Emotional Intelligence and Conflict Management: An Empirical Study in Indian Context
|
|
|
- Aldous Shepherd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Engineering, Business and Enterprise Applications (IJEBEA) ISSN (Print): ISSN (Online): Emotional Intelligence and Conflict Management: An Empirical Study in Indian Context Tanu Sharma & Anil Sehrawat Jaypee University of Information technology, Waknaghat, Solan, Himachal Pradesh , INDIA Abstract: The role of Emotional intelligence in the workplace has attracted the attention of researchers in the last two decades. Researchers have made many claims about the relationship between emotional intelligence and performance, job satisfaction, work motivation. The present study aims at extending the existing empirical base of emotional intelligence in Indian Context. The objective of the present study are to explore relationship between emotional intelligence and different styles of conflict management and to find out whether people differing in levels of emotional intelligence show a preference for a particular style of conflict management. Keywords: Emotional intelligence, conflict management, job satisfaction, performance, diversity. I. Introduction Salovey and Mayer [1] coined the term Emotional Intelligence to explain a different type of Intelligence but it became popular with the publication of Goleman s book Emotional Intelligence [2].Thereafter it became an important topic of research in the field of management.mayer & Salovey (1997), defined emotional intelligence as the ability to perceive accurately, appraise, and express emotion; the ability to understand emotion and emotional knowledge; and the ability to regulate emotions to promote emotional and intellectual growth. Gardner explained emotional intelligence as a deep awareness of one's own emotions and the ability to label and draw upon those emotions as a resource to guide behavior [3]. Goleman defines EI as the capacity for organizing our own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves and for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationships [2, p.317]. Mayer and Salovey classified emotional intelligence in five domains- self-awareness, managing emotions, motivating oneself, empathy, and handling relationships[1]. Goleman later developed his four dimension model of emotional intelligence to include knowing and managing one s emotions, self-motivation, empathy toward others, and social deftness [2]. According to Goleman there are five components of EQ at work. Self-Awareness refers to the ability to recognize and understand one s own moods, emotions, and drives, as well as their effect on others; Self-Regulation refers to the ability to control or redirect one s disruptive impulses and moods; Motivation refers to a passion to work for reasons that go beyond money or status; Empathy refers to the ability to understand the emotional framework of others, and Social Skill refers to proficiency in managing relationships and building networks [6]. Scholars like Neisser noted the distinction between academic intelligence and social intelligence [7]. Marlowe defined social intelligence as the ability to understand other people and social interactions and using this knowledge to lead and guide others to mutually satisfying outcomes [8]. Goleman has acclaimed EI as the best predictor of work and life success [2, 5]. Many scholars have made claim about the potential of EI to predict work outcomes, such as job satisfaction, turnover [5], and performance [9]. Researchers agreed that emotional intelligence is important for academic and career achievement [10, 11]. The use of EI tests for personnel selection purposes has been advocated, claiming a strong correlation between EI and job performance. Goleman also claimed that employees with high EI are star performers. [5] These claims, however, have been strongly criticized as being implausible and lacking empirical support [12] 2000a). Scholars have criticized these claims argue that these claims are based on unpublished studies, anecdotal accounts, and misinterpreted data [13, 14]. The interest in EQ is growing with increasing organizational change and organizational contextual volatility [15]. Moreover, global mergers and acquisitions, growing number of MNC s have increased the pace of organizational change and cultural diversity. Organizational change is frequently associated with emotional conflict or interpretative conflict [15]. In such a situation awareness of the style employees use to handle conflicts would be helpful [16, 17, 18]. The term conflict has been employed in different ways reflecting the different levels at which conflicts exist [19, 20]. Thomas has given two broad uses of the term conflict. The first use refers to incompatible response tendencies within an individual, e.g., behavioral conflicts where one must choose whether or not to pursue a particular course of action or a goal, or role conflict where one must choose between several competing sets of role demands. The second use refers to conflicts that occur between different individuals, groups, organizations, or other social units [20]. Hence, the terms interpersonal, inter-group, and IJEBEA ; 2014, IJEBEA All Rights Reserved Page 104
2 inter-organizational conflict are used. Putnam and Poole and Thomas on the basis of their analysis of numerous conceptualizations and definitions of conflict identified three characteristics: interdependence, disagreement, and interference [22, 20, 21]. Interdependence exists when each party involved depends, at least in part on the actions of the other for the attainment of their goals. Without Interdependence, the actions of each party have no impact on the outcomes of the other party. Therefore, interdependence is an essential pre-condition of any conflict situation, providing an interpersonal context in which conflicts may arise. Disagreement exists when parties involved think that different values, needs, interests, opinions, goals, or objectives exist. IN interpersonal conflict, disagreement is a key component. However, disagreeing parties will not experience conflict when the point of disagreement is irrelevant or unimportant (for e.g., when there is no interdependence, or when the issue of disagreement is minor). Interference exists when one party interferes with or opposes the other party s attainment of its, objectives, goals or interests. Many researchers believe that the core process of interpersonal conflict is the behavior where one or more disputants oppose their counterpart s interests or goals[23]. The role of negative emotion (jealousy, anger, anxiety, or frustration)has been emphasized into into conceptualizations of conflict by many researchers [24, 25, 26, 27, 20, 21. These emotions are thought to emerge when there are major disagreements, or when parties interfere with the attainment of each others important goals. Therefore, a fourth property, negative emotion, can also be added. In this study, we focus on interpersonal conflict which has been defined in many different ways [21, 23]. Researchers Within the conflict domain have identified a number of conflict management styles and their role in satisfactory management and resolution of conflicts have been identified [28, 29, 22, 30, 21, 23]. Several measures assessing styles of conflict management have also been developed [31, 32, 33]. Traditionally, five different styles of conflict management: asserting, accommodating, compromising, problem-solving, and