September 16 th 2010 International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer
|
|
|
- Damon Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 September 16 th 2010 International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer Next 16 th of September it will be celebrated the 2010 edition of the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer, which commemorates the signature of the Montreal Protocol in acknowledgement of the importance of the same for the protection of health and the environment. 1. The theme for the Ozone Day this year is "Ozone layer protection: governance and compliance at their best". Due that this year it is celebrated the greatest milestone of the Montreal Protocol s history, we are not only on the right path for totally phasing out chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), Halons and carbon tetrachloride (CTC); but we have also guaranteed the universal ratification of the Protocol by all Member States to the United Nations (UN). 2. The Ozone Layer protection - Why is important to protect the Ozone Layer? According to scientific evidence, ozone layer depletion has reached such magnitude that the recovery of the ozone layer could only be achieved by midcentury in the Arctic region and the mid latitudes, while on the Antarctic it will only happen after 2065, solely and exclusively if all countries comply with the obligations committed under the Montreal Protocol and its Amendments 1. Notwithstanding who is the main emitting country of ozone depleting substances, the damaging destruction effects of said substances have a global impact where human beings, plants, animals and our environment are affected some way or another. We all have, globally, a degree of responsibility and can contribute with actions allowing us to protect global health and our environment. 3. Health and the Environment. Ozone layer depletion entails an inadequate protection of the Earth s surface against UV-B radiation, which is very intense and when it filters in higher proportions than normally, it causes problems to human health, such as more intense skin burns, skin cancer, a decrease of the immunologic system of human beings, premature skin aging and eye diseases. According to data provided by Environment Canada 2, scientific studies have confirmed that non-melanoma skin cancer arises as a response to UV-B radiation and it is estimated that a 10% sustained destruction of the ozone layer would lead to a 26% increase of non-melanoma skin cancer cases (about 300 thousand new cases yearly globally). Cataracts are a disease that causes clouding of the eyes lens, are the main cause of permanent blindness and they are the result of an overexposure to UV radiation. A 10% sustained loss of the ozone layer could cause globally nearly 2 million of new cataract cases each year. UV-B radiation also reduces plant growth, health of wildlife, of animals in general and damages ecosystems for which the food is affected and therefore, all type of life in the world. 4. The International Convention The Montreal Protocol on substances that deplete the ozone layer is considered to be a model for other international treaties, mainly due to the maturity degree it has reached. All the goals achieved can contribute to the development 1 For more information consult the page Milestones: Vienna Convention ; Montreal Protocol- 1987; London Amendment ; Copenhagen Amendment- 1992; Montreal Amendment 1997; Beijing Amendment Environment Canada webpage on health and effects of UV-B radiation
2 of new even more successful international instruments where a higher consistency degree could be ensured and it will be achieved, to certain extent, avoiding the weaknesses that the Montreal Protocol has had to face. CFC production and consumption and most part of Methyl Bromide consumption have been faced out, but there is still work to be done which implies the participation of all stakeholders, including governments, industry and civil society organizations and main groups. We are at a fundamental moment of the process for which we cannot reduce efforts and loose the achievements achieved. On the contrary, we must strengthen ourselves and extend the participation at a general population level since the action of each one of us is a key element for the success on the protection of the ozone layer. 5. Production and consumption of Ozone Depleting Substances Global production and consumption of all Ozone Depleting Substances have been drastically reduced since the entry in force of the Montreal Protocol and continues to be reduced nowadays. It is worth noting that according to the Montreal Protocol, developed countries had to reduce their consumption in a first stage and now it is the turn for developing countries to demonstrate that they are also capable to contribute for the protection of the atmosphere and of complying with Multilateral Environment Agreements. This is the year when we have the obligation to completely phase out production and consumption of one of the most widely used substance, CFCs. a. CFC, CTC and Halons In Latin America and the Caribbean, cumulative production of CFCs between 1986 and 2000 was equivalent to 5,8% of the cumulative global production and nearly one third of the total production of developing countries during this period. Mexico, Brazil, Venezuela and Argentina (in decreasing order) have been the only producers in the region. The four mentioned countries have shut down their CFC production. Consumption of these controlled substances has also been decreasing in the Latin America and Caribbean region. Graph 1: Evolución del Consumo de los CFC, TCC y Halones en América Latina y El Caribe Toneladas PAO 100,000 50,000 0 Línea de Base Consumo Regional Note 1: In this graph, it is necessary to use the correction factor and express ODP consumption tonnes because data of different type of substances were added. The regional consumption start point of CFC, CTC and Halons was 73,830 ODP tonnes 3 in year 1989 and in year 2005 the region had reduced the consumption of such substances to less than 10 thousand ODP tonnes, with which the expected reduction goal was overcome according to the Montreal Protocol. 3 ODP tonnes are equivalent to metric tonnes multiplied by the Ozone Depletion Potential, which is a factor established in a comparative way between the different controlled substances 2
3 In year 2007, the CFC consumption reduction goal was also attained as established under the Montreal Protocol, having reached a total consumption of 1650 tonnes. By the end of present year 2010, countries of the region should be capable of maintain CFC zero consumption level, which is expected to be efficiently complied with given the aforementioned background. This success is highly satisfactory, but there is much left to do regarding other substances such as hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC) and methyl bromide, which are also damaging substances for the ozone layer. b. Methyl Bromide In some countries of the Latin America and Caribbean region, the Methyl Bromide use if of utmost importance for agriculture. In this case, the regional situation is not so encouraging due that technical and commercial difficulties have arisen for the sustained substitution. Graph 2: Evolución del Consumo del Bromuro de Metilo en América Latina y El Caribe Toneladas métricas 10,000 5, Consumo Regional Línea de base Note 2: Methyl Bromide Ozone Depletion Potential is 0.55 with respect to the assigned value for CFCs that have been taken as reference, that is, they have been assigned a value of Methyl Bromide regional consumption tripled between 1991 and 1994 having reached a maximum value of 8500 metric tonnes, although after this initial period said consumption has gradually decreased. Consequently, in years 2005 and 2007 consumption levels were reduced to 5276 and 4136 metric tonnes, respectively, for which there was continuation with the CFC trend of overcoming the reduction goals provided by the Montreal Protocol. The complete reduction of Methyl Bromide use was agreed for year 2005 and for the year of which there is gathered data for all countries, the regional consumption is of nearly 3400 metric tonnes. c. HCFC HCFC consumption in developed countries had decreased 72% with respect to the baseline in year 2005, while future consumption reductions are expected to continue at a much slower pace during the next years. Regarding consumption in developing countries, it reached about 20 thousand ODP tonnes in 2005 and recent studies indicate that this number could have increased double-fold by year 2015 if no adjustment would have existed as agreed in year Current trends of HCFC uses must be reverted to comply with the adjustments agreed in the 19th Meeting of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol. The decision anticipates one decade the HCFC production and consumption phase out 3
