PENETRATION DATA FOR A MEDIUM CALIBER TUNGSTEN SINTER ALLOY PENETRATOR INTO ALUMINUM ALLOY 7020 IN THE VELOCITY REGIME FROM 250 M/S TO 1900 M/S
|
|
|
- Lydia Bennett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 23RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN ABRIL PENETRATION DATA FOR A MEDIUM CALIBER TUNGSTEN SINTER ALLOY PENETRATOR INTO ALUMINUM ALLOY 7020 IN THE VELOCITY REGIME FROM 250 M/S TO 1900 M/S Matthias Wickert Fraunhofer Ernst-Mach-Institut, Eckerstr. 4, Freiburg, Germany Phone: Fax: matthias.wickert@emi.fraunhofer.de Penetration data over a wide velocity range are of general interest for the ballistic research community. An important material class for light vehicle structures are aluminum alloys. Aluminum Alloy 7020 has been chosen to examine the semi-infinite penetration of a tungsten sinter alloy medium caliber type penetrator in the wide velocity regime from 250 m/s to 1900 m/s. Three response regions are identified. Rigid body penetration is observed up to 700 m/s with the onset of plastic deformation of the penetrator s frustrum nose. A maximum depth of penetration of 1.4 of the penetrator s length is measured before the transition to hydrodynamic penetration with irregular shaped broad penetration craters sets in. Between 700 m/s and 1000 m/s a drastic drop up to 40% of the depth of penetration is observed due to strong bending of the penetration craters and the fragmentation of the penetrator. A penetration of 1.4 of the penetrator s length is exceeded again beyond impact INTRODUCTION High strength aluminum alloys are used for structural elements in infantry fighting vehicles. If such an element is considered as a target, the line-of-sight thickness might be drastically increased due to the target inclination relative to the shot line. Considering a target obliquity of 60 NATO and an azimuth angle of 45 NATO the resulting line-of-sight thickness is increased by a factor of 2.9. Since only few penetration data of tungsten sinter alloy penetrators in aluminum have been available so far, a test series was devoted to the penetration performance of a medium calibre type penetrator with a length over diameter ratio of 15 into the high strength Aluminum Alloy 7020 within the impact velocity regime from 250 m/s to 1900 m/s. All tests have been performed at the same gun facility employing single-stage powder gun setup and two-stage light-gas gun setup. 1437
2 1438 TERMINAL BALLISTICS EXPERIMENTAL SETUP The penetrator was shot with 0 NATO obliquity against the semi-infinite aluminum target represented by layering plates with a thickness of 60 mm and lateral dimensions of 125 mm x 125 mm. The high strength Aluminum Alloy 7020 with the composition AlZn4.5Mg1 is specified by the manufacturer with a minimum ultimate tensile strength of 350 N/mm², an elongation of 10% and a density of 2.77 g/cm³. The tests were performed with a 90 mm long threaded penetrator with a frustrum nose, see figure 1. The nominal diameter is 6 mm. The mass of the penetrator is 46.7 g. The penetrator is made of a tungsten sinter alloy with a density of 17.7 g/cm³, an ultimate tensile strength of 1370 N/mm² and an elongation of 11.5%. Figure 1 Frustrum nose tungsten sinter alloy penetrator. RESULTS Table 1 gives the penetration data measured in line-of-sight direction. For high velocity the penetration in the aluminum alloy shall be compared to the penetration in RHA. In test the same penetrator was fired with a velocity of 1501 m/s and -0.1 /0 yaw against a semi-infinite RHA target with a hardness of BHN 300. The penetration of 71.5 mm in RHA compares to a value of 153 mm in Aluminum Alloy 7020 interpolated by the tests and Thus at 1500 m/s the tungsten sinter alloy penetrator exceeds in Aluminum Alloy 7020 the penetration in RHA by a factor of 2.1. For comparison images of the penetration craters of test and are shown in figure 2. Images of the penetration craters for almost all aluminum targets are displayed in figure 3.
3 Penetration data for a medium caliber tungsten sinter alloy penetrator into aluminum alloy 7020 in the velocity regime from 250 m/s to 1900 m/s 1439 Figure 2 Comparison of penetration craters into RHA (10759) and Aluminum Alloy 7020 (10762) at high striking velocity. Table 1 Semi-infinite penetration data for Aluminum Alloy Velocity [m/s] Test ID Pitch/Yaw [ ] Penetration [mm] Penetration [P/L] / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / /
4 1440 TERMINAL BALLISTICS Figure 3 Penetration craters in Aluminum Alloy 7020 with respect to impact velocity.
5 Penetration data for a medium caliber tungsten sinter alloy penetrator into aluminum alloy 7020 in the velocity regime from 250 m/s to 1900 m/s 1441 Comparing the cross-sectional shapes of the projectile nose, the onset of projectile deformation can be observed at 664 m/s in test In figure 3 the nose shape is compared for this and the nearby-velocity tests. At 540 m/s in test the frustrum nose shape is still intact whereas at 695 m/s in test the nose shape has deformed to a flat shape. 540 m/s (10798) 664 m/s (10804) 695 m/s (10808) Figure 3 Onset of frustrum projectile nose deformation. The penetration data are graphically presented in figure 4 with three response regions. Up to 700 m/s a parabolic fit function is inserted based on the penetration data up to 540 m/s without plastic deformation of the penetrator nose, reflecting that the amount of displaced target material is proportional to the kinetic energy of the projectile.
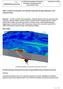
6 1442 TERMINAL BALLISTICS Response Region I II III Penetration [P/L] v [m/s] Figure 4 Drop of semi-infinite penetration into Aluminum Alloy 7020 at 700 m/s. A steep increase in penetration up to 1.4 penetrator lengths is observed up to a velocity of 700 m/s with penetration craters that are straight or modestly bent. The penetrator is visible to a large extent in the target cross section images and fits tightly in the smooth crater channels. For the following three tests at velocities of 785 m/s, 869 m/s and 884 m/s drastically reduced penetration values are observed about 40% less than the penetration measured at 695 m/s. At 946 m/s the depth of penetration is still 9% less than at the test at 695 m/s. There is no indication that this reduction of penetration performance is related to an increased yaw in the corresponding velocity regime. But the penetration craters are either strongly bowed as in test or crater branching does occur as in test In all of these tests the penetrator is strongly fragmented and the penetration channels are at least in some sections much wider than the penetrator diameter. Not until 1071 m/s the penetration performance exceeds the value at 695 m/s. This corresponds to a velocity increase of almost 400 m/s or, respectively, an increase of the kinetic energy of the penetrator by a factor of 2.4. Beyond velocities of 1000 m/s the penetration craters are to a large portion directed along the line-of-sight axis with modest bowing at the end. The walls of the crater walls are irregular and the penetrator is fragmented and eroded.
