6 pts. B) State two mechanisms to explain the effect shown in the figure.
|
|
|
- Marsha Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question 1. (10 points) The rate of uptake of glucose into rat adipocytes is increased by addition of insulin to the medium. The increase reaches a maximum within 30 seconds at 37 C and is energy dependent. The transport of glucose into the cell, however, takes place by facilitated diffusion. The rates of glucose entry as a function of the extracellular glucose concentration in the absence and the presence of insulin are shown in the figure below. 4 pts. A) What is the effect of insulin on the K m and V max of the transport process? 6 pts. B) State two mechanisms to explain the effect shown in the figure. 1
2 Question 2. (24 points) A muscle biopsy was performed on a person who is incapable of doing prolonged physical work. His mitochondria were isolated and found to be atypical in structure. The respiratory functions of these mitochondria were determined. They are able to carry out electron transport to O 2 ; however, during active O 2 consumption, there is no membrane potential across the inner mitochondrial membrane. On the other hand, the matrix ph is 9 when the external ph is 7. RT= 0.6 kcal/mol F= 23 kcal/mol volt 6 pts. A) Calculate the protomotive force in these mitochondria. 6 pts. B) G for the synthesis of ATP in these mitochondria is kcal/mol. What is the minimun number of protons that must be translocated to drive the synthesis of one molecule of ATP? 2
3 6 pts. C) In normal mitochondria, the membrane potential across the inner membrane is volt, while the ph is 2 during respiration. What is the minimum number of protons required for the synthesis of one molecule of ATP in this case? 6 pts. D) What might cause the atypical mitochondria to retain the ability to form a ph gradient but be unable to develop a membrane potential? Be brief. 3
4 Question 3. (18 points) The elongation rate constants for actin filaments are: k on (ATP) k off (M -1 sec -1 ) (sec -1 ) barbed end (+) 12 x pointed end (-) 1.2 x An actin filament 0.1 µm in length is placed in a solution of 75 mm KCl, 5 mm Mg +2 and 2 mm ATP; actin monomer with bound ATP is added at a concentration of µm. The size of the filament is measured as a function of time. 6 pts. A) Determine the value of the critical concentration for the barbed end and for the pointed end. 6 pts. B) What happens to the size of the filament and at the two ends of the filament under these conditions? 6 pts. C) A bacterium binds to the barbed end of the filament in a way that does not prevent binding of actin monomers. Indicate whether or not the bacterium moves; if it does, in which direction and at what speed. Remember that the actin monomer can be represented by a sphere with a diameter of 5 nm. 4
5 Question 4. (15 points) Aldehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction : O O R--CH + NAD + + H 2 O R--C--O - + NADH + 2H + Using fast measurements techniques, the following rate profile was obtained for the reaction of 1 pmole of enzyme with propionaldehyde and NAD + : NADH (pmoles) 0.9 time Write the simplest kinetic scheme (sequence of reactions) to explain the results. Assume that NAD + binds to the enzyme before the aldehyde, and that either NADH or the carboxylic acid is released first from the enzyme. 5
6 Question 5. (20 points) Influenza hemagglutinin (HAO) is a membrane protein with a single transmembrane domain at the COOH-terminal end. The effect of a reducing environment on the folding of HAO in the endoplasmic reticulum was investigated in these studies. CHO 15B cells, expressing HAO, were pulse-labeled for 2 min with 35 S-methionine. Dithiothreitol (DTT), a reducing agent, was added at 5 mm during the chase with nonradioactive methionine. Then, DTT was washed out of the cells for 2 and 30 min. In one plate, glucose was present so that there was an adequate amount of ATP; in another plate, inhibitors of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation were present to deplete the cells of ATP. At various times, the cells were lysed and the extracts were examined by non-reducing SDS-PAGE to determine the mobility of HAO. The results are shown in the figure. Conditions: +ATP -ATP top of gel Wash: Wash: -DTT +DTT 2 min 30 min +DTT 2 min 30 min Indicate the structures of the bands in the various lanes. (If you need to write on the back of the page, please indicate) 6
7 Question 6. (24 points) The following studies were done to study the cell cycle of Hela cells. The growth rate of an asynchronously growing culture is shown in Figure 5. Examination of a dish of fixed cells revealed that 10% of the cells are in mitosis. 3 H-Thymidine was added to the medium at time 0; after the given times, the cells were fixed and prepare for autoradiography. Figure 6 shows the fraction of labeled mitotic cells as a function of time after addition of the radioactive thymidine. In Figure 7, the number of silver grains per mitotic cell is plotted as a function of time after addition of 3 H- thymidine. Determine the doubling time and indicate the duration of the phases of the cell cycle in Hela cells. 7
