Unapproved Genetically Modified Wheat Discovered in Oregon: Status and Implications
|
|
|
- Linda Reed
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unapproved Genetically Modified Wheat Discovered in Oregon: Status and Implications Tadlock Cowan Analyst in Natural Resources and Rural Development June 7, 2013 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional Research Service R43100
2 Summary The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) announced on May 31, 2013, that a variety of genetically engineered (GE) wheat had been discovered in a field in eastern Oregon. No varieties of genetically modified wheat have been approved, or deregulated, by the Animal and Plant and Health Inspection Service (APHIS), the USDA agency responsible for regulating the release of GE plants into the environment. Release of GE plants into the natural environment is regulated by APHIS under the Plant Protection Act (PPA, 7 U.S.C et seq.), as amended. APHIS began a formal investigation in early May after notification by an Oregon State University scientist that preliminary tests of the wheat samples from the Oregon farm indicated the possible presence of GE glyphosate-tolerant wheat plants. Test results by APHIS indicated the presence of a glyphosate-tolerant variety field-tested by Monsanto Company, a major corporate presence in agricultural biotechnology, under APHIS approval at approximately 100 field trials in 16 states between 1998 and The agency approved field testing of GE wheat in Oregon in At this time, APHIS does not know how the presence of the unapproved wheat variety occurred, how the wheat could have gotten into the field after so many years, whether violations under the PPA occurred, or whether the growth of the wheat is more widespread. Answers to these questions are among the objectives of the APHIS investigation. The safety of GE organisms for food and feed is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 301 et seq.). A voluntary consultation on the safety of food derived from the GE wheat variety was completed by FDA in FDA determined that the GE wheat variety was as safe for food and feed as non-ge wheat, and that there were no public health concerns. As of early June 2013, APHIS has stated that there is no evidence that GE wheat has entered commerce. Initial tests of wheat imported by Japan, South Korea, and the European Union have found no evidence of the unapproved GE trait. The presence of GE wheat in the market could have significant trade implications if the variety turns out to be widespread. The United States is a major wheat exporter, exporting about 50% of its wheat crop. About 90% of Oregon s wheat crop is exported. Many countries, including Japan, the European Union, and South Korea, have zerotolerance policies regarding imports of unapproved GE varieties. Japan, the largest buyer of U.S. wheat, and South Korea have temporarily halted imports of U.S. soft white wheat grown in Oregon and the Pacific Northwest. Monsanto Company, the variety s developer, provided a validated testing method for the presence of the GE trait to APHIS and to government regulators in Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and the European Union. If APHIS s investigation shows that the GE wheat is isolated to the one field and a few unintended volunteer wheat plants, the trade implications are likely to be minimal. Should the investigation show that the contamination is from commingled seed, or that the GE wheat is widely dispersed, the trade implications could be more significant. Congressional Research Service
3 Contents Genetically Engineered Wheat: Background... 1 Federal Regulation of Genetically Engineered Plants... 2 Safety of GE Wheat for Food and Feed... 3 United States Wheat Export Markets... 4 Policy Implications... 4 Contacts Author Contact Information... 5 Congressional Research Service
4 Genetically Engineered Wheat: Background Between 1998 and 2005, the Monsanto Company field-tested a variety of genetically engineered (GE) wheat that was tolerant of glyphosate, a widely used, broad-spectrum herbicide marketed by the Monsanto Company under its trade name, Roundup. 1 Many crop varieties, including soybeans, cotton, alfalfa, sugar beets, and canola, have been similarly engineered to be tolerant of glyphosate. These varieties constitute the largest acreage of GE plants globally. In 2005, Monsanto halted its field trials of GE wheat and withdrew its application for deregulated status. There was concern that the Canadian and Australian Wheat Boards might not approve the glyphosate-tolerant variety, leading Monsanto to reevaluate the marketability of the GE wheat variety at that time. With Monsanto s withdrawal of its application to deregulate and commercialize the GE wheat, no GE wheat varieties have been approved by the U.S. Department of Agriculture s (USDA s) Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS), the principal regulator of GE plants released into the environment. A letter from USDA s Grain Inspection, Packers, and Stockyards Administration (GIPSA) stated further that there are no transgenic wheat varieties for sale or in commercial production in the United States at this time. 2 In spring 2013, an eastern Oregon farmer, spraying glyphosate in preparation for planting, discovered volunteer wheat plants in part of the 80-acre field that were not killed by the herbicide. 3 On April 30, 2013, the grower took samples of the plants to be tested at Oregon State University. Preliminary tests by a scientist at the university indicated the possible presence of GE glyphosate-tolerant wheat plants. On May 3, the scientist notified APHIS of the preliminary test results, and APHIS began a formal investigation. 4 Subsequent test results by APHIS indicated the presence of a glyphosate-tolerant wheat variety field-tested by Monsanto under APHIS approval at approximately 100 field trials in 16 states between 1998 and The agency approved field testing of GE wheat in Oregon in As of early June, APHIS does not yet know how the presence of the unapproved wheat variety occurred, how the GE wheat appeared in the field after so many years, whether regulatory violations occurred, or whether the growth of the wheat is more widespread than a single field in Oregon. Answering these questions is among the primary objectives of the APHIS investigation. 1 Monsanto Company is the world s largest seed owner and a major corporate presence in global agricultural biotechnology. While there are no commercialized GE wheat varieties, most of the world s acreage planted to GE crops is planted in glyphosate-tolerant varieties developed and licensed by Monsanto (e.g., soybean, canola, cotton). For more information on the seed industry and biotechnology, see CRS Report RL32809, Agricultural Biotechnology: Background, Regulation, and Policy Issues, by Tadlock Cowan. 2 See May 31, 2013, letter from John B. Pitchford, Director, Departmental Initiatives and International Affairs, USDA, Grain Inspection, Packers and Stockyards Administration, at 3 Volunteers are plants that have germinated and grown in a place where they were not intentionally planted. 4 APHIS has referred the investigation to its Investigative and Enforcement Services, in addition to its onsite investigation. APHIS also has a memorandum of understanding with USDA s Agricultural Marketing Service and Grain Inspection, Packers, and Stockyards Administration to provide technical sampling and testing expertise when needed. Congressional Research Service 1