7 Penetration data for a medium caliber tungsten sinter alloy penetrator into aluminum alloy 7020 in the velocity regime from 250 m/s to 1900 m/s 1443 DISCUSSION Tungsten sinter alloy penetrators are often designed for high performance in steel targets. For high impact velocities pure hydrodynamic theory estimates the ratio P/L for a tungsten sinter alloy penetrator with the density ρ p =17.7 g/cm³ and steel with the density ρ st =7.85 g/cm³ according to eq.(1) to 1.5. P ρ P = (1) L ρ t For an aluminum target with ρ al =2.77 g/cm³ the estimate is 2.5. For long rod penetration in steel, this estimate by pure hydrodynamic theory describes the magnitude of penetration values achieved for high velocities beyond 2500 m/s reasonably well, whereas for the penetration in aluminum a magnitude of 3.5 is reported [1] attributed to a strong contribution of secondary penetration effects. Tate s [2] modified hydrodynamic theory takes strength effects into account and estimates the necessary velocity v thres for a penetrator beginning to deform by eq. (2). v thres Yp Rt = 2 (2) ρ t Below this velocity rigid body penetration will occur. By approximating the dynamic strength of the projectile Y p and the target R t by the tensile strength data given before, the threshold velocity for the RHA target is about 290 m/s whereas the limit velocity for the Aluminum Alloy 7020 is estimated by 860 m/s. Due to the much higher threshold velocity, rigid body penetration effects become much more visible in aluminum targets compared to steel targets. The data presented for the aluminum penetration by a tungsten sinter alloy penetrator reflect this transition from rigid body penetration to hydrodynamic penetration with rod erosion and mass consumption. For the tungsten sinter alloy penetrator used in the experiments, rigid body penetration yields very high penetration values up to a velocity of 700 m/s. Then the penetration performance drops more than 40 % and beyond velocities of 1000 m/s the penetration performance exceeds the maximum depth for rigid body penetration again. Maximum rigid body penetration and the transition velocity depend strongly on the shape and hardness of the projectile nose. Forrestal and Piekutowski [3] have demonstrated for the penetration of a steel projectile into Aluminum 6061-T6511, that for an ogival nose shape rigid body penetration can be observed up to velocities as high as 1400 m/s with a resulting penetration of about 4 P/L whereas for a spherical nose
8 1444 TERMINAL BALLISTICS rigid body penetration was observed only up to a velocity of 1000 m/s with 1.3 P/L. Also the positive effect of high projectile hardness on the maximum rigid body penetration performance is demonstrated there. For the tungsten sinter alloy penetrator in the response region of rigid body penetration into the Aluminum Alloy 7020 the penetration data can well be fitted by a parabolic curve. The onset of projectile nose deformation in tests and is correlated with reduced penetration relative to the parabolic fit curve. The specific characteristics of the penetration behaviour for the transition from rigid body penetration to hydrodynamic penetration will depend strongly on nose form and strength of the penetrator. CONCLUSIONS For the tungsten sinter alloy penetrator with frustum nose design rigid body penetration into the Aluminum Alloy 7020 was observed up to 700 m/s with a maximum penetration of 1.4 P/L. In the transition region the penetration performance for the examined penetrator design drops by 40% before the same penetration performance is reached again at velocities beyond 1000 m/s and rises to 2 P/L at 1500 m/s. The onset of the plastic deformation of the frustrum penetrator nose was observed at 661 m/s with reduced penetration relative to a parabolic fit curve for rigid body penetration. Penetrator erosion and mass consumption become important for velocities greater than 1000 m/s with irregular crater walls and a modest bowing at the end of the penetration crater. At a velocity of 1924 m/s the hydrodynamic penetration limit is closely reached with minor secondary penetration effects due to rigid body penetration in the final penetration phase. REFERENCES [1] A. J. Stilp, V. Hohler, Long rod penetration mechanics, Chapter No. 5 in High velocity impact dynamics, Editor J. A. Zukas, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1990) [2] A. Tate, Further results in the theory of long rod penetration, J. Mech. Solids, Vol. 17, (1969) [3] M. J. Forrestal, A. J. Piekutowski, Penetration experiments with 6061-T6511 aluminum targets and spherical-nose steel projectiles at striking velocities between 0.5 and 3 km/s, International Journal of Impact Engineering 24, (2000)
PENETRATION EXPERIMENTS WITH T6511 ALUMINUM TARGETS AND SPHERICAL-NOSE STEEL PROJECTILES AT STRIKING VELOCITIES BETWEEN 0.5 AND 3.
 5+%4999-~32zzL3- PENETRATION EXPERIMENTS WITH 6061 -T6511 ALUMINUM TARGETS AND SPHERICAL-NOSE STEEL PROJECTILES AT STRIKING VELOCITIES BETWEEN 0.5 AND 3.0 kit1/s MICHAEL J. FORRESTAL* AND ANDREWJ. PIEKUTOWSKI**
5+%4999-~32zzL3- PENETRATION EXPERIMENTS WITH 6061 -T6511 ALUMINUM TARGETS AND SPHERICAL-NOSE STEEL PROJECTILES AT STRIKING VELOCITIES BETWEEN 0.5 AND 3.0 kit1/s MICHAEL J. FORRESTAL* AND ANDREWJ. PIEKUTOWSKI**
BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF MONOBLOCK AND JACKETED MEDIUM-CALIBER PENETRATORS AGAINST COMPOSITE ARMOR AND SPACED TARGETS
 BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF MONOBLOCK AND JACKETED MEDIUM-CALIBER PENETRATORS AGAINST COMPOSITE ARMOR AND SPACED TARGETS H. Kaufmann 1, S. Lampert 2, G. Heizmann 2, B. Lehmann 2 1 RUAG Land Systems, Allmendstrasse
BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF MONOBLOCK AND JACKETED MEDIUM-CALIBER PENETRATORS AGAINST COMPOSITE ARMOR AND SPACED TARGETS H. Kaufmann 1, S. Lampert 2, G. Heizmann 2, B. Lehmann 2 1 RUAG Land Systems, Allmendstrasse
On the role of nose profile in long-rod penetration
 International Journal of Impact Engineering 22 (1999) 551 557 On the role of nose profile in long-rod penetration Z. Rosenberg*, E. Dekel RAFAEL, P.O. Box 2250, Haifa, Israel Received 10 May 1997; received
International Journal of Impact Engineering 22 (1999) 551 557 On the role of nose profile in long-rod penetration Z. Rosenberg*, E. Dekel RAFAEL, P.O. Box 2250, Haifa, Israel Received 10 May 1997; received
INFLUENCE OF LINERS ON THE DEBRIS CLOUD EXPANSION BEHIND SINGLE-PLATE TARGETS PERFORATED BY ROD PROJECTILES
 XXXX TB41 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 21, Interlaken, Switzerland INFLUENCE OF LINERS ON THE DEBRIS CLOUD EXPANSION BEHIND SINGLE-PLATE TARGETS PERFORATED BY ROD PROJECTILES Karl
XXXX TB41 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 21, Interlaken, Switzerland INFLUENCE OF LINERS ON THE DEBRIS CLOUD EXPANSION BEHIND SINGLE-PLATE TARGETS PERFORATED BY ROD PROJECTILES Karl
IMPACT AND PENETRATION PERFORMANCE OF A TUNGSTEN WIRE/TITANIUM COMPOSITE MATERIAL
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 IMPACT AND PENETRATION PERFORMANCE OF A TUNGSTEN WIRE/TITANIUM COMPOSITE MATERIAL TD Andrews 1, SP Godfrey 1, GD Howard 1,
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 IMPACT AND PENETRATION PERFORMANCE OF A TUNGSTEN WIRE/TITANIUM COMPOSITE MATERIAL TD Andrews 1, SP Godfrey 1, GD Howard 1,
Influence of Target Convexity and Concavity on the Ballistic Limit of Thin Aluminum Plate against by Sharp Nosed Projectile
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 3 (2013), pp. 365-372 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Influence of Target
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 3 (2013), pp. 365-372 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Influence of Target
Analytical and Numerical Consideration of Projectile Density Effect on Its Penetration Ability in Alumina Armor
 Journal of Mechanical Research and Application ISSN: 2251-7383, eissn: 2251-7391 Vol. 3, No. 1, 211, 21-28 JMRA Analytical and Numerical Consideration of Projectile Density Effect on Its Penetration Ability
Journal of Mechanical Research and Application ISSN: 2251-7383, eissn: 2251-7391 Vol. 3, No. 1, 211, 21-28 JMRA Analytical and Numerical Consideration of Projectile Density Effect on Its Penetration Ability
BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF THIN TITANIUM PLATES. Matthew Burkins
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 ABRIL BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF THIN TITANIUM PLATES Matthew Burkins U.S. Army Research Laboratory, ATTN: AMSRD-ARL-WM-TA, APG, MD, 21005-5066,
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 ABRIL BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF THIN TITANIUM PLATES Matthew Burkins U.S. Army Research Laboratory, ATTN: AMSRD-ARL-WM-TA, APG, MD, 21005-5066,
BALLISTIC IMPACT ON CERAMIC ARMOUR WITH DIFFERENT NOSED PROJECTILES: NUMERICAL STUDY
 International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (IJMME), Vol. 7 (2012), No. 1, 69 77. BALLISTIC IMPACT ON CERAMIC ARMOUR WITH DIFFERENT NOSED PROJECTILES: NUMERICAL STUDY B.M. Fadhil* Engineering
International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (IJMME), Vol. 7 (2012), No. 1, 69 77. BALLISTIC IMPACT ON CERAMIC ARMOUR WITH DIFFERENT NOSED PROJECTILES: NUMERICAL STUDY B.M. Fadhil* Engineering
INVESTIGATION OF SEVERAL POSSIBILITIES TO DISTURB THE JETTING PROCESS OF 40 MM / 60 CHARGES
 WM33 XXXX 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland INVESTIGATION OF SEVERAL POSSIBILITIES TO DISTURB THE JETTING PROCESS OF 40 MM / 60 CHARGES C. Voumard2, H.
