(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
|
|
|
- Charity Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
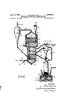
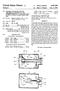
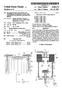
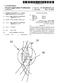
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1 Leigh (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUPPLYING SOLID FEED MATERIALS FOR A DIRECT SMELTING PROCESS (76) Inventor: David John Leigh, Kensington, WA (US) Correspondence Address: MILES & STOCKBRIDGE P.C. Suite Pinnacle Drive McLean, VA (US) (21) Appl. No.: 10/267,037 (22) Filed: Oct. 9, 2002 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 9, 2001 (AU)... PR 8172 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl.... C21B 13/00 (52) U.S. Cl /267; 75/503 (57) ABSTRACT A process and apparatus for Supplying Solid feed materials for a direct Smelting process to Solids injection lances of a direct Smelting vessel is disclosed. The feed materials Supply apparatus includes a Supply line (L) for conveying iron containing material and Solid carbonaceous material under pressure to Solids injection lances (7), and the Supply line includes a main feeder line Section (15) and a plurality of branch line sections (17) extending from the main feeder line Section. Each branch line Section is connected to one Solids injection lance for Supplying iron-containing material and carbonaceous material to that lance. The apparatus further includes an assembly for dispensing iron-containing material under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line and an assembly for dispensing carbonaceous material under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line. 9 CCA FUX FROUS NJECTION MJECTION NJEcton
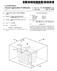
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 3 US 2003/ A1 i oc ) i
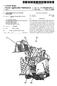
3 Patent Application Publication. Sheet 2 of 3 US 2003/ A1 2 to Q o es s ió O - O
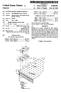
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 3 US 2003/ A1 Figure 3 -a- DIRECTION OF FLOW EE PECE NEXT PPE SIZE LARGER Df RECTION OF FLOW
5 SUPPLYING SOLID FEED MATERLALS FOR A DIRECT SMELTING PROCESS The present invention relates to a process and an apparatus for Supplying Solid feed materials for a direct Smelting process to Solids injection lances of a direct Smelt ing vessel A known direct smelting process that is generally referred to as the HISmelt process is described in Interna tional Application PCT/AU96/00197 (WO96/31627) and in other patent applications in the name of the applicant The following discussion of the HISmelt process is not to be taken as an admission of common general knowl edge The HISmelt process includes the steps of: 0005 (a) forming a molten bath of iron and slag in a vessel; 0006 (b) injecting into the bath: 0007 (i) an iron-containing feed material, typi cally iron ore or partially reduced iron ore, and 0008 (ii) a solid carbonaceous material, typically coal, which acts as a reductant of the iron-con taining feed material and a Source of energy; and 0009 (c) Smelting iron-containing feed material to iron in the bath The term smelting is herein understood to mean thermal processing wherein chemical reactions that reduce iron-containing material take place to produce molten iron The iron-containing feed material and the Solid carbonaceous material are injected into the molten bath through a number of Solids injection lances which are inclined to the Vertical So as to extend downwardly and inwardly through the side wall of the vessel and into the lower region of the vessel So as to deliver the Solids materials deep into the molten bath The HISmelt process also includes post-combust ing reaction gases, Such as CO and H2, that are released from the bath into a Space above the bath with oxygen-containing gas and transferring the heat generated by post-combustion to the bath to contribute to the thermal energy required to Smelt iron-containing feed material Typically, the oxygen-containing gas is a blast of hot air, which may be oxygen enriched, that is injected into an upper region of the vessel through a downwardly extend ing hot air injection lance. Offgases resulting from post combustion of reaction gases in the vessel are taken away from an upper part of the vessel through an offgas duct The HISmelt process enables large quantities of molten iron to be produced by direct Smelting in a Single compact vessel However, in order to achieve this it is necessary to Supply large quantities of Solid feed materials, namely iron-containing feed material, carbonaceous material, and fluxes, to the Solids injection lances The Supply of Solid feed materials must continue throughout a Smelting campaign, which desirably is at least 12 months Moreover, it must be possible to vary the supply of Solid feed materials during the course of a Smelting cam paign to accommodate different operating conditions, including unexpected perturbations in the process, at differ ent Stages of a Smelting campaign The present invention provides an effective and reliable process and apparatus for Supplying Solid feed materials to Solids injection lances during a HISmelt Smelt ing campaign According to the present invention there is pro Vided an apparatus for Supplying Solid feed materials for a direct Smelting process to Solids injection lances of a direct Smelting vessel, the feed materials Supply apparatus includ Ing: 0020 (a) a supply line for conveying iron-contain ing material and Solid carbonaceous material under pressure to Solids injection lances, the Supply line including a main feederline Section and a plurality of branch line Sections extending from the main feeder line Section, with each branch line Section being connected to one Solids injection lance for Supplying iron-containing material and carbonaceous material to that lance; 0021 (b) an assembly for dispensing iron-contain ing material under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line; 0022 (c) an assembly for dispensing carbonaceous material under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line The term iron-containing material includes iron ore, partially reduced iron ore, DRI, and iron-containing wastes produced in Steelmaking plants The term carbonaceous material includes coal and coke breeze Preferably the iron-containing material dispensing assembly includes a pressurised vessel that contains iron containing material Preferably the iron-containing material dispensing assembly includes a means for controlling the flow rate of iron-containing material to the Supply line Preferably the iron-containing material dispensing assembly includes a means for Supplying carrier gas to transport iron-containing material under pressure into the Supply line Preferably the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly includes a pressurised vessel that contains carbon aceous material Preferably the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly includes a means for controlling the flow rate of carbonaceous material to the Supply line Preferably the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly includes a means for Supplying carrier gas to transport carbonaceous material under pressure into the Supply line Preferably the apparatus includes an assembly for dispensing flux under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line.
