RANGELAND SEEDING. Goals. Burn assessment. Site prep. --Tip Hudson, WSU Extension rangeland & livestock regional specialist
|
|
|
- Derek Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RANGELAND SEEDING --Tip Hudson, WSU Extension rangeland & livestock regional specialist Goals Goals for seeding rangeland are diverse. Increased plant diversity, improved forage quantity or quality for livestock, tall grass for structural diversity, plants producing large or abundant seed for wildlife, native forbs (wildflowers) for a beautiful spring view, or easily established, deep-rooting grasses for soil stabilization in disturbed areas are just some of the potential goals for managing a piece of property. Reclamation of burned soils may also dictate a particular plan of action and species mix. Burn assessment Areas which are most at risk of soil erosion are those which previously did not have much perennial grass cover. These often include areas where the forest canopy was mostly closed, leaving little herbaceous cover in the understory, such as grasses and forbs. While the roots of shrubs and short trees function well as rebar for soil, the grasses and forbs are really what hold the finer particles together and prevent sediment loss in two primary ways: absorbing the energy of raindrops before the drops impact and dislodge soil; and holding soil particles and aggregates together with their shallow, fibrous roots. In areas with little grass before the fire or with grasses visibly burned into the ground (crowns and meristematic tissue killed by high temperature) it will be very important to apply seed the fall after the fire. Fall-planted seed will not germinate until spring, leaving little cover this winter, but these plants will provide long-term protection starting the year after the fire. Where a fire burned hot enough to create hydrophobic soils, more aggressive practices may be necessary to prevent soil erosion and to prepare soil for seeding. Under these hydrophobic conditions, contour felling and other forestry practices recommended by NRCS and DNR are likely the best short-term control measures. Perhaps the biggest factor is whether we receive heavy fall rain before a protective snow layer is present. Site prep Timing October 1 to first snowfall is the ideal window for applying grass seed. This is early enough to catch fall rain, late enough that it won t germinate and frost-kill the seedlings. Most seedings on non-irrigated land should occur in the fall (October 1-first snowfall). Fall seedings are typically more successful on non-irrigated acreage in the Intermountain West because seedlings are able to take advantage of fall and winter moisture, it is late enough that seedlings won t germinate and frost-
2 kill, and soils dry out relatively quickly in the spring depending on unpredictable spring precipitation, making spring seedings notoriously unsuccessful. Weed control Control weeds and other undesirable vegetation prior to seeding. Consider the timing necessary to accomplish this. Where there is a sufficient remnant population of desirable perennial plants, it may be advantageous to use selective herbicides to kill the undesirables and interseed into the existing plant community. Some herbicides that work by inhibiting germination should usually not be used in combination with a seeding. A good example is cheatgrass control. Imazapic is a germination inhibitor and it is very good at stopping or preventing cheatgrass invasion/dominance. It has little to no effect, at recommended rates, on perennial plants. It does, however, cause a problem for annual and perennial grass seed, so attempting cheatgrass control and fall seeding during the same year is a waste of seed. Soil conditions Grass seed must contact the soil to germinate. Usually harrowing or raking will expose enough soil to accomplish this. After a fire mechanical treatment may not be necessary. Once applied, the seed also needs to have ~1/8 soil coverage. A culti-packer or roller works best, but going over the field again with a harrow or drag works as well. On rangeland areas with abundant rocks or shrubs, or on sites with high slope, it may be impossible to conduct any site prep. On these areas, one is limited to a controlled burn before seeding, livestock impact after seeding, or take your chances with whatever litter cover is on site. Where enough slope exists to allow water runoff and soil erosion to occur, and where there is little remaining rooted vegetation to stabilize soil, it may be necessary to artificially create enough surface roughness to generate microsites for germination and physical barriers for water that may try to carry your seed away. If raking, lightly cultivating, or harrowing, travel with the contour of the slope as much as possible to minimize the potential for soil erosion. Seed application methods There are two methods for seeding: broadcast and direct/drilled. Broadcast seeding is easier on rough terrain where there are rocks, slopes, uneven ground, other vegetation, but has a lower success rate than drilled seed. If broadcast seeding, consider dragging something like a harrow over the site to scarify the soil surface and provide opportunity for seeds to contact mineral soil. Grain drills generally do not work except in deeper, rock-free soils, but a rangeland drill is designed to work around these obstacles and dramatically increases the success rate (germination and establishment of seeds). Regardless of site preparation measures, the site conditions ideal for perennial seeds are as follows: 1. Seeds must contact bare mineral soil. If they are sitting on top of dead plant material seeds will either dry out or be consumed by birds and rodents. This can be usually be accomplished by a field entry with a harrow or pasture drag. If this is a pasture that has been plowed, disked, and rolled, the soil should be firm; fluffed soil from excessive tillage won t provide enough stability for the roots and is susceptible to wind and water erosion. Tillage is not recommended for low
3 rainfall sites. Seeding into unplowed but harrowed or raked soil is preferable to avoid soil erosion and mass germination of weed seeds that are already in the soil seed bank. 2. If tillage is used to prepare the seedbed, Topsoil (first ½-1 ) should be well-pulverized and mollified. This means loose, not cloddy, but not so powdery loose that crusting takes place. Crusting will prevent seedling emergence. TILLAGE (PLOWING/DISKING) IS NOT USUALLY RECOMMENDED FOR DRYLAND SEEDING. 3. The seed site should be free of invasive plants. The presence of annual weeds or perennials that are competing for the same resources as the seedling is the most common and significant obstacle to establishment. This doesn t mean eliminating all live vegetation on the entire seeding area, as dryland areas typically have spaces between plants, but reseeding is usually done where all or part of the existing vegetation is unwanted and some level and form of vegetation control is beneficial. This is most effectively accomplished using selective herbicides or controlled grazing on annual grasses. 4. The area should be free of the seed of competitive species. This typically means ensuring that the existing undesirable vegetation doesn t produce seed in the growing season prior to planting. If this is a concern, it may be beneficial to summer fallow the site: kill the undesirable vegetation in the fall and/or spring and give the site one full growing season to see what comes up. If you don t want it, kill it, and plant the following fall with a better chance of success. 5. There should be a moderate amount of mulch or plant residue on or in the soil surface. (Don t scrape a site clean with a tractor!) With a fall planting, there is generally a sufficient amount of dead plant material from this year s growing season that is incorporated through the winter. (Adapted from Kingery, 1997) Aftercare for new plants If seeding is for pasture forage, do not graze until the following year, and then only if plants cannot be pulled by hand. If you can pull the grass plants out, roots and all, they are not ready for grazing. Weed control may still be necessary, especially in year 1 and 2 post-seeding. Any kind of soil disturbance often stimulates weed seeds which are already in the soil seed bank to germinate and establish. It is not uncommon to have a profusion of weeds you didn t even know were there to show up following a light mechanical treatment. Herbicide recommendations are dependent entirely on the weed species present. Seed selection Select seed that is well-suited to your site and your goals. A seed guide from any of the major seed dealers is a good place to start. A seed mix is preferable to a single species because each species has different strengths and weaknesses and a combination of species has much greater biological resiliency to grazing, fire, insects, drought, prolonged cold, excess moisture, etc., than a monoculture.
