Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity.
|
|
|
- Christal Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity. Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density and specific gravity of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance. If a substance has a lot of mass in small volume we would say it is dense. For instance, fishing weights usually weigh only a few ounces, but they are heavy for their size. Fishing weights are often made out of lead, one of the densest metals. Hay, on the other hand is not dense; its mass per volume is very small. Bales of hay, while not dense, are very heavy due to their size and have been know to kill people they roll on. So having a lot of mass does not make something dense, it must be a lot of mass packed into a small volume. Density is calculated as mass divided by volume. In chemistry, the most common units of density are g/ml (used for liquids) and g/cm 3 (used for solids). Recall that a milliliter and a cubic centimeter are the same volume. Density = mass volume Below are densities for some common substances. Since two substances rarely have the same density, density can be used to identify materials. Solids (25 o C) Density (g/cm 3 ) Liquids (25 o C) Density (g/ml) Gases (0 o C, 1 atm) Density (g/l) Hay bale Gasoline 0.74 Helium Ice (0 o C) 0.92 Honey 1.42 Nitrogen 1.25 Aluminum 2.70 Olive oil 0.92 Air 1.29 Zinc 7.14 Water 1.00 Oxygen 1.43 Tin 7.31 Urine Carbon dioxide 1.96 Steel 7.48 Blood 1.03 Sulfur hexafluoride 6.17 Brass 8.74 Mercury 13.6 Copper 8.96 Lead 11.4 Buoyancy stems from differences in density. Helium balloons float in air, because helium is less dense than air. In fact, the earth s atmosphere contains almost no helium because the gravitational pull is not strong enough to prevent its loss to outer space. Or helium supply comes from gases trapped in ores deep in the earth, a resource we are using up at an alarming rate. Other examples of how buoyancy is determined by density include oil floating on water and stones sinking in a river. Water is an unusual substance in that its solid form is less dense than its liquid form. The less dense ice floating in water allows pond life to survive over the winter. Volume by displacement If an object does not have a regular, easily measured shape, its volume can be determined by displacement. First, choose a partially filled graduated cylinder large enough to accommodate the object with enough liquid to completely submerge it. Carefully measure the volume in the cylinder. Submerge the object in the cylinder and measure the volume again. The difference between the two volumes is equal to the volume of the object. Once you have determined the volume, divide by the mass to find the density of the irregular object.
2 Specific Gravity Specific gravity is a ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water. Because specific gravity is unitless, it will be the same no matter which system of measurement is used. Specific Gravity = density of substance density of water For mercury, the specific gravity is equal to 13.6 g/ml divided by 1.00 g/ml = When using the metric system, the specific gravity is essentially the density written without a unit. Note if using imperial units, the specific gravity of mercury would be 113 lb/gal divided by 8.3 lb/gal for water which still equals Specific gravity is measured using a hydrometer. To use this instrument, float it in the liquid to be measured and read where the liquid surface hits the scale. The lower the hydrometer floats, the less dense the liquid. Hydrometers can be used to determine the amount of solids in a urine sample a higher specific gravity indicates less water present and possibly dehydration. Hydrometers are also used to determine alcohol content in beer. Brewers take a specific gravity reading before and after fermentation. As sugars convert to alcohol, the specific gravity decreases. The percent alcohol can be determined by comparing the initial and final specific gravity. Laboratory Activity Materials: metal cylinder Graduated cylinders aluminum foil hydrometers Ruler Deionized water isopropanol Procedure A. Density of an Unknown Metal 1. Obtain an unknown metal sample and record the mass measured with a balance. 2. Find the volume of the cylinder by displacement. Fill a 25 ml graduated cylinder about halfway with water. Carefully read and record the volume to the correct number of significant figures. Angle the graduated cylinder and gently slide in the metal. If liquid splashes out, start over. Record the new volume. Subtract the two water volumes to find the volume of the metal. 3. Calculate the density of the metal. Determine the identity by comparing your value to the densities of metals in the table in the background section. B. Thickness of Aluminum Foil 1. Obtain a piece of aluminum foil and measure its length and width in centimeters with a ruler. Be sure to record the correct number of significant figures. 2. Record the mass of the aluminum foil. Fold the foil if necessary so that it only touches the pan of the balance. 3. Use the density of aluminum given in the table to find volume of the foil sheet. Given that the volume of the foil sheet is length x width x height, find the thickness (height) of the foil.
3 C. Density and Specific Gravity of Liquids. 1. Record the mass of a dry 100 ml graduated cylinder to the correct number of significant figures. Write this number in the table on the first line in the column for water. 2. Fill the graduated cylinder roughly 2/3 full with deionized water and record the mass. The amount of water is not important do not try to fill exactly to a line! Record this value in the second line in the column for water. 3. Read the volume of the graduated cylinder to the correct number of significant figures. Use volume and mass to calculate the density of water. 4. Repeat steps 1-3 with a different dry graduated cylinder for isopropyl alcohol. Record the values in the isopropyl column. 5. Two large graduated cylinders in the front of the room ( or in the fume hood) will contain water and isopropyl alcochol. Rotate the floating hydrometer so that you can see the side with wider markings. Use these markings to measure the specific gravity of water and isopropyl alcohol. Record each in the appropriate column. Waste Disposal deionized water sink Isopropyl alcohol return to the bottle.
4
5 Name Team Name CHM101 Lab Density and Specific Gravity Grading Rubric To participate in this lab you must have splash-proof goggles, proper shoes and attire. Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Safety and proper waste disposal procedures observed 2 Followed procedure correctly without depending too much on instructor or lab partner 3 Work space and glassware was cleaned up 1 Lab Report Part A (data recorded with correct sig figs and units, calculations shown clearly, all questions answered) Part B (data recorded with correct sig figs and units, calculations shown clearly, all questions answered) Part C (data recorded with correct sig figs and units, calculations shown clearly, all questions answered) Post Lab: Question 1 1 Post Lab: Question 2 (work shown in detail with units) 2 Post Lab: Question 3 (work shown in detail with units) 2 Total 20 Subject to additional penalties at the discretion of the instructor.
