RNA and Protein Synthesis
|
|
|
- Cameron Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College RNA and Protein Synthesis Considerable evidence suggests that RNA molecules evolved prior to DNA molecules and proteins, and that many processes now involving DNA and proteins were previously accomplished by RNA alone. Many RNA molecules have enzymatic activity, and like DNA contain genetic information stored as nucleotide sequences. In living cells encountered today, RNA molecules are formed from DNA templates through transcription, but this was not always so. It is no wonder then that RNA molecules play such important roles within living cells. Types of RNA molecules: Although cellular RNA molecules are typically made via transcription using DNA as a template, they are coded for by different genes and have a variety of different functions. RNA molecules typically found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells include: 1) Messenger-RNA (m-rna) Messenger-RNA molecules are coded for by regions of DNA called structural genes, and carry the nucleotide sequences determining what types of proteins the cell will make. They carry this "message" from the nucleus or nucleoid to the ribosomes where proteins are made. 2) Ribosomal-RNA (r-rna) Ribosomal-RNA molecules bind with proteins to form ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis. In prokaryotic cells r-rna molecules occur as 23S, 16S and 5S segments. The 23S and 5S segments occur within the 50S ribosomal subunits, while the 16S segments occur within the 30S subunits. Ribosomal-RNA is largely responsible for ribosome function (except for the formation of peptide bonds) and coordinates the attachment of t-rna anti-codons with m-rna codons during translation. Most of the RNA within a prokaryotic cell is ribosomal. 3) Transfer-RNA (t-rna) Transfer-RNA molecules are relatively small, being only 74 to 93 nucleotides in length. Their function is to carry individual amino acid molecules to the ribosomes for protein synthesis. Each t-rna molecule is folded upon itself to form a shape roughly similar to a cloverleaf. The top or "stem" forms the amino acid binding site and typically has the base sequence CCA at the 3' end. The side loops are called T and D loops, and the bottom loop contains the anti-codon region (as set of three bases). Aminoacyl-t-RNA-synthetase enzymes catalyze the formation of covalent bonds binding amino acids to t-rna molecules. There are typically many different aminoacyl-t-rna-synthetase enzymes within each cell because each one catalyzes only the reaction binding a specific amino acid to the CCA sequence of each t- RNA molecule. The resulting complex is called aminoacyl-t-rna. Eukaryotic cells typically contain additional types of RNA not found in prokaryotic cells. Though these are not directly involved in protein synthesis, they are of considerable importance. Some additional types of RNA include:
2 1) Small or short-rna (s-rna) Small-RNA molecules bind with proteins to form structures called spliceosomes and are involved in a process called posttranscriptional modification. In eukaryotic cells, nearly all RNA molecules undergo some modification following transcription, so these small-rna molecules play a vital role. In the case of m-rna molecules, post-transcriptional modification involves the removal of multiple sections called introns (intervening regions) from the original RNA transcript. The remaining sections, called exons (expressed regions) are then bond together to form a shorter m-rna molecule (in some cases over half the original m-rna transcript is composed of introns). Post-transcriptional modification also involves the application of a methylated-guanine "cap" (which is attached to the 5' end before transcription is completed), and a poly-adenine "tail". The splicing of exons following the removal of introns can occur in a variety of ways in some m-rna molecules, and this increases the variety of proteins that can be generated. 2) Micro-RNA (mi-rna) Micro-RNA molecules are very small, usually only 21 bases in length. They regulate the expression of genes by binding with m-rna molecules. At this time, researchers believe there are probably hundreds of genes coding for different mi-rna molecules, and that the potential for regulating cellular processes by means of mi-rna is enormous. 