4 Dryland grass species descriptions (not for irrigated pasture) Bluebunch wheatgrass ($) an excellent native species adapted to low rainfall areas that is highly palatable; seed is more expensive than introduced species; exercise care in grazing to avoid late spring damage Basin wildrye Very large native plant that once occupied much of the Yakima floodplain; highly salt-tolerant and has an excellent root system; good for wildlife cover as well as livestock **Crested wheatgrass (Hycrest or Nordan) easy to establish, short-lived if not grazed **Hard fescue used in roadcuts to stabilize soil; easy to establish and tremendous root system. **Intermediate wheatgrass a good introduced grass for alkaline soils; relatively unpalatable Figure 2. Bluebunch wheatgrass plant. Photo by Tip Hudson **Siberian wheatgrass (Vavilov) introduced, short bunchgrass that does well above 7 rainfall zones Slender wheatgrass relatively unpalatable but produces a vigorous root system; good for reclamation Thickspike wheatgrass ($) a very tough grass that is good for shallow, rocky soils; tolerates grazing well; more palatable than crested wheatgrass **Good choice for value and ease of establishment $ Expensive seed Recommended seed mixes If you were to order a custom mix for post-fire rehabiliation, NRCS, WSU, and the WSU Plant Materials Center folks would recommend: Blue Wildrye 6 lbs/ac Mountain Brome 4 lbs Slender wheatgrass 4 lbs Bluebunch wheatgrass 4 lbs Landmark Seed has this available ( ); talk to Harold Wood. If you have areas that are exceptionally steep and burned very hot (enough to kill perennial grasses) you could add winter wheat (annual grass with rapid spring growth).
5 Functional seed mixes that are on hand locally include: Old Mill Country Store (Ellensburg) erosion control mix (good mix, not for pasture) Hard fescue - 20 each Annual ryegrass Sheep fescue Creep red fescue Canada bluegrass Mid-State Coop, dryland range mix (good all-purpose mix, very drought-tolerant, not great if grazed range) 25 Oahe intermediate wheatgrass 24 Hycrest crested wheatgrass 20 Sheep fescue 19 Hard fescue 10 Gulf annual ryegrass Phil Hess (509) [local forest consultant] custom forest mix (temporarily on hand) (not ideal for grazing land) 40% siberian or crested 20% hard fescue 20% sheep fescue 10% sherman big bluegrass 10% sandberg bluegrass Seed dealers Old Mill Country Store: (509) Midstate Co-op: (509) Arnold s Ranch & Home: Cle Elum Farm & Home: Kern Company: Smith Kem: Seed suppliers/dealers BFI Native Seed (Jerry Benson): (509) Landmark Seed: ( Rainier Seed: (800) Grassland West (grasslandwest.com) Seed application contractors BFI Native Seed: (509) No-till pasture drill available for rent The South Yakima Conservation District has a no-till pasture drill available at a rate of $2/acre with a $100 refundable deposit. It is a 7 rancher model with a hitch assembly no trailer required and requires a ~50-horse tractor. The drill uses a sponge metering system and has one seed bin. Interested customers can contact the SYCD at (509) to schedule usage. Yakima County residents have first priority, so call well in advance of anticipated use. Late summer/early fall are good times to interseed existing grass stands or to establish a new stand in dead turf (irrigated pastures). The drill will also work on rangeland areas without much exposed rock or dense sagebrush. Dryland seedings should be done after plants are dormant, usually after October 15.
6 Weed Whackerz (Brett Graham): Clean Image Services:
Practical Applications
 Practical Applications wsm.wsu.edu/discovery/index.php/tag/cheatgrass/ Rachel Mealor Extension Range Specialist Department of Renewable Resources and Brian Mealor Extension Weed Specialist Department of
Practical Applications wsm.wsu.edu/discovery/index.php/tag/cheatgrass/ Rachel Mealor Extension Range Specialist Department of Renewable Resources and Brian Mealor Extension Weed Specialist Department of
Seeding. Rangeland. Tommy G. Welch, Barron S. Rector and James S. Alderson*
 Seeding Rangeland. Tommy G. Welch, Barron S. Rector and James S. Alderson* Soil and water conservation, high quality forage production for livestock and wildlife, revegetation of deteriorated rangeland
Seeding Rangeland. Tommy G. Welch, Barron S. Rector and James S. Alderson* Soil and water conservation, high quality forage production for livestock and wildlife, revegetation of deteriorated rangeland
Big Horn Bas in Irrigation
 GROWERS GUIDE Big Horn Bas in Irrigation Water Management Program Big Horn Bas in Irrigation Water Management Program Index: Basic Crop Information Water Requirements Growing Seasons Drought Tolerant Crop
GROWERS GUIDE Big Horn Bas in Irrigation Water Management Program Big Horn Bas in Irrigation Water Management Program Index: Basic Crop Information Water Requirements Growing Seasons Drought Tolerant Crop
44 GRASSLAND RESTORATION
 Table of Contents 6 TABLES 6 FIGURES 8 LIMITATIONS 9 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION 9 Background 10 Management Contexts 11 Rangeland Seeding Objectives 11 Potential Natural Community and. Plant Succession 12
Table of Contents 6 TABLES 6 FIGURES 8 LIMITATIONS 9 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION 9 Background 10 Management Contexts 11 Rangeland Seeding Objectives 11 Potential Natural Community and. Plant Succession 12
Seed Mixes for Western Montana
 Seed Mixes for Western Montana By Karli Becher and Ben Montgomery, Ronan NRCS Field Office Looking for general seed mix suggestions? The Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) in Ronan and the Lake
Seed Mixes for Western Montana By Karli Becher and Ben Montgomery, Ronan NRCS Field Office Looking for general seed mix suggestions? The Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) in Ronan and the Lake
From the Ground Up- Field Soil Considerations
 From the Ground Up- Field Soil Considerations Ted Bilderback Nursery Extension Specialist Department of Horticulture Science North Carolina State University Ted_Bilderback@ncsu.edu http://www.ces.ncsu.edu/depts/hort/nursery/
From the Ground Up- Field Soil Considerations Ted Bilderback Nursery Extension Specialist Department of Horticulture Science North Carolina State University Ted_Bilderback@ncsu.edu http://www.ces.ncsu.edu/depts/hort/nursery/
Options for Improving Forage Production on Pastures and Hay Lands Fraser Stewart, Manitoba Forage Council 2004
 Options for Improving Forage Production on Pastures and Hay Lands Fraser Stewart, Manitoba Forage Council 2004 The productivity of a forage field depends upon many factors including available moisture
Options for Improving Forage Production on Pastures and Hay Lands Fraser Stewart, Manitoba Forage Council 2004 The productivity of a forage field depends upon many factors including available moisture
Two, Four, Eight Let s Renovate. Dr. AJ Foster Regional Agronomy Specialist University of Missouri Extension Stoddard County
 Two, Four, Eight Let s Renovate Dr. AJ Foster Regional Agronomy Specialist University of Missouri Extension Stoddard County What we ll be covering: Introduction Definitions Know your forage options Existing