4 for all the Parties. Likewise, it controls the level of production and consumption from which developing countries must start their reductions, respects the deadlines necessary for the introduction of alternatives and fosters for said refrigerants not be replaced with high global warming potential substances or with other environmental risks. Some statistics indicate that anticipated HCFC phase out could result in reductions between 18 and 25 billion equivalent carbon dioxide tonnes of emissions. Annually, this represents a cut of or higher than 3.5% of all global greenhouse gases emissions. Unmistakably, Montreal Protocol s commitments for an anticipated HCFC phase out have the double purpose of addressing climate change and ozone depletion. Graph 3: 6000 Evolución del consumo de los HCFC en América Latina y El Caribe 4000 Toneladas PAO Consumo Regional 2008 Note 3: HCFCs have been used as transition replacement substances for CFCs, for this reason the growth pace of HCFC consumption has gone along the respective CFC decrease. HCFC baseline will be established based on the consumption average. 6. Actions that we all can start. The next two years are crucial for preparing and starting with the application of the National HCFC Phase out Management Plan in all developing countries, through which the foundations will be laid for attaining the gradual reduction of HCFC consumption and production as from The following are specially highlighted: The need to establish and modify promptly the laws and decrees that establish the CFC licensing systems as to include also HCFC importation controls. Manufacturing industries that consume HCFC should change the production systems to alternative technologies, particularly for low-global Warming Potential (GWP) options. The owners of refrigeration and air conditioning equipment should avoid acquiring new equipment based on HCFC to reduce future demands of these substances, and consider the economic feasibility of replacing their current equipment for new equipment with high energy efficiency and that use refrigerants that do not deplete the ozone layer or have high GWP. Consumers should select products and equipment that do not have or have had HCFCs used for their manufacturing, particularly in electrical appliances or in construction thermal insulation. 7. Situation of the Ozone Layer During the months from September to December each year, the phenomenon called Ozone Layer Hole appears on the Antarctic territory. This problem begins with the arrival of the austral spring to recompose when warm air coming from other regions penetrates the polar vortex. (The polar vortex is a region that flows around the Antarctic, with high speed of stratospheric winds and which gas mass does not mix with those outside until late spring). 4
5 The total size of ozone loss in the current year, as in previous cases, depends of the meteorological conditions prevailing in the stratosphere, particularly during September and October. This phenomenon will continue while the atmosphere continues having chloride and bromide excesses coming from chemical substances emissions of anthropogenic origin. It is worth noting that this is a dynamic phenomenon, that it varies daily and that it is strongly affected by the meteorological conditions therein. The meteorological conditions in the Antarctic stratosphere from late July to early August of each year, determine the ozone losses. A key factor in the destruction of the ozone layer is the atmosphere s temperature, since if it is sufficiently cold, polar stratospheric clouds (PSC) will form (containing small crystals) that facilitates the ozone depletion reaction with the arrival of the first sunlight. On this regard it can be said that this year s atmospheric temperature was sufficiently low for these polar stratospheric clouds to form. Until mid July 2010, the minimum temperatures were below the longterm average. Since then the minimum temperature has been oscillating around the long-term average. The average temperature over the S region were close to or below the long-term mean until the middle of July. A sudden stratospheric warming that started around mid July and lasted until early August pushed the cold air away from the pole. The cold air mass was less cold than at the same time in This warming event caused a temperature increase of more than 20 K, culminating on 31 July. Since the onset of such low temperatures on 8 May the area with temperatures low enough to form polar stratospheric clouds (PSC) was above or oscillating around the average until mid July. This area reached a peak of 26 million km 2 on 14 July. Then the sudden stratospheric warming event caused the area to drop to around 18 million km 2 over the course of the next two weeks and reaching the long term ( ) low on some days. During August the area has remained well below the long-term average, although it has increased somewhat. The geographical extent of the south polar vortex has been higher than the average on almost every day since early April. It should be pointed out, however, that vortex size gives no direct indication of the degree of ozone loss that might occur later in the season. At the altitude of 18 km the vortex is now almost entirely depleted of hydrochloric acid (HCl), one of the reservoir gases that can be transformed to active chlorine. The area affected by HCl removal is relatively small in comparison to recent years. In the sunlit collar along the vortex edge there is now up to 1.5 ppbv of active chlorine (chlorine monoxide, ClO), and ozone depletion has just started. The mixing ratio of ClO is lower than at the same date in recent years (back to 2004). Satellite observations show that the area where total ozone is less than 220 DU ( ozone hole area ) is low compared to recent years. However, the onset of ozone depletion varies considerably from one year to the next, depending on the position of the polar vortex and availability of daylight after the polar night. As the sun returns to Antarctica after the polar night, it is expected that ozone destruction will speed up. It is still too early to give a definitive statement about the development of this year's ozone hole and the degree of ozone loss that will occur. This will, to a large extent, depend on the meteorological conditions. However, the drop in the occurrence of polar stratospheric clouds since the middle of July and the comparatively small mixing ratios of chlorine monoxide point towards a relatively small ozone hole in The largest extension registered of the ozone layer hole on the Antarctic was in year 2006, when due to a especially cold Winter, it extended on a surface of 29,5 million square kilometers, with an ozone loss valuated in 40 million tonnes. 5
