Approved Package of Practice for Cotton in Karnataka State
|
|
|
- Amanda Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Approved Package of Practice for Cotton in Karnataka State Cotton is a major commercial crop grown in almost all the Agro-climatic zones of Karnataka. All the four cultivated species of cotton viz,. Gossypium arboreum, G. herbaceum, G. barbadense, and G. hirsutum are grown in the state where in Gossypium hirsutum has the major share of the hybrid cotton grown. Area under cotton during the year , was 3.7 lakh hectares with a production and productivity of 6.0 lakh bales and 365 kg lint/ha respectively. Area under Bt cotton was to the extent of 0.8 lakh hectares during The package of practices developed for different species of cotton and agro-climatic situations is summarized as below. 1. CROP IMPROVEMENT 1.1 Cotton varieties / hybrids released for cultivation in the state Varieties/ Zone and Crop Time of Special Yield (q/ha) hybrids situation duration ( days) sowing characters Irrigated Rainfed Inter specific hybrids Varalaxmi 2, 3, 8, 9 Irrigated / 190 May 15 th Extra long staple (ELS) cotton DCH 32 2, 3, 8, 9 Irrigated / DHB , 3, 8, 9 Irrigated/ Intra hirsutum hybrids NHH 44 2, 3, 8, Irrigated / DHH 11 2, 3, 8, Irrigated / Suvida (DHH 543) Bunny (NCH 145) 2, 3, 8, Irrigated / 2, 3, Irrigated / Hirsutum varieties Abadhita 2, 3, 8, Rainfed RAMPBS 155 2, Irrigated Sahana 2, 3, 8, Irrigated / 190 May 15 th 180 May 15 th 160 May 15 th 160 May 15 th Feb-Mar 160 May 15 th 165 May 15 th 160 May 15 th 170, May 15 th 160 May 15 th Feb-Mar Extra long staple (ELS) cotton Long staple cotton and tolerant to leaf reddening Having better regenerative character Bigger boll size and good boll opening. Average boll size good boll opening Bigger boll size and good boll opening Tolerant to bollworm Round boll shape, Tolerant to leaf reddening Tolerant to bollworm
2 LRA , Irrigated Ganesh - (ACP - 71 Gouri (AH 107) 3, Irrigated 3, Irrigated RAH 100 2, 3, Irrigated Desi cotton varieties Jayadhar 2, 3, 8 Rainfed Renuka 2, 3, Rainfed DDHC 11 2, 3, 8 Rainfed RAHS 14 2, 3, Rainfed DLSA 17 2, 3, 8 Rainfed 160 Feb-Mar Suitable for summer season also Feb-Mar Suitable for intercropping with maize 160 Feb-Mar Suitable for double cropping system 165 May 15 th Sept. 190 Sept 180 Sept 180 Sept 160 May 15 th Resistant to pest and diseases. Suitable for intercropping under conditions Suitable for saline soils. Long Staple cotton with good boll opening CROP PRODUCTION 2.1 Seed, seed treatment. Use delinted seeds for uniform and higher germination. Adopt the following method for delinting of cotton seeds. Soak 1 kg of cotton seeds in 100 ml commercial grade Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) for ten minutes. Wash the acid treated seeds with 2% Calcium Chloride (CaCl2), then with clean water and dry the seeds under sunlight and use for sowing after recommended seed treatment. Treat the seeds required for one hectare area with 500g Azospirillum and 500g Phosphorous Solubilising Bacteria (PSB) before sowing which can save 20 kg N and 10 P2O5 /ha. Treat the seeds with 10 g Imidacloprid 70WS or 5 g Thiomethaxam 70 WS to reduce the sucking pest incidence up to days of sowing. 2.2 Seed rate and methods of sowing Methods of sowing Seed rate (kg / ha) Varieties Hybrids Drill sown Hand dibbling
3 2.3 Time of sowing Early sowing in the season is recommended for higher yields. Situation Time of sowing I. Rainfed a. Herbaceum varieties (Jayadhar/DDHc-11 etc. ) - September b. Arboreum varieties (DLSa-17)S May c. Hirsutum varieties/hybrids (Inter specific and Intra hirsutum) May 15 th II. Irrigated a. Hybrids May 15 th b. Summer cotton February March 2.4 Planting geometry. Planting geometry can be modified and adopted based on soil type and fertility. Following planting geometries have been recommended under different soils and various growing situations. 1. Rainfed situation (For varieties) 60cm x 30 cm or 90cm x 20 cm 2. Irrigated ( For varieties and summer cotton ) 75 cm X 30 cm ( Average soils) 90 cm x 30 cm (Fertile soils) 3. Transitional Zone (Zone-8, Assured rainfall areas for Hybrids) a. Interspecific hybrids b. Intra hirsutum hybrids 4. Heavy rainfall tract (zone 9 - Malanad) and Irrigated areas a. Interspecific hybrids b. Intra hirsutum hybrids 90 cm x 60 cm 90 cm x 60 cm or 90 cm x 30 cm 90 cm x 60 cm (Average fertility soils) 90 cm x 60 cm or 90 cm x 30 cm 120 cm x 60 cm ( Fertile soils) 2.5 Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) Organic Fertilizer: Apply 10 t/ha and 5 t/ha under irrigated and conditions respectively Apply Poultry 2t/ha instead of FYM under irrigated conditions only. Incorporate cotton stalks (Crop 2 t/ha along with 3 t/ha and 1 t/ha. 2-3 weeks before sowing under irrigated conditions. Grow sunhemp (as green manure) between two rows of cotton and incorporate in situ after 30 DAS in.irrigated and assured rainfall areas which helps in increasing the soil fertility and reducing weed population. Incorporate 3 t/ha along with green leaf 2t/ha (Ex situ), 2 to 3 weeks before sowing in irrigated and assured rainfall areas
4 2.5.2 Bio fertilisers Treat the seeds required for one hectare area with 500 g Azospirillum and 500 g Phosphorous Solubilising Bacteria (PSB) before sowing which can save 20 kg N and 10 kg P2O5 /ha Inorganic fertilizers Zones/ Varieties/Hybrids Recommended quantity nutrients (kg/ha) I. Rainfed (varieties) Nitrogen Phosphorus Potash 1. Northern dry tract (zone 1, 3) Transitional tract (zone 8) II. Rainfed (hybrids) 1. Malanad tract (zone 9) Transitional tract (zone 8) III. a. Irrigated (varieties) In all zones III. a. Irrigated (hybrids) 1. Inter specific hybrids 2. Intra hirsutum hybrids IV. Summer cotton 1. Varieties Intra hirsutum hybrids Split application of fertlisers Incorporate organics (FYM/Compost/Crop residues) into the soil 2-3 weeks before sowing. For cotton apply entire recommended nutrients as basal at the time of sowing. Under assured rainfall conditions apply 50% N, entire dose of P2O5 and K2O as basal at the time of sowing and top dress remaining 50% N at 60 DAS. Under irrigated conditions, apply 50 % N & K2O and entire P2O5 as basal at sowing and top dress 50 % N & K2O at 30 DAS and remaining 25% N & K2O at 60 DAS. Under irrigated conditions in Zone -3 apply 25 % N & K2O and entire P2O5 as basal at sowing and top dress 50 % N & K2O in three equal splits at 50, 80 and 110 DAS. Under heavy rainfall areas (Malanad), apply N, P2O5 and K2O in three equal splits i.e Basal, 60 and 90 DAS. In all the situations give foliar sprays of 2% Urea or DAP + 1% MOP at 80, 100 & 120 DAS 2.6. Post sowing operations and weed management Keep the plots weed free up to 60 days as the crop growth is slow during this period and this is the critical crop growth stage for crop weed competition. Three four intercultivations at an interval of 15 days after 30 DAS helps in controlling weeds and acts as dust mulch in conserving the available soil moisture. In situations weeds can be managed effectively by 2-3 intercultivations followed by hand weeding. In transitional and irrigated areas integrated weed management proved effective in controlling the weeds. Pre emergent application of Diuron 1.25 kg/ha or Pendimethalin (30 3 lit/ha in lits of water, immediately after sowing (with sufficient soil moisture) coupled with one hand weeding and intercultivation is recommended
5 2.7 Irrigation Water requirement and number of irrigations. Soil type Crop Irrigation No. of Depth of Total crop duration interval irrigations each water irrigation requirement (cm) (cm) Black soils 180 days 20 days cm cm Light/red/sandy loam soils days 15 days cm cm Schedule irrigation at 0.6 IW/CPE through out the crop growth Methods of irrigation Adopt furrow method of irrigation with following specifications. Adopt Alternatively Alternate Furrow Irrigation (AAFI) in heavy soils (Vertisols), which saves time, labour, irrigation water (to the extent of 30%) and minimizes the long term ill effects of irrigation on soil properties. Particulars In heavy or black soils In light or red soils or sandy loam soils Furrow length m m Slope in furrows % % Stream size 2 3 lit/sec 3 4 lit/sec Critical stages of irrigation Critical Stages of crop growth Days after sowing (DAS) Sympodial branching and square formation stage Flowering and fruiting stage Peak boll formation Boll development and boll opening stage Heavy and frequent irrigation enhances the vegetative growth leading to ineffectiveness of plant protection measures, resulting in higher incidence of pest/diseases Provide drainage in heavy soils to avoid water logging due to low infiltration rate Under canal command areas where in the canal opening is not assured at scheduled time, ensure early sowing with protective irrigation by open/bore well water. Under constraints of irrigation water, foliar spray of Kaolin (60 g/lit) with 1 g teepol or soap, at 3 days after last irrigation reduces transpiration losses from the crop canopy, thus helps the crop to utilize the available soil moisture efficiently. 2.8 Drip irrigation in cotton Drip irrigation can be a viable option under constraints of irrigation water in zone 3 and 8 for hybrid cotton cultivation. It can save electricity, labour and 50% of irrigation water as against the surface furrow irrigation Planting geometry of 90 cm x 60 cm (Normal planting) can be adopted under drip irrigation, but paired row planting at 60 cm 120 cm 60 cm can save 50% laterals as against the normal planting
