Nanogrinding of SiC wafers with high flatness and low subsurface damage
|
|
|
- Megan Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) Nanogrinding of SiC wafers with high flatness and low subsurface damage HUO Feng-wei, GUO Dong-ming, KANG Ren-ke, FENG Guang Key Laboratory for Precision and Non traditional Machining of Ministry of Education, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian , China Received 20 August 2012; accepted 8 October 2012 Abstract: Nanogrinding of SiC wafers with high flatness and low subsurface damage was proposed and nanogrinding experiments were carried out on an ultra precision grinding machine with fine diamond wheels. Experimental results show that nanogrinding can produce flatness less than 1.0 μm and a surface roughness R a of 0.42 nm. It is found that nanogrinding is capable of producing much flatter SiC wafers with a lower damage than double side lapping and mechanical polishing in much less time and it can replace double side lapping and mechanical polishing and reduce the removal amount of chemical mechanical polishing. Key words: SiC wafer; nanogrinding; cup wheel; flatness; surface roughness; damage 1 Introduction SiC single crystal has a unique combination of electrical and thermophysical properties such as wide energy band gap, high thermal conductivity, large break down field and high saturation velocity. These properties make it an ideal semiconductor material for high temperature, high power, high voltage and high frequency electronic devices. In addition, it is used as the substrate material for III V nitride film deposition for manufacturing electronic and optoelectronic devices [1,2]. While manufacturing these devices, high quality epitaxial SiC thin film or gallium nitride film is required, but they can only be grown on SiC wafers with extremely flat, smooth and damage free surfaces [3,4]. SiC wafer preparation starts with growth of single crystal ingots and then a series of steps are needed to turn an ingot into acceptable wafers. They typically consist of slicing, double side lapping, mechanical polishing (MP) and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) [5,6]. However, good quality SiC wafers are very difficult to obtain, as SiC is extremely hard, extremely brittle and extremely chemically stable. Double side lapping is usually applied after slicing to remove the slicing induced waviness and yield acceptable flatness, but it involves material removal through brittle fracture characterized by chipping and cracking and would generate large subsurface damages. This damaged layer is then removed by mechanical polishing. Mechanical polishing of SiC wafers is typically accomplished with diamond slurries in multiple steps where the grain size is successively reduced until a surface roughness (R a ) 1 nm or less is produced [5]. Since very smooth surface can only be obtained by using diamond slurry of small grain size down to submicron, the material removal rate is typically less than 1 μm/h and the total process time for mechanical polishing is more than 6 h. Nevertheless, it results in insufficiently smooth wafer surfaces characterized by deep and wide scratches [7 9]. The mechanical polishing step is followed by chemical mechanical polishing. Chemical mechanical polishing can achieve damage-free surfaces. However, it is typically very slow, as effective CMP process is not available since SiC is generally unaffected by exposure to acid or alkali at temperatures less than about 300 C. The material removal rate of chemical mechanical polishing is typically 50 to 150 nm/h [10]. Mechanical polishing and chemical mechanical polishing are the most time-consuming and therefore most expensive machining operations in SiC wafers preparation processes. Therefore, there is a need to develop a new method for flattening SiC wafers with lower cost and higher efficiency. Nanogrinding is an aspect of advanced grinding that has been growing rapidly in recent years [11]. It utilizes ultra precision machines with high Foundation item: Project ( ) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Corresponding author: HUO Feng-wei; Tel: ; huofw@dlut.edu.cn DOI: /S (11)
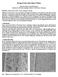
2 3028 HUO Feng-wei, et al/trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) motion accuracy and high stiffness, and it can precisely control the kinetics of the grinding wheel at the nanometer level and generate surfaces with high dimension and form accuracy [11,12]. The surface roughness and subsurface damage can be sharply reduced by using fine diamond wheel and controlling the grain depth cut down to nanometer level [13,14]. In this work, nanogrinding of SiC wafers with fine diamond wheels was proposed. Its capability to achieve flatter wafers with a lower subsurface damage at higher throughput in comparison with the conventional technologies is investigated. 2 Experimental Both the wheel spindle and the rotary table spindle were supported by high accuracy air bearings with axial and radial motion error less than 50 nm. The radius and the rim width of the cup wheel were 175 mm and 3 mm, respectively. #600, #2000 and #12000 vitrified diamond cup wheels were used for rough, fine and finish grinding, respectively. The wheel rotational speed was 2000 r/min and the rotary table rotational speed was 100 r/min. The wheel infeed rate was 2, 1 and 0.25 μm/min for the #600, #2000 and #12000 diamond cup wheels, respectively, and the corresponding material removal amount was 30, 10 and 5 μm, respectively. The cup wheels were trued and dressed using a cast iron lapping plate with #360 silicon carbide abrasives. Deionized water was used as the coolant. 2.1 SiC wafers SiC single crystal is commercially available in various polytypes such as 2H, 3C, 4H and 6H. 4H-SiC is the most favorable substrate for high-power, high-frequency and high temperature device applications and it is more available. Thus 50.8 mm N-type 4H-SiC wafers having an off-axis orientation of 4 degrees were selected. Sliced SiC wafers were used as the grinding specimens. Double side lapped, mechanical polished and chemical mechanical polished SiC wafers were used for contrast and comparison with grinding results. All the SiC wafers were research grade and were made by TankeBlue Semiconductor Co. Ltd., Beijing, China. 2.2 Nanogrinding experiments Nanogrinding experiments were performed on an ultra precision surface grinding machine (Okamoto, VG401MK). It uses a rotary table and a cup wheel to perform an infeed grinding, as shown in Fig. 1. The wafer is fixed on the center of the rotary table and the cup wheel is offset by a distance of the wheel radius relative to the rotational axis of the rotary table. While grinding, both the cup wheel and the rotary table rotate and the cup wheel is fed down to the wafer [12,15]. 2.3 Characterization of SiC wafer surfaces After nanogrinding experiments, the ground specimens were measured to determine the surface roughness, surface morphology and flatness. The surface roughness and the morphology of double side lapped, mechanical polished and chemical mechanical polished wafers were measured as well for contrast and comparison. Flatness was measured with a Tropel Flatmaster 200 surface form measurement. Surface topography was measured with a Zygo Newview D surface profiler over a scanning area of 70 μm 53 μm. The surface morphology was examined using a field emission environmental scanning electron microscope (SEM, SUPRA 55, Carl Zeiss, Germany). Atomic force microscope (AFM, XE200, Park Systems Inc, Korea) was used to characterize the scratches induced by nanogrinding and mechanical polishing. 3 Results Photographs of the ground SiC wafers are shown in Fig. 2. There are a large number of obvious grinding traces on the wafer ground with the #600 diamond wheel and only a few faint grinding traces could be seen on the wafer with the #2000 wheel. Whereas grinding with the #12000 diamond wheel produced a nominally defect-free specular surface. Fig. 1 Photograph of grinding set-up Fig. 2 Photographs of SiC wafers ground with #600, #2000 and #12000 diamond wheels, respectively
3 HUO Feng-wei, et al/trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) Surface roughness The surface topography of the SiC wafers measured using the 3D surface profiler is shown in Fig. 3. Figures 3(a) (c) are Zygo images of typical double side lapped, mechanical polished and chemical mechanical polished SiC wafers, respectively. Figures 3(d) (f) are Zygo images of SiC wafers after grinding with #600, #2000 and #12000 diamond wheels, respectively. It can be seen that the surface of the double side lapped wafer was extremely rough. It was characterized by a surface roughness R a of nm, rms of nm and PV of 1582 nm. The surface roughness R a, rms and PV of the mechanical polished wafer were 0.612, 0.76 and nm respectively. The SiC wafer after chemical mechanical polishing had a surface roughness R a of nm, rms of nm and PV of nm. The wafer ground with the #600 diamond wheel had a surface roughness R a of nm, rms of nm and PV of 1067 nm. Whereas, grinding with the #2000 diamond wheel resulted in a surface roughness R a of 2.58 nm, rms of 3.41 nm and PV of nm. They were 0.421, and nm respectively when grinding with the #12000 diamond wheel. 3.2 Surface morphology Figures 4(a) (d) are the SEM images of the double side lapped and ground SiC wafers. SEM observation shows that the lapped wafer surface consists of a great number of small fracture craters induced by lateral cracks propagation. This indicates that material is removed predominately by brittle fracture in lapping. However, the material is removed predominately by plastic deformation in nanogrinding, as can be seen from the smooth grooves generated by individual diamond grains and the residual plastic chips adhered to the outside of the grooves. The majority of the wafer surface is smooth and exhibits a ductile removal appearance even when ground with the #600 diamond wheel, though chipping pits and medium cracks can be seen occasionally. A #2000 diamond wheel can produce a smoother wafer surface, but slight brittle fractures still exist. The grooves on the SiC wafer ground with #12000 diamond wheel were very smooth and no brittle fracture was observed even at the high magnification. Fig. 3 Surface topographies of SiC wafers: ((a) Double side polished; (b) Mechanical polished; (c) Chemical mechanical polished; (d) Ground with #600 diamond wheel; (e) Ground with #2000 diamond wheel; (f) Ground with #12000 diamond wheel
