Chapter 4.!Extensions to Mendelian Genetics.! Gene Interactions
|
|
|
- Kelly Julianna Griffith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4!Extensions to Mendelian Genetics! Gene Interactions 1
2 Gene Interactions Extensions to Mendelian Genetics Just as different alleles of 1 gene can interact in complex ways, 2 different genes can also act together to modify a phenotype: 2 genes 1 phenotype (Additive Gene Action) Complementation (complementary gene action) Epistasis (recessive and dominant) Redundancy 2
3 Multifactorial Inheritance Vast majority of traits are determined by multiple factors: genetic as well as environmental. Gene interactions between two or more genes Example: Lentil Seed color. F1 all same, F2: 4 different phenotypes F2 phenotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1 (same as F2 dihybrids in Mendel s original crosses). Difference: in original crosses: 2 independent traits/phenotypes=2 independent genes; Seed color and seed shape here: multiple phenotypes of 1 trait=2 independent genes Seed color only. 3
4 (Additive Gene Action) You can tell this genotype is caused by more than one gene : because there are 4 phenotypes not 3 in F2 1 gene F2 would have 3 phenotypes 1:2:1 ratio 4
5 F2 phenotypes Dominance Relationships: Tan is dominant to green Gray is dominant to green Brown is dominant to gray, green and tan. Tan and Gray are incompletely dominant, giving rise to brown. Genotypic classes: Brown: A_B_ Tan: A_bb Gray: aab_ Green: aabb 5
6 Complementary Gene Action Each genotypic class may not always dictate a unique phenotype A pair of genes can often work together to create a specific phenotype. We call this complementary interaction. With this type of interaction we see 2 different phenotypes instead of the 4 seen in 2 genes 1 phenotype Two or more genotypic classes may display an identical phenotype. Example: Two lines of pure breeding white flowered pea plants falling into different genotypic classes: AAbb & aabb The must have a dominant allele in both genes to result in the purple flower phenotype 6
7 7
8 8
9 Epistasis One gene s allele masks the phenotype of the other gene s alleles. Four genotypic classes produce fewer than four phenotypes. Different types of epistasis: Recessive epistasis: when the recessive allele of one gene masks the effects of either allele of the second gene. Dominant epistasis: when the dominant allele of one gene masks the effects of either allele of the second gene. 9
10 Recessive Epistasis Example 1: Coat color of Labrador retriever Example 2: ABO blood groups: Bombay phenotype. Phenotypic ratios are 9:3:4 in F2. 10
11 Coat-Color Inheritance in Labrador Retrievers P X golden black F1 black 11
12 Recessive Epistasis: a recessive mutation in one gene masks the phenotypic effects of another F1 F2 X Appears like incomplete dominance because some of the progeny look like neither parent, but the ratio is wrong. 9 : 3 : 4 12
13 Dihybrid Cross: BbEe x BbEe F2 BE Be be be BE AACC AACc Aa c CC BBEE BBEe BbEE Aa BbEe c Cc Be AACc BBEe BBee AAcc Aa BbEe c Cc Aa Bbee c cc be Aa BbEE c CC BbEe Aa c Cc abbee c a c CC abbee c a c Cc be AACc BbEe Bbee Aa c cc abbee c a c Cc abbee c a c cc 9 black: 3 brown: 4 golden (9 B-E-: 3 bbe-: 3 B-ee: 1 bbee) 13
14 Molecular Explanation Pigment production (B) and subsequent incorporation (E) into the hair shaft are controlled by two separate genes. To be black, both genes must function. Mutations in B (b) lead to brown pigment. Mutations in E (e) lead to no pigment in coat. 3 gene B gene E
15 Recessive Epistasis Two genes involved in coat color determination. Gene B determines whether black (B) or brown (bb) pigment is produced. Gene E determines if pigment is deposited in hair golden retrievers (ee) make either black (B-) or brown (bb) pigment (look at noses) but not in fur The recessive allele is epistatic to (stands over) other genes when homozygous -- hence the name recessive epistasis Phenotypes do not segregate according to Mendelian ratios (the phenotypic ratios are modified Mendelian ratios). epistasis - (Greek, to stand upon or stop) the differential phenotypic expression of a genotype at one locus caused by the genotype at another, non allelic, locus. A mutation that exerts its expression by canceling the expression of the alleles of another gene. 15
16 Dominant Epistasis caused by the dominant allele of one gene, masking the action of either allele of the other gene. Ratio is 12:3:1 instaed f 9:3:3:1 Example: Summer Squash 16
17 17
18 Redundancy: Duplicate Genes Petal color in snapdragons - if Mendel had used snap dragons for his experiments, he wouldn t be famous! P F1 AABB X A-Baabb F2 15/16 red; 1/16 white 18
19 A-B- X A-B- AB AB Ab ab ab AACC AABB AABb AACc AaBB c CC AaBb Ab AACc AABb AAbb AAcc AaBb c Cc Aabb ab AaBB c CC AaBb c Cc aabba c a c CC aabb ab AACc AaBb Aabb c cc aabba c a c Cc aabb c a c cc 15/16 A-B- red; 1/16 aabb white Whenever a dominant gene is present, the trait is expressed. One allele is sufficient to produce the pigment. 19
20 Hints for figuring out gene interactions: Look at the F2 phenotypic ratios!! If one gene is involved in the trait, then the monohybrid phenotypic ratio is: 3:1 or 1:2:1 or 2:1 If two genes are involved in the trait, then the dihybrid phenotypic ratio is: 9:3:3:1 or some permutation (9:4:3 or 9:7 or 12:3:1) "The 1/16 class is always the double homozygous recessive. " Look for internal 3:1 ratios, which will indicate dominance/recessive relationships for alleles within a gene. 20
21 Hints for figuring out gene interactions: 2 Genes 1 Phenotype (Additive Gene Action): You can tell this genotype is caused by more than one gene because there are 4 phenotypes not 3 in F2 (9:3:3:1) 1 gene F2 would have 3 phenotypes 1:2:1 ratio Complementary Gene Action: one good copy of each gene is needed for expression of the final phenotype 9:7 ratio Epistasis: one gene can mask the effect of another gene 9:3:4 ratio for recessive epistasis 12:3:1 ratio for dominant epistasis Duplicate genes: only double mutant has mutant phenotype 15:1 ratio 21
22 variations on Mendelian inheritance Gene interaction Inheritance pattern A-/B- A-/bb aa/b- aabb ratio Additive Each genotype results in a unique phenotype :3:3:1 Complementary At least one dominant allele from each of two genes needed for phenotype :7 Recessive Epistasis Homozyous recessive genotype at one locus masks expression at second locus :3:4 Dominant Epistasis Dominant allele at one locus masks expression at second locus :3:1 Duplicate Genes One dominant allele from either of twogenes needed for phenotype :1 22
23 true breeding brown dogs X true breeding white dogs F1 = all white F2 = 118 white black 3 10 brown 1 # Find the genotypes of the dogs in each class: What is the ratio? How many genes? 2 Sample Problem What is the ratio of white to colored dogs? 12:4 = 3:1 This means that white is dominant to colored so let s call one gene: W= white w=colored 23
24 What is the ratio of black to brown dogs? 3 : 1 So black must be dominant to brown. So we will call the second gene: B=black and b=brown What class of dogs are the double recessive homozygotes and what is their genotype? Brown - wwbb What is the genotype of the black dogs? Must be wwb- What are the genotypes of the white dogs? F2 = 118 white 32 black 10 brown W_ B_ and W_bb # This is an example of dominant 24 epistasis (white).