6 0.032 Preferably the flux dispensing assembly includes a pressurised vessel that contains flux Preferably the flux dispensing assembly includes a means for controlling the flow rate of flux into the Supply line Preferably the flux dispensing assembly includes a means for Supplying carrier gas to transport flux under pressure into the Supply line Preferably each dispensing assembly is connected to the main feederline Section of the Supply line at a different connection location along the main feeder line Section Preferably the connection of the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly to the main feeder line Section is upstream of the connection of the iron-containing material dispensing assembly to the main feeder line Section Preferably the connection of the flux dispensing assembly to the main feeder line Section is intermediate the connections of the carbonaceous material dispensing assem bly to the iron-containing material dispensing assembly and the main feeder line Section Preferably each branch line section is substantially the same in terms of configuration, ie Straight Sections and bends and pipe dimeter(s) in the branch line Sections Preferably the supply line includes only two branch line Sections With this arrangement, preferably the branch line Sections are connected to a pair of lances at diametrically opposed locations on the vessel. 0041) Preferably each branch line section includes a Straight Section that is connected to the Solids injection lance and the length of the Straight Section is at least 10 times the diameter of the Straight Section Preferably the apparatus includes a means for detecting and unblocking blockages in the Supply line Preferably the detecting/unblocking apparatus includes a plurality of assemblies for Selectively pressurising or venting the Supply line at a Series of locations along the length of the Supply line Preferably the apparatus includes a plurality of the above-described Supply lines, with the branch line Sections of each Supply line being connected to Solids injection lances, and with Separate dispensing assemblies for iron containing material and carbonaceous material and option ally flux being connected to each Supply line With this arrangement, if there is a blockage or other interruption to the Supply of feed materials in one or more of the Supply lines, it is Still possible to continue Supplying feed materials to the vessel via the remaining unaffected and operational Supply line or lines and Solids injection lances connected to the Supply line or lines According to the present invention there is also provided a process for Supplying Solid feed materials for a direct Smelting process to Solids injection lances of a direct Smelting vessel, the process including the Step of Supplying Solid feed materials and carrier gas to a plurality of Solids injection lances via a Supply line that has a main feeder line Section and a plurality of branch line Sections extending from the main feeder line Section, with each branch line being connected to one of the lances Preferably the process includes maintaining the Same mass flow rate of Solid feed materials to each lance Preferably the solid feed materials include one or more of iron-containing material, carbonaceous material, and flux Preferably the iron-containing material is substan tially fine material of less than 6 mm diameter Preferably the carbonaceous material is substan tially fine material of less than 3 mm diameter Preferably the carrier gas is nitrogen Preferably the process includes supplying solid feed materials and carrier gas into the main feeder line Section via Separate dispensing assemblies for each feed material Preferably the process includes maintaining a pres sure head of at least 250 Pa at the dispensing assembly end of the main feeder line Section of the Supply line Preferably the process includes maintaining a pres sure head of at least 300 Pa at the dispensing assembly end of the main feeder line Section of the Supply line Preferably the process includes supplying solid feed materials and carrier gas in the Supply line at a Solids: gas ratio of at least 10 kg Solids/Nm gas Preferably the process includes Supplying the fol lowing feed materials into the Supply line at the following minimum velocities. Material Minimum Velocity mfs Coalf coke breeze 8 Ore/partially reduced 1O iron ore DRI/steel plant wastes Flux According to the present invention there is also provided a direct Smelting apparatus that includes the above described feed materials Supply apparatus According to the present invention there is also provided a direct Smelting process that includes the above described process for Supplying Solid feed materials. 0059) The present invention is described further by way of example with reference to the accompanying drawings of which: 0060 FIG. 1 illustrates in diagrammatic form a preferred embodiment of the feed materials Supply apparatus in accor dance with the present invention; 0061 FIG. 2 illustrates in detail in diagrammatic form one unit of the feed materials Supply apparatus shown in FIG. 1; and 0062 FIG. 3 is a side elevation of a preferred embodi ment of a bend in the Supply line of the feed materials apparatus shown in FIGS. 1 and 2.
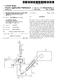
7 0.063 FIG. 1 illustrates a feed material supply apparatus for Supplying Solid feed materials, namely coal, flux and iron ore, and carrier gas to 8 Solids injection lances 7 that extend through the side wall 5 of a direct smelting vessel SRV and downwardly and inwardly into the vessel The direct smelting vessel SRV may be any suit able vessel for carrying out a direct Smelting process Such as the HISmelt process described above Australian patent application 27990/01 in the name of the applicant includes a description of the general con struction of a HISmelt vessel and the disclosure in the Australian patent application is incorporated herein by cross-reference In basic terms, the HISmelt vessel described in Australian patent application 27990/01 has: a hearth that includes a base and Sides formed from refractory bricks, Side walls which form a generally cylindrical barrel extending upwardly from the Sides of the hearth and include an upper barrel Section and a lower barrel Section; a roof; an outlet for offgases, a forehearth for discharging molten metal continu ously; and a tap-hole for discharging molten slag In use, the vessel contains a molten bath of iron and Slag which includes a layer of molten metal and a layer of molten Slag on the metal layer The vessel is fitted with a downwardly extending gas injection lance for delivering a hot air blast into an upper region of the vessel and eight Solids injection lances, iden tified by the numeral 7 in the figures, extending downwardly and inwardly through the Side walls and into the Slag layer for injecting iron ore, Solid carbonaceous material, and fluxes entrained in an oxygen-deficient carrier gas into the metal layer The gas injection lance receives an oxygen enriched hot air flow through a hot gas delivery duct which extends from a hot gas Supply Station located Some distance away from the reduction vessel The position of the solids injection lances 7 is Selected So that their outlet ends are above the Surface of the metal layer during operation of the process. This position of the lances reduces the risk of damage through contact with molten metal and also makes it possible to cool the lances by forced internal water cooling without Significant risk of water coming into contact with the molten metal in the vessel The feed materials supply apparatus is arranged to Supply coal, flux and iron ore to diametrically opposed pairs of the solids injection lances The feed materials supply apparatus for each pair of Solids injection lances 7 includes: 0073 (a) a series of feed material dispensing assem blies, namely a coal dispensing assembly, a flux dispensing assembly, and an iron ore dispensing assembly, and 0074 (b) a supply line generally identified by the letter L that conveys the feed materials to the lances More particularly, there is a separate supply of each of coal, flux, and iron ore for each of the 4 pairs of lances 7. In other words, the apparatus includes 4 independent feed materials Supply units for Supplying the feed materials to the lances 7. Consequently, the apparatus ensures a high level of reliability for the direct Smelting process Specifically, should one or more of the units be non-operational the remaining unit or units can continue to Supply each of the feed materials, optionally at increased feed rates to compensate for the reduction in feed material Supply through the non-operational unit or units The feed material dispensing assemblies include pressurised vessels 9, 11, 13 that are constructed to dispense the respective Solid feed materials with a carrier gas, typi cally nitrogen, into the Supply lines L With regard to FIG. 2, the carrier gas is supplied under pressure to the dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13 via gas supply lines In addition, the feed material dispensing assem blies includes valves 41 that control the flow of gas dis charged from the dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13 into the Supply lines L In addition, the feed material dispensing assem blies include lock hoppers (not shown) for Supplying the respective feed materials to the dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13 and bulk storage bins (not shown) for Supplying feed mate rials to the lock hoppers The Supply lines L have an abrasion resistant liner Selected to Survive a direct Smelting campaign, typically 12 months In order to minimise manufacture and operating costs, desirably the Supply lines L are the minimum possible lengths Each Supply line L includes a single main feeder line 15 connected to the dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13, a junction 19 connected to a downstream end of the feederline 15, and a pair of branch lines 17 extending from the junction 19 and connected to the lances 7. One branch line 17 is connected to one of the lances 7 and the other of the branch lines 7 is connected to the other of the lances The dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13 are connected Separately to each feeder line 15, with the coal dispensing vessel 9 being connected upstream of the other vessels 11, 13 and the flux dispensing vessels 11 being connected upstream of the iron ore dispensing vessels The coal storage vessels 9 are connected upstream of the other vessels 11, 13 because the natural properties of coal assist in facilitating the conveying of Solid feed mate rials in the Supply lines L The junctions 19 may be any suitable type of feed splitter. One suitable junction is a Clyde splitter box In use, one or more of coal, flux, and iron ore are Supplied under pressure with carrier gas from the respective dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13 into the feeder lines 15 and are conveyed via the feeder lines 15 and the branch lines 17 to the Solids injection lances The arrangement is such that, depending on pro cess requirements, at any given time, only one of the feed materials, or a blend of two of the feed materials, or a blend
