Bacterial DNA replication
|
|
|
- Dortha McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1
2 Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Helicase Polymerase Core ssdna binding Remove +sc at fork (swivel) Decatenation Ligase Function Primase Primer removal Clamp loader Sliding clamp DnaB Primase (DnaG) pol I s 5-3 exo pol III (α, ε, θ subunits) γ complex β SSB gyrase topo IV E. coli DNA ligase SV40 (simian virus 40) T antigen pol α primase FEN 1 (also RNaseH) pol δ, ε RF-C PCNA RF-A topo I or topo II topo II DNA ligase I other model systems include bacteriophage T4 and yeast The ends of (linear) eukaryotic chromosomes cannot be replicated by the replisome. Not enough nucleotides for primase to start last lagging strand fragment Chromosome ends shorten every generation! 2
3 Telomere shortening signals trouble! Telomere binding proteins (TBPs) 1. Telomere shortening releases telomere binding proteins (TBPs) 2. Further shortening affects expression of telomereshortening sensitive genes 3. Further shortening leads to DNA damage and mutations. Telomerase replicates the ends (telomeres) Telomere ssdna Telomerase extends the leading strand! Synthesis is in the 5 -->3 direction. Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP). The enzyme contains RNA and proteins. The RNA templates DNA synthesis. The proteins include the telomerase reverse transcriptase TERT. 3
4 Telomerase cycles at the telomeres TERT protein Telomere ssdna TER RNA template Telomerase extends a chromosome 3 overhang 4
5 Conserved structures in TER and TERT Core secondary structures shared in ciliate and vertebrate telomerase RNAs (TERs). (Sequences highly variable.) nucleotides 1000s of nucleotides 1300 nucleotides TERT protein sequences conserved Starting and stopping summary 1. DNA replication is controlled at the initiation step. 2. DNA replication starts at specific sites in E. coli and yeast. 3. In E. coli, DnaA recognizes OriC and promotes loading of the DnaB helicase by DnaC (helicase loader) 4. DnaA and DnaC reactions are coupled to ATP hydrolysis. 5. Bacterial chromosomes are circular, and termination occurs opposite OriC. 6. In E. coli, the helicase inhibitor protein, Tus, binds 10 ter DNA sites to trap the replisome at the end. 7. Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear, and the chromosome ends cannot be replicated by the replisome. 8. Telomerase extends the leading strand at the end. 9. Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) with RNA (template) and reverse-transcriptase subunits. 5
6 DNA methods summary 1. Restriction enzymes cut at specific DNA sites. (N) 2. Vectors allow genes to be cloned and proteins expressed. (N) 3. Gel electrophoresis separates DNA on the basis of size. 4. DNAs can be synthesized (up to ~100 bases commercially). (N) 5. PCR amplifies any target DNA sequence. (N) 6. Genes and genomes can be sequenced by chain termination. (N) 7. Oligonucleotides can be used to change bases by site- directed mutagenesis. (N) 8. Southern blotting detects sequences by hybridization. 9. Microarrays detect gene expression patterns over the genome. 10. Genes can be knocked out (deleted) or replaced in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (N) Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sites 6
7 Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sites 3 types of ends: 5 overhang, blunt and 3 overhang Cognate methyl transferases protect host genome from digestion. Restriction-modification systems degrade foreign DNA. Average frequency of restriction sites in random DNA sequences Site size Average frequency 1/256 (1/4 x 1/4 x 1/4 x 1/4) 1/4,096 1/65,536 The average occurrence of each sequence = 1/4 n, where n = the site length and all bases are equally represented 7
8 Lots of different recognition sites known Core four bases Flanking bases None A----T C----G G----C T----A A simple cloning procedure 1. Cut insert and vector DNA with a restriction enzyme 2. Mix and join ends with DNA ligase. The ends should match for efficient ligation. 8
9 Cloning without DNA ligase Ligation-independent cloning Gateway cloning 1. Prepare open vector and insert with the same long sticky ends No dt in template T T + Pol I Klenow fragment + datp 2. Mix and let the ends anneal. A T T A A T T A 1. Prepare an insert flanked by sites for a site-specific DNA recombinase. 2. Mix insert with the closed vector containing the recipient recombination site and recombinase enzyme. E Transform the nicked plasmid. The plasmid is repaired in vivo. 3. (Have lunch.) Transform. Vectors allow DNA sequences to be cloned - 1 Ori + selectable marker + cloning site (polylinker) Phage λ for cloning big (7-25 kb) DNA pieces 9
