DNA Replica,on. An,parallel Elonga,on. DNA polymerases. Add nucleo1des only to the free 3 end of a growing strand
|
|
|
- Catherine James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DNA Replica,on nucleoside triphosphate Nucleodes that are added to a growing DNA Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (dntp) supply nucleodes to growing DNA As monomer dntp joins DNA loses two phosphate groups as a molecule of pyrophosphate Fig. 6 4 New end end end end Sugar Phosphate A Base T A T G G G G end T A DNA polymerase T A Pyrophosphate end Nucleoside triphosphate end end An,parallel Elonga,on DNA polymerases Add nucleodes only to the free end of a growing Therefore DNA elongates only in to direcon DNA polymerase synthesizes leading connuously moving toward the replicaon fork
2 Fig. Fig. 6 5 Overview Origin of replication Primer Parental DNA Overall directions of replication Origin of replication RNA primer Sliding clamp DNA poll III lagging Strand constructed away from replicaon fork Okazaki fragments series of segments An,parallel Elonga,on joined together by DNA ligase
3 Fig. Fig. 6 6a Overview Origin of replication Overall directions of replication Fig. 6 6b Fig. 6 6b RNA primer
4 Fig. Fig. 6 6b3 RNA primer Okazaki fragment Fig. 6 6b4 RNA primer Okazaki fragment Fig. 6 6b5 RNA primer Okazaki fragment
5 Fig. Fig. 6 6b6 RNA primer Okazaki fragment Overall direction of replication Fig. 6 7 Overview Origin of replication Single- binding protein Overall directions of replication Helicase Parental DNA DNA pol III Primer Primase DNA pol III 4 DNA pol I 3 DNA ligase DNA replicaon complex The DNA Replica,on omplex proteins that parcipate in replicaon DNA replicaon machine Recent studies probably staonary during the replicaon process support a model in which DNA polymerase molecules reel in parental DNA and extrude newly made daughter DNA molecules DNA Replication Review
6 Proofreading Proofreading and Repairing DNA Eukaryoc DNA ploymerases replace any incorrect nucleodes Mismatch repair repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing DNA can be damaged by chemicals, radioacve emissions, X rays, UV light, and certain molecules (in cigareoe smoke for example) Nucleo,de excision repair nuclease cuts out and replaces damaged stretches of DNA Fig. 6 8 Thymine dimer Nuclease DNA polymerase DNA ligase Replica,ng the Ends of DNA Molecules Limitaons of DNA polymerase create problems for the linear DNA of eukaryoc chromosomes Standard replicaon machinery provides no way to complete the ends repeated rounds of replicaon produce shorter DNA molecules
7 Fig. Fig. 6 9 Ends of parental DNA s Last fragment Previous fragment Parental RNA primer Removal of primers and replacement with DNA where a end is available Second round of replication New leading New lagging Further rounds of replication Shorter and shorter daughter molecules Telomeres Replica,ng the Ends of DNA Molecules Nucleode sequences At ends of eukaryoc chromosomal DNA molecules Do not prevent the shortening of DNA molecules Postpone the erosion of genes near the ends of DNA molecules It has been proposed that the shortening of telomeres is connected to aging Fig. 6 0 µm
8 Then what about gametes? If germ cell chromosomes became shorter in every cell cycle telomerase Replica,ng the Ends of DNA Molecules genes eventually damaged and gametes they produce catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in germ cells fountain of youth? hop:// html Replica,ng the Ends of DNA Molecules The shortening of telomeres might protect cells from cancerous growth by liming the number of cell divisions evidence of telomerase acvity in cancer cells may allow cancer cells to persist DNA packaging Bacterial chromosome ircular, small amount of protein supercoiled, in nucleoid region Eukaryoc chromosome Linear, large amount of protein
9 DNA packaging hroma,n complex of DNA and protein Histones proteins that are responsible for the first level of DNA packing in chroman Fig. 6 a DNA double helix ( nm in diameter) Histones Nucleosome (0 nm in diameter) Histone tail DNA, the double helix Histones Nucleosomes, or beads on a string (0-nm fiber) H Fig. 6 b hromatid (700 nm) 30-nm fiber Loops Scaffold 300-nm fiber Replicated chromosome (,400 nm) 30-nm fiber Looped domains (300-nm fiber) Metaphase chromosome
10 DNA packaging hroman is organized into fibers 0 nm fiber DNA winds around histones to form nucleosome beads Nucleosomes are strung together like beads on a string by linker DNA 30 nm fiber Interacons between nucleosomes cause the thin fiber to coil or fold into this thicker fiber 300 nm fiber DNA packaging The 30 nm fiber forms looped domains that aoach to proteins Metaphase chromosome Looped domains coil further Width of a chromad is 700 nm 30-nm fiber 30-nm fiber LoopsScaffold Looped domains (300-nm fiber) 300-nm fiber hromatid (700 nm) Replicated chromosome (,400 nm) Metaphase chromosome Most chroman DNA packaging loosely packed during interphase Euchroma,n condenses prior to mitosis Loosely packed chroman Heterochroma,n Highly condensed chroman centromeres and telomeres During interphase Dense packing of the heterochroman makes it difficult for the cell to express genec informaon coded in these regions
11 You should now be able to:. Describe the contribuons of the following people: Griffith; Avery, Mcary, and MacLeod; Hershey and hase; hargaff; Watson and rick; Franklin; Meselson and Stahl. Describe the structure of DNA 3. Describe the process of DNA replicaon; include the following terms: anparallel structure, DNA polymerase, leading, lagging, Okazaki fragments, DNA ligase, primer, primase, helicase, topoisomerase, single binding proteins 4. Describe the funcon of telomeres 5. ompare a bacterial chromosome and a eukaryoc chromosome