4 3030 HUO Feng-wei, et al/trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) Fig. 4 SEM images of SiC wafers: (a) Double side lapped; (b) Ground with #600 diamond wheel; (c) Ground with #2000 diamond wheel; (d) Ground with #12000 diamond wheel The width of the generated grooves is very small while ground with the #12000 cup wheel, as can be seen that the maximum was measured to be 70 nm, and an overwhelming majority of the grooves is less than 20 nm in width. This indicates that single crystal silicon carbide is completely ductile when ground with the #12000 diamond wheel, as shown in Fig. 4(d). AFM measurements with a scan area of 20 μm 20 μm in noncontact mode show that there are high density of grooves on both surfaces of the wafer ground with the #12000 diamond wheel and the mechanical polished wafer, as seen in Fig. 5. However, the grooves on the ground surface are much finer and they are much similar in width and depth than that on the mechanical polished surface. Most of these grooves on the ground wafer were measured to be only 2 3 nm in depth. On the contrary, large scratches up to 10 nm in depth and 0.3 μm in width were found on the mechanical polished wafer surface. 3.3 Flatness The surface of the sliced wafer is extremely rough and has obvious waviness, as shown in Fig. 6. Its flatness was measured to be μm. However, it reduced to μm after grinding with a #600 diamond wheel. Further flatness measurements showed that grinding with #600, #2000 or #12000 diamond wheels resulted in similar flatness. This indicates that nanogrinding can produce SiC wafers with lower bow, warp and total thickness variation (TTV). Fig. 5 AFM micrographs of SiC wafers: (a) Mechanical polished; (b) Ground with #12000 wheel
5 HUO Feng-wei, et al/trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) Fig. 6 Flatness error of sliced (a) and ground with #600 diamond wheel (b) SiC wafers 4 Discussion The grinding wheel in nanogrinding typically rotates at a high speed in the range of r/min; whereas the lapping plate in lapping rotate at a speed less than 300 r/min and polishing is typically done at lower speeds. It takes several hours to lap the sliced wafer to an acceptable flatness. However, the experiments show that the sliced wafer could be flattened by nanogrinding for less than 15 min. Therefore, nanogrinding is a faster and more cost effective process than lapping and polishing. In infeed grinding using a rotary table and a cup wheel, the rotational speeds of the rotary table range from 50 to 500 r/min and the infeed rate may range from several tens microns down to submicron per minute. Since the wheel depth of cut is the ratio of the infeed rate to the rotational speeds of the rotary table, the wheel depth of cut can be set to be several tens of nanometers or less. The depth of cut made by individual diamond grains is generally equal to or smaller than the wheel depth of cut. The wheel depth of cut in these grinding experiments was calculated to be 20, 10 and 2.5 nm for the #600, #2000 and #12000 cup wheel, respectively [13,14]. When cutting at depth of cut of such a nanometer scale, the resultant subsurface damage can be very low. Moreover, the depths of cut of the individual abrasive grains can be set to be a level equal to or less than the critical depth of cut so that ductile mode grinding can be realized based on ductile removal rather than brittle fracture, and thereby making it possible to suppress the generation of microcracks [15]. For example, the undeformed chip thickness cut by a single grain was measured to be only 2 3 nm when ground SiC wafer with #12000 diamond wheel using the grinding conditions described in the previous section. When ground at an undeformed chip thickness of such level, only a few layers of atoms are removed from the wafer surface each time, the resisting shear stresses at the cutting edges of the diamond grains become extremely large, the plastic yield limit is lower than the brittle fracture limit, the material is removed in ductile mode and it was unlikely to induce any cracks [12,15]. Mechanical polishing basically uses the same ductile mode removal mechanism as grinding with diamond abrasives in submicron level or less and very gentle polishing pressure. However, mechanical polishing suffers deep scratching, as shown in Fig. 5(a). Scratching is a primary defect that is caused by very low levels of large, oversize particles in the slurry. Despite the grain size distribution of the diamond slurry used in mechanical polishing is stringently controlled, the existence of oversize grains is inevitable. When the wafer being polished is placed in contact with the slurry on the polishing pad, the oversize grains will support a disproportionate amount of the load placed on the wafer and have tendency to produce high depth of cut. If the grain depth of cut exceeds the critical depth of cut, brittle fracture that can extend into the crystal structure beneath the wafer surface by more than several microns may occur. On the contrary, no obviously large, deep scratches generate when ground with the #12000 diamond cup wheel. It is well accepted that the subsurface damage generally increases linearly with increasing surface roughness during grinding, lapping or polishing hard and brittle materials [16,17]. A comparison of the surface roughness of SiC wafers obtained from grinding, mechanical polishing and double side lapping enabled us to evaluate the subsurface damage induced by these three processes. It can be found that the surface roughness of the SiC wafer ground with the #600 diamond wheel is significantly smaller than that of the double side lapped. Grinding with a #2000 diamond wheel produces a relatively rough surface than mechanical polishing. However, the surface roughness with a #12000 diamond wheel is significantly smaller than mechanical polishing. Moreover, the surface roughness of the SiC wafer ground
6 3032 HUO Feng-wei, et al/trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) with the #12000 diamond wheel is very close to that of the chemical mechanical polishing, as shown in Fig. 7. Therefore, the subsurface damage induced by grinding with #12000 diamond cup wheel is better than that by mechanical polishing. Thus, the removal amount for chemical mechanical polishing can be reduced significantly. 5 Conclusions 1) Nanogrinding can produce a flatness less than 1.0 μm and a surface roughness R a of 0.42 nm for 508 mm SiC wafers. 2) Grinding with #600 diamond wheel is less damaged than double side lapping and grinding with #12000 diamond wheel is less damaged than mechanical polishing. 3) Nanogrinding is capable of producing much flatter SiC wafers with a lower damage than double side lapping and mechanical polishing in much less time. 4) Nanogrinding can replace double side lapping and mechanical polishing and reduce the removal amount for chemical mechanical polishing. References Fig. 7 Comparison of surface roughness among chemical mechanical polishing (CMP), nanogrinding and mechanical polishing (MP) In traditional wafer preparation processes, the flatness of SiC wafers mainly depends on double side lapping. Mechanical polishing does not improve wafers flatness since they use soft polishing pad and the pad is prone to deform according to the shape of the wafers. On the contrary, the flatness may deteriorate after a great amount of polishing due to edge effect [5]. During double side lapping, the down force exerted by the upper lapping plate has a tendency to bend the wafer, and hence it is difficult for double side lapping to produce very flat SiC wafers. Nevertheless, SiC wafers with high warp, bow and TTV are undesirable. Producing a large number of high quality SiC wafers with low bow, warp and TTV remains a constant technical commercial goal. Since nanogrinding utilizes ultra precision machines with high motion accuracy and high stiffness, it can precisely control the kinetics of the grinding wheel at the nanometer level. The cutting paths of the individual grains are highly deterministic, all the irregularities on the wafer surface can be removed and hence it is possible to control the wafer flatness to a higher degree. The above analyses show that nanogrinding is capable of producing much flatter SiC wafers with lower damages than double side lapping and mechanical polishing in much less