Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviors of Polish Managers
|
|
|
- Alicia Warren
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Intercultural Management Vol. 5, No. 1, March 2013, pp Jerzy Mączyński Łukasz Sułkowski Michał Chmielecki Agnieszka Zajączkowska Społeczna Akademia Nauk w Łodzi Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviors of Polish Managers Abstract: 1996/1997 under the GLOBE research project. As was unexpected, our research results indicate the Polish middle managers under Key-words: followers evaluations of Polish middle managers in regard to their traits and behaviors in the years of 2008/2009; 2010/2011; 2012 and evaluations from
2 6 J. Mączyński, Ł. Sułkowski, M.Chmielecki, A. Zajączkowska the part of managers investigated during 1996/1997 under the GLOBE research project. The Poland of today is facing an immense political and socioeconomic change, and is designing the suitable institutions and legislations that should be advantageous to a democratic system. Therefore we have assumed that there is a good reason to predict that the political and economic transformation in Poland should be beneficial for shaping organizational culture and managerial practices and values. Method The leadership measurements asked followers to assess their superiors according to seven traits that are presented below: 1. Performance Orientation: improvement oriented, excellence oriented, achievement oriented. 2. Team Orientation: group oriented, collaborative, loyal, consultative. 3. Humane Orientation: generous, compassionate. 4. Autocratic Orientation: dictatorial, bossy, elitist. 5. Integrity Leadership Dimension: honest, sincere, just, trustworthy. 6. Visionary Leadership Dimension: foresight, prepared, anticipatory, plans ahead. 7. Inspirational Leadership Dimension: enthusiastic, positive, morale booster, motive arouser. In generating leadership traits and behaviors, the items were based on several existing leadership theories, as described by House, et al., [1997]. All scales developed in GLOBE study are based on extensive pilot study [see House, et al., 2004]. Questionnaire items developed in GLOBE project were translated from English to Polish, and after that translated back into English language. Back-translation was checked by the GLOBE coordinating team. Analysis of Research Results Research data analyzed in our paper concerning Polish managers investigated during 1996/1997 were drawn from extensive cross-cultural research under the GLOBE project, which was developed to study societal, organizational and leadership traits and behaviors through the use of multiple methods and at multiple levels of analysis [House, et al., 1997 a; b]. In turn research data concerning Polish managers studied in the years of 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012 have been collected partly by the authors of this paper. In the years of 1996/1997 two hundred seventy seven Polish middle managers completed the Leader Attribute Questionnaire developed by GLOBE research project. In the remaining years we have been able to conduct a follow-up study among 342 followers employed by several organizations located in different
3 Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviorsof Polish Managers 7 parts of Poland (including Legnica, Świdnica, Wrocław, Łódź, Warszawa). Followers of Polish middle managers, tested in those years, completed identical questionnaires as followers investigated under the GLOBE project. 1. Performance Orientation Under the GLOBE project, performance orientation is defined as the extent to which organization encourages and rewards innovation, setting high standards, challenging goals, and performance improvement. The differences between compared groups of managers on Performance Orientation are presented in Figure 1. Figure 1: Differences between Polish managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and of 2012 on Performance Orientation. Our research data displayed in Figure 1, indicate that Polish managers investigated in 2008/2009; 2010/2011; 2012 according to their followers demonstrate lower level of Performance Orientation than managers estimated under the GLOBE project in 1996/1997. It may appear that newer generations of Polish managers demonstrate weaker motivation to improve their work performance and develop their potentials. Based on the GLOBE research results, societies whose members express strong Performance Orientation, value education and learning, accentuate results, set high performance goals, and value taking initiative [House, et al., 2004]. David C. McClelland [1987] introduced the concept of need for achievement, which was defined as a tendency to do better all the time. He noted that
4 8 J. Mączyński, Ł. Sułkowski, M.Chmielecki, A. Zajączkowska organizational members with high need for achievement tend to achieve satisfaction from progressive work improvement, prefer to work on tasks with moderate chances of success, assume personal responsibility for their activities, look for frequent feedback, search for knowledge on how to perform work better, and are in general innovative. GLOBE findings on Performance Orientation practices, proved that performance oriented societies are more economically prosperous. Measures of economic health used by GLOBE, found strong and significant correlation with three scales: economic prosperity(correlation=.573, p<.001), public support for economic prosperity(correlation=.547, p<.001), and societal support for economic prosperity(correlation=.367, p<.05, House, 2004, p.254). It is worthwhile to mention, that Hofstede and Bond [1988] proved that Confucian Dynamism was significantly correlated with economic growth among 22 nations under study. Their description of Confucian Dynamism has a great deal in common with McClelland s need for achievement and GLOBE s Performance Orientation lending support for the argument that societal and organizational practices that encourage achievement orientation are solution to economic and business development and success. 2. Team Orientation Team Orientation is a leadership attribute that emphasizes effective team building, cooperation, loyalty, consultation and implementation of common goals by team members. Figure 2 presents the data concerning differences between Polish middle managers studied under the GLOBE study and our follow-up investigation. Figure 2: Differences between Polish managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and of 2012 on Team Orientation.
5 Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviorsof Polish Managers 9 From the results presented in Figure 2, it can be clearly seen that Polish middle managers investigated in the years of 2008/2009; 2010/2011 and 2012, in comparison with managers studied under the GLOBE project, score significantly lower on team orientation. It can be concluded that managers investigated under our follow-up study express lower consideration towards followers interests and views. In the GLOBE research it has been found that team-oriented leaders tend to emphasize mutual interests rather than differences. Explain the importance of cooperation, between team members for shared organizational goals, as well as individual objectives. Encourage team members to exchange information and elicit additional ideas, and help each other. Diverse studies provide ample evidence that leader s skills in team-building are highly relevant for strengthening followers identification with the organization s mission and managerial effectiveness [Peters and Austin, 1985; Tichy and Devanna, 1986]. 3. Humane Orientation Humane Orientation can be defined as the degree to which society or organization encourage and rewards people for being generous, altruistic, friendly, caring and kind to others. Humane Orientation is operationalized as the degree of concern, sensitivity, friendship, tolerance, and support that is extended to others at the societal, organizational, and leadership levels [House, et al., 2004, p.595]. Figure 3 displays the data related to differences between Polish middle managers investigated under the GLOBE study and our follow-up investigation. Figure 3: Differences between Polish managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012 on Humane Orientation.
6 10 J. Mączyński, Ł. Sułkowski, M.Chmielecki, A. Zajączkowska Our research results presented in Figure 3, indicate that Polish managers, from the point of view of their followers, investigated under the follow-up study display lower level of humane orientation than Polish managers studied under the GLOBE project. As viewed by the GLOBE study, highly humane-oriented behaviors are concerned with expressing care, nurturance, and help to others, while low humane orientation imply encouraging self-interest and lack of consideration to other people. Humane orientation of managers is closely related to the economic, physical, and psychological well-being of their followers. As revealed by the GLOBE study results, the more an organization value Humane Orientation, the higher the members of that organization rate Participative Leadership style as a desired attribute and the lower they rate Autocratic Leadership behavior as essential factor for being effective [House, et al., 2004; Mączyński, et al., 1994; Mączyński, 2001; 2002]. 4. Autocratic Orientation Autocratic leadership attribute, under the GLOBE project is defined as being dictatorial, bossy and making decisions in a command manner. The differences between analyzed groups of middle Polish managers are shown in Figure 4. Figure 4: Differences between Polish managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012 on Autocratic Orientation.