25 Same Genotype may produce different Phenotypes Penetrance: Genotype does not necessarily define phenotype. The proportion of individuals with a given genotype express the phenotype determines penetrance. 100% penetrance = all individuals show phenotype. 50% penetrance = half the individuals show phenotype. Example: retinoblastoma: only 75% individuals affected. Expressivity: the degree or intensity with which a particular genotype is expressed in a phenotype in a given individual. Retinoblastoma: some have both eyes affected, some only one. 25
26 Modifier Effects Modifier Genes: they have a subtle, secondary effect which alters the phenotypes produced by the primary genes. E.G. Tail length in mice. The mutant allele t causes a shortening of the tail. Not all short tails are of the same length: another gene affects the actual length. (Variable expressivity). Modifying environment: The environment may influence the effect of a genotype on the phenotype. E.G.: Siamese cats: temperature dependent color of coat. Color shows up only in extremities, where the temp is lower (enzyme for pigment formation is active only at lower temp.) 26
27 Modifying environment: The environmental influence of a genotype on the phenotype= phenocopy 27
28 Modifying environment: The environmental influence of a genotype on the phenotype= phenocopy 28
29 Homework Problems Chapter 4 # 15, 16, 19, 26 $DON T T forget to take the online QUIZ!! 29
Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits. Chapter 11
 Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Chapter 11 Impacts, Issues: The Color of Skin Like most human traits, skin color has a genetic basis; more than 100 gene products affect the synthesis and deposition
Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Chapter 11 Impacts, Issues: The Color of Skin Like most human traits, skin color has a genetic basis; more than 100 gene products affect the synthesis and deposition
Inheritance Pattern Complexity
 Inheritance Pattern Complexity complexity from how genes transmitted Sex linkage Linkage (coming soon!) complexity from how genes function dominance relationships multiple alleles pleiotropy conditional
Inheritance Pattern Complexity complexity from how genes transmitted Sex linkage Linkage (coming soon!) complexity from how genes function dominance relationships multiple alleles pleiotropy conditional
! Allele Interactions
 Chapter 4!Extensions to Mendelian Genetics! Allele Interactions 1 INTRODUCTION Mendelian inheritance describes inheritance patterns that obey two laws Law of segregation Law of independent assortment Simple
Chapter 4!Extensions to Mendelian Genetics! Allele Interactions 1 INTRODUCTION Mendelian inheritance describes inheritance patterns that obey two laws Law of segregation Law of independent assortment Simple
Chapter 4 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Extensions of Mendelian Genetics. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Extensions of Mendelian Genetics Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Factors that cause deviation from normal monohybrid and dihybrid ratios: X-linkage
Chapter 4 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Extensions of Mendelian Genetics Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Factors that cause deviation from normal monohybrid and dihybrid ratios: X-linkage
D) Gene Interaction Takes Place When Genes at Multiple Loci Determine a Single Phenotype.
 D) Gene Interaction Takes Place When Genes at Multiple Loci Determine a Single Phenotype. In the dihybrid crosses, each locus had an independent effect on the phenotype. When Mendel crossed a homozygous
D) Gene Interaction Takes Place When Genes at Multiple Loci Determine a Single Phenotype. In the dihybrid crosses, each locus had an independent effect on the phenotype. When Mendel crossed a homozygous
Multiple Choice (3.35 each) Total = 100pts. Choice the choice that best answers the question! Good luck!