6
7 Density and Specific Gravity: Data Sheet Name Include the proper units for all measurements and show all your work for any calculations. Report your answers to the correct number of significant digits. A. Density of an Unknown Metal Mass of metal Volume of water Volume of water + metal Volume of metal Show calculations for the density of the metal. Write out all units and use correct significant figures. Based on density, what is your unknown metal? Explain your choice. B. Thickness of Aluminum Foil Length of foil Width of foil Mass of foil Use the density of aluminum and mass to find the volume of the aluminum foil: Use volume of the foil, length and width to calculate thickness (height) of the aluminum foil: (V = l x w x h) Report Page 1 of 3
8 C. Density and Specific Gravity of Liquids Mass of empty cylinder Mass of cylinder with liquid Mass of liquid Volume of liquid (read the cylinder!) Density of liquid (calculate from data above) Specific Gravity (measure with hydrometer) Water Isopropanol How does you calculated density and measured specific gravity compare for the water? How do they compare for the isopropanol? Report Page 2 of 3
9 Density and Specific Gravity: Post Lab Questions Name Q1. Calculate your percent error for the density of water. Percent Error = true value - your value true value 100% Q2. An irregular object with a mass of 92.5 g is placed in a graduated cylinder containing 54.3 ml of water. The new volume is 88.0 ml. What is the density of the object? Q3. Determine the volume in quarts of 25.6 kg of oil. The oil has a density of g/ml. Report Page 3 of 3
Introduction to Density
 Introduction to Density INTRODUCTION Which is heavier, a pound of aluminum or a pound of lead? The answer, of course, is neither, but many people confuse the words "heavy" and "dense". "Heavy" refers to
Introduction to Density INTRODUCTION Which is heavier, a pound of aluminum or a pound of lead? The answer, of course, is neither, but many people confuse the words "heavy" and "dense". "Heavy" refers to
D =? D = M = 10 g = 5 g/cm 3 M = 10 g V 2 cm 3 V = 2 cm 3 5 g/cm 3
 Using the formula for density, answer the following calculation problems. M D = (g/ml or g/cm 3 ) Density = Mass D = M M = (g) Volume V D V V = (ml or cm 3 ) For all of your problems, please complete them
Using the formula for density, answer the following calculation problems. M D = (g/ml or g/cm 3 ) Density = Mass D = M M = (g) Volume V D V V = (ml or cm 3 ) For all of your problems, please complete them
Name # Date Period! FINDING&VOLUME&AND&DENSITY& !!! !!!!!!!
 Name # Date Period FINDING&VOLUME&AND&DENSITY& TherectangularshapedboxinFigure1isfilledwithdrysand.Findthe volumeanddensityofthesand. 1.Firstfindthevolumeofthebox.Thisisalsothevolumeofthesand. Usethediagramtofindthedimensionsofthebox.
Name # Date Period FINDING&VOLUME&AND&DENSITY& TherectangularshapedboxinFigure1isfilledwithdrysand.Findthe volumeanddensityofthesand. 1.Firstfindthevolumeofthebox.Thisisalsothevolumeofthesand. Usethediagramtofindthedimensionsofthebox.
Density What is density? How do you measure density?
 Density What is density? How do you measure density? What is density? Density describes how much mass is in a given volume of a material. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. Volume: the amount of
Density What is density? How do you measure density? What is density? Density describes how much mass is in a given volume of a material. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. Volume: the amount of
2.3 Density and Density Calculations
 2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
Density Answers to the End of module questions
 IDS 101 Density Answers to the End of module questions 1. You are experimenting with the mysterious substance X. You carefully measure the mass of a uniform 2 ml sample of pure substance X. You slice it
IDS 101 Density Answers to the End of module questions 1. You are experimenting with the mysterious substance X. You carefully measure the mass of a uniform 2 ml sample of pure substance X. You slice it
EXPERIMENT 3: Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties
 EXPERIMENT 3: Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties Materials: Hot plate Digital balance Capillary tubes (3) Thermometer Beakers (250 ml) Watch glass Graduated Cylinder (10 ml) Mel-Temp
EXPERIMENT 3: Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties Materials: Hot plate Digital balance Capillary tubes (3) Thermometer Beakers (250 ml) Watch glass Graduated Cylinder (10 ml) Mel-Temp
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET
 SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET PART 1 - Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. 1.) 0.02 2.) 0.020 3.) 501 4.) 501.0 5.) 5,000 6.) 5,000. 7.) 6,051.00 8.) 0.0005 9.) 0.1020
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET PART 1 - Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. 1.) 0.02 2.) 0.020 3.) 501 4.) 501.0 5.) 5,000 6.) 5,000. 7.) 6,051.00 8.) 0.0005 9.) 0.1020
Experiment 1: The Densities of Liquids and Solids (from Masterson & Hurley)
 Experiment 1: The Densities of Liquids and Solids (from Masterson & Hurley) One of the fundamental properties of any sample of matter is its density, which is its mass per unit of volume. The density of
Experiment 1: The Densities of Liquids and Solids (from Masterson & Hurley) One of the fundamental properties of any sample of matter is its density, which is its mass per unit of volume. The density of
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter.