5 Federal Regulation of Genetically Engineered Plants The basic federal guidance for regulating biotechnology products is the Coordinated Framework for Regulation of Biotechnology published in 1986 by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP). 5 A key regulatory principle in the U.S. biotechnology regulatory structure is that genetically engineered products should continue to be regulated according to their characteristics and unique features, not their production method that is, whether or not they were created through biotechnology. The framework provides a regulatory approach intended to ensure the safety of biotechnology research and products, using existing statutory authority and previous agency experience with traditional breeding techniques. Three lead federal agencies regulate genetically modified organisms: USDA s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS); the Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration (FDA); and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). APHIS regulates plants engineered to be herbicide-tolerant. EPA, with APHIS, regulates plants that contain pesticides, such as the many corn varieties that are engineered with Bacillus thuringiensis to be resistant to certain pests, such as corn borer. 6 FDA has regulatory authority under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act for the safety and nutritional quality of GE foods and feeds. APHIS regulates the importation, interstate movement, and field testing of GE plants and organisms that are or might be plant pests under the Plant Protection Act (PPA; 7 U.S.C et seq.). APHIS also regulates animal biologics (i.e., viruses, serums, toxins for animal vaccines) under the Virus, Serum, and Toxins Act (21 U.S.C. 151 et seq.). Specifically, GE plants that are or might be plant pests are considered regulated articles under APHIS regulations (7 C.F.R ). APHIS authorization must be obtained prior to import, interstate movement, or environmental release, including field testing. More specifically, a regulated plant cannot be introduced into the environment, or even field tested, unless its developer obtains APHIS authorization through (1) the permit process or (2) the notification process. Permits impose restrictions on movement and planting to prevent escape of plant material that may pose a pest risk. Sponsors follow APHIS guidance on testing and movements to ensure that the plant will not damage agriculture, human health, or the environment. Most GE crops have been developed under the notification option, an expedited procedure that is less rigorous than permitting. Notification can be used in lieu of permitting when the plant species is not considered a noxious weed (or weed in the release area), and other APHIS standards are met Federal Register, EPA regulates pesticides under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (7 U.S.C 121 et seq.), as amended. 7 The notification procedure is the streamlined authorization process used only for GE plants that qualify based on APHIS regulatory criteria. Permits may be used for any GE plant, but are required for plants that do not meet APHIS s criteria for the expedited notification procedure. In addition to following conditions required by regulations under the (continued...) Congressional Research Service 2
6 Regardless of the process chosen, after testing is completed, a developer next seeks nonregulated status from APHIS, the typical route to full commercialization and no further formal oversight. The developer must provide APHIS with extensive information on plant biology and genetics, and potential environmental and plant pest impacts that may result from the modification. APHIS conducts a formal environmental assessment (EA) under the National Environmental Protection Act and has public comment periods before deciding whether to approve the developer s request for non-regulated status. Once the GE plant is deregulated, it is no longer subject to APHIS regulation under 7 C.F.R. Part 340. While a plant remains under APHIS regulatory control (i.e., it remains a regulated article ), APHIS imposes conditions on field testing, harvesting, and transporting GE materials. APHIS could also impose penalties up to $1 million for violations under the PPA. Should tests show the presence of an unapproved GE trait in shipments of grains or in commercial seed, APHIS would determine whether remedial action was necessary to protect plant health or the environment under the authority of the PPA. Given that FDA has concluded that there are no health or safety concerns from consuming food or feed derived from the GE wheat (see below), APHIS has stated that it would not take steps to remove low-level presence (LLP) of this variety from the food supply. 8 Low-level presence is the commingling of genes and gene products from unintended plant sources, whether conventionally bred plants or those derived from biotechnology. APHIS s LLP policy was clarified in March 2007 and considers six safety-related criteria when determining a GE plant material s potential to pose a risk to plant health or to the environment. 9 Safety of GE Wheat for Food and Feed While the glyphosate-tolerant GE wheat was never deregulated by APHIS, Monsanto submitted materials to FDA on the biological characteristics of the GE variety for a determination of the variety s safety. FDA completed a voluntary consultation on the safety of food and feed derived from the glyphosate-tolerant GE wheat in 2004, and agreed with Monsanto that the GE wheat was not materially different in composition, safety, or any other relevant parameter from wheat now grown, marketed, and consumed. 10 In other words, FDA concluded that food and feed derived from GE wheat was as safe as and nutritionally equivalent to food and feed derived from non-ge wheat. Once a determination is made by FDA on the substantial equivalence of a GE variety compared to a non-ge variety, FDA s role in the regulatory process typically ends. (...continued) Plant Protection Act, permits impose additional conditions specific to the application. 8 APHIS. Biotechnology Regulatory Services. Questions and Answers: USDA Investigating Detection of Positive Genetically Engineered Glyphosate-Resistant Wheat in Oregon, May 2013, biotechnology/2013/faq_brs_ge_wheat_detection.pdf. 9 APHIS. Biotechnology Regulatory Services. Low-Level Presence, March 2007, publications/biotechnology/content/printable_version/fs_llppolicy pdf. 10 FDA s summary of their consultative process can be found at the following FDA site: FoodScienceResearch/Biotechnology/Submissions/ucm htm. Congressional Research Service 3
7 United States Wheat Export Markets APHIS has stated that, as of early June 2013, there is no evidence that GE wheat has entered commerce. Initial tests of wheat imported by Japan, Korea, and the European Union have found no evidence of the unapproved GE trait. Although the United States produces only about 10% of the world s wheat, it is consistently the world s largest wheat exporter. The United States exports about 50% of its wheat crop, and Oregon exports nearly 90% of its wheat crop. 11 In its March 2013 National Agricultural Statistical Service (NASS) Prospective Plantings report, USDA projected U.S. winter wheat seedings in fall 2012 for harvest in 2013 of million acres, up 1.3% (or 704,000 acres) from million acres in 2012, and also up from million acres in Many countries have zero-tolerance policies regarding imports of unapproved GE varieties. Japan, the largest buyer of U.S. wheat, and South Korea have temporarily halted imports of U.S. soft white wheat grown in Oregon and the Pacific Northwest. Japan has continued to purchase U.S. hard red spring wheat and hard red winter wheat. Monsanto Company, the variety s developer, provided a validated testing method for the presence of the GE trait to APHIS and to government regulators in Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and the European Union. 12 According to a Monsanto spokesman, the test would allow governments to test for the original GE trait named the MON71800 genetic event while distinguishing it from similar traits approved and used in other crops. Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack stated that APHIS will use an independent test to reassure wheat importers that their wheat shipments are free of any GE trait. Policy Implications Incidents of regulatory noncompliance have continued to raise concerns about the adequacy of biotechnology regulatory structures. In December 2008, a small amount of unapproved GE cotton was harvested along with commercially available GE cotton. The unapproved GE cotton variety produces a pesticide that is a plant-incorporated protectant (PIP). In August 2006, traces of an unapproved variety of GE rice Liberty Link were reported in commercial rice samples from parts of the southern United States. APHIS subsequently retroactively approved the variety, but not before rice prices fell and the European Union and Japan refused to buy from the United States. In 2001, a variety of GE corn known as StarLink was discovered in taco shells made by Kraft Foods. The GE corn had been approved by APHIS, but only as an animal feed and not for human consumption. In that case, hundreds of corn products were recalled, and Aventis, the developer of the GE corn, paid over $120 million to settle various lawsuits The United States top wheat export markets are Japan, Mexico, Nigeria, the Philippines, Egypt, South Korea, and Taiwan. 12 A Monsanto spokesman told CRS that the test the company provided to APHIS and other governments was an event-specific assay that can determine the specific glyphosate-tolerant trait of the GE wheat variety (MON71800), but avoids false positives. False positives can result from less accurate strip tests and dip-stick tests that might not differentiate the presence of a glyphosate-tolerance trait in other approved crop varieties (e.g., soybeans) from the specific genetic MON71800 event of the glyphosate-tolerant wheat. 13 On June 4, a Kansas wheat farmer filed suit in federal court against Monsanto for gross negligence over the GE wheat discovery. The suit is seeking unspecified damages for lower wheat prices triggered by the export limits. See Congressional Research Service 4
