Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG
|
|
|
- Dwain Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS
2 Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in ocean and coastal ecosystems. Recent decades have seen more frequent and stronger climate variations and changes compared to the relative stability of the climate from Ocean warming have direct consequences for species distribution and habitats and also indirect consequences for food web in marine ecosystems. Understanding the functioning of marine ecosystem and how they respond to global change is essential to manage marine living resources such as fisheries effectively, to the sustainable development.
3 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Climate-induced change in small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control mechanism Main scientific issues essential to be address
4 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Climate-induced change in small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control mechanism Main scientific issues essential to be address
5 Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Long-term variations of physical environment parameters in the ocean plays an important role on influencing the marine ecosystem dynamics. Oceanic temperature variation not only affects directly the metabolic rates of the organisms but also influences other oceanic states, such as sea level and therefore local currents. Variations of oceanic temperature can influence the substrate structure, photosynthetic light intensity, watercolumn stratification and nutrient cycling and therefore productivity of living marine resources.
6 Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Climate changes impacting the ocean ecosystem can be marked by the air temperature (AT), monthly mean sea surface temperature (SST) and sea surface salinity (SSS). Investigations of the Bohai Sea ecosystem shows that population of phytoplankton and zooplankton, benthic community biomass, fish resources and species diversity change with influence of AT, SST and SSS. In , the total biomass had decreased by 30% and the total biomass of phytoplankton and zooplankton had decreased by 50% compared with
7 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Climate-induced change in small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control mechanism Main scientific issues essential to be address
8 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Nature factors impact an important long-term changes on biomass yields of resources populations in the ocean and coastal ecosystems. The altering in the abundance of the species of various ecotypes are correlated with climate change. Small pelagic fish and shellfish species, such as Pacific herring and prawn, are more sensitive to climate change. The Yellow Sea ecosystem study is an example of the impact.
9 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Yellow Sea ecosystem: 1) primary production 60gC m -2 yr-1, relative low 2) phytoplankton biomass relatively stable over the past 30 years 3) zooplankton annual biomass declined by amount 50% from 1959 through There is a similar trend in the East China Sea.
10 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Extreme overexploitation is one factor causing decline in abundance for the most important commercial demersal species in the Yellow Sea, such as small yellow croaker, hairtail, large yellow croaker, flatfish and Pacific cod. The fluctuation in abundance for some demersal species may be affected by both natural force and human activities. Biotic communities of the YS ecosystem are complex in species composition, spatial distribution, and community structure with the marked seasonal variation.
11 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Fish resources in YS ecosystem are multi-species. Warm temperature species are the major component, accounting for about 60% of the total biomass of the resources. Warm-water species and cold temperature species account for 15% and 25 % respectively. Demersal and sem-idemesal fish species account for 58% and pelagic species for about 42%.
12 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate About 20 major species account 92% of the total biomass of the resources population and about 80% species account for the other 8% population. The dramatic shifts of species dominance in the ecosystem occurred from the1950s through the 1980s. The dominant species in the 1950s and early 1960s were small yellow croaker and hairtail, while Pacific herring and chub mackerel became dominance in the 1970s. Some small-size, fast-growing, short-lived and lowvalue species such as Japanese anchovy and half-fin anchovy increased markedly in abundance in the1980s and have taken a prominent position in the ecosystem resources.
13 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Rainfall, wind and daylight appear to be the major factors affecting fluctuations of recruitment. The long-term changes in herring abundance may be correlated with the 36-years cycle of dryness-wetness oscillations in eastern China. Proportion of major species and feeding habits in the biomass yields, based on the Yellow Sea surveys in and
14 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Two types of species shifts in the ecosystem resources are systematic replacement and ecological replacement. Systematic replacement occurs when one dominant species declines by overexploitation and another competitive species increase. Ecological replacement occurs when minor changes in the natural environment impact stock abundance, especially small pelagic species. The natural environment variations have an important effect on long-term changes in dominant species of various ecotypes.
15 Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate The warm and temperate species (A and B) increase during warm years in 1960s and 1980s. Boreal species (C) trend to increase in cold years as 1970s.
16 Wetness grade Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Rainfall Catch (10 3 mt) Relationship between the fluctuations in herring bundance of the Yellow Sea and the 36-yr cycle of wetness oscillation in eastern China.
17 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Climate-induced change in small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control mechanism Main scientific issues essential to be address
18 Climate-induced change of small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Resources of small pelagic fish are abundant in China coastal waters and offshore. The mean annual catch accounted 39% in total marine catch in last decade. The highest production is 7.18 million tons in Catch Total Marine catch Pelagic catch Year
19 Climate-induced change of small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters The mean annual pelagic catch of China was 4.15 million tons from 1990 through species which annual production was ever more then 100 thousand tons. Annual catch of 4 important species are showed here (1000 tons). Species Japanese anchovy Spanish mackerel Silver pomfret Pacific herring Total pelagic catch
20 Climate-induced change of small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Japanese anchovy is the most abundant pelagic species distributed widely in the northwest of Pacific. The anchovy stocks in winter are located mainly in the area of the depths 40-80m with water temperature of 7-14 o C in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. It s biomass was estimated at the average of 3.0 million tons in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea based on the winter surveys by R/V Dei Dou conducted The biomass of the stock fluctuated in the levels of million tons. The total Chinese yield of anchovy was 54,000 tons in 1990 and it reached 1,373,000 tons in 1998.