avoiding are classified. These styles are seen as general strategies or behavioral orientations that individuals adopt for managing and resolving conflicts. Asserting style occurs when individuals strive to win. In this style one party gains at the cost of the gains of other party. Conflict, therefore, is considered a win- lose situation. Like asserting, accommodating style occurs when individuals sacrifice their own needs and desires in order to satisfy the needs of other parties. This occurs as individuals oblige or yield to others positions, or cooperate in an attempt to resolve conflicts. Compromising style frequently splits the difference or involves give and take behaviors where each party wins some and loses some. Problem-solving style occurs when individuals involved in conflict try to fully satisfy the concerns of all parties. In this style, actions are aimed at the achievement of goals and objectives of all parties. Hence, it results as a win-win solution. At last, avoiding style occurs when individuals are indifferent to the concerns of other party and refuse to act or participate in conflict. Here, one party withdraws, physically or psychologically, abdicating all responsibility for the solution. Literature in this field reflects that cooperative styles (problem solving, accommodating and compromising) are positively associated with constructive conflict management and with individual and organizational outcomes [34] and show substantial concern for the other party. Among these three, problem solving style is generally perceived as the most appropriate, most effective, and highly competent style in managing conflicts [35, 36]. Weider-Hatfield and Hatfield found problem-solving positively related to interpersonal outcomes [37]. Burke suggested that, in general, problem solving style was related to the effective management of conflict, while asserting and avoiding were related to the infective management of conflict [38]. Lawrence and Lorsch suggested that a confrontation style dealing with intergroup conflict was used to a significantly greater degree in higher than lower performing organizations [39]. Scholars believe that an individual s EI influences one s way of handling interpersonal conflict. Individuals with high EI may be more effective in resolving conflict than those with low EI [5, 40]. Jordon and Troth emphasized that individuals with high EI prefer to seek cooperative solutions when confronted with conflict [13]. Goleman suggested that emotionally intelligent employees are better at negotiation and effectively handling of their conflicts with organizational members [5]. A growing number of scholars suggest that emotional intelligence (EI) plays an important role in managing interpersonal conflicts [16]. However, there is little or no empirical data on relationships between EI and handling interpersonal conflicts conducted in an Indian organizational context. To bridge the gap, the present study seeks to explore the relationship between Emotional Intelligence and conflict management styles. II. Method and Objectives of the study The objective of the study was to explore the relationship between emotional intelligence and conflict management. Sample A sample of 100 working mid-level managers from different organizations of north India was selected. The subjects thus covered in the study were the willing participants drawn from a mix of socio-economic backgrounds in the years age range. Data Collection IJEBEA ; 2014, IJEBEA All Rights Reserved Page 105
3 The study was limited to organizations established in North India. The managers were contacted personally with each organization and requested to complete the survey questionnaire in 30 minutes. All participants completed the surveys in their scheduled time. Instrumentation Emotional Competence Inventory (ECI) by Boyatzis et al. was used in this study to measure emotional intelligence [41]. It consists of 80 items that reflect adaptive tendency toward emotional intelligence. Each item in the questionnaire described a work-related behavior. Respondents used a 7-point Likert scale. Higher the score, greater the tendency an individual possessed to exhibit emotionally intelligent behavior. ECI is divided into the following four sub-skills, as defined in Goleman's (2001) emotional intelligence model: Self-awareness, Self-management, Social awareness, and Relationship management. An average for each cluster was found by summing responses (1-7) to the corresponding questions that pertain to a cluster. A questionnaire measuring Interpersonal Conflict and Conflict Management Styles adapted by Barki and Hartwick was used In addition to the ECI [42]. In this questionnaire, twenty items, adapted from previous measures were used to assess the extent to which students employed five styles (problem-solving, asserting, avoiding, compromising, and accommodating) [31, 33]. For each style, two items inquired respondent s own behaviors, and two items asked about the behaviors of the other party(ies). Conceptually, these indices measure the overall usage of each style by everyone involved, and not only the respondent s own usage of the style. The style items assessed these behaviors on 7-point scales ranging from 1 (never) to 7 (always). III. Results First of all, the reliability of the data was tested by computing Cronbach s Alpha Model. The variable wise reliability coefficients are emotional intelligence α =.823 and conflict management α =.673.The descriptive statistics of the data are given in table 1. Table 1: Descriptive Statistics of the Data N=100 Variable Range of scores Min score Max score Mean score Std. Dev. Self-awareness Self-management Social-awareness Social-skill Emotional Intelligence Problem Solving Asserting Avoiding Compromising Accommodating The Pearson correlation coefficients were used to examine any relationship that may exist between emotional intelligence measure and different styles of conflict management. Table 2: Correlation between the Emotional Intelligence sub-scales and Conflict Management styles Variables Problem Solving Asserting Avoiding Compromising Accommodating Self Awareness * ** Self Management 0.394** 0.405** ** 0.350** Social Awareness 0.475** 0.507** ** 0.363** Social Skills 0.332** 0.441** ** 0.290** Emotional Intelligence 0.409** 0.474** ** 0.238** ** Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level, * Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed) Table 2 presents the correlations between EI skills and different styles of conflict management. Self awareness has a significant positive correlation with asserting and compromising styles of conflict management, and there is no relationship between problem solving, avoiding and accommodating styles of conflict management. Self management has significant and positive correlation with problem solving, asserting, compromising and accommodating styles of conflict management. It has significant relationship with avoiding styles of conflict management. Social awareness is positively and significantly correlated with problem solving, asserting, compromising and accommodating styles of conflict management. It has no relationship with avoiding style of conflict management. Social skills are positively correlated with problem solving, asserting, compromising and accommodating styles of conflict management. Emotional intelligence as a single variable has a positive and IJEBEA ; 2014, IJEBEA All Rights Reserved Page 106