7 Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviorsof Polish Managers 11 From a comparison of the results presented in Figure 4, it can be easily seen that Polish middle managers investigated under the follow-up study score higher on Autocratic dimension than middle managers investigated in 1996/1997 under the GLOBE project. It is worthwhile to mention that the GLOBE results revealed that Polish managers were expected to behave more often in a highly autocratic manner than their western counterparts [Szabo, et al., 1997]. Some of the research data from the GLOBE project indicate that Polish managers report that their followers tend not to question their superiors, but instead significantly more often pointed to their superiors as the authority responsible for dealing with on-going work events and making organizational decisions. On the other hand western managers report that followers in a situation where there is disagreement with their superiors express a tendency to question their orders rather than obey them [Szabo, et al., 1997]. It should be noted that the current situation in Poland is vastly different from the circumstances that prevailed under previous system. There is no longer such a strong tendency to apply coercion as a means for obtaining managerial control. As a consequence employees nowadays have much more power and a concurrent expectation that their views will be asked for and will be taking into consideration. In other words, managers should no longer function effectively by applying traditional autocratic leadership style. Polish organizations of today need more participative managerial practices compatible with human resources conception [Mączyński, 1998]. 5. Integrity Leadership Dimension Integrity as leadership attribute within the GLOBE project is defined as being trustworthy, just, honest and sincere. Figure 6 reports the differences between analyzed groups of Polish middle managers on Integrity Leadership Dimension. From a comparison of our research results displayed in Figure 6, it can be concluded that Polish middle managers investigated under our follow-up study score significantly lower on Integrity Leadership Dimension, than their counterparts studied in 1996/1997 under the GLOBE project. Leaders with high integrity have insight into the needs, interests, and values of their followers, and are able to arouse strong emotions and identification with organizational goals. High integrity leaders are likely to set an example through their own behavior for followers to stimulate enthusiasm and effort. Through this process such a leaders are able to exert substantial influence on the satisfaction and motivation of their followers. According to Yukl subordinates are usually more satisfied with a leader who is friendly and helpful, shows trust and respect, and demonstrates concern for their needs and feelings [Yukl, 1994, p.446].
8 12 J. Mączyński, Ł. Sułkowski, M.Chmielecki, A. Zajączkowska Figure 5: Differences between Polish managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012 on Integrity Leadership Dimension. Followers of high integrity leader have a feelings of trust, admiration, respect and loyalty towards the leader, and they are willing to do more than they were expected to do. Followers are more aware of the importance of the goal outcomes, and are willing to devote their own self-interest for the sake of the organization. 6. Visionary Leadership Dimension Under the GLOBE project Visionary Leadership is characterized by the following terms: foresight, anticipatory, prepared, intellectually stimulating, future oriented, inspirational. Cultural future orientation is the degree to which a society or organization encourages and rewards future-oriented behaviors such as planning and delaying gratification. An important aspect of visionary leadership is envisioning the future, providing long-term direction and articulating it to followers. Thomas and Greenberger[1995] concluded that the ability to create vision is to some extent dependent on future-time perspective characterized by the leader. A leader who is focused on future orientation is willing to direct his energy toward the future. Figure 6 displays the differences between compared groups of Polish middle managers on Visionary Leadership Dimension.
9 Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviorsof Polish Managers 13 Figure 6: Differences between Polish managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012 on Visionary Leadership Dimension. The data presented in Figure 6, show substantial evidence of differences in mean score on Visionary Leadership between compared groups of respondents. Polish middle managers investigated on our follow-up study display significantly lower level of visionary leadership attribute than their counterparts studied in the years of 1996/1997 under the GLOBE project. GLOBE study discovered that future-oriented practices are positively correlated with societal health and general satisfaction [House, et al., 2004, p.316]. Hofstede and Bond [1988] postulated that Confucian Dynamism is, in essence, a dynamic, future oriented mentality, as opposed to a static oriented mind-set. Hofstede [1991;2000] concluded that a long-term orientation is essential for a high tendency to save while a short-term orientation results in a tendency to enjoy leisure in the present time and emphasize only immediate concerns of the people. Organizations that value future orientation, reveal a tendency to endorse the effectiveness of Visionary Leadership. Visionary leaders have the ability to inspire and motivate followers to work hard in order to achieve organizational goals. 7. Inspirational Leadership Dimension Under the GLOBE project, Inspirational Leadership reflects the ability to inspire, to motivate, to encourage, to built confidence, and to expect high work performance from the part of followers. The last Figure(Number 7) displays the differences between compared groups of Polish middle managers on Inspirational Leadership Dimension.
10 14 J. Mączyński, Ł. Sułkowski, M.Chmielecki, A. Zajączkowska Figure 7: Differences between Polish middle managers of 1996/1997, 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012 on Inspirational Leadership Dimension. Results presented in Figure 7, indicate that Polish middle managers studied under our follow-up study display significantly lower level of Inspirational Leadership attribute than their counterparts investigated in the years of 1996/1997 under the GLOBE research project. Based on the GLOBE research results it can be concluded that an Inspirational Leadership behavior is concerned with an attempt to develop enthusiasm and commitment by arousing strong emotions pertaining to followers needs, values, dreams and ideas. Inspirational leadership behavior may appeal to followers desire to be important, to feel useful and take advantage of their skills, to accomplish worthwhile organizational objectives, to perform an exceptional task, to be a member of outstanding team, or to participate in an fascinating and inspiring effort to perform tasks better. To be able to articulate suitable inspirational appeals, the leader should have insight into the values, expectations, and fears of the followers or team to be influenced. The effectiveness of an inspirational leadership behavior also depends on the leader s communication skills, such as the ability to use creative ideas, and employ suitable voice and gestures to generate enthusiasm, excitement and motivation [Yukl, 1998]. Conclusion In summary, our overall purpose in this paper was to compare followers evaluation of Polish middle managers in respect to their leadership attributes,
11 Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviorsof Polish Managers 15 in the years of 2008/2009, 2010/2011, 2012 and during 1996/1997 within the GLOBE research project. Our findings with respect to attributes associated with leadership effectiveness are largely consistent, in our follow-up study, across the years of investigation and regions of Poland under the study. At the same time data collected in our follow-up study differ significantly with the results received under the GLOBE investigation. It was surprising and to some extent unexpected that new generation of Polish middle managers investigated in the years of 2008/2009, 2010/2011 and 2012, among other aspects, disclosed substantially less negative attitude towards autocratic leadership attribute than did their counterparts investigated under the GLOBE project in 1996/1997. Based upon our research data, it could be concluded that the more autocratic leadership style is applied towards followers, there is less opportunity to manifest humane orientation, team orientation, integrity, visionary and inspirational leadership attributes in organizational practices. It has been internationally accepted that managerial leadership style is influenced by the concept of national culture which is labeled Power Distance. Based on a survey of employees in 40 countries, Hofstede defines this construct as the extent to which a society accepts the fact that power in institutions and organizations is distributed equally [1980, p.45]. High power distance is dysfunctional since it discourage members of the society or organization from debate and voicing of divergent views. Asking questions may be regarded as criticizing and blaming, and therefore may not be allowed. In contrast within the low power distance societies, the flexible distribution of power is expected to reinforce entrepreneurial innovation, broader participation in decision making, and to restrain the abuse of power and corruption. Relatively high levels of power distance in Poland are also in line with results of studies conducted by Sułkowski [2008; 2009], who suggests that through the use of empowerment techniques one could awaken initiative and responsibility for one s own life. According to Sułkowski Evolutionary research may be used to interpret sources of behaviors connected with power and to show possibilities of limiting some dangers [2009, p.67]. Within the GLOBE research, we found that societies who score lower on Power Distance practices and values tend to be more economically prosperous and competitively successful, enjoy higher levels of societal health, and human development [House, et al., 2004, p.556]. We have assumed that the current circumstances in Poland are vastly different from the situation that prevailed at the time when our original
