Heat Storage Performance of a Honeycomb Ceramic Monolith
|
|
|
- Gregory Walsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Send Orders for Reprints to The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, 7, Heat Storage Performance of a Honeycomb Ceramic Monolith Xiaoni Qi * and Yongqi Liu Open Access College of Traffic and Vehicle Engineering, Shandong University of Technology, Zhangzhou Road 12, Zibo , China Abstract: Honeycomb ceramic is the key component of the regenerative system. The three-dimensional numerical model has been established for thermal process in honeycomb regenerator. The numerical simulation was performed using FLU- ENT, a commercial computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code, to compare simulation results to the test data. The regenerative process of a honeycomb ceramic regenerator was simulated under different conditions. The results under different flow rates, different flowing time, different materials and different wall thickness were investigated. The work in this paper provides a theory basis and guide to the exploitation and appliance of HTAC system and the results of the numerical calculation can be used as the foundation of engineering design. The results may be utilized for design of porous media reactors and process optimization. Keywords: Ceramic honeycomb, heat transfer characteristics, numerical simulation, heat storage performance. 1. INTRODUCTION High temperature air combustion (HiTAC) is characterized by reactants of high-temperature and low-oxygen concentration. Many researchers have recently realized significant energy savings, NOx emissions reduction and heat transfer uniformity in industrial heating furnaces resulting from such novel combustion 1. A regenerative burner is very effective for reducing fuel consumption in an industrial furnace [1-4]. A typical regenerative burner consists of at least two burners and two regenerators. While one of the burners is fired using cold air fed to the base of its regenerator, exhaust gas is drawn through the other burner and down into its associated regenerator to preheat the packing, then discharged to the atmosphere. When the regenerator being heated is sufficiently charged, the reversing system operates, cold air flows to the newly heated regenerator and is preheated, the previously cooled regenerator being reheated by the exhaust gas from the other burner firing. The regenerative burner shows a high heat recovery efficiency of 80-95% and the combustion air is preheated to over 1000 C. The classical books [5-7] provide analytical methods and mathematical models for calculating temperature profiles, effectiveness and other thermal performance parameters of regenerators. H. Hausen and Rummel [5] presented the first approximate solution to determine the spatial temperature distribution in solid material at a certain time and at a certain cross-section in a heat regenerator. They assumed time independent fluid flow temperature, but the assumption does not hold well in practice. Rummel introduced some constants to the heat transfer coefficient to get away from this assumption. However, the constants should be determined by *Address correspondence to this author at the College of Traffic and Vehicle Engineering, Shandong University of Technology, Zhangzhou Road 12, Zibo , China; Tel: ; Xiaoniqi1987@126.com experiment. An analytical model limited to a small wall thickness was developed by Klein et al. [8]. End temperatures of this solution agree approximately with experiments for fast switching limiting case. But there were little comparison about temperatures along the regenerator. Generally, the use of the dynamically operated regenerative burners was avoided and consequently measurements were made easier. Since a complete understanding of the heat transfer in industrial furnaces is always required in the design and optimization of dynamic heating processes. Our ambition in this work was to carry out studies on the start-up process in a furnace equipped with reverse regenerative burner systems. In this paper a three-dimensional numerical simulation model for a ceramic honeycomb regenerator used for a Hi- TAC burner was developed. This kind of regenerator is either a fixed bed with randomly packed ceramic balls or having honeycomb structure with identical cells. In this work, it is based on finite volume methods and the commercial Computational Fluid Dynamics software Fluent is used to simulate the dynamic process. Moreover, the model considers the temperature dependent thermal properties. By comparison, one-dimensional numerical simulation is not capable of considering all the above effects. The aim of the model is to obtain the temperature distribution of solid matrix and gases along the regenerator, the pressure difference across the regenerator at different operating conditions. It was verified with experiments that were performed on the same regenerator. 2. SIMULATION MODEL Fig. (1) shows the dimensions of one heat regenerator used in a HiTAC regenerative burner. Regenerator dimension is150w!150h! 300L. All flue gases generated by combustion are sucked again by the burners and pass X/ Bentham Open
2 114 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume 7 Qi and Liu through the regenerators. The switching time can be set to a value between 15 and 60 s Geometry Parameters of Honeycomb Cell A three-dimensional simulation model was developed to find out the temperature distribution of the solid storing material and flowing gases and other thermal and flow parameters for this regenerator and compare results with experiments. Because of geometric symmetry of the honeycomb structure, mathematical analysis was made on one honeycomb cell, or matrix, that formed a small part of the regenerator cross-section along the flow path (Fig. 1). properties between the gas and the air has small influences on the heat transfer performance of the honeycomb regenerator, the physical properties of the air is used instead of the gas in the numerical simulation for convenience. In fact the specific heat of flue gas is a little larger than that of the air, so the heat transfer between the flue gas and the honeycomb is a little more than the heat transfer between the honeycomb and the air if both of the switching times are the same. The temperatures of the air and the gas flowing through the honeycomb vary greatly, so their physical properties vary greatly correspondingly. The physical properties are assumed to vary linearly with the temperature. And the solid material is assumed to be Mullite, the thermal conductivity of which changes linearly with temperature. The physical property parameters of air and Mullite are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. Fig. (2). Three-dimensional computational zone. Table 1. Physical property parameters of air [19]. Temperature (T) 1473 K Density (ρ) kg / m 3 Isobaric specific heat (Cp) KJ / (kg! K ) Dynamic viscosity (µ) 53.5e- 6 kg / (m! s) Thermal conductivity (λ) 9.15e-2 W (m! K ) Fig. (1). Honeycomb regenerator and dimension of the ceramic material and flow path. In our test lab, there are 10 types of honeycomb cells, the side of which ranges from 2.1 mm to 5.0 mm. For such simple geometry with very small side, the flow is always laminar at nominal operating conditions, and flue gases emissivity is low inside regenerator cells due to very short beam length, so the heat transfer by radiation is not taken into account in this work Computational Zone Fig. (2) shows the three-dimensional zone in the simulation. It includes the solid material and flow path (the gas phase). The honeycomb cell is square--axisymmetric, the velocity, temperature and pressure distribution are all symmetric. So half the wall thickness, 1/4 flow path and the whole length of the cell is taken as the computational zone Physical Property Parameters of Gas and Honeycomb The flue-gas and the preheated air flow through the honeycomb alternately. As the difference of the physical Inlet velocity (V) 7 m! s Prandt number (Pr) Governing Equations In the honeycomb cell, gas attributes to the threedimensional unsteady laminar flow. There are three different forms of heat transfer process, that is, the thermal conductivity of gas or air in itself; convection heat transfer between honeycomb and flue or air; thermal conductivity, thermal storage and thermal rejection internal honeycomb. In order to simplify the calculation, we made the following assumptions: The differences between the flue gas and air is ignored and the physical parameters of air are used instead of that of flue gas; radiation heat transfer in the channel is ignored; Heat loss from the regenerator to the environment is ignored; The surface area and body mass distribution of the cell is uniform; The Cell surface is smooth. A typical set of equations for regenerative problem was used: equation of mass conservation, Navier-Stokes, thermal conductivity equation for gas, thermal conductivity equation for porous media and Ideal gas state equation.