8 At this time, APHIS does not know whether the GE wheat incident has similar characteristics to these earlier cases. If APHIS s investigation shows that the GE wheat is isolated to the one field and a few volunteer wheat plants, the trade implications are likely to be minimal. Should the investigation show that the contamination is from commingled seed, and not just the few volunteer plants in an Oregon field, and that the GE wheat or seed is widely dispersed, the trade implications could be more significant. The incident is also likely to continue fueling criticism of those opposed to GE crops in general, and those who question the strength and reliability of APHIS s regulatory oversight of GE plants. Author Contact Information Tadlock Cowan Analyst in Natural Resources and Rural Development tcowan@crs.loc.gov, Congressional Research Service 5
Unapproved Genetically Modified Wheat Discovered in Oregon and Montana: Status and Implications
 Discovered in Oregon and Montana: Status and Implications name redacted Analyst in Natural Resources and Rural Development December 4, 2014 Congressional Research Service 7-... www.crs.gov R43100 Summary
Discovered in Oregon and Montana: Status and Implications name redacted Analyst in Natural Resources and Rural Development December 4, 2014 Congressional Research Service 7-... www.crs.gov R43100 Summary
Report of LibertyLink Rice Incidents
 Report of LibertyLink Rice Incidents Introduction This report summarizes the U.S. Department of Agriculture s (USDA) response to the low-level presence of two regulated lines of genetically engineered
Report of LibertyLink Rice Incidents Introduction This report summarizes the U.S. Department of Agriculture s (USDA) response to the low-level presence of two regulated lines of genetically engineered
USDA-APHIS Biotechnology Regulatory Services Janet L. Bucknall Associate Deputy Administrator
 USDA-APHIS Biotechnology Regulatory Services Janet L. Bucknall Associate Deputy Administrator National Conference of State Legislatures Capitol Forum, Washington DC December 8, 2015 USDA APHIS BRS Mission
USDA-APHIS Biotechnology Regulatory Services Janet L. Bucknall Associate Deputy Administrator National Conference of State Legislatures Capitol Forum, Washington DC December 8, 2015 USDA APHIS BRS Mission
Regulation of Agricultural Biotechnology in the United States: Overview
 Regulation of Agricultural Biotechnology in the United States: Overview Webinar for: National Agricultural Law Center July 15, 2015 Michael J. Firko, Ph.D. APHIS Deputy Administrator (BRS) History of Plant
Regulation of Agricultural Biotechnology in the United States: Overview Webinar for: National Agricultural Law Center July 15, 2015 Michael J. Firko, Ph.D. APHIS Deputy Administrator (BRS) History of Plant
The Regulation of GM crops in the United States
 The Regulation of GM crops in the United States GMO Technology Conference: The Regulation and Use of GMO Technology in Ireland 10-11 October 2013 // The Printworks, Dublin Castle Coordinated Framework
The Regulation of GM crops in the United States GMO Technology Conference: The Regulation and Use of GMO Technology in Ireland 10-11 October 2013 // The Printworks, Dublin Castle Coordinated Framework
Deregulating Genetically Engineered Alfalfa and Sugar Beets: Legal and Administrative Responses
 Deregulating Genetically Engineered Alfalfa and Sugar Beets: Legal and Administrative Responses Tadlock Cowan Analyst in Natural Resources and Rural Development Kristina Alexander Legislative Attorney
Deregulating Genetically Engineered Alfalfa and Sugar Beets: Legal and Administrative Responses Tadlock Cowan Analyst in Natural Resources and Rural Development Kristina Alexander Legislative Attorney
Incident Report GENETICALLY MODIFIED WHEAT 2018
 Incident Report GENETICALLY MODIFIED WHEAT 2018 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (Canadian Food Inspection Agency), 2018. CFIA P0951-18 ISBN: 978-0-660-26780-7 Catalogue No.: A104-141/2018E-PDF
Incident Report GENETICALLY MODIFIED WHEAT 2018 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (Canadian Food Inspection Agency), 2018. CFIA P0951-18 ISBN: 978-0-660-26780-7 Catalogue No.: A104-141/2018E-PDF
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21418 Updated March 8, 2005 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Regulation of Plant-Based Pharmaceuticals Summary Geoffrey S. Becker Resources, Science, and Industry Division
Order Code RS21418 Updated March 8, 2005 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Regulation of Plant-Based Pharmaceuticals Summary Geoffrey S. Becker Resources, Science, and Industry Division
Bugbears? Maize GE Benefits & Bugbears in the U.S. Benefits & Bugbears. Bugbears? Natural Corn Plant Sex. v , Purdue Univ.
 Maize GE Benefits & Bugbears in the R.L. (Bob) Nielsen Agronomy Department University,, Email: rnielsen@purdue.edu Web: www.kingcorn.org/rln-bio.htm Links Links to to this this presentation can can be
Maize GE Benefits & Bugbears in the R.L. (Bob) Nielsen Agronomy Department University,, Email: rnielsen@purdue.edu Web: www.kingcorn.org/rln-bio.htm Links Links to to this this presentation can can be
Identify government agencies involved in biotechnology. 1. What is the role of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in biotechnology?
 UNIT II - ISSUES IN BIOTECHNOLOGY Lesson 2: Agencies Involved in Biotechnology Competency/Objective: Identify government agencies involved in biotechnology. Study Questions References 1. What is the role
UNIT II - ISSUES IN BIOTECHNOLOGY Lesson 2: Agencies Involved in Biotechnology Competency/Objective: Identify government agencies involved in biotechnology. Study Questions References 1. What is the role
Re: Application for importation and trial release of Roundup Ready canola line RT73.
 Re: Application for importation and trial release of Roundup Ready canola line RT73. With reference to Monsanto s application for importation and trial release of Roundup Ready canola RT73, reference number
Re: Application for importation and trial release of Roundup Ready canola line RT73. With reference to Monsanto s application for importation and trial release of Roundup Ready canola RT73, reference number
Maize GE Benefits & Bugbears in the U.S.
 FAR FAR New New Zealand Zealand Maize Maize Conference Conference 12-13 12-13 Feb Feb 2003, 2003, Hamilton, Hamilton, New New Zealand Zealand Maize GE Benefits & Bugbears in the U.S. R.L. (Bob) Nielsen
FAR FAR New New Zealand Zealand Maize Maize Conference Conference 12-13 12-13 Feb Feb 2003, 2003, Hamilton, Hamilton, New New Zealand Zealand Maize GE Benefits & Bugbears in the U.S. R.L. (Bob) Nielsen
CSPI s Comments to EPA FIFRA SAP on Bt Corn and Rootworm Resistance
 CSPI s Comments to EPA FIFRA SAP on Bt Corn and Rootworm Resistance Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project Center for Science in the Public Interest December 4, 2013 Summary of my comments Background
CSPI s Comments to EPA FIFRA SAP on Bt Corn and Rootworm Resistance Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project Center for Science in the Public Interest December 4, 2013 Summary of my comments Background
Regulatory slowdown on GM crop decisions
 CORRESPONDENCE Regulatory slowdown on GM crop decisions 2006 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/naturebiotechnology To the editor: The speed of regulatory decision-making is an important constraint
CORRESPONDENCE Regulatory slowdown on GM crop decisions 2006 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/naturebiotechnology To the editor: The speed of regulatory decision-making is an important constraint
Environmental release of plants with novel traits in Canada: A product-based approach to regulatory oversight
 Environmental release of plants with novel traits in Canada: A product-based approach to regulatory oversight Cindy Pearson CFIA Plant Biosafety Office OUTLINE Canadian regulatory framework for biotechnology
Environmental release of plants with novel traits in Canada: A product-based approach to regulatory oversight Cindy Pearson CFIA Plant Biosafety Office OUTLINE Canadian regulatory framework for biotechnology
Regulation of New Plant Breeding Techniques in Canada and the United States
 Regulation of New Plant Breeding Techniques in Canada and the United States New Breeding Techniques RNA interference Cisgenesis and intragenesis Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis Grafting (on transgenic