12 16 J. Mączyński, Ł. Sułkowski, M.Chmielecki, A. Zajączkowska data were collected in 1996/97 under the GLOBE project. That s why we have speculated that profound changes in social, economic and organizational arrangements in Poland should diminish Power Distance in organizational practices, and lead to more negative attitude towards autocratic managerial behaviors from the part of newer generation of Polish managers. Our research results clearly show a resistance to immense political and socioeconomic change. Organizational practices in Polish organizations remain relatively autocratic. Interpreting our findings in this light leads to the conclusion that profound changes in political and socioeconomic systems are not sufficient factors that would have the power to modify organizational values and subsequent practices and behaviors. It would mean that deep changes in the mentality of people are needed to generate beneficial changes in the cultural values and succeeding attitudes and behaviors [Hofstede, 1980; 1991; 2000; Martan, 1993; Mączyński, et al., 2010]. It should be emphasized, that progressing autocratic managerial practices may produce unfortable situation for Polish organizations, and would become dysfunctional for organizational survival and development. This leads to the conclusion that in order to cope successfully with the current worldwide economic crisis, Polish managers would have to acquire such values and managerial behaviors, which would favor, among other aspects, application and development of human capital and potentials of their followers. We hope that potential benefits resulted from our research on leadership traits and behaviors may have significant implications for improving managerial performance. Conclusions drawn from our findings might be helpful, among other aspects, in selection and placement of candidates for managerial positions and formal management training programs. Bibliography Hofstede, G. (1980). Culture s consequences: International differences in work-related values. CA: Sage, Beverly Hills. Hofstede, G. (1991). Cultures and organizations: Software of the mind. London: McGraw- Hill. Hofstede, G. (2000). Kultury i organizacje. Zaprogramowanie umysłu. Warszawa: Polskie Wydawnictwo Ekonomiczne. Hofstede, G., and Bond, M.H. (1988). The Confucius connection: From cultural roots to economic growth. Organizational Dynamics, 16(4), pp House, R.J., Hanges, P.I., & Ruiz-Quintanilla, S.A. (1997). GLOBE: The global leadership and organizational behavior effectiveness research program. Polish Psychological Bulletin, 28, pp House, R.J., Hanges, P.J., & Ruiz-Quintanilla, S.A., Dorfman, P.W., Javidan, M.,Dickson,
13 Longitudinal Studies on Traits and Behaviorsof Polish Managers 17 M.W., Gupta, V., & 159 co-authors (1999). Cultural influences on leadership and organizations: Project GLOBE. [in:] W. Mobley, J. Gessner, & V. Arnold (eds.), Advances in global leadership., JAI Press, Stamford, pp House R.J., Wright, N.S., & Aditya, R.N. (1997). Cross-cultural research on organizational leadership: A critical analysis and proposed theory. [in:] P.C. Early & M. Erez (eds.), New perspectives in international organizational psychology. San Francisco, pp New Lexington. House, R.J., et al. (2004). Culture, leadership, and organizations. The GLOBE study of 62 societies. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, London, New Delhi. Mączyński, J. (1998). Diagnosing decision participation. Warsaw: Polish Academy of Sciences Press. Mączyński, J. (2001). The cultural impact on the leadership style of Polish managers. [in:] Polish Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 1(1), pp Mączyński, J. (2002). Cultural determinants of leadership style of Polish managers. [in:] G. Reber (eds.) Management in einer Welt der Globalisierung und Diverität. Schäffer- Poeschel Verlag, Stuttgart, pp Mączyński, J., Jago, A.G., Reber, G. & Böhnisch, W. (1994). Culture and leadership styles: A comparison of Polish, Austrian and US managers. Polish Psychological Bulletin, 25, pp Mączyński, J., Łobodziński, A., Wyspiański, D., Kwiatkowski, P. (2010). Differences on organizational practices and preferred leader attributes between Polish managers investigated in 1996/1997 and 2008/2009. Polish Psychological Bulletin, vol. 41, pp Martan, L. (1993). The necessary change of human mentality. Organization and Management, 73, pp Mc Clleland, D.C. (1987). Human motivation. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Peters, T.J., and Austin, N. (1985). A passion for excellence: The leadership difference. New York: Random House. Sułkowski, Ł. (2008). Empowerment methods in social projects managements. Intercultural Management Studies, pp Sułkowski, Ł. (2009). Universal sources of hierarchy and power from the perspective of neoevolutionism. Journal of Intercultural Management, vol. 1, No. 2, pp Szabo, et al. (1997). Autocratic polish versus participative Austrian leaders: More than a cliché? Polish Psychological Bulletin, vol. 28, No. 3, pp Thomas, M.A., Greenberger, D.B. (1985). The relationship between leadership and time orientation. Journal of Management Inquiry, 4, pp Tichy, N.M., and Devanna, M.A. (1986). The transformational leader. New York: John Wiley. Yukl, G. (1994). Leadership in organizations. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Other Papers. A Seven Nations Study of Leadership Attributes
 Other Papers Polish Psychological Bulletin 2017, vol. 48(2) 307 314 DOI - 10.1515/ppb-2017-0035 Jerzy Mączyński * Łukasz Sułkowski ** A Seven Nations Study of Attributes Abstract: The overall purpose of
Other Papers Polish Psychological Bulletin 2017, vol. 48(2) 307 314 DOI - 10.1515/ppb-2017-0035 Jerzy Mączyński * Łukasz Sułkowski ** A Seven Nations Study of Attributes Abstract: The overall purpose of
CHAPTER 13: LEADING COURSE PROGRESS PLANNING AHEAD CHAPTER 13 STUDY QUESTIONS STUDY QUESTION 1: WHAT IS THE NATURE OF LEADERSHIP?
 COURSE PROGRESS CHAPTER 13: LEADING BOH4M Unit 3: Leading Ø Unit 1: Management Fundamentals Ø Unit 2: Planning, Controlling, and Strategizing Ø Unit 3: Leading Ø Chapter 13: Leading Ø Chapter 15: Individual
COURSE PROGRESS CHAPTER 13: LEADING BOH4M Unit 3: Leading Ø Unit 1: Management Fundamentals Ø Unit 2: Planning, Controlling, and Strategizing Ø Unit 3: Leading Ø Chapter 13: Leading Ø Chapter 15: Individual
A leader lives in each of us. Leadership is one of the four functions of management.
 MODULE 16 A leader lives in each of us MODULE GUIDE 16.1 What are the foundations for effective leadership? What are current issues and directions in leadership development? Leadership is one of the four
MODULE 16 A leader lives in each of us MODULE GUIDE 16.1 What are the foundations for effective leadership? What are current issues and directions in leadership development? Leadership is one of the four
Publishing as Prentice Hall
 17-1 eleventh edition Define leader and leadership Compare and contrast early theories of leadership Describe the three major contingency theories of leadership Describe contemporary views of leadership
17-1 eleventh edition Define leader and leadership Compare and contrast early theories of leadership Describe the three major contingency theories of leadership Describe contemporary views of leadership
Management Principles
 Management Principles WEEK 7 Leadership Part IV: Leading L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S Chapter 16: Leadership 1. Define leader and explain the difference between managers and leaders. 2. Summarize the
Management Principles WEEK 7 Leadership Part IV: Leading L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S Chapter 16: Leadership 1. Define leader and explain the difference between managers and leaders. 2. Summarize the
Principles of Management
 Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW Dr Mariusz Maciejczak Principles of Management www.maciejczak.pl Basic reading The presentation has been prepared based on the book 1 Leaders and Power Leadership
Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW Dr Mariusz Maciejczak Principles of Management www.maciejczak.pl Basic reading The presentation has been prepared based on the book 1 Leaders and Power Leadership
Part 4: Leading. Chapter 11. Leadership and Trust. PowerPoint Presentation by Mohammed Ramadan Copyright 2018 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Part 4: Leading Chapter 11 Leadership and Trust PowerPoint Presentation by Mohammed Ramadan Copyright 2018 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S After reading this chapter,
Part 4: Leading Chapter 11 Leadership and Trust PowerPoint Presentation by Mohammed Ramadan Copyright 2018 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S After reading this chapter,
The nature of Leadership Leading Leadership and vision vision: Visionary leader Power and influence power Sources of position power Reward power
 Chapter 12 Leadership is hard, and most managers find it especially difficult when going to a new organisation, as there current leadership doesn't work. The nature of Leadership Leading is the process
Chapter 12 Leadership is hard, and most managers find it especially difficult when going to a new organisation, as there current leadership doesn't work. The nature of Leadership Leading is the process
Joseph A. Agada 1 1 Department of Business Administration and Management Studies, Federal Polytechnic Idah, Kogi
 Leadership Style, Motivation and Delegation in one Selected Tertiary Institution in Kogi State, Nigeria Joseph A. Agada 1 1 Department of Business Administration and Management Studies, Federal Polytechnic
Leadership Style, Motivation and Delegation in one Selected Tertiary Institution in Kogi State, Nigeria Joseph A. Agada 1 1 Department of Business Administration and Management Studies, Federal Polytechnic
6/19/2013. Introduction. Leadership contd.. Leadership. Kinds of leadership
 Principles of Management -Leadership- Introduction People in organization rarely, if ever, work entirely alone. Formal and informal groups exists in organizations. Groups exerts a very strong influence
Principles of Management -Leadership- Introduction People in organization rarely, if ever, work entirely alone. Formal and informal groups exists in organizations. Groups exerts a very strong influence
Lesson 14. Being an Effective Leader
 Lesson 14 Being an Effective Leader Learning Objectives 1. Define leader and leadership. 2. Compare and contrast early theories of leadership. 3. Describe the three major contingency theories of leadership.