 1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
v = 5.00cm x 3.00cm x 2.00cm 2. What is the volume of a marble that has a mass of 3.0 g and a density of 2.7 g/ml? Formula (density) Substitution
 Name: STUDY GUIDE: MEASUREMENT, DENSITY, MASS, VOLUME, AND DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS (2016) 1. A solid block is 5.00 cm high, 3.00 cm wide, and 2.00 cm long. It has a mass of 129 g. What is the density? Formula
Name: STUDY GUIDE: MEASUREMENT, DENSITY, MASS, VOLUME, AND DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS (2016) 1. A solid block is 5.00 cm high, 3.00 cm wide, and 2.00 cm long. It has a mass of 129 g. What is the density? Formula
1 Elements. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Look at the illustration and identify one source of iron that comes to Earth from somewhere else.
 CHAPTER 4 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
CHAPTER 4 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
Copper Odyssey. Chemical Reactions of Copper
 Name Lab Partner(s) Copper Odyssey Chemical Reactions of Copper Date Period Elemental copper metal will be converted into copper (II) ion and then brought through a series of compound conversions until
Name Lab Partner(s) Copper Odyssey Chemical Reactions of Copper Date Period Elemental copper metal will be converted into copper (II) ion and then brought through a series of compound conversions until
DETERMINATION OF DENSITY
 DETERMINATION OF DENSITY Dr. Barbara B. Bunn. Adapted from Experiments in General Chemistry ; Wiley 1996J.G. Wardeska, T.T-S. Huang, R.W. Kopp; used by permission. Tested by Ms. Janice Orr s Chemistry
DETERMINATION OF DENSITY Dr. Barbara B. Bunn. Adapted from Experiments in General Chemistry ; Wiley 1996J.G. Wardeska, T.T-S. Huang, R.W. Kopp; used by permission. Tested by Ms. Janice Orr s Chemistry
Name Honors Chemistry / /
 Name Honors Chemistry / / SOL Questions Chapter 1 Each of the following questions below appeared on an SOL Chemistry Exam. For each of the following bubble in the correct answer on your scantron. 1. The
Name Honors Chemistry / / SOL Questions Chapter 1 Each of the following questions below appeared on an SOL Chemistry Exam. For each of the following bubble in the correct answer on your scantron. 1. The
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use.
 This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example,
 SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example, density, thermal or electrical conductivity, solubility,
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example, density, thermal or electrical conductivity, solubility,
DETERMINATION of the EMPIRICAL FORMULA
 DETERMINATION of the EMPIRICAL FORMULA One of the fundamental statements of the atomic theory is that elements combine in simple whole number ratios. This observation gives support to the theory of atoms,
DETERMINATION of the EMPIRICAL FORMULA One of the fundamental statements of the atomic theory is that elements combine in simple whole number ratios. This observation gives support to the theory of atoms,
EXPERIMENT. The Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid; The Molar Volume of Hydrogen
 EXPERIMENT The Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid; The Molar Volume of Hydrogen PURPOSE In this experiment you will determine the volume of the hydrogen gas which is produced when a sample of
EXPERIMENT The Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid; The Molar Volume of Hydrogen PURPOSE In this experiment you will determine the volume of the hydrogen gas which is produced when a sample of
COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER
 COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of dissolved substances. Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater, measured in parts per thousand
COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of dissolved substances. Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater, measured in parts per thousand
Salinity in Seawater
 Salinity in Seawater Objective To familiarize students with the different methods used for measuring salinity of water. Introduction: Salinity exerts profound impacts on the marine environment. It controls
Salinity in Seawater Objective To familiarize students with the different methods used for measuring salinity of water. Introduction: Salinity exerts profound impacts on the marine environment. It controls
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 10 (2 Weeks) Chemistry 100 Laboratory TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION It is useful to classify reactions into different types, because products of reactions can be predicted.
EXPERIMENT 10 (2 Weeks) Chemistry 100 Laboratory TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION It is useful to classify reactions into different types, because products of reactions can be predicted.
1.4 Density. Question Paper. Subject Physics (0625) Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) General Physics A* A B C D E U
 1.4 ensity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic General Physics Sub-Topic 1.4 ensity ooklet Question Paper Time llowed: 33 minutes Score:
1.4 ensity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic General Physics Sub-Topic 1.4 ensity ooklet Question Paper Time llowed: 33 minutes Score:
Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide
 Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide The quantitative stoichiometric relationships governing mass and amount will be studied using the combustion reaction of magnesium metal. Magnesium
Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide The quantitative stoichiometric relationships governing mass and amount will be studied using the combustion reaction of magnesium metal. Magnesium
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 Water Sampler # 15010 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Purpose: Contents: For the collection of water samples at varying depths or distances away from a shoreline. One (1) Assembled Water Sampler One (1) Cord (15
Water Sampler # 15010 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Purpose: Contents: For the collection of water samples at varying depths or distances away from a shoreline. One (1) Assembled Water Sampler One (1) Cord (15
Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3
 Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK. Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70)
 Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 1.1 1.2 1.3 Warm Ups Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic
Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 1.1 1.2 1.3 Warm Ups Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic
Eutrophication: Too Much of a Good Thing?
 Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab DATASHEET FOR IN-TEXT LAB Eutrophication: Too Much of a Good Thing? Plants depend on nutrients such as phosphates and nitrates to survive. However, when people release
Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab DATASHEET FOR IN-TEXT LAB Eutrophication: Too Much of a Good Thing? Plants depend on nutrients such as phosphates and nitrates to survive. However, when people release
There are 2 different types of numbers Exact -Measured
 Significant Figures When measuring or using our calculators we must determine the correct answer; our calculators are mindless drones and don t know the correct answer. There are 2 different types of numbers
Significant Figures When measuring or using our calculators we must determine the correct answer; our calculators are mindless drones and don t know the correct answer. There are 2 different types of numbers
The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel.
