NORMS PROMOTING CREATIVITY AND INNOVATION IN SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTERPRISES
|
|
|
- Theodore Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NORMS PROMOTING CREATIVITY AND INNOVATION IN SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTERPRISES Ľubica Lesáková Faculty of Economics, Matej Bel University, Tajovského St. 10, Banská Bystrica, Slovak Republik, Abstract Organizational culture plays an important role in supporting the creative processes, because it can promote or hinder innovation-enhancing norms. Innovative small and medium enterprises tend to develop culture, which emphasize and reward values and norms that support the generation and implementation of new ideas. Such a system encourages everyone in enterprise to develop original and useful proposals. They promote innovative ways of solving problems and finding solutions. Over the years, researchers have documented a variety of norms that promote consistently creativity and innovation in organizational settings. The aim of the article is to present the organizational culture, especially the innovation-enhancing norms, as important elements, that promote creativity and innovation in small and medium enterprises. The paper was elaborated a sa part of VEGA project 1/0654/11 Innovative Small and Medium Enterprises as a Part of Knowledge-Based Economy in the SR. Key words: small and medium enterprises, organizational culture, behavioral norms, creativity, innovation. 1. Introduction There are many driving forces that promote creativity and innovation in enterprises. In the last decade managers and theorists started to recognize, that one of the main driving forces behind creativity and innovation, is the organizational culture, especially the innovation-enhancing norms that promote creativity and innovation ( Andriopoulos C., Dawson P., 2010). It can be stated, that the components of organizational culture (shared values, beliefs and behavioral norms) are key in promoting the generation and implementation of new and useful ideas. In accordance with shared norms, staff will decide on wheater creative and innovative behaviour is a part of the internal environment in which small and medium enterprises operate. Moreover, the dominant values, beliefs and behavioral norms, which are incorporated in the management practices of the small and medium enterprises, may directly or indirectly support or hinder creativity and innovation in the workplace. Innovative small and medium enterprises tend to develop culture, which emphasize and reward values and norms that support the generation and implementation of new ideas. Such a systems encourage everyone in enterprise to develop original and useful proposals. They promote innovative ways of solving 44
2 problems and finding solutions. Innovative enterprises value flexibility, mobilize freedom within the work setting and encourage co-operative team work. These are important in promoting the creativity and innovation. The aim of the paper is to present the organizational culture, especially the innovation-enhancing norms, as an important elements, that promote creativity and innovation in small and medium enterprises. The paper was elaborated a sa part of VEGA project 1/0654/11 Innovative small and medium enterprises as a part of knowledge-based economy in the SR. 2. Norms promoting creativity and innovation Innovation usually involves risk taking, nonstandard solutions and unconventional teamwork practices (elements that are not easily managed by formal control systems). The effective management of culture is critical in mobilizing organizational creativity and innovation. Crutial in this efforts is the establishment and continuous encouragement of behavioural norms that promote the generation and implementation of new solutions. These norms refer to the socially created expectations that guide the acceptance of attitudes and behaviour in the work setting ( Grieves J., 2010,). Over the years, researchers have documented a variety of norms that promote consistently creativity and innovation in oganizational settings. Main of these norms are discusses in more detail below. It may sound obvious, but promoting behaviour, which supports idea generating, is a key for mobilizing creativity in the work. Managers building the creative environment need to promote open communication and forum of intra- and extra-organizational debate. Sustaining such an information flow is crutial. Lack of information hinders creativity in organizational settings; building organizational culture needs to encourage open discussion, constructive conflict, fair evaluation of ideas and fast approvals ( Bessant J., Tidd J., 2009). All this of course, needs to happen in a positive cooperative atmosphere, because conflict across enterprise could bring the opposite results. Creativity is promoted in such an environment, where continuous learning is a firm-wide expectation. Employees should have a continuously curious attitude; this will allow them to discover and explore new ideas and potentially identify new and valuable solutions. Keeping staff s knowledge and skills up to date, is a key in this respect. The creative process often involves a risk taking. The generation of ideas requires experimentation and, as such, taking risks is usually unavoidable (and often necessary). Encouraging risk taking behaviour needs therefore to be a part of the creative culture. To mobilize and encourage risk taking, managers need to avoid applying too many controls in the creative process, because it may likely to stop experimentation and to slow down creative flow. However, creative small and medium enterprises have to face a commercial reality, because excessive risk taking may lead to costly results on profit and loss account. Experimentation and risk taking may lead to mistakes. Mistakes are therefore an everyday practice in creative environment. Supporting a culture that tolerates mistakes and handles them effectively, is important in encouraging staff to 45
3 think and act creatively. Creative enterprises need to have faith in their employees to try new things, even if this leads to failure or disappointing results. Enterprises, that punish employee mistake, discourage creativity and inhibit innovation. Creative small and medium enterprises need therefore to acknowledge failure and constantly create opportunities to openly discuss mistakes and learn from the falls of the creative process. The successful management of mistakes often relies on manager s skills to clarify which mistakes are acceptable and which are not. Positive examples confirm, that behaviour that is promoting change in the work setting may influence positively organizational creativity and innovation. To support creativity, the culture must tolerate uncertainty, promote and reward positive attitudes towards change and encourage employees to change constantly the status quo and explore new ways of finding creative solutions ( Monch A., 2006). Change and constant experimentation may likely lead in the workplace to conflict; conflict between colleagues, conflict between departments, conflict between individual s creative freedom and the constraints set by the client s commercial reality. Managers in creative enterprises often complain about handling a conflict between the creatives and the non-creatives. This is the reason why many creative enterprises try to employ managers with technical as well as business experience with the aim to overcome the gap between these two disciplines. The literature suggests that enterprises need to expect and tolerate conflict and handle it effectively in order to support creative behaviour in the worksetting. As the starting point of creativity often comes out from individual expression; it is important to acknowledge and to be sensitive to different styles of working. At the same time, managers need to train employees in the process of constructive confrontation in order to promote constructive feedback and an open, supportive culture in the workplace. 3. Norms promoting implementation of innovative ideas Though creativity is important, commercial reality requires implementation; ideas need to be turned into innovations that will positively influence the corporate profit. In order to encourage action, several norms are important. The main norms are: an emphasis on team work and effective group functioning, a focus on speed and urgency, a need for flexibility and adaptability and a sence of autonomy (Walmsley B., 2009). The need for team work and effective group functioning is common in creative environment. Depending on the enterprise, teams may be fixed for each project, or staff may join different teams depending on the nature of the project. Staff may join different teams in order to promote a new perspective and encourage emploees to utilize their work capabilities and interpersonal skills. Employees need to be encouraged to work and communicate effectively. Implementation is successful when teams work harmoniously, communicate well and have common goals (Lesáková L. et al., 2009b). Promoting behaviours that support speed and urgency is important for quick translating ideas into innovations. After the initial experimentation stage, 46