Lesson 14 Being an Effective Leader Learning Objectives 1. Define leader and leadership. 2. Compare and contrast early theories of leadership. 3. Describe the three major contingency theories of leadership.
Cross-Cultural Leadership, Diversity,
 Cross-Cultural Leadership, Diversity, CHAPTER 14 Learning Objectives Understand why cross-cultural research on leadership is important. Understand different types of cross-cultural research. Understand
Cross-Cultural Leadership, Diversity, CHAPTER 14 Learning Objectives Understand why cross-cultural research on leadership is important. Understand different types of cross-cultural research. Understand
MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS. Lesson 4
 MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS Lesson 4 Leadership The Nature of Leadership Leading is a process of directing and influencing the task oriented activities of group members or the entire organisation Leadership
MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS Lesson 4 Leadership The Nature of Leadership Leading is a process of directing and influencing the task oriented activities of group members or the entire organisation Leadership
The definition of leadership
 The definition of leadership Leadership is the lifting of a man s vision to higher sight, the raising of a man s performance to a higher standard, the building of a man s personality beyond its normal
The definition of leadership Leadership is the lifting of a man s vision to higher sight, the raising of a man s performance to a higher standard, the building of a man s personality beyond its normal
Chapter 16: Leadership
 Chapter 16: Leadership 1 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Define leader and leadership. Compare and contrast early theories of leadership. Describe the three
Chapter 16: Leadership 1 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Define leader and leadership. Compare and contrast early theories of leadership. Describe the three
Leadership In Organizations: National Implications
 VOLUME 7, NUMBER 1, 2004 Leadership In Organizations: National Implications Alicia Kritsonis MBA Graduate Student California State University, Dominquez Hills ABSTRACT The purpose of this article is to
VOLUME 7, NUMBER 1, 2004 Leadership In Organizations: National Implications Alicia Kritsonis MBA Graduate Student California State University, Dominquez Hills ABSTRACT The purpose of this article is to
Organizational Communication: Relationships with Organization Climate and its Impacts An Empirical Study
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. II, Issue 2/ May 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.1 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Organizational Communication: Relationships with Organization Climate
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. II, Issue 2/ May 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.1 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Organizational Communication: Relationships with Organization Climate
CHAPTER 17 LEADERSHIP. Leadership is a process of influencing a group to achieve goals
 CHAPTER 17 LEADERSHIP Leadership is a process of influencing a group to achieve goals Early Leadership Theories Trait Theories (1920s -1930s) Research focused on identifying personal characteristics that
CHAPTER 17 LEADERSHIP Leadership is a process of influencing a group to achieve goals Early Leadership Theories Trait Theories (1920s -1930s) Research focused on identifying personal characteristics that
Chapter. Leadership and Management Behavior in Multinational Companies
 Chapter 15 Leadership and Management Behavior in Multinational Companies Leadership The GLOBE s universal definition of Leadership: the ability of an individual to influence, motivate, and enable others
Chapter 15 Leadership and Management Behavior in Multinational Companies Leadership The GLOBE s universal definition of Leadership: the ability of an individual to influence, motivate, and enable others
CHAPTER 2 MODELS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 CHAPTER 2 MODELS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR AN ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR SYSTEM The primary purpose of organizational behavior system (OBS) is to identify and then help manipulate the major human and organizational
CHAPTER 2 MODELS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR AN ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR SYSTEM The primary purpose of organizational behavior system (OBS) is to identify and then help manipulate the major human and organizational
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
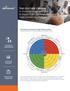 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
What leadership practices work internationally and Why? Darlene Fisher: Core team member - IB Leadership Pathways Developers
 What leadership practices work internationally and Why? Darlene Fisher: Core team member - IB Leadership Pathways Developers My reality and research Some questions for today What is leadership? Where does
What leadership practices work internationally and Why? Darlene Fisher: Core team member - IB Leadership Pathways Developers My reality and research Some questions for today What is leadership? Where does
Chapter 1. Leadership CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Leadership CHAPTER OUTLINE Chapter 1 I. THE NATURE OF LEADERSHIP A. Leadership is the process by which a person exerts influence over other people and inspires, motivates, and directs their activities
Leadership CHAPTER OUTLINE Chapter 1 I. THE NATURE OF LEADERSHIP A. Leadership is the process by which a person exerts influence over other people and inspires, motivates, and directs their activities
9-1. Managing Leadership. Essentials of Contemporary Management, 3Ce. Copyright 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 9 9-1 Managing Leadership Learning Objectives 9-2 1. Describe what leadership is and on what bases of power leaders influence others. 2. Describe the early trait and behavioural theories of leadership
9 9-1 Managing Leadership Learning Objectives 9-2 1. Describe what leadership is and on what bases of power leaders influence others. 2. Describe the early trait and behavioural theories of leadership
PRESENTATION STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION PHD THESIS DR. ARNOUD VAN DER MAAS STRATAEGOS CONSULTING
 PRESENTATION STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION PHD THESIS DR. ARNOUD VAN DER MAAS STRATAEGOS CONSULTING There is nothing more difficult to take at hand, more perilous to conduct, or more uncertain in its success,
PRESENTATION STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION PHD THESIS DR. ARNOUD VAN DER MAAS STRATAEGOS CONSULTING There is nothing more difficult to take at hand, more perilous to conduct, or more uncertain in its success,
International Research on Leadership
 International Research on Leadership William W. Liddell, Brock University, St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada Project GLOBE (Global Leadership and Organizational Behavior Effectiveness) is a major long-term
International Research on Leadership William W. Liddell, Brock University, St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada Project GLOBE (Global Leadership and Organizational Behavior Effectiveness) is a major long-term
What is a Responsibility-Based Workplace Model?