8 Question 7. (18 points) AZT (azidodideoxythymidine), a drug used in the treatment of AIDS, acts by inhibiting the viral reverse transcriptase, which is critical for the life cycle of HIV. AZT must be triply phosphorylated to form azttp (azidodideoxythymidine triphosphate) in order to mimic dtpp (deoxythimidine triphosphate), a substrate for DNA synthesis. When reverse transcriptase mistakes aztpp for dttp, viral DNA synthesis terminates. aztpp cannot be given to patients because it can not get into cells. On the other hand, AZT does enter cells and is phosphorylated by the cellular thymidine phosphorylation pathway. The structures of AZT and aztpp are: 5 pts. A) Why can AZT get into a cell while azttp can not? (Not more than 15 words). 8 pts. B) The values of Km for dttp with reverse transcriptase were determined at various concentrations of azttp. azttp (µm) Km(apparent) (µm) What is the value of K I (include units) for azttp? 5 pts. C) The K I of azttp for inhibition of cellular DNA polymerase is ~ 230 µm. Explain why azttp can be used to inhibit HIV reverse transcriptase without affecting cellular (nonviral) DNA replication? 8
9 Question 8. (15 points) A mutant Gαs subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein was found to have decreased GTPase activity although it bound nucleotides. It was noticed that cells expressing the mutant Gαs had increased protein kinase A (PKA) activity compared to cells with wild type Gαs. 5 pts. A) What is the explanation for the increased PKA activity? 10 pts. B) The mutant Gαs was expressed in liver cells. Describe the effect of the mutant on glycogen metabolism (breakdown and synthesis). Be sure to identify the critical enzymes involved in the process. 9
10 Question 9. (16 points) Cyclin B is a 48 kd protein involved in the cell cycle. Its levels are known to rise and fall as cells proceed through their development cycle. Xenopus egg extracts are used as an in vitro model for cell cycle studies. Such extracts are effectively frozen in late meiosis until Ca 2+ is added, after which cyclin levels drop precipitously and the extract proceeds into interphase. Radiolabelled cyclin was added to Xenopus egg extract. Ca 2+ was then added and samples were taken at 0, 5, and 10 minutes after the calcium addition. The experiment was also run in the presence of lactacystin. The resultant samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography, giving the following results: - lactacystin + lactacystin Size (kda) min. after Ca 2+ addition pts. A) What is the band in lanes 1 and 4? 3 pts. B) The ladder in lanes 2, 5 and 6 appear to occur at regular increments of ~7kD. What is the source of this pattern? 10
11 5 pts. C) Propose a mechanism responsible for the decrease in cyclin levels observed in Xenopus extracts upon Ca ++ addition. 5 pts. D) What features might you find on cyclin B that is important for this mechanism? How would you test this? 11
12 Question 10. (16 points) 6 pts. A) The velocity of an enzymatic reaction was measured as a function of substrate concentration at three concentrations of enzyme : 0.5 nm, 5 nm and 25 nm. On one set of axes, draw the Lineweaver-Burk plots of the results with the enzyme concentrations. 10 pts.b) Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) catalyzes the reaction: The intial velocity of ATCase as a function of aspartate concentration is shown in Figure A. Succinate binds to the same site on ATCase as aspartate. Using the aspartate concentration corresponding to C in Figure A, the initial velocity of the reaction is measured as a function of succinate concentration; the results are shown in Figure B. 12
13 A. B. v v [aspartate] [succinate] Which of the following statements are true and which are false? a) Succinate acts as a competitive inhibitor at low concentrations and as a noncompetitive inhibitor at high concentrations. b) There are cooperative interactions between the binding site for aspartate. c) Succinate binds preferentially to the T state of ATCase, which has low affinity for aspartate. d) Succinate binds preferentially to the R state of ATCase, which has a high affinity for aspartate. e) Succinate is an allosteric inhibitor of ATCase. 12
14 Question 11. (24 points) Refer to the colored photocopy for figures. The most prominent divergent region in the 130 kda motor domain (S1 fragment) of myosin occurs at the 50K/20K junction, a region of the molecule involved in actin binding. In the Figure, the junctional region is at the 50kDa cleft. Myosin chimeras have been constructed by substituting a 9-amino-acid junctional region of Dictyostelium myosin with those from myosins of other species. The purified wild-type and chimeric myosins were assayed for ATPase activity under three conditions, all at saturating ATP concentration. The motile activity of the myosins was measured in a sliding filament in vitro motility assay (last column). In this assay, the myosin was applied to a glass slide so as to coat its surface, then a solution of fluorescent F-actin was introduced and movement initiated by the addition of ATP. In this system multiple myosin molecules interact with an actin filament. Movement at 30 C was recorded and analyzed. The results are shown in the Table. High salt Mg 2+ -ATPase Actin-activated Sliding velocity Ca 2+ -ATPase Mg 2+ -ATPase (Pi/head/sec) (Pi/head/sec) (Pi/head/sec) (µm s -1 ) Wild type myosin (Dictyostelium) Chimera with Rabbit skeletal myosin Chimera with chicken smooth muscle It is evident that the Vmax values for the actin-activated ATPase activities of the chimeras differ by a factor of 9; however, the velocities measured in the in vitro motility assays are within a factor of 2. The actin-activated myosin ATPase cycle is shown in the Figure. 12
15 8 pts. A) Why is there a difference between the values of the Mg 2+ -ATPase and the actin-activated Mg 2+ -ATPase activities for each myosin? What is the effect of actin on the mechanism of the reaction? 8 pts. B) What is the explanation for the Ca 2+ -ATPase activities compared to those for the Mg 2+ -ATPase activities of the various myosins. 8 pts. C) How is it possible for the actin-activated ATPase activities not to be correlated with the sliding velocities? Explain in terms of the cycle shown in the figure. 12