6 8. Historic registers from the ozone layer hole A summary with the data daily observed in the Southern hemisphere during the months of September and October of the last 20 years is presented below, wherein the average observed area and minimum detected concentration are highlighted. INFORMATION SOURCE: Year Average area of ozone layer (million km2) Minimum concentration (Dobson units) UNEP s OznoAction Team will continue following up on the information provided by the World Meteorological Organization and from NASA, based on which it will be produced an update of the present report by End of September This article was prepared by UNEP s OzonAction Programme, on September 15 th 2010; it is not an official document. UNEP is not liable for the accuracy or scope of the same. For more information, please contact the Regional Coordinator of the OzonAction Networks. Mirian Vega: mirian.vega@unep.org 4 World Meteorological Organization, 6
3 - Environmental Ozone Indicators
 3 - Environmental Ozone Indicators A. Introduction: Ozone (O3) is a triatomic allotrope of oxygen. It is naturally occurring process called photochemical analysis; the ozone exists throughout the year
3 - Environmental Ozone Indicators A. Introduction: Ozone (O3) is a triatomic allotrope of oxygen. It is naturally occurring process called photochemical analysis; the ozone exists throughout the year
4. Stratospheric ozone depletion
 112 4. Stratospheric ozone depletion The thickness of the ozone layer above Europe has decreased significantly since the beginning of the 198s, and is declining at a rate of 4 5 % per decade. The gradual
112 4. Stratospheric ozone depletion The thickness of the ozone layer above Europe has decreased significantly since the beginning of the 198s, and is declining at a rate of 4 5 % per decade. The gradual
The role of the Montreal Protocol in protecting present and future climate: A scientific perspective
 ATOC4800/ATOC5000/ENVS5830: Policy Implications of Climate : Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment, Prof. Weiqing Han University of Colorado Boulder Boulder, CO 20 February 2019 The role of the
ATOC4800/ATOC5000/ENVS5830: Policy Implications of Climate : Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment, Prof. Weiqing Han University of Colorado Boulder Boulder, CO 20 February 2019 The role of the
HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT 02 OCTOBER 2013
 HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT 02 OCTOBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at the Human influence on the environment in terms of: o Composition of the atmosphere and ozone layer (Depleting
HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT 02 OCTOBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at the Human influence on the environment in terms of: o Composition of the atmosphere and ozone layer (Depleting
FAQ - OZONE DAY. Overview:
 FAQ - OZONE DAY Overview: 1. OZONE DAY What is that? 2. What exactly would happen without the ozone layer? 3. How do we harm the ozone layer? 4. What is the Montreal Protocol? 5. Are the greenhouse effect
FAQ - OZONE DAY Overview: 1. OZONE DAY What is that? 2. What exactly would happen without the ozone layer? 3. How do we harm the ozone layer? 4. What is the Montreal Protocol? 5. Are the greenhouse effect
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part III
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part III A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes TODAY: The STORY OF THE DISCOVERY OF THE OZONE HOLE:
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part III A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes TODAY: The STORY OF THE DISCOVERY OF THE OZONE HOLE:
COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT. Reviewing Regulation (EC) No 2037/2000 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
 EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 1.8.2008 SEC(2008) 2367 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Reviewing Regulation (EC) No 2037/2000 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 1.8.2008 SEC(2008) 2367 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Reviewing Regulation (EC) No 2037/2000 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
Lovelock detects CCl 3. F (CFC-11) in the atmosphere of both hemispheres Rowland & Molina's Nature paper. CFC + hυ Cl + CCl 2
 1972-1974 1972 Lovelock detects CCl 3 F (CFC-11) in the atmosphere of both hemispheres. 1974 Rowland & Molina's Nature paper Review suggests that tropospheric sinks for CFC's (e.g. oxidation, dissolution
1972-1974 1972 Lovelock detects CCl 3 F (CFC-11) in the atmosphere of both hemispheres. 1974 Rowland & Molina's Nature paper Review suggests that tropospheric sinks for CFC's (e.g. oxidation, dissolution
PRESS BACKGROUNDER. Basic facts and data on the science and politics of ozone protection
 May 1999 - Ver. 1.1 PRESS BACKGROUNDER For use of the media only; not an official document. Basic facts and data on the science and politics of ozone protection 1. The Ozone Layer Ozone molecules (O 3
May 1999 - Ver. 1.1 PRESS BACKGROUNDER For use of the media only; not an official document. Basic facts and data on the science and politics of ozone protection 1. The Ozone Layer Ozone molecules (O 3
2016 edition. Printed with soy ink on 100% recycled paper
 The illustration on the cover shows the distribution of ozone above the Antarctic in October 215 (the monthly average in Dobson Unit) based on the data of the Japan Meteorological Agency. 215.1 216 edition
The illustration on the cover shows the distribution of ozone above the Antarctic in October 215 (the monthly average in Dobson Unit) based on the data of the Japan Meteorological Agency. 215.1 216 edition
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2006 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2006 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER **************************
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2006 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER **************************
CELEBRATION OF THE WORLD OZONE DAY-2014 INTERNATIONAL DAY FOR THE PRESERVATION OF THE OZONE LAYER. Theme: Ozone layer protection -The mission goes on
 CELEBRATION OF THE WORLD OZONE DAY-2014 INTERNATIONAL DAY FOR THE PRESERVATION OF THE OZONE LAYER Theme: Ozone layer protection -The mission goes on Organized by Gujarat Cleaner Production Centre- ENVIS
CELEBRATION OF THE WORLD OZONE DAY-2014 INTERNATIONAL DAY FOR THE PRESERVATION OF THE OZONE LAYER Theme: Ozone layer protection -The mission goes on Organized by Gujarat Cleaner Production Centre- ENVIS
Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate
 Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate 2018-19 Q.1. Name the layers of the atmosphere. Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere GREENHOUSE EARTH: Q.2. (a) What is the
Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate 2018-19 Q.1. Name the layers of the atmosphere. Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere GREENHOUSE EARTH: Q.2. (a) What is the
C O N T E N T S 4 FOREWORD 6 THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 11 THE WORLD BANK AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL
 C O N T E N T S 4 FOREWORD 6 THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 11 THE WORLD BANK AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 16 THE WORLD BANK CHINA MONTREAL PROTOCOL PROGRAM 31 THE WAY FORWARD 3 F O R E
C O N T E N T S 4 FOREWORD 6 THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 11 THE WORLD BANK AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 16 THE WORLD BANK CHINA MONTREAL PROTOCOL PROGRAM 31 THE WAY FORWARD 3 F O R E
Stratospheric Chemistry HS 2017 Solution to Homework Problem Set 3
 Stratospheric Chemistry HS 2017 Solution to Homework Problem Set 3 For questions: andrea.stenke@env.ethz.ch (CHN P14) Problem 1: The Montreal Protocol and Climate (a) Chemical Formulas CFC-11 : CFCl 3
Stratospheric Chemistry HS 2017 Solution to Homework Problem Set 3 For questions: andrea.stenke@env.ethz.ch (CHN P14) Problem 1: The Montreal Protocol and Climate (a) Chemical Formulas CFC-11 : CFCl 3
Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica?