 White Paper: What is a Responsibility-Based Workplace Model? Publication Date: 1 March 2006 Written by: Judy Ryan, Owner Expanding Human Potential Contact Judy Ryan at 314.878.9100 What is a Responsibility-Based
White Paper: What is a Responsibility-Based Workplace Model? Publication Date: 1 March 2006 Written by: Judy Ryan, Owner Expanding Human Potential Contact Judy Ryan at 314.878.9100 What is a Responsibility-Based
Autocratic or Democratic? Which Type of Construction Leaders Do You Prefer? Thomas Ho 20 November 2014
 Autocratic or Democratic? Which Type of Construction Leaders Do You Prefer? Thomas Ho 20 November 2014 What is Leadership? The famous Chinese philosopher Lao-tzu said : to lead the people, walk behind
Autocratic or Democratic? Which Type of Construction Leaders Do You Prefer? Thomas Ho 20 November 2014 What is Leadership? The famous Chinese philosopher Lao-tzu said : to lead the people, walk behind
Motivation & Leadership. Section #1: Motivation
 Motivation & Leadership Section #1: Motivation 1 S1 Learning Targets 1. I can explain the meaning of motivation 2. I can describe the various theories of motivation. 3. I can explain how expectations affect
Motivation & Leadership Section #1: Motivation 1 S1 Learning Targets 1. I can explain the meaning of motivation 2. I can describe the various theories of motivation. 3. I can explain how expectations affect
LEADERSHIP AND CHANGE
 LEADERSHIP AND CHANGE Leadership and Management If followers are over budget on travel expenses or fail to come to work on time, then managers use various levers in the accounting or performance management
LEADERSHIP AND CHANGE Leadership and Management If followers are over budget on travel expenses or fail to come to work on time, then managers use various levers in the accounting or performance management
The Relationship Between Followers Personality and Preferences in Leadership
 The Relationship Between Followers Personality and Preferences in Leadership Lucinda Parmer University of Houston-Downtown Mark Green Our Lady of the Lake University-San Antonio Phyllis Duncan Our Lady
The Relationship Between Followers Personality and Preferences in Leadership Lucinda Parmer University of Houston-Downtown Mark Green Our Lady of the Lake University-San Antonio Phyllis Duncan Our Lady
Chapter 17 LEADERSHIP. Prentice Hall,
 Chapter 17 LEADERSHIP Prentice Hall, 2002 17-1 You should learn to: Learning Objectives 1. Explain the difference between managers and leaders 2. Describe the trait and behavioral theories of leadership
Chapter 17 LEADERSHIP Prentice Hall, 2002 17-1 You should learn to: Learning Objectives 1. Explain the difference between managers and leaders 2. Describe the trait and behavioral theories of leadership
BBS Notes - 3rd Year Organizational Behavior LEADERSHIP
 1. What is charismatic leadership? 1 8.0 LEADERSHIP Charismatic theory of leadership primary focuses on the ability of a leader. As per this theory, effectiveness of leadership depends upon leader's ability
1. What is charismatic leadership? 1 8.0 LEADERSHIP Charismatic theory of leadership primary focuses on the ability of a leader. As per this theory, effectiveness of leadership depends upon leader's ability
Universally Enforced Attributes of Leadership with Current Prevalent Leadership Theories Taught at Texas A&M University
 of with Current Prevalent Theories Taught at Texas A&M University J. Muenich and J. Williams Texas A&M University College Station, T Abstract Globalization is changing the shape of today s world. The result
of with Current Prevalent Theories Taught at Texas A&M University J. Muenich and J. Williams Texas A&M University College Station, T Abstract Globalization is changing the shape of today s world. The result
Presented by: Kamelia Gulam
 Chapter: 12 Leadership 0 Presented by: Kamelia Gulam 1 After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Contrast leadership and management 2. List the traits of effective leaders 3. Define and give
Chapter: 12 Leadership 0 Presented by: Kamelia Gulam 1 After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Contrast leadership and management 2. List the traits of effective leaders 3. Define and give
LEADERSHIP STYLES AND INFLUENCE STRATEGIES: THE MODERATING EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CLIMATE
 Advances in Industrial Organizational Psychology B.J. Fallon, H.P. Pfister, J. Brebner (eds.) Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. (North-Holland), 1989 59 pp. 59-65. LEADERSHIP STYLES AND INFLUENCE STRATEGIES:
Advances in Industrial Organizational Psychology B.J. Fallon, H.P. Pfister, J. Brebner (eds.) Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. (North-Holland), 1989 59 pp. 59-65. LEADERSHIP STYLES AND INFLUENCE STRATEGIES:
Response Questions: Unit One. Anitra Lindsay. Capella University ED Professor Ordu
 Response Questions: Unit One Anitra Lindsay Capella University ED 8720 Professor Ordu July 13, 2008 Response Questions Describe your personal position with regard to Theory X and Theory Y. How does either
Response Questions: Unit One Anitra Lindsay Capella University ED 8720 Professor Ordu July 13, 2008 Response Questions Describe your personal position with regard to Theory X and Theory Y. How does either
A STUDY ON PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORIES OF MOTIVATION FOR INCREASING PRODUCTIVITY IN AN ORGANISATION AND ITS EFFECTIVENESS ON MANAGEMENT
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Management Studies (IJIRMS) Volume 2, Issue 11, December 2017. pp.13-19. A STUDY ON PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORIES OF MOTIVATION FOR INCREASING PRODUCTIVITY IN AN
International Journal of Innovative Research in Management Studies (IJIRMS) Volume 2, Issue 11, December 2017. pp.13-19. A STUDY ON PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORIES OF MOTIVATION FOR INCREASING PRODUCTIVITY IN AN
Change Management and the Role of Leadership in Facilitating Organizational Change in Corporate Takeovers
 Change Management and the Role of Leadership in Facilitating Organizational Change in Corporate Takeovers Radu Florea, PhD Cand. Abstract Facilitating organizational change depends to a great extent on
Change Management and the Role of Leadership in Facilitating Organizational Change in Corporate Takeovers Radu Florea, PhD Cand. Abstract Facilitating organizational change depends to a great extent on
Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management
 Subject Name Paper Name Paper No. 14 Module Name/Title Module Id Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management Organizational Leadership FT/FBM/09 Objectives To know about difference between
Subject Name Paper Name Paper No. 14 Module Name/Title Module Id Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management Organizational Leadership FT/FBM/09 Objectives To know about difference between
Organizational Behaviour
 Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Organisational Dynamics Leadership Theories The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education
Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Organisational Dynamics Leadership Theories The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education
Influence of Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture and Trust on Organizational Commitment
 International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research (IJMSR) Volume 4, Issue 9, September 2016, PP 47-51 ISSN 2349-0330 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0349 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0349.0409006
International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research (IJMSR) Volume 4, Issue 9, September 2016, PP 47-51 ISSN 2349-0330 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0349 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0349.0409006
Registration Details. How to Interpret the Report?