6 Enzymes II W. H. Freeman and Company
 6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
A. Incorrect! Enzymes are not altered or consumed by the reactions they catalyze.
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Cellular Metabolism No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about enzymes is correct? (A) Enzymes are consumed in a reaction. (B) Enzymes act by lowering
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Cellular Metabolism No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about enzymes is correct? (A) Enzymes are consumed in a reaction. (B) Enzymes act by lowering
Enzymes Part III: regulation I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Lecture 13. Motor Proteins I
 Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008
 BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008 NAME (printed very legibly) Key UT-EID EXAMINATION 3 Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008 NAME (printed very legibly) Key UT-EID EXAMINATION 3 Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
Unit 1 Human cells. 1. Division and differentiation in human cells
 Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Practice Problems 5. Location of LSA-GFP fluorescence
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 5 1. Soluble proteins that are normally secreted from the cell into the extracellular environment must go through a series of steps referred to as the secretory pathway.
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 5 1. Soluble proteins that are normally secreted from the cell into the extracellular environment must go through a series of steps referred to as the secretory pathway.
(a) Rearrange the Michaelis Menten equation to give V 0 as a function of V 0 /[S]. (b) What is the significance of the slope, the vertical intercept,
![(a) Rearrange the Michaelis Menten equation to give V 0 as a function of V 0 /[S]. (b) What is the significance of the slope, the vertical intercept, (a) Rearrange the Michaelis Menten equation to give V 0 as a function of V 0 /[S]. (b) What is the significance of the slope, the vertical intercept,](/thumbs/78/78783979.jpg) 1. Active yet responsive. What is the biochemical advantage of having a K M approximately equal to the substrate con- centration normally available to an enzyme? 2. Destroying the Trojan horse. Penicillin
1. Active yet responsive. What is the biochemical advantage of having a K M approximately equal to the substrate con- centration normally available to an enzyme? 2. Destroying the Trojan horse. Penicillin
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I)
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Sequence of C-terminal tail regions of myosin heavy chains in class XI of Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb
 Fig. S1 Sequence of C-terminal tail regions of myosin heavy chains in class XI of Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb myosin XI-2, -F and K) and BY-2 cell (Nt 170-kD myosin and Nt 175-kD myosin). Amino acids identical
Fig. S1 Sequence of C-terminal tail regions of myosin heavy chains in class XI of Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb myosin XI-2, -F and K) and BY-2 cell (Nt 170-kD myosin and Nt 175-kD myosin). Amino acids identical
7.014 Quiz I Solutions
 7.014 Quiz I Solutions Class Average = 64.7 Median = 66 Grade Range % A 79-100 22 B 60-78 37 C 50 59 24 D 38 49 15 F 0 37 2 Question 1 (32 points) You are a biology specialist on a space exploration team.
7.014 Quiz I Solutions Class Average = 64.7 Median = 66 Grade Range % A 79-100 22 B 60-78 37 C 50 59 24 D 38 49 15 F 0 37 2 Question 1 (32 points) You are a biology specialist on a space exploration team.
MCB130 midterm exam. 1) The exam has 6 pages (not including this page). Check that you have all 6 pages
 MCB130 midterm exam 1) The exam has 6 pages (not including this page). Check that you have all 6 pages 2) Please write your name and SID on the top of each page. The pages will be separated for grading
MCB130 midterm exam 1) The exam has 6 pages (not including this page). Check that you have all 6 pages 2) Please write your name and SID on the top of each page. The pages will be separated for grading
Name period date AP BIO- 2 nd QTR 6 Week Test Review
 Name period date AP BIO- 2 nd QTR 6 Week Test Review Cellular Respiration 1. In the following reaction, C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy, identify which is reduced and which is oxidized: a. Glucose
Name period date AP BIO- 2 nd QTR 6 Week Test Review Cellular Respiration 1. In the following reaction, C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy, identify which is reduced and which is oxidized: a. Glucose
MCB110 FINAL. Dec 13, Your name and student ID
 MCB110 FINAL Dec 13, 2007 Your name and student ID. QUESTION POINTS 1 (15 points) 2 (15 points) 3 (15 points) 4 (20 points) 5 (25 points) 6 (20 points) 7 (20 points) 8 (20 points) 9 (25 points) 10 (25
MCB110 FINAL Dec 13, 2007 Your name and student ID. QUESTION POINTS 1 (15 points) 2 (15 points) 3 (15 points) 4 (20 points) 5 (25 points) 6 (20 points) 7 (20 points) 8 (20 points) 9 (25 points) 10 (25
Q2 (1 point). How many carbon atoms does a glucose molecule contain?