Two, Four, Eight Let s Renovate Dr. AJ Foster Regional Agronomy Specialist University of Missouri Extension Stoddard County What we ll be covering: Introduction Definitions Know your forage options Existing
Dryland Pasture for Horses
 Dryland Pasture for Horses Many small ranches and horse facilities in the area utilize some dry, non-irrigated land for horse pasture. These pastures are often used as holding areas or exercise runs. They
Dryland Pasture for Horses Many small ranches and horse facilities in the area utilize some dry, non-irrigated land for horse pasture. These pastures are often used as holding areas or exercise runs. They
Grassed Waterway Improvement and Gully Restoration
 Revised April 2007 Agdex 573-5 Grassed Waterway Improvement and Gully Restoration Each year, tonnes of topsoil are eroded from localized areas on some Alberta farms. This loss is serious for several reasons:
Revised April 2007 Agdex 573-5 Grassed Waterway Improvement and Gully Restoration Each year, tonnes of topsoil are eroded from localized areas on some Alberta farms. This loss is serious for several reasons:
The use of buckwheat as a precise weed control tool
 The use of buckwheat as a precise weed control tool Thomas Björkman Department of Horticultural Sciences, Cornell University, Geneva, NY 14456 tnb1@cornell.edu New England farmers have long used buckwheat
The use of buckwheat as a precise weed control tool Thomas Björkman Department of Horticultural Sciences, Cornell University, Geneva, NY 14456 tnb1@cornell.edu New England farmers have long used buckwheat
Restoration Theory and Practice
 Restoration Theory and Practice An Overview PCAP 2014 Native Prairie Restoration/Reclamation Workshop January 29 th, 2014 Regina, Sk Larry K. Gabruch Native Plant Solutions, Saskatoon OVERVIEW Project
Restoration Theory and Practice An Overview PCAP 2014 Native Prairie Restoration/Reclamation Workshop January 29 th, 2014 Regina, Sk Larry K. Gabruch Native Plant Solutions, Saskatoon OVERVIEW Project
Seeding of Areas Burned by Wildfires. Revised Range Branch Ministry of Forests, Lands, and Natural Resource Operations
 Seeding of Areas Burned by Wildfires Revised 07 Range Branch Ministry of Forests, Lands, and Natural Resource Operations Seeding of areas burned by wildfires July 07 Broad scale seeding of all burned areas
Seeding of Areas Burned by Wildfires Revised 07 Range Branch Ministry of Forests, Lands, and Natural Resource Operations Seeding of areas burned by wildfires July 07 Broad scale seeding of all burned areas
Case Study: Legume Inter-Seeding Field Trials, Lake County, MT Sprinkler-Irrigated Sites
 Page 1 Case Study: Legume Inter-Seeding Field Trials, Lake County, MT Sprinkler-Irrigated Sites Field studies conducted in Lake County by the Lake County Conservation District (LCCD) and the NRCS Field
Page 1 Case Study: Legume Inter-Seeding Field Trials, Lake County, MT Sprinkler-Irrigated Sites Field studies conducted in Lake County by the Lake County Conservation District (LCCD) and the NRCS Field
ESTABLISHING ALFALFA USING NO-TILL TECHNIQUES
 ESTABLISHING ALFALFA USING NO-TILL TECHNIQUES Gary Bates Forage Specialist The University of Tennessee There have been many changes in agriculture over the last 50 years. One of the greatest has been the
ESTABLISHING ALFALFA USING NO-TILL TECHNIQUES Gary Bates Forage Specialist The University of Tennessee There have been many changes in agriculture over the last 50 years. One of the greatest has been the
into Existing Forage Stands
 Sod-Seeding into Existing Forage Stands Manitoba has nearly 4 million acres (1.6 million hectares) of unimproved pasture and hayland. However, productivity from much of this area is limited due to a number
Sod-Seeding into Existing Forage Stands Manitoba has nearly 4 million acres (1.6 million hectares) of unimproved pasture and hayland. However, productivity from much of this area is limited due to a number
Applying best stubble heights on rangelands RANGELAND HEALTH BROCHURE 6
 Applying best stubble heights on rangelands RANGELAND HEALTH BROCHURE 6 Contents What is stubble height?...................................... 1 What is a key area?.........................................
Applying best stubble heights on rangelands RANGELAND HEALTH BROCHURE 6 Contents What is stubble height?...................................... 1 What is a key area?.........................................
~ ERNST. lmj SEEDS PLANTING GUIDE. I I (800)
 MINIMUM-TILL EQUIPMENT Minimum-till equipment is used to incorporate a portion of the surface vegetation into the soil and level uneven surfaces. One of the most common tools is a disc, which cuts through
MINIMUM-TILL EQUIPMENT Minimum-till equipment is used to incorporate a portion of the surface vegetation into the soil and level uneven surfaces. One of the most common tools is a disc, which cuts through
EC Know and Control Downy Brome
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1970 EC70-188 Know and Control Downy Brome
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1970 EC70-188 Know and Control Downy Brome
7.0 GRAZING MANAGEMENT
 GRAZING MANAGEMENT 7.1 Assessing Grazing Resources 7.1.1 Tame pastures 7.1.2 Annual pastures 7.1.3 Native range 7.1.4 Forest pastures 7.1.5 Combined native and tame pastures 7.1.6 Riparian pastures 7.2
GRAZING MANAGEMENT 7.1 Assessing Grazing Resources 7.1.1 Tame pastures 7.1.2 Annual pastures 7.1.3 Native range 7.1.4 Forest pastures 7.1.5 Combined native and tame pastures 7.1.6 Riparian pastures 7.2
href=" 1d3227ea7bfd4d1085ec1738dce6dd611d">Pr esentation<
 SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE Pr
SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE Pr
IMPROVING PASTURES BY RENOVATION Ed Ballard,Retired Animal Systems Educator University of Illinois Extension
 IMPROVING PASTURES BY RENOVATION Ed Ballard,Retired Animal Systems Educator University of Illinois Extension In Illinois, pastures are generally relegated to land that is too steep and rocky for row crops.
IMPROVING PASTURES BY RENOVATION Ed Ballard,Retired Animal Systems Educator University of Illinois Extension In Illinois, pastures are generally relegated to land that is too steep and rocky for row crops.
Bald Fire Salvage and Restoration Project
 Bald Fire Salvage and Restoration Project Range Report Prepared by: KC Pasero Rangeland Management Specialist Hat Creek Ranger District /s/ KC Pasero April 27, 2015 Introduction The Bald Fire Salvage and
Bald Fire Salvage and Restoration Project Range Report Prepared by: KC Pasero Rangeland Management Specialist Hat Creek Ranger District /s/ KC Pasero April 27, 2015 Introduction The Bald Fire Salvage and
SEED
 PROTECTS THE SOIL SAVES YOU MONEY www.pennington.com 1-800-285-SEED WHO IS PENNINGTON SEED? Pennington has a long history in the farming industry starting with the first members of the Pennington family
PROTECTS THE SOIL SAVES YOU MONEY www.pennington.com 1-800-285-SEED WHO IS PENNINGTON SEED? Pennington has a long history in the farming industry starting with the first members of the Pennington family
Grazing Systems. " Grazing period = The season and number of days during which a pasture is grazed.