 NAME DATE Multiple Choice (3.35 each) Total = 100pts. Choice the choice that best answers the question! Good luck! 1. Could the characteristic followed in the pedigree be caused by an autosomal dominant
NAME DATE Multiple Choice (3.35 each) Total = 100pts. Choice the choice that best answers the question! Good luck! 1. Could the characteristic followed in the pedigree be caused by an autosomal dominant
Mendelian Genetics 1
 Mendelian Genetics Genetics Mendel and the Gene Idea Genetics: The study of heredity. 2 Heredity Two possible explanations for heredity: The Blending Hypothesis Genetic material from the parents mix. Similar
Mendelian Genetics Genetics Mendel and the Gene Idea Genetics: The study of heredity. 2 Heredity Two possible explanations for heredity: The Blending Hypothesis Genetic material from the parents mix. Similar
ch03 Student: If a phenotype is controlled by the genotypes at two different loci the interaction of these genes is called
 ch03 Student: 1. Which of the following is not a phenotypic description of allele interactions affecting the expression of traits? incomplete dominance codominance polymorphic multifactorial E. pleiotrophic
ch03 Student: 1. Which of the following is not a phenotypic description of allele interactions affecting the expression of traits? incomplete dominance codominance polymorphic multifactorial E. pleiotrophic
Chapter 4. Modification of Mendelian Ratios
 Chapter 4. Modification of Mendelian Ratios Inheritance Patterns are Often More Complex than Predicted by Simple Mendelian Genetics The relationship between genotype and phenotype is rarely as simple as
Chapter 4. Modification of Mendelian Ratios Inheritance Patterns are Often More Complex than Predicted by Simple Mendelian Genetics The relationship between genotype and phenotype is rarely as simple as
B.6.F predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and non Mendelian inheritance
 B.6.F predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and non Mendelian inheritance Gregor Mendel Austrian monk * Studied science and mathematics
B.6.F predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and non Mendelian inheritance Gregor Mendel Austrian monk * Studied science and mathematics
Chapter 5. Gene Interactions
 Chapter 5 Gene Interactions Figure 5-1 Coat color in mammals is an example of a phenotypic trait that is controlled by more than one locus and the alleles at these loci can interact to alter the expected
Chapter 5 Gene Interactions Figure 5-1 Coat color in mammals is an example of a phenotypic trait that is controlled by more than one locus and the alleles at these loci can interact to alter the expected
Mendel and The Gene Idea
 Mendel and The Gene Idea Gregor Mendel was a monk who experimented with pea plants and was also a scientist He is known as the Father of Genetics. Mendel s two fundamental principles of heredity are now
Mendel and The Gene Idea Gregor Mendel was a monk who experimented with pea plants and was also a scientist He is known as the Father of Genetics. Mendel s two fundamental principles of heredity are now
Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits. Chapter 11 Updated Reading Not
 Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Chapter 11 Updated Reading 11.1-11.3 Not 11.5-11.7 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles,
Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Chapter 11 Updated Reading 11.1-11.3 Not 11.5-11.7 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles,
Biology. Chapter 13. Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 13 Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits 13.1 How Do Alleles Contribute to Traits? Blending inheritance 19th century idea Failed to explain
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 13 Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits 13.1 How Do Alleles Contribute to Traits? Blending inheritance 19th century idea Failed to explain
Genetics, Fall 2005 TEST 2, 11/16/05 Page 1
 Genetics, Fall 2005 TEST 2, 11/16/05 Page 1 STUDENT NAME: Give a brief definition of the following terms (5 points each; only nine definitions count for the grade): 1. phenotype 2. homozygous 3. codominance
Genetics, Fall 2005 TEST 2, 11/16/05 Page 1 STUDENT NAME: Give a brief definition of the following terms (5 points each; only nine definitions count for the grade): 1. phenotype 2. homozygous 3. codominance
Non Mendelian Genetics
 Non Mendelian Genetics TEKS 6 Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to: 6F
Non Mendelian Genetics TEKS 6 Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to: 6F
Would expect variation to disappear Variation in traits persists (Example: freckles show up in unfreckled parents offspring!)
 Genetics Early Ideas about Heredity People knew that sperm and eggs transmitted information about traits Blending theory mother and father s traits blended together Problem: Would expect variation to disappear
Genetics Early Ideas about Heredity People knew that sperm and eggs transmitted information about traits Blending theory mother and father s traits blended together Problem: Would expect variation to disappear
Exploring Mendelian Genetics. Dihybrid crosses. Dihybrid crosses
 Objective 8: Predict the results of dihybrid genetic crosses by using Punnett squares Exploring Mendelian Genetics 11.3 Dihybrid cross--a cross that involves two pairs of contrasting traits. A cross between
Objective 8: Predict the results of dihybrid genetic crosses by using Punnett squares Exploring Mendelian Genetics 11.3 Dihybrid cross--a cross that involves two pairs of contrasting traits. A cross between
A/A;b/b x a/a;b/b. The doubly heterozygous F1 progeny generally show a single phenotype, determined by the dominant alleles of the two genes.
 Name: Date: Title: Gene Interactions in Corn. Introduction. The phenotype of an organism is determined, at least in part, by its genotype. Thus, given the genotype of an organism, and an understanding
Name: Date: Title: Gene Interactions in Corn. Introduction. The phenotype of an organism is determined, at least in part, by its genotype. Thus, given the genotype of an organism, and an understanding
Outer. Last. Possible gamete combinations for parent 1: RY RY ry ry F (first) O (outer) I (inner) L (last)
 Dihybrid Crosses Explained: Mendel s Law of Independent Assortment says that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. What does that mean? It means that the
Dihybrid Crosses Explained: Mendel s Law of Independent Assortment says that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. What does that mean? It means that the
Content Objectives Write these down!
 Content Objectives Write these down! I will be able to identify: Key terms associated with Mendelian Genetics The patterns of heredity explained by Mendel The law of segregation The relationship between
Content Objectives Write these down! I will be able to identify: Key terms associated with Mendelian Genetics The patterns of heredity explained by Mendel The law of segregation The relationship between
Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Name Period Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea If you have completed a first-year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics.
Name Period Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea If you have completed a first-year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics.
Observing Patterns In Inherited Traits
 Observing Patterns In Inherited Traits Ø Where Modern Genetics Started/ Gregor Mendel Ø Law of Segregation Ø Law of Independent Assortment Ø Non-Mendelian Inheritance Ø Complex Variations in Traits Genetics:
Observing Patterns In Inherited Traits Ø Where Modern Genetics Started/ Gregor Mendel Ø Law of Segregation Ø Law of Independent Assortment Ø Non-Mendelian Inheritance Ø Complex Variations in Traits Genetics:
Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Chapter 4: Mendel and the Gene Idea. The Experiments of Gregor Mendel 2. Beyond Mendelian Genetics 3. Human Genetics . The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Chapter Reading pp. 268-276 TECHNIQUE Parental generation
Chapter 4: Mendel and the Gene Idea. The Experiments of Gregor Mendel 2. Beyond Mendelian Genetics 3. Human Genetics . The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Chapter Reading pp. 268-276 TECHNIQUE Parental generation
BIOLOGY 321 SPRING2013 ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #4 Answers to Edition 9 text questions:
 BIOLOGY 321 SPRING2013 ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #4 Answers to Edition 9 text questions: http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/answers4.9.pdf Chapter 2 NOTE ON 38: substitute dominant for mutant in part
BIOLOGY 321 SPRING2013 ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #4 Answers to Edition 9 text questions: http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/answers4.9.pdf Chapter 2 NOTE ON 38: substitute dominant for mutant in part
Early Ideas of Heredity. Early Ideas of Heredity. Early Ideas of Heredity. Early Ideas of Heredity. Patterns of Inheritance.