 Q1 (1 point). Name three amino acids that are typically found at the surface of integrated membrane proteins.. Q2 (1 point). How many carbon atoms does a glucose molecule contain? Q3 (1 point). What do
Q1 (1 point). Name three amino acids that are typically found at the surface of integrated membrane proteins.. Q2 (1 point). How many carbon atoms does a glucose molecule contain? Q3 (1 point). What do
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10
 Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Question 2 (15 points)
 Question 2 (15 points) Your undergraduate TAs were not very successful at performing the Protein Biochemistry experiments during Run-Through Week. Describe how the following mistakes would affect the purification
Question 2 (15 points) Your undergraduate TAs were not very successful at performing the Protein Biochemistry experiments during Run-Through Week. Describe how the following mistakes would affect the purification
green B 1 ) into a single unit to model the substrate in this reaction. enzyme
 Teacher Key Objectives You will use the model pieces in the kit to: Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating enzymatic activity.
Teacher Key Objectives You will use the model pieces in the kit to: Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating enzymatic activity.
Nucleic Acids and Proteins
 DNA Structure 7.1 Nucleic Acids and Proteins Topic 7 DNA is composed of subunits called nucleotides The four types of bases on nucleotides are: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thyamine Purines: two ring
DNA Structure 7.1 Nucleic Acids and Proteins Topic 7 DNA is composed of subunits called nucleotides The four types of bases on nucleotides are: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thyamine Purines: two ring
1. ADHERE AND DEFEND: Our bacterium has entered the host. Now it needs to adhere and get past the normal microbiota.
 North Seattle College Stage 02 Colonization and Infection This explanatory model will tell the story of how one bacterium adheres to a host and, through binary fission, ends up making two daughter cells.
North Seattle College Stage 02 Colonization and Infection This explanatory model will tell the story of how one bacterium adheres to a host and, through binary fission, ends up making two daughter cells.
BC 367, Exam 2 November 13, Part I. Multiple Choice (3 pts each)- Please circle the single best answer.
 Name BC 367, Exam 2 November 13, 2008 Part I. Multiple Choice (3 pts each)- Please circle the single best answer. 1. The enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyzes the following reaction. What kind of enzyme
Name BC 367, Exam 2 November 13, 2008 Part I. Multiple Choice (3 pts each)- Please circle the single best answer. 1. The enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyzes the following reaction. What kind of enzyme
cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular processes (transcription, replication, microtubules)
 DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
Microbial Metabolism. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
G = H (T S) I. Cellular Metabolism & Reaction Coupling Figure 1: Metabolism
 I. Cellular Metabolism & Reaction Coupling Figure 1: Metabolism Metabolism represents the sum total of ALL chemical reactions within the cell. These reactions can be regarded as either catabolic or anabolic
I. Cellular Metabolism & Reaction Coupling Figure 1: Metabolism Metabolism represents the sum total of ALL chemical reactions within the cell. These reactions can be regarded as either catabolic or anabolic
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05
 Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05 Class Average = 83 Standard Deviation = 9 Range Grade % 87-100 A 43 74-86 B 39 55-73 C 17 > 54 D 1 Question 1 (56 points) While studying deep sea bacteria, you discover
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05 Class Average = 83 Standard Deviation = 9 Range Grade % 87-100 A 43 74-86 B 39 55-73 C 17 > 54 D 1 Question 1 (56 points) While studying deep sea bacteria, you discover
Student name ID # Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores Total
 Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Metabolism. BIOL 3702: Chapter 10. Introduction to Metabolism. Energy and Work. BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 AY Dr. Cooper 1. Metabolism (cont.
 Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Biology (Microbiology): Exam #2
 NAME: ANSWER KEY PLEDGE: Biology 50-384 (Microbiology): Exam #2 1. You have isolated mutants in the following genes in the motile bacterium E. coli. These mutations result in the formation of a nonfunctional
NAME: ANSWER KEY PLEDGE: Biology 50-384 (Microbiology): Exam #2 1. You have isolated mutants in the following genes in the motile bacterium E. coli. These mutations result in the formation of a nonfunctional
Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 19 Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide 19.1 and 19.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges
Chapter 19 Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide 19.1 and 19.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges
Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 9 9.1 and 9.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges of
Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 9 9.1 and 9.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges of
7.06 Problem Set #3, 2006
 7.06 Problem Set #3, 2006 1. You are studying the EGF/Ras/MAPK pathway in cultured cells. When the pathway is activated, cells are signaled to proliferate. You generate various mutants described below.
7.06 Problem Set #3, 2006 1. You are studying the EGF/Ras/MAPK pathway in cultured cells. When the pathway is activated, cells are signaled to proliferate. You generate various mutants described below.