10 Vectors allow DNA sequences to be cloned - 2 Shuttle vectors: move genes between organisms Expression vectors: Make your favorite protein Reporter genes: β-gal, GFP... Vectors allow DNA sequences to be cloned -3 Transient transfection: eukaryotes Stable transduction 10
11 Gel electrophoresis separates DNA on the basis of size Agarose: big fragments (>300 bp) Acrylamide: smaller fragments, higher resolution Mobility proportional to log MW. Chemical DNA synthesis Sequential rounds of coupling, oxidation and deprotection of the 5 OH build up the oligonucleotide
12 Chemical DNA synthesis Sequential rounds of coupling, oxidation and deprotection of the 5 OH build up the oligonucleotide. 3 5 Frontiers in DNA synthesis Currently: nucleotides routine (Assemble 5 kb) 10,000 = largest. Primer set for the human genome (30,000 genes) ~ $10 4 Goal 1: Make yeast chromosome 3: 300 kb without errors! (Jeff Boeke) Goal 2: Assemble 16 X 10 6 w/o errors for ~$1000 (George Church) 12
13 DNA sequencing by partial chain termination ddntps terminate the chain DNA sequencing by partial chain termination ddntps terminate the chain Small amount of ddgtp + excess dgtp partially terminates chains at Cs in the template 13
14 DNA sequencing by partial chain termination 1. All fragments start at the primer 2. All fragments ending in a particular base have a different length and a different color tag 3. Separating the mixture of products by size reveals the sequence. Two strategies for genome sequencing Hierarchical Shotgun Sequencing Sequencing 14
15 PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): isolate and amplify any DNA sequence Copies: N cycles amplifies the target sequence 2 N -fold. Site-directed mutagenesis 1. Anneal divergent mutagenic primers. 2. Replicate entire plasmid with a DNA pol lacking 5 -->3 exonuclease. 3. Select against parental strands. 15
16 Gene replacement in mice -- make donor cells 1. Insert drug markers into genome of ES cells 2. Select to enrich for homologous recombinants Neo r confers resistance to G-418. tk HSV confers sensitivity to ganciclovir. Check insertion site by Southern blotting Southern blotting detects DNA sequences by hybridization 1. Digest DNA using restriction enzyme(s) 2. Run gel 3. Transfer DNA from gel to (nitrocellulose) paper. 4. Denature DNA, hybridize probe DNA, and wash off excess probe. 5. Detect the probe on the paper. E.g. by autoradiography. Northern blotting detects RNA on the gel. 16
17 Microarrays detect expressed genes by hybridization Each spot has a different synthetic oligonucleotide complementary to a specific gene. 1. Label cdnas with red fluorophore in one condition and green fluorophore in another reference condition. 2. Mix red and green DNA and hybridize to a microarray. 3. Relative to the reference, Red=enriched, yellow = =, green = depleted. Gene replacement in mice -- germline incorporation Transgenic mice express a new gene Which mouse expresses extra copies of the growth hormone gene? 1. Inject ES cells into early embryos, 2. Transfer embryos to foster mother, 3. Breed chimeric mice and screen for progeny with mutant germ line, 4. Screen progeny DNA for mutation, 5. Mate heterozygotes (X+/X-), 6. Screen progeny DNA for KO genotype (X-/X-). Entire process takes a year. 17
18 Gene replacement in plants -- engineered crops E.g. Golden rice synthesizes β-carotene DNA methods summary 1. Restriction enzymes cut at specific DNA sites. (N) 2. Vectors allow genes to be cloned and proteins expressed. (N) 3. Gel electrophoresis separates DNA on the basis of size. 4. DNAs can be synthesized (up to ~100 bases commercially). (N) 5. PCR amplifies any target DNA sequence. (N) 6. Genes and genomes can be sequenced by chain termination. (N) 7. Oligonucleotides can be used to change bases by site- directed mutagenesis. (N) 8. Southern blotting detects sequences by hybridization. 9. Microarrays detect gene expression patterns over the genome. 10. Genes can be knocked out (deleted) or replaced in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (N) 18
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 26, 2005
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. January 25, 2006
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
 CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 24, 2005
 DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
Chapter 30. Replication. Meselson Stahl Experiment. BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2 Conceptual Mechanism of.
 BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three
BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three
Introducing new DNA into the genome requires cloning the donor sequence, delivery of the cloned DNA into the cell, and integration into the genome.
 Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
The replication forks Summarising what we know:
 When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
Biologia Genômica. 2º Semestre, Replicação de DNA em Bactérias e no Núcleo Eucariótico. Prof. Marcos Túlio
 Biologia Genômica 2º Semestre, 2017 Replicação de DNA em Bactérias e no Núcleo Eucariótico Prof. Marcos Túlio mtoliveria@fcav.unesp.br Faculdade de Ciências Agrárias e Veterinárias de Jaboticabal Instituto
Biologia Genômica 2º Semestre, 2017 Replicação de DNA em Bactérias e no Núcleo Eucariótico Prof. Marcos Túlio mtoliveria@fcav.unesp.br Faculdade de Ciências Agrárias e Veterinárias de Jaboticabal Instituto
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
CHAPTER 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY AND GENOMICS. Section A: DNA Cloning
 Section A: DNA Cloning 1. DNA technology makes it possible to clone genes for basic research and commercial applications: an overview 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA 3. Genes can
Section A: DNA Cloning 1. DNA technology makes it possible to clone genes for basic research and commercial applications: an overview 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA 3. Genes can
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA
 Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Recombinant DNA Technology
 History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
Learning Objectives :
 Learning Objectives : Understand the basic differences between genomic and cdna libraries Understand how genomic libraries are constructed Understand the purpose for having overlapping DNA fragments in
Learning Objectives : Understand the basic differences between genomic and cdna libraries Understand how genomic libraries are constructed Understand the purpose for having overlapping DNA fragments in
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis
 3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
Biochemistry. DNA Polymerase. Structure and Function of Biomolecules II. Principal Investigator
 Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Recombinant DNA Technology. The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology. yeast. Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology.
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
M Keramatipour 2. M Keramatipour 1. M Keramatipour 4. M Keramatipour 3. M Keramatipour 5. M Keramatipour
 Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication
 Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW
 AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
DNA replication. - proteins for initiation of replication; - proteins for polymerization of nucleotides.
 DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information
 Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Hershey & Chase Avery, MacLeod, & McCarty DNA: The Genetic Material
 DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
Replication. Obaidur Rahman
 Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
The Polymerase Chain Reaction. Chapter 6: Background
 The Polymerase Chain Reaction Chapter 6: Background Invention of PCR Kary Mullis Mile marker 46.58 in April of 1983 Pulled off the road and outlined a way to conduct DNA replication in a tube Worked for
The Polymerase Chain Reaction Chapter 6: Background Invention of PCR Kary Mullis Mile marker 46.58 in April of 1983 Pulled off the road and outlined a way to conduct DNA replication in a tube Worked for
Lecture 25 (11/15/17)
 Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
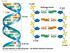 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
CHAPTER 08: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 08: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA technology Intentionally
CHAPTER 08: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA technology Intentionally
Cyclin- Dependent Protein Kinase. Function
 Complex Cyclin Cyclin- Dependent rotein Kinase Function promotes passage through restriction G1-CDK Complex Cyclin D CDK4 or CDK6 point in late G1 G1/S-CDK Complex Cyclin E CDK2 commits the cell to DA
Complex Cyclin Cyclin- Dependent rotein Kinase Function promotes passage through restriction G1-CDK Complex Cyclin D CDK4 or CDK6 point in late G1 G1/S-CDK Complex Cyclin E CDK2 commits the cell to DA
Directe d Mutagenesis
