PTAC 1302 INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS TECHNOLOGY
|
|
|
- Jeremy Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course Overview History of the Process Industry Green Technologies and Related Industries (Optional) Your Career as a Process Technician 1. Describe the following components (aspects) of the PTAC Program: Individual expectations Program purpose Program value Industry involvement 2. Review course objectives 1. Explain the growth and development of the process industries. 2. Report the impact of the industry on: The community Other industries The environment The economy 3. Identify industry responses to current issues and trends such as: Global competition Safety and environmental regulations Technology advancements 4. Explain and describe the responsibility of the following regulatory agencies: EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) OSHA (Occupational Safety & Health Administration DOT (Department of Transportation) NRC (Nuclear Regulatory Comission) Homeland Security Local and state regulatory agencies 1. Describe Green technologies relevant to the industries in your area. BioMass Solar Wind Hydro/Water Nuclear Recycling Technology 1. Describe the roles, responsibilities, and expectations of the process technician: Work environment (all weather, drug and alcohol free, team-structured, constantly changing and 24 hours per day operations). Employer expectations. Equipment and process operations, maintenance and control. Physical requirements (lifting, pulling, climbing, etc.). Page 1 of 15
2 Your Career as a Process Technician (cont.) Working as Teams Basic Physics Following all procedures, safety systems, and rules for everyone s safety and the protection of the environment Housekeeping/Auditing is 24/7 2. Describe the impact of shift work on: Individual (Health and Safety) Family relationships. 3. Describe changes and future trends in the role of the process technician. 4. List the factors responsible for future role changes of the process technician. 5. Describe the difference between organized and non-organized (union and non-union) operations. 1. Describe the differences between work groups and teams. 2. Describe the different types of teams encountered in the process industries. 3. Identify the characteristics of a "High Performance" or an effective team. 4. Define the terms: Synergy Team Dynamics 5. Describe the steps or stages through which a team evolves (forming, storming, norming, and performing). 6. Identify factors that contribute to the failure of a team including: Failure to achieve the defined outcome Failure as a team to work together and achieve full synergy 7. Define workforce diversity and its impact on workplace relations: In a team environment Work group (co-worker) 1. Define the application of physics in the process industries. 2. Define matter and the states in which it exists. 3. Use physical property characteristics to describe various states of matter (liquid, gas, and solids). 4. Define and provide examples of the following terms: Mass Density Elasticity Viscosity Buoyancy Specific Gravity Flow Evaporation Pressure Velocity Friction Temperature Page 2 of 15
3 Basic Physics (cont.) British Thermal Unit Calorie Electricity 5. Describe the three (3) methods of BTU (British Thermal Unit) transfer: Convection Conduction Radiation 6. Describe how Boyle's Law explains the relationship between pressure and volume of gases. 7. Describe how Charles' Law explains the relationship between temperature and volume of gases. 8. Describe how Dalton's Law explains the relationship between total and partial pressure of a gas. 9. Describe how the General Gas Law explains the relationship between temperature, pressure, and volume of gas. 10. Describe how Bernoulli's Law explains the flow of liquids and gasses. 11. Describe force and leverage and their application to the process industry. 12. Convert between scales using mass, flow and temperature which are commonly used in the process industry. Basic Chemistry 1. Define the application of chemistry in the process industries. 2. Describe the relationship between molecules, atoms, protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3. Define the difference between organic and inorganic chemistry. 4. Explain the difference between chemical properties and physical properties. 5. Define and provide examples of the following terms: Hydrocarbon Boiling Point Chemical Reaction Oxidation/ Reduction Acidic Alkaline Exothermic Endothermic Compounds Mixtures Solutions Homogenous Equilibrium Catalyst 6. Describe the difference between an acid and a base (caustic). 7. Describe the method of measurement for acids and bases. (What is ph?) Page 3 of 15
4 Safety, Health, and the Environment Principles of Quality 1. Discuss the safety, health, and environmental hazards found in the process industries. 2. Describe the intent and application of the primary regulations impacting the process industries: CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) CFR 29 OSHA Process Safety Management (PSM) OSHA Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) OSHA Hazard Communication (HAZCOM) OSHA Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) DOT CFR Hazardous Materials General Requirements for Shipments and Packaging EPA CFR Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) 40 CFR Clean Air Act 3. Describe the role of the process technician in achieving successful compliance with regulations. 4. Describe the personal attitudes and behaviors that can help to prevent workplace accidents and incidents. 5. Describe the components of the fire triangle and the fire and fire tetrahedron. 6. Identify the consequences of non-compliance with regulations: Legal Moral and Ethical Safety, Health, and Environmental Economics 7. Explain the managerial and engineering controls used in the industry to minimize hazards and maximize worker and system protection in the workplace. 8. Describe (demonstrate, if possible) the correct use of personal protective equipment (PPE). 9. Describe the intent of the OSHA Voluntary Protection Program (VPP). 10. Describe the application of the International Organization of Standards (ISO) as it relates to the process industries. 1. Identify responses in the process industries to quality issues. 2. Describe the role each of the following played in quality implementation: W. E. Deming Joseph Juran Philip Crosby 3. Describe the four (4) components of Total Quality Management (TQM) and how it is applied in today's workplace. 4. Describe the application of the International Organization of Standards, ISO-9000, as it relates to the process industries. 5. Describe the use of Statistical Process Control (SPC) in the workplace. Describe the roles and responsibilities of the process technician in supporting quality improvement within the workplace. Page 4 of 15
5 Piping and Valves 1. Describe the purpose or function of piping and valves in the process industries. 2. Identify the different materials used to manufacture piping and valve components: Carbon Steel Stainless Steel Iron Plastic Exotic Metals (alloys) 3. Identify the different types of piping and valve connecting methods: Screwed Flanged Welded Glued or bonded 4. Identify the different types of pipe fittings used in the industry and their application: Coupling Elbow Tee Cross Union Nipple Bushing Plug Cap 5. Identify the different types of valves used in the industry and there application: Ball Butterfly Check Diaphragm Gate Globe Plug Relief/Safety 6. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of a valve: Loss or Product Damage al Damage and Cost of Cleanup 7. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with piping and valves: Page 5 of 15
6 Piping and Valves (cont) Tanks, Drums, and Vessels Look: Do: o o o o Inspect for connection leaks Inspect for wear from corrosion or erosion Check for loose valve parts Verify proper positioning of valves o Grease and lubricate o Adjust packing o Labeling 8. Identify the symbols used to represent the different types of piping and valve components presented in this session: 1. Describe the purpose or function of tanks, drums, and vessels in the process industries. 2. Explain the relationship of pressure to the vessel shape and wall thickness. 3. Describe the purpose of dikes, firewalls and containment walls around tanks, drums, and vessels. 4. Define and provide examples of the following terms as they relate to tanks, drums, and vessels: Floating Roof Sphere Blanket Vapor Recovery Foam Chamber Vortex Breaker Sump (Possum Belly) Baffle Mixer Weir Gauge Hatch Boot Manway Heat Tracing (steam or electrical) 5. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with tank farm operations: Listen: abnormal noise Touch: abnormal heat on vessels and piping Look: Monitor levels Check firewalls and sumps Page 6 of 15