4 significant correlation with problem solving, asserting, compromising and accommodating styles of conflict management. However, there is no correlation between EI and avoiding style of conflict management. The results show that EI of an individual affects his handling of a conflict situation. It means that knowledge of self and of others helps in the resolution of conflicts and through collaborative and cooperative methods. IV. Discussion In the present study, presents the correlation between sub-scales- self awareness, self management, Social awareness and social skills of emotional intelligence and five styles- problem-solving, asserting, avoiding, compromising and accommodating of handling conflict. The literature suggests that EI has been associated with cooperative solutions, which results in more effective conflict management. The results showed significant influence of EI on problem solving, asserting, compromising and accommodating styles. EI has no significant relationship with avoiding style. Social awareness or empathy refers to the awareness of others feelings, needs, and concerns. According to Goleman empathy involves understanding others, developing others, and having a service orientation [2]. It implies that the more an individual understands others/colleagues, the more likely he or she will use the problem solving style to handle conflict. EI is positively correlated asserting dominating style of handling conflict. It is surprising because asserting style maximizes one s own needs at the expense of the other individuals needs [43]. This result matches with the study of Yu, Sardessai, Lu and Zhao [44]. Further exploration found that integrating, dominating, and compromising share one characteristic: concern for self. Concern for self is one of the two basic dimensions that differentiate the five styles of handling conflict. Concern for self explains the degree to which a person attempts to satisfy his or her own interests [45]. However, no specific reason can be given for this outcome but we can say that in South Asia people use self-awareness in deciding their self-interests. V. Managerial implications The globalization and privatization of the workplace has lead to increasing organizational change and organizational contextual volatility, which, in turn, produce increasing differences and conflicts [46] as cited in [44]. Furthermore, Indian organizations are involved in margers and acquisitions at international level that result in workforce diversity and cultural differences that is another major reason of conflicts among employees. Therefore, the findings of this study have importance to Indian organizations in managing conflicts. The problem-solving style is generally perceived to be a more appropriate, effective, and competent style in managing conflict. Individuals who have batter self-awareness also recognize their strengths, weaknesses, needs, and drives. Additionally, these people know how their feelings affect themselves, other people, and their job performance [6]. Self-regulation is an important component of social development and it contributes to the quality of interpersonal relationships [47]. Empathy involves understanding others, developing others, and having a service orientation [2]. Self-regulation and empathy can be developed [48 49]. To manage a conflict effectively it becomes necessary for a manager to adopt and develop an integrative style. Salopek noted in an interview with Goleman that emotional intelligence abilities are learned and tend to improve as one ages and matures. Therefore, organizations have to consciously and continuously strive to inculcate self-regulation and empathy among their managers through an effective programme of training and development [50]. VI. Limitations and future directions The limitations of the study are first, it is an exploratory study that examines the relationship between EI and conflict management styles in the Indian context. As in any cross-sectional studies, data collected at a single moment in time may limit the accuracy of this research. As such, a longitudinal study could be considered in order to get convincing evidence of the relationship between EI and conflict management styles. Second in this study, the data is self reported, therefore, subject to limitation of the process. In addition, the scales used to evaluate EI and conflict management styles were developed by Western scholars and tested in a Western setting. Thus, the investigators indigenous culture is likely to bias the design of the research instrument (Hofstede, 1991; Adler et al., 1989). Therefore, it would be desirable to develop a scale to measure EI and conflict management styles based on the Indian context. References [1] Salovey, P & Mayer, J. D. (1990), Emotional intelligence, Imagination, Cognition, and Personality, Vol. 9, pp [2] Goleman, D. (1995), Emotional Intelligence, Bantam Books, New York. [3] Mayer, J., & Salovey, P. (1997), What is emotional intelligence?, in P. Salovey and D. Sluyter (Eds.) Emotional Development and Emotional Intelligence: implication for educators, Basic Books, New York, pp [4] Gardner, H. (1983).Intelligence Reframed. New York: Bantam Books. [5] Goleman, D. (1998), Working with Emotional Intelligence, Bantam Books, New York. [6] Goleman, D. (1999), What makes a leader?, Harvard Business Review, Vol. 76 No. 6, pp [7] Neisser, U. (1976), Cognition and reality, Freeman, San Francisco. [8] Marlowe Jr., H. A. (1986), Social intelligence: Evidence for multidimensionality and construct independence, Journal of Educational Psychology, Vol. 78, pp IJEBEA ; 2014, IJEBEA All Rights Reserved Page 107
5 [9] Bachman, J, Stein, S, Campbell, K, & Sitarenious,G, (2000), Emotional intelligence in the collection of debt. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 8, 176 [10] Lord, R. G., De Vader, C. L., & Alliger, G. M. (1986), A meta-analysis of the relationship between personality traits and leadership perceptions: An application of validity generalization procedures Organizational Behavior and Human Performances, Vol. 23, pp [11] Wentzel, K. (1991), Relationship between social competence and academic achievement in early adolescence, Child Development, Vol. 62, pp [12] Mayer, J.D., Salovey, P. and Caruso, D.R. (2000), Competing models of emotional intelligence, in R. Sternberg (Ed.) Handbook of Intelligence, Cambridge, New York, pp [13] Barrett, L.F., Lane, R.D., Sechrest, L., & Schwartz, G. E. (2000). Sex differences in emotional awareness. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin, 26(9), [14] Jordan, P. L. and Troth, A. C. (2002), Emotional intelligence and conflict resolution: implications for human resource development, Advances in Developing Human Resources, Vol. 4 No. 1, pp [15] Downing, S. J. (1997), Learning the plot: emotional momentum in search of dramatic logic, Management Learning, Vol. 28 No. 1, pp [16 Rahim, M.A. (2001), Managing Conflict in Organizations, 3rd edition, Quorum Books, Westport, CT. [17] Rahim, M.A. (1985), A strategy for managing conflict in complex organizations, Human Relations, Vol. 38, pp [18] Rahim, M.A. (1986), Managing Conflict in Organizations, Praeger, New York. [19] Deutsch, M. (1990), Sixty years of conflict, International Journal of Conflict Management, Vol. 1 No. 3, pp [20] Thomas, K. W. (1992a), Conflict and conflict management: Reflections and update, Journal of Organizational Behaviour, Vol. 13, pp [21] Thomas, K. W. (1992b), Conflict and negotiation processes in organizations, in M. D. Dunnette and L. M. Hough (Eds.) Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology 2 nd ed., Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, CA, pp [22] Putnam, L. L. & Poole, M. S. (1987). Conflict and Negotiation. In Jablin, F. M., Roberts, K. H., & Porter, L. W. (Eds.), Handbook of Organizational Communication, ( ). Newbury Park, CA: Sage. [23] Wall, J. A. Jr. and Callister, R. R. (1995), Conflict and its management, Journal of Management, Vol 21 No. 3, pp [24] Amason, A. (1996) Distinguishing effects of functional and dysfunctional conflict on strategic decision making: Resolving a paradox for top management teams. Academy of Management Journal, 39, [25] Jehn, K A multimethod examination of the benefits and detriments of intragroup conflict. Administrative Science Quarterly, 40, [26] Pinkley, R Dimensions of the conflict frame: Disputant interpretations of conflict. Journal of Applied Psychology, 75, [27] Pondy, L.R. (1967). Organizational conflict: concepts and models, Administrative Science Quarterly, 12(2), [28] Blake, R. R. and Mouton, J. S. (1964), The Managerial Grid, Houston, Gulf,, TX. [29] Pruitt, D. G. and Rubin, J. Z. (1986), Social Conflict: Escalation, Stalemate, and Settlement, Random House, New York. [30] Thomas, K. W. (1976), Conflict and conflict management, in M. D. Dunnette (Ed.) Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, CA, pp [31] Killman, R. H. and Thomas, K. W. (1977), Developing a forced choice measure of conflict handling behavior: The MODE instrument, Educational and Psychological Measurement, Vol. 37, pp [32] Putnam, L. L. and Wilson, C. (1982), Communicative strategies in organizational conflict: Reliability and validity of a measurement scale, in M. Burgoon (Ed.) Communication Yearbook 6, Sage, Newbury Park, pp [33] Rahim, M.A. (1983), A measure of the styles of handling interpersonal conflict, Academy of Management Journal, Vol. 26 No. 2, pp [34] Rahim, M.A. and Magner, N.R. (1995), Confirmatory factor analysis of the styles of handling interpersonal conflict: first-order factor model and its invariance across groups, Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 80 No. 1, pp [35] Gross, M. A. and Guerrero, L. K. (2000), Managing conflict appropriately and effectively: an application of the competence model to Rahim s organizational conflict styles, The International Journal of Conflict Management, Vol. 11 No. 3, pp [36] Papa, M.J. and Canary, D.J. (1995), Conflict in organizations: a competence-based approach, in A.M. Nicotera (Ed.) Conflict and Organizations: Communicative Processes, State University of New York Press, Albany, NY, pp [37] Weider-Hatfield, D. and Hatfield, J.D. (1995), Relationship s among conflict management styles, levels of conflict, and reactions to work, Journal of Social Psychology, Vol. 135 No. 6, pp [38] Burke, R. J. (1970), Methods of resolving superior-subordinate conflict: The constructive use of subordinate differences and disagreements, Organizational Behaviour and Human Performance, Vol. 5, pp [39] Lawrence, P. R. and Lorsch, J. W. (1967), Differentiation and integration in complex organizations, Administrative Science Quarterly, Vol. 12, pp [40] Mayer, J.D., Salovey, P. and Caruso, D.R. (1997), The emotional IQ test, Virtual Knowledge, Needham, MA. [41] Boyatzis, R., Goleman, D., & Hay McBer. (1999). Emotional competency inventory. Boston: HayGroup. [42] Barki, H. and Hartwick, J. (2001), Interpersonal conflict and its management in information system development, MIS Quarterly, Vol. 25 No. 2, pp [43] Spitzberg, B.H., Canary, D.J. and Cupach, W.R. (1994), A competence-based approach to the study of interpersonal conflict, in D. Cahn (Ed.) Conflict in Personal Relationships, Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, pp [44] Yu, C. S., Sardessai, R. M., Lu, J. and Zhao, J. H. (2006), Relationship of emotional intelligence with conflict management styles: an empirical study in china, Int. J. Management and Enterprise Development, Vol. 3 Nos. 1/2, pp [45] Rahim, M.A., Magner, N.R. and Shapiro, D.L. (2000), Do justice perceptions influence styles of handling conflict with supervisors? What justice perceptions, precisely?, International Journal of Conflict Management, Vol. 11 No. 1, pp [46] Sommer, R.A. (2003), Small and medium sized enterprises: no longer just coping with the supply chain, International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, Vol. 1 No. 1, pp [47] Davis, M.H. (1983), Measuring individual differences in empathy: evidence for a multidimensional approach, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Vol. 44, pp [48] Saarni, C. (1999), The Development of Emotional Competence, Guilford Press, New York. [49] Kestenbaum, R., Farber, E. A., & Sroufe, L. A. (1989), Individual differences in empathy among preschoolers: Relation to attachment history, New Directions for Child Development, Vol. 44, pp [50] Salopek, J. (1998), Train your brain, Training and Development, Vol. 52, IJEBEA ; 2014, IJEBEA All Rights Reserved Page 108
1. Presenter: 2. Title of Presentation. Testing the Emotional Intelligence of Leaders as an Antecedent to Leader-Member Exchanges: A Field Study
 1. Presenter: John E. Barbuto, Jr. Associate Professor of Leadership University of Nebraska-Lincoln 300 Ag Hall Lincoln, NE 68583-0709 (402) 472-8736 jbarbuto@unl.edu 2. Title of Presentation Testing the
1. Presenter: John E. Barbuto, Jr. Associate Professor of Leadership University of Nebraska-Lincoln 300 Ag Hall Lincoln, NE 68583-0709 (402) 472-8736 jbarbuto@unl.edu 2. Title of Presentation Testing the
ОРГАНИЗАЦИОННАЯ ПСИХОЛОГИЯ
 . С. 23 27 ОРГАНИЗАЦИОННАЯ ПСИХОЛОГИЯ Emotional Intelligence and work performance of executives Govind Singh KUSHWAHA PhD, G.B. Pant University of Technology & Agriculture, U S Nagar, India, drgovindsingh@hotmail.com
. С. 23 27 ОРГАНИЗАЦИОННАЯ ПСИХОЛОГИЯ Emotional Intelligence and work performance of executives Govind Singh KUSHWAHA PhD, G.B. Pant University of Technology & Agriculture, U S Nagar, India, drgovindsingh@hotmail.com
Emotional Competence and Leadership Excellence at Johnson & Johnson: The Emotional Intelligence and Leadership Study
 Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence in Organizations Leadership & EI at J&J 1 Emotional Competence and Leadership Excellence at Johnson & Johnson: The Emotional Intelligence and Leadership
Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence in Organizations Leadership & EI at J&J 1 Emotional Competence and Leadership Excellence at Johnson & Johnson: The Emotional Intelligence and Leadership
Emotional Intelligence and Managerial Effectiveness * Bhawna Chahar
 4DInternational Journal of Mgt.And Science ISSN-2250-0669 4DCross Connect.com,Inc-2011 www.4dinternationaljournal.com Volume-4,Issue-2, July 2014 Abstract Emotional Intelligence and Managerial Effectiveness
4DInternational Journal of Mgt.And Science ISSN-2250-0669 4DCross Connect.com,Inc-2011 www.4dinternationaljournal.com Volume-4,Issue-2, July 2014 Abstract Emotional Intelligence and Managerial Effectiveness
RelationshipofEmotionalIntelligencefromtheDiversityPerspectiveinProjectOutcomesinTechnologyProjects
 Global Journal of Management and Business Research: G Interdisciplinary Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Management and Business Research: G Interdisciplinary Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Emotional Profile of a Leader: Top 10 Leadership Competencies Identified.