4 which is a key in generating creative outputs, decisions need to be made quickly. Norms like speed, a sence of urgency and commitment to achieving deadlines (even if teams need to work long hours to achieve their goals) are also important. It seems that creativeness and the williness to discover and to deliver something new and novel, drive people to excel and redefines acceptable working hours. Promoting flexibility and adaptability in the workplace is a key factor in supporting implementation. The constructive confrontation in the creative process requires from staff to be open minded and flexible in their thinking. Changing the status quo and the way in which things can be done in a different way, is important for generating new solutions. Employees need to be perpetually challenged; this requires from employees strong characters that can constantly deal with change and cope with the inevitable conflict. Sustaining a sence of autonomy in the workplace is also important in promoting implementation in the work setting. Individuals need to be autonomous and take action without being asked to do so. This does not only promote the generation of new ideas, but also the quick implementation of valuable concepts. Developing a culture for creativity and innovation requires from managers to support perpetualy the generation and implementation of ideas in the workplace. This requires that managers avoid in the managerial work some mistakes (Monch A., 2006). Despite the fact, that innovation requires autonomy and personal initiative, overemphasizing individual accountability can be detrimental to the creative process. Though to staff has to be to given individual targets and has to be evaluated against their achieved outcomes, overemphasizing individual accountability can create a climate of fear and may discourage employees from taking the risks. It also goes against the requirement for open communication, constructive feedback and the necessity of an open learning culture. Moreover, though individual performance appraisals serve as essential human resource management tools, they need to be carefully implemented and not promote a risk averse culture. Though enterprises need to consider also financial constraints, overemphasizing quantitative goals and financial budgets rarely promotes a culture of perpetual discovery and innovation. Objectives and financial constraints will certainly set the frame, in which the creative process will be initiated, but employees also need to be encouraged to act outside the firm and, if necessary, negotiate with the client or their company for exta resources. The way how enterprises handle the inevitable mistakes can increase or constrain creative processes at work. Punishing mistakes is a common fall in business environments; it creates a culture of fear and hinders organizational creativity. Managers need to acknowledge mistakes as part of the learning experience. Creative thinking involves (often long) trial-and-error processes and punishing mistakes can be detrimental to the generation of new ideas. Enterprises that are innovation driven, tend to promote a forgiveness culture ( Berchicci L., 47
5 2009). Such a managerial attitude mobilizes an action across the enterprise, where people focus on doing things rather than on hesitating because of fear of failure. Promoting internal competition is often used as a mean for mobilizing initiative within a work settings. However, innovation usually entails collaboration across intra- or extra-organizational boundaries. Consequently, promoting internal competition may hinder effective team working and stimulate organizational politicking that may be detrimental to the creative process. Though managers increasingly acknowledge the value of creativity and innovation as a means of developing and sustaining competitive advantage, paradoxically, many enterprises strive to be the same as their competitors. They use similar processes, generate similar products and avoid the implementation of risky novel ideas and practices. Innovation requires managers to be different, because the profit from successful innovations is far greater than that achieved through imitation. 4. Principles of creativity and innovation Organizational culture is important determinant of organizational creativity and innovation. Several authors have proposed principles, that enterprises should follow in order to build and sustain a culture that promotes the generation and implementation of new ideas and novel outcomes ( Beerel A., 2009, Grieves J., 2010). Building of an innovative culture requires creating an environment of faith and trust, in which good ideas have a chance to become great products. Truly innovative companies maintain creativity and innovation as a key corporate priority. Rather than focusing on safe ready made solutions, visionary managers see and continuously support the world of discovery and the fact that innovation helps to increase profitability (Lesáková L., 2009a). Be truly experimental in all parts of the businesss process is a critical part of the creative process. Especially in the early stages of creative discovery, encouraging employees in creative endeavours and taking sensible risk, is important. Creative employees need to be constantly challenged and highly experimental work can help in this respect. Building close relationships between marketing and technical people. Promoting close and meaningful relationships between the technical innovators and the marketing people is another essential principle for promoting a culture of creativity and change. Although such arrangements may create some conflict, open communication and constructive criticism between marketing and technical people is critical. Some authors encourage enterprises to bring together these two functions formally and informally ( Andriopoulos C., Dawson P., 2010). Such a relationship does not solve the traditional tensions between cost control and experimentation, but also helps to provide a balance between the ideas of creative discovery and the concept of feasibility. Building customer intimacy. The commercial reality requires from enterprises to anticipate and to meet market driven requirements. Innovative enterprises achieve the customer intimacy by observing potential users, videotaping 48
6 their actions, interviewing key stakeholders and studying customer s lifestyles and product decisions. They also increasingly employ sociologists, antropologists, who are becoming part of the creative process; larger enterprises increasingly employ them as full-time staff, while smaller firms often subcontract their services. Being creative in enterprises should not be a privilege of selected few employees. Visionary leaders try to engage the whole enterprise in generating and implementing new solutions. Creating a sense of community, where everyone works to achieve a common goal and beliefs in the value of discovery and innovation, is critical. This is organized both formally and informally. Formally, through planned communication activities such as: regular meetings motivating staff and providing opportunities for feedback, through s celebrating achievements, through internet that bring the employees together. Informally, by leading by example, initiating social get togethers, engaging staff in discussions and others (Berchicci L., 2009). Acknowledging the individual, providing opportunities for personal expression and encouraging employees to work on challenging projects, that all is important in mobilizing culture of creativity and innovation. Innovative companies create a fun working environment and support employees in achieving their ambitions. A key principle for fostering creative culture in enterprises is a collaborative approach to management, in which employees are constantly aware of the company s actions and are able to present their views and opinions in numerous formal and informal occasions. Creating a no fear climate and culture that supports experimentation is essential in mobilizing innovation-enhancing behaviour. The fair of failure can be detrimental to organizational creativity. Creating a system that supports individuals in their creative endeavours helps to foster a no fear climate in the workplace. 