WM33 XXXX 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland INVESTIGATION OF SEVERAL POSSIBILITIES TO DISTURB THE JETTING PROCESS OF 40 MM / 60 CHARGES C. Voumard2, H.
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 144 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 144 (2016 ) 124 131 12th International Conference on Vibration Problems, ICOVP 2015 Experimental study of plain and reinforced
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 144 (2016 ) 124 131 12th International Conference on Vibration Problems, ICOVP 2015 Experimental study of plain and reinforced
BALLISTIC TESTING OF AUSTRALIAN BISALLOY STEEL FOR ARMOR APPLICATIONS
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 BALLISTIC TESTING OF AUSTRALIAN BISALLOY STEEL FOR ARMOR APPLICATIONS W.A. Gooch 1, D.D. Showalter 1, M.S. Burkins 1, V. Thorn
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 BALLISTIC TESTING OF AUSTRALIAN BISALLOY STEEL FOR ARMOR APPLICATIONS W.A. Gooch 1, D.D. Showalter 1, M.S. Burkins 1, V. Thorn
Fundamental Course in Mechanical Processing of Materials. Exercises
 Fundamental Course in Mechanical Processing of Materials Exercises 2017 3.2 Consider a material point subject to a plane stress state represented by the following stress tensor, Determine the principal
Fundamental Course in Mechanical Processing of Materials Exercises 2017 3.2 Consider a material point subject to a plane stress state represented by the following stress tensor, Determine the principal
STUDY OF DAMAGE OF GAS-FILLED SPHERICAL PRESSURE VESSEL SUBJECTED TO HYPERVELOCITY IMPACT BY SPACE DEBRIS WITH DIFFERENT VELOCITY
 STUDY OF DAMAGE OF GAS-FILLED SPHERICAL PRESSURE VESSEL SUBJECTED TO HYPERVELOCITY IMPACT BY SPACE DEBRIS WITH DIFFERENT VELOCITY Cai Yuan (1), Pang Baojun (2), Jia Bin (3) ABSTRACT As an important component
STUDY OF DAMAGE OF GAS-FILLED SPHERICAL PRESSURE VESSEL SUBJECTED TO HYPERVELOCITY IMPACT BY SPACE DEBRIS WITH DIFFERENT VELOCITY Cai Yuan (1), Pang Baojun (2), Jia Bin (3) ABSTRACT As an important component
Quantitative Evidence of Reaction During Hypervelocity Penetration of Aluminum Through Oxygenated Fluids
 Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive Faculty and Researcher Publications Faculty and Researcher Publications 2013 Quantitative Evidence of Reaction During Hypervelocity Penetration of Aluminum Through
Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive Faculty and Researcher Publications Faculty and Researcher Publications 2013 Quantitative Evidence of Reaction During Hypervelocity Penetration of Aluminum Through
BALLISTIC IMPACT ON THIN SANDIWCH PANELS AND MULTI-LAYERED PLATES
 BALLISTIC IMPACT ON THIN SANDIWCH PANELS AND MULTI-LAYERED PLATES D.W. ZHOU 1, TWI LTD, Cambridge, UK dzhou@cantab.net W.J. STRONGE 2 Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK ABSTRACT
BALLISTIC IMPACT ON THIN SANDIWCH PANELS AND MULTI-LAYERED PLATES D.W. ZHOU 1, TWI LTD, Cambridge, UK dzhou@cantab.net W.J. STRONGE 2 Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK ABSTRACT
FEM Analysis of Ogive Nose Projectile Impact on Aluminum Plates
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn : 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 5, Issue 4 (December 2012), PP. 01-07 FEM Analysis of Ogive Nose Projectile Impact
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn : 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 5, Issue 4 (December 2012), PP. 01-07 FEM Analysis of Ogive Nose Projectile Impact
PROTECTIVE POWER OF THICK COMPOSITE LAYERS AGAINST MEDIUM-CALIBER LONG-ROD PENETRATORS
 TB07 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland PROTECTIVE POWER OF THICK COMPOSITE LAYERS AGAINST MEDIUM-CALIBER LONG-ROD PENETRATORS H.-J. Ernst1, T. Wolf1 and
TB07 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland PROTECTIVE POWER OF THICK COMPOSITE LAYERS AGAINST MEDIUM-CALIBER LONG-ROD PENETRATORS H.-J. Ernst1, T. Wolf1 and
Seismic Design Guidelines to Mitigate Upheaval Buckling Of Small Diameter Pipes
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Seismic Design Guidelines to Mitigate Upheaval Buckling Of Small Diameter Pipes H. Shinkai
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Seismic Design Guidelines to Mitigate Upheaval Buckling Of Small Diameter Pipes H. Shinkai
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE TEST METHOD STANDARD
 METRIC 21 August 1998 SUPERSEDING MIL-STD-376 28 June 1993 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE TEST METHOD STANDARD BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE RANKING OF CERAMIC ARMOR PLATES AGAINST HIGH DENSITY PENETRATORS AMSC N/A FSC
METRIC 21 August 1998 SUPERSEDING MIL-STD-376 28 June 1993 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE TEST METHOD STANDARD BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE RANKING OF CERAMIC ARMOR PLATES AGAINST HIGH DENSITY PENETRATORS AMSC N/A FSC
S?W3--96-a Penetration into Limestone Targets with Ogive-Nose Steel Projectiles
 CON)=- q b, o l 2 - - S S?W3--96-a99 963 Penetration into Limestone Targets with Ogive-Nose Steel Projectiles D. J. Frew@,M. J. Forrestal@,S. J. Hanchak, andm. L. Green@ Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg,
CON)=- q b, o l 2 - - S S?W3--96-a99 963 Penetration into Limestone Targets with Ogive-Nose Steel Projectiles D. J. Frew@,M. J. Forrestal@,S. J. Hanchak, andm. L. Green@ Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg,
Bullet Impact on Steel and Kevlar /Steel Armor - Computer Modeling and Experimental Data*
 Bullet Impact on Steel and Kevlar /Steel Armor - Computer Modeling and Experimental Data* Dale S. Preece Sandia National Laboratories P.O. Box 5800 Albuquerque, NM 87185-1156 Vanessa S. Berg Sandia National
Bullet Impact on Steel and Kevlar /Steel Armor - Computer Modeling and Experimental Data* Dale S. Preece Sandia National Laboratories P.O. Box 5800 Albuquerque, NM 87185-1156 Vanessa S. Berg Sandia National
EXPERIMENTAL SIMULATION OF FRAGMENTATION EFFECTS OF AN IMPROVISED EXPLOSIVE DEVICE. A. Karpenko 1 and M. Ceh 2
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 EXPERIMENTAL SIMULATION OF FRAGMENTATION EFFECTS OF AN IMPROVISED EXPLOSIVE DEVICE A. Karpenko 1 and M. Ceh 2 1 Armatec Survivability
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 EXPERIMENTAL SIMULATION OF FRAGMENTATION EFFECTS OF AN IMPROVISED EXPLOSIVE DEVICE A. Karpenko 1 and M. Ceh 2 1 Armatec Survivability
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE PENETRATION OF 7.62 AP PROJECTILES INTO CERAMIC ARMOURS
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE PENETRATION OF 7.62 AP PROJECTILES INTO CERAMIC ARMOURS J. Buchar 1, S. Rolc 2 and G. Cozzani 3
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE PENETRATION OF 7.62 AP PROJECTILES INTO CERAMIC ARMOURS J. Buchar 1, S. Rolc 2 and G. Cozzani 3
ON THE CRITICAL THICKNESS OF CERAMIC TO SHATTER WC-Co BULLET CORES
 ON THE CRITICAL THICKNESS OF CERAMIC TO SHATTER WC-Co BULLET CORES P. J. Hazell 1 and C. J. Roberson 2 1 Engineering Systems Department, Cranfield University, Royal Military College of Science, Shrivenham,