 Grazing Systems Grazing systems are controlled grazing management practices that manipulate livestock to systematically control periods of grazing, deferment, or rest. An extremely important concept in
Grazing Systems Grazing systems are controlled grazing management practices that manipulate livestock to systematically control periods of grazing, deferment, or rest. An extremely important concept in
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science. Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices
 Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices 1 Terms Conservation tillage Continuous cropping Conventional tillage Crop rotation Double cropping Organic farming
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices 1 Terms Conservation tillage Continuous cropping Conventional tillage Crop rotation Double cropping Organic farming
Permanent Pastures For Delaware
 Revision Date: 9/1/1998 Richard Barczewski, PhD Animal Scientist Richard W Taylor, PhD Extension Specialist III AF-10 Permanent Pastures For Delaware Pasture, like any other crop, must be properly managed
Revision Date: 9/1/1998 Richard Barczewski, PhD Animal Scientist Richard W Taylor, PhD Extension Specialist III AF-10 Permanent Pastures For Delaware Pasture, like any other crop, must be properly managed
INCREASING NATIVE PLANT DIVERSITY IN CRESTED WHEATGRASS STANDS: THEORY, PRACTICE AND PROBLEMS. Val Anderson and Robert Cox Brigham Young University
 INCREASING NATIVE PLANT DIVERSITY IN CRESTED WHEATGRASS STANDS: THEORY, PRACTICE AND PROBLEMS Val Anderson and Robert Cox Brigham Young University Sagebrush-grass Steppe Areas 50 million hectares in Western
INCREASING NATIVE PLANT DIVERSITY IN CRESTED WHEATGRASS STANDS: THEORY, PRACTICE AND PROBLEMS Val Anderson and Robert Cox Brigham Young University Sagebrush-grass Steppe Areas 50 million hectares in Western
Successful Food Plots for Wildlife Clifton Martin OSU Extension Muskingum County
 Successful Food Plots for Wildlife Clifton Martin OSU Extension Muskingum County A frame pictures. Image source, bugwood.org Food plots alone do not create large antlered, trophy sized whitetail deer.
Successful Food Plots for Wildlife Clifton Martin OSU Extension Muskingum County A frame pictures. Image source, bugwood.org Food plots alone do not create large antlered, trophy sized whitetail deer.
Establishing Native Forbs
 Establishing Native Forbs Native forbs are broadleaf plants native to Missouri s natural communities. They come in a variety of colors and shapes, and provided critical food and shelter for many wildlife
Establishing Native Forbs Native forbs are broadleaf plants native to Missouri s natural communities. They come in a variety of colors and shapes, and provided critical food and shelter for many wildlife
Cool Season Grass Establishment. Doug Shoup Southeast Area Agronomist
 Cool Season Grass Establishment Doug Shoup Southeast Area Agronomist Introduction Smooth Brome and tall fescue are important cool season grasses for eastern Kansas Well adapted High production Quality
Cool Season Grass Establishment Doug Shoup Southeast Area Agronomist Introduction Smooth Brome and tall fescue are important cool season grasses for eastern Kansas Well adapted High production Quality
8/31/2010. Diversity - the number of different forage plants that are well represented (20% or more of plant cover) in a pasture
 2 nd Iowa GLCI Grazing Conference Aug 23-24, 2010 Management for Diverse Pastures? Diverse Pastures??? di verse -- adj. 1. of a different kind, form, etc.; unlike: 2. of various kinds or forms; multi-form.
2 nd Iowa GLCI Grazing Conference Aug 23-24, 2010 Management for Diverse Pastures? Diverse Pastures??? di verse -- adj. 1. of a different kind, form, etc.; unlike: 2. of various kinds or forms; multi-form.
Joe Grant UC Cooperative Extension San Joaquin County. Janine Hasey UC Cooperative Extension Sutter, Yuba & Colusa Counties
 Joe Grant UC Cooperative Extension San Joaquin County Janine Hasey UC Cooperative Extension Sutter, Yuba & Colusa Counties Young Almond & Walnut Orchards Workshop, January 14, 2016 http://anrcatalog.ucanr.edu
Joe Grant UC Cooperative Extension San Joaquin County Janine Hasey UC Cooperative Extension Sutter, Yuba & Colusa Counties Young Almond & Walnut Orchards Workshop, January 14, 2016 http://anrcatalog.ucanr.edu
Site Preparation: The First Step to Regeneration
 Site Preparation: The First Step to Regeneration People have been clearing land for agricultural purposes for centuries. They recognized early that weeds, brush, and stones had to be removed if crops were
Site Preparation: The First Step to Regeneration People have been clearing land for agricultural purposes for centuries. They recognized early that weeds, brush, and stones had to be removed if crops were
Range Effectiveness Evaluations Part 2 Rangeland Health and Plant Residue
 Range Effectiveness Evaluations 2004 Part 2 Rangeland Health and Plant Residue FRPA Values Soils Biodiversity Forage and associated plant communities Fish and fish habitat Water (WQOs) Wildlife (also WHAs
Range Effectiveness Evaluations 2004 Part 2 Rangeland Health and Plant Residue FRPA Values Soils Biodiversity Forage and associated plant communities Fish and fish habitat Water (WQOs) Wildlife (also WHAs
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices Interest Approach Ask students what challenges the first farmers faced as colonists moved across North America. Some of the challenges involved
Animal, Plant & Soil Science D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices Interest Approach Ask students what challenges the first farmers faced as colonists moved across North America. Some of the challenges involved
Rachel Mealor Extension Range Specialist Department of Renewable Resources. Revegetation: Seeding Essentials for Reclaiming Disturbed Lands
 Rachel Mealor Extension Range Specialist Department of Renewable Resources Revegetation: Seeding Essentials for Reclaiming Disturbed Lands Where we are headed Designing a seed mix Seedbed preparation Using
Rachel Mealor Extension Range Specialist Department of Renewable Resources Revegetation: Seeding Essentials for Reclaiming Disturbed Lands Where we are headed Designing a seed mix Seedbed preparation Using
GRASSLAND WEED MANAGEMENT AND FOCUS ON CONTROL OF COMMON RUSH WITHOUT USING CHEMICALS
 GRASSLAND WEED MANAGEMENT AND FOCUS ON CONTROL OF COMMON RUSH WITHOUT USING CHEMICALS Ian Cairns May 2016 Reversion of improved marginal grassland it s a natural process! Over time, quality and productivity
GRASSLAND WEED MANAGEMENT AND FOCUS ON CONTROL OF COMMON RUSH WITHOUT USING CHEMICALS Ian Cairns May 2016 Reversion of improved marginal grassland it s a natural process! Over time, quality and productivity
Overview: History & Tradition. An Overview of Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health: Carrying Capacity Surveys.