21 Climate-induced change of small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Year Biomass (million tons) Landing (million tons) Yearly variations of anchovy biomass and landings
22 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Climate-induced change in small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control mechanism Main scientific issues essential to be address
23 Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control echanism During past four decades, productivity and community structure of the Bohai Sea ecosystem has been highly variable. Decadal-scale variations are described using the survey data from , and Result indicates that a large productivity variation in ecosystem is an important characteristics of coastal ecosystem dynamics. Productivity changes at different trophic levels are described by primary production zooplankton biomass fish productivity.
24 Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control echanism Primary production It was at a relatively high in the Bohai Sea before 1982 Yearly average abundance of phytoplankton showed an declining trend from 1959 to 1998 and a sharp drop from 1982 to 1992 Phytoplankton abundance in 1998 was about 38% in 1982 In the same period, the number of phytoplankton species also decreased Peak of primary production season was in summer A large seasonal variations of phytoplankton abundance occurred in 1992 and 1998.
25 Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control echanism Zooplankton biomass Secondary production presents the variations of zooplankton biomass in the Bohai Sea. Annually averaged, the zooplankton biomass decreased by about 40% from the late 1950 s (107.3 mg m -3 ) to early 1990 s (64.0 mg m -3 ). The particularly high values were observed in spring and summer of 1998, but the biomass of zooplankton in 1998 was an exception. The biomass in 1998 accounted for three to six times as much as the mean value at the same season from 1959 to 1982, and four times as much as 1992.
26 Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control echanism Fish productivity The seasonal variations of fish in the Bohai Sea are important. The most species emigrate to the Yellow Sea in late autumn for over-wintering and return to the Bohai Sea in spring for spawning. The catch per hour of hauling data indicated that the top production began to decrease since the 1950 s and was serious in the late 1990 s. The biomass in was slightly lower on average than the previous year surveys. The biomass in was the lowest in all surveys with a sharp decline, accounting for only 5% of the 1959 values.
27 Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control echanism The community structure of fishery resources tends to be simple by decreasing of species numbers. The species richness, diversity and evenness also decreased from the beginning of 1980 s to late 1990 s. The shift of dominant species was observed by the surveys in Large-size demersal species were replaced by small pelagic species, such as half-fin anchovy (Setipinna taty), anchovy (Engraulis japonicus), and this replacement has continued thereafter. As a result, the trophic level in the fish productivity decreased from 4.3 in 1959, to 3.8 in , 3.6 in , and 3.3 in
28 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Physical oceanography and climate variations to induce changes of marine ecosystems Living resource dynamics in relation to ocean and climate Climate-induced change in small pelagic fish productivity in Chinese waters Decadal-scale variation of ecosystem productivity and control mechanism Main scientific issues essential to be address
29 Main scientific issues essential to be address Some ocean areas are particularly sensitive to gradual long-term changes in climate, and will be subject to intensive studies. They are the continental margins, meso-pelagic zone, intermediate waters, regions of upwelling and deep mixing. The continental margins are a critical boundary because they are most directly relevant to human development. However, marine food webs in continental margins are heavily impacted by fishing activities and closely relate to the biogeochemical cycles. The meso-pelagic zone is an important ocean region for recycling of nutrients and also an important region for pelagic food webs.
30 Main scientific issues essential to be address Marine ecosystem intensive studies frame enclosed with food web
31 Main scientific issues essential to be address Food webs study is very important in marine ecosystem intensive research. GLOBEC and IMBER projects will investigate closely the impact of global change on food web structure and function. GLOBEC has developed a focus on zooplankton that is important prey for fish. Zooplankton forms an important route for the transport of carbon up the marine food webs to higher trophic levels and down the webs in forms of faecal pellets and excretion products. One of the major questions studied by GLOBEC is what are the impacts of global change on fish population dynamics using coupled physical, biological and chemical models linked to appropriate observation systems?
32 Main scientific issues essential to be address Study on the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea ecosystem dynamics is focusing on the coupling of physical environment and biological progress. Its goals are to identify key processes of ecosystem dynamics improve predictive and modeling capabilities provide scientific understanding to ecosystems responded to climate change and rational management system of living marine resources.
33 Main scientific issues essential to be address To understand ecosystem dynamics and its mechanism of living resources, there are 6 key scientific problems in the coastal ocean regions: energy flow and conversion of key species recruitment of zooplankton population renovation of bio-elements ecological effect of key physical process coupling of pelagic benthic system and contribution of microbial food loop.
