Department of Electrical Engineering. Jungli, Taiwan
|
|
|
- Emory Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Fabrication of CMOS Integrated Circuits Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
2 Background Outline The CMOS Process Flow Design Rules Latchup Antenna Rules & Layer Density Rules CMOS Process Enhancements Summary Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2
3 Introduction An integrated circuit is created by stacking layers of various materials in a pre-specified p sequence Both the electrical properties of the material and the geometrical patterns of the layer are important in establishing the characteristics of devices and networks Most layers are created first, and then patterned using lithographic sequence Doped silicon layers are the exception to this rule Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 3
4 Material Growth and Deposition Silicon Dioxide (SiO 2 ) It is an excellent electrical insulator It can be grown on a silicon wafer or deposited on top of the wafer Thermal oxide Si+O 2 SiO 2 (dry oxidation), using heat as a catalyst Growth rate is lower Si+2H 2 O SiO 2 +2H 2 (wet oxidation) Growth rate is faster The surface of the silicon is recessed from its original location CVD oxide SiH 4 (gas)+2o 2 (gas) SiO 2 (solid)+2h 2 O(gas) Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 4
5 Material Growth and Deposition Silicon Nitride (Si 3 N 4 ) A.k.a. nitride 3SiH 4 (gas)+4nh 3 (gas) Si 3 N 4 (solid)+12h 2 (gas) Nitrides act as strong barriers to most atoms, this makes them ideal for use as an overglass layer Polycrystal y Silicon Called polysilicon or just poly for short It is used as the gate material in MOSFETs SiH 4 Si+2H 2 It adheres well to silicon dioxide Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 5
6 Material Growth and Deposition Metals Aluminum (Al) is the most common metal used for interconnect wiring in ICs It is prone to electromigration J=I/A; A=wt is the cross-section area Layout engineers cannot alter the thickness t of the layer Electromigration is thus controlled by specifying the minimum width w to keep J below a max. value Copper (Cu) has recently been introduced as a replacement to aluminum Its resistivity itiit is about one-half the value of Al Standard patterning techniques cannot be used on copper layers; specialized techniques had to be developed Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 6
7 Material Growth and Deposition Doped Silicon Layers Silicon wafer is the starting point of the CMOS fabrication process A doped silicon layer is a patterned n- or p-type section of the wafer surface This is accomplished by a technique called ion implantation Basic section of an ion implanter Ion source Accelerator Magnetic Mass Separator Ion beam wafer Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 7
8 Material Growth and Deposition The process of deposition causes that the top surface has hillocks If we continue to add layers (e.g., metal layers), the surface will get increasing rough and may lead to breaks in fine line features and other problems Surface planarization is required Chemical-Mechanical Polishing (CMP) It uses a combination of chemical etching and mechanical sanding to produce planar surfaces on silicon wafers Surface planarization poly substrate substrate Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 8
9 Lithography One of the most critical problems in CMOS fabrication is the technique used to create a pattern Photolithography The photolithographic process starts with the desired pattern definition for the layer A mask is a piece of glass that has the pattern defined using a metal such as chromium Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 9
10 Transfer a Mask to Silicon Surface The process for transferring the mask pattern to the surface of a silicon region Coat photoresist Exposure step Etching Coat photoresist Liquid photoresist is sprayed onto a spinning wafer Exposure Photoresist is sensitive to light, such as ultraviolet (UV) Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 10
11 Transfer a Mask to Silicon Surface The figure shown as below depicts the main idea UV mask Hardened resist layer wafer photoresist wafer The hardened resist layer is used to protect underlying regions from the etching process Etching The chemicals are chosen to attack and remove the material layer not shielded by the hardened photoresist Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 11
12 Dopping The figure shows the etching process Hardened resist layer Patterned oxide layer Substrate Oxide layer Substrate Creation of doped silicon Arsenic ions Lateral dopping Substrate N+ N+ Substrate Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 12
13 Dopping The conductive characteristics of intrinsic silicon can be changed by introducing impurity atoms into the silicon crystal lattice Impurity elements that use (provide) electrons are called as acceptor (donor) Silicon that contains a majority of donors (acceptor) is known as n-type (p-type) When n-type and p-type materials are merged together, the region where the silicon changes from n-type to p-type is called junction Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 13