 Ozone Depletion and Climate Change Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica? In a recent (last August 2016) BBC documentary on the Antarctic weather changes, it has
Ozone Depletion and Climate Change Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica? In a recent (last August 2016) BBC documentary on the Antarctic weather changes, it has
WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2010 OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2010 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER **************************
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2010 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER **************************
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY FINAL UNEP/WMO "SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2002" PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY FINAL UNEP/WMO "SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2002" PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER Released
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY FINAL UNEP/WMO "SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2002" PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER Released
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough
UNEP fifth Global Environment Outlook (GEO-5) assessment report
 UNEP fifth Global Environment Outlook (GEO-5) assessment report Click here to read/download the full report Click here to read/download related Press Release The following pages include reference to: -
UNEP fifth Global Environment Outlook (GEO-5) assessment report Click here to read/download the full report Click here to read/download related Press Release The following pages include reference to: -
Air Pollution Chapter 21. Atmosphere as a Resource
 Air Pollution Chapter 21 Atmosphere as a Resource Atmospheric Composition Nitrogen 78.08% Oxygen 20.95% Argon 0.93% Carbon dioxide 0.04% Ecosystem services Blocks UV radiation Moderates the climate Redistributes
Air Pollution Chapter 21 Atmosphere as a Resource Atmospheric Composition Nitrogen 78.08% Oxygen 20.95% Argon 0.93% Carbon dioxide 0.04% Ecosystem services Blocks UV radiation Moderates the climate Redistributes
Environmental Science 101 Air Resources. Fall Learning Objectives: Reading Assignment:
 1 Environmental Science 101 Air Resources Fall 2012 Lecture Outline: 11. OZONE DEPLETION A. Nature and Importance of the Ozone Shield B. Formation and Breakdown of the Shield 1. Ozone Formation 2. Chloroflourocarbons
1 Environmental Science 101 Air Resources Fall 2012 Lecture Outline: 11. OZONE DEPLETION A. Nature and Importance of the Ozone Shield B. Formation and Breakdown of the Shield 1. Ozone Formation 2. Chloroflourocarbons
RECENT MAJOR FINDINGS AND CURRENT SCIENTIFIC UNDERSTANDING
 The provisions of the 1987 Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer include the requirement that the Parties to the Protocol base their future decisions on the current scientific, environmental,
The provisions of the 1987 Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer include the requirement that the Parties to the Protocol base their future decisions on the current scientific, environmental,
Antarctic Climate Change and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion. Karen L. Smith Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Earth 2 Class October 19, 2013
 Antarctic Climate Change and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Karen L. Smith Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Earth 2 Class October 19, 2013 Antarctic Climate Change Antarctic climate change over the past
Antarctic Climate Change and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Karen L. Smith Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Earth 2 Class October 19, 2013 Antarctic Climate Change Antarctic climate change over the past
Chapter 20 Air Pollution
 Chapter 20 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 20 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
Chapter 20 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 20 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
TROPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration
 GE 101, February 6, 14 Finish insolation variation Global environmental issues associated with insolation TRPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration MID-LATITUDES: insolation
GE 101, February 6, 14 Finish insolation variation Global environmental issues associated with insolation TRPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration MID-LATITUDES: insolation
Lecture 29 Air Pollution. Air Pollution. Clean Boundary Layer. Clean Boundary Layer
 Lecture 29 Air Pollution Air Pollution Conditions that promote air pollution episodes Ozone Hole Air Pollution Elevated levels of aerosols and harmful gases Most pollution enters atmosphere near the surface.
Lecture 29 Air Pollution Air Pollution Conditions that promote air pollution episodes Ozone Hole Air Pollution Elevated levels of aerosols and harmful gases Most pollution enters atmosphere near the surface.
I. Pollutants A. Harmful substances the enter the environment
 I. Pollutants A. Harmful substances the enter the environment II. Two Classifications A. Particulates 1. Tiny substances (liquid or solid) suspended in the atmosphere 2. Examples: Dust, Ash, and Soot 3.
I. Pollutants A. Harmful substances the enter the environment II. Two Classifications A. Particulates 1. Tiny substances (liquid or solid) suspended in the atmosphere 2. Examples: Dust, Ash, and Soot 3.
Environmental Impacts of. Energy Production
 CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
The 2018 WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion
 The 2018 WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion Co-chairs: David Fahey Paul A. Newman John Pyle Bonfils Safari Scientific Steering Committee: Co-chairs + Martyn Chipperfield David Karoly Doug
The 2018 WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion Co-chairs: David Fahey Paul A. Newman John Pyle Bonfils Safari Scientific Steering Committee: Co-chairs + Martyn Chipperfield David Karoly Doug
Looking Ahead: HCFCs, HFC, CTC and other Chemicals Addressing HCFC, CFC and HFC in a Package: World Bank and GEF Cooperation
 Looking Ahead: HCFCs, HFC, CTC and other Chemicals Addressing HCFC, CFC and HFC in a Package: World Bank and GEF Cooperation Steve Gorman Ninth Annual Financial Agents Workshop The World Bank Washington,
Looking Ahead: HCFCs, HFC, CTC and other Chemicals Addressing HCFC, CFC and HFC in a Package: World Bank and GEF Cooperation Steve Gorman Ninth Annual Financial Agents Workshop The World Bank Washington,
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 1998
 World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 44 SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 1998 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 44 SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 1998 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
Welcome to the MARR WGs Session
 The World s Most Successful Ozone/Climate Change Multi-Stewardship Initiative Welcome to the MARR WGs Session Genoa de Bruin Climate Change Specialist, MOPIA Thursday, 8 th November, 2017 Winnipeg, Manitoba,
The World s Most Successful Ozone/Climate Change Multi-Stewardship Initiative Welcome to the MARR WGs Session Genoa de Bruin Climate Change Specialist, MOPIA Thursday, 8 th November, 2017 Winnipeg, Manitoba,
Scenarios of ODSs and ODS substitutes. Guus Velders
 Scenarios of ODSs and ODS substitutes Guus Velders 1 02 May 2011 Chapter 5: WMO/UNEP Ozone assessment: 2010 A focus on information and options for policymakers: Metrics: update of lifetimes, GWPs, ODPs
Scenarios of ODSs and ODS substitutes Guus Velders 1 02 May 2011 Chapter 5: WMO/UNEP Ozone assessment: 2010 A focus on information and options for policymakers: Metrics: update of lifetimes, GWPs, ODPs
K EY F INDING #9. Arctic Ozone Depletion
 K EY F INDING #9 Ultraviolet radiation (UV) reaching the earth s surface is a growing concern in the Arctic, largely due to depletion of stratospheric ozone caused by emissions of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
K EY F INDING #9 Ultraviolet radiation (UV) reaching the earth s surface is a growing concern in the Arctic, largely due to depletion of stratospheric ozone caused by emissions of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2006
 Reprinted from World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 50 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2006 National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Reprinted from World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 50 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2006 National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Stratospheric Ozone. Science Concepts. Stratospheric Ozone. Ozone Chemistry Creation Process Destruction Processes Equilibrium.