 Mettl Leadership Assessment - Demo sample_report@mettl.com Test Taken on: June 14, 2017 07:02:4 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample_report@mettl.com First Name: Sample
Mettl Leadership Assessment - Demo sample_report@mettl.com Test Taken on: June 14, 2017 07:02:4 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample_report@mettl.com First Name: Sample
TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP THE ART OF SUCCESSFULLY MANAGING TRANSFORMATIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGES
 TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP THE ART OF SUCCESSFULLY MANAGING TRANSFORMATIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGES Ionel Scaunasu, PhD Applicant University "Wallachia" Targoviste ABSTRACT: Companies today face new challenges
TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP THE ART OF SUCCESSFULLY MANAGING TRANSFORMATIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGES Ionel Scaunasu, PhD Applicant University "Wallachia" Targoviste ABSTRACT: Companies today face new challenges
MBH1683 Leading Organisational Change
 MBH1683 Leading Organisational Change Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L6 The Leadership of Change www.mba638.wordpress.com 1 Learning Objectives Discuss whether there is one best way of leading or whether
MBH1683 Leading Organisational Change Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L6 The Leadership of Change www.mba638.wordpress.com 1 Learning Objectives Discuss whether there is one best way of leading or whether
TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP AND ITS FUNCTIONALITY IN ARTS ORGANIZATION
 International Journal of Business and Society, Vol. 18 S4, 2017, 710-717 TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP AND ITS FUNCTIONALITY IN ARTS ORGANIZATION Qistina Donna Lee Abdullah Universiti Malaysia Sarawak Khashini
International Journal of Business and Society, Vol. 18 S4, 2017, 710-717 TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP AND ITS FUNCTIONALITY IN ARTS ORGANIZATION Qistina Donna Lee Abdullah Universiti Malaysia Sarawak Khashini
Transactional Leadership
 DePaul University From the SelectedWorks of Marco Tavanti 2008 Transactional Leadership Marco Tavanti, DePaul University Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marcotavanti/15/ Transactional Leadership
DePaul University From the SelectedWorks of Marco Tavanti 2008 Transactional Leadership Marco Tavanti, DePaul University Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marcotavanti/15/ Transactional Leadership
Does Transformational Leadership Leads To Higher Employee Work Engagement. A Study of Pakistani Service Sector Firms
 Does Transformational Leadership Leads To Higher Employee Work Engagement. A Study of Pakistani Service Sector Firms M. Waqas Raja PhD Scholar COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Chak Shahzad Campus,
Does Transformational Leadership Leads To Higher Employee Work Engagement. A Study of Pakistani Service Sector Firms M. Waqas Raja PhD Scholar COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Chak Shahzad Campus,
Managers Play a Key Role in Transforming the Fear and Uncertainty of a Layoff into Trust By Kevin Scheid
 BCWI research has revealed the financial downturn has increased the level of fear and uncertainty among staff in many Christian organizations. As leaders in ministry, what are the levers we can employ
BCWI research has revealed the financial downturn has increased the level of fear and uncertainty among staff in many Christian organizations. As leaders in ministry, what are the levers we can employ
1/16/2009. Chapter Seventeen. Learning Objectives. The Nature of Leadership. Managing Leadership and Influence Processes
 Chapter Seventeen Managing Leadership and Influence Processes Slide content created by Charlie Cook, The University of West Alabama Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives
Chapter Seventeen Managing Leadership and Influence Processes Slide content created by Charlie Cook, The University of West Alabama Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives
Lesson 11: Leadership
 Lesson 11: Leadership Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Contrast leadership and management. 2. Summarize the conclusions of trait theories of leadership. 3. Identify
Lesson 11: Leadership Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Contrast leadership and management. 2. Summarize the conclusions of trait theories of leadership. 3. Identify
ECI - Emotional Competency Inventory
 TM ECI - Emotional Competency Inventory A Primer on Emotional Intelligence John Mitchell - KM Advisors ACC Chicago October 19, 2010 Hay & Emotional Intelligence Background: Competency Methodology McClelland,
TM ECI - Emotional Competency Inventory A Primer on Emotional Intelligence John Mitchell - KM Advisors ACC Chicago October 19, 2010 Hay & Emotional Intelligence Background: Competency Methodology McClelland,
LISA SMITH. Report Generated: 03/04/2008
 Administered By: Report Prepared for: ACheck America - HQ COMPLIMENTARY MERIT Applicant Name: LISA SMITH Report Generated: 03/04/2008 Report Version 2.0: Recruitment Report Intended Use Reminder The MERIT
Administered By: Report Prepared for: ACheck America - HQ COMPLIMENTARY MERIT Applicant Name: LISA SMITH Report Generated: 03/04/2008 Report Version 2.0: Recruitment Report Intended Use Reminder The MERIT
An Executive Briefing Identifying and Retaining Top Performers
 An Executive Briefing Identifying and Retaining Top Performers Sponsored by Your local Profiles representative and Profiles International, Inc. Today s Objectives To IDENTIFY the characteristics of top
An Executive Briefing Identifying and Retaining Top Performers Sponsored by Your local Profiles representative and Profiles International, Inc. Today s Objectives To IDENTIFY the characteristics of top
How leaders create engaged performance and how to measure it
 How leaders create engaged performance and how to measure it Capturing value in human resources 2008 conference, Stockholm, 21-22 October 2008 Georg Vielmetter Draft presentation including explanatory
How leaders create engaged performance and how to measure it Capturing value in human resources 2008 conference, Stockholm, 21-22 October 2008 Georg Vielmetter Draft presentation including explanatory
What Is Motivation? Motivation works best when individual needs are compatible with organizational goals.
 7 Motivation 1 What Is Motivation? Motivation Is the result of an interaction between the person and a situation; it is not a personal trait. Is the set of forces that initiates, directs, and makes people
7 Motivation 1 What Is Motivation? Motivation Is the result of an interaction between the person and a situation; it is not a personal trait. Is the set of forces that initiates, directs, and makes people
Role of Leader in Improving Institutional Climate
 International Journal of Scientific Research and Management (IJSRM) Volume 5 Issue 10 Pages 72707275 2017 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 23213418 Index Copernicus value (2015): 57.47 DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i10.12
International Journal of Scientific Research and Management (IJSRM) Volume 5 Issue 10 Pages 72707275 2017 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 23213418 Index Copernicus value (2015): 57.47 DOI: 10.18535/ijsrm/v5i10.12
LEADERSHIP. Emergency Preparedness Leadership Training Series
 LEADERSHIP Emergency Preparedness Leadership Training Series Series Schedule Dates: April 1, 2015, Noon to 1 p.m. (PT) 2:00 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. (CT) Introductory webinar. Overview of successful leadership
LEADERSHIP Emergency Preparedness Leadership Training Series Series Schedule Dates: April 1, 2015, Noon to 1 p.m. (PT) 2:00 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. (CT) Introductory webinar. Overview of successful leadership
Considerations Regarding Improving Business Competiveness From An Entrepreneurial Perspective
 Considerations Regarding Improving Business Competiveness From An Entrepreneurial Perspective Manoela POPESCU Faculty of Touristic and Commercial Management, Dimitrie Cantemir Christian University, 174
Considerations Regarding Improving Business Competiveness From An Entrepreneurial Perspective Manoela POPESCU Faculty of Touristic and Commercial Management, Dimitrie Cantemir Christian University, 174
Chapter 10: Servant Leadership
 Chapter 10: Servant Leadership Description Servant leadership is an approach focusing on leadership from the point of view of the leader and his or her behaviors Servant leadership emphasizes that leaders
Chapter 10: Servant Leadership Description Servant leadership is an approach focusing on leadership from the point of view of the leader and his or her behaviors Servant leadership emphasizes that leaders
CHAPTER II A BRIEF HISTORY OF FOLLOWERSHIP. Early Trends. expanded follower roles, leaders formerly had exclusive rights to the domain of
 CHAPTER II A BRIEF HISTORY OF FOLLOWERSHIP Early Trends According to Offermann, followers have power. That power resides in the ability of followers to either support or sabotage the success of leaders.
CHAPTER II A BRIEF HISTORY OF FOLLOWERSHIP Early Trends According to Offermann, followers have power. That power resides in the ability of followers to either support or sabotage the success of leaders.
The function of management
 The function of management Managing In The New Era The Internet changes the way management must think and act chief Web officer will be one of the most important jobs will oversee information systems and
The function of management Managing In The New Era The Internet changes the way management must think and act chief Web officer will be one of the most important jobs will oversee information systems and
Creating a Customer Centric Organization
 RESEARCH BRIEF Creating a Customer Centric Organization The Key Drivers of Customer Loyalty Bill Kowalski Integrity Solutions The Sales Management Association +1 312 278-3356 www.salesmanagement.org 2009
RESEARCH BRIEF Creating a Customer Centric Organization The Key Drivers of Customer Loyalty Bill Kowalski Integrity Solutions The Sales Management Association +1 312 278-3356 www.salesmanagement.org 2009
Power, Influence, and Leadership. 2. Introduction. 2.1 Overview. Notes: Copyright 2016 Educational Design Technology (EDT) background music
 Power, Influence, and Leadership 2. Introduction 2.1 Overview background music 2.2 Learning Objectives No audio 1. Scene 1 1.1 Aspects of Leadership no audio 1.2 Power & Influence Power is an integral
Power, Influence, and Leadership 2. Introduction 2.1 Overview background music 2.2 Learning Objectives No audio 1. Scene 1 1.1 Aspects of Leadership no audio 1.2 Power & Influence Power is an integral
EQ Competencies Assessment
 EQ Competencies Assessment The research validates that what separates superior leaders from average leaders is Emotional Intelligence (EQ). When measuring IQ, Technical Expertise and EQ, the results validated
EQ Competencies Assessment The research validates that what separates superior leaders from average leaders is Emotional Intelligence (EQ). When measuring IQ, Technical Expertise and EQ, the results validated
Registration Details. How to Interpret the Report?