time and it could replace double side lapping and mechanical polishing and reduce the removal amount for chemical mechanical polishing. These results provide useful information for preparing high quality SiC wafers with high efficiency and low cost. [1] POWELL A R, ROWLAND L B. SiC materials-progress, status, and potential roadblocks [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2002, 90(6): [2] ALVI N H, RIAZ M, TZAMALIS G, NUR O, WILLANDER M. Fabrication and characterization of high-brightness light emitting diodes based on n-zno nanorods grown by a low-temperature chemical method on p-4h-sic and p-gan [J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2010, 25(6): [3] LEE K S, LEE S H, NAHM K S, KIM K C, KIM M. Effect of substrate surface state on the crystal quality of homoepitaxially grown 6H-SiC epilayers [J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2004, 45(4): [4] CHEN X F, XU X G, HU X B, LI J, JIANG S Z, NING L N, WANG Y M, JIANG M H. Anisotropy of chemical mechanical polishing in silicon carbide substrates [J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2007, 142(1): [5] KATO T, WADA K, HOZOMI E, TANIGUCHI H, MIURA T, NISHIZAWA S, ARAI K. High throughput SiC wafer polishing with good surface morphology [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, : [6] CHEN X F, LI J, MA D Y, HU X, XU X G, JIANG M H. Fine Machining of large-diameter 6H-SiC wafers [J]. Journal of Material Science and Technology, 2006, 22(5): [7] CHEN X F, XU X G, LI J, JIANG S Z, NING L N, WANG Y M, MA D Y, HU X B, JIANG M H. Surface polishing of 6H-SiC substrates [J]. Journal of Material Science and Technology, 2007, 23(3): [8] YAGI K, MURATA J, KUBOTA A, SANO Y, HARA H, ARIMA K, OKAMOTO T, MIMURA H, YAMAUCHI K. Defect-free planarization of 4H SiC(0001) substrate using reference plate [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 47(1): [9] LEE H, PARK B, JEONG S, JOO S, JEONG H. The effect of mixed abrasive slurry on CMP of 6H-SiC substrates [J]. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 2009, 10(3): [10] GRIM J R, BENAMARA M, SKOWRONSKI M, EVERSON W J, HEYDEMANN V D. Transmission electron microscopy analysis of mechanical polishing-related damage in silicon carbide wafers [J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology. 2006, 21(12): [11] JACKSON M J, DAVIM J P. Machining with abrasives [M]. New York: Springer, 2011: [12] YIN L, PICKERING J P, RAMESH K, HUANG H, SPOWAGE A C,
7 HUO Feng-wei, et al/trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) VANCOILLE E Y J. Planar nanogrinding of a fine grained WC-Co composite for an optical surface finish [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2005, 26(7 8): [13] HUO F W, ZHAO H H, ZHAO D J. Nanogrinding of silicon wafer using a novel vitrified diamond wheel [J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2011, 26(8): [14] ZHANG Z Y, HUO F W, WU Y Q, HUANG H. Grinding of silicon wafers using an ultrafine diamond wheel of a hybrid bond material [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2011, 51(1): [15] BIFANO T G, BIERDEN P A. Fixed-abrasive grinding of brittle hard-disk [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 1997, 37(7): [16] HED P P, EDWARDS D F. Relationship between subsurface damage depth and surface roughness during grinding of optical glass with diamond tools [J]. Applied Optics, 1987, 26(13): [17] LI S Y, WANG Z, WU Y L. Relationship between subsurface damage and surface roughness of optical materials in grinding and lapping processes [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 205(1 3): 高平整度和低损伤碳化硅晶片的纳米磨削技术 霍凤伟, 郭东明, 康仁科, 冯光 大连理工大学精密与特种加工教育部重点实验室大连 摘要 : 采用细粒度砂轮的纳米磨削来实现碳化硅晶片高平整度和低损伤加工新方法 磨削试验表明采用纳米磨削 50.8 mm 碳化硅晶片时其平整度在 1.0 μm 以内, 表面粗糙度可达 0.42 nm 纳米磨削比双面研磨和机械抛光更能高效地对碳化硅晶片做更高平整度 更低损伤加工, 可以取代双面研磨和机械抛光, 并减小化学机械抛光去除量 研究结果对高效低成本制备高质量碳化硅晶片有参考价值 关键词 : 碳化硅晶片 ; 纳米磨削 ; 杯形砂轮 ; 平整度 ; 表面粗糙度 ; 损伤 (Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Bimodal-grained Ti fabricated by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 1170 1175 Bimodal-grained Ti fabricated by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering Yan LONG, Wen-jing GUO, Ying LI Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 1170 1175 Bimodal-grained Ti fabricated by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering Yan LONG, Wen-jing GUO, Ying LI Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory
Automated, reliable lapping and polishing systems make light work of hard silicon carbide and sapphire wafers
 Automated, reliable lapping and polishing systems make light work of hard silicon carbide and sapphire wafers Author: Mark Kennedy www.logitech.uk.com Overview The lapping and polishing of wafers made
Automated, reliable lapping and polishing systems make light work of hard silicon carbide and sapphire wafers Author: Mark Kennedy www.logitech.uk.com Overview The lapping and polishing of wafers made
Recrystallization behavior of cold rolled Al Zn Mg Cu fabricated by twin roll casting
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2226 2231 Recrystallization behavior of cold rolled Al Zn Mg Cu fabricated by twin roll casting Yun-Soo LEE, Won-Kyoung KIM, Dong-A JO, Cha-Yong LIM, Hyoung-Wook
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2226 2231 Recrystallization behavior of cold rolled Al Zn Mg Cu fabricated by twin roll casting Yun-Soo LEE, Won-Kyoung KIM, Dong-A JO, Cha-Yong LIM, Hyoung-Wook
Ceramic Processing Research
 Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 100~106 (2010) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Factors affecting surface roughness of Al 2 O 3 films deposited on Cu substrates
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 100~106 (2010) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Factors affecting surface roughness of Al 2 O 3 films deposited on Cu substrates
Interfacial structure and mechanical properties of hot-roll bonded joints between titanium alloy and stainless steel using niobium interlayer
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2839 2844 Interfacial structure and mechanical properties of hot-roll bonded joints between titanium alloy and stainless steel using niobium interlayer Dong-sheng
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2839 2844 Interfacial structure and mechanical properties of hot-roll bonded joints between titanium alloy and stainless steel using niobium interlayer Dong-sheng
GRINDING AND OTHER ABRASIVE PROCESSES
 GRINDING AND OTHER ABRASIVE PROCESSES Grinding Related Abrasive Process Abrasive Machining Material removal by action of hard, abrasive particles usually in the form of a bonded wheel Generally used as
GRINDING AND OTHER ABRASIVE PROCESSES Grinding Related Abrasive Process Abrasive Machining Material removal by action of hard, abrasive particles usually in the form of a bonded wheel Generally used as
PROCESS PARAMETERS IN GRINDING OF Si 3 N 4 CERAMICS WITH VIRTRIFIED BOND DIAMOND GRINDING WHEEL
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol.13, No.4, October-December 2018, p.1205-1211 PROCESS PARAMETERS IN GRINDING OF Si 3 N 4 CERAMICS WITH VIRTRIFIED BOND DIAMOND GRINDING WHEEL Z. H.
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol.13, No.4, October-December 2018, p.1205-1211 PROCESS PARAMETERS IN GRINDING OF Si 3 N 4 CERAMICS WITH VIRTRIFIED BOND DIAMOND GRINDING WHEEL Z. H.
Characteristics of machined surface controlled by cutting tools and conditions in machining of brittle material
 Characteristics of machined surface controlled by cutting tools and conditions in machining of brittle material Yong-Woo KIM 1, Soo-Chang CHOI 1, Jeung-Woo PARK 2, Deug-Woo LEE 3 1. Department of Nano
Characteristics of machined surface controlled by cutting tools and conditions in machining of brittle material Yong-Woo KIM 1, Soo-Chang CHOI 1, Jeung-Woo PARK 2, Deug-Woo LEE 3 1. Department of Nano
Deterministic Microgrinding, Lapping, and Polishing of Glass-Ceramics
 Deterministic Microgrinding, Lapping, and Polishing of Glass-Ceramics Introduction Glass-ceramics are attractive structural materials due to their good mechanical properties, chemical stability at higher
Deterministic Microgrinding, Lapping, and Polishing of Glass-Ceramics Introduction Glass-ceramics are attractive structural materials due to their good mechanical properties, chemical stability at higher
Structural and mechanical properties of CuZr/AlN nanocomposites
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 380 384 Structural and mechanical properties of CuZr/AlN nanocomposites Man GU 1,2, Yu-cheng WU 1,3, Ming-hua JIAO 3,4, Xin-min HUANG 1 1. School of Materials
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 380 384 Structural and mechanical properties of CuZr/AlN nanocomposites Man GU 1,2, Yu-cheng WU 1,3, Ming-hua JIAO 3,4, Xin-min HUANG 1 1. School of Materials
MECHANICAL MICROMACHINING OF HIGH ASPECT RATIO MICRO-STRUCTURES
 MECHANICAL MICROMACHINING OF HIGH ASPECT RATIO MICRO-STRUCTURES Hans H. Gatzen, Caspar Morsbach, Alexey Karyazin Institute for Microtechnology, Hanover University, Germany Key Words: precision machining,
MECHANICAL MICROMACHINING OF HIGH ASPECT RATIO MICRO-STRUCTURES Hans H. Gatzen, Caspar Morsbach, Alexey Karyazin Institute for Microtechnology, Hanover University, Germany Key Words: precision machining,
Improving the Surface Roughness of a CVD Coated Silicon Carbide Disk By Performing Ductile Regime Single Point Diamond Turning.