5. Conclusion The concept of organizational culture is one of the widely researched management topics. Culture plays an important role in supporting the creative process, because it can promote or hinder innovation-enhancing behavioural norms. Norms like risk taking, a tolerance of mistakes, and continuous support for change, are some of the attitudes and behaviors, those innovative enterprises try to promote in their culture. Organizational culture is increasingly seen as an element which, if effectively managed, could provide enterprises with managerial effectiveness. Encouraging and sustaining an organizational culture, which promotes the generation and implementation of new ideas among organizational members, is considered central to development of creative and innovative worksettings. Culture is considered as a form of social control that is characterized as a shared phenomenon, which exists in both visible artefacts and mission statements as well as in less visible and deeper levels. Strong cultures are not necessary conductive in generating and implementing new ideas in enterprises ( Grieves J., 2010). What is required is 49
7 culture, which helps to foster innovation-enhancing norms and at the same time promotes the social cohesion, necessary for turning ideas into innovations. Bibliography 1. Andriopoulos C., Dawson P., 2010, Managing Change and Innovation, SAGE Publications Ltd, London; 2. Beerel A., 2009, Leadership and Change Management, : SAGE Publications Ltd., London; 3. Berchicci L., 2009, Innovating for Sustainability, MPG Books Ltd., Bodmin, London; 4. Bessant J., Tidd J., 2009, Innovation and Entrepreneurship, John Wiley and Sons Ltd., Chichester, England; 5. Frappaolo C Knowledge Management. Chichester : Capstone Publishing Ltd., ISBN Grieves J., 2010, Organizational Change. Themes and Issues, Oxford University Press, London; 7. Lesáková L., 2009a., Determinants of Innovation Activities in Small and Medium Enterprises in Slovakia, in: Innovation - Factor Determining Competitiveness of Small and Medium Enterprises in the Global Business Environment, Faculty of Economics, Matej Bel University, Banska Bystrica; 8. Lesáková L. et al., 2009b, Innovative Management in the Knowledgebased Economy, Banska Bystrica, Faculty of Economics, Matej Bel University; 9. Monch A., 2006, Change Management, Carl Hanser Verlag, Munchen; 10. Walmsley B., 2009, Managing Change. Skills for success, Hodder Education Hachette Livre UK Company, London. 50
S & T Management Core Competency Profile
 (Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
(Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
VISION MISSION VALUES LEADERSHIP-PRINCIPLES
 VISION MISSION VALUES LEADERSHIP-PRINCIPLES VISION The Way We Are We are the formative force of the front-end module market! MISSION The Way We Are Innovation, know-how, internationality, flexibility,
VISION MISSION VALUES LEADERSHIP-PRINCIPLES VISION The Way We Are We are the formative force of the front-end module market! MISSION The Way We Are Innovation, know-how, internationality, flexibility,
Performance Skills Leader. Individual Feedback Report
 Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
BC Assessment - Competencies
 BC Assessment - Competencies This document provides a list and description of all of BC Assessment s core competencies, as well as the level of competency required for a given position, as defined in each
BC Assessment - Competencies This document provides a list and description of all of BC Assessment s core competencies, as well as the level of competency required for a given position, as defined in each
COMPETENCY PROFILE FOR THE RESEARCH, ANALYSIS AND LIBRARY SPECIALISTS GROUP
 COMPETENCY PROFILE FOR THE RESEARCH, ANALYSIS AND LIBRARY SPECIALISTS GROUP Introduction What is a competency profile? Competencies are specific behavioural manifestations of knowledge, skills and qualities
COMPETENCY PROFILE FOR THE RESEARCH, ANALYSIS AND LIBRARY SPECIALISTS GROUP Introduction What is a competency profile? Competencies are specific behavioural manifestations of knowledge, skills and qualities
S E L E C T D E V E L O P L E A D H O G A N L E A D V A L U E S CORE VALUES AND MOTIVATORS FOR LEADERSHIP ROLES. Report for: John Doe ID: HA154779
 S E L E C T D E V E L O P L E A D H O G A N L E A D V A L U E S CORE VALUES AND MOTIVATORS FOR LEADERSHIP ROLES Report for: John Doe ID: HA154779 Date: November, 09 2 0 0 9 H o g a n A s s e s s m e n
S E L E C T D E V E L O P L E A D H O G A N L E A D V A L U E S CORE VALUES AND MOTIVATORS FOR LEADERSHIP ROLES Report for: John Doe ID: HA154779 Date: November, 09 2 0 0 9 H o g a n A s s e s s m e n
Behavioural Attributes Framework
 Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
CORE COMPETENCIES. For all faculty and staff
 SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
COMPETENCY PROFILE FOR THE PROFESSIONALS AND TECHNICAL SPECIALISTS GROUP
 COMPETENCY PROFILE FOR THE PROFESSIONALS AND TECHNICAL SPECIALISTS GROUP Introduction What is a competency profile? Competencies are specific behavioural manifestations of knowledge, skills and qualities
COMPETENCY PROFILE FOR THE PROFESSIONALS AND TECHNICAL SPECIALISTS GROUP Introduction What is a competency profile? Competencies are specific behavioural manifestations of knowledge, skills and qualities
Contents 5. Building and Maintaining an Effective Team 6. An Overview of Planning and Estimating
 TEAMFLY vi Contents 5. Building and Maintaining an Effective Team 77 The Mechanics of Building a Team 78 Team Leadership Starts on Day One! 83 Fostering Teamwork and Synergism 88 Getting the Most from
TEAMFLY vi Contents 5. Building and Maintaining an Effective Team 77 The Mechanics of Building a Team 78 Team Leadership Starts on Day One! 83 Fostering Teamwork and Synergism 88 Getting the Most from
Competency Catalog June 2010
 Competency Catalog June 2010 Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are those generic or cross-organizational competencies that are applicable to various functions and/or posts. They focus on
Competency Catalog June 2010 Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are those generic or cross-organizational competencies that are applicable to various functions and/or posts. They focus on
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT CONTRIBUTION TO ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE IN THE CONTEXT OF GLOBALIZATION
 HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT CONTRIBUTION TO ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE IN THE CONTEXT OF GLOBALIZATION Luţ Dina Maria lecturer, PHD student Christian University Dimitrie Cantemir Faculty of Management in
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT CONTRIBUTION TO ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE IN THE CONTEXT OF GLOBALIZATION Luţ Dina Maria lecturer, PHD student Christian University Dimitrie Cantemir Faculty of Management in
High Performance Organization
 Kai Laamanen HPO description 1 (6) 15.10.2007 High Performance Organization Leaders of today face ever-increasing complexity in private business and public sector. Innotiimi meets the growing need for
Kai Laamanen HPO description 1 (6) 15.10.2007 High Performance Organization Leaders of today face ever-increasing complexity in private business and public sector. Innotiimi meets the growing need for
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK 1 Introduction to the Leadership Competency Framework The Leadership Competency Framework focuses on three levels of management: Team Leaders/Supervisors responsible for
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK 1 Introduction to the Leadership Competency Framework The Leadership Competency Framework focuses on three levels of management: Team Leaders/Supervisors responsible for
Cultural Intelligence
 July 2007 Cultural Intelligence - A concept for bridging and benefiting from cultural differences By Elisabeth Plum (Translated and commented by Dympna Cunnane) What have international relations, mergers
July 2007 Cultural Intelligence - A concept for bridging and benefiting from cultural differences By Elisabeth Plum (Translated and commented by Dympna Cunnane) What have international relations, mergers
TQM Implementation for Effective Project Management