7 Tanks, Drums, and Vessels (cont.) Pumps Corrosion and Discoloration Feel: excessive vibration-pumps/mixers Smell: abnormal odors-leaks 6. Identify the symbols used to represent the different types of tanks, drums, and vessels presented in this session. 7. Identify and describe the various types of reactors and their purpose. 8. Identify possible impacts from the following: Improper valve lineup Loss of nitrogen flow Cross contamination Failure of vent system Leaks/Spills Chemical Reactions (such as corrosion, ph, etc.) 1. Describe the purpose or function of pumps in the process industries. 2. Explain the difference between the two common types of pumps used in the process industries: Centrifugal (horizontal and vertical) Positive displacement (rotary and reciprocating) 3. Identify the primary parts of a typical centrifugal pump: 4. Describe the operations of a centrifugal pump. 5. Explain the difference between the rotary and reciprocating positive displacement pumps Identify the primary parts of various positive displacement pumps: 7. Describe the operations of a positive displacement pump. 8. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of both the positive displacement and centrifugal pump: 9. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with pumps: Listen: abnormal noise Inspect: excessive heat and vibration (be aware of high temperatures) Look: Check oil levels Look: Check for Leaks at seals and flanges Look: Discharge Pressure 10. Identify the symbols used to represent the different types of pumps. Page 7 of 15
8 Compressors Steam Turbines 1. Describe the purpose or function of compressors in the process industries. 2. Explain the difference between a pump and compressor in terms of what function each performs. 3. Explain the difference between the two (2) more common types of compressors used in the process industries: Dynamic (centrifugal and axial) Positive Displacement (rotary and reciprocating) 4. Identify the primary parts of a typical centrifugal compressor: 5. Describe the operations of a centrifugal compressor. 6. Explain the difference between rotary and reciprocating positive displacement compressors. 7. Identify the primary parts of a positive displacement compressor. 8. Describe the operations of a positive displacement compressor. 9. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of both the positive displacement and centrifugal compressor: 10. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with compressors: Look: Check oil levels, check for leaks at seals and flange Check suction and discharge pressures Listen: Inspect for abnormal noise Inspect: Inspect for excessive heat and vibration (be aware of high temperatures) 11. Identify the symbols used to represent the different types of compressors presented in this session. 1. Describe the purpose or function of steam turbines in the process industries. 2. Identify the primary parts of a typical (non-condensing) steam turbine: Casing Shaft Moving and fixed blades Governor Nozzle Inlet (Suction) Outlet (Discharge) Trip and Throttle Valve 3. Describe how a steam turbine operates. 4. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of a steam turbine: Page 8 of 15
9 Steam Turbines (cont.) 5. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with a steam turbine: Look: o Check oil levels-lubrication o Check bearings o Check for leaks at seals and flanges o Check RPMs Listen: for abnormal noise Inspect: Check for excessive vibration (be aware of high temperatures) 6. Identify the symbols used to represent the steam turbine and associated equipment presented in this session. Electricity and Motors 1. Explain the difference between AC and DC current. 2. Identify what current (AC, DC, 3-phase, single phase) is most commonly used in the Processing Industry. 3. Explain basic motor controllers 4. Describe the purpose or function of the electric motor in the process industries. 5. Identify the primary parts of a typical electric motor: 6. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper inspection and operation of an AC motor: 7. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with an electric motor: Look: o Check lubrication o Check for loose covers and shrouds Listen: for abnormal noise Inspect: o Check for excessive heat o Check for excessive vibration (be aware of high temperatures) 8. Identify the symbols used to represent electric motors and associated equipment presented in this session. Page 9 of 15
10 Heat Exchangers (Part 1) Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers (Part 2) Air Cooled Exchangers PTAC 1302 INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS TECHNOLOGY 1. Describe the purpose or function of heat exchangers in the process industries. 2. Recall the three (3) methods of heat (BTU) transfer: Convection Conduction Radiation 3. Identify the primary parts of a typical shell and tube exchanger. 4. Describe the operations of a typical shell and tube exchanger. 5. Describe the different applications of a typical shell and tube exchanger: Reboiler (forced feed and thermo siphon) Heater/preheater After-cooler Condenser Chiller Interchanger 6. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of a heat exchanger: al 7. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with a heat exchanger: Look: o Check for external leaks head, flanges, and bleeders o Check for internal tube leaks sample results o Check inlet and outlet pressures o Check inlet and outlet temperatures Listen: Inspect for abnormal noise Inspect: Check for excessive vibration (be aware of high temperatures) 8. Identify the symbols used to represent the heat exchanger and associated equipment presented in this session. 1. Describe the purpose or function of an air cooled heat exchanger in the process industries. 2. Identify the primary parts and support systems of a typical air cooled exchanger. 3. Describe the operation of an air cooled exchanger 4. Describe the different applications or use of water from a cooling tower: Process condensers Lubricating system coolers (Rotating Equipment) 5. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of an air cooled exchanger 6. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with an air cooled exchanger: Look: Leaks Page 10 of 15
11 Heat Exchangers (Part 2) Air Cooled Exchangers (cont.) Heat Exchangers (Part 3) Cooling Towers Furnaces Listen: Inspect for abnormal noise (fans and motors) Inspect: Check for excessive vibration (fans and motors) be aware of high temperatures ntify the symbols used to represent air cooled exchangers, and associated equipment. 1. Describe the purpose or function of a cooling tower in the process industries. 2. Identify the primary parts and support systems of a typical cooling tower. 3. Describe the operation of a Cooling Tower 4. Discuss the hazards associated with improper operation of a Cooling tower and the potential fire hazard when shutting one down. 5. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with a Cooling Tower: Look: Leaks Listen: for abnormal noise (fans and motors) be aware of high temperatures 6. Identify the symbols used with cooling towers and associated equipment presented in this session 1. Describe the purpose or function of a furnace in the process industries. 2. Describe the types of fuel used in a furnace Natural gas Fuel oil Process oil Process gas Fuel gas 3. Identify the primary parts of a typical furnace. 4. Describe the different types of furnaces by draft: Natural draft Forced draft Induced draft Balanced draft 5. Describe the different furnace designs: Cylindrical Cabin A-Frame 6. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with a furnace. Look: positive/negative pressure, flame inspection, hot spots Listen: abnormal noise (i.e., incomplete combustion Inspect: visible emissions, on-line analysis 7. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of a furnace: Page 11 of 15
12 Furnaces (cont.) Protection (PPE) Boilers Identify the symbols used with furnaces and associated equipment presented in this session 1. Describe the fundamental principles of boiler operation. 2. Describe the operation of boilers in different applications in the process industries. 3. Identify the primary parts and support systems of a typical fuel-fired boiler. 4. Describe the types of fuel used in a boiler: Natural gas Fuel oil Fuel gas Process oil Process gas 5. Describe the different types of boilers by draft: Natural draft Forced draft Induced draft Balanced draft 6. Describe the difference in fire tube and water tube boilers. 7. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with operating boilers: Look: Fire eye, boiler level, boiler pressure Listen: abnormal noises Check: safety systems associated with a boiler Inspect: water level, water quality 8. Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of a boiler: 9. Identify the symbols used with boilers and associated equipment presented in this session 1. Describe the purpose or function of a distillation column or tower in the process industries. 2. Identify the primary parts and support systems of a typical tray-type distillation column: 3. Describe the distillation process. 4. Describe the use of packing as it pertains to distillation Discuss the hazards associated with the improper operation of a distillation column: Page 12 of 15