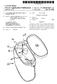
8 of the 3 feed materials are conveyed via the feeder lines 15 and the branch lines 17 to the Solid injection lances Each given pair of branch lines 17 is constructed to have the same configuration of Straight Sections and bends and pipe diameters So that there is Substantially equal resistance to mass flow of feed materials through each branch line 17 from the junctions 19 to the lances In the arrangement shown in the Figures, each branch line 17 includes a first straight section 21, a first T-bend 23, a second straight section 25, a second T-bend 27, and a third straight section ) With reference to FIG.3, the T-bends 23, 27 are 90 degrees expanded T-bends that have dead-end Sections 31 that can be accessed via a port The branch lines 17 are constructed so that the length of the third Straight Sections 29, ie the Sections that are connected to the lances 7, are not less than 10 pipe diam eters. This ensures that the highest wear region of the branch lines 17, which is typically 2-7 pipe diameters downstream of the second T-bends 27, is external to the Solids injection lances On the basis of experimental work carried out by the applicant, preferred operating parameters are as follows: 0094 Solids: Gas Ratio Min Nominal Max Solids:Gas ratio 10 kg/nm 15 kg/nm 18 kg/nm Conveying Velocity Material Min Nominal Max** coalf coke breeze 8 mis 10 m?s 16 m?s orefreverts/dri fluxfoust 10 ms 8 mis 12 m/s 10 m?s 16 m?s 16 m?s **This is the normal operating maximum. Short term (<1 hour) excursions about these values will be possible Minimum Pressure Head (based on gas properties only) Material coalf coke breeze orefreverts/dri fluxiclust Min 3OO Pa 3OO Pa 3OO Pa In general terms, the objective of the selection of operating parameters is to operate at as low as possible gas Velocity to minimise carrier gas Volumes and line wear, bearing in mind that the risk of line blockages increases as the Velocity decreases The apparatus also includes a means for detecting and unblocking blockages in Supply lines L With reference to FIG. 2, the detecting/unblocking means includes pressure measurement equipment PT in each of the dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13, the feeder lines 15, and the branch lines 17. The detecting/unblocking means also includes a data processing System (not shown) for process ing measured pressures and determining pressure differen tials and, more particularly, whether pressure differentials are outside prescribed ranges, thereby indicating a line blockage With further reference to FIG. 2, the detecting/ unblocking means also includes assemblies 51 for pressuris ing/venting the Supply lines L at a number of points along the length of the Supply lines L for unblocking line block ages In use, when a blockage is detected in a supply line L., Valves 43 are closed to prevent continued Supply of feed materials to a blocked Supply line L and pipework on both Sides of a blockage is pressurised by Supplying gas via the pressurising/venting points 51 and then one Side of the blockage is vented quickly to atmosphere. The applicant has found that this technique is an effective means of clearing line blockages. 0102) Many modifications may be made to the preferred embodiment of the present invention described above with out departing from the Spirit and Scope of the present invention. 0103) In this regard, it is understood that the control means associated with the dispensing vessels 9, 11, 13 may be a mechanical feed System or a pressure System using differential pressure or any combination thereof. 1. An apparatus for Supplying Solid feed materials for a direct Smelting process to Solids injection lances of a direct Smelting vessel, the feed materials Supply apparatus includ ing: (a) a Supply line for conveying iron-containing material and Solid carbonaceous material under pressure to Solids injection lances, the Supply line including a main feeder line Section and a plurality of branch line Sec tions extending from the main feeder line Section, with each branch line Section being connected to one Solids injection lance for Supplying iron-containing material and carbonaceous material to that lance; (b) an assembly for dispensing iron-containing material under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line, and (c) an assembly for dispensing carbonaceous material under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line. 2. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the iron-containing material dispensing assembly includes a pressurised vessel containing iron-containing material. 3. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the iron-containing material dispensing assembly a means for controlling the flow rate of iron-containing material to the Supply line. 4. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the iron-containing material dispensing assembly includes a means for Supplying carrier gas to transport iron-containing material under pressure into the Supply line.
9 5. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly includes a pres Surised vessel containing carbonaceous material. 6. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly includes a means for controlling the flow rate of carbonaceous material to the Supply line. 7. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly includes a means for Supplying carrier gas to transport carbonaceous material under pressure into the Supply line. 8. The supply apparatus defined in claim 1 further includes an assembly for dispensing flux under pressure into the main feeder line Section of the Supply line. 9. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 8 wherein the flux dispensing assembly includes a pressurised vessel con taining flux. 10. The supply apparatus defined in claim 8 wherein the flux dispensing assembly includes a means for controlling the flow rate of flux into the Supply line. 11. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 8 wherein the flux dispensing assembly includes a means for Supplying carrier gas to transport flux under pressure into the Supply line. 12. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein each dispensing assembly is connected to the main feeder line Section of the Supply line at a different connection location along the main feeder line Section. 13. The supply apparatus defined in claim 12 wherein the connection of the carbonaceous material dispensing assem bly to the main feeder line section is upstream of the connection of the iron-containing material dispensing assembly to the main feeder line Section. 14. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 8 wherein the connection of the flux dispensing assembly to the main feeder line Section is intermediate the connections of the carbonaceous material dispensing assembly to the iron containing material dispensing assembly and the main feeder line Section. 15. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein each branch line Section is Substantially the Same in terms of configuration, ie Straight Sections and bends and pipe dime ter(s) in the branch line Sections. 16. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 wherein the Supply line includes only two branch line Sections. 17. The supply apparatus defined in claim 16 wherein the branch line Sections are connected to a pair of lances at diametrically opposed locations on the vessel. 18. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 17 wherein each branch line Section includes a Straight Section that is connected to the Solids injection lance and the length of the Straight Section is at least 10 times the diameter of the Straight Section. 19. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 further includes a means for detecting and unblocking blockages in the Supply line. 20. The supply apparatus defined in claim 19 wherein the detecting/unblocking apparatus includes a plurality of assemblies for Selectively pressurising or venting the Supply line at a Series of locations along the length of the Supply line. 21. The Supply apparatus defined in claim 1 includes more than one Said Supply line, with the branch line Sections of each Supply line being connected to Solids injection lances, and with Separate dispensing assemblies for iron-containing material and carbonaceous material and optionally flux being connected to each Supply line. 22. A process for Supplying Solid feed materials for a direct Smelting process to Solids injection lances of a direct Smelting vessel, which process includes a step of Supplying Solid feed materials and carrier gas to a plurality of Solids injection lances via a Supply line that has a main feeder line Section and a plurality of branch line Sections extending from the main feeder line Section, with each branch line being connected to one of the lances. 23. The process defined in claim 22 includes maintaining the same mass flow rate of Solid feed materials to each lance. 24. The process defined in claim 22 wherein the solid feed materials include one or more of iron-containing material, carbonaceous material, and flux. 25. The process defined in claim 24 wherein the iron containing material is Substantially fine material of less than 6 mm diameter. 26. The process defined in claim 25 wherein the carbon aceous material is Substantially fine material of less than 3 mm diameter. 27. The process defined in claim 22 includes Supplying Solid feed materials and carrier gas into the main feeder line Section via Separate dispensing assemblies for each feed material. 28. The process defined in claim 22 includes maintaining a pressure head of at least 250 Pa at the dispensing assembly end of the main feeder line Section of the Supply line. 29. The process defined in claim 22 includes Supplying Solid feed materials and carrier gas in the Supply line at a Solids: gas ratio of at least 10 kg Solids/Nm gas. 30. The process defined in claim 22 includes supplying the following feed materials into the Supply line at the following minimum velocities: Material Minimum Velocity mfs Coalf coke breeze 8 Ore/partially reduced 1O iron ore DRI/steel plant wastes Flux 8
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007O157761A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0157761 A1 Bratina (43) Pub. Date: (54) USE OF AN INDUCTION FURNACE FOR Publication Classification THE PRODUCTION
US 2007O157761A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0157761 A1 Bratina (43) Pub. Date: (54) USE OF AN INDUCTION FURNACE FOR Publication Classification THE PRODUCTION
July 14, B. S. OLD ET AL 2,894,831 PROCESS OF FLUIDIZED BED REDUCTION OF IRON ORE FOLLOWED BY ELECTRIC FURNACE. MELTING
 July 14, 1959 - B. S. OLD ET AL 2,894,831 PROCESS OF FLUIDIZED BED REDUCTION OF IRON ORE FOLLOWED BY ELECTRIC FURNACE. MELTING Filed Nov. 28, i956.. 2. Sheets-Sheet l AAC/WG Gas. BY INVENTORS B2Uce Scot