 Mettl Leadership Development Report sample sample.report@mettl.com Test Taken on: September 13, 2017 0:4:09 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample.report@mettl.com First
Mettl Leadership Development Report sample sample.report@mettl.com Test Taken on: September 13, 2017 0:4:09 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample.report@mettl.com First
MОTIVATION AND PERFORMANCE. CORRELATION STUDY
 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND EDUCATION IN THE AIR FORCE-AFASES 2016 MОTIVATION AND PERFORMANCE. CORRELATION STUDY Georgiana CORCACI University "Petre Andrei" Iasi, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND EDUCATION IN THE AIR FORCE-AFASES 2016 MОTIVATION AND PERFORMANCE. CORRELATION STUDY Georgiana CORCACI University "Petre Andrei" Iasi, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences
The Emotional Competence Framework
 The Emotional Competence Self-Awareness Personal Competence Emotional awareness: Recognising one s emotions and their effects. Know which emotions they are feeling and why Realise the links between their
The Emotional Competence Self-Awareness Personal Competence Emotional awareness: Recognising one s emotions and their effects. Know which emotions they are feeling and why Realise the links between their
LEADERSHIP STYLES IN SMALL ENTERPRISES OF A TRANSITION COUNTRY: AN EMPIRICAL RESEARCH IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
 LEADERSHIP STYLES IN SMALL ENTERPRISES OF A TRANSITION COUNT...Page 1 of 11 LEADERSHIP STYLES IN SMALL ENTERPRISES OF A TRANSITION COUNTRY: AN EMPIRICAL RESEARCH IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA MARIO BUBLE,
LEADERSHIP STYLES IN SMALL ENTERPRISES OF A TRANSITION COUNT...Page 1 of 11 LEADERSHIP STYLES IN SMALL ENTERPRISES OF A TRANSITION COUNTRY: AN EMPIRICAL RESEARCH IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA MARIO BUBLE,
MANAGEMENT OF ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR MBA I semester. Prepared by K.L REVATHI
 MANAGEMENT OF ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR MBA I semester Prepared by K.L REVATHI HISTORY OF MANAGEMENT Mary Parker defines the term management as the art of getting things done through others. Ivancerich, Donnelly
MANAGEMENT OF ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR MBA I semester Prepared by K.L REVATHI HISTORY OF MANAGEMENT Mary Parker defines the term management as the art of getting things done through others. Ivancerich, Donnelly
Management. Part IV: Leading Ch. 13. Leadership
 Management Part IV: Leading Ch. 13. Leadership Dan C. Lungescu, PhD, assistant professor 2015-2016 Course outline Management Part I: Introduction Part II: Planning Part III: Organizing Part IV: Leading
Management Part IV: Leading Ch. 13. Leadership Dan C. Lungescu, PhD, assistant professor 2015-2016 Course outline Management Part I: Introduction Part II: Planning Part III: Organizing Part IV: Leading
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit VI
 UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Motivation and Leadership Reading Assignment Chapter 13: Motivation and Performance Chapter 14: Leadership Suggested Reading See information below. Learning Activities (Non-Graded)
UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Motivation and Leadership Reading Assignment Chapter 13: Motivation and Performance Chapter 14: Leadership Suggested Reading See information below. Learning Activities (Non-Graded)
The Leadership Style Preference among Sabah Ethnicities
 The Leadership Style Preference among Sabah Ethnicities Dg Kamisah A.B (Corresponding author) Faculty of Business Management P.O.Box 71, 88997 Kota Kinabalu, Sabah Universiti Teknologi MARA E-mail: dkamisah@yahoo.com
The Leadership Style Preference among Sabah Ethnicities Dg Kamisah A.B (Corresponding author) Faculty of Business Management P.O.Box 71, 88997 Kota Kinabalu, Sabah Universiti Teknologi MARA E-mail: dkamisah@yahoo.com
HarbisonWalker International. Core Competencies
 HarbisonWalker International Core Competencies HWI Core Competency Model 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Core Competencies Accountability/Drive 3 Innovation 4 Collaboration 5 Customer Focus 6 Adapting to Change 7
HarbisonWalker International Core Competencies HWI Core Competency Model 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Core Competencies Accountability/Drive 3 Innovation 4 Collaboration 5 Customer Focus 6 Adapting to Change 7
The Servant Leader:! Enabling Exceptional Performance
 The Servant Leader: Enabling Exceptional Performance Chris De Santis with help from Warren Bennis, Robert Thomas, Daniel Goleman, Robert Greenleaf, Peter Drucker, Joseph Nye, Sylvia Hewlett, Carol Dweck
The Servant Leader: Enabling Exceptional Performance Chris De Santis with help from Warren Bennis, Robert Thomas, Daniel Goleman, Robert Greenleaf, Peter Drucker, Joseph Nye, Sylvia Hewlett, Carol Dweck
LEADING FROM THE HEART AND WITH YOUR PEOPLE
 LEADING FROM THE HEART AND WITH YOUR PEOPLE WHY PARTICIPATIVE LEADERSHIP? Share decision making with group members Fosters a team approach to work and problem solving Helps to inspire and motivate people
LEADING FROM THE HEART AND WITH YOUR PEOPLE WHY PARTICIPATIVE LEADERSHIP? Share decision making with group members Fosters a team approach to work and problem solving Helps to inspire and motivate people
LEADERSHIP WHAT IS A LEADER? CHAPTER 12 THE MANAGER AS A LEADER
 CHAPTER 12 THE MANAGER AS A LEADER ANYONE CAN STEER THE SHIP, BUT IT TAKES A LEADER TO CHART THE COURSE LEADERSHIP WHAT IS A LEADER? Manager who earns the respect and cooperation of employees to effectively
CHAPTER 12 THE MANAGER AS A LEADER ANYONE CAN STEER THE SHIP, BUT IT TAKES A LEADER TO CHART THE COURSE LEADERSHIP WHAT IS A LEADER? Manager who earns the respect and cooperation of employees to effectively
Leadership CHAPTER SIXTEEN INTRODUCTION DETAILED LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER SIXTEEN Leadership INTRODUCTION I must follow the people. Am I not their leader? Benjamin Disraeli. The current chapter discusses leadership, a topic as complex as this quotation indicates. Indeed,
CHAPTER SIXTEEN Leadership INTRODUCTION I must follow the people. Am I not their leader? Benjamin Disraeli. The current chapter discusses leadership, a topic as complex as this quotation indicates. Indeed,
Interpreting Your Leadership Circle Profile
 Interpreting Your Leadership Circle Profile The Leadership Circle Profile is the most comprehensive leadership assessment system available. It is organized into a very powerful system for understanding
Interpreting Your Leadership Circle Profile The Leadership Circle Profile is the most comprehensive leadership assessment system available. It is organized into a very powerful system for understanding
A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT
 A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT ENHANCING LEADERSHIP CAPABILITY Questions to consider What values should guide my actions? How do I best set an example for others? How do I articulate a vision of the future? How
A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT ENHANCING LEADERSHIP CAPABILITY Questions to consider What values should guide my actions? How do I best set an example for others? How do I articulate a vision of the future? How
4. A mission statement must be converted into goals to become operational and useful. Ans: True Page: 32 Difficulty: Easy
 Chapter 2 Models of Organizational Behavior True/False Questions 1. The philosophy of organizational behavior held by a manager stems from fact premises and value premises. Page: 31 2. Value premises represent
Chapter 2 Models of Organizational Behavior True/False Questions 1. The philosophy of organizational behavior held by a manager stems from fact premises and value premises. Page: 31 2. Value premises represent
Competencies. Working in Partnership. Creativity and Innovation Organisational and People Development
 Competencies Leadership Competency Framework - Summary Technical Expertise Demonstrates an avid interest in continuously enhancing current skills and learning new ones; applies advanced functional or technical
Competencies Leadership Competency Framework - Summary Technical Expertise Demonstrates an avid interest in continuously enhancing current skills and learning new ones; applies advanced functional or technical
Leadership. The Nature of Leadership 12/18/2012. Learning Objectives. The Nature of Leadership. The Nature of Leadership. The Nature of Leadership