14 MOS Transistor Basic structure of a NMOS transistor Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 14
15 Fabrication Steps for an NMOS Patterning SiO 2 Layer p-substrate Implant or Diffusion Thin Oxide n + n + p-substrate Implant of Impurities Gate Oxidation p-substrate Contact Cuts n + n + p-substrate SiO 2 by deposition Polysilicon Al contacts Patterning Polysilicon p-substrate Patterning Al layer n + n + p-substrate Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 15
16 Basic CMOS Technology Four dominant CMOS technologies N-well process P-well process Twin-tub process Silicon on insulator (SOI) N-well (P-well) process Starts with a lightly doped p-type (n-type) substrate (wafer), create the n-type (p-type) well for the p-channel (n-channel) devices, and build the n-channel (p-channel) transistor in the native p-substrate (n-substrate) Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 16
17 N-Well CMOS Process Cross Section of Physical Structure Mask (top view) n-well mask p-substrate n-well n-well active mask nitride oxide n-well p-substrate Active Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 17
18 N-Well CMOS Process p-channel stop Implant (Boron) Resist channel stop mask n-well p-substrate Channel stop n-well p-substrate Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 18
19 N-Well CMOS Process polysilicon mask p-substrate n-well polysilicon n + mask n + n + n-well p-substrate n + mask Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 19
20 N-Well CMOS Process Light implant heavier implant oxide poly poly n - n - n - n - n + n + Shadow drain implant LDD (lightly doped drain) structure p + mask n + n + p + p + p-substrate n-well p + mask Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 20
21 N-Well CMOS Process contact mask n + n + p + p + n-well p-substrate contact mask metal mask n + n + p + p + n-well p-substrate metal mask Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 21
22 CMOS Inverter in N-Well Process in Vdd out Vss in out Vdd Vss Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 22
23 CMOS Inverter in N-Well Process p + p + n + n + n-well p-substrate contact cut polysilicon metal gate oxide field oxide p + p + n + n + n-well p-substrate Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 23
24 A Sample of Multi-Layer Metal Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 24
25 Design Rules Design rules (layout rules) Provide a necessary communication link between circuit designers and process engineers during manufacturing phase The goal of design rules is to achieve the optimum yield of a circuit with the smallest area cost Design rules specify to the designer certain geometric constraints on the layout artwork so that the patterns on the processed wafer will preserve the topology and geometry of the designs Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 25
26 Design Rules The design rules primarily address two issues The geometrical reproduction of features that can be reproduced by the mask-making and lithographical process The interactions between different layers Lambda-based rules Based on a single parameter, lambda, which characterizes the linear feature the resolution of the complete wafer implementation process Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 26
27 Examples of Design Rules Same Potential Different Potential 9 0 Well or Active Polysilicon 3 2 Contact or Via 2 Hole 2 Metal1 3 3 Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 27
28 Transistor Layout Trans sistor Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 28
29 Design Rules for Vias & Contacts 4 Via Metal to Metal to 1 Poly Contact Active Contact Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 29
30 Design Rule Checker Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 30
31 Latchup Latchup is defined as the generation of a low- impedance path in CMOS chips between power supply rail and the ground rail due to interaction of parasitic pnp and npn bipolar transistors These BJTs form a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) with positive feedback and virtually short circuit the power rail to ground, thus causing excessive current flows and even permanent device damage Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 31
32 Latchup of a CMOS Inverter Vdd p + n + n + p + p + n + NPN PNP R well N-well R substrate P-substrate R well 2.0mA I ramp V ne I ramp R substrate Trigger point V ne Holding Voltage Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 32
33 Latchup Triggering Latchup can be triggered by transient current or voltages that may occur internally to a chip during power-up or externally due to voltages or currents beyond normal operating ranges Two possible triggering mechanisms Lateral triggering & vertical triggering Ex: the static trigger point of lateral triggering is I ntrigger Vpnp on α npn R well Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 33
34 Latchup Prevention Reducing the value of resistors and reducing the gain of the parasitic transistors are the basis for eliminating latchup Latchup can be prevented in two basic methods Latchup resistant CMOS process Layout techniques I/O latchup prevention n Reducing the gain of parasitic transistors is achieved through the use of guard rings Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 34
