Higher National Unit specification General information Unit title: Unit code: Superclass: Publication date: Source: Version: Unit purpose Outcomes
|
|
|
- Juliana Harrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H92E 35 Superclass: RH Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is designed to enable learners to understand the principles underlying immunological techniques, and to develop an understanding of how antibodies are produced in vivo and their use in diagnostics and research. Learners will also develop practical skills in techniques relevant to immunology. The Unit is suitable for learners studying at HND level, and will provide the necessary underpinning knowledge and skills to enable progression to further study of immunology at degree level or to seek employment in science based industries. Outcomes On successful completion of the Unit the learner will be able to: 1 Describe and explain the principles of acquired immunity. 2 Explain the procedures used in the production of polyclonal and monoclonal antisera. 3 Explain the underlying principles of immunological techniques and their use in diagnostics and research. 4 Perform practical experiments related to immunology. Credit points and level 1 Higher National Unit credit at SCQF level 8: (8 SCQF credit points at SCQF level 8) H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 1
2 Higher National Unit specification: General information (cont) Recommended entry to the Unit Entry is at the discretion of the centre, however it is recommended that learners should have completed the HN Units H92W 33 Fundamental Chemistry: An Introduction and H Cell Biology: Theory and Laboratory Skills or equivalent. Core Skills Achievement of this Unit gives automatic certification of the following Core Skills component: Complete Core Skill None Core Skill component Critical Thinking at SCQF level 6 There are also opportunities to develop aspects of Core Skills which are highlighted in the Support Notes of this Unit specification. Context for delivery If this Unit is delivered as part of a Group Award, it is recommended that it should be taught and assessed within the subject area of the Group Award to which it contributes. The Assessment Support Pack (ASP) for this Unit provides assessment and marking guidelines that exemplify the national standard for achievement. It is a valid, reliable and practicable assessment. Centres wishing to develop their own assessments should refer to the ASP to ensure a comparable standard. A list of existing ASPs is available to download from SQA s website ( Equality and inclusion This Unit specification has been designed to ensure that there are no unnecessary barriers to learning or assessment. The individual needs of learners should be taken into account when planning learning experiences, selecting assessment methods or considering alternative evidence. Further advice can be found on our website H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 2
3 Higher National Unit specification: Statement of standards Acceptable performance in this Unit will be the satisfactory achievement of the standards set out in this part of the Unit specification. All sections of the statement of standards are mandatory and cannot be altered without reference to SQA. Where evidence for Outcomes is assessed on a sample basis, the whole of the content listed in the Knowledge and/or Skills section must be taught and available for assessment. Learners should not know in advance the items on which they will be assessed and different items should be sampled on each assessment occasion. Outcome 1 Describe and explain the principles of acquired immunity. Knowledge and/or Skills Role of T cell lymphocytes in activating B lymphocytes Role of B lymphocytes in the production of antibodies Structure and function of the components of antibodies Properties of an antigen and an immunogen Binding between antibody and antigen with reference to valency, specificity, affinity/avidity and factors affecting binding equilibrium Outcome 2 Explain the procedures used in the production of polyclonal and monoclonal antisera. Knowledge and/or Skills Principle of immunisation Choice of animal available for production of antisera Need for immunisation schedules Use of adjuvants Formation and selection of hybridoma cells in monoclonal antibody production Outcome 3 Explain the underlying principles of immunological techniques and their use in diagnostics and research. Knowledge and/or Skills Principles and uses of precipitation reactions Principles and uses of agglutination reactions Basic principles of immunoassay design: solid phase, choice of primary antibody and secondary antibody-enzyme conjugates, detection methods Principles and uses of immunoassays using labelled antibodies or antigens H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 3
4 Higher National Unit specification: Statement of standards (cont) Outcome 4 Perform practical experiments related to immunology. Knowledge and/or Skills Immunology experiments Working safely, within current health and safety regulations Consistent and accurate results Recording observations and results Evaluation skills Result analysis and conclusions Evidence Requirements for this Unit Written and/or oral recorded evidence for Outcomes 1 3 should be assessed using a holistic closed-book assessment under supervised conditions. The assessment will use a sampling approach to the Knowledge and/or Skills as detailed below. It is recommended that the assessment should be completed within 90 minutes. Written and/or oral recorded evidence for Outcome 4 should be assessed by production of a full laboratory report, or by completion of an appropriate pro forma. An assessor s observation checklist could be used to record performance evidence of practical experiments. Outcome 1 The assessment will sample three of the five Knowledge and/or Skills items. Learners will not have prior knowledge of which items are being assessed. Those items which are not sampled must be covered in the alternative (re-sit) assessment. Where an item is sampled, a leaner s response will be judged satisfactory where the evidence shows that the learner can: Explain the role of T cell lymphocytes in activating B lymphocytes. Explain the role of B lymphocytes in the production of antibodies. Explain the function of the structural components of antibodies. Describe the properties of an antigen and an immunogen. Describe the binding between antibody and antigen with reference to either valency, specificity, affinity/avidity or factors affecting binding equilibrium. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 4
5 Higher National Unit specification: Statement of standards (cont) Outcome 2 The assessment will sample three of the five Knowledge and/or Skills items. Learners will not have prior knowledge of which items are being assessed. Those items which are not sampled must be covered in the alternative (re-sit) assessment. Where an item is sampled, a leaner s response will be judged satisfactory where the evidence shows that the learner can: Explain the principle of immunisation (primary and secondary response). Explain why a particular animal is chosen for the production of antisera. Explain why a particular immunisation schedule is chosen. Explain why certain adjuvants are chosen. Describe how hybridoma cells are formed and selected in monoclonal antibody production. Outcome 3 The assessment will sample three of the four Knowledge and/or Skills items. Learners will not have prior knowledge of which items are being assessed. Those items which are not sampled must be covered in the alternative (re-sit) assessment. Where an item is sampled, a leaner s response will be judged satisfactory where the evidence shows that the learner can: Explain the principles and uses of precipitation reactions. Explain the principles and uses of agglutination reactions. Explain the choice of the different solid phases, the choice of primary antibody, secondary antibody-enzyme conjugates, and the different detection methods used in immunoassays. Explain the principles and uses of immunoassays using labelled antibodies or antigens. Outcome 4 Learners will perform a minimum of one practical experiment, the content of which will be related to Outcome 3. A learner s response will be judged satisfactory where the evidence shows that the learner can achieve all of the following: Plan and perform experiments related to immunological techniques. Work in a safe manner regarding current health and safety regulations. Achieve consistent and accurate results. Record experimental observations and results clearly and accurately. Evaluate validity of results in terms of sources of and values of experimental errors. Analyse results correctly and state valid conclusions. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 5
6 Higher National Unit specification: Statement of standards (cont) An assessor observation checklist will be used to record the learner s planning and performance of the practical work in line with health and safety requirements. Learners should complete a laboratory diary throughout the practical experiments. Learners must report the practical experiments by production of a full laboratory report. Where a learner does not perform an assessed practical experiment to the required standard, they will be given the chance to either reattempt the same practical experiments, or to undertake a different practical experiment of similar complexity. Where a laboratory report does not meet the required standard, then the learner will be given a single opportunity to re-draft. If the required standard is still not attained, then an alternative practical experiment will be set. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 6