July 14, 1959 - B. S. OLD ET AL 2,894,831 PROCESS OF FLUIDIZED BED REDUCTION OF IRON ORE FOLLOWED BY ELECTRIC FURNACE. MELTING Filed Nov. 28, i956.. 2. Sheets-Sheet l AAC/WG Gas. BY INVENTORS B2Uce Scot
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020079273A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0079273 A1 Davies et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) UPGRADING SOLID MATERIAL Inventors: Mark
(19) United States US 20020079273A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0079273 A1 Davies et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) UPGRADING SOLID MATERIAL Inventors: Mark
United States Patent [I91 [ill Patent Number: 6,010,083 Roe et al. [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 4,2000
![United States Patent [I91 [ill Patent Number: 6,010,083 Roe et al. [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 4,2000 United States Patent [I91 [ill Patent Number: 6,010,083 Roe et al. [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 4,2000](/thumbs/90/102456941.jpg) United States Patent [I91 [ill Patent Number: 6,010,083 Roe et al. [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 4,2000 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 3,954,662 511976 Salyer et al.... 2521382 GENERATING HIGH QUALITY FOAM
United States Patent [I91 [ill Patent Number: 6,010,083 Roe et al. [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 4,2000 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 3,954,662 511976 Salyer et al.... 2521382 GENERATING HIGH QUALITY FOAM
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008393822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,393,822 B2 Hotchkin (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) ROADWAY BARRIER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Darren John Hotchkin, Labertouche
(12) United States Patent US008393822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,393,822 B2 Hotchkin (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) ROADWAY BARRIER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Darren John Hotchkin, Labertouche
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100038405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0038405 A1 Garner (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2010 (54) SPINDLE-INTEGRATED COOLING AND COLLECTION DEVICE FOR
(19) United States US 20100038405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0038405 A1 Garner (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2010 (54) SPINDLE-INTEGRATED COOLING AND COLLECTION DEVICE FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080276627A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0276627 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2008 (54) FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEMAND METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20080276627A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0276627 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2008 (54) FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEMAND METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 US0096.70593B2 (12) United States Patent Kato et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2017 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR RECHARGING RAW MATERAL POLYCRYSTALLINE
US0096.70593B2 (12) United States Patent Kato et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2017 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR RECHARGING RAW MATERAL POLYCRYSTALLINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100146890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0146890 A1 Kristensen (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 17, 2010 (54) FOUNDATION FOR ENABLING ANCHORING OFA WIND TURBINE
(19) United States US 20100146890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0146890 A1 Kristensen (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 17, 2010 (54) FOUNDATION FOR ENABLING ANCHORING OFA WIND TURBINE
IIIIIi. 0 o_l_ll_. ""' Llillg
 IIIIIi. 0 o_l_ll_ ""' Llillg 11111_ 11111_ DOE Docket S-70,579 u 0 C SPLIT FLOW GASIFIER o Inventor - John S. Halow DISCLAIMER H Thisreportwaspreparedasan accountof worksponsoredby an agencyof the UnitedStates
IIIIIi. 0 o_l_ll_ ""' Llillg 11111_ 11111_ DOE Docket S-70,579 u 0 C SPLIT FLOW GASIFIER o Inventor - John S. Halow DISCLAIMER H Thisreportwaspreparedasan accountof worksponsoredby an agencyof the UnitedStates
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003OOO9978A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0009978A1 Haslem et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) PLASTICSLAB BOLSTER UPPER (22) Filed: Jul. 12,
US 2003OOO9978A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0009978A1 Haslem et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) PLASTICSLAB BOLSTER UPPER (22) Filed: Jul. 12,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100163550A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0163550 A1 BELSH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2010 (54) HEATING AND MELTING OF MATERIALS BYELECTRIC INDUCTION
(19) United States US 20100163550A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0163550 A1 BELSH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2010 (54) HEATING AND MELTING OF MATERIALS BYELECTRIC INDUCTION
3.430,865 3/1969 McDougal. 239/427.5
 US00601 0083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: R0e et al. () Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 9 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 3.954,662 5/1976 Salyer et al.... 2/382 GENERATING HIGH QUALITY FOAM
US00601 0083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: R0e et al. () Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 9 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 3.954,662 5/1976 Salyer et al.... 2/382 GENERATING HIGH QUALITY FOAM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016024.3609A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0243609 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) QUASI SELF-DESTRUCTIVE CORE FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016024.3609A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0243609 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) QUASI SELF-DESTRUCTIVE CORE FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090317637A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0317637 A1 Luhrs et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) MATERIAL WITH CORE-SHELL STRUCTURE (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20090317637A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0317637 A1 Luhrs et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) MATERIAL WITH CORE-SHELL STRUCTURE (75) Inventors:
(10) Patent No.: US 7.628,197 B2
 US007628197B2 (12) United States Patent Verma (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) () (51) (52) (58) (56) WATER QUENCH FITTING FOR PYROLYSIS FURNACE EFFLUENT Inventor: Vijender Kumar Verma, Sugar Land, TX (US)
US007628197B2 (12) United States Patent Verma (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) () (51) (52) (58) (56) WATER QUENCH FITTING FOR PYROLYSIS FURNACE EFFLUENT Inventor: Vijender Kumar Verma, Sugar Land, TX (US)
Onuma et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 3, VALVE GATE INJECTION MOLDING 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 III IIHIIII United States Patent 19 11 USOO5378138A Patent Number: Onuma et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 1995 54 VALVE GATE INJECTION MOLDING 56) References Cited APPARATUS U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,026,518
III IIHIIII United States Patent 19 11 USOO5378138A Patent Number: Onuma et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 1995 54 VALVE GATE INJECTION MOLDING 56) References Cited APPARATUS U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,026,518
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,128,753. Sharp 45) Dec. 5, 1978
 29 se 2. SR 1.2/s/78 OR 4 g 2B S3 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,128,753 Sharp 45) Dec. 5, 1978 (54) LASER BEAM WELDING OTHER PUBLICATIONS (75) Inventor: Charles M. Sharp, Nether Heyford, Electronic
29 se 2. SR 1.2/s/78 OR 4 g 2B S3 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,128,753 Sharp 45) Dec. 5, 1978 (54) LASER BEAM WELDING OTHER PUBLICATIONS (75) Inventor: Charles M. Sharp, Nether Heyford, Electronic
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0318104A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0318104 A1 Ott et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016 (54) GRADIENT SINTERED METAL PREFORM Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016.0318104A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0318104 A1 Ott et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016 (54) GRADIENT SINTERED METAL PREFORM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060214543A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0214543 A1 Johnson (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 28, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF MAKING AND (52) U.S. Cl.... 312/1403
(19) United States US 20060214543A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0214543 A1 Johnson (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 28, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF MAKING AND (52) U.S. Cl.... 312/1403
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0210492 A1 Kivijarvi et al. US 20140210492A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 31, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) MOISTUREMETER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0210492 A1 Kivijarvi et al. US 20140210492A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 31, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) MOISTUREMETER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 201600 16855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0016855A1 WU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) FABRICATION OF CARBON Publication Classification NANOTUBE-NONOXDESTRUCTURAL
(19) United States US 201600 16855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0016855A1 WU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) FABRICATION OF CARBON Publication Classification NANOTUBE-NONOXDESTRUCTURAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009007 O194A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0070194 A1 SONG (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF PROVIDING ESTIMATED COST Publication Classification FOR KEYWORD
(19) United States US 2009007 O194A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0070194 A1 SONG (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF PROVIDING ESTIMATED COST Publication Classification FOR KEYWORD
-64.--Cee--sear ATTO&WEYS. April 13, 1971 L. F. ROBERTSON ET All 3,574,585. Ame S W, TAHOWAS. Filed Aug. 19, 1968 N 3. Sheets-Sheet L.