35 Guard Rings Guard rings are that p+ diffusions in the p- substrate and n+ diffusions in the n-well to collect injected minority carriers Vdd emitter p + p-plus n-plus n + n-plus N-well base collector (substrate) Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 35
36 I/O Latchup Prevention A p+ guard ring is shown below for an n+ source/drain V ss n+ P+ collects hole current thereby shielding n+ source/drain p+ + p+ + + hole current N-well A n+ guard ring is shown below for a p+ source/drain V dd n+ collects electron current thereby shielding p+ source/drain electron current - p+ - - n+ p+ N-well Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 36
37 Antenna Rules When a metal wire contacted to a transistor gate is plasma-etched, it can charge up to a voltage sufficient to break down thin gate oxide The metal can be contacted to diffusion to provide a path for the charge to bleed away Antenna rules specify the maximum area of metal that t can be connected to a gate without a source or drain to act as a discharge element The design rule normally defines the maximum ratio of metal area to gate area such that charge on the metal will not damage the gate The ratios can vary from 100:1 to 5000:1 depending on the thickness of the gate oxide (and hence breakdown voltage) of the transistor in question Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 37
38 Antenna Rule Violation and Fix Wire attracts t charge during plasma processing and builds up voltage V=Q/C L2 Length L2 exceeds allowed limit Any source/drain can act as a discharge element Gate may be connected to source/drain at any metal layer in an auto routing situation L1 metal 4 metal 3 metal 2 metal tl 1 Added link solves problem-l1 satisfies design rule Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 38
39 Antenna Diode Addition An alternative method is to attach source/drain diodes to problem nets as shown below These diodes d can be simple junctions ns of n-diffusion n to p- substrate rather than transistor source/drain regions L2 Antenna diode may be added Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 39
40 Layer Density Rules For advanced processes, a minimum and maximum density of a particular layer within a specific area should be specified Layer density rules Layer density rules are required as a result of the CMP process and the desire to achieve uniform etch rates For example, a metal layer might have to have 30% minimum and 70% maximum fill within a 1mm by 1mm area For digital circuits, layer density levels are normally reached with normal routing Analog & RF circuits are almost spares Gate and metal layers may have to be added manually or by a fill program after design has been completed Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 40
41 CMOS Process Enhancements Multiple threshold voltages Low-V t more on current, but greater subthreshold leakage High-V t less current, but smaller subthreshold h leakage User low-v t devices on critical paths and higher-v t devices elsewhere to limit leakage power Multiple masks and implantation steps are used to set the various thresholds Silicon on insulator (SOI) process The transistors are fabricated on an insulator Two major insulators are used, SiOs and sapphire Two major advantages: elimination of the capacitance between the source/drain regions and body, leading to higher-speed devices; lower subthreshold leakage Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 41
42 CMOS Process Enhancements High-k gate dielectrics MOS needs high gate capacitance to attract charge to channel very thin SiO 2 gate dieletrics Scaling trends indicate the gate leakage will be unacceptably large in such thin gates Gates could use thicker dielectrics and hence leak less if a material a with a higher dielectric c constant were availablea a Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 42
43 Summary Some of more common CMOS technologies have been covered A representative set of n-well process has been introduced Concepts of design rules have been presented The important condition i known as latchup has been introduced with necessary design rules to avoid this condition i in CMOS chips Antenna rules & layer density rules should be considered in modern manufacturing process Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 43
PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS
 Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology
 Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
CHAPTER - 4 CMOS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY
 CHAPTER - 4 CMOS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY Samir kamal Spring 2018 4.1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Introduce the CMOS designer to the technology that is responsible for the semiconductor devices that might be designed
CHAPTER - 4 CMOS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY Samir kamal Spring 2018 4.1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Introduce the CMOS designer to the technology that is responsible for the semiconductor devices that might be designed