13 Distillation (cont.) 6. Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with distillation column operations: Process Control Instrumentation Listen: Inspect for abnormal noise (pumps and reboilers) Look: Check for leaks Look: Check samples for separation Look: Check temperature and pressure differentials (be aware of high temperatures) Identify the symbols used with distillation columns and associated equipment presented in this session. 1. Describe the purpose or function of process control instrumentation in the process industries. 2. Describe the difference between process control indicators and control loop inputs. 3. Describe the major types of process control instrumentation: Electronic Pneumatic Digital Analog 4. Define a generic control loop and provide an example. 5. Identify four key variables which are controlled by process control instrumentation: Temperature Pressure Level Flow 6. Identify typical process control instruments, their applications and functions. 7. Describe distributive control systems and how they are applied in the process industries. 8. Discuss the hazards associated with process control instruments (i.e., positioners, fail open/fail closed, leaks). Look: Valve position Listen: Leaks on pneumatic air systems Check: valve stroke Describe the monitoring and maintenance activities associated with process control instrumentation. 10. Identify symbols used to represent process control instruments. Process Utilities 1. Discuss the different types of process utilities and their applications: Water Systems (Boiler feed water, Drinking water, Cooling water, Fire water, Service water, Process water, Potable water, Condensate) Steam Electrical Air Systems (Plant, instrument air, breathing) Page 13 of 15
14 Process Utilities (cont.) Sour water Gas Systems (Fuel Gas, Natural gas, nitrogen, etc.) CO2 (carbon monoxide) 2. Describe the different types of equipment associated with each of the utility systems found in the process industries. Process Auxiliaries Process Print Reading Identify symbols used to represent process utilities. 1. Describe the purpose or function of the different process auxiliary systems and their applications. 2. Discuss the different types of waste water systems and their applications in process: Treated water Waste water (Sewer, Storm, Oily) 3. Discuss the equipment associated with flare systems found in the process industries. 4. Discuss the parts associated with refrigeration systems found in the process industries Discuss the parts associated with lubrication systems found in the process industries. 6. Discuss the parts associated with hot oil systems found in the process industries. Identify symbols used to represent process auxiliary systems. 1. Describe the purpose or function of process systems drawings. 2. Identify the common components and information within process systems drawings. 3. Identify the different drawing types and their uses: Block Flow Diagrams Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) Piping and Instrument Diagrams (P&ID) Plan drawing Engineering Flow Drawing (EFD) Electrical Drawings: Mechanical - Wiring Diagrams Schematics Isometrics Identify the different components and their symbols in each of the drawings listed above. Process Facility Tour (optional) Establish the relationship between content in the course and actual equipment in a process by conducting a facility tour. Consider the following: 1. Transportation 2. Access to the facility/safety orientation 3. Tour Guide 4. Proper clothing (PPE) *Suggested alternatives to touring process facility: College physical plant Public/municipal utilities Page 14 of 15
BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE. Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology
 BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology Instructor: Paul Meiller Office Phone: 979.230.3618 Alt. Phone: Office: No office email: paul.meiller@brazosport.edu I. COURSE
BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology Instructor: Paul Meiller Office Phone: 979.230.3618 Alt. Phone: Office: No office email: paul.meiller@brazosport.edu I. COURSE
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology
 Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology Instructor: David Hendrix Office Phone: 979.230.3449 Alt Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: HS.212F Email: david.hendrix@brazosport.edu
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology Instructor: David Hendrix Office Phone: 979.230.3449 Alt Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: HS.212F Email: david.hendrix@brazosport.edu
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology
 Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology Instructor: Edie Myer Office Phone: N/A Alt Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: N/A email: edie.myer@brazosport.ed I. COURSE DESCRIPTION:.
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1302 Introduction to Process Technology Instructor: Edie Myer Office Phone: N/A Alt Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: N/A email: edie.myer@brazosport.ed I. COURSE DESCRIPTION:.
PTAC PROCESS TECHNOLOGY II - SYSTEMS. Last Reviewed: Page 1 of 10
 Systems Overview Water Systems: Potable Water Fire Water Water Systems: Service/Utility Waste Water Storm Water 1. Describe how process industry facilities are divided into systems. Identify the types
Systems Overview Water Systems: Potable Water Fire Water Water Systems: Service/Utility Waste Water Storm Water 1. Describe how process industry facilities are divided into systems. Identify the types
Brazosport College. Syllabus for PTAC Process Technology I Equipment
 Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1410 - Process Technology I Equipment Instructor: Gregg Curry Office Phone: N/A Alt. Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: N/A email: gregg.curry@brazosport.edu I. COURSE DESCRIPTION
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1410 - Process Technology I Equipment Instructor: Gregg Curry Office Phone: N/A Alt. Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: N/A email: gregg.curry@brazosport.edu I. COURSE DESCRIPTION
Appendix B. Glossary of Steam Turbine Terms
 Operator s Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and Troubleshooting. Robert X. Perez and David W. Lawhon. 2016 Scrivener Publishing
Operator s Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and Troubleshooting. Robert X. Perez and David W. Lawhon. 2016 Scrivener Publishing
PROCESS OPERATIONS. Introduction to Operations. Diagrams for the Operating Unit. Revised 11/30/18 1
 TOPIC Introduction to Operations Diagrams for the Operating Unit OBJECTIVES 1. Discuss the importance of this course as a capstone experience in the Process Technology program and how the material learned
TOPIC Introduction to Operations Diagrams for the Operating Unit OBJECTIVES 1. Discuss the importance of this course as a capstone experience in the Process Technology program and how the material learned
CAMS Mechanical Engineering Assessment Planning Assignment 1 - Site & Development Engineer
 Mechanical Engineering Unit 1.0 - Rotating Equipment ME1.1 Turbines including types and Supporting Systems - Steam; Gas; Control System; Governing System; Hydraulic System; Lubrication System and Lube
Mechanical Engineering Unit 1.0 - Rotating Equipment ME1.1 Turbines including types and Supporting Systems - Steam; Gas; Control System; Governing System; Hydraulic System; Lubrication System and Lube
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION
 SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17413 ( EME ) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17413 ( EME ) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Downsizing a Claus Sulfur Recovery Unit
 INFRASTRUCTURE MINING & METALS NUCLEAR, SECURITY & ENVIRONMENTAL Downsizing a Claus Sulfur Recovery Unit OIL, GAS & CHEMICALS By Charles L. Kimtantas and Martin A. Taylor ckimtant@bechtel.com & mataylo1@bechtel.com
INFRASTRUCTURE MINING & METALS NUCLEAR, SECURITY & ENVIRONMENTAL Downsizing a Claus Sulfur Recovery Unit OIL, GAS & CHEMICALS By Charles L. Kimtantas and Martin A. Taylor ckimtant@bechtel.com & mataylo1@bechtel.com
Code. 1) Code. Standard or Specification. Bolting
 Code 1. Code 1) Code (1) ASME B 31.1 : Power Piping (2) ASME B 31.3 : Process Piping (3) ASME B 31.4 : Pipeline Transportation Systems for Liquid Hydrocarbons and Other Liquids 2) Material Code Bolting
Code 1. Code 1) Code (1) ASME B 31.1 : Power Piping (2) ASME B 31.3 : Process Piping (3) ASME B 31.4 : Pipeline Transportation Systems for Liquid Hydrocarbons and Other Liquids 2) Material Code Bolting
Module 9 : Sewage And Storm water Pumping Stations. Lecture 11 : Sewage And Storm water Pumping Stations