 Learning Objectives Leadership Chapter 10 website Mark Gosling Office: D404 Phone: 5417 Email: markg@mail.nkuht.com.tw LO1 What is leadership LO2 What traits does a leader have? LO3 Talk about leadership
Learning Objectives Leadership Chapter 10 website Mark Gosling Office: D404 Phone: 5417 Email: markg@mail.nkuht.com.tw LO1 What is leadership LO2 What traits does a leader have? LO3 Talk about leadership
Motivational Needs Assessment
 Self Assessments for Book So You Think You Can LEAD? Instructions: Motivational Needs Assessment Based on David McClelland s Theory of Learned Motives Place an X in the box in front of the statement in
Self Assessments for Book So You Think You Can LEAD? Instructions: Motivational Needs Assessment Based on David McClelland s Theory of Learned Motives Place an X in the box in front of the statement in
Leadership Theory and Practice Bronwyn Coulton Professional Practice Manager Northland Kindergarten Association Te amorangi ki mua, te hapai o ki
 Leadership Theory and Practice Bronwyn Coulton Professional Practice Manager Northland Kindergarten Association Te amorangi ki mua, te hapai o ki muri The leader at the front and the workers behind the
Leadership Theory and Practice Bronwyn Coulton Professional Practice Manager Northland Kindergarten Association Te amorangi ki mua, te hapai o ki muri The leader at the front and the workers behind the
Chapter 10 LEADERSHIP [PowerPoint Slide 1]
![Chapter 10 LEADERSHIP [PowerPoint Slide 1] Chapter 10 LEADERSHIP [PowerPoint Slide 1]](/thumbs/89/98634656.jpg) Chapter 10 LEADERSHIP [PowerPoint Slide 1] Chapter 10 explains the nature of organizational leadership and what a leader must do to be effective. Here we synthesize a number of ideas particularly relevant
Chapter 10 LEADERSHIP [PowerPoint Slide 1] Chapter 10 explains the nature of organizational leadership and what a leader must do to be effective. Here we synthesize a number of ideas particularly relevant
DANTES Fact Sheet. Study Guide. Subject Standardized Tests ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR TEST INFORMATION CONTENT
 DANTES Fact Sheet Study Guide Subject Standardized Tests ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR TEST INFORMATION This test was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that
DANTES Fact Sheet Study Guide Subject Standardized Tests ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR TEST INFORMATION This test was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that
DNA 25. Dina Sample. Talent. ABC Corp NEW 25. Copyright Target Training International, Ltd.
 DNA 25 Talent ABC Corp 12-23-2015 NEW 25 Introduction Your success in any job depends on the value of your contribution to the organization. Managers, mentors and professional coaches can encourage, advise
DNA 25 Talent ABC Corp 12-23-2015 NEW 25 Introduction Your success in any job depends on the value of your contribution to the organization. Managers, mentors and professional coaches can encourage, advise
A Study On Organizational Climate At Jbm Auto Systems Pvt Ltd, Chennai
 A Study On Organizational Climate At Jbm Auto Systems Pvt Ltd, Chennai M. Venkatesh, PG Scholar, P.S.R. Engineering College, Sivakasi. 1. S. Saranya Jegajothi, AP/MBA., P.S.R. Engineering College, Sivakasi.
A Study On Organizational Climate At Jbm Auto Systems Pvt Ltd, Chennai M. Venkatesh, PG Scholar, P.S.R. Engineering College, Sivakasi. 1. S. Saranya Jegajothi, AP/MBA., P.S.R. Engineering College, Sivakasi.
Executive Director Performance Review
 Executive Director Performance Review Board Toolkit October 2012 The board s role in growing and developing the organization includes assessment of the Executive Director. The performance review process
Executive Director Performance Review Board Toolkit October 2012 The board s role in growing and developing the organization includes assessment of the Executive Director. The performance review process
by Frederic J. Gratto
 by Frederic J. Gratto In a profession as technical as facilities management all the hardware in the world can be a mighty force. Nonetheless, the software of management skill matters more than ever before.
by Frederic J. Gratto In a profession as technical as facilities management all the hardware in the world can be a mighty force. Nonetheless, the software of management skill matters more than ever before.
Motivating and Rewarding Employees
 11Chapter Motivating and Rewarding Employees Pearson Education Limited 2015 11-1 Learning Outcomes Define and explain motivation. Compare and contrast early theories of motivation. Compare and contrast
11Chapter Motivating and Rewarding Employees Pearson Education Limited 2015 11-1 Learning Outcomes Define and explain motivation. Compare and contrast early theories of motivation. Compare and contrast
Introducing Management
 Introducing Management Definitions Management roles Management & leadership Core qualities of managers Levels of management Competency-driven management Challenges of managing diverse workforces in diverse
Introducing Management Definitions Management roles Management & leadership Core qualities of managers Levels of management Competency-driven management Challenges of managing diverse workforces in diverse
ASSESSING LEADERSHIP STYLE IN MULTICULTURAL TEAM
 ASSESSING LEADERSHIP STYLE IN MULTICULTURAL TEAM B. B. Biradar 1, Dr. Vishnukant. S. Chatpalli 2 1 Research Scholar, Dept of Business Administration, Rani Channamma University, Belagavi (India) 2 Professor,
ASSESSING LEADERSHIP STYLE IN MULTICULTURAL TEAM B. B. Biradar 1, Dr. Vishnukant. S. Chatpalli 2 1 Research Scholar, Dept of Business Administration, Rani Channamma University, Belagavi (India) 2 Professor,
myskillsprofile MLQ30 Management and Leadership Report John Smith
 myskillsprofile MLQ30 Management and Leadership Report John Smith Management and Leadership Questionnaire 2 INTRODUCTION The Management and Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ30) assesses management and leadership
myskillsprofile MLQ30 Management and Leadership Report John Smith Management and Leadership Questionnaire 2 INTRODUCTION The Management and Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ30) assesses management and leadership
CHAPTER 12 THE MANAGER AS A LEADER
 CHAPTER 12 pp smartboard.notebook CHAPTER 12 THE MANAGER AS A LEADER ANYONE CAN STEER THE SHIP, BUT IT TAKES A LEADER TO CHART THE COURSE 1 WHAT IS A LEADER? Manager who earns the respect and cooperation
CHAPTER 12 pp smartboard.notebook CHAPTER 12 THE MANAGER AS A LEADER ANYONE CAN STEER THE SHIP, BUT IT TAKES A LEADER TO CHART THE COURSE 1 WHAT IS A LEADER? Manager who earns the respect and cooperation
International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2014, Vol 1, No.6,
 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2014, Vol 1, No.6, 49-54. 49 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Study of Importance of Empowered
International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2014, Vol 1, No.6, 49-54. 49 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Study of Importance of Empowered
A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT
 A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT Learning Objective Goal To strengthen leadership capability and organizational culture by providing an integrated leadership framework (language and linked set of tools) Outcome To
A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT Learning Objective Goal To strengthen leadership capability and organizational culture by providing an integrated leadership framework (language and linked set of tools) Outcome To
BOH4M Final Exam Review
 Unit 1: Foundations of Management Four Functions of Management: BOH4M Final Exam Review Management Functions Planning setting objectives and determining what actions should be taken to accomplish them
Unit 1: Foundations of Management Four Functions of Management: BOH4M Final Exam Review Management Functions Planning setting objectives and determining what actions should be taken to accomplish them
1300 mindworx Overview
 TECHNOLOGY RECRUITMENT SPECIALISTS > Contract Recruitment > Permanent Recruitment > Direct Contractor Payroll > Strategic HR Consulting 1300 mindworx www.mindworx.com.au Overview Define Psychometrics Link
TECHNOLOGY RECRUITMENT SPECIALISTS > Contract Recruitment > Permanent Recruitment > Direct Contractor Payroll > Strategic HR Consulting 1300 mindworx www.mindworx.com.au Overview Define Psychometrics Link
