Low Carbon Technology Plan
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Low Carbon Technology Plan May 19, 2008 Council for Science and Technology Policy
2 Table of Contents Introduction 1 1. Technological Strategy of Japan for Realizing a Low Carbon Society 4 (1) Technologies Required for Short and Medium-Term Measures (until around 2030) 4 (2) Technologies Required for Medium and Long-Term Measures (after the Year 2030) 7 (3) Deployment Measures for Society and the Necessary Institutional Reform 8 2. Contributing to International GHG Emission Reduction 11 (1) International Expansion and Contribution of Environment and Energy Technologies 11 (2) Contribution to Making an International Scheme Promotion Strategy for Developing Innovative Environment and Energy Technologies 14 (1) Investment in R&D 15 (2) R&D Structure 16 Recommendations 17 Attachment 1: Development and Diffusion of Environment & Energy Technology 20 Attachment 2: Environment & Energy Technology Assessment 21
3 Introduction In July 2008, Japan is hosting the G8 Summit in Toyako, Hokkaido with clear recognition on environment and climate change issues as part of the main agendas. As Japan has predominant technologies in this field, we should take the initiative in developing innovative technologies to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, deploy them throughout our country and the international society and play a leading role in the challenge against climate change issues. Japan has already announced its target of halving total emissions of GHGs throughout the world by In order to reach the fundamental solution of the climate change issues, there is no doubt that substantial reduction of GHG emissions and stabilization of the atmospheric concentration is needed in realizing a low carbon society. In order to reduce GHG emissions, it is essential to 1) promote improvement and deployment of existing technologies with immediate policy support, and 2) steadily advance research and development (R&D) of innovative technologies. The latter is particularly important, taking into consideration the estimate that approximately 60 per cent of the energy-related CO 2 emissions to be halved by 2050 will depend on the development and introduction of innovative technologies. In order to introduce and deploy innovative technologies, new approaches toward an institutional scheme are essential. Especially regarding the creation of a scheme for the Post-Kyoto Protocol, attention needs to be paid to the introduction and deployment of innovative technologies. This plan not only aims at substantial reduction of GHG emissions but also gives extra consideration on important issues such as energy security, harmonization of the environment and economy and contributions to developing countries. First, we rely on overseas countries for the major part of our energy resources - fossil fuels. Fossil fuels will remain as a major energy resource for the purpose of a stable supply of energy even when the utilization of renewable energy and nuclear energy shall be expanded upon. In addition, rapid increases in the energy demand by BRIC countries will likely cause increased global competition and conflicts in acquiring 1
4 resources, with a significant implication on the energy security of Japan. Accordingly the development and global diffusion of our excellent low carbon technologies will improve global energy efficiency, and contribute to stabilizing the international energy supply. In other words, research, development and deployment of the innovative low carbon energy technologies will contribute to energy security in both Japan and other countries in the world. Second, becoming a low carbon society with drastically reduced GHG emissions will be a significant shift from our present society, which is dependent on fossil fuels. We believe that in a low carbon society innovative technologies will create new industries and bring about new wealth to the country and the world. Economic development since the industrial revolution to date has been achieved by new innovative technologies. Japan should lead the world in innovative low carbon technologies, hold to the firm belief of making a global contribution and propose new technological and institutional innovations to the rest of the world as well as boost the country s economy. Third, developing countries contributing significantly in increasing GHG emissions are the key for stabilization of the global climate. Although 60 percent of current CO 2 emissions from energy sources come from developed countries whereas remaining 40 percent from developing countries, with the economic development of the developing countries in the future, it is estimated that the percentage of emission contributions from developing countries will be over 50 per cent by the year At the same time, many developing countries are extremely vulnerable to climate changes. It is expected that impacts of the climate change (flooding/drought, impacts on agriculture, industry and human health, and so forth) will last for a long time, even after GHG emissions have started to drop. Because of this, adaptation methods to the climate change are especially important. Japan has to make an effort to develop technology in the fields of adaptation as well as mitigation, try to conserve the ecosystem and promote international contributions through a system such as financial support. On the basis of the perspective mentioned above, this plan covers the following four aspects: 1) A full review of GHG emission reduction technologies available from the country 2
5 2) Technology deployment measures and the necessary institutional reform with consideration to the supply and demand of energy and the viewpoint and behavior of consumers 3) The potential of satisfying both economic development and emission reduction in developing countries based on the transfer and deployment of innovative technologies from Japan 4) The necessity of international financial support to underwrite the additional cost of reducing GHG emissions and realizing the leadership of our nation through proactive international cooperation 3
6 1. Technological Strategy of Japan for Realizing a Low Carbon Society As the energy consumption rate by the manufacturing industry has been reduced by approximately half since the oil crisis of the late 1970's, Japan has put a lot of effort into energy conservation all over the nation and we need to make even more efforts in the future. However, in order to significantly reduce GHG emissions in the future it will be necessary to develop innovative technologies that enable drastic reductions because it will be limited if we depend only on improving existing technologies. In addition, not only the actual development of technologies is important but also the deployment of them throughout the society is getting more important. That is to say, improving existing technologies and then diffusing throughout society over the short and medium-terms and developing innovative technologies over the medium and long-terms are the key to success. (1) Technologies Required for Short and Medium-Term Measures (until around 2030)(Refer to Attachments 1 and 2) On the energy supply side, securing a stable supply of energy resources and promoting a low carbon society is needed for the moment. On the energy demand side, in order to preserve consumers' quality of life(qol) while reducing their demand for energy, with the deployment of existing technologies that can be expected to reduce GHG emissions over the short and medium-terms, the development of the technologies for improving efficiency, reducing costs and assessing the performance of individual technologies accurately will be promoted. In addition, to achieve more significant emission reductions, it is necessary to take account of the effect of each individual technology, the institutional reform required for deployment, the cost etc. and pay attention to the appropriate timing of that introduction so as to enable optimizing the technology and the system architecture. Furthermore, regarding large scale facilities such as power plants, it will be necessary to introduce the most effective reduction technology so that agrees with the timing of systematic updates. Regarding the commercial/residential sector where the amount of GHG being emitted is significantly increasing, it will be necessary to work on this together as the entire nation more proactively such as appropriately improving social infrastructures. On top of this, it will be necessary to develop and introduce technologies which enable further improved efficiency in the industrial sector such as manufacturing and processing. Regarding biomass utilization, development of technology enabling ecosystem 4
7 conservation and sustainable production without compromising to food production will be promoted. (a) Technologies with a Significant Reduction Effect Regarding the energy supply side, in accordance with the expansion of usage in developing countries, it is required to make coal and natural gas fired power generation more efficient and to promote activities such as environmental arrangements for the steady use and expansion of nuclear power generation(light-water reactors), which will have a significant reduction effect in the current situation. In addition, although the effectiveness in reducing GHG emissions is rather insignificant, in time with the renewal of electric power transmission cables that will commence in 2020, developing technologies for the high-efficiency superconducting power transmission, which is competitive in the international market, will be promoted. Regarding the energy demand side, on the other hand, it is planned to deploy and expand use of more efficient heat pumps, and to increase the efficiency of and lower the cost of cooling mediums and heat exchangers in thermal fields; to promote electrification through the introduction of hybrid and electric vehicles and so forth in the transport sector; and to increase the efficiency of and deploy technologies that are very efficient in reducing emissions such as energy saving household appliances and Information Technology (IT) devices and other related power electronics. Main Technologies: (Energy Supply side) Advanced use of light-water reactors, High-efficiency fired power generation (coal and natural gas) (Energy Demand side) Hybrid vehicle, Plug-in hybrid vehicle, Electric vehicle, Fuel cell vehicle, High-efficiency lighting, High-efficiency heat pump, High-efficiency home electronics and information devices (b) Technologies to Reduce Greenhouse Gases in Entire Regions In order to reduce energy demands even more, efforts will be made to improve energy efficiency not only at the equipment level but also at the region level including residences, offices, transportation facilities and lifelines utilizing IT, and so forth. In particular developing and maintaining a way of assessing and visualizing energy efficiency not only at residences and offices but also at the regional level and energy conservation technology and promoting the development and deployment of 5
8 technologies through the concept of environmental model cities will be important. In addition, in order to reduce greenhouse gases through innovation of the social system and life styles, the development and deployment of the following technologies will all be promoted; increasing the efficiency of traffic and commodity distribution with an Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); using natural energy through local production for local consumption; production and usage of biofuel from cellulosic resources; longer lifespan of and saving of energy at residences through the changeover to a stock style society; saving more energy in the public transportation system such as more efficient use of rolling stocks; and highly used technologies such as IT that enables telework. Main Technologies: (Commercial/residential Sector) Energy efficient housing, HEMS/BEMS, CASBEE (Comprehensive Assessment System for Building Environmental Efficiency) (Regional and Local Area) Utilization of biomass fuel, High-efficiency rolling stock, Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS), Areal use of energy(local area EMS, cascade utilization of energy), Telework (advanced usage of IT) (c) Linking Technologies to Enhance the Efficiency of Reducing GHG Emissions Regarding technologies of which the efficiency of each elemental technology is increased through being linked with other technologies and that can be expected to be effectively diffused such as a combination of renewable energy and electric power storage, and a distributed thermoelectric supply (co-generation) system, the development and deployment of technologies while connecting multiple technologies will be promoted. Main Technologies: Renewable energy (photovoltaic power generation and wind power generation) and Electric power storage (secondary battery and capacitor), Stationary fuel cells, High-efficiency fired power generation (coal and natural gas) and Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage (CCS) 6