34 Thanks! C.
Development in plankton community: the Barents Sea. E. Eriksen SEAPOP, April 2017
 Development in plankton community: the Barents Sea E. Eriksen SEAPOP, 27-28 April 2017 Arctic ocean The Barents Sea short description The Barents Sea is a shelf sea (~ 1.6 million km 2 ) and a transition
Development in plankton community: the Barents Sea E. Eriksen SEAPOP, 27-28 April 2017 Arctic ocean The Barents Sea short description The Barents Sea is a shelf sea (~ 1.6 million km 2 ) and a transition
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13
 OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for future research
 PICES XVII End-to-end food webs: Impacts of a changing ocean October 28 28 Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for
PICES XVII End-to-end food webs: Impacts of a changing ocean October 28 28 Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for
The Influence of Freshwater on Fishery Production on Continental Shelves: The Mississippi River
 The Influence of Freshwater on Fishery Production on Continental Shelves: The Mississippi River Churchill B. Grimes and Steve Lindley National Marine Fisheries Service Santa Cruz, California, USA Fishery
The Influence of Freshwater on Fishery Production on Continental Shelves: The Mississippi River Churchill B. Grimes and Steve Lindley National Marine Fisheries Service Santa Cruz, California, USA Fishery
the future? From the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, October 20, 2005 Assessing the potential impacts of global warming Courtesy of Nate Mantua
 the future? From the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, October 20, 2005 Assessing the potential impacts of global warming Courtesy of Nate Mantua Climate Change: Assessing its Implications for Marine Ecosystems
the future? From the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, October 20, 2005 Assessing the potential impacts of global warming Courtesy of Nate Mantua Climate Change: Assessing its Implications for Marine Ecosystems
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer. I. Ocean Circulation
 Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
LME 23 Baltic Sea 1/12. LME overall risk 2
 Bordering countries: Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden LME Total area: 396,838 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary
Bordering countries: Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden LME Total area: 396,838 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
Overfishing of planktivorous fishes may result in smaller plankton and less efficient energy flow to higher trophic levels
 Overfishing of planktivorous fishes may result in smaller plankton and less efficient energy flow to higher trophic levels Tore Johannessen Institute of Marine Research Flødevigen Victoria 6-11 March 2017
Overfishing of planktivorous fishes may result in smaller plankton and less efficient energy flow to higher trophic levels Tore Johannessen Institute of Marine Research Flødevigen Victoria 6-11 March 2017
Patterns of Productivity
 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
BONUS INSPIRE PROJECT (01. February January 2018) The final publishable summary report Date 31. March 2018
 BONUS INSPIRE PROJECT (01. February 2014 31. January 2018) The final publishable summary report Date 31. March 2018 1 Project outline of goals and results envisaged at the beginning of the project cycle
BONUS INSPIRE PROJECT (01. February 2014 31. January 2018) The final publishable summary report Date 31. March 2018 1 Project outline of goals and results envisaged at the beginning of the project cycle
Productivity and fisheries. Energy flow. Biological pyramids. Why study production processes?
 Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters. Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU
 Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Marine Life. Communities
 Marine Life Communities Habitat, Population, Community, Niche Every marine organism lives in a unique set of physical conditions within a given region of ocean, termed its habitat. A group of marine organism
Marine Life Communities Habitat, Population, Community, Niche Every marine organism lives in a unique set of physical conditions within a given region of ocean, termed its habitat. A group of marine organism
Production and Life OCEA 101
 Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
LME 22 North Sea 1/12. LME overall risk 2
 Bordering countries: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, United Kingdom. LME Total area: 690,041 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary
Bordering countries: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, United Kingdom. LME Total area: 690,041 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary
High Latitude Environment
 9. Habitats: High Latitude Ecosystems High Latitude Environments Seasonal Processes Sea ice Food Fall Reproduction Bentho-pelagic coupling Food Weds Climate Change Effects Dr Rhian G. Waller 26th April
9. Habitats: High Latitude Ecosystems High Latitude Environments Seasonal Processes Sea ice Food Fall Reproduction Bentho-pelagic coupling Food Weds Climate Change Effects Dr Rhian G. Waller 26th April
Predicting and adapting to biome-scale marine resource changes in the North Pacific
 Predicting and adapting to biome-scale marine resource changes in the North Pacific PICES International Symposium Understanding Changes in Transitional Areas of the Pacific April 25, 2018 Presented by:
Predicting and adapting to biome-scale marine resource changes in the North Pacific PICES International Symposium Understanding Changes in Transitional Areas of the Pacific April 25, 2018 Presented by:
Need & Opportunities for more integrated farming practices in coastal and offshore aquaculture. Patrick Sorgeloos Ghent University, Belgium
 Need & Opportunities for more integrated farming practices in coastal and offshore aquaculture Patrick Sorgeloos Ghent University, Belgium The Ny-Ålesund Symposium 2016 Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard-Norway, September
Need & Opportunities for more integrated farming practices in coastal and offshore aquaculture Patrick Sorgeloos Ghent University, Belgium The Ny-Ålesund Symposium 2016 Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard-Norway, September