DNA Model Building and Replica3on
 DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
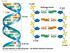 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
The DNA Molecule: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Slide hapter 6 he DN Molecule: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil ampbell and Jane Reece Lectures by hris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Slide hapter 6 he DN Molecule: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil ampbell and Jane Reece Lectures by hris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions Concept 16.1: DNA is the genetic material The Search for the Genetic Material: Scientific Inquiry
 Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chromosomes. Nucleosome. Chromosome. DNA double helix. Coils. Supercoils. Histones
 Chromosomes Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Evidence That DNA Can Transform Bacteria Frederick Griffith s experiment 1928 Griffith called the phenomenon transformation
Chromosomes Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Evidence That DNA Can Transform Bacteria Frederick Griffith s experiment 1928 Griffith called the phenomenon transformation
BIOLOGY. The Molecular Basis of Inheritance CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life s Operating Instructions
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life s Operating Instructions
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James
BIOLOGY. Chapter 14 DNA Structure and Function
 BIOLOY hapter 14 DN Structure and Function Figure 14.11 Figure 16.22a Figure 14.11 DN double helix (2 nm in diameter) Nucleosome (10 nm in diameter) DN, the double helix Histones Histones Histone tail
BIOLOY hapter 14 DN Structure and Function Figure 14.11 Figure 16.22a Figure 14.11 DN double helix (2 nm in diameter) Nucleosome (10 nm in diameter) DN, the double helix Histones Histones Histone tail
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
BIOLOGY DNA. DNA: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance. DNA s Discovery. Watson and Crick. Rosalind Franklin. The Players. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA
 6 MPBELL BIOLOY ENH EDIION Reece Urry ain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson DN: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance DN Deoxyribonucleic acid DN he blueprint to making proteins!!! hromosomes located inside the nucleus
6 MPBELL BIOLOY ENH EDIION Reece Urry ain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson DN: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance DN Deoxyribonucleic acid DN he blueprint to making proteins!!! hromosomes located inside the nucleus
You Should Be Able To
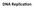 DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
10/23/2011. Quiz Oct Overview: Life s Operating Instructions DNA
 hapter 6 DN: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Quiz Oct 23 20. In the protein coupled receptor - IP3 pathway, the α subunit of the -protein activates what molecule? 2. In the protein coupled receptor -
hapter 6 DN: he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Quiz Oct 23 20. In the protein coupled receptor - IP3 pathway, the α subunit of the -protein activates what molecule? 2. In the protein coupled receptor -
Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of. Chapter 16. Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme
 Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 hapter 16 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Dr. Wendy Sera Houston ommunity ollege Biology 1406 Key oncepts in hapter 16 1. DN is the genetic material 2. Many proteins work together in DN replication and
hapter 16 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Dr. Wendy Sera Houston ommunity ollege Biology 1406 Key oncepts in hapter 16 1. DN is the genetic material 2. Many proteins work together in DN replication and
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 hapter 6 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Dr. Wendy Sera Key oncepts in hapter 6. DN is the genetic material. Many proteins work together in DN replication and repair. 3. chromosome consists of a DN molecule
hapter 6 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Dr. Wendy Sera Key oncepts in hapter 6. DN is the genetic material. Many proteins work together in DN replication and repair. 3. chromosome consists of a DN molecule
Chapter 16. The Molecular Basis of Inheritance. Biology Kevin Dees
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance DNA Life s instructions!!!! Deoxyribonucleic Acid Nucleic acid polymer from nucleotide monomers Unique in that it can: Self replicate Carry information History
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance DNA Life s instructions!!!! Deoxyribonucleic Acid Nucleic acid polymer from nucleotide monomers Unique in that it can: Self replicate Carry information History
AP Biology Day 27. Wednesday, October 26, 2016
 AP Biology Day 27 Wednesday, October 26, 2016 Do-Now 1. Double check Is your unit log complete? Is your lab notebook up to date with scores? Did you write your Unit 4 log standards? Did you begin filling
AP Biology Day 27 Wednesday, October 26, 2016 Do-Now 1. Double check Is your unit log complete? Is your lab notebook up to date with scores? Did you write your Unit 4 log standards? Did you begin filling
