2.5. Equipment and materials supplied by user Template preparation by cloning into plexsy_invitro-2 vector 4. 6.
|
|
|
- Martina Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Manual 15 Reactions LEXSY in vitro Translation Cell-free protein expression kit based on Leishmania tarentolae contains the vector plexsy_invitro-2 Cat. No. EGE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE Jena Bioscience GmbH Löbstedter Str Jena, Germany Tel.: Fax: Last update: Mar 30, 2011
2 Content 1. Introduction 3 2. Kit components and storage conditions LEXSY cell extract plexsy_invitro-2 vector Sequencing primers Nuclease-free water Equipment and materials supplied by user 3 3. Protocol section Template preparation by cloning into plexsy_invitro-2 vector Cell-free translation Detection of synthesized proteins Isolation of synthesized proteins 6 4. Licensing information 8 5. Literature 8 6. Appendix Map of vector plexsy_invitro Architecture of SITS and EGFP gene DNA Sequence and description of vector plexsy_invitro Influence of temperature on in vitro EGFP synthesis DNA sequences of the primers for LEXSY in vitro Translation Kit 12 2
3 1. Introduction The LEXSY in vitro translation system is a rapid, convenient, flexible and cost efficient tool to produce recombinant proteins for biochemical, biophysical and structural analysis (Mureev et al., 2009). Its key component is the transcription-translation linked cell extract of the eukaryotic protozoan host Leishmania tarentolae, which can be programmed by DNA templates encoding the user s gene of interest. The LEXSY cell extract for in vitro translation contains functional ribosomes and all essential components of the eukaryotic translation and folding machinery. For target mrna generation the heterologous T7 RNA polymerase was added to the extracts. To ensure a low background the translation of endogenous host mrnas is efficiently blocked by an antisense oligonucleotide making use of the unique gene organization of Leishmania (LeBowitz et al., 1993). 2. Kit components and storage conditions The kit is shipped on dry ice. Upon arrival of the kit all its components should be stored at the appropriate temperature as indicated below LEXSY cell extract (Cat. No. EGE-260) 1 vial with 250 μl of frozen LEXSY cell extract (sufficient for 15 reactions) store at -80 C, stable for at least 12 month without loss of activity freeze unused aliquots in liquid nitrogen and store at -80 C avoid more than two freeze-thaw cycles 2.2. plexsy_invitro-2 vector (Cat. No. EGE-262) 0.36 µg/μl in 25 μl 10 mm TrisHCl ph 8.0 (0.155 μm) store at -20 C 2.3. Sequencing primers (see Appendix 6.5. for sequences) PM-116 forward sequencing primer H4132 PM-101 reverse sequencing primer A μm in 50 μl 10 mm TrisHCl ph 8.0 store at -20 C 2.4. Nuclease-free water 1.2 ml store at -20 C 2.5. Equipment and materials supplied by user Standard molecular biology equipment and reagents for PCR, cloning, DNA and protein handling, including gene specific primers for primary PCR amplification of target ORF Incubators at 20 C - 37 C Bench-top centrifuge at room temperature and 4 C Cooling and freezing capacities at +4 C, -20 C and -80 C Liquid nitrogen equipment 3
4 3. Protocol section 3.1. Template preparation by cloning into plexsy_invitro-2 vector The map, sequence and features of the plexsy_invitro-2 vector are provided in Appendix This vector contains the EGFP gene which can be used as a positive control for transcription/translation reactions. The vector incorporates the species independent translation initiation sequence (SITS) upstream of the EGFP ORF. SITS consists of a poly-tttta 5 UTR fused to a sequence forming three stem-loop structures in mrna (Mureev et al., 2009). Translation of this sequence results in the addition of 17 amino acids to the N terminus of the target protein. This configuration ensures the highest yield of recombinant protein synthesis in the LEXSY in vitro system. The plexsy_invitro-2 vector offers three cloning strategies: 1. replacement of vector EGFP control gene by target gene 2. fusion of target gene to N of vector EGFP gene 3. fusion of target gene to C of vector EGFP gene To clone the target protein coding sequence into the plexsy_invitro-2 vector: Perform PCR amplification of the gene of interest with primers containing the chosen cloning sites of MCS1 and/or MCS2, e.g. NcoI x NotI. Make sure that insertion is in frame with SITS. For incorporation of affinity tags into the C-terminus of the recombinant proteins, include the appropriate sequences into the reverse primer. For N EGFP fusions insert the target gene into the MCS1 (NcoI-XhoI polylinker) of the plexsy_invitro-2 vector. For C EGFP fusions insert the target gene into the MCS2 (HindIII-SmaI polylinker) Open the plexsy_invitro-2 vector with the appropriate restriction enzymes and clone the PCR product into the vector by standard techniques Prepare plasmid DNA with a column based kit (Jena Bioscience, Cat. No. PP203) Adjust the plasmid concentration to approx. 