9 (2) Technologies Required for Medium and Long-Term Measures (after the Year 2030) (Refer to Attachments 1 and 2) It is necessary to work on the R&D of strategic technologies that can be expected to greatly reduce GHG emissions in the future and that significantly change the social structure and drastically reduce emissions through their introduction. (a) Innovative Technologies with a Significant Reduction Effect R&D will be promoted on technologies that are still in the basic study phase but that will have a significant reduction effect after realization aiming at practical application around the year On the energy supply side, in particular, the development of thin-film photovoltaic cells that can enhance generating efficiency and new third-generation photovoltaic cells will be promoted. In addition, the development and demonstration of next generation light-water reactors that will be used as replacements around the year 2030 and fast breeder reactors and electrical storage devices that aim at practical application no later than 2050 will be also promoted. On the energy demand side, the development of iron and steel process using as reducing agent of a part of coal and the technology of innovative batteries that are the keystone to electric vehicles from the point of view of further reducing GHG emissions from the transport sectors will be promoted. Also, technology development related to energy generating residences will be promoted. Regarding use of hydrogen, efficient hydrogen storage and transport technologies and lowering the cost of hydrogen production that does not depend on the fossil fuels and so forth will be required. Main Technologies: (Energy Supply side) Nuclear power generation (next generation light-water reactors and fast breeder reactor and its fuel cycle technology), Third generation photovoltaic cells, Hydrogen production technology (Energy Demand side) Hydrogen reduction iron and steel making process (b) Fundamental Technologies for Realizing the Breakthrough of Technologies In order to make a new technology practicable it is first necessary to overcome many technical obstacles. For realizing breakthroughs with obstacles, research on 7
10 basic and fundamental techniques to develop new mediums and materials (heat-resistant and high-temperature materials, superconductive materials, platinum substitution catalysts and so forth) will be promoted. On these fundamental R&D, the government promotes cooperation between related institutions and research organizations internally and internationally, and support efficient R&D, for the purpose of fundamental research for clarification of principals and phenomena at universities and public research organizations that are participating in developing innovative technologies, and achieving the goal of reduce emissions. (c) Technologies Whose Realization is Expected to Take a Long Time Regarding technologies whose realization is expected in the year 2050 or later, long term R&D will be strategically promoted for the ultimate of zero GHG emissions as well. It is also required to work on the technology development of nuclear fusion and space solar power systems, which are extensive energy sources that do not depend on fossils fuels, over the long-term. (3) Deployment measures for Society and the Necessary Institutional Reform A continuous implementation will take place not only with the deployment of products of high energy efficiency but also with reforming the social system to realize a low carbon society. National policies affect the deployment of excellent technologies. Environment and energy technologies are not an exception to this so it will be necessary to enhance the ability to make propositions regarding policy options such as the best mix of technology development and deployment in order to apply technologies that are advantageous to the nation. In addition, it is important that an institution and scheme that can effectively mediate between developments and deployments are in place since deployments are to make progress of the development of technologies. (a) Deployment Measures for Society With consideration to the fact that there are many technologies that are difficult to deploy if only the market is relied upon, promotion of deployment through economic incentives such as carbon pricing should be considered. In addition regulatory reforms and infrastructure construction will be promoted through amplification of objective products of the Top Runner Program, an investigation on preferential treatment for cars 8
11 that display appropriate environmental and energy performance, establishment of a financial institution when more effective GHG emission countermeasure technology is used by medium and small companies (domestic CDM and so forth) and realization of the scheme to increase investment and loans (Socially Responsible Investment (SRI) and so forth.) In particular the aim is to promote the enforcement of various policies to enhance regulatory reform and infrastructure construction and the realization of self-directed diffusion of those technologies in their final form using a product performance display system to promote the introduction of low carbon technologies and to raise the awareness of the nation through the system for evaluating, indicating, and approving performance of energy efficient residences and so forth. (b) Revolution of Social System It is necessary to inspect the achievements of technology developments and institutions through implementing a pilot project utilizing Super Area Initiative system to promote diffusion such as environmental model cities and technology demonstrations. Regarding housing and building, improving and making more familiar indications and certificates in order to establish an evaluation technique for energy consumption and GHG emissions and visualize the energy efficiency when actually they are in use are necessary. Also provisions for enhancement of compliance to acts such as the Rationalization in Energy Use Law are to be planned and implemented. Based on that, it is necessary to promote consumer behavior where technologies with high environment and energy conservation capabilities are chosen through enhancing a consciousness to restructure into a low carbon society by displaying carbon disclosure and energy consumption efficiency evaluated using the LCA method for household appliances, IT devices, cars and residences. In the commercial/residential sector, specific countermeasures are urgently required as the increasing tendency for GHG emission continues. For instance, when a residence is newly constructed or rebuilt, consideration needs to be given to encouraging or requiring the glass windows to have an insulating effect, use of energy saving devices such as energy efficient fluorescent lights, heat pumps and so forth and new energy devices such as solar batteries, and to provide aid for use of products and buildings that fulfill certain levels of performance in addition to regulations related to improving the energy saving performance of residences. It would be desirable to implement fiscal and financial measures to support 9
12 activities in improving energy saving performance that contribute to the point of view that reducing GHG emissions is of public benefit to the whole of society although they are carried out by individuals and the respective stakeholders. In this regard, however, it is necessary to form a preliminary national agreement in appropriate combination with the regulatory measures. (c) Role Sharing between the Public and Private Sectors in Deployment The appropriate division of roles between the public and private sectors is required, for example, in improving the environment so it is easier for business enterprises to act upon the enforcement of appropriate deployment and promotion plans at the demonstration and deployment stages as well as the government working on high risk R&D technologies. Furthermore, the burden of cost for introducing and diffusion of technologies where financial incentives are ineffective at the moment, such as CCS and solar energy, needs reviewing. (d) Social Enlightenment In order to enhance the awareness of the nation on energy saving and promoting their understanding of the situation regarding environment and energy in Japan and all over the world, efforts need to be made to enable understanding and dissemination of knowledge on the situation with energy, resources and energy consumption, the current situation and future vision of sustainable energy systems targeting those that are conducive to countermeasures against global warming (for example, the usability and issues of nuclear power generation and natural energy). In addition, providing energy and environment education to children through to adults is needed to nurture a culture that values global environmental protection. (e) Development of Human Resources As well as cultivating human resources whose priority is the environment and energy field, it is required to nurture a research environment that will attract a lot of human resources to the field. In addition, in order to accelerate R&D of environment and energy technologies further, the national awareness of these technologies and strengthening basic research at universities and public research organizations needs to be deepened. Accordingly, the development of excellent human resources can create innovative technologies and nurture those of the next generation. In addition more 10
13 researchers and engineers from all over the countries including Asian countries, will be encouraged to participate. 2. Contributing to International GHG Emission Reduction In order to enable all countries to work on reducing GHG emissions using a variety of approaches, increasing use of the environment and energy technologies of the nation will be necessary in a timely manner. Especially, as well as taking advantage of achievements made in international partnerships and so forth, it is necessary to improve energy efficiency globally through the diffusion and transfer of technologies to developing countries in cooperative sector oriented approaches such as the Asia-Pacific Partnership on Clean Development and Climate (APP). In addition, an international collaborative research will be proactively promoted from the point of view of generating excellent results via gathering technologies from all countries as well as contributing to the activities of international organizations such as IEA, IPCC and so forth. (1) International Expansion and Contribution of Environment and Energy Technologies (a) Expansion of Technologies Effective in Foreign Countries Regarding technologies that are expected to be effective in GHG reduction in foreign countries, for example developing countries (such as a combination of highly-efficient coal fired power generation and CCS), it is required to promote the transfer of technology through financial aid and international expansion, along with using the practice of reducing national emissions as a model for developing countries. To developing countries whose energy demands are expected to increase, with nonproliferation, nuclear power safety and nuclear security as the base premise, it is necessary to proactively contribute to the infrastructure development of those countries and to expand use of the excellent nuclear power technology (next generation light-water reactors and small & medium sized reactors) of the nation internationally for the smooth introduction of nuclear power generation. In addition, international expansion is being proactively planned to promote the introduction of excellent Japanese technologies such as utilizing solar energy in areas with a lot of sunny days in the year, high-efficiency home electronics and information devices, high-efficiency heat pumps and so forth. 11
