Mechanisms of Diffusion II. Ionic Crystals L5 11/3/03-1-
|
|
|
- Whitney Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanisms of Diffusion II. Ionic Crystals 3.05 L5 11/3/03-1-
2 Charges on point imperfections Point imperfections in ionic crystals are generally electrically charged L5 11/3/03 - (a) Unit cell in perfect crystal; charge-neutral. (b) Removal of a cation to a surface step, leaving a unit cell with a cation vacancy. Net charge associated with defective cell is 1. (c) Formation of anion interstitial; net charge is 1.
3 Kröger-Vink notation X = what is at the site (El or V) X Z Y where Y= what site is defective (El or i) Z = effective charge at the site ( = +; '= ) Examples Intrinsic defects: Schottky and Frenkel Defects involving impurities 3.05 L5 11/3/03-3
4 Schottky disorder Charge-compensating anion vacancies + cation vacancies e.g. in MgO Formation: null = V Mg + V O Equilibrium: K S = [V Mg Charge neutrality: [V Mg ] = [V O ] ] [V O ] = exp G S f kt 3.05 L5 11/3/03-4
5 Frenkel pair Charge-compensating vacancy-interstitial pair e.g. cation Frenkel pair in LiF Formation: Equilibrium: Li Li = V Li K F = [V Li + Li i ] [Li Li ] = exp Charge neutrality: [V Li ] = [Li Li ] G F f kt 3.05 L5 11/3/03-5
6 Self-diffusion in KCl Analogous to self-diffusion in metals with and f G f S SS f H [ V S K ]= exp = exp exp kt k kt K =1 K [ V K ] giving for the self-diffusivity on the cation sites m f m + S S f H CV + H S D K = ga f exp S CV exp k kt 3.05 L5 11/3/03-6
7 Extrinsic defects Isovalent impurities e.g. CaO in MgO MgO Incorporation: CaO Ca Mg + O O Equilibrium: K S = [V Mg ] [V O ] = exp G S f Charge neutrality: [V Mg ] = [V O ] kt 3.05 L5 11/3/03-7
8 Extrinsic defects, cont d Aliovalent impurities e.g. CaO in ZrO Incorporation: CaO ZrO Ca Zr + V O + OO 4 Equilibrium: K S = [V Zr ] [V O ] = exp G S f kt 4 Charge neutrality: 4[V Zr ] + Ca [ Zr ] = [V O ] 3.05 L5 11/3/03-8
9 Cation diffusion in KCl with Ca Impurity incorporation CaCl Schottky equilibrium K S = [ V K Neutrality condition KCl Ca K + V K + Cl Cl ][V Cl ] = exp G S f kt [V Cl ] + [Ca K ] = [ V K ] 3.05 L5 11/3/03-9
10 Diffusion in KCl with Ca, cont d This leads to 1 4[ V K ] [Ca K ] pure [ V K ]= [Ca K ] and to two regimes: Intrinsic: Small impurity concentration or high T [ V K ] pure >> [Ca K ], then [ V K ]= [ V K ] pure Extrinsic: High impurity concentration or low T V K << [Ca K ], then [ V K ]= [Ca K ] [ ] pure 3.05 L5 11/3/03-10
11 Diffusion in KCl with Ca, cont d This leads to this behavior for the cation diffusivity ln [ V K ] ln D K Intrinsic H S f k Intrinsic m H CV f + H S k ln [ Ca K ] Extrinsic Extrinsic m H CV k 1 T 1 T +=JE L=?=?O??A JH=JE 3.05 L5 11/3/03-11
12 e.g., cation diffusion in FeO (note various valence states of Fe are possible) FeO can be oxidized to make a cation deficient oxide Fe 1 x O e 0 neutral oxygen atom 3+ Oxygen atom approaches, attracts two electrons from Fe and gets ionized. e 3+ Oxygen-deficient crystal. Note cation vacancy and two ferric cations. oxidation reaction: 3.05 L5 11/3/ O = O x x O + V Fe + h Fe, where h Fe = Fe Fe Fe Fe
13 Oxidation reaction: 1 x O = O O + V Fe Equilibrium constant for this reaction: K eq = + h Fe [ [ V Fe ] p O h Fe ] = exp G kt Charge neutrality: [ V Fe ] = [h Fe ] Cation vacancy concentration: [ G 3kT V ] = (1 4) 13 exp ( p ) Fe O 16 Diffusion in impure FeO will have three regimes: 1. High T, low oxygen pressure, dominated by Schottky defect equilibria. High oxygen pressure, dominated by oxidation reaction 3. Low T, low oxygen pressure, dominated by extrinsic impurities 3.05 L5 11/3/03-13
14 Oxidation reaction: 1 O = O x O + V Fe + h Fe Equilibrium constant for this reaction: K eq = [ ] [ V Fe ] h Fe p O = exp G kt Charge neutrality: [ ] = h Fe V Fe [ ] Cation vacancy concentration: [ V Fe ] = 14 ( ) 13 exp G ( ) 16 3kT p O Diffusion in impure FeO will have three regimes: 1. High T, low oxygen pressure, dominated by Schottky defect equilibria. High oxygen pressure, dominated by oxidation reaction 3. Low T, low oxygen pressure, dominated by extrinsic impurities 3.05 L5 11/3/03-14-
15 Cation diffusivity Arrhenius plot Intrinsic ln D Fe H f CV + k m H CV diffusivity varies as (P O ) 1/6 H 3 + k m H CV Extrinsic m H CV k Position of middle segment will depend on oxygen pressure, hence this region will not be observable at low oxygen pressures or high impurity contents 1 T 3.05 L5 11/3/03-15
16 Microstructural processes Densification of powder compacts by sintering Creep deformation at high temperatures Grain growth Solid solid transformation kinetics, including oxidation of metals Electrical conduction Ionic conductors for chemical and gas sensors, solid electrolytes, fuel cells Sensors emissions HC NO x 3.05 L5 11/3/ " # air-to-fuel ratio
17 3.05 L5 11/3/03-17-
A great many properties of crystals are determined by imperfections.