 TQM Implementation for Effective Project Management Ion STANCIU Faculty of Tourism and Commercial Management Email: Ion_stanciu@hotmail.com Bogdănel DRĂGUŢ Faculty of Tourism and Commercial Management
TQM Implementation for Effective Project Management Ion STANCIU Faculty of Tourism and Commercial Management Email: Ion_stanciu@hotmail.com Bogdănel DRĂGUŢ Faculty of Tourism and Commercial Management
Leadership Agility Profile: 360 Assessment. Prepared for J. SAMPLE DATE
 Prepared for J. SAMPLE About this Report Introduction LEADERSHIP that special quality that enables leaders to achieve extraordinary success. In today's uncertain world the need for leadership is at an
Prepared for J. SAMPLE About this Report Introduction LEADERSHIP that special quality that enables leaders to achieve extraordinary success. In today's uncertain world the need for leadership is at an
The components of an innovative organization part 2
 The components of an innovative organization part 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2009 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.managing-innovation.com 2 3. KEY INDIVIDUALS Key individuals are those figures that have a critical importance
The components of an innovative organization part 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2009 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.managing-innovation.com 2 3. KEY INDIVIDUALS Key individuals are those figures that have a critical importance
NORTHUMBRIA POLICE ICF COMPETENCIES
 NORTHUMBRIA POLICE ICF COMPETENCIES What is ICF? Since May 2007, the new Integrated Competency Framework (ICF) has applied to all recruitment process within Northumbria Police. The Integrated Competency
NORTHUMBRIA POLICE ICF COMPETENCIES What is ICF? Since May 2007, the new Integrated Competency Framework (ICF) has applied to all recruitment process within Northumbria Police. The Integrated Competency
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
Profile Comparison Top-Leader
 Limbic Personality GmbH Profile Comparison Top-Leader Peter Mustermann Presented by The Limbic Personality Profile Comparison for Top Leaders There are a lot of leaders in the market but only those with
Limbic Personality GmbH Profile Comparison Top-Leader Peter Mustermann Presented by The Limbic Personality Profile Comparison for Top Leaders There are a lot of leaders in the market but only those with
Putting our behaviours into practice
 Putting our behaviours into practice Introduction Our behaviours are an important part of One Housing. They are designed to shape how we work - they are the ideas and approaches that form the foundation
Putting our behaviours into practice Introduction Our behaviours are an important part of One Housing. They are designed to shape how we work - they are the ideas and approaches that form the foundation
9-1. Managing Leadership. Essentials of Contemporary Management, 3Ce. Copyright 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 9 9-1 Managing Leadership Learning Objectives 9-2 1. Describe what leadership is and on what bases of power leaders influence others. 2. Describe the early trait and behavioural theories of leadership
9 9-1 Managing Leadership Learning Objectives 9-2 1. Describe what leadership is and on what bases of power leaders influence others. 2. Describe the early trait and behavioural theories of leadership
Respect Innovate Support Excel
 SRUC Shared Values The work of every employee at SRUC contributes to the achievement of our strategic outcomes, it is therefore important that we all have a clear understanding of what our role is and
SRUC Shared Values The work of every employee at SRUC contributes to the achievement of our strategic outcomes, it is therefore important that we all have a clear understanding of what our role is and
6 CRITICAL LEADERSHIP CAPACITIES TO GET YOUR ORGANISATION FROM HERE TO THERE
 The defining trait of organisations that successfully grow and navigate critical change is the practice of regularly revising their form of leadership, thinking and operations. Simply put, these great
The defining trait of organisations that successfully grow and navigate critical change is the practice of regularly revising their form of leadership, thinking and operations. Simply put, these great
DEAF DIRECT: Performance Management Policy: April Performance Management Policy
 Performance Management Policy 1 Contents Introduction Aims of the Performance Management Process Benefits of the Performance Management Process Key Principles of the Process Job Descriptions Planning Performance
Performance Management Policy 1 Contents Introduction Aims of the Performance Management Process Benefits of the Performance Management Process Key Principles of the Process Job Descriptions Planning Performance
City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council
 City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council 1.CM.250 Issue 3 Nov-2014 Process Owner: Organisational Development Team Authorisation: Deborah Morley Page
City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council 1.CM.250 Issue 3 Nov-2014 Process Owner: Organisational Development Team Authorisation: Deborah Morley Page
Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara
 Leads Innovation Leadership Styles Manages Change Models Integrity, Trust & Transparency Strategic Thinking and Planning Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara Conflict Management
Leads Innovation Leadership Styles Manages Change Models Integrity, Trust & Transparency Strategic Thinking and Planning Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara Conflict Management
The components of an innovative organization part 2
 The components of an innovative organization part 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2009 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.managing-innovation.com 2 3. KEY INDIVIDUALS Key individuals are those figures that have a critical importance
The components of an innovative organization part 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2009 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.managing-innovation.com 2 3. KEY INDIVIDUALS Key individuals are those figures that have a critical importance
UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators
 UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators Rev. 08/21/2014 COM M UNI C AT I O N Shares and receives information using clear oral, written, and interpersonal communication skills. Behavioral
UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators Rev. 08/21/2014 COM M UNI C AT I O N Shares and receives information using clear oral, written, and interpersonal communication skills. Behavioral
OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION
 OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION By always VALUING PEOPLE Leading myself and others Working together as a team ACHIEVING THE VISION... Delivering great service Taking a professional
OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION By always VALUING PEOPLE Leading myself and others Working together as a team ACHIEVING THE VISION... Delivering great service Taking a professional
DNA 25. Dina Sample. Talent. ABC Corp NEW 25. Copyright Target Training International, Ltd.
 DNA 25 Talent ABC Corp 12-23-2015 NEW 25 Introduction Your success in any job depends on the value of your contribution to the organization. Managers, mentors and professional coaches can encourage, advise
DNA 25 Talent ABC Corp 12-23-2015 NEW 25 Introduction Your success in any job depends on the value of your contribution to the organization. Managers, mentors and professional coaches can encourage, advise
cambridge Institute for Family Enterprise
 Professionalizing the Family Business: It s Not What You Think It Is John A. Davis Cambridge Institute for Family Enterprise cambridge Institute for Family Enterprise At some point in the life of a family
Professionalizing the Family Business: It s Not What You Think It Is John A. Davis Cambridge Institute for Family Enterprise cambridge Institute for Family Enterprise At some point in the life of a family
Managing Up, Down, and Around
 Managing Up, Down, and Around Rich Orbé-Austin, PhD Dynamic Transitions Psychological Consulting January 2018 Session Objectives! To discuss the distinct challenges of management! To distinguish the varied
Managing Up, Down, and Around Rich Orbé-Austin, PhD Dynamic Transitions Psychological Consulting January 2018 Session Objectives! To discuss the distinct challenges of management! To distinguish the varied
Transforming Healthcare Organizations. Healthier Workers. Healthier Leaders. Healthier Organizations.