 April 13, 1971 L. F. ROBERTSON ET All ELECTRIC GLASS MELING FURNACE AND METHOD OF METTING GLASS Filed Aug. 19, 1968 N 3. Sheets-Sheet L. Y s R N INVENTORS LEON F. AOAAEAT SON/ Ame S W, TAHOWAS -64.--Cee--sear
April 13, 1971 L. F. ROBERTSON ET All ELECTRIC GLASS MELING FURNACE AND METHOD OF METTING GLASS Filed Aug. 19, 1968 N 3. Sheets-Sheet L. Y s R N INVENTORS LEON F. AOAAEAT SON/ Ame S W, TAHOWAS -64.--Cee--sear
Reduction in Charge Requirements of Hismeltiron-Making Process in Indian Context
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-12, pp-102-108 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Reduction in Charge Requirements of Hismeltiron-Making
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-12, pp-102-108 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Reduction in Charge Requirements of Hismeltiron-Making
58 Field of Search /540,583, direction, and are moved rapidly onto a selected one of a
 USOO5887699A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,887,699 Tharpe (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999 54 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR CONVEYING 3,645,391 2/1972 Hirakawa et al.... 209/583 X AND SORTING
USOO5887699A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,887,699 Tharpe (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999 54 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR CONVEYING 3,645,391 2/1972 Hirakawa et al.... 209/583 X AND SORTING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,861,865 B2
 USOO786 1865B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Green (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 2011 (54) PACKAGING ASSEMBLY 4,949,898 A 8, 1990 Nederveld 5,035,323 A 7, 1991 Daniels et al.... 206/386 (75)
USOO786 1865B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Green (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 2011 (54) PACKAGING ASSEMBLY 4,949,898 A 8, 1990 Nederveld 5,035,323 A 7, 1991 Daniels et al.... 206/386 (75)
United States Patent (19) Welch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Welch et al. 54 (76) CRAWLNG INSEC-PROOF PET BOWL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Harland A. Welch, 13005 Pollard Dr., Austin, Tex. 78727; Lorenzo Perales, 8307-A Bowling Grn.;
United States Patent (19) Welch et al. 54 (76) CRAWLNG INSEC-PROOF PET BOWL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Harland A. Welch, 13005 Pollard Dr., Austin, Tex. 78727; Lorenzo Perales, 8307-A Bowling Grn.;
MANUFACTURE OF IRON OR STEEL (preliminary treatment of ferrous ores or scrap C22B 1/00; electric heating H05B)
 CPC - C21B - 2017.08 C21B MANUFACTURE OF IRON OR STEEL (preliminary treatment of ferrous ores or scrap C22B 1/00; electric heating H05B) The production of iron or steel starting from iron ores, e.g. the
CPC - C21B - 2017.08 C21B MANUFACTURE OF IRON OR STEEL (preliminary treatment of ferrous ores or scrap C22B 1/00; electric heating H05B) The production of iron or steel starting from iron ores, e.g. the
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050O23278A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0023278A1 Yong (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) THERMAL INSULATION LINER (76) Inventor: Lawrence Joon Leong
(19) United States US 20050O23278A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0023278A1 Yong (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) THERMAL INSULATION LINER (76) Inventor: Lawrence Joon Leong
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013026.6816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0266816 A1 Xu (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING HYBRID (52) U.S. Cl. CORE USPC... 428/450; 427/201
US 2013026.6816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0266816 A1 Xu (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING HYBRID (52) U.S. Cl. CORE USPC... 428/450; 427/201
March 9, J. B. williamson 2,073,358 SELF SUPPORTING TANK ROOF.
 March 9, 1937. J. B. williamson 2,073,8 SELF SUPPORTING TANK ROOF. Filed March 22, 19 3. Sheets-Sheet 1 X S. as N,. inventor /277zes A. Wz7/ea resort BY..... Attorney March 9, 1937. J. B. WILLIAMSON 2,073,8
March 9, 1937. J. B. williamson 2,073,8 SELF SUPPORTING TANK ROOF. Filed March 22, 19 3. Sheets-Sheet 1 X S. as N,. inventor /277zes A. Wz7/ea resort BY..... Attorney March 9, 1937. J. B. WILLIAMSON 2,073,8
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O191209A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0191209 A1 Reisman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) MODULAR STORAGE SHED SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 52/36.2:52/79.1
US 2006O191209A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0191209 A1 Reisman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) MODULAR STORAGE SHED SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 52/36.2:52/79.1
(12) United States Patent
 USOO94351.86B2 (12) United States Patent Bakke (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.435,186 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SUBSEA PROCESSING SYSTEM (75) Inventor: William Bakke, Royken (NO) (73) Assignee:
USOO94351.86B2 (12) United States Patent Bakke (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.435,186 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SUBSEA PROCESSING SYSTEM (75) Inventor: William Bakke, Royken (NO) (73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Chielens et al.
 United States Patent (19) Chielens et al. 54 METHOD OF CONTROLLING COOLING OF A CONTINUOUS CASTING 75 Inventors: Alain Chielens, Marcq en Baroeul; Philippe Benoit; Bernard Roggo, both of Lambersart, all
United States Patent (19) Chielens et al. 54 METHOD OF CONTROLLING COOLING OF A CONTINUOUS CASTING 75 Inventors: Alain Chielens, Marcq en Baroeul; Philippe Benoit; Bernard Roggo, both of Lambersart, all
United States Patent (19) Schnaars
 United States Patent (19) Schnaars (54) (76) 21 22 (51) 52 (58 (56) PROCESS AND APPARATUS FOR APPLYING ANADHESIVE TO THE INTERIOR SURFACE OF A BULK BAG AND GLUING A PLASTC LNER WITHIN THE BAG Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Schnaars (54) (76) 21 22 (51) 52 (58 (56) PROCESS AND APPARATUS FOR APPLYING ANADHESIVE TO THE INTERIOR SURFACE OF A BULK BAG AND GLUING A PLASTC LNER WITHIN THE BAG Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,785,137 B2
 USOO7785.137B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,785,137 B2 Porter et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 31, 2010 (54) INTEGRAL METERJAW ASSEMBLY (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/517,
USOO7785.137B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,785,137 B2 Porter et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 31, 2010 (54) INTEGRAL METERJAW ASSEMBLY (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/517,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201502O3411A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0203411 A1 XU (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2015 (54) ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING HYBRID Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201502O3411A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0203411 A1 XU (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2015 (54) ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING HYBRID Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) BOOver
 United States Patent (19) BOOver 54, WASTEBASKET FOR REMOVING AND RETANING ATRASH CAN LNER 76 Inventor: Richard C. Boover, 3869 W. Loyola Dr. Kenner, La. 70062 21 Appl. No.: 738,090 22 Filed: Oct. 25,
United States Patent (19) BOOver 54, WASTEBASKET FOR REMOVING AND RETANING ATRASH CAN LNER 76 Inventor: Richard C. Boover, 3869 W. Loyola Dr. Kenner, La. 70062 21 Appl. No.: 738,090 22 Filed: Oct. 25,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0034439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0034439 A1 Galea (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 17, 2005 (54) ATTACHMENT FOR A SUGARCANE HARVESTER (76) Inventor: Emanuel
(19) United States US 2005.0034439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0034439 A1 Galea (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 17, 2005 (54) ATTACHMENT FOR A SUGARCANE HARVESTER (76) Inventor: Emanuel
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2001
 US 2001 OO15079A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0015079 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING DOPANT (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO15079A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0015079 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING DOPANT (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0099618A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0099618 A1 ZAKI et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 1, 2008 (54) OXYGEN REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2008.0099618A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0099618 A1 ZAKI et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 1, 2008 (54) OXYGEN REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0036060 A1 BrezOVec et al. US 2016.0036060A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) COMPOSITE ELECTRODE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0036060 A1 BrezOVec et al. US 2016.0036060A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) COMPOSITE ELECTRODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201403.36021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0336021 A1 JONES (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2014 (54) EXERCISE DEVICE Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 201403.36021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0336021 A1 JONES (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 13, 2014 (54) EXERCISE DEVICE Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150090202A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0090202 A1 Nenmeni et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR DRUM LEVEL (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150090202A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0090202 A1 Nenmeni et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR DRUM LEVEL (52) U.S. Cl.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Eriksson et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1985 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURING FERROSILICON 75 Inventors: Sune Eriksson; Sven Santén, both of Hofors, Sweden 73 Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Eriksson et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1985 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURING FERROSILICON 75 Inventors: Sune Eriksson; Sven Santén, both of Hofors, Sweden 73 Assignee:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Majurinen 54 BUILDING BLOCKSYSTEM MAGNETC (75) Inventor: Joel Majurinen, Espoo, Finland 73) Assignee: Insinooritoimisto Joel Majurinen KY, Helsinki, Finland (21) Appl. No.: 610,411