6 Operate drip system daily or once in three days and replenish 75 per cent cumulative ET of corresponding days by drip for hybrid cotton and 50 percent for hirsutum varieties.(table.1) Table. 1: Time schedule of drip operation based on daily ET (Zone 3 and 8) Month Evaporation *Time of drip operation based on ET (Minutes) (mm/day) Zone 3 Zone 8 Zone 3 Zone 8 Hybrids Varieties Hybrid Varietties January February March April May June August September October November December Replenishing 75% and 50% daily ET for hybrids and varieties respectively. Drippers having discharge capacity of 4 lit/sec to be used. Laterals to be placed at 90 cm apart and drippers at 60 cm under normal planting In case of paired row planting (60 cm 120 cm 60 cm) the above time of drip operation has to be doubled as the number of laterals and drippers are reduced to 50 % as compared to normal planting of 90 cm x 60 cm Fertilizer management in drip irrigation system Apply 10 percent of recommended fertilizers as basal at the time of sowing and apply remaining fertilizers in equal splits through fertigation between 30 to 120 DAS at six days interval. Urea, MOP and DAP can be used for fertigation instead of costly liquid fertlisers. Follow weed, pest and diseases management practices as mentioned in irrigated cotton 2.9 Cotton based cropping systems Crop rotations. I year II- Year III-Year Cotton Groundnut Rabi Jowar or wheat Cotton Cotton Green gram Rabi Jowar or Wheat Cotton Cotton Soyabean Wheat or Rabi Jowar Cotton Cotton Maize Chickpea Cotton Cotton Sunflower Chickpea Cotton
7 2.9.2 Intercropping and mixed/relay cropping systems. In situations cotton based intercropping and mixed cropping systems are remunerative and act as insurance against the risk of erratic rainfall. Under conditions adopt the following intercropping systems. 1. Cotton + onion (1: 5) 2. Cotton + chilli (1: 1) 3. Cotton + groundnut (1: 3) 4. Cotton + green gram (1: 3) 5. Cotton + soybean (1: 3) 6. Cotton + peas (1: 2) Under irrigated conditions following inter cropping systems are recommended. 1. Cotton + chilli (1: 1) 2. Cotton + onion (1: 5) 3. Cotton + soybean (1: 2). 4. Cotton + Sunhemp(As green manure) (1: 2) 5. In black soils of Tung Bhadra Project (TBP area), Cotton + onion (1: 2) and Cotton + chilli (1: 1) are recommended. Under low rainfall areas Cotton (desi) + Onion + Coriander, Cotton (desi) + onion + chilli mixed/relay cropping systems are recommended. In heavy rainfall areas (Malanad) (zone-9), Cotton + paddy (1:6) intercropping system is recommended Physiological disorders in cotton. Square drying, flowers and premature boll dropping and leaf reddening are the major Physiological disorders in cotton. These can be effectively managed and minimized by the following measures. Squares, flowers and boll dropping can be minimized by foliar sprays of 0.25ml/lit of water during pre flowering (55-60 DAS) and peak flowering stage ( DAS) of the crop. Twice foliar sprays of 1% MgSO4 or 2% urea or DAP at 90 DAS and 110 DAS reduces the leaf reddening during winter season.
8 3 CROP PROTECTION 3.1 Major diseases, symptoms and their control measures. Sl No. Name of the disease Symptoms of the disease Suggested control measures 1 Seedling rot 2 Grey mildew / areolate mildew 3 Bacterial blight Decay of the seedlings before emergence, girdling of the seedling stems and root rot. Some times mustard like seeds appear on the roots. A whitish mycelial growth appears chiefly on the under surface of the leaves. Under congenial conditions defoliation is observed in diploid cottons. Water soaked angular leaf spots appear on the leaves, later spread to the veins and vein lets Drenching of 2 g/litre of water around the diseased seedlings. Foliar sprays of 1g /litre of water as and when symptoms seen. Foliar sprays of Streptocycline 0.5 gm/litre and 3 g / litre of water as and when symptoms seen 4 Rust Circular brown to reddish pustules appear during boll maturation stage on lower surface of leaves and later on they coalesce in to large spots lowering photosynthesis, affecting nutrient supply from source to sink thus affecting the yields.. 5 Wilt Adult plants become weak coupled with yellowing of leaves with senescence and drying 6 Boll rot The bolls nearer to the ground becomes decay, with mycelial growth and some times bacterial ooze comes out of the bolls Foliar sprays of Copper- 3g/litre or 2gm/litre of water, as and when symptoms are seen. Drenching of 2g/litre of water around the diseased plants Efficient pest management is the best method to control the boll rot. Yet, foliar sprays of 3g/litre and Streptocycline 0.5 gm/litre or 2g /litre and 2g/litre of water at boll initiation stage and a second need based spray after days in heavy rainfall /irrigated areas on interspecific hybrids
9 3.2 Major insect Pests, symptoms and their control measures. Sl. No Pests Damage Symptoms Management strategies I. Sucking Pests 1. Jassids Yellowing, reddening along the leaf margin and complete drying of leaves * Treat the seeds with 10 g Imidacloprid 70WS or 5 g Thiomethaxam 70 WS * Foliar application if needed further with 2. Thrips White streaks on leaves and complete dr[ying of leaves NSKE(5%) or 0.5 ml Imidacloprid 17.8 SL or 1.5ml Oxydemton methyl 25EC or 3. Aphids Yellowing, crinkling and development of black sooty mildew on leaves 2.0ml Dimethoate 30 EC or 1.0 ml Monochrotophos 36 SL or 0.2 g Thiomethoxam 25WG or 0.2g Acetamiprid 20 SP per liter of water OR * Smear with 1.0 ml Imidacloprid 17.8 SL in 20 ml water approximately to a length of an inch at top tender green portion of the stem. II. Other Sucking pests 4. Serpentine Makes zig zag tunnels or mines Spraying of any systemic insecticides leaf miner on leaves. Infestation starts at very early stage of plant growth ( two leaf stage) mentioned above. 5. White flies Yellowing, crinkling and development of black sooty mold on leaves. Premature dropping of squares and bolls 6. Mites White streaks on leaves, yellow spots on lower side of the leaves. 7. Dusky cotton Bad boll opening and bugs deterioration of seed quality 8. Red cotton bugs Suck the sap from the matured bolls. Quality of the lint deteriorates. Erection of yellow sticky 50 /ha, Foliar sprays of 5.0% or 1.5 ml Triazophos 40 EC per liter of water. Sprays of water soluble 5 g or 2.5 ml Dicofol 20 EC per liter of water Any contact insecticides
10 III. Bollworms 1. Spotted bollworm 2. American bollworm 3. Pink bollworm Feeds on squares, flowers and bolls. Flaring up of squares and damage holes on bolls Feeds on squares, flowers and small as well as big sized bolls. Flaring up symptoms and dropping of squares. Bored entry holes on boll. Feeds on squares, flowers and developing bolls. Rosetted flowers. No damage symptoms on bolls as it feeds inside. * Installation of pheromone 5/ha for monitoring of bollworm moths activity. Use separate traps for each kind of boll bollworms. Change the lure at every days. * Release egg parasitoid i.e. Trichogramma 2.5 lakh/ha (Tricho card) twice a week at DAS * Spraying of neem based insecticides or Endosulfon ml/liter after 5-7 days of T.chilonis release. * If T.chilonis is not available pray ovicides like Profenophos ml/lit or Thiodicarb g/lit. * Under irrigated situations spray Methomyl g/lit. * Spray Ha 500 LE/ha + 5 % jaggery water + 0.1% Boric acid (Spray during morning or evening hours) at DAS * Nipping and disposal of terminal shoots at DAS to reduce egg laying by bollworm moths and to prevent aphid breeding. * Selective use of following insecticides based on incidence of bollworms: Emamectin benzoate g/lit or Indoxcarb ml/lit or Spinosad ml/lit or Carbaryl 50% 3.0 g/lit or Quinolpho ml/lit or Cholrpyriphos ml/lit.water * Spray with recommended synthetic pyrethroids in severe cases of bollworm incidence (0.5ml of Decamethtrin 2.8 EC or Cypermethrin 10 EC or Fenvalrate 10 EC or β- Cyfluthrin 25 SC or 0.25ml/lit Alphamethrin 10 EC, however its use should be avoided or restricted to one or two spays after 100 days of sowing alternating with Insecticides of other groups. Specific recommendations for Pink Boll Worm (PBW) management: * Use delta traps (5.0/ha) for monitoring PBW activities * Twist tying of PB Ropel 200/ha at DAS Or Mass trapping and killing of moths through pheromone 30/ha * Supervisory control by spraying recommended Pyrethroides or Profenophos or thiodicarb in addition to regular boll management activity.