3 Heat Storage Performance of a Honeycomb Ceramic Monolith The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume Table 2. Temperature K Physical property parameters of Mullite. Density kg / m 3 Thermal Conductivity W (m! K ) Isobaric Specific Heat J / (kg! K ) Mass conservation equation:!" +! "u!x! "u +!("v)!y +! "w =0 (1)!z Navier-Stokes equations:! "v! "w +div("uu)=div(#gradu) $!p!x +div("vu)=div(#gradv) $!p!y +div("wu)=div(#gradw) $!p!z An energy balance was made in every domain in the channel, the flowing gases and solid domains. The problem is transient and the general energy balance equation is:! "T +div("uu)=div(#gradu) $!p!x where ST, a sink or source heat, is zero in this case. The expression within brackets is the heat flux vector, which in this case includes the contributions from conduction and convection, respectively. The heat is transported by convection and conduction in the flow domain and only by conduction in solid domain. Therefore, the energy equation of the solid material domain is:! "T s =div( # c p gradt s ) And the energy equation of the flowing gases domain is:! "T g +div( # c p gradt g )=div( # c p gradt g ) Energy conservation Equation:! "T +div("ut )=div( # c p gradt ) Ideal gas state equation: p =!R g T (6) 2.5. Boundary Conditions Since the symmetry of the flow and heat transfer in the three-dimensional flow zone of the honeycomb, the four (2) (3) (4) (5) exterior sides along the direction of the gas flow are defined as symmetric boundary as shown in Fig. (2). The solid surface of both ends of honeycomb is defined as adiabatic boundary condition. Coupling boundary conditions are applied on the two interior surfaces where the honeycomb is in contact with the flowing gas. Because the heat transfer between the honeycomb and the gas is continuous and the temperature and the heat flux are both affected by the interaction with the wall, no matter if the temperature or the heat flux on the interface are parts of the results. Obviously the two contact surfaces cannot be used as the first, second or third type of pre-specified boundary conditions. Boundary conditions such as these dynamically determined by the thermal transformation process cannot be predetermined, is known as conjugate heat transfer. The coupled boundary conditions at the intersection of the two-phase interface can be listed as the following expressions: Tw honeycomb = Tw gas (Continuous Temperature) q w honeycomb = q w gas (Continuous heat flux) where the subscript--honeycomb and gas mean the simulation regions respectively, w means the interface between the two regions. The gas mass flow rates of the two heat-exchange stages in one working cycle should be the same. However, the inlet temperature of flue gas is 1473 K. So the inlet velocity of gas is V=7 m/s. During the heating period, the inlet end of hot flue gas is defined as the inlet boundary condition, where the speed and the pressure are set to a specific value and 0 Pa, respectively. While the other end of the cold-side is set to pressure outlet. During the cooling period, the inlet end of cold air is defined as velocity inlet and the pressure is 0 Pa, the other end is set to pressure outlet. As the honeycomb hole is 5 mm, the gas inlet velocity is 7 m/s, the dynamic viscosity is Pa! s, the density is kg / m 3, and the Reynolds number is about 60. For such simple geometry with very small diameter, the flow is always laminar since local Re ranges between 90 and 1000 at nominal operating conditions and therefore, the velocity profile and pressure drop across the regenerator can be determined from the solution of Navier-Stokes equation. Since the local Remax is much smaller than 2000 (the critical Reynolds in a smooth tube), the flow can be considered as laminar. In practice, the actual critical Reynolds number may be reduced because of the wall roughness, and the flow near the wall region tends to be turbulent, which may strengthen the local heat transfer. However, this effect can be corrected by means of experiments, or suitable correction factor is used in the numerical heat transfer 19. The local heat transfer caused by the roughness is ignored and the surface of the cellular surface is assumed to be smooth Switching Condition Heating or cooling period is half of one cycle time. The ending of heating period is the starting time of cooling period. Similarly, the ending of cooling period is the starting time of heating period. The switching operation is instantaneous and it did not take time. The physical properties and
4 116 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume 7 Qi and Liu the temperature of honeycomb, the temperature, physical properties and flowing condition of gas do not change before and after the moment. When the heating period is over, the cooling process makes end that is pressure outlet before the switching time changes to velocity inlet and the heating end that is velocity inlet before the switching time changes to pressure outlet. Correspondingly, when the cooling period is finished, the heating process makes end that is pressure outlet before the switching time changes to velocity inlet, and the cooling end that is velocity inlet before the switching time changes to pressure outlet. A commutation cycle consists of a heating period and a cooling period. The calculation repeats the cycle until the process becomes a stable state Initial Conditions When the furnace starts working, the temperature of regenerator increases slowly from the ambient temperature, so the initial temperature values of honeycomb and air are set to ambient temperature, T 0 = 300K ; the initial velocity of gas is set to 0, u = v = w = 0m/s ; the initial pressure is 0, P 0 = 0Pa. The initial temperature of the cellular ceramic body is set to 300 K when the detailed starting characteristics is investigated. In other cases, the initial value of the temperatures are set to 900 K, which is the mean value of the inlet temperature of flue gas K and the inlet temperature of air. This way the time that the honeycomb regenerator takes to reach to the stable working conditions greatly reduces as well as it saves the computing time Computation Ending Condition When the difference of the exit temperature of air and flue gas at the end of one cycle between those at the end of the previous cycle is less than 0.2 C, then we consider that the honeycomb regenerator has reached to stable working condition, and the calculation process is completed. until the temperature profiles just before the changeover are the same as the previous data, periodic steady state. The meshing of the computational zone is shown in Fig. (3). The governing integral equations for the conservation of mass and momentum, and for energy and other scalars such as turbulence and chemical species were solved through control-volume-based technique. Pressure and velocity field are computed by Semi-Implicit Method for Pressure-Linked Equations (SIMPLE) algorithms. The convergence criterion for energy equation was that the residual error was less than 10-6, whereas for other governing equations it was In this study, all residual errors of the degree of freedom were set by10-3, which is satisfactory for simulation analysis. Experiments were carried out on honeycomb regenerators that are contained in a methane oxidation reactor. For completeness, a simple description of the reactor is given here. Tests of temperatures were carried out in a reverse flow reactor. The reactor is 600 mm wide, 600 mm high and 300 mm long. The entire configuration of the test apparatus is shown in Fig. (4). In a reverse flow reactor, the feed is periodically switched between the two reactor ends using switching valves. When switching valves 1 and 4 are open, the feed flows to the reactor from left to right (forward flow), indicated by the solid arrows. When switching valves 2 and 3 are open, the feed flows to the reactor from right to left (reverse flow), indicated by the dotted arrows. The total cycle consists of these two operations, and the term switch time denotes the time at which the flow is changed from forward to reverse flow or from reverse to forward flow. The sum of the times for forward and reverse flow is the cycle time. In this experiment the flue gas is substituted by hot air. Thermal energy carried by hot air can be captured by the solid heat storage medium. Then, with switching the flow direction, the captured thermal energy within the heat storage medium can be used to preheat the air. In the experiments, the ceramic honeycomb monoliths were used as heat storage medium. The monoliths consist of a structure of parallel channels with porous walls. The monolith properties are as same as that used in the model. Fig. (3). Meshing of the computational zone Computational Process The computations are initiated using cold start initial conditions and executed for one complete cycle of operation, i.e., the duration for both the regeneration and the combustion periods. The results are then saved in the computer and the final temperatures are set to be the initial conditions of the next run. The computations were executed repeatedly Fig. (4). Configuration of the test apparatus. To prevent heat loss from the reactor to the surroundings, the reactor was surrounding with a 350 mm thick layer of
5 Heat Storage Performance of a Honeycomb Ceramic Monolith The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume insulation ceramic fiber blanket. Thermal conductivity of the ceramic fiber blanket is W (m! K ). solution was obtained from the commercially available CFD code FLUENT to investigate the thermal storage behavior of the honeycomb regenerator. The thermal behavior of the channel has been simulated numerically for some cases. In this part the heat transfer performance of ceramic honeycomb will be discussed under different conditions by changing the different parameters. All conditions can be summarized in four cases: the gas inlet velocity, the specific heat of regenerator, the flowing time through the regenerative and the wall thickness of the ceramic body Influence of Different Flowing Time Fig. (5). Experimental and mathematical temperature of flue gas inlet. Air and the hot air were supplied to the reactor using an air compressor. The flow rate of inlet was measured using a flow rate meter. Thermal profiles from the reactor were obtained using twelve thermocouples (denoted from 1 to 12 in Fig. 1). All thermocouples were placed along the centerline of the reactors. The data acquisition system recorded all sensor values. Data were saved as data files for analysis. The calculated temperatures of flue gas inlet were compared with the ones measured as shown in Fig. (5). The temperature of those 12 points was measured by 12 thermocouples. During the measurements there should be no flame in the combustion space. Therefore, the measurements were performed in the 2 second gap between the intervals. It is shown in Fig. (5) that the measured temperatures of inlet flue gas are generally more than the simulated values. The reason may be that the radiation of the hot air is ignored in the model. However, the tendency of the temperature is the same as the experiment. 4. RESULTS For a 3-D numerical simulation model, the structure and meshes were constructed by GAMBIT, and then numerical Figs. (6-9) show the temperature and velocity distribution at different time. It is apparent that this is a transient process in which the temperature and the velocity change with time. It can be clearly seen from the color in the figures that the inlet temperature of the ceramic regenerator increases with the increasing time. This is due to the stronger heat transference between the ceramic and the hot gas, and the temperature around the inlet of the ceramic almost equals to the hot gas. In the early period of the heat exchange, the heat transfer between the regenerator and the hot gas occurs mainly in the inlet zone. The high temperature zone gradually goes to lower temperature zone with the carrying out of the heat transfer, and the ceramic regenerator temperature in the axial direction gradually increases. By comparing the temperature and the velocity map, it can be seen that both the distribution maps are very similar. This is because the relationship of the ideal gas ρv = nrt. When the gas temperature decreases, its density decreases, and the gas velocity is bound to increase according to the mass conservative law. That is to say that the gas velocity varies with temperature. Therefore, the velocity distribution and temperature distribution are very similar. It can be seen from the temperature distribution of the outlet section that the outlet temperature is getting more and more higher. It means that the regenerative capacity of regenerator is getting worse over time, because the temperature difference between the gas and the wall is getting even more smaller, and the heat transfer coefficient decreases. Therefore, in order to obtain a higher recovery rate, the appropriate flowing time should be determined. If the flowing time is too Fig. (6). Temperature distribution in the central section (7 m/s, 6 s).