United States Patent (19) Majurinen 54 BUILDING BLOCKSYSTEM MAGNETC (75) Inventor: Joel Majurinen, Espoo, Finland 73) Assignee: Insinooritoimisto Joel Majurinen KY, Helsinki, Finland (21) Appl. No.: 610,411
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150.073589A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0073589 A1 Khodl et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 12, 2015 (54) AUTONOMOUS MOBILE PICKING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20150.073589A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0073589 A1 Khodl et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 12, 2015 (54) AUTONOMOUS MOBILE PICKING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,349,717 B1
 USOO6349717B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,349,717 B1 Thompson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2002 (54) OVEN RACKSYSTEM HAVING CUTOUT 5,775,209 A 7/1998 Tiemann... 99/426 AREA
USOO6349717B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,349,717 B1 Thompson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2002 (54) OVEN RACKSYSTEM HAVING CUTOUT 5,775,209 A 7/1998 Tiemann... 99/426 AREA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Toupin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2012
 US 20120276366A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0276366 A1 Toupin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2012 (54) FLEXIBLE SLATEVENEER (52) U.S. Cl.... 428/314.4
US 20120276366A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0276366 A1 Toupin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2012 (54) FLEXIBLE SLATEVENEER (52) U.S. Cl.... 428/314.4
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O166804A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hansen (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2005 (54) PALLET CONSTRUCTED OF RUBBER (52) U.S. Cl.... 108/56.3; 108/57.17 COMPOSITE
(19) United States US 2005O166804A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hansen (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2005 (54) PALLET CONSTRUCTED OF RUBBER (52) U.S. Cl.... 108/56.3; 108/57.17 COMPOSITE
Ea?t. - Lizzli" United States Patent (19) critime 5,254,171. Hayakawa et al. Oct. 19, S 2 a BIASECR PLASMACVDAPPARATUS
 United States Patent (19) Hayakawa et al. 11 45) USOO525417A Patent Number: Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1993 54 BIASECR PLASMACVDAPPARATUS COMPRISING SUSCEPTOR, CLAMP, AND CHAMBER WALL HEATING AND COOLNG
United States Patent (19) Hayakawa et al. 11 45) USOO525417A Patent Number: Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1993 54 BIASECR PLASMACVDAPPARATUS COMPRISING SUSCEPTOR, CLAMP, AND CHAMBER WALL HEATING AND COOLNG
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Brandenberger 54 OXY GEN SUPPLIED THERMAL LANCE 75) Inventor: Ernst Brandenberger, Wetzikon, Switzerland 73) Assignee: Kubatec Kunststoff- und Bautechnik AG, Triesen, Liechtenstein
United States Patent (19) Brandenberger 54 OXY GEN SUPPLIED THERMAL LANCE 75) Inventor: Ernst Brandenberger, Wetzikon, Switzerland 73) Assignee: Kubatec Kunststoff- und Bautechnik AG, Triesen, Liechtenstein
(12) United States Patent
 US008348.043B2 (12) United States Patent Smith (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) APPARATUS HAVING A BILL VALIDATOR AND A METHOD OF SERVICING
US008348.043B2 (12) United States Patent Smith (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) APPARATUS HAVING A BILL VALIDATOR AND A METHOD OF SERVICING
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,331,757 B2. Janssen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2008
 United States Patent USOO733177B2 (12) () Patent No.: Janssen et al. () Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2008 (4) TURBINE SHAFT AND PRODUCTION OF A,7,797 A 4/199 Marliere et al. TURBINE SHAFT.487,082 A * 1/1996
United States Patent USOO733177B2 (12) () Patent No.: Janssen et al. () Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2008 (4) TURBINE SHAFT AND PRODUCTION OF A,7,797 A 4/199 Marliere et al. TURBINE SHAFT.487,082 A * 1/1996
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O24.1336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/024.1336A1 Brisberger (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR COATING THE SURFACE OF ELONGATED METAL PRODUCTS
(19) United States US 2004O24.1336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/024.1336A1 Brisberger (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR COATING THE SURFACE OF ELONGATED METAL PRODUCTS
Koi...K.K. WOP). Kengo
 US 2002O112788A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0112788A1 Tanaka et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NI-TI-CU SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2002O112788A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0112788A1 Tanaka et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NI-TI-CU SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O15681 1A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0156811 A1 Borowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 20, 2006 (54) CONTAINER WITH MEASURING DEVICE (22) Filed:
US 2006O15681 1A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0156811 A1 Borowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 20, 2006 (54) CONTAINER WITH MEASURING DEVICE (22) Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7431,305 B2
 USOO743 13 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7431,305 B2 Fiedler (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 7, 2008 (54) OIL SCRAPER RING RING GROOVE (58) Field of Classification Search... 277/435, ARRANGEMENT
USOO743 13 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7431,305 B2 Fiedler (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 7, 2008 (54) OIL SCRAPER RING RING GROOVE (58) Field of Classification Search... 277/435, ARRANGEMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0318201 A1 UnderWOOd et al. US 2016.03182O1A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) MACHINES AND METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0318201 A1 UnderWOOd et al. US 2016.03182O1A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) MACHINES AND METHODS
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ling et al. (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DISTRIBUTING WATER PURIFYING CHEMICALS 75 Inventors: Tommy Ling, Svalov; Kjell E. Stendahl, Helsingborg, both of Sweden 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Ling et al. (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DISTRIBUTING WATER PURIFYING CHEMICALS 75 Inventors: Tommy Ling, Svalov; Kjell E. Stendahl, Helsingborg, both of Sweden 73) Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O1834.83A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Ambrose (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2005 (54) COMPOSTING OF ORGANIC WASTE (76) Inventor: Harvey Ambrose, Oshawa (CA)
(19) United States US 2005O1834.83A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Ambrose (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2005 (54) COMPOSTING OF ORGANIC WASTE (76) Inventor: Harvey Ambrose, Oshawa (CA)
Patent Application Publication Jun. 22, 2006 F.G. 1 K22 XAA.ZXZXZXZX2XZX2XZXZXZXAX2X, 6 SXXXXXX-XXXXXAS A. ZXZZX2/2S/2XZXZX2XZ2S/2S/2XA2x2x2X2S-- 4b
 (19) United States US 20060135O15A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0135015 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR MAKING FLEXIBLE AUTOMOBILE INTERIOR MATERAL AND (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20060135O15A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0135015 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR MAKING FLEXIBLE AUTOMOBILE INTERIOR MATERAL AND (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Jokela USOO6654663B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 25, 2003 (54) AUTOMATED ASSEMBLY LINE (75) Inventor: Markku Jokela, Virkkala (FI) (73) Assignee: PMJ automec Oyj,
(12) United States Patent Jokela USOO6654663B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 25, 2003 (54) AUTOMATED ASSEMBLY LINE (75) Inventor: Markku Jokela, Virkkala (FI) (73) Assignee: PMJ automec Oyj,
45) Moir /147. O'Rourke /147. Bain /133. Lilly /133. Larrouze et al /146X Rees et al /146
 United States Patent (19) Echols et al. 11 45) Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,473,322 Sep. 25, 1984 54) 76 (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 (56) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR LINING SHAFTS Inventors: Appl. No.: 36,961.