 Transforming Healthcare Organizations Healthier Workers. Healthier Leaders. Healthier Organizations. Acknowledgements: Authored by Dr. Graham Dickson, LEADS Canada The following document is a summary of
Transforming Healthcare Organizations Healthier Workers. Healthier Leaders. Healthier Organizations. Acknowledgements: Authored by Dr. Graham Dickson, LEADS Canada The following document is a summary of
CITB-ConstructionSkills BEHAVIOURAL COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 STRATEGIC AWARENESS Definition The ability to stand back and think about the broader perspective in order to visualise the way forward. Thinks ahead and plans for the future Continuously looks for better
STRATEGIC AWARENESS Definition The ability to stand back and think about the broader perspective in order to visualise the way forward. Thinks ahead and plans for the future Continuously looks for better
The importance of control in managerial work
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The importance of control in managerial work Andrea Cambalikova and Juraj Misun University of Economics in Bratislava, Faculty of Business Management, Department of Management
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The importance of control in managerial work Andrea Cambalikova and Juraj Misun University of Economics in Bratislava, Faculty of Business Management, Department of Management
Bank of Kathmandu Limited
 KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT HRD Climate Survey and Analysis Report of Bank of Kathmandu Limited Submitted to: Asst. Prof. Seema Singh Human Resource Development Submitted by: Ginish Jung
KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT HRD Climate Survey and Analysis Report of Bank of Kathmandu Limited Submitted to: Asst. Prof. Seema Singh Human Resource Development Submitted by: Ginish Jung
COUNTRY REPORT. Conduction of Online Survey in Estonia /O1/
 COUNTRY REPORT Conduction of Online Survey in Estonia /O1/ A. ACTIVITY INFORMATION Report objective: Time frame for online survey conduction /O1/: Deadline for submitting the report: To collect and analyze
COUNTRY REPORT Conduction of Online Survey in Estonia /O1/ A. ACTIVITY INFORMATION Report objective: Time frame for online survey conduction /O1/: Deadline for submitting the report: To collect and analyze
THE FIVE DYSFUNCTIONS OF A TEAM
 Members of truly cohesive teams: 1. Trust one another. 2. Engage in unfiltered conflict around ideas. 3. Commit to decisions and plans of action. 4. Hold one another accountable for delivering against
Members of truly cohesive teams: 1. Trust one another. 2. Engage in unfiltered conflict around ideas. 3. Commit to decisions and plans of action. 4. Hold one another accountable for delivering against
Corporate culture as a part of hiring process for cultural fit in Slovak enterprises
 Corporate culture as a part of hiring process for cultural fit in Slovak enterprises Alexandra Turáková* Prešovská univerzita v Prešove Katedra marketingu a medzinárodného obchodu Prešovská ul. 5, 080
Corporate culture as a part of hiring process for cultural fit in Slovak enterprises Alexandra Turáková* Prešovská univerzita v Prešove Katedra marketingu a medzinárodného obchodu Prešovská ul. 5, 080
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing
 A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing 9.14.2015 HR Toolkit http://www.unitedwayofcolliercounty.org/maphr 2015 Competence is the ability of an individual to do a job properly. Job competencies
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing 9.14.2015 HR Toolkit http://www.unitedwayofcolliercounty.org/maphr 2015 Competence is the ability of an individual to do a job properly. Job competencies
Hafan Cymru Job Description
 Job title Grade / Salary Scale Location Contract hours Working Pattern Responsible to Responsible for (staff / finance / Service Users /Customers Job Purpose Competency and Level required Project Manager
Job title Grade / Salary Scale Location Contract hours Working Pattern Responsible to Responsible for (staff / finance / Service Users /Customers Job Purpose Competency and Level required Project Manager
Positive Workplace Behaviours Guidance
 Positive behaviours in our workplace enable us to make a positive difference to the lives of everyone. How well we behave in our organisation is central to how well we deliver better services. Great results
Positive behaviours in our workplace enable us to make a positive difference to the lives of everyone. How well we behave in our organisation is central to how well we deliver better services. Great results
Unit 1. I.T.S Management & IT Institute Mohan Nagar, Ghaziabad
 Organization Behavior Unit 1 I.T.S Management & IT Institute Mohan Nagar, Ghaziabad Unit-1: Contents Concept, Nature, Importance & Characteristics of OB Conceptual Foundations Models of Organization Behavior
Organization Behavior Unit 1 I.T.S Management & IT Institute Mohan Nagar, Ghaziabad Unit-1: Contents Concept, Nature, Importance & Characteristics of OB Conceptual Foundations Models of Organization Behavior
John Kotter. Leading Change Heart of Change Our Iceberg Is Melting A Sense of Urgency. Slide 2
 5 John Kotter Leading Change Heart of Change Our Iceberg Is Melting A Sense of Urgency Slide 2 Succeeding in a Changing World Did not try to change They tried and failed They tried and succeeded but did
5 John Kotter Leading Change Heart of Change Our Iceberg Is Melting A Sense of Urgency Slide 2 Succeeding in a Changing World Did not try to change They tried and failed They tried and succeeded but did
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing. HR Toolkit
 A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing HR Toolkit 2015 Competency models help make transparent the skills an agency needs to be successful. Start by identifying competencies that predict
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing HR Toolkit 2015 Competency models help make transparent the skills an agency needs to be successful. Start by identifying competencies that predict
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
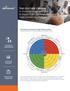 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
10 Human Resources management policies to support innovation Creating a Company Culture for Continuous Innovation
 10 Human Resources management policies to support innovation 10.2 Creating a Company Culture for Continuous Innovation Keywords Culture analysis; Innovation; Knowledge management; Knowledge sharing; Leadership;
10 Human Resources management policies to support innovation 10.2 Creating a Company Culture for Continuous Innovation Keywords Culture analysis; Innovation; Knowledge management; Knowledge sharing; Leadership;
EMPLOYEE ASSISTANCE PROGRAM. Workplace Training Programs
 EMPLOYEE ASSISTANCE PROGRAM Workplace Training Programs The Solutions Group offers more than 100 different training seminars and workshops, including Leadership Training, Employee Training and Work-Life
EMPLOYEE ASSISTANCE PROGRAM Workplace Training Programs The Solutions Group offers more than 100 different training seminars and workshops, including Leadership Training, Employee Training and Work-Life
Suggested Attributes to Determine Performance Evaluation Ratings
 Below are attributes to consider when looking for behaviors that represent an overall rating and/or a rating for each core expectation category. What behaviors define what a 5, 4, 3, and 2 rating looks
Below are attributes to consider when looking for behaviors that represent an overall rating and/or a rating for each core expectation category. What behaviors define what a 5, 4, 3, and 2 rating looks
IMPLEMENTATION OF KNOWLEDGE, SKILL AND ABILITY IN AN ORGANISATION FOR EFFECTIVE JOB PERFORMANCE.