0.2 μm. To do this, measure the DNA concentration spectrophotometrically and calculate its molar concentration using the formula below conc( ng / μl) 1000 = conc( nm ) length( N, bp) 0.68 Use the DNA as a template for the in vitro translation reaction at final concentration of 20 nm as described below Cell-free translation The typical reaction volume for translation is 20 μl. The yield of in vitro synthesized EGFP in the system programmed with the EGFP control plasmid plexsy_invitro-2 is approx. 200 μg/ml. The amount of synthesized EGFP protein in 10 μl of loaded reaction is sufficient to be clearly visible on a SDS-PAGE gel viewed under unfiltered UV light of a transilluminator (ATTENTION! Do not boil the sample - this step will destroy the EGFP chromophore). The incubation time of in vitro translation reactions is typically 2 hours. The user must take into account that some polypeptides need additional time to fold into active protein. After translation the sample can be stored at 4 C for several hours or overnight for protein maturation. The low protease activity of the extracts allows extended incubation of many translated proteins in the translation mixture at 4 C without detectable protein degradation. 4
5 The incubation temperature of the translation reaction is a compromise in-between protein yield and folding efficiency. Temperature increase improves the total protein yield but usually decreases the fraction of active protein (Appendix 6.4.). We recommend performing standard translation reactions at C. Positive and negative control reactions with plexsy_invitro-2 vector or without exogenous DNA resp. should be included into each experiment. Standard translation protocol Thaw the LEXSY cell extract on ice and keep on ice before use Note: keep all reagents on ice during pipetting of the reaction mixes. Thaw the extracts immediately before use and start the reactions within 10 minutes after thawing. Freeze unused extracts with liquid nitrogen and store at 80 C. Avoid more than two freeze-thaw cycles. Assemble the translation reaction mixes in final volume of 20 μl on ice according to the table below. Add the LEXSY cell extract in the last step and mix well by pipetting up and down avoiding air bubbles. Incubate translation reaction mixes at C for 2 hours. Transcription-translation reaction set-up Component Volume per reaction (μl) Volume per positive control reaction (μl) Volume per negative control reaction (μl) Nuclease-free water variable Template DNA (20 nm final concentration) variable LEXSY cell extract Detection of in vitro synthesized proteins Translation of target proteins can be detected by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Fusion proteins resulting from in frame fusions to EGFP can be detected directly on the SDS-PAGE by in situ fluorescence scanning. The plexsy_invitro-2 vector also includes a sequence for the myc-tag that can be detected by Western blotting with specific antibodies. For detection of EGFP control protein and EGFP fusion proteins Mix 10 μl of translation mix with 10 μl of 2X SDS loading buffer. Do not boil the sample! Resolve the sample on a 12% PAGE gel. Do not subject the gel to staining or fixation! Visualize EGFP by fluorescence scanning (EGFP Ex/Em 488/507 nm) or view it on the UV transilluminator (see Fig. 1 for typical results). 5