 An Overview of Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health: For More Information Visit: http://fresc.usgs.gov/products/rangehealth/ Download Assessment Manual from: http://fresc.usgs.gov/products/papers/1385_pellant.pdf
An Overview of Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health: For More Information Visit: http://fresc.usgs.gov/products/rangehealth/ Download Assessment Manual from: http://fresc.usgs.gov/products/papers/1385_pellant.pdf
History. Grass Seed Production. Uses. Uses. Oregon Grass Seed. Environment Requirements 2/7/2008
 History Grass Seed Production Seed from the pastures and hay fields of European immigrants Grass seed did not become an important agricultural crop until after the destructive 1930's Dust Bowl Important
History Grass Seed Production Seed from the pastures and hay fields of European immigrants Grass seed did not become an important agricultural crop until after the destructive 1930's Dust Bowl Important
Management of Established Grass Stands for Early Successional Habitat
 Management of Established Grass Stands for Early Successional Habitat In the beginning 4-5 years after establishment Introduced Cool-Season Native Warm-Season Which field would wildlife prefer to walk
Management of Established Grass Stands for Early Successional Habitat In the beginning 4-5 years after establishment Introduced Cool-Season Native Warm-Season Which field would wildlife prefer to walk
Improving Reclamation on Oil and Gas Well Pads in the Rocky Mountain West
 Improving Reclamation on Oil and Gas Well Pads in the Rocky Mountain West IPAMS 2008 ROCKY MOUNTAIN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE September 5, 2008 Ed Redente, Ph.D. MWH Americas, Inc. 3665 JFK Parkway,
Improving Reclamation on Oil and Gas Well Pads in the Rocky Mountain West IPAMS 2008 ROCKY MOUNTAIN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE September 5, 2008 Ed Redente, Ph.D. MWH Americas, Inc. 3665 JFK Parkway,
8/10/2011. Lesson Overview. Rangelands. Rangelands. Brush management on rangelands. Advantages and disadvantages. Specific mechanical treatments
 Lesson Overview Brush management on rangelands Advantages and disadvantages Specific mechanical treatments Brush dominates areas across TX that were previously dominated by grasses. Coping with dense brush
Lesson Overview Brush management on rangelands Advantages and disadvantages Specific mechanical treatments Brush dominates areas across TX that were previously dominated by grasses. Coping with dense brush
WHY GROW MEDIC? Training Kit No. 1
 Training Kit No. 1 WHY GROW MEDIC? Script: Brian and Lynne Chatterton. Photos: Florita Botts. Additional Photos: Brian Chatterton. Production: Florita Botts. THE FAILURE OF THE CEREAL - FALLOW ROTATION
Training Kit No. 1 WHY GROW MEDIC? Script: Brian and Lynne Chatterton. Photos: Florita Botts. Additional Photos: Brian Chatterton. Production: Florita Botts. THE FAILURE OF THE CEREAL - FALLOW ROTATION
EC Know and Control : Downy Brome
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1974 EC74-188 Know and Control : Downy Brome
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1974 EC74-188 Know and Control : Downy Brome
Engaging Livestock in Weed Management
 Engaging Livestock in Weed Management Grazing is Powerful Over Grazing Saudi Arabia A Western Perspective Rangeland Ecology & Management University of Idaho Karen Launchbaugh Sheep Reduce Forbs Goats Reduce
Engaging Livestock in Weed Management Grazing is Powerful Over Grazing Saudi Arabia A Western Perspective Rangeland Ecology & Management University of Idaho Karen Launchbaugh Sheep Reduce Forbs Goats Reduce
This section provides useful information on the characteristics of soil and important soil management practices.
 7.0 SOIL MANAGEMENT This section provides useful information on the characteristics of soil and important soil management practices. What Is Soil? The four main components of soil are mineral and organic
7.0 SOIL MANAGEMENT This section provides useful information on the characteristics of soil and important soil management practices. What Is Soil? The four main components of soil are mineral and organic
The Manitoba Water Services Board SECTION Standard Construction Specifications Revised May 2015 Page 1 of 5
 Revised May 2015 Page 1 of 5 Part 1 General 1.1 DESCRIPTION OF WORK.1 This work shall include the supply of all materials. Seeding shall include the preparation of the seed bed and the supply and placement
Revised May 2015 Page 1 of 5 Part 1 General 1.1 DESCRIPTION OF WORK.1 This work shall include the supply of all materials. Seeding shall include the preparation of the seed bed and the supply and placement
Lessons from Floodplain and Riparian Revegetation. Katrina Strathmann Project Manager/Plant Ecologist Mid-Columbia Fisheries Enhancement Group
 Lessons from Floodplain and Riparian Revegetation Katrina Strathmann Project Manager/Plant Ecologist Mid-Columbia Fisheries Enhancement Group Why revegetation fails (the short list) Low fall and/or spring
Lessons from Floodplain and Riparian Revegetation Katrina Strathmann Project Manager/Plant Ecologist Mid-Columbia Fisheries Enhancement Group Why revegetation fails (the short list) Low fall and/or spring
The Art and Science of Pasture Management
 Connecticut Horse Environmental Awareness Program The Art and Science of Pasture Management Is the area you call pasture looking more like a dusty weed patch than a healthy grass population that provides
Connecticut Horse Environmental Awareness Program The Art and Science of Pasture Management Is the area you call pasture looking more like a dusty weed patch than a healthy grass population that provides
Rangeland CEAP Literature Synthesis: Conclusions and Recommendations
 Rangeland CEAP Literature Synthesis: Conclusions and Recommendations David D. Briske, Academic Coordinator, Texas A&M University, College Station TX Leonard Jolley, Range and Pastureland CEAP Director,
Rangeland CEAP Literature Synthesis: Conclusions and Recommendations David D. Briske, Academic Coordinator, Texas A&M University, College Station TX Leonard Jolley, Range and Pastureland CEAP Director,
Metcel VMF Herbicide EPA Reg. No FOR USE ON PASTURE AND RANGELAND
 SUPPLEMENTAL LABELING Metcel VMF Herbicide EPA Reg. No. 352-439-85588 FOR USE ON PASTURE AND RANGELAND DIRECTIONS FOR USE Metcel VMF Herbicide is recommended for the control of broadleaf weeds, brush and
SUPPLEMENTAL LABELING Metcel VMF Herbicide EPA Reg. No. 352-439-85588 FOR USE ON PASTURE AND RANGELAND DIRECTIONS FOR USE Metcel VMF Herbicide is recommended for the control of broadleaf weeds, brush and
Sagebrush Rangelands in Nevada
 BACKGROUND INFORMATION Sagebrush Rangelands in Nevada Sagebrush Species and Their General Biology: There are at least 28 species of sagebrush and many more subspecies or varieties, found in the Intermountain
BACKGROUND INFORMATION Sagebrush Rangelands in Nevada Sagebrush Species and Their General Biology: There are at least 28 species of sagebrush and many more subspecies or varieties, found in the Intermountain
We are talking about prairie fire ecology for several reasons.