 Defect in ceramics A great many properties of crystals are determined by imperfections. Electrical conductivity Diffusion transport imperfection Optical properties Rate of kinetic process Precipitation
Defect in ceramics A great many properties of crystals are determined by imperfections. Electrical conductivity Diffusion transport imperfection Optical properties Rate of kinetic process Precipitation
Defects and Diffusion
 Defects and Diffusion Goals for the Unit Recognize various imperfections in crystals Point imperfections Impurities Line, surface and bulk imperfections Define various diffusion mechanisms Identify factors
Defects and Diffusion Goals for the Unit Recognize various imperfections in crystals Point imperfections Impurities Line, surface and bulk imperfections Define various diffusion mechanisms Identify factors
Imperfections, Defects and Diffusion
 Imperfections, Defects and Diffusion Lattice Defects Week5 Material Sciences and Engineering MatE271 1 Goals for the Unit I. Recognize various imperfections in crystals (Chapter 4) - Point imperfections
Imperfections, Defects and Diffusion Lattice Defects Week5 Material Sciences and Engineering MatE271 1 Goals for the Unit I. Recognize various imperfections in crystals (Chapter 4) - Point imperfections
MSE 351 Engineering Ceramics I
 Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana MSE 351 Engineering Ceramics I Ing. Anthony Andrews (PhD) Department of Materials Engineering Faculty of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering
Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana MSE 351 Engineering Ceramics I Ing. Anthony Andrews (PhD) Department of Materials Engineering Faculty of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering
Physical Ceramics. Principles for Ceramic Science and Engineering. Yet-Ming Chiang Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts
 Physical Ceramics Principles for Ceramic Science and Engineering Yet-Ming Chiang Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts Dunbar P. Birnie, III University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona
Physical Ceramics Principles for Ceramic Science and Engineering Yet-Ming Chiang Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts Dunbar P. Birnie, III University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona
Electrical conduction in ceramics
 Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali Materiali Inorganici Funzionali Electrical conduction in ceramics Prof. Antonella Glisenti - Dip. Scienze Chimiche - Università degli Studi di Padova Conductivity
Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali Materiali Inorganici Funzionali Electrical conduction in ceramics Prof. Antonella Glisenti - Dip. Scienze Chimiche - Università degli Studi di Padova Conductivity
Defect in crystals. Primer in Materials Science Spring
 Defect in crystals Primer in Materials Science Spring 2017 11.05.2017 1 Introduction The arrangement of the atoms in all materials contains imperfections which have profound effect on the behavior of the
Defect in crystals Primer in Materials Science Spring 2017 11.05.2017 1 Introduction The arrangement of the atoms in all materials contains imperfections which have profound effect on the behavior of the
Materials Science. Imperfections in Solids CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS. Types of Imperfections
 In the Name of God Materials Science CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
In the Name of God Materials Science CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III
 Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Bulk Diffusion in Alumina: Solving the Corundum Conundrum
 Bulk Diffusion in Alumina: Solving the Corundum Conundrum Nicholas D.M. Hine 1,2,3 K. Frensch 3, W.M.C Foulkes 1,2, M.W. Finnis 2,3, A. H. Heuer 3,4 1 Theory of Condensed Matter Group, Cavendish Laboratory,
Bulk Diffusion in Alumina: Solving the Corundum Conundrum Nicholas D.M. Hine 1,2,3 K. Frensch 3, W.M.C Foulkes 1,2, M.W. Finnis 2,3, A. H. Heuer 3,4 1 Theory of Condensed Matter Group, Cavendish Laboratory,
1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following.
 315 Problems 1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following. (a) Find the temperature and partial pressure of O 2 where Ni(s), Ni(l), and NiO(s) are in equilibrium.
315 Problems 1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following. (a) Find the temperature and partial pressure of O 2 where Ni(s), Ni(l), and NiO(s) are in equilibrium.
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics
 Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Review of structures for ceramics How are impurities accommodated in the ceramic lattice? In what ways are ceramic phase diagrams similar
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Review of structures for ceramics How are impurities accommodated in the ceramic lattice? In what ways are ceramic phase diagrams similar
NPTEL COURSE ADVANCED CERAMICS FOR STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 NPTEL COURSE ADVANCED CERAMICS FOR STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q1: What do you understand by Ceramics? Ans: Ceramics are a group of chemical compounds, either simple (consisting of only
NPTEL COURSE ADVANCED CERAMICS FOR STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q1: What do you understand by Ceramics? Ans: Ceramics are a group of chemical compounds, either simple (consisting of only
Electrical Properties of Polymers, Ceramics, Dielectrics, and Amorphous Materials. Dae Yong JEONG Inha University
 Electrical Properties of Polymers, Ceramics, Dielectrics, and Amorphous Materials Dae Yong JEONG Inha University Review & Introduction We learned about the electronic transfer in Metal and Semiconductor.
Electrical Properties of Polymers, Ceramics, Dielectrics, and Amorphous Materials Dae Yong JEONG Inha University Review & Introduction We learned about the electronic transfer in Metal and Semiconductor.