6 118 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume 7 Qi and Liu Fig. (7). Velocity distribution in the central section (7 m/s, 6 s). Fig. (8). Temperature distribution in the central section (7 m/s, 30 s). Fig. (9). Velocity distribution in the central section (7 m/s, 30 s). long, the heat in the gas cannot be fully absorbed by the wall, the outlet temperature is high; if the flowing time is too short and the regenerator cannot be fully heated, it is difficult to obtain a good warm-up effect, the temperature of regenerator reduces.
7 Heat Storage Performance of a Honeycomb Ceramic Monolith The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume Influence of Inlet Velocity Figs. (10, 11) show temperature distributions as t=50 s under v=7 m/s and v=15m/s, respectively. The temperature distribution differs greatly under different velocities. As the inlet velocity of gas increases, the high temperature zone moves gradually to the outlet direction and the high temperature zone becomes bigger. The outlet temperature of the gas is greater when the inlet velocity of gas is greater. As the inlet velocity is greater, the mass flow rate unit time is greater and the heat carrying by the gas is greater, since the time of heat transfer between the gas and the wall is not sufficient. Therefore, in order to prevent the gas outlet temperature from being higher, the influence of the gas flow rate on heat transfer must be fully considered, and the combustion system must be reasonable in practical application. 5. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Honeycomb regenerator is an important part of high temperature air combustion system. This paper focuses on the flow and heat transfer of the flue gas and ceramic. In addition, the heat transfer of honeycomb is considered as well. In this paper, numerical simulation method is used to study the factors that influence the heat transfer characteristics of the gas and the honeycomb in the start-up period. Moreover, the model was validated with the experimental data. The following conclusions were obtained: (1) Numerical model of honeycomb regenerator was presented and the whole start-up process was simulated by means of CFD commercial software Fluent. Fig. (10). Temperature distribution in the central section (t=50 s, v=7 m/s). Fig. (11). Temperature distribution in the central section (t=50 s, v=15 m/s).
8 120 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, Volume 7 Qi and Liu (2) The flue gas and air inlet temperature curves change with the cycle and the changing discipline of the gas inlet temperatures were obtained. And then the heat transfer between the gas and the honeycomb was analyzed. According to the analysis, the duration time of start-up period can be roughly calculated, which provides reference for further study. (3) The velocity distributions on the cross-section or the section along the length were obtained, which verified the laminar flow of the channel. This conclusion provides reference to optimizing the flow. (4) The gas and the honeycomb temperature distributions on the cross-section or the section along the length at the end of the heating period were obtained. The characteristics and the reason of the temperature distribution were analyzed, which provides a reference for further research. (5) The pressure distribution along the honeycomb were obtained, the reasons for the loss of production and the method to reduce the pressure loss were analyzed. (6) The transient temperature curves of flue gas inlet and air inlet were obtained, and the temperature fluctuations by the intersection of cold and hot airstream forward were analyzed. (7) The influence of switching time on the heat transfer efficiency and temperature efficiency was analyzed. And the principle of best switching time was presented, which can be used as the foundation of engineering design. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Declared none. REFERENCES [1] H. Tsuji, A. Gupta, T. Hasegawa, M. Katsuki, K. Kishimoto, and M. Morita, High Temperature Air Combustion; from Energy Conservation to Pollution Reduction, CRC Press LLC, New York, [2] R. Tanaka, New progress of energy saving technology toward the 21 st century: frontier of combustion & heat transfer technology, In: Proceedings of 11 th IFRF, The Netherlands, [3] M. Mortberg, N. Rafidi, and W. Blasiak, Measurements of temperature heat flux and flue gas composition in HTAC flame, In: Proceedings of Challenges in Reheating Furnaces Conference, IOM Communications Ltd, London, 1995, pp [4] J.A. Wunning, J.G. Wunning, Flameless oxidation to reduce thermal NO-formation, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., vol. 23, pp , April [5] H. Hausen, Heat Transfer in Counter Flow, Parallel Flow and Cross Flow, McGraw-Hill, New York, [6] F.W. Schmidt, A.J. Willmot, Thermal Energy Storage and Regeneration, McGraw-Hill, New York, [7] W.M. Kays, and A.L. London, Compact Heat Exchanger, McGraw-Hill, New York, [8] H. Klein, and G. Eigenberger, Approximate solution for metallic regenerative heat exchangers, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, vol. 44, pp , April Received: January 6, 2015 Revised: May 20, 2015 Accepted: June 19, 2015 Qi and Liu; Licensee Bentham Open This is an open access article licensed under the terms of the ( which permits unrestricted, noncommercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the work is properly cited.
The 3-D Numerical Simulation of a Walking Beam Type Slab Heating Furnace with Regenerative Burners
 The 3-D Numerical Simulation of a Walking Beam Type Slab Heating Furnace with Regenerative Burners Jiin-Yuh Jang, Chien-Nan Lin, Sheng-Chih Chang, Chao-Hua Wang Abstract: This study investigates the furnace
The 3-D Numerical Simulation of a Walking Beam Type Slab Heating Furnace with Regenerative Burners Jiin-Yuh Jang, Chien-Nan Lin, Sheng-Chih Chang, Chao-Hua Wang Abstract: This study investigates the furnace
Evaluation of new combustion technologies for CO 2 and NO x reduction in steel industries
 Evaluation of new combustion technologies for CO 2 and NO x reduction in steel industries W. Blasiak, K. Narayanan & W. Yang Division of Energy and Furnace Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH),
Evaluation of new combustion technologies for CO 2 and NO x reduction in steel industries W. Blasiak, K. Narayanan & W. Yang Division of Energy and Furnace Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH),
CFD ANALYSIS OF CONVECTIVE FLOW IN A SOLAR DOMESTIC HOT WATER STORAGE TANK
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 4, Issue 1, January-2013 1 CFD ANALYSIS OF CONVECTIVE FLOW IN A SOLAR DOMESTIC HOT WATER STORAGE TANK Mr. Mainak Bhaumik M.E. (Thermal
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 4, Issue 1, January-2013 1 CFD ANALYSIS OF CONVECTIVE FLOW IN A SOLAR DOMESTIC HOT WATER STORAGE TANK Mr. Mainak Bhaumik M.E. (Thermal
MODELLING COMBUSTION AND THERMAL NO X FORMATION IN ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF FERRO-SILICON AND SILICON-METAL
 MODELLING COMBUSTION AND THERMAL NO X FORMATION IN ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF FERRO-SILICON AND SILICON-METAL B. Ravary, C. Colomb 1 and S. T. Johansen 2 ERAMET Norway AS, c/o SINTEF Materials,
MODELLING COMBUSTION AND THERMAL NO X FORMATION IN ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF FERRO-SILICON AND SILICON-METAL B. Ravary, C. Colomb 1 and S. T. Johansen 2 ERAMET Norway AS, c/o SINTEF Materials,
Thermal Management of Densely-packed EV Battery Set
 EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 2015 Thermal Management of Densely-packed EV Battery Set Abstract Z. Lu 1, X.Z. Meng 1, W.Y. Hu 2, L.C. Wei 3, L.Y. Zhang 1, L.W. Jin 1* 1 Building Environment and Equipment
EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 2015 Thermal Management of Densely-packed EV Battery Set Abstract Z. Lu 1, X.Z. Meng 1, W.Y. Hu 2, L.C. Wei 3, L.Y. Zhang 1, L.W. Jin 1* 1 Building Environment and Equipment
Simulation of Flameless Combustion of Natural Gas in a Laboratory Scale Furnace
 Turkish J. Eng. Env. Sci. 30 (2006), 135 143. c TÜBİTAK Simulation of Flameless Combustion of Natural Gas in a Laboratory Scale Furnace Sébastien MURER, Barbara PESENTI and Paul LYBAERT Thermal Engineering
Turkish J. Eng. Env. Sci. 30 (2006), 135 143. c TÜBİTAK Simulation of Flameless Combustion of Natural Gas in a Laboratory Scale Furnace Sébastien MURER, Barbara PESENTI and Paul LYBAERT Thermal Engineering
Numerical Investigation of Swirl's Effects in the Outer Annulus of a Reverse-flow Gas Turbine Combustor
 Numerical Investigation of Swirl's Effects in the Outer Annulus of a Reverse-flow Gas Turbine Combustor Mostafa Ghanei Tayeblou and Kavous Ariafar Department of Civil Engineering Islamic Azad University,
Numerical Investigation of Swirl's Effects in the Outer Annulus of a Reverse-flow Gas Turbine Combustor Mostafa Ghanei Tayeblou and Kavous Ariafar Department of Civil Engineering Islamic Azad University,
Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software To cite this article: D Zahariea 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software To cite this article: D Zahariea 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Experimental Investigation of Heat Transfer Characteristics of Calcined Petroleum Coke Fin-and-Tube Waste Heat Exchanger
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 20 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, 7, 20-25 Open Access Experimental Investigation of Heat Transfer Characteristics of Calcined Petroleum
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 20 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2014, 7, 20-25 Open Access Experimental Investigation of Heat Transfer Characteristics of Calcined Petroleum
Numerical Modeling of Buoyancy-driven Natural Ventilation in a Simple Three Storey Atrium Building
 Numerical Modeling of Buoyancy-driven Natural Ventilation in a Simple Three Storey Atrium Building Shafqat Hussain and Patrick H. Oosthuizen Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Queen s
Numerical Modeling of Buoyancy-driven Natural Ventilation in a Simple Three Storey Atrium Building Shafqat Hussain and Patrick H. Oosthuizen Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Queen s
Self-Aspirating Radiant Tube Burner
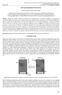 Self-Aspirating Radiant Tube Burner Chanon Chuenchit and Sumrerng Jugjai * Combustion and Engine Research Laboratory (CERL), Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s
Self-Aspirating Radiant Tube Burner Chanon Chuenchit and Sumrerng Jugjai * Combustion and Engine Research Laboratory (CERL), Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s
Performance Analysis for Natural Draught Cooling Tower & Chimney through Numerical Simulation
 Performance Analysis for Natural Draught Cooling Tower & Chimney through Numerical Simulation Kanteyya A 1, Kiran Kumar Rokhade 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, HKESSLN College
Performance Analysis for Natural Draught Cooling Tower & Chimney through Numerical Simulation Kanteyya A 1, Kiran Kumar Rokhade 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, HKESSLN College
Numerical modelling of shielding gas flow and heat transfer in laser welding process
 Numerical modelling of shielding gas flow and heat transfer in laser welding process Alireza Javidi Shirvan 1, Isabelle Choquet 1, Håkan Nilsson 2 1 University West, Department of Engineering Science,
Numerical modelling of shielding gas flow and heat transfer in laser welding process Alireza Javidi Shirvan 1, Isabelle Choquet 1, Håkan Nilsson 2 1 University West, Department of Engineering Science,
ESTIMATION OF THE GAS EXHAUST RATE REQUIRED ON AN ALUMINIUM REDUCTION CELL DURING START-UP USING TASCflow3D
 ESTIMATION OF THE GAS EXHAUST RATE REQUIRED ON AN ALUMINIUM REDUCTION CELL DURING START-UP USING TASCflow3D Marc Dupuis (GéniSim Eng.) Edgar Dernedde (Kroll International) ABSTRACT During the start-up
ESTIMATION OF THE GAS EXHAUST RATE REQUIRED ON AN ALUMINIUM REDUCTION CELL DURING START-UP USING TASCflow3D Marc Dupuis (GéniSim Eng.) Edgar Dernedde (Kroll International) ABSTRACT During the start-up
Project Background (long term goals)
 ANNUAL REPORT 2012 UIUC, August 16, 2012 Modeling Heat Transfer in SEN during Preheating & Cool-down Yonghui Li (Ph.D. Student) Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at
ANNUAL REPORT 2012 UIUC, August 16, 2012 Modeling Heat Transfer in SEN during Preheating & Cool-down Yonghui Li (Ph.D. Student) Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at
NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE
 S643 NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE by Yong-Hui XIE *, Dong-Ting YE, and Zhong-Yang SHEN School of Energy
S643 NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE by Yong-Hui XIE *, Dong-Ting YE, and Zhong-Yang SHEN School of Energy
Theory Comparison between Propane and Methane Combustion inside the Furnace
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Theory
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Theory
Numerical Simulation on Effects of Electromagnetic Force on the Centrifugal Casting Process of High Speed Steel Roll
 Modeling and Numerical Simulation of Material Science, 2014, 4, 20-24 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/mnsms) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/mnsms.2014.41004 Numerical Simulation
Modeling and Numerical Simulation of Material Science, 2014, 4, 20-24 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/mnsms) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/mnsms.2014.41004 Numerical Simulation
CFD tools and lower order modeling for regenerative chambers with gas recirculation system
 CFD tools and lower order modeling for regenerative chambers with gas recirculation system Ing. Alessandro Spoladore Prof. Carlo Cravero Università di Genova Facoltà di Ingegneria DIME 1 Computational
CFD tools and lower order modeling for regenerative chambers with gas recirculation system Ing. Alessandro Spoladore Prof. Carlo Cravero Università di Genova Facoltà di Ingegneria DIME 1 Computational
Heat transfer enhancement in fire tube boiler using hellically ribbed tubes
 Heat transfer enhancement in fire tube boiler using hellically ribbed tubes Miss Simantini Balasaheb Kute --------------------------------------------------------***-------------------------------------------------------------
Heat transfer enhancement in fire tube boiler using hellically ribbed tubes Miss Simantini Balasaheb Kute --------------------------------------------------------***-------------------------------------------------------------
JERNKONTORETS FORSKNING
 JERNKONTORETS FORSKNING Serie Nr Datum Forskningsuppgift nr D 803 2003-11-25 51046 (TO 51-37) PERFORMANCE OF REHEATING FURNACES EQUIPPED WITH HIGHLY PREHEATED AIR Final report by Birgitta Lindblad, Jernkontoret
JERNKONTORETS FORSKNING Serie Nr Datum Forskningsuppgift nr D 803 2003-11-25 51046 (TO 51-37) PERFORMANCE OF REHEATING FURNACES EQUIPPED WITH HIGHLY PREHEATED AIR Final report by Birgitta Lindblad, Jernkontoret
Experimental and modelling study of low-nox industrial burners
 Experimental and modelling study of low-nox industrial burners A. Frassoldati 1, A. Cuoci 1, T. Faravelli 1, E. Ranzi 1, D. Astesiano 2, M. Valenza 2, P. Sharma 3 1. Dipartimento di Chimica Materiali e
Experimental and modelling study of low-nox industrial burners A. Frassoldati 1, A. Cuoci 1, T. Faravelli 1, E. Ranzi 1, D. Astesiano 2, M. Valenza 2, P. Sharma 3 1. Dipartimento di Chimica Materiali e
COMSOL Multiphysics Simulation of Flow in a Radial Flow Fixed Bed Reactor (RFBR)
 COMSOL Multiphysics Simulation of Flow in a Radial Flow Fixed Bed Reactor (RFBR) Anthony G. Dixon *,1, Dominic Polcari 1, Anthony Stolo 1 and Mai Tomida 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Worcester
COMSOL Multiphysics Simulation of Flow in a Radial Flow Fixed Bed Reactor (RFBR) Anthony G. Dixon *,1, Dominic Polcari 1, Anthony Stolo 1 and Mai Tomida 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Worcester
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR NATURAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL RADIATION IN PASSIVE CONTAINMENT COOLING SYSTEM
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR NATURAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL RADIATION IN PASSIVE CONTAINMENT COOLING SYSTEM Weizhong Zhang and Qian Lin Advanced Nuclear Power Technology R&D Center, Shanghai Nuclear Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR NATURAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL RADIATION IN PASSIVE CONTAINMENT COOLING SYSTEM Weizhong Zhang and Qian Lin Advanced Nuclear Power Technology R&D Center, Shanghai Nuclear Engineering
Quenching steels with gas jet arrays
 Quenching steels with gas jet arrays PAUL F STRATTON ANDREW P RICHARDSON BOC Rother Valley Way, Holbrook, Sheffield UNITED KINGDOM Paul.stratton@boc.com http://www.catweb.boc.com Abstract: - Single components
Quenching steels with gas jet arrays PAUL F STRATTON ANDREW P RICHARDSON BOC Rother Valley Way, Holbrook, Sheffield UNITED KINGDOM Paul.stratton@boc.com http://www.catweb.boc.com Abstract: - Single components
Dr. J. Wolters. FZJ-ZAT-379 January Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ
 Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ ZAT-Report FZJ-ZAT-379 January 2003 Benchmark Activity on Natural Convection Heat Transfer Enhancement in Mercury with Gas Injection authors Dr. J. Wolters abstract A
Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ ZAT-Report FZJ-ZAT-379 January 2003 Benchmark Activity on Natural Convection Heat Transfer Enhancement in Mercury with Gas Injection authors Dr. J. Wolters abstract A
Numerical Simulation of a Batch-Type Reheating Furnace
 World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2018, 6, 713-722 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet ISSN Online: 2331-4249 ISSN Print: 2331-4222 Numerical Simulation of a Batch-Type Reheating Furnace Francisco