 Stratospheric Ozone 12-1 Stratospheric Ozone Ozone Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFCs Science Concepts Ozone Chemistry Creation Process Destruction Processes Equilibrium CFC Chemistry Antarctic Ozone Hole
Stratospheric Ozone 12-1 Stratospheric Ozone Ozone Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFCs Science Concepts Ozone Chemistry Creation Process Destruction Processes Equilibrium CFC Chemistry Antarctic Ozone Hole
Overview of Chapter 19
 19 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 19 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere Acid
19 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 19 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere Acid
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES. Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 1.8.2008 COM(2008) 505 final 2008/0165 (COD) C6-0297/08 Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of [ ] on substances that
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 1.8.2008 COM(2008) 505 final 2008/0165 (COD) C6-0297/08 Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of [ ] on substances that
On the road back to normalcy. 20% healing of the Antarctic Ozone Hole during
 On the road back to normalcy. 20% healing of the Antarctic Ozone Hole during 2000-2017 By Jos de Laat, Michiel van Weele, and Ronald van der A October, 2017 De Bilt, The Netherlands In recent years it
On the road back to normalcy. 20% healing of the Antarctic Ozone Hole during 2000-2017 By Jos de Laat, Michiel van Weele, and Ronald van der A October, 2017 De Bilt, The Netherlands In recent years it
OZONE LAYER PROTECTION PROGRAMME IN INDONESIA
 Historical Perspective and Progress as of 18 November 2014 OZONE LAYER PROTECTION PROGRAMME IN INDONESIA By Anton SRI PROBIYANTONO BRIEF 1970s Scientists discovered ODS 1985 Vienna Convention for the Protection
Historical Perspective and Progress as of 18 November 2014 OZONE LAYER PROTECTION PROGRAMME IN INDONESIA By Anton SRI PROBIYANTONO BRIEF 1970s Scientists discovered ODS 1985 Vienna Convention for the Protection
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Slide 2 of 30
 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 2 of 30 Ozone Depletion What are two types of global change of concern to biologists? the ozone layer high in the atmosphere the global climate system 3 of 30 Ozone
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 2 of 30 Ozone Depletion What are two types of global change of concern to biologists? the ozone layer high in the atmosphere the global climate system 3 of 30 Ozone
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Slide 1 of 30
 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 1 of 30 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Researchers are gathering data to monitor and evaluate the effects of human activities on important systems in the biosphere.
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 1 of 30 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Researchers are gathering data to monitor and evaluate the effects of human activities on important systems in the biosphere.
Directed Reading. Section: Global Change. than in the rest of the United States. b. In the United States and Canada, many lakes are dying as their ph
 Section: Global Change In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Scientists have discovered that acid rain is caused
Section: Global Change In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Scientists have discovered that acid rain is caused
INFORMATION NOTE. Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer
 INFORMATION NOTE Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer 1. Background 1.1 At the meeting held on 10 July 2009, the Subcommittee on Ozone Layer Protection (Products Containing Scheduled
INFORMATION NOTE Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer 1. Background 1.1 At the meeting held on 10 July 2009, the Subcommittee on Ozone Layer Protection (Products Containing Scheduled
Depleting The Ozone Layer. environmentalists have extensively studied the effects of the depletion of the ozone layer for the
 Abdul 1 Paula Abdul Dr. Koster CRTW 201 19 April 2005 Depleting The Ozone Layer What would the Earth be like if the ozone layer were to be non existent? Scientists and environmentalists have extensively
Abdul 1 Paula Abdul Dr. Koster CRTW 201 19 April 2005 Depleting The Ozone Layer What would the Earth be like if the ozone layer were to be non existent? Scientists and environmentalists have extensively
CCSP 2.4 March 11, Convening Lead Authors: A.R. Ravishankara, NOAA; Michael J. Kurylo, NASA
 381 Executive Summary 382 383 Convening Lead Authors: A.R. Ravishankara, NOAA; Michael J. Kurylo, NASA 384 385 386 387 388 389 Lead Authors: Richard Bevilacqua, NRL / DoD; Jeff Cohen, USEPA; John Daniel,
381 Executive Summary 382 383 Convening Lead Authors: A.R. Ravishankara, NOAA; Michael J. Kurylo, NASA 384 385 386 387 388 389 Lead Authors: Richard Bevilacqua, NRL / DoD; Jeff Cohen, USEPA; John Daniel,
How is the atmosphere different from outer space? a mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth
 Chapter 15 Atmosphere Section 1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth's atmosphere. Explain why air pressure changes with altitude. Explain how air temperature changes with atmospheric composition.