11 3.3 Integrated Pest Management in Bt- Cotton under Irrigated conditions Seed treatment with 0.5ml Imidacloprid 17.8SL or 0.2 g Thiomethaxam 25WG or 0.2g Acetamiprid 20 SP per lit. of water for sucking pest management. OR Stem smearing with 1ml Imidacloprid 17.8 SL in 20ml water. Monitoring bollworm moth activity with pheromone 5.0/ha Erecting of bird 20-25/ha to sustain insectivorous birds in the field. Hand collection and disposal of grownup larvae. Spry Ha 500 LE/ha+5% jaggery in water+ 0.1% Boric acid (Spray in morning or evening hours) when early stage larval incidence is persisting. Apply stomach and contact insecticide when larval incidence cross ETL. Apply recommended synthetic parathyroids at days after sowing for Bt resistant population of American bollworm and pink boll worms. Erection of yellow sticky 50 /ha and application of NSKE 5.0% or 1.5 ml Triazophos 40EC per liter of water for whitefly management Manage mite, dusky cotton and red cotton bugs with application of suitable insecticide/acaricide Conservation of soil moisture till boll opening stage is essential. Economic Threshold Level for Chemical Application. Insect Pests Jassids Aphids Thrips Whitefly American bollworm Spotted bollworm Pink bollworm 2.0 nymphs/leaf 10 aphids/leaf 10 thirps/leaf 5 whiteflies/leaf 1.0 larvae/plant 5.0% damage 10 % damage ETL
12 4. Economics of cotton cultivation 4.1 The details on cost of cultivation, gross and net returns of hybrid cotton-non Bt are given in the following table. Cost of cultivation of Hybrid cotton - Non Bt. (Per Acre) Sl. No Particulars Physical unit per acre Unit cost (Rs) Total cost per Acre (Rs/acre) Irrigated Rainfed Irrigated Rainfed Irrigated Rainfed 1 Tractor ploughing 5hrs 5hrs Tractor cultivator 2hrs 2hrs Twice harrowing (by 1 pair 1 pair bullocks) 4 FYM application 6 L 4 L Opening seed line (by 0.5 pair 0.5 pair bullocks) 6 Seed dibbling 5 L 5 L Weedicide application (Optional) 8 Fertiliser application 5 L 5 L Thinning 2 L 2 L Twice intercultivation 1 pair 1 pair Twice hand weeding 15 L 10 L Irrigation (4-5 times) 12 L Spraying(6-Irri, 5-) 18 L 15 L A. Total cost of cultural operations (Rs) * Kapas picking Rs.2 /kg Rs.2/kg B. Total cost of kapas picking (Rs) Cost of seed 0.75 kg 0.75 kg Rs.800/kg Rs. 800/kg N: P: K(Basal + Top dress + Rec. Foliar sprays of DAP, MgSO4, planofix) 60:30:30 N : P: K (kg/ac) 32:16:16 N : P: K (kg/ac) N-Rs. 11/kg P- Rs. 24/kg K-Rs. 8 /kg N-Rs. 11/kg P- Rs. 24/kg K-Rs. 8 /kg Weedicide cost (optional) Additional micronutrient Foliar sprays(optional) 5 FYM 4 tons 4 tons Rs.300/t Rs.300/t PPchemicals 6 sprays 5 sprays C. Total cost of inputs (Rs) Grading& kapas packing in docras/ transportation to market 2 Land rent D. Total post harvest management cost (Rs) E. Total cost of cultivation (Rs)/acre 16,000 12,000 * Varies as per the actual quantity of kapas obtained from an acre. Total cost of cultivation: Irrigated -- Rs. 16,000 per acre. ( Rs.40,000 per hectare) Rainfed -- Rs. 12,000 per acre. ( Rs.30,000 per hectare) Gross returns: Irrigated -- 15q/ac Rs.2000/q = Rs.30,000/ac ( Rs.75,000/ha) Rainfed -- 10q/ac Rs.2000/q = Rs.20,000/ac ( Rs. 50,000/ha) Net returns: Irrigated : (30,000 16,000) = Rs /ac ( Rs. 35,000/ha) Rainfed : ( 20,000 12,000) = Rs. 8000/ac ( Rs. 20,000/ha)
13 Sl. No 4.2 The details on cost of cultivation, gross and net returns of hybrid cotton- Bt are given in the following table. Cost of cultivation of Hybrid cotton - Bt. (Per Acre) Particulars Physical unit per acre Unit cost (Rs) Total cost per Acre (Rs/acre) Irrigated Rainfed Irrigated Rainfed Irrigated Rainfed 1 Tractor ploughing 5hrs 5hrs Tractor cultivator 2hrs 2hrs Twice harrowing (by 1 pair 1 pair bullocks) 4 FYM application 6 L 4 L Opening seed line (by 0.5 pair 0.5 pair bullocks) 6 Seed dibbling 5 L 5 L Weedicide application (Optional) 8 Fertiliser application 5 L 5 L Thinning 2 L 2 L Twice intercultivation 1 pair 1 pair Twice hand weeding 15 L 10 L Irrigation (4-5 times) 12 L Spraying(4-Irri, 3-) 12 L 9 L A. Total cost of cultural operations (Rs) * Kapas picking Rs.2 /kg Rs.2/kg B. Total cost of kapas picking (Rs) Cost of seed 0.75 kg 0.75 kg Rs1500/kg Rs1500/kg N: P: K(Basal + Top dress + Rec. Foliar sprays of DAP, MgSO4, planofix) 60:30:30 N : P: K (kg/ac) 32:16:16 N : P: K (kg/ac) N-Rs. 11/kg P- Rs. 24 /kg K-Rs. 8 /kg N-Rs. 11/kg P- Rs. 24 /kg K-Rs. 8 /kg Weedicide cost (optional) Additional micronutrient Foliar sprays(optional) 5 FYM 4 tons 4 tons Rs.300/t Rs.300/t PPchemicals 4 sprays 3 sprays C. Total cost of inputs (Rs) Grading& kapas packing in docras/ transportation to market 2 Land rent D. Total post harvest management cost (Rs) E. Total cost of cultivation (Rs)/acre 15,525 11,525 * Varies as per the actual quantity of kapas obtained from an acre. Total cost of cultivation: Irrigated -- Rs. 15,525 per acre. ( Rs. 38,813 per hectare) Rainfed -- Rs. 11,525 per acre. ( Rs. 28,813 per hectare) Gross returns: Irrigated -- 15q/ac Rs.2000/q = Rs.30,000/ac ( Rs.75,000/ha) Rainfed -- 10q/ac Rs.2000/q = Rs.20,000/ac ( Rs. 50,000/ha) Net returns: Irrigated : (30,000 15,525) = Rs. 14,475/ac ( Rs. 36,188/ha) Rainfed : ( 20,000 11,525) = Rs. 8475/ac ( Rs. 21,188/ha)
14 4.3 The details on cost of cultivation, gross and net returns of desi cotton are given in the following table Cost of cultivation of desi (Herbaceum/Arboreum) Cotton (Per Acre) Sl.No. Particulars Physical unit per acre * Ploughing once in 3 years ** Picking cost varies as per kapas picked from the area. Total cost of cultivation: Rs per acre ( Rs. 13,200 per hectare) Gross returns: 4q/ac Rs.1700/q = Rs.6,800/ac ( Rs.17,000/ha) Net returns: ( 6, ) = Rs. 1520/ac ( Rs.3,800/ha) Unit cost (Rs) Total cost per acre (Rs) 1 Tractor cultivator * 2 hrs Twice harrowing (by bullocks) 1 pair FYM application 2 L Opening seed line (by bullocks) 0.5 pair Seed dibbling 5 L Fertiliser application 2 L Intercultivation 1 pair Hand weeding 5 L Spraying (One spray) 3 L A. Total cost of cultural operations (Rs) **Kapas picking 400 Rs. 2/kg 800 B. Total cost of kapas picking (Rs/ac) Cost of seed 2 kg Rs. 40/kg 80 2 N : P: K (kg/ac) 16:10:10 N : P: K (kg/ac) N-Rs. 11/kg P- Rs. 24 /kg K-Rs. 8 /kg 3 FYM 2 tons/ha Rs.300/t PPchemicals 1 spray 1 spray 250 C. Total cost of inputs (Rs) Grading& kapas packing in docras/ transportation to market 2 Land rent D. Total post harvest management cost (Rs) 1250 E. Total cost of cultivation (Rs)/acre
Central Institute for Cotton Research
 Central Institute for Cotton Research Sixth Weekly Advisory for Cotton Cultivation: 21 st August to 1 st September 2012 "The advisory is based on inputs received from the State Agricultural Universities
Central Institute for Cotton Research Sixth Weekly Advisory for Cotton Cultivation: 21 st August to 1 st September 2012 "The advisory is based on inputs received from the State Agricultural Universities
Adoption Behaviour of ELS cotton growers in Vellore district of Tamil Nadu
 Research Article Research Note 6025 Vol. 30 No. 1, 2018 DOI:https://doi.org/10.26725/JEE.2018.1.30.5996-5999 Vol. 30 No. 1, 2018 DOI:https://doi.org/10.26725/JEE.2018.1.30.6025-6030 Adoption Behaviour
Research Article Research Note 6025 Vol. 30 No. 1, 2018 DOI:https://doi.org/10.26725/JEE.2018.1.30.5996-5999 Vol. 30 No. 1, 2018 DOI:https://doi.org/10.26725/JEE.2018.1.30.6025-6030 Adoption Behaviour
SORGHUM GROWERS GUIDE
 SORGHUM GROWERS GUIDE Contents Introduction... 2 Soils and climate... 2 Fertilisation... 2 Varietal choice... 2 Characteristics of Seed Co Sorghum varieties... 3 MACIA... 3 Plant height cms... 3 Production
SORGHUM GROWERS GUIDE Contents Introduction... 2 Soils and climate... 2 Fertilisation... 2 Varietal choice... 2 Characteristics of Seed Co Sorghum varieties... 3 MACIA... 3 Plant height cms... 3 Production
Recommended package of practices: Rabi sorghum
 Recommended package of practices: Rabi sorghum 1. Crop based cropping system Rabi sorghum is sown after a fallow period (kharif) in certain medium to deep soil areas where the rainfall frequency is high.