Regulation of New Plant Breeding Techniques in Canada and the United States New Breeding Techniques RNA interference Cisgenesis and intragenesis Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis Grafting (on transgenic
PRINSIP BIOTEKNOLOGY. Application of Biotech on Plants, Agriculture
 PRINSIP BIOTEKNOLOGY Application of Biotech on Plants, Agriculture Materi Traditional methods, selective breeding Recombinant DNA technology How to deliver genes in plants The major concerns about GMO
PRINSIP BIOTEKNOLOGY Application of Biotech on Plants, Agriculture Materi Traditional methods, selective breeding Recombinant DNA technology How to deliver genes in plants The major concerns about GMO
GE crops and gene flow Roundup Ready Wheat and related Problems. Steve Strauss and Carol Mallory-Smith Oregon State University
 GE crops and gene flow Roundup Ready Wheat and related Problems Steve Strauss and Carol Mallory-Smith Oregon State University Plan The problem Gene flow concepts Two case studies with Oregon focus Roundup
GE crops and gene flow Roundup Ready Wheat and related Problems Steve Strauss and Carol Mallory-Smith Oregon State University Plan The problem Gene flow concepts Two case studies with Oregon focus Roundup
Agricultural Biotechnology: Background and Recent Issues
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Congressional Research Service Reports Congressional Research Service 2010 Agricultural Biotechnology: Background and Recent
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Congressional Research Service Reports Congressional Research Service 2010 Agricultural Biotechnology: Background and Recent
Genetically Engineered Crops in the United States
 Genetically Engineered Crops in the United States James MacDonald USDA Economic Research Service Briefing to OECD Network on Farm-Level Analysis Paris, June, 2014 An ERS Report Genetically Engineered Crops
Genetically Engineered Crops in the United States James MacDonald USDA Economic Research Service Briefing to OECD Network on Farm-Level Analysis Paris, June, 2014 An ERS Report Genetically Engineered Crops
Case3:08-cv JSW Document277 Filed02/12/10 Page1 of 18
 Case3:08-cv-00484-JSW Document277 Filed02/12/10 Page1 of 18 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE NORTHERN DISTRICT OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO DIVISION CENTER FOR FOOD SAFETY, et al., ) Case No.: 3:08-cv-00484-JSW
Case3:08-cv-00484-JSW Document277 Filed02/12/10 Page1 of 18 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE NORTHERN DISTRICT OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO DIVISION CENTER FOR FOOD SAFETY, et al., ) Case No.: 3:08-cv-00484-JSW
Post-Market Oversight of Biotech Foods
 Post-Market Oversight of Biotech Foods IS THE SYSTEM PREPARED? MICHAEL R. TAYLOR and JODY S. TICK APRIL 2003 A report commissioned by the Pew Initiative on Food and Biotechnology and prepared by Resources
Post-Market Oversight of Biotech Foods IS THE SYSTEM PREPARED? MICHAEL R. TAYLOR and JODY S. TICK APRIL 2003 A report commissioned by the Pew Initiative on Food and Biotechnology and prepared by Resources
DELIVERING A SYSTEM FOR HIGHER YIELD IN CANOLA
 DELIVERING A SYSTEM FOR HIGHER YIELD IN CANOLA System of Solutions Come Together in Our Pipeline Development Process Monsanto s R&D Pipeline Designed to Address Farmers Challenges Increase Yield Impact
DELIVERING A SYSTEM FOR HIGHER YIELD IN CANOLA System of Solutions Come Together in Our Pipeline Development Process Monsanto s R&D Pipeline Designed to Address Farmers Challenges Increase Yield Impact
IS THE US FDA REGULATION AND EVALUATION OF GENETICALLY ENGINEEERED FOODS SUFFICIENT? Teresa Marek FOOD REGULATION IN THE UNITED STATES
 IS THE US FDA REGULATION AND EVALUATION OF GENETICALLY ENGINEEERED FOODS SUFFICIENT? by Teresa Marek FOOD REGULATION IN THE UNITED STATES Professor Neal Fortin April 25, 2008-1 - IS THE US FDA REGULATION
IS THE US FDA REGULATION AND EVALUATION OF GENETICALLY ENGINEEERED FOODS SUFFICIENT? by Teresa Marek FOOD REGULATION IN THE UNITED STATES Professor Neal Fortin April 25, 2008-1 - IS THE US FDA REGULATION
USDA APHIS Requirements for Rookies Doug Grant, Ph.D. Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch
 USDA APHIS Requirements for Rookies Doug Grant, Ph.D. Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January 30, 2014 APHIS BRS For Rookies
USDA APHIS Requirements for Rookies Doug Grant, Ph.D. Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January 30, 2014 APHIS BRS For Rookies
HOW OUR FOOD IS GROWN
 OPEN TO YOUR QUESTIONS ABOUT HOW OUR FOOD IS GROWN Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are a major topic of discussion today. Across our society, media and the Internet, a growing number of people have
OPEN TO YOUR QUESTIONS ABOUT HOW OUR FOOD IS GROWN Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are a major topic of discussion today. Across our society, media and the Internet, a growing number of people have
The Role of USDA APHIS in Regulating Biotechnology in the U.S.
 The Role of USDA APHIS in Regulating Biotechnology in the U.S. John Turner Director, Environmental Risk Analysis Programs Specialty Crop Regulatory Assistance Workshop December 6-8, 2011 What Does APHIS
The Role of USDA APHIS in Regulating Biotechnology in the U.S. John Turner Director, Environmental Risk Analysis Programs Specialty Crop Regulatory Assistance Workshop December 6-8, 2011 What Does APHIS
Frequently Asked Questions about Biotechnology
 You are here: Home / Agriculture All USDA Information For... Frequently Asked Questions about Biotechnology 1. What is Agricultural Biotechnology? Agricultural biotechnology is a range of tools, including
You are here: Home / Agriculture All USDA Information For... Frequently Asked Questions about Biotechnology 1. What is Agricultural Biotechnology? Agricultural biotechnology is a range of tools, including
USDA Regulation of Organisms Developed Through Modern Breeding Technologies
 USDA Regulation of Organisms Developed Through Modern Breeding Technologies Neil E. Hoffman USDA-Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Riverdale, Maryland neil.e.hoffman@aphis.usda.gov The federal
USDA Regulation of Organisms Developed Through Modern Breeding Technologies Neil E. Hoffman USDA-Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Riverdale, Maryland neil.e.hoffman@aphis.usda.gov The federal
Genetically Modified Organisms
 Genetically Modified Organisms 1 Genetically Modified Organisms Farmers have been genetically modifying plants for 1000s of years Must take undesirable traits with those selected for Modern technology
Genetically Modified Organisms 1 Genetically Modified Organisms Farmers have been genetically modifying plants for 1000s of years Must take undesirable traits with those selected for Modern technology
Commercializing StarLink Corn: A Working Paper Chronology of U.S. Regulation By D. L. Uchtmann and S. P. Moose 1
 Commercializing StarLink Corn: A Working Paper Chronology of U.S. Regulation By D. L. Uchtmann and S. P. Moose 1 StarLink corn has become famous because of publicity surrounding its discovery in taco shells
Commercializing StarLink Corn: A Working Paper Chronology of U.S. Regulation By D. L. Uchtmann and S. P. Moose 1 StarLink corn has become famous because of publicity surrounding its discovery in taco shells
Unapproved genetically modified wheat from Monsanto found in Oregon field
 Unapproved genetically modified wheat from Monsanto found in Oregon field By Steven Mufson, Published: May 30, 2013 David King, founder and chairman of the Seed Library of Los Angeles, speaks to activists
Unapproved genetically modified wheat from Monsanto found in Oregon field By Steven Mufson, Published: May 30, 2013 David King, founder and chairman of the Seed Library of Los Angeles, speaks to activists
GMOs: the Myths, Concerns, propaganda and drivers of GMOs. into Nigeria
 GMOs: the Myths, Concerns, propaganda and drivers of GMOs by Nnimmo Bassey @ Just Governance: The Nigerian Biosafety Act and GMOs - Implications for Nigerians and Africa Abuja, 24 May 2016 into Nigeria
GMOs: the Myths, Concerns, propaganda and drivers of GMOs by Nnimmo Bassey @ Just Governance: The Nigerian Biosafety Act and GMOs - Implications for Nigerians and Africa Abuja, 24 May 2016 into Nigeria
USDA APHIS Biotechnology Regulatory Services Update
 USDA APHIS Biotechnology Regulatory Services Update Doug Grant, Ph.D. Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January 24, 2013 Biotechnology
USDA APHIS Biotechnology Regulatory Services Update Doug Grant, Ph.D. Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January 24, 2013 Biotechnology
ISSUES WITH GMO ALFALFA IN THE MARKETPLACE. William T. W. Woodward 1