 We are talking about prairie fire ecology for several reasons. First, the historical fire regime was one of very frequent fires. You ll learn about fire effects in two different ecosystems that once experienced
We are talking about prairie fire ecology for several reasons. First, the historical fire regime was one of very frequent fires. You ll learn about fire effects in two different ecosystems that once experienced
Mike Pellant Bureau of Land Mgt. Boise, ID. An Overview on Research and Studies on Diversifying Crested Wheatgrass Seedings
 Mike Pellant Bureau of Land Mgt. Boise, ID An Overview on Research and Studies on Diversifying Crested Wheatgrass Seedings Topics Evolution from conversion to Crested WG to seeding diversification? Why
Mike Pellant Bureau of Land Mgt. Boise, ID An Overview on Research and Studies on Diversifying Crested Wheatgrass Seedings Topics Evolution from conversion to Crested WG to seeding diversification? Why
SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE MANAGEMENT 1 Kent L Brittan ABSTRACT
 SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE MANAGEMENT 1 Kent L Brittan ABSTRACT Good site selection and proper seedbed preparation whether conventional or no-till can have a significant impact the success
SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE MANAGEMENT 1 Kent L Brittan ABSTRACT Good site selection and proper seedbed preparation whether conventional or no-till can have a significant impact the success
Pasture Renovation and Improvement
 Pasture Renovation and Improvement Stephen K. Barnhart Extension Agronomist Forages Iowa State University Extension Ames, Iowa 50011-1010 Phone 515-294-7835 Email sbarnhar@iastate.edu Evaluate your Pasture?
Pasture Renovation and Improvement Stephen K. Barnhart Extension Agronomist Forages Iowa State University Extension Ames, Iowa 50011-1010 Phone 515-294-7835 Email sbarnhar@iastate.edu Evaluate your Pasture?
A problem often associated with non-uniform pasture production is a mis-match between forage needs and for availability. Evaluate your Pasture?
 Pasture Renovation and Improvement Evaluate your Pasture? This can range from: Stephen K. Barnhart Extension Agronomist Forages Iowa State University Extension Ames, Iowa 50011-1010 Phone 515-294-7835
Pasture Renovation and Improvement Evaluate your Pasture? This can range from: Stephen K. Barnhart Extension Agronomist Forages Iowa State University Extension Ames, Iowa 50011-1010 Phone 515-294-7835
Pinyon and Juniper Investigation Nevada Youth Range Camp
 Curriculum Material 10-10 Pinyon and Juniper Investigation Nevada Youth Range Camp Sherman Swanson State Range Specialist This curriculum is used at Nevada Youth Range Camp for teaching high school age
Curriculum Material 10-10 Pinyon and Juniper Investigation Nevada Youth Range Camp Sherman Swanson State Range Specialist This curriculum is used at Nevada Youth Range Camp for teaching high school age
Solving the SOIL HEALTH Puzzle? WE HAVE YOU COVERED. lacrosseseed.com soil1st.com SEED. Soil First Mix Decision Tree
 Solving the SOIL HEALTH Puzzle? WE HAVE YOU COVERED lacrosseseed.com soil1st.com info@laxseed.com 800.356.SEED Mix Decision Tree START DECISION TREE AFTER CORN GRAIN GOING TO SOYBEANS COVER CROP TYPE CONDITIONS/DESIRED
Solving the SOIL HEALTH Puzzle? WE HAVE YOU COVERED lacrosseseed.com soil1st.com info@laxseed.com 800.356.SEED Mix Decision Tree START DECISION TREE AFTER CORN GRAIN GOING TO SOYBEANS COVER CROP TYPE CONDITIONS/DESIRED
 www.dakotalakes.com beck@dakotalakes.com Wheat Health Management Cook and Veseth Crop rotation is probably the single most critical factor affecting the health and productivity of a future wheat crop.
www.dakotalakes.com beck@dakotalakes.com Wheat Health Management Cook and Veseth Crop rotation is probably the single most critical factor affecting the health and productivity of a future wheat crop.
California s Rangelands. Annual Grassland Dominated Systems
 *Grazing Systems on California s Rangelands Annual Grassland Dominated Systems What is a Grazing System & are they applicable for California Grazing Systems refers to specialized grazing management that
*Grazing Systems on California s Rangelands Annual Grassland Dominated Systems What is a Grazing System & are they applicable for California Grazing Systems refers to specialized grazing management that
Control of Sericea Lespedeza using Late-Season Prescribed Burning
 Control of Sericea Lespedeza using Late-Season Prescribed Burning KC Olson, W. H. Fick, J. A. Alexander, J. Lemmon, G. A. Gatson Department of Animal Sciences & Industry, Kansas State University Department
Control of Sericea Lespedeza using Late-Season Prescribed Burning KC Olson, W. H. Fick, J. A. Alexander, J. Lemmon, G. A. Gatson Department of Animal Sciences & Industry, Kansas State University Department
PenningtonCoverCrops.com SOIL-911
 PenningtonCoverCrops.com 1-844-SOIL-911 Who is Pennington Seed? Pennington has a long history in the farming industry starting with the first members of the Pennington family that moved from Europe to
PenningtonCoverCrops.com 1-844-SOIL-911 Who is Pennington Seed? Pennington has a long history in the farming industry starting with the first members of the Pennington family that moved from Europe to
KEEPING livestock well fed during the
 Forage Production KEEPING livestock well fed during the winter months can be one of the largest costs associated with livestock operations. Forage can provide much needed nutrients, so it is critical in
Forage Production KEEPING livestock well fed during the winter months can be one of the largest costs associated with livestock operations. Forage can provide much needed nutrients, so it is critical in
Making the Most of Cover Crop Mixtures Charlie White, Penn State Extension 501 ASI Building, University Park, PA
 Making the Most of Cover Crop Mixtures Charlie White, Penn State Extension 501 ASI Building, University Park, PA 16802 cmw29@psu.edu Introduction Cover crops are an important tool that farmers can use
Making the Most of Cover Crop Mixtures Charlie White, Penn State Extension 501 ASI Building, University Park, PA 16802 cmw29@psu.edu Introduction Cover crops are an important tool that farmers can use
Invasive Species Management Plans for Florida
 Invasive Species Management Plans for Florida Cogongrass Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv. Poaceae INTRODUCTION Cogongrass is an aggressive, rhizomatous, perennial grass that is distributed throughout the
Invasive Species Management Plans for Florida Cogongrass Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv. Poaceae INTRODUCTION Cogongrass is an aggressive, rhizomatous, perennial grass that is distributed throughout the
Managing Saline Areas with forages. Glenn Friesen Forage Specialist MAFRI, Carman December 15, 2009
 Managing Saline Areas with forages Glenn Friesen Forage Specialist MAFRI, Carman December 15, 2009 April 18, 2007 April 18, 2007 Is it Salinity? Saline soils Normal ph, High concentrations of soluble
Managing Saline Areas with forages Glenn Friesen Forage Specialist MAFRI, Carman December 15, 2009 April 18, 2007 April 18, 2007 Is it Salinity? Saline soils Normal ph, High concentrations of soluble