FABRICATION of MOSFETs
 FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation CMOS Processing Technology Topics CMOS Processing Technology Semiconductor Processing How do we make a transistor? Fabrication Process Wafer Processing Silicon single crystal
VLSI Design and Simulation CMOS Processing Technology Topics CMOS Processing Technology Semiconductor Processing How do we make a transistor? Fabrication Process Wafer Processing Silicon single crystal
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time Etching Dry etch (anisotropic) SiO
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time Etching Dry etch (anisotropic) SiO
Manufacturing Process
 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
EE 560 FABRICATION OF MOS CIRCUITS. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 FABRICATION OF MOS CIRCUITS 2 CMOS CHIP MANUFACTRING STEPS Substrate Wafer Wafer Fabrication (diffusion, oxidation, photomasking, ion implantation, thin film deposition, etc.) Finished Wafer Wafer
1 EE 560 FABRICATION OF MOS CIRCUITS 2 CMOS CHIP MANUFACTRING STEPS Substrate Wafer Wafer Fabrication (diffusion, oxidation, photomasking, ion implantation, thin film deposition, etc.) Finished Wafer Wafer
Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Steven Levitan Fall 2008 1 The Manufacturing Process For a great tour through the IC manufacturing
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Steven Levitan Fall 2008 1 The Manufacturing Process For a great tour through the IC manufacturing
CMOS Technology. Flow varies with process types & company. Start with substrate selection. N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI
 CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part 2
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
UT Austin, ECE Department VLSI Design 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout Rules
 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
CS/ECE 5710/6710. N-type Transistor. N-type from the top. Diffusion Mask. Polysilicon Mask. CMOS Processing
 CS/ECE 5710/6710 CMOS Processing Addison-Wesley N-type Transistor D G +Vgs + Vds S N-type from the top i electrons - Diffusion Mask Mask for just the diffused regions Top view shows patterns that make
CS/ECE 5710/6710 CMOS Processing Addison-Wesley N-type Transistor D G +Vgs + Vds S N-type from the top i electrons - Diffusion Mask Mask for just the diffused regions Top view shows patterns that make
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
EE 434 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology
 EE 434 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Quiz 7 The layout of a film resistor with electrodes A and B is shown. If the sheet resistance of the film is 40 /, determine the resistance between nodes A and
EE 434 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Quiz 7 The layout of a film resistor with electrodes A and B is shown. If the sheet resistance of the film is 40 /, determine the resistance between nodes A and
Fabrication and Layout
 Fabrication and Layout Kenneth Yun UC San Diego Adapted from EE271 notes, Stanford University Overview Semiconductor properties How chips are made Design rules for layout Reading Fabrication: W&E 3.1,
Fabrication and Layout Kenneth Yun UC San Diego Adapted from EE271 notes, Stanford University Overview Semiconductor properties How chips are made Design rules for layout Reading Fabrication: W&E 3.1,
This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes.
 IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003
 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
9/4/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
CMOS FABRICATION. n WELL PROCESS
 CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
VLSI Digital Systems Design
 VLSI Digital Systems Design CMOS Processing cmpe222_03process_ppt.ppt 1 Si Purification Chemical purification of Si Zone refined Induction furnace Si ingot melted in localized zone Molten zone moved from
VLSI Digital Systems Design CMOS Processing cmpe222_03process_ppt.ppt 1 Si Purification Chemical purification of Si Zone refined Induction furnace Si ingot melted in localized zone Molten zone moved from
Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1
 Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1 LECTURE 030 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - I (References [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate integrated
Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1 LECTURE 030 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - I (References [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate integrated
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
Manufacturing Process
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Manufacturing Process July 30, 2002 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Manufacturing Process July 30, 2002 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten
We are moving to 155 Donner Lab From Thursday, Feb 2 We will be able to accommodate everyone!