Recommended package of practices: Rabi sorghum 1. Crop based cropping system Rabi sorghum is sown after a fallow period (kharif) in certain medium to deep soil areas where the rainfall frequency is high.
Central Institute for Cotton Research
 Central Institute for Cotton Research Eighth Weekly Advisory for Cotton Cultivation: 11 to 18 September 2012 "The advisory is based on inputs received from the State Agricultural Universities of the respective
Central Institute for Cotton Research Eighth Weekly Advisory for Cotton Cultivation: 11 to 18 September 2012 "The advisory is based on inputs received from the State Agricultural Universities of the respective
Central Institute for Cotton Research
 Central Institute for Cotton Research Seventh Weekly Advisory for Cotton Cultivation: 3 to 9 September 2012 "The advisory is based on inputs received from the State Agricultural Universities of the respective
Central Institute for Cotton Research Seventh Weekly Advisory for Cotton Cultivation: 3 to 9 September 2012 "The advisory is based on inputs received from the State Agricultural Universities of the respective
BLACKGRAM. Powdery mildew resistant variety: LBG-17.
 BLACKGRAM Selection of varieties: Varieties suitable for all seasons: LBG-20 (Teja), T-9, LBG-623, WBG-26 (Usha), PBG-1, LBG-752, MBG-207 Powdery mildew resistant variety: LBG-17. YMV resistant/tolerant
BLACKGRAM Selection of varieties: Varieties suitable for all seasons: LBG-20 (Teja), T-9, LBG-623, WBG-26 (Usha), PBG-1, LBG-752, MBG-207 Powdery mildew resistant variety: LBG-17. YMV resistant/tolerant
Application of 50 kg K2O/ha, 30 days prior to harvesting of plant cane with irrigation water, resulted in better sprouting of winter harvested cane.
 AGRONOMY Agronomical requirements for sugarcane varieties CoH 35, CoS 8436, CoH 99, CoH 92, CoH 110 and CoH 119 released for cultivation in Haryana and also for CoH 92 released at national level have been
AGRONOMY Agronomical requirements for sugarcane varieties CoH 35, CoS 8436, CoH 99, CoH 92, CoH 110 and CoH 119 released for cultivation in Haryana and also for CoH 92 released at national level have been
Institute of Organic Farming Directorate of Research University of Agricultural Sciences Dharwad , Karnataka
 ICAR Network Project on Organic Farming Dharwad Centre Package Developed by Principal Investigator Dr. H.B.Babalad Co- Principal Investigators Dr. R.K Patil Dr. K.K.Math Dr. M.G.Palakashappa Dr. M.N.Sreenivasa
ICAR Network Project on Organic Farming Dharwad Centre Package Developed by Principal Investigator Dr. H.B.Babalad Co- Principal Investigators Dr. R.K Patil Dr. K.K.Math Dr. M.G.Palakashappa Dr. M.N.Sreenivasa
Research Paper INTRODUCTION
 ADVNACE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 1 Issue 2 (December, 2010) Page : 114-119 Received : August, 2010; Accepted : September, 2010 Research Paper Role of organic sources in enhancing the
ADVNACE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 1 Issue 2 (December, 2010) Page : 114-119 Received : August, 2010; Accepted : September, 2010 Research Paper Role of organic sources in enhancing the
Presented by : Digambar Singh
 Presented by : Digambar Singh 2/8/2014 1 Aphids Caterpillar/Fruit Borer Mealybug Leaf Miner Fruit fly Mealy Bug Mealy bugs are insects in the family Pseudococcidae. SYMPTOMS : They are considered pests
Presented by : Digambar Singh 2/8/2014 1 Aphids Caterpillar/Fruit Borer Mealybug Leaf Miner Fruit fly Mealy Bug Mealy bugs are insects in the family Pseudococcidae. SYMPTOMS : They are considered pests
CARE Climate Change Adaptation(CCA) Plan
 CARE Climate Change Adaptation(CCA) Plan a. Introduction: b. Background: The project Reversing Environmental Degradation and Rural Poverty through Adaptation to Climate Change in Drought Stricken Areas
CARE Climate Change Adaptation(CCA) Plan a. Introduction: b. Background: The project Reversing Environmental Degradation and Rural Poverty through Adaptation to Climate Change in Drought Stricken Areas
Package of Practices of maize cultivation in Andhra Pradesh
 Package of Practices of maize cultivation in Andhra Pradesh Package of practices of Maize for Kharif and Rabi Season Rabi Recommended hybrid and varieties Hybrid/ Variety Hybrids Rainfed/ irrigated Duration
Package of Practices of maize cultivation in Andhra Pradesh Package of practices of Maize for Kharif and Rabi Season Rabi Recommended hybrid and varieties Hybrid/ Variety Hybrids Rainfed/ irrigated Duration
Improved Cultivation Practices for Clusterbean in Kharif and Summer Season
 Improved Cultivation Practices for Clusterbean in Kharif and Summer Season Raj Singh Central Arid Zone Research Institute ISO 9001 : 2008 (Indian Council of Agricultural Research) Jodhpur - 342 003 (Rajasthan)
Improved Cultivation Practices for Clusterbean in Kharif and Summer Season Raj Singh Central Arid Zone Research Institute ISO 9001 : 2008 (Indian Council of Agricultural Research) Jodhpur - 342 003 (Rajasthan)
COTTON PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGIES
 COTTON PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGIES Desi Cotton Varieties (G.arboreum.L) Amerecian Cotton Varieties (G. hirsutum L.) Intra-specific Cotton Varieties / Hybrids Egyption Cotton Varieties / Inter-specific Cotton
COTTON PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGIES Desi Cotton Varieties (G.arboreum.L) Amerecian Cotton Varieties (G. hirsutum L.) Intra-specific Cotton Varieties / Hybrids Egyption Cotton Varieties / Inter-specific Cotton
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS Crop Improvement. National Trials
 B -1 RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS Crop Improvement National Trials In the initial evaluation trial of G. hirsutum, CA 105, GISV 272 and GJHV 398 were found to be the best in terms of seed cotton yield in north,
B -1 RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS Crop Improvement National Trials In the initial evaluation trial of G. hirsutum, CA 105, GISV 272 and GJHV 398 were found to be the best in terms of seed cotton yield in north,
Millets. Land preparation. 1. Jowar. Varieties along with recommended area
 Millets 1. Jowar Varieties: PSV-1, Palem-2, CSV-10, CSV-11, CSV-13, CSV-15 and Srisaila (PSV 56) RABI Varieties : NTJ-2, NTJ-4, CSV 216R, CSV 14R, M35-1, Kinnera Early rabi areas of Rayala seema : CSV
Millets 1. Jowar Varieties: PSV-1, Palem-2, CSV-10, CSV-11, CSV-13, CSV-15 and Srisaila (PSV 56) RABI Varieties : NTJ-2, NTJ-4, CSV 216R, CSV 14R, M35-1, Kinnera Early rabi areas of Rayala seema : CSV
Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum
 Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum Importance o It is regarded as queen of oilseeds Because of its quality (fatty acid composition) Its resistance to oxidation and rancidity o India is considered as basic
Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum Importance o It is regarded as queen of oilseeds Because of its quality (fatty acid composition) Its resistance to oxidation and rancidity o India is considered as basic
Sheela Kumare A model farmer from village Lonsawali
 Sheela Kumare A model farmer from village Lonsawali Profile of Mahila Kisan : Name: Village: GP: Block: District: Livelihood Group Name: Food Security Level: Sheela Kumare Lonsawali Lonsawali Wardha Wardha
Sheela Kumare A model farmer from village Lonsawali Profile of Mahila Kisan : Name: Village: GP: Block: District: Livelihood Group Name: Food Security Level: Sheela Kumare Lonsawali Lonsawali Wardha Wardha
Common millet management
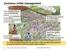 Common millet management Soil compaction due to tracking animals and tractors No protection measures against wind and soil erosion Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of harvested fields No soil water
Common millet management Soil compaction due to tracking animals and tractors No protection measures against wind and soil erosion Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of harvested fields No soil water
12. Water Management Technology Options for Non-Rice Crops
 12. Water Management Technology Options for Non-Rice Crops Special irrigation techniques for non-rice crops: Paired row technique: It is a method in which accommodating crop rows on both sides of furrow
12. Water Management Technology Options for Non-Rice Crops Special irrigation techniques for non-rice crops: Paired row technique: It is a method in which accommodating crop rows on both sides of furrow
Split application of nutrients through fertigation in Bt cotton
 J. Cotton Res. Dev. 28 (2) 238-242 (July, 2014) Split application of nutrients through fertigation in Bt cotton D.D.PAWAR*, S.K. DINGRE AND U. S. SURVE Inter faculty Department of Irrigation Water Management,
J. Cotton Res. Dev. 28 (2) 238-242 (July, 2014) Split application of nutrients through fertigation in Bt cotton D.D.PAWAR*, S.K. DINGRE AND U. S. SURVE Inter faculty Department of Irrigation Water Management,
Adoption Level of Farmers on Maize Cultivation Practices
 Journal of Extension Education Vol. 26 No. 4, 2014 Adoption Level of Farmers on Maize Cultivation Practices D. Yavana Priya 1, K.A. Ponnusamy 2 and J. Venkatapirabu 3 ABSTRACT The study to measure the
Journal of Extension Education Vol. 26 No. 4, 2014 Adoption Level of Farmers on Maize Cultivation Practices D. Yavana Priya 1, K.A. Ponnusamy 2 and J. Venkatapirabu 3 ABSTRACT The study to measure the
Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.