 IMPLEMENTATION OF KNOWLEDGE, SKILL AND ABILITY IN AN ORGANISATION FOR EFFECTIVE JOB PERFORMANCE. Dr.K.R.Mahalaxmi 1 Madhunica Priyadharshini M. 2 Assistant Professor 1 PG Student 2 1,2 Department of Management
IMPLEMENTATION OF KNOWLEDGE, SKILL AND ABILITY IN AN ORGANISATION FOR EFFECTIVE JOB PERFORMANCE. Dr.K.R.Mahalaxmi 1 Madhunica Priyadharshini M. 2 Assistant Professor 1 PG Student 2 1,2 Department of Management
Key Competences Which behaviours should you be looking for?
 Key Competences Which behaviours should you be looking for? www.bucksandberks.co.uk Key competences: Which behaviours should you be looking for? When carrying out employee reviews, it can be hard to know
Key Competences Which behaviours should you be looking for? www.bucksandberks.co.uk Key competences: Which behaviours should you be looking for? When carrying out employee reviews, it can be hard to know
For internal circulation of BSNL only
 E4-E5 E5 (MANAGEMENT) Leadership & Team Building Leadership Fundamentals Understand.. Learning Objectives why leadership is important the difference between Management v/s Leadership components of effective
E4-E5 E5 (MANAGEMENT) Leadership & Team Building Leadership Fundamentals Understand.. Learning Objectives why leadership is important the difference between Management v/s Leadership components of effective
getabstract compressed knowledge Motivating Employees by Anne Bruce and James S. Pepitone 1999 McGraw-Hill 160 pages
 Motivating Employees by Anne Bruce and James S. Pepitone 1999 McGraw-Hill 160 pages Focus Leadership Strategy Sales & Marketing Corporate Finance Human Resources Technology Production & Logistics Small
Motivating Employees by Anne Bruce and James S. Pepitone 1999 McGraw-Hill 160 pages Focus Leadership Strategy Sales & Marketing Corporate Finance Human Resources Technology Production & Logistics Small
Employee Performance Review
 Employee Performance Review Employee s Name Title Department Supervisor s Name Type of Review (Initial/Annual/Follow-up) Date Tips for Completing the Employee Performance Review A current Position Description
Employee Performance Review Employee s Name Title Department Supervisor s Name Type of Review (Initial/Annual/Follow-up) Date Tips for Completing the Employee Performance Review A current Position Description
For internal circulation of BSNL only. Mobile Phone:
 E3-E4 E4 MANAGEMENT Leadership & Team Building Mobile Phone:09412739203 Email: chaubemc@bsnl.co.in Leadership Fundamentals Understand.. Learning Objectives why leadership is important the difference between
E3-E4 E4 MANAGEMENT Leadership & Team Building Mobile Phone:09412739203 Email: chaubemc@bsnl.co.in Leadership Fundamentals Understand.. Learning Objectives why leadership is important the difference between
The study of organisational culture Hofstede: Hofstede developed 5 dimensions of culture operating within organisational culture:
 Informal Organisation: perceptions of the organisation -The unofficial and less visible part of the organisation -What the workers really think about the organisation? -What is portrayed to the public
Informal Organisation: perceptions of the organisation -The unofficial and less visible part of the organisation -What the workers really think about the organisation? -What is portrayed to the public
ANA Adopted Values and Associated Behaviors. May 27, 2015
 Background ANA Adopted Values and Associated Behaviors May 27, 2015 - Values work launched at the February Directors Retreat. - A Values work group (Directors) determined and recommended a draft of 5 ANA
Background ANA Adopted Values and Associated Behaviors May 27, 2015 - Values work launched at the February Directors Retreat. - A Values work group (Directors) determined and recommended a draft of 5 ANA
Performance Leader Navigator Individual Feedback Report For: Chris Anderson
 For: Chris Anderson Finding your way in today's world of work Copyright ã 2007, 2008 Wilson Learning Worldwide Inc. This report includes ratings from: Self 1 Manager 1 Direct Report 5 Peer 3 Customer 4
For: Chris Anderson Finding your way in today's world of work Copyright ã 2007, 2008 Wilson Learning Worldwide Inc. This report includes ratings from: Self 1 Manager 1 Direct Report 5 Peer 3 Customer 4
Policy & Procedure : Job Banding & Competency Framework
 Policy & Procedure : Job Banding & Competency Framework Document owner: Personnel Manager Document version: V1 Document status: Agreed SMT Date: 1 September 2008 1. Background This Policy & Procedure is
Policy & Procedure : Job Banding & Competency Framework Document owner: Personnel Manager Document version: V1 Document status: Agreed SMT Date: 1 September 2008 1. Background This Policy & Procedure is
Organization Realignment
 Organization Realignment Collective Wisdom Fresh Ideas We are all drawn to tangible, concrete ideas. Consequently we find that when we are considering organizational change, there is a strong temptation
Organization Realignment Collective Wisdom Fresh Ideas We are all drawn to tangible, concrete ideas. Consequently we find that when we are considering organizational change, there is a strong temptation
The Power of People. Our University Our Future Our People
 The Power of People Our University Our Future Our People 2016-2021 The Power of People The Power of People builds on the significant achievements of Talent First, the University s People Strategy 2013-2015,
The Power of People Our University Our Future Our People 2016-2021 The Power of People The Power of People builds on the significant achievements of Talent First, the University s People Strategy 2013-2015,
Thinking about competence (this is you)
 CPD In today s working environment, anyone who values their career must be prepared to continually add to their skills, whether it be formally through a learning programme, or informally through experience
CPD In today s working environment, anyone who values their career must be prepared to continually add to their skills, whether it be formally through a learning programme, or informally through experience
Personal Qualities Framework for G3
 Personal Qualities Framework for G3 The following table below provides a summary of PQF behaviours by NCA grade. PQF - BEHAVIOURS DD G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 WORKING WITH OTHERS Communication A A B B C C D Teamwork
Personal Qualities Framework for G3 The following table below provides a summary of PQF behaviours by NCA grade. PQF - BEHAVIOURS DD G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 WORKING WITH OTHERS Communication A A B B C C D Teamwork
Facilities Training Brochure
 Facilities Training Brochure Training for Facilities Supervisors Mastery Series FY19 Spring Semester Fundamental Series Advanced Series Fundamental Supervisory Series Revised Dec 2018: Victoria O Connor
Facilities Training Brochure Training for Facilities Supervisors Mastery Series FY19 Spring Semester Fundamental Series Advanced Series Fundamental Supervisory Series Revised Dec 2018: Victoria O Connor
What are the common and unique Public Service competencies?