 Emotional Profile of a Leader: Top 10 Leadership Competencies Identified. Abstract The paper is an attempt to develop An Emotional Profile of Leader and identify the top 10 leadership competencies focusing
Emotional Profile of a Leader: Top 10 Leadership Competencies Identified. Abstract The paper is an attempt to develop An Emotional Profile of Leader and identify the top 10 leadership competencies focusing
A Cross-Cultural Study on the Differences in Conflict Management Process between Chinese Employees and American Employees Xiao-Li SONG
 2016 3 rd International Conference on Social Science (ICSS 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-410-3 A Cross-Cultural Study on the Differences in Conflict Management Process between Chinese Employees and American
2016 3 rd International Conference on Social Science (ICSS 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-410-3 A Cross-Cultural Study on the Differences in Conflict Management Process between Chinese Employees and American
IMPACT OF CORE SELF EVALUATION (CSE) ON JOB SATISFACTION IN EDUCATION SECTOR OF PAKISTAN Yasir IQBAL University of the Punjab Pakistan
 IMPACT OF CORE SELF EVALUATION (CSE) ON JOB SATISFACTION IN EDUCATION SECTOR OF PAKISTAN Yasir IQBAL University of the Punjab Pakistan ABSTRACT The focus of this research is to determine the impact of
IMPACT OF CORE SELF EVALUATION (CSE) ON JOB SATISFACTION IN EDUCATION SECTOR OF PAKISTAN Yasir IQBAL University of the Punjab Pakistan ABSTRACT The focus of this research is to determine the impact of
The power of EI: The soft skills the sharpest leaders use. Comparisons across data from Korn Ferry Hay Group leadership and employee surveys
 The power of EI: The soft skills the sharpest leaders use Comparisons across data from Korn Ferry Hay Group leadership and employee surveys What s emotional intelligence got to do with leadership? Organizations
The power of EI: The soft skills the sharpest leaders use Comparisons across data from Korn Ferry Hay Group leadership and employee surveys What s emotional intelligence got to do with leadership? Organizations
THE INFLUENCE OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE ON CRISIS MANAGEMENT
 THE INFLUENCE OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE ON CRISIS MANAGEMENT *Abbas S. Ardestani and Yahiya Amirzadeh Department of Management, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran *Author for
THE INFLUENCE OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE ON CRISIS MANAGEMENT *Abbas S. Ardestani and Yahiya Amirzadeh Department of Management, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran *Author for
Organizational Behaviour
 Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Dr Jan P Bosman, Ph.D The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private higher
Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Dr Jan P Bosman, Ph.D The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private higher
Hybrid online mediation in hierarchical labor disputes. By Katalien Bollen [author]
![Hybrid online mediation in hierarchical labor disputes. By Katalien Bollen [author] Hybrid online mediation in hierarchical labor disputes. By Katalien Bollen [author]](/thumbs/72/67293570.jpg) Hybrid online mediation in hierarchical labor disputes By Katalien Bollen [author] One of the ways to implement online tools in mediation processes is the use of an online tool in order to prepare the
Hybrid online mediation in hierarchical labor disputes By Katalien Bollen [author] One of the ways to implement online tools in mediation processes is the use of an online tool in order to prepare the
Role of Emotional Intelligence on the Relationship among Leadership Styles, Decision Making Styles and Organizational Performance: A Review
 From the SelectedWorks of Rana Rashid Rehman May, 2011 Role of Emotional Intelligence on the Relationship among Leadership Styles, Decision Making Styles and Organizational Performance: A Review Rana Rashid
From the SelectedWorks of Rana Rashid Rehman May, 2011 Role of Emotional Intelligence on the Relationship among Leadership Styles, Decision Making Styles and Organizational Performance: A Review Rana Rashid
MEASUREMENT OF TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT EFFECTIVENESS AN EMPIRICAL STUDY
 MEASUREMENT OF TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT EFFECTIVENESS AN EMPIRICAL STUDY DR. V.RAMA DEVI*; MR.NAGURVALI SHAIK** *PROFESSOR, KLU BUSINESS SCHOOL KL UNIVERSITY, VADDESWARAM, GUNTUR (DT.) ANDHRA PRADESH **KLU
MEASUREMENT OF TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT EFFECTIVENESS AN EMPIRICAL STUDY DR. V.RAMA DEVI*; MR.NAGURVALI SHAIK** *PROFESSOR, KLU BUSINESS SCHOOL KL UNIVERSITY, VADDESWARAM, GUNTUR (DT.) ANDHRA PRADESH **KLU
Understanding Precedents for Frontline Employee Turnover in Luxury Hotels: Emotional Intelligence as a Unifying Factor
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Tourism Travel and Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally 2015 ttra International Conference Understanding Precedents for
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Tourism Travel and Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally 2015 ttra International Conference Understanding Precedents for
LEARN TO CONTROL YOUR EMOTIONS Hogan Assessment Systems, Inc.