 Improving the Surface Roughness of a CVD Coated Silicon Carbide Disk By Performing Ductile Regime Single Point Diamond Turning Deepak Ravindra (Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering) & John
Improving the Surface Roughness of a CVD Coated Silicon Carbide Disk By Performing Ductile Regime Single Point Diamond Turning Deepak Ravindra (Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering) & John
Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg 3Sn 1Mn magnesium alloy
 Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg 3Sn 1Mn magnesium alloy YANG Ming-bo 1, 2, 3, QIN Cai-yuan 1, PAN Fu-sheng 3 1. Materials Science and Engineering College, Chongqing
Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg 3Sn 1Mn magnesium alloy YANG Ming-bo 1, 2, 3, QIN Cai-yuan 1, PAN Fu-sheng 3 1. Materials Science and Engineering College, Chongqing
Advanced Manufacturing Choices
 Advanced Manufacturing Choices Table of Content Mechanical Removing Techniques Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB) Ultrasonic Machining In ultrasonic machining (USM),
Advanced Manufacturing Choices Table of Content Mechanical Removing Techniques Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB) Ultrasonic Machining In ultrasonic machining (USM),
Preparation and properties of porous silicon carbide ceramics through coat mix and composite additives process
 Preparation and properties of porous silicon carbide ceramics through coat mix and composite additives process ZHAO Hong sheng, LIU Zhong guo, YANG Yang, LIU Xiao xue, ZHANG Kai hong, LI Zi qiang Institute
Preparation and properties of porous silicon carbide ceramics through coat mix and composite additives process ZHAO Hong sheng, LIU Zhong guo, YANG Yang, LIU Xiao xue, ZHANG Kai hong, LI Zi qiang Institute
Effect of electromagnetic field on microstructure and macrosegregation of flat ingot of 2524 aluminium alloy
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2408 2413 Effect of electromagnetic field on microstructure and macrosegregation of flat ingot of 2524 aluminium alloy Yu-bo ZUO, Jian-zhong CUI, Dan MOU, Qing-feng
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2408 2413 Effect of electromagnetic field on microstructure and macrosegregation of flat ingot of 2524 aluminium alloy Yu-bo ZUO, Jian-zhong CUI, Dan MOU, Qing-feng
A Study on the Grindability of Ceramics by Wet Lapping
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Number 5 (2017) pp. 681-685 A Study on the Grindability of Ceramics by Wet Lapping Seong-kyum Kim 1 and Haeng-muk Cho 1*
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Number 5 (2017) pp. 681-685 A Study on the Grindability of Ceramics by Wet Lapping Seong-kyum Kim 1 and Haeng-muk Cho 1*
Shear hydro-bending of 5A02 aluminum alloys rectangular tubes
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s382 s388 Shear hydro-bending of 5A02 aluminum alloys rectangular tubes HAN Cong, XU Yong-chao, WANG Yong, ZANG Chao, YUAN Shi-jian School of Materials Science
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s382 s388 Shear hydro-bending of 5A02 aluminum alloys rectangular tubes HAN Cong, XU Yong-chao, WANG Yong, ZANG Chao, YUAN Shi-jian School of Materials Science
The Study of SEM Examination of Crept Ceramic Samples Prepared by Cross Polishing Method
 The Study of SEM Examination of Crept Ceramic Samples Prepared by Cross Polishing Method Alper Uludag Faculty of Aeronautics and Astronautics Anadolu University Eskisehir, Turkey alperuludag@anadolu.edu.tr
The Study of SEM Examination of Crept Ceramic Samples Prepared by Cross Polishing Method Alper Uludag Faculty of Aeronautics and Astronautics Anadolu University Eskisehir, Turkey alperuludag@anadolu.edu.tr
Similar physical simulation of microflow in micro-channel by centrifugal casting process
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1094 1100 Similar physical simulation of microflow in micro-channel by centrifugal casting process Ming-xing REN 1, Guo-tian WANG 2, Bang-sheng LI 1,2, Zhen-long
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1094 1100 Similar physical simulation of microflow in micro-channel by centrifugal casting process Ming-xing REN 1, Guo-tian WANG 2, Bang-sheng LI 1,2, Zhen-long
American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (2): 40-44, 2010 ISSN Science Publications
 American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (2): 40-44, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications Fabrication of X-Ray Optics for a Portable Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer Using Electrolytic
American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (2): 40-44, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications Fabrication of X-Ray Optics for a Portable Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer Using Electrolytic
Grinding of Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Al 2 O 3 or SiC Particles
 Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:79 83 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Grinding of Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Al 2 O 3 or SiC Particles Z. W. Zhong
Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:79 83 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Grinding of Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Al 2 O 3 or SiC Particles Z. W. Zhong
Effect of wet shot peening on Ti 6Al 4V alloy treated by ceramic beads
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 690 696 Effect of wet shot peening on Ti 6Al 4V alloy treated by ceramic beads Guo-qing CHEN 1, Yan JIAO 1, Tang-yong TIAN 1, Xin-hua ZHANG 2, Zhi-qiang LI 2,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 690 696 Effect of wet shot peening on Ti 6Al 4V alloy treated by ceramic beads Guo-qing CHEN 1, Yan JIAO 1, Tang-yong TIAN 1, Xin-hua ZHANG 2, Zhi-qiang LI 2,
Fabrication and application of high quality diamond coated. CMP pad conditioners
 Fabrication and application of high quality diamond coated CMP pad conditioners Hua Wang 1,a, Fanghong Sun 1,b* 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240, China
Fabrication and application of high quality diamond coated CMP pad conditioners Hua Wang 1,a, Fanghong Sun 1,b* 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240, China
Effect of Residual Phase and Grain Size on Corrosion Resistance of SiC Ceramics in Mixed HF-HNO 3 Acid Solution
 第 31 卷第 6 期无机材料学报 Vol. 31 No. 6 2016 年 6 月 Journal of Inorganic Materials Jun., 2016 Article ID: 1000-324X(2016)06-0661-06 DOI: 10.15541/jim20150579 Effect of Residual Phase and Grain Size on Corrosion
第 31 卷第 6 期无机材料学报 Vol. 31 No. 6 2016 年 6 月 Journal of Inorganic Materials Jun., 2016 Article ID: 1000-324X(2016)06-0661-06 DOI: 10.15541/jim20150579 Effect of Residual Phase and Grain Size on Corrosion
Grinding of hard-material-coated forming tools on machining centers
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia CIRP 1 (2012 ) 388 392 5 th CIRP Conference on High Performance Cutting 2012 Grinding of hard-material-coated forming tools on machining centers S. Rausch
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia CIRP 1 (2012 ) 388 392 5 th CIRP Conference on High Performance Cutting 2012 Grinding of hard-material-coated forming tools on machining centers S. Rausch
Microstructure and mechanical properties of ceramic coatings formed on 6063 aluminium alloy by micro-arc oxidation
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3323 3328 Microstructure and mechanical properties of ceramic coatings formed on 6063 aluminium alloy by micro-arc oxidation Nan XIANG 1,2, Ren-guo SONG 1,2,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3323 3328 Microstructure and mechanical properties of ceramic coatings formed on 6063 aluminium alloy by micro-arc oxidation Nan XIANG 1,2, Ren-guo SONG 1,2,