 Cropping 101 Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.edu This overview provides summaries of 1. Key
Cropping 101 Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.edu This overview provides summaries of 1. Key
Bharati Kursange A Confident farmer of Village Vihirgaon
 Profile of Mahila Kisan : Bharati Kursange A Confident farmer of Village Vihirgaon Name: Village: GP: Block: District: Livelihood Group Name: Food Security Level: Bharati Giridhar Kursange Vihirgaon Chikhali
Profile of Mahila Kisan : Bharati Kursange A Confident farmer of Village Vihirgaon Name: Village: GP: Block: District: Livelihood Group Name: Food Security Level: Bharati Giridhar Kursange Vihirgaon Chikhali
BOLLWORM MANAGEMENT IN COTTON PRODUCTION TO MEET THE QUALITY COTTON REQUIREMENTS OF THE INDUSTRY. B. Dhara Jothi
 - 90 - BOLLWORM MANAGEMENT IN COTTON PRODUCTION TO MEET THE QUALITY COTTON REQUIREMENTS OF THE INDUSTRY B. Dhara Jothi Senior Scientist, Central Institute for Cotton Research, Regional Station, Coimbatore-641003.
- 90 - BOLLWORM MANAGEMENT IN COTTON PRODUCTION TO MEET THE QUALITY COTTON REQUIREMENTS OF THE INDUSTRY B. Dhara Jothi Senior Scientist, Central Institute for Cotton Research, Regional Station, Coimbatore-641003.
1256 Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) for hirsutum cotton under cotton- wheat cropping system in canal command area of North West Rajasthan, India
 1256 Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) for hirsutum cotton under cotton- wheat cropping system in canal command area of North West Rajasthan, India Dr. Prem lal Nehra Sr., Rajasthan Agricultural University,
1256 Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) for hirsutum cotton under cotton- wheat cropping system in canal command area of North West Rajasthan, India Dr. Prem lal Nehra Sr., Rajasthan Agricultural University,
EFFICACY AND ECONOMICS OF VARIOUS PEST MANAGEMENT MODULES
 Agric. Sci. Digest, 32 (4) 296-300, 2012 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.ar.arccjour ccjournals.com / indianjournals.com nals.com EFFICACY AND ECONOMICS OF VARIOUS PEST MANAGEMENT MODULES
Agric. Sci. Digest, 32 (4) 296-300, 2012 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.ar.arccjour ccjournals.com / indianjournals.com nals.com EFFICACY AND ECONOMICS OF VARIOUS PEST MANAGEMENT MODULES
STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF RATIOS AND LEVELS OF NPK FERTILIZER NUTRIENTS ON THE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYBRID SUNFLOWER UNDER RAINFED FARMING SITUATIONS
 STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF RATIOS AND LEVELS OF NPK FERTILIZER NUTRIENTS ON THE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYBRID SUNFLOWER UNDER RAINFED FARMING SITUATIONS Lokanath H. Malligawad, Agronomist (Groundnut), Oilseeds
STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF RATIOS AND LEVELS OF NPK FERTILIZER NUTRIENTS ON THE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYBRID SUNFLOWER UNDER RAINFED FARMING SITUATIONS Lokanath H. Malligawad, Agronomist (Groundnut), Oilseeds
1._. Crop Production and Management. Lesson at a Glance
 1._ Crop Production and Management Lesson at a Glance Agriculture: The applied branch of biology which deals with cultivation of plants and rearing of animals is called agriculture. Generally, the art
1._ Crop Production and Management Lesson at a Glance Agriculture: The applied branch of biology which deals with cultivation of plants and rearing of animals is called agriculture. Generally, the art
Total Fertilizer (kg/ha)
 Tomato Fertigation The nutrient requirement for hybrids is 2:25:25 kg of NPK per ha. 75 % of P (87.5 kg P which comes to 72 kg of superphosphate) is applied as basal. The remaining quantity of 2:62.5:25
Tomato Fertigation The nutrient requirement for hybrids is 2:25:25 kg of NPK per ha. 75 % of P (87.5 kg P which comes to 72 kg of superphosphate) is applied as basal. The remaining quantity of 2:62.5:25
(A) garden (B) agriculture (C) crop (D) all of the above
 CROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT 1.Why storage of food is done? 2.Write any two sources of irrigation? 3.What are the two common forms by which we add nutrients in soil? 4.What do you mean by seed drill?
CROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT 1.Why storage of food is done? 2.Write any two sources of irrigation? 3.What are the two common forms by which we add nutrients in soil? 4.What do you mean by seed drill?
Lesson 4 Sunflower Helianthus annuus
 Lesson 4 Sunflower Helianthus annuus About sunflower It was an ornamental before 1969 in India It is popular oil seed crop today Its name is with reasoning Annual but there are perennials Competing with
Lesson 4 Sunflower Helianthus annuus About sunflower It was an ornamental before 1969 in India It is popular oil seed crop today Its name is with reasoning Annual but there are perennials Competing with
Sorghum grown under poor management
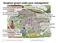 Sorghum grown under poor management Compaction of soil with tracking animals and tractors Use of poor seeds No hedges to protect the soil from erosion by wind Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of
Sorghum grown under poor management Compaction of soil with tracking animals and tractors Use of poor seeds No hedges to protect the soil from erosion by wind Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of
Recommended package of practices: Kharif sorghum
 Recommended package of practices: Kharif sorghum Preparation of land One deep ploughing with mould board plough in summer followed by 3 to 4 harrowings to maintain weed free conditions. Making compartmental
Recommended package of practices: Kharif sorghum Preparation of land One deep ploughing with mould board plough in summer followed by 3 to 4 harrowings to maintain weed free conditions. Making compartmental
Integrated Pest Management
 Integrated Pest Management System or strategy Utilizes all methods of pest suppression Compatible Maintain pests below economically damaging level Environmentally sound Economically sound Biological Control
Integrated Pest Management System or strategy Utilizes all methods of pest suppression Compatible Maintain pests below economically damaging level Environmentally sound Economically sound Biological Control
CONTRIBUTORS 6/30/14. Major crops in Bangladesh. CDB strategy for cotton expansion
 // CONTRIBUTORS MD. FAKHRE ALAM IBNE TABIB, PhD DEPUTY DIRECTOR COTTON DEVELOPMENT BOARD DHAKA REGION, DHAKA. Dr. Md. Fakhre Alam Ibne Tabib, Deputy Director, CDB Prof. Dr. M. Abdul Karim, Department of
// CONTRIBUTORS MD. FAKHRE ALAM IBNE TABIB, PhD DEPUTY DIRECTOR COTTON DEVELOPMENT BOARD DHAKA REGION, DHAKA. Dr. Md. Fakhre Alam Ibne Tabib, Deputy Director, CDB Prof. Dr. M. Abdul Karim, Department of
Nutrient management. Cassava
 Nutrient management Cassava Fertilizer use By applying mineral fertilizers to their cassava, smallholder farmers can increase their yields from about 10 tonnes to as much as 16 tonnes of fresh roots per
Nutrient management Cassava Fertilizer use By applying mineral fertilizers to their cassava, smallholder farmers can increase their yields from about 10 tonnes to as much as 16 tonnes of fresh roots per
PLANTING GEOMETRY AND ITS EFFECT ON GROWTH AND YIELD. 3. Sowi ng behind the country plough (manual and mechanical drilling)
 PLANTING GEOMETRY AND ITS EFFECT ON GROWTH AND YIELD Methods of Sowing and Transplanting 1. Broadcasting 2. Dibbling 3. Sowi ng behind the country plough (manual and mechanical drilling) 4. Seed Drilling
PLANTING GEOMETRY AND ITS EFFECT ON GROWTH AND YIELD Methods of Sowing and Transplanting 1. Broadcasting 2. Dibbling 3. Sowi ng behind the country plough (manual and mechanical drilling) 4. Seed Drilling
Effect of Split Application of Fertilizers on Growth, Yield and Economics of Bt Cotton Hybrid under Rainfed Condition
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Special Issue-6 pp. 373-378 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Effect of Split Application
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Special Issue-6 pp. 373-378 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Effect of Split Application
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM
 STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 7 TH April 2015 9 TH APRIL 2015 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON TUESDAY 7 TH
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 7 TH April 2015 9 TH APRIL 2015 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON TUESDAY 7 TH
AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION UMMEDGANJ, KOTA (Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture & Technology, Udaipur)
 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION UMMEDGANJ, KOTA (Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture & Technology, Udaipur) Dr. Pramod Dashora Assoc. Professor (Agronomy) Ph : 0744-2844369 (O) Fax : 0744-2844306 Mob.
AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION UMMEDGANJ, KOTA (Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture & Technology, Udaipur) Dr. Pramod Dashora Assoc. Professor (Agronomy) Ph : 0744-2844369 (O) Fax : 0744-2844306 Mob.