 -Spring 006 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 4 CMOS Manufacturing Process Design Rules EECS141 1 Good News! We are moving to 155 Donner Lab From Thursday, Feb We will be able to accommodate everyone!
-Spring 006 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 4 CMOS Manufacturing Process Design Rules EECS141 1 Good News! We are moving to 155 Donner Lab From Thursday, Feb We will be able to accommodate everyone!
Manufacturing Process
 CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process 1 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi AlCu Tungsten SiO n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V DD
CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process 1 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi AlCu Tungsten SiO n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V DD
CMOS Fabrication. Dr. Bassam Jamil. Adopted from slides of the textbook
 CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
EEC 118 Lecture #5: MOS Fabrication. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #5: MOS Fabrication Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 3 this week, report due next week HW 3 due this Friday at 4
EEC 118 Lecture #5: MOS Fabrication Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 3 this week, report due next week HW 3 due this Friday at 4
ECE321 Electronics I
 ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 19: CMOS Fabrication Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Miller Effect Interconnect
ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 19: CMOS Fabrication Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Miller Effect Interconnect
CMOS Processing Technology
 CHAPTER 2 CMOS Processing Technology Outline 2 1. CMOS Technologies 2. Layout Design Rules 3. CMOS Process Enhancements 4. Technology-related CAD Issues 5. Manufacturing Issues CMOS Technologies 3 n-well
CHAPTER 2 CMOS Processing Technology Outline 2 1. CMOS Technologies 2. Layout Design Rules 3. CMOS Process Enhancements 4. Technology-related CAD Issues 5. Manufacturing Issues CMOS Technologies 3 n-well
CMOS Processing Technology
 CHAPTER 2 CMOS Processing Technology Outline 2 1. CMOS Technologies 2. Layout Design Rules 3. CMOS Process Enhancements 4. Technology-related CAD Issues 5. Manufacturing Issues CMOS Technologies 3 n-well
CHAPTER 2 CMOS Processing Technology Outline 2 1. CMOS Technologies 2. Layout Design Rules 3. CMOS Process Enhancements 4. Technology-related CAD Issues 5. Manufacturing Issues CMOS Technologies 3 n-well
CMOS Manufacturing Process
 CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V
CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Fabrication and Layout
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design Fabrication and Layout ECEN 454 3.1 A Glimpse at MOS Device Polysilicon Aluminum ECEN 475 4.2 1 Material Classification Insulators Glass, diamond, silicon oxide
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design Fabrication and Layout ECEN 454 3.1 A Glimpse at MOS Device Polysilicon Aluminum ECEN 475 4.2 1 Material Classification Insulators Glass, diamond, silicon oxide
HOMEWORK 4 and 5. March 15, Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook:
 HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
CMOS Manufacturing process. Design rule set
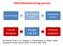 CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
Microelectronics. Integrated circuits. Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, Expected decrease in line width
 Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
EE40 Lec 22. IC Fabrication Technology. Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009
 Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
IC Fabrication Technology Part III Devices in Semiconductor Processes
 EE 330 Lecture 10 IC Fabrication Technology Part III Metalization and Interconnects Parasitic Capacitances Back-end Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes Resistors Diodes Review from Last Lecture
EE 330 Lecture 10 IC Fabrication Technology Part III Metalization and Interconnects Parasitic Capacitances Back-end Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes Resistors Diodes Review from Last Lecture
ECE 659. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, Digital EE141 Integrated Circuits 2nd Manufacturing.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Manufacturing Process July 0, 00 1 CMOS Process 1 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi AlCu Tungsten
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Manufacturing Process July 0, 00 1 CMOS Process 1 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi AlCu Tungsten
VLSI Systems and Computer Architecture Lab
 ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων CMOS Technology Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής 1 From the book: An Introduction ti to VLSI Process By: W. Maly ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Διάρθρωση 1. N well CMOS 2. Active
ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων CMOS Technology Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής 1 From the book: An Introduction ti to VLSI Process By: W. Maly ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Διάρθρωση 1. N well CMOS 2. Active
VLSI. Lecture 1. Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University. Based on slides of David Money Harris
 VLSI Lecture 1 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Based on slides of David Money Harris Goals of This Course Learn the principles of VLSI design Learn to design
VLSI Lecture 1 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Based on slides of David Money Harris Goals of This Course Learn the principles of VLSI design Learn to design
Review of CMOS Processing Technology
 - Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
- Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE
 Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
CMOS VLSI Design. Introduction. All materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN. Introduction
 CMOS VLSI Design Introduction ll materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN Introduction Chapter previews the entire field, subsequent chapters elaborate on specific
CMOS VLSI Design Introduction ll materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN Introduction Chapter previews the entire field, subsequent chapters elaborate on specific
Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits
 Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits OUTLINE History Basic Processes Implant; Oxidation; Photolithography; Masks Layout and Process Flow Device Cross Section Evolution Lecture 38, 12/05/05 Reading This
Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits OUTLINE History Basic Processes Implant; Oxidation; Photolithography; Masks Layout and Process Flow Device Cross Section Evolution Lecture 38, 12/05/05 Reading This
Lect. 2: Basics of Si Technology
 Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 4. Basic Integrated Circuit Processing
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 4 Basic Integrated Circuit Processing Lecture Outline Details of the physical structure of devices will be very important in developing models for electrical behavior
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 4 Basic Integrated Circuit Processing Lecture Outline Details of the physical structure of devices will be very important in developing models for electrical behavior
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II?? - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II?? - Masking - Photolithography - Deposition - Etching - Diffusion Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow
Cost of Integrated Circuits
 Cost of IC Design 1 Cost of Integrated Circuits NRE (Non-Recurrent Engineering) costs fixed design time and effort, mask generation independent of sales volume / number of products one-time cost factor
Cost of IC Design 1 Cost of Integrated Circuits NRE (Non-Recurrent Engineering) costs fixed design time and effort, mask generation independent of sales volume / number of products one-time cost factor
Complexity of IC Metallization. Early 21 st Century IC Technology
 EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Lecture # 25 Microfabrication Handout of This Lecture. Today: how are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other
EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Lecture # 25 Microfabrication Handout of This Lecture. Today: how are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other
VLSI Technology. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam
 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. Andy Neureuther
 EECS 40 Spring 2003 Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. ndy Neureuther How are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other films Pattern transfer by lithography
EECS 40 Spring 2003 Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. ndy Neureuther How are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other films Pattern transfer by lithography
Lecture 2. Fabrication and Layout
 Lecture 2 Fabrication and Layout Mark Horowitz Modified by Azita Emami Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University azita@stanford.edu 1 Overview Reading W&E 3.1(scan), 3.2.1, 3.3.1 - Fabrication W&E
Lecture 2 Fabrication and Layout Mark Horowitz Modified by Azita Emami Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University azita@stanford.edu 1 Overview Reading W&E 3.1(scan), 3.2.1, 3.3.1 - Fabrication W&E
Chapter 4 : ULSI Process Integration (0.18 m CMOS Process)
 Chapter : ULSI Process Integration (0.8 m CMOS Process) Reference. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (00). - (00). Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Basic Principles(/e)
Chapter : ULSI Process Integration (0.8 m CMOS Process) Reference. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (00). - (00). Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Basic Principles(/e)
Lecture 2: CMOS Fabrication Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Lecture 2: CMOS Fabrication Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This
Lecture 2: CMOS Fabrication Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This
Microelettronica. Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication. 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica
 Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor.
 Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor. Gate electrode Drain electrode Source electrode Gate oxide Gate length Page 1 Step 0 The positively doped silicon wafer is first coated with an insulating
Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor. Gate electrode Drain electrode Source electrode Gate oxide Gate length Page 1 Step 0 The positively doped silicon wafer is first coated with an insulating
EE 143 CMOS Process Flow
 EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 84 D D G Sub G Sub S S G D S G D S + + + + - MOS Substrate Well - MOS Substrate EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 85 hotoresist Si 3 4 SiO 2 Substrate selection: moderately high resistivity,
EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 84 D D G Sub G Sub S S G D S G D S + + + + - MOS Substrate Well - MOS Substrate EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 85 hotoresist Si 3 4 SiO 2 Substrate selection: moderately high resistivity,
Figure 2.3 (cont., p. 60) (e) Block diagram of Pentium 4 processor with 42 million transistors (2000). [Courtesy Intel Corporation.
 Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Chapter 3 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world) are manufactured every year. VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) ULSI (Ultra Large Scale
Exam 1 Friday Sept 22
 Exam 1 Friday Sept 22 Students may bring 1 page of notes Next weeks HW assignment due on Wed Sept 20 at beginning of class No 5:00 p.m extension so solutions can be posted Those with special accommodation
Exam 1 Friday Sept 22 Students may bring 1 page of notes Next weeks HW assignment due on Wed Sept 20 at beginning of class No 5:00 p.m extension so solutions can be posted Those with special accommodation
Chapter 2 Problems. The CMOS technology we need to realize is shown below, from Figure 1-34 in the text. S P + N P + N WELL P +
 Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
Czochralski Crystal Growth
 Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
UNIT 4. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun
 UNIT 4 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus METALLIZATION: Applications and choices, physical vapor deposition, patterning, problem areas.
UNIT 4 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus METALLIZATION: Applications and choices, physical vapor deposition, patterning, problem areas.
EE 330 Lecture 12. Devices in Semiconductor Processes
 EE 330 Lecture 12 Devices in Semiconductor Processes Review from Lecture 9 Copper Interconnects Limitations of Aluminum Interconnects Electromigration Conductivity not real high Relevant Key Properties
EE 330 Lecture 12 Devices in Semiconductor Processes Review from Lecture 9 Copper Interconnects Limitations of Aluminum Interconnects Electromigration Conductivity not real high Relevant Key Properties
Isolation Technology. Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
 INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY 0. Silicon crystal growth and wafer preparation 1. Processing Steps 1.1. Photolitography 1.2. Oxidation 1.3. Layer Deposition 1.4. Etching 1.5. Diffusion 1.6 Backend: assembly,
INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY 0. Silicon crystal growth and wafer preparation 1. Processing Steps 1.1. Photolitography 1.2. Oxidation 1.3. Layer Deposition 1.4. Etching 1.5. Diffusion 1.6 Backend: assembly,
Process Integration. MEMS Release Techniques Sacrificial Layer Removal Substrate Undercut
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 9/13/2007 Fabrication Technology Lecture 1 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world)
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 9/13/2007 Fabrication Technology Lecture 1 Silicon Device Fabrication Technology Over 10 15 transistors (or 100,000 for every person in the world)
Microelectronics Devices
 Microelectronics Devices Yao-Joe Yang 1 Outline Basic semiconductor physics Semiconductor devices Resistors Capacitors P-N diodes BJT/MOSFET 2 Type of Solid Materials Solid materials may be classified
Microelectronics Devices Yao-Joe Yang 1 Outline Basic semiconductor physics Semiconductor devices Resistors Capacitors P-N diodes BJT/MOSFET 2 Type of Solid Materials Solid materials may be classified
Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University
![Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University](/thumbs/75/72824557.jpg) 2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
EE 143 FINAL EXAM NAME C. Nguyen May 10, Signature:
 INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Very Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Design
 Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Very Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Design Bradley A. Minch Mixed Analog-Digital VLSI Circuits and Systems Lab Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 5401 minch@ece.cornell.edu
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Very Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Design Bradley A. Minch Mixed Analog-Digital VLSI Circuits and Systems Lab Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 5401 minch@ece.cornell.edu
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST
 Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Is Now Part of To learn more about ON Semiconductor, please visit our website at
 Is Now Part of To learn more about ON Semiconductor, please visit our website at www.onsemi.com ON Semiconductor and the ON Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC
Is Now Part of To learn more about ON Semiconductor, please visit our website at www.onsemi.com ON Semiconductor and the ON Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC
conductor - gate insulator source gate n substrate conductor - gate insulator gate substrate n open switch closed switch however: closed however:
 MOS Transistors Readings: Chapter 1 N-type drain conductor - gate insulator source gate drain source n p n substrate P-type drain conductor - gate insulator source drain gate source p p substrate n 42
MOS Transistors Readings: Chapter 1 N-type drain conductor - gate insulator source gate drain source n p n substrate P-type drain conductor - gate insulator source drain gate source p p substrate n 42