Chapter 15 Atmosphere Section 1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth's atmosphere. Explain why air pressure changes with altitude. Explain how air temperature changes with atmospheric composition.
working towards reducing global-warming HFCs under the Montreal Protocol
 International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer 2016 Address by the Minister of Education, Innovation, Gender Relations and Sustainable Development Dr. Gale Rigobert Today, 16 th September, Saint
International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer 2016 Address by the Minister of Education, Innovation, Gender Relations and Sustainable Development Dr. Gale Rigobert Today, 16 th September, Saint
3 RD EXTRAORDINARY MEETING OF THE PARTIES TO THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER JULY 2016 VIENNA, AUSTRIA
 3 RD EXTRAORDINARY MEETING OF THE PARTIES TO THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER 22-23 JULY 2016 VIENNA, AUSTRIA STATEMENT BY INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE
3 RD EXTRAORDINARY MEETING OF THE PARTIES TO THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER 22-23 JULY 2016 VIENNA, AUSTRIA STATEMENT BY INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE
Peace Independence Democracy Unity Prosperity. Decree on The Control of the Import, Export and Use of Ozone Depleting Substances
 The Prime Minister s LAO PEOPLE S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC Peace Independence Democracy Unity Prosperity ----------===000===---------- Office No.162/PM Vientiane, Date 13 October 2003 Decree on The Control
The Prime Minister s LAO PEOPLE S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC Peace Independence Democracy Unity Prosperity ----------===000===---------- Office No.162/PM Vientiane, Date 13 October 2003 Decree on The Control
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES SEC(92)387 final Brusse Is. 4 March 1992 COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL The Participation of the European Community and Member States Negotiation
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES SEC(92)387 final Brusse Is. 4 March 1992 COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL The Participation of the European Community and Member States Negotiation
What Exactly is a Greenhouse Gas?
 1 What Exactly is a Greenhouse Gas? You may have stood in a greenhouse and felt the heat, but what do greenhouse gases have to do with greenhouses? A greenhouse gas is any gas that absorbs and re-emits
1 What Exactly is a Greenhouse Gas? You may have stood in a greenhouse and felt the heat, but what do greenhouse gases have to do with greenhouses? A greenhouse gas is any gas that absorbs and re-emits
Climate Change and Ozone Loss
 Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Global HFC phase-down: A concrete step in delivering the Paris Agreement and in achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
 Global HFC phase-down: A concrete step in delivering the Paris Agreement and in achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Presented by Eshrat Sharmen Akand Senior Programme Officer 1 Why global phase
Global HFC phase-down: A concrete step in delivering the Paris Agreement and in achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Presented by Eshrat Sharmen Akand Senior Programme Officer 1 Why global phase
Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration OZONE LAYER PROTECTION:
 Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration OZONE LAYER PROTECTION: What Taiwan Has Been Doing Ozone Layer Protection : What Taiwan Has Been Doing Taiwan is not a Party to the Montreal Protocol, but
Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration OZONE LAYER PROTECTION: What Taiwan Has Been Doing Ozone Layer Protection : What Taiwan Has Been Doing Taiwan is not a Party to the Montreal Protocol, but
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion
 Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
3/4/2014. Air Pollution. Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion. Major Air Pollutants. Primary Pollutants
 Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings,
Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings,
AIRAH Refrigerants Update controls on refrigerants
 AIRAH Refrigerants Update controls on refrigerants Speaker: Patrick McInerney Stratospheric clouds above Davis Station, Antarctica Key points of presentation Outlook for refrigerants Phase-out of HCFCs
AIRAH Refrigerants Update controls on refrigerants Speaker: Patrick McInerney Stratospheric clouds above Davis Station, Antarctica Key points of presentation Outlook for refrigerants Phase-out of HCFCs
(First Earth Summit-1992)
 Summits related to Climate Change India launched an international solar alliance of over 120 countries (Completely or partially between tropic of cancer and Capricorn) at the Paris COP21 climate summit.
Summits related to Climate Change India launched an international solar alliance of over 120 countries (Completely or partially between tropic of cancer and Capricorn) at the Paris COP21 climate summit.
The State of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 The State of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion September 2003 I. Executive Summary Ozone, composed of three molecules of oxygen bonded together, forms a protective barrier in the Earth's upper atmosphere.
The State of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion September 2003 I. Executive Summary Ozone, composed of three molecules of oxygen bonded together, forms a protective barrier in the Earth's upper atmosphere.
B REGULATION (EC) No 1005/2009 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 16 September 2009 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
 2009R1005 EN 25.11.2013 002.001 1 This document is meant purely as a documentation tool and the institutions do not assume any liability for its contents B REGULATION (EC) No 1005/2009 OF THE EUROPEAN
2009R1005 EN 25.11.2013 002.001 1 This document is meant purely as a documentation tool and the institutions do not assume any liability for its contents B REGULATION (EC) No 1005/2009 OF THE EUROPEAN
Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1. Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE
 Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page:
 ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page: http://atoc.colorado.edu/~whan/atoc4800_5000 Announcements 1. No Exams and Extra-credits;
ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page: http://atoc.colorado.edu/~whan/atoc4800_5000 Announcements 1. No Exams and Extra-credits;
G-5 ACTIVITY ON VOLCANISM & CLIMATE THE ANSWERS!
 G-5 ACTIVITY ON VOLCANISM & CLIMATE THE ANSWERS! #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted in the largest GLOBAL cooling: #1 Low latitude eruption both hemispheres #2 Large amount of eruptive material
G-5 ACTIVITY ON VOLCANISM & CLIMATE THE ANSWERS! #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted in the largest GLOBAL cooling: #1 Low latitude eruption both hemispheres #2 Large amount of eruptive material
ACID RAIN. CE 326 Principles of Environmental Engineering Prof. Tim Ellis January 22, 2007
 ACID RAIN CE 326 Principles of Environmental Engineering Prof. Tim Ellis January 22, 2007 More accurate term may be acid deposition Occurs in two forms wet deposition (acidic rain, fog, and snow) dry deposition
ACID RAIN CE 326 Principles of Environmental Engineering Prof. Tim Ellis January 22, 2007 More accurate term may be acid deposition Occurs in two forms wet deposition (acidic rain, fog, and snow) dry deposition
SAP-2010-FAQs-update.pdf
 ATM 507 Lecture 10 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 23 Midterm Oct. 25? Today s topics Polar Ozone, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from the 2010 WMO report
ATM 507 Lecture 10 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 23 Midterm Oct. 25? Today s topics Polar Ozone, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from the 2010 WMO report
Percentages of Gases in the Atmosphere
 Chapter 7 - Atmosphere and Climate 7.1 The atmosphere atmosphere - thin layer of gases that surrounds the earth - extends from the surface of the Earth to hundreds of kilometers above the surface - without
Chapter 7 - Atmosphere and Climate 7.1 The atmosphere atmosphere - thin layer of gases that surrounds the earth - extends from the surface of the Earth to hundreds of kilometers above the surface - without
blic Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
 blic Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized C O N T E N T S 4 FOREWORD 6 THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 12 THE WORLD
blic Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized C O N T E N T S 4 FOREWORD 6 THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT AND THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL 12 THE WORLD
Module 3, Investigation 2: Briefing The loss of stratospheric ozone: Where are lives at risk?
