Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
|
|
|
- Eileen Fields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA
2 Transcription factor binding sites convey specificity to regulation RNA
3 Systematic Discovery of TFBS by Comparative genomics: key learnings Checking for promoter region only is bad! Checking for full loci (entire trx unit) is highly recommended! Check for modules of several factor binding sites Genomic sequences come in different qualities Need to mask problematic bad sequences, parts which do not make sense Do we detect transcription factor binding sites because they were conserved during evolution? Or the sequences have been conserved because they contain a functional transcription factor binding site?
4 Transcript Imaging
5 The functional complexity of the human transcriptome is not yet fully elucidated Transcribed portions of the genome are larger and more complex than expected; transcripts based on untranslated regions or noncoding RNA 65 % of the polyadenylated transcriptome maps to known genes and 35% to non annotated genomic regions Sultan et al (2008) Science, 321, 956
6 Functional classes of eukaryotic promoters 3 RNA Polymerases: Pol I rrna Pol II mrna (small RNAs) Pol III small RNAs Pol IV, V plants 3 categories of promoters Architecture of yeast RNA polymerase II (backbone models for the 10 subunits as ribbon diagram) Cramer P et al. Science 288:
7
8 Definition of regulatory elements
9 Definition of regulatory elements
10 Binding Assay on Random DNA oligomers: PCR Binding Site Selection
11 Pol I promoters
12 Eukaryotic Pol II promoter: upstream and core NF-kB Fos Oct-1 CBFA-1 CREB etc Transcription activators TATA Basal machinery INR GENE RNA PolII 12 TFIIA 3 TFIIB 1 TFIID (TBP) ca. 14 (1) TFIIE 2 TFIIF 2 TFIIH ca. 9 upstream (regulatory, enhancer) core
13 The core Pol II promoter in more detail BRE TATA box G/CG/CG/CCGCC TATAAA Initiator PyPyANT/APyPy DPE GA/TCGTG TFIIB TFIID TFIID TFIID TFIIA TBP TAF II 250 TAF II 150 TAF II 60 TAF II 40
14 The TATA box Matrices are derived from known binding sites or binding assays on random DNA oligomers
15 Definition of the upstream promoter elements β Example: CAAT (4 bases) average match 1 / 4>4 (1/256 bp), 12 10>6 matches in the genome!
16 Transcriptional enhancers/silencers: First identified in viruses, then in cellular genes Activate (or repress) transcription independently of position (distance) and orientation (no polarity) Are made (and can be created) from partially redundant modules Confer cell-specific or temporal regulation No activity + Reporter Gene Low activity High activity
17 Identification of enhancer modules Enhancer activity is the result of interaction between individual modules «Super enhancers» controversial class of enhancers reported in genomic proximity with high level of mediator binding (p300, CBP, and histone marks) Pott S. (2015) Nature 47:8
18 Pol III promoters
19
20 Systematic discovery of transcriptional regulatory motifs by comparative genomics Paper presentation
21 The Basics of Transcription - I Methods used to study transcription: in vitro assays Transcription proceeds in several steps DNA-dependent RNA polymerases General Transcription Factors: GTFs
22 The Players in Transcription Regulation DNA-binding transcription factors (upstream factors) Chromatin regulators Coactivators and corepressors: Mediator, etc.. Basal Machinery: RNA Pol, GTFs Chromatin regulators Mediator Coactivator Basal Machinery TFIIH TFIIE TFIID RNAPII TFIIA TFIIB TFIIF DNA-binding TFs Gene
23 In Vivo Transcription Assays
24 In Vitro Transcription Assays Purified DNA templates (plasmids) are transcribed in the test tube with nuclear extracts, highly purified or recombinant transcription factors Criteria: accuracy and quantity of transcripts The ultimate goal is the reconstitution of regulated gene expression from recombinant (i.e. completely defined) components
25 In Vitro Transcription Assays All methods require some knowledge about the DNA fragment containing the promoter of interest where is the natural start site (+1)? 5 3 mrna