14 It is also very important to strive to protect intellectual property with an appropriate method from the point of view of developing industry in Japan and then diffusion to the world. Furthermore, technologies not only to reduce emissions but also to adapt to a changing climate are important in order to respond to accelerating climate change. For example, reforestation is effective as an act of adaptation to global warming such as restoring vegetation in dry areas. As a technology that can be expected to be adopted by developing countries, the development of new breeds tolerant to droughts and so forth will be promoted. (b) Infrastructure Development for International Expansion In order to develop a foundation for the introduction and application of brilliant technologies from individual countries all over the world, the government should promote international standardization (energy saving standards, emission assessment criteria and so forth) and proactively establish global standards and international rules for appropriately evaluating the effect of reductions in GHG emissions. In addition, global application of them will increase through the provision of information on countermeasures that are effective in reducing GHG emission nationally, such as with the Top Runner Program and the knowledge gathered therein. Meanwhile, regarding large scale technology developments that require long periods of time for R&D, international cooperation with developed countries is promoted proactively in order that they can share the financial resources and spread the merits internationally by sharing technologies. Furthermore, it is necessary to take national measures from the viewpoint of promoting the reduction of GHG emissions in other countries with a financial support scheme related to the reduction in developing countries based on the fact that there is a way of thinking of having a surcharge for reductions adding up to the total reductions in the nation by supporting reductions in developing countries financially. In order to realize a low carbon society, technologies with brilliant environmental performance will be utilized to the upmost extent when implementing projects in developing countries. In addition, an international approach is required to enhance in cooperation with the other related countries in order to include highly effective technologies for use in reducing GHG emissions such as nuclear power generation and CCS in the subject of the CDM projects. In order to smoothly transfer excellent national technologies to developing countries, it is necessary to take advantage of the vitality of private companies, remove 12
15 any obstacles to technology transfers and promote their sale in that the government and the industrial world have worked together and based on the fact that these technologies would have been mainly developed and reserved by private companies. In the case that low carbon devices are sold to developing countries through doing business, problems such as the size of the market, the understanding of consumers and equipment costs will arise. In cases like that, it is necessary for the government to take the initiative in preparing incentives in order for private companies with leading-edge environmental technologies to maintain their edge and motivation to make an international contribution with consideration given to autonomous activities related to the technology transfer of private companies as a public activity that helps solve the global environmental issues. The government provides support including the provision of public funds if necessary in order to secure appropriate consideration for private companies. As stated above, brilliant environment and energy technologies of the nation need to be considered as new global intellectual assets that work to reduce GHG emissions with the cooperation of all countries. In this case, however, it is difficult to work on the activities mentioned above without the cooperation of private companies because they have retained the actual effective environment and energy technologies and product manufacturing ability, knowledge and intellectual properties. It is necessary to promote fair international activities in utilizing global intellectual assets effectively with the cooperation of developed countries and avoid private companies of any unfair trading penalized country in order to apply globally the technologies and intellectual properties that private companies have made the effort to develop in the midst of hard international competition. It is also necessary to reinforce strategies for the provision of technological information to developing countries, and select the appropriate technologies based on the actual situation of each country and to combine them. Along with that support will be enhanced to improve the conflict-resolution skills through developing human resources and so forth in order to promote settlement of the technologies in developing countries. (c) Promotion of R&D through International Links and Cooperation It will be necessary to set the security of the technological rights of Japan as a precondition, apply the financial resources of foreign countries and proactively promote international cooperation in R&D that is of high risk and needs massive investment over a long term of period that our nation cannot take care of independently (nuclear fusion, 13
16 CCS, space solar power systems and so forth). Regarding nuclear power, international cooperation will be promoted through a scheme involving countries such as the Generation IV International Forum (GIF). Regarding third-generation photovoltaic cells, international cooperation should be promoted in order to hasten R&D. (2) Contribution to Making an International Scheme (a) Technology Development that Corresponds to a New Reduction Scheme It is required to promote technology development of ships and aircraft of low-fuel consumption to reduce GHG emissions from the international ships and aircraft because a new target has been discussed for reducing carbon dioxide emissions in an international agreement. In addition Japan will play an active role in making international schemes such as the establishment of international standards related to international lines and waterways, and an approach to evaluating forests and soil as carbon sinks. (b) International Contribution to Earth Observation, Climate Change Projection and Impact Assessment International climatic stabilization policy is formulated based on scientific knowledge related to the climate and scientific achievements represented by IPCC are making main stream for policy foundation. It is important to promote excellent climatic science of the nation and secure a unique policy foundation. Observation and accuracy of regional climate change predictions will be improved to contribute more for the IPCC fifth assessment report and provide useful information and knowledge for use in establishing an international scheme. In addition, it is also necessary to contribute internationally by providing earth observation data and results of environmental assessment and predictions for regional areas to foreign countries including developing countries. 3. Promotion Strategy for Developing Innovative Environment and Energy Technologies R&D of environment and energy technology will be promoted more than ever in order to realize brilliant technologies and R&D capabilities and lead the world in fundamentally reducing GHG emissions. This plan is a part of the Strategy for Revolutionary Technology and R&D on reducing GHG emissions will be effectively promoted based on policies that promote R&D within the strategy through the following; 14
17 (1) Investment in R&D (a) Acceleration of Innovative Technology Development Improvement of conventional technologies is the main method of reducing GHG emissions over the short-term; however, it will reach the critical limit in the case of aiming at drastic reductions needed in the future and it will be important to develop innovative technologies that lead to drastic reductions in emissions over the medium to long-term. Therefore, regarding investment in R&D, it is concentrated to improve existing technologies over the short-term, then to emphasize the development of innovative technologies with a view to long-term stabilization of the climate in the future. In this case, it will be important to review the development of individual technologies at the appropriate time and consistently promote the most effective R&D. It will also be necessary to clearly reveal a future energy system and technical road map through sufficient investigation in advance and to promote that R&D in order to make steady achievements. (b) Prioritizing of R&D by the Government The government emphasizes a plan of diffusion promotion plan of the technologies while practical R&D are carried out in the private sector. However, the government will need to emphasize technologies of high risk in their R&D (mainly innovative technologies). The government shall invest concentrating heavily on technologies with significant reduction effects from the viewpoint of fundamentally reducing GHG emissions. In addition, emphasis shall be placed on R&D with high usability by industry, society and the world. On this occasion, it will be necessary for our nation to cultivate human resources based on the long-term strategy as well as increasing the international standard. It will also be important to promote basic research so as to create innovative technologies simultaneously. For this reason, the Council for Science and Technology Policy, Cabinet Office decides a resource allocation policy every year and related ministries and agencies will distribute resources based on it, and will be based on the government line of investing approximately US 30 billion dollars over five years on R&D in the fields of the environment and energy. (c) Incentive for Private Sector R&D 15
18 Considering the fact that smooth formation of an early market would be a great incentive for technology development, priority will be given to technologies that lead to significant reductions in GHG emissions in procuring them nationally after sufficient early evaluation of the possibility of realizing positive effects on the economy and reduction effects. In addition, unifying the different industries and fields will be promoted as well as sharing goals, objectives and overall vision of the main bodies that carry out R&D through the establishment and continuous review of a road map related to research, development and preeminence of the market. (2) R&D Structure (a) Establishment of a National R&D System It is essential to realize more innovative technologies early on by integrally promoting basic research through to application and development research of innovative technologies. For this reason, it will be necessary to establish a research system that can quickly combine the collective efforts of industry-academia-government within the framework of the relevant and ministries and agencies and a scheme to put together the knowledge of research organizations that belong to it. On this occasion, it will be important to aim at solidarity of the goal and the direction using a technology road map and establish an uninterrupted system by centralizing management for the R&D project on a large scale. In addition, considering the fact that it requires long-term R&D to introduce innovative technologies into the market, the schedule includes promoting a long-term overview of appropriate early assessment and corresponding stable policies as well as establish a scheme for contiguous supply of financial resources for use in R&D through the cooperation of funding organizations. (b) R&D Management From the point of view of promoting R&D in an effective manner, it is very important to set clear midterm and overall goals, strictly evaluate them with international R&D trends taken into consideration, review the road map while R&D is underway according to any changes in the surrounding environment and quickly distribute resources. 16