Chapter 4. Ionic conductivity of GDC. electrolyte
 Chapter 4 Ionic conductivity of GDC electrolyte 4.1 Introduction Solid oxides with fluorite structure, such as, ZrO 2 and CeO 2, when doped with aliovalent cations become oxygen ion conductor and are used
Chapter 4 Ionic conductivity of GDC electrolyte 4.1 Introduction Solid oxides with fluorite structure, such as, ZrO 2 and CeO 2, when doped with aliovalent cations become oxygen ion conductor and are used
POINT DEFECTS IN CRYSTALS
 POINT DEFECTS IN CRYSTALS Overview Vacancies & their Clusters Interstitials Defects in Ionic Crytals Frenkel defect Shottky defect Part of MATERIALS SCIENCE & ENGINEERING A Learner s Guide AN INTRODUCTORY
POINT DEFECTS IN CRYSTALS Overview Vacancies & their Clusters Interstitials Defects in Ionic Crytals Frenkel defect Shottky defect Part of MATERIALS SCIENCE & ENGINEERING A Learner s Guide AN INTRODUCTORY
Crystal Defects. Perfect crystal - every atom of the same type in the correct equilibrium position (does not exist at T > 0 K)
 Crystal Defects Perfect crystal - every atom of the same type in the correct equilibrium position (does not exist at T > 0 K) Real crystal - all crystals have some imperfections - defects, most atoms are
Crystal Defects Perfect crystal - every atom of the same type in the correct equilibrium position (does not exist at T > 0 K) Real crystal - all crystals have some imperfections - defects, most atoms are
Role of small amount of MgO and ZrO 2 on creep behaviour of high purity Al 2 O 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 28, No. 3, June 2005, pp. 281 285. Indian Academy of Sciences. Role of small amount of MgO and ZrO 2 on creep behaviour of high purity Al 2 O 3 L N SATAPATHY* and S SWAROOP Ceramic
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 28, No. 3, June 2005, pp. 281 285. Indian Academy of Sciences. Role of small amount of MgO and ZrO 2 on creep behaviour of high purity Al 2 O 3 L N SATAPATHY* and S SWAROOP Ceramic
Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities)
 Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities) 1 Structural Imperfections A perfect crystal has the lowest internal energy E Above absolute zero
Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities) 1 Structural Imperfections A perfect crystal has the lowest internal energy E Above absolute zero
Point Defects in Metals
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Point Defects in Metals 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for lead at its melting temperature of 327 C (600 K). Assume an energy
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Point Defects in Metals 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for lead at its melting temperature of 327 C (600 K). Assume an energy
From sand to silicon wafer
 From sand to silicon wafer 25% of Earth surface is silicon Metallurgical grade silicon (MGS) Electronic grade silicon (EGS) Polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) Single crystal Czochralski drawing Single
From sand to silicon wafer 25% of Earth surface is silicon Metallurgical grade silicon (MGS) Electronic grade silicon (EGS) Polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) Single crystal Czochralski drawing Single
Point Defects LATTICE VACANCIES 585. DIFFUSION 588 Metals 591. COLOR CENTERS 592 F centers 592 Other centers in alkali halides 593 PROBLEMS 595
 ch20.qxd 9/22/04 5:27 PM Page 583 20 Point Defects LATTICE VACANCIES 585 DIFFUSION 588 Metals 591 COLOR CENTERS 592 F centers 592 Other centers in alkali halides 593 PROBLEMS 595 1. Frenkel defects 595
ch20.qxd 9/22/04 5:27 PM Page 583 20 Point Defects LATTICE VACANCIES 585 DIFFUSION 588 Metals 591 COLOR CENTERS 592 F centers 592 Other centers in alkali halides 593 PROBLEMS 595 1. Frenkel defects 595
Physics of Transition Metal Oxides
 Physics of Transition Metal Oxides Lecture 11 Defects in oxides Defects in oxides: We have looked at a variety of defects already. Today we discuss structural defects, giving rise to distinct phases impurity
Physics of Transition Metal Oxides Lecture 11 Defects in oxides Defects in oxides: We have looked at a variety of defects already. Today we discuss structural defects, giving rise to distinct phases impurity
a) The self-diffusion coefficient of a metal with cubic structure can be expressed as
 EXERCISES KJM5120 Chapter 5; Diffusion 1. Random (self) diffusion a) The self-diffusion coefficient of a metal with cubic structure can be expressed as 1 n D = s 6 t 2 where n/t represents the jump frequency
EXERCISES KJM5120 Chapter 5; Diffusion 1. Random (self) diffusion a) The self-diffusion coefficient of a metal with cubic structure can be expressed as 1 n D = s 6 t 2 where n/t represents the jump frequency
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS ev /atom = exp. kt ( =
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
Order in materials. Making Solid Stuff. Primary Bonds Summary. How do they arrange themselves? Results from atomic bonding. What are they?
 Making Solid Stuff Primary Bonds Summary What are they? Results from atomic bonding So the atoms bond together! Order in materials No long range order to atoms Gases little or no interaction between components
Making Solid Stuff Primary Bonds Summary What are they? Results from atomic bonding So the atoms bond together! Order in materials No long range order to atoms Gases little or no interaction between components
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
Intrinsic Defects and Defect
 Chapter 4 Intrinsic Defects and Defect Concentrations in MgAl 2 O 4 Spinel 4.1 Introduction MgAl 2 O 4 spinel is an important industrial ceramic with a range of applications that take advantage of its
Chapter 4 Intrinsic Defects and Defect Concentrations in MgAl 2 O 4 Spinel 4.1 Introduction MgAl 2 O 4 spinel is an important industrial ceramic with a range of applications that take advantage of its
Electrolytes: Stabilized Zirconia
 Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali Materiali Inorganici Funzionali Electrolytes: Stabilized Zirconia Prof. Antonella Glisenti - Dip. Scienze Chimiche - Università degli Studi di Padova Bibliography
Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali Materiali Inorganici Funzionali Electrolytes: Stabilized Zirconia Prof. Antonella Glisenti - Dip. Scienze Chimiche - Università degli Studi di Padova Bibliography
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number:
 Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
Learning Objectives. Chapter Outline. Solidification of Metals. Solidification of Metals
 Learning Objectives Study the principles of solidification as they apply to pure metals. Examine the mechanisms by which solidification occurs. - Chapter Outline Importance of Solidification Nucleation
Learning Objectives Study the principles of solidification as they apply to pure metals. Examine the mechanisms by which solidification occurs. - Chapter Outline Importance of Solidification Nucleation
Material Science. Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore India
 Material Science Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 India Chapter 5. Diffusion Learning objectives: - To know the
Material Science Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 India Chapter 5. Diffusion Learning objectives: - To know the
Diffusion in Oxides. Department of Geological Sciences Case Western Reserve University Euclid Avenue Cleveland, Ohio U.S.A.
 Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry Vol. 72 pp. 757-825, 2010 Copyright Mineralogical Society of America 17 Diffusion in Oxides James A. Van Orman 1,2 and Katherine L. Crispin 1 1 Department of Geological
Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry Vol. 72 pp. 757-825, 2010 Copyright Mineralogical Society of America 17 Diffusion in Oxides James A. Van Orman 1,2 and Katherine L. Crispin 1 1 Department of Geological
» Please take out your periodic table.
 » Please take out your periodic table. Ionic Compounds Before we begin What are ions? How are they made? (Hint: Remember what happens to VALENCE electrons.) (Put a line down the middle of the white board.)
» Please take out your periodic table. Ionic Compounds Before we begin What are ions? How are they made? (Hint: Remember what happens to VALENCE electrons.) (Put a line down the middle of the white board.)
INGE Engineering Materials. Chapter 3 (cont.)
 Some techniques used: Chapter 3 (cont.) This section will address the question how do we determine the crystal structure of a solid sample? Electron microscopy (by direct and indirect observations) Scanning
Some techniques used: Chapter 3 (cont.) This section will address the question how do we determine the crystal structure of a solid sample? Electron microscopy (by direct and indirect observations) Scanning
Module 10. Crystal Defects in Metals I. Lecture 10. Crystal Defects in Metals I
 Module 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I Lecture 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Introduction Keywords:
Module 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I Lecture 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Introduction Keywords:
Diffusion phenomenon
 Module-5 Diffusion Contents 1) Diffusion mechanisms and steady-state & non-steady-state diffusion 2) Factors that influence diffusion and nonequilibrium transformation & microstructure Diffusion phenomenon
Module-5 Diffusion Contents 1) Diffusion mechanisms and steady-state & non-steady-state diffusion 2) Factors that influence diffusion and nonequilibrium transformation & microstructure Diffusion phenomenon
Chapter 5. Imperfections in Solids
 Chapter 5 Imperfections in Solids Chapter 5 2D Defects and Introduction to Diffusion Imperfections in Solids Issues to Address... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
Chapter 5 Imperfections in Solids Chapter 5 2D Defects and Introduction to Diffusion Imperfections in Solids Issues to Address... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
Short-Circuit Diffusion L6 11/14/06
 Short-Circuit Diffusion in Crystals 1 Today s topics: Diffusion spectrum in defective crystals Dislocation core structure and dislocation short circuits Grain boundary structure Grain boundary diffusion
Short-Circuit Diffusion in Crystals 1 Today s topics: Diffusion spectrum in defective crystals Dislocation core structure and dislocation short circuits Grain boundary structure Grain boundary diffusion
ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 4-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types
Chapter 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 4-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types
 Defects in solids http://www.bath.ac.uk/podcast/powerpoint/inaugural_lecture_250407.pdf http://www.materials.ac.uk/elearning/matter/crystallography/indexingdirectionsandplanes/indexing-of-hexagonal-systems.html
Defects in solids http://www.bath.ac.uk/podcast/powerpoint/inaugural_lecture_250407.pdf http://www.materials.ac.uk/elearning/matter/crystallography/indexingdirectionsandplanes/indexing-of-hexagonal-systems.html
E45 Midterm 01 Fall 2007! By the 0.2% offset method (shown on plot), YS = 500 MPa
 1.!Mechanical Properties (20 points) Refer to the following stress-strain plot derived from a standard uniaxial tensile test of a high performance titanium alloy to answer the following questions. Show
1.!Mechanical Properties (20 points) Refer to the following stress-strain plot derived from a standard uniaxial tensile test of a high performance titanium alloy to answer the following questions. Show
Imperfections in the Atomic and Ionic Arrangements
 Objectives Introduce the three basic types of imperfections: point defects, line defects (or dislocations), and surface defects. Explore the nature and effects of different types of defects. Outline Point
Objectives Introduce the three basic types of imperfections: point defects, line defects (or dislocations), and surface defects. Explore the nature and effects of different types of defects. Outline Point
CHAPTER 5: DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS
 CHAPTER 5: DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How does diffusion occur? Why is it an important part of processing? How can the rate of diffusion be predicted for some simple cases? How does diffusion
CHAPTER 5: DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How does diffusion occur? Why is it an important part of processing? How can the rate of diffusion be predicted for some simple cases? How does diffusion
Stacking Oranges. Packing atoms together Long Range Order. What controls the nearest number of atoms? Hard Sphere Model. Hard Sphere Model.
 { Stacking atoms together Crystal Structure Stacking Oranges Packing atoms together Long Range Order Crystalline materials... atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays typical of: -metals -many ceramics -some
{ Stacking atoms together Crystal Structure Stacking Oranges Packing atoms together Long Range Order Crystalline materials... atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays typical of: -metals -many ceramics -some
The Nernst-Einstein equation indicates that the ratio β /D for a given material varies only with temperature. Calculate β/d for oxygen ions in Zr 0.