 ISSUES WITH GMO ALFALFA IN THE MARKETPLACE William T. W. Woodward 1 A GMO (genetically modified organisms) debate that has continued in the past few years on crops such as corn, cotton, canola, soybean,
ISSUES WITH GMO ALFALFA IN THE MARKETPLACE William T. W. Woodward 1 A GMO (genetically modified organisms) debate that has continued in the past few years on crops such as corn, cotton, canola, soybean,
Developments in Biotechnology in the U.S. Wheat Sector. Shannon Schlecht, Director of Policy U.S. Wheat Associates
 Developments in Biotechnology in the U.S. Wheat Sector Shannon Schlecht, Director of Policy U.S. Wheat Associates Biotech Defined Biotechnologically derived crops also referred to as: Genetically modified
Developments in Biotechnology in the U.S. Wheat Sector Shannon Schlecht, Director of Policy U.S. Wheat Associates Biotech Defined Biotechnologically derived crops also referred to as: Genetically modified
NewLeaf Potatoes: Friend or Foe A study of the GMO potato. By Rick Swenson English 320 Final Paper Dr. Sullivan 5/6/04
 NewLeaf Potatoes: Friend or Foe A study of the GMO potato By Rick Swenson English 320 Final Paper Dr. Sullivan 5/6/04 Introduction: In 1995 a new potato variety was introduced to the market, this new potato
NewLeaf Potatoes: Friend or Foe A study of the GMO potato By Rick Swenson English 320 Final Paper Dr. Sullivan 5/6/04 Introduction: In 1995 a new potato variety was introduced to the market, this new potato
1 A Genetically Modified Solution? Th e u n i t e d n a t i o n s World Food Program has clearly stated, Hunger
 1 A Genetically Modified Solution? Th e u n i t e d n a t i o n s World Food Program has clearly stated, Hunger and malnutrition are in fact the number one risk to health worldwide greater than AIDS, malaria,
1 A Genetically Modified Solution? Th e u n i t e d n a t i o n s World Food Program has clearly stated, Hunger and malnutrition are in fact the number one risk to health worldwide greater than AIDS, malaria,
GMO Crops, Trade Wars, and a New Site Specific Mutagensis System. A. Lawrence Christy, Ph.D.
 GMO Crops, Trade Wars, and a New Site Specific Mutagensis System A. Lawrence Christy, Ph.D. Background PhD in Plant Physiology from Ohio State University 12 years with Monsanto R&D in PGR s and herbicides
GMO Crops, Trade Wars, and a New Site Specific Mutagensis System A. Lawrence Christy, Ph.D. Background PhD in Plant Physiology from Ohio State University 12 years with Monsanto R&D in PGR s and herbicides
WITHERING ON THE VINE:
 WITHERING ON THE VINE: WILL AGRICULTURAL BIOTECH S PROMISES BEAR FRUIT? By Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project February 2, 2005 CENTER FOR SCIENCE IN THE PUBLIC INTEREST 1875 Connecticut Avenue,
WITHERING ON THE VINE: WILL AGRICULTURAL BIOTECH S PROMISES BEAR FRUIT? By Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project February 2, 2005 CENTER FOR SCIENCE IN THE PUBLIC INTEREST 1875 Connecticut Avenue,
In a decision that has outraged organic and conventional alfalfa
 Ready or Not, Genetically Engineered Crops Explode on Market USDA allows new GE crops over objections of growers, environmentalists, manufacturers, and retailers By Stephanie Davio and Jay Feldman In a
Ready or Not, Genetically Engineered Crops Explode on Market USDA allows new GE crops over objections of growers, environmentalists, manufacturers, and retailers By Stephanie Davio and Jay Feldman In a
PLANTING TROUBLE: ARE FARMERS SQUANDERING BT CORN TECHNOLOGY?
 PLANTING TROUBLE: ARE FARMERS SQUANDERING BT CORN TECHNOLOGY? AN ANALYSIS OF USDA DATA SHOWING SIGNIFICANT NONCOMPLIANCE WITH EPA S REFUGE REQUIREMENTS by Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project
PLANTING TROUBLE: ARE FARMERS SQUANDERING BT CORN TECHNOLOGY? AN ANALYSIS OF USDA DATA SHOWING SIGNIFICANT NONCOMPLIANCE WITH EPA S REFUGE REQUIREMENTS by Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project
GM Foods: Possible Risks and Opportunities. Dr. Frank Shotkoski, Cornell University, USA
 GM Foods: Possible Risks and Opportunities Dr. Frank Shotkoski, Cornell University, USA crops have been genetically modified during mestication Domestication Selection Mutagenesis Hybridization Transgenic/Cisgenic
GM Foods: Possible Risks and Opportunities Dr. Frank Shotkoski, Cornell University, USA crops have been genetically modified during mestication Domestication Selection Mutagenesis Hybridization Transgenic/Cisgenic
Bt d-endotoxins are globular protein molecules, which accumulate as protoxins in crystalline form during late stage of the sporulation.
 Bt Corn Bt d-endotoxins are globular protein molecules, which accumulate as protoxins in crystalline form during late stage of the sporulation. Protoxins are liberated in the midgut after solubilization
Bt Corn Bt d-endotoxins are globular protein molecules, which accumulate as protoxins in crystalline form during late stage of the sporulation. Protoxins are liberated in the midgut after solubilization
Stewardship and Integrated Pest Management for generic / off patent GM crops
 Stewardship and Integrated Pest Management for generic / off patent GM crops Georges FREYSSINET 1 Stewardship and Integrated Pest Management for generic GM crops Generic Off Patent GM crops Stewardship
Stewardship and Integrated Pest Management for generic / off patent GM crops Georges FREYSSINET 1 Stewardship and Integrated Pest Management for generic GM crops Generic Off Patent GM crops Stewardship
Evogene - Bayer CropScience Multi-year Collaboration to Improve Wheat Seed. December 13, 2010
 Evogene - Bayer CropScience Multi-year Collaboration to Improve Wheat Seed December 13, 2010 1 2 Agenda Evogene Bayer CropScience Collaboration Wheat Background Complementary Capabilities Create Opportunity
Evogene - Bayer CropScience Multi-year Collaboration to Improve Wheat Seed December 13, 2010 1 2 Agenda Evogene Bayer CropScience Collaboration Wheat Background Complementary Capabilities Create Opportunity
2015 Pesticide Safety: Understnding GMO's
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Cranberry Station Extension meetings Cranberry Station Outreach and Public Service Activities 4-2015 2015 Pesticide Safety: Understnding GMO's
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Cranberry Station Extension meetings Cranberry Station Outreach and Public Service Activities 4-2015 2015 Pesticide Safety: Understnding GMO's
FDA Regulation of Food
 FDA Regulation of Food from New Plant Varieties Patrick Cournoyer, PhD U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition Office of Food Additive Safety Does FDA regulate genome
FDA Regulation of Food from New Plant Varieties Patrick Cournoyer, PhD U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition Office of Food Additive Safety Does FDA regulate genome
Loomis/CBC Joint Symposium and Workshop Genome Editing Putting Together the Pieces Innovation and USDA Regulation of the Products of Biotechnology
 Loomis/CBC Joint Symposium and Workshop Genome Editing Putting Together the Pieces Innovation and USDA Regulation of the Products of Biotechnology May 9, 2018 Sally L. McCammon Science Advisor Biotechnology
Loomis/CBC Joint Symposium and Workshop Genome Editing Putting Together the Pieces Innovation and USDA Regulation of the Products of Biotechnology May 9, 2018 Sally L. McCammon Science Advisor Biotechnology
Virus disease resistance Herbicide tolerance, modified product quality, pollination control system Herbicide tolerance, insect resistance
 Pocket K No. 2 Plant Products of Biotechnology Plant products of biotechnology have been available in the market for some time now. These modified crops look like their traditional counterparts, but they
Pocket K No. 2 Plant Products of Biotechnology Plant products of biotechnology have been available in the market for some time now. These modified crops look like their traditional counterparts, but they
Chapter 6: Plant Biotechnology
 Chapter 6: Plant Biotechnology Chapter Contents 6.1 The Future of Agriculture: Plant Transgenics 6.2 Methods Used in Plant Transgenesis 6.3 Practical Applications 6.4 Health and Environmental Concerns
Chapter 6: Plant Biotechnology Chapter Contents 6.1 The Future of Agriculture: Plant Transgenics 6.2 Methods Used in Plant Transgenesis 6.3 Practical Applications 6.4 Health and Environmental Concerns
Kansas State University Working with Industry Boot Camp
 Kansas State University Working with Industry Boot Camp Session III: How to Formalize the Relationship Connie M. Armentrout, Director, Academic Technology Licensing Monsanto Company Technology Alliances
Kansas State University Working with Industry Boot Camp Session III: How to Formalize the Relationship Connie M. Armentrout, Director, Academic Technology Licensing Monsanto Company Technology Alliances
Yield10 Bioscience, Inc.