 1 P age Module 9 : Sewage And Storm water Pumping Stations Lecture 11 : Sewage And Storm water Pumping Stations 2 P age 9.1 Introduction There are certain locations where it is possible to convey sewage
1 P age Module 9 : Sewage And Storm water Pumping Stations Lecture 11 : Sewage And Storm water Pumping Stations 2 P age 9.1 Introduction There are certain locations where it is possible to convey sewage
Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition. Acknowledgment
 Dedication Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition Forewords Acknowledgment iii xiii xv xvii xix Chapter 1 Introduction to Pipeline Systems 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Liquid Pipelines
Dedication Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition Forewords Acknowledgment iii xiii xv xvii xix Chapter 1 Introduction to Pipeline Systems 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Liquid Pipelines
OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES
 Training Title OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates REF PE015 Operation Skills Enhancement -Measurement & Instrument
Training Title OPERATION SKILLS ENHANCEMENT-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENT FOR PROCESS VARIABLES Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates REF PE015 Operation Skills Enhancement -Measurement & Instrument
Coker Safety and Reliability Lessons Learned
 Coker Safety and Reliability Lessons Learned Dale Wilborn 2015 Coking.com Conference COKER SAFETY & RELIABILITY Current Situation The Delayed Coker industry has had many incidents with severe consequences,
Coker Safety and Reliability Lessons Learned Dale Wilborn 2015 Coking.com Conference COKER SAFETY & RELIABILITY Current Situation The Delayed Coker industry has had many incidents with severe consequences,
MEC-MOS-E-2004 Gas Turbine Maintenance Engineer PERSONAL DATA EDUCATION LANGUAGES COMPUTER SKILLS TRAINING COURSES AND CERTIFICATIONS
 100771-MEC-MOS-E-2004 Gas Turbine Maintenance Engineer Holds a B. Sc. and M. Sc. in Mechanical Power Engineering. Has about 11 years hands-on experience in power plant projects including installation for
100771-MEC-MOS-E-2004 Gas Turbine Maintenance Engineer Holds a B. Sc. and M. Sc. in Mechanical Power Engineering. Has about 11 years hands-on experience in power plant projects including installation for
SEA Certified Piping Design Engineer
 SEA Certified Piping Design Engineer Certification Course Course Title Eligibility Criteria : SEA CERTIFIED PIPING DESIGN ENGINEER : Mechanical Engineer, Chemical & Petroleum Engineer Duration of Course
SEA Certified Piping Design Engineer Certification Course Course Title Eligibility Criteria : SEA CERTIFIED PIPING DESIGN ENGINEER : Mechanical Engineer, Chemical & Petroleum Engineer Duration of Course
CombiSump. Vertical long shaft sump pump,according to ISO 2858,EN 733 (DIN 24255), API 610
 CombiSump Vertical long shaft sump pump,according to ISO 2858,EN 733 (DIN 24255), API 610 CombiSump CombiSump is the sump pump solution for thin liquids. The pump is part of Johnson Pump s Combi-system,
CombiSump Vertical long shaft sump pump,according to ISO 2858,EN 733 (DIN 24255), API 610 CombiSump CombiSump is the sump pump solution for thin liquids. The pump is part of Johnson Pump s Combi-system,
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC Process Technology I Equipment
 Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1410 - Process Technology I Equipment Instructor: Abigale Antoine Office Phone: N/A Alt. Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: N/A Email: abigale.antoine@brazosport.edu I. COURSE
Brazosport College Syllabus for PTAC 1410 - Process Technology I Equipment Instructor: Abigale Antoine Office Phone: N/A Alt. Phone: 979.230.3618 Office: N/A Email: abigale.antoine@brazosport.edu I. COURSE
NUCLEAR TRAINING CENTRE COURSE 134 FOR ONTARIO HYDRO USE ONLY
 NUCLEAR TRAINING CENTRE COURSE 134 FOR ONTARIO HYDRO USE ONLY NUCLEAR TRAINING COURSE COURSE 134 1 - Level 3 - Equipment & System Principles 4 - TURBINE, GENERATOR & AUXILIARIES Index 134.00-0 Objectives
NUCLEAR TRAINING CENTRE COURSE 134 FOR ONTARIO HYDRO USE ONLY NUCLEAR TRAINING COURSE COURSE 134 1 - Level 3 - Equipment & System Principles 4 - TURBINE, GENERATOR & AUXILIARIES Index 134.00-0 Objectives
100 Safety and Soft 114 Fall Protection 150 Environmental Skills Awareness 116 Compressed Gas 101 Personal Protective Cylinder Safety
 100 and Soft Skills 101 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) 101-01 Personal Protective Equipment 101-02 Hearing and Noise 101-03 Respiratory Protection Program 102 Worksite 102-01 Slip, Trip, and Fall
100 and Soft Skills 101 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) 101-01 Personal Protective Equipment 101-02 Hearing and Noise 101-03 Respiratory Protection Program 102 Worksite 102-01 Slip, Trip, and Fall
Assessment Schedule - TS.5
 The Assessor shall determine the business s commitment and support to good and safe working practices; also that it has a positive culture in all aspects of its work. In particular, the assessor shall
The Assessor shall determine the business s commitment and support to good and safe working practices; also that it has a positive culture in all aspects of its work. In particular, the assessor shall
IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Refinery Personnel
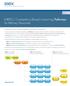 International Human Resources Development Corporation V.2.0 IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Refinery Personnel COMPETENCY-BASED TRAINING PATHWAYS FOR REFINERY TECHNICIANS Our highly regarded
International Human Resources Development Corporation V.2.0 IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Refinery Personnel COMPETENCY-BASED TRAINING PATHWAYS FOR REFINERY TECHNICIANS Our highly regarded
B. System Design and Performance Requirements
 15625 Water Chillers This document provides design standards only, and is not intended for use, in whole or in part, as a specification. Do not copy this information verbatim in specifications or in notes
15625 Water Chillers This document provides design standards only, and is not intended for use, in whole or in part, as a specification. Do not copy this information verbatim in specifications or in notes
Table of Contents. iii. vi Tables. Figures. viii Foreword. ix Acknowledgments
 Figures vi Tables viii Foreword ix Acknowledgments xi About the authors xiii Chapter 1. Fundamentals 1 Fluid Properties 1 Temperature 2 Pressure 3 Gravity and Miscibility 3 Solubility 4 The Ideal Gas Law
Figures vi Tables viii Foreword ix Acknowledgments xi About the authors xiii Chapter 1. Fundamentals 1 Fluid Properties 1 Temperature 2 Pressure 3 Gravity and Miscibility 3 Solubility 4 The Ideal Gas Law
BCE Program March-2017 Electrical Power Systems Time: min Quiz 1 Model A رقم المجموعة:
 Quiz 1 Model A (A) it is discovered since very long time (B) it can be generated by different power stations (C) it can be easy controlled 2. To install Nuclear Power plants it is required to have a very
Quiz 1 Model A (A) it is discovered since very long time (B) it can be generated by different power stations (C) it can be easy controlled 2. To install Nuclear Power plants it is required to have a very
IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Petrochemicals Technicians
 International Human Resources Development Corporation V.1.0 IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Petrochemicals Technicians Competency-Based Training pathways for petrochemicals Technicians
International Human Resources Development Corporation V.1.0 IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Petrochemicals Technicians Competency-Based Training pathways for petrochemicals Technicians
4th Class Power Engineering (PEN) Curriculum Mapping
 Curriculum Mapping Program Curriculum A collection of 25 CTS courses have been developed to align with the revised (2017) 4th Class Power Engineering course outline. These courses, when combined, cover
Curriculum Mapping Program Curriculum A collection of 25 CTS courses have been developed to align with the revised (2017) 4th Class Power Engineering course outline. These courses, when combined, cover
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Styrene
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Styrene The feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 100,000 tonne/y, styrene plant is being investigated. As part of
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Styrene The feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 100,000 tonne/y, styrene plant is being investigated. As part of
Control Valve Sourcebook Chemical Process Overview
 Control Valve Sourcebook Chemical Process Overview Ammonia Production Topic Page I Purification of Feedstock............... II Reforming........................ III Shift Conversion....................
Control Valve Sourcebook Chemical Process Overview Ammonia Production Topic Page I Purification of Feedstock............... II Reforming........................ III Shift Conversion....................