Climate, biomass, and the trophic role of midwater fishes in the southern California Current
 Climate, biomass, and the trophic role of midwater fishes in the southern California Current Tony Koslow Scripps Ititution of Oceanography, University of California, S.D., La Jolla, CA USA Co authors:
Climate, biomass, and the trophic role of midwater fishes in the southern California Current Tony Koslow Scripps Ititution of Oceanography, University of California, S.D., La Jolla, CA USA Co authors:
LME 01 East Bering Sea
 LME 01 East Bering Sea Bordering country: United States of America LME Total area: 1,193,601 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity 2 Chlorophyll-A Primary productivity 2 3 Sea Surface
LME 01 East Bering Sea Bordering country: United States of America LME Total area: 1,193,601 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity 2 Chlorophyll-A Primary productivity 2 3 Sea Surface
Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth 1, and Evan Howell 1 Julia Blanchard 3
 Projected expansion of the subtropical biome and contraction of the temperate and equatorial upwelling biomes in the North Pacific under global warming Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth
Projected expansion of the subtropical biome and contraction of the temperate and equatorial upwelling biomes in the North Pacific under global warming Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
LME 06 Southeast U.S. Continental Shelf
 LME 06 Southeast U.S. Continental Shelf Bordering countries: United States of America, Bahamas LME Total area: 303,029 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary
LME 06 Southeast U.S. Continental Shelf Bordering countries: United States of America, Bahamas LME Total area: 303,029 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary
Predicting Trophic Interactions and Habitat Utilization in the California Current Ecosystem
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Predicting Trophic Interactions and Habitat Utilization in the California Current Ecosystem Jerome Fiechter UC Santa Cruz,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Predicting Trophic Interactions and Habitat Utilization in the California Current Ecosystem Jerome Fiechter UC Santa Cruz,
CHANGES IN ENVIRONMENT: IMPLICATIONS FOR FISHERIES IN INDIAN WATERS
 CHANGES IN ENVIRONMENT: IMPLICATIONS FOR FISHERIES IN INDIAN WATERS CHAPTER 33 V. Kripa Fishery Environment Management Division ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute Introduction The coastal
CHANGES IN ENVIRONMENT: IMPLICATIONS FOR FISHERIES IN INDIAN WATERS CHAPTER 33 V. Kripa Fishery Environment Management Division ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute Introduction The coastal
4/28/2013. Transmission of Light in Seawater. Color in the Ocean Color of ocean ranges from deep blue to yellow-green Factors Turbidity from runoff
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
LME 34 Bay of Bengal 1/13. LME overall risk 2
 LME 34 Bay of Bengal Bordering countries: Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Maldives, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand. LME Total area: 3,657,502 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity
LME 34 Bay of Bengal Bordering countries: Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Maldives, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand. LME Total area: 3,657,502 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity
Stock Assessment and ABC Calculation for Japanese Sardine (Sardinops Melanostictus) in the Northwestern Pacific under Japanese TAC System
 125 Stock Assessment and ABC Calculation for Japanese Sardine (Sardinops Melanostictus) in the Northwestern Pacific under Japanese TAC System Hiroshi NISHIDA National Research Institute of Fisheries Science,
125 Stock Assessment and ABC Calculation for Japanese Sardine (Sardinops Melanostictus) in the Northwestern Pacific under Japanese TAC System Hiroshi NISHIDA National Research Institute of Fisheries Science,
Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea
 Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea Sinjae Yoo Indicators of Status and Change within North Pacific Marine Ecosystems: A FUTURE Workshop Honolulu, 2011.04.26-28 Purpose To introduce monitoring and assessment
Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea Sinjae Yoo Indicators of Status and Change within North Pacific Marine Ecosystems: A FUTURE Workshop Honolulu, 2011.04.26-28 Purpose To introduce monitoring and assessment
Marine Microbial Processes
 Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving
Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving
Equatorial Pacific HNLC region
 Equatorial Pacific HNLC region Another region with high nitrogen left over after the growing season Iron and grazing constraints on primary production in the central equatorial Pacific: An EqPac synthesis
Equatorial Pacific HNLC region Another region with high nitrogen left over after the growing season Iron and grazing constraints on primary production in the central equatorial Pacific: An EqPac synthesis
Impacts of climate change and variability on the Northeast Shelf ecosystem and its inhabitants
 Impacts of climate change and variability on the Northeast Shelf ecosystem and its inhabitants Kevin Friedland National Marine Fisheries Service Narragansett Laboratory Themes - A few things to keep in
Impacts of climate change and variability on the Northeast Shelf ecosystem and its inhabitants Kevin Friedland National Marine Fisheries Service Narragansett Laboratory Themes - A few things to keep in
LIST OF POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF DECADAL PREDICTION
 LIST OF POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF DECADAL PREDICTION Document prepared for CLIVAR Pacific Panel by: William Crawford, Rodney Martinez and Toshio Suga. October 2006 The decadal time period falls between
LIST OF POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF DECADAL PREDICTION Document prepared for CLIVAR Pacific Panel by: William Crawford, Rodney Martinez and Toshio Suga. October 2006 The decadal time period falls between
Capacity Building in MEBM: sea-enclosing
 Capacity Building in MEBM: sea-enclosing and land-reclamation in developing countries Su Jilan* and Liu Hui *Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration Yellow Sea Fisheries Res Inst,