 Yield10 Bioscience, Inc. (NASDAQCM:YTEN) Third Quarter 2018 Conference Call Yield10 is developing new technologies to achieve step-changes in crop yield to enhance global food security November 8, 2018
Yield10 Bioscience, Inc. (NASDAQCM:YTEN) Third Quarter 2018 Conference Call Yield10 is developing new technologies to achieve step-changes in crop yield to enhance global food security November 8, 2018
Regulatory experiences and ideas. Steve Strauss Oregon State University
 Regulatory experiences and ideas Steve Strauss Oregon State University Steve.Strauss@oregonstate.edu Plan My experience with GMO trees, regulations A scary lesson in regulatory compliance Ideas for regulatory
Regulatory experiences and ideas Steve Strauss Oregon State University Steve.Strauss@oregonstate.edu Plan My experience with GMO trees, regulations A scary lesson in regulatory compliance Ideas for regulatory
tractors. Using herbicides avoids that, while herbicide tolerant crops make the use of herbicides simpler.
 Benefits of GM crops Monsanto, as a company is committed to sustainable agriculture and development and recognises that there are many challenges in delivering the results of research to the great diversity
Benefits of GM crops Monsanto, as a company is committed to sustainable agriculture and development and recognises that there are many challenges in delivering the results of research to the great diversity
Coexistence of Biotech, Organic and Conventional Crops: Facts. Issues and a Path Forward
 Coexistence of Biotech, Organic and Conventional Crops: Facts. Issues and a Path Forward Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project Center for Science in the Public Interest June 2, 2015 Summary of
Coexistence of Biotech, Organic and Conventional Crops: Facts. Issues and a Path Forward Gregory Jaffe Director, Biotechnology Project Center for Science in the Public Interest June 2, 2015 Summary of
CONTENTS SUMMARY MOST RECENT DEVELOPMENTS BACKGROUND AND ANALYSIS Adoption of Biotechnology in Agriculture Current Applications U.S. Food Products Con
 Order Code IB10131 CRS Issue Brief for Congress Received through the CRS Web Agricultural Biotechnology: Overview and Selected Issues Updated June 4, 2004 Geoffrey S. Becker Resources, Science, and Industry
Order Code IB10131 CRS Issue Brief for Congress Received through the CRS Web Agricultural Biotechnology: Overview and Selected Issues Updated June 4, 2004 Geoffrey S. Becker Resources, Science, and Industry
Wisconsin Briefs. from the Legislative Reference Bureau GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROPS. Brief December 2012
 Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau Wisconsin Briefs from the Legislative Reference Bureau Brief 12-10 December 2012 GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROPS INTRODUCTION The development of genetically modified (GM)
Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau Wisconsin Briefs from the Legislative Reference Bureau Brief 12-10 December 2012 GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROPS INTRODUCTION The development of genetically modified (GM)
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry FDA recommendations for sampling and testing yellow corn and dry-milled yellow corn shipments intended for human food use for Cry9C protein residues Final Guidance This guidance represents
Guidance for Industry FDA recommendations for sampling and testing yellow corn and dry-milled yellow corn shipments intended for human food use for Cry9C protein residues Final Guidance This guidance represents
Non GMO Crop Production. Joe Lawrence
 Non GMO Crop Production Joe Lawrence 1 Crops of Potential Interest: DAIRY Field Crops where certain varieties/hybrids contain GE Traits Corn Cotton Alfalfa Canola Soybean Sugar Beets Conventional term
Non GMO Crop Production Joe Lawrence 1 Crops of Potential Interest: DAIRY Field Crops where certain varieties/hybrids contain GE Traits Corn Cotton Alfalfa Canola Soybean Sugar Beets Conventional term
GMO Questions from the Community WFSG Meeting July 19, Q: May we get a copy of/receive the presenters power points?
 GMO Questions from the Community WFSG Meeting July 19, 2012 Categories: I. Questions to GMO companies: General 1. Q: May we get a copy of/receive the presenters power points? 2. Q: Why don t you hire independent
GMO Questions from the Community WFSG Meeting July 19, 2012 Categories: I. Questions to GMO companies: General 1. Q: May we get a copy of/receive the presenters power points? 2. Q: Why don t you hire independent
Regulating Transgenic "Pharm" Plants: Pre-Commercialization Review and Post-Commercialization Monitoring
 Regulating Transgenic "Pharm" Plants: Pre-Commercialization Review and Post-Commercialization Monitoring The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Regulating Transgenic "Pharm" Plants: Pre-Commercialization Review and Post-Commercialization Monitoring The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
5/24/ Food & Agriculture National Conference. Jim Schweigert. Managing the First Genetically Engineered. Events to Go Off Patent 1.
 Events to Go Off Patent Panel Jarrett Abramson Senior Intellectual Property Counsel at International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) CGIAR Consortium Jim Schweigert President Gro Alliance Stacey
Events to Go Off Patent Panel Jarrett Abramson Senior Intellectual Property Counsel at International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) CGIAR Consortium Jim Schweigert President Gro Alliance Stacey
Managing the First Genetically Engineered Events to Go Off Patent
 Managing the First Genetically Engineered Events to Go Off Patent Panel Jarrett Abramson Senior Intellectual Property Counsel at International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) CGIAR Consortium
Managing the First Genetically Engineered Events to Go Off Patent Panel Jarrett Abramson Senior Intellectual Property Counsel at International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) CGIAR Consortium
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL32809 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Agricultural Biotechnology: Background and Recent Issues March 7, 2005 Geoffrey S. Becker Specialist in Agricultural Policy Resources,
Order Code RL32809 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Agricultural Biotechnology: Background and Recent Issues March 7, 2005 Geoffrey S. Becker Specialist in Agricultural Policy Resources,
Genetically Engineered Crops: What are They? Who s Growing Them? Who s Eating Them? Who Cares?