ON THE CRITICAL THICKNESS OF CERAMIC TO SHATTER WC-Co BULLET CORES P. J. Hazell 1 and C. J. Roberson 2 1 Engineering Systems Department, Cranfield University, Royal Military College of Science, Shrivenham,
3. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL MATERIALS
 3. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL MATERIALS Igor Kokcharov 3.1 TENSION TEST The tension test is the most widely used mechanical test. Principal mechanical properties are obtained from the test. There
3. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL MATERIALS Igor Kokcharov 3.1 TENSION TEST The tension test is the most widely used mechanical test. Principal mechanical properties are obtained from the test. There
Seismic Design Guidelines To Mitigate Upheaval Buckling Of Small Diameter Pipes
 Seismic Design Guidelines To Mitigate Upheaval Buckling Of Small Diameter Pipes Hajime Shinkai 1 ABSTRACT This paper describes The Draft Seismic Design Guidelines to Mitigate Upheaval Buckling of Small
Seismic Design Guidelines To Mitigate Upheaval Buckling Of Small Diameter Pipes Hajime Shinkai 1 ABSTRACT This paper describes The Draft Seismic Design Guidelines to Mitigate Upheaval Buckling of Small
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN APRL 2007
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRL 2007 ON THE ROLE OF INTERMEDIATE LAYER LOCATION IN PREVENTION OF SYMPATHETIC DOTONATION BETWEEN REACTIVE ARMOR SANDWICHWES S. Chanukaev
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRL 2007 ON THE ROLE OF INTERMEDIATE LAYER LOCATION IN PREVENTION OF SYMPATHETIC DOTONATION BETWEEN REACTIVE ARMOR SANDWICHWES S. Chanukaev
EFFECT OF PROJECTILE TYPE, SIZE AND IMPACT VELOCITY ON BALLISTIC IMPACT FAILURE BEHAVIOR OF TROGAMID CX-7323 NYLON
 EFFECT OF PROJECTILE TYPE, SIZE AND IMPACT VELOCITY ON BALLISTIC IMPACT FAILURE BEHAVIOR OF TROGAMID CX-7323 NYLON Nicholas Tsantinis*, John W. Song US ARMY NSRDEC, AMSRD-NSR-WS-DB Natick, MA. 01760 Roy
EFFECT OF PROJECTILE TYPE, SIZE AND IMPACT VELOCITY ON BALLISTIC IMPACT FAILURE BEHAVIOR OF TROGAMID CX-7323 NYLON Nicholas Tsantinis*, John W. Song US ARMY NSRDEC, AMSRD-NSR-WS-DB Natick, MA. 01760 Roy
Simulation of perforation behaviour of carbon fiber reinforced 6061-T6 aluminum metal matrix composite by a tungsten projectile
 Simulation of perforation behaviour of carbon fiber reinforced 6061-T6 aluminum metal matrix composite by a tungsten projectile W.-S. Lee*, C.-H. Lai* & S.-T. Chiou* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Simulation of perforation behaviour of carbon fiber reinforced 6061-T6 aluminum metal matrix composite by a tungsten projectile W.-S. Lee*, C.-H. Lai* & S.-T. Chiou* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Title: LS-DYNA FEA Simulation of Projectile Penetration through Aluminum-Foam Sandwich Panel
 LS-DYNA FEA Simulation of Projectile Penetration Through Aluminum- Title: LS-DYNA FEA Simulation of Projectile Penetration through Aluminum-Foam Sandwich Panel Keywords: LS-DYNA, projectile, blast, penetration,
LS-DYNA FEA Simulation of Projectile Penetration Through Aluminum- Title: LS-DYNA FEA Simulation of Projectile Penetration through Aluminum-Foam Sandwich Panel Keywords: LS-DYNA, projectile, blast, penetration,
An Explosive Fragment Projector for IM testing
 An Explosive Fragment Projector for IM testing G.G. Goviazin, R.E. Ceder, T. Eliash Rafael, Manor Advanced Defense Technologies Division ISRAEL Email: talel@rafael.co.il Abstract Fragment Attack (FA) testing,
An Explosive Fragment Projector for IM testing G.G. Goviazin, R.E. Ceder, T. Eliash Rafael, Manor Advanced Defense Technologies Division ISRAEL Email: talel@rafael.co.il Abstract Fragment Attack (FA) testing,
HAYNES Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy
 HAYNES Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy Principal Features Lightweight, High Strength HAYNES Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy (UNS R56320) is both lightweight and strong. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio which provides a major
HAYNES Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy Principal Features Lightweight, High Strength HAYNES Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy (UNS R56320) is both lightweight and strong. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio which provides a major
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE)
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code :Strength of Materials-II (16CE111) Course & Branch: B.Tech - CE Year
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code :Strength of Materials-II (16CE111) Course & Branch: B.Tech - CE Year
DETERMINATION OF DYNAMIC TENSILE STRENGTH OF METALS FROM JET BREAK-UP STUDIES
 WM37 XXXX 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland DETERMINATION OF DYNAMIC TENSILE STRENGTH OF METALS FROM JET BREAK-UP STUDIES Manjit Singh 1, M.S. Bola 1 and
WM37 XXXX 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland DETERMINATION OF DYNAMIC TENSILE STRENGTH OF METALS FROM JET BREAK-UP STUDIES Manjit Singh 1, M.S. Bola 1 and
Experimental Analysis and Parametric Optimization of 6065-Aluminium Alloy in Rotary Friction Welding
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 8, Number 1 (2018), pp. 111-118 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Analysis and Parametric
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 8, Number 1 (2018), pp. 111-118 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Experimental Analysis and Parametric
ME-313 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS October 11, 2000 TEST I OPEN TEXT BOOK
 ME-313 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS October 11, 000 TEST I OEN TEXT BOOK Name: 1. Three plates of are bolted together as shown in the figure below. Design the bolted connection by choosing both plate thickness
ME-313 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS October 11, 000 TEST I OEN TEXT BOOK Name: 1. Three plates of are bolted together as shown in the figure below. Design the bolted connection by choosing both plate thickness
STRAIN RATE EFFECT ON THE FAILURE STRAIN AND HARDNESS OF METALLIC ARMOR PLATES SUBJECTED TO HIGH VELOCITY PROJECTILE IMPACT
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 1, No. 2 (2006) 166-175 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College STRAIN RATE EFFECT ON THE FAILURE STRAIN AND HARDNESS OF METALLIC ARMOR PLATES
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 1, No. 2 (2006) 166-175 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College STRAIN RATE EFFECT ON THE FAILURE STRAIN AND HARDNESS OF METALLIC ARMOR PLATES
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN APRIL 2007
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 SIMULATION OF BALLISTIC IMPACT OF A TUNGSTEN CARBIDE SPHERE ON A CONFINED SILICON CARBIDE TARGET C. G. Fountzoulas, B. A. Cheeseman