7 Higher National Unit Support Notes Unit Support Notes are offered as guidance and are not mandatory. While the exact time allocated to this Unit is at the discretion of the centre, the notional design length is 40 hours. Guidance on the content and context for this Unit This Unit is intended as part of the framework for HND Applied Biological Sciences but may be suitable for inclusion in other HN Science awards. It is designed to develop the theoretical and practical aspects of immunological techniques, and to enable an understanding of the way antibodies are produced in vivo, how polyclonal and monoclonal antiserum is prepared and how these antibodies are used in different types of immunoassays. Outcome 1 Describe and explain the principles of aquired immunity General overview of the immune system including innate and acquired immune response. T cell types (helper and killer T cells) and their activation by antigen presenting cells. T cell-dependant B cell activation to produce plasma cells and memory cells. Clonal selection and expansion. Role of cytokine in B and T cell regulation. Structure of antibodies: light and heavy chains, antigen binding sites at F(ab), Fc linked to effector function, variable and constant domains, hinge region, diversity of hypervariable region (VDJ rearrangement) and affinity maturation, isotypes of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgE, IgD, IgG, IgM) and valency of these isotypes. Antigen and epitope definition, properties of B cell and T cell recognised epitopes. Immunogenicity of antigens: foreignness to host, molecular size, chemical composition and degradability of protein. Binding between antibody and antigen: non-covalent forces involved, definition of and difference between affinity and avidity, antibody specificity and cross-reactivity, effect of temperature, ph, concentration and time on antibody-antigen binding equilibrium. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 7
8 Higher National Unit Support Notes (cont) Outcome 2 Explain the procedures used in the production of polyclonal and monoclonal antisera Immunisation: differences in antibody production between primary and secondary response, preparation of vaccine: methods of making haptens immunogenic using carriers, use of adjuvants in animals (Freund s complete and incomplete adjuvant). Choice of animal and methods to obtain antisera from them, need for Home Office licence for animal experiments, immunisation schedules (boosters, timings of immunisations). Formation of hybridoma cells: isolation of B cells, use of PEG to fuse with myeloma cells. Selection of hybridoma cells: use of HAT medium, role of each component within HAT medium. Screening of hybridomas for monoclonal antibodies: use of ELISA. Outcome 3 Explain the underlying principles of immunological techniques and their use in diagnostics and research Precipitation reaction: principles of antigen excess, antibody excess and equivalence. Precipitation assays: Single Radial Immunodiffusion and/or Ouchterlony. Agglutination reaction: interaction between antibody and particular antigen, prozone effect. Agglutination assays: haemagglutination/blood typing, passive and indirect agglutination, agglutination inhibition. Basic principles of immunoassay design. Solid phase: paramagnetic beads, polystyrene plates, glass fibre matrix. Primary antibody detecting antigen: monoclonal or polyclonal. Secondary antibody-enzyme conjugates: choice of secondary antibodies to bind primary antibody. Enzyme conjugate: Horse Radish Peroxidase, Alkaline Phosphatase, betagalactosidase, Biotin. Substrates: TMB, pnpp. Types of detection: Chromogenic/Colourimetric, Chemiluminescence, Fluorescence, Radioactivity. Types of assays: competitive, non-competitive, homogenous, and heterogeneous. Link these definitions to appropriate immunoassays from list below. Principles of labelled antibody assays: the principles underlying ELISA (direct, indirect, sandwich and competitive), Western Blotting and Immunofluorescence microscopy (direct versus indirect method with fluorochrome labelled antibodies using light microscopy). H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 8
9 Higher National Unit Support Notes (cont) Labelled antibody assays: the uses of techniques applying labelled antibodies and antigens are extremely widespread and examples should be chosen with consideration of the background and aspirations of the learner. Examples might include: diagnostic kits using RIA, EIA eg ELISA for screening of hybridoma supernatants or MEIA; Tuberculosis test using ELISPOT assay, drug testing using FPIA; disease marker detection by Flow cytometry, diagnostic tests using Immunofluorescence microscopy. Summary of uses of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies: protein purification (affinity chromatography), tumour detection, tumour killing, diagnostic kits, research applications, food industry applications. Outcome 4 Perform practical experiments related to immunology Guidance on suitable practical experiments for assessment purposes is given elsewhere in this document. However, it is envisaged that learners will also participate in a range of other practical experiments which will both develop their laboratory skills and support the theory covered in Outcome 3. In carrying out such activities, learners should follow Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and carry out or be familiar with the risk and Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) assessments on all procedures undertaken. Opportunities should be taken to develop awareness of the sources of experimental error and of the accuracy of measurements, with quantification of errors where possible. Guidance on approaches to delivery of this Unit Outcomes 1 4 would best be delivered in order. However, to understand the principles of immunoassays in Outcome 3, it would be beneficial to support the learning by incorporating several practical experiments and hands-on simulations. It is envisaged that delivery of Outcome 1 could commence with a general overview of the response of the innate and adaptive immune system to an infection with bacteria or virus. The main cellular players of both immune systems (eg T helper cells, B cells, macrophages, platelets) can be introduced using cut-outs and playing out the processes of inflammation. The humoral immune response could then be covered, starting with the activation of T helper cells through antigen presenting cells, eg macrophages, leading to the subsequent activation of B cells and antibody production. Learners should be aware of the general structure of the IgG antibody with specific emphasis on the structure and function of the antigen binding sites, and this could be introduced through model building. At this level, only a limited explanation of the VDJ rearrangement and affinity maturation (with emphasis on the development from IgM affinity to IgG affinity) should be given to explain the variety of antigen binding sites of B cell receptors/antibodies. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 9
10 Higher National Unit Support Notes (cont) Delivery of the topic antigen and immunogen could include comparing different infectious and non-infectious agents in regards to their antigenicity and immunogenicity. The antibody-antigen equilibrium should be introduced using the reversible chemical equation between antigen and antibody as well as the equilibrium constant. The effects of temperature, ph, concentration and time on antibody-antigen binding equilibrium should be briefly covered to show their importance in immunoassay design. Outcome 2 is intended to give a brief introduction to the topic of immunisation and vaccine design in order to raise polyclonal antibodies in animals. Therefore it is suggested to only focus on Freund s complete and Freund s incomplete adjuvants and the way their components contribute to a greater vaccine efficiency. The procedure of making monoclonal antibodies must be covered in great detail. This should include the role of each component within HAT medium and PEG in cell fusion. The screening of hybridoma supernatants for the correct antibodies with ELISA could be mentioned at this stage, but ELISA should be described in detail in Outcome 3. It is envisaged that Outcome 3 commences with the more basic homogenous techniques of precipitation and agglutination to promote understanding of large (visible) antibody-antigen lattices forming in equivalence zone. The understanding of the principles can be supported by incorporating practical experiments like the Ouchterlony test or blood typing. Moving on from these cheaper, more time-consuming techniques learners could be introduced to the basic setup of modern immunoassays, leading on to principles of ELISA, Western Blotting and Immunofluorescence. It is recommended to emphasise the choices the learners will have to make when designing an immunoassay: direct versus indirect assay, homogenous versus heterogeneous assay, competitive versus non-competitive assay. Learners should discuss which of these types of assays leads to greater signal amplification/ sensitivity, is less time-consuming and comes with greater cost. Immunoassay development is a fast moving field. Therefore newer assays like FPIA could be introduced beside classical ones like ELISA to show parallels and differences. It is envisaged to conclude the Outcome with internet research on uses of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies in assays used in a research, clinical, diagnostic or food industry setting. A visit to a local company or NHS laboratory using these types of immunoassays would demonstrate their practical applications. It is envisaged that Outcome 4 will be delivered alongside the theoretical based Outcome 3. A range of practical experiments could be utilised to both support understanding of the underlying theory and to prepare learners for undertaking the assessed practical experiments. Aspects suitable for experimental investigation might include Serial Radial Immunodiffusion to detect IgA in saliva, Ouchterlony test, Haemagglutination, Western Blotting and SAPS Botrytis ELISA. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 10