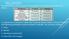 BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
GREENHOUSE LAB EXPERIMENTAL FOUNDATIONS OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE BROUGHT ON BY CARBON DIOXIDE POLLUTION
 GREENHOUSE LAB EXPERIMENTAL FOUNDATIONS OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE BROUGHT ON BY CARBON DIOXIDE POLLUTION STUDENT VERSION: PART 1...1-10 PART 2...11-14 PART 3...15-17 TEACHER INFORMATION PAGES: PART 1...18-26
GREENHOUSE LAB EXPERIMENTAL FOUNDATIONS OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE BROUGHT ON BY CARBON DIOXIDE POLLUTION STUDENT VERSION: PART 1...1-10 PART 2...11-14 PART 3...15-17 TEACHER INFORMATION PAGES: PART 1...18-26
Significance of Water Observation Lab
 Significance of Water Observation Lab It has been said that the chemistry of life is water chemistry. Because of its chemical properties, water is the medium in which most of life s chemical reactions
Significance of Water Observation Lab It has been said that the chemistry of life is water chemistry. Because of its chemical properties, water is the medium in which most of life s chemical reactions
Can you identify the properties and physical states of water?
 Unit 1 What is the Water Cycle? Activity A Can you identify the properties and physical states of water? Introduction Water is a substance with which students may believe they are very familiar. This activity
Unit 1 What is the Water Cycle? Activity A Can you identify the properties and physical states of water? Introduction Water is a substance with which students may believe they are very familiar. This activity
TESTING THE WATERS HOW GOOD IS THAT BOTTLED WATER AND HOW EFFECTIVE IS YOUR WATER FILTER
 TESTING THE WATERS HOW GOOD IS THAT BOTTLED WATER AND HOW EFFECTIVE IS YOUR WATER FILTER TEACHER NOTES This experiment is designed for students working singly or in groups of two. One run through the series
TESTING THE WATERS HOW GOOD IS THAT BOTTLED WATER AND HOW EFFECTIVE IS YOUR WATER FILTER TEACHER NOTES This experiment is designed for students working singly or in groups of two. One run through the series
Sunlight (solar energy) CO2 + H2O. Cellular Respiration (mitochondria) 36 ATP
 Aerobic & Anaerobic Conditions HASPI Medical Biology Lab 11 Background/Introduction The Flow of Energy & Cycling of Matter Photosynthesis and cellular respiration (including aerobic and anaerobic respiration)
Aerobic & Anaerobic Conditions HASPI Medical Biology Lab 11 Background/Introduction The Flow of Energy & Cycling of Matter Photosynthesis and cellular respiration (including aerobic and anaerobic respiration)
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK
 4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST SPRING 2009 Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST SPRING 2009 Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS
 ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
EXPERIMENT 6. Determination of the Ideal Gas Law Constant - R. Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following reaction,
 EXPERIMENT 6 Determination of the Ideal Gas Law Constant - R Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following reaction, Mg + 2 HCl MgCl 2 + H 2 (g) In this experiment you will use
EXPERIMENT 6 Determination of the Ideal Gas Law Constant - R Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following reaction, Mg + 2 HCl MgCl 2 + H 2 (g) In this experiment you will use
Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill
 Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill Lesson Overview: Students use the dimensions of the cargo hold of a ship s hull to calculate the volume of material that can be contained. Students will then use the
Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill Lesson Overview: Students use the dimensions of the cargo hold of a ship s hull to calculate the volume of material that can be contained. Students will then use the
CHAPTER 1. Conversions. General Plan for Converting Measurements. State the relationship between the unit given and the unit sought as an equality.
 CHAPTER 1 Conversions One of the aims of chemistry is to describe changes to tell what changed, how it changed, and what it changed into. Another aim of chemistry is to look at matter and its changes and
CHAPTER 1 Conversions One of the aims of chemistry is to describe changes to tell what changed, how it changed, and what it changed into. Another aim of chemistry is to look at matter and its changes and
To identify and classify various types of chemical reactions.
 Cycle of Copper Reactions Minneapolis Community and Technical College v.11.17 Objectives: To observe and document copper s chemical changes in five different reactions and verify that copper is conserved
Cycle of Copper Reactions Minneapolis Community and Technical College v.11.17 Objectives: To observe and document copper s chemical changes in five different reactions and verify that copper is conserved
ALTERNATIVE TRANSPORTATION FUELS LAB
 ALTERNATIVE TRANSPORTATION FUELS LAB Purpose: To examine the energy content of various alternative fuels which could be used for powering our vehicles in the future. As gasoline becomes increasingly expensive,
ALTERNATIVE TRANSPORTATION FUELS LAB Purpose: To examine the energy content of various alternative fuels which could be used for powering our vehicles in the future. As gasoline becomes increasingly expensive,
Experiment 2: The Chromatography of Organic Compounds
 Experiment 2: The Chromatography of Organic Compounds INTRODUCTION When performing an organic reaction, it is very common to observe the formation of other compounds in addition to your desired product;
Experiment 2: The Chromatography of Organic Compounds INTRODUCTION When performing an organic reaction, it is very common to observe the formation of other compounds in addition to your desired product;
Water: A Valuable, Yet Limited Resource
 Water: A Valuable, Yet Limited Resource Subject: Science Target Grades 4-5 Duration: One class period Materials per class 3 100-ml graduated cylinders container of water (10-ml/student) Water Cycle with
Water: A Valuable, Yet Limited Resource Subject: Science Target Grades 4-5 Duration: One class period Materials per class 3 100-ml graduated cylinders container of water (10-ml/student) Water Cycle with
Acid Rain. Evaluation copy. Figure 1: Typical rain ph in United States.