 Directe d Mutagenesis A Practical Approac h M. J. McPHERSON 1. Mutagenesis facilitated by the removal or introduction of unique restriction sites 1 P. Carte r 1. Introduction to site-directed mutagenesis
Directe d Mutagenesis A Practical Approac h M. J. McPHERSON 1. Mutagenesis facilitated by the removal or introduction of unique restriction sites 1 P. Carte r 1. Introduction to site-directed mutagenesis
Site-directed Mutagenesis
 Site-directed Mutagenesis Applications Subtilisin (Met à Ala mutation resistant to oxidation) Fluorescent proteins Protein structure-function Substrate trapping mutants Identify regulatory regions/sequences
Site-directed Mutagenesis Applications Subtilisin (Met à Ala mutation resistant to oxidation) Fluorescent proteins Protein structure-function Substrate trapping mutants Identify regulatory regions/sequences
DNA Technology. B. Using Bacteria to Clone Genes: Overview:
 DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
Molecular Biology and Genetics. Prof. Mohammad El-Khateeb Dr. Mamoun Ahram
 Molecular Biology and Genetics Prof. Mohammad El-Khateeb Dr. Mamoun Ahram Curriculum (Part I: molecular biology) DNA and RNA structures Restriction endonucleases and their applications (RFLP and cloning)
Molecular Biology and Genetics Prof. Mohammad El-Khateeb Dr. Mamoun Ahram Curriculum (Part I: molecular biology) DNA and RNA structures Restriction endonucleases and their applications (RFLP and cloning)
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
Replication of DNA Virus Genomes. Lecture 7 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2013
 Replication of DNA Virus Genomes Lecture 7 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2013 It s all about Initiation Problems faced by DNA replication machinery Viruses must replicate their genomes to make new progeny
Replication of DNA Virus Genomes Lecture 7 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2013 It s all about Initiation Problems faced by DNA replication machinery Viruses must replicate their genomes to make new progeny
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology. 10/1/ MDufilho
 Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology 10/1/2017 1 MDufilho The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology? Recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) technology Intentionally modifying
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology 10/1/2017 1 MDufilho The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology? Recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) technology Intentionally modifying
DNA Technology. Asilomar Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg
 DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
Viral DNA replication
 Viral DNA replication Lecture 8 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2017 The more the merrier --ANONYMOUS Viral DNA genomes must be replicated to make new progeny Parvovirus Retrovirus Poliovirus VII Hepatitis
Viral DNA replication Lecture 8 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2017 The more the merrier --ANONYMOUS Viral DNA genomes must be replicated to make new progeny Parvovirus Retrovirus Poliovirus VII Hepatitis
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
AP Biology. Chapter 20. Biotechnology: DNA Technology & Genomics. Biotechnology. The BIG Questions. Evolution & breeding of food plants
 What do you notice about these phrases? radar racecar Madam I m Adam Able was I ere I saw Elba a man, a plan, a canal, Panama Was it a bar or a bat I saw? Chapter 20. Biotechnology: DNA Technology & enomics
What do you notice about these phrases? radar racecar Madam I m Adam Able was I ere I saw Elba a man, a plan, a canal, Panama Was it a bar or a bat I saw? Chapter 20. Biotechnology: DNA Technology & enomics
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
Friday, April 17 th. Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation. AP Biology
 Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
September 19, synthesized DNA. Label all of the DNA strands with 5 and 3 labels, and clearly show which strand(s) contain methyl groups.
 KEY DNA Replication and Mutation September 19, 2011 1. Below is a short DNA sequence located on the E. coli chromosome. In class we talked about how during the process of DNA replication, an enzyme adds
KEY DNA Replication and Mutation September 19, 2011 1. Below is a short DNA sequence located on the E. coli chromosome. In class we talked about how during the process of DNA replication, an enzyme adds
Unit 6: Gene Activity and Biotechnology
 Chapter 16 Outline The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Level 1 Items students should be able to: 1. Recognize scientists and the experiments that lead to the understanding of the molecular basis of inheritance.