6 Fig. 1 Visualization of EGFP-tagged translation products resolved on a SDS-PAGE gel by fluorescent scanning. DNA templates encoding a set of C EGFP tagged proteins (PP2B phosphatases (lanes 1, 2), eif1a (lane 3), eif4g (lane 4), eif4a (lanes 5, 6), eif4e (lane 7), eif5a (lane 8), eif6 (lane 9), PABP (lane 10), eef2 kinase (lane 11), eif SUI (lane 12), eif2α (lane 13), DHH1 (lane14)) were translated in the LEXSY in vitro translation system and 5 μl of end point reaction mixture were resolved on a 4-12% PAA gel. The EGFP-fluorescence was detected on a scanner with 488 nm excitation laser and 520 nm emission filter Isolation of in vitro synthesized proteins Recombinant proteins produced in the LEXSY in vitro translation kit can be easily isolated by affinity chromatography. While numerous affinity tags may be employed we currently do not recommend the use of Ni-NTA chromatography for proteins expressed with this kit. Below we provide a protocol for one-step isolation of GFP tagged proteins using GFP-Cap matrix (Jena Bioscience, Cat. No. PR-949) that displays picomolar affinity to GFP protein. See Fig. 2 for typical purification results. To isolate GFP-tagged proteins from translation mixture Increase ionic strength in the sample by adjusting NaCl concentration to 150 mm Add μl of GFP-Cap S resin to the sample and incubate with gentle rotation for 20 minutes at 4 C. Do not allow beads to settle Centrifuge 2 min, 2000 x g, 4 C. Discard the supernatant 6
7 Wash resin 2-3 times with washing buffer (10 mm Tris-HCl ph 7.5, 500 mm NaCl, 0.5 mm EDTA). Sediment beads and discard the supernatant as described above To analyze the bound protein, resuspend the resin in 20 μl of 1x SDS-loading buffer and boil for 5 minutes. The protein can be eluted from the matrix by lowering the ph. Add 50 μl of 0.1 M Gly-HCl ph 2.2 to the resin and incubate for 20 seconds. Pellet the beads at 2000 x g for 30 seconds and collect supernatant with eluted protein. Neutralize the supernatant with 1/10 volume of 1 M Tris base. Fig. 2 SDS-PAGE analysis of in vitro translated proteins isolated with the GFP-Cap resin (Coomassie staining). Each translation reaction mixture (150 μl) was programmed with 20 nm of ethanol-precipitated DNA template. The products were isolated with 20 μl of GFP-Cap beads, eluted with 20 μl of SDS-loading buffer and resolved on 4-12% PAGE. Target proteins listed on top of the gel. 7
8 4. Licensing information Purchase of the LEXSY in vitro Translation Kit includes a non-exclusive and non-transferable license for non-commercial research. Commercial use of the LEXSY in vitro Translation Kit, however, requires separate licensing. Commercial use includes but is not limited to: the use of any protein or other substance produced by LEXSY Kits as reagents in screening to discover and/or promote candidate compounds for sale to a customer, distributor, wholesaler or other end user in therapeutic, diagnostic, prophylactic, and/or veterinary areas. the manufacture, sale or offer to sell any product containing proteins or other substances produced with LEXSY Kits. "Contract research" to any third party or "Contract manufacturing" for any third party that has not been granted a license to use LEXSY Kit. Please contact us at expression@jenabioscience.com. 5. Literature (1) Mureev et al. (2009) Species-independent translational leaders facilitate cell-free expression. Nature Biotechnology 27: 747 (2) LeBowitz et al. (1993) Coupling of polyadenylation site selection and trans-splicing in Leishmania. Genes & Dev. 7: 996 Please, visit for further literature on LEXSY. 8
9 6. Appendix 6.1. Map of vector plexsy_invitro-2 MCS1 SspI (3321) BsmFI (23)Af lii (30) NcoI (151) BglII (157) XhoI (161) ScaI (2997) T7Po bla Leader-EGFP-MYC plexsy_invitro-2 MCS2 HindIII (907) SalI (913) XbaI (920) BamHI (926) BamHI (2278) 3437 bp ori E.c. to 3'utr SmaI (931) NotI (942) SphI (1058) MluI (1093) KpnI (1099) PstI (1105) SpeI (1150) Pv uii (1222) EcoRI (1270) PciI (1626) Pv uii (1448) Fig. 3: Map of plexsy_invitro-2 (Cat. No. EGE-262) expression vector with cloning sites for target gene in frame fusions (see Appendix 6.2 and 6.3 for sequence and description). 3 utr is derived from 1.4k-IR camcb of L. tarentolae. MCS1 and MCS2 are multicloning sites for replacement of vector EGFP control gene or N or C fusions resp. SITS is species independent translation sequence (Mureev et al., 2009 and Appendix 6.2.). See text for details. 9