Appendix 8.5 Equipment Summary & Specification Sheets
 Appendix 8.5 Equipment Summary & Specification Sheets 59 EQUIPMENT NR. : NAME : REACTORS, COLUMNS & VESSELS SUMMARY R0 Monolith Reactor R02 Riser Regenerator C0 Depropanizer C04 Deethanizer C05 PP splitter
Appendix 8.5 Equipment Summary & Specification Sheets 59 EQUIPMENT NR. : NAME : REACTORS, COLUMNS & VESSELS SUMMARY R0 Monolith Reactor R02 Riser Regenerator C0 Depropanizer C04 Deethanizer C05 PP splitter
Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Level 3
 Level 3 C1 Shaft Alignment II Duration: 10 hours 3 hours 7 hours This unit is designed to introduce knowledge of the procedures for shaft alignment using the reverse dial method. It is also designed to
Level 3 C1 Shaft Alignment II Duration: 10 hours 3 hours 7 hours This unit is designed to introduce knowledge of the procedures for shaft alignment using the reverse dial method. It is also designed to
FIREMAN BOILER OPERATOR SYLLABUS
 GENERAL INFORMATION: FIREMAN BOILER OPERATOR SYLLABUS This Syllabus has been approved by the Technical Safety Authority of Saskatchewan and is intended to assist candidates studying for the Fireman s examination.
GENERAL INFORMATION: FIREMAN BOILER OPERATOR SYLLABUS This Syllabus has been approved by the Technical Safety Authority of Saskatchewan and is intended to assist candidates studying for the Fireman s examination.
Building Maintenance & Property Management Syllabus Outline
 Building Maintenance & Property Management Syllabus Outline Building Maintenance & Property Management Program The knowledge-based Building Maintenance & Property Management Course is an accelerated method
Building Maintenance & Property Management Syllabus Outline Building Maintenance & Property Management Program The knowledge-based Building Maintenance & Property Management Course is an accelerated method
Gas Dehydration Field Manual
 Gas Dehydration Field Manual Maurice Stewart Ken Arnold AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD * PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO QulfProfcsiion»l Publishing Is an Imprint
Gas Dehydration Field Manual Maurice Stewart Ken Arnold AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD * PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO QulfProfcsiion»l Publishing Is an Imprint
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics. Design Project. Production of Acetone
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Acetone We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 15,000 metric tons/year, acetone plant.
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Acetone We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 15,000 metric tons/year, acetone plant.
Natural Gas Processing
 Natural Gas Processing Technology and Engineering Design Alireza Bahadori, Ph.D. School of Environment, Science and Engineering, Southern Cross University, Lismore, NSW, Australia AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG
Natural Gas Processing Technology and Engineering Design Alireza Bahadori, Ph.D. School of Environment, Science and Engineering, Southern Cross University, Lismore, NSW, Australia AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG
Steam Turbine Bingo Instructions
 Steam Turbine Bingo Instructions Host Instructions: Decide when to start and select your goal(s) Designate a judge to announce events Cross off events from the list below when announced Goals: First to
Steam Turbine Bingo Instructions Host Instructions: Decide when to start and select your goal(s) Designate a judge to announce events Cross off events from the list below when announced Goals: First to
IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Refinery Technicians
 International Human Resources Development Corporation V.1.0 IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Refinery Technicians Competency-Based Training pathways for Refinery Technicians Our highly
International Human Resources Development Corporation V.1.0 IHRDC s Competency-Based e-learning Pathways for Refinery Technicians Competency-Based Training pathways for Refinery Technicians Our highly
SECTION COOLING TOWER
 PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SECTION INCLUDES A. Mechanical induced draft Cooling Tower B. Controls C. Ladder and handrails 1.2 REFERENCES SECTION 23 65 00 COOLING TOWER A. ANSI/AFBMA 9 - Load Rating and Fatigue
PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SECTION INCLUDES A. Mechanical induced draft Cooling Tower B. Controls C. Ladder and handrails 1.2 REFERENCES SECTION 23 65 00 COOLING TOWER A. ANSI/AFBMA 9 - Load Rating and Fatigue
20/06/2011 Seminar on Geothermal Exploitation Santiago de Chile
 Contents Power Plants Steam Power plants Binary Power plants Geothermal Power Plants Single flash systems Binary systems 1 Equipment Well head Gathering piping system Steam separators and moisture separators
Contents Power Plants Steam Power plants Binary Power plants Geothermal Power Plants Single flash systems Binary systems 1 Equipment Well head Gathering piping system Steam separators and moisture separators
Comparing Evaporative Technologies for the Recycling of Produced Waters
 Comparing Evaporative Technologies for the Recycling of Produced Waters Relatively recent advance refinements of evaporative technologies have enabled a cost effective solution for a variety of wastewater
Comparing Evaporative Technologies for the Recycling of Produced Waters Relatively recent advance refinements of evaporative technologies have enabled a cost effective solution for a variety of wastewater
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics Design Project. Production of Ethanol
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics Design Project Production of Ethanol Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 30,000 tonne/y of ethanol from ethylene.
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics Design Project Production of Ethanol Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 30,000 tonne/y of ethanol from ethylene.
COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM DESIGNS BEGIN WITH THE DEMANDS
 COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM DESIGNS BEGIN WITH THE DEMANDS BY: BILL SCALES, P.E. SCALES INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC. The purpose of an assessment of an existing compressed air system, or design of a new one,
COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM DESIGNS BEGIN WITH THE DEMANDS BY: BILL SCALES, P.E. SCALES INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC. The purpose of an assessment of an existing compressed air system, or design of a new one,
Steam Power Station (Thermal Station)
 Steam Power Station (Thermal Station) A generating station which converts heat energy into electrical energy through turning water into heated steam is known as a steam power station. A steam power station
Steam Power Station (Thermal Station) A generating station which converts heat energy into electrical energy through turning water into heated steam is known as a steam power station. A steam power station
VVER-440/213 - The reactor core
 VVER-440/213 - The reactor core The fuel of the reactor is uranium dioxide (UO2), which is compacted to cylindrical pellets of about 9 height and 7.6 mm diameter. In the centreline of the pellets there
VVER-440/213 - The reactor core The fuel of the reactor is uranium dioxide (UO2), which is compacted to cylindrical pellets of about 9 height and 7.6 mm diameter. In the centreline of the pellets there
BHS-FILTRATION INC. BHS VACUUM BELT FILTER, CANDLE & PRESSURE PLATE FILTER TECHNOLOGIES FOR BIO-ENERGY APPLICATIONS
 BHS-FILTRATION INC. BHS VACUUM BELT FILTER, CANDLE & PRESSURE PLATE FILTER TECHNOLOGIES FOR BIO-ENERGY APPLICATIONS 1. Crop Feedstocks for Bio-Ethanol 2. Cellulose Feedstocks for Bio-Ethanol 3. Wood Feedstocks
BHS-FILTRATION INC. BHS VACUUM BELT FILTER, CANDLE & PRESSURE PLATE FILTER TECHNOLOGIES FOR BIO-ENERGY APPLICATIONS 1. Crop Feedstocks for Bio-Ethanol 2. Cellulose Feedstocks for Bio-Ethanol 3. Wood Feedstocks
SECTION FUEL-FIRED UNIT HEATERS
 SECTION 23 55 33 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. This Section includes gas-fired unit heaters. SPEC WRITER NOTES: 1. Use this section only for NCA projects. 2. Delete between // // if not applicable
SECTION 23 55 33 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. This Section includes gas-fired unit heaters. SPEC WRITER NOTES: 1. Use this section only for NCA projects. 2. Delete between // // if not applicable
Mechanical-Electrical Technology MECHANICAL-ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY Sacramento City College Catalog
 Mechanical-Electrical Technology MET Degree: A.S. Mechanical-Electrical Technology Certificates of Achievement: Mechanical-Electrical Technology Mechanical Systems Technician Certificate: Commercial Building
Mechanical-Electrical Technology MET Degree: A.S. Mechanical-Electrical Technology Certificates of Achievement: Mechanical-Electrical Technology Mechanical Systems Technician Certificate: Commercial Building