 Background Have you heard of the ozone hole? In the 1970s, scientists began noticing a hole developing in the stratospheric ozone layer high above Antarctica. Scientists attributed the ozone destruction
Background Have you heard of the ozone hole? In the 1970s, scientists began noticing a hole developing in the stratospheric ozone layer high above Antarctica. Scientists attributed the ozone destruction
CHINA S ACTIVITIES AND CONTRIBUTIONS IN PROTECTING THE OZONE LAYER
 CHINA S ACTIVITIES AND CONTRIBUTIONS IN PROTECTING THE OZONE LAYER L. H. Lu and C. S. Ren Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, P. R. China. Keywords: Ozone depletion, Antarctic ozone hole,
CHINA S ACTIVITIES AND CONTRIBUTIONS IN PROTECTING THE OZONE LAYER L. H. Lu and C. S. Ren Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, P. R. China. Keywords: Ozone depletion, Antarctic ozone hole,
Chapter 17: Atmospheric Science and Air Pollution I. Central Case: The 1952 Killer Smog of London
 Chapter 17: Atmospheric Science and Air Pollution I. Central Case: The 1952 Killer Smog of London A. Thick smog first settled over the city on December 5, 1952, when many residents stoked: B. A wind finally
Chapter 17: Atmospheric Science and Air Pollution I. Central Case: The 1952 Killer Smog of London A. Thick smog first settled over the city on December 5, 1952, when many residents stoked: B. A wind finally
Environmental Toxicology
 The Science of Chemical Safety Essential Toxicology - 3 Environmental Toxicology John Duffus & Howard Worth IUPAC Educators Resource Material IUPAC 1 Environmental Toxicology Large exposures to chemicals
The Science of Chemical Safety Essential Toxicology - 3 Environmental Toxicology John Duffus & Howard Worth IUPAC Educators Resource Material IUPAC 1 Environmental Toxicology Large exposures to chemicals
STRATEGIES FOR COPING WITHOUT CFCS
 STRATEGIES FOR COPING WITHOUT CFCS A WHITE PAPER WRITTEN FOR DEVELOPMENT OF CORPORATE POLICY BY THOMAS A. DAMBERGER, CEM REGIONAL ENERGY SERVICES 393 EAST WALNUT PASADENA, CA 91188-0008 (818) 405-5641
STRATEGIES FOR COPING WITHOUT CFCS A WHITE PAPER WRITTEN FOR DEVELOPMENT OF CORPORATE POLICY BY THOMAS A. DAMBERGER, CEM REGIONAL ENERGY SERVICES 393 EAST WALNUT PASADENA, CA 91188-0008 (818) 405-5641
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
HUMAN IMPACT on the BIOSPHERE part 4
 HUMAN IMPACT on the BIOSPHERE part 4 Charting a course for the Future http://www.claybennett.com/pages2/mistletoe.html ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS DEAD ZONES OZONE DEPLETION ACID RAIN GLOBAL WARMING WASTE http://www.acmecompany.com/stock_thumbnails/13808.greenhouse_effect_2.jpg
HUMAN IMPACT on the BIOSPHERE part 4 Charting a course for the Future http://www.claybennett.com/pages2/mistletoe.html ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS DEAD ZONES OZONE DEPLETION ACID RAIN GLOBAL WARMING WASTE http://www.acmecompany.com/stock_thumbnails/13808.greenhouse_effect_2.jpg
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2
 Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014
 Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014 MRS 1 Due Tuesday Second exam will be postponed until after spring break The sun drives the climate of Earth http://www.spaceweather.com/images2002/18mar02/cme_c3_big.gif
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014 MRS 1 Due Tuesday Second exam will be postponed until after spring break The sun drives the climate of Earth http://www.spaceweather.com/images2002/18mar02/cme_c3_big.gif
New Jersey Clean Air Council Primer on Highly Warming Gases and Related Topics
 New Jersey Clean Air Council Primer on Highly Warming Gases and Related Topics Air Quality, Energy and Sustainability New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection December 12, 2018 Commissioner s
New Jersey Clean Air Council Primer on Highly Warming Gases and Related Topics Air Quality, Energy and Sustainability New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection December 12, 2018 Commissioner s
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 2/28/2013
 Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 2/28/2013 MRS 1 Due Tuesday The Earth s atmosphere has changed substantially over our planet s history First gases surrounding Earth were originally hydrogen and helium (during
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 2/28/2013 MRS 1 Due Tuesday The Earth s atmosphere has changed substantially over our planet s history First gases surrounding Earth were originally hydrogen and helium (during
Chapter 4: The Global Energy System
 Discovering Physical Geography Third Edition by Alan Arbogast Chapter 4: The Global Energy System The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Solar Energy Solar Energy as Radiation Electromagnetic energy transmitted
Discovering Physical Geography Third Edition by Alan Arbogast Chapter 4: The Global Energy System The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Solar Energy Solar Energy as Radiation Electromagnetic energy transmitted
Synthesis of the 2014 Reports of the Scientific, Environmental Effects, and Technology & Economic Assessment Panels of the Montreal Protocol
 United Nations Environment Programme Ozone Secretariat Synthesis of the 2014 Reports of the Scientific, Environmental Effects, and Technology & Economic Assessment Panels of the Montreal Protocol October
United Nations Environment Programme Ozone Secretariat Synthesis of the 2014 Reports of the Scientific, Environmental Effects, and Technology & Economic Assessment Panels of the Montreal Protocol October
Module 2. Components of Global Change.