10 6.2. Architecture of SITS and EGFP gene AatII T7Po GACGT C TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGACATCTTAAG TTTATTTTAT TTTATTTTAT TTTATTTTAT TTTATTTTAT TTTATTTTAT NcoI BglII TTTATTTTAT TTAA CC ATG ACA GTA ATG TAT AAA GTC TGT AAA GAC ATT AAA CAC GTA AGT GAA ACC ATG GAG M T V M Y K V C K D I K H V S E T M E EGFP SITS poly-tttta MCS 1 XhoI ATC TCG AGC AAG GGC GAG GAG CT G T T C ACC GGG GT G GT G CCC AT C CT G GT C GAG CT G GAC GGC GAC GT A AAC I S S K G E E L F T G V V P I L V E L D G D V N GGC CAC AAG T T C AGC GT G T CC GGC GAG GGC GAG GGC GAT GCC ACC T AC GGC AAG CT G ACC CT G AAG T T C AT C G H K F S V S G E G E G D A T Y G K L T L K F I T GC ACC ACC GGC AAG CT G CCC GT G CCC T GG CCC ACC CT C GT G ACC ACC CT G ACC T AC GGC GT G CAG T GC T T C C T T G K L P V P W P T L V T T L T Y G V Q C F AGC CGC TAC CCC GAC CAC ATG AAG CAG CAC GAC TTC TTC AAG TCC GCC ATG CCC GAA GGC TAC GTC CAG GAG S R Y P D H M K Q H D F F K S A M P E G Y V Q E CGC ACC AT C T T C T T C AAG GAC GAC GGC AAC T AC AAG ACC CGC GCC GAG GT G AAG T T C GAG GGC GAC ACC CT G R T I F F K D D G N Y K T R A E V K F E G D T L GT G AAC CGC AT C GAG CT G AAG GGC AT C GAC T T C AAG GAG GAC GGC AAC AT C CT G GGG CAC AAG CT G GAG T AC V N R I E L K G I D F K E D G N I L G H K L E Y AAC TAC AAC AGC CAC AAC GTC TAT ATC ATG GCC GAC AAG CAG AAG AAC GGC ATC AAG GTG AAC TTC AAG ATC N Y N S H N V Y I M A D K Q K N G I K V N F K I CGC CAC AAC ATC GAG GAC GGC AGC GTG CAG CTC GCC GAC CAC TAC CAG CAG AAC ACC CCC ATC GGC GAC GGC R H N I E D G S V Q L A D H Y Q Q N T P I G D G CCC GTG CTG CTG CCC GAC AAC CAC TAC CTG AGC ACC CAG TCC GCC CTG AGC AAA GAC CCC AAC GAG AAG CGC P V L L P D N H Y L S T Q S A L S K D P N E K R GAT CAC AT G GT C CT G CT G GAG T T C GT G ACC GCC GCC GGG AT C ACT CT C GGC AT G GAC GAG CT A T AC AAG GAG D H M V L L E F V T A A G I T L G M D E L Y K E c-myc tag MCS 2 HindIII SalI XbaI SmaI NotI CAG AAG CTG ATC TCG GAG GAG GAT CTG CAA GCT TGT CGA CCT CTA GAG GAT CCC CGG GGC TAA GCGGCCGC Q K L I S E E D L Q A C R P L E D P R G Fig. 4: DNA sequences of SITS and EGFP gene. MCS1 and MCS2 are multicloning sites for replacement of vector EGFP control gene or N or C fusions resp. SITS is species independent translation sequence (Mureev et al., 2009). 10
11 6.3. DNA Sequence and description of vector plexsy_invitro-2 nt 7-23 nt nt nt nt nt nt nt nt nt nt nt 1689 nt T7 promoter poly-tttta region SITS (species independent translation initiation sequence) Multiple cloning site 1 (MCS1) for N fusion to EGFP or replacement N Leader region ORF for Leader-EGFP-MYC fusion protein c-myc-tag Multiple cloning site 2 (MCS2) for C fusion to EGFP or replacement 3 utr T 7 terminator puc18-derived sequence origin of replication E. coli ORF bla gene GACGTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGACATCTTAAGTTTATTTTATTTTATTTTATTTTATTTTATTTT ATTTTATTTTATTTTATTTTATTTTATTTAACCATGACAGTAATGTATAAAGTCTGTAAAGACATTAAA CACGTAAGTGAAACCATGGAGATCTCGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAGCTGTTCACCGGGGTGGTGCCC ATCCTGGTCGAGCTGGACGGCGACGTAAACGGCCACAAGTTCAGCGTGTCCGGCGAGGGCGAG GGCGATGCCACCTACGGCAAGCTGACCCTGAAGTTCATCTGCACCACCGGCAAGCTGCCCGTGC CCTGGCCCACCCTCGTGACCACCCTGACCTACGGCGTGCAGTGCTTCAGCCGCTACCCCGACCA CATGAAGCAGCACGACTTCTTCAAGTCCGCCATGCCCGAAGGCTACGTCCAGGAGCGCACCATC TTCTTCAAGGACGACGGCAACTACAAGACCCGCGCCGAGGTGAAGTTCGAGGGCGACACCCTG GTGAACCGCATCGAGCTGAAGGGCATCGACTTCAAGGAGGACGGCAACATCCTGGGGCACAAG CTGGAGTACAACTACAACAGCCACAACGTCTATATCATGGCCGACAAGCAGAAGAACGGCATCAA GGTGAACTTCAAGATCCGCCACAACATCGAGGACGGCAGCGTGCAGCTCGCCGACCACTACCAG CAGAACACCCCCATCGGCGACGGCCCCGTGCTGCTGCCCGACAACCACTACCTGAGCACCCAG TCCGCCCTGAGCAAAGACCCCAACGAGAAGCGCGATCACATGGTCCTGCTGGAGTTCGTGACCG CCGCCGGGATCACTCTCGGCATGGACGAGCTATACAAGGAGCAGAAGCTGATCTCGGAGGAGG ATCTGCAAGCTTGTCGACCTCTAGAGGATCCCCGGGGCTAAGCGGCCGCCCTCCTCCTCCTTTC TTGTTCCTTTCACGTCGCCTTCTCGGTTGTAGCTGGCAGACGACGAGTCTTACTTTTACGTGTACT TCTCTATAGATGATGTATGATCTCTCTGCATGCGTGTTCGTGCATGTGTCCGTGTGTTGGGTACG CGTGGTACCCTGCAGGAAGGAAGCTGAGTTGGCTGCTGCCACCGCTGAGCAATAACTAGTAATT ACTAGCATAACCCCTTGGGGCCTCTAAACGGGTCTTGAGGGGGTTTTTTGCTGAAAGGAGGACA GCTGATGATTGTCATGCTTGCCATCTGTTTTCTTGCAAGGTCAGAGGAATTCGTAATCATGGTCAT AGCTGTTTCCTGTGTGAAATTGTTATCCGCTCACAATTCCACACAACATACGAGCCGGAAGCATAA AGTGTAAAGCCTGGGGTGCCTAATGAGTGAGCTAACTCACATTAATTGCGTTGCGCTCACTGCCC GCTTTCCAGTCGGGAAACCTGTCGTGCCAGCTGCATTAATGAATCGGCCAACGCGCGGGGAGAG GCGGTTTGCGTATTGGGCGCTCTTCCGCTTCCTCGCTCACTGACTCGCTGCGCTCGGTCGTTCG GCTGCGGCGAGCGGTATCAGCTCACTCAAAGGCGGTAATACGGTTATCCACAGAATCAGGGGAT AACGCAGGAAAGAACATGTGAGCAAAAGGCCAGCAAAAGGCCAGGAACCGTAAAAAGGCCGCGT TGCTGGCGTTTTTCCATAGGCTCCGCCCCCCTGACGAGCATCACAAAAATCGACGCTCAAGTCAG AGGTGGCGAAACCCGACAGGACTATAAAGATACCAGGCGTTTCCCCCTGGAAGCTCCCTCGTGC GCTCTCCTGTTCCGACCCTGCCGCTTACCGGATACCTGTCCGCCTTTCTCCCTTCGGGAAGCGT GGCGCTTTCTCATAGCTCACGCTGTAGGTATCTCAGTTCGGTGTAGGTCGTTCGCTCCAAGCTGG GCTGTGTGCACGAACCCCCCGTTCAGCCCGACCGCTGCGCCTTATCCGGTAACTATCGTCTTGA