Chapter 16 Outline The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Level 1 Items students should be able to: 1. Recognize scientists and the experiments that lead to the understanding of the molecular basis of inheritance.
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
Synthetic Biology for
 Synthetic Biology for Plasmids and DNA Digestion Plasmids Plasmids are small DNA molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA They are most commonly found as double stranded, circular DNA Typical plasmids
Synthetic Biology for Plasmids and DNA Digestion Plasmids Plasmids are small DNA molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA They are most commonly found as double stranded, circular DNA Typical plasmids
Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases
 nature methods Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases Daniel G Gibson, Lei Young, Ray-Yuan Chuang, J Craig Venter, Clyde A Hutchison III & Hamilton O Smith Supplementary figures
nature methods Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases Daniel G Gibson, Lei Young, Ray-Yuan Chuang, J Craig Venter, Clyde A Hutchison III & Hamilton O Smith Supplementary figures
Covalently bonded sugar-phosphate backbone with relatively strong bonds keeps the nucleotides in the backbone connected in the correct sequence.
 Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis
 CSS451 CSS/HRT 451 Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis Chapter 4-5 T-DNA LB auxin cytokin opine Oncogenic genes RB vir genes ori opine catabolism Guo-qing Song Part 1 Basic principles Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis
CSS451 CSS/HRT 451 Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis Chapter 4-5 T-DNA LB auxin cytokin opine Oncogenic genes RB vir genes ori opine catabolism Guo-qing Song Part 1 Basic principles Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA
 Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR
 DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications
 Chapter Outline Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications Section 1: The Human Genome KEY IDEAS > Why is the Human Genome Project so important? > How do genomics and gene technologies affect
Chapter Outline Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications Section 1: The Human Genome KEY IDEAS > Why is the Human Genome Project so important? > How do genomics and gene technologies affect
BIOTECHNOLOGY OLD BIOTECHNOLOGY (TRADITIONAL BIOTECHNOLOGY) MODERN BIOTECHNOLOGY RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY.
 BIOTECHNOLOGY Biotechnology can be defined as the use of micro-organisms, plant or animal cells or their components or enzymes from organisms to produce products and processes (services) useful to human
BIOTECHNOLOGY Biotechnology can be defined as the use of micro-organisms, plant or animal cells or their components or enzymes from organisms to produce products and processes (services) useful to human
Initiation of Replication. This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication.
 Initiation of Replication This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication. Replicons and origins of replication The unit of DNA replication
Initiation of Replication This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication. Replicons and origins of replication The unit of DNA replication
Chapter 17. PCR the polymerase chain reaction and its many uses. Prepared by Woojoo Choi
 Chapter 17. PCR the polymerase chain reaction and its many uses Prepared by Woojoo Choi Polymerase chain reaction 1) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): artificial amplification of a DNA sequence by repeated
Chapter 17. PCR the polymerase chain reaction and its many uses Prepared by Woojoo Choi Polymerase chain reaction 1) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): artificial amplification of a DNA sequence by repeated
The GeneEditor TM in vitro Mutagenesis System: Site- Directed Mutagenesis Using Altered Beta-Lactamase Specificity
 Promega Notes Magazine Number 62, 1997, p. 02 The GeneEditor TM in vitro Mutagenesis System: Site- Directed Mutagenesis Using Altered Beta-Lactamase Specificity By Christine Andrews and Scott Lesley Promega
Promega Notes Magazine Number 62, 1997, p. 02 The GeneEditor TM in vitro Mutagenesis System: Site- Directed Mutagenesis Using Altered Beta-Lactamase Specificity By Christine Andrews and Scott Lesley Promega
Biotechnology and Genomics in Public Health. Sharon S. Krag, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Manipulating DNA. Nucleic acids are chemically different from other macromolecules such as proteins and carbohydrates.