3) Small interfering-rna (si-rna) Small interfering-rna molecules (also called short interfering or silencing-rna) are typically nucleotides in length, and doublestranded. Like mi-rna they play a significant role in regulating the expression of eukaryotic genes. Translation Protein synthesis: The term "translate" means to give an equivalent in another language, therefore, when not applied to biological activities, translation refers to the process of reproducing a written or spoken text in a different language while retaining the original meaning. When applied to biological systems, it has essentially the same meaning. Translation is protein synthesis. During translation, information contained in m-rna molecules in the form of nucleotide sequences (transcribed from small sections of DNA; also nucleotide sequences), is translated into information contained in polypeptides in the form of amino acid sequences. The language change is from nucleotide sequence to amino acid sequence. Some polypeptides are fully functional proteins, while others undergo modification to become functional units. Recall that proteins with quaternary structure contain multiple polypeptide chains. Some background information: When the structure of DNA was first determined (through the efforts of Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, James Watson and Francis Crick see Wikipedia DNA) in the early 1950s, researchers were uncertain how this relatively simple molecule could contain the information necessary to control the physiological processes within living cells. It became obvious that protein structure was dependent on the nucleotide sequences of DNA molecules, but it was not immediately apparent how this could be. Proteins typically contain 20 different amino acids, and the primary structure of each polypeptide is
3 determined by the sequence or arrangement of these monomers (just as the sequence or arrangement of letters determines the informational content of words on a page). Each DNA molecule (and each m-rna molecule) contains only four different nitrogenous bases, so researchers knew individual bases (translated separately) could not determine amino acid sequences. When "read" in pairs (groups of 2), the bases could be arranged to yield 16 different sets, but this was still not enough. Then researchers considered translating base sequences arranged in sets of three. In this configuration, they form 64 possible sets (3-letter "words"), which is more than enough to code for 20 different amino acids. By synthesizing nucleotide sequences containing only one type of base, i.e., polyadenine, polycytosine, polyguanine, etc. researchers were able to determine portions of the "genetic code", the sets of bases coding for different types of amino acid; polyadenine sequences yielded polypeptides containing only lysine, polycytosine sequences yielded polypeptides containing only proline, polyguanine sequences yielded polypeptides containing only glycine, etc. Eventually the entire genetic code was revealed. The Genetic Code: The genetic code typically presented in biology textbooks (and in the lecture syllabus) is made up of nucleotides (bases) arranged in groups of three. These groups are called codons, and occur within messenger-rna molecules and DNA molecules. Since nucleotides arranged in sets of three form 64 different combinations (64, 3-letter "words"), and because proteins typically contain only 20 different amino acids, there is considerable overlap. Most of the amino acids incorporated into proteins are "coded for" by multiple different codons, so the genetic code contains redundancy. Some references refer to the code as being degenerate, but the overlap has benefit because it reduces the potentially lethal effects of certain types of mutation as will be explained later. In addition to the codons translated into amino acids, the genetic code contains four codons with alternate functions. The codon "AUG" codes for the amino acid methionine, but also serves as a start or initiator codon. The codons "UAA", "UAG", and "UGA" do not code for any amino acids, and were initially referred to as non-sense codons; these code for "stop" or termination of the growing polypeptide chain. Named "Ocher", "Amber" and "Umber" (color names), these three terminator codons play an essential role in protein synthesis. Although similar in all living organisms, the genetic code as presented in most texts is not universal. Variations are common within mitochondria. For example, mitochondria found within animals and eukaryotic microbes use "UGA" as the code for tryptophan instead of stop, most animal mitochondria use "AUA" as the code for methionine rather than isoleucine, all mitochondria associated with vertebrate animals use "AGA" and "AGG" as chain terminators, and yeast mitochondria use "CUA, CUG, CUC and CUU" to code for threonine instead of leucine. Only plant mitochondria use the universal code. Beyond that, researchers have now developed strains of E. coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae that use specific redundant codons as the codes for amino acids not normally incorporated into proteins. The code apparently has considerable versatility. Translation: The translation process occurs in association with ribosomes and involves the three types of RNA common to all types of cells, i.e., m-rna, r-rna and t-rna. Since m-rna molecules carry the genetic message, they must interact directly with the ribosomes.