 Genetically Engineered Crops: What are They? Who s Growing Them? Who s Eating Them? Who Cares? Margaret Smith Dept. Plant Breeding and Genetics Cornell University Topics Why the controversy? What is genetic
Genetically Engineered Crops: What are They? Who s Growing Them? Who s Eating Them? Who Cares? Margaret Smith Dept. Plant Breeding and Genetics Cornell University Topics Why the controversy? What is genetic
FDA Regulation of Food from GE Crops
 FDA Regulation of Food from GE Crops Patrick Cournoyer, Ph.D. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition Office of Food Additive Safety Overview Historical perspective:
FDA Regulation of Food from GE Crops Patrick Cournoyer, Ph.D. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition Office of Food Additive Safety Overview Historical perspective:
Case 2:13-cv KHV-KMH Document 37 Filed 03/07/14 Page 1 of 33 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF KANSAS
 Case 2:13-cv-02562-KHV-KMH Document 37 Filed 03/07/14 Page 1 of 33 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF KANSAS IN RE: MONSANTO COMPANY GENETICALLY- MDL No: 2473 ENGINEERED WHEAT LITIGATION
Case 2:13-cv-02562-KHV-KMH Document 37 Filed 03/07/14 Page 1 of 33 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF KANSAS IN RE: MONSANTO COMPANY GENETICALLY- MDL No: 2473 ENGINEERED WHEAT LITIGATION
Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
 Details Utah State University Engineering in This is a project resulting from the Engineering Workshop for Teachers to provide teaching materials for genetic engineering topics. Please direct any feedback
Details Utah State University Engineering in This is a project resulting from the Engineering Workshop for Teachers to provide teaching materials for genetic engineering topics. Please direct any feedback
Testimony of the Biotechnology Industry Organization. Submitted to the California Assembly Committee on Agriculture.
 Testimony of the Biotechnology Industry Organization Submitted to the California Assembly Committee on Agriculture Regarding Assembly Bill 984: Manufacturer Liability On behalf of the members of the Biotechnology
Testimony of the Biotechnology Industry Organization Submitted to the California Assembly Committee on Agriculture Regarding Assembly Bill 984: Manufacturer Liability On behalf of the members of the Biotechnology
Position Paper. Regulation of Plant Biotechnology Products Containing Two or More Traits Combined By Conventional Plant Breeding
 Position Paper Regulation of Plant Biotechnology Products Containing Two or More Traits Combined By Conventional Plant Breeding 24 January 2005 We support the following policy regarding plant biotechnology
Position Paper Regulation of Plant Biotechnology Products Containing Two or More Traits Combined By Conventional Plant Breeding 24 January 2005 We support the following policy regarding plant biotechnology
Office of Pest Management Policy (OPMP)
 Office of Pest Management Policy (OPMP) US Department of Agriculture Sheryl H. Kunickis, Ph.D. Director 7 U.S. Code 7653 - Office of Pest Management Policy a) Purpose The purpose of this section is to
Office of Pest Management Policy (OPMP) US Department of Agriculture Sheryl H. Kunickis, Ph.D. Director 7 U.S. Code 7653 - Office of Pest Management Policy a) Purpose The purpose of this section is to
Genetically Modified Organisms
 Genetically Modified Organisms 1 Genetically Modified Organisms! Farmers have been genetically modifying plants for 1000s of years! Modern technology allows for the insertion of desirable genes into target
Genetically Modified Organisms 1 Genetically Modified Organisms! Farmers have been genetically modifying plants for 1000s of years! Modern technology allows for the insertion of desirable genes into target
State of Organic Seed Report 2010: Organic Seed Survey Results
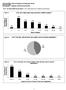 Q #1: In which state do you farm? 1027 responses from 45 states and territories. Figure 1. Q #2: How many years have you been certified organic? 31% 3% 21% 19% 14% 7% 4% 1%
Q #1: In which state do you farm? 1027 responses from 45 states and territories. Figure 1. Q #2: How many years have you been certified organic? 31% 3% 21% 19% 14% 7% 4% 1%
PROTECTING HEALTH, ENVIRONMENT
 PROTECTING HEALTH, ENVIRONMENT AND AGRICULTURE: AUTHORISATION OF GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROPS AND FOOD IN THE UNITED STATES AND THE EUROPEAN UNION MARGARET ROSSO GROSSMAN Millions of agricultural producers
PROTECTING HEALTH, ENVIRONMENT AND AGRICULTURE: AUTHORISATION OF GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROPS AND FOOD IN THE UNITED STATES AND THE EUROPEAN UNION MARGARET ROSSO GROSSMAN Millions of agricultural producers
2008/SOM1/HLPDAB/008 Agenda Item: 2
 2008/SOM1/HLPDAB/008 Agenda Item: 2 United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS): Implications of Transparent Policies and Regulations in Agricultural
2008/SOM1/HLPDAB/008 Agenda Item: 2 United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS): Implications of Transparent Policies and Regulations in Agricultural
Managing Pesticide Resistance
 Kentucky Pesticide Education Program copyright 2016 University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Managing Pesticide Resistance Pesticide resistance presents an increasing challenge to growers. A resistant
Kentucky Pesticide Education Program copyright 2016 University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Managing Pesticide Resistance Pesticide resistance presents an increasing challenge to growers. A resistant
GMO CONTAMINATION PREVENTION
 UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA Southwest Research and Outreach Center GMO CONTAMINATION PREVENTION What Does it Take? By Jim Riddle, Organic Outreach Coordinator Best Management Practices for Producers of GMO
UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA Southwest Research and Outreach Center GMO CONTAMINATION PREVENTION What Does it Take? By Jim Riddle, Organic Outreach Coordinator Best Management Practices for Producers of GMO
Biotechnology and Genetically Modified Crops
 Biotechnology and Genetically Modified Crops Suggestions for Your Presentation Use a Video to start your presentation. A couple of videos were provided with this slide deck that could be used or use another
Biotechnology and Genetically Modified Crops Suggestions for Your Presentation Use a Video to start your presentation. A couple of videos were provided with this slide deck that could be used or use another
Food & Agricultural Biotechnology CPE Questions
 Food & Agricultural Biotechnology CPE Questions 1. What genetic traits are expressed by the biotechnology crops that have been introduced? a. insect protection b. herbicide resistance c. virus resistance
Food & Agricultural Biotechnology CPE Questions 1. What genetic traits are expressed by the biotechnology crops that have been introduced? a. insect protection b. herbicide resistance c. virus resistance
Biotechnology Regulatory Services Program Update and Hot Topics. National Plant Board
 Biotechnology Regulatory Services Program Update and Hot Topics National Plant Board Doug Grant Chief, WR Compliance Assurance Branch Denver, CO August 9, 2011 Outline Program Update RR Sugarbeet Partial
Biotechnology Regulatory Services Program Update and Hot Topics National Plant Board Doug Grant Chief, WR Compliance Assurance Branch Denver, CO August 9, 2011 Outline Program Update RR Sugarbeet Partial
Global Review of Commercialized Transgenic Crops: 2002 Feature: Bt Maize
 I S A A A INTERNATIONAL SERVICE FOR THE ACQUISITION OF AGRI-BIOTECH APPLICATIONS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Global Review of Commercialized Transgenic Crops: 2002 Feature: Bt Maize by Clive James Chair, ISAAA Board
I S A A A INTERNATIONAL SERVICE FOR THE ACQUISITION OF AGRI-BIOTECH APPLICATIONS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Global Review of Commercialized Transgenic Crops: 2002 Feature: Bt Maize by Clive James Chair, ISAAA Board
Pocket K No. 2. Plant Products of Biotechnology
 Pocket K No. 2 Plant Products of Biotechnology Plant products of biotechnology have been available in the market for 21 years in 2016. These modified crops look like their traditional counterparts, but
Pocket K No. 2 Plant Products of Biotechnology Plant products of biotechnology have been available in the market for 21 years in 2016. These modified crops look like their traditional counterparts, but