26 Many transcripts will be accurately initiated on the promoter of interest, but there will be a degree of non-specific background transcription spurious promoters; gaps/nicks in template DNA Different methods are available for quantitating in vitro transcripts: primer extension assay run-off assay G-less cassettes S1 nuclease protection assay
27 Methods: primer extension, run off transcripts and G-less cassettes
28 Methods: S1 Nuclease Protection Assay Single strand-specific nuclease enzymes will not digest doublestranded nucleic acid substrates this includes RNA:RNA or RNA:DNA hybrids S1 endonuclease mrna is hybridised to an uniformly radiolabelled single-stranded DNA fragment containing the start site; the probe can also be end-labelled mrna hybridised to the DNA-fragment will protect it right up to the start sequence from degradation
29 Methods: S1 Nuclease Protection Assay 1. In vitro Transcription RNA 2. Prepare radiolabeled probe * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * 3. Hybridize radiolabeled probe with RNA 4. Digest with nuclease S1 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
30 Basal vs Activated Transcription: an in vitro concept NF-kB Fos Pu.1 Oct-1 CBFA-1 etc Transcription activators TATA Basal machinery INR TFIIH TFIIE TFIID GENE RNAPII TFIIA TFIIB TFIIF RNAPII 12 TFIIA 3 TFIIB 1 TFIID (TBP) ca. 14 (1) TFIIE 2 TFIIF 2 TFIIH 10 upstream (regulatory, enhancer) core Cofactors, Mediator
31 Transcription Cycle: Multiple Steps, Multiple Opportunities for Regulation
32 Transcription Cycle: Status of Promoter- Proximal Pol II : Paused, Stalled, Poised, etc? Paused: elongation complexes halted temporarily Stalled: elongation complexes that have stopped RNA synthesis Poised: RNA polymerase detected near a gene promoter (ChIP assay terminology) Backtracked: halted elongation complexes that move backwards Arrested: complexes cannot restart transcription without additional factors
33 Transcription Initiation Steps Increasing Commitment Promoter (Start Site) Recognition Promoter Binding Promoter Melting Transcript Initiation Promoter Escape/Clearance Transcript Elongation
34 Sequential assembly of Initiation Complex Stepwise recruitement of general transcription factors or TFIIA PIC: preinitiation complex (DNA, RNAPII, TBP, TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIF, TFIIE, TFIIH Buratowski S and Sharp PA. Cell 56:549
35 Recruitment of preassembled RNAPII holoenzyme and general transcription factors two component pathway
36 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases: Original Discovery AMANITIN BINDING AS STABLE COMPLEX TO CALF THYMUS RNA POLYMERASE B (1970) Kédinger C. and Chambon P. FEBS Letter 9: alpha-amanitin, a toxin from the mushroom Amanita phalloides, is a potent inhibitor of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II
37
38 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases: Contacts between Alpha-amanitin and RNA Pol II as of Today Bruekner F. and Cramer P. (2008) Nature S&MB 15: alpha-amanitin chemical formula and stick model shown in orange, RNA Pol II residues and as ribbon model in grey
39 Engel Nature 2013
40 Cramer P et al. (2008) Ann Rev Biophys 37: Cramer P et al. (2000, 2001) Science 288: 642
41 RNA Polymerase I Initiation Engel Nature 2013
42 RNA Polymerase I : Purification and Crystalization litres S. cerevisiae Engel C. and Cramer P. (2013) Nature 502:
43 RNA Polymerase I Engel C. and Cramer P. (2013) Nature 502:
44 RNA Polymerase II All eukaryotic RNAPIIs characterized so far contain 12 different subunits (involved in transcription initiation, elongation and termination) RPB1 to RPB12 RNAPIIs are highly conserved across eukaryotic species 53% overall identity between yeast and human RNAPII The two largest subunits, RPB1 and RPB2, contain the catalytic center Four subunits (RPB3, RPB10, RPB11 and RPB12) serve as an assembly scaffold for RPB1/RPB2 Post-transcriptional mechanisms also depend on RNAPII capping splicing 3 end formation
45 Cramer, Bushnell and Kornberg (2001). Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 Angstrom resolution. Science 292,
46 RNA Polymerase II: Initiation-elongation transition Kostrewa D, Cramer P. (2009). Nature 462:
47 Structural Conservation: 53% overall Identity between Yeast and Human all across distributed Residues Identical Between Yeast and Human RNAPII Residues Identical Between Yeast and E. coli
48 Structural Conservation: overall Homology Sequence Homology Between Yeast RNAPII and Bacterial RNAPs Structural Homology Between Yeast RNAPII and Bacterial RNAPs
49 Differences between Pol I and Pol II
50 The Carboxy Terminal Domain: CTD repeating heptapeptide sequences: 52 repeats human, 26 in yeast Tyr-Ser-Pro-Thr-Ser-Pro-Ser YSPTSPS n target for phosphorylation RNA Pol II O = phosphorylated RNA Pol II A = unphosphorylated form RNA Pol II is phosphorylated at Ser5 (Ser7)to initiate elongation RNA Pol II is phosphorylated at Ser2 after bp +50 during elongation Phosphorylation is removed for termination
51 The Carboxy Terminal Domain: CTD
52 The Carboxy Terminal Domain: CTD RNA Kinase chip-chip occupancy. Mayer A and Cramer P (2010) Nature 17: 1272
53 RNA Polymerase III : Rapid Repression by Maf1 ensures cell survival during stress Pol III specific subunits on Pol II structure (C53, C34, C82) ribbon diagram of Maf1 crystal Vannini A. and Cramer P. (2010) Cell 143:59-70
54 Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic RNA Polymerases In the presence of σ factors, bacterial RNA polymerases (RNAPs) can recognize promoters without the help of any other transcription factors Although eukaryotic RNAPs are structurally much more complex, they do not have any obvious sequence-specific binding activities by themselves. Promoter recognition requires large number of additional factors (GTFs).
55
56 Cramer et al. (2008) Ann Rev Biophys 37:
57 E. coli RNA polymerase Hochschild A and Dove SL. Cell 92: 597 (1998)
58
59 σ 54 is dedicated for long-range activation: response to nitrogen deprivation in prokaryotes Su et al. DNA looping and enhancer activity at glutamine synthetase gene. (1990) PNAS 87: 5504
60 Nothing in life is to be feared, it is only to be understood. Now is the time to understand more, so that we may fear less Marie Curie Sklodowska
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
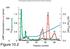 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Prof. Michael Hampsey
 The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time.
 All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Complex Transcription Machinery
 Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
Transcription. Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally
 Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Biochemistry Eukaryotic Transcription
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription
 Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription Key learning goals: Understand what a promoter sequence is Understand the role of sigma factors in prokaryotic RNAP initiation Understand what an open complex is,
Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription Key learning goals: Understand what a promoter sequence is Understand the role of sigma factors in prokaryotic RNAP initiation Understand what an open complex is,
Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
 CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated February 2013)
 URS AACTGT ATATTA - 35-10 transcription Pribnow Box discriminator +1 AGGAGGT TTA TCCTCCA ATT Gene C TGA TAG ACT ATC rho or GC hairpin loop transcription termination DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated
URS AACTGT ATATTA - 35-10 transcription Pribnow Box discriminator +1 AGGAGGT TTA TCCTCCA ATT Gene C TGA TAG ACT ATC rho or GC hairpin loop transcription termination DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 11. Transcription. The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU
 Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA
 1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
DNA Evolution of knowledge about gene. Contains information about RNAs and proteins. Polynucleotide chains; Double stranded molecule;
 Evolution of knowledge about gene G. Mendel Hereditary factors W.Johannsen, 1909 G.W.Beadle, E.L.Tatum, 1945 Ingram, 1957 Actual concepts The gene hereditary unit located in chromosomes Hypotheses One