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 LEURE PRESENIONS For MPBELL BIOLOY, NINH EDIION Jane B. Reece, Lisa. Urry, Michael L. ain, Steven. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson hapter 16 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lectures by
LEURE PRESENIONS For MPBELL BIOLOY, NINH EDIION Jane B. Reece, Lisa. Urry, Michael L. ain, Steven. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson hapter 16 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lectures by
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 6 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance MPBELL BIOLOY ENH EDIION Reece Urry ain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Life s Operating Instructions In 953, James Watson and Francis rick introduced an elegant double-helical
6 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance MPBELL BIOLOY ENH EDIION Reece Urry ain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Life s Operating Instructions In 953, James Watson and Francis rick introduced an elegant double-helical
DNA Replication and Repair
 DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DNA Replication. Packet #17 Chapter #16
 DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
1. DNA Structure. Genetic Material: Protein or DNA? 10/28/2015. Chapter 16: DNA Structure & Replication. 1. DNA Structure. 2.
 hapter 6: DN Structure & Replication. DN Structure 2. DN Replication. DN Structure hapter Reading pp. 33-38 enetic Material: Protein or DN? Until the early 950 s no one knew for sure, but it was generally
hapter 6: DN Structure & Replication. DN Structure 2. DN Replication. DN Structure hapter Reading pp. 33-38 enetic Material: Protein or DN? Until the early 950 s no one knew for sure, but it was generally
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis
 Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life s Operating
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life s Operating
Chapter 13 Active Reading Guide The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 13 Active Reading Guide The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Section 1 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. Why did researchers originally think that
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 13 Active Reading Guide The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Section 1 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. Why did researchers originally think that
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
The Molecul Chapter ar Basis 16: The M of olecular Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1
 he Chapter Molecular 16: he Basis Molecular of Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1 dditional Evidence hat DN Is the Genetic Material It was known that DN is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting
he Chapter Molecular 16: he Basis Molecular of Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1 dditional Evidence hat DN Is the Genetic Material It was known that DN is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting
Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA Replication D. The Mechanism of DNA Replication E. DNA Proofreading
Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA Replication D. The Mechanism of DNA Replication E. DNA Proofreading
DNA and Its Role in Heredity. DNA and Its Role in Heredity. A. DNA: The Genetic Material. A. DNA: The Genetic Material.
 DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA E. DNA Proofreading and Repair F. Practical Applications of DNA A.
DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA E. DNA Proofreading and Repair F. Practical Applications of DNA A.
DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul. Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47204 1 DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m47204 1 DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
2. Why did researchers originally think that protein was the genetic material?
 AP Biology Chapter 13 Reading Guide The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 13.1 DNA is the Genetic Material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. Why did researchers originally
AP Biology Chapter 13 Reading Guide The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 13.1 DNA is the Genetic Material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. Why did researchers originally
DNA Replication * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45475 1 DNA Replication * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m45475 1 DNA Replication * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
Chapter 16 : The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 : The Molecular Basis of Inheritance over view : - In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the world with an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid(dna).
Chapter 16 : The Molecular Basis of Inheritance over view : - In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the world with an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid(dna).
The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 hapter 16 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil ampbell and Jane Reece Lectures by hris Romero Scientific History he march to understanding that DN is
hapter 16 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil ampbell and Jane Reece Lectures by hris Romero Scientific History he march to understanding that DN is
DNA is the genetic material [2].