 The Nernst-Einstein equation indicates that the ratio β /D for a given material varies only with temperature. Calculate β/d for oxygen ions in 0.8 Y 0.2 1.9 at 800 C. 1 The Nernst-Einstein equation indicates
The Nernst-Einstein equation indicates that the ratio β /D for a given material varies only with temperature. Calculate β/d for oxygen ions in 0.8 Y 0.2 1.9 at 800 C. 1 The Nernst-Einstein equation indicates
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Materials Science and Engineering
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Materials Science and Engineering GRAIN BOUNDARY SEGREGATION AND BLOCKING EFFECT IN DOPED TITANIUM OXIDE AT HIGH TEMPERATURE EQUILIBRIUM
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Materials Science and Engineering GRAIN BOUNDARY SEGREGATION AND BLOCKING EFFECT IN DOPED TITANIUM OXIDE AT HIGH TEMPERATURE EQUILIBRIUM
Hei Wong.
 Defects and Disorders in Hafnium Oxide and at Hafnium Oxide/Silicon Interface Hei Wong City University of Hong Kong Email: heiwong@ieee.org Tokyo MQ2012 1 Outline 1. Introduction, disorders and defects
Defects and Disorders in Hafnium Oxide and at Hafnium Oxide/Silicon Interface Hei Wong City University of Hong Kong Email: heiwong@ieee.org Tokyo MQ2012 1 Outline 1. Introduction, disorders and defects
Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali. Materiali Inorganici Funzionali. Electrolytes: Ceria
 Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali Materiali Inorganici Funzionali Electrolytes: Ceria Prof. Antonella Glisenti - Dip. Scienze Chimiche - Università degli Studi di Padova Bibliography 1. N.Q. Minh,
Laurea Magistrale in Scienza dei Materiali Materiali Inorganici Funzionali Electrolytes: Ceria Prof. Antonella Glisenti - Dip. Scienze Chimiche - Università degli Studi di Padova Bibliography 1. N.Q. Minh,
General Characteristics of Solid State
 General Characteristics of Solid State (i) They have definite mass, volume and shape. (ii) Intermolecular distances are short. (iii) Intermolecular forces are strong. (iv) Their constituent particles (atoms,
General Characteristics of Solid State (i) They have definite mass, volume and shape. (ii) Intermolecular distances are short. (iii) Intermolecular forces are strong. (iv) Their constituent particles (atoms,
Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS)
 Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What are anistropic substances. 2. Why are amorphous solids isotropic in nature?. Why glass is regarded as an amorphous solid? 4.
Unit-1 THE SOLID STATE QUESTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What are anistropic substances. 2. Why are amorphous solids isotropic in nature?. Why glass is regarded as an amorphous solid? 4.
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT. Sub-topics. Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface
 IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
Solid. Imperfection in solids. Examples of Imperfections #2. Examples of Imperfections #1. Solid
 Solid Imperfection in solids By E-mail: Patama.V@chula.ac.th Solid State of materials Rigid Strong bonding ionic, van der aals, metal bonding normally has crystal structure Examples of Imperfections #
Solid Imperfection in solids By E-mail: Patama.V@chula.ac.th Solid State of materials Rigid Strong bonding ionic, van der aals, metal bonding normally has crystal structure Examples of Imperfections #
Introduction to Materials Science
 EPMA Powder Metallurgy Summer School 27 June 1 July 2016 Valencia, Spain Introduction to Materials Science Prof. Alberto Molinari University of Trento, Italy Some of the figures used in this presentation
EPMA Powder Metallurgy Summer School 27 June 1 July 2016 Valencia, Spain Introduction to Materials Science Prof. Alberto Molinari University of Trento, Italy Some of the figures used in this presentation
Electrical conductivity of Ca-doped YFeO 3
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 19, bruary 01, pp. 47-53 Electrical conductivity of Ca-doped 3 K T Jacob a *, G Rajitha a & N Dasgupta b a Department of Materials Engineering, Indian
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 19, bruary 01, pp. 47-53 Electrical conductivity of Ca-doped 3 K T Jacob a *, G Rajitha a & N Dasgupta b a Department of Materials Engineering, Indian
ACTIVATION ENERGIES FOR SINTERING AND GRAIN GROWTH IN SINTERED MAGNESITES
 ACTIVATION ENERGIES FOR SINTERING AND GRAIN GROWTH IN SINTERED MAGNESITES 149 ACTIVATION ENERGY FOR SINTERING AND GRAIN GROWTH PROCESSES IN SINTERED NATURAL MAGNESITE WITH AND WITHOUT TITANIA 9.1 INTRODUCTION
ACTIVATION ENERGIES FOR SINTERING AND GRAIN GROWTH IN SINTERED MAGNESITES 149 ACTIVATION ENERGY FOR SINTERING AND GRAIN GROWTH PROCESSES IN SINTERED NATURAL MAGNESITE WITH AND WITHOUT TITANIA 9.1 INTRODUCTION
Ionic transport of α-alumina below 1000 C An in-situ impedance spectroscopy study
 Ionic transport of α-alumina below 1000 C An in-situ impedance spectroscopy study Johan Öijerholm Licentiate thesis, Stockholm 2004 Department of Materials Science and Engineering Division of Corrosion
Ionic transport of α-alumina below 1000 C An in-situ impedance spectroscopy study Johan Öijerholm Licentiate thesis, Stockholm 2004 Department of Materials Science and Engineering Division of Corrosion
Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects
 Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects Coordination Close packed structures Cubic close packing Hexagonal close packing Metallic structures Ionic structures with interstitial sites Important
Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects Coordination Close packed structures Cubic close packing Hexagonal close packing Metallic structures Ionic structures with interstitial sites Important
Lab 1 The Defect Structure of cubic Bi 2 O 3 Nb 2 O 5 Solid Solutions
 Lab 1 The Defect Structure of cubic Bi 2 O 3 Nb 2 O 5 Solid Solutions 27-202 Fall 2002 Objective The objective of this lab is to identify the defect structure and charge compensation mechanism in Bi 2
Lab 1 The Defect Structure of cubic Bi 2 O 3 Nb 2 O 5 Solid Solutions 27-202 Fall 2002 Objective The objective of this lab is to identify the defect structure and charge compensation mechanism in Bi 2
Some structural aspects of ionic conductivity in zirconia stabilised by yttria and calcia
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 24, No. 1, 2006 Some structural aspects of ionic conductivity in zirconia stabilised by yttria and calcia M. M. BUĆKO * AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 24, No. 1, 2006 Some structural aspects of ionic conductivity in zirconia stabilised by yttria and calcia M. M. BUĆKO * AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty
X-ray Diffraction Study on Structural Characteristics of Pure and Doped Perovskite BaTiO 3
 Egypt. J. Solids, Vol. (31), No. (1), (2008) 55 X-ray Diffraction Study on Structural Characteristics of Pure and Doped Perovskite BaTiO 3 F. F. Hammad 1, A. K. Mohamed 1 and A. M. El-Shabiny 2 1) Inorganic
Egypt. J. Solids, Vol. (31), No. (1), (2008) 55 X-ray Diffraction Study on Structural Characteristics of Pure and Doped Perovskite BaTiO 3 F. F. Hammad 1, A. K. Mohamed 1 and A. M. El-Shabiny 2 1) Inorganic
Defects and transport in Ce-doped La 27 W 5 O 55.5
 Defects and transport in Ce-doped La 27 W 5 O 55.5 Nadezda Alyeshkina Master Thesis in Materials, Energy and Nanotechnology UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY June 2013 ii Preface This thesis represents
Defects and transport in Ce-doped La 27 W 5 O 55.5 Nadezda Alyeshkina Master Thesis in Materials, Energy and Nanotechnology UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY June 2013 ii Preface This thesis represents
CHAPTER 6 OUTLINE. DIFFUSION and IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS
 CHAPTER 6 DIFFUSION and IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS OUTLINE 1. TYPES OF DIFFUSIONS 1.1. Interdiffusion 1.2. Selfdiffusion 1.3.Diffusion mechanisms 1.4.Examples 2. TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS 2.1.Point Defects 2.2.Line
CHAPTER 6 DIFFUSION and IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS OUTLINE 1. TYPES OF DIFFUSIONS 1.1. Interdiffusion 1.2. Selfdiffusion 1.3.Diffusion mechanisms 1.4.Examples 2. TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS 2.1.Point Defects 2.2.Line
The Structure of Materials
 The Structure of Materials Samuel M. Allen Edwin L. Thomas Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts / John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto
The Structure of Materials Samuel M. Allen Edwin L. Thomas Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts / John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto
EGN 3365 Review on Metals, Ceramics, & Polymers, and Composites by Zhe Cheng
 EGN 3365 Review on Metals, Ceramics, & Polymers, and Composites 2017 by Zhe Cheng Expectations on Chapter 11 Chapter 11 Understand metals are generally categorized as ferrous alloys and non-ferrous alloys
EGN 3365 Review on Metals, Ceramics, & Polymers, and Composites 2017 by Zhe Cheng Expectations on Chapter 11 Chapter 11 Understand metals are generally categorized as ferrous alloys and non-ferrous alloys
Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction
 Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction Callister, William D. ISBN-13: 9780470419977 Table of Contents List of Symbols. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Historical Perspective. 1.2 Materials Science and
Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction Callister, William D. ISBN-13: 9780470419977 Table of Contents List of Symbols. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Historical Perspective. 1.2 Materials Science and
Unit 1 The Solid State
 Points to Remember Amorphous and Crystalline Solids Unit 1 The Solid State Amorphous- short range order, Irregular shape eg-glass Crystalline Solids- long range order, regular shape eg : NaCl Molecular
Points to Remember Amorphous and Crystalline Solids Unit 1 The Solid State Amorphous- short range order, Irregular shape eg-glass Crystalline Solids- long range order, regular shape eg : NaCl Molecular
FUEL CELL CHARGE TRANSPORT
 FUEL CELL CHARGE TRANSPORT M. OLIVIER marjorie.olivier@fpms.ac.be 19/05/2008 INTRODUCTION Charge transport completes the circuit in an electrochemical system, moving charges from the electrode where they
FUEL CELL CHARGE TRANSPORT M. OLIVIER marjorie.olivier@fpms.ac.be 19/05/2008 INTRODUCTION Charge transport completes the circuit in an electrochemical system, moving charges from the electrode where they
3. Anisotropic blurring by dislocations
 Dynamical Simulation of EBSD Patterns of Imperfect Crystals 1 G. Nolze 1, A. Winkelmann 2 1 Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Berlin, Germany 2 Max-Planck- Institute of Microstructure
Dynamical Simulation of EBSD Patterns of Imperfect Crystals 1 G. Nolze 1, A. Winkelmann 2 1 Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Berlin, Germany 2 Max-Planck- Institute of Microstructure
It was already showed that spinel present a grain boundary sliding deformation
 Stoichiometry defect at grain boundary observed by nano-scale TEM microanalysis in spinel MgAl2O4 N. Nuns, F. Béclin, J. Crampon Laboratoire de Structure et Propriétés de l'etat Solide, ESA 8008 Bat C6,
Stoichiometry defect at grain boundary observed by nano-scale TEM microanalysis in spinel MgAl2O4 N. Nuns, F. Béclin, J. Crampon Laboratoire de Structure et Propriétés de l'etat Solide, ESA 8008 Bat C6,
Transport Properties of Cerium Oxide Pure Non Doped
 , March 13-15, 2013, Hong Kong Transport Properties of Cerium Oxide Pure Non Doped Băilă Diana Irinel, Lazăr Livia Veronica, Members, IAENG Abstract In the last years, the solid electrolyte fuel cells
, March 13-15, 2013, Hong Kong Transport Properties of Cerium Oxide Pure Non Doped Băilă Diana Irinel, Lazăr Livia Veronica, Members, IAENG Abstract In the last years, the solid electrolyte fuel cells
High Conductivity Oxides for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells ABEL FERNANDEZ MATERIALS 286G JUNE 2016
 High Conductivity Oxides for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells ABEL FERNANDEZ MATERIALS 286G JUNE 2016 How do Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Work? O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 Cathode Electrolyte O 2- O 2- O 2- Porous cathode reduces
High Conductivity Oxides for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells ABEL FERNANDEZ MATERIALS 286G JUNE 2016 How do Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Work? O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 Cathode Electrolyte O 2- O 2- O 2- Porous cathode reduces
Point Defects in 3D and 1D Nanomaterials: The Model Case of Titanium Dioxide
 IP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Point Defects in 3D and 1D Nanomaterials: The Model Case of tanium Dioxide To cite this article: Philippe Knauth 2010 IP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Point Defects in 3D and 1D Nanomaterials: The Model Case of tanium Dioxide To cite this article: Philippe Knauth 2010 IP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
SOLID STATE
