HSC 8 - Sim Distribution 42. Sim Distribution Example Magnetite Oxidation Example 14022-ORC-J 1 (22) Pelletized magnetite (Fe3O4) ore can be oxidized to hematite (Fe2O3) in a shaft furnace. The typical
CHAPTER VII MELTING D-R PELLETS. the volume of gases evolved, the movements of the solid-liquid
 CHAPTER VII 172. MELTING D-R PELLETS The mathematical model described in Chapter V is utilized to determine the temperature distribution, the change of chemical composition, the volume of gases evolved,
CHAPTER VII 172. MELTING D-R PELLETS The mathematical model described in Chapter V is utilized to determine the temperature distribution, the change of chemical composition, the volume of gases evolved,
THE VALUE OF ENERGY AND RESOURCES TOWARDS AN EFFICIENT FUTURE STEELMAKING
 THE VALUE OF ENERGY AND RESOURCES TOWARDS AN EFFICIENT FUTURE STEELMAKING Authors: Dr. Alexander Fleischanderl 1), Dr. Thomas Steinparzer 2) 1) Technology Officer Up-stream, Vice President, PhD in process
THE VALUE OF ENERGY AND RESOURCES TOWARDS AN EFFICIENT FUTURE STEELMAKING Authors: Dr. Alexander Fleischanderl 1), Dr. Thomas Steinparzer 2) 1) Technology Officer Up-stream, Vice President, PhD in process
Shenwu s Innovative Smelting Technology via Rotary Hearth Furnace. 2 nd INDIA INTERNATIONAL DRI SUMMIT 1 ST AUG, 2014 HOTEL LE MERIDIEN, NEW DELHI 1
 Shenwu s Innovative Smelting Technology via Rotary Hearth Furnace 2 nd INDIA INTERNATIONAL DRI SUMMIT 1 ST AUG, 2014 HOTEL LE MERIDIEN, NEW DELHI 1 Content 1 Introduction 2 R&D on RHF 3 Industrialization
Shenwu s Innovative Smelting Technology via Rotary Hearth Furnace 2 nd INDIA INTERNATIONAL DRI SUMMIT 1 ST AUG, 2014 HOTEL LE MERIDIEN, NEW DELHI 1 Content 1 Introduction 2 R&D on RHF 3 Industrialization
Biomass Gasification
 Biomass Gasification Efficient use of Energy Turning waste to energy, liabilities to assets and visions into reality. Table of Contents THE HTI ADVANTAGE...................... 1 FEED SYSTEMS..........................
Biomass Gasification Efficient use of Energy Turning waste to energy, liabilities to assets and visions into reality. Table of Contents THE HTI ADVANTAGE...................... 1 FEED SYSTEMS..........................
High efficient multi-fuel CYMIC concept for biomass, rejects and coal for Hamburger Hungaria Katriina Jalkanen Valmet Technologies Oy
 High efficient multi-fuel CYMIC concept for biomass, rejects and coal for Hamburger Hungaria 28.4.2016 Katriina Jalkanen Valmet Technologies Oy CYMIC Multi-Fuel Design Concept: general and case example
High efficient multi-fuel CYMIC concept for biomass, rejects and coal for Hamburger Hungaria 28.4.2016 Katriina Jalkanen Valmet Technologies Oy CYMIC Multi-Fuel Design Concept: general and case example
Novel Ironmaking Technology with Low Energy Requirement and CO 2 Emission
 Novel Ironmaking Technology with Low Energy Requirement and CO 2 Emission University of Utah PI: H. Y. Sohn Postdoc: G. Han Lab Assts: M.E. Choi, Y. Zhang, Josh Ramos, H. Wang Supported by DOE/AISI Partner
Novel Ironmaking Technology with Low Energy Requirement and CO 2 Emission University of Utah PI: H. Y. Sohn Postdoc: G. Han Lab Assts: M.E. Choi, Y. Zhang, Josh Ramos, H. Wang Supported by DOE/AISI Partner
Essar Steel (I) Ltd. Hazira
 Essar Steel (I) Ltd. Hazira Presentation on : Technological conjunction of Iron & Steel Making at Essar Steel India Ltd. By : Mr. Hitesh Sheth (Hitesh.Sheth@essar.com) Ms. Neeru Singh (Neeru.Singh@essar.com)
Essar Steel (I) Ltd. Hazira Presentation on : Technological conjunction of Iron & Steel Making at Essar Steel India Ltd. By : Mr. Hitesh Sheth (Hitesh.Sheth@essar.com) Ms. Neeru Singh (Neeru.Singh@essar.com)
Peridur organic binder for pelletization
 Peridur organic binder for pelletization Advantages of using Peridur Peridur provides: Excellent pellet growth behavior Peridur can deal with changes in iron ore mineralogy, as well as variations in blaine
Peridur organic binder for pelletization Advantages of using Peridur Peridur provides: Excellent pellet growth behavior Peridur can deal with changes in iron ore mineralogy, as well as variations in blaine
RECYCLING PRACTICES OF SPENT MgO-C REFRACTORIES
 Journal of Minerals & Materials Characterization & Engineering, Vol. 1, No.2, pp69-78, 2002 Printed in the USA. All rights reserved RECYCLING PRACTICES OF SPENT MgO-C REFRACTORIES Kyei-Sing Kwong and James
Journal of Minerals & Materials Characterization & Engineering, Vol. 1, No.2, pp69-78, 2002 Printed in the USA. All rights reserved RECYCLING PRACTICES OF SPENT MgO-C REFRACTORIES Kyei-Sing Kwong and James
INDUSTRIAL ACCESSORIES COMPANY
 INDUSTRIAL ACCESSORIES COMPANY Industrial Accessories Company is an industrial design/build and original equipment manufacturer of baghouses, flue gas desulfurization, heavy metal mitigating sorbent injection
INDUSTRIAL ACCESSORIES COMPANY Industrial Accessories Company is an industrial design/build and original equipment manufacturer of baghouses, flue gas desulfurization, heavy metal mitigating sorbent injection