 Module 2. Components of Global Change. Atmospheric Ozone Ozone Depletion Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect Biodiversity Declines Invasions Human Activity & Environmental Degradation Global Change
Module 2. Components of Global Change. Atmospheric Ozone Ozone Depletion Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect Biodiversity Declines Invasions Human Activity & Environmental Degradation Global Change
Statement of Mack McFarland, Ph.D. Global Environmental Manager
 Statement of Mack McFarland, Ph.D. Global Environmental Manager DuPont Fluoroproducts E.I. DuPont de Nemours and Company, Inc before the Committee on Oversight and Government Reform U.S. House of Representatives
Statement of Mack McFarland, Ph.D. Global Environmental Manager DuPont Fluoroproducts E.I. DuPont de Nemours and Company, Inc before the Committee on Oversight and Government Reform U.S. House of Representatives
Ozonesonde. Ozonesonde
 Ozonesonde Introduction In this exercise you will participate in a group activity which involves measuring and then interpreting the profile of ozone in the atmosphere from the ground to the stratosphere.
Ozonesonde Introduction In this exercise you will participate in a group activity which involves measuring and then interpreting the profile of ozone in the atmosphere from the ground to the stratosphere.
Name: Class: Date: 6. Most air pollution is produced by a. thermal inversions. c. ozone layer depletion. b. fuel burning. d. volcanic eruptions.
 Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Assessment for Decision-Makers
 Assessment for Decision-Makers Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2014 WMO Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 56 World Meteorological Organization United Nations Environment
Assessment for Decision-Makers Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2014 WMO Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 56 World Meteorological Organization United Nations Environment
Chillventa, October 2018
 Country situation - strengthening of capacities under the HPMP, stakeholder involvement and communication tools Natasha Kochova MOEPP - National Ozone Unit Republic of Macedonia + 389 71 342-437 n.kochova@ozoneunit.mk
Country situation - strengthening of capacities under the HPMP, stakeholder involvement and communication tools Natasha Kochova MOEPP - National Ozone Unit Republic of Macedonia + 389 71 342-437 n.kochova@ozoneunit.mk
Lecture 17. Air Pollution. Lecture 17
 Lecture 17 Air Pollution Lecture 17 1. Atmosphere Origin 2. Atmosphere as a Resource 3. Types and Sources of Air Pollution 4. Effects of Air Pollution 5. Controlling Air Pollution 6. Ozone Depletion in
Lecture 17 Air Pollution Lecture 17 1. Atmosphere Origin 2. Atmosphere as a Resource 3. Types and Sources of Air Pollution 4. Effects of Air Pollution 5. Controlling Air Pollution 6. Ozone Depletion in
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone Recovery? Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA- IASB. ATC14, October, Jülich, Germany
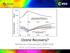 SCIAMACHY book Ozone Recovery? Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA- IASB ATC14, 27-31 October, Jülich, Germany 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974:
SCIAMACHY book Ozone Recovery? Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA- IASB ATC14, 27-31 October, Jülich, Germany 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974:
Green Chemistry Five ways in which the Chemical industry can become Greener Changing to renewable sources Use of alternatives to hazardous chemicals
 Green Chemistry Green Chemistry refers to the processes in the chemical industry that are being reinvented to make them more sustainable. The term sustain means to keep going. If we use resources faster
Green Chemistry Green Chemistry refers to the processes in the chemical industry that are being reinvented to make them more sustainable. The term sustain means to keep going. If we use resources faster
ANNUAL REPORT
 ANNUAL REPORT 2016 2017 REFRIGERANT RECLAIM AUSTRALIA CHAIRMAN S REPORT 2016/17 has been another very successful year for Refrigerant Reclaim Australia and the refrigerant product stewardship program.
ANNUAL REPORT 2016 2017 REFRIGERANT RECLAIM AUSTRALIA CHAIRMAN S REPORT 2016/17 has been another very successful year for Refrigerant Reclaim Australia and the refrigerant product stewardship program.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 215 216 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 215 216 REFRIGERANT RECLAIM AUSTRALIA CHAIRMAN S REPORT RRA has enjoyed another very successful year in 215/216. Our continued success is due to the ongoing commitment of the
215 216 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 215 216 REFRIGERANT RECLAIM AUSTRALIA CHAIRMAN S REPORT RRA has enjoyed another very successful year in 215/216. Our continued success is due to the ongoing commitment of the
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I
 Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
The Kigali Amendment and Opportunities for Energy Efficiency. Helen Walter-Terrinoni
 The Kigali Amendment and Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Helen Walter-Terrinoni Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer (protocol to the Vienna Convention for the Protection of
The Kigali Amendment and Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Helen Walter-Terrinoni Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer (protocol to the Vienna Convention for the Protection of
The Earth s Atmosphere-I. GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology
 The Earth s Atmosphere-I GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Overview What is the composition of Atmosphere? How did the atmosphere arrive at its current state? 2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere
The Earth s Atmosphere-I GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Overview What is the composition of Atmosphere? How did the atmosphere arrive at its current state? 2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere
9th Period Environmental Science Chapter 15: The Atmosphere
 Section 15.1: Earth s Atmosphere 9th Period Environmental Science Chapter 15: The Atmosphere Properties of the Atmosphere: nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor and 1% other gases. air pressure is higher at the
Section 15.1: Earth s Atmosphere 9th Period Environmental Science Chapter 15: The Atmosphere Properties of the Atmosphere: nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor and 1% other gases. air pressure is higher at the
Climate and Atmosphere-- United States
 Climate and Atmosphere-- United States EarthTrends Country Profiles United States North America Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions {a} World (in thousand metric tons of CO2) Total Emissions, 1998 5,447,640
Climate and Atmosphere-- United States EarthTrends Country Profiles United States North America Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions {a} World (in thousand metric tons of CO2) Total Emissions, 1998 5,447,640
Instructor's Guide for Computer Resources
 Studying Earth's Environment From Space Module 1: Stratospheric Ozone Instructor's Guide for Computer Resources STRATOSPHERIC OZONE MODULE Release: June 2000 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Earth Sciences
Studying Earth's Environment From Space Module 1: Stratospheric Ozone Instructor's Guide for Computer Resources STRATOSPHERIC OZONE MODULE Release: June 2000 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Earth Sciences