 SOLID STATE Short Answer Questions: 1. Derive Bragg s equation? Ans. Bragg s equation: W.H. Bragg has proposed an equation to explain the relation between inter planar distance (d) and wave length ( λ
SOLID STATE Short Answer Questions: 1. Derive Bragg s equation? Ans. Bragg s equation: W.H. Bragg has proposed an equation to explain the relation between inter planar distance (d) and wave length ( λ
Imperfections in Solids. Imperfections in Solids. Point Defects. Types of Imperfections
 Imperfections in Solids In this topic we will try to answer the following questions: What types of defects arise in solids? Are these defects undesirable? How do defects affect material properties? Can
Imperfections in Solids In this topic we will try to answer the following questions: What types of defects arise in solids? Are these defects undesirable? How do defects affect material properties? Can
The Diffusion Equation I L2 10/31/06
 The Diffusion Equation I 3.205 L2 10/31/06 1 Fick s Laws of Diffusion Fick s first law r J = "D#c The diffusivity, D, is a second-rank tensor Fick s second law "c "t = #$ % J r 3.205 L2 10/31/06 2 Self-diffusion
The Diffusion Equation I 3.205 L2 10/31/06 1 Fick s Laws of Diffusion Fick s first law r J = "D#c The diffusivity, D, is a second-rank tensor Fick s second law "c "t = #$ % J r 3.205 L2 10/31/06 2 Self-diffusion
Point coordinates. x z
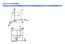 Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry. Lecture Notes No. 6 THE IMPERFECT SOLID STATE
 3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 6 THE IMPERFECT SOLID STATE 1. INTRODUCTION Real crystals are never perfect: they always contain a considerable density of defects and imperfections
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 6 THE IMPERFECT SOLID STATE 1. INTRODUCTION Real crystals are never perfect: they always contain a considerable density of defects and imperfections
Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic. Ceramics. Ceramics exhibit ionic, covalent bonding or a combination of the two (like in Al 2 O 3 )
 What are Ceramics? CERAMIC MATERIALS Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic and crystalline materials that are typically produced using clays and other minerals from the earth or chemically processed powders
What are Ceramics? CERAMIC MATERIALS Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic and crystalline materials that are typically produced using clays and other minerals from the earth or chemically processed powders
Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids
 Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects exist in solids? How do defects affect material properties? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects exist in solids? How do defects affect material properties? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
Oxidation Reactions. This oxide will from only if thermodynamics favour a reaction of the form: M + O 2 = MO 2. Which must form rapidly (favourable(
 Oxidation of s Oxidation is a general term used to define the reaction between a metal or alloy and its environment. s or alloys are oxidised when heated to elevated temperatures es in air or highly oxidised
Oxidation of s Oxidation is a general term used to define the reaction between a metal or alloy and its environment. s or alloys are oxidised when heated to elevated temperatures es in air or highly oxidised
Properties of Ceramic Materials
 1-5 Superplasticity: There are two basic types of superplasticity, termed transformation and structural superplasticity respectively. (A third type of superplasticity, termed temperature-cycling superplasticity,
1-5 Superplasticity: There are two basic types of superplasticity, termed transformation and structural superplasticity respectively. (A third type of superplasticity, termed temperature-cycling superplasticity,
How Trivalent Amphoteric Dopants in BaTiO 3 Ceramics Improve Reliability of Capacitors
 How Trivalent Amphoteric Dopants in BaTiO 3 Ceramics Improve Reliability of Capacitors Yoed Tsur and Clive A. Randall Center for Dielectric Studies Materials Research Laboratory The Pennsylvania State
How Trivalent Amphoteric Dopants in BaTiO 3 Ceramics Improve Reliability of Capacitors Yoed Tsur and Clive A. Randall Center for Dielectric Studies Materials Research Laboratory The Pennsylvania State
Mechanical prop: Fe-C System (1) Mechanical prop: Fe-C system (2)
 Mechanical prop: Fe-C System (1) Effect of wt% C Pearlite (med) ferrite (soft) TS(MPa) 1100 YS(MPa) 900 700 500 300 Hypo C o < 0.76 wt% C Hypoeutectoid 0 0.5 1 0.76 Hyper hardness %EL 100 Pearlite (med)
Mechanical prop: Fe-C System (1) Effect of wt% C Pearlite (med) ferrite (soft) TS(MPa) 1100 YS(MPa) 900 700 500 300 Hypo C o < 0.76 wt% C Hypoeutectoid 0 0.5 1 0.76 Hyper hardness %EL 100 Pearlite (med)
Mat E 272 Lecture 26: Oxidation and Corrosion
 Mat E 272 Lecture 26: Oxidation and Corrosion December 11, 2001 Introduction: Environmental degradation of materials is one of the most costly failure modes, accounting for over 5 percent of the total
Mat E 272 Lecture 26: Oxidation and Corrosion December 11, 2001 Introduction: Environmental degradation of materials is one of the most costly failure modes, accounting for over 5 percent of the total
NMC EXAM BRUSH-UP NOVEMBER 2009
 NMC EXAM BRUSH-UP NOVEMBER 2009 OVERVIEW 1. Crystal Structures 2. Solidification and Crystal Defects in Solids 3. Heat Treatments 4. Electrical Properties of Materials 5. Magnetic Properties of Materials
NMC EXAM BRUSH-UP NOVEMBER 2009 OVERVIEW 1. Crystal Structures 2. Solidification and Crystal Defects in Solids 3. Heat Treatments 4. Electrical Properties of Materials 5. Magnetic Properties of Materials
Kinetics. Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces
 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
An application of Nanoparticles. Application of ZrO 2 as a Catalyst and a Catalyst Support
 An application of Nanoparticles Application of ZrO 2 as a Catalyst and a Catalyst Support Introduction Characteristics of ZrO 2 High T m (>3000K) Low K c High resistance for corrosion Refractories, pigments,
An application of Nanoparticles Application of ZrO 2 as a Catalyst and a Catalyst Support Introduction Characteristics of ZrO 2 High T m (>3000K) Low K c High resistance for corrosion Refractories, pigments,
Characteristics of yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia powder used in optical fiber connector ferrule
 Ceramics International 31 (2005) 297 303 www.elsevier.com/locate/ceramint Characteristics of yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia powder used in optical fiber connector ferrule Chih-Liang Yang a, Hsing-I.