11 Higher National Unit Support Notes (cont) Guidance on approaches to assessment of this Unit Evidence can be generated using different types of assessment. The following are suggestions only. There may be other methods that would be more suitable to learners. Outcomes 1 3 could be assessed by a single holistic closed-book assessment with an appropriate cut-off score that covers the sampling requirements as detailed in the Evidence Requirements. Assessment should be carried out in supervised conditions, and it is recommended that the assessment be completed within 90 minutes. Where evidence of Outcomes 1 3 is assessed by sampling, the whole of the content listed in the Knowledge and/or Skills must be taught and available for assessment. Learners should not know in advance the items on which they will be assessed, and different items should be sampled on each assessment occasion. Any items not sampled in the first assessment, must be included in the alternative (re-sit) assessment. In Outcome 4 learners are required to undertake one assessed practical experiment, the content of which will be related to Outcome 3. Examples of suitable experiments are given below. However, this list is not prescriptive, and other practical experiments of similar complexity may be used by the centre. Suitable practical experiments for Outcome 3 are: Serial Radial Immunodiffusion to detect IgA in saliva Ouchterlony test Haemagglutination Western Blotting SAPS Botrytis ELISA Assessed practical experiments will usually be performed individually. However, there may be some experiments that are suitable to be undertaken in pairs or small groups. If this is the case then the assessor should ensure that all participants are actively involved and are able to adequately demonstrate the required skills. An exemplar instrument of assessment with marking guidelines has been produced to indicate the national standard of achievement at SCQF level 8. Centres are reminded that prior verification of centre-devised assessments would help to ensure that the national standard is being met. Where learners experience a range of assessment methods, this helps them to develop different skills that should be transferable to work or further and higher education. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 11
12 Higher National Unit Support Notes (cont) Opportunities for e-assessment E-assessment may be appropriate for some assessments in this Unit. By e-assessment we mean assessment which is supported by Information and Communication Technology (ICT), such as e-testing or the use of e-portfolios or social software. Centres which wish to use e-assessment must ensure that the national standard is applied to all learner evidence and that conditions of assessment as specified in the Evidence Requirements are met, regardless of the mode of gathering evidence. The most up-to-date guidance on the use of e-assessment to support SQA s qualifications is available at Opportunities for developing Core and other essential skills The delivery and assessment of this Unit will provide learners with the opportunity to develop the Core Skills of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) at SCQF level 4, Numeracy at SCQF level 5 and Problem Solving at SCQF level 6. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Providing/Creating Information at SCQF level 4 Learners will make effective and appropriate use of ICT packages to produce a laboratory report in an appropriate format. Packages used will likely include word processing, spreadsheets, and graph drawing software. Learners will also be required to utilise internet search engines to source information on research topics. Numeracy Using Number at SCQF level 5 In context with the immunoassay practical experiment learners might be required to solve simple equations and perform data analysis, eg calculation of ring area and line of best fit. Problem Solving Reviewing and Evaluating at SCQF level 6 Following assessed practical experiments learners will be required to review and evaluate the effectiveness of the exercise with a thorough interpretation of random and systematic sources or error. Learners will be required to reach sound conclusions on the basis of the data collected and the inherent errors. Sustainability Sustainability can be embedded in delivery of the Unit in a variety of ways. For example, by encouraging minimum usage, correct disposal procedures and possible recycling during practical experiments. Citizenship Citizenship will be encouraged by developing learners who are scientifically literate on topics such as the use of animals in research. This will enable learners to make effective choices and contributions to public debates on the issue. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 12
13 This Unit has the Critical Thinking components of Problem Solving embedded in it. This means that when candidates achieve the Unit, their Core Skills profile will also be updated to show they have achieved Critical Thinking at SCQF level 6 H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 13
14 History of changes to Unit Version Description of change Date 02 Core Skills Component Critical Thinking at SCQF level 6 embedded July 2015 Scottish Qualifications Authority 2015 This publication may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational purposes provided that no profit is derived from reproduction and that, if reproduced in part, the source is acknowledged. Additional copies of this Unit specification can be purchased from the Scottish Qualifications Authority. Please contact the Business Development and Customer Support team, telephone H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 14
15 General information for learners This section will help you decide whether this is the Unit for you by explaining what the Unit is about, what you should know or be able to do before you start, what you will need to do during the Unit and opportunities for further learning and employment. This is a 1 credit Unit at SCQF level 8, which you are likely to be studying as part of the second year of an HND Science programme. Before progressing to this Unit it would be beneficial to have completed the HN Units H92W 33 Fundamental Chemistry: An Introduction and H Cell Biology: Theory and Laboratory Skills. This Unit will provide you with the underpinning knowledge to understand how polyclonal and monoclonal antisera are produced and how they have their applications in some of the most common immunological techniques used in a wide variety of research, clinical and industrial laboratories. Emphasis is on you being provided with the opportunity to gain hands-on experience of some of these techniques. On completion of the Unit you should be able to: 1 Describe and explain the principles of acquired immunity. 2 Explain the procedures used in the production of polyclonal and monoclonal antisera. 3 Explain the underlying principles of immunological techniques and their use in diagnostics and research. 4 Perform practical experiments related to immunology. Outcome 1 In this Outcome you will find out how B and T-lymphocytes are involved in the production of polyclonal antibodies and you will learn about the structure and diverse functions of these antibodies. You will also discover the reasons why some molecules (antigens) are very good at causing the production of antibodies whereas other molecules are not. Finally, you will learn about the optimal conditions for an antigen and an antibody to bind to each other. Outcome 2 In this Outcome you will explore how immunisation works and the methods used to produce polyclonal antiserum and monoclonal antibodies. You will find out how the production of maximal antibody amounts is achieved using different animals and vaccine designs. Outcome 3 In this Outcome you will be given information about the underlying principles of a variety of immunological techniques such as precipitation, agglutination and immunoassays involving labelled antibodies and antigens. You will also explore details about the applications of the techniques. Many of these techniques are in regular use in a wide range of laboratories, including those involved in clinical medicine, research and industry. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 15
16 General information for learners (cont) Outcome 4 In this Outcome you will undertake practical experiments, based on the content of Outcome 3. During this practical work, you will also be expected to develop good laboratory practices as well as improve your skills of manipulation, observation and measurement. You will also be encouraged to develop safe working practices and to strive constantly to improve the accuracy and reliability of your results. The reporting and analysis of experimental data is an important aspect of the practical sessions. Assessment For Outcomes 1 to 3 you will take a closed-book, end of Unit assessment. Outcome 4 will be assessed after you have learned the necessary practical skills, and will take the form of one practical experiment, for which you will report your results either in a full laboratory report, or by completion of a pro forma. Core Skills You will have opportunities to develop the Core Skills of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) at SCQF level 4, Numeracy at SCQF level 5 and Problem Solving at SCQF level 6. H92E 35, Immunological Techniques (SCQF level 8) 16