Capacity Building in MEBM: sea-enclosing and land-reclamation in developing countries Su Jilan* and Liu Hui *Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration Yellow Sea Fisheries Res Inst,
Advice July 2014
 7.3.19 Advice July 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Bay of Biscay and Atlantic Iberian waters Sardine in Divisions VIIIc and IXa Advice for 2015 ICES advises on the basis of precautionary considerations, and taking
7.3.19 Advice July 2014 ECOREGION STOCK Bay of Biscay and Atlantic Iberian waters Sardine in Divisions VIIIc and IXa Advice for 2015 ICES advises on the basis of precautionary considerations, and taking
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf
 Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Figure 1: map of East Asia showing land masses and water bodies. Source: PEMSEA
 Annex 1. Technical Background The Seas of East Asia1 The seas of East Asia are defined as the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea, the South China Sea, the Gulf of Thailand, the Sulu-Celebes (Sulawesi) Sea,
Annex 1. Technical Background The Seas of East Asia1 The seas of East Asia are defined as the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea, the South China Sea, the Gulf of Thailand, the Sulu-Celebes (Sulawesi) Sea,
Ecosystem dynamics and fisheries management in the Barents sea
 Ecosystem dynamics and fisheries management in the Barents sea A.Filin 1, S. Tjelmeland 2, J.E. Stiansen 2 1 Polar Research Institute of Marine Fisheries and Oceanography (PINRO), Murmansk, Russia 2 Institute
Ecosystem dynamics and fisheries management in the Barents sea A.Filin 1, S. Tjelmeland 2, J.E. Stiansen 2 1 Polar Research Institute of Marine Fisheries and Oceanography (PINRO), Murmansk, Russia 2 Institute
Production vs Biomass
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Relating the distribution of zooplankton abundance in the coastal waters of central Fujian Province to the seasonal variation of water masses
 32 4 2012 2 ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA Vol. 32 No. 4 Feb. 2012 DOI 10. 5846 /stxb201012261848.. 2012 32 4 1097-1104. Tian F G Xu Z L. Relating the distribution of zooplankton abundance in the coastal waters
32 4 2012 2 ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA Vol. 32 No. 4 Feb. 2012 DOI 10. 5846 /stxb201012261848.. 2012 32 4 1097-1104. Tian F G Xu Z L. Relating the distribution of zooplankton abundance in the coastal waters
Classification of systems. Aquatic Ecosystems. Lakes 9/9/2013. Chapter 25
 Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture Dan Cogalniceanu Course content Overview of marine systems
 Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability
 Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
LME 61 Antarctica 1/11. LME overall risk 2. Bordering country: Antarctica LME Total area: 3,486,169 km 2 List of indicators
 LME 61 Antarctica Bordering country: Antarctica LME Total area: 3,486,169 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary productivity Sea Surface Temperature 3 3 Fish
LME 61 Antarctica Bordering country: Antarctica LME Total area: 3,486,169 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary productivity Sea Surface Temperature 3 3 Fish
Zooplankton and Micronekton Distribution and Interaction with Predators at the Northwest Atlantic Shelf Break and its Canyons
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Zooplankton and Micronekton Distribution and Interaction with Predators at the Northwest Atlantic Shelf Break and its Canyons
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Zooplankton and Micronekton Distribution and Interaction with Predators at the Northwest Atlantic Shelf Break and its Canyons
populations and human systems in marine ecosystem models
 Coupling across individuals, populations and human systems in marine ecosystem models Eileen Hofmann Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University Outline of Lecture Scales and relevance
Coupling across individuals, populations and human systems in marine ecosystem models Eileen Hofmann Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University Outline of Lecture Scales and relevance
Using climate model output to project climate change impacts over the 21 st Century in the North Pacific Subtropical Ecosystem
 Using climate model output to project climate change impacts over the 21 st Century in the North Pacific Subtropical Ecosystem Jeffrey Polovina and Phoebe Woodworth-Jefcoats Pacific Islands Fisheries Science
Using climate model output to project climate change impacts over the 21 st Century in the North Pacific Subtropical Ecosystem Jeffrey Polovina and Phoebe Woodworth-Jefcoats Pacific Islands Fisheries Science
Climate Change and Plankton Communities: Disruptions at the Base of the Food Web
 Climate Change and Plankton Communities: Disruptions at the Base of the Food Web Walker O. Smith, Jr. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary With contributions from D. Steinberg,
Climate Change and Plankton Communities: Disruptions at the Base of the Food Web Walker O. Smith, Jr. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary With contributions from D. Steinberg,
Interannual variations of nutrients and primary production over the southeastern Beirng Sea shelf during spring of 1997,1998,and 1999
 Interannual variations of nutrients and primary production over the southeastern Beirng Sea shelf during spring of 1997,1998,and 1999 TaeKeun Rho,Terry E. Whitledge, and John J. Goering Institute of Marine
Interannual variations of nutrients and primary production over the southeastern Beirng Sea shelf during spring of 1997,1998,and 1999 TaeKeun Rho,Terry E. Whitledge, and John J. Goering Institute of Marine
LME 05 Gulf of Mexico
 LME 05 Gulf of Mexico Bordering countries: Mexico, United States of America LME Total area: 1,530,387 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary productivity Sea
LME 05 Gulf of Mexico Bordering countries: Mexico, United States of America LME Total area: 1,530,387 km 2 List of indicators LME overall risk 2 Productivity Chlorophyll-A 2 2 Primary productivity Sea
8/7/18. UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere
 UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
