MATTHEW A. WICKHAM 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Collin Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ION IMPLANTATION TO ADJUST NMOS THRESHOLD VOLTAGES MATTHEW A. WICKHAM 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT NMOS processes require a variety of threshold voltages for differing applications. For this experiment, the threshold voltages of NMOS devices were altered by a using several different ion implant doses (none, 1, 2, 4, and 8e12/cm2) of boron. This shifted the threshold voltage in good agreement with literature values [1]. One of the most important applications of ion implantation in MOS technology is the control of threshold voltages within the devices. By implanting a specific quantity of B atoms in the channels of an NMDS device will bring the threshold voltage to a more positive value. This change is in proportion to the amount of atoms implanted into the channel over the gate oxide capacitance per unit area [1]. Ion implantations are used to control the threshold voltage (Vt) of MDS devices, since they have the advantage of being able to introduce a precisely controlled amount of dopant material into the substrate. Implants can also be performed at lower temperatures, and can be masked with a wider range of materials than diffusions. Lattice damage may occur during an implant, as well as the fact that not all of the implanted atoms may be electrically active [1]. However, under the conditions where an amorphous layer is not formed, temperatures as high as 1000C are needed to anneal the crystal damage, and activate the implanted ions. Typical anneal times are on the order of thirty minutes, and result in virtually all of the species becoming electrically active [2,3]. NMOS devices have gained in popularity as their threshold voltages are typically half of that for the p channel devices [4]. The smaller threshold voltage is benifical for several reasons; 1.) it allows for the use of smaller power-supply, and hence less power, 2. ) it becomes compatible in operation with bipolar devices, and 3.) it makes room for a higher packing density [5]. To lower the threshold voltage, several methods can be used. The use of the crystal orientation <100> will yield a lower Vt up to one third of <111> orientated silicon), but it will also cut down on the mobility of the holes. The addition of silicon 210
2 nitride (Si3N4) to the silicon (Si02) dielectric layer will increase the dielectric constant, thereby lowering lyti. ~ silicon gate, polysilicon doped with phosphorus to be conductive, will have a lower work function difference with the oxide, than the metal (aluminum), lowering the threshold voltage. Ion implantation can also be used to fabricate both enhancement and depletion mode devices on the same wafer [5]. For this final reason the effects of ion implantation were chosen for study. The onset of inversion exists when enough gate voltage is applied to bend the band edge to a point where p-type (n-type) material in bulk becomes equally n-type (p-type) at the surface. The inversion layer is formed when the gate voltage exceeds the threshold voltage [2]. The gate of the capacitor being the top (aluminum), deposited atop a Si02 dielectric, with the bottom plate being the silicon substrate (doped p+). ~ MOS device is considered to be in the depletion mode if it is on with the gate voltage equal to zero, and in the enhancement mode if it is off with a gate voltage equal to zero. NMOS devices are ideally enhancement mode devices, but nonidealities tend to shift the threshold voltage toward the negative. Until about 1977, PMOS technology was dominant due to the fact that NMOS transistors were typically of the depletion mode type [6]. For this reason, an experiment was designed to involve a preliminary investigation into threshold voltage adjustments performed with an ion implanter. EX~M~NT Since a variety of threshold voltages may be required for various devices, a process for which differing threshold voltages could be obtained was designed. Several different implant doses (none, 1,2,4, and 8e12/cm2) were performed to examine the shift of the threshold voltage due to these doses. ~s the metal gate process is now in use at R.I.T., that is what was used for this experiment. First a mask of several differing size capacitors was designed on ICE,an in house C~D tool, and the mask was fabricated through reversal processing of the retical. The capacitor sizes ranged from squares of 10x10 microns square, 400x400 microns square. Other shapes, both rectangles and hallow squares were designed, but overall differing shapes did not affect the threshold voltage. Ten p-type wafers of <100> orientation were obtained, and scribed with numbers one through ten. The average resistivity of these wafers was 5.50 ohm-cm. The wafers were then cleaned with a standard RCt~ clean (fifteen minutes in NH4OH/H202/H20 (1:1:5), two minute rinse, two minute HF/H20 (10:1), two minute rinse, fifteen minutes in HC1/H202/H20 (1:1:5), and a final five minute rinse). 211