World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2018, 6, 713-722 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet ISSN Online: 2331-4249 ISSN Print: 2331-4222 Numerical Simulation of a Batch-Type Reheating Furnace Francisco
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF NATURAL DRAFT WET COOLING TOWER AT OPTIMIZED INJECTION HEIGHT
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF NATURAL DRAFT WET COOLING TOWER AT OPTIMIZED INJECTION HEIGHT 1 ALOK SINGH, 2 SANJAY SONI, 3 R. S. RANA 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Mechanical Engineering Department
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF NATURAL DRAFT WET COOLING TOWER AT OPTIMIZED INJECTION HEIGHT 1 ALOK SINGH, 2 SANJAY SONI, 3 R. S. RANA 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Mechanical Engineering Department
Investigating Two Configurations of a Heat Exchanger in an Indirect Heating Integrated Collector Storage Solar Water Heating System
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 7 (2013) 66-73 D DAVID PUBLISHING Investigating Two Configurations of a Heat Exchanger in an Indirect Heating Integrated Collector Storage Solar Water Heating System
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 7 (2013) 66-73 D DAVID PUBLISHING Investigating Two Configurations of a Heat Exchanger in an Indirect Heating Integrated Collector Storage Solar Water Heating System
LECUTRE 32: Steady state heat flow in furnaces and heat exchangers
 LECUTRE 32: Steady state heat flow in furnaces and heat exchangers Contents Estimation of heat losses in furnaces Heat exchanger Performance of a heat exchanger Regenerator Key words: Heat exchanger, Regenerator,
LECUTRE 32: Steady state heat flow in furnaces and heat exchangers Contents Estimation of heat losses in furnaces Heat exchanger Performance of a heat exchanger Regenerator Key words: Heat exchanger, Regenerator,
Development of a novel reformer for tar-free syngas production
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 246 251 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Development of a novel reformer for tar-free syngas
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 246 251 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Development of a novel reformer for tar-free syngas
Development of Micro Combustion Systems: Insights through Computations and Experiments
 Development of Micro Combustion Systems: Insights through Computations and Experiments Sudarshan Kumar 1 Abstract This paper reports the experimental and numerical investigations on the performance of
Development of Micro Combustion Systems: Insights through Computations and Experiments Sudarshan Kumar 1 Abstract This paper reports the experimental and numerical investigations on the performance of
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMIC COMBUSTION MODELLING OF A BAGASSE BOILER
 REFEREED PAPER COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMIC COMBUSTION MODELLING OF A BAGASSE BOILER DU TOIT P AND VAN DER MERWE SW John Thompson, Sacks Circle, Bellville South, 7530, South Africa philipd@johnthompson.co.za
REFEREED PAPER COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMIC COMBUSTION MODELLING OF A BAGASSE BOILER DU TOIT P AND VAN DER MERWE SW John Thompson, Sacks Circle, Bellville South, 7530, South Africa philipd@johnthompson.co.za
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BY AENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2016 Special 10(6): pages 72-78 Open Access Journal Cfd Analysis Of
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BY AENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2016 Special 10(6): pages 72-78 Open Access Journal Cfd Analysis Of
Computational Analysis of Blast Furnace Pulverized Coal Injection For Iron Making
 Computational Analysis of Blast Furnace Pulverized Coal Injection For Iron Making 1 Gourav Kumar Thakur, 2 Kawal lal Kurrey, 3 Abhishek bhushan 1 M.tech scholar Ccet Bhilai 2 Assistant professor ccet Bhilai
Computational Analysis of Blast Furnace Pulverized Coal Injection For Iron Making 1 Gourav Kumar Thakur, 2 Kawal lal Kurrey, 3 Abhishek bhushan 1 M.tech scholar Ccet Bhilai 2 Assistant professor ccet Bhilai
A numerical simulation of the combustion processes of wood pellets
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 149 A numerical simulation of the combustion processes of wood pellets J. Ahn 1 & H. J. Kim 2 1 School of Mechanical Systems Engineering,
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 149 A numerical simulation of the combustion processes of wood pellets J. Ahn 1 & H. J. Kim 2 1 School of Mechanical Systems Engineering,
Effects of shaft supporting structure on performance test of axial flow fan
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of shaft supporting structure on performance test of axial flow fan To cite this article: R Ma et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of shaft supporting structure on performance test of axial flow fan To cite this article: R Ma et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Model development of a blast furnace stove
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 1758 1765 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Model development of a blast furnace stove Jonas
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 1758 1765 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Model development of a blast furnace stove Jonas
Finite Element Simulation Research on Medium Plate Multi-Pass Welding Temperature Field
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 786 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 786-790 Open Access Finite Element Simulation Research on Medium Plate Multi-Pass Welding Temperature
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 786 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 786-790 Open Access Finite Element Simulation Research on Medium Plate Multi-Pass Welding Temperature
INVESTIGATION OF FLOW CHARACTERISTICS OF HELLER-TYPE COOLING TOWERS WITH DIFFERENT COOLING DELTA ANGLES
 PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. MECH. ENG. VOL. 47, NO. 2, PP. 143 150 (2003) INVESTIGATION OF FLOW CHARACTERISTICS OF HELLER-TYPE COOLING TOWERS WITH DIFFERENT COOLING DELTA ANGLES Nimród KAPÁS Department
PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. MECH. ENG. VOL. 47, NO. 2, PP. 143 150 (2003) INVESTIGATION OF FLOW CHARACTERISTICS OF HELLER-TYPE COOLING TOWERS WITH DIFFERENT COOLING DELTA ANGLES Nimród KAPÁS Department
CHAPTER 3 HEURISTIC APPROACH TO MODELING THE BOILER FURNACE
 CHAPTER 3 HEURISTIC APPROACH TO MODELING THE BOILER FURNACE 3.1 INTRODUCTION Modeling and simulation of boiler systems has been an interesting subject of investigation for many years. Mathematical modeling
CHAPTER 3 HEURISTIC APPROACH TO MODELING THE BOILER FURNACE 3.1 INTRODUCTION Modeling and simulation of boiler systems has been an interesting subject of investigation for many years. Mathematical modeling
A Numerical Investigation of the Temperature Uniformity of a Billet due to Thermal Radiation in a Reheating Furnace
 Article A Numerical Investigation of the Temperature Uniformity of a Billet due to Thermal Radiation in a Reheating Furnace Tanawat Khoukit and Chittin Tangthieng* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Article A Numerical Investigation of the Temperature Uniformity of a Billet due to Thermal Radiation in a Reheating Furnace Tanawat Khoukit and Chittin Tangthieng* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Numerical study of the influence of injection/production well perforation location on CO 2 -EGS system
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 00 (2013) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia GHGT-11 Numerical study of the influence of injection/production well perforation location on
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 00 (2013) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia GHGT-11 Numerical study of the influence of injection/production well perforation location on
Investigating two configurations of a heat exchanger in an Indirect Heating Integrated Collector Storage Solar Water Heating System (IHICSSWHS)
 European Association for the Development of Renewable Energies, Environment and Power Quality (EA4EPQ) International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 12) Santiago de Compostela
European Association for the Development of Renewable Energies, Environment and Power Quality (EA4EPQ) International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 12) Santiago de Compostela
Evaluating Performance of Steam Turbine using CFD
 Evaluating Performance of Steam Turbine using CFD Sivakumar Pennaturu Department of Mechanical Engineering KL University, Vaddeswaram, Guntur,AP, India Dr P Issac prasad Department of Mechanical Engineering
Evaluating Performance of Steam Turbine using CFD Sivakumar Pennaturu Department of Mechanical Engineering KL University, Vaddeswaram, Guntur,AP, India Dr P Issac prasad Department of Mechanical Engineering