United States Patent (19) Echols et al. 11 45) Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,473,322 Sep. 25, 1984 54) 76 (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 (56) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR LINING SHAFTS Inventors: Appl. No.: 36,961.
United States Patent (19) Silvestri, Jr.
 United States Patent (19) Silvestri, Jr. 54 EXTENDED FUELCYCLEOPERATION FOR PRESSURIZED WATER REACTOR PLANTS 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21 Appi. No.: 3,174 George J. Silvestri, Jr., Morton, Pa. Westinghouse
United States Patent (19) Silvestri, Jr. 54 EXTENDED FUELCYCLEOPERATION FOR PRESSURIZED WATER REACTOR PLANTS 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21 Appi. No.: 3,174 George J. Silvestri, Jr., Morton, Pa. Westinghouse
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Lange 54) TOY BRICK AND COMBINATION OF TOY BRCKS 76) inventor: Helmut Lange, Bez. Hamburg 1, Industrie-str. 5, 2 Schenefeld, Germany 22 Filed: Oct. 9, 1973 (21) Appl. No.: 404,763
United States Patent (19) Lange 54) TOY BRICK AND COMBINATION OF TOY BRCKS 76) inventor: Helmut Lange, Bez. Hamburg 1, Industrie-str. 5, 2 Schenefeld, Germany 22 Filed: Oct. 9, 1973 (21) Appl. No.: 404,763
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200700.95443A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0095443 A1 Dolman (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2007 (54) WEAR RESISTANT CAST IRON (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 200700.95443A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0095443 A1 Dolman (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2007 (54) WEAR RESISTANT CAST IRON (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9502143B2 (10) Patent No.: Ganesan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) FLOATING NUCLEAR POWER REACTOR (58) Field of Classification Search WITH A SELF-COOLING CONTAINMENT
(12) United States Patent USOO9502143B2 (10) Patent No.: Ganesan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) FLOATING NUCLEAR POWER REACTOR (58) Field of Classification Search WITH A SELF-COOLING CONTAINMENT
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rudolph et al. (54) PROCESS OF GASIFYING SOLID FUELS 75) Inventors: Paul Rudolph, Bad Homburg; Rainer Reimert, Idstein; Osman Turna, Frankfurt am Main, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany
United States Patent (19) Rudolph et al. (54) PROCESS OF GASIFYING SOLID FUELS 75) Inventors: Paul Rudolph, Bad Homburg; Rainer Reimert, Idstein; Osman Turna, Frankfurt am Main, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Egan (54) (75) (73) 21) 22 51 52 (58) (56) CANT LEVER RETAINING WALL SYSTEM USING DSCRETE PRECAST FACNG PANELS Inventor: Assignee: Philip D. Egan, Great Falls, Va. The Reinforced
United States Patent (19) Egan (54) (75) (73) 21) 22 51 52 (58) (56) CANT LEVER RETAINING WALL SYSTEM USING DSCRETE PRECAST FACNG PANELS Inventor: Assignee: Philip D. Egan, Great Falls, Va. The Reinforced
IIII. United States Patent (19) Smith 108/56.1; 211/189, 182, 195. preferably rectangular in shape and the support frame has
 United States Patent (19) Smith 54. STORAGE/SHIPPING RACK FOR FENCE SECTION 76) Inventor: Lee Roy Smith, 110 Two Rivers Ct., Nashville, Tenn. 37214 21 Appl. No.: 526,549 22 Filed: Sep. 12, 1995 (51) Int.
United States Patent (19) Smith 54. STORAGE/SHIPPING RACK FOR FENCE SECTION 76) Inventor: Lee Roy Smith, 110 Two Rivers Ct., Nashville, Tenn. 37214 21 Appl. No.: 526,549 22 Filed: Sep. 12, 1995 (51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160083658A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0083658 A1 SANNER (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) METHODS FOR PRODUCTION OF LIQUID Publication Classification
US 20160083658A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0083658 A1 SANNER (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) METHODS FOR PRODUCTION OF LIQUID Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0086889 A1 Oh et al. US 20150.086889A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD FOR RECOVERING PERFORMANCE OF FUEL-CELL STACK
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0086889 A1 Oh et al. US 20150.086889A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD FOR RECOVERING PERFORMANCE OF FUEL-CELL STACK
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,831,939 B2. Bratina et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2004
 USOO6831939B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bratina et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2004 (54) DUALUSE OF AN INDUCTION FURNACE 4,612,041 A 9/1986 Matsuoka et al. TO PRODUCE HOT METAL OR
USOO6831939B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bratina et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2004 (54) DUALUSE OF AN INDUCTION FURNACE 4,612,041 A 9/1986 Matsuoka et al. TO PRODUCE HOT METAL OR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,568,305 B2
 USOO85683 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,568,305 B2 Lins et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2013 (54) MINIMALLY-INVASIVE PORTAL SYSTEM 2,300,040 A * 10/1942 Betts... 600,220 FOR
USOO85683 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,568,305 B2 Lins et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2013 (54) MINIMALLY-INVASIVE PORTAL SYSTEM 2,300,040 A * 10/1942 Betts... 600,220 FOR
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/45
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00021A2* (11) EP 1 00 21 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2000 Bulletin 2000/4 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00021A2* (11) EP 1 00 21 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2000 Bulletin 2000/4 (1) Int
United States Patent (19) Udo
 United States Patent (19) Udo 11) 451 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 1989 (54) 75 (73) (21) (22) 51 (52) 58) COOLING APPARATUS FOR ELECTRIC ARC FURNACE ELECTRODES Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Udo 11) 451 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 1989 (54) 75 (73) (21) (22) 51 (52) 58) COOLING APPARATUS FOR ELECTRIC ARC FURNACE ELECTRODES Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200602891.59A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Davila (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR COLLECTING ESCAPNG HYDROCARBONS FROMA BREACHED WELL
(19) United States US 200602891.59A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Davila (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR COLLECTING ESCAPNG HYDROCARBONS FROMA BREACHED WELL
United States Patent (19) Woodard
 United States Patent (19) Woodard (54) (75) 73 21 22) (51) (52) 58 56) SEMPERMEABLE MEMBRANE DRYER FOR AIR COMPRESSOR SYSTEM Inventor: Michael K. Woodard, Hampton, Va. Assignee: Newport News Shipbuilding
United States Patent (19) Woodard (54) (75) 73 21 22) (51) (52) 58 56) SEMPERMEABLE MEMBRANE DRYER FOR AIR COMPRESSOR SYSTEM Inventor: Michael K. Woodard, Hampton, Va. Assignee: Newport News Shipbuilding
PILOT PLANT PRODUCTION OF FERRONICKEL FROM NICKEL OXIDE ORES AND DUSTS IN A DC ARC FURNACE. Abstract
 PILOT PLANT PRODUCTION OF FERRONICKEL FROM NICKEL OXIDE ORES AND DUSTS IN A DC ARC FURNACE I.J Kotzé (Pyrometallurgy Division, Mintek, South Africa) E-mail for correspondence: isabelk@mintek.co.za Abstract
PILOT PLANT PRODUCTION OF FERRONICKEL FROM NICKEL OXIDE ORES AND DUSTS IN A DC ARC FURNACE I.J Kotzé (Pyrometallurgy Division, Mintek, South Africa) E-mail for correspondence: isabelk@mintek.co.za Abstract
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited
 Serial Number Filing Date Inventor 08/95.994 9 September 1997 Eugene E. Nolting Jon Colfield Roy Richard Steven Peterson NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests
Serial Number Filing Date Inventor 08/95.994 9 September 1997 Eugene E. Nolting Jon Colfield Roy Richard Steven Peterson NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O136579 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0136579 A1 McGovern et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MINORCOMPONENTRATIOBALANCING (52) U.S. Cl. IN FILTRATION