3 blanket boron implant was then performed at 6OKeV for the following: wafers 1,2 -- no implant wafers 3,4 -- implant 1e12/square cm. wafers 5,6 -- implant 2e12/square cm. wafers 7,8 -- implant 4e12/square cm. wafers 9,10 -- implant 8e12/square cm. ñfter this a thin gate oxide was grown at 1000C for forty minutes. This resulted in an oxide thickness of approximately 470 angstroms, and was also long enough to anneal out damage as well as to make the boron electrically active C2 3]. ~luminum was then evaporated on the frontside of the wafers and patterned with KT1820 photoresist. The photoresist having been spun on with the wafertrac, exposed with a Kasper aligner, and developed with the wafertrac also. The aluminum was the patterned with aluminum etch, and rinsed. Then the photoresist was stripped of with the plasma asher in an oxygen ambient. ~luminum was then evaporated on the backside of the wafers to produce an extremely large capacitor in parallel with the much smaller frontside capacitors, to make the stray capacitance negligible. The odd numbered wafers were then sinter ed in a forming gas ambient for twenty-five minutes at 450C. Finally, the capacitors were tested with capacitance-voltage measurements. RESULTS/ANALYSIS Capacitance-voltage graphs were taken of all the wafers to determine the actual threshold voltages of the implanted doses. The plots were taken from the 400x400 micron squared capacitor, as it gave the most repeatable results. Figure 1 shows a plot of a capacitor which was not adjusted by implant or sintering after metal deposition. It shows a threshold voltage (marked Vt) of magnitude 0.89V. foo.ooj~ H so.000.~4/div E_ -~ r~i~r~r~i 0 io.0o VOLTS 2.000/div ( V) Figure 1: Capacitance vs. Voltage (no implant or sintering) 212
4 The positive accumulation voltage implies an n-type substrate, which was not the actual case since p-type substrates were used. This can be explained by the fact that the ramp voltage was applied to the substrate, and not the gate, during the capacitance-voltage measurement, which will invert the voltage. Figure 2 shows a plot of a capacitor which received a dose of 4e12/square cm., and was not sinter ed after metal deposition. It shows that the magnitude of the threshold voltage has shifted to 1.85V, however the accumulation voltage had the same problem encountered in Figure 1. VOLTS 2.000/div C V).00 Figure 2: Capacitance vs. Voltage (4e12/cm2 dose, no sinter) It is also noticed that the values for the maximum capacitance decrease with the increasing dose, assymtotically approaches 250 pf, and the value of the minimum capacitance increases with increasing dose, approaching about 200 pf. These changing values of capacitance are due to mobility in the substrate, the fact that there are species in the substrate. ~t a high enough implant capacitor would break down completely, and be of no capacitance-voltage plot would become a straight line. the higher more mobile dose, the use, as the Figure 3 shows a plot of threshold voltage magnitude versus implant dose for the values used. It can be seen from this graph that sintering the wafers after metal deposition to tie up the loose bonds between the metal and the oxide had little effect on the overall adjustment. Sintered capacitors had a slightly higher threshold voltage, but not appreciable. 213
5 ~1 c 6 ~c5.a ()~~ Figure 3: Threshold Voltage Magnitude vs. Implant Dose CONCLUSIONS It is now possible to predict the threshold voltage shift for various implant doses at 6OKeV. This is of much use as threshold voltages will be important in the upcoming CMOS and NMOS projects. The oxide quality, and processing cleanliness of the NMOS/CMOS processes will also be evaluated through the comparison of past and future results. The lowest dose implant preformed was 1e12/square cm. This was due to the fact that the implanter beam current was to high to accomplish any lower doses. It may be of use to study lower implant doses, as well as different implant energies and their effect on the threshold voltage shifting. More experimentation needs to be done to gain more insight into this process at R.I.T. ACKNOWL EDBMENTS Rob Pearson for his help in the formation of the pro5ect, Mike Jackson for his support and guidance throughout the process, Frank the implant guy, and Michelle Myer for her support, and a shoulder to lean on. REFERENCES El] S. Wolf and R.N.TauiDer, in SILICON PROCESSING FOR THE VLSI ERA, (Lattice Press, California, 1986), pp , 305,325 2] W. Till and J. Luxon, in INTEGRATED CIRCUITS: MATERIALS, DEVICES,AND FABRICATION, (Prentice Hall, Inc., New Jersey, 1982), Pp. 80,196 3] J. Mayer and L. Eriksson, in ION IMPLANTATION IN SEMICONDUCTORS SILICON AND GERMANIUM, (Academic Press, New York, 1970), p.232 4) A. Mukherjec, in INTRODUCTiON TO NMOS AND CMOS VLSI SYSTEMS DESIGN,(Prcfltice-Hahi, New Jersey, 1986), p.15 5] J. Millman, in MICROELECTRONICS, (McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York, 1979), pp.113-il4, ] R. Pierret, in MODULAR SERIES ON SOLID STATE DEVICES: FIELD ~~CT DEVICES; VOL. IV, (Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., California, 1983), pp.43-sb, 95-98
Chapter 2 Problems. The CMOS technology we need to realize is shown below, from Figure 1-34 in the text. S P + N P + N WELL P +
 Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS
 Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Isolation Technology. Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
CMOS Technology. Flow varies with process types & company. Start with substrate selection. N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI
 CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
Brian Izzio 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student. Rochester Institute of Technology
 CAPACITAWZE-VOI~TAGE characterization FOR POLYSILICON GATE MOS CAPACITORS DJTRODUcTION Brian Izzio 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology ABSTRACT The effects of
CAPACITAWZE-VOI~TAGE characterization FOR POLYSILICON GATE MOS CAPACITORS DJTRODUcTION Brian Izzio 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology ABSTRACT The effects of
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
EE 143 FINAL EXAM NAME C. Nguyen May 10, Signature:
 INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes.
 IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003
 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
CMOS Fabrication. Dr. Bassam Jamil. Adopted from slides of the textbook
 CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
VLSI Technology. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam
 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Introduction to VLSI Technology, Crystal Growth, Oxidation, Epitaxial Process, Diffusion Process, Ion Implantation, Lithography, Etching, Metallization, VLSI Process Integration,
CMOS VLSI Design. Introduction. All materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN. Introduction
 CMOS VLSI Design Introduction ll materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN Introduction Chapter previews the entire field, subsequent chapters elaborate on specific
CMOS VLSI Design Introduction ll materials are from the textbook Weste and Harris, 3 rd Edition CMOS VLSI DESIGN Introduction Chapter previews the entire field, subsequent chapters elaborate on specific
VLSI. Lecture 1. Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University. Based on slides of David Money Harris
 VLSI Lecture 1 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Based on slides of David Money Harris Goals of This Course Learn the principles of VLSI design Learn to design
VLSI Lecture 1 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Based on slides of David Money Harris Goals of This Course Learn the principles of VLSI design Learn to design
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 MOSFET I Metal gate vs self-aligned poly gate So far, we have discussed about
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 MOSFET I Metal gate vs self-aligned poly gate So far, we have discussed about
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Very Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Design
 Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Very Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Design Bradley A. Minch Mixed Analog-Digital VLSI Circuits and Systems Lab Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 5401 minch@ece.cornell.edu
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Very Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Design Bradley A. Minch Mixed Analog-Digital VLSI Circuits and Systems Lab Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 5401 minch@ece.cornell.edu
CS/ECE 5710/6710. N-type Transistor. N-type from the top. Diffusion Mask. Polysilicon Mask. CMOS Processing
 CS/ECE 5710/6710 CMOS Processing Addison-Wesley N-type Transistor D G +Vgs + Vds S N-type from the top i electrons - Diffusion Mask Mask for just the diffused regions Top view shows patterns that make
CS/ECE 5710/6710 CMOS Processing Addison-Wesley N-type Transistor D G +Vgs + Vds S N-type from the top i electrons - Diffusion Mask Mask for just the diffused regions Top view shows patterns that make
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology
 Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
Chapter 3 CMOS processing technology (How to make a CMOS?) Si + impurity acceptors(p-type) donors (n-type) p-type + n-type => pn junction (I-V) 3.1.1 (Wafer) Wafer = A disk of silicon (0.25 mm - 1 mm thick),
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time IC Fabrication Technology Crystal Preparation
CMOS FABRICATION. n WELL PROCESS
 CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
FABRICATION of MOSFETs
 FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
Chapter 4. UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication. Oxidation
 Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
UT Austin, ECE Department VLSI Design 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout Rules
 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
Microelectronic Device Instructional Laboratory. Table of Contents
 Introduction Process Overview Microelectronic Device Instructional Laboratory Introduction Description Flowchart MOSFET Development Process Description Process Steps Cleaning Solvent Cleaning Photo Lithography
Introduction Process Overview Microelectronic Device Instructional Laboratory Introduction Description Flowchart MOSFET Development Process Description Process Steps Cleaning Solvent Cleaning Photo Lithography
Microelectronics. Integrated circuits. Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, Expected decrease in line width
 Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Microelectronics Introduction to the IC technology M.Rencz 11 September, 2002 9/16/02 1/37 Integrated circuits Development is controlled by the roadmaps. Self-fulfilling predictions for the tendencies
Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Steven Levitan Fall 2008 1 The Manufacturing Process For a great tour through the IC manufacturing
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1A: Manufacturing& Layout David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Steven Levitan Fall 2008 1 The Manufacturing Process For a great tour through the IC manufacturing
HOMEWORK 4 and 5. March 15, Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook:
 HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