CFD Modelling of an Aerosol Exposure Chamber for Medical Studies G. Manenti, M. Derudi, G. Nano, R. Rota
 CFD Modelling of an Aerosol Exposure Chamber for Medical Studies G. Manenti, M. Derudi, G. Nano, R. Rota Dip. di Chimica, Materiali e Ingegneria Chimica G. Natta, Politecnico di Milano, via Mancinelli
CFD Modelling of an Aerosol Exposure Chamber for Medical Studies G. Manenti, M. Derudi, G. Nano, R. Rota Dip. di Chimica, Materiali e Ingegneria Chimica G. Natta, Politecnico di Milano, via Mancinelli
Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor
 Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor S.S.Vinay l, S.D.Ravi 2, G PremaKumar 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l M.E Student, Bangalore University, Bangalore. 2 Project Assistant, CGPL, Dept
Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor S.S.Vinay l, S.D.Ravi 2, G PremaKumar 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l M.E Student, Bangalore University, Bangalore. 2 Project Assistant, CGPL, Dept
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS OPTIMISATION OF A PELLET BURNER
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2012, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 1175-1186 1175 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS OPTIMISATION OF A PELLET BURNER by Lars B. WESTERLUND *, Roger L. HERMANSSON, and Michel J. CERVANTES Divisions
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2012, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 1175-1186 1175 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS OPTIMISATION OF A PELLET BURNER by Lars B. WESTERLUND *, Roger L. HERMANSSON, and Michel J. CERVANTES Divisions
XVII th World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR)
 XVII th World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR) Hosted by the Canadian Society for Bioengineering (CSBE/SCGAB) Québec City, Canada June 13-17, 2010
XVII th World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR) Hosted by the Canadian Society for Bioengineering (CSBE/SCGAB) Québec City, Canada June 13-17, 2010
Analysis of Flue Gas Flow Behavior in Economiser Duct Using Cfd
 Analysis of Flue Gas Flow Behavior in Economiser Duct Using Cfd Anand Kumar S Malipatil 1, Shivaraj 2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-Gulbarga Abstract-- Energy saving and efficiency are the
Analysis of Flue Gas Flow Behavior in Economiser Duct Using Cfd Anand Kumar S Malipatil 1, Shivaraj 2 Department of Thermal Power Engineering, VTU-Gulbarga Abstract-- Energy saving and efficiency are the
Simulation of Atmospheric Air Micro Plasma Jet for Biomedical Applications
 Simulation of Atmospheric Air Micro Plasma Jet for Biomedical Applications Luke T. Gritter 1, Jeffrey S. Crompton *1, and Kyle C. Koppenhoefer 1 1 AltaSim Technologies, LLC 130 E. Wilson Bridge Rd, Suite
Simulation of Atmospheric Air Micro Plasma Jet for Biomedical Applications Luke T. Gritter 1, Jeffrey S. Crompton *1, and Kyle C. Koppenhoefer 1 1 AltaSim Technologies, LLC 130 E. Wilson Bridge Rd, Suite
Temperature Field Calculation and Analysis within Steel Tube Reinforced Columns
 The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 212, 6, 15-2 15 Open Access Temperature Field Calculation and Analysis within Steel Tube Reinforced Columns Lei Xu * and Jiangang Sun School of Civil & Architectural
The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 212, 6, 15-2 15 Open Access Temperature Field Calculation and Analysis within Steel Tube Reinforced Columns Lei Xu * and Jiangang Sun School of Civil & Architectural
Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting
 Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting Wei Zuo a, Shun Kang b Key Laboratory of Condition Monitoring and Control for Power Plant Equipment, Ministry
Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting Wei Zuo a, Shun Kang b Key Laboratory of Condition Monitoring and Control for Power Plant Equipment, Ministry
Optimizing Sidewell Furnaces through Mathematical Modelling
 Optimizing Sidewell Furnaces through Mathematical Modelling Abstract Yasar Kocaefe 1, Rung Tien Bui 2, André Charette 3 1. Research Professor 2. Emeritus Professor 3. Emeritus Professor University of Quebec
Optimizing Sidewell Furnaces through Mathematical Modelling Abstract Yasar Kocaefe 1, Rung Tien Bui 2, André Charette 3 1. Research Professor 2. Emeritus Professor 3. Emeritus Professor University of Quebec
MODERN PRACTICES FOR MEASUREMENT OF GAS PATH PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF AN AXIAL TURBINE
 Review of the Air Force Academy No.1 (33)/2017 MODERN PRACTICES FOR MEASUREMENT OF GAS PATH PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF AN AXIAL TURBINE Daniel OLARU, Valeriu VILAG, Gheorghe
Review of the Air Force Academy No.1 (33)/2017 MODERN PRACTICES FOR MEASUREMENT OF GAS PATH PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF AN AXIAL TURBINE Daniel OLARU, Valeriu VILAG, Gheorghe
Optimization and control of working parameters of hot blast furnace
 Optimization and control of working of hot blast furnace Heng Wang 1, Shukun Cao 1, QuanchengDong 1, Yi Cui 1, Zijian Cao 1, Shuqiang Xu 1 Xiangwen Song 1, Hao Shen 1 1 336 West Road Jinan, School of Mechanical
Optimization and control of working of hot blast furnace Heng Wang 1, Shukun Cao 1, QuanchengDong 1, Yi Cui 1, Zijian Cao 1, Shuqiang Xu 1 Xiangwen Song 1, Hao Shen 1 1 336 West Road Jinan, School of Mechanical
OPTIMALLY DESIGNING REGENERATIVE SOAKING PIT BY MEANS OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION
 OPTIMALLY DESIGNING REGENERATIVE SOAKING PIT BY MEANS OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION RAO Wen-tao ZHU Tong Abstract: Gas consumption will be decreased if the combustion system of soaking pit is rebuilt applying
OPTIMALLY DESIGNING REGENERATIVE SOAKING PIT BY MEANS OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION RAO Wen-tao ZHU Tong Abstract: Gas consumption will be decreased if the combustion system of soaking pit is rebuilt applying
A Simple Engineering Analysis Method to Evaluate the Geothermal Potential from a Hot Water Aquifer
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 05 Melbourne, Australia, 9-5 April 05 A Simple Engineering Analysis Method to Evaluate the Geothermal Potential from a ot Water Aquifer Xiaoyu Lu, Kenichi Soga, Xiaohui
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 05 Melbourne, Australia, 9-5 April 05 A Simple Engineering Analysis Method to Evaluate the Geothermal Potential from a ot Water Aquifer Xiaoyu Lu, Kenichi Soga, Xiaohui
CFD-BASED INVESTIGATION OF HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF FLUE GAS-WATER HEAT EXCHANGER PANELS PRODUCED WITH A NOVEL MANUFACTURING PROCESS
 CFD-BASED INVESTIGATION OF HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF FLUE GAS-WATER HEAT EXCHANGER PANELS PRODUCED WITH A NOVEL MANUFACTURING PROCESS T. FUKUE 1, C. SPITAS 2, M. DWAIKAT 3 and M. ISHIZUKA 4 1 Department
CFD-BASED INVESTIGATION OF HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF FLUE GAS-WATER HEAT EXCHANGER PANELS PRODUCED WITH A NOVEL MANUFACTURING PROCESS T. FUKUE 1, C. SPITAS 2, M. DWAIKAT 3 and M. ISHIZUKA 4 1 Department
IFRF Combustion Journal Article Number , November 2006 ISSN X
 IR Combustion Journal Article Number 63, November 6 ISSN 156-479X CD as applied to high temperature air combustion in industrial furnaces Yang Weihong and Blasiak Wlodzimierz Division of Energy and urnace
IR Combustion Journal Article Number 63, November 6 ISSN 156-479X CD as applied to high temperature air combustion in industrial furnaces Yang Weihong and Blasiak Wlodzimierz Division of Energy and urnace
A NOVEL TECHNIQUE FOR EXTRACTION OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY FROM ABANDONED OIL WELLS
 A NOVEL TECHNIQUE FOR EXTRACTION OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY FROM ABANDONED OIL WELLS Seyed Ali Ghoreishi-Madiseh McGill University 3450 University St., Room 125 Montreal, QC, Canada H3A2A7 e-mail: seyed.ghoreishimadiseh
A NOVEL TECHNIQUE FOR EXTRACTION OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY FROM ABANDONED OIL WELLS Seyed Ali Ghoreishi-Madiseh McGill University 3450 University St., Room 125 Montreal, QC, Canada H3A2A7 e-mail: seyed.ghoreishimadiseh
Performance Improvement on Water-cooled Cold-Plate
 Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia, January 17-19, 2007 104 Performance Improvement on Water-cooled Cold-Plate SHYAN-FU CHOU,
Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia, January 17-19, 2007 104 Performance Improvement on Water-cooled Cold-Plate SHYAN-FU CHOU,
CFD Modelling and Analysis of Different Plate Heat Exchangers
 CFD Modelling and Analysis of Different Plate Heat Exchangers Ahmed Y Taha Al-Zubaydi a *, Guang Hong b and W. John Dartnall c Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, UTS, Sydney, Australia