Process Flow in Cross Sections
 Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 MOSFET I Metal gate vs self-aligned poly gate So far, we have discussed about
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 MOSFET I Metal gate vs self-aligned poly gate So far, we have discussed about
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 02 MOS Transistors - I Hello and welcome to today
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 02 MOS Transistors - I Hello and welcome to today
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication
 Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
Process Integration. NMOS Generic NMOS Process Flow. CMOS - The MOSIS Process Flow
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Lecture 200 BiCMOS Technology (12/12/01) Page 200-1
 Lecture 200 BiCMOS Technology (12/12/01) Page 200-1 LECTURE 200 BICMOS TECHNOLOGY (READING: Text-Sec. 2.11) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate BiCMOS technology Outline Introduction Physical process illustration
Lecture 200 BiCMOS Technology (12/12/01) Page 200-1 LECTURE 200 BICMOS TECHNOLOGY (READING: Text-Sec. 2.11) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate BiCMOS technology Outline Introduction Physical process illustration
Fabrication Process. Crystal Growth Doping Deposition Patterning Lithography Oxidation Ion Implementation CONCORDIA VLSI DESIGN LAB
 Fabrication Process Crystal Growth Doping Deposition Patterning Lithography Oxidation Ion Implementation 1 Fabrication- CMOS Process Starting Material Preparation 1. Produce Metallurgical Grade Silicon
Fabrication Process Crystal Growth Doping Deposition Patterning Lithography Oxidation Ion Implementation 1 Fabrication- CMOS Process Starting Material Preparation 1. Produce Metallurgical Grade Silicon
A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process
 Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
EE CMOS TECHNOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text
 1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
FABRICATION ENGINEERING MICRO- NANOSCALE ATTHE AND. Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL. of Minnesota. University OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 AND FABRICATION ENGINEERING ATTHE MICRO- NANOSCALE Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL University of Minnesota New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Preface xiii prrt i OVERVIEW AND MATERIALS
AND FABRICATION ENGINEERING ATTHE MICRO- NANOSCALE Fourth Edition STEPHEN A. CAMPBELL University of Minnesota New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Preface xiii prrt i OVERVIEW AND MATERIALS
Fabrication Technology
 Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS. CHAPTER 3 Conventional Si Processing
 3. Conventional licon Processing Micromachining, Microfabrication. EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 3 Conventional Processing Why silicon? Abundant, cheap, easy to process. licon planar Integrated
3. Conventional licon Processing Micromachining, Microfabrication. EE 5344 Introduction to MEMS CHAPTER 3 Conventional Processing Why silicon? Abundant, cheap, easy to process. licon planar Integrated
Make sure the exam paper has 9 pages total (including cover page)
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2010 EE143 Midterm Exam #2 Family Name First name SID Signature Solution Make sure the exam
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2010 EE143 Midterm Exam #2 Family Name First name SID Signature Solution Make sure the exam
The Physical Structure (NMOS)
 The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 3D Perspective 2 3 Fabrication
The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 3D Perspective 2 3 Fabrication
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Franssila: Chapters 26,28 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Franssila: Chapters 26,28 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Complementary
EE6303 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS UNIT I IC FABRICATION
 SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY TIRUPACHUR DEPARTMENT OFELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6303 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND APPLICATIONS 1. Define an Integrated circuit.
SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY TIRUPACHUR DEPARTMENT OFELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6303 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND APPLICATIONS 1. Define an Integrated circuit.
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology. IC Fabrication Process Overview
 Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 00 by Prentice Hall Chapter 9 IC Fabrication Process Overview /4 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you
Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Michael Quirk & Julian Serda October 00 by Prentice Hall Chapter 9 IC Fabrication Process Overview /4 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you