In the center of Texas exists the Texas Hill Country, an area which encompasses 25
 In the center of Texas exists the Texas Hill Country, an area which encompasses 25 counties and is where I live. Over time, land has been handed down, divided, and sold to new landowners. This turnover
In the center of Texas exists the Texas Hill Country, an area which encompasses 25 counties and is where I live. Over time, land has been handed down, divided, and sold to new landowners. This turnover
BMP No. 2 Vegetative Establishment of Silviculturally Disturbed Areas
 BMP No. 2 Vegetative Establishment of Silviculturally Disturbed Areas Establishment of grass and herb cover on disturbed areas, including roads, trails, and landings, is used to stabilize the soil and
BMP No. 2 Vegetative Establishment of Silviculturally Disturbed Areas Establishment of grass and herb cover on disturbed areas, including roads, trails, and landings, is used to stabilize the soil and
ALTERNATE FORAGE CROPS WHEN IRRIGATION WATER IS LIMITED
 Drought Management Drought Management Factsheet - No. 6 in Series Order No. 665.000-6 Revised June 2015 ALTERNATE FORAGE CROPS WHEN IRRIGATION WATER IS LIMITED Key Points 1. Choosing annuals versus perennial
Drought Management Drought Management Factsheet - No. 6 in Series Order No. 665.000-6 Revised June 2015 ALTERNATE FORAGE CROPS WHEN IRRIGATION WATER IS LIMITED Key Points 1. Choosing annuals versus perennial
TALL FESCUE MANAGEMENT GUIDE
 TALL FESCUE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Introduction Where is Tall Fescue Suited? Tall fescue is an exciting grass species that has proven itself to be an answer to pasture persistence and performance in hot summer
TALL FESCUE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Introduction Where is Tall Fescue Suited? Tall fescue is an exciting grass species that has proven itself to be an answer to pasture persistence and performance in hot summer
ADOPT Project Forage Termination Strategies on Succeeding Annual Crops
 heatland Conservation Area Inc W Agri-ARM Research Update 2015 ADOPT Project Forage Termination Strategies on Succeeding Annual Crops Presentation Outline Project introduction SMA literature summary 2013-14
heatland Conservation Area Inc W Agri-ARM Research Update 2015 ADOPT Project Forage Termination Strategies on Succeeding Annual Crops Presentation Outline Project introduction SMA literature summary 2013-14
Targeted Grazing for vegetation management and landscape enhancement. Products of Livestock Grazing. Products of Targeted Grazing
 Targeted Grazing for vegetation management and landscape enhancement Products of Livestock Grazing Karen Launchbaugh Meat & Livestock Products Manage Plant Communities Products of Targeted Grazing Targeted
Targeted Grazing for vegetation management and landscape enhancement Products of Livestock Grazing Karen Launchbaugh Meat & Livestock Products Manage Plant Communities Products of Targeted Grazing Targeted
Cheatgrass fuels rangeland fires.
 A Burning Issue: Cheatgrass fuels rangeland fires. Control the weeds that fuel wildfires with herbicide www.bettervm.basf.us.com Cheatgrass infestation increases the frequency of major rangeland wildfires
A Burning Issue: Cheatgrass fuels rangeland fires. Control the weeds that fuel wildfires with herbicide www.bettervm.basf.us.com Cheatgrass infestation increases the frequency of major rangeland wildfires
Managing Nitrogen Requirements for Big Horn Basin Crops
 Managing Nitrogen Requirements for Big Horn Basin Crops Jay Norton Assistant Professor and Soil Fertility Extension Specialist Department of Renewable Resources University of Wyoming Westi Ag Days, Worland,
Managing Nitrogen Requirements for Big Horn Basin Crops Jay Norton Assistant Professor and Soil Fertility Extension Specialist Department of Renewable Resources University of Wyoming Westi Ag Days, Worland,
A windbreak across a large field distributes snow throughout the field, providing winter protection and moisture for crop production.
 In areas of high winds and blowing snow, windbreaks can reduce the amount of effort spent on snow management. They can be designed to spread snow across a large area or to confine it to a relatively small
In areas of high winds and blowing snow, windbreaks can reduce the amount of effort spent on snow management. They can be designed to spread snow across a large area or to confine it to a relatively small
EXTENDING THE GRAZING SEASON USING SPECIES AND VARIETIES. S. Ray Smith 1
 EXTENDING THE GRAZING SEASON USING SPECIES AND VARIETIES S. Ray Smith 1 During the last 10 years there have been several new forage species that have emerged as useful in grazing systems and many new varieties
EXTENDING THE GRAZING SEASON USING SPECIES AND VARIETIES S. Ray Smith 1 During the last 10 years there have been several new forage species that have emerged as useful in grazing systems and many new varieties
Improving Rainfall Effectiveness On Rangeland
 L-5029 Improving Rainfall Effectiveness On Rangeland Allan McGinty, Thomas L. Thurow and Charles A. Taylor, Jr.* Rainfall is a major limiting factor for livestock production from Texas rangelands. Everything
L-5029 Improving Rainfall Effectiveness On Rangeland Allan McGinty, Thomas L. Thurow and Charles A. Taylor, Jr.* Rainfall is a major limiting factor for livestock production from Texas rangelands. Everything
Conservation Practices for Landlords There is growing concern over the possible
 Conservation Practices for Landlords There is growing concern over the possible impact of rented land on soil conservation. Concerns regarding conservation practices are not new; however, the recent increase
Conservation Practices for Landlords There is growing concern over the possible impact of rented land on soil conservation. Concerns regarding conservation practices are not new; however, the recent increase
2017 MB Envirothon. Theme Training Document
 2017 MB Envirothon Theme Training Document Envirothon Training Soil and Water Conservation Stewardship: Beneficial Management Practices Types of BMPs Water Management BMPs: Water Retention Wetland Restoration
2017 MB Envirothon Theme Training Document Envirothon Training Soil and Water Conservation Stewardship: Beneficial Management Practices Types of BMPs Water Management BMPs: Water Retention Wetland Restoration
BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES FOR GRAZING
 BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES FOR GRAZING Courtesy NRCS INTRODUCTION The purpose of the brochure is to give the reader some basic range management practices useful for reducing impacts to surface and ground
BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES FOR GRAZING Courtesy NRCS INTRODUCTION The purpose of the brochure is to give the reader some basic range management practices useful for reducing impacts to surface and ground
Improving Pasture Productivity through Forage Management
 Improving Pasture Productivity through Forage Management David Otte Green Valley Seed Kahoka, Missouri dlotte@centurytel.net I must confess that putting these thoughts and ideas onto paper is more difficult