 ISBN 0-478-24459-2 June 2004 HR Framework: Building capability for public service What are the common and unique Public Service competencies? Competencies are defined as knowledge, skills, attributes and
ISBN 0-478-24459-2 June 2004 HR Framework: Building capability for public service What are the common and unique Public Service competencies? Competencies are defined as knowledge, skills, attributes and
CELONA APRIL BARCELONA APRIL BARCELONA APRIL 200. Principles of action. Principles of action
 CELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 200 Principles of action Principles of action LONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 2003. ..BARCELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA
CELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 200 Principles of action Principles of action LONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA APRIL 2003. ..BARCELONA APRIL 2003...BARCELONA
Correct principles are like compasses: they are always pointing the way. And if you know how to read them, we won t get lost, confused, or fooled by
 LEADERSHIP & ETHICS Correct principles are like compasses: they are always pointing the way. And if you know how to read them, we won t get lost, confused, or fooled by conflicting voices and values. -Stephen
LEADERSHIP & ETHICS Correct principles are like compasses: they are always pointing the way. And if you know how to read them, we won t get lost, confused, or fooled by conflicting voices and values. -Stephen
INNOVATION CULTURE AUDIT
 INNOVATION CULTURE AUDIT To get a quick snapshot of how the culture of your organisation performs across the dimensions that matter, take a few minutes to complete this questionnaire. Please rate your
INNOVATION CULTURE AUDIT To get a quick snapshot of how the culture of your organisation performs across the dimensions that matter, take a few minutes to complete this questionnaire. Please rate your
Description. Award Categories. Customer Service. Engagement
 Description The Rowan Recognition program recognizes and rewards faculty and staff for work and behaviors that support the mission, goals, values and initiatives of Rowan University. The work and behavior
Description The Rowan Recognition program recognizes and rewards faculty and staff for work and behaviors that support the mission, goals, values and initiatives of Rowan University. The work and behavior
Subject Name Paper Name Module Title Module Id Pre- Requisites Objectives. Keywords
 Items Subject Name Paper Name Module Title Module Id Pre- Requisites Objectives Keywords Description of Module Human Resource Management International Human Resource Management Management of Conflict Module
Items Subject Name Paper Name Module Title Module Id Pre- Requisites Objectives Keywords Description of Module Human Resource Management International Human Resource Management Management of Conflict Module
Dictionary of Functional Competencies for Career Banding
 Dictionary of Functional Competencies for Career Banding NC Office of State Personnel Revised April 18, 2007 Advocacy: Skills and abilities in developing and presenting the client s, patient s, and/or
Dictionary of Functional Competencies for Career Banding NC Office of State Personnel Revised April 18, 2007 Advocacy: Skills and abilities in developing and presenting the client s, patient s, and/or
Understanding leadership. To develop knowledge and understanding of leadership as required by a practising or potential first line manager.
 Module 1 Understanding leadership To develop knowledge and understanding of leadership as required by a practising or potential first line manager. Learning outcomes (the learner will) Understand leadership
Module 1 Understanding leadership To develop knowledge and understanding of leadership as required by a practising or potential first line manager. Learning outcomes (the learner will) Understand leadership
Dear IKEA friends, November Peter, Jonas and Mathias Kamprad. Inter IKEA Systems B.V IKEA key values
 IKEA key values Dear IKEA friends, Over the past few years the three of us have had the privilege to meet more than 2,000 IKEA leaders at the IKEA Way seminars. After listening to the feedback, as well
IKEA key values Dear IKEA friends, Over the past few years the three of us have had the privilege to meet more than 2,000 IKEA leaders at the IKEA Way seminars. After listening to the feedback, as well
Summary. I. The ABS Transformation
 Measuring culture change progress and leadership performance in the Australian Bureau of Statistics during Transformation Delivered by Samantha Palmer, General Manager, People, Capability and Communication,
Measuring culture change progress and leadership performance in the Australian Bureau of Statistics during Transformation Delivered by Samantha Palmer, General Manager, People, Capability and Communication,
Managing Change. Comportamiento organizacional. M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1
 Managing Change M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1 Outline Forces of Change External Forces Internal Forces Models of Planned Change Lewin s Change Model A Systems Model of Change Kotter s Eight Steps for
Managing Change M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1 Outline Forces of Change External Forces Internal Forces Models of Planned Change Lewin s Change Model A Systems Model of Change Kotter s Eight Steps for
Effectiveness Assessment Tool for High-Performance Social Change Organizations: An Overview
 Working Paper #1 Effectiveness Assessment Tool for High-Performance Social Change Organizations: An Overview Cheyanne Scharbatke-Church A high-performance social change organization is one that considers
Working Paper #1 Effectiveness Assessment Tool for High-Performance Social Change Organizations: An Overview Cheyanne Scharbatke-Church A high-performance social change organization is one that considers
ANALYST COMMENTS WRITTEN FOR: Carol SAMPLE
 For the position of: Prepared for: WSheaffer Client #: Analyst: WendyS QC: WendyS Profile #: Date: 1:Assertive, competitive 2:Cautious, helpful 3:Sociable, empathetic 4:Analytical, objective 5:Fast-paced,
For the position of: Prepared for: WSheaffer Client #: Analyst: WendyS QC: WendyS Profile #: Date: 1:Assertive, competitive 2:Cautious, helpful 3:Sociable, empathetic 4:Analytical, objective 5:Fast-paced,
Denis THIERY Chairman & Chief Executive Officer. Gilles WOZELKA Chief People & Transformation Officer
 GROUP CORE VALUES Message from Denis THIERY How Did We Choose Our Core Values? Neopost s four values - Focus on Customers, Foster Teamwork, Promote Innovation and Drive to Succeed - are the true cornerstones
GROUP CORE VALUES Message from Denis THIERY How Did We Choose Our Core Values? Neopost s four values - Focus on Customers, Foster Teamwork, Promote Innovation and Drive to Succeed - are the true cornerstones
COMPETENCY DICTIONARY
 COMPETENCY DICTIONARY COMPETENCY DICTIONARY 2 3 WHY WE DID IT? Working together as the Standard Profil Family, we identified a set of observable and quantifiable knowledge, skill and attitude, which plays
COMPETENCY DICTIONARY COMPETENCY DICTIONARY 2 3 WHY WE DID IT? Working together as the Standard Profil Family, we identified a set of observable and quantifiable knowledge, skill and attitude, which plays
The 10 Core Values of Zappos
 The 10 Core Values of Zappos Core values are what support the vision, shape the culture and reflect what the company values. They are the essence of the company s identity the principles, beliefs or philosophy
The 10 Core Values of Zappos Core values are what support the vision, shape the culture and reflect what the company values. They are the essence of the company s identity the principles, beliefs or philosophy
Dictionary of Functional Competencies for Career Banding
 Dictionary of Functional Competencies for Career Banding NC Office of State Personnel April 6, 2006 Advocacy: Demonstrates skills and abilities needed to effectively develop and present the client s, patient
Dictionary of Functional Competencies for Career Banding NC Office of State Personnel April 6, 2006 Advocacy: Demonstrates skills and abilities needed to effectively develop and present the client s, patient
Stages of Organisational Consciousness: Part II
 Stages of Organisational Consciousness: Part II Shaun McCarthy Managing Director and Chairman of Human Synergistics Australia March 2014 In our earlier paper, Stages of Organisational Consciousness: Part
Stages of Organisational Consciousness: Part II Shaun McCarthy Managing Director and Chairman of Human Synergistics Australia March 2014 In our earlier paper, Stages of Organisational Consciousness: Part
Staff Work Book. Social Policy Edition. Performance Review and Development. Name:
 Performance Review and Development Social Policy Edition Staff Work Book For staff who are required to register with: Scottish Social Service Council, Health Professions Council, Nursing and Midwifery
Performance Review and Development Social Policy Edition Staff Work Book For staff who are required to register with: Scottish Social Service Council, Health Professions Council, Nursing and Midwifery
Improving Change Management Application through Cultural Awareness and Adaptation
 Improving Change Management Application through Cultural Awareness and Adaptation By Rashelle Esparza and Robert Stise, Prosci Percent of respondents Abstract Prosci research explored the impact that culture
Improving Change Management Application through Cultural Awareness and Adaptation By Rashelle Esparza and Robert Stise, Prosci Percent of respondents Abstract Prosci research explored the impact that culture
Society Time for Change
 Well-Being, W ell-being ell-b, Good od Work Work & Society Time for Change 0161 232 4910 www.robertsoncooper.com www.carycooperblog.com The Business ess Well-Being Well Well-Being Being Network Annual
Well-Being, W ell-being ell-b, Good od Work Work & Society Time for Change 0161 232 4910 www.robertsoncooper.com www.carycooperblog.com The Business ess Well-Being Well Well-Being Being Network Annual
Assistant Deputy Minister, Finance and Corporate Services Ministry of Children and Family Development Victoria
 Assistant Deputy Minister, Finance and Corporate Services Ministry of Children and Family Development Victoria The Ministry of Children and Family Development supports healthy child development by its
Assistant Deputy Minister, Finance and Corporate Services Ministry of Children and Family Development Victoria The Ministry of Children and Family Development supports healthy child development by its
Fig.1. Project Organization Chart.