 LEARN TO CONTROL YOUR EMOTIONS. 2013 Hogan Assessment Systems, Inc. THE CURRENT GENERATION IS THE MOST EDUCATED AND TECHNOLOGICALLY ADVANCED TO EVER ENTER THE WORKFORCE. However, according to recent numbers
LEARN TO CONTROL YOUR EMOTIONS. 2013 Hogan Assessment Systems, Inc. THE CURRENT GENERATION IS THE MOST EDUCATED AND TECHNOLOGICALLY ADVANCED TO EVER ENTER THE WORKFORCE. However, according to recent numbers
10 more years boosting performance. How EI is making a difference in the workplace.
 10 more years boosting performance. How EI is making a difference in the workplace. Emotional Intelligence research series. Korn Ferry Hay Group s partnership with Richard Boyatzis and Dan Goleman provides
10 more years boosting performance. How EI is making a difference in the workplace. Emotional Intelligence research series. Korn Ferry Hay Group s partnership with Richard Boyatzis and Dan Goleman provides
Leading with Emotional Intelligence. by David Cory, M.A., 2010
 by David Cory, M.A., 2010 2010 THE EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE TRAINING COMPANY Leading with Emotional Intelligence by David Cory, M.A. Abstract To lead with emotional intelligence is to inspire, motivate and
by David Cory, M.A., 2010 2010 THE EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE TRAINING COMPANY Leading with Emotional Intelligence by David Cory, M.A. Abstract To lead with emotional intelligence is to inspire, motivate and
Feedback Report. ESCI - University Edition. Sample Person Hay Group 11/21/06
 Feedback Report ESCI - University Edition Sample Person Hay Group 11/21/06 Introduction What Is Emotional and Social Intelligence? Emotional and Social Intelligence, commonly refered to as EI, is the capacity
Feedback Report ESCI - University Edition Sample Person Hay Group 11/21/06 Introduction What Is Emotional and Social Intelligence? Emotional and Social Intelligence, commonly refered to as EI, is the capacity
at work TIPS, TOOLS & INTELLIGENCE FOR DEVELOPING TALENT
 DECEMBER 2016 ISSUE 1612 at work TIPS, TOOLS & INTELLIGENCE FOR DEVELOPING TALENT CAREER DEVELOPMENT USING EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN THE WORKPLACE Meloney Sallie-Dosunmu career development VOL. 33 ISSUE
DECEMBER 2016 ISSUE 1612 at work TIPS, TOOLS & INTELLIGENCE FOR DEVELOPING TALENT CAREER DEVELOPMENT USING EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN THE WORKPLACE Meloney Sallie-Dosunmu career development VOL. 33 ISSUE
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS RELATED TO BURNOUT AMONG MANAGERS
 GJBM Emotional Intelligence as Related to Burnout Among Managers ISSN: 0973-8533 Vol. 2 No. 1, June 2008 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS RELATED TO BURNOUT AMONG MANAGERS Kiran Sahu* and Shelley Yadav** ABSTRACT
GJBM Emotional Intelligence as Related to Burnout Among Managers ISSN: 0973-8533 Vol. 2 No. 1, June 2008 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS RELATED TO BURNOUT AMONG MANAGERS Kiran Sahu* and Shelley Yadav** ABSTRACT
Transactional Leadership
 DePaul University From the SelectedWorks of Marco Tavanti 2008 Transactional Leadership Marco Tavanti, DePaul University Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marcotavanti/15/ Transactional Leadership
DePaul University From the SelectedWorks of Marco Tavanti 2008 Transactional Leadership Marco Tavanti, DePaul University Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marcotavanti/15/ Transactional Leadership
International Journal of Management (IJM), ISSN (Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 1, Number 2, July - Aug (2010), IAEME
 International Journal of Management (IJM), ISSN 0976 6502(Print), ISSN 0976 6510(Online) Volume 1, Number 2, July - Aug (2010), pp. 70-75 IAEME, http://www.iaeme.com/ijm.html IJM International Journal
International Journal of Management (IJM), ISSN 0976 6502(Print), ISSN 0976 6510(Online) Volume 1, Number 2, July - Aug (2010), pp. 70-75 IAEME, http://www.iaeme.com/ijm.html IJM International Journal
International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Reviews Vol.4 No.2, July., 2013; p (ISSN: )
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS PREDICTOR OF BANK MANAGERS LEADERSHIP PERFORMANCE IN NIGERIA By WASIU OLAYIWOLA AKANDE Department of Management and Accounting, Faculty of Administration, Obafemi Awolowo University,
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS PREDICTOR OF BANK MANAGERS LEADERSHIP PERFORMANCE IN NIGERIA By WASIU OLAYIWOLA AKANDE Department of Management and Accounting, Faculty of Administration, Obafemi Awolowo University,
Developing human capital by linking emotional intelligence with personal competencies in Indian business organizations
 Int. Journal of Business Science and Applied Management, Volume 5, Issue 2, 2010 Developing human capital by linking emotional intelligence with personal competencies in Indian business organizations Kavita
Int. Journal of Business Science and Applied Management, Volume 5, Issue 2, 2010 Developing human capital by linking emotional intelligence with personal competencies in Indian business organizations Kavita
Emotional Intelligence & Leadership Global Health Institute Chiang Mai Thailand
 Emotional Intelligence & Leadership Global Health Institute Chiang Mai Thailand University of Minnesota Jenny The Best & Worst of Times Instructions: Think of a person in your current or past workplace
Emotional Intelligence & Leadership Global Health Institute Chiang Mai Thailand University of Minnesota Jenny The Best & Worst of Times Instructions: Think of a person in your current or past workplace
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS A DETERMINANT OF CONFLICT STYLE ADOPTION OF MANAGERS: A THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVE
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS A DETERMINANT OF CONFLICT STYLE ADOPTION OF MANAGERS: A THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVE SMARTY MUKUNDAN*; DR. ZAKKARIYA K.A.** *ASST PROFESSOR FISAT BUSINESS SCHOOL, MOOKKANNOOR P.O,