CHAPTER - 4 CMOS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY
 CHAPTER - 4 CMOS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY Samir kamal Spring 2018 4.1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Introduce the CMOS designer to the technology that is responsible for the semiconductor devices that might be designed
CHAPTER - 4 CMOS PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY Samir kamal Spring 2018 4.1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Introduce the CMOS designer to the technology that is responsible for the semiconductor devices that might be designed
Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University
![Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University](/thumbs/75/72824557.jpg) 2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
2014 Ajay Kumar Gautam [VLSI TECHNOLOGY] VLSI Technology for 3RD Year ECE/EEE Uttarakhand Technical University Page1 Syllabus UNIT 1 Introduction to VLSI Technology: Classification of ICs, Scale of integration,
Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1
 Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1 LECTURE 030 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - I (References [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate integrated
Lecture 030 Integrated Circuit Technology - I (5/8/03) Page 030-1 LECTURE 030 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - I (References [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate integrated
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 02 MOS Transistors - I Hello and welcome to today
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 02 MOS Transistors - I Hello and welcome to today
EE 330 Lecture 8. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
EE 330 Lecture 8 IC Fabrication Technology Part II - Oxidation - Epitaxy - Polysilicon - Interconnects Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Bulk Source Gate Drain p-channel MOSFET Lightly-doped n-type
Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Chapter 2 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 CMOS Process (n-well) Both NMOS and PMOS must be built in the same silicon material. PMOS in n-well NMOS
Process Integration. MEMS Release Techniques Sacrificial Layer Removal Substrate Undercut
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Problem 1 Lab Questions ( 20 points total)
 Problem 1 Lab Questions ( 20 points total) (a) (3 points ) In our EE143 lab, we use Phosphorus for the source and drain diffusion. However, most advanced processes use Arsenic. What is the advantage of
Problem 1 Lab Questions ( 20 points total) (a) (3 points ) In our EE143 lab, we use Phosphorus for the source and drain diffusion. However, most advanced processes use Arsenic. What is the advantage of
CHAPTER 4: Oxidation. Chapter 4 1. Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are:
 Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
Chapter 4 1 CHAPTER 4: Oxidation Oxidation of silicon is an important process in VLSI. The typical roles of SiO 2 are: 1. mask against implant or diffusion of dopant into silicon 2. surface passivation
EE 143 MICROFABRICATION TECHNOLOGY FALL 2014 C. Nguyen PROBLEM SET #9
 Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROBLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROBLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
Graduate Student Presentations
 Graduate Student Presentations Dang, Huong Chip packaging March 27 Call, Nathan Thin film transistors/ liquid crystal displays April 4 Feldman, Ari Optical computing April 11 Guerassio, Ian Self-assembly
Graduate Student Presentations Dang, Huong Chip packaging March 27 Call, Nathan Thin film transistors/ liquid crystal displays April 4 Feldman, Ari Optical computing April 11 Guerassio, Ian Self-assembly
PRELIMINARY FORMATION OF DEEP TRENCH C~P~CITORS
 PRELIMINARY FORMATION OF DEEP TRENCH C~P~CITORS Christopher 3. Waskiewicz 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology ABSTRACT ~ Tegal 700 plasma etcher was used to etch
PRELIMINARY FORMATION OF DEEP TRENCH C~P~CITORS Christopher 3. Waskiewicz 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology ABSTRACT ~ Tegal 700 plasma etcher was used to etch
VLSI Systems and Computer Architecture Lab
 ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων CMOS Technology Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής 1 From the book: An Introduction ti to VLSI Process By: W. Maly ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Διάρθρωση 1. N well CMOS 2. Active
ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων CMOS Technology Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής 1 From the book: An Introduction ti to VLSI Process By: W. Maly ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ VLSI Διάρθρωση 1. N well CMOS 2. Active
UNIT 4. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun
 UNIT 4 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus METALLIZATION: Applications and choices, physical vapor deposition, patterning, problem areas.
UNIT 4 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus METALLIZATION: Applications and choices, physical vapor deposition, patterning, problem areas.