GTCCAACCCGGTAAGACACGACTTATCGCCACTGGCAGCAGCCACTGGTAACAGGATTAGCAGA GCGAGGTATGTAGGCGGTGCTACAGAGTTCTTGAAGTGGTGGCCTAACTACGGCTACACTAGAA GAACAGTATTTGGTATCTGCGCTCTGCTGAAGCCAGTTACCTTCGGAAAAAGAGTTGGTAGCTCT TGATCCGGCAAACAAACCACCGCTGGTAGCGGTGGTTTTTTTGTTTGCAAGCAGCAGATTACGCG CAGAAAAAAAGGATCTCAAGAGGATCCTTTGATCTTTTCTACGGGGTCTGACGCTCAGTGGAACG AAAACTCACGTTAAGGGATTTTGGTCATGAGATTATCAAAAAGGATCTTCACCTAGATCCTTTTAAA TTAAAAATGAAGTTTTAAATCAATCTAAAGTATATATGAGTAAACTTGGTCTGACAGTTACCAATGC TTAATCAGTGAGGCACCTATCTCAGCGATCTGTCTAGTTCGTTCATCCATAGTTGCCTGACTCCCC GTCGTGTAGATAACTACGATACGGGAGGGCTTACCATCTGGCCCCAGTGCTGCAATGATACCGC GAGACCCACGCTCACCGGCTCCAGATTTATCAGCAATAAACCAGCCAGCCGGAAGGGCCGAGC GCAGAAGTGGTCCTGCAACTTTATCCGCCTCCATCCAGTCTATTAATTGTTGCCGGGAAGCTAGA GTAAGTAGTTCGCCAGTTAATAGTTTGCGCAACGTTGTTGCCATTGCTACAGGCATCGTGGTGTC ACGCTCGTCGTTTGGTATGGCTTCATTCAGCTCCGGTTCCCAACGATCAAGGCGAGTTACATG ATCCCCCATGTTGTGCAAAAAAGCGGTTAGCTCCTTCGGTCCTCCGATCGTTGTCAGAAGTAA 11
12 GTTGGCCGCAGTGTTATCACTCATGGTTATGGCAGCACTGCATAATTCTCTTACTGTCATGCCATC CGTAAGATGCTTTTCTGTGACTGGTGAGTACTCAACCAAGTCATTCTGAGAATAGTGTATGCGGC GACCGAGTTGCTCTTGCCCGGCGTCAATACGGGATAATACCGCGCCACATAGCAGAACTTTAAAA GTGCTCATCATTGGAAAACGTTCTTCGGGGCGAAAACTCTCAAGGATCTTACCGCTGTTGAGATC CAGTTCGATGTAACCCACTCGTGCACCCAACTGATCTTCAGCATCTTTTACTTTCACCAGCGTTTC TGGGTGAGCAAAAACAGGAAGGCAAAATGCCGCAAAAAAGGGAATAAGGGCGACACGGAAATGT TGAATACTCATACTCTTCCTTTTTCAATATTATTGAAGCATTTATCAGGGTTATTGTCTCATGAGCG GATACATATTTGAATGTATTTAGAAAAATAAACAAATAGGGGTTCCGCGCACATTTCCCCGAAAAG TGCCACCT 6.4. Influence of temperature on in vitro EGFP synthesis Fig. 5: Influence of temperature on EGFP synthesis and folding efficiency in the LEXSY cell-free translation system. The yield of total full-sized EGFP was evaluated by Western blotting; the yield of properly folded EGFP was evaluated with direct fluorescence measurement Sequences of the primers for LEXSY in vitro Translation Kit Insert sequencing forward primer H4132 Anneals to SITS leader sequence 5 -CATGACAGTAATGTATAAAGTC-3 Cat. No. PM-116 Insert sequencing reverse primer A264 Anneals to 3 utr 1.4k camcb 5 -CATCTATAGAGAAGTACACGTAAAAG-3 Cat. No. PM
2.5. Equipment and materials supplied by user PCR based template preparation Influence of temperature on in vitro EGFP synthesis 11
 Manual 15 Reactions LEXSY in vitro Translation Cell-free protein expression kit based on Leishmania tarentolae for PCR-based template generation Cat. No. EGE-2010-15 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT INTENDED
Manual 15 Reactions LEXSY in vitro Translation Cell-free protein expression kit based on Leishmania tarentolae for PCR-based template generation Cat. No. EGE-2010-15 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT INTENDED
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual
 MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
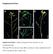 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), , DOI: /bi00034a013
 Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR
 Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Hes6. PPARα. PPARγ HNF4 CD36
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were
 1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells
 Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Expression of Recombinant Proteins
 Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Load-dependent modulation of non-muscle myosin-2a function by tropomyosin 4.2 Nikolas Hundt 1, Walter Steffen 2, Salma Pathan-Chhatbar 1, Manuel H. Taft 1, Dietmar J. Manstein
Supplementary Information Load-dependent modulation of non-muscle myosin-2a function by tropomyosin 4.2 Nikolas Hundt 1, Walter Steffen 2, Salma Pathan-Chhatbar 1, Manuel H. Taft 1, Dietmar J. Manstein
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
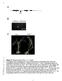 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification
 Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Additional descriptions of plasmid constructions and the oligonucleotides used Plasmid or Oligonucleotide
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Additional descriptions of plasmid constructions and the oligonucleotides used Plasmid or Oligonucleotide former/ working Description a designation Plasmids pes213a b pes213-tn5
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Additional descriptions of plasmid constructions and the oligonucleotides used Plasmid or Oligonucleotide former/ working Description a designation Plasmids pes213a b pes213-tn5