 Acid Rain Experiment 2 Acid rain is a topic of great concern to environmental engineers. It can kill fish by lowering the ph of lakes and rivers. It can harm trees and plants by burning their leaves and
Acid Rain Experiment 2 Acid rain is a topic of great concern to environmental engineers. It can kill fish by lowering the ph of lakes and rivers. It can harm trees and plants by burning their leaves and
Sci-Tech. Connections. The Heat's On. Hot Potatoes Grade 7 Sampler
 Sci-Tech Connections The Heat's On Hot Potatoes Grade 7 Sampler HOT POTATOES EXPECTATIONS work cooperatively, respect each other, work safely, and keep a clean work space use the terms heat and cooling
Sci-Tech Connections The Heat's On Hot Potatoes Grade 7 Sampler HOT POTATOES EXPECTATIONS work cooperatively, respect each other, work safely, and keep a clean work space use the terms heat and cooling
Eutrophication Using Up Oxygen In Water
 Eutrophication Using Up Oxygen In Water Topic Water pollution causing oxygen depletion in water by living organisms Introduction Farming is a major cause of freshwater pollution. Sewage and farm animal
Eutrophication Using Up Oxygen In Water Topic Water pollution causing oxygen depletion in water by living organisms Introduction Farming is a major cause of freshwater pollution. Sewage and farm animal
An Oxidation-Reduction Titration: The Reaction of Fe 2+ and Ce 4+
 An Oxidation-Reduction Titration: The Reaction of Fe 2+ and Ce 4+ LAB ADV COMP 8 From Advanced Chemistry with Vernier, Vernier Software & Technology, 2004 INTRODUCTION A titration, as you recall, is a
An Oxidation-Reduction Titration: The Reaction of Fe 2+ and Ce 4+ LAB ADV COMP 8 From Advanced Chemistry with Vernier, Vernier Software & Technology, 2004 INTRODUCTION A titration, as you recall, is a
Experiment 2: Preparation of the Artificial Sweetener Dulcin
 Experiment 2: Preparation of the Artificial Sweetener Dulcin Organic compounds known as sugars are carbohydrates that occur widely in nature. For example, sucrose (aka table sugar) is found in sugar can,
Experiment 2: Preparation of the Artificial Sweetener Dulcin Organic compounds known as sugars are carbohydrates that occur widely in nature. For example, sucrose (aka table sugar) is found in sugar can,
Science Class 8 Topic: Elements And Compounds Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Elements And Compounds Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1.Choose the best answer. 1. Which of the following is an element? a) steam b) sugar c)dry ice d) sulphur 2. Which
Science Class 8 Topic: Elements And Compounds Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1.Choose the best answer. 1. Which of the following is an element? a) steam b) sugar c)dry ice d) sulphur 2. Which
Chem 2115 Experiment #9. Consumer Chemistry: Determining the Iron Content in Supplements
 Chem 2115 Experiment #9 Consumer Chemistry: Determining the Iron Content in Supplements OBJECTIVE: The goal of this experiment is to use the quantitative technique of spectrophotometry to determine the
Chem 2115 Experiment #9 Consumer Chemistry: Determining the Iron Content in Supplements OBJECTIVE: The goal of this experiment is to use the quantitative technique of spectrophotometry to determine the
The determination of copper in brass
 The determination of copper in brass Objective - To determine the amount of copper in a brass sample Background Brass is an alloy made of copper and zinc. Most brass contains about 60% copper. The proportions
The determination of copper in brass Objective - To determine the amount of copper in a brass sample Background Brass is an alloy made of copper and zinc. Most brass contains about 60% copper. The proportions
GEL Hydrogeology (Groundwater) LAB 2: POROSITY & HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY - Porosity Segment - Grade: /25
 GEL 4250 - Hydrogeology (Groundwater) LAB 2: POROSITY & HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY - Porosity Segment - Name: Section: Grade: /25 COMPLETE & TURN IN ONLY PAGES THAT HAVE A FIELD FOR YOUR NAME. ALL OTHER PAGES
GEL 4250 - Hydrogeology (Groundwater) LAB 2: POROSITY & HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY - Porosity Segment - Name: Section: Grade: /25 COMPLETE & TURN IN ONLY PAGES THAT HAVE A FIELD FOR YOUR NAME. ALL OTHER PAGES
Experiment 3: The Chromatography of Organic Compounds
 Experiment 3: The Chromatography of Organic Compounds INTRODUCTION Very often, in an organic synthesis, a reaction will proceed to produce multiple products or perhaps will only partially form the desired
Experiment 3: The Chromatography of Organic Compounds INTRODUCTION Very often, in an organic synthesis, a reaction will proceed to produce multiple products or perhaps will only partially form the desired
1 Elements. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Look at the illustration and identify one source of iron that comes to Earth from somewhere else.
 CHAPTER 3 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
CHAPTER 3 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
Chapter 4.1. Estimating Manure Inventory. learning objectives
 Estimating Manure Inventory learning objectives Briefly explain the importance of determining manure weight or volume. Estimate the weight of solid manure in a pile. Estimate the volume of liquid manure
Estimating Manure Inventory learning objectives Briefly explain the importance of determining manure weight or volume. Estimate the weight of solid manure in a pile. Estimate the volume of liquid manure
Station 1 Dry Ice Experiments / Producing CO 2 in a reaction
 Station 1 Dry Ice Experiments / Producing CO 2 in a reaction 1. WHAT IS DRY ICE Put a flat chunk of dry ice on the counter and see how easy it "floats" on top of the counter when you give it a small push.
Station 1 Dry Ice Experiments / Producing CO 2 in a reaction 1. WHAT IS DRY ICE Put a flat chunk of dry ice on the counter and see how easy it "floats" on top of the counter when you give it a small push.