Unit title: Biochemistry: Theory and Laboratory Skills (SCQF level 7)
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H922 34 Superclass: RH Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H922 34 Superclass: RH Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification: general information
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H31F 34 Superclass: AE Publication date: April 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H31F 34 Superclass: AE Publication date: April 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Conform to General Workplace Health, Safety and Welfare (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H106 12 Superclass: TE Publication date: March 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Summary This Unit is suitable for candidates
National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H106 12 Superclass: TE Publication date: March 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Summary This Unit is suitable for candidates
Unit title: Travel and Tourism in the UK (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit specification General information Unit code: H90R 46 Superclass: NK Publication date: September 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
National Unit specification General information Unit code: H90R 46 Superclass: NK Publication date: September 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
National Unit Specification: general information. UNIT Creative Project (SCQF level 6) CODE F58F 12 SUMMARY OUTCOMES RECOMMENDED ENTRY
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F58F 12 SUMMARY The purpose of this Unit is to allow candidates to plan, implement and evaluate a creative project. Candidates will be required to
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F58F 12 SUMMARY The purpose of this Unit is to allow candidates to plan, implement and evaluate a creative project. Candidates will be required to
Hospitality: Financial and Control Systems
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Hospitality: Financial and Control Systems Unit code: DL3T 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to introduce candidates
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Hospitality: Financial and Control Systems Unit code: DL3T 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to introduce candidates
On successful completion of the Unit candidates will be able to carry out a simple earthing exercise on a simulated electrical installation.
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5HE 11 SUMMARY This Unit is designed for candidates with little or no prior knowledge of earthing systems for electrical installations but who wish
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5HE 11 SUMMARY This Unit is designed for candidates with little or no prior knowledge of earthing systems for electrical installations but who wish
UNIT Market Operations and the Scottish Economy (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F391 11 SUMMARY This Unit is intended to introduce candidates to basic ideas in Economics. It is intended for candidates who have no previous knowledge
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F391 11 SUMMARY This Unit is intended to introduce candidates to basic ideas in Economics. It is intended for candidates who have no previous knowledge
UNIT Applications of Programmable Logic Controllers (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5H0 12 SUMMARY This Unit is designed to develop the candidate s skills in solving typical industrial related problems by the application of Programmable
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5H0 12 SUMMARY This Unit is designed to develop the candidate s skills in solving typical industrial related problems by the application of Programmable
Building Services Engineering: Basic Plumbing Operations (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FT7Y 11 Superclass: TH Publication date: April 2016 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 03 Summary This is a mandatory Unit of
National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FT7Y 11 Superclass: TH Publication date: April 2016 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 03 Summary This is a mandatory Unit of
UNIT Postiche Application and Styling: An Introduction (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F4C6 11 SUMMARY This Unit is a general introduction to the use of temporary postiche applications. On completion of this Unit the candidate will have
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F4C6 11 SUMMARY This Unit is a general introduction to the use of temporary postiche applications. On completion of this Unit the candidate will have
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Forestry Industries Market Evaluation. Unit code: F3YL 35
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Forestry Industries Market Evaluation Unit code: F3YL 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to give the candidate understanding
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Forestry Industries Market Evaluation Unit code: F3YL 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to give the candidate understanding
Planning and Sustainable Development in Tourism (SCQF level 8)
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: DK02 35 Superclass: NK Publication date: July 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 04 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: DK02 35 Superclass: NK Publication date: July 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 04 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Creative Digital Media: Production Project
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5CY 10 SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Creative Digital Media (Intermediate 1) Course but may also be taken as a free-standing
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5CY 10 SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Creative Digital Media (Intermediate 1) Course but may also be taken as a free-standing
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F6JJ 34. Unit purpose:
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Building an e-business Unit code: F6JJ 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with an understanding
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Building an e-business Unit code: F6JJ 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with an understanding
Group Award Specification for:
 Group Award Specification for: Award in Customer Service: Principles and Practices Group Award Code: GG2A 45 Validation date: January 2013 Date of original publication: February 2013 Version: 1 Contents
Group Award Specification for: Award in Customer Service: Principles and Practices Group Award Code: GG2A 45 Validation date: January 2013 Date of original publication: February 2013 Version: 1 Contents
Higher National Unit specification: general information
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FG67 34 Superclass: KH Publication date: August 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FG67 34 Superclass: KH Publication date: August 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
National 5 Creative Industries: Skills for Work Course Specification
 National 5 Creative Industries: Skills for Work Course Specification Valid from August 2013 This edition: August 2013, version 2.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational
National 5 Creative Industries: Skills for Work Course Specification Valid from August 2013 This edition: August 2013, version 2.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational
Serology as a Diagnostic Technique
 Serology as a Diagnostic Technique Characteristics of Any Diagnostic Techniques Any useful detection strategy must be: Specific: yield a positive response for only the target organism or molecule. Sensitive:
Serology as a Diagnostic Technique Characteristics of Any Diagnostic Techniques Any useful detection strategy must be: Specific: yield a positive response for only the target organism or molecule. Sensitive:
Higher National Unit specification: general information. Digital Marketing Communications: An Introduction
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FK93 34 Superclass: CE Publication date: June 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FK93 34 Superclass: CE Publication date: June 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
UNIT Hairdressing: Salon Awareness (Intermediate 1)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE DX0M 10 COURSE Hairdressing (Intermediate 1) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 1) Course and
National Unit Specification: general information CODE DX0M 10 COURSE Hairdressing (Intermediate 1) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 1) Course and
UNIT Hairdressing: Working in a Salon Environment (Intermediate 2)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F343 11 COURSE Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) Course and
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F343 11 COURSE Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) Course and
National 4 Sport and Recreation: Skills for Work Course Specification
 National 4 Sport and Recreation: Skills for Work Course Specification Valid from August 2013 This edition: August 2013, version 2.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational
National 4 Sport and Recreation: Skills for Work Course Specification Valid from August 2013 This edition: August 2013, version 2.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational
The Unit has been developed to enable candidates to demonstrate knowledge, comprehension and application of the design checking process.