 Patterns of Inheritance Chapter 12 Before the 20 th century, 2 concepts were the basis for ideas about heredity: -heredity occurs within species -traits are transmitted directly from parent to offspring
Patterns of Inheritance Chapter 12 Before the 20 th century, 2 concepts were the basis for ideas about heredity: -heredity occurs within species -traits are transmitted directly from parent to offspring
Mendelian & Non Mendelian Genetics. Copy Dr. M. A. Fouad
 Mendelian & Non Mendelian Genetics Copy right @ Dr. M. A. Fouad Mendelian Genetics Mendel s Law of Austrian monk born in 1822 in monastery known for research and teaching after his death (1884) acknowledgment
Mendelian & Non Mendelian Genetics Copy right @ Dr. M. A. Fouad Mendelian Genetics Mendel s Law of Austrian monk born in 1822 in monastery known for research and teaching after his death (1884) acknowledgment
Chapter 02 Mendel s Principles of Heredity
 Chapter 02 Mendel s Principles of Heredity Multiple Choice Questions 1. What was the importance of Mendel performing reciprocal crosses? To be able to breed plants all year round To obtain enough plants
Chapter 02 Mendel s Principles of Heredity Multiple Choice Questions 1. What was the importance of Mendel performing reciprocal crosses? To be able to breed plants all year round To obtain enough plants
5. Alternate versions of the same gene, like purple and white flower color, are termed.
 Name Period If you have completed a first- year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics. For other students, this may be your
Name Period If you have completed a first- year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics. For other students, this may be your
CHAPTER 10: Patterns of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 10: Patterns of Inheritance BIO 121 Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns Genetics can explain how these poodles look different. Section 10.1 Puppies Punchstock/Banana Stock RF Genetics
CHAPTER 10: Patterns of Inheritance BIO 121 Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns Genetics can explain how these poodles look different. Section 10.1 Puppies Punchstock/Banana Stock RF Genetics
Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea Name Period If you have completed a first-year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics.
Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea Name Period If you have completed a first-year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics.
Chapter 11 Reading Guide: Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Chapter 11 Reading Guide: Mendel and the Gene Idea Since you have completed a first-year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics.
Chapter 11 Reading Guide: Mendel and the Gene Idea Since you have completed a first-year high school biology course, some of this chapter will serve as a review for the basic concepts of Mendelian genetics.
Exam 1 Answers Biology 210 Sept. 20, 2006
 Exam Answers Biology 20 Sept. 20, 2006 Name: Section:. (5 points) Circle the answer that gives the maximum number of different alleles that might exist for any one locus in a normal mammalian cell. A.
Exam Answers Biology 20 Sept. 20, 2006 Name: Section:. (5 points) Circle the answer that gives the maximum number of different alleles that might exist for any one locus in a normal mammalian cell. A.
Exploring Mendelian Genetics 11-3
 Exploring Mendelian Genetics 11- GENES are more complicated than Mendel thought Some traits have MORE than 2 allele choices = MULTIPLE ALLELE TRAIT http://www.eslkidstuff.com/images/tallshort.gif EX: blood
Exploring Mendelian Genetics 11- GENES are more complicated than Mendel thought Some traits have MORE than 2 allele choices = MULTIPLE ALLELE TRAIT http://www.eslkidstuff.com/images/tallshort.gif EX: blood
AP Biology. Extending Mendelian genetics. Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance. Incomplete dominance. Incomplete dominance.
 female / eggs Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance Extending Mendelian genetics Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each
female / eggs Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance Extending Mendelian genetics Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each
Chapter 9. Gene Interactions. As we learned in Chapter 3, Mendel reported that the pairs of loci he observed segregated independently
 Chapter 9 Gene Interactions Figure 9-1 The coat colour on this juvenile horse is called Bay Roan Tobiano. Bay is the brown base coat colour; Roan is the mixture of white hairs with the base coat, making
Chapter 9 Gene Interactions Figure 9-1 The coat colour on this juvenile horse is called Bay Roan Tobiano. Bay is the brown base coat colour; Roan is the mixture of white hairs with the base coat, making
11 3 Exploring Mendelian
 11 3 Exploring Mendelian 11-3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics Genetics 2 of 31 What is the principle of independent assortment? 3 of 31 The principle of independent assortment states that genes for different
11 3 Exploring Mendelian 11-3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics Genetics 2 of 31 What is the principle of independent assortment? 3 of 31 The principle of independent assortment states that genes for different
Patterns of Inheritance
 Patterns of Inheritance Learning Outcomes Explain the Laws of Segregation and of Independent Assortment and what features of meiosis they correspond to. Explain the terms gene, allele, dominant, recessive,
Patterns of Inheritance Learning Outcomes Explain the Laws of Segregation and of Independent Assortment and what features of meiosis they correspond to. Explain the terms gene, allele, dominant, recessive,
Biology Genetics Practice Quiz
 Biology Genetics Practice Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The table above shows information related to blood types. What genotype(s)
Biology Genetics Practice Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The table above shows information related to blood types. What genotype(s)
Chapter 9. Objectives. Table of Contents. Gregor Mendel. Gregor Mendel, continued. Section 1 Mendel s Legacy. Section 2 Genetic Crosses
 Fundamentals of Genetics Table of Contents Objectives Describe how Mendel was able to control how his pea plants were pollinated. Describe the steps in Mendel s experiments on true-breeding garden peas.