Name Lab Section Date. Sediment Lab
 Name Lab Section Date. Investigating Stokes Law Sediment Lab ds = density of solid, g/cm dw = density of water, g/cm g = gravity, 980 cm/second 2 D = particle diameter in centimeters μ = molecular viscosity,
Name Lab Section Date. Investigating Stokes Law Sediment Lab ds = density of solid, g/cm dw = density of water, g/cm g = gravity, 980 cm/second 2 D = particle diameter in centimeters μ = molecular viscosity,
Analysis of Calcium Carbonate Tablets
 Experiment 9 Analysis of Calcium Carbonate Tablets Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To perform a gravimetric exercise to determine weight percent of active ingredient in a
Experiment 9 Analysis of Calcium Carbonate Tablets Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To perform a gravimetric exercise to determine weight percent of active ingredient in a
2015 CORNELL SOIL HEALTH TRAIN-THE-TRAINER WORKSHOP AUGUST 5-8, 2015 ITHACA, NY. Wet Aggregate Stability Test
 2015 CORNELL SOIL HEALTH TRAIN-THE-TRAINER WORKSHOP AUGUST 5-8, 2015 ITHACA, NY Background / References: Wet Aggregate Stability Test The Wet Aggregate Stability (WAS) Test assesses the extent to which
2015 CORNELL SOIL HEALTH TRAIN-THE-TRAINER WORKSHOP AUGUST 5-8, 2015 ITHACA, NY Background / References: Wet Aggregate Stability Test The Wet Aggregate Stability (WAS) Test assesses the extent to which
Effects of Turbidity on Living Things
 3.4 Investigate Effects of Turbidity on Living Things Macroinvertebrates can serve as an indicator of water quality in an ecosystem. That is just one example of how living things can serve as an indicator
3.4 Investigate Effects of Turbidity on Living Things Macroinvertebrates can serve as an indicator of water quality in an ecosystem. That is just one example of how living things can serve as an indicator
IDENTIFYING UNKNOWN SUBSTANCES
 IDENTIFYING UNKNOWN SUBSTANCES LAB 15 EXPERIMENT STUDENT BOOK Chapter 1, page 25 TOOLBOX Page 4 and 36 Goal Identify unknown substances with the help of different tests. 1. What is the independent variable
IDENTIFYING UNKNOWN SUBSTANCES LAB 15 EXPERIMENT STUDENT BOOK Chapter 1, page 25 TOOLBOX Page 4 and 36 Goal Identify unknown substances with the help of different tests. 1. What is the independent variable
Science Grade 07 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 03: Effects of Human Activity on Water
 Unit: 04 Lesson: 03 Suggested Duration: 7 days Grade 07 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 03: Effects of Human Activity on Water This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
Unit: 04 Lesson: 03 Suggested Duration: 7 days Grade 07 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 03: Effects of Human Activity on Water This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
It is not essential for students to conduct an investigation for every question they generate or generate questions based on prior investigations.
 Scientific Inquiry 5-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the foundations of technological design and the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary
Scientific Inquiry 5-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the foundations of technological design and the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary
Understanding the Environmental Requirements for Fish
 Lesson C3 2 Understanding the Environmental Requirements for Fish Unit C. Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 3. Fish Management Lesson 2. Understanding the Environmental Requirements for Fish New
Lesson C3 2 Understanding the Environmental Requirements for Fish Unit C. Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 3. Fish Management Lesson 2. Understanding the Environmental Requirements for Fish New
Oceanopgraphy: 3014 lab 6 Experiments:
 LAB 6: EXPERIMENTS ON LAB 5 NAME OF THE GROUP MEMBERS 1 2 3 4 5 Things that are needed for the experiments Salt Beakers Pipette Petri dish Graduated cylinder Deionized water Thermometer Dropper Burette
LAB 6: EXPERIMENTS ON LAB 5 NAME OF THE GROUP MEMBERS 1 2 3 4 5 Things that are needed for the experiments Salt Beakers Pipette Petri dish Graduated cylinder Deionized water Thermometer Dropper Burette
Gravimetric Analysis: Determination of % Sulfur in Fertilizer
 Gravimetric Analysis: Determination % Sulfur in Fertilizer This is another "real world" sample experiment in this case we will analyze a fertilizer sample for the sulfate content and express the result
Gravimetric Analysis: Determination % Sulfur in Fertilizer This is another "real world" sample experiment in this case we will analyze a fertilizer sample for the sulfate content and express the result
Lab #3: Law of Definite Proportions
 Name Lab #3: Law of Definite Proportions Sept. 21, 2016 Purpose To find the percent composition and therefore definite ratio of the elements in magnesium oxide. Background When magnesium and oxygen are
Name Lab #3: Law of Definite Proportions Sept. 21, 2016 Purpose To find the percent composition and therefore definite ratio of the elements in magnesium oxide. Background When magnesium and oxygen are
EOC 7th Grade District Common Assessment
 EOC 7th Grade District Common Assessment 1. Todd needs to measure 50 grams of table salt for an experiment. Which measuring device will most accurately measure 50 grams? 2. What is the length (in millimeters)
EOC 7th Grade District Common Assessment 1. Todd needs to measure 50 grams of table salt for an experiment. Which measuring device will most accurately measure 50 grams? 2. What is the length (in millimeters)
Science Physical Science Grades 6 and 8
 Science Physical Science Grades 6 and 8 Subject: Physical Science: Thermal Energy Level: Grade 6 and 8 The Hot in the Cold Abstract: Students will conduct an experiment and collect data on the exchange
Science Physical Science Grades 6 and 8 Subject: Physical Science: Thermal Energy Level: Grade 6 and 8 The Hot in the Cold Abstract: Students will conduct an experiment and collect data on the exchange
AT HOME SCIENTIST! SHARKS
 SHARKS Sharks are amazing and often misunderstood creatures of the sea. Without them, the ocean food chain would be affected, and the balance of life in the ocean would be disrupted. Have you wondered
SHARKS Sharks are amazing and often misunderstood creatures of the sea. Without them, the ocean food chain would be affected, and the balance of life in the ocean would be disrupted. Have you wondered
Physical Behavior of Metals
 Activity 4 Physical Behavior of Metals GOALS In this activity you will: Discover what an alloy is. Make a brass-coated penny. Determine how the properties of a metal are affected by making it into an alloy.