Effects of tribological behavior of DLC film on micro-deep drawing processes
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2877 2882 Effects of tribological behavior of DLC film on micro-deep drawing processes Chun-ju WANG 1,2,3, Chuan-jie WANG 1,2, Bin GUO 1,2,3, De-bin SHAN 1,2,3
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2877 2882 Effects of tribological behavior of DLC film on micro-deep drawing processes Chun-ju WANG 1,2,3, Chuan-jie WANG 1,2, Bin GUO 1,2,3, De-bin SHAN 1,2,3
Removal of boron from metallurgical grade silicon by electromagnetic induction slag melting
 Removal of boron from metallurgical grade silicon by electromagnetic induction slag melting LUO Da-wei 1, LIU Ning 1, LU Yi-ping 1, ZHANG Guo-liang 1, LI Ting-ju 1, 2 1. School of Materials Science and
Removal of boron from metallurgical grade silicon by electromagnetic induction slag melting LUO Da-wei 1, LIU Ning 1, LU Yi-ping 1, ZHANG Guo-liang 1, LI Ting-ju 1, 2 1. School of Materials Science and
Molecular dynamics study on temperature and strain rate dependences of mechanical tensile properties of ultrathin nickel nanowires
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 3(013) 3353 3361 Molecular dynamics study on temperature and strain rate dependences of mechanical tensile properties of ultrathin nickel nanowires Wei-dong WANG, Cheng-long
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 3(013) 3353 3361 Molecular dynamics study on temperature and strain rate dependences of mechanical tensile properties of ultrathin nickel nanowires Wei-dong WANG, Cheng-long
Development of High-Performance Vitrified Grinding Wheels using Ultrafine-Crystalline cbn Abrasive Grains
 Development of High-Performance Vitrified Grinding Wheels using Ultrafine-Crystalline cbn Abrasive Grains Yoshio ICHIDA 1, Masakazu FUJIMOTO 1, Yuichiro INOUE 1 and Keisuke MATSUI 1 1 Graduate School of
Development of High-Performance Vitrified Grinding Wheels using Ultrafine-Crystalline cbn Abrasive Grains Yoshio ICHIDA 1, Masakazu FUJIMOTO 1, Yuichiro INOUE 1 and Keisuke MATSUI 1 1 Graduate School of
Microstructure refining and property improvement of ZK60 magnesium alloy by hot rolling
 Microstructure refining and property improvement of ZK60 magnesium alloy by hot rolling WANG Xin 1, CHEN Wen-zhen 1, HU Lian-xi 1, WANG Guo-jun 2, WANG Er-de 1 1. School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Microstructure refining and property improvement of ZK60 magnesium alloy by hot rolling WANG Xin 1, CHEN Wen-zhen 1, HU Lian-xi 1, WANG Guo-jun 2, WANG Er-de 1 1. School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Leaching behavior of metals from limonitic laterite ore by high pressure acid leaching
 Leaching behavior of metals from limonitic laterite ore by high pressure acid leaching GUO Xue-yi, SHI Wen-tang, LI Dong, TIAN Qing-hua School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University,
Leaching behavior of metals from limonitic laterite ore by high pressure acid leaching GUO Xue-yi, SHI Wen-tang, LI Dong, TIAN Qing-hua School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University,
Research On Silicon Carbide Ceramic By Ultrasonic Grinding Processing
 Research On Silicon Carbide Ceramic By Ultrasonic Grinding Processing Qidong Geng a, Chunyan Li b and Jun Wang c School of mechanical engineering, Yancheng Institute of Technology, Yancheng 224051, China
Research On Silicon Carbide Ceramic By Ultrasonic Grinding Processing Qidong Geng a, Chunyan Li b and Jun Wang c School of mechanical engineering, Yancheng Institute of Technology, Yancheng 224051, China
ZHANG Xin. National Center for Climate Change Strategy and International Cooperation
 ZHANG Xin National Center for Climate Change Strategy and International Cooperation 2017.9 1 2 3 4 Important requirement and work on Climate Change in China National Greenhous Gas Inventory and methodology
ZHANG Xin National Center for Climate Change Strategy and International Cooperation 2017.9 1 2 3 4 Important requirement and work on Climate Change in China National Greenhous Gas Inventory and methodology
MSEC IMPROVING THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF A CVD COATED SILICON CARBIDE DISK BY PERFORMING DUCTILE REGIME SINGLE POINT DIAMOND TURNING
 Proceedings of the 8 International Manufacturing Science And Engineering Conference MSEC8 October 7-, 8, Evanston, Illinois, USA MSEC8-74 IMPROVING THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF A CVD COATED SILICON CARBIDE
Proceedings of the 8 International Manufacturing Science And Engineering Conference MSEC8 October 7-, 8, Evanston, Illinois, USA MSEC8-74 IMPROVING THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF A CVD COATED SILICON CARBIDE
Boron removal from metallurgical silicon using CaO SiO 2 CaF 2 slags
 Boron removal from metallurgical silicon using CaO SiO CaF slags CAI Jing 1, LI Jin tang 1, CHEN Wen hui 1, CHEN Chao, LUO Xue tao 1 1. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, College of Materials,
Boron removal from metallurgical silicon using CaO SiO CaF slags CAI Jing 1, LI Jin tang 1, CHEN Wen hui 1, CHEN Chao, LUO Xue tao 1 1. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, College of Materials,
Evaluation of the Surface of Nitinol after MR Polishing Process
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2015, 3, 208-217 Published Online February 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.32031 Evaluation of the Surface
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2015, 3, 208-217 Published Online February 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.32031 Evaluation of the Surface
Interfacial reactions between Ti 1100 alloy and ceramic mould during investment casting
 Interfacial reactions between Ti 1100 alloy and ceramic mould during investment casting ZHAO Er-tuan 1, KONG Fan-tao 1, CHEN Yu-yong 1, LI Bao-hui 2 1. National Key Laboratory of Precision Hot Processing
Interfacial reactions between Ti 1100 alloy and ceramic mould during investment casting ZHAO Er-tuan 1, KONG Fan-tao 1, CHEN Yu-yong 1, LI Bao-hui 2 1. National Key Laboratory of Precision Hot Processing
Fine debismuthizing with calcium, magnesium and antimony
 Fine debismuthizing with calcium, magnesium and antimony LU Dian-kun 1, JIN Zhe-nan 1, JIANG Kai-xi 2 1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China; 2. Beijing
Fine debismuthizing with calcium, magnesium and antimony LU Dian-kun 1, JIN Zhe-nan 1, JIANG Kai-xi 2 1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China; 2. Beijing
Anti-oxidation properties of ZrB 2 modified silicon-based multilayer coating for carbon/carbon composites at high temperatures
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2094 2099 Anti-oxidation properties of ZrB 2 modified silicon-based multilayer coating for carbon/carbon composites at high temperatures He-jun LI, Xi-yuan YAO,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2094 2099 Anti-oxidation properties of ZrB 2 modified silicon-based multilayer coating for carbon/carbon composites at high temperatures He-jun LI, Xi-yuan YAO,
PRECISION MACHINING & FINISHING. Micron+ NE X T GENERATION MICRON+
 PRECISION MACHINING & FINISHING NE X T GENERATION MICRON+ Toolmakers can achieve highly consistent engineered abrasive tools using, which increases productivity and dramatically improves workpiece quality.
PRECISION MACHINING & FINISHING NE X T GENERATION MICRON+ Toolmakers can achieve highly consistent engineered abrasive tools using, which increases productivity and dramatically improves workpiece quality.