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 SIMULATION OF BALLISTIC IMPACT OF A TUNGSTEN CARBIDE SPHERE ON A CONFINED SILICON CARBIDE TARGET C. G. Fountzoulas, B. A. Cheeseman
A Coupled Thermal and Mechanical Model of Sliding Wear
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (4) A Coupled Thermal and Mechanical Model of Sliding Wear S. S. Akarca, W. J. Altenhof, and A. T. Alpas Department of Mechanical, Automotive,
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (4) A Coupled Thermal and Mechanical Model of Sliding Wear S. S. Akarca, W. J. Altenhof, and A. T. Alpas Department of Mechanical, Automotive,
Residual velocity of the non-deformable projectile after perforating the ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete
 Structures Under Shock and Impact XIII 257 Residual velocity of the non-deformable projectile after perforating the ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete R. Sovják 1, T. Vavřiník 1, M. Frydrýn
Structures Under Shock and Impact XIII 257 Residual velocity of the non-deformable projectile after perforating the ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete R. Sovják 1, T. Vavřiník 1, M. Frydrýn
Effects of Various Reinforcements in Oblique Loading of Rectangular Thin Walled Structure using FEA
 Effects of Various Reinforcements in of Rectangular Thin Walled Structure using FEA Abhishek Pratap Singh 1, Rahul Mishra 2 1 M.E. Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor, IES Institute of Technology & Management,
Effects of Various Reinforcements in of Rectangular Thin Walled Structure using FEA Abhishek Pratap Singh 1, Rahul Mishra 2 1 M.E. Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor, IES Institute of Technology & Management,
ENGINEERING MATERIAL 100
 Department of Applied Chemistry Division of Science and Engineering SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MATERIAL 100 Experiments 4 and 6 Mechanical Testing and Applications of Non-Metals Name: Yasmin Ousam
Department of Applied Chemistry Division of Science and Engineering SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MATERIAL 100 Experiments 4 and 6 Mechanical Testing and Applications of Non-Metals Name: Yasmin Ousam
Gun Propellants For The 27 mm Cal. Gun Eurofighter Jet
 Gun Propellants For The 27 mm Cal. Gun Eurofighter Jet Dr. Dietmar ller Fraunhofer Institut Chemische Technologie ( ICT ), D-76327 Pfinztal, Germany mue@ict.fhg.de Walter Langlotz Diehl BGT Defence GmbH
Gun Propellants For The 27 mm Cal. Gun Eurofighter Jet Dr. Dietmar ller Fraunhofer Institut Chemische Technologie ( ICT ), D-76327 Pfinztal, Germany mue@ict.fhg.de Walter Langlotz Diehl BGT Defence GmbH
TB18 BEHAVIOR AND PERFORMANCE OF AMORPHOUS AND NANOCRYSTALLINE METALS IN BALLISTIC IMPACTS
 TB18 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland BEHAVIOR AND PERFORMANCE OF AMORPHOUS AND NANOCRYSTALLINE METALS IN BALLISTIC IMPACTS L. Magness1, L.Kecskes1, M.Chung2,
TB18 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland BEHAVIOR AND PERFORMANCE OF AMORPHOUS AND NANOCRYSTALLINE METALS IN BALLISTIC IMPACTS L. Magness1, L.Kecskes1, M.Chung2,
On the Quasi-Static Perforation Resistance of Circular AA5083-H116 Aluminium Plates
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Technology (2) On the Quasi-Static Perforation Resistance of Circular AA5083-H116 Aluminium Plates F. Grytten 1, T. Børvik 1,2, O.S. Hopperstad 1 and M. Langseth
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Technology (2) On the Quasi-Static Perforation Resistance of Circular AA5083-H116 Aluminium Plates F. Grytten 1, T. Børvik 1,2, O.S. Hopperstad 1 and M. Langseth
EFFECT OF LOW VELOCITY IMPACT ON DEFORMATION BEHAVIOUR OF METALLIC PRESSURE VESSEL
 EFFECT OF LOW VELOCITY IMPACT ON DEFORMATION BEHAVIOUR OF METALLIC PRESSURE VESSEL N. H. Farhood, S. Karuppanan, H. H. Ya and A. N. Mengal Department of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Petronas,
EFFECT OF LOW VELOCITY IMPACT ON DEFORMATION BEHAVIOUR OF METALLIC PRESSURE VESSEL N. H. Farhood, S. Karuppanan, H. H. Ya and A. N. Mengal Department of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Petronas,
MASS PER CUBIC FOOT (METER), YIELD, AND AIR CONTENT (GRAVIMETRIC) OF FRESHLY MIXED CONCRETE (Kansas Test Method KT-20)
 5.9.20 MASS PER CUBIC FOOT (METER), YIELD, AND AIR CONTENT (GRAVIMETRIC) OF FRESHLY MIXED CONCRETE (Kansas Test Method ) 1. SCOPE This method of test covers the procedure for determining the mass per cubic
5.9.20 MASS PER CUBIC FOOT (METER), YIELD, AND AIR CONTENT (GRAVIMETRIC) OF FRESHLY MIXED CONCRETE (Kansas Test Method ) 1. SCOPE This method of test covers the procedure for determining the mass per cubic
Investigation of Materials for Liners of Shaped Charge Warhead and Their Optimum Standoff Distances
 Investigation of Materials for Liners of Shaped Charge Warhead and Their Optimum Standoff Distances Kulsirikasem W*, Julniphitwong A and Tanapornraweekit G Defence Technology Institute (PO), 47/433 4 th
Investigation of Materials for Liners of Shaped Charge Warhead and Their Optimum Standoff Distances Kulsirikasem W*, Julniphitwong A and Tanapornraweekit G Defence Technology Institute (PO), 47/433 4 th
Analysis and Correction of a Design Failure
 Analysis and Correction of a Design Failure Brett Sorensen U.S. Army Research Laboratory AMSRD-ARL-WM-TC, APG, MD 21005 Abstract This paper presents a case study of an incremental design process of a kinetic
Analysis and Correction of a Design Failure Brett Sorensen U.S. Army Research Laboratory AMSRD-ARL-WM-TC, APG, MD 21005 Abstract This paper presents a case study of an incremental design process of a kinetic
Main Processing of Tungsten Alloy Swaging Rod: 1). Mixing 2). Pressing 3). Sintering 4). Heat treatment 5). Swaging 6). Machining Tungsten Alloy Rods
 Tungsten Alloy Military Swaging Rod Tungsten Alloy Swaging Rod for Military Swaging greatly increases tungsten alloy rod's ultimate tensile strength. The ultimate tensile strength of regular tungsten alloy
Tungsten Alloy Military Swaging Rod Tungsten Alloy Swaging Rod for Military Swaging greatly increases tungsten alloy rod's ultimate tensile strength. The ultimate tensile strength of regular tungsten alloy
May 21-24,1995 A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF GRAIN SIZE ON THE BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF SILICON CARBIDE. Carl F. Cline
 w-9.5053 7-5 3 UCRL-JC-118421 PREPRINT A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF GRAIN SIZE ON THE BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF SILICON CARBIDE. Carl F. Cline This paper was prepared forthe 15th International Symposium on
w-9.5053 7-5 3 UCRL-JC-118421 PREPRINT A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF GRAIN SIZE ON THE BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF SILICON CARBIDE. Carl F. Cline This paper was prepared forthe 15th International Symposium on
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 8, 1994 WIT Press, ISSN