Lecture 7: 9/7. CHAPTER 7 Kinetics and Regulation
 Lecture 7: 9/7 CHAPTER 7 Kinetics and Regulation Chapter 7 Outline The rate or velocity of an enzymatic reaction Consider a simple reaction: The velocity or rate of the reaction is determined by measuring
Lecture 7: 9/7 CHAPTER 7 Kinetics and Regulation Chapter 7 Outline The rate or velocity of an enzymatic reaction Consider a simple reaction: The velocity or rate of the reaction is determined by measuring
Examination I Key MCMP 208 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences I February 7, 2017
 Examination I Key MCMP 208 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences I February 7, 2017 Correct answers in multiple choice questions are indicated in RED and underlined. Correct answers to essay questions
Examination I Key MCMP 208 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences I February 7, 2017 Correct answers in multiple choice questions are indicated in RED and underlined. Correct answers to essay questions
Enzyme kinetics. Irreversible inhibition inhibitor is bound tightly to enzyme - very slow dissociation can be covalent or non covalently bound
 Enzymes can be regulated by acceleration and inhibition inhibition very common - several different mechanisms competitive / non competitive reversible / irreversible Irreversible inhibition inhibitor is
Enzymes can be regulated by acceleration and inhibition inhibition very common - several different mechanisms competitive / non competitive reversible / irreversible Irreversible inhibition inhibitor is
5. Which of the following enzymes catalyze the attachment of an amino acid to trna in the formation of aminoacyl trna?
 Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
Technical University of Denmark. Written examination, 29 May 2012 Course name: Life Science. Course number: Aids allowed: Written material
 1 Technical University of Denmark Written examination, 29 May 2012 Course name: Life Science Course number: 27008 Aids allowed: Written material Exam duration: 4 hours Weighting: The exam set consists
1 Technical University of Denmark Written examination, 29 May 2012 Course name: Life Science Course number: 27008 Aids allowed: Written material Exam duration: 4 hours Weighting: The exam set consists
The Effects of Malonate Inhibiting Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH) Activity in the Krebs Cycle
 Group 01, Section 073, Bio 122 1 Bio 122 Lab; Section 073; Group 01: Dawn McDougall Krupa Patel Ria Raju* Bill Tashjian The Effects of Malonate Inhibiting Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH) Activity in the
Group 01, Section 073, Bio 122 1 Bio 122 Lab; Section 073; Group 01: Dawn McDougall Krupa Patel Ria Raju* Bill Tashjian The Effects of Malonate Inhibiting Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH) Activity in the
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
BIOL 461/ 661 Cell Biology 4 Credits Instructor: Dr. Kristin O Brien. T/TH 11:30-1:00, Irving I 208 Office hours: M 9-10, TH 3-4
 BIOL 461/ 661 Cell Biology 4 Credits Instructor: Dr. Kristin O Brien Prerequisites: BIOL 362 Principals of Genetics Office: 226 Arctic Health CHEM 321 Organic Chemistry Laboratory: 229 Arctic Health T/TH
BIOL 461/ 661 Cell Biology 4 Credits Instructor: Dr. Kristin O Brien Prerequisites: BIOL 362 Principals of Genetics Office: 226 Arctic Health CHEM 321 Organic Chemistry Laboratory: 229 Arctic Health T/TH
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
BIO 315 Lab Exam I. Section #: Name:
 Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
PROTOCOL 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon
 PROTOCOL ATP Synthase Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 DESCRIPTION ATP Synthase Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL ATP Synthase Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 DESCRIPTION ATP Synthase Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
BIO 315 Lab Exam I. Section #: Name:
 Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Buffer (20X) Detergent (10X) NADH Reagent 1 (20X) Reagent 2 (100X) 96-well microplate (12 strips) 1
 PROTOCOL Complex I Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MS141 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION Complex I Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit Included in this kit is
PROTOCOL Complex I Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MS141 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION Complex I Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit Included in this kit is
namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES PAPER: THEORY
 namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE:
namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE:
MIT Invitational Tournament Cell Biology Exam
 1 MIT Invitational Tournament Cell Biology Exam January 24 th, 2015 Total Points: 140 Duration: 60 Minutes Instructions: This test is composed of 16 pages including this cover. Please check to make sure
1 MIT Invitational Tournament Cell Biology Exam January 24 th, 2015 Total Points: 140 Duration: 60 Minutes Instructions: This test is composed of 16 pages including this cover. Please check to make sure
Name. Student ID. Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004
 Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
th is is re vi sio n. com
 Section (a) Cells and organelles th is is re vi sio n. com 1. Make a diagram to show the structure of a liver cell as seen using an electron microscope. On your diagram, label the following: nucleus nuclear