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part 2
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part 2 Quiz 8 A 2m silicon crystal is cut into wafers using a wire saw. If the wire diameter is 220um and the wafer thickness is 350um, how many wafers will this
EE 330 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology Part II. -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects
 EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time Etching Dry etch (anisotropic) SiO
EE 330 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Part II -Oxidation -Epitaxy -Polysilicon -Planarization -Resistance and Capacitance in Interconnects Review from Last Time Etching Dry etch (anisotropic) SiO
Lecture 2: CMOS Fabrication Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Lecture 2: CMOS Fabrication Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This
Lecture 2: CMOS Fabrication Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This
EE 434 Lecture 9. IC Fabrication Technology
 EE 434 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Quiz 7 The layout of a film resistor with electrodes A and B is shown. If the sheet resistance of the film is 40 /, determine the resistance between nodes A and
EE 434 Lecture 9 IC Fabrication Technology Quiz 7 The layout of a film resistor with electrodes A and B is shown. If the sheet resistance of the film is 40 /, determine the resistance between nodes A and
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology
 Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Chapter 2 MOS Fabrication Technology Abstract This chapter is concerned with the fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology. Various processes such as wafer fabrication, oxidation, mask
Is Now Part of To learn more about ON Semiconductor, please visit our website at
 Is Now Part of To learn more about ON Semiconductor, please visit our website at www.onsemi.com ON Semiconductor and the ON Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC
Is Now Part of To learn more about ON Semiconductor, please visit our website at www.onsemi.com ON Semiconductor and the ON Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC
Microelettronica. Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication. 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica
 Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Process Integration. NMOS Generic NMOS Process Flow. CMOS - The MOSIS Process Flow
 Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Process Integration Self-aligned Techniques LOCOS- self-aligned channel stop Self-aligned Source/Drain Lightly Doped Drain (LDD) Self-aligned silicide (SALICIDE) Self-aligned oxide gap MEMS Release Techniques
Department of Electrical Engineering. Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 3 Fabrication of CMOS Integrated Circuits Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Background Outline The CMOS Process Flow Design Rules Latchup
Chapter 3 Fabrication of CMOS Integrated Circuits Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Background Outline The CMOS Process Flow Design Rules Latchup
ABSTRACT. which indicates the implanted region did not adequately inhibit the diffusion of oxygen.
 . INVESTIGATION OF LOCOS PROCESS USING NITROGEN IMPL~NTAT ION Joseph W. Walters 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT A localized oxidation
. INVESTIGATION OF LOCOS PROCESS USING NITROGEN IMPL~NTAT ION Joseph W. Walters 5th Year Microelectronic Engineering Student Rochester Institute of Technology INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT A localized oxidation
3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005
 3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005 1) This is an open book, take-home quiz. You are not to consult with other class members or anyone else. You may discuss the
3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005 1) This is an open book, take-home quiz. You are not to consult with other class members or anyone else. You may discuss the
MOLYBDENUM AS A GATE ELECTRODE FOR DEEP SUB-MICRON CMOS TECHNOLOGY
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Vol. 611 2000 Materials Research Society MOLYBDENUM AS A GATE ELECTRODE FOR DEEP SUB-MICRON CMOS TECHNOLOGY Pushkar Ranade, Yee-Chia Yeo, Qiang Lu, Hideki Takeuchi, Tsu-Jae King, Chenming
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Vol. 611 2000 Materials Research Society MOLYBDENUM AS A GATE ELECTRODE FOR DEEP SUB-MICRON CMOS TECHNOLOGY Pushkar Ranade, Yee-Chia Yeo, Qiang Lu, Hideki Takeuchi, Tsu-Jae King, Chenming
Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. Andy Neureuther
 EECS 40 Spring 2003 Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. ndy Neureuther How are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other films Pattern transfer by lithography
EECS 40 Spring 2003 Lecture 19 Microfabrication 4/1/03 Prof. ndy Neureuther How are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other films Pattern transfer by lithography
Complexity of IC Metallization. Early 21 st Century IC Technology
 EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Lecture # 25 Microfabrication Handout of This Lecture. Today: how are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other
EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Lecture # 25 Microfabrication Handout of This Lecture. Today: how are Integrated Circuits made? Silicon wafers Oxide formation by growth or deposition Other
Microelectronics Devices