19 Recommendations We need not only to make this low carbon technology plan as a strategy for reducing the GHG emissions of the nation, but also to share with the many other countries in the world the way of thinking of this plan. We then contribute to developing and diffusing climate change countermeasures in the world through the excellent innovative low carbon technologies of the nation and be a leader in use of them. In order to realize this, the government should release the following strategies as a message to the international society. Strategy 1: Japan will lead the world in the development of low carbon technologies and associated international cooperation and proactively diffuse their achievements to the international society. 1) While Japan is the world s second largest economy and accounts for 8 to 9 per cent of global GDP, its GHG emission is approximately 5 percent in the world. This energy efficiency has been realized primarily through the two oil crises in 1970s, because of which Japan had to come up with new energy efficient technologies in order to overcome the critical problem of its low self sufficient ratio of energy supply. Since then Japan has developed energy efficient and low carbon technologies of the world s highest standard through the R&Ds under the public and private coordination. In order to cope with today s serious situations of the environment and energy issues, however, Japan should continue to improve existing technologies and to initiate the development of innovative technologies. In order to accelerate technology developments as a global commitment it needs to establish a global long-term roadmap for technology development. Moreover, it will promote the international cooperation that secures enough investment for low carbon R&D in major countries. Furthermore, it needs to make the best effort to deploy low carbon technologies throughout the world promptly so as to overcome these global issues. Japan will play a leading global role in this area including technology transfer to other countries in the world. 2) Environment and Energy technologies are required globally, regardless of being a developed or developing nation. Regarding the promotion of world-wide deployment of environment and energy technologies, aiming at the situation 17
20 where they will be capable of supporting the preservation of the global environment in the future, the government shall pay attention to securing the intellectual property rights of private companies, lead the appropriate implementation of smooth and quick technology transfers and develop the appropriate environment such as putting the relevant structures and institutions in place. 3) Regarding the United States, which is economically three times bigger than Japan but discharges four times the amount of the energy derived CO 2, discussions shall take place to include the United States in consideration to the new policy issued in April this year, set by the Bush administration, that targets being low carbon societies and sets technology innovation as the main instrument in doing so. Japan shall clearly mention that we will strengthen international cooperation in developing environment and energy technology and its deployment in its relationship with the United States. Using existing frameworks such as the Global Nuclear Energy Partnership (GNEP)and APP. It is required to establish a scheme for the fair transfer of environment and energy technologies involving the major developed countries, which includes the United States and the developing countries that will receive them and to promote prompt effective deployment of the same. Strategy 2: The main actors to transfer Environment and Energy technologies shall be private companies while the government provides indirect support. 1) Environment and energy technology for short and medium-term diffusion can be expected to include nuclear power generation, high-efficiency power generation using coal and natural gas, means of transportation such as hybrid vehicles with low CO 2 emissions, heat pumps, high-efficiency home electronics and information devices. These technologies are to be mainly developed and owned by private companies, and hence the main leader in transferring technology shall be the private sector. 2) In the case that the economy of the destination country where a technology is to be transformed rather poor or with an underdeveloped market, the government will promote support that includes the application of public funds if necessary by keeping in mind that private companies will hesitate to transfer technologies if 18
21 there is no guarantee of consideration being given to that transfer. Strategy 3: International cooperation in environmental model cities shall be used as the effective method to transfer technology in the commercial/residential sector. 1) The amount of CO 2 being emitted by the commercial/residential sector is increasing not only in our own country but all over the world. As environment and energy technology for the commercial/residential sector, heat pumps, stationary fuel cells, high-efficiency home electronics and information devices, high-efficiency lighting and an integration of them all will be included. This needs to be executed with greater development of a systematic scheme for improving the energy saving performance of new buildings and reformed buildings and energy saving initiatives in whole areas by considering buildings as a group will be promoted simultaneously. Policies, like with environmental model cities that promote energy saving from the side, are effective and will enable the realization of low carbon urban lifestyles through utilizing various technologies and social systems. 2) In order to stimulate the incentive of citizens in the promotion of environmental model cities, it is required to review allowing preferential treatment for low emission economical cars, a support system for the establishment of heat pumps and fuel cells and the development of a social system with the institution that efforts made by individuals are awarded with eco-points in certain areas. 3) From the point of view of transferring technologies to reduce GHG emissions internationally, the establishment of environmental model cities is considered to be effective. If it is possible to put in place an international cooperation scheme with environment model cities all over the world, including other Asian countries that share a similar climate to Japan, it would enable the founding a plan for environment model cities to be shared and stimulate the transfer of technology that conserves energy. 19
ACE: Actions for Cool Earth. Proactive Diplomatic Strategy for Countering Global Warming
 ACE: Actions for Cool Earth Proactive Diplomatic Strategy for Countering Global Warming 1. Basic Concept November 2013 Ministry of Foreign Affairs Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Ministry of the
ACE: Actions for Cool Earth Proactive Diplomatic Strategy for Countering Global Warming 1. Basic Concept November 2013 Ministry of Foreign Affairs Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Ministry of the
Submission on Innovative Technology Development
 Submission on Innovative Technology Development The Government of Japan submitted the document below as submission regarding the paragraph 1 of the Bali Action Plan in May 2008; http://unfccc.int/files/meetings/ad_hoc_working_groups/lca/application/pdf/submissionjapan.pdf
Submission on Innovative Technology Development The Government of Japan submitted the document below as submission regarding the paragraph 1 of the Bali Action Plan in May 2008; http://unfccc.int/files/meetings/ad_hoc_working_groups/lca/application/pdf/submissionjapan.pdf
ROLE OF ENERGY SUPPLIER FOR HEAT PUMP DEPLOYMENT
 - 1 - ROLE OF ENERGY SUPPLIER FOR HEAT PUMP DEPLOYMENT MIKIO MATSUMURA, General Manager (Planning) Sales Department, The KANSAI Electric Power Co., Inc.,6-16, Nakanoshima, 3-chome, Kita-ku, Osaka, Japan
- 1 - ROLE OF ENERGY SUPPLIER FOR HEAT PUMP DEPLOYMENT MIKIO MATSUMURA, General Manager (Planning) Sales Department, The KANSAI Electric Power Co., Inc.,6-16, Nakanoshima, 3-chome, Kita-ku, Osaka, Japan
Green Growth and Green Innovation: Korean Case Oct. STEPI
 Green Growth and Green Innovation: Korean Case 2010. Oct. STEPI 목차 I. Introduction II. What is Green Growth and Green Innovation III. Status and Strategies for GT Development in Korea IV. Conclusion 1.
Green Growth and Green Innovation: Korean Case 2010. Oct. STEPI 목차 I. Introduction II. What is Green Growth and Green Innovation III. Status and Strategies for GT Development in Korea IV. Conclusion 1.
Status and Strategy for Green Technology Development in Korea
 Status and Strategy for Green Technology Development in Korea 2010. 9. 9 Jin Gyu Jang, Ph.D. Science and Technology Policy Institute Contents I II III Introduction Status of GT development in Korea Strategies
Status and Strategy for Green Technology Development in Korea 2010. 9. 9 Jin Gyu Jang, Ph.D. Science and Technology Policy Institute Contents I II III Introduction Status of GT development in Korea Strategies
The Strategic Energy Plan of Japan -Meeting global challenges and securing energy futures- (Revised in June 2010)
 The Strategic Energy Plan of Japan -Meeting global challenges and securing energy futures- (Revised in June 2010) [Summary] June, 2010 Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan Strategic Energy Plan
The Strategic Energy Plan of Japan -Meeting global challenges and securing energy futures- (Revised in June 2010) [Summary] June, 2010 Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan Strategic Energy Plan
2007 EU-U.S. SUMMIT STATEMENT ENERGY SECURITY, EFFICIENCY, AND CLIMATE CHANGE
 2007 EU-U.S. SUMMIT STATEMENT ENERGY SECURITY, EFFICIENCY, AND CLIMATE CHANGE Ensuring secure, affordable supplies of energy and tackling climate change are central, interlinked global challenges facing
2007 EU-U.S. SUMMIT STATEMENT ENERGY SECURITY, EFFICIENCY, AND CLIMATE CHANGE Ensuring secure, affordable supplies of energy and tackling climate change are central, interlinked global challenges facing
U.S. Climate Change Technology Program (CCTP) Overview
 U.S. Climate Change Technology Program (CCTP) Overview Program (CCTP) Overview Dr. Harlan L. Watson Senior Climate Negotiator and Special Representative U.S. Department of State Dialogue on Long-Term Cooperative
U.S. Climate Change Technology Program (CCTP) Overview Program (CCTP) Overview Dr. Harlan L. Watson Senior Climate Negotiator and Special Representative U.S. Department of State Dialogue on Long-Term Cooperative
Environmental Action Plan By the Japanese Electric Utility Industry
 Environmental Action Plan By the Japanese Electric Utility Industry November 2013 The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan (FEPC) 1. About us Electricity supply in Japan is carried out by privately-owned
Environmental Action Plan By the Japanese Electric Utility Industry November 2013 The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan (FEPC) 1. About us Electricity supply in Japan is carried out by privately-owned
Keynote Speech by H.E. Ichiro Kamoshita, Minister of the Environment of Japan, in the Session on Climate Change
 Keynote Speech by H.E. Ichiro Kamoshita, Minister of the Environment of Japan, in the Session on Climate Change Introduction Here at the beginning of the session on Climate Change, as the chair of the
Keynote Speech by H.E. Ichiro Kamoshita, Minister of the Environment of Japan, in the Session on Climate Change Introduction Here at the beginning of the session on Climate Change, as the chair of the
ENERGY TECHNOLOGY ROADMAPS
 ENERGY TECHNOLOGY ROADMAPS Status report Introduction Current trends in energy supply and use are clearly unsustainable economically, environmentally and socially. Without decisive action, energy related
ENERGY TECHNOLOGY ROADMAPS Status report Introduction Current trends in energy supply and use are clearly unsustainable economically, environmentally and socially. Without decisive action, energy related
Gist of the Kyoto Protocol Target Achievement Plan
 1 (Tentative Translation) Gist of the Kyoto Protocol Target Achievement Plan In line with the Climate Change Policy Law, the Kyoto Protocol Target Achievement Plan was stipulated to set forth necessary
1 (Tentative Translation) Gist of the Kyoto Protocol Target Achievement Plan In line with the Climate Change Policy Law, the Kyoto Protocol Target Achievement Plan was stipulated to set forth necessary
New Low Carbon Technology Plan
 New Low Carbon Technology Plan September 13, 2013 Council for Science and Technology Policy Table of Contents Introduction... 1 1. Roadmap of Innovative Technologies and Measures for Their Domestic Diffusion...
New Low Carbon Technology Plan September 13, 2013 Council for Science and Technology Policy Table of Contents Introduction... 1 1. Roadmap of Innovative Technologies and Measures for Their Domestic Diffusion...