Section (a) Cells and organelles th is is re vi sio n. com 1. Make a diagram to show the structure of a liver cell as seen using an electron microscope. On your diagram, label the following: nucleus nuclear
DNA DNA Profiling 18. Discuss the stages involved in DNA profiling 19. Define the process of DNA profiling 20. Give two uses of DNA profiling
 Name: 2.5 Genetics Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.5.1 Heredity and Variation 1. Discuss the diversity of organisms 2. Define the term species 3. Distinguish between
Name: 2.5 Genetics Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.5.1 Heredity and Variation 1. Discuss the diversity of organisms 2. Define the term species 3. Distinguish between
PROTOCOL 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon
 PROTOCOL Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP30 Rev.4 DESCRIPTION Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick
PROTOCOL Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP30 Rev.4 DESCRIPTION Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick
1. Which process decreases when the human body temperature decreases? D. Shivering (Total 1 mark) D. Liver (Total 1 mark)
 1. Which process decreases when the human body temperature decreases? A. Blood flow to the internal organs B. Secretion of sweat C. Secretion of insulin D. Shivering 2. Which organ secretes enzymes that
1. Which process decreases when the human body temperature decreases? A. Blood flow to the internal organs B. Secretion of sweat C. Secretion of insulin D. Shivering 2. Which organ secretes enzymes that
Dr. Jeffrey P. Thompson bio350
 Chapter 8 Enzymes Green light GFP Blue light Modern day catalysis Catalysis (reaction promotion) may have gotten its beginning g in an RNA- dominated world. Most catalysis today has evolved into using
Chapter 8 Enzymes Green light GFP Blue light Modern day catalysis Catalysis (reaction promotion) may have gotten its beginning g in an RNA- dominated world. Most catalysis today has evolved into using
amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide glucose
 Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
Higher Human Biology. Unit 1: Human Cells
 Calderglen High School Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Homework Questions Contents Page Sub-Topic 1: Differentiation and stem cells 3-5 Sub-Topic 2: DNA and its replication 6-10 Sub-Topic 3: RNA,
Calderglen High School Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Homework Questions Contents Page Sub-Topic 1: Differentiation and stem cells 3-5 Sub-Topic 2: DNA and its replication 6-10 Sub-Topic 3: RNA,
Notes on experimental technique: 1. Enzyme activity was measured by noting the increase in absorbance at 341 nm, as NADPH +
 Case 2 Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and cell growth Focus concept The activity of the pentose phosphate pathway enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase has been found to be important in
Case 2 Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and cell growth Focus concept The activity of the pentose phosphate pathway enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase has been found to be important in
Regulation of enzyme synthesis
 Regulation of enzyme synthesis The lac operon is an example of an inducible operon - it is normally off, but when a molecule called an inducer is present, the operon turns on. The trp operon is an example
Regulation of enzyme synthesis The lac operon is an example of an inducible operon - it is normally off, but when a molecule called an inducer is present, the operon turns on. The trp operon is an example
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
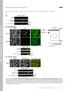 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Experimental Design. Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Michaelis Menton Kinetics and Inhibition. Lecture 14: Enzymes & Kinetics III E + S ES E + P
 Lecture 14: Enzymes & Kinetics III Michaelis Menton Kinetics and Inhibition Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Experimental Design k 1 k cat E + S ES E + P k -1 I want to measure the reactivity of my enzyme
Lecture 14: Enzymes & Kinetics III Michaelis Menton Kinetics and Inhibition Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Experimental Design k 1 k cat E + S ES E + P k -1 I want to measure the reactivity of my enzyme
Cell cycle oscillations
 Positive and negative feedback produce a cell cycle Fast Slow Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 1 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine
Positive and negative feedback produce a cell cycle Fast Slow Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 1 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine
7.06 EXAM b)(5 points) How would you show that this protein specifically interacts with the minus ends of microtubules?
 7.06 EXAM 3 1998 1: /20 2: /20 3: /20 4: /20 5: /20 TOTAL /100 Question 1 (20 pts) You are studying microtubule (MT) associated proteins. I) (12 points) a)(5 points) You identify a gene encoding a protein
7.06 EXAM 3 1998 1: /20 2: /20 3: /20 4: /20 5: /20 TOTAL /100 Question 1 (20 pts) You are studying microtubule (MT) associated proteins. I) (12 points) a)(5 points) You identify a gene encoding a protein
The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation. The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton.