LME 32 Arabian Sea 1/13. LME overall risk 2
 LME 32 Arabian Sea Bordering countries: Bahrain, Djibouti, India, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen. LME Total area: 3,950,421 km 2 List of indicators
LME 32 Arabian Sea Bordering countries: Bahrain, Djibouti, India, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen. LME Total area: 3,950,421 km 2 List of indicators
The use of ecological models to assess indicators in support of the EU Marine Strategy Framework Directive
 The use of ecological models to assess indicators in support of the EU Marine Strategy Framework Directive Chiara Piroddi Brussels, 20-21 January 2016 Background * EU FP7 project Ocean of Tomorrow : DEVelopment
The use of ecological models to assess indicators in support of the EU Marine Strategy Framework Directive Chiara Piroddi Brussels, 20-21 January 2016 Background * EU FP7 project Ocean of Tomorrow : DEVelopment
Environmental studies for the assessment of myctophid resources in the Arabian Sea
 Environmental studies for the assessment of myctophid resources in the Arabian Sea Submitted to Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE) Ministry of Earth Sciences Government of India Kochi
Environmental studies for the assessment of myctophid resources in the Arabian Sea Submitted to Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE) Ministry of Earth Sciences Government of India Kochi
Integrated End-to-End and Fisheries Bio-Economic Modeling for Evaluating Ecosystem-Wide Effects of Human Pressures in the Baltic Sea
 Integrated End-to-End and Fisheries Bio-Economic Modeling for Evaluating Ecosystem-Wide Effects of Human Pressures in the Baltic Sea J. Rasmus Nielsen, Artur Palacz, Sieme Bossier, Francois Bastardie,
Integrated End-to-End and Fisheries Bio-Economic Modeling for Evaluating Ecosystem-Wide Effects of Human Pressures in the Baltic Sea J. Rasmus Nielsen, Artur Palacz, Sieme Bossier, Francois Bastardie,
Module 4. The Georges Bank Fisheries
 Module 4. The Georges Bank Fisheries Ocean Ecosystems Resources Energy Flow Ocean Ecosystem Problems Where is Georges Bank? What Makes a Good Fishery? Population Dynamics - the basics Sustainable Yield
Module 4. The Georges Bank Fisheries Ocean Ecosystems Resources Energy Flow Ocean Ecosystem Problems Where is Georges Bank? What Makes a Good Fishery? Population Dynamics - the basics Sustainable Yield
Approaching Coastal Aquaculture from an Ecosystem Perspective
 Approaching Coastal Aquaculture from an Ecosystem Perspective M. Rawson 1, Chen 2 C., Ji R.1, Zhu 3 M., Wang 4 D., C. Yarish 5, J. Sullivan 1 1 Georgia Sea Grant College Program, School of Marine Program,
Approaching Coastal Aquaculture from an Ecosystem Perspective M. Rawson 1, Chen 2 C., Ji R.1, Zhu 3 M., Wang 4 D., C. Yarish 5, J. Sullivan 1 1 Georgia Sea Grant College Program, School of Marine Program,
21 st Century Climate Change Impacts on Marine Fisheries
 21 st Century Climate Change Impacts on Marine Fisheries Anne B. Hollowed, NOAA, NMFS, Alaska Fisheries Science Center, Seattle, WA USA International Workshop on Climate and Oceanic Fisheries, Rarotonga,
21 st Century Climate Change Impacts on Marine Fisheries Anne B. Hollowed, NOAA, NMFS, Alaska Fisheries Science Center, Seattle, WA USA International Workshop on Climate and Oceanic Fisheries, Rarotonga,
California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web
 TEACHER PAGES What role do plankton play in the food web? California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
TEACHER PAGES What role do plankton play in the food web? California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
Predicting Trophic Interactions and Habitat Utilization in the California Current Ecosystem
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Predicting Trophic Interactions and Habitat Utilization in the California Current Ecosystem Jerome Fiechter UC Santa Cruz,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Predicting Trophic Interactions and Habitat Utilization in the California Current Ecosystem Jerome Fiechter UC Santa Cruz,
SALMON AS INTEGRATIVE SAMPLERS
 SALMON AS INTEGRATIVE SAMPLERS OF HIGH SEAS FOOD WEBS POSTER: INTEGRATING STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSES OF ZOOPLANKTON & RETURNING ADULT SALMON TISSUES TO INFORM HIGH SEAS NORTH PACIFIC FOOD WEB DYNAMICS Brian
SALMON AS INTEGRATIVE SAMPLERS OF HIGH SEAS FOOD WEBS POSTER: INTEGRATING STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSES OF ZOOPLANKTON & RETURNING ADULT SALMON TISSUES TO INFORM HIGH SEAS NORTH PACIFIC FOOD WEB DYNAMICS Brian
derived from coastal ecosystems and therefore may not be applicable to gyre ecosystems. Workshop objectives
 SSTO REVIEW ECOSYSTEM MODELS FOR THE SUBARCTIC PACIFIC GYRES APPENDIX E: BASS/MODEL WORKSHOP TO REVIEW ECOSYSTEM MODELS FOR THE SUBARCTIC PACIFIC GYRES Workshop objectives The BASS/MODEL workshop on trophic
SSTO REVIEW ECOSYSTEM MODELS FOR THE SUBARCTIC PACIFIC GYRES APPENDIX E: BASS/MODEL WORKSHOP TO REVIEW ECOSYSTEM MODELS FOR THE SUBARCTIC PACIFIC GYRES Workshop objectives The BASS/MODEL workshop on trophic
Responses of Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystems to Anthropogenic Climate Change
 Responses of Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystems to Anthropogenic Climate Change 1900 2100 Ryan R. Rykaczewski University of South Carolina ryk @ sc.edu We are united by an interest in understanding ecosystem
Responses of Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystems to Anthropogenic Climate Change 1900 2100 Ryan R. Rykaczewski University of South Carolina ryk @ sc.edu We are united by an interest in understanding ecosystem
Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin
 The BACC Author Team Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin 4u Springer Contents Preface The BACC Author Team Acknowledgements V VII XIII 1 Introduction and Summary 1 1.1 The BACC Approach
The BACC Author Team Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin 4u Springer Contents Preface The BACC Author Team Acknowledgements V VII XIII 1 Introduction and Summary 1 1.1 The BACC Approach
LATIDITUDINAL CHANGES OF PLANKTON AND NEKTON BIOMASSES IN THE WESTERN TRANSITION ZONE
 LATIDITUDINAL CHANGES OF PLANKTON AND NEKTON BIOMASSES IN THE WESTERN TRANSITION ZONE Vadim F. Savinykh,, Vladimir A. Shelekhov,, Svetlana V. Davydova,, Svetlana V. Naydenko, Alexey A. Baytaluk, Gennady