Evolution of knowledge about gene G. Mendel Hereditary factors W.Johannsen, 1909 G.W.Beadle, E.L.Tatum, 1945 Ingram, 1957 Actual concepts The gene hereditary unit located in chromosomes Hypotheses One
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Methoden zur Analyse von Transkriptionsfaktoren. Seminar: BCII, Lausen
 Methoden zur Analyse von Transkriptionsfaktoren Seminar: BCII, Lausen Gene expression: from transcription to translation Orphanides G, Reinberg D.Cell. 2002 Feb 22;108(4):439-51. Schematic of a gene regulatory
Methoden zur Analyse von Transkriptionsfaktoren Seminar: BCII, Lausen Gene expression: from transcription to translation Orphanides G, Reinberg D.Cell. 2002 Feb 22;108(4):439-51. Schematic of a gene regulatory
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
Nucleotide Entry Port. Scaffold Subunits. Polymerase Activity β Sliding Clamp. Clamp Loader. Promoter Recognition
 Nucleotide Entry ort α (2) Scaffold Subunits olymerase Activity Sliding Clamp σ Clamp Loader romoter Recognition -35-10 NNAAA AA T A TTTTNNAAAANNN TT T N N17 N6 α α α α α α α α α α α α α α +1 α α α α Subunit
Nucleotide Entry ort α (2) Scaffold Subunits olymerase Activity Sliding Clamp σ Clamp Loader romoter Recognition -35-10 NNAAA AA T A TTTTNNAAAANNN TT T N N17 N6 α α α α α α α α α α α α α α +1 α α α α Subunit
Francisco Navarro. Departamento de Biología Experimental Área de Genética Universidad de Jaén
 Regulación de la expresión génica Francisco Navarro Departamento de Biología Experimental Área de Genética Universidad de Jaén Gene expression From genes to proteins Gene expression From genes to proteins
Regulación de la expresión génica Francisco Navarro Departamento de Biología Experimental Área de Genética Universidad de Jaén Gene expression From genes to proteins Gene expression From genes to proteins
BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt
 BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt Introduction to molecular biology Combining genetics, biochemistry, structural chemistry Information flow in biological systems: The Central Dogma
BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt Introduction to molecular biology Combining genetics, biochemistry, structural chemistry Information flow in biological systems: The Central Dogma
Lecture 11. Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription. Transcription Initiation Complex
 Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 MODULAR STRUCTURE OF UPSTREAM TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS Experimental
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 MODULAR STRUCTURE OF UPSTREAM TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS Experimental
Introduction. Matıas Montes 1, *, Sandra Moreira-Ramos 1, *, Diego A. Rojas 2, *, Fabiola Urbina 1, Norbert F. K aufer 3 and Edio Maldonado 1
 RNA polymerase II components and Rrn7 form a preinitiation complex on the HomolD box to promote ribosomal protein gene expression in Schizosaccharomyces pombe Matıas Montes 1, *, Sandra Moreira-Ramos 1,
RNA polymerase II components and Rrn7 form a preinitiation complex on the HomolD box to promote ribosomal protein gene expression in Schizosaccharomyces pombe Matıas Montes 1, *, Sandra Moreira-Ramos 1,
IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III
 10 January, 2018 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III Document Filetype: PDF 312 KB 0 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III The actual replication enzyme in E. Both will
10 January, 2018 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III Document Filetype: PDF 312 KB 0 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III The actual replication enzyme in E. Both will
RNA POLYMERASE FUNCTIONS E-BOOK
 08 March, 2018 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK Document Filetype: PDF 431.06 KB 0 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mrna and
08 March, 2018 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK Document Filetype: PDF 431.06 KB 0 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mrna and
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Transcription. By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt
 Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs
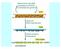 Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
DNA Bending and Wrapping around RNA Polymerase: a Revolutionary Model Describing Transcriptional Mechanisms
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 1999, p. 457 478 Vol. 63, No. 2 1092-2172/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. DNA Bending and Wrapping around
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 1999, p. 457 478 Vol. 63, No. 2 1092-2172/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. DNA Bending and Wrapping around
Differential Gene Expression
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics
 Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics David Hendrix Oregon State University Feb 15th 2016 Transcriptomics High-throughput Sequencing (deep sequencing) High-throughput sequencing (also
Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics David Hendrix Oregon State University Feb 15th 2016 Transcriptomics High-throughput Sequencing (deep sequencing) High-throughput sequencing (also
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
CONTENTS. LIST OF FIGURES... i. LIST OF TABLES... iii. SUMMARY OF THE WORK DONE... vi
 CONTENTS SECTION ~ LIST OF FIGURES... i LIST OF TABLES... iii LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS USED... ~... iv SUMMARY OF THE WORK DONE... vi 1. INTROD UCTION... :.................................... 1 1.1. AN OVERVIEW
CONTENTS SECTION ~ LIST OF FIGURES... i LIST OF TABLES... iii LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS USED... ~... iv SUMMARY OF THE WORK DONE... vi 1. INTROD UCTION... :.................................... 1 1.1. AN OVERVIEW
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature21393 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT SpMED Immuno-purification and subunit localization Wild-type and subunit deletion mutant SpMEDs (Extended Data Table 1) were immunopurified through TAP-tagged
doi:10.1038/nature21393 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT SpMED Immuno-purification and subunit localization Wild-type and subunit deletion mutant SpMEDs (Extended Data Table 1) were immunopurified through TAP-tagged
Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes. Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes?
 Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
RNA Polymerase II The Transcription Machine
 RNA Polymerase II The Transcription Machine Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2006 Jiyoti Verma 1, Aruna Naorem 2, Anand Kumar 3, Manimala Sen 4 and Parag Sadhale 5 It was 2005 December. The distinguished speaker
RNA Polymerase II The Transcription Machine Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2006 Jiyoti Verma 1, Aruna Naorem 2, Anand Kumar 3, Manimala Sen 4 and Parag Sadhale 5 It was 2005 December. The distinguished speaker
(c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/ :57 PM
 C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
Synthetic cells: do bacteria need all its genes? No.
 NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
Bi 8 Lecture 5. Ellen Rothenberg 19 January 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 5 MORE ON HOW WE KNOW WHAT WE KNOW and intro to the protein code Ellen Rothenberg 19 January 2016 SIZE AND PURIFICATION BY SYNTHESIS: BASIS OF EARLY SEQUENCING complex mixture of aborted DNA
Bi 8 Lecture 5 MORE ON HOW WE KNOW WHAT WE KNOW and intro to the protein code Ellen Rothenberg 19 January 2016 SIZE AND PURIFICATION BY SYNTHESIS: BASIS OF EARLY SEQUENCING complex mixture of aborted DNA
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
RNA Metabolism Chap 26, part I
 RNA Metabolism Chap 26, part I mrna (selective and regulated) trna rrna other (specialized) RNAs (eukaryotes!!!) processing transcriptome (Surprisingly, much of your genome is transcribed!) RNA is the
RNA Metabolism Chap 26, part I mrna (selective and regulated) trna rrna other (specialized) RNAs (eukaryotes!!!) processing transcriptome (Surprisingly, much of your genome is transcribed!) RNA is the
Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase.
 Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme,
Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme,
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302. February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm
 RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
Molecular Genetics of the RNA Polymerase II General Transcriptional Machinery
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 1998, p. 465 503 Vol. 62, No. 2 1092-2172/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Molecular Genetics of the RNA Polymerase II General
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 1998, p. 465 503 Vol. 62, No. 2 1092-2172/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Molecular Genetics of the RNA Polymerase II General
Biochemistry 111. Carl Parker x A Braun
 Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x6368 101A Braun csp@caltech.edu Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside
Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x6368 101A Braun csp@caltech.edu Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Initiation de la transcription et Facteurs de transcription
 Initiation de la transcription et Facteurs de transcription Aurélio Balsalobre Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal Laboratoire de génétique moléculaire Jeudi 18 octobre 2012 Plan du cours Introduction
Initiation de la transcription et Facteurs de transcription Aurélio Balsalobre Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal Laboratoire de génétique moléculaire Jeudi 18 octobre 2012 Plan du cours Introduction
BCH 4054 Fall 2000 Chapter 31 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4054 Fall 2000 Chapter 31 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 31 Transcription and Regulation of Gene Expression 2 Messenger RNA Central Dogma (Francis Crick, 1958) DNA RNA Protein (Fig 31.1) Jacob-Monod Hypothesis:
BCH 4054 Fall 2000 Chapter 31 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 31 Transcription and Regulation of Gene Expression 2 Messenger RNA Central Dogma (Francis Crick, 1958) DNA RNA Protein (Fig 31.1) Jacob-Monod Hypothesis:
Promoter Architectures and Developmental Gene Regulation
 Promoter Architectures and Developmental Gene Regulation Vanja Haberle a,b,1 and Boris Lenhard a,* a Institute of Clinical Sciences and MRC Clinical Sciences Center, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College
Promoter Architectures and Developmental Gene Regulation Vanja Haberle a,b,1 and Boris Lenhard a,* a Institute of Clinical Sciences and MRC Clinical Sciences Center, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College
DNA Transcription. Visualizing Transcription. The Transcription Process
 DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
Initiation and termination of transcription, Post transcription modification of the RNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Initiation and termination of transcription, Post transcription modification of the RNA Mitesh Shrestha Transcription: overview In prokaryotes transcription and translation are coupled. Proteins are synthesized
Initiation and termination of transcription, Post transcription modification of the RNA Mitesh Shrestha Transcription: overview In prokaryotes transcription and translation are coupled. Proteins are synthesized
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF GENE REGULATION
 TARTU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF BILOGY AND GEOGRAPHY DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF GENE REGULATION TARTU 2005 Sten Ilmjärv 2 TABLE OF CONTENT TABLE OF CONTENT...2 GLOSSARY...3 INTRODUCTION...4 1. THE GENE...5 2. GENE
TARTU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF BILOGY AND GEOGRAPHY DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF GENE REGULATION TARTU 2005 Sten Ilmjärv 2 TABLE OF CONTENT TABLE OF CONTENT...2 GLOSSARY...3 INTRODUCTION...4 1. THE GENE...5 2. GENE
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression
 Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Answers to Module 1. An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth.
 Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
5. Which of the following enzymes catalyze the attachment of an amino acid to trna in the formation of aminoacyl trna?
 Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Chapter Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms
 Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
DNA REPLICATION. DNA structure. Semiconservative replication. DNA structure. Origin of replication. Replication bubbles and forks.
 DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points?
 BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Resources. This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11
 Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
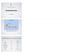 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 06 Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Transcription Activation Domains In
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 06 Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Transcription Activation Domains In
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Practice Exam A. Briefly describe how IL-25 treatment might be able to help this responder subgroup of liver cancer patients.
 Practice Exam 2007 1. A special JAK-STAT signaling system (JAK5-STAT5) was recently identified in which a gene called TS5 becomes selectively transcribed and expressed in the liver upon induction by a
Practice Exam 2007 1. A special JAK-STAT signaling system (JAK5-STAT5) was recently identified in which a gene called TS5 becomes selectively transcribed and expressed in the liver upon induction by a
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs. Effector Domain. Zinc Fingers. Zinc Fingers, continued. Zif268
 DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
Why does this matter?
 Background Why does this matter? Better understanding of how the nucleosome affects transcription Important for understanding the nucleosome s role in gene expression Treats each component and region of
Background Why does this matter? Better understanding of how the nucleosome affects transcription Important for understanding the nucleosome s role in gene expression Treats each component and region of
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