 Microelectronics Devices Yao-Joe Yang 1 Outline Basic semiconductor physics Semiconductor devices Resistors Capacitors P-N diodes BJT/MOSFET 2 Type of Solid Materials Solid materials may be classified
Microelectronics Devices Yao-Joe Yang 1 Outline Basic semiconductor physics Semiconductor devices Resistors Capacitors P-N diodes BJT/MOSFET 2 Type of Solid Materials Solid materials may be classified
Make sure the exam paper has 9 pages total (including cover page)
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2010 EE143 Midterm Exam #2 Family Name First name SID Signature Solution Make sure the exam
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2010 EE143 Midterm Exam #2 Family Name First name SID Signature Solution Make sure the exam
TOWARD MEMS!Instructor: Riadh W. Y. Habash
 TOWARD MEMS!Instructor: Riadh W. Y. Habash Students are presented with aspects of general production and manufacturing of integrated circuit (IC) products to enable them to better liaise with and participate
TOWARD MEMS!Instructor: Riadh W. Y. Habash Students are presented with aspects of general production and manufacturing of integrated circuit (IC) products to enable them to better liaise with and participate
Process Flow in Cross Sections
 Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Process Flow in Cross Sections Process (simplified) 0. Clean wafer in nasty acids (HF, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4,...) --> wear gloves! 1. Grow 500 nm of SiO 2 (by putting the wafer in a furnace with O 2 2. Coat
Manufacturing Process
 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
EE40 Lec 22. IC Fabrication Technology. Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009
 Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Suggested Reading EE40 Lec 22 IC Fabrication Technology Prof. Nathan Cheung 11/19/2009 300mm Fab Tour http://www-03.ibm.com/technology/manufacturing/technology_tour_300mm_foundry.html Overview of IC Technology
Czochralski Crystal Growth
 Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
We are moving to 155 Donner Lab From Thursday, Feb 2 We will be able to accommodate everyone!
 -Spring 006 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 4 CMOS Manufacturing Process Design Rules EECS141 1 Good News! We are moving to 155 Donner Lab From Thursday, Feb We will be able to accommodate everyone!
-Spring 006 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 4 CMOS Manufacturing Process Design Rules EECS141 1 Good News! We are moving to 155 Donner Lab From Thursday, Feb We will be able to accommodate everyone!
Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits
 Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits OUTLINE History Basic Processes Implant; Oxidation; Photolithography; Masks Layout and Process Flow Device Cross Section Evolution Lecture 38, 12/05/05 Reading This
Microfabrication of Integrated Circuits OUTLINE History Basic Processes Implant; Oxidation; Photolithography; Masks Layout and Process Flow Device Cross Section Evolution Lecture 38, 12/05/05 Reading This
Surface micromachining and Process flow part 1
 Surface micromachining and Process flow part 1 Identify the basic steps of a generic surface micromachining process Identify the critical requirements needed to create a MEMS using surface micromachining
Surface micromachining and Process flow part 1 Identify the basic steps of a generic surface micromachining process Identify the critical requirements needed to create a MEMS using surface micromachining
9/4/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
EE 560 FABRICATION OF MOS CIRCUITS. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 FABRICATION OF MOS CIRCUITS 2 CMOS CHIP MANUFACTRING STEPS Substrate Wafer Wafer Fabrication (diffusion, oxidation, photomasking, ion implantation, thin film deposition, etc.) Finished Wafer Wafer
1 EE 560 FABRICATION OF MOS CIRCUITS 2 CMOS CHIP MANUFACTRING STEPS Substrate Wafer Wafer Fabrication (diffusion, oxidation, photomasking, ion implantation, thin film deposition, etc.) Finished Wafer Wafer
Amorphous and Polycrystalline Thin-Film Transistors
 Part I Amorphous and Polycrystalline Thin-Film Transistors HYBRID AMORPHOUS AND POLYCRYSTALLINE SILICON DEVICES FOR LARGE-AREA ELECTRONICS P. Mei, J. B. Boyce, D. K. Fork, G. Anderson, J. Ho, J. Lu, Xerox
Part I Amorphous and Polycrystalline Thin-Film Transistors HYBRID AMORPHOUS AND POLYCRYSTALLINE SILICON DEVICES FOR LARGE-AREA ELECTRONICS P. Mei, J. B. Boyce, D. K. Fork, G. Anderson, J. Ho, J. Lu, Xerox
Instructor: Dr. M. Razaghi. Silicon Oxidation
 SILICON OXIDATION Silicon Oxidation Many different kinds of thin films are used to fabricate discrete devices and integrated circuits. Including: Thermal oxides Dielectric layers Polycrystalline silicon
SILICON OXIDATION Silicon Oxidation Many different kinds of thin films are used to fabricate discrete devices and integrated circuits. Including: Thermal oxides Dielectric layers Polycrystalline silicon
A LOW SERIES RESISTANCE, HIGH DENSITY, TRENCH CAPACITOR FOR HIGH-FREQUENCY APPLICATIONS
 A LOW SERIES RESISTANCE, HIGH DENSITY, TRENCH CAPACITOR FOR HIGH-FREQUENCY APPLICATIONS Gordon Grivna, Sudhama Shastri, Yujing Wu, & Will Cai Sept, 2008 www.onsemi.com Presentation Outline 1. Introduction
A LOW SERIES RESISTANCE, HIGH DENSITY, TRENCH CAPACITOR FOR HIGH-FREQUENCY APPLICATIONS Gordon Grivna, Sudhama Shastri, Yujing Wu, & Will Cai Sept, 2008 www.onsemi.com Presentation Outline 1. Introduction
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST
 Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
Silicon Wafer Processing PAKAGING AND TEST Parametrical test using test structures regularly distributed in the wafer Wafer die test marking defective dies dies separation die fixing (not marked as defective)
EE 143 CMOS Process Flow
 EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 84 D D G Sub G Sub S S G D S G D S + + + + - MOS Substrate Well - MOS Substrate EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 85 hotoresist Si 3 4 SiO 2 Substrate selection: moderately high resistivity,
EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 84 D D G Sub G Sub S S G D S G D S + + + + - MOS Substrate Well - MOS Substrate EE 143 CMOS rocess Flow CT 85 hotoresist Si 3 4 SiO 2 Substrate selection: moderately high resistivity,
VLSI Digital Systems Design
 VLSI Digital Systems Design CMOS Processing cmpe222_03process_ppt.ppt 1 Si Purification Chemical purification of Si Zone refined Induction furnace Si ingot melted in localized zone Molten zone moved from
VLSI Digital Systems Design CMOS Processing cmpe222_03process_ppt.ppt 1 Si Purification Chemical purification of Si Zone refined Induction furnace Si ingot melted in localized zone Molten zone moved from
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 33 Problems in LOCOS + Trench Isolation and Selective Epitaxy So, we are discussing
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 33 Problems in LOCOS + Trench Isolation and Selective Epitaxy So, we are discussing
EEC 118 Lecture #5: MOS Fabrication. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #5: MOS Fabrication Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 3 this week, report due next week HW 3 due this Friday at 4
EEC 118 Lecture #5: MOS Fabrication Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 3 this week, report due next week HW 3 due this Friday at 4
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 6 CMOS Fabrication Process & Design Rules guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 6 CMOS Fabrication Process & Design Rules guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Chapter 5. UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication. Diffusion
 Chapter 5 UEEP613 Microelectronic Fabrication Diffusion Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 4 Jun 01 Chapter 5 Diffusion...131 5.0 Introduction... 131 5.1 Model of Diffusion in Solid... 133 5. Fick s Diffusion
Chapter 5 UEEP613 Microelectronic Fabrication Diffusion Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 4 Jun 01 Chapter 5 Diffusion...131 5.0 Introduction... 131 5.1 Model of Diffusion in Solid... 133 5. Fick s Diffusion
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication
 Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
Lecture 22: Integrated circuit fabrication Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Layering 4 3 Patterning 7 4 Doping 8 4.1 Thermal diffusion......................... 10 4.2 Ion implantation.........................
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 7: CMOS Manufacturing Process Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
Chapter 4 : ULSI Process Integration (0.18 m CMOS Process)
 Chapter : ULSI Process Integration (0.8 m CMOS Process) Reference. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (00). - (00). Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Basic Principles(/e)
Chapter : ULSI Process Integration (0.8 m CMOS Process) Reference. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (00). - (00). Semiconductor Physics and Devices- Basic Principles(/e)
CMOS Manufacturing process. Design rule set
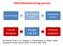 CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
Fabrication Technology
 Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
Fabrication Technology By B.G.Balagangadhar Department of Electronics and Communication Ghousia College of Engineering, Ramanagaram 1 OUTLINE Introduction Why Silicon The purity of Silicon Czochralski
Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology
 Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology Background The following contains a brief description of isolation technologies used for radiation hardened integrated circuits. The technologies mentioned are junction
Radiation Tolerant Isolation Technology Background The following contains a brief description of isolation technologies used for radiation hardened integrated circuits. The technologies mentioned are junction
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation CMOS Processing Technology Topics CMOS Processing Technology Semiconductor Processing How do we make a transistor? Fabrication Process Wafer Processing Silicon single crystal
VLSI Design and Simulation CMOS Processing Technology Topics CMOS Processing Technology Semiconductor Processing How do we make a transistor? Fabrication Process Wafer Processing Silicon single crystal
Fabrication and Layout
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design Fabrication and Layout ECEN 454 3.1 A Glimpse at MOS Device Polysilicon Aluminum ECEN 475 4.2 1 Material Classification Insulators Glass, diamond, silicon oxide
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design Fabrication and Layout ECEN 454 3.1 A Glimpse at MOS Device Polysilicon Aluminum ECEN 475 4.2 1 Material Classification Insulators Glass, diamond, silicon oxide
Figure 2.3 (cont., p. 60) (e) Block diagram of Pentium 4 processor with 42 million transistors (2000). [Courtesy Intel Corporation.
 Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
Figure 2.1 (p. 58) Basic fabrication steps in the silicon planar process: (a) oxide formation, (b) selective oxide removal, (c) deposition of dopant atoms on wafer, (d) diffusion of dopant atoms into exposed
conductor - gate insulator source gate n substrate conductor - gate insulator gate substrate n open switch closed switch however: closed however:
 MOS Transistors Readings: Chapter 1 N-type drain conductor - gate insulator source gate drain source n p n substrate P-type drain conductor - gate insulator source drain gate source p p substrate n 42
MOS Transistors Readings: Chapter 1 N-type drain conductor - gate insulator source gate drain source n p n substrate P-type drain conductor - gate insulator source drain gate source p p substrate n 42
An SOI Process for Fabrication. of Solar Cells, Transistors and Electrostatic Actuators. Berkeley Sensor and Actuator Center
 An SOI Process for Fabrication of Solar Cells, Transistors and Electrostatic Actuators Colby L Bellew, Seth Hollar and K.S.J. Pister University of California at Berkeley Berkeley Sensor and Actuator Center
An SOI Process for Fabrication of Solar Cells, Transistors and Electrostatic Actuators Colby L Bellew, Seth Hollar and K.S.J. Pister University of California at Berkeley Berkeley Sensor and Actuator Center
EE THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6. Basic Concepts
 EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
Fabrication and Layout
 Fabrication and Layout Kenneth Yun UC San Diego Adapted from EE271 notes, Stanford University Overview Semiconductor properties How chips are made Design rules for layout Reading Fabrication: W&E 3.1,
Fabrication and Layout Kenneth Yun UC San Diego Adapted from EE271 notes, Stanford University Overview Semiconductor properties How chips are made Design rules for layout Reading Fabrication: W&E 3.1,
A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in
 Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
Chapter 5 PROCESSING OF DEVICES A discussion of crystal growth, lithography, etching, doping, and device structures is presented in the following overview gures. SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE PROCESSING: AN OVERVIEW
Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE
 Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
Transistors on a Chip Lecture #18 Fabrication OUTLINE IC Fabrication Technology Introduction the task at hand Doping Oxidation Thin-film deposition Lithography Etch Lithography trends Plasma processing
Lect. 2: Basics of Si Technology
 Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from fractions of nanometer to several micro-meters
PREMETAL PLANARIZATION USING SPIN-ON-DIELECTRIC. Fred Whitwer, Tad Davies, Craig Lage National Semiconductor Corp., Puyallup, WA, 98373
 PREMETAL PLANARIZATION USING SPIN-ON-DIELECTRIC Fred Whitwer, Tad Davies, Craig Lage National Semiconductor Corp., Puyallup, WA, 98373 ABSTRACT A silicate type spin-on-glass (SOG) has been used to planarize
PREMETAL PLANARIZATION USING SPIN-ON-DIELECTRIC Fred Whitwer, Tad Davies, Craig Lage National Semiconductor Corp., Puyallup, WA, 98373 ABSTRACT A silicate type spin-on-glass (SOG) has been used to planarize
EE CMOS TECHNOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text
 1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
1 EE 212 FALL 1999-00 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text In this set of notes we will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors
Summary of Selected EMCR732 Projects for Spring 2005 Mike Aquilino Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Summary of Selected EMCR732 Projects for Spring 2005 Mike Aquilino Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Summary of Selected EMCR732 Projects for Spring 2005 Mike Aquilino Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY
ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline:
 ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline: Fabrication of p-n junctions Contact Potential Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the necessary steps to fabricate
ECE 440 Lecture 27 : Equilibrium P-N Junctions I Class Outline: Fabrication of p-n junctions Contact Potential Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the necessary steps to fabricate
Doping and Oxidation
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