LATIDITUDINAL CHANGES OF PLANKTON AND NEKTON BIOMASSES IN THE WESTERN TRANSITION ZONE Vadim F. Savinykh,, Vladimir A. Shelekhov,, Svetlana V. Davydova,, Svetlana V. Naydenko, Alexey A. Baytaluk, Gennady
To upscale or downscale? Thoughts on bridging disparate scales of space and time in linking the planetary to the plankton
 To upscale or downscale? Thoughts on bridging disparate scales of space and time in linking the planetary to the plankton Nate Mantua University of Washington JISAO/SMA Climate Impacts Group PICES/CLIVAR
To upscale or downscale? Thoughts on bridging disparate scales of space and time in linking the planetary to the plankton Nate Mantua University of Washington JISAO/SMA Climate Impacts Group PICES/CLIVAR
Ecology. Climate. Global Climate. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
LME 20 Barents Sea. Contents 1/9. LME overall risk 2. Bordering countries: Norway, Russia, Svalbard LME Total area: 2,023,335 km 2
 Bordering countries: Norway, Russia, Svalbard LME Total area: 2,023,335 km 2 Contents LME overall risk 2 Productivity 2 Chlorophyll-A 2 Primary productivity 3 Sea Surface Temperature 3 Fish and Fisheries
Bordering countries: Norway, Russia, Svalbard LME Total area: 2,023,335 km 2 Contents LME overall risk 2 Productivity 2 Chlorophyll-A 2 Primary productivity 3 Sea Surface Temperature 3 Fish and Fisheries
UPDATE AND DISCUSSION
 UPDATE AND DISCUSSION Agenda Item K.2.b Supplemental NWFSC and SWFSC Presentation November 2012 Objectives Provide a brief update on the state of the California Current Integrated Ecosystem Assessment
UPDATE AND DISCUSSION Agenda Item K.2.b Supplemental NWFSC and SWFSC Presentation November 2012 Objectives Provide a brief update on the state of the California Current Integrated Ecosystem Assessment
SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATIONS IN SURFACE ZOOPLANKTON BIOMASS DISTRIBUTION IN THE GULF OF AQABA, RED SEA
 SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATIONS IN SURFACE ZOOPLANKTON BIOMASS DISTRIBUTION IN THE GULF OF AQABA, RED SEA Tariq Al-Najjar Marine Science Station, P.O. Box 195, Aqaba, Jordan tnajjar65@hotmail.com (Received
SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATIONS IN SURFACE ZOOPLANKTON BIOMASS DISTRIBUTION IN THE GULF OF AQABA, RED SEA Tariq Al-Najjar Marine Science Station, P.O. Box 195, Aqaba, Jordan tnajjar65@hotmail.com (Received
Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the
 Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems?
 Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Questions 3-6 refer to the diagram of surface currents in the oceans. 3. A current responsible for moving heat away from the equator.
 1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
The role of squid in linking marine ecosystems Alexander I. ARKHIPKIN
 The role of squid in linking marine ecosystems Alexander I. ARKHIPKIN Fisheries Department Falkland Islands Government Stanley FALKLAND ISLANDS Highly migratory fish Pacific salmons Open ocean coastal
The role of squid in linking marine ecosystems Alexander I. ARKHIPKIN Fisheries Department Falkland Islands Government Stanley FALKLAND ISLANDS Highly migratory fish Pacific salmons Open ocean coastal
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016
 SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
Marine Processes and Ecology
 T-TH 10:00-11:45 Discussion Sections TH 12:30-13:40 Textbook: Charlie Miller, Biological Oceanography Others listed in the syllabus (optional) Textbooks available at the Science Library: Oceanography:
T-TH 10:00-11:45 Discussion Sections TH 12:30-13:40 Textbook: Charlie Miller, Biological Oceanography Others listed in the syllabus (optional) Textbooks available at the Science Library: Oceanography:
California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web
 What role do plankton play in the food web? : California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, and
What role do plankton play in the food web? : California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, and
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Columbia River Plume correlation with Oregon/Washington dead zones
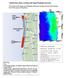 Columbia River Plume correlation with Oregon/Washington dead zones The location of the Oregon and Washington dead zones strongly correlate with Columbia River Plum summer flow patterns. OSU map OSU Map
Columbia River Plume correlation with Oregon/Washington dead zones The location of the Oregon and Washington dead zones strongly correlate with Columbia River Plum summer flow patterns. OSU map OSU Map
Ecosystem Research Initiative (ERI) in the St. Lawrence Estuary, eastern Canada:
 Ecosystem Research Initiative (ERI) in the St. Lawrence Estuary, eastern Canada: Testing an approach for science support to ecosystem-based management Boulogne Sur Mer November 5-7, 2008 Outline of the
Ecosystem Research Initiative (ERI) in the St. Lawrence Estuary, eastern Canada: Testing an approach for science support to ecosystem-based management Boulogne Sur Mer November 5-7, 2008 Outline of the
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Modelling of higher trophic levels with an large ecosystem model: -state of the art -limitations -perspectives. Piet Ruardij
 Modelling of higher trophic levels with an large ecosystem model: -state of the art -limitations -perspectives Piet Ruardij 1 Modelling the North Sea: Actual situation: 8+1 coupled hydrodynamical-ecosystems
Modelling of higher trophic levels with an large ecosystem model: -state of the art -limitations -perspectives Piet Ruardij 1 Modelling the North Sea: Actual situation: 8+1 coupled hydrodynamical-ecosystems
RE: Commercial Leasing for Wind Power on the Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) Offshore Massachusetts Request for Interest (RFI)
 New England Fishery Management Council 50 WATER STREET NEWBURYPORT, MASSACHUSETTS 01950 PHONE 978 465 0492 FAX 978 465 3116 John Pappalardo, Chairman Paul J. Howard, Executive Director March 28, 2011 Ms.
New England Fishery Management Council 50 WATER STREET NEWBURYPORT, MASSACHUSETTS 01950 PHONE 978 465 0492 FAX 978 465 3116 John Pappalardo, Chairman Paul J. Howard, Executive Director March 28, 2011 Ms.