Japan s Vision and Actions toward Low-Carbon Growth and a Climate-Resilient World
 Japan s Vision and Actions toward Low-Carbon Growth and a Climate-Resilient World In order to effectively address the issue of climate change, it is necessary for both developed and developing countries
Japan s Vision and Actions toward Low-Carbon Growth and a Climate-Resilient World In order to effectively address the issue of climate change, it is necessary for both developed and developing countries
Breaking the Climate Deadlock A Global Deal for Our Low-Carbon Future. Executive Summary. Report submitted to the G8 Hokkaido Toyako Summit June 2008
 Report submitted to the G8 Hokkaido Toyako Summit June 2008 Breaking the Climate Deadlock A Global Deal for Our Low-Carbon Future Executive Summary The Office of Tony Blair The Climate Group Executive
Report submitted to the G8 Hokkaido Toyako Summit June 2008 Breaking the Climate Deadlock A Global Deal for Our Low-Carbon Future Executive Summary The Office of Tony Blair The Climate Group Executive
Proposal for Future Energy Policy
 Proposal for Future Energy Policy -For a Rich and Vigorous Economic Society- Outline November 14, 2017 Basic structure of Japan s energy policy Basic Act on Energy Policy (enacted in 2002) April 2014(Fourth)Strategic
Proposal for Future Energy Policy -For a Rich and Vigorous Economic Society- Outline November 14, 2017 Basic structure of Japan s energy policy Basic Act on Energy Policy (enacted in 2002) April 2014(Fourth)Strategic
A. Achieving sustainable development in Asia and the Pacific
 Inputs from the Asian and Pacific region to the Commission on Sustainable Development at its fifteenth session Policy options related to energy for sustainable development, industrial development, air
Inputs from the Asian and Pacific region to the Commission on Sustainable Development at its fifteenth session Policy options related to energy for sustainable development, industrial development, air
Declaration of the 3rd ASEM Environment Ministers Meeting April
 Declaration of the 3rd ASEM Environment Ministers Meeting April 24-26 2007 The ASEM heads of state and government at the ASEM Summit in Helsinki (11. September 2006) called for the continuation of the
Declaration of the 3rd ASEM Environment Ministers Meeting April 24-26 2007 The ASEM heads of state and government at the ASEM Summit in Helsinki (11. September 2006) called for the continuation of the
TABLE OF CONTENTS TECHNOLOGY AND THE GLOBAL ENERGY ECONOMY TO 2050
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1 TECHNOLOGY AND THE GLOBAL ENERGY ECONOMY TO 2050 PART 2 THE TRANSITION FROM PRESENT TO 2050 Introduction 1 1 2 Overview of scenarios Electricity generation Electricity networks
TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1 TECHNOLOGY AND THE GLOBAL ENERGY ECONOMY TO 2050 PART 2 THE TRANSITION FROM PRESENT TO 2050 Introduction 1 1 2 Overview of scenarios Electricity generation Electricity networks
Countermeasure Area Promotion Plan
 Global Warming Countermeasure Area Promotion Plan FY2018 - FY2020 Digest Bright Environmental Outlook, Bright Citizens February 2018 The Global Warming Countermeasure Area Promotion Plan was formulated
Global Warming Countermeasure Area Promotion Plan FY2018 - FY2020 Digest Bright Environmental Outlook, Bright Citizens February 2018 The Global Warming Countermeasure Area Promotion Plan was formulated
Act on Promoting Green Procurement
 Act on Promoting Green The Act on Promotion of of Eco-Friendly Goods and Services by the State and Other Entities (Act No.100 of May 31, 2000, promulgated on May 31, 2000 and enforced on April 1, 2001)
Act on Promoting Green The Act on Promotion of of Eco-Friendly Goods and Services by the State and Other Entities (Act No.100 of May 31, 2000, promulgated on May 31, 2000 and enforced on April 1, 2001)
PROMOTION OF TECHNICAL RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT FOR PREVENTION OF GLOBAL WARMING An Overview
 April 21, 2003 PROMOTION OF TECHNICAL RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT FOR PREVENTION OF GLOBAL WARMING An Overview I. Purpose Japan has made a commitment under the Kyoto Protocol to reduce its greenhouse gas
April 21, 2003 PROMOTION OF TECHNICAL RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT FOR PREVENTION OF GLOBAL WARMING An Overview I. Purpose Japan has made a commitment under the Kyoto Protocol to reduce its greenhouse gas
Issues in Climate Change and Energy Security in Northeast Asia
 Issues in Climate Change and Energy Security in Northeast Asia Seung Jick Yoo (Senior Research Fellow, Korea Energy Economics Institute) 1. Introduction Traditionally, energy security concerns are related
Issues in Climate Change and Energy Security in Northeast Asia Seung Jick Yoo (Senior Research Fellow, Korea Energy Economics Institute) 1. Introduction Traditionally, energy security concerns are related
CCS Policy Development in Japan
 CCS Policy Development in Japan IEA-GHG 3rd MEETING of the OXY-FUEL COMBUSTION NETWORK 5 March 2008 Yokohama Symposia, Yokohama, Japan Makoto Akai, AIST 2 Contents Background Technical R&D Research on
CCS Policy Development in Japan IEA-GHG 3rd MEETING of the OXY-FUEL COMBUSTION NETWORK 5 March 2008 Yokohama Symposia, Yokohama, Japan Makoto Akai, AIST 2 Contents Background Technical R&D Research on
U.S. Reflections on Outcomes and Implications of Bali
 U.S. Reflections on Outcomes and Implications of Bali Dr. Harlan L. Watson Senior Climate Negotiator and Special Representative U.S. Department of State IISD Conference on A Way Forward: Canadian and International
U.S. Reflections on Outcomes and Implications of Bali Dr. Harlan L. Watson Senior Climate Negotiator and Special Representative U.S. Department of State IISD Conference on A Way Forward: Canadian and International
The Innovation for Green Economy and Society
 The Innovation for Green Economy and Society (tentative translation) Minister of the Environment, Dr. Tetsuo Saito April 20, 2009 Delay in measures for climate change will cause the serious environmental
The Innovation for Green Economy and Society (tentative translation) Minister of the Environment, Dr. Tetsuo Saito April 20, 2009 Delay in measures for climate change will cause the serious environmental
Ralf Dahrendorf Taskforce on the Future of the European Union
 Ralf Dahrendorf Taskforce on the Future of the European Union Working group IV Financial and economic crisis liberal solutions for a Europe that works A liberal perspective on energy and environmental
Ralf Dahrendorf Taskforce on the Future of the European Union Working group IV Financial and economic crisis liberal solutions for a Europe that works A liberal perspective on energy and environmental
Key Words Low-Carbon Society, Backcasting, Narrative Scenario, Ecological Modernization, Simulation model
 FY2006 Research Results (S-3-1 Abstract) S-3 Low-Carbon Society Scenario toward 2050: Scenario Development and its Implication for Policy Measures 1. Long-term Scenario Development Study to Integrate Environmental
FY2006 Research Results (S-3-1 Abstract) S-3 Low-Carbon Society Scenario toward 2050: Scenario Development and its Implication for Policy Measures 1. Long-term Scenario Development Study to Integrate Environmental
DENSO ECO VISION 2025
 1st edition June, 2016 DENSO ECO VISION 2025 I II Commitment Environmental policy -Target 3 -Action III Environmental action plan (6th) I Commitment ( - 2050) DENSO group preserves the earth and delivers
1st edition June, 2016 DENSO ECO VISION 2025 I II Commitment Environmental policy -Target 3 -Action III Environmental action plan (6th) I Commitment ( - 2050) DENSO group preserves the earth and delivers
New Management Plan. Rolling Plan (Supplemental Presentation Materials) April 28, 2017
 New Management Plan Rolling Plan 2017 (Supplemental Presentation Materials) April 28, 2017 Review of Previous Midterm Management Plan Previous Midterm Management Plan ʻSTEER FOR 2020ʼ Implementation of
New Management Plan Rolling Plan 2017 (Supplemental Presentation Materials) April 28, 2017 Review of Previous Midterm Management Plan Previous Midterm Management Plan ʻSTEER FOR 2020ʼ Implementation of
Japanese Energy Efficient Technologies
 Japanese Energy Efficient Technologies World Energy Outlook It is well appreciated that energy consumption levels have been quickly increasing in the regions such as Asia where economic development has
Japanese Energy Efficient Technologies World Energy Outlook It is well appreciated that energy consumption levels have been quickly increasing in the regions such as Asia where economic development has
Keidanren Action Plan on the Environment (Section on Global Warming Measures) Reassessment Report
 Keidanren Action Plan on the Environment (Section on Global Warming Measures) Reassessment Report 19 November 2013 Keidanren 1. Overview of the Keidanren Action Plan on the Environment (1) Background Prior
Keidanren Action Plan on the Environment (Section on Global Warming Measures) Reassessment Report 19 November 2013 Keidanren 1. Overview of the Keidanren Action Plan on the Environment (1) Background Prior
Environmental Management at Konica Minolta Eco Vision 2050 Carbon Minus by 2050: Evolution of Long-Term Environmental Target Eco Vision 2050 Aiming to
 Environmental Management at Konica Minolta Eco Vision 2050 Carbon Minus by 2050: Evolution of Long-Term Environmental Target Eco Vision 2050 Aiming to Achieve Carbon Minus Status by 2050 Given the urgency
Environmental Management at Konica Minolta Eco Vision 2050 Carbon Minus by 2050: Evolution of Long-Term Environmental Target Eco Vision 2050 Aiming to Achieve Carbon Minus Status by 2050 Given the urgency
It is important to take best practices and lessons from existing arrangements and institutions on adaptation into our consideration of the 2015
 Submission by Japan Information, views and proposals on matters related to the work of Ad Hoc Working Group on the Durban Platform for Enhanced Action (ADP) (10 September, 2013) Japan welcomes the opportunity
Submission by Japan Information, views and proposals on matters related to the work of Ad Hoc Working Group on the Durban Platform for Enhanced Action (ADP) (10 September, 2013) Japan welcomes the opportunity
The Status and Direction of Energy Conservation Technologies in the Consumer Sector
 8 The Status and Direction of Energy Conservation Technologies in the Consumer Sector KAZUAKI MIYAMOTO Environment and Energy Research Unit 8.1 Introduction Based primarily on the experience of having
8 The Status and Direction of Energy Conservation Technologies in the Consumer Sector KAZUAKI MIYAMOTO Environment and Energy Research Unit 8.1 Introduction Based primarily on the experience of having
Chapter 3 Policies and Measures
 Chapter 3 Policies and Measures In Japan, the Global Warming Prevention Headquarters was established in December 1997 by order of the Cabinet to implement specific and effective countermeasures against
Chapter 3 Policies and Measures In Japan, the Global Warming Prevention Headquarters was established in December 1997 by order of the Cabinet to implement specific and effective countermeasures against
Climate change: a development perspective
 Climate change: a development perspective A Note for the Special UN General Assembly Session on Climate Change by Martin Khor, Director, Third World Network A. Background and Latest Scientific Information
Climate change: a development perspective A Note for the Special UN General Assembly Session on Climate Change by Martin Khor, Director, Third World Network A. Background and Latest Scientific Information
The Green Vision. Scenario for Europe. How to achieve net-zero CO 2. emissions by 2050
 The Green Vision Scenario for Europe How to achieve net-zero CO 2 emissions by 2050 The first political EU-wide climate scenario based on a carbon budget Summary for policy makers What is a carbon budget?