Fundamentals of Genetics Table of Contents Objectives Describe how Mendel was able to control how his pea plants were pollinated. Describe the steps in Mendel s experiments on true-breeding garden peas.
Biol 1408 : Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Biol 08 : Chapter Patterns of Inheritance We previously discussed mono - hybrid crosses The Experiment P generation (true-breeding parents) Purple flowers White flowers F generation All plants have purple
Biol 08 : Chapter Patterns of Inheritance We previously discussed mono - hybrid crosses The Experiment P generation (true-breeding parents) Purple flowers White flowers F generation All plants have purple
Complex inheritance of traits does not follow inheritance patterns described by Mendel.
 Section 2: Complex inheritance of traits does not follow inheritance patterns described by Mendel. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the differences
Section 2: Complex inheritance of traits does not follow inheritance patterns described by Mendel. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the differences
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.14 - MENDELIAN GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MENDEL S EXPERIMENT Gregor Mendel designed an experiment to study inheritance in pea plants. Character a feature that can be inherited, and shows variation between individuals
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MENDEL S EXPERIMENT Gregor Mendel designed an experiment to study inheritance in pea plants. Character a feature that can be inherited, and shows variation between individuals
Modified Mendelian Ratios Ch. 13
 Modified Mendelian Ratios Ch. 13 1. Multiple alleles (more than 2 alleles for gene in population) Example: Blood Groups Karl Landsteiner 1900 s Chromosome 9 I gene ABO blood system = polymorphic I gene
Modified Mendelian Ratios Ch. 13 1. Multiple alleles (more than 2 alleles for gene in population) Example: Blood Groups Karl Landsteiner 1900 s Chromosome 9 I gene ABO blood system = polymorphic I gene
Some Vocab. Genotype allele combination. Phenotype physical appearance
 Genetics Some Vocab. Genotype allele combination Capital letter = dominant allele Lowercase letter = recessive allele Ex AA, Aa, aa Phenotype physical appearance Ex green, yellow Some Vocab. Homozygous
Genetics Some Vocab. Genotype allele combination Capital letter = dominant allele Lowercase letter = recessive allele Ex AA, Aa, aa Phenotype physical appearance Ex green, yellow Some Vocab. Homozygous
Lecture 3 Monohybrid and Dihybrid Crosses
 THE MONOHYBRID CROSS Lecture 3 Monohybrid and Dihybrid Crosses FOLLOWING THE INHERITANCE OF ONE TRAIT Monohybrid cross Parents differ by a single trait. Crossing two pea plants that differ in stem size,
THE MONOHYBRID CROSS Lecture 3 Monohybrid and Dihybrid Crosses FOLLOWING THE INHERITANCE OF ONE TRAIT Monohybrid cross Parents differ by a single trait. Crossing two pea plants that differ in stem size,
#3: Random Fertilization. If DNA replication and cell division are both so precise, and so accurate, why are we all so unique??
 Today: Microbial Genetics Wrap-up Mendelian Genetics Adding Chromosomes to the Mix?? Tomorrow: UW Fieldtrip! Back to Eukaryotes: Bringing in Mendel If DNA replication and cell division are both so precise,
Today: Microbial Genetics Wrap-up Mendelian Genetics Adding Chromosomes to the Mix?? Tomorrow: UW Fieldtrip! Back to Eukaryotes: Bringing in Mendel If DNA replication and cell division are both so precise,
MENDELIAN GENETICS This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law.
 MENDELIAN GENETICS This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law. Gregor Mendel! 19 th century Austrian monk! Interested in heredity!
MENDELIAN GENETICS This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law. Gregor Mendel! 19 th century Austrian monk! Interested in heredity!
Extensions of Mendelism
 Chapter 4. Extensions of Mendelism 1. Allelic Variation and gene function 2. Gene action : from genotype to phenotype Allelic Variation and gene function Mendel's experiments established that genes can
Chapter 4. Extensions of Mendelism 1. Allelic Variation and gene function 2. Gene action : from genotype to phenotype Allelic Variation and gene function Mendel's experiments established that genes can
Mendelian Genetics. What is Gregor Mendel known for and what organism did he use? When did Mendel conduct most of his work?
 Mendelian Genetics What is Gregor Mendel known for and what organism did he use? When did Mendel conduct most of his work? What Mendel called particles are actually Define the following: Trait- Heredity-
Mendelian Genetics What is Gregor Mendel known for and what organism did he use? When did Mendel conduct most of his work? What Mendel called particles are actually Define the following: Trait- Heredity-
1/21/ Exploring Mendelian Genetics. What is the principle of independent assortment? Independent Assortment. Biology.
 Biology 1 of 31 11-3 Exploring Mendelian Exploring Genetics Mendelian Genetics 2 of 31 What is the principle of independent assortment? 3 of 31 1 The principle of independent assortment states that genes
Biology 1 of 31 11-3 Exploring Mendelian Exploring Genetics Mendelian Genetics 2 of 31 What is the principle of independent assortment? 3 of 31 1 The principle of independent assortment states that genes
Part I: Predicting Genetic Outcomes
 Part I: Predicting Genetic Outcomes Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in every cell of living organisms, and all of the cells in each organism contain the exact same copy of that organism s DNA. Because
Part I: Predicting Genetic Outcomes Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in every cell of living organisms, and all of the cells in each organism contain the exact same copy of that organism s DNA. Because
Course Overview. Interacting genes. Complementation. Complementation. February 15
 Course Overview Interacting genes http://www.erin.utoronto.ca/~w3bio/bio207/index.htm February 15 Outline Week Topic Chapter 1 Course objectives and Introduction to genetics Ch. 1 & Ch. 2 2 Human Pedigrees
Course Overview Interacting genes http://www.erin.utoronto.ca/~w3bio/bio207/index.htm February 15 Outline Week Topic Chapter 1 Course objectives and Introduction to genetics Ch. 1 & Ch. 2 2 Human Pedigrees
Crossing and Probabilities
 Let us review Crossing and Probabilities RR= homozygous dominant for Rr = homozygous recessive for white. P gen: RR x rr F1 gen: Rr F2 gen: Purple: 1RR, 2 Rr = total 3 Purple White : 1 rr = 1 total white
Let us review Crossing and Probabilities RR= homozygous dominant for Rr = homozygous recessive for white. P gen: RR x rr F1 gen: Rr F2 gen: Purple: 1RR, 2 Rr = total 3 Purple White : 1 rr = 1 total white
(A) Type AB only. (B) Type A or Type B only. (C) Type A, AB, and B only. (D) All four types are possible: type A, AB, B or O.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 02:Mendelian Genetics and its Extensions No. 1 of 10 1. In the case of a couple, where the husband has type A blood and the wife has type B, the blood types of their children should
Genetics - Problem Drill 02:Mendelian Genetics and its Extensions No. 1 of 10 1. In the case of a couple, where the husband has type A blood and the wife has type B, the blood types of their children should
Mendel & Inheritance. SC.912.L.16.1 Use Mendel s laws of segregation and independent assortment to analyze patterns of inheritance.