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Structural Steel Design and Detailing Unit code: DW4A 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide the candidate with
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Structural Steel Design and Detailing Unit code: DW4A 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide the candidate with
To achieve this Unit, candidates should attain 70% of available marks for each Outcome.
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit code: DE5H 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide students with basic knowledge about company law. It is intended for
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit code: DE5H 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide students with basic knowledge about company law. It is intended for
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Photography: Professional Studies. Unit code: F1T7 36
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Photography: Professional Studies Unit code: F1T7 36 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to give candidates opportunities
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Photography: Professional Studies Unit code: F1T7 36 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to give candidates opportunities
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. IT in Business: Spreadsheets. Unit code: F84V 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: IT in Business: Spreadsheets Unit code: F84V 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to allow candidates to develop an understanding
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: IT in Business: Spreadsheets Unit code: F84V 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to allow candidates to develop an understanding
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Construction Site Surveying C. Unit code: DW44 35
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Construction Site Surveying C Unit code: DW44 35 Unit purpose: To develop candidate knowledge and skills in a range of more
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Construction Site Surveying C Unit code: DW44 35 Unit purpose: To develop candidate knowledge and skills in a range of more
CHAPTER 3 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE I
 CHAPTER 3 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE I See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY ANALYSIS; (6), EQUILIBRIUM DIALYSIS; (7) CROSS-REACTIVITY Electrophoretic separation of serum proteins identifies the GAMMA-GLOBULIN fraction
CHAPTER 3 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE I See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY ANALYSIS; (6), EQUILIBRIUM DIALYSIS; (7) CROSS-REACTIVITY Electrophoretic separation of serum proteins identifies the GAMMA-GLOBULIN fraction
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F5GF 35
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Managing People Unit code: F5GF 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates to develop the knowledge and skills
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Managing People Unit code: F5GF 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates to develop the knowledge and skills
This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Beauty (Higher) Course and can also be taken as a free-standing Unit.
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5B2 12 COURSE Beauty (Higher) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Beauty (Higher) Course and can also be taken as a free-standing
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F5B2 12 COURSE Beauty (Higher) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Beauty (Higher) Course and can also be taken as a free-standing
Protein homology. Antigens & Antibodies I. Administrative issues:
 Administrative issues: Recommended text: Goldsby/Kuby Immunology, 6th edition (Note that Innate Immunity is not adequately covered in the 5th edition.) Text book reading assignments are to supplement the
Administrative issues: Recommended text: Goldsby/Kuby Immunology, 6th edition (Note that Innate Immunity is not adequately covered in the 5th edition.) Text book reading assignments are to supplement the
Higher National Unit specification: general information. Trade Union Organising and Representation: Equality Legislation Relating to the Workplace
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H2XE 34 Superclass: AJ Publication date: November 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H2XE 34 Superclass: AJ Publication date: November 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F7JR 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Cost Accounting Unit code: F7JR 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to introduce candidates to costing techniques that
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Cost Accounting Unit code: F7JR 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to introduce candidates to costing techniques that
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Building Management Systems. Unit code: DP0Y 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Building Management Systems Unit code: DP0Y 34 Unit purpose: The purpose of this unit is to develop the candidate understanding
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Building Management Systems Unit code: DP0Y 34 Unit purpose: The purpose of this unit is to develop the candidate understanding
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Creative Industries: An Introduction. Unit code: DM0V 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: DM0V 34 Unit purpose: To introduce candidates to the concept, history and workings of the Creative Industries and to develop
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: DM0V 34 Unit purpose: To introduce candidates to the concept, history and workings of the Creative Industries and to develop
This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) Course and can also be taken as a free-standing Unit.
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F344 11 COURSE Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) Course and
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F344 11 COURSE Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) SUMMARY This Unit has been designed as a mandatory Unit of the Hairdressing (Intermediate 2) Course and
Higher National Group Award Graded Unit Specification
 Higher National Group Award Graded Unit Specification General Information for Centres This Group Award Graded Unit has been validated as part of the HNC Acting and Performance. Centres are required to
Higher National Group Award Graded Unit Specification General Information for Centres This Group Award Graded Unit has been validated as part of the HNC Acting and Performance. Centres are required to
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Unit title: Marine Engineering: Naval Architecture. Unit code: F911 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit code: F911 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates to develop their knowledge and understanding of Naval Architecture.
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit code: F911 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates to develop their knowledge and understanding of Naval Architecture.
UNIT Sport and Recreation: Developing Volunteering (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F7JG 12 SUMMARY The purpose of the Unit is to enable candidates involved in sport and recreation, to develop transferable skills while working in a
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F7JG 12 SUMMARY The purpose of the Unit is to enable candidates involved in sport and recreation, to develop transferable skills while working in a
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit title: Make-up Artistry: Special Effects. Unit code: F0JG 35
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: F0JG 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates to develop specialised make up effects used within the film/television
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: F0JG 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates to develop specialised make up effects used within the film/television
Graded Unit title: Professional Cookery: Graded Unit 1
 Higher National Graded Unit specification General information for centres This Graded Unit has been validated as part of the HNC in Professional Cookery. Centres are required to develop the assessment
Higher National Graded Unit specification General information for centres This Graded Unit has been validated as part of the HNC in Professional Cookery. Centres are required to develop the assessment
MOLECULAR RECOGNITION
 MOLECULAR RECOGNITION Bioanalytical Methods Classification 1. Biassay: molecular recognition, signal generation and detection in solution or on inert solid phase 2. Biosensor: molecular recognition system
MOLECULAR RECOGNITION Bioanalytical Methods Classification 1. Biassay: molecular recognition, signal generation and detection in solution or on inert solid phase 2. Biosensor: molecular recognition system
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit title: Incubation of Hatching Eggs. Unit code: F439 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: F439 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to give candidates the knowledge and skills required to manage a poultry hatchery.
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: F439 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to give candidates the knowledge and skills required to manage a poultry hatchery.