About BCI, Better Cotton, Minimum Production Criteria s (MPCs) and the process we followed to grow Better Cotton:
 About BCI, Better Cotton, Minimum Production Criteria s (MPCs) and the process we followed to grow Better Cotton: BCI exists to make global cotton production better for the people who produce it, better
About BCI, Better Cotton, Minimum Production Criteria s (MPCs) and the process we followed to grow Better Cotton: BCI exists to make global cotton production better for the people who produce it, better
Dept. of Agronomy, College of Agriculture, UAS, Raichur, Karnataka , India
 International Journal of Agriculture, Environment & Biotechnology Citation: IJAEB: 6(4): 623-628 December 2013 DOI Number 10.5958/j.2230-732X.6.4.041 Soil Science Uptake of NPK, Availability of NPK and
International Journal of Agriculture, Environment & Biotechnology Citation: IJAEB: 6(4): 623-628 December 2013 DOI Number 10.5958/j.2230-732X.6.4.041 Soil Science Uptake of NPK, Availability of NPK and
How to use Artificial Fertilizers. AT UGANDA LIMITED SOILS BROCHURE SERIES No. 02
 How to use Artificial Fertilizers AT UGANDA LIMITED SOILS BROCHURE SERIES No. 02 Introduction One way of enriching and replenishing the soil is by addition of artificial fertilizers. These fertilizers,
How to use Artificial Fertilizers AT UGANDA LIMITED SOILS BROCHURE SERIES No. 02 Introduction One way of enriching and replenishing the soil is by addition of artificial fertilizers. These fertilizers,
Research Project Form (RPF-II) ( )
 Research Project Form (RPF-II) (2007-08) (ANNUAL PROGRESS REPORT OF RESEARCH PROJECTS) Part-I : General Information 600 Project Code : 6001 Institute Project Code No. : 6002 ICAR Project Code No. : 601
Research Project Form (RPF-II) (2007-08) (ANNUAL PROGRESS REPORT OF RESEARCH PROJECTS) Part-I : General Information 600 Project Code : 6001 Institute Project Code No. : 6002 ICAR Project Code No. : 601
Technology 8: Extent of micro- and secondary nutrient deficiencies in Indian soils and their correction
 Technology 8: Extent of micro- and secondary nutrient deficiencies in Indian soils and their correction (i) Zinc Survey of Indian soils revealed that about 49% of 2.52 lakh soil samples analyzed were found
Technology 8: Extent of micro- and secondary nutrient deficiencies in Indian soils and their correction (i) Zinc Survey of Indian soils revealed that about 49% of 2.52 lakh soil samples analyzed were found
CROP MANAGEMENT Rain fed crops Trainer's guideline
 Inter Aide Agro-Phalombe PO Box 318 Zomba CROP MANAGEMENT Rain fed crops Trainer's guideline Laurence Mathieu-Colas and Goulven Le Bahers* Laston Maxwell Makina** September 2009 Objective of the training:
Inter Aide Agro-Phalombe PO Box 318 Zomba CROP MANAGEMENT Rain fed crops Trainer's guideline Laurence Mathieu-Colas and Goulven Le Bahers* Laston Maxwell Makina** September 2009 Objective of the training:
The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect
 Chapter 2 The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect 2.1 Introduction Sugarcane growing countries of the world are lying between the latitude 36.70 0 north and 31.00 0 south of the equator extending from tropical
Chapter 2 The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect 2.1 Introduction Sugarcane growing countries of the world are lying between the latitude 36.70 0 north and 31.00 0 south of the equator extending from tropical
Nutrient management practices for organic cotton production
 International Journal of Agricultural Sciences Volume 9 Issue 2 June, 2013 776-782 RESEARCH PAPER Nutrient management practices for organic cotton production R.F. CHANNAGOUDAR*, H.B. BABALAD, R.K. PATIL,
International Journal of Agricultural Sciences Volume 9 Issue 2 June, 2013 776-782 RESEARCH PAPER Nutrient management practices for organic cotton production R.F. CHANNAGOUDAR*, H.B. BABALAD, R.K. PATIL,
Integrated Pest Management in Sunflower
 Integrated Pest Management in Sunflower Insect pests of sunflowers Establishment Vegetative growth Budding flowering Maturity True and False Wireworms Cutworms Black scarab beetles Thrips Wingless cockroaches
Integrated Pest Management in Sunflower Insect pests of sunflowers Establishment Vegetative growth Budding flowering Maturity True and False Wireworms Cutworms Black scarab beetles Thrips Wingless cockroaches
Pest Management in Canola
 Pest Management in Canola Contents Canola aphids Diamondback moth (DBM) Native budworm Insecticide options in canola Key messages Key canola pests Pest group Emergence Vegetative Flowering Grain fill Earth
Pest Management in Canola Contents Canola aphids Diamondback moth (DBM) Native budworm Insecticide options in canola Key messages Key canola pests Pest group Emergence Vegetative Flowering Grain fill Earth
Cannabis Conundrum. PART 1 Commercial Production
 Cannabis Conundrum Canadian Industrial Hemp Industry PART 1 Commercial Production UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT EXTENSION Northwest Crops and Soils Program 2019 Industrial Hemp Conference: A Grower s Tutorial
Cannabis Conundrum Canadian Industrial Hemp Industry PART 1 Commercial Production UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT EXTENSION Northwest Crops and Soils Program 2019 Industrial Hemp Conference: A Grower s Tutorial
GRAMIN KRISHI MAUSAM SEWA
 GRAMIN KRISHI MAUSAM SEWA INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT NORTH EASTERN GAHAT ZONE RRTTS, G.UDAYAGIRI, OUAT, KANDHMAL, ODISHA-762100 MULTIMODEL ENSEMBLE BASED DISTRICT LEVEL WEATHER FORECAST FOR THE STATE:
GRAMIN KRISHI MAUSAM SEWA INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT NORTH EASTERN GAHAT ZONE RRTTS, G.UDAYAGIRI, OUAT, KANDHMAL, ODISHA-762100 MULTIMODEL ENSEMBLE BASED DISTRICT LEVEL WEATHER FORECAST FOR THE STATE:
HEAT USE EFFICIENCY AND HELIO-THERMAL UNITS FOR MAIZE GENOTYPES AS INFLUENCED BY DATES OF SOWING UNDER SOUTHERN TRANSITIONAL ZONE OF KARNATAKA STATE
 I.J.S.N., VOL. 2(3) 2011: 529-533 ISSN 2229 6441 HEAT USE EFFICIENCY AND HELIO-THERMAL UNITS FOR MAIZE GENOTYPES AS INFLUENCED BY DATES OF SOWING UNDER SOUTHERN TRANSITIONAL ZONE OF KARNATAKA STATE 1 Girijesh,
I.J.S.N., VOL. 2(3) 2011: 529-533 ISSN 2229 6441 HEAT USE EFFICIENCY AND HELIO-THERMAL UNITS FOR MAIZE GENOTYPES AS INFLUENCED BY DATES OF SOWING UNDER SOUTHERN TRANSITIONAL ZONE OF KARNATAKA STATE 1 Girijesh,
ORGANIC NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT IN CHILLIES BENGAL GRAM BABY CORN SEQUENCE
 Int. J. Agrl.Sc Sc. & Vet.Med. Med. 2013 2013 P M Shanmugam and K Siddeswaran, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2320-3730 www.ijasvm.com Vol. 1, No. 3, August 2013 2013 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved
Int. J. Agrl.Sc Sc. & Vet.Med. Med. 2013 2013 P M Shanmugam and K Siddeswaran, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2320-3730 www.ijasvm.com Vol. 1, No. 3, August 2013 2013 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved
XIII-Workshop. Venue : Jawahar Lal Nehru Krishi Vishwavidyalaya, Jabalpur Date : 15 th 18 th December, 1993
 4. Insect and Nematode Control For the control of jassids and shoot and fruit borer in okra 4 sprays with endosulfan at 500 g a.i./ ha at 14 days interval starting from 15 days after germination has been
4. Insect and Nematode Control For the control of jassids and shoot and fruit borer in okra 4 sprays with endosulfan at 500 g a.i./ ha at 14 days interval starting from 15 days after germination has been
MICRO-SPRINKLER IRRIGATION AND FUSTIGATION AND LAND CONFIGURATION AS A BEST MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY PACKAGE FOR GROUNDNUT
 MICRO-SPRINKLER IRRIGATION AND FUSTIGATION AND LAND CONFIGURATION AS A BEST MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY PACKAGE FOR GROUNDNUT R. Vijayalakshmi 1, V. Veerabadran 2, K.Shanmugasundram 3, V.Kumar 4 ABSTRACT Field
MICRO-SPRINKLER IRRIGATION AND FUSTIGATION AND LAND CONFIGURATION AS A BEST MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY PACKAGE FOR GROUNDNUT R. Vijayalakshmi 1, V. Veerabadran 2, K.Shanmugasundram 3, V.Kumar 4 ABSTRACT Field
NORTHERN FEBRUARY 2017 SUNFLOWER CONTENTS
 NORTHERN FEBRUARY 2017 SUNFLOWER CONTENTS Sunflowers What s new Introduction A.1 Agronomy at a glance...xvi A.2 Crop overview...xvii A.3 Key management issues...xvii A.4 End uses...xviii 1 Planning/Paddock
NORTHERN FEBRUARY 2017 SUNFLOWER CONTENTS Sunflowers What s new Introduction A.1 Agronomy at a glance...xvi A.2 Crop overview...xvii A.3 Key management issues...xvii A.4 End uses...xviii 1 Planning/Paddock
Soybean cultivator SYLLABUS/ CURRICULUM
 Soybean cultivator SYLLABUS/ CURRICULUM This program is aimed at training candidates for the job of a Soybean Cultivator, in the Agriculture Sector/Industry and aims at building the following key competencies
Soybean cultivator SYLLABUS/ CURRICULUM This program is aimed at training candidates for the job of a Soybean Cultivator, in the Agriculture Sector/Industry and aims at building the following key competencies
Sorghum Farming. Introduction
 Sorghum Farming Introduction For a very long time, sorghum has been the mostly cultivated cereal crop especially in semi arid areas. It is rich in vitamins and carbohydrates which keep families strong
Sorghum Farming Introduction For a very long time, sorghum has been the mostly cultivated cereal crop especially in semi arid areas. It is rich in vitamins and carbohydrates which keep families strong
Procedures for Tomato Variety Field Trials
 AVRDC The World Vegetable Center AVRDC Publication Number: 11-751 International Cooperators Guide Procedures for Tomato Variety Field Trials Peter Hanson, Li-ju Lin, Gregory C. Luther, Wen-shi Tsai, R.