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AS A DETERMINANT OF CONFLICT STYLE ADOPTION OF MANAGERS: A THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVE SMARTY MUKUNDAN*; DR. ZAKKARIYA K.A.** *ASST PROFESSOR FISAT BUSINESS SCHOOL, MOOKKANNOOR P.O,
16 Human Resource Development, Emotional Intelligence and Social Capital for Senior Managers in the Hospitality Industry in Zimbabwe
 16 Human Resource Development, Emotional Intelligence and Social Capital for Senior Managers in the Hospitality Industry in Zimbabwe By VONAI CHIRASHA Department of Human Resource Management, Midlands
16 Human Resource Development, Emotional Intelligence and Social Capital for Senior Managers in the Hospitality Industry in Zimbabwe By VONAI CHIRASHA Department of Human Resource Management, Midlands
AN INTRODUCTION TO NEGOTIATION AND CONFLICT MANAGEMENT
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NEGOTIATION AND CONFLICT MANAGEMENT Timeframe: Learning outcome: Recommended reading: Multimedia: Section overview: 10 hours Define the broad concepts Bakhare, R. (2010). The Manager
AN INTRODUCTION TO NEGOTIATION AND CONFLICT MANAGEMENT Timeframe: Learning outcome: Recommended reading: Multimedia: Section overview: 10 hours Define the broad concepts Bakhare, R. (2010). The Manager
Author's Abstract: COPYRIGHT 2006 Heldref Publications
 The Journal of Psychology, May 2006 v140 i3 p269(20) Choice of conflict-handling strategy: a matter of context. Gerard A. Callanan; Cynthia D. Benzing; David F. Perri. Author's Abstract: COPYRIGHT 2006
The Journal of Psychology, May 2006 v140 i3 p269(20) Choice of conflict-handling strategy: a matter of context. Gerard A. Callanan; Cynthia D. Benzing; David F. Perri. Author's Abstract: COPYRIGHT 2006
The Impact of Emotional Intelligence on Employees Performance Qadar Baksh Baloch, Maimoona Saleem, Gohar Zaman & Asma Fida
 The Impact of Emotional Intelligence on Employees Performance Qadar Baksh Baloch, Maimoona Saleem, Gohar Zaman & Asma Fida Abstract Developing countries, like Pakistan, are rich in emotional sentiments
The Impact of Emotional Intelligence on Employees Performance Qadar Baksh Baloch, Maimoona Saleem, Gohar Zaman & Asma Fida Abstract Developing countries, like Pakistan, are rich in emotional sentiments
IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 RESEARCH AND PRACTICE IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Lu, L. & Lin, G. C. (2002). Work Values and Job Adjustment of Taiwanese workers, Research and Practice in Human Resource Management, 10(2), 70-76. Work
RESEARCH AND PRACTICE IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Lu, L. & Lin, G. C. (2002). Work Values and Job Adjustment of Taiwanese workers, Research and Practice in Human Resource Management, 10(2), 70-76. Work
Leadership Case Study: Emotional Intelligence Effect in Our Life
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Leadership Case Study: Emotional Intelligence Effect in Our Life Selçuk Genç June 2015 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/67210/ MPRA Paper No. 67210, posted 14.
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Leadership Case Study: Emotional Intelligence Effect in Our Life Selçuk Genç June 2015 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/67210/ MPRA Paper No. 67210, posted 14.
EQ Competencies Assessment
 EQ Competencies Assessment The research validates that what separates superior leaders from average leaders is Emotional Intelligence (EQ). When measuring IQ, Technical Expertise and EQ, the results validated
EQ Competencies Assessment The research validates that what separates superior leaders from average leaders is Emotional Intelligence (EQ). When measuring IQ, Technical Expertise and EQ, the results validated
Styles of Managing Interpersonal Conflict: A Case Study On Student Affairs Department, Universiti Utara Malaysia
 Styles of Managing Interpersonal Conflict: A Case Study On Student Affairs Department, Universiti Utara Malaysia by Mohd Amy Azhar Mohd Harif Assoc. Prof., Ph.d, C.A.(M) (corresponding author) College
Styles of Managing Interpersonal Conflict: A Case Study On Student Affairs Department, Universiti Utara Malaysia by Mohd Amy Azhar Mohd Harif Assoc. Prof., Ph.d, C.A.(M) (corresponding author) College
Stand: Semester / Term: Duration: Module No.: 1 Semester DLMMANE. Regularly offered in: Module Type(s): Compulsory WS, SS
 Module Title: Management (English) Module No.: DLMMANE Semester / Term: -- Duration: 1 Semester Module Type(s): Compulsory Regularly offered in: WS, SS Workload: 300 h Credit Points: 10 Admission Requirements:
Module Title: Management (English) Module No.: DLMMANE Semester / Term: -- Duration: 1 Semester Module Type(s): Compulsory Regularly offered in: WS, SS Workload: 300 h Credit Points: 10 Admission Requirements:
HIGH PERFORMANCE TEAMS
 HIGH PERFORMANCE TEAMS Tri-State Consortium of Opportunity Programs in Higher Education Leadership institute April 11-15, 2015 Glenn B. Lang, EdD doctorg96@gmail.com None of us is smart as all of us Ken
HIGH PERFORMANCE TEAMS Tri-State Consortium of Opportunity Programs in Higher Education Leadership institute April 11-15, 2015 Glenn B. Lang, EdD doctorg96@gmail.com None of us is smart as all of us Ken
Modeling Emotionally Intelligent Behaviour at Workplace- An Interpretive Structural Modeling Technique
 Volume 8, Issue 3, September 2015 Modeling Emotionally Intelligent Behaviour at Workplace- An Interpretive Structural Modeling Technique Shitika Research Scholar, ITM University, Gurgaon MD, Styrax Consultants
Volume 8, Issue 3, September 2015 Modeling Emotionally Intelligent Behaviour at Workplace- An Interpretive Structural Modeling Technique Shitika Research Scholar, ITM University, Gurgaon MD, Styrax Consultants
more primal: Great leadership works through the emotions (Boyatzis, Goleman and McKee, 2002).