The Green Vision Scenario for Europe How to achieve net-zero CO 2 emissions by 2050 The first political EU-wide climate scenario based on a carbon budget Summary for policy makers What is a carbon budget?
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): ENERGY
 Country Partnership Strategy: People s Republic of China, 2016 2020 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): ENERGY Sector Road Map A. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Reduction in energy intensity.
Country Partnership Strategy: People s Republic of China, 2016 2020 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): ENERGY Sector Road Map A. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Reduction in energy intensity.
Chair s Summary G8 Environment Ministers Meeting. Kobe, Japan May 24-26, 2008
 Chair s Summary G8 Environment Ministers Meeting Kobe, Japan May 24-26, 2008 1. The G8 Ministers and European Commissioner responsible for the environment met in Kobe from May 24 to 26, 2008. They were
Chair s Summary G8 Environment Ministers Meeting Kobe, Japan May 24-26, 2008 1. The G8 Ministers and European Commissioner responsible for the environment met in Kobe from May 24 to 26, 2008. They were
David Hone World Business Council for Sustainable Development Energy and Climate
 1 Directions to 2050 Realizing the full potential of technology Actions to promote RD&DD Involving developing countries Utilising the market David Hone Energy and Climate Our energy system 2 Liquids Oil
1 Directions to 2050 Realizing the full potential of technology Actions to promote RD&DD Involving developing countries Utilising the market David Hone Energy and Climate Our energy system 2 Liquids Oil
China s policies and actions to mitigate climate change
 India-China Joint Workshop on National Actions Plans on Climate Change China s policies and actions to mitigate climate change Xu Huaqing New Delhi, 21 st October 2009 Outline Political Context Guidelines
India-China Joint Workshop on National Actions Plans on Climate Change China s policies and actions to mitigate climate change Xu Huaqing New Delhi, 21 st October 2009 Outline Political Context Guidelines
Norwegian submission to ADP on Workstream 2 on pre-2020 ambition
 Norwegian submission to ADP on Workstream 2 on pre-2020 ambition Norway is pleased to present views on the process of Workstream 2 under Ad Hoc Working Group on the Durban Platform for Enhanced Action,
Norwegian submission to ADP on Workstream 2 on pre-2020 ambition Norway is pleased to present views on the process of Workstream 2 under Ad Hoc Working Group on the Durban Platform for Enhanced Action,
CLEAN TECHNOLOGY FUND INVESTMENT CRITERIA FOR PUBLIC SECTOR OPERATIONS 1
 CTF/TFC.2/3 January 16, 2009 Meeting of the CTF Trust Fund Committee Washington, D.C. January 29-30, 2009 CLEAN TECHNOLOGY FUND INVESTMENT CRITERIA FOR PUBLIC SECTOR OPERATIONS 1 1 These criteria are applicable
CTF/TFC.2/3 January 16, 2009 Meeting of the CTF Trust Fund Committee Washington, D.C. January 29-30, 2009 CLEAN TECHNOLOGY FUND INVESTMENT CRITERIA FOR PUBLIC SECTOR OPERATIONS 1 1 These criteria are applicable
(Summary) Yuhji Matsuo* Yasuaki Kawakami* Ryo Eto* Yoshiaki Shibata* Shigeru Suehiro** Akira Yanagisawa*
 Position of Hydrogen Energy and Prospect of Its Introduction Toward a Low-Carbon Society in 25 in Japan (Summary) Yuhji Matsuo* Yasuaki Kawakami* Ryo Eto* Yoshiaki Shibata* Shigeru Suehiro** Akira Yanagisawa*
Position of Hydrogen Energy and Prospect of Its Introduction Toward a Low-Carbon Society in 25 in Japan (Summary) Yuhji Matsuo* Yasuaki Kawakami* Ryo Eto* Yoshiaki Shibata* Shigeru Suehiro** Akira Yanagisawa*
Small and Medium Enterprise Charter
 Small and Medium Enterprise Charter (Approved at the June 18, 2010 Cabinet Meeting) (Provisional Translation) The Government has formulated the Small and Medium Enterprise Charter as per the attached Exhibit.
Small and Medium Enterprise Charter (Approved at the June 18, 2010 Cabinet Meeting) (Provisional Translation) The Government has formulated the Small and Medium Enterprise Charter as per the attached Exhibit.
The Mid- to Long-Term Global Vision for Challenges against Global Warming
 The Mid- to Long-Term Global Vision for Challenges against Global Warming Date: October 27, 2009 Location: Shin-Marunouchi Building The Canon Institute for Global Studies (CIGS) Zhou Dadi,
The Mid- to Long-Term Global Vision for Challenges against Global Warming Date: October 27, 2009 Location: Shin-Marunouchi Building The Canon Institute for Global Studies (CIGS) Zhou Dadi,
Responses for Full Liberalization of the Retail Sale of Electricity
 Efforts to Achieve the Corporate Vision Responses for Full Liberalization of the Retail Sale of Electricity A year has passed since the full liberalization of the retail sale of electricity started in
Efforts to Achieve the Corporate Vision Responses for Full Liberalization of the Retail Sale of Electricity A year has passed since the full liberalization of the retail sale of electricity started in
Contribution to Global Warming Prevention by IT Solutions
 Contribution to Global Warming Prevention by IT Solutions Contribution to Global Warming Prevention by IT 1 Situation Surrounding Global Warming Prevention Awareness of global warming issue IPCC* 1 stated
Contribution to Global Warming Prevention by IT Solutions Contribution to Global Warming Prevention by IT 1 Situation Surrounding Global Warming Prevention Awareness of global warming issue IPCC* 1 stated
Memo on the Renewable Energy and Climate Change Package
 MEMO/08/33 Brussels, 23 January 2008 Memo on the Renewable Energy and Climate Change Package 1. INTRODUCTION In recent decades, our lifestyle and growing wealth has had a profound effect on the energy
MEMO/08/33 Brussels, 23 January 2008 Memo on the Renewable Energy and Climate Change Package 1. INTRODUCTION In recent decades, our lifestyle and growing wealth has had a profound effect on the energy
Toyama Framework on Material Cycles
 Toyama Framework on Material Cycles We, the G7 Ministers and high representatives, and European Commissioner responsible for the environment, based on our discussion on resource efficiency and the 3Rs
Toyama Framework on Material Cycles We, the G7 Ministers and high representatives, and European Commissioner responsible for the environment, based on our discussion on resource efficiency and the 3Rs
Japan s Energy Mix and Clean Coal Technology
 Japan s Energy Mix and Clean Coal Technology Takafumi KAKUDO Director, Coal Division Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Principles of Japan s Energy Policy
Japan s Energy Mix and Clean Coal Technology Takafumi KAKUDO Director, Coal Division Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Principles of Japan s Energy Policy
States and Regions commitments to the Clean Revolution and the Green Economy
 States and Regions commitments to the Clean Revolution and the Green Economy Following the commitments outlined in the 2010 Cancun Statement of Federated States & Regional Governments on Low Carbon & Climate
States and Regions commitments to the Clean Revolution and the Green Economy Following the commitments outlined in the 2010 Cancun Statement of Federated States & Regional Governments on Low Carbon & Climate
Keidanren's Views on Climate Change Policy
 Keidanren's Views on Climate Change Policy IMF-Japan High Level Tax Conference For Asian and Pacific Countries January 31, 2012 Masami Hasegawa Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) 1 1.What is Keidanren?
Keidanren's Views on Climate Change Policy IMF-Japan High Level Tax Conference For Asian and Pacific Countries January 31, 2012 Masami Hasegawa Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) 1 1.What is Keidanren?