 THE PROJECT ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE A project organization is a structure that facilitates the coordination and implementation of project activities. Its main reason is to create an environment that fosters
THE PROJECT ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE A project organization is a structure that facilitates the coordination and implementation of project activities. Its main reason is to create an environment that fosters
THE WORLD OF ORGANIZATION
 22 THE WORLD OF ORGANIZATION In today s world an individual alone can not achieve all the desired goals because any activity requires contributions from many persons. Therefore, people often get together
22 THE WORLD OF ORGANIZATION In today s world an individual alone can not achieve all the desired goals because any activity requires contributions from many persons. Therefore, people often get together
The practice of constantly assessing personal knowledge and skills and following paths for improvement. have been done by
 Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Training & Development Brochure
 Training & Development Brochure Learning & Development Team Performance Being Intentional Ethics Employee Engagement Team Building The 5 Essential Leadership Questions Education & Training Compliance Training:
Training & Development Brochure Learning & Development Team Performance Being Intentional Ethics Employee Engagement Team Building The 5 Essential Leadership Questions Education & Training Compliance Training:
CHAPTER-VI SUMMARY & CONCLUSION
 CHAPTER-VI SUMMARY & CONCLUSION SUMMARY The thesis Occupational stress in relation to emotional intelligence among different levels of managers is composed of six chapters. The first chapter of the thesis
CHAPTER-VI SUMMARY & CONCLUSION SUMMARY The thesis Occupational stress in relation to emotional intelligence among different levels of managers is composed of six chapters. The first chapter of the thesis
Watson-Glaser III Critical Thinking Appraisal (US)
 Watson-Glaser III Critical Thinking Appraisal (US) Development Report Candidate Name: Organization: Pearson Sample Corporation Date of Testing: 21-11-2017 (dd-mm-yyy) 21-11-2017 Page 1 of 15 How to Use
Watson-Glaser III Critical Thinking Appraisal (US) Development Report Candidate Name: Organization: Pearson Sample Corporation Date of Testing: 21-11-2017 (dd-mm-yyy) 21-11-2017 Page 1 of 15 How to Use
Investors in People Introducing the sixth generation Standard. Gordon Stopani Accredited Practitioner
 Investors in People Introducing the sixth generation Standard Gordon Stopani Accredited Practitioner What is Investors in People (IIP)? People Management Standard Tool for supporting the achievement of
Investors in People Introducing the sixth generation Standard Gordon Stopani Accredited Practitioner What is Investors in People (IIP)? People Management Standard Tool for supporting the achievement of
Developing Strategic Leadership
 Secondary Leadership Paper 31 1998-2008 Anniversary Edition Developing Strategic Leadership Brent Davies & Barbara J Davies Introduction: What is Strategic Leadership? One of the key challenges, when taking
Secondary Leadership Paper 31 1998-2008 Anniversary Edition Developing Strategic Leadership Brent Davies & Barbara J Davies Introduction: What is Strategic Leadership? One of the key challenges, when taking
Introducing Management
 Introducing Management Definitions Management roles Management & leadership Core qualities of managers Levels of management Competency-driven management Challenges of managing diverse workforces in diverse
Introducing Management Definitions Management roles Management & leadership Core qualities of managers Levels of management Competency-driven management Challenges of managing diverse workforces in diverse
Individual Feedback Report for
 Individual Feedback Report for Individual Name: John A. Smith Company Name: ABC Company Report Date: 23 Jan 2006 Harcourt Assessment, Inc San Antonio, TX 78259 Sample Report Page 1 Values Arrangement List
Individual Feedback Report for Individual Name: John A. Smith Company Name: ABC Company Report Date: 23 Jan 2006 Harcourt Assessment, Inc San Antonio, TX 78259 Sample Report Page 1 Values Arrangement List
MENTAL HEALTH IN THE WORKPLACE: ORGANIZATIONAL FACTORS AND RESOURCES ESDC OPEN HOUSE 2015
 MENTAL HEALTH IN THE WORKPLACE: ORGANIZATIONAL FACTORS AND RESOURCES ESDC OPEN HOUSE 2015 Andrew Harkness Strategy Advisor, Organizational Health Initiatives Workplace Safety and Prevention Services Agenda
MENTAL HEALTH IN THE WORKPLACE: ORGANIZATIONAL FACTORS AND RESOURCES ESDC OPEN HOUSE 2015 Andrew Harkness Strategy Advisor, Organizational Health Initiatives Workplace Safety and Prevention Services Agenda
COURSE ASSESSMENT in Consulting and Influencing Skills (CIS)
 COURSE ASSESSMENT in Consulting and Influencing Skills (CIS) 1 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Arena of Consultancy: Talent Management and Retention... 3 3. Competency Profile based on Interview
COURSE ASSESSMENT in Consulting and Influencing Skills (CIS) 1 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Arena of Consultancy: Talent Management and Retention... 3 3. Competency Profile based on Interview