CFD Modelling and Analysis of Different Plate Heat Exchangers Ahmed Y Taha Al-Zubaydi a *, Guang Hong b and W. John Dartnall c Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, UTS, Sydney, Australia
By Kimbal A. Hall, PE. Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY. May ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC. 30 Shrewsbury Street Holden, MA 01520
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 36 3050 THREE STAGE MIXER TO BE INSTALLED IN THE PERCHLORATE BLENDING STATION FOR THE CITY OF REDLANDS, CALIFORNIA GFS-411507-1R2 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 36 3050 THREE STAGE MIXER TO BE INSTALLED IN THE PERCHLORATE BLENDING STATION FOR THE CITY OF REDLANDS, CALIFORNIA GFS-411507-1R2 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted
40-Ton Articulated Truck Cooling System Modelling Using STAR-CCM+
 40-Ton Articulated Truck Cooling System Modelling Using STAR-CCM+ Gary Yu, Martin Timmins and Mario Ciaffarafa DENSO Marston Ltd, Bradford, BD17 7JR, UK DENSO Marston Founded in 1904 Acquired by DENSO
40-Ton Articulated Truck Cooling System Modelling Using STAR-CCM+ Gary Yu, Martin Timmins and Mario Ciaffarafa DENSO Marston Ltd, Bradford, BD17 7JR, UK DENSO Marston Founded in 1904 Acquired by DENSO
Study on Heat Transfer Characteristic of Furnace Bottom for Waste Heat Recovery
 International Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences (IJEAS) Study on Heat Transfer Characteristic of Furnace Bottom for Waste Heat Recovery Ruiyu Yang, Yanxia Wang Abstract The temperature of Calcined
International Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences (IJEAS) Study on Heat Transfer Characteristic of Furnace Bottom for Waste Heat Recovery Ruiyu Yang, Yanxia Wang Abstract The temperature of Calcined
LECUTRE 34: Heat flow in furnaces and exchangers
 LECUTRE 34: Heat flow in furnaces and exchangers Contents Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3 Exercise 4 Exercise 1 a) Regenerator receives hot flue gases at 1400 and cold air at 25, the flue gases leave
LECUTRE 34: Heat flow in furnaces and exchangers Contents Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3 Exercise 4 Exercise 1 a) Regenerator receives hot flue gases at 1400 and cold air at 25, the flue gases leave
BOUNDARY SETTING IN SIMULATING GREENHOUSE VENTILATION BY FLUENT SOFTWARE
 BOUNDARY SETTING IN SIMULATING GREENHOUSE VENTILATION BY FLUENT SOFTWARE Cuiping Hou 1, 2, Chengwei Ma 1,2,* 1 College of Water Conservancy and Civil Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing,
BOUNDARY SETTING IN SIMULATING GREENHOUSE VENTILATION BY FLUENT SOFTWARE Cuiping Hou 1, 2, Chengwei Ma 1,2,* 1 College of Water Conservancy and Civil Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing,
Optimum design on impeller blade of mixed-flow pump based on CFD
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 187 195 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation Optimum design on impeller blade of mixed-flow
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 187 195 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation Optimum design on impeller blade of mixed-flow
Flameless Oxidation Technology
 Flameless Oxidation Technology A.Milani, J.G.Wünning WS Wärmeprozesstechnik Dornierstr 14 71272 Germany WS Abstract Flameless combustion is the most significant recent advancement in high temperature combustion
Flameless Oxidation Technology A.Milani, J.G.Wünning WS Wärmeprozesstechnik Dornierstr 14 71272 Germany WS Abstract Flameless combustion is the most significant recent advancement in high temperature combustion
Numerical and analytical analysis of groundwater influence on the pile ground heat exchanger with cast-in spiral coils
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 61 (2014 ) 1784 1788 The 6 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2014 Numerical and analytical analysis of groundwater
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 61 (2014 ) 1784 1788 The 6 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2014 Numerical and analytical analysis of groundwater
Numerical Analysis of Two-phase Flow and Heat Transfer in External Cyclic Purification Hot-dip Galvanizing Bath
 2nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2016) Numerical Analysis of Two-phase Flow and Heat Transfer in External Cyclic Purification Hot-dip Galvanizing Bath Hui SUN1,
2nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2016) Numerical Analysis of Two-phase Flow and Heat Transfer in External Cyclic Purification Hot-dip Galvanizing Bath Hui SUN1,
Advanced combustion systems for tube manufacturing
 Advanced combustion systems for tube manufacturing As part of a major energy reduction programme Tenaris has successfully implemented advanced combustion systems for high temperature furnaces in its tube
Advanced combustion systems for tube manufacturing As part of a major energy reduction programme Tenaris has successfully implemented advanced combustion systems for high temperature furnaces in its tube
Optimization of Air Preheater Design for the Enhancement of Heat Transfer Coefficient
 Optimization of Air Preheater Design for the Enhancement of Heat Transfer Coefficient P. N. Sapkal 1, P. R. Baviskar 2, M. J. Sable 3 & P. A. Makasare 4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rajarshi Shahu
Optimization of Air Preheater Design for the Enhancement of Heat Transfer Coefficient P. N. Sapkal 1, P. R. Baviskar 2, M. J. Sable 3 & P. A. Makasare 4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rajarshi Shahu
COMPUTER MODELLING OF HIGH TEMPERATURE AIR COMBUSTION
 HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta COMPUTER MODELLING OF HIGH TEMPERATURE AIR COMBUSTION Cauchi J, Ghirlando R.*, and Farrugia
HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta COMPUTER MODELLING OF HIGH TEMPERATURE AIR COMBUSTION Cauchi J, Ghirlando R.*, and Farrugia
CCC Annual Report. UIUC, August 20, Modeling SEN Preheating. Yonghui Li. Department of Mechanical Science & Engineering
 CCC Annual Report UIUC, August 20, 2014 Modeling SEN Preheating Yonghui Li Department of Mechanical Science & Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Objectives Develop an accurate preheating
CCC Annual Report UIUC, August 20, 2014 Modeling SEN Preheating Yonghui Li Department of Mechanical Science & Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Objectives Develop an accurate preheating
RESIDUAL STRESS AND DISTORTION ANALYSIS IN LASER BEAM WELDING PROCESSES
 Ind. J. Sci. Res. and Tech. 015 3():0-5/Kanthi ISSN:-31-96 (Online) RESIDUAL STRESS AND DISTORTION ANALYSIS IN LASER BEAM WELDING PROCESSES Rajesh Goud Kanthi School of Mechanical Engineering,CEST, Fiji
Ind. J. Sci. Res. and Tech. 015 3():0-5/Kanthi ISSN:-31-96 (Online) RESIDUAL STRESS AND DISTORTION ANALYSIS IN LASER BEAM WELDING PROCESSES Rajesh Goud Kanthi School of Mechanical Engineering,CEST, Fiji
CFD ANALYSIS OF SOLAR HEATER WATER PIPE WITH DIFFERENT INCLINATION
 International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD) ISSN(P): 2249-6890; ISSN(E): 2249-8001 Vol. 4, Issue 2, Apr 2014, 55-62 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. CFD ANALYSIS OF
International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD) ISSN(P): 2249-6890; ISSN(E): 2249-8001 Vol. 4, Issue 2, Apr 2014, 55-62 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. CFD ANALYSIS OF
Research Article Heat Transfer Characteristics of Calcined Petroleum Coke in Waste Heat Recovery Process
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 06, Article ID 698, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/0./06/698 Research Article Heat ransfer Characteristics of Calcined Petroleum Coke in Waste Heat Recovery Process
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 06, Article ID 698, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/0./06/698 Research Article Heat ransfer Characteristics of Calcined Petroleum Coke in Waste Heat Recovery Process
A CFD Analysis of the Operating Conditions of a Multitube Pd Membrane for H 2 Purification
 A CFD Analysis of the Operating Conditions of a Multitube Pd Membrane for H 2 Purification B. Castro-Dominguez 1*, R. Ma 1, A.G Dixon 1 and Y. H. Ma 1 1 Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Department of Chemical
A CFD Analysis of the Operating Conditions of a Multitube Pd Membrane for H 2 Purification B. Castro-Dominguez 1*, R. Ma 1, A.G Dixon 1 and Y. H. Ma 1 1 Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Department of Chemical
Liquid-Solid Phase Change Modeling Using Fluent. Anirudh and Joseph Lam 2002 Fluent Users Group Meeting
 Liquid-Solid Phase Change Modeling Using Fluent Anirudh and Joseph Lam 2002 Fluent Users Group Meeting Solidification Model FLUENT can be used to solve fluid flow problems involving both solidification
Liquid-Solid Phase Change Modeling Using Fluent Anirudh and Joseph Lam 2002 Fluent Users Group Meeting Solidification Model FLUENT can be used to solve fluid flow problems involving both solidification