Texture evolution and its simulation of cold drawing copper wires produced by continuous casting
 Texture evolution and its simulation of cold drawing copper wires produced by continuous casting CHEN Jian 1, 2, YAN Wen 1, 2, LI Wei 3, MIAO Jian 4, FAN Xin-hui 2 1. Department of Applied Physics, Northwestern
Texture evolution and its simulation of cold drawing copper wires produced by continuous casting CHEN Jian 1, 2, YAN Wen 1, 2, LI Wei 3, MIAO Jian 4, FAN Xin-hui 2 1. Department of Applied Physics, Northwestern
Influence of high-speed milling parameter on 3D surface topography and fatigue behavior of TB6 titanium alloy
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 650 660 Influence of high-speed milling parameter on 3D surface topography and fatigue behavior of TB6 titanium alloy Chang-feng YAO, Dao-xia WU, Qi-chao JIN,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 650 660 Influence of high-speed milling parameter on 3D surface topography and fatigue behavior of TB6 titanium alloy Chang-feng YAO, Dao-xia WU, Qi-chao JIN,
ЗАГАЛЬНІ ПИТАННЯ ТЕОРІЇ ТЕРТЯ ТА ЗНОШУВАННЯ A REVIEW OF STUDIES REGARDING DUCTILE REGIME MACHINING OF SEMICONDUCTORS, CERAMICS AND GLASS
 ЗАГАЛЬНІ ПИТАННЯ ТЕОРІЇ ТЕРТЯ ТА ЗНОШУВАННЯ УДК 621.315.592:621.91:620.181 A. M. Kovalchenko, Candidate of Technical Sciences Senior Researcher A REVIEW OF STUDIES REGARDING DUCTILE REGIME MACHINING OF
ЗАГАЛЬНІ ПИТАННЯ ТЕОРІЇ ТЕРТЯ ТА ЗНОШУВАННЯ УДК 621.315.592:621.91:620.181 A. M. Kovalchenko, Candidate of Technical Sciences Senior Researcher A REVIEW OF STUDIES REGARDING DUCTILE REGIME MACHINING OF
Welding characteristics of AZ31B magnesium alloy using DC-PMIG welding
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 315 322 Welding characteristics of AZ31B magnesium alloy using DC-PMIG welding Zhao-dong ZHANG, Li-ming LIU, Gang SONG Key Laboratory of Liaoning Advanced Welding
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 315 322 Welding characteristics of AZ31B magnesium alloy using DC-PMIG welding Zhao-dong ZHANG, Li-ming LIU, Gang SONG Key Laboratory of Liaoning Advanced Welding
Simulation of extrusion process of complicated aluminium profile and die trial
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1732 1737 Simulation of extrusion process of complicated aluminium profile and die trial HE Zhao 1, WANG He-nan 1, WANG Meng-jun 1,2, LI Guang-yao 2 1. Key Laboratory
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1732 1737 Simulation of extrusion process of complicated aluminium profile and die trial HE Zhao 1, WANG He-nan 1, WANG Meng-jun 1,2, LI Guang-yao 2 1. Key Laboratory
Mechanical properties of strengthened surface layer in Ti 6Al 4V alloy induced by wet peening treatment
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 2868 2873 Mechanical properties of strengthened surface layer in Ti 6Al 4V alloy induced by wet peening treatment Kang LI 1, Xue-song FU 1, Guo-qing CHEN 1, Wen-long
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 2868 2873 Mechanical properties of strengthened surface layer in Ti 6Al 4V alloy induced by wet peening treatment Kang LI 1, Xue-song FU 1, Guo-qing CHEN 1, Wen-long
Smart phone 产业领域机器人应用解决方案
 Smart phone 产业领域机器人应用解决方案 25th, August 2016 Page: 1 Content 1. KUKA 2. Electronics Market/Division 3. Applications 4. Products and Services 5. Future and Innovation 6. References 7. Summary Page: 2 KUKA
Smart phone 产业领域机器人应用解决方案 25th, August 2016 Page: 1 Content 1. KUKA 2. Electronics Market/Division 3. Applications 4. Products and Services 5. Future and Innovation 6. References 7. Summary Page: 2 KUKA
Microstructure and properties of CuCr contact materials with different Cr content
 Microstructure and properties of CuCr contact materials with different Cr content XIU Shi-xin 1, YANG Ren 2, XUE Jun 3, WANG Jin-xing 3, WANG Jia-yi 1 1. State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and
Microstructure and properties of CuCr contact materials with different Cr content XIU Shi-xin 1, YANG Ren 2, XUE Jun 3, WANG Jin-xing 3, WANG Jia-yi 1 1. State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and
Precision Dicing of Optical Materials
 Precision Dicing of Optical Materials L. G. Carpenter, C. Holmes, P. A. Cooper, J. C. Gates and P. G. R. Smith Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Highfield, Southampton, Hampshire,
Precision Dicing of Optical Materials L. G. Carpenter, C. Holmes, P. A. Cooper, J. C. Gates and P. G. R. Smith Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Highfield, Southampton, Hampshire,
Synchrotron X-Ray Topography Measurements on 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layer
 Synchrotron X-Ray Topography Measurements on 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layer Isaho KAMATA, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) Kamata@criepi.denken.or.jp Silicon carbide has excellent
Synchrotron X-Ray Topography Measurements on 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layer Isaho KAMATA, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) Kamata@criepi.denken.or.jp Silicon carbide has excellent
Experimental Investigations on Material Removal Rate and Surface Roughness in Lapping of Substrate Wafers: A Literature Review
 Key Engineering Materials Vol. 404 (2009) pp 23-31 online at http://www.scientific.net (2009) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 2009/Jan/07 Experimental Investigations on Material
Key Engineering Materials Vol. 404 (2009) pp 23-31 online at http://www.scientific.net (2009) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 2009/Jan/07 Experimental Investigations on Material
Rotary Dressers. Diamond Tools. Rotary Dressers
 Rotary Dressers Diamond Tools Rotary Dressers Super-fine diamond grit and super-fine ceramics technology result in an innovative A.L.M.T. grinding wheel. Application of both acquired material technology
Rotary Dressers Diamond Tools Rotary Dressers Super-fine diamond grit and super-fine ceramics technology result in an innovative A.L.M.T. grinding wheel. Application of both acquired material technology
Monitoring for Ultra-Precision Cutting Process of Single Crystal Silicon
 International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 1st Century Oct. 19-, 005, Nagoya, Japan Copyright 005 Monitoring for Ultra-Precision Cutting Process of Single Crystal Silicon Ryuichi IWAMOTO
International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 1st Century Oct. 19-, 005, Nagoya, Japan Copyright 005 Monitoring for Ultra-Precision Cutting Process of Single Crystal Silicon Ryuichi IWAMOTO
Ductile or Partial Ductile Mode Machining of Brittle Materials
 Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:579 585 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Ductile or Partial Ductile Mode Machining of Brittle Materials Z. W. Zhong School of MPE, Nanyang Technological
Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:579 585 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Ductile or Partial Ductile Mode Machining of Brittle Materials Z. W. Zhong School of MPE, Nanyang Technological
Superlubricity behaviors of Nitinol 60 alloy under oil lubrication
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 354 359 Superlubricity behaviors of Nitinol 60 alloy under lubrication Qun-feng ZENG, Guang-neng DONG Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for Modern Design and
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 354 359 Superlubricity behaviors of Nitinol 60 alloy under lubrication Qun-feng ZENG, Guang-neng DONG Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for Modern Design and
Application of Ultrasonic Assisted Machining Technique for Glass-Ceramic Milling
 Application of Ultrasonic Assisted Machining Technique for Glass-Ceramic Milling S. Y. Lin, C. H. Kuan, C. H. She, W. T. Wang Abstract In this study, ultrasonic assisted machining (UAM) technique is applied
Application of Ultrasonic Assisted Machining Technique for Glass-Ceramic Milling S. Y. Lin, C. H. Kuan, C. H. She, W. T. Wang Abstract In this study, ultrasonic assisted machining (UAM) technique is applied
Surface Characterisation of Germanium detectors
 Surface Characterisation of Germanium detectors T.Engert 1,2, I.Kojouharov 1, J.Gerl 1, A.Boston 2, P.Nolan 2 1 GSI, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 University of Liverpool Outline Background > Detector technology
Surface Characterisation of Germanium detectors T.Engert 1,2, I.Kojouharov 1, J.Gerl 1, A.Boston 2, P.Nolan 2 1 GSI, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 University of Liverpool Outline Background > Detector technology
Characteristics of the Fine Grained CVD Diamond Film and its Industrial Applications. K. Kazahaya, A. Yamakawa and T. Fukunisi
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 2004-02-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 257-258, pp 553-558 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.257-258.553 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Characteristics of the Fine
Key Engineering Materials Online: 2004-02-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 257-258, pp 553-558 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.257-258.553 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Characteristics of the Fine
SPDT Effects on Surface Quality & Subsurface Damage in Ceramics
 SPDT Effects on Surface Quality & Subsurface Damage in Ceramics Deepak Ravindra & John Patten (Manufacturing Research Center- Western Michigan University) Jun Qu (Oak Ridge National Laboratory) Presentation
SPDT Effects on Surface Quality & Subsurface Damage in Ceramics Deepak Ravindra & John Patten (Manufacturing Research Center- Western Michigan University) Jun Qu (Oak Ridge National Laboratory) Presentation
Ductile streaks in precision grinding of hard and brittle materials
 Sādhan ā Vol. 28, Part 5, October 2003, pp. 915 924. Printed in India Ductile streaks in precision grinding of hard and brittle materials V C VENKATESH, S IZMAN, S SHARIF, T T MON and M KONNEH Department
Sādhan ā Vol. 28, Part 5, October 2003, pp. 915 924. Printed in India Ductile streaks in precision grinding of hard and brittle materials V C VENKATESH, S IZMAN, S SHARIF, T T MON and M KONNEH Department
The Influence of Abrasive Size on High-Pressure Chemical Mechanical Polishing of Sapphire Wafer
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PRECISION ENGINEERING AND MANUFACTURING-GREEN TECHNOLOGY Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 157-162 APRIL 2015 / 157 DOI: 10.1007/s40684-015-0020-0 ISSN 2288-6206 (Print) / ISSN 2198-0810 (Online)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PRECISION ENGINEERING AND MANUFACTURING-GREEN TECHNOLOGY Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 157-162 APRIL 2015 / 157 DOI: 10.1007/s40684-015-0020-0 ISSN 2288-6206 (Print) / ISSN 2198-0810 (Online)