![DNA is the genetic material [2]. DNA is the genetic material [2].](/thumbs/75/71793754.jpg) GUIDED READING - Ch. 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not
GUIDED READING - Ch. 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not
Transformation: change in genotype & phenotype due to assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
 DNA Replication Chapter 16: DNA as Genetic Material Genes are on Chromosomes T.H. Morgan o Working with Drosophila (fruit flies) o Genes are on chromosomes o But is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes
DNA Replication Chapter 16: DNA as Genetic Material Genes are on Chromosomes T.H. Morgan o Working with Drosophila (fruit flies) o Genes are on chromosomes o But is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes
Overview: Life s Opera6ng Instruc6ons
 h. 9 Molecular Biology BIOL 60 Overview: Life s Opera6ng Instruc6ons James Watson and Francis rick 953 - produced double- helical model for the structure of DN Structural Model of DN Rosalind Franklin
h. 9 Molecular Biology BIOL 60 Overview: Life s Opera6ng Instruc6ons James Watson and Francis rick 953 - produced double- helical model for the structure of DN Structural Model of DN Rosalind Franklin
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. The search for identifying
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. The search for identifying
Genetic material must be able to:
 Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 LEURE PRESENIONS For MPBELL BIOLOY, NINH EDIION Jane B. Reece, Lisa. Urry, Michael L. ain, Steven. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson hapter 6 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lectures by
LEURE PRESENIONS For MPBELL BIOLOY, NINH EDIION Jane B. Reece, Lisa. Urry, Michael L. ain, Steven. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson hapter 6 he Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lectures by
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication. Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes.
 DNA replication Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. Figure 10.8 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/ DNAi_replication_schematic-lg.mov
DNA replication Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. Figure 10.8 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/ DNAi_replication_schematic-lg.mov
DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 2 Chapter 16 Activity #2 BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA: Nucleotides: NAME DATE PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION 1. 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose) 2. Nitrogenous
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 2 Chapter 16 Activity #2 BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA: Nucleotides: NAME DATE PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION 1. 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose) 2. Nitrogenous
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule.
 1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
AP Biology Chapter 16 Notes:
 AP Biology Chapter 16 Notes: I. Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance a. Overview: i. April 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick great the double helix model of DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid ii. DNA
AP Biology Chapter 16 Notes: I. Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance a. Overview: i. April 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick great the double helix model of DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid ii. DNA
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.8 DNA REPLICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
Friday, April 17 th. Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation. AP Biology
 Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE
 STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
Chapter 16. The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical model for the
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical model for the
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical model for the structure of
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Lecture Outline Overview In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical model for the structure of
Essential Questions. DNA: The Genetic Material. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions Which experiments led to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material? What is the basic structure of DNA? What is the basic structure of eukaryotic chromosomes? Vocabulary Review nucleic
Essential Questions Which experiments led to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material? What is the basic structure of DNA? What is the basic structure of eukaryotic chromosomes? Vocabulary Review nucleic
Brief History. Many people contributed to our understanding of DNA
 DNA (Ch. 16) Brief History Many people contributed to our understanding of DNA T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Erwin Chargaff (1947) Hershey & Chase (1952)
DNA (Ch. 16) Brief History Many people contributed to our understanding of DNA T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Erwin Chargaff (1947) Hershey & Chase (1952)
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
Proposed Models of DNA Replication. Conservative Model. Semi-Conservative Model. Dispersive model
 5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
14 DNA STRUCTURE, REPLICATION, AND ORGANIZATION
 14 DNA STRUCTURE, REPLICATION, AND ORGANIZATION Chapter Outline 14.1 ESTABLISHING DNA AS THE HEREDITARY MOLECULE Experiments began when Griffith found a substance that could genetically transform pneumonia
14 DNA STRUCTURE, REPLICATION, AND ORGANIZATION Chapter Outline 14.1 ESTABLISHING DNA AS THE HEREDITARY MOLECULE Experiments began when Griffith found a substance that could genetically transform pneumonia
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In April 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
DNA The Genetic Material
 DNA The Genetic Material 2006-2007 Chromosomes related to phenotype T.H. Morgan working with Drosophila fruit flies associated phenotype with specific chromosome white-eyed male had specific X chromosome
DNA The Genetic Material 2006-2007 Chromosomes related to phenotype T.H. Morgan working with Drosophila fruit flies associated phenotype with specific chromosome white-eyed male had specific X chromosome
DNA Structure. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
Hershey & Chase Avery, MacLeod, & McCarty DNA: The Genetic Material
 DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material. The Nature of Genetic Material. Chemical Nature of Nucleic Acids. Chromosomes - DNA and protein
 Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
The flow of Genetic information
 The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 11 DNA Replication
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
Welcome to Class 18! Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives. Replication is semiconservative! Replication: DNA DNA! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Wednesday, April 9 th. DNA The Genetic Material Replication. Chapter 16
 Wednesday, April 9 th DNA The Genetic Material Replication Chapter 16 Modified from Kim Foglia Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick
Wednesday, April 9 th DNA The Genetic Material Replication Chapter 16 Modified from Kim Foglia Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Erwin Chargaff
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Erwin Chargaff
DNA is a functional genetic material as it:
 DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