MEDICAL IMMUNOLOGY 544. Dr. George A. Gutman
 I M M U N O L O G Y CORE NOTES MEDICAL IMMUNOLOGY 544 FALL 2011 Dr. George A. Gutman SCHOOL OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE (Copyright) 2011 Regents of the University of California TABLE OF
I M M U N O L O G Y CORE NOTES MEDICAL IMMUNOLOGY 544 FALL 2011 Dr. George A. Gutman SCHOOL OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE (Copyright) 2011 Regents of the University of California TABLE OF
Antibody Structure. Antibodies
 Antibodies Secreted by B lymphocytes Great diversity and specificity: >10 9 different antibodies; can distinguish between very similar molecules Tag particles for clearance/destruction Protect against
Antibodies Secreted by B lymphocytes Great diversity and specificity: >10 9 different antibodies; can distinguish between very similar molecules Tag particles for clearance/destruction Protect against
Antibody Structure supports Function
 Antibodies Secreted by B lymphocytes Great diversity and specificity: >10 9 different antibodies; can distinguish between very similar molecules Tag particles for clearance/destruction Protect against
Antibodies Secreted by B lymphocytes Great diversity and specificity: >10 9 different antibodies; can distinguish between very similar molecules Tag particles for clearance/destruction Protect against
Assays for Immunogenicity: Are We There Yet?
 Assays for Immunogenicity: Are We There Yet? Mark Wener, MD Department of Laboratory Medicine & Rheumatology Division Department of Medicine University of Washington Seattle, WA 98195 wener@uw.edu Goals:
Assays for Immunogenicity: Are We There Yet? Mark Wener, MD Department of Laboratory Medicine & Rheumatology Division Department of Medicine University of Washington Seattle, WA 98195 wener@uw.edu Goals:
Basic Antibody Structure. Multiple myeloma = cancerous plasma cells Monomer = 150,000. Chapter 4. Immunoglobulin Structure and Function
 Chapter 4. Immunoglobulin Structure and Function. Functional Regions. Types of chains. Constant & Variable regions 4. Glycoprotein * * * Heavy chain= 446 aa Light chain= 4aa Each heavy and light chain
Chapter 4. Immunoglobulin Structure and Function. Functional Regions. Types of chains. Constant & Variable regions 4. Glycoprotein * * * Heavy chain= 446 aa Light chain= 4aa Each heavy and light chain
Custom Antibodies Services. GeneCust Europe. GeneCust Europe
 GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 2 route de Remich L-5690 Ellange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com Custom
GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 2 route de Remich L-5690 Ellange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com Custom
Guidance for the Implementation of Graded Units in Higher National Certificates and Diplomas
 Guidance for the Implementation of Graded Units in Higher National Certificates and Diplomas Publication date: April 2008 Publication code: CA4405 Published by the Scottish Qualifications Authority The
Guidance for the Implementation of Graded Units in Higher National Certificates and Diplomas Publication date: April 2008 Publication code: CA4405 Published by the Scottish Qualifications Authority The
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. IT Infrastructure: Service Delivery. Unit code: F0DY 35
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: IT Infrastructure: Service Delivery Unit code: F0DY 35 Unit purpose: This Unit develops the candidate s knowledge and understanding
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: IT Infrastructure: Service Delivery Unit code: F0DY 35 Unit purpose: This Unit develops the candidate s knowledge and understanding
Antibodies and Antigens in the Blood Bank 9/7/2015 NAHLA BAKHAMIS 1
 Antibodies and Antigens in the Blood Bank NAHLA BAKHAMIS 9/7/2015 NAHLA BAKHAMIS 1 Outline Antibodies structure, classes and functions Most important Abs in the blood bank effective roles of Abs Zeta potential
Antibodies and Antigens in the Blood Bank NAHLA BAKHAMIS 9/7/2015 NAHLA BAKHAMIS 1 Outline Antibodies structure, classes and functions Most important Abs in the blood bank effective roles of Abs Zeta potential
Antibodies and Antigens In the blood bank
 Antibodies and Antigens In the blood bank 1 Nice game!! http://nobelprize.org/ 2 Karl Landsteiner discovered blood groups in 1901. Awarded Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1930 3 Why we study
Antibodies and Antigens In the blood bank 1 Nice game!! http://nobelprize.org/ 2 Karl Landsteiner discovered blood groups in 1901. Awarded Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1930 3 Why we study
Biology Assignment General assessment information
 Biology Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Biology Course assessment. It
Biology Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Biology Course assessment. It
Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development
 Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development Rebecca Brunette, PhD Scientist, Analytical Biology SNBL USA Preclinical Immunotoxicology The study of evaluating adverse effects
Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development Rebecca Brunette, PhD Scientist, Analytical Biology SNBL USA Preclinical Immunotoxicology The study of evaluating adverse effects
Biology Assignment General assessment information
 Biology Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Biology Course assessment. It
Biology Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Biology Course assessment. It
LECTURE: 26 SIMPLE SEROLOGICAL LABORATORY TECHNIQUES LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 LECTURE: 26 Title SIMPLE SEROLOGICAL LABORATORY TECHNIQUES LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Define the term "simple serological techniques". Describe the benefit of the use of serological
LECTURE: 26 Title SIMPLE SEROLOGICAL LABORATORY TECHNIQUES LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Define the term "simple serological techniques". Describe the benefit of the use of serological
Step-by-Step Description of ELISA
 Step-by-Step Description of ELISA The protocols in this kit rely on indirect antibody capture ELISA. The steps in this assay are: Step 1: Antigen is added to the wells of the microplate strip and incubated
Step-by-Step Description of ELISA The protocols in this kit rely on indirect antibody capture ELISA. The steps in this assay are: Step 1: Antigen is added to the wells of the microplate strip and incubated
Hospitality: Practical Cake Craft Practical Activity General assessment information
 Hospitality: Practical Cake Craft Practical Activity General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the practical activity Component
Hospitality: Practical Cake Craft Practical Activity General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the practical activity Component
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE: UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION. -Module Number Session
 -SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE: UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Module Number- 6260046 -Session-1996-97 -Superclass- -Title- BA MARKETING MIX -----------------------------------------
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE: UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Module Number- 6260046 -Session-1996-97 -Superclass- -Title- BA MARKETING MIX -----------------------------------------
SPHERO TM Coated Particles
 SPHERO TM Coated Particles Manufactured by either passive adsorption or covalent coupling depending upon the intended application Stable for several years under proper storage condition Available in a
SPHERO TM Coated Particles Manufactured by either passive adsorption or covalent coupling depending upon the intended application Stable for several years under proper storage condition Available in a
How to run Alpha assay: How to setup an Alpha assay Make your own assay!
 How to run Alpha assay: How to setup an Alpha assay Make your own assay! 1 2009 PerkinElmer AlphaLISA kits - recommendations before starting the assay Samples: Phenol red and hemoglobin: choose AlphaLISA
How to run Alpha assay: How to setup an Alpha assay Make your own assay! 1 2009 PerkinElmer AlphaLISA kits - recommendations before starting the assay Samples: Phenol red and hemoglobin: choose AlphaLISA
Media Assignment General assessment information
 Media Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the Assignment Component of National 5 Media Course assessment. It
Media Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the Assignment Component of National 5 Media Course assessment. It
Psychology Assignment General assessment information
 Psychology Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Psychology Course assessment.
Psychology Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Psychology Course assessment.