A. Operation and Maintenance Data: For pumps and controls, to include in operation and maintenance manuals.
 Page 221429-1 SECTION 221429 - PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
Page 221429-1 SECTION 221429 - PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
Corrosion in GASCO Habshan CBA Units and its mitigation
 Corrosion in GASCO Habshan CBA Units and its mitigation Orlando de Matos Inspection Department Head MESPON 2016 - Abu Dhabi 9 th to 11 th October 2016 AGENDA Introduction Process Description for CBA Units
Corrosion in GASCO Habshan CBA Units and its mitigation Orlando de Matos Inspection Department Head MESPON 2016 - Abu Dhabi 9 th to 11 th October 2016 AGENDA Introduction Process Description for CBA Units
Technology Specification
 Technology Specification GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PROCESS FEEDSTOCK CORE TECHNOLOGY COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION OF THE MODULES Introduction KENTEC Energy is a technology company supplying and developing gasification
Technology Specification GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PROCESS FEEDSTOCK CORE TECHNOLOGY COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION OF THE MODULES Introduction KENTEC Energy is a technology company supplying and developing gasification
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Acrylic Acid
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Acrylic Acid We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 50,000 metric tons/year, acrylic acid
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Acrylic Acid We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 50,000 metric tons/year, acrylic acid
ChE 455 Fall 2001 Major 1. Ethylene Oxide Production
 10/19/01 ChE 455 Fall 2001 Major 1 Ethylene Oxide Production Ethylene oxide is a chemical used to make ethylene glycol (the primary ingredient in antifreeze). It is also used to make poly(ethylene oxide),
10/19/01 ChE 455 Fall 2001 Major 1 Ethylene Oxide Production Ethylene oxide is a chemical used to make ethylene glycol (the primary ingredient in antifreeze). It is also used to make poly(ethylene oxide),
MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT DESIGN Online Course Part I: Introduction to Mechanical Equipment
 MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT DESIGN Online Course Part I: Introduction to Mechanical Equipment STUDY NOTES Curso impartido por: Instructor: Javier Tirenti www.etcfunsafe.com Table of contents Introduction... 3
MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT DESIGN Online Course Part I: Introduction to Mechanical Equipment STUDY NOTES Curso impartido por: Instructor: Javier Tirenti www.etcfunsafe.com Table of contents Introduction... 3
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics. Design Project. Production of Ammonia
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ammonia Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 50,000 tonne/y of ammonia from a syngas
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ammonia Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 50,000 tonne/y of ammonia from a syngas
B. Wiring Diagrams: For power, signal, and control wiring.
 Page 221429-1 SECTION 221429 - PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
Page 221429-1 SECTION 221429 - PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
CONTENTS 3 SPLIT CASE PUMPS 4 HORIZONTAL END-SUCTION PUMPS 5 MULTI STAGE PUMPS. HORIZONTAL 6 MULTI STAGE PUMPS. VERTICAL 7 VERTICAL IN LINE PUMPS
 G IN ER EN GI NE GM BH PE N VA LV ES PU M M S MP AU RU PU INDUSTRIAL FOR WATER APPLICATIONS Water Supply Well Systems Irrigation Cooling Water Waste Water Sludge Desalination Fire Fighting CONTENTS 2 3
G IN ER EN GI NE GM BH PE N VA LV ES PU M M S MP AU RU PU INDUSTRIAL FOR WATER APPLICATIONS Water Supply Well Systems Irrigation Cooling Water Waste Water Sludge Desalination Fire Fighting CONTENTS 2 3
Read Only Copy Not For Distribution. Chapter 17. Private Potable Water Supply Systems 17.1 GENERAL REGULATIONS 17.2 QUANTITY OF WATER REQUIRED
 Chapter 17 Private Potable Water Supply Systems 17.1 GENERAL REGULATIONS 17.1.1 Applicability The regulations in this chapter apply to any private potable water supply system where plumbing fixtures are
Chapter 17 Private Potable Water Supply Systems 17.1 GENERAL REGULATIONS 17.1.1 Applicability The regulations in this chapter apply to any private potable water supply system where plumbing fixtures are
SECTION HVAC WATER TREATMENT
 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION SECTION 23 25 00 SPEC WRITER NOTES: 1. Use this section only for NCA projects. 2. Delete between //-----// if not applicable to project. Also delete any other item or paragraph
PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION SECTION 23 25 00 SPEC WRITER NOTES: 1. Use this section only for NCA projects. 2. Delete between //-----// if not applicable to project. Also delete any other item or paragraph
A. This Section includes the following sump pumps and accessories, inside the building, for building storm drainage systems:
 SECTION 221429 - SUMP PUMPS PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
SECTION 221429 - SUMP PUMPS PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
Recent Technologies for Steam Turbines
 Recent Technologies for Steam Turbines Kenji Nakamura Takahiro Tabei Tetsu Takano A B S T R A C T In response to global environmental issues, higher efficiency and improved operational reliability are
Recent Technologies for Steam Turbines Kenji Nakamura Takahiro Tabei Tetsu Takano A B S T R A C T In response to global environmental issues, higher efficiency and improved operational reliability are
University of Delaware
 University Contact: Energy & Engineering Group (302) 831-1744 SECTION 22 13 00 _SANITARY SEWER PIPING SYSTEMS PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Sanitary sewer piping buried 2. Sanitary
University Contact: Energy & Engineering Group (302) 831-1744 SECTION 22 13 00 _SANITARY SEWER PIPING SYSTEMS PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Sanitary sewer piping buried 2. Sanitary
P A C K A G E R. Oil & Gas
 P A C K A G E R P R O D U C T S D I S T R I B U T O R Oil & Gas S T O C K I S T P I P E S V A LV E S F I T T I N G S F L A N G E S SEAMLESS & WELDED PIPES Carbon Steel Low Temperature Pipes Stainless Steel
P A C K A G E R P R O D U C T S D I S T R I B U T O R Oil & Gas S T O C K I S T P I P E S V A LV E S F I T T I N G S F L A N G E S SEAMLESS & WELDED PIPES Carbon Steel Low Temperature Pipes Stainless Steel
Fiberglass Cooling Towers
 Fiberglass Cooling Towers Available in sizes from 100 to 240 tons. FC Series 700 Fiberglass Cooling Tower Available in sizes from 170 to 240 tons. No other fiberglass cooling tower comes with as many high-quality
Fiberglass Cooling Towers Available in sizes from 100 to 240 tons. FC Series 700 Fiberglass Cooling Tower Available in sizes from 170 to 240 tons. No other fiberglass cooling tower comes with as many high-quality
The following sub-systems are provided and the integration of these is described below:
 The following sub-systems are provided and the integration of these is described below: Pretreatment Plant The Pretreatment Plant typically comprises an amine system for gas sweetening and a molecular
The following sub-systems are provided and the integration of these is described below: Pretreatment Plant The Pretreatment Plant typically comprises an amine system for gas sweetening and a molecular
AMCOT COOLING TOWER CORPORATION LRC-H & LRC-LNS CROSS FLOW COOLING TOWER OPERATIONS AND MAINTAINENCE MANUAL
 AMCOT COOLING TOWER CORPORATION LRC-H & LRC-LNS CROSS FLOW COOLING TOWER 1. Preface OPERATIONS AND MAINTAINENCE MANUAL 1-800-444-8693 Operation and Maintenance Manual For Amcot LRC-H Cooling Tower & LRC-LNS
AMCOT COOLING TOWER CORPORATION LRC-H & LRC-LNS CROSS FLOW COOLING TOWER 1. Preface OPERATIONS AND MAINTAINENCE MANUAL 1-800-444-8693 Operation and Maintenance Manual For Amcot LRC-H Cooling Tower & LRC-LNS
-SQA- SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE: UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION. -Module Number Session
 -SQA- SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE: UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Module Number- 3251013 -Session-1993-94 -Superclass- XH -Title- MATERIALS HANDLING 2 -DESCRIPTION-
-SQA- SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE: UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Module Number- 3251013 -Session-1993-94 -Superclass- XH -Title- MATERIALS HANDLING 2 -DESCRIPTION-
Geothermal Power Plant
 Geothermal Power Plant The Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc., Japan Hachijo-jima Geothermal Power Plant 3,300kW 0A3-E-009 Outline All equipment and system except for the civil work and geothermal wells were
Geothermal Power Plant The Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc., Japan Hachijo-jima Geothermal Power Plant 3,300kW 0A3-E-009 Outline All equipment and system except for the civil work and geothermal wells were
TABLE OF CONTENT
 Page : 1 of 28 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION
Page : 1 of 28 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION
Vocabulary. Heat production and transfer
 Kick off 1 Heat is the transfer of energy between objects that are usually at different temperatures. Match the types of energy with the pictures. 1 chemical 3 mechanical 2 nuclear 4 electrical 2 Heat
Kick off 1 Heat is the transfer of energy between objects that are usually at different temperatures. Match the types of energy with the pictures. 1 chemical 3 mechanical 2 nuclear 4 electrical 2 Heat
Questions. Downdraft biomass gasifier. Air. Air. Blower. Air. Syngas line Filter VFD. Gas analyzer(s) (vent)
 Question 1 Questions Biomass gasification is a process where organic matter liberates flammable gases such as hydrogen (H 2 ) and carbon monoxide (CO) when heated to high temperatures. A gasifier is a
Question 1 Questions Biomass gasification is a process where organic matter liberates flammable gases such as hydrogen (H 2 ) and carbon monoxide (CO) when heated to high temperatures. A gasifier is a
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Ethylbenzene
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ethylbenzene We continue to investigate the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 80,000 tonne/y, ethylbenzene facility.