AZERBAIJAN ECONOMIC REFORMS REVIEW
 April 2017 AZERBAIJAN ECONOMIC REFORMS REVIEW Editor-in-chief : Dr. Vusal Musayev PhD in Economics London University THE STRATEGIC ROADMAP FOR THE PRODUCTION OF CONSUMER GOODS IN AZERBAIJAN AT THE LEVEL
April 2017 AZERBAIJAN ECONOMIC REFORMS REVIEW Editor-in-chief : Dr. Vusal Musayev PhD in Economics London University THE STRATEGIC ROADMAP FOR THE PRODUCTION OF CONSUMER GOODS IN AZERBAIJAN AT THE LEVEL
Progress of Medium- and Long-term Efforts to Decommission Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP of TEPCO (Statement)
 Progress of Medium- and Long-term Efforts to Decommission Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP of TEPCO (Statement) November 27, 2012 Japan Atomic Energy Commission Tokyo Electric Co., Ltd. (TEPCO) announced the Roadmap
Progress of Medium- and Long-term Efforts to Decommission Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP of TEPCO (Statement) November 27, 2012 Japan Atomic Energy Commission Tokyo Electric Co., Ltd. (TEPCO) announced the Roadmap
7 Summary and Conclusion: Implications for Renewable Energy Instruments and Markets
 7 Summary and Conclusion: Implications for Renewable Energy Instruments and Markets This research study presents the first systematic comparison of renewable energy instruments and markets in Germany,
7 Summary and Conclusion: Implications for Renewable Energy Instruments and Markets This research study presents the first systematic comparison of renewable energy instruments and markets in Germany,
Japan s International Cooperation on Climate Change -- Contribution through ODA --
 Japan s International Cooperation on Climate Change -- Contribution through ODA -- Messages from Japan November 2006 Ministry of Foreign Affairs 1. Achieving sustainable development through environmental
Japan s International Cooperation on Climate Change -- Contribution through ODA -- Messages from Japan November 2006 Ministry of Foreign Affairs 1. Achieving sustainable development through environmental
such as improvement of transportation and well-being of the elderly, reduction of administrative costs for infrastructure per capita, and urban heat i
 Submission by the Government of Japan Information, views and proposals on matters related to the work of Ad Hoc Working Group on the Durban Platform for Enhanced Action (ADP), Workstream 2, Urban environment
Submission by the Government of Japan Information, views and proposals on matters related to the work of Ad Hoc Working Group on the Durban Platform for Enhanced Action (ADP), Workstream 2, Urban environment
Chapter 4 Eighty Percent Reduction Scenario in Japan
 Chapter 4 Eighty Percent Reduction Scenario in Japan Toshihiko Masui, Ken Oshiro, and Mikiko Kainuma Abstract Toward the achievement of the 2 C target, Japan has set several GHG mitigation targets after
Chapter 4 Eighty Percent Reduction Scenario in Japan Toshihiko Masui, Ken Oshiro, and Mikiko Kainuma Abstract Toward the achievement of the 2 C target, Japan has set several GHG mitigation targets after
Climate Change Research, Education and Outreach Activities at AIT
 Climate Change Research, Education and Outreach Activities at AIT The Second International Conference on Sustainability Science in Asia (ICSS-Asia) March 2-4, 2011, Hanoi, Vietnam Dr. Sangam Shrestha Assistant
Climate Change Research, Education and Outreach Activities at AIT The Second International Conference on Sustainability Science in Asia (ICSS-Asia) March 2-4, 2011, Hanoi, Vietnam Dr. Sangam Shrestha Assistant
Through our innovation in energy and environment technology, we are contributing to the creation of responsible and sustainable societies.
 Through our innovation in energy and environment technology, we are contributing to the creation of responsible and sustainable societies. On behalf of Fuji Electric, I would like to express our sincere
Through our innovation in energy and environment technology, we are contributing to the creation of responsible and sustainable societies. On behalf of Fuji Electric, I would like to express our sincere
Declaration of Biodiversity by Keidanren
 Declaration of Biodiversity by Keidanren Revised Edition October 16, 2018 Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) Revision to Declaration of Biodiversity by Keidanren and Action Policy Formulation of Declaration
Declaration of Biodiversity by Keidanren Revised Edition October 16, 2018 Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) Revision to Declaration of Biodiversity by Keidanren and Action Policy Formulation of Declaration
CHINA 2050 HIGH RENEWABLE ENERGY PENETRATION SCENARIO AND ROADMAP STUDY. Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission
 CHINA 2050 HIGH RENEWABLE ENERGY PENETRATION SCENARIO AND ROADMAP STUDY Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission ENERGY RESEARCH INSTITUTE NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND REFORM COMMISSION
CHINA 2050 HIGH RENEWABLE ENERGY PENETRATION SCENARIO AND ROADMAP STUDY Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission ENERGY RESEARCH INSTITUTE NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND REFORM COMMISSION
Toyota Environmental Challenge 2050
 1 2 As if to demonstrate the fact of global warming, extreme weather patterns worldwide have been provoking successive disasters. If current conditions continue and increased measures are not taken to
1 2 As if to demonstrate the fact of global warming, extreme weather patterns worldwide have been provoking successive disasters. If current conditions continue and increased measures are not taken to
Environment. Priority Areas
 Priority Areas As a global leader, seeking to build a truly global company, Bridgestone s business presence spans multiple countries, with hundreds of production, development and corporate locations, employing
Priority Areas As a global leader, seeking to build a truly global company, Bridgestone s business presence spans multiple countries, with hundreds of production, development and corporate locations, employing
emissions, capability to take emission reduction measures and national conditions differ from country to country. After the Paris Agreement, it may be
 Climate Change Measures in China after Paris Agreement Li Zhidong * This paper intends to outline China s intended nationally determined contributions (INDC) and discuss China s domestic initiatives and
Climate Change Measures in China after Paris Agreement Li Zhidong * This paper intends to outline China s intended nationally determined contributions (INDC) and discuss China s domestic initiatives and
Future key factors of PV power generation to become a mainstream power source - Action plans of -
 Future key factors of PV power generation to become a mainstream power source - Action plans of PV150@2030 - New installation target of 150 GW by 2030 was proposed based on the forecast on
Future key factors of PV power generation to become a mainstream power source - Action plans of PV150@2030 - New installation target of 150 GW by 2030 was proposed based on the forecast on
Country Report. Hirofumi Kyutoku Managing Director The Japan Gas Association (JGA)
 Country Report Hirumi Kyutoku Managing Director The Japan Gas Association (JGA) July 9, 2009 The 10 th Round Table Meeting in Chiba Prefecture, Japan I. Introduction 1-1. Natural Gas Situation in Japan
Country Report Hirumi Kyutoku Managing Director The Japan Gas Association (JGA) July 9, 2009 The 10 th Round Table Meeting in Chiba Prefecture, Japan I. Introduction 1-1. Natural Gas Situation in Japan
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/ENERGY/2014/5/Rev.1 Distr.: General 28 November 2014 Original: English only Economic Commission for Europe Committee on Sustainable Energy Twenty-third session
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/ENERGY/2014/5/Rev.1 Distr.: General 28 November 2014 Original: English only Economic Commission for Europe Committee on Sustainable Energy Twenty-third session
9. Vision 5: Becoming a trustworthy industry with noble aspiration
 9. Vision 5: Becoming a trustworthy industry with noble aspiration Strategic points for realizing the vision Initiatives to strengthen compliance Strengthening the influence in the creation of global compliance
9. Vision 5: Becoming a trustworthy industry with noble aspiration Strategic points for realizing the vision Initiatives to strengthen compliance Strengthening the influence in the creation of global compliance
The Global Calculator:
 International Forum for Sustainable Asia and the Pacific July 12-13 2016 : Exploring a low-carbon future www.globalcalculator.org Pascal Vermeulen CLIMACT What is it? A free and interactive tool that helps
International Forum for Sustainable Asia and the Pacific July 12-13 2016 : Exploring a low-carbon future www.globalcalculator.org Pascal Vermeulen CLIMACT What is it? A free and interactive tool that helps
CSR Management. Corporate Philosophy. CSR Activities Concepts and Systems. Review activities according to plans each year
 NGK Group Profile CSR Management Environmental Social Governance Content Index CSR Management CSR Activities Concepts and Systems Through its products and services, the NGK Group works to create new value
NGK Group Profile CSR Management Environmental Social Governance Content Index CSR Management CSR Activities Concepts and Systems Through its products and services, the NGK Group works to create new value
CO 2 tax or fee as a single economic instrument for climate protection policy promoting Renewable Energy Sources and enhancing Energy Efficiency
 CO 2 tax or fee as a single economic instrument for climate protection policy promoting Renewable Energy Sources and enhancing Energy Efficiency G. Graniæ REVIEW This paper presents the analysis of the
CO 2 tax or fee as a single economic instrument for climate protection policy promoting Renewable Energy Sources and enhancing Energy Efficiency G. Graniæ REVIEW This paper presents the analysis of the
NRCan s Six Priorities for Action SDS Now and for the Future SDS Now and for the Future SUSTAINABLE STRATEGY
 NRCan s Six Priorities for Action The previous section described the key public issues that will determine the realization of NRCan s vision of a sustainable future. As an advocate for natural resources,
NRCan s Six Priorities for Action The previous section described the key public issues that will determine the realization of NRCan s vision of a sustainable future. As an advocate for natural resources,
Innovative Technology Development. May 2007
 Innovative Technology Development May 2007 Innovative Technologies for Significant Reductions of CO2 Emissions 1. Innovative Zero-emissions Coal-fired Power Generation The combination of the efficiency
Innovative Technology Development May 2007 Innovative Technologies for Significant Reductions of CO2 Emissions 1. Innovative Zero-emissions Coal-fired Power Generation The combination of the efficiency
Green Growth: A New Growth Paradigm in Korea
 November 21 2011 Low Carbon Green Growth in Korea and ASEAN: Policy and Lesson Singapore Green Growth: A New Growth Paradigm in Korea Jung, Tae Yong Deputy Executive Director Table of Contents I. Green
November 21 2011 Low Carbon Green Growth in Korea and ASEAN: Policy and Lesson Singapore Green Growth: A New Growth Paradigm in Korea Jung, Tae Yong Deputy Executive Director Table of Contents I. Green
Korea s Green Growth Vision and Five-Year Plan
 Korea s Green Growth Vision and Five-Year Plan Nov 2009 JinBae Hong Director, Presidential Committee on Green Growth Why is Korea striving for Green Growth? Climate change impact - average temperature
Korea s Green Growth Vision and Five-Year Plan Nov 2009 JinBae Hong Director, Presidential Committee on Green Growth Why is Korea striving for Green Growth? Climate change impact - average temperature
December 2010 Se Chang Ahn
 Green Growth: Addressing Energy & Climate Challenges December 2010 Se Chang Ahn 1 Outline I. Why Green Growth? II. Key Progress of Green Growth III. Clean Energy Strategies for Green Growth IV. Global
Green Growth: Addressing Energy & Climate Challenges December 2010 Se Chang Ahn 1 Outline I. Why Green Growth? II. Key Progress of Green Growth III. Clean Energy Strategies for Green Growth IV. Global
Konica Minolta Environmental Policy
 Konica Minolta s Environmental Policy, Vision, and Strategy Konica Minolta Environmental Policy The Konica Minolta Group aims to promote sustainable development and profitable growth. We integrate environmental,
Konica Minolta s Environmental Policy, Vision, and Strategy Konica Minolta Environmental Policy The Konica Minolta Group aims to promote sustainable development and profitable growth. We integrate environmental,
Initiative for Disaster Reduction through ODA
 Initiative for Disaster Reduction through ODA January 18, 2005 Government of Japan Ⅰ Japan s basic position on disaster reduction The disaster caused by the major earthquake off the coast of Sumatra and
Initiative for Disaster Reduction through ODA January 18, 2005 Government of Japan Ⅰ Japan s basic position on disaster reduction The disaster caused by the major earthquake off the coast of Sumatra and
Green IT Initiative as a policy to provide a solution
 Green IT Initiative as a policy to provide a solution Presentation in ICCP/WPIE Workshop in Copenhagen Takayuki Sumita METI, Japan May, 2008 Current Status of the Global Environmental Issue and Measures
Green IT Initiative as a policy to provide a solution Presentation in ICCP/WPIE Workshop in Copenhagen Takayuki Sumita METI, Japan May, 2008 Current Status of the Global Environmental Issue and Measures
A Clean Planet for all. A European strategic long term vision for a prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy
 A Clean Planet for all A European strategic long term vision for a prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy Political context Parties of the Paris Agreement to present long-term low
A Clean Planet for all A European strategic long term vision for a prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy Political context Parties of the Paris Agreement to present long-term low
Japan s Assistance Initiatives to Address Climate Change 2017
 Japan s Assistance Initiatives to Address Climate Change 2017 1. Vision With the early entry into force of the Paris Agreement in November last year, the world is now moving toward its implementation.