QImaging Camera Application Notes Multicolor Immunofluorescence Imaging
 QImaging Camera Application Notes Multicolor Immunofluorescence Imaging In order to image localization of intracellular proteins with high specificity, it is frequently necessary to multiplex antibody
QImaging Camera Application Notes Multicolor Immunofluorescence Imaging In order to image localization of intracellular proteins with high specificity, it is frequently necessary to multiplex antibody
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ANALYSIS
 -SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Unit number- 6430959 -Unit title- -Superclass category- FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ANALYSIS AK -Date of publication-
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Unit number- 6430959 -Unit title- -Superclass category- FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ANALYSIS AK -Date of publication-
Media Assignment General assessment information
 Media Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Media Course assessment. It must
Media Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Media Course assessment. It must
The Principles of Money. SCQF level 4. Unit Code: FC hour Unit
 The Principles of Money SCQF level 4 Unit Code: FC64 04 40 hour Unit What is this Unit about? This Unit focuses on opportunities to explore basic financial encounters. It will help you gain a better understanding
The Principles of Money SCQF level 4 Unit Code: FC64 04 40 hour Unit What is this Unit about? This Unit focuses on opportunities to explore basic financial encounters. It will help you gain a better understanding
Classical Studies Assignment General assessment information
 Classical Studies Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Classical Studies Course
Classical Studies Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Classical Studies Course
Immunoglobulins. Biological Properties
 Immunoglobulins Biological Properties Introduction Many important biological properties are attributed to antibodies that differ depending on isotype These include; - Neutralization of toxins - Immobilization
Immunoglobulins Biological Properties Introduction Many important biological properties are attributed to antibodies that differ depending on isotype These include; - Neutralization of toxins - Immobilization
Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function
 Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function Immunoglobulins:Structure and Function Definition: Glycoprotein molecules that are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which function as antibodies
Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function Immunoglobulins:Structure and Function Definition: Glycoprotein molecules that are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which function as antibodies
Assays and Strategies for Immunogenicity Assessment. Steven J Swanson, Ph.D. Executive Director, Medical Sciences Clinical Immunology, Amgen
 Assays and Strategies for Immunogenicity Assessment Steven J Swanson, Ph.D. Executive Director, Medical Sciences Clinical Immunology, Amgen General Antibody Assay Strategy Correlation of clinical findings
Assays and Strategies for Immunogenicity Assessment Steven J Swanson, Ph.D. Executive Director, Medical Sciences Clinical Immunology, Amgen General Antibody Assay Strategy Correlation of clinical findings
CHAPTER 7 CELLULAR BASIS OF ANTIBODY DIVERSITY: CLONAL SELECTION
 CHAPTER 7 CELLULAR BASIS OF ANTIBODY DIVERSITY: CLONAL SELECTION The specificity of humoral immune responses relies on the huge DIVERSITY of antigen combining sites present in antibodies, diversity which
CHAPTER 7 CELLULAR BASIS OF ANTIBODY DIVERSITY: CLONAL SELECTION The specificity of humoral immune responses relies on the huge DIVERSITY of antigen combining sites present in antibodies, diversity which
Scottish Vocational Qualifications. Qualification Verification Summary Report SVQ Management
 Scottish Vocational Qualifications Qualification Verification Summary Report 2017 SVQ Management 1 Introduction This verification group covers the following awards: GC49 22 SVQ 2 in Team Leading at SCQF
Scottish Vocational Qualifications Qualification Verification Summary Report 2017 SVQ Management 1 Introduction This verification group covers the following awards: GC49 22 SVQ 2 in Team Leading at SCQF
Immunological Techniques
 Midterm Extra Office Hours Take Regular Office Hours: Tuesdays 11-12 Extra office hours: Wed, Feb 7 12-1pm Thurs, Feb 8 11am-12 Fri, Feb 9 2-4pm I WILL NOT BE HOLDING OFFICE HOURS ON TUESDAY Feb 13!! Dina,
Midterm Extra Office Hours Take Regular Office Hours: Tuesdays 11-12 Extra office hours: Wed, Feb 7 12-1pm Thurs, Feb 8 11am-12 Fri, Feb 9 2-4pm I WILL NOT BE HOLDING OFFICE HOURS ON TUESDAY Feb 13!! Dina,
SynAbs S.A. Driving mab innovation for the IVD & BioPharma R&D markets
 SynAbs S.A. Driving mab innovation for the IVD & BioPharma R&D markets February 20, 2016 SynAbs in a nutshell (1/2) Rat monoclonal antibodies, service and catalog Innovative guinea pig monoclonals! Mouse
SynAbs S.A. Driving mab innovation for the IVD & BioPharma R&D markets February 20, 2016 SynAbs in a nutshell (1/2) Rat monoclonal antibodies, service and catalog Innovative guinea pig monoclonals! Mouse
National 5 Religious, Moral and Philosophical Studies Assignment General assessment information
 National 5 Religious, Moral and Philosophical Studies Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component
National 5 Religious, Moral and Philosophical Studies Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Isotyping Reagents
 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Isotyping Reagents Catalog Number: SEK003 Storage Temperature: 2-8 C Fax : +86-10-58628220 Tel : +86-400-890-9989 http://www.sinobiological.com Description Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Isotyping Reagents Catalog Number: SEK003 Storage Temperature: 2-8 C Fax : +86-10-58628220 Tel : +86-400-890-9989 http://www.sinobiological.com Description Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Arrangements for: SQA Advanced Certificate in Accounting (GM96 47) SQA Advanced Diploma in Accounting (GM8G 48) Date of publication: August 2017
 Arrangements for: SQA Advanced Certificate in Accounting (GM9 7) SQA Advanced Diploma in Accounting (GM8G 8) Date of publication: August 7 Version: (August 7) Published by the Scottish Qualifications Authority
Arrangements for: SQA Advanced Certificate in Accounting (GM9 7) SQA Advanced Diploma in Accounting (GM8G 8) Date of publication: August 7 Version: (August 7) Published by the Scottish Qualifications Authority
Ig Isotype (Human) Quantitative Antibody Array
 Ig Isotype (Human) Quantitative Antibody Array Catalog Number AA0113 8 Samples/Slide Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Introduction and Background A. Overview The human immune system
Ig Isotype (Human) Quantitative Antibody Array Catalog Number AA0113 8 Samples/Slide Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Introduction and Background A. Overview The human immune system
The Biotechnology Education Company. Quantitative ELISA. Storage: See Page 3 for specific storage instructions EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE:
 The Biotechnology Education Company Revised and Updated Quantitative ELISA Storage: See Page 3 for specific storage instructions EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: EDVO-Kit # 278 The objective of this experiment is
The Biotechnology Education Company Revised and Updated Quantitative ELISA Storage: See Page 3 for specific storage instructions EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: EDVO-Kit # 278 The objective of this experiment is
PeliClass human IgG subclass ELISA kit Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
 PeliClass human IgG subclass ELISA kit Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Catalog No: M1551 Size: six pre-coated 8-well strips for each of the four IgG subclasses Test description The PeliClass human subclass
PeliClass human IgG subclass ELISA kit Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Catalog No: M1551 Size: six pre-coated 8-well strips for each of the four IgG subclasses Test description The PeliClass human subclass
Applications of HTRF and Tag-lite Assays for HTP Antibody Screening
 Applications of HTRF and Tag-lite Assays for HTP Antibody Screening Brigitte Devaux, PhD Bristol Myers Squibb, Redwood City CA HTRF Symposium April 25, 2013 1 Introduction Generate human therapeutic antibodies
Applications of HTRF and Tag-lite Assays for HTP Antibody Screening Brigitte Devaux, PhD Bristol Myers Squibb, Redwood City CA HTRF Symposium April 25, 2013 1 Introduction Generate human therapeutic antibodies
The World Leader in SPR Technology. Jimmy Page, PhD, Biacore, Inc.