(19) United States US 2016O136579 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0136579 A1 McGovern et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MINORCOMPONENTRATIOBALANCING (52) U.S. Cl. IN FILTRATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100310968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0310968 A1 Kluge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2010 (54) BLOCKING LAYER (76) Inventors: Claus Peter Kluge,
(19) United States US 20100310968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0310968 A1 Kluge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2010 (54) BLOCKING LAYER (76) Inventors: Claus Peter Kluge,
(CA); Ghyslain Durand, (21) Appl.No.: 13/184,501. KY (U S); Gregory Phillip Paradat, Lakewood, WA (U S);
 US 20120047786Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047786 A1 Dextraze et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) MODULAR FIREARM STOCK SYSTEM (76) Inventors:
US 20120047786Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047786 A1 Dextraze et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) MODULAR FIREARM STOCK SYSTEM (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169663 A1 Berg et al. US 2007 O1696.63A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SIDEFRAME PEDESTAL Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169663 A1 Berg et al. US 2007 O1696.63A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SIDEFRAME PEDESTAL Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0009683A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009683 A1 Hamilton et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW BORON E-GLASS COMPOSITION (52) U.S. Cl.... 501/35; 501/36;
(19) United States US 2005.0009683A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009683 A1 Hamilton et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW BORON E-GLASS COMPOSITION (52) U.S. Cl.... 501/35; 501/36;
FIRST OPERATING EXPERIENCES WITH POST-COMBUSTION LANCES AT BOF SHOP LD3
 JOACHIIM LEHNER 1, MARTIN.W. EGGER 1, HARALD. PANHOFER 1, MICHAEL.J. STRELBISKY 2 FIRST OPERATING EXPERIENCES WITH POST-COMBUSTION LANCES AT BOF SHOP LD3 Abstract The application of post-combustion (secondary
JOACHIIM LEHNER 1, MARTIN.W. EGGER 1, HARALD. PANHOFER 1, MICHAEL.J. STRELBISKY 2 FIRST OPERATING EXPERIENCES WITH POST-COMBUSTION LANCES AT BOF SHOP LD3 Abstract The application of post-combustion (secondary
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0367533 A1 SCHNABEL US 20150367533A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD FOR PRODUCING ANATURAL FIBER-RENFORCED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0367533 A1 SCHNABEL US 20150367533A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD FOR PRODUCING ANATURAL FIBER-RENFORCED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O228683A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0228683 A1 Saylor et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED USE OF A PORTABLE IMAGE Publication
US 2005O228683A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0228683 A1 Saylor et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED USE OF A PORTABLE IMAGE Publication
United States Patent (19) Boot
 United States Patent (19) Boot 54 AUTOMATIC BRICKPLACING MACHINE LOADER 75 Inventor: Phillip H. Boot, Sydney, Australia 73 Assignee: Panelbrick Industries Pty. Limited, Australia 21 Appl. No.: 70,323 22,
United States Patent (19) Boot 54 AUTOMATIC BRICKPLACING MACHINE LOADER 75 Inventor: Phillip H. Boot, Sydney, Australia 73 Assignee: Panelbrick Industries Pty. Limited, Australia 21 Appl. No.: 70,323 22,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0060682A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0060682 A1 Yeh et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH TEMPERATURE SPM TREATMENT FORPHOTORESIST STRIPPING (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008.0060682A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0060682 A1 Yeh et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH TEMPERATURE SPM TREATMENT FORPHOTORESIST STRIPPING (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060225818A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0225818 A1 Baliktay (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) PROCESS FOR CASTING A (52) U.S. Cl.... 148/557; 148/671
(19) United States US 20060225818A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0225818 A1 Baliktay (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) PROCESS FOR CASTING A (52) U.S. Cl.... 148/557; 148/671
Lecture 17 Alternative Charge Materials in EAF
 Lecture 17 Alternative Charge Materials in EAF Contents: Introduction Types of metallic charge materials Carbon content in DRI Charging methods Key words: Sponge iron, DRI, electric arc furnace, UHP furnaces
Lecture 17 Alternative Charge Materials in EAF Contents: Introduction Types of metallic charge materials Carbon content in DRI Charging methods Key words: Sponge iron, DRI, electric arc furnace, UHP furnaces
Davez.2%% NNINTN NNIN NNNNN FG. I. 2 FG. 2. Oct. 24, 1961 G. K. CHRISTIANSEN 3,005,282. Godtfred Kirk Christion sen Z27 WYZVY O 44 NNNNN 22E7) NNN
 Oct. 4, 1961 G. K. CHRISTIASE TOY BUILDIG BRICK Filed July 8, l958 Sheets-Sheet FG. I. FG.. 5 M Z L E7) I 1 1. 4. Z7 WYZVY O 44 IT II IVETOR Godtfred Kirk Christion sen Davez.%% ATTOREYS Oct. 4, 1961 G.
Oct. 4, 1961 G. K. CHRISTIASE TOY BUILDIG BRICK Filed July 8, l958 Sheets-Sheet FG. I. FG.. 5 M Z L E7) I 1 1. 4. Z7 WYZVY O 44 IT II IVETOR Godtfred Kirk Christion sen Davez.%% ATTOREYS Oct. 4, 1961 G.
s SEs &S> US 7,645,098 B1 C C & C CCCXCXC. g) 3. & C. C 3. C & Ss. Rainey. Jan. 12, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 USOO7645098B1 (12) United States Patent Rainey (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 12, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) MODULAR RETAINING WALL BLOCKWITH ENHANCED STACKING ABILITY
USOO7645098B1 (12) United States Patent Rainey (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 12, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) MODULAR RETAINING WALL BLOCKWITH ENHANCED STACKING ABILITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090241 809A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0241809 A1 Head (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) MATERLALS SAFETY CAGE AND ASSOCATED METHODS (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 20090241 809A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0241809 A1 Head (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) MATERLALS SAFETY CAGE AND ASSOCATED METHODS (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0069407 A1 STENKAMP et al. US 201600694O7A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (30) LINING CARRIER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0069407 A1 STENKAMP et al. US 201600694O7A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (30) LINING CARRIER
SHADEED IRON & STEEL OMAN, SOHAR PORT THE FIRST HOTLINK STEEL PLANT
 OMAN, SOHAR PORT THE FIRST HOTLINK STEEL PLANT 1 TOPICS Introduction SHADEED Project History SHADEED Design Basis DRI Hotlink Technology Advantages of Hotlink Melt shop Design basis Conclusions 2 SHADEED
OMAN, SOHAR PORT THE FIRST HOTLINK STEEL PLANT 1 TOPICS Introduction SHADEED Project History SHADEED Design Basis DRI Hotlink Technology Advantages of Hotlink Melt shop Design basis Conclusions 2 SHADEED
United States Patent (19) Peet
 United States Patent (19) Peet 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58) (56) SUPERHEATER OUTLET STEAM TEMPERATURE CONTROL Inventor: Assignee: William J. Peet, Cambridge, Canada The Babcock & Wilcox Company, New
United States Patent (19) Peet 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58) (56) SUPERHEATER OUTLET STEAM TEMPERATURE CONTROL Inventor: Assignee: William J. Peet, Cambridge, Canada The Babcock & Wilcox Company, New