Japan s Assistance Initiatives to Address Climate Change 2017 1. Vision With the early entry into force of the Paris Agreement in November last year, the world is now moving toward its implementation.
Becoming an Innovative Energy & Service Company that Continues to Be the First Choice of Customers
 Osaka Gas Group Long-Term Management Vision 2030 and Medium-Term Management Plan 2020 [Going Forward Beyond Borders] Becoming an Innovative Energy & Service Company that Continues to Be the First Choice
Osaka Gas Group Long-Term Management Vision 2030 and Medium-Term Management Plan 2020 [Going Forward Beyond Borders] Becoming an Innovative Energy & Service Company that Continues to Be the First Choice
Promote Agriculture among Young People in Asia
 Promote Agriculture among Young People in Asia M.R. Davari YPARD Iran Representative and YPARD Asia Program Officer (mrdavari@gmail.com) The global population is projected to rise from its present level
Promote Agriculture among Young People in Asia M.R. Davari YPARD Iran Representative and YPARD Asia Program Officer (mrdavari@gmail.com) The global population is projected to rise from its present level
THE ASIA PACIFIC PARTNERSHIP: ITS ROLE IN PROMOTING A POSITIVE CLIMATE FOR INVESTMENT, ECONOMIC GROWTH AND GREENHOUSE GAS REDUCTIONS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 THE ASIA PACIFIC PARTNERSHIP: ITS ROLE IN PROMOTING A POSITIVE CLIMATE FOR INVESTMENT, ECONOMIC GROWTH AND GREENHOUSE GAS REDUCTIONS By W. David Montgomery Sugandha D. Tuladhar * EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Background:
THE ASIA PACIFIC PARTNERSHIP: ITS ROLE IN PROMOTING A POSITIVE CLIMATE FOR INVESTMENT, ECONOMIC GROWTH AND GREENHOUSE GAS REDUCTIONS By W. David Montgomery Sugandha D. Tuladhar * EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Background:
The Law on Promoting Green Purchasing and the Green Contract Law
 The Law on Promoting Green Purchasing and the Green Contract Law Environment and Economy Division Environmental Policy Bureau Ministry of the Environment, Japan Takashi Minemura Outline of the Law on Promoting
The Law on Promoting Green Purchasing and the Green Contract Law Environment and Economy Division Environmental Policy Bureau Ministry of the Environment, Japan Takashi Minemura Outline of the Law on Promoting
Evaluation of Operating Results for Japan Atomic Energy Agency in FY2015
 Evaluation of Operating Results for Japan Atomic Energy Agency in FY2015 September 2016 Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Nuclear Regulation
Evaluation of Operating Results for Japan Atomic Energy Agency in FY2015 September 2016 Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Nuclear Regulation
Co-Benefit Approach in JICA
 Co-Benefit Approach in JICA The 18 th Asia-Pacific Seminar on Climate Change Ha Noi, 3th March 2009 by Akiko URAKAMI, Office for Climate Change Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) Table of Contents
Co-Benefit Approach in JICA The 18 th Asia-Pacific Seminar on Climate Change Ha Noi, 3th March 2009 by Akiko URAKAMI, Office for Climate Change Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) Table of Contents
Summary of the Chair. Conclusions and Recommendations of the Parliamentarian Forum on Energy Legislation and Sustainable Development
 Summary of the Chair Conclusions and Recommendations of the Parliamentarian Forum on Energy Legislation and Sustainable Development Introduction 1. We, parliamentarians and legislators of African and other
Summary of the Chair Conclusions and Recommendations of the Parliamentarian Forum on Energy Legislation and Sustainable Development Introduction 1. We, parliamentarians and legislators of African and other
Current situation and Issues
 Overview of the 2nd Fundamental Plan for Establishing a Sound Material Cycle Society(decided by the Cabinet on March,2008) Current situation and Issues All three indicators; resource productivity, cyclinical
Overview of the 2nd Fundamental Plan for Establishing a Sound Material Cycle Society(decided by the Cabinet on March,2008) Current situation and Issues All three indicators; resource productivity, cyclinical
Becoming a net-zero emissions city through transformative changes in lifestyle, work-style and urban infrastructure
 Becoming a net-zero emissions city through transformative changes in lifestyle, work-style and urban infrastructure Kyoto is one of the world s most unique historical cities: one that has developed over
Becoming a net-zero emissions city through transformative changes in lifestyle, work-style and urban infrastructure Kyoto is one of the world s most unique historical cities: one that has developed over
MAFF UPDATE. Summary of the Basic Plan for Food, Agriculture and Rural Areas
 A weekly update of news from the Japanese MAFF International Policy Planning Division, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Kasumigaseki 1-2-1, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8950 Ministry of Agriculture,
A weekly update of news from the Japanese MAFF International Policy Planning Division, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Kasumigaseki 1-2-1, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8950 Ministry of Agriculture,
30.X CLIMATE CHANGE - Council conclusions. The Council adopted the following conclusions: "The Council of the European Union,
 CLIMATE CHANGE - Council conclusions The Council adopted the following conclusions: "The Council of the European Union, 1. RECALLS the (Environment) Council conclusions of 20 February 2007 as well as the
CLIMATE CHANGE - Council conclusions The Council adopted the following conclusions: "The Council of the European Union, 1. RECALLS the (Environment) Council conclusions of 20 February 2007 as well as the
are country driven and in conformity with, and supportive of, national development priorities;
 OPERATIONAL PROGRAM NUMBER 7 REDUCING THE LONG-TERM COSTS OF LOW GREENHOUSE GAS-EMITTING ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES 7.1 The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) seeks to stabilize atmospheric
OPERATIONAL PROGRAM NUMBER 7 REDUCING THE LONG-TERM COSTS OF LOW GREENHOUSE GAS-EMITTING ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES 7.1 The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) seeks to stabilize atmospheric
CSR & Sustainability China
 order the FULL report COMPLIMENTARY at www.elcamedia.com Emerging markets series elcamedia CSR consultancy CSR & Sustainability China SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT in China s 12 th Five Year Plan ElcaMedia CSR
order the FULL report COMPLIMENTARY at www.elcamedia.com Emerging markets series elcamedia CSR consultancy CSR & Sustainability China SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT in China s 12 th Five Year Plan ElcaMedia CSR
Energy-Efficient Technologies and Renewables in Relation to Japan s Energy Security
 Energy-Efficient Technologies and Renewables in Relation to Japan s Energy Security Haruki Tsuchiya Research Institute for Systems Technology Tokyo, Japan Commissioned by the Pacific Asia Regional Energy
Energy-Efficient Technologies and Renewables in Relation to Japan s Energy Security Haruki Tsuchiya Research Institute for Systems Technology Tokyo, Japan Commissioned by the Pacific Asia Regional Energy
6% 25% 5 by20 y 20 80 by2050
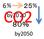 6% 25% by2020 80% by2050 LDP DPJ Low Carbon Green Growth and Development Green New Deal 20 Apr 2009 Minister for MoE Tetsuo SAITO Action Plan for the Creation of a Low-Carbon Society 29 Jul 2008 Cabinet
6% 25% by2020 80% by2050 LDP DPJ Low Carbon Green Growth and Development Green New Deal 20 Apr 2009 Minister for MoE Tetsuo SAITO Action Plan for the Creation of a Low-Carbon Society 29 Jul 2008 Cabinet
Achieving a Low-Carbon Society
 107 Achieving a Low-Carbon Society Hitachi s Approach Achieving a low-carbon society is an urgent challenge shared widely around the world. Among the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the
107 Achieving a Low-Carbon Society Hitachi s Approach Achieving a low-carbon society is an urgent challenge shared widely around the world. Among the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the