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system
 Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental Information. Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids. Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites. to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
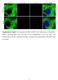 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
ORFs and genes. Please sit in row K or forward
 ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Supplementary Figure 1A A404 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid
 Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
ENDEXT Technology. Instruction manual for protein synthesis. with wheat germ cell-free system
 ENDEXT Technology Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system 1 Protocol Overview Plasmid DNA construction (see Section 3.1) Preparation of plasmid DNA for transcription (see
ENDEXT Technology Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system 1 Protocol Overview Plasmid DNA construction (see Section 3.1) Preparation of plasmid DNA for transcription (see
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines
 Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
RPA-AB RPA-C Supplemental Figure S1: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification.
 RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base. excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps
 Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR
 Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System
 Cat. # 3281 For Research Use Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage...
Cat. # 3281 For Research Use Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage...
Supplementary Information. Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins
 Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Legends for supplementary figures 1-3
 High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
evaluated with UAS CLB eliciting UAS CIT -N Libraries increase in the
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Overexpression Normal expression Overexpression Normal expression. 26 (21.1%) N (%) P-value a N (%)
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
Wet Lab Tutorial: Genelet Circuits
 Wet Lab Tutorial: Genelet Circuits DNA 17 This tutorial will introduce the in vitro transcriptional circuits toolkit. The tutorial will focus on the design, synthesis, and experimental testing of a synthetic
Wet Lab Tutorial: Genelet Circuits DNA 17 This tutorial will introduce the in vitro transcriptional circuits toolkit. The tutorial will focus on the design, synthesis, and experimental testing of a synthetic
ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1. ΔPDD1 x wild type. 70 kd Pdd1. Pdd3
 Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Classic cloning with pask-iba and pexpr-iba vectors
 Classic cloning with pask-iba and pexpr-iba vectors General protocol Last date of revision March 2017 Version PR08-0008 For research use only Important licensing information Products featuring CMV promoter,
Classic cloning with pask-iba and pexpr-iba vectors General protocol Last date of revision March 2017 Version PR08-0008 For research use only Important licensing information Products featuring CMV promoter,
Cell-Free Protein Expression Kit
 Cell-Free Protein Expression Kit Handbook Version v.01, January 2018 Cat# 507024 (Sigma 70 Master Mix Kit, 24 Rxns) Cat# 507096 (Sigma 70 Master Mix Kit, 96 Rxns) Please refer to this product in your publication
Cell-Free Protein Expression Kit Handbook Version v.01, January 2018 Cat# 507024 (Sigma 70 Master Mix Kit, 24 Rxns) Cat# 507096 (Sigma 70 Master Mix Kit, 96 Rxns) Please refer to this product in your publication
Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
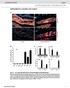 doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Human Cell-Free Protein Expression Maxi System
 Cat. # 3285 For Research Use Human Cell-Free Protein Expression Maxi System Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 4 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 IV. Storage...
Cat. # 3285 For Research Use Human Cell-Free Protein Expression Maxi System Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 4 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 IV. Storage...