Activity 4 Physical Behavior of Metals GOALS In this activity you will: Discover what an alloy is. Make a brass-coated penny. Determine how the properties of a metal are affected by making it into an alloy.
Grade 8 SCIENCE Unit 3 FLUIDS Chapter 7 QUESTIONS
 Grade 8 SCIENCE Unit 3 FLUIDS Chapter 7 QUESTIONS Page 272 1. A FLUID is a substance that can be made to FLOW. If a material, FLOWS, it is a FLUID. If you can STIR it, it is behaving like a FLUID. 2. Particle
Grade 8 SCIENCE Unit 3 FLUIDS Chapter 7 QUESTIONS Page 272 1. A FLUID is a substance that can be made to FLOW. If a material, FLOWS, it is a FLUID. If you can STIR it, it is behaving like a FLUID. 2. Particle
Periodic Trends and the Properties of Elements The Alkaline Earth Metals
 Introduction Periodic Trends and the Properties of Elements The Alkaline Earth Metals The periodic table is the most recognized symbol of chemistry across the world. It is a valuable tool that allows scientists
Introduction Periodic Trends and the Properties of Elements The Alkaline Earth Metals The periodic table is the most recognized symbol of chemistry across the world. It is a valuable tool that allows scientists
The Planet s Lungs: Planting Giant Sequoias to Combat Carbon Dioxide
 The Planet s Lungs: Planting Giant Sequoias to Combat Carbon Dioxide By Matthew Auman Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing. This is not controversial. Global warming has been cited
The Planet s Lungs: Planting Giant Sequoias to Combat Carbon Dioxide By Matthew Auman Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing. This is not controversial. Global warming has been cited
One to two class periods depending on how much of the lab set-up is done before hand and the length of the pre-lab and follow-up discussions.
 Can Gases Act Like a Greenhouse? Adapted from www.planetconnecticut.org Students conduct a controlled experiment to confirm whether a gas -- in this case, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) -- can act like a greenhouse.
Can Gases Act Like a Greenhouse? Adapted from www.planetconnecticut.org Students conduct a controlled experiment to confirm whether a gas -- in this case, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) -- can act like a greenhouse.
Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect: A laboratory exercise
 Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect: A laboratory exercise A laboratory exercise prepared by Beyond Benign as part of the Green Chemistry in Higher Education program: A workshop for EPA Region 2 Colleges
Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect: A laboratory exercise A laboratory exercise prepared by Beyond Benign as part of the Green Chemistry in Higher Education program: A workshop for EPA Region 2 Colleges
Lab #7H Photosynthesis and Respiration
 Lab #7H Photosynthesis and Respiration Plants make sugar, storing the energy of the sun into chemical energy, by the process of photosynthesis. When they require energy, they can tap the stored energy
Lab #7H Photosynthesis and Respiration Plants make sugar, storing the energy of the sun into chemical energy, by the process of photosynthesis. When they require energy, they can tap the stored energy
FOSS Journal. (Name) 2
 FOSS Journal (Name) 2 Rubric - 40 pts. You are graded on your FOSS journaling. You are expected to complete all notes, even if you are absent. Please check with classmates to see if you can copy notes.
FOSS Journal (Name) 2 Rubric - 40 pts. You are graded on your FOSS journaling. You are expected to complete all notes, even if you are absent. Please check with classmates to see if you can copy notes.
Deciding how to handle waste produced from manufacturing
 27 Reclaiming the Metal l a b o r at o ry Deciding how to handle waste produced from manufacturing is challenging. It can be diluted or incinerated, as you saw in previous activities. In some cases, it
27 Reclaiming the Metal l a b o r at o ry Deciding how to handle waste produced from manufacturing is challenging. It can be diluted or incinerated, as you saw in previous activities. In some cases, it
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROCHEMISTRY: CURRENT, VOLTAGE, & BATTERIES. Introduction. Electrochemistry Revised 4/28/14
 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROCHEMISTRY: CURRENT, VOLTAGE, & BATTERIES Introduction Electrochemical Cells In this part of the experiment, four half cells are created by immersing metal strips of zinc, copper,
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROCHEMISTRY: CURRENT, VOLTAGE, & BATTERIES Introduction Electrochemical Cells In this part of the experiment, four half cells are created by immersing metal strips of zinc, copper,
Engineering Aquatic Ecosystems
 Grade: 9-12 Version 2 Sept. 2017 Engineering Aquatic Ecosystems Design and develop a self-sustaining ecosystem that can support at least five complimentary organisms in a closed-loop system www.seiinc.org
Grade: 9-12 Version 2 Sept. 2017 Engineering Aquatic Ecosystems Design and develop a self-sustaining ecosystem that can support at least five complimentary organisms in a closed-loop system www.seiinc.org
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Lab: Ocean Salinity and Density M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
CHEM 1215 LAB NOTES EXPT #2: PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES 1
 CHEM 1215 LAB NOTES EXPT #2: PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES 1 TECHNIQUES: chemical and physical changes, reactions, observations READING: PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES e.g. Tro chapter 1 SAFETY: Safety
CHEM 1215 LAB NOTES EXPT #2: PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES 1 TECHNIQUES: chemical and physical changes, reactions, observations READING: PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES e.g. Tro chapter 1 SAFETY: Safety
EMG 807 Post-test. 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of
 EMG 807 Post-test 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of a. Energy that we use. b. Power that we use. c. Force that we use. a. i only
EMG 807 Post-test 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of a. Energy that we use. b. Power that we use. c. Force that we use. a. i only
Significance of Water Observation Lab
 Significance of Water Observation Lab It has been said that the chemistry of life is water chemistry. Because of its chemical properties, water is the medium in which most of life s chemical reactions
Significance of Water Observation Lab It has been said that the chemistry of life is water chemistry. Because of its chemical properties, water is the medium in which most of life s chemical reactions
Chapter 3: Ocean Water
 Chapter 3: Ocean Water CHAPTER 3 PROJECT - DENSITY BOTTLES During the Golf Ball Density lab, you will see the ways in which fresh water interacts with salt water when the two are mixed. The two forms of
Chapter 3: Ocean Water CHAPTER 3 PROJECT - DENSITY BOTTLES During the Golf Ball Density lab, you will see the ways in which fresh water interacts with salt water when the two are mixed. The two forms of
Investigating Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
 Investigating Energy Flow in an Ecosystem Introduction Energy flows from one organism to another as food. Energy enters into a food web either as solar energy captured as part of photosynthesis or as chemical
Investigating Energy Flow in an Ecosystem Introduction Energy flows from one organism to another as food. Energy enters into a food web either as solar energy captured as part of photosynthesis or as chemical
Chapter 3 - Energy and Matter Practice Problems
 Chapter 3 - Energy and Matter Practice Problems 1) Helium is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture. C) element. D) homogeneous mixture. E) electron. 2) Air is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture.