Dynamic recrystallization rules in needle piercing extrusion for AISI304 stainless steel pipe
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s519 s527 Dynamic recrystallization rules in needle piercing extrusion for AISI304 stainless steel pipe GUO Liang-gang 1, DONG Ke-ke 1, ZHANG Bao-jun 1, YANG
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s519 s527 Dynamic recrystallization rules in needle piercing extrusion for AISI304 stainless steel pipe GUO Liang-gang 1, DONG Ke-ke 1, ZHANG Bao-jun 1, YANG
Micro Laser Assisted Machining (µ-lam) of Semiconductors and Ceramics. Machining Direction
 Micro Laser Assisted Machining (µ-lam) of Semiconductors and Ceramics John Patten, Director, Manufacturing Research Center Western Michigan University Machining Direction IR laser Machining Direction Work
Micro Laser Assisted Machining (µ-lam) of Semiconductors and Ceramics John Patten, Director, Manufacturing Research Center Western Michigan University Machining Direction IR laser Machining Direction Work
Cylindrical grinding of Al/SiC metal matrix composites
 Material Science Research India Vol. 7(2), 425-433 (2010) Cylindrical grinding of Al/SiC metal matrix composites C.THIAGARAJAN¹*, R. SIVARAMAKRISHNAN² and S. SOMASUNDARAM³ ¹Department of Production Engineering,
Material Science Research India Vol. 7(2), 425-433 (2010) Cylindrical grinding of Al/SiC metal matrix composites C.THIAGARAJAN¹*, R. SIVARAMAKRISHNAN² and S. SOMASUNDARAM³ ¹Department of Production Engineering,
Superabrasives Products. Solutions for Industry
 Superabrasives Products Solutions for Industry www.master-abrasives.co.uk Introduction Master Abrasives Master Abrasives has a hard and long earned reputation in the UK abrasives market for providing solutions
Superabrasives Products Solutions for Industry www.master-abrasives.co.uk Introduction Master Abrasives Master Abrasives has a hard and long earned reputation in the UK abrasives market for providing solutions
Analysis of deformation characteristic in multi-way loading forming process of aluminum alloy cross valve based on finite element model
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 199 207 Analysis of deformation characteristic in multi-way loading forming process of aluminum alloy cross valve based on finite element model Da-wei ZHANG 1,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 199 207 Analysis of deformation characteristic in multi-way loading forming process of aluminum alloy cross valve based on finite element model Da-wei ZHANG 1,
Comparison of microstructural stability of IN939 superalloy with two different manufacturing routes during long-time aging
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1717 1729 Comparison of microstructural stability of IN939 superalloy with two different manufacturing routes during long-time aging M. R. JAHANGIRI 1, H. ARABI
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1717 1729 Comparison of microstructural stability of IN939 superalloy with two different manufacturing routes during long-time aging M. R. JAHANGIRI 1, H. ARABI
Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon
 Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Microstructures and mechanical properties of pure magnesium bars by high ratio extrusion and its subsequent annealing treatment
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s445 s449 Microstructures and mechanical properties of pure magnesium bars by high ratio extrusion and its subsequent annealing treatment SUN Hong-fei 1,2, LI
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s445 s449 Microstructures and mechanical properties of pure magnesium bars by high ratio extrusion and its subsequent annealing treatment SUN Hong-fei 1,2, LI
Modelization and comparison of Norton-Hoff and Arrhenius constitutive laws to predict hot tensile behavior of Ti 6Al 4V alloy
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s457 s464 Modelization and comparison of Norton-Hoff and Arrhenius constitutive laws to predict hot tensile behavior of Ti 6Al 4V alloy ZHANG Chao 1, 2, LI Xiao-qiang
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s457 s464 Modelization and comparison of Norton-Hoff and Arrhenius constitutive laws to predict hot tensile behavior of Ti 6Al 4V alloy ZHANG Chao 1, 2, LI Xiao-qiang
The Effect of Laser Heating on the Ductile to Brittle Transition of Silicon
 The Effect of Laser Heating on the Ductile to Brittle Transition of Silicon Deepak Ravindra & Bogac Poyraz Manufacturing Research Center Western Michigan University Dr.John Patten Director -Manufacturing
The Effect of Laser Heating on the Ductile to Brittle Transition of Silicon Deepak Ravindra & Bogac Poyraz Manufacturing Research Center Western Michigan University Dr.John Patten Director -Manufacturing
Preparation and Polishing Properties of Spherical Porous Silica Abrasive
 American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (1): 32-39, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications Preparation and Polishing Properties of Spherical Porous Silica Abrasive Hong Lei, Hu Li, Ping Liu and Ruling
American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (1): 32-39, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications Preparation and Polishing Properties of Spherical Porous Silica Abrasive Hong Lei, Hu Li, Ping Liu and Ruling
Advances in 3E of Polymer Processing and Sustainable Manufacturing. Weimin Yang
 US NSF CHINA NSF WORKSHOP ON SUSTAINABLE MANUFACTURING Advances in 3E of Polymer Processing and Sustainable Manufacturing Beijing University of Chemical Technology Weimin Yang Wuhan, China March 13-15,
US NSF CHINA NSF WORKSHOP ON SUSTAINABLE MANUFACTURING Advances in 3E of Polymer Processing and Sustainable Manufacturing Beijing University of Chemical Technology Weimin Yang Wuhan, China March 13-15,
Thermodynamics and kinetics of carbothermal reduction of zinc ferrite by microwave heating
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3808 3815 Thermodynamics and kinetics of carbothermal reduction of zinc ferrite by microwave heating Xin WANG 1,2,3, Da-jin YANG 4, Shao-hua JU 1,2,3, Jin-hui
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3808 3815 Thermodynamics and kinetics of carbothermal reduction of zinc ferrite by microwave heating Xin WANG 1,2,3, Da-jin YANG 4, Shao-hua JU 1,2,3, Jin-hui
Crack initiation and fracture features of Fe Co B Si Nb bulk metallic glass during compression
 Focussed on Crack Paths Crack initiation and fracture features of Fe Co B Si Nb bulk metallic glass during compression S. Lesz, A. Januszka, S. Griner, R. Nowosielski Silesian University of Technology,
Focussed on Crack Paths Crack initiation and fracture features of Fe Co B Si Nb bulk metallic glass during compression S. Lesz, A. Januszka, S. Griner, R. Nowosielski Silesian University of Technology,
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1383~1390
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1383~1390 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x Environmentally conscious hard turning of cemented carbide
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1383~1390 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x Environmentally conscious hard turning of cemented carbide
Grain refinement of pure aluminum by direct current pulsed magnetic field and inoculation
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1295 1300 Grain refinement of pure aluminum by direct current pulsed magnetic field and inoculation Hang CHEN, Jin-chuan JIE, Ying FU, Hong-jun MA, Ting-ju LI
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1295 1300 Grain refinement of pure aluminum by direct current pulsed magnetic field and inoculation Hang CHEN, Jin-chuan JIE, Ying FU, Hong-jun MA, Ting-ju LI
Effects of welding current on properties of A-TIG welded AZ31 magnesium alloy joints with TiO 2 coating
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2507 2515 Effects of welding current on properties of A-TIG welded AZ31 magnesium alloy joints with TiO 2 coating Jun SHEN, Da-jun ZHAI, Kai LIU, Zhong-ming CAO
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2507 2515 Effects of welding current on properties of A-TIG welded AZ31 magnesium alloy joints with TiO 2 coating Jun SHEN, Da-jun ZHAI, Kai LIU, Zhong-ming CAO
Physics and Material Science of Semiconductor Nanostructures
 Physics and Material Science of Semiconductor Nanostructures PHYS 570P Prof. Oana Malis Email: omalis@purdue.edu Today Bulk semiconductor growth Single crystal techniques Nanostructure fabrication Epitaxial
Physics and Material Science of Semiconductor Nanostructures PHYS 570P Prof. Oana Malis Email: omalis@purdue.edu Today Bulk semiconductor growth Single crystal techniques Nanostructure fabrication Epitaxial
Internal stress analysis of electroplated films based on electron theory
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 2413 2418 Internal stress analysis of electroplated films based on electron theory Feng-zhang REN 1,2, Li-tao YIN 1, Shan-shan WANG 1, Yi XIONG 1, A. A. VOLINSKY
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 2413 2418 Internal stress analysis of electroplated films based on electron theory Feng-zhang REN 1,2, Li-tao YIN 1, Shan-shan WANG 1, Yi XIONG 1, A. A. VOLINSKY
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy cast by metal mould and lost foam casting
 Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy cast by metal mould and lost foam casting LI Ji-lin, CHEN Rong-shi, KE Wei State Key Laboratory for Corrosion and Protection, Institute of Metal
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy cast by metal mould and lost foam casting LI Ji-lin, CHEN Rong-shi, KE Wei State Key Laboratory for Corrosion and Protection, Institute of Metal
Rapid electroplating of Cu coatings by mechanical attrition method
 Rapid electroplating of Cu coatings by mechanical attrition method NING Zhao-hui( 宁朝晖 ), HE Ye-dong( 何业东 ) Beijing Key Laboratory for Corrosion, Erosion and Surface Technology, University of Science and
Rapid electroplating of Cu coatings by mechanical attrition method NING Zhao-hui( 宁朝晖 ), HE Ye-dong( 何业东 ) Beijing Key Laboratory for Corrosion, Erosion and Surface Technology, University of Science and
Recrystallization of Al 5.8Mg Mn Sc Zr alloy
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3235 3241 Recrystallization of Al 5.8Mg Mn Sc Zr alloy Ying WANG 1, Qing-lin PAN 1,2, Yan-fang SONG 1, Chen LI 1, Zhi-feng LI 1, Qin CHEN 1, Zhi-min YIN 1 1.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3235 3241 Recrystallization of Al 5.8Mg Mn Sc Zr alloy Ying WANG 1, Qing-lin PAN 1,2, Yan-fang SONG 1, Chen LI 1, Zhi-feng LI 1, Qin CHEN 1, Zhi-min YIN 1 1.