 Mendel & Inheritance SC.912.L.16.1 Use Mendel s laws of segregation and independent assortment Mendel s Law of Segregation: gene pairs separate when gametes (sex cells) are formed; each gamete as only
Mendel & Inheritance SC.912.L.16.1 Use Mendel s laws of segregation and independent assortment Mendel s Law of Segregation: gene pairs separate when gametes (sex cells) are formed; each gamete as only
 http://www.simonmawer.com/mendel's_garden.jpg 1 http://khzs.fme.vutbr.cz/iahrwg2009/img/map_cz.gif 2 http://www.haverford.edu/biology/meneely/brno.htm 3 http://biology.clc.uc.edu/fankhauser/travel/berlin/for_web/
http://www.simonmawer.com/mendel's_garden.jpg 1 http://khzs.fme.vutbr.cz/iahrwg2009/img/map_cz.gif 2 http://www.haverford.edu/biology/meneely/brno.htm 3 http://biology.clc.uc.edu/fankhauser/travel/berlin/for_web/
I.New Explanations of Inheritance A. Understanding Gene Function 1. Prokaryote gene regulation a. genes that code for enzymes
 I.New Explanations of Inheritance A. Understanding Gene Function 1. Prokaryote gene regulation a. genes that code for enzymes using lactose are expressed only when lactose is present b. Expression of this
I.New Explanations of Inheritance A. Understanding Gene Function 1. Prokaryote gene regulation a. genes that code for enzymes using lactose are expressed only when lactose is present b. Expression of this
Fall 2004 Animal Science 213 Animal Genetics EXAM Points Exam must be completed in INK!
 Fall 2004 Animal Science 213 Animal Genetics EXAM 3 125 Points Exam must be completed in INK! Name: KEY Multiple Choice (4 points each) 1. If an individual plant homozygous dominant for the single gene
Fall 2004 Animal Science 213 Animal Genetics EXAM 3 125 Points Exam must be completed in INK! Name: KEY Multiple Choice (4 points each) 1. If an individual plant homozygous dominant for the single gene
Mendel and the Gene Idea
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea Lectures
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea Lectures
Genetics is the study of inheritance The field of genetics began with the work of Gregor Mendel He had no knowledge of chromosomes, meiosis, or DNA
 Inheritance 1 Mendel and the Black Box 2 The Experimental Subjects: Pisum sativum 3 Starting the Experiments: Purple and White Flowers 4 Mendel s Generations Illustrated 5 Crosses Involving Two Characters
Inheritance 1 Mendel and the Black Box 2 The Experimental Subjects: Pisum sativum 3 Starting the Experiments: Purple and White Flowers 4 Mendel s Generations Illustrated 5 Crosses Involving Two Characters
Genetics: Mendelian Genetics (1) Patterns of Inheritance
 Genetics: Mendelian Genetics (1) Patterns of Inheritance Outline 1. Key concepts 2. A few terms 3. Mendel s Experimental Approach 4. Monohybrid 5. Dihybrid 6. Extending Medelian Genetics 7. Mendilian Inheritance
Genetics: Mendelian Genetics (1) Patterns of Inheritance Outline 1. Key concepts 2. A few terms 3. Mendel s Experimental Approach 4. Monohybrid 5. Dihybrid 6. Extending Medelian Genetics 7. Mendilian Inheritance
Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance
 Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance Modified from Kim Foglia Extending Mendelian genetics Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single
Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance Modified from Kim Foglia Extending Mendelian genetics Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single
Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits
 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits Solving a Genetic Mystery LIFE SCIENCE DISCIPLINARY CORE IDEAS Copyright Rebecca Rehder Wingerden Activity- Modeling Mendel s Peas STAMP Date Introduction:
Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits Solving a Genetic Mystery LIFE SCIENCE DISCIPLINARY CORE IDEAS Copyright Rebecca Rehder Wingerden Activity- Modeling Mendel s Peas STAMP Date Introduction:
Genetics. Ms. Gunjan M. Chaudhari
 Genetics Ms. Gunjan M. Chaudhari UNIT 1 Introduction to genetics Genetics:: The scientific study of heredity Heredity : The passing on of characteristics (traits) from parents to offspring Importance of
Genetics Ms. Gunjan M. Chaudhari UNIT 1 Introduction to genetics Genetics:: The scientific study of heredity Heredity : The passing on of characteristics (traits) from parents to offspring Importance of
Classical (Mendelian) Genetics. Gregor Mendel
 Classical (Mendelian) Genetics Gregor Mendel Vocabulary Genetics: The scientific study of heredity Allele: Alternate forms of a gene/factor. Genotype: combination of alleles an organism has. Phenotype:
Classical (Mendelian) Genetics Gregor Mendel Vocabulary Genetics: The scientific study of heredity Allele: Alternate forms of a gene/factor. Genotype: combination of alleles an organism has. Phenotype:
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel TEKS 6 Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected
Genetics & The Work of Mendel TEKS 6 Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected
Tuesday February 28 th! Unit 5 Test on Thurs Feb 9/Fri Feb 10 Quiz TODAY! Due: Blue People of Troublesome Creek Pedigree! Starter:
 Tuesday February 28 th! Unit 5 Test on Thurs Feb 9/Fri Feb 10 Quiz TODAY! Due: Blue People of Troublesome Creek Pedigree! Starter: 5.4 Complex Patterns of Heredity Today s Objectives: I can describe outcome
Tuesday February 28 th! Unit 5 Test on Thurs Feb 9/Fri Feb 10 Quiz TODAY! Due: Blue People of Troublesome Creek Pedigree! Starter: 5.4 Complex Patterns of Heredity Today s Objectives: I can describe outcome
Active Learning Exercise 8 Mendelian Genetics & the Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 8 Mendelian Genetics & the Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Reference: Chapter 14-15 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) Note: In addition to the
Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 8 Mendelian Genetics & the Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Reference: Chapter 14-15 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) Note: In addition to the
Biol 331 Genetics Exam 1a Fall 2016
 Biol 331 Genetics Exam 1a Fall 2016 Multiple Choice. (2points each) 1. An allele is. A. one of the bases in DNA B. an alternate form of a gene C. another term for epistasis D. present only in males and
Biol 331 Genetics Exam 1a Fall 2016 Multiple Choice. (2points each) 1. An allele is. A. one of the bases in DNA B. an alternate form of a gene C. another term for epistasis D. present only in males and
Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS USING TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum) SEEDLINGS
 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS USING TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum) SEEDLINGS By Dr. Elaine Winshell Updated and Revised by Dr. Susan Petro Objectives To apply Mendel s Law of Segregation To use Punnett squares
INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS USING TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum) SEEDLINGS By Dr. Elaine Winshell Updated and Revised by Dr. Susan Petro Objectives To apply Mendel s Law of Segregation To use Punnett squares
Chapter 14. Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea Overview: Drawing from the Deck of Genes What genetic principles account for the passing of traits from parents to offspring? The blending hypothesis is the idea that
Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea Overview: Drawing from the Deck of Genes What genetic principles account for the passing of traits from parents to offspring? The blending hypothesis is the idea that
Chapter 2 Mendelian Genetics
 Chapter 2 Mendelian Genetics Synopsis: The first part of Chapter 2 covers the basic principles of inheritance that can be summarized as Mendel s Laws of Segregation (for one gene) and Independent Assortment
Chapter 2 Mendelian Genetics Synopsis: The first part of Chapter 2 covers the basic principles of inheritance that can be summarized as Mendel s Laws of Segregation (for one gene) and Independent Assortment
Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Chapter 4 Mendel and the Gene Idea PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Chapter 4 Mendel and the Gene Idea PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Unit 10: Genetics. Chapter 9: Read P
 Unit 10: Genetics Chapter 9: Read P. 145-167 10.0 Genetics The Definition of Genetics The study of heredity and how traits are passed on through generations. Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics Gregor
Unit 10: Genetics Chapter 9: Read P. 145-167 10.0 Genetics The Definition of Genetics The study of heredity and how traits are passed on through generations. Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics Gregor
Lab Mendelian Genetics-Exploring Genetic Probability -Revisiting Mendel s Observations
 NAMES: (one packet per partner pair to be turned in) DATE: Lab Mendelian Genetics-Exploring Genetic -Revisiting Mendel s Observations Purpose: Students will 1. Learn that probability is strongly related
NAMES: (one packet per partner pair to be turned in) DATE: Lab Mendelian Genetics-Exploring Genetic -Revisiting Mendel s Observations Purpose: Students will 1. Learn that probability is strongly related
Genetics: the scientific study of heredity
 GENETICS 1 Mendel 1884) 2 Mendel Mendel was an Austrian monk who was in charge of the mo His work with pea plants has led to him being considered the Fath Genetics: the scientific study of heredity 3 Purple
GENETICS 1 Mendel 1884) 2 Mendel Mendel was an Austrian monk who was in charge of the mo His work with pea plants has led to him being considered the Fath Genetics: the scientific study of heredity 3 Purple
IN: Make a quick diagram of.. What GENETICS means to me. No words. Color.
 IN: Make a quick diagram of.. What GENETICS means to me. No words. Color. Variation and Distribution of Genetic Traits I. Mendel and Inheritance Patterns A. GREGOR MENDEL (1822-1884) - Father of Genetics
IN: Make a quick diagram of.. What GENETICS means to me. No words. Color. Variation and Distribution of Genetic Traits I. Mendel and Inheritance Patterns A. GREGOR MENDEL (1822-1884) - Father of Genetics
Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders)
 Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders) Chapter 2 Transmission Genetics 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Mendel performed many types of crosses, including those in which the same genotypes are crossed
Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders) Chapter 2 Transmission Genetics 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Mendel performed many types of crosses, including those in which the same genotypes are crossed
Chp 10 Patterns of Inheritance
 Chp 10 Patterns of Inheritance Dogs, one of human s longest genetic experiments Over 1,000 s of years, humans have chosen and mated dogs with specific traits. A process called -artificial selection The
Chp 10 Patterns of Inheritance Dogs, one of human s longest genetic experiments Over 1,000 s of years, humans have chosen and mated dogs with specific traits. A process called -artificial selection The
Phenotypic Expression & Multi-Factorial Traits (Learning Objectives)
 Phenotypic Expression & Multi-Factorial Traits (Learning Objectives) Understand and explain the factors affecting the phenotypic expression of Mendelian inheritance and provide examples for each: a) Lethal
Phenotypic Expression & Multi-Factorial Traits (Learning Objectives) Understand and explain the factors affecting the phenotypic expression of Mendelian inheritance and provide examples for each: a) Lethal
Chapter 14. Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea Gregor Mendel Gregor Mendel documented a particular mechanism for inheritance. Mendel developed his theory of inheritance several decades before chromosomes were observed
Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea Gregor Mendel Gregor Mendel documented a particular mechanism for inheritance. Mendel developed his theory of inheritance several decades before chromosomes were observed
Scrambling information
 Scrambling information Introduction to Genetics GENETICS branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation of organisms. Chromosomes carry the hereditary information (genes) Arrangement of nucleotides
Scrambling information Introduction to Genetics GENETICS branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation of organisms. Chromosomes carry the hereditary information (genes) Arrangement of nucleotides
Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance
 Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance 1 Extending Mendelian genetics Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each gene has only
Chapter 14. Beyond Mendel s Laws of Inheritance 1 Extending Mendelian genetics Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each gene has only
Review. 0 Genotype: alleles that are present 0 Phenotype: physical appearance. 0 If Red is dominant to white, what is the phenotype of the above?