 , the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
ab Mitochondrial Viability Assay
 ab129732 Mitochondrial Viability Assay Instructions for Use For measuring mitochondrial/cellular viability in high throughput This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab129732 Mitochondrial Viability Assay Instructions for Use For measuring mitochondrial/cellular viability in high throughput This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
2012 GENERAL [5 points]
![2012 GENERAL [5 points] 2012 GENERAL [5 points]](/thumbs/75/72452386.jpg) GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
Basic PCR Technique. Presented by : Noorul Hidayah Badri
 Basic PCR Technique Presented by : Noorul Hidayah Badri What is PCR? PCR is aninvitro technique which allow the amplification of a specific DNA region. PCR is like selecting a specific page from book and
Basic PCR Technique Presented by : Noorul Hidayah Badri What is PCR? PCR is aninvitro technique which allow the amplification of a specific DNA region. PCR is like selecting a specific page from book and
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Respiration. 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able. to:
 Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able 2.2.5 1. Definition of the term: aerobic respiration. 2. Explain the role of aerobic respiration what does it
Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able 2.2.5 1. Definition of the term: aerobic respiration. 2. Explain the role of aerobic respiration what does it
7.06 Cell Biology QUIZ #3
 Recitation Section: 7.06 Cell Biology QUIZ #3 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes, but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write your answers
Recitation Section: 7.06 Cell Biology QUIZ #3 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes, but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write your answers
Exam 2 Study Guide. Monday, July 30 th 125 points. 3 short answer questions approximately 7 points each
 Exam 2 Study Guide Monday, July 30 th 125 points 3 short answer questions approximately 7 points each No complete sentences required, though you can write them if you want Variable points (denoted next
Exam 2 Study Guide Monday, July 30 th 125 points 3 short answer questions approximately 7 points each No complete sentences required, though you can write them if you want Variable points (denoted next
Bioreaction Kinetics Seungwook Kim Chem. & Bio. Eng.
 Bioreaction Kinetics 2 2004 Seungwook Kim Chem. & Bio. Eng. Reference Chemistry and the Living Organism, 6 th edition, Molly M. Bloomfield, Lawrence J. Stephens, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Enzymes 1. Most
Bioreaction Kinetics 2 2004 Seungwook Kim Chem. & Bio. Eng. Reference Chemistry and the Living Organism, 6 th edition, Molly M. Bloomfield, Lawrence J. Stephens, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Enzymes 1. Most
Student Centered Education Problem-based Test: Replication of Mitochondrial DNA During the Cell Cycle
 Student Centered Education Problem-based Test: Replication of Mitochondrial DNA During the Cell Cycle Gy orgy Setalo Jr.* From the Department of Medical Biology, Medical School, University of Pecs, H-7624
Student Centered Education Problem-based Test: Replication of Mitochondrial DNA During the Cell Cycle Gy orgy Setalo Jr.* From the Department of Medical Biology, Medical School, University of Pecs, H-7624
Cloning and Expression of a Haloacid Dehalogenase Enzyme. By: Skyler Van Senior Research Advisor: Dr. Anne Roberts
 Cloning and Expression of a Haloacid Dehalogenase Enzyme By: Skyler Van Senior Research Advisor: Dr. Anne Roberts utline The gene being cloned is JHP1130 from Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) JHP1130 is
Cloning and Expression of a Haloacid Dehalogenase Enzyme By: Skyler Van Senior Research Advisor: Dr. Anne Roberts utline The gene being cloned is JHP1130 from Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) JHP1130 is
John s Student Union Study Guide for Final Exam
 John s Student Union Study Guide for Final Exam 1. What organelle do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common? Ribosomes 2. Covalent vs Ionic bonds: Covalent: sharing electrons (Polar & Nonpolar) Ionic:
John s Student Union Study Guide for Final Exam 1. What organelle do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common? Ribosomes 2. Covalent vs Ionic bonds: Covalent: sharing electrons (Polar & Nonpolar) Ionic:
National 5 Biology. Unit 1 Homework. Cell Biology
 National 5 Biology Unit 1 Homework Cell Biology Sub-topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. Identify the organelles labelled A - E in the following diagrams of an animal and a plant cell. 5 2. The following diagram
National 5 Biology Unit 1 Homework Cell Biology Sub-topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. Identify the organelles labelled A - E in the following diagrams of an animal and a plant cell. 5 2. The following diagram
Curriculum Correlation
 Curriculum Correlation A: Scientific Investigation Skills and Career Exploration A1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION SKILLS SECTIONS A1. demonstrate scientific investigation skills in the four areas of skills
Curriculum Correlation A: Scientific Investigation Skills and Career Exploration A1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION SKILLS SECTIONS A1. demonstrate scientific investigation skills in the four areas of skills
1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called.
 Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Biology Semester Exam Study Guide--January 2016
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Inserting genes into plasmids
 Inserting genes into plasmids GENE cut from genome or other plasmid w/ two different enzymes PLASMID cut with same two enzymes BTEC 120 - Molecular & Cell Biotechnology 18 Inserting genes into plasmids
Inserting genes into plasmids GENE cut from genome or other plasmid w/ two different enzymes PLASMID cut with same two enzymes BTEC 120 - Molecular & Cell Biotechnology 18 Inserting genes into plasmids
Supplementary Materials for
 www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/1/e1400205/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Myosin-binding protein C corrects an intrinsic inhomogeneity in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling Michael
www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/1/e1400205/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Myosin-binding protein C corrects an intrinsic inhomogeneity in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling Michael
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) Combo (Activity + Profiling) Microplate Assay Kit
 ab110671 Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) Combo (Activity + Profiling) Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the activity and relative quantity of PDH in a Human, Bovine, Mouse or Rat sample This product
ab110671 Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) Combo (Activity + Profiling) Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the activity and relative quantity of PDH in a Human, Bovine, Mouse or Rat sample This product
Please sign below if you wish to have your grades posted by the last five digits of your SSN
 BIO 226R EXAM II (Sample) PRINT YOUR NAME SSN Please sign below if you wish to have your grades posted by the last five digits of your SSN Signature BIO 226R Exam II has 6 pages, and 27 questions. There
BIO 226R EXAM II (Sample) PRINT YOUR NAME SSN Please sign below if you wish to have your grades posted by the last five digits of your SSN Signature BIO 226R Exam II has 6 pages, and 27 questions. There
 Fig. S1 Fig. S3 Fig. S4 Fig. S5 Fig. S9 Legend for supplementary figures Fig. S1. RFLP analysis of A7339G clones Platelets from the patient were isolated by centrifugation mixed with mtdna-less rho-0
Fig. S1 Fig. S3 Fig. S4 Fig. S5 Fig. S9 Legend for supplementary figures Fig. S1. RFLP analysis of A7339G clones Platelets from the patient were isolated by centrifugation mixed with mtdna-less rho-0
SensoLyte 620 HCV Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 620 HCV Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71146 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Convenient Format: Complete kit including all the assay components. Optimized Performance: Optimal
SensoLyte 620 HCV Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71146 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Convenient Format: Complete kit including all the assay components. Optimized Performance: Optimal
PROTOCOL. Monoamine Oxidase B Enzyme Specific Activity Assay Kit (human) MS747 Rev.0 DESCRIPTION ADDITIONAL MATERIALS REQUIRED
 PROTOCOL Monoamine Oxidase B Enzyme Specific Activity Assay Kit (human) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MS747 Rev.0 DESCRIPTION MAOB Enzyme Specific Activity Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Monoamine Oxidase B Enzyme Specific Activity Assay Kit (human) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MS747 Rev.0 DESCRIPTION MAOB Enzyme Specific Activity Assay Kit Sufficient materials
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
Page Monday December 19, 2016
 replication and Page 5-55 Monday December 9, 06 Notebook check 0: exam review notebook pages 5-55 Proteins Enzymes Activation energy Photo Cellular respiration, replication and Learning goal: Describe
replication and Page 5-55 Monday December 9, 06 Notebook check 0: exam review notebook pages 5-55 Proteins Enzymes Activation energy Photo Cellular respiration, replication and Learning goal: Describe
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
* + * RecA * + + for RecA-dependent strand + + MIT Department of Biology 7.28, Spring Molecular Biology
 MIT Department of Biology 7.28, Spring 2005 - Molecular Biology 1) Question 1. 1A. You are studying the function of in vitro along with a lab partner. You run several reactions to examine the requirements
MIT Department of Biology 7.28, Spring 2005 - Molecular Biology 1) Question 1. 1A. You are studying the function of in vitro along with a lab partner. You run several reactions to examine the requirements
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
Where Are The Protein-synthesizing Instructions Stored On A Dna Molecule
 Where Are The Protein-synthesizing Instructions Stored On A Dna Molecule DNA contains all the information a cell needs in order to make certain proteins. Where are the protein-synthesizing instructions
Where Are The Protein-synthesizing Instructions Stored On A Dna Molecule DNA contains all the information a cell needs in order to make certain proteins. Where are the protein-synthesizing instructions
Multiple Choice Review Cells
 Multiple Choice Review Cells 1. Various materials are transported into and out of cells by simple diffusion. The rate at which these materials diffuse is related to the surface area to volume ratio of
Multiple Choice Review Cells 1. Various materials are transported into and out of cells by simple diffusion. The rate at which these materials diffuse is related to the surface area to volume ratio of
5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. SESSION 13 and SESSION
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. SESSION 13 and SESSION
Unit IIB Exam (v. 1.0)
 Unit IIB Exam (v. 1.0) 1. The lac operon. (PT1-5) a. Is found only in eukaryotic cells b. Codes for the sequence of amino acids in lactase c. Regulates the transcription of mrna d. Regulates transcription
Unit IIB Exam (v. 1.0) 1. The lac operon. (PT1-5) a. Is found only in eukaryotic cells b. Codes for the sequence of amino acids in lactase c. Regulates the transcription of mrna d. Regulates transcription
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
UNIT 2 HUMAN BIOLOGY NOTES
 DNA, genes and chromosomes CHAPTER 13 DNA THE CODE FOR LIFE - DNA is short for deoxyribonucleic acid found in cells of organisms. The DNA is embedded within the nucleus of a cell. - DNA is a long stranded
DNA, genes and chromosomes CHAPTER 13 DNA THE CODE FOR LIFE - DNA is short for deoxyribonucleic acid found in cells of organisms. The DNA is embedded within the nucleus of a cell. - DNA is a long stranded
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #2 March 20, 2003
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #2 March 20, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #2 March 20, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