National Organic Program March 20, Cheri Courtney Director, Accreditation and International Activities Division USDA National Organic Program
 National Organic Program March 20, 2013 Cheri Courtney Director, Accreditation and International Activities Division USDA National Organic Program Why Organic? Environmentally sound farming systems Biodiversity
National Organic Program March 20, 2013 Cheri Courtney Director, Accreditation and International Activities Division USDA National Organic Program Why Organic? Environmentally sound farming systems Biodiversity
By Doug Gurian-Sherman, Ph.D. Senior Scientist and Director of Sustainable Agriculture, Center for Food Safety
 June 2, 2016 Invited Comments to the National Research Council Committee on Future Biotechnology Products and Opportunities to Enhance the Capabilities of the Biotechnology Regulatory System By Doug Gurian-Sherman,
June 2, 2016 Invited Comments to the National Research Council Committee on Future Biotechnology Products and Opportunities to Enhance the Capabilities of the Biotechnology Regulatory System By Doug Gurian-Sherman,
USDA APHIS Requirements
 USDA APHIS Requirements Catharine Cook, Senior Regulatory Biotechnologist Eastern Compliance Assurance Branch USDA APHIS BRS ROP National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January
USDA APHIS Requirements Catharine Cook, Senior Regulatory Biotechnologist Eastern Compliance Assurance Branch USDA APHIS BRS ROP National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January
National Organic Program Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)
 National Organic Program Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) Miles McEvoy, Deputy Administrator 1/18/2012 1 GMO OVERVIEW The Organic Food Production Act (OFPA) of 1990 does not mention biotechnology, genetic
National Organic Program Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) Miles McEvoy, Deputy Administrator 1/18/2012 1 GMO OVERVIEW The Organic Food Production Act (OFPA) of 1990 does not mention biotechnology, genetic
Foreign Agricultural Service Update United States Department of Agriculture
 Foreign Agricultural Service Update United States Department of Agriculture Mark Rasmussen Plant Division/Office of Agreements and Scientific Affairs ! Lead agricultural trade agency within USDA! Three
Foreign Agricultural Service Update United States Department of Agriculture Mark Rasmussen Plant Division/Office of Agreements and Scientific Affairs ! Lead agricultural trade agency within USDA! Three
Unit Plan 5: Bioethics
 Unit Plan 5: Bioethics Each unit is complete with the corresponding slides found in the main Genetic Engineering PowerPoint. Teachers have the liberty to cover the material on an as-needed basis based
Unit Plan 5: Bioethics Each unit is complete with the corresponding slides found in the main Genetic Engineering PowerPoint. Teachers have the liberty to cover the material on an as-needed basis based
USDA APHIS Requirements
 USDA APHIS Requirements Douglas Grant Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch USDA APHIS BRS ROP National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January 28, 2016 APHIS BRS Requirements
USDA APHIS Requirements Douglas Grant Chief, Western Compliance Assurance Branch USDA APHIS BRS ROP National Alliance of Independent Crop Consultants Annual Meeting January 28, 2016 APHIS BRS Requirements
Genetically Modified Organisms II. How are transgenic plants generated? The components of T DNA transfer. Plants
 Genetically Modified Organisms II Plants How are transgenic plants generated? The bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a pathogen of plants that causes crown gall tumors. Crown gall tumor Agrobacterium
Genetically Modified Organisms II Plants How are transgenic plants generated? The bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a pathogen of plants that causes crown gall tumors. Crown gall tumor Agrobacterium
Applicants: E. A. Grabau & P.M. Phipps, Virginia Tech, VA
 Petition for the Determination of Nonregulated Status For Sclerotinia Blight Resistant (aka Blight Blocker) Transgenic Peanut Events N70, P39, and W171 Applicants: E. A. Grabau & P.M. Phipps, Virginia
Petition for the Determination of Nonregulated Status For Sclerotinia Blight Resistant (aka Blight Blocker) Transgenic Peanut Events N70, P39, and W171 Applicants: E. A. Grabau & P.M. Phipps, Virginia
What is DNA? Gene (skin colour) Gene (iris colour)
 What is DNA? Gene (skin colour) Adenine Thymine Gene (iris colour) Guanine Cytosine 1 is deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule found in the cells of all living organisms. It carries the information responsible
What is DNA? Gene (skin colour) Adenine Thymine Gene (iris colour) Guanine Cytosine 1 is deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule found in the cells of all living organisms. It carries the information responsible
Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Benefits and Weed Management Recommendations
 1 Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Benefits and Weed Management Recommendations It s the System that Makes the Difference Key Reasons Demand for Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Expected to More than Double
1 Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Benefits and Weed Management Recommendations It s the System that Makes the Difference Key Reasons Demand for Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Expected to More than Double
Regulatory Challenges Presented by Genome Editing Industry Perspective. 29 Nov 2017 / Felicity Keiper
 Regulatory Challenges Presented by Genome Editing Industry Perspective 29 Nov 2017 / Felicity Keiper Genome Editing in Plant Breeding Genome editing for targeted modifications/introductions of one or more
Regulatory Challenges Presented by Genome Editing Industry Perspective 29 Nov 2017 / Felicity Keiper Genome Editing in Plant Breeding Genome editing for targeted modifications/introductions of one or more
Introduction. Comments Received on Preliminary Work Plan
 Introduction This is the Environmental Protection Agency s (EPA or the Agency) Final Work Plan (FWP) for the registration review of glyphosate. This FWP includes the expected registration review timeline.
Introduction This is the Environmental Protection Agency s (EPA or the Agency) Final Work Plan (FWP) for the registration review of glyphosate. This FWP includes the expected registration review timeline.
Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Benefits and Weed Management Recommendations
 1 Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Benefits and Weed Management Recommendations It s the System that Makes the Difference Key Reasons Demand for Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Expected to More than Double
1 Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Benefits and Weed Management Recommendations It s the System that Makes the Difference Key Reasons Demand for Roundup Ready Xtend Crop System Expected to More than Double
GM crops in Australia Costs, profits and economic risks
 GM crops in Australia Costs, profits and economic risks Max Foster Economist Overview Adoption and performance of current GM crops in Australia cotton Canola/rapeseed Risks with GM crops in Australia Market
GM crops in Australia Costs, profits and economic risks Max Foster Economist Overview Adoption and performance of current GM crops in Australia cotton Canola/rapeseed Risks with GM crops in Australia Market
Who Am I? Farmer, Dietitian, Promoter of Food & Farming
 Schmidt Farms Inc. 3 rd Generation in USA 2100 Acres in Maryland Corn (biotech & conventional production; formerly certified organic) Soybeans (food, feed & seed) Wheat (feed & seed) Barley (seed) 150
Schmidt Farms Inc. 3 rd Generation in USA 2100 Acres in Maryland Corn (biotech & conventional production; formerly certified organic) Soybeans (food, feed & seed) Wheat (feed & seed) Barley (seed) 150
Agricultural Biotechnology
 Agricultural Biotechnology Kent J. Bradford Department of Plant Sciences Seed Biotechnology Center University of California Davis, CA 95616 530-754-7333 sbc@ucdavis.edu Domestication: The Original Crop
Agricultural Biotechnology Kent J. Bradford Department of Plant Sciences Seed Biotechnology Center University of California Davis, CA 95616 530-754-7333 sbc@ucdavis.edu Domestication: The Original Crop