The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 148 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2016, 10, 148-159 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal Content list available at: www.benthamopen.com/tomej/
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 148 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2016, 10, 148-159 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal Content list available at: www.benthamopen.com/tomej/
Following the world economic crisis, the primary goals of
 Tenova FlexyTech regenerative flameless burners With more than 40 years experience in R&D on combustion systems, furnace design and installation of Tenova s Flexy Tech regenerative flameless burners combine
Tenova FlexyTech regenerative flameless burners With more than 40 years experience in R&D on combustion systems, furnace design and installation of Tenova s Flexy Tech regenerative flameless burners combine
ISSN (ONLINE): , ISSN (PRINT):
 SPECIAL ISSUE (ICRAME-2015) International Conference on Recent Advances in Mechanical Engineering In collaboration with International Journal of Engineering and Management Research (IJEMR) Page Number:
SPECIAL ISSUE (ICRAME-2015) International Conference on Recent Advances in Mechanical Engineering In collaboration with International Journal of Engineering and Management Research (IJEMR) Page Number:
OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS
 OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic University of Belgrade-Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Laboratory of Thermal
OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic University of Belgrade-Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Laboratory of Thermal
Numerical Study on the Effects of Flue-Gas Inlet Type for the Flue-Gas-Desulfurization Wet Scrubber
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET1021041 241
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET1021041 241
Heat and Mass Transfer in Convective Drying Processes
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Heat and Mass Transfer in Convective Drying Processes Camelia GAVRILA* Adrian Gabriel GHIAUS* Ion GRUIA** *Technical University of Civil Engineering Bucharest
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Heat and Mass Transfer in Convective Drying Processes Camelia GAVRILA* Adrian Gabriel GHIAUS* Ion GRUIA** *Technical University of Civil Engineering Bucharest
CFD analysis of double-chambered crematories using biomass producer gas as a fuel source
 CFD analysis of double-chambered crematories using biomass producer gas as a fuel source Yaowateera Achawangkul 1, Naoki Maruyama 1, Chatchawan Chaichana 2 Masafumi Hirota 1, Akira Nishimura 1, Pimpawat
CFD analysis of double-chambered crematories using biomass producer gas as a fuel source Yaowateera Achawangkul 1, Naoki Maruyama 1, Chatchawan Chaichana 2 Masafumi Hirota 1, Akira Nishimura 1, Pimpawat
Batch Annealing Model for Cold Rolled Coils and Its Application
 China Steel Technical Report, No. 28, pp.13-20, (2015) Chun-Jen Fang and Li-Wen Wu 13 Batch Annealing Model for Cold Rolled Coils and Its Application CHUN-JEN FANG and LI-WEN WU New Materials Research
China Steel Technical Report, No. 28, pp.13-20, (2015) Chun-Jen Fang and Li-Wen Wu 13 Batch Annealing Model for Cold Rolled Coils and Its Application CHUN-JEN FANG and LI-WEN WU New Materials Research
Topic: TSF: Thermal Systems and Fluid Mechanics
 The 23 rd Conference of the Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand November 4 7, 2009, Chiang Mai Validation of a 3D Model for Predicting Pressure Drop of a Clean Diesel Particulate Filter Ekathai
The 23 rd Conference of the Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand November 4 7, 2009, Chiang Mai Validation of a 3D Model for Predicting Pressure Drop of a Clean Diesel Particulate Filter Ekathai
Effect of Rotation Speed of a Rotary Thermal Wheel on Ventilation Supply Rates of Wind Tower System
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 1705 1710 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Effect of Rotation Speed of a Rotary Thermal Wheel
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 1705 1710 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Effect of Rotation Speed of a Rotary Thermal Wheel
Numerical study on the thermodynamic characteristics. in a Twin Swirl pulverized coal Combustor
 ICCM2015, 14-17 th July, Auckland, NZ Abstract Numerical study on the thermodynamic characteristics in a Twin Swirl pulverized coal Combustor Yinli LIU, * Hao TANG, Yongfen WANG College of Energy and Power
ICCM2015, 14-17 th July, Auckland, NZ Abstract Numerical study on the thermodynamic characteristics in a Twin Swirl pulverized coal Combustor Yinli LIU, * Hao TANG, Yongfen WANG College of Energy and Power
Flow and heat distribution analysis of different transformer sub-stations
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Flow and heat distribution analysis of different transformer sub-stations To cite this article: H Hasini et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Flow and heat distribution analysis of different transformer sub-stations To cite this article: H Hasini et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Performance estimation on micro gas turbine plant recuperator
 Performance estimation on micro gas turbine plant recuperator Laura Alina STIKA 1, Jeni Alina POPESCU,1, Sorin Gabriel TOMESCU 1, Valeriu-Alexandru VILAG 1 Corresponding author 1 National Research and
Performance estimation on micro gas turbine plant recuperator Laura Alina STIKA 1, Jeni Alina POPESCU,1, Sorin Gabriel TOMESCU 1, Valeriu-Alexandru VILAG 1 Corresponding author 1 National Research and
COOLING EFFECT ENHANCEMENT IN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING SYSTEM
 Fifth International Conference on CFD in the Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 13-15 December 2006 COOLING EFFECT ENHANCEMENT IN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING SYSTEM Jae-Sang BAEK and Youn J. KIM*
Fifth International Conference on CFD in the Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 13-15 December 2006 COOLING EFFECT ENHANCEMENT IN MAGNETRON SPUTTERING SYSTEM Jae-Sang BAEK and Youn J. KIM*
CFD Analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger to Evaluate the Effect of Parameters on Its Performance
 PP 14-19 CFD Analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger to Evaluate the Effect of Parameters on Its Performance Arpit Thakur 1, Aashish Sharma 2 1,2 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional
PP 14-19 CFD Analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger to Evaluate the Effect of Parameters on Its Performance Arpit Thakur 1, Aashish Sharma 2 1,2 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional
Research Article Experimental Investigation of Flow Resistance in a Coal Mine Ventilation Air Methane Preheated Catalytic Oxidation Reactor
 Chemistry Volume 2015, Article ID 375789, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375789 Research Article Experimental Investigation of Flow Resistance in a Coal Mine Ventilation Air Methane Preheated Catalytic
Chemistry Volume 2015, Article ID 375789, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375789 Research Article Experimental Investigation of Flow Resistance in a Coal Mine Ventilation Air Methane Preheated Catalytic
INVESTIGATION ON DRAG COEFFICIENT OF SUPERCIRTICAL WATER CROSS-FLOW PAST CYLINDER BIOMASS PARTICEL AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBERS
 INVESTIGATION ON DRAG COEFFICIENT OF SUPERCIRTICAL WATER CROSS-FLOW PAST CYLINDER BIOMASS PARTICEL AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBERS by Zhen-Qun WU, Hui JIN, Yi-Fei REN, Lie-Jin GUO State Key Laboratory of Multiphase
INVESTIGATION ON DRAG COEFFICIENT OF SUPERCIRTICAL WATER CROSS-FLOW PAST CYLINDER BIOMASS PARTICEL AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBERS by Zhen-Qun WU, Hui JIN, Yi-Fei REN, Lie-Jin GUO State Key Laboratory of Multiphase
Effect of Tower Area Change on the Potential of Solar Tower
 The nd Joint International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment (SEE 006) B-09 (O) - November 006, Bangkok, Thailand Effect of Tower rea Change on the Potential of Solar Tower tit Koonsrisuk
The nd Joint International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment (SEE 006) B-09 (O) - November 006, Bangkok, Thailand Effect of Tower rea Change on the Potential of Solar Tower tit Koonsrisuk
Tananop Piemsinlapakunchon, and Manosh C. Paul
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 2017 Vol II, July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Tananop Piemsinlapakunchon, and Manosh C. Paul , July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. is 0.8 cm above the air inlet. This
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 2017 Vol II, July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Tananop Piemsinlapakunchon, and Manosh C. Paul , July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. is 0.8 cm above the air inlet. This