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ethylbenzene We continue to investigate the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 80,000 tonne/y, ethylbenzene facility.
U. S. Army Corps of Engineers Air Stripping Performance Checklist
 U. S. Army Corps of Engineers Air Stripping Performance Checklist Installation Name Site Name / I.D. Evaluation Team Site Visit Date This checklist is designed to facilitate the performance evaluation
U. S. Army Corps of Engineers Air Stripping Performance Checklist Installation Name Site Name / I.D. Evaluation Team Site Visit Date This checklist is designed to facilitate the performance evaluation
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Phthalic Anhydride
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Phthalic Anhydride Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 75,000 tonne/y of phthalic anhydride
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Phthalic Anhydride Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 75,000 tonne/y of phthalic anhydride
N N O V A T I O N E F F I C I E N C Y Q U A L I T Y VTG. Vertical Turbine Generator
 N N O V A T I O N E F F I C I E N C Y Q U A L I T Y VTG For more than 60 years the name Ruhrpumpen has been synonymous worldwide with innovation and reliability for pumping technology Ruhrpumpen is an
N N O V A T I O N E F F I C I E N C Y Q U A L I T Y VTG For more than 60 years the name Ruhrpumpen has been synonymous worldwide with innovation and reliability for pumping technology Ruhrpumpen is an
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Ç engel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Objectives Develop the conservation
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Ç engel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Objectives Develop the conservation
Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter
 Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter Consider the separation of a mixture of 50 mol/hr of propane C 3 H 8 (1) and 50 mol/hr propene, C 3 H 6 (2) at a pressure of 1.1 bar and a
Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter Consider the separation of a mixture of 50 mol/hr of propane C 3 H 8 (1) and 50 mol/hr propene, C 3 H 6 (2) at a pressure of 1.1 bar and a
Combined Heat and Power
 Lecture 12 Combined Heat and Power Combustion Turbines and Co-generation Combustion Turbines and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems See B. K. Hodge, Chapter 5 and Chapter 11. ISBN: 978-0-470-14250-9
Lecture 12 Combined Heat and Power Combustion Turbines and Co-generation Combustion Turbines and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems See B. K. Hodge, Chapter 5 and Chapter 11. ISBN: 978-0-470-14250-9
EXTRACTION EQUIPMENT:- 1. Single stage mixer settler 2. Multi stage mixer settler 3. Spay tower 4. Packed tower 5. Tray tower
 EXTRACTION EQUIPMENT:- 1. Single stage mixer settler 2. Multi stage mixer settler 3. Spay tower 4. Packed tower 5. Tray tower DEFINATION:- EXTRACTION Extraction is the method of separating the liquid mixture
EXTRACTION EQUIPMENT:- 1. Single stage mixer settler 2. Multi stage mixer settler 3. Spay tower 4. Packed tower 5. Tray tower DEFINATION:- EXTRACTION Extraction is the method of separating the liquid mixture
ES Fluid & Thermal Systems Page 1 of 6 STEAM TURBINE LABORATORY
 ES 202 - Fluid & Thermal Systems Page 1 of 6 STEAM TURBINE LABORATORY Objective The objective of this laboratory experience is to demonstrate how mechanical power can be generated using a steam turbine
ES 202 - Fluid & Thermal Systems Page 1 of 6 STEAM TURBINE LABORATORY Objective The objective of this laboratory experience is to demonstrate how mechanical power can be generated using a steam turbine
About Praxair. Air Separation. Applications. our purpose. 1 Where your talent makes an impact
 About Praxair Air Separation Applications our purpose 1 Where your talent makes an impact who we are 2 Where your talent makes an impact Energy Metals Chemicals Manufacturing Electronics Food Healthcare
About Praxair Air Separation Applications our purpose 1 Where your talent makes an impact who we are 2 Where your talent makes an impact Energy Metals Chemicals Manufacturing Electronics Food Healthcare
Training Program for Urea Engineers. Tailor Made to Your Wishes
 Training Program for Urea Engineers Tailor Made to Your Wishes v6 Choose the Modules of Your Interest and Compose your Preferred Training Program ü Highly awarded by all previous participants ü Covering
Training Program for Urea Engineers Tailor Made to Your Wishes v6 Choose the Modules of Your Interest and Compose your Preferred Training Program ü Highly awarded by all previous participants ü Covering
2/24/2011. Energy Efficiency. Fluid Sealing Association. The Beginning. Fluid Sealing Association
 Sealing Systems Energy Efficiency Fluid Sealing Association Friction is Only The Beginning Fluid Sealing Association 1 Sealing Systems Impact Efficiency Friction losses are only the beginning There is
Sealing Systems Energy Efficiency Fluid Sealing Association Friction is Only The Beginning Fluid Sealing Association 1 Sealing Systems Impact Efficiency Friction losses are only the beginning There is
FXV. Closed Circuit Cooling Towers. Closed Circuit Cooling Towers. Product Detail FXV - C 1. Engineering Data FXV Models... C2
 - C 1 Product Detail Engineering Data Models... C2 Structural Support Models... C6 Engineering Specifications... C8 - C 2 Engineering Data Models REMARK: Do not use for construction. Refer to factory certified
- C 1 Product Detail Engineering Data Models... C2 Structural Support Models... C6 Engineering Specifications... C8 - C 2 Engineering Data Models REMARK: Do not use for construction. Refer to factory certified
Modular Oil & Gas Equipment Onshore & Offshore
 Modular Oil & Gas Equipment Onshore & Offshore Separators & Desalters AI Energy Solutions onshore and offshore oil process solutions offer innovative technologies packaged with global project management
Modular Oil & Gas Equipment Onshore & Offshore Separators & Desalters AI Energy Solutions onshore and offshore oil process solutions offer innovative technologies packaged with global project management
Sulfur Tail Gas Thermal Oxidizer Systems By Peter Pickard
 Sulfur Tail Gas Thermal Oxidizer Systems By Peter Pickard Introduction SRU s (Sulfur Recovery Units) are critical pieces of equipment in refineries and gas plants. SRUs remove sulfur compounds from certain