 The World Leader in SPR Technology Jimmy Page, PhD, Biacore, Inc. Objectives of Biacore Experiments Yes/No Data» Is there binding?» Ligand Fishing Concentration Analysis: How MUCH? Active Concentration
The World Leader in SPR Technology Jimmy Page, PhD, Biacore, Inc. Objectives of Biacore Experiments Yes/No Data» Is there binding?» Ligand Fishing Concentration Analysis: How MUCH? Active Concentration
Meter Systems in Measurement and Control Engineering
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Meter Systems in Measurement and Control Engineering Unit code: DX4H 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Meter Systems in Measurement and Control Engineering Unit code: DX4H 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates
Arrangements for: National Progression Award in (NPA): Play in a Sports Environment. at SCQF level 6. Group Award Code: G9GE 46
 Arrangements for: National Progression Award in (NPA): Play in a Sports Environment at SCQF level 6 Group Award Code: G9GE 46 Validation date: May 2009 Date of original publication: August 2009 Version:
Arrangements for: National Progression Award in (NPA): Play in a Sports Environment at SCQF level 6 Group Award Code: G9GE 46 Validation date: May 2009 Date of original publication: August 2009 Version:
ELISA IMMUNOASSAY FOR DISEASE DETECTION
 Unit 6/ Module 1 /Version B pg. 1 California Lutheran University s Enriched Science (CLUES) and California State University Program for Education and Research in Biotechnology (C-SUPERB) ELISA IMMUNOASSAY
Unit 6/ Module 1 /Version B pg. 1 California Lutheran University s Enriched Science (CLUES) and California State University Program for Education and Research in Biotechnology (C-SUPERB) ELISA IMMUNOASSAY
FORENSIC SEROLOGY. Chapter PRENTICE HALL 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458
 Chapter 8 FORENSIC SEROLOGY 8-1 Nature of Blood The word blood refers to a highly complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances. Plasma, which is the fluid portion of blood, is
Chapter 8 FORENSIC SEROLOGY 8-1 Nature of Blood The word blood refers to a highly complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances. Plasma, which is the fluid portion of blood, is
ELISA IMMUNOASSAY FOR HUMAN
 Unit 6/ Module 1 /Version A pg. 1 California Lutheran University s Enriched Science (Clues) and California State University Program for Education and Research in Biotechnology (C-SUPERB) ELISA IMMUNOASSAY
Unit 6/ Module 1 /Version A pg. 1 California Lutheran University s Enriched Science (Clues) and California State University Program for Education and Research in Biotechnology (C-SUPERB) ELISA IMMUNOASSAY
Supplementary Figure 1. Utilization of publicly available antibodies in different applications.
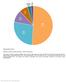 Supplementary Figure 1 Utilization of publicly available antibodies in different applications. The fraction of publicly available antibodies toward human protein targets is shown with data for the following
Supplementary Figure 1 Utilization of publicly available antibodies in different applications. The fraction of publicly available antibodies toward human protein targets is shown with data for the following
Chapter 2. Antibodies
 Chapter 2. Antibodies An iddy-biddy antibody Just nanometers long Saved the butt of a sumo man Hundreds of kilos strong Anonymous The main elements of the immune system are firstly antibodies, secondly
Chapter 2. Antibodies An iddy-biddy antibody Just nanometers long Saved the butt of a sumo man Hundreds of kilos strong Anonymous The main elements of the immune system are firstly antibodies, secondly
See more signal with less noise
 See more signal with less noise SeraCare KPL Antibodies & Conjugates See more signal with less noise In nature many animals use camouflage to escape detection. An animal s survival often depends upon its
See more signal with less noise SeraCare KPL Antibodies & Conjugates See more signal with less noise In nature many animals use camouflage to escape detection. An animal s survival often depends upon its
Human IL10RB ELISA Pair Set ( CRFB4 )
 Human IL10RB ELISA Pair Set ( CRFB4 ) Catalog Number : SEK10945 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the
Human IL10RB ELISA Pair Set ( CRFB4 ) Catalog Number : SEK10945 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the
Converting your ELISA from horseradish peroxidase to alkaline phosphatase using NovaBright chemiluminescence detection reagents
 Application note DynaLight Substrate with RapidGlow Enhancer Converting your ELISA from horseradish peroxidase to alkaline phosphatase using NovaBright chemiluminescence detection reagents Introduction
Application note DynaLight Substrate with RapidGlow Enhancer Converting your ELISA from horseradish peroxidase to alkaline phosphatase using NovaBright chemiluminescence detection reagents Introduction
Mouse ICAM-1 / CD54 ELISA Pair Set
 Mouse ICAM-1 / CD54 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK50440 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the General
Mouse ICAM-1 / CD54 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK50440 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the General
Arrangements for: National Certificate in Retailing at SCQF level 5. Group Award Code: GF6T 45. Validation date: May 2012
 Arrangements for: National Certificate in Retailing at SCQF level 5 Group Award Code: GF6T 45 Validation date: May 2012 Date of original publication: September 2012 Version: 06 Acknowledgement SQA acknowledges
Arrangements for: National Certificate in Retailing at SCQF level 5 Group Award Code: GF6T 45 Validation date: May 2012 Date of original publication: September 2012 Version: 06 Acknowledgement SQA acknowledges
Higher Beauty: Skills for Work Specification (Code C262 76)
 Higher Beauty: Skills for Work Specification (Code C262 76) Valid from August 2014 This edition, August 2014 version 2.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational purposes
Higher Beauty: Skills for Work Specification (Code C262 76) Valid from August 2014 This edition, August 2014 version 2.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational purposes
For the quantitative detection of human IL6 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine.
 m andw da a For the quantitative detection of human IL6 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity Range (calibration
m andw da a For the quantitative detection of human IL6 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity Range (calibration
SAMPLE LITERATURE Please refer to included weblink for correct version.
 REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #269 Introduction to ELISA Reactions Experiment Objective: This experiment introduces concepts and methodologies of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). See page 3 for
REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #269 Introduction to ELISA Reactions Experiment Objective: This experiment introduces concepts and methodologies of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). See page 3 for