Ceramics International 31 (2005) 297 303 www.elsevier.com/locate/ceramint Characteristics of yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia powder used in optical fiber connector ferrule Chih-Liang Yang a, Hsing-I.
Effect of CO Gas Concentration on Reduction Rate of Major Mineral Phase in Sintered Iron Ore
 , pp. 570 575 Effect of CO Gas Concentration on Reduction Rate of Major Mineral Phase in Sintered Iron Ore Daisuke NOGUCHI, 1) * Ko-ichiro OHNO, 2) Takayuki MAEDA, 2) Kouki NISHIOKA 3) and Masakata SHIMIZU
, pp. 570 575 Effect of CO Gas Concentration on Reduction Rate of Major Mineral Phase in Sintered Iron Ore Daisuke NOGUCHI, 1) * Ko-ichiro OHNO, 2) Takayuki MAEDA, 2) Kouki NISHIOKA 3) and Masakata SHIMIZU
Ionic Conductivity and Solid Electrolytes II: Materials and Applications
 Ionic Conductivity and Solid Electrolytes II: Materials and Applications Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Lecture #27 June 4, 2003 References A. Manthiram & J. Kim Low Temperature Synthesis of Insertion
Ionic Conductivity and Solid Electrolytes II: Materials and Applications Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Lecture #27 June 4, 2003 References A. Manthiram & J. Kim Low Temperature Synthesis of Insertion
Physics of Materials: Defects in Solids. Dr. Anurag Srivastava. Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior
 : Defects in Solids Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior What you have learnt so far? Properties of Materials affected by defects
: Defects in Solids Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior What you have learnt so far? Properties of Materials affected by defects
3. Cubic zirconia single crystals
 3.1. Structure and phase relationship of cubic zirconium dioxide 3. Cubic zirconia single crystals 3.1. Structure and phase relationship of cubic zirconium dioxide Pure zirconia (ZrO 2 ) undergoes two
3.1. Structure and phase relationship of cubic zirconium dioxide 3. Cubic zirconia single crystals 3.1. Structure and phase relationship of cubic zirconium dioxide Pure zirconia (ZrO 2 ) undergoes two
Phase Transformation of Materials
 2009 fall Phase Transformation of Materials 10.08.2009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous class Interstitial
2009 fall Phase Transformation of Materials 10.08.2009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous class Interstitial
12/10/09. Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids. Imperfections in Solids. Polycrystalline Materials ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 4: ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? How do defects affect material
Chapter 4: ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? How do defects affect material
ION PROBE MEASUREMENT OF OXYGEN SELF-DIFFUSION IN A DAVID JOHN REED -lz::: B.S.E.E., University of Utah 1967.
 1 ION PROBE MEASUREMENT OF OXYGEN SELF-DIFFUSION IN A1 2 0 3 by DAVID JOHN REED -lz::: B.S.E.E., University of Utah 1967 Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF
1 ION PROBE MEASUREMENT OF OXYGEN SELF-DIFFUSION IN A1 2 0 3 by DAVID JOHN REED -lz::: B.S.E.E., University of Utah 1967 Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF
Development of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions and Future Trends
 Special Issue Oxygen Storage Materials for Automotive Catalysts Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions 1 Review Development of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions and Future Trends Hideo Sobukawa This review summarizes
Special Issue Oxygen Storage Materials for Automotive Catalysts Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions 1 Review Development of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions and Future Trends Hideo Sobukawa This review summarizes
diffusion is not normally subject to observation by noting compositional change, because in pure metals all atoms are alike.
 71 CHAPTER 4 DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS 4.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous chapters we learnt that any given atom has a particular lattice site assigned to it. Aside from thermal vibration about its mean position
71 CHAPTER 4 DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS 4.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous chapters we learnt that any given atom has a particular lattice site assigned to it. Aside from thermal vibration about its mean position
Material Science. Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore India
 Material Science Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 India Chapter 3. Imperfections in Solids Learning objectives:
Material Science Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 India Chapter 3. Imperfections in Solids Learning objectives:
Point coordinates. Point coordinates for unit cell center are. Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111
 Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