AVRDC The World Vegetable Center AVRDC Publication Number: 11-751 International Cooperators Guide Procedures for Tomato Variety Field Trials Peter Hanson, Li-ju Lin, Gregory C. Luther, Wen-shi Tsai, R.
08. WATER BUDGETING AND ITS IMPORTANCE - IRRIGATION SCHEDULING - APPROACHES
 08. WATER BUDGETING AND ITS IMPORTANCE - IRRIGATION SCHEDULING - APPROACHES Water budgeting: Allocation of the water receipt including anticipated within the crop period and its detailed account of expenditure
08. WATER BUDGETING AND ITS IMPORTANCE - IRRIGATION SCHEDULING - APPROACHES Water budgeting: Allocation of the water receipt including anticipated within the crop period and its detailed account of expenditure
National Agromet Advisory Service Bulletin Based on Extended Range Weather Forecast (ERFS)
 National Agromet Advisory Service Bulletin Based on Extended Range Weather Forecast (ERFS) Validity: 10 to 23 August 2018 Date of issue: 10 August 2018 Issued by Indian Council of Agricultural Research
National Agromet Advisory Service Bulletin Based on Extended Range Weather Forecast (ERFS) Validity: 10 to 23 August 2018 Date of issue: 10 August 2018 Issued by Indian Council of Agricultural Research
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(8):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3597-3605 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.432
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3597-3605 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.432
Cluster Demonstration on Kharif Groundnut var. Devi
 Cluster Demonstration on Kharif Groundnut var. Devi Crop & variety Groundnut, Devi Season & Year Kharif, 2016 Village Mandapada, GP- Ranagundi, Block- Danagadi Area (ha) 30 ha No. of beneficiaries- 44
Cluster Demonstration on Kharif Groundnut var. Devi Crop & variety Groundnut, Devi Season & Year Kharif, 2016 Village Mandapada, GP- Ranagundi, Block- Danagadi Area (ha) 30 ha No. of beneficiaries- 44
Maharashtra. Groundnut
 Maharashtra Groundnut By the end of first week of September rice crop condition is improving in all the districts of Konkan and in Kolhapur, western Talukas of Pune and Satara districts and many other
Maharashtra Groundnut By the end of first week of September rice crop condition is improving in all the districts of Konkan and in Kolhapur, western Talukas of Pune and Satara districts and many other
Influence of Organic Manures and Rock Phosphate Application on of Bengal Gram (cicer arietinum l.).
 Influence of Organic Manures and Rock Phosphate Application on of Bengal Gram (cicer arietinum l.). T.SARAVANAN* AND P.PANNEERSELVAM Department of Crop Management,Vanavarayar Institute of Agriculture,
Influence of Organic Manures and Rock Phosphate Application on of Bengal Gram (cicer arietinum l.). T.SARAVANAN* AND P.PANNEERSELVAM Department of Crop Management,Vanavarayar Institute of Agriculture,
JUNAGADH AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
 JUNAGADH AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY RECOMMENDATIONS/TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPED DURING LAST 12 YEARS (2001-02 TO 2012-13) New technologies were developed in the different disciplines. Nearly 402 recommendations/new
JUNAGADH AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY RECOMMENDATIONS/TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPED DURING LAST 12 YEARS (2001-02 TO 2012-13) New technologies were developed in the different disciplines. Nearly 402 recommendations/new
Cotton Crop Protection Strategies 2018
 Cotton Crop Protection Strategies 2018 Dr V. S. Nagrare, Dr Nandini Gokte-Narkhedkar, Dr V. N. Waghmare ICAR-Central Institute for Cotton Research, Nagpur (No part of this advisory may be reproduced in
Cotton Crop Protection Strategies 2018 Dr V. S. Nagrare, Dr Nandini Gokte-Narkhedkar, Dr V. N. Waghmare ICAR-Central Institute for Cotton Research, Nagpur (No part of this advisory may be reproduced in
Field Problems in Direct-Seeded Rice Using Drumseeder -- and Solutions
 Field Problems in Direct-Seeded Rice Using Drumseeder -- and Solutions Dr. P. Bala Hussain Reddy, SMS (Agrl. Extension), Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Nellore District, Andhra Pradesh, India S. Sreenivasulu, SMS
Field Problems in Direct-Seeded Rice Using Drumseeder -- and Solutions Dr. P. Bala Hussain Reddy, SMS (Agrl. Extension), Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Nellore District, Andhra Pradesh, India S. Sreenivasulu, SMS
Green Bean Production and Management
 WISCONSIN VEGETABLE SUSTAINABILITY GREEN/SNAP BEAN SPECIFIC PROTOCOL - DRAFT 1/25/2012 Developed by the Wisconsin Institute for Sustainable Agriculture, University of Wisconsin - Madison Note: To determine
WISCONSIN VEGETABLE SUSTAINABILITY GREEN/SNAP BEAN SPECIFIC PROTOCOL - DRAFT 1/25/2012 Developed by the Wisconsin Institute for Sustainable Agriculture, University of Wisconsin - Madison Note: To determine
EFFECT OF MOISTURE CONSERVATION PRACTICES, PHOSPHORUS LEVELS AND BACTERIAL INOCULATION ON GROWTH, YIELD AND ECONOMICS OF CHICKPEA (CICER ARIETINUM L.
 Legume Res., 29 (1) : 68-72, 2006 EFFECT OF MOISTURE CONSERVATION PRACTICES, PHOSPHORUS LEVELS AND BACTERIAL INOCULATION ON GROWTH, YIELD AND ECONOMICS OF CHICKPEA (CICER ARIETINUM L.) L.R. Meena 1, R.K.
Legume Res., 29 (1) : 68-72, 2006 EFFECT OF MOISTURE CONSERVATION PRACTICES, PHOSPHORUS LEVELS AND BACTERIAL INOCULATION ON GROWTH, YIELD AND ECONOMICS OF CHICKPEA (CICER ARIETINUM L.) L.R. Meena 1, R.K.
IRRIGATION AND WATER REQUIREMENTS IN BANANA... 8
 (iii) CONTENTS Paae PREFACE... CHRONOLOGY OF EVENTS AND SUBJECT AREAS.... TERMS OF REFERENCE FOR RAPPORTEURS... ix xi... XIII CHAPTER I - REPORT ON BANANA CROP - by Mr P.S.N. Sastry........ I 1.1 INTRODUCTION............................
(iii) CONTENTS Paae PREFACE... CHRONOLOGY OF EVENTS AND SUBJECT AREAS.... TERMS OF REFERENCE FOR RAPPORTEURS... ix xi... XIII CHAPTER I - REPORT ON BANANA CROP - by Mr P.S.N. Sastry........ I 1.1 INTRODUCTION............................
USING TITHONIA AS A FERTILISER
 USING TITHONIA AS A FERTILISER Compiled by RESCAP WHAT IS TITHONIA? Tithonia was initially introduced from Central America as an ornamental. It is now a common flower that grows along roads and on waste
USING TITHONIA AS A FERTILISER Compiled by RESCAP WHAT IS TITHONIA? Tithonia was initially introduced from Central America as an ornamental. It is now a common flower that grows along roads and on waste
ANNUAL REPORT ALL INDIA CO-ORDINATED RESEARCH PROJECT ON SUGARCANE ZARS, VC FARM (UAS,BENGALORE), MANDYA (KARNATAKA)
 ANNUAL REPORT 2015-16 ALL INDIA CO-ORDINATED RESEARCH PROJECT ON SUGARCANE ZARS, VC FARM (UAS,BENGALORE), MANDYA (KARNATAKA) RESULTS OF AGRONOMY AND ENTOMOLOGY TRIALS 2. AICRP on Sugarcane (Agronomy) Experiment
ANNUAL REPORT 2015-16 ALL INDIA CO-ORDINATED RESEARCH PROJECT ON SUGARCANE ZARS, VC FARM (UAS,BENGALORE), MANDYA (KARNATAKA) RESULTS OF AGRONOMY AND ENTOMOLOGY TRIALS 2. AICRP on Sugarcane (Agronomy) Experiment
Management of major insect pests of black gram under dryland conditions
 2015; 3 (1): 115-121 ISSN 2320-7078 JEZS 2015; 3 (1): 115-121 2015 JEZS Received: 05-12-2014 Accepted: 20-12-2014 C. Gailce Leo Justin P. Anandhi D. Jawahar Management of major insect pests of black gram
2015; 3 (1): 115-121 ISSN 2320-7078 JEZS 2015; 3 (1): 115-121 2015 JEZS Received: 05-12-2014 Accepted: 20-12-2014 C. Gailce Leo Justin P. Anandhi D. Jawahar Management of major insect pests of black gram
INHERITANT SOCIAL BENEFITS OF ORGANIC FARMING
 INHERITANT SOCIAL BENEFITS OF ORGANIC FARMING WELCOME TO ONE AND ALL INTRODUCTION Anandi Enterprises is implementing organic cotton project with 6 ICS, in the Districts of salem, Namakkal & Tiruvannamalai
INHERITANT SOCIAL BENEFITS OF ORGANIC FARMING WELCOME TO ONE AND ALL INTRODUCTION Anandi Enterprises is implementing organic cotton project with 6 ICS, in the Districts of salem, Namakkal & Tiruvannamalai
Realization of Target Yield in Bt Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) with Different Methods of Establishment under Varied Dates of Planting
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3005-3010 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.351
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3005-3010 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.351
Agronomy Agronomy I: Agronomy IIa: Agronomy IIb: Agronomy III: Agronomy IV: IV a: IV b IV c: Agronomy V: Agronomy VI: PHYSIOLOGY: Phy.