 Lesson Overview 14.3 Studying the Human Genome Nucleic acids are chemically different from other macromolecules such as proteins and carbohydrates. Nucleic acids are chemically different from other macromolecules
Lesson Overview 14.3 Studying the Human Genome Nucleic acids are chemically different from other macromolecules such as proteins and carbohydrates. Nucleic acids are chemically different from other macromolecules
DNA Replication. Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow!
 DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
Some types of Mutagenesis
 Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Q1 (1 point): Explain why a lettuce leaf wilts when it is placed in a concentrated salt solution.
 Short questions 1 point per question. Q1 (1 point): Explain why a lettuce leaf wilts when it is placed in a concentrated salt solution. Answer: Water is sucked out of the cells by osmosis (this reduces
Short questions 1 point per question. Q1 (1 point): Explain why a lettuce leaf wilts when it is placed in a concentrated salt solution. Answer: Water is sucked out of the cells by osmosis (this reduces
DNA sequencing. Course Info
 DNA sequencing EECS 458 CWRU Fall 2004 Readings: Pevzner Ch1-4 Adams, Fields & Venter (ISBN:0127170103) Serafim Batzoglou s slides Course Info Instructor: Jing Li 509 Olin Bldg Phone: X0356 Email: jingli@eecs.cwru.edu
DNA sequencing EECS 458 CWRU Fall 2004 Readings: Pevzner Ch1-4 Adams, Fields & Venter (ISBN:0127170103) Serafim Batzoglou s slides Course Info Instructor: Jing Li 509 Olin Bldg Phone: X0356 Email: jingli@eecs.cwru.edu
Chapter 13 DNA The Genetic Material Replication
 Chapter 13 DNA The Genetic Material Replication Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944)
Chapter 13 DNA The Genetic Material Replication Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944)
Lecture 18. PCR Technology. Growing PCR Industry
 Lecture 18 PCR Technology Growing PCR Industry Basic PCR, Cloning of PCR product, RT-PCR, RACE, Quantitative PCR, Multiplex PCR, Hot start PCR, Touchdown PCR,PCR sequencing.. How PCR started The DNA duplex
Lecture 18 PCR Technology Growing PCR Industry Basic PCR, Cloning of PCR product, RT-PCR, RACE, Quantitative PCR, Multiplex PCR, Hot start PCR, Touchdown PCR,PCR sequencing.. How PCR started The DNA duplex
TRANSGENIC TECHNOLOGIES: Gene-targeting
 TRANSGENIC TECHNOLOGIES: Gene-targeting Reverse Genetics Wild-type Bmp7 -/- Forward Genetics Phenotype Gene or Mutations First Molecular Analysis Second Reverse Genetics Gene Phenotype or Molecular Analysis
TRANSGENIC TECHNOLOGIES: Gene-targeting Reverse Genetics Wild-type Bmp7 -/- Forward Genetics Phenotype Gene or Mutations First Molecular Analysis Second Reverse Genetics Gene Phenotype or Molecular Analysis
DNA The Genetic Material
 DNA The Genetic Material 2006-2007 Chromosomes related to phenotype T.H. Morgan working with Drosophila fruit flies associated phenotype with specific chromosome white-eyed male had specific X chromosome
DNA The Genetic Material 2006-2007 Chromosomes related to phenotype T.H. Morgan working with Drosophila fruit flies associated phenotype with specific chromosome white-eyed male had specific X chromosome
Building with DNA 2. Andrew Tolonen Genoscope et l'université d'évry 08 october atolonen at
 Building with DNA 2 Andrew Tolonen Genoscope et l'université d'évry 08 october 2014 atolonen at genoscope.cns.fr @andrew_tolonen www.tolonenlab.org Yesterday we talked about ways to assemble DNA building
Building with DNA 2 Andrew Tolonen Genoscope et l'université d'évry 08 october 2014 atolonen at genoscope.cns.fr @andrew_tolonen www.tolonenlab.org Yesterday we talked about ways to assemble DNA building
STRUCTURE AND DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS OF DNA
 STRUCTURE AND DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS OF DNA UNIVERSITY OF PAPUAN NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LECTURE
STRUCTURE AND DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS OF DNA UNIVERSITY OF PAPUAN NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LECTURE
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr.
 MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
Lecture 3 (FW) January 28, 2009 Cloning of DNA; PCR amplification Reading assignment: Cloning, ; ; 330 PCR, ; 329.
 Lecture 3 (FW) January 28, 2009 Cloning of DNA; PCR amplification Reading assignment: Cloning, 240-245; 286-87; 330 PCR, 270-274; 329. Take Home Lesson(s) from Lecture 2: 1. DNA is a double helix of complementary
Lecture 3 (FW) January 28, 2009 Cloning of DNA; PCR amplification Reading assignment: Cloning, 240-245; 286-87; 330 PCR, 270-274; 329. Take Home Lesson(s) from Lecture 2: 1. DNA is a double helix of complementary
7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Chapter 20: Biotechnology
 Chapter 20: Biotechnology 1. DNA Sequencing 2. DNA Cloning 3. Studying Gene Expression 4. Manipulating Genomes 5. herapeutic & Diagnostic echniques 1. DNA Sequencing Chapter Reading pp. 409-412 DNA Sequencing
Chapter 20: Biotechnology 1. DNA Sequencing 2. DNA Cloning 3. Studying Gene Expression 4. Manipulating Genomes 5. herapeutic & Diagnostic echniques 1. DNA Sequencing Chapter Reading pp. 409-412 DNA Sequencing
1. A brief overview of sequencing biochemistry
 Supplementary reading materials on Genome sequencing (optional) The materials are from Mark Blaxter s lecture notes on Sequencing strategies and Primary Analysis 1. A brief overview of sequencing biochemistry
Supplementary reading materials on Genome sequencing (optional) The materials are from Mark Blaxter s lecture notes on Sequencing strategies and Primary Analysis 1. A brief overview of sequencing biochemistry
T and B cell gene rearrangement October 17, Ram Savan
 T and B cell gene rearrangement October 17, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #9 Slide 1 of 28 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 (Last Friday): Structural features of the BCR and TCR
T and B cell gene rearrangement October 17, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #9 Slide 1 of 28 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 (Last Friday): Structural features of the BCR and TCR
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
Manipulation of Purified DNA
 Manipulation of Purified DNA To produce the recombinant DNA molecule, the vector, as well as the DNA to be cloned, must be cut at specific points and then joined together in a controlled manner by DNA
Manipulation of Purified DNA To produce the recombinant DNA molecule, the vector, as well as the DNA to be cloned, must be cut at specific points and then joined together in a controlled manner by DNA
Biotechnology. Chapter 13
 Biotechnology Chapter 13 Genetic Changes Humans have been changing the genetics of other species for thousands of years Artificial selection of plants and animals Tomato plants look nothing like their
Biotechnology Chapter 13 Genetic Changes Humans have been changing the genetics of other species for thousands of years Artificial selection of plants and animals Tomato plants look nothing like their
DNA Replication. The Organization of DNA. Recall:
 Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
Cat # Box1 Box2. DH5a Competent E. coli cells CCK-20 (20 rxns) 40 µl 40 µl 50 µl x 20 tubes. Choo-Choo Cloning TM Enzyme Mix
 Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual
 XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual An RNA-guided recombinant endonuclease for efficient targeted DNA cleavage Catalog Numbers CE1000-50K, CE1000-50, CE1000-250, CE1001-250, CE1001-1000 Table of
XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual An RNA-guided recombinant endonuclease for efficient targeted DNA cleavage Catalog Numbers CE1000-50K, CE1000-50, CE1000-250, CE1001-250, CE1001-1000 Table of
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review
 AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still
The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still
Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template.
 Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template. Fengtao Luo 1, Xiaolan Du 1, Tujun Weng 1, Xuan Wen 1, Junlan Huang 1, Lin Chen 1 Running title: Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis
Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template. Fengtao Luo 1, Xiaolan Du 1, Tujun Weng 1, Xuan Wen 1, Junlan Huang 1, Lin Chen 1 Running title: Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