 Review by Tangela Richardson Great Leaders move us. They ignite our passion and inspire the best in us. When we try to explain why they are so effective, we speak of strategy, vision, or powerful ideas.
Review by Tangela Richardson Great Leaders move us. They ignite our passion and inspire the best in us. When we try to explain why they are so effective, we speak of strategy, vision, or powerful ideas.
TIONAL EFFECTIVENESS
 ROLE OF EMPLOYEE COMMITMENT IN ORGANIZA ANIZATIO TIONAL EFFECTIVENESS G.P.P.. Mishra* THE study leads us to believe that in the eyes of employees they do a lot for their organization and they also have
ROLE OF EMPLOYEE COMMITMENT IN ORGANIZA ANIZATIO TIONAL EFFECTIVENESS G.P.P.. Mishra* THE study leads us to believe that in the eyes of employees they do a lot for their organization and they also have
CONFLICT MANAGEMENT. Goal conflict is situation in which desired end states or preferred outcomes appear to be incompatible.
 CONFLICT MANAGEMENT Introduction To Conflict: Conflict is difficult to define, because it occurs in many different settings. The essence of conflict seems to be disagreement, contradiction, or incompatibility.
CONFLICT MANAGEMENT Introduction To Conflict: Conflict is difficult to define, because it occurs in many different settings. The essence of conflict seems to be disagreement, contradiction, or incompatibility.
The Nature and Extent of Conflict Among Volunteer Leaders in the 4-H Horse Project: Implications for Effective Program Management
 February 2012 Volume 50 Number 1 Article Number 1FEA2 Return to Current Issue The Nature and Extent of Conflict Among Volunteer Leaders in the 4-H Horse Project: Implications for Effective Program Management
February 2012 Volume 50 Number 1 Article Number 1FEA2 Return to Current Issue The Nature and Extent of Conflict Among Volunteer Leaders in the 4-H Horse Project: Implications for Effective Program Management
Daftar Pustaka. Allard, P. (2002), Life sentences: Denying welfare benefits to women convicted of
 Daftar Pustaka Allard, P. (2002), Life sentences: Denying welfare benefits to women convicted of drug offenses. Washington, DC: The Sentencing Project. Amason, A. C., dan Schweiger, D. M. (1994), Resolving
Daftar Pustaka Allard, P. (2002), Life sentences: Denying welfare benefits to women convicted of drug offenses. Washington, DC: The Sentencing Project. Amason, A. C., dan Schweiger, D. M. (1994), Resolving
Saville Consulting Wave Professional Styles Handbook
 Saville Consulting Wave Professional Styles Handbook PART 1: OVERVIEW Chapter 2: Applications This manual has been generated electronically. Saville Consulting do not guarantee that it has not been changed
Saville Consulting Wave Professional Styles Handbook PART 1: OVERVIEW Chapter 2: Applications This manual has been generated electronically. Saville Consulting do not guarantee that it has not been changed
Organizationa Behavior and Management
 Organizationa Behavior and Management Ninth Edition John M. Ivancevich Hugli Roy and Lillie Cram Cullen Chair and Professor of Organizational Behavior and Management, C. T. Bauer College of Business, University
Organizationa Behavior and Management Ninth Edition John M. Ivancevich Hugli Roy and Lillie Cram Cullen Chair and Professor of Organizational Behavior and Management, C. T. Bauer College of Business, University
Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management
 Subject Name Paper Name Paper No. 14 Module Name/Title Module Id Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management Organizational Leadership FT/FBM/09 Objectives To know about difference between
Subject Name Paper Name Paper No. 14 Module Name/Title Module Id Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management Organizational Leadership FT/FBM/09 Objectives To know about difference between
Power, Conflict, and Effectiveness: A Cross-Cultural Study in the United States and Bulgaria
 European Psychologist Power, Conflict, and Effectiveness: A Cross-Cultural Study in the United States and M. Afzalur Rahim 1, David Antonioni 2, Krum Krumov 3, and Snejana Ilieva 3 1 Western Kentucky University,
European Psychologist Power, Conflict, and Effectiveness: A Cross-Cultural Study in the United States and M. Afzalur Rahim 1, David Antonioni 2, Krum Krumov 3, and Snejana Ilieva 3 1 Western Kentucky University,
The Effect of Inter-functional Coordination on Organizational Commitment in the Hotel Industry
 The Effect of Inter-functional Coordination on Organizational Commitment in the Hotel Industry Cheng Peng Hospitality Management Program Department of Consumer Sciences The Ohio State University and R.
The Effect of Inter-functional Coordination on Organizational Commitment in the Hotel Industry Cheng Peng Hospitality Management Program Department of Consumer Sciences The Ohio State University and R.
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, UNL Libraries Libraries at University of Nebraska-Lincoln December 2007 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE Joan
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, UNL Libraries Libraries at University of Nebraska-Lincoln December 2007 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE Joan
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN ORGANIZATIONS
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN ORGANIZATIONS Éva Fenyvesi 1 - Judit Vágány 2 Judit Daróczi, Kárpátiné 3 1 college professor, Budapest Business School, Faculty of Commerce, Catering and Tourism Department of
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN ORGANIZATIONS Éva Fenyvesi 1 - Judit Vágány 2 Judit Daróczi, Kárpátiné 3 1 college professor, Budapest Business School, Faculty of Commerce, Catering and Tourism Department of
+ Capacity for Health. Presents
 + Capacity for Health 1 Presents Managing in Times of Change and Transition Part II Team Management Presenter: Doris Ferrer Roach, J.D. Executive Coach and Management Consultant + 3 levels of change management
+ Capacity for Health 1 Presents Managing in Times of Change and Transition Part II Team Management Presenter: Doris Ferrer Roach, J.D. Executive Coach and Management Consultant + 3 levels of change management
Using Your Emotional Intelligence as a Consultant. Jill Dann FBCS CITP
 Using Your Emotional Intelligence as a Consultant Jill Dann FBCS CITP Presentation Summary 1. Complete the consulting skills assessment form. 2. Look at the emotional intelligence competencies involved
Using Your Emotional Intelligence