4 Translation can be broken into a series of stages as follows: 1) Initiation - Initially, the small ribosomal subunit (30S in prokaryotes, 40S in eukaryotes) binds to m-rna at a site "upstream" of the initiator codon. Some bacterial m-rna molecules carry the nucleotide sequence "5'-AGGAGG" (the Shine-Dalgarno sequence) which binds to the complimentary sequence "3'-UCCUCCA" (the anti-shine- Dalgarno sequence) on the 16S ribosomal-rna portion of the ribosome. In bacteria lacking a Shine-Dalgarno sequence, the binding of m-rna to the small ribosomal subunit involves interaction between ribosomal proteins and purine rich regions of RNA upstream of the initiator. In eukaryotes a sequence beginning with "A" or "G" followed by "CCACC" (the Kozak concensus sequence) serves as the ribosome binding site. Once the binding of m-rna to the small ribosomal subunit has occurred, a number of translation initiation factors (IF) bind to the ribosome along with a t-rna carrying the amino acid methionine. In prokaryotes, this is N-formylmethionine (fmet) rather than the methionine commonly incorporated into proteins. Following the binding of this aminoacyl-t-rna molecule, the second ribosomal subunit (50S in prokaryotes or 60S in eukaryotes) binds to the m-rna. 2) Elongation The large ribosomal subunit has three t-rna binding sites designated as the A-site, the P-site and the E-site. The A-site is the amino acid binding site and binds with incoming t-rna molecules (aminoacyl-t-rna), i.e., those carrying individual amino acids to the ribosome. The P-site is the polypeptide binding site, and once translation has begun, will bind with the peptidyl-t-rna molecule, i.e., the one holding the growing polypeptide chain. The E-site binds with the exiting-t-rna, i.e., the free t- RNA molecule remaining after the amino acid it was carrying has been added to the growing peptide chain. The binding of aminoacyl-t-rna molecules involves interaction between t-rna anticodons and m-rna codons. Hydrogen bonds forming between the complimentary bases insure that each amino acid will be incorporated in the correct location. A ribosomal enzyme called peptidyl transferase catalyzes chemical reactions resulting in the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids. Without this enzyme activity, proteins cannot be made. Peptidyl transferase activity apparently involves RNA molecules, not ribosomal proteins. Translation requires that the ribosomes travel along m-rna molecules from the 5' ends toward the 3'ends. As they do, the codons associated with the A-site change and new aminoacyl-t-rna molecules can bind. As peptide bonds are formed between adjacent amino acids, the growing peptide chain is transferred from the t-rna in the P-site to the one occupying the A-site (explaining the name peptidyl transferase). The t-rna released by the transfer of the peptide chain, occupies the E-site until the ribosome moves, and is then released. These "exiting" t-rna molecules can again interact with aminoacyl-t-rna synthase enzymes, pick up new amino acids, and return to the ribosome, i.e., they can be used over and over again.
5 3) Termination Translation is terminated when the ribosome reaches a stop or terminator codon. In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the process involves the interaction of two or more proteins called chain release factors. When a stop codon is recognized, the finished polypeptide chain is released from the last t-rna, i.e., the covalent bond attaching the last amino acid added to its corresponding t-rna molecule is hydrolyzed. Following this reaction, the t-rna is released from the ribosome, and the two ribosomal subunits separate, releasing the m-rna. Since messenger-rna molecules have a relatively short life expectancy (about 2 minutes in some eukaryotic cells), bacteria often increase translation efficiency by binding multiple ribosomes to the same m-rna during translation. A group of ribosomes bound to and translating the same m-rna is called a polyribosome or polysome. 0 In eukaryotic cells, m-rna molecules typically carry the information copied from individual genes (transcription is monocistronic), but in prokaryotic cells, m-rna molecules often carry the information copied from multiple genes (transcription is polycistronic). Polycistronic m-rna molecules carry information that is translated into multiple polypeptides. In E.coli the m-rna copied from the tryptophan biosynthesis operon contains about 7000bp and is translated into five different enzymes. Each protein is coded for by a section of m-rna having its own start and stop signals, i.e., initiation and termination sequences. For a fun and simple review of the translation process take a look at this site.
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
C. Incorrect! Threonine is an amino acid, not a nucleotide base.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
Nucleic acids and protein synthesis
 THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
DNA - DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID
 DNA - DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID blueprint of life (has the instructions for making an organism) established by James Watson and Francis Crick codes for your genes shape of a double helix made of repeating
DNA - DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID blueprint of life (has the instructions for making an organism) established by James Watson and Francis Crick codes for your genes shape of a double helix made of repeating
Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
1. DNA, RNA structure. 2. DNA replication. 3. Transcription, translation
 1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Molecular Genetics. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 12 Molecular Genetics section 3 DNA,, and Protein DNA codes for, which guides protein synthesis. What You ll Learn the different types of involved in transcription and translation the role of polymerase
12 Molecular Genetics section 3 DNA,, and Protein DNA codes for, which guides protein synthesis. What You ll Learn the different types of involved in transcription and translation the role of polymerase
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
 Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Bio11 Announcements. Ch 21: DNA Biology and Technology. DNA Functions. DNA and RNA Structure. How do DNA and RNA differ? What are genes?
 Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
 DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It holds all of our genetic information which is passed down through sexual reproduction DNA has three main functions: 1. DNA Controls
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It holds all of our genetic information which is passed down through sexual reproduction DNA has three main functions: 1. DNA Controls
DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E
 DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E How this Unit is broken down Chapter 10.1 10.3 The structure of the genetic material Chapter 10.4 & 10.5 DNA replication Chapter 10.6 10.15 The flow of genetic information
DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E How this Unit is broken down Chapter 10.1 10.3 The structure of the genetic material Chapter 10.4 & 10.5 DNA replication Chapter 10.6 10.15 The flow of genetic information
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
THE GENETIC CODE Figure 1: The genetic code showing the codons and their respective amino acids
 THE GENETIC CODE As DNA is a genetic material, it carries genetic information from cell to cell and from generation to generation. There are only four bases in DNA and twenty amino acids in protein, so
THE GENETIC CODE As DNA is a genetic material, it carries genetic information from cell to cell and from generation to generation. There are only four bases in DNA and twenty amino acids in protein, so
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
DNA Structure and Protein synthesis
 DNA Structure and Protein synthesis What is DNA? DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes are made of DNA It carries genetic information: controls the activities of cells by providing instructions for making
DNA Structure and Protein synthesis What is DNA? DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes are made of DNA It carries genetic information: controls the activities of cells by providing instructions for making
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
2. From the first paragraph in this section, find three ways in which RNA differs from DNA.
 Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
DNA. translation. base pairing rules for DNA Replication. thymine. cytosine. amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are?
 2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
 Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Ch 10.4 Protein Synthesis
 Ch 10.4 Protein Synthesis I) Flow of Genetic Information A) DNA is made into RNA which undergoes transcription and translation to be made into a protein. II) RNA Structure and Function A) RNA contains
Ch 10.4 Protein Synthesis I) Flow of Genetic Information A) DNA is made into RNA which undergoes transcription and translation to be made into a protein. II) RNA Structure and Function A) RNA contains
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
7.2 Protein Synthesis. From DNA to Protein Animation
 7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Protein Synthesis. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46032 1 Protein Synthesis OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46032 1 Protein Synthesis OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
From Gene to Protein. Chapter 17. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
 Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Living organisms are complex systems. Hundreds of thousands of proteins exist inside each one of us to help carry out our daily functions. These proteins are produced locally,
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Living organisms are complex systems. Hundreds of thousands of proteins exist inside each one of us to help carry out our daily functions. These proteins are produced locally,
PUC Vikasana Program- 2012
 Chromosome Nucleus DNA PUC Vikasana Program- 2012 Introduction Molecular biology is the study of biology at a molecular level. Macromolecules and the macromolecular mechanisms. Interactions between the
Chromosome Nucleus DNA PUC Vikasana Program- 2012 Introduction Molecular biology is the study of biology at a molecular level. Macromolecules and the macromolecular mechanisms. Interactions between the
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Do you remember. What is a gene? What is RNA? How does it differ from DNA? What is protein?
 Lesson 1 - RNA Do you remember What is a gene? What is RNA? How does it differ from DNA? What is protein? Gene Segment of DNA that codes for building a protein DNA code is copied into RNA form, and RNA
Lesson 1 - RNA Do you remember What is a gene? What is RNA? How does it differ from DNA? What is protein? Gene Segment of DNA that codes for building a protein DNA code is copied into RNA form, and RNA
Summary 12 1 DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis Chromosomes and DNA Replication. Name Class Date
 Chapter 12 Summary DNA and RNA 12 1 DNA To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical structure of the gene. Frederick Griffith first learned that some factor from dead, disease-causing
Chapter 12 Summary DNA and RNA 12 1 DNA To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical structure of the gene. Frederick Griffith first learned that some factor from dead, disease-causing
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Biology Multiple Choice 016074 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY Test Code: 016074 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested
Biology Multiple Choice 016074 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY Test Code: 016074 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The virulent strain of the bacterium S. pneumoniae causes disease because it a. has
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The virulent strain of the bacterium S. pneumoniae causes disease because it a. has
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!!
 What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR
 UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR RNA, as previously mentioned, is an acronym for ribonucleic acid. There are many forms
UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR RNA, as previously mentioned, is an acronym for ribonucleic acid. There are many forms
Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping
 Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the discovery of DNA structure. amount of base pairs five-carbon sugar purine DNA polymerases Franklin
Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the discovery of DNA structure. amount of base pairs five-carbon sugar purine DNA polymerases Franklin
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Unit VII DNA to RNA to protein The Central Dogma
 Unit VII DNA to RNA to protein The Central Dogma DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid, the material that contains information that determines inherited characteristics. A DNA molecule is shaped like a spiral staircase
Unit VII DNA to RNA to protein The Central Dogma DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid, the material that contains information that determines inherited characteristics. A DNA molecule is shaped like a spiral staircase
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
 TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION Bell Ringer (5 MINUTES) 1. Have your homework (any missing work) out on your desk and ready to turn in 2. Draw and label a nucleotide. 3. Summarize the steps of DNA replication.
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION Bell Ringer (5 MINUTES) 1. Have your homework (any missing work) out on your desk and ready to turn in 2. Draw and label a nucleotide. 3. Summarize the steps of DNA replication.
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7)
 Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
DNA, RNA, protein synthesis. Sections , , and
 DNA, RNA, protein synthesis Sections 14.1 14.5, 15.1 15.5, and 16.4 16.6 05-09-16 Today s class Extra-credit essay Activity on mitosis, meiosis, and inheritance Lecture and activities on the lecture Extra-credit
DNA, RNA, protein synthesis Sections 14.1 14.5, 15.1 15.5, and 16.4 16.6 05-09-16 Today s class Extra-credit essay Activity on mitosis, meiosis, and inheritance Lecture and activities on the lecture Extra-credit
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
DNA and RNA. Chapter 12
 DNA and RNA Chapter 12 Warm Up Exercise Test Corrections Make sure to indicate your new answer and provide an explanation for why this is the correct answer. Do this with a red pen in the margins of your
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 Warm Up Exercise Test Corrections Make sure to indicate your new answer and provide an explanation for why this is the correct answer. Do this with a red pen in the margins of your
Student Exploration: RNA and Protein Synthesis Due Wednesday 11/27/13
 http://www.explorelearning.com Name: Period : Student Exploration: RNA and Protein Synthesis Due Wednesday 11/27/13 Vocabulary: Define these terms in complete sentences on a separate piece of paper: amino
http://www.explorelearning.com Name: Period : Student Exploration: RNA and Protein Synthesis Due Wednesday 11/27/13 Vocabulary: Define these terms in complete sentences on a separate piece of paper: amino
Comparing RNA and DNA
 RNA The Role of RNA Genes contain coded DNA instructions that tell cells how to build proteins. 1 st step in decoding these genetic instructions = copy part of the base sequence from DNA into RNA. 2 nd
RNA The Role of RNA Genes contain coded DNA instructions that tell cells how to build proteins. 1 st step in decoding these genetic instructions = copy part of the base sequence from DNA into RNA. 2 nd
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review
 AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations
 Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
Pauling/Itano Experiment
 Chapter 12 Pauling/Itano Experiment Linus Pauling and Harvey Itano knew that hemoglobin, a molecule in red blood cells, contained an electrical charge. They wanted to see if the hemoglobin in normal RBC
Chapter 12 Pauling/Itano Experiment Linus Pauling and Harvey Itano knew that hemoglobin, a molecule in red blood cells, contained an electrical charge. They wanted to see if the hemoglobin in normal RBC
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung. Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo
 Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
 By the end of this lesson, I can Relate how Griffith s bacterial experiments showed that a hereditary factor was involved in transformation. Summarize how Avery s experiments led his group to conclude
By the end of this lesson, I can Relate how Griffith s bacterial experiments showed that a hereditary factor was involved in transformation. Summarize how Avery s experiments led his group to conclude
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
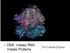 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
 Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein
 Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein I. Overview A. DNA ultimately determines every aspect of a cell from shape to function 1. DNA = 2. Nucleotides of DNA have three units a. A nitrogen-containing
Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein I. Overview A. DNA ultimately determines every aspect of a cell from shape to function 1. DNA = 2. Nucleotides of DNA have three units a. A nitrogen-containing
14 Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 CMPBELL BIOLOY IN FOCS rry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 14 ene Expression: From ene to Protein Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Flow of enetic Information
CMPBELL BIOLOY IN FOCS rry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 14 ene Expression: From ene to Protein Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Flow of enetic Information
Biomolecules: lecture 6
 Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Flow of Genetic Information
 Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication.
 Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication. The difference between replication, transcription, and translation. How
Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication. The difference between replication, transcription, and translation. How
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide
 Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
RNA and Protein Synthesis
 RNA and Protein Synthesis CTE: Agriculture and Natural Resources: C5.3 Understand various cell actions, such as osmosis and cell division. C5.4 Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, bacteria, and
RNA and Protein Synthesis CTE: Agriculture and Natural Resources: C5.3 Understand various cell actions, such as osmosis and cell division. C5.4 Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, bacteria, and
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Chapter 13
 RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review
 DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
Neurospora mutants. Beadle & Tatum: Neurospora molds. Mutant A: Mutant B: HOW? Neurospora mutants
 Chapter 10: Central Dogma Gene Expression and Regulation Mutant A: Neurospora mutants Mutant B: Not made Not made Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are
Chapter 10: Central Dogma Gene Expression and Regulation Mutant A: Neurospora mutants Mutant B: Not made Not made Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE. Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below.
 Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
BIOLOGY. Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins
 BIOLOGY Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins CMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 17 Protein Synthesis 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 17-1 Figure 17.1a n albino racoon Condition
BIOLOGY Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins CMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 17 Protein Synthesis 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 17-1 Figure 17.1a n albino racoon Condition
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
translation The building blocks of proteins are? amino acids nitrogen containing bases like A, G, T, C, and U Complementary base pairing links
 The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
Activity A: Build a DNA molecule
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Building DNA Vocabulary: double helix, DNA, enzyme, lagging strand, leading strand, mutation, nitrogenous base, nucleoside, nucleotide, replication Prior Knowledge Questions
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Building DNA Vocabulary: double helix, DNA, enzyme, lagging strand, leading strand, mutation, nitrogenous base, nucleoside, nucleotide, replication Prior Knowledge Questions
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation
 Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS
 1 CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS * Some contents are adapted from Dr. Jean Gao at UT Arlington Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University 2 Genetics The discovery of
1 CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS * Some contents are adapted from Dr. Jean Gao at UT Arlington Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University 2 Genetics The discovery of