 Impact effects on the primary fragmentation generated by the HE81 mortar grenade on conventional concrete and steel fibers reinforced concrete M.F. Canovas," R.G. Pamies^ J.R. Simon del Potrcf & E.M. Almansa^
Impact effects on the primary fragmentation generated by the HE81 mortar grenade on conventional concrete and steel fibers reinforced concrete M.F. Canovas," R.G. Pamies^ J.R. Simon del Potrcf & E.M. Almansa^
Accurate Prediction of Projectile Residual Velocity for Impact on Single and Multi-Layered Steel and Aluminum Plates
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Penetration/Explosive Modeling Accurate Prediction of Projectile Residual Velocity for Impact on Single and Multi-Layered Steel and Aluminum Plates M. Raguraman
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Penetration/Explosive Modeling Accurate Prediction of Projectile Residual Velocity for Impact on Single and Multi-Layered Steel and Aluminum Plates M. Raguraman
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF HIGH SPEED IMPACT ON ALUMINIUM PLATE
 Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design Albufeira/Portugal 11-15 June 2017. Editors J.F. Silva Gomes and S.A. Meguid. Publ. INEGI/FEUP (2017) PAPER REF: 6664
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design Albufeira/Portugal 11-15 June 2017. Editors J.F. Silva Gomes and S.A. Meguid. Publ. INEGI/FEUP (2017) PAPER REF: 6664
Deformation, plastic instability
 Deformation, plastic instability and yield-limited design Engineering Materials 2189101 Department of Metallurgical Engineering Chulalongkorn University http://pioneer.netserv.chula.ac.th/~pchedtha/ Material
Deformation, plastic instability and yield-limited design Engineering Materials 2189101 Department of Metallurgical Engineering Chulalongkorn University http://pioneer.netserv.chula.ac.th/~pchedtha/ Material
Penetration of steel plates by long ceramic rods
 Metallurgical and Materials Applications of Shock-Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena L.E. Murr, K.P. Staudhammer and M.A. Meyers (Editors) ic 1995 Elsevier Science B. V. All rights reserved. 543 64 Penetration
Metallurgical and Materials Applications of Shock-Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena L.E. Murr, K.P. Staudhammer and M.A. Meyers (Editors) ic 1995 Elsevier Science B. V. All rights reserved. 543 64 Penetration
4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering (ICSEEE 2015)
 4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering (ICSEEE 2015) Ballistic Performance of Laminated Functionally Graded Composites of TiB2-based Ceramic and Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering (ICSEEE 2015) Ballistic Performance of Laminated Functionally Graded Composites of TiB2-based Ceramic and Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Quasi-Static and Dynamic Ballistic Damage Mechanisms in Confined Ceramic Tiles
 Quasi-Static and Dynamic Ballistic Damage Mechanisms in Confined Ceramic Tiles D. Sherman To cite this version: D. Sherman. Quasi-Static and Dynamic Ballistic Damage Mechanisms in Confined Ceramic Tiles.
Quasi-Static and Dynamic Ballistic Damage Mechanisms in Confined Ceramic Tiles D. Sherman To cite this version: D. Sherman. Quasi-Static and Dynamic Ballistic Damage Mechanisms in Confined Ceramic Tiles.
Jongen Werkzeugtechnik. Working depth. Drilling by JONGEN. 3 x D. BP 04 to 12
 Jongen Werkzeugtechnik Working depth 3 x D Drilling by JONGEN BP 04 to 12 THE TOOL New at Jongen: universally applicable high-performance drill for use on lathes and milling centers. It offers the highest
Jongen Werkzeugtechnik Working depth 3 x D Drilling by JONGEN BP 04 to 12 THE TOOL New at Jongen: universally applicable high-performance drill for use on lathes and milling centers. It offers the highest
Numerical Analysis of Behavior of UHPC Panels under High Velocity Impact Loading
 Numerical Analysis of Behavior of UHPC Panels under High Velocity Impact Loading Sanghee Kim 1) and Thomas Kang 2) 1), 2) Department of Architecture and Architectural Engineering, Seoul National University,
Numerical Analysis of Behavior of UHPC Panels under High Velocity Impact Loading Sanghee Kim 1) and Thomas Kang 2) 1), 2) Department of Architecture and Architectural Engineering, Seoul National University,
Modern armour configurations against 14.5 mm AP
 Modern armour configurations against 14.5 mm AP Diederen, A.M. 1, Broos, J.P.F. 1, Peijen, M.C.P. 2 1 TNO Prins Maurits Laboratory, P.O. Box 45, NL-2280 AA Rijswijk, The Netherlands 2 Royal Netherlands
Modern armour configurations against 14.5 mm AP Diederen, A.M. 1, Broos, J.P.F. 1, Peijen, M.C.P. 2 1 TNO Prins Maurits Laboratory, P.O. Box 45, NL-2280 AA Rijswijk, The Netherlands 2 Royal Netherlands
3D SIMULATION ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT PROTECTION MATERIAL IMPACTING BY 7.62 MM AMMUNITION
 3D SIMULATION ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT PROTECTION MATERIAL IMPACTING BY 7.62 MM AMMUNITION Juraj HUB 1, Pavel KNEYS 2 * 1 Department of Aircraft and Rocket Technology, University of Defence, Kounicova 65,
3D SIMULATION ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT PROTECTION MATERIAL IMPACTING BY 7.62 MM AMMUNITION Juraj HUB 1, Pavel KNEYS 2 * 1 Department of Aircraft and Rocket Technology, University of Defence, Kounicova 65,
Impact behaviour of lightweight armours V. Sanchez-Galvez E. T.S. Ingenieros de Caminos, Universidad Politecnica de Madrid, Spain
 Impact behaviour of lightweight armours V. Sanchez-Galvez E. T.S. Ingenieros de Caminos, Universidad Politecnica de Madrid, Spain Abstract Lightweight armours are being increasingly introduced as protective
Impact behaviour of lightweight armours V. Sanchez-Galvez E. T.S. Ingenieros de Caminos, Universidad Politecnica de Madrid, Spain Abstract Lightweight armours are being increasingly introduced as protective
PROTECTION PERFORMANCE OF THE MONOLAYER AND MULTI-LAYERED STEEL PLATES AGAINST 7.62-MM APM2 PROJECTILE IN ARMORED VEHICLES
 PROTECTION PERFORMANCE OF THE MONOLAYER AND MULTI-LAYERED STEEL PLATES AGAINST 7.62-MM APM2 PROJECTILE IN ARMORED VEHICLES N. Shash and V. N. Zuzov Bauman Moscow State Technical University, Moscow, Russia
PROTECTION PERFORMANCE OF THE MONOLAYER AND MULTI-LAYERED STEEL PLATES AGAINST 7.62-MM APM2 PROJECTILE IN ARMORED VEHICLES N. Shash and V. N. Zuzov Bauman Moscow State Technical University, Moscow, Russia
FRAGMENT SIMULATING PROJECTILE PENETRATION INTO LAYERED TARGETS
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 18, 2011, No. 5/6, p. 353 361 353 FRAGMENT SIMULATING PROJECTILE PENETRATION INTO LAYERED TARGETS Petr Pěchouček*, Stanislav Rolc, Jaroslav Buchar Fragment Simulating Projectile
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 18, 2011, No. 5/6, p. 353 361 353 FRAGMENT SIMULATING PROJECTILE PENETRATION INTO LAYERED TARGETS Petr Pěchouček*, Stanislav Rolc, Jaroslav Buchar Fragment Simulating Projectile
MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF FV535 STEEL AGAINST BALLISTIC IMPACT AT HIGH TEMPERATURES. B. Erice, F. Gálvez, D. Cendón and V. Sánchez-Gálvez.
 MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF FV535 STEEL AGAINST BALLISTIC IMPACT AT HIGH TEMPERATURES B. Erice, F. Gálvez, D. Cendón and V. Sánchez-Gálvez. Department of Materials Science, CISDEM, Polytechnic University of
MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF FV535 STEEL AGAINST BALLISTIC IMPACT AT HIGH TEMPERATURES B. Erice, F. Gálvez, D. Cendón and V. Sánchez-Gálvez. Department of Materials Science, CISDEM, Polytechnic University of
MIL-HDBK-1013/1A. Section 7: STANDOFF WEAPONS HARDENING
 Section 7: STANDOFF WEAPONS HARDENING 7.1 Introduction. This section begins with a description of the threat from a standoff Rocket Propelled Grenade (RPG) type of attack, followed by the general mechanisms
Section 7: STANDOFF WEAPONS HARDENING 7.1 Introduction. This section begins with a description of the threat from a standoff Rocket Propelled Grenade (RPG) type of attack, followed by the general mechanisms
Mechanical Properties of Materials
 INTRODUCTION Mechanical Properties of Materials Many materials, when in service, are subjected to forces or loads, it is necessary to know the characteristics of the material and to design the member from
INTRODUCTION Mechanical Properties of Materials Many materials, when in service, are subjected to forces or loads, it is necessary to know the characteristics of the material and to design the member from
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Penetration resistance of laminated plates from steel and flbreglass-reinforced polyester A.M. Eleiche*, M.S. Abdel-Kader\ A. Almohandes' "Mechanical Engineering Department, UAE University, United Arab
Penetration resistance of laminated plates from steel and flbreglass-reinforced polyester A.M. Eleiche*, M.S. Abdel-Kader\ A. Almohandes' "Mechanical Engineering Department, UAE University, United Arab
EFFECT OF THE BONDING LAYER ON BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF PERSONAL PROTECTIVE PLATE ARMOR
 EFFECT OF THE BONDING LAYER ON BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF PERSONAL PROTECTIVE PLATE ARMOR M.F. Buchely 1, J.D. Acuna 2, A. Maranon 3* 1,2,3 Structural Integrity Research group, Mechanical Engineering Department,
EFFECT OF THE BONDING LAYER ON BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF PERSONAL PROTECTIVE PLATE ARMOR M.F. Buchely 1, J.D. Acuna 2, A. Maranon 3* 1,2,3 Structural Integrity Research group, Mechanical Engineering Department,
2. TEST METHOD FOR OVERLAP SPLICE STRENGTH OF CONTINUOUS FIBER SHEETS (JSCE-E )
 2. TEST METHOD FOR OVERLAP SPLICE STRENGTH OF CONTINUOUS FIBER SHEETS (JSCE-E 542-2000) 1. Scope This specification describes the test method for the overlap splice strength of continuous fiber sheets
2. TEST METHOD FOR OVERLAP SPLICE STRENGTH OF CONTINUOUS FIBER SHEETS (JSCE-E 542-2000) 1. Scope This specification describes the test method for the overlap splice strength of continuous fiber sheets
Quasi-static and impact perforation of polymer-metal bi-layer plates by a blunt indenter. Abstract
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Quasi-static and impact perforation of polymer-metal bi-layer plates by a blunt indenter I. Mohagheghian a,b, G.J. McShane
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Quasi-static and impact perforation of polymer-metal bi-layer plates by a blunt indenter I. Mohagheghian a,b, G.J. McShane
Numerical and Experimental Methods for. Numerical and Experimental Methods for. Penetrating Glass and Plywood
 Numerical and Experimental Methods for Numerical and Experimental Methods for Estimating Impact Acceleration of Small-Caliber Projectile Penetrating Glass and Plywood 49th Annual Fuze Conference April
Numerical and Experimental Methods for Numerical and Experimental Methods for Estimating Impact Acceleration of Small-Caliber Projectile Penetrating Glass and Plywood 49th Annual Fuze Conference April
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES.
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES. Hardness, strength, ductility and elasticity are among the mechanical properties of a material that would probably first come to mind. In order to know how each of these characteristics
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES. Hardness, strength, ductility and elasticity are among the mechanical properties of a material that would probably first come to mind. In order to know how each of these characteristics
Mesoscale modeling of failure in partially sintered metals and homogenization to macroscale
 9. LS-DYNA Forum, Bamberg 2010 Mesoscale modeling of failure in partially sintered metals and homogenization to macroscale Nathanaël Durr, Martin Sauer Fraunhofer Institute for High-Speed Dynamics, Freiburg,
9. LS-DYNA Forum, Bamberg 2010 Mesoscale modeling of failure in partially sintered metals and homogenization to macroscale Nathanaël Durr, Martin Sauer Fraunhofer Institute for High-Speed Dynamics, Freiburg,
New Nano-Precipitates Hardened Steels of Wide Range of Strength and Toughness and High Resistance to Piercing With Projectiles *
 PROBLEMS OF MECHATRONICS ARMAMENT, AVIATION, SAFETY ENGINEERING ISSN 2081-5891 4 (10), 2012, 39-54 New Nano-Precipitates Hardened Steels of Wide Range of Strength and Toughness and High Resistance to Piercing
PROBLEMS OF MECHATRONICS ARMAMENT, AVIATION, SAFETY ENGINEERING ISSN 2081-5891 4 (10), 2012, 39-54 New Nano-Precipitates Hardened Steels of Wide Range of Strength and Toughness and High Resistance to Piercing
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF EXPLOSIVELY FORMED PROJECTILES (EFP)
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF EXPLOSIVELY FORMED PROJECTILES (EFP) S. Rolc 1, J. Buchar 2 and Z. Akstein 3 1 VOP-026 Sternberk, s.p.,
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF EXPLOSIVELY FORMED PROJECTILES (EFP) S. Rolc 1, J. Buchar 2 and Z. Akstein 3 1 VOP-026 Sternberk, s.p.,
Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Perforation of Thin Polycarbonate Plate by Projectiles of Different Nose Shape
 357 Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Perforation of Thin Polycarbonate Plate by Projectiles of Different Nose Shape Abstract The present study is based on experimental investigation and numerical
357 Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Perforation of Thin Polycarbonate Plate by Projectiles of Different Nose Shape Abstract The present study is based on experimental investigation and numerical
REVISED PAGES IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS REFERENCES QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS. 166 Chapter 6 / Mechanical Properties of Metals
 1496T_c06_131-173 11/16/05 17:06 Page 166 166 Chapter 6 / Mechanical Properties of Metals IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS Anelasticity Design stress Ductility Elastic deformation Elastic recovery Engineering
1496T_c06_131-173 11/16/05 17:06 Page 166 166 Chapter 6 / Mechanical Properties of Metals IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS Anelasticity Design stress Ductility Elastic deformation Elastic recovery Engineering
60mm ANTOS Commando Mortar 60mm Mortar bombs & 81mm Light Weight Mortar. IT&T McLean, VA
 60mm ANTOS Commando Mortar 60mm Mortar bombs & 81mm Light Weight Mortar IT&T McLean, VA 60 mm ULTRALIGHT MORTAR ANTOS Commando General description for ANTOS Commando 60mm ANTOS Commando is designed for:
60mm ANTOS Commando Mortar 60mm Mortar bombs & 81mm Light Weight Mortar IT&T McLean, VA 60 mm ULTRALIGHT MORTAR ANTOS Commando General description for ANTOS Commando 60mm ANTOS Commando is designed for:
MACHINES DESIGN SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL MACHINES DESIGN
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL C O N T E N T 2 1. MACHINE DESIGN 03-21 2. FLEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS. 22-34 3. JOURNAL BEARINGS... 35-65 4. CLUTCH AND BRAKES.
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL C O N T E N T 2 1. MACHINE DESIGN 03-21 2. FLEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS. 22-34 3. JOURNAL BEARINGS... 35-65 4. CLUTCH AND BRAKES.