Supplemental Information. Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous. MicroRNAs in C. elegans. Inventory of Supplementary Information
 Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE S1. Identification of BmCREC. (A) Amino acid sequences of BmCREC show the peptides identified in LC-MS/MS analysis (marked by red letters
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE S1. Identification of BmCREC. (A) Amino acid sequences of BmCREC show the peptides identified in LC-MS/MS analysis (marked by red letters
SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer
 TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FILE
 Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
NAME:... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:... Maximum marks: 50. Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer Science, UKZN
 COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
PCR analysis was performed to show the presence and the integrity of the var1csa and var-
 Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
FAT10 and NUB1L bind the VWA domain of Rpn10 and Rpn1 to enable proteasome-mediated proteolysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FAT10 and NUB1L bind the VWA domain of Rpn10 and Rpn1 to enable proteasome-mediated proteolysis Neha Rani, Annette Aichem, Gunter Schmidtke, Stefan Kreft, and Marcus Groettrup
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FAT10 and NUB1L bind the VWA domain of Rpn10 and Rpn1 to enable proteasome-mediated proteolysis Neha Rani, Annette Aichem, Gunter Schmidtke, Stefan Kreft, and Marcus Groettrup
High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria
 High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria Eric R Geertsma & Bert Poolman Supplementary text and figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of SfiI sites yielding identical 3 extensions
High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria Eric R Geertsma & Bert Poolman Supplementary text and figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of SfiI sites yielding identical 3 extensions
Table S1. Sequences of mutagenesis primers used to create altered rdpa- and sdpa genes
 Supplementary Table and Figures for Structural Basis for the Enantiospecificities of R- and S-Specific Phenoxypropionate/α-Ketoglutarate Dioxygenases by Tina A. Müller, Maria I. Zavodszky, Michael Feig,
Supplementary Table and Figures for Structural Basis for the Enantiospecificities of R- and S-Specific Phenoxypropionate/α-Ketoglutarate Dioxygenases by Tina A. Müller, Maria I. Zavodszky, Michael Feig,
Protocol: Generating RNA Baits for Capture-based enrichment Tung lab, Duke University, September 10 th, 2015
 Protocol: Generating RNA Baits for Capture-based enrichment Tung lab, Duke University, September 10 th, 2015 1. Extract high quality, genomic DNA (gdna) from a primary tissue sample. *Note that you do
Protocol: Generating RNA Baits for Capture-based enrichment Tung lab, Duke University, September 10 th, 2015 1. Extract high quality, genomic DNA (gdna) from a primary tissue sample. *Note that you do
PCR Cloning II fusion domains for purification His 6 GST chitin binding protein MBP
 PCR cloning : why secondary amplification? May 26, 2009 secondary amplification amplification of the coding sequence alone or of defined fragments ligation into expression vector insertion of fusion domains
PCR cloning : why secondary amplification? May 26, 2009 secondary amplification amplification of the coding sequence alone or of defined fragments ligation into expression vector insertion of fusion domains
II 0.95 DM2 (RPP1) DM3 (At3g61540) b
 Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR.
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE-/- hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE+/+
 ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS. E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean SYHT0H2 by Real-time PCR. Validated Method
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics Unit Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean SYHT0H2 by Real-time PCR
EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics Unit Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean SYHT0H2 by Real-time PCR
Annex 6.5 CDC real-time rubella RT-PCR protocol targeting rubella p150 gene (154 nt region)
 Annex 6.5 CDC real-time rubella RT-PCR protocol targeting rubella p150 gene (154 nt region) NOTE: This document is intended to provide basic test method details and is not an SOP. Laboratories need to
Annex 6.5 CDC real-time rubella RT-PCR protocol targeting rubella p150 gene (154 nt region) NOTE: This document is intended to provide basic test method details and is not an SOP. Laboratories need to
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Cotton Event MON Using Real-time PCR. Protocol
 Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Cotton Event MON 88913 Using Real-time PCR Protocol 5 May 2009 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Cotton Event MON 88913 Using Real-time PCR Protocol 5 May 2009 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics
Molecular Techniques Third-year Biology
 PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
mrnadembeads Purification Mini Kit (cat #06011) Instruction manual for mrna purification
 mrnadembeads Purification Mini Kit (cat #06011) Instruction manual for mrna purification Ademtech * Bioparc BioGalien 27 Allée Charles Darwin * 33600 Pessac France Tel : + 33 (0) 57 02 02 01, Fax : + 33
mrnadembeads Purification Mini Kit (cat #06011) Instruction manual for mrna purification Ademtech * Bioparc BioGalien 27 Allée Charles Darwin * 33600 Pessac France Tel : + 33 (0) 57 02 02 01, Fax : + 33
5.2 Protein purification
 Purification of a His 6 -tagged Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP). Protein purification.. Purification of a His 6 -tagged Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) Principle You can add either a N- or C-terminal His
Purification of a His 6 -tagged Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP). Protein purification.. Purification of a His 6 -tagged Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) Principle You can add either a N- or C-terminal His