RECYCLING OF STEELMAKING DUSTS THE RADUST CONCEPT -
 Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, 41 B (2005) 1-16 RECYCLING OF STEELMAKING DUSTS THE RADUST CONCEPT - H. Jalkanen *#, H. Oghbasilasie * and K. Raipala ** * Helsinki University of Technology, Department
Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, 41 B (2005) 1-16 RECYCLING OF STEELMAKING DUSTS THE RADUST CONCEPT - H. Jalkanen *#, H. Oghbasilasie * and K. Raipala ** * Helsinki University of Technology, Department
Development of the Process for Producing Pre-reduced Agglomerates
 Development of the Process for Producing Pre-reduced Agglomerates JFE TECHNICAL REPORT No. 13 (May 9) MACHIDA Satoshi *1 SATO Hideaki * TAKEDA Kanji *3 Abstract: The Japanese steel industry, accounting
Development of the Process for Producing Pre-reduced Agglomerates JFE TECHNICAL REPORT No. 13 (May 9) MACHIDA Satoshi *1 SATO Hideaki * TAKEDA Kanji *3 Abstract: The Japanese steel industry, accounting
Heat exchangers and thermal energy storage concepts for the off-gas heat of steelmaking devices
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Heat exchangers and thermal energy storage concepts for the off-gas heat of steelmaking devices To cite this article: T Steinparzer et al 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Heat exchangers and thermal energy storage concepts for the off-gas heat of steelmaking devices To cite this article: T Steinparzer et al 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
direct from 1st quarter 2015 inside this issue The Value of DRI : Using the Product for Optimum Steelmaking
 direct from 1st quarter 2015 inside this issue 2 commentary: Synergy in Motion: Combining People, Process & Performance 3 Technical Excellence with a Human Touch: Engineering, the Midrex Way 8 The Value
direct from 1st quarter 2015 inside this issue 2 commentary: Synergy in Motion: Combining People, Process & Performance 3 Technical Excellence with a Human Touch: Engineering, the Midrex Way 8 The Value
Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) plant 2 x 600 MW Coal based Thermal power plant Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu. By MK Parameswaran 23 rd Dec, 2016
 Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) plant 2 x 600 MW Coal based Thermal power plant Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu. By MK Parameswaran 23 rd Dec, 2016 Introduction Flue Gas Desulfurization is a process of removing
Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) plant 2 x 600 MW Coal based Thermal power plant Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu. By MK Parameswaran 23 rd Dec, 2016 Introduction Flue Gas Desulfurization is a process of removing
Cement industry Industrial emissions IPPC
 This project is funded by the European Union Cement industry Industrial emissions IPPC Andrzej Werkowski, Expert GHG Inventory and MRV of Industrial Emissions Workshop, Tbilisi, 27-28 March 2017 Multiple
This project is funded by the European Union Cement industry Industrial emissions IPPC Andrzej Werkowski, Expert GHG Inventory and MRV of Industrial Emissions Workshop, Tbilisi, 27-28 March 2017 Multiple
calcium oxide removes acidic oxides basic oxides acidic oxides basic oxides Iron obtained from the blast furnace is contaminated with
 1 Iron from a blast furnace is treated with and with calcium oxide to make steel. Which substances in the are removed? removes calcium oxide removes acidic oxides basic oxides acidic oxides basic oxides
1 Iron from a blast furnace is treated with and with calcium oxide to make steel. Which substances in the are removed? removes calcium oxide removes acidic oxides basic oxides acidic oxides basic oxides
SOME ENERGY-EFFICIENT TECHNOLOGIES IN JAPAN
 SOME ENERGY-EFFICIENT TECHNOLOGIES IN JAPAN (EXECUTIVE SESSION) November, 2007 JAPAN EXTERNAL TRADE ORGANIZATION JAPAN CONSULTING INSTITUTE SOME ENERGY-EFFICIENT TECHNOLOGIES IN JAPAN 1. Power Generation
SOME ENERGY-EFFICIENT TECHNOLOGIES IN JAPAN (EXECUTIVE SESSION) November, 2007 JAPAN EXTERNAL TRADE ORGANIZATION JAPAN CONSULTING INSTITUTE SOME ENERGY-EFFICIENT TECHNOLOGIES IN JAPAN 1. Power Generation
HOW A BLAST FURNACE WORKS
 HOW A BLAST FURNACE WORKS Introduction The purpose of a blast furnace is to chemically reduce and physically convert iron oxides into liquid iron called "hot metal". The blast furnace is a huge, steel
HOW A BLAST FURNACE WORKS Introduction The purpose of a blast furnace is to chemically reduce and physically convert iron oxides into liquid iron called "hot metal". The blast furnace is a huge, steel
IRISH CEMENT PLATIN INVESTING IN OUR FUTURE
 IRISH CEMENT PLATIN INVESTING IN OUR FUTURE INTRODUCTION Investing in our future. The next phase of investment in Platin will see further energy efficiency improvements with on site electricity generation
IRISH CEMENT PLATIN INVESTING IN OUR FUTURE INTRODUCTION Investing in our future. The next phase of investment in Platin will see further energy efficiency improvements with on site electricity generation