 Review 0 Genotype: alleles that are present 0 Phenotype: physical appearance 0 Rr 0 RR 0 rr 0 If Red is dominant to white, what is the phenotype of the above? 2 Vocab to Remember! 0 Allele 0 Gene 0 Trait
Review 0 Genotype: alleles that are present 0 Phenotype: physical appearance 0 Rr 0 RR 0 rr 0 If Red is dominant to white, what is the phenotype of the above? 2 Vocab to Remember! 0 Allele 0 Gene 0 Trait
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.3 EXTENSIONS TO MENDELIAN INHERITANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT Independent Assortment is Mendel s Second Law Independent Assortment: States that alleles of two genes assort independently A dihybrid cross is used
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT Independent Assortment is Mendel s Second Law Independent Assortment: States that alleles of two genes assort independently A dihybrid cross is used
Why peas? Pea S by Mendel. F 1 generation
 Fig. 07.0 Mendelian Genetics Mendelian Genetics Outline I. Mendel s Ideas About Genetics. Experimental Design with garden peas 2. Monohybrid Crosses. Principle of Segregation 2. Principle of Dominance
Fig. 07.0 Mendelian Genetics Mendelian Genetics Outline I. Mendel s Ideas About Genetics. Experimental Design with garden peas 2. Monohybrid Crosses. Principle of Segregation 2. Principle of Dominance
EOC Review Reporting Category 2 Mechanisms of Genetics
 EOC Review Reporting Category 2 Mechanisms of Genetics The student will demonstrate an understanding of the mechanisms of genetics. Langham Creek High School 2012-2013 By PresenterMedia.com TEK 6A Identify
EOC Review Reporting Category 2 Mechanisms of Genetics The student will demonstrate an understanding of the mechanisms of genetics. Langham Creek High School 2012-2013 By PresenterMedia.com TEK 6A Identify
Codominant. Both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways.
 Codominant Both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. Codominance Alleles for a gene are both dominant Both alleles are expressed when present Examples: Roan cow or horse Codominance:
Codominant Both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. Codominance Alleles for a gene are both dominant Both alleles are expressed when present Examples: Roan cow or horse Codominance:
Two possible explanations for dominant mutations Haploinsufficiency vs Dominant negative
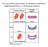 Two possible explanations for dominant mutations Haploinsufficiency vs Dominant negative Incomplete dominance for flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa R 1 R 1 R 2 R 2 R 1 R 2 R 1 Red pigment R 2 No pigment
Two possible explanations for dominant mutations Haploinsufficiency vs Dominant negative Incomplete dominance for flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa R 1 R 1 R 2 R 2 R 1 R 2 R 1 Red pigment R 2 No pigment
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
 Non-Mendelian Inheritance Objectives Predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and non-mendelian inheritance (TEKS 6F) Background Information
Non-Mendelian Inheritance Objectives Predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and non-mendelian inheritance (TEKS 6F) Background Information
Incomplete Dominance And Codominance Worksheet Answer Key
 Incomplete Dominance And Codominance Worksheet Answer Key INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE AND CODOMINANCE WORKSHEET ANSWER KEY PDF - Are you looking for incomplete dominance and codominance worksheet answer key Books?
Incomplete Dominance And Codominance Worksheet Answer Key INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE AND CODOMINANCE WORKSHEET ANSWER KEY PDF - Are you looking for incomplete dominance and codominance worksheet answer key Books?
Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders) Chapter 2 Transmission Genetics. 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/genetic-analysis-an-integrated-approach-2ndedition-sanders-test-bank/ Genetics:
Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/genetic-analysis-an-integrated-approach-2ndedition-sanders-test-bank/ Genetics:
OpenStax-CNX module: m Laws of Inheritance. OpenStax College. Abstract. By the end of this section, you will be able to:
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44479 1 Laws of Inheritance OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44479 1 Laws of Inheritance OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
. Definition The passing down of characteristics from generation to generation resulting in continuity and variation within a species
 Section 3: The Basics of genetics. Definition The passing down of characteristics from generation to generation resulting in continuity and variation within a species Important Terms. Genes A specific
Section 3: The Basics of genetics. Definition The passing down of characteristics from generation to generation resulting in continuity and variation within a species Important Terms. Genes A specific
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853 where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science
Genetics & The Work of Mendel He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853 where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science
Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders) Chapter 2 Transmission Genetics. 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders) Chapter 2 Transmission Genetics 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Mendel performed many types of crosses, including those in which the same genotypes are crossed
Genetics: An Integrated Approach (Sanders) Chapter 2 Transmission Genetics 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Mendel performed many types of crosses, including those in which the same genotypes are crossed
Genetics. The beginning Drawing from the deck of genes. From general observations it can been seen that there is variation in
 Genetics The beginning Drawing from the deck of genes Gregor Mendel Peas From general observations it can been seen that there is variation in characteristics amongst individuals in a population. What
Genetics The beginning Drawing from the deck of genes Gregor Mendel Peas From general observations it can been seen that there is variation in characteristics amongst individuals in a population. What
LECTURE 1 : GENETICS
 LECTURE 1 : GENETICS Introduction to Genetics and heredity Gregor Mendel Genetic terminology (glossary) Monohybrid crosses Patterns of inheritance Dihybrid crosses Test cross Introduction to Genetics GENETICS
LECTURE 1 : GENETICS Introduction to Genetics and heredity Gregor Mendel Genetic terminology (glossary) Monohybrid crosses Patterns of inheritance Dihybrid crosses Test cross Introduction to Genetics GENETICS