Sulfur Tail Gas Thermal Oxidizer Systems By Peter Pickard Introduction SRU s (Sulfur Recovery Units) are critical pieces of equipment in refineries and gas plants. SRUs remove sulfur compounds from certain
TM Series Induced Draft Cooling Tower Specifications
 Delta Cooling Towers, Inc. 41 Pine Street P.O. Box 315 Rockaway, New Jersey 07866-0315 Telephone 973.586.2201 Fax 973.586.2243 www.deltacooling.com sales@deltacooling.com TM Series Induced Draft Cooling
Delta Cooling Towers, Inc. 41 Pine Street P.O. Box 315 Rockaway, New Jersey 07866-0315 Telephone 973.586.2201 Fax 973.586.2243 www.deltacooling.com sales@deltacooling.com TM Series Induced Draft Cooling
Industrial Manufacturing
 Integrated Solutions for the Industrial Manufacturing Industry A Relentless Ally for American Manufacturing about us ENPRO, INC. has been in the business of helping our customers solve their process problems
Integrated Solutions for the Industrial Manufacturing Industry A Relentless Ally for American Manufacturing about us ENPRO, INC. has been in the business of helping our customers solve their process problems
NSSS Design (Ex: PWR) Reactor Coolant System (RCS)
 NSSS Design (Ex: PWR) Reactor Coolant System (RCS) Purpose: Remove energy from core Transport energy to S/G to convert to steam of desired pressure (and temperature if superheated) and moisture content
NSSS Design (Ex: PWR) Reactor Coolant System (RCS) Purpose: Remove energy from core Transport energy to S/G to convert to steam of desired pressure (and temperature if superheated) and moisture content
SIMPACK - MODEL DEVELOPMENT PACKAGE FOR POWER PLANTS
 SIMPACK - MODEL DEVELOPMENT PACKAGE FOR POWER PLANTS 1.0 OVERVIEW SIMPACK is a totally integrated set of simulation software development modules for power plants. It is template based modeling tool and
SIMPACK - MODEL DEVELOPMENT PACKAGE FOR POWER PLANTS 1.0 OVERVIEW SIMPACK is a totally integrated set of simulation software development modules for power plants. It is template based modeling tool and
Products II 1 VERTICAL LINE SHAFT PRODUCT AND OIL LUBRICATED PUMPS II 2 SUBMERSIBLE PUMPS II 3 MIX FLOW PRODUCT AND OIL LUBRICATED PUMPS
 II Products II 1 VERTICAL LINE SHAFT PRODUCT AND OIL LUBRICATED PUMPS PAGE II-2 II 2 SUBMERSIBLE PUMPS PAGE II-4 II 3 MIX FLOW PRODUCT AND OIL LUBRICATED PUMPS PAGE II-5 II 4 AXIAL FLOW PRODUCT AND OIL
II Products II 1 VERTICAL LINE SHAFT PRODUCT AND OIL LUBRICATED PUMPS PAGE II-2 II 2 SUBMERSIBLE PUMPS PAGE II-4 II 3 MIX FLOW PRODUCT AND OIL LUBRICATED PUMPS PAGE II-5 II 4 AXIAL FLOW PRODUCT AND OIL
PREMIER Low Profile Induced Draft Cooling Tower Specifications
 Fa Delta Cooling Towers, Inc. 185 US Highway 206 Roxbury Township, NJ 07836 973.586.2201 973.586.2243 fax www.deltacooling.com sales@deltacooling.com PREMIER Low Profile Induced Draft Cooling Tower Specifications
Fa Delta Cooling Towers, Inc. 185 US Highway 206 Roxbury Township, NJ 07836 973.586.2201 973.586.2243 fax www.deltacooling.com sales@deltacooling.com PREMIER Low Profile Induced Draft Cooling Tower Specifications
AIR TREATMENT BREATHING AIR PURIFIERS. DBS Series
 AIR TREATMENT BREATHING AIR PURIFIERS DBS Series Optimal Performance and Operation The DBS series breathing air purifier from Gardner Denver will provide the clean, dry air necessary to keep your workers
AIR TREATMENT BREATHING AIR PURIFIERS DBS Series Optimal Performance and Operation The DBS series breathing air purifier from Gardner Denver will provide the clean, dry air necessary to keep your workers
Turbo Machines Pumps and Turbines ME 268
 Turbo Machines Pumps and Turbines ME 268 Turbo Machines Turbo machines are dynamic fluid machines that either extract energy from a fluid (turbine) or add energy to a fluid (pump) as a result of dynamic
Turbo Machines Pumps and Turbines ME 268 Turbo Machines Turbo machines are dynamic fluid machines that either extract energy from a fluid (turbine) or add energy to a fluid (pump) as a result of dynamic
CombiSump. Vertical long shaft sump pump, according to ISO 2858, EN 733, API 610 (VS4)
 CombiSump Vertical long shaft sump pump, according to ISO 2858, EN 33, API 6 (VS4) Johnson Pump, An SPX FLOW Brand CombiSump SPX FLOW develops, manufactures and markets Johnson Pump branded positive displacement
CombiSump Vertical long shaft sump pump, according to ISO 2858, EN 33, API 6 (VS4) Johnson Pump, An SPX FLOW Brand CombiSump SPX FLOW develops, manufactures and markets Johnson Pump branded positive displacement
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS MAINTENANCE & FAILURE ANALYSIS
 Training Title CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS MAINTENANCE & FAILURE ANALYSIS Training Duration 5 days Training Dates & Venue Centrifugal Compressors Maintenance & Failure Analysis 5 14 18 Apr $3,750 Riyadh, KSA
Training Title CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS MAINTENANCE & FAILURE ANALYSIS Training Duration 5 days Training Dates & Venue Centrifugal Compressors Maintenance & Failure Analysis 5 14 18 Apr $3,750 Riyadh, KSA
C. ASSE 1013 Performance Requirements for Reduced Pressure Principle Backflow Preventers.
 PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Purpose: A. This standard is intended to provide useful information to the Professional Service Provider (PSP) to establish a basis of design. The responsibility of the engineer is
PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Purpose: A. This standard is intended to provide useful information to the Professional Service Provider (PSP) to establish a basis of design. The responsibility of the engineer is
Magnetically Coupled Submerged Cryogenic Pumps and Expanders for Ammonia Applications
 Paper 4d Magnetically Coupled Submerged Cryogenic Pumps and Expanders for Ammonia Applications Liquefied Ammonia, or Liquid NH3, is (like LNG or liquefied natural gas) a cryogenic fluid and production
Paper 4d Magnetically Coupled Submerged Cryogenic Pumps and Expanders for Ammonia Applications Liquefied Ammonia, or Liquid NH3, is (like LNG or liquefied natural gas) a cryogenic fluid and production
4th Class Curriculum Document SOPEEC Syllabus, dated November 2017 Previous Syllabus dated 2012 Updated. July 2017 By BFB
 4th Class Curriculum Document SOPEEC Syllabus, dated November 2017 Previous Syllabus dated 2012 Updated July 2017 By BFB The SOPEEC syllabi are the official governing document for SOPEEC examinations.
4th Class Curriculum Document SOPEEC Syllabus, dated November 2017 Previous Syllabus dated 2012 Updated July 2017 By BFB The SOPEEC syllabi are the official governing document for SOPEEC examinations.