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1
 Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean Event DP Using Real-time PCR. Validated Method
 Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean Event DP-356043-5 Using Real-time PCR Validated Method 29 March 2010 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean Event DP-356043-5 Using Real-time PCR Validated Method 29 March 2010 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular
A Genetically Encoded Toolbox for Glycocalyx Engineering: Tunable Control of Cell Adhesion,
 TITLE A Genetically Encoded Toolbox for Glycocalyx Engineering: Tunable Control of Cell Adhesion, Survival, and Cancer Cell Behaviors AUTHORS Carolyn R. Shurer *, Marshall J. Colville *, Vivek K. Gupta,
TITLE A Genetically Encoded Toolbox for Glycocalyx Engineering: Tunable Control of Cell Adhesion, Survival, and Cancer Cell Behaviors AUTHORS Carolyn R. Shurer *, Marshall J. Colville *, Vivek K. Gupta,
WEPRO7240/7240H/7240G Expression Kit. Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system
 ENDEXT Technology WEPRO7240/7240H/7240G Expression Kit Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system (Catalog No. CFS-TRI-7240, CFS-TRI-7240H, CFS-TRI-7240G) CellFree Sciences
ENDEXT Technology WEPRO7240/7240H/7240G Expression Kit Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system (Catalog No. CFS-TRI-7240, CFS-TRI-7240H, CFS-TRI-7240G) CellFree Sciences
NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples
 NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples VERSION 2.0 SUMMARY This procedure describes the use of nested Sequence-Based
NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples VERSION 2.0 SUMMARY This procedure describes the use of nested Sequence-Based
Nongenetic Reprogramming of the Ligand Specificity. of Growth Factor Receptors by Bispecific DNA Aptamers
 Supporting Information For Nongenetic Reprogramming of the Ligand Specificity of Growth Factor Receptors by Bispecific DNA Aptamers Ryosuke Ueki,* Saki Atsuta, Ayaka Ueki and Shinsuke Sando* Department
Supporting Information For Nongenetic Reprogramming of the Ligand Specificity of Growth Factor Receptors by Bispecific DNA Aptamers Ryosuke Ueki,* Saki Atsuta, Ayaka Ueki and Shinsuke Sando* Department
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. In Vitro Bacterial Split Fluorescent Protein Fold n Glow Solubility Assay Kits
 In Vitro Bacterial Split Fluorescent Protein Fold n Glow Solubility Assay Kits Catalog Numbers APPA001 In Vitro Bacterial Split GFP "Fold 'n' Glow" Solubility Assay Kit (Green) APPA008 In Vitro Bacterial
In Vitro Bacterial Split Fluorescent Protein Fold n Glow Solubility Assay Kits Catalog Numbers APPA001 In Vitro Bacterial Split GFP "Fold 'n' Glow" Solubility Assay Kit (Green) APPA008 In Vitro Bacterial
Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit)
 Product Name: Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit) Cat. # Product Size DS610 Long ssdna Preparation Kit for 1.5 kb (LsODN Preparation Kit) plsodn-1 10 μg (0.5 μg/μl) plsodn-2d 10 μg (0.5
Product Name: Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit) Cat. # Product Size DS610 Long ssdna Preparation Kit for 1.5 kb (LsODN Preparation Kit) plsodn-1 10 μg (0.5 μg/μl) plsodn-2d 10 μg (0.5
Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit)
 Product Name: Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit) Cat. # Product Size DS610 Long ssdna Preparation Kit for 1.5 kb (LsODN Preparation Kit) plsodn-1 10 μg (0.5 μg/μl) plsodn-2d 10 μg (0.5
Product Name: Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit) Cat. # Product Size DS610 Long ssdna Preparation Kit for 1.5 kb (LsODN Preparation Kit) plsodn-1 10 μg (0.5 μg/μl) plsodn-2d 10 μg (0.5
WEPRO1240/1240H/1240G Expression Kit. Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system
 ENDEXT Technology WEPRO1240/1240H/1240G Expression Kit Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system (Catalog No. CFS-TRI-1240, CFS-TRI-1240H, CFS-TRI-1240G) CellFree Sciences
ENDEXT Technology WEPRO1240/1240H/1240G Expression Kit Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system (Catalog No. CFS-TRI-1240, CFS-TRI-1240H, CFS-TRI-1240G) CellFree Sciences
Supplemental Data. Bennett et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Oilseed Rape RF1 using Real-time PCR. Protocol
 Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Oilseed Rape RF1 using Real-time PCR Protocol 7 July 2011 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Oilseed Rape RF1 using Real-time PCR Protocol 7 July 2011 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics
I. Things to keep in mind before you start this protocol
 Inverse PCR and Sequencing Protocol on 5 Fly Preps For recovery of sequences flanking piggybac elements This protocol is an adaptation of "Inverse PCR and Cycle Sequencing Protocols" by E. Jay Rehm Berkeley
Inverse PCR and Sequencing Protocol on 5 Fly Preps For recovery of sequences flanking piggybac elements This protocol is an adaptation of "Inverse PCR and Cycle Sequencing Protocols" by E. Jay Rehm Berkeley
BioDynamics Laboratory Inc.
 Product Name: Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit) Cat. # Product Size DS610 Long ssdna Preparation Kit for 1.5 kb (LsODN Preparation Kit) plsodn-1 10 µg (0.5 µg/µl) plsodn-2d 10 µg (0.5
Product Name: Long ssdna Preparation Kit (LsODN Preparation Kit) Cat. # Product Size DS610 Long ssdna Preparation Kit for 1.5 kb (LsODN Preparation Kit) plsodn-1 10 µg (0.5 µg/µl) plsodn-2d 10 µg (0.5
Creation of A Caspese-3 Sensing System Using A Combination of Split- GFP and Split-Intein
 Supplementary Information Creation of A Caspese-3 Sensing System Using A Combination of Split- GFP and Split-Intein Seiji Sakamoto,* Mika Terauchi, Anna Hugo, Tanner Kim, Yasuyuki Araki and Takehiko Wada*
Supplementary Information Creation of A Caspese-3 Sensing System Using A Combination of Split- GFP and Split-Intein Seiji Sakamoto,* Mika Terauchi, Anna Hugo, Tanner Kim, Yasuyuki Araki and Takehiko Wada*