DYNAMIC FRAGMENTATION OF ALUMINA WITH ADDITIONS OF NIOBIA AND SILICA UNDER IMPACT
 XXXX TB40 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland DYNAMIC FRAGMENTATION OF ALUMINA WITH ADDITIONS OF NIOBIA AND SILICA UNDER IMPACT L.H.L. Louro1, A.V. Gomes1,
XXXX TB40 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, 7 11 May 2001, Interlaken, Switzerland DYNAMIC FRAGMENTATION OF ALUMINA WITH ADDITIONS OF NIOBIA AND SILICA UNDER IMPACT L.H.L. Louro1, A.V. Gomes1,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Steel for the reinforcement and prestressing of concrete Test methods Part 3: Prestressing steel
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 15630-3 First edition 2002-04-15 Steel for the reinforcement and prestressing of concrete Test methods Part 3: Prestressing steel Aciers pour l'armature et la précontrainte du
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 15630-3 First edition 2002-04-15 Steel for the reinforcement and prestressing of concrete Test methods Part 3: Prestressing steel Aciers pour l'armature et la précontrainte du
CE 221: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS I CHAPTER 3: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 CE 221: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS I CHAPTER 3: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS By Dr. Krisada Chaiyasarn Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Thammasat university Outline Tension and compression
CE 221: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS I CHAPTER 3: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS By Dr. Krisada Chaiyasarn Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Thammasat university Outline Tension and compression
Analysis of the energy absorption of aluminium tubes for crash boxes
 Analysis of the energy absorption of aluminium tubes for crash boxes 2nd Workshop on Structural Analysis of Lightweight Structures Natters, May 30-2012 F.O. Riemelmoser (FH Kärnten) M. Kotnik (SZ Oprema
Analysis of the energy absorption of aluminium tubes for crash boxes 2nd Workshop on Structural Analysis of Lightweight Structures Natters, May 30-2012 F.O. Riemelmoser (FH Kärnten) M. Kotnik (SZ Oprema
Testing and modelling on an energy absorbing rock bolt
 Testing and modelling on an energy absorbing rock bolt A. Ansell Department of Structural Engineering, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden Abstract Dynamic loads on underground structures,
Testing and modelling on an energy absorbing rock bolt A. Ansell Department of Structural Engineering, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden Abstract Dynamic loads on underground structures,
The Impacting Dynamic Response of Energetic Materials PTFE/Al
 2016 International Conference on Materials, Information, Mechanical, Electronic and Computer Engineering (MIMECE 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-420-2 The Impacting Dynamic Response of Energetic Materials PTFE/Al
2016 International Conference on Materials, Information, Mechanical, Electronic and Computer Engineering (MIMECE 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-420-2 The Impacting Dynamic Response of Energetic Materials PTFE/Al
Question Paper Code : 11410
 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 11410 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Fourth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME 2254 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Common to Automobile Engineering and Production
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 11410 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Fourth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME 2254 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Common to Automobile Engineering and Production
ME 207 Material Science I
 ME 207 Material Science I Chapter 4 Properties in Bending and Shear Dr. İbrahim H. Yılmaz http://web.adanabtu.edu.tr/iyilmaz Automotive Engineering Adana Science and Technology University Introduction
ME 207 Material Science I Chapter 4 Properties in Bending and Shear Dr. İbrahim H. Yılmaz http://web.adanabtu.edu.tr/iyilmaz Automotive Engineering Adana Science and Technology University Introduction
FORMING OF FULLERENE-DISPERSED ALUMINUM COMPOSITE BY THE COMPRESSION SHEARING METHOD
 FORMING OF FULLERENE-DISPERSED ALUMINUM COMPOSITE BY THE COMPRESSION SHEARING METHOD Noboru NAKAYAMA Akita Prefectural University, 84-4 Tsuchiya-Ebinokuti, Yurihonjyo, Akita/ 15-55, JAPAN nakayama@akita-pu.ac.jp
FORMING OF FULLERENE-DISPERSED ALUMINUM COMPOSITE BY THE COMPRESSION SHEARING METHOD Noboru NAKAYAMA Akita Prefectural University, 84-4 Tsuchiya-Ebinokuti, Yurihonjyo, Akita/ 15-55, JAPAN nakayama@akita-pu.ac.jp
Reproducible evaluation of material properties. Static Testing Material response to constant loading
 Material Testing Material Testing Reproducible evaluation of material properties Static Testing Material response to constant loading Dynamic Testing Material response to varying loading conditions, including
Material Testing Material Testing Reproducible evaluation of material properties Static Testing Material response to constant loading Dynamic Testing Material response to varying loading conditions, including
True Stress and True Strain
 True Stress and True Strain For engineering stress ( ) and engineering strain ( ), the original (gauge) dimensions of specimen are employed. However, length and cross-sectional area change in plastic region.
True Stress and True Strain For engineering stress ( ) and engineering strain ( ), the original (gauge) dimensions of specimen are employed. However, length and cross-sectional area change in plastic region.
TITANIUM ALLOYS FOR ARMOR APPLICATIONS. Matthew Burkins, U.S. Army Research Laboratory
 TITANIUM ALLOYS FOR ARMOR APPLICATIONS Matthew Burkins, U.S. Army Research Laboratory Titanium alloys have long been used for reducing system weight in aerospace components. The high cost of titanium,
TITANIUM ALLOYS FOR ARMOR APPLICATIONS Matthew Burkins, U.S. Army Research Laboratory Titanium alloys have long been used for reducing system weight in aerospace components. The high cost of titanium,
Determination of the main characteristics of semi-rigid beam-to-column connections through numerical and experimental method
 Determination of the main characteristics of semi-rigid beam-to-column connections through numerical and experimental method K. Vértes & M. Iványi Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department
Determination of the main characteristics of semi-rigid beam-to-column connections through numerical and experimental method K. Vértes & M. Iványi Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department
Reproducible evaluation of material properties. Static Testing Material response to constant loading
 Material Testing Material Testing Reproducible evaluation of material properties Static Testing Material response to constant loading Dynamic Testing Material response to varying loading conditions, including
Material Testing Material Testing Reproducible evaluation of material properties Static Testing Material response to constant loading Dynamic Testing Material response to varying loading conditions, including
Rod End. General Catalog A-941
 Rod End General Catalog A Technical Descriptions of the Products B Product Specifications (Separate) Features and Types... Features of the Rod End... Features... Special Bearing Alloy... Performance Test
Rod End General Catalog A Technical Descriptions of the Products B Product Specifications (Separate) Features and Types... Features of the Rod End... Features... Special Bearing Alloy... Performance Test
Chapter 4 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL. By: Ardiyansyah Syahrom
 Chapter 4 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL By: Ardiyansyah Syahrom Chapter 2 STRAIN Department of Applied Mechanics and Design Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 1 Expanding
Chapter 4 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL By: Ardiyansyah Syahrom Chapter 2 STRAIN Department of Applied Mechanics and Design Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 1 Expanding
National Physical Laboratory Hampton Road Teddington Middlesex United Kingdom TW11 0LW
 NPL REPORT DEPC MPE 007 Methodology for determining the resistance of welded corrosion resistant alloys to stress corrosion using the four-point bend method A Turnbull and W Nimmo NOT RESTRICTED NOVEMBER
NPL REPORT DEPC MPE 007 Methodology for determining the resistance of welded corrosion resistant alloys to stress corrosion using the four-point bend method A Turnbull and W Nimmo NOT RESTRICTED NOVEMBER
How bending affects the ballistic properties of Armox
 DEGREE PROJECT, IN MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING, SECOND LEVEL, SWEDEN 2014 How bending affects the ballistic properties of Armox RICHARD TENGGREN KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 1 Abstract This
DEGREE PROJECT, IN MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING, SECOND LEVEL, SWEDEN 2014 How bending affects the ballistic properties of Armox RICHARD TENGGREN KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 1 Abstract This