 D-1- Agronomy Experiments were laid out as per the technical programme approved during the AICCIP meeting held at PAU, Ludhiana for the year 2008-09. Following experiments were carried out by various centres
D-1- Agronomy Experiments were laid out as per the technical programme approved during the AICCIP meeting held at PAU, Ludhiana for the year 2008-09. Following experiments were carried out by various centres
Success Story No.1 Red gram Transplantation Reviving Red gram area; Replenishing the Protein Bowl
 Success Story No.1 Red gram Transplantation Reviving Red gram area; Replenishing the Protein Bowl Pulses Scenario In Tamil Nadu pulses are grown in an area of 8.8 lakh ha with an annual production of 5.08
Success Story No.1 Red gram Transplantation Reviving Red gram area; Replenishing the Protein Bowl Pulses Scenario In Tamil Nadu pulses are grown in an area of 8.8 lakh ha with an annual production of 5.08
Vegetable Gardening and Season Extension
 Vegetable Gardening and Season Extension Vern Grubinger www.uvm.edu/vtvegandberry Overview Introduction Soil Health: fertilizers, cover crops, compost Pest Management: insects, diseases, weeds Season Extension:
Vegetable Gardening and Season Extension Vern Grubinger www.uvm.edu/vtvegandberry Overview Introduction Soil Health: fertilizers, cover crops, compost Pest Management: insects, diseases, weeds Season Extension:
A) PLANT BREEDING (CROP IMPROVEMENT): The following 25 rice varieties were developed and released from this research station.
 A) PLANT BREEDING (CROP IMPROVEMENT): The following 25 rice varieties were developed and released from this research station. S. No Variety (Paddy) Year of release Special Characters 1. BCP 1 1948 Traditional
A) PLANT BREEDING (CROP IMPROVEMENT): The following 25 rice varieties were developed and released from this research station. S. No Variety (Paddy) Year of release Special Characters 1. BCP 1 1948 Traditional
Biologically-Based, Insect Pest Management in Tomato and Pepper
 Biologically-Based, Insect Pest Management in Tomato and Pepper Southern Wisconsin Vegetable Workshop February 1, 2013 Russell L. Groves Department of Entomology University of Wisconsin 1630 Linden Drive
Biologically-Based, Insect Pest Management in Tomato and Pepper Southern Wisconsin Vegetable Workshop February 1, 2013 Russell L. Groves Department of Entomology University of Wisconsin 1630 Linden Drive
Lesson 6 Safflower Carthamus tinctorious
 Lesson 6 Safflower Carthamus tinctorious Economic Importance o Rich in PUFA (78%) to reduce blood cholesterols o Used for preparation of: Margarine, and salad dressing Varnishes, paints and surface coating
Lesson 6 Safflower Carthamus tinctorious Economic Importance o Rich in PUFA (78%) to reduce blood cholesterols o Used for preparation of: Margarine, and salad dressing Varnishes, paints and surface coating
Effect of High Density Planting System (HDPS) and Varieties on Yield, Economics and Quality of Desi Cotton
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 233-238 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.025
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 233-238 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.025
Evaluation of Conventional and Aerobic Farming Practices in a Paddy based. cropping system - A case study in Karnataka, India
 INT J CURR SCI 2016, 19(2): E 122-127 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2250-1770 Evaluation of Conventional and Aerobic Farming Practices in a Paddy based cropping system - A case study in Karnataka, India Sreenivasa
INT J CURR SCI 2016, 19(2): E 122-127 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2250-1770 Evaluation of Conventional and Aerobic Farming Practices in a Paddy based cropping system - A case study in Karnataka, India Sreenivasa
Effect of High Density Planting and Weed Management Practices on Productivity and Economic Analysis of Bt Cotton
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2225-2230 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.261
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2225-2230 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.261
International Journal of Agriculture Innovations and Research Volume 4, Issue 1, ISSN (Online)
 Manuscript Processing Details (dd/mm/yyyy) : Received : 03/08/2015 Accepted on : 12/08/2015 Published : 19/08/2015 Effective Agricultural Management Practices for Farmers through Field Farmers School Programmes
Manuscript Processing Details (dd/mm/yyyy) : Received : 03/08/2015 Accepted on : 12/08/2015 Published : 19/08/2015 Effective Agricultural Management Practices for Farmers through Field Farmers School Programmes
Department of Agriculture Entomology Brsa Agricultural University, Kanke, Ranchi
 Technology Developed Department of Agriculture Entomology Brsa Agricultural University, Kanke, Ranchi 1. Development of IPM modules in rice crop Gallmidge resistant varieties viz., Lalat, RD-202, BG-380-2,
Technology Developed Department of Agriculture Entomology Brsa Agricultural University, Kanke, Ranchi 1. Development of IPM modules in rice crop Gallmidge resistant varieties viz., Lalat, RD-202, BG-380-2,
SWEET POTATO (Ipomoea batatas (L) Lam)
 A CROP PRODUCTION TECHNICAL GUIDE SWEET POTATO (Ipomoea batatas (L) Lam) Prepared by Pathleen Titus, CARDI Caribbean Agricultural Research and Development Institute St Vincent and the Grenadines May 2008
A CROP PRODUCTION TECHNICAL GUIDE SWEET POTATO (Ipomoea batatas (L) Lam) Prepared by Pathleen Titus, CARDI Caribbean Agricultural Research and Development Institute St Vincent and the Grenadines May 2008
SESAME (Sesamum indicum)
 SESAME (Sesamum indicum) CROP IMPROVEMENT I. SEASON AND VARIETIES DISTRICT/SEASON A) Rainfed 1. Adipattam (Jun - Jul) All districts 2. Karthigaipattam (Oct - Nov) All districts B) Irrigated - Masipattam
SESAME (Sesamum indicum) CROP IMPROVEMENT I. SEASON AND VARIETIES DISTRICT/SEASON A) Rainfed 1. Adipattam (Jun - Jul) All districts 2. Karthigaipattam (Oct - Nov) All districts B) Irrigated - Masipattam
Impact of climate change on wheat productivity in Ludhiana and Bathinda of Punjab
 Indian J. Agric. Res., 49 (4) 2015: 368-372 Print ISSN:0367-8245 / Online ISSN:0976-058X AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijarjournal.com Impact of climate change on
Indian J. Agric. Res., 49 (4) 2015: 368-372 Print ISSN:0367-8245 / Online ISSN:0976-058X AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijarjournal.com Impact of climate change on
Class IX Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Science
 What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? (i) Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source of energy. (ii) Pulses give us proteins. (iii) Fruits and vegetables
What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? (i) Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source of energy. (ii) Pulses give us proteins. (iii) Fruits and vegetables
 Question 1: What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? (i) Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source of energy. (ii) Pulses give us proteins. (iii) Fruits and
Question 1: What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? (i) Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source of energy. (ii) Pulses give us proteins. (iii) Fruits and
Dr. Sarath Nissanka, R&D Coordinator, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
 Crop Trial Undertaken by University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, (Faculty of Agriculture-Department of Crop Science) in Collaboration with BioAg Pty Ltd (Australia) Crop: Green Chili Trial Dates: Commencement:
Crop Trial Undertaken by University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, (Faculty of Agriculture-Department of Crop Science) in Collaboration with BioAg Pty Ltd (Australia) Crop: Green Chili Trial Dates: Commencement:
CERTIFICATE IN SERICULTURE (CIS) BLP-004 : CROP PROTECTION
 No. of Printed Pages : 7 BLP-004 N CERTIFICATE IN SERICULTURE (CIS) 0") Term-End Examination CD CD December, 2013 BLP-004 : CROP PROTECTION Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Answer any two questions
No. of Printed Pages : 7 BLP-004 N CERTIFICATE IN SERICULTURE (CIS) 0") Term-End Examination CD CD December, 2013 BLP-004 : CROP PROTECTION Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Answer any two questions
Class IX Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Science
 Class IX Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Science Question 1: What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? (i) Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source
Class IX Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Science Question 1: What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? (i) Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source
MAIZE (Zea mays L.) Family Poaecea(Gramineae) By Dr. S A. Abolusoro
 MAIZE (Zea mays L.) Family Poaecea(Gramineae) By Dr. S A. Abolusoro Origin Maize was domesticated in Southern Mexico around 4000BC. On arrival of European in America,maize had already spread from chile
MAIZE (Zea mays L.) Family Poaecea(Gramineae) By Dr. S A. Abolusoro Origin Maize was domesticated in Southern Mexico around 4000BC. On arrival of European in America,maize had already spread from chile
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 25 TH MARCH to 28 TH MARCH 2016
 STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 25 TH MARCH to 28 TH MARCH 2016 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON FRIDAY 25 TH
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 25 TH MARCH to 28 TH MARCH 2016 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON FRIDAY 25 TH