Assessing the effects of climate change on U.S. West Coast sablefish productivity and on the performance of alternative management strategies
 Assessing the effects of climate change on U.S. West Coast sablefish productivity and on the performance of alternative management strategies Melissa A. Haltuch 1, Z. Teresa A mar 2, Nicholas A. Bond 3,
Assessing the effects of climate change on U.S. West Coast sablefish productivity and on the performance of alternative management strategies Melissa A. Haltuch 1, Z. Teresa A mar 2, Nicholas A. Bond 3,
Fish Conservation and Management
 Fish Conservation and Management CONS 486 Trophic pyramids, food webs, and trophic cascades oh my! Ross Chapter 2, Diana Chapter 1 Trophic interactions Limnological classification review Trophic pyramids
Fish Conservation and Management CONS 486 Trophic pyramids, food webs, and trophic cascades oh my! Ross Chapter 2, Diana Chapter 1 Trophic interactions Limnological classification review Trophic pyramids
Climate Change and Phenology in Narragansett Bay Phytoplankton. Introduction
 Sarah Blackstock OCG561: Biological Oceanography Susanne Menden-Deuer Research Project 3 December 2013 Climate Change and Phenology in Narragansett Bay Phytoplankton Introduction As time-series on plankton
Sarah Blackstock OCG561: Biological Oceanography Susanne Menden-Deuer Research Project 3 December 2013 Climate Change and Phenology in Narragansett Bay Phytoplankton Introduction As time-series on plankton
Study on the Diagnostics and Projection of Ecosystem Change Associated with Global Change
 Study on the Diagnostics and Projection of Ecosystem Change Associated with Global Change Project Representative Eitaro Wada Frontier Research Center for Global Change, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science
Study on the Diagnostics and Projection of Ecosystem Change Associated with Global Change Project Representative Eitaro Wada Frontier Research Center for Global Change, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science
observatory framework
 From marine terrestrial interactions to the warm blob : integrating land-oceanatmospheric research in a coastal observatory framework Brian Hunt, Jennifer Burt, Wiley Evans, William Floyd, Ian Giesbrecht,
From marine terrestrial interactions to the warm blob : integrating land-oceanatmospheric research in a coastal observatory framework Brian Hunt, Jennifer Burt, Wiley Evans, William Floyd, Ian Giesbrecht,
Filling the gaps: The Case of the Yellow Sea
 Filling the gaps: The Case of the Yellow Sea Sinjae Yoo KORDI, South Korea 1. Background 2. Knowledge gaps 3. YSLME Acknowledgements Details of the YSLME plan is an outcome of joint efforts by many members
Filling the gaps: The Case of the Yellow Sea Sinjae Yoo KORDI, South Korea 1. Background 2. Knowledge gaps 3. YSLME Acknowledgements Details of the YSLME plan is an outcome of joint efforts by many members
RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD
 RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD Jeffery Scott, Michael Follows Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program in Atmospheres, Oceans and Climate INTRODUCTION: Marine
RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD Jeffery Scott, Michael Follows Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program in Atmospheres, Oceans and Climate INTRODUCTION: Marine
Assessing impacts of climate changes on fisheries: An EAF perspective
 Assessing impacts of climate changes on fisheries: An EAF perspective Chang Ik Zhang 1 and Do Hoon Kim 2 1 Pukyong National University 2 National Fisheries R&D Institute Outline Impacts of climate changes
Assessing impacts of climate changes on fisheries: An EAF perspective Chang Ik Zhang 1 and Do Hoon Kim 2 1 Pukyong National University 2 National Fisheries R&D Institute Outline Impacts of climate changes
Investigating Alternate Trophic Pathways through Gelatinous Zooplankton and Planktivorous Fishes in an Upwelling Ecosystem Using End-to-End Models
 Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry Marine Environmental Modeling & Analysis, Eds., K. Omori, X. Guo, N. Yoshie, N. Fujii, I. C. Handoh, A. Isobe and S. Tanabe, pp. 57 63. by TERRAPUB,
Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry Marine Environmental Modeling & Analysis, Eds., K. Omori, X. Guo, N. Yoshie, N. Fujii, I. C. Handoh, A. Isobe and S. Tanabe, pp. 57 63. by TERRAPUB,
Instructions: Answer the questions 1-8 to set up basic rules for how lateral current direction controls vertical motion of seawater.
 Activity 1.1. Vertical Ocean Circulation NAME Reading: Ocean circulation is an important aspect of ocean health because it controls redistribution of both heat and nutrients. Humans indirectly affect ocean
Activity 1.1. Vertical Ocean Circulation NAME Reading: Ocean circulation is an important aspect of ocean health because it controls redistribution of both heat and nutrients. Humans indirectly affect ocean
Summary. Maritimes Region Ecosystem Status Report 2004/003
 Ecosystem Status Report 2004/003 2002 State of the Ocean: Chemical and Biological Oceanographic Conditions in the Gulf of Maine - Bay of Fundy, Scotian Shelf and the Southern Gulf of St. Lawrence Background
Ecosystem Status Report 2004/003 2002 State of the Ocean: Chemical and Biological Oceanographic Conditions in the Gulf of Maine - Bay of Fundy, Scotian Shelf and the Southern Gulf of St. Lawrence Background
The Open Ocean. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
Warming of the Arctic Ocean, Marine Ecological Consequences
 Warming of the Arctic Ocean, Marine Ecological Consequences Short version of a presentation at the summer school in Potsdam, 25 th June 2014 eva-maria.noethig@awi.de Only for working purposes Do not use
Warming of the Arctic Ocean, Marine Ecological Consequences Short version of a presentation at the summer school in Potsdam, 25 th June 2014 eva-maria.noethig@awi.de Only for working purposes Do not use