Some observations on the wear of diamond tools in ultra-precision cutting of single-crystal silicon
 Wear 255 (2003) 1380 1387 Case study Some observations on the wear of diamond tools in ultra-precision cutting of single-crystal silicon Jiwang Yan a,, Katsuo Syoji b, Jun ichi Tamaki a a Department of
Wear 255 (2003) 1380 1387 Case study Some observations on the wear of diamond tools in ultra-precision cutting of single-crystal silicon Jiwang Yan a,, Katsuo Syoji b, Jun ichi Tamaki a a Department of
Crystal Growth and Wafer Fabrication. K.Sivasankaran, Assistant Professor (Senior), VLSI Division, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT
 Crystal Growth and Wafer Fabrication K.Sivasankaran, Assistant Professor (Senior), VLSI Division, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT Crystal growth Obtaining sand Raw Polysilicon Czochralski Process
Crystal Growth and Wafer Fabrication K.Sivasankaran, Assistant Professor (Senior), VLSI Division, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT Crystal growth Obtaining sand Raw Polysilicon Czochralski Process
Experiment setup and crop model calibration for assessing the impacts of haze on crop growth and yield. Weihong Luo Nanjing Agricultural University
 Experiment setup and crop model calibration for assessing the impacts of haze on crop growth and yield Weihong Luo Nanjing Agricultural University Outline Impacts of haze on crop growth Model applications
Experiment setup and crop model calibration for assessing the impacts of haze on crop growth and yield Weihong Luo Nanjing Agricultural University Outline Impacts of haze on crop growth Model applications
Effect of Wall Groove Characteristics on Yield Stress Measurement of Magnetorheological Fluid
 Journal of Magnetics 22(2), 281-285 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.2.281 Effect of Wall Groove Characteristics on Yield Stress Measurement of
Journal of Magnetics 22(2), 281-285 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.2.281 Effect of Wall Groove Characteristics on Yield Stress Measurement of
Influence of aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ80 and ZK60 magnesium alloys
 Influence of aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ80 and ZK60 magnesium alloys LI Yan 1, ZHANG Zhi-min 1, XUE Yong 1, 2 1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, North University
Influence of aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ80 and ZK60 magnesium alloys LI Yan 1, ZHANG Zhi-min 1, XUE Yong 1, 2 1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, North University
Creep-feed grinding of tungsten carbide using small diameter electroplated diamond wheels
 Creep-feed grinding of tungsten carbide using small diameter electroplated diamond wheels This paper, by Z. Shi, H. Attia, D. Chellan and T. Wang, is concerned with an experimental investigation into creep-feed
Creep-feed grinding of tungsten carbide using small diameter electroplated diamond wheels This paper, by Z. Shi, H. Attia, D. Chellan and T. Wang, is concerned with an experimental investigation into creep-feed
Sensitivity model for prediction of bead geometry in underwater wet flux cored arc welding
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1977 1984 Sensitivity model for prediction of bead geometry in underwater wet flux cored arc welding Yong-hua SHI, Ze-pei ZHENG, Jin HUANG School of Mechanical
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1977 1984 Sensitivity model for prediction of bead geometry in underwater wet flux cored arc welding Yong-hua SHI, Ze-pei ZHENG, Jin HUANG School of Mechanical
Influence of Crystal Orientations on the Bendability of an Al-Mg-Si Alloy
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 4 (2010) pp. 614 to 619 Special Issue on Crystallographic Orientation Distribution and Related Properties in Advanced Materials II #2010 The Japan Institute of Light
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 4 (2010) pp. 614 to 619 Special Issue on Crystallographic Orientation Distribution and Related Properties in Advanced Materials II #2010 The Japan Institute of Light
T-11 FLARED CUPS. Specification. Wheel Shape. Wheel Size
 GENERAL T-11 FLARED CUPS Type 11 flared cups have widespread applications in both rough grinding and tool room application. Resin Bond Rough Grinding Resin bonded abrasives are a mixture of abrasive grains
GENERAL T-11 FLARED CUPS Type 11 flared cups have widespread applications in both rough grinding and tool room application. Resin Bond Rough Grinding Resin bonded abrasives are a mixture of abrasive grains
Correlating oriented grain number density of recrystallisation in particle-containing aluminium alloys
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 220 225 Correlating oriented grain number density of recrystallisation in particle-containing aluminium alloys Qing-long ZHAO 1, Hui-di ZHANG 1, Ke HUANG 2, Knut
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 220 225 Correlating oriented grain number density of recrystallisation in particle-containing aluminium alloys Qing-long ZHAO 1, Hui-di ZHANG 1, Ke HUANG 2, Knut
Dicing of Ultra-thin Silicon Wafers
 Dicing of Ultra-thin Silicon Wafers Hans H. Gatzen, Gerald Guenzel Institute for Microtechnology, Hanover University, Germany Keywords: dicing, ultra thin wafers, silicon, chipping, machining Abstract:
Dicing of Ultra-thin Silicon Wafers Hans H. Gatzen, Gerald Guenzel Institute for Microtechnology, Hanover University, Germany Keywords: dicing, ultra thin wafers, silicon, chipping, machining Abstract:
Abstract. Introduction
 Accelerating Silicon Carbide Power Electronics Devices into High Volume Manufacturing with Mechanical Dicing System By Meng Lee, Director, Product Marketing and Jojo Daof, Senior Process Engineer Abstract
Accelerating Silicon Carbide Power Electronics Devices into High Volume Manufacturing with Mechanical Dicing System By Meng Lee, Director, Product Marketing and Jojo Daof, Senior Process Engineer Abstract
Beam Dump Window Design for CSNS
 Submitted to Chinese Physics C Beam Dump Window Design for CSNS NIE Xiao-Jun( 聂小军 ) 1 LIU Lei( 刘磊 ) 1 WANG Hai-Jing ( 王海静 ) 1,2 Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049,
Submitted to Chinese Physics C Beam Dump Window Design for CSNS NIE Xiao-Jun( 聂小军 ) 1 LIU Lei( 刘磊 ) 1 WANG Hai-Jing ( 王海静 ) 1,2 Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049,
Metastable phase of β-eucryptite and thermal expansion behavior of eucryptite particles reinforced aluminum matrix composite
 Metastable phase of β-eucryptite and thermal expansion behavior of eucryptite particles reinforced aluminum matrix composite WANG Li-dong 1, CUI Ye 1, YANG Cong-tao 2, WANG Kang-peng 1, FEI Wei-dong 1,
Metastable phase of β-eucryptite and thermal expansion behavior of eucryptite particles reinforced aluminum matrix composite WANG Li-dong 1, CUI Ye 1, YANG Cong-tao 2, WANG Kang-peng 1, FEI Wei-dong 1,
THE VDI-3198 INDENTATION TEST EVALUATION OF A RELIABLE QUALITATIVE CONTROL FOR LAYERED COMPOUNDS
 THE VDI-3198 INDENTATION TEST EVALUATION OF A RELIABLE QUALITATIVE CONTROL FOR LAYERED COMPOUNDS N. Vidakis *, A. Antoniadis *, N. Bilalis** * Technological Educational Institute of Crete, Greece ** Technical
THE VDI-3198 INDENTATION TEST EVALUATION OF A RELIABLE QUALITATIVE CONTROL FOR LAYERED COMPOUNDS N. Vidakis *, A. Antoniadis *, N. Bilalis** * Technological Educational Institute of Crete, Greece ** Technical