Chapter 3 - Energy and Matter Practice Problems 1) Helium is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture. C) element. D) homogeneous mixture. E) electron. 2) Air is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture.
Hot Water Lab September 4, 2003
 Lab Partners: Johnny Smith Janie B. Good Susie S. Marte Hot Water Lab September 4, 2003 Period 2 September 10, 2003 Introduction: The purpose of the hot water lab is to determine the of the water with
Lab Partners: Johnny Smith Janie B. Good Susie S. Marte Hot Water Lab September 4, 2003 Period 2 September 10, 2003 Introduction: The purpose of the hot water lab is to determine the of the water with
INDEX METALS FERRIC METALS NON-FERRIC METALS WORKING WITH METALS METAL FORMING TECHNIQUES ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF METAL EXTRACTION
 METALS INDEX METALS FERRIC METALS NON-FERRIC METALS WORKING WITH METALS METAL FORMING TECHNIQUES ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF METAL EXTRACTION METALS CHEMICAL ELEMENTS FOUND IN NATURE IN SOLID STATE AT ROOM
METALS INDEX METALS FERRIC METALS NON-FERRIC METALS WORKING WITH METALS METAL FORMING TECHNIQUES ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF METAL EXTRACTION METALS CHEMICAL ELEMENTS FOUND IN NATURE IN SOLID STATE AT ROOM
Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: NGSS Cross-cutting Concepts: NGSS Disciplinary Core Ideas:
 FCJJ 37 - Science Kit Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: Asking questions and defining problems Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations
FCJJ 37 - Science Kit Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: Asking questions and defining problems Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations
Solid State Diffusion of Metals
 Solid State Diffusion of Metals Theodore Greene College of Engineering & Technology Wentworth Institute of Technology Boston, MA 02115 Copyright Edmonds Community College 2015 This material may be used
Solid State Diffusion of Metals Theodore Greene College of Engineering & Technology Wentworth Institute of Technology Boston, MA 02115 Copyright Edmonds Community College 2015 This material may be used
GRAVIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF SULFATE IN AN UNKNOWN SOLUTION
 GRAVIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF SULFATE IN AN UNKNOWN SOLUTION AIM The main objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of sulfate ion in an unknown solution by using gravimetry. INTRODUCTION
GRAVIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF SULFATE IN AN UNKNOWN SOLUTION AIM The main objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of sulfate ion in an unknown solution by using gravimetry. INTRODUCTION
KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS
 Soil Columns 40- to 2-3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 4 L A B O R AT O R Y Students investigate the composition of two different types of soil by separating the soils with water. By creating and
Soil Columns 40- to 2-3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 4 L A B O R AT O R Y Students investigate the composition of two different types of soil by separating the soils with water. By creating and
TREATMENT PLANT OPERATOR TRAINEE Examination Study Guide
 TREATMENT PLANT OPERATOR TRAINEE Examination Study Guide Mobile County Personnel Board 1809 Government St., Mobile AL 36606 May, 2018 A calculator and this page will be made available to examinees when
TREATMENT PLANT OPERATOR TRAINEE Examination Study Guide Mobile County Personnel Board 1809 Government St., Mobile AL 36606 May, 2018 A calculator and this page will be made available to examinees when
Study of a Freshwater Stream Ecosystem
 Practical Related Task - Ecology Field Work Instructional Approach Study of a Fresh Ecosystem Name: Group: Date: Aims: After the course, students should be able to: 1. Classify and identify organisms commonly
Practical Related Task - Ecology Field Work Instructional Approach Study of a Fresh Ecosystem Name: Group: Date: Aims: After the course, students should be able to: 1. Classify and identify organisms commonly
Name Date SEQL Student Pre/Post-Test-6 th Grade Science KEY
 IN.1.B.5,6,7.d-Measure length to the nearest millimeter, mass to the nearest gram, volume to the nearest milliliter, force (weight) to the nearest Newton, temperature to the nearest degree Celsius, time
IN.1.B.5,6,7.d-Measure length to the nearest millimeter, mass to the nearest gram, volume to the nearest milliliter, force (weight) to the nearest Newton, temperature to the nearest degree Celsius, time
Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology
 Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com Science Objectives Identify characteristics of different soils to demonstrate that a suspect has been at a scene.
Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com Science Objectives Identify characteristics of different soils to demonstrate that a suspect has been at a scene.
1. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide. She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard.
 1. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide. She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard. After 15 minutes, Marie found some shiny beads in the mixture. a. (i) Marie collected
1. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide. She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard. After 15 minutes, Marie found some shiny beads in the mixture. a. (i) Marie collected