Improving Pasture Productivity through Forage Management David Otte Green Valley Seed Kahoka, Missouri dlotte@centurytel.net I must confess that putting these thoughts and ideas onto paper is more difficult
Ponds Planning, Design, Construction
 United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service Ponds Planning, Design, Construction Agriculture Handbook Number 590 Estimating storm runoff The amount of precipitation,
United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service Ponds Planning, Design, Construction Agriculture Handbook Number 590 Estimating storm runoff The amount of precipitation,
Focus. After the Conservation Reserve Program: Economic Decisions with Farming and Grazing in Mind
 FARM Assistance Focus After the Conservation Reserve Program: Economic Decisions with Farming and Grazing in Mind DeDe Jones Department of Agricultural Economics, Texas AgriLife Extension Service Texas
FARM Assistance Focus After the Conservation Reserve Program: Economic Decisions with Farming and Grazing in Mind DeDe Jones Department of Agricultural Economics, Texas AgriLife Extension Service Texas
A Pictorial Comparison of Seasonal Timing and Frequency of Prescribed Fire in Longleaf Pine Stands
 FORESTRY & WATER RESOURCES A Pictorial Comparison of Seasonal Timing and Frequency of Prescribed Fire in Longleaf Pine Stands When using prescribed fire in longleaf pine stands, land managers should consider
FORESTRY & WATER RESOURCES A Pictorial Comparison of Seasonal Timing and Frequency of Prescribed Fire in Longleaf Pine Stands When using prescribed fire in longleaf pine stands, land managers should consider
LECTURE - 5 TILLAGE - OBJECTIVES AND TYPES. FURROW TERMINOLOGY AND METHODS OF PLOUGHING. FIELD CAPACITY AND FIELD EFFICIENCY TILLAGE Mechanical
 LECTURE - 5 TILLAGE - OBJECTIVES AND TYPES. FURROW TERMINOLOGY AND METHODS OF PLOUGHING. FIELD CAPACITY AND FIELD EFFICIENCY TILLAGE Mechanical manipulation of soil to provide favourable condition for
LECTURE - 5 TILLAGE - OBJECTIVES AND TYPES. FURROW TERMINOLOGY AND METHODS OF PLOUGHING. FIELD CAPACITY AND FIELD EFFICIENCY TILLAGE Mechanical manipulation of soil to provide favourable condition for
Rangeland Roots Vegetation
 Rangeland Roots Vegetation Created by: IRRC Date: Subject: Science Grade Level: 4 th + Time Required: 1hour Standards: Standard: 3 Biology Overview Goal(s) & Objective(s) Materials Students fill in the
Rangeland Roots Vegetation Created by: IRRC Date: Subject: Science Grade Level: 4 th + Time Required: 1hour Standards: Standard: 3 Biology Overview Goal(s) & Objective(s) Materials Students fill in the
Review of Management Scenarios for the Chesapeake Bay Program s Phase 6 Watershed Model. David T. Lightle Erosion Model Consultant December 17, 2016
 Review of Management Scenarios for the Chesapeake Bay Program s Phase 6 Watershed Model David T. Lightle Erosion Model Consultant December 17, 2016 Resources Used Resources provided consisted of a limited
Review of Management Scenarios for the Chesapeake Bay Program s Phase 6 Watershed Model David T. Lightle Erosion Model Consultant December 17, 2016 Resources Used Resources provided consisted of a limited
Tillage RootMax Annual Ryegrass
 Tillage RootMax Annual Ryegrass Tillage RootMax Annual Ryegrass is the premium annual ryegrass in today s marketplace. It has been screened and selected for winter hardiness, rooting depth, and especially
Tillage RootMax Annual Ryegrass Tillage RootMax Annual Ryegrass is the premium annual ryegrass in today s marketplace. It has been screened and selected for winter hardiness, rooting depth, and especially
Making Pasture Weed Control Decisions
 Making Pasture Weed Control Decisions Rocky Lemus 1 and Jason Weirich 1 Extension Forage Specialist Visit us at http://msucares.com/crops/forages/index.html As we approach spring growth, weed control becomes
Making Pasture Weed Control Decisions Rocky Lemus 1 and Jason Weirich 1 Extension Forage Specialist Visit us at http://msucares.com/crops/forages/index.html As we approach spring growth, weed control becomes
Shrub Microsite Influences Post-fire Perennial Grass Establishment
 Shrub Microsite Influences Post-fire Perennial Grass Establishment Chad S. Boyd and Kirk W. Davies SUMMARY Woody plants can cause localized increases in resources (i.e., resource islands) that can persist
Shrub Microsite Influences Post-fire Perennial Grass Establishment Chad S. Boyd and Kirk W. Davies SUMMARY Woody plants can cause localized increases in resources (i.e., resource islands) that can persist
Frost Seeding Legumes and Grasses into Pastures
 Page 1 of 5 Frost Seeding Legumes and Grasses into Pastures Mike Rankin Crops and Soils Agent UW Extension - Fond du Lac County Why Frost Seed? Frost seeding legumes and grasses is increasingly being used
Page 1 of 5 Frost Seeding Legumes and Grasses into Pastures Mike Rankin Crops and Soils Agent UW Extension - Fond du Lac County Why Frost Seed? Frost seeding legumes and grasses is increasingly being used
Soil Management and Fertilizer Use: Cover Crops
 1 of 7 29/06/2007 16:33 Soil Management and Fertilizer Use: Cover Crops Author: OMAFRA Staff Creation Date: 01 March 2002 Last Reviewed: 01 March 2002 Agronomy Guide > Pub 811: Soil Management and Fertilizer
1 of 7 29/06/2007 16:33 Soil Management and Fertilizer Use: Cover Crops Author: OMAFRA Staff Creation Date: 01 March 2002 Last Reviewed: 01 March 2002 Agronomy Guide > Pub 811: Soil Management and Fertilizer
Pasture Production with Selected Forage Species
 Bringing information and education into the communities of the Granite State Pasture Production with Selected Forage Species Carl Majewski, Extension Field Specialist, Food & Agriculture Many species of
Bringing information and education into the communities of the Granite State Pasture Production with Selected Forage Species Carl Majewski, Extension Field Specialist, Food & Agriculture Many species of
Kent and Linda Solberg
 Kent and Linda Solberg Summer 2015 Continuous Living Cover Series Kent & Linda Solberg Profile Verndale, MN July 7, 2014 When Kent & Linda Solberg moved to their farm in 2003, they found thistles and sandburs
Kent and Linda Solberg Summer 2015 Continuous Living Cover Series Kent & Linda Solberg Profile Verndale, MN July 7, 2014 When Kent & Linda Solberg moved to their farm in 2003, they found thistles and sandburs
0.0. Pervious CN = 40. (Unconnected impervious) (Total impervious) Total impervious area (percent) Composite CN
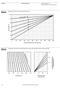 Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
Agriculture and Society: Part II. PA E & E Standards 4.4
 Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Pasture Management Andrea Lawseth, M.Sc., P.Ag. COABC Conference February 29, 2015
 Pasture Management Andrea Lawseth, M.Sc., P.Ag. COABC Conference February 29, 2015 Outline Benefits of Good Pasture Management Pasture Degradation Pasture Renovation Seed Mixtures Weed Management Grazing
Pasture Management Andrea Lawseth, M.Sc., P.Ag. COABC Conference February 29, 2015 Outline Benefits of Good Pasture Management Pasture Degradation Pasture Renovation Seed Mixtures Weed Management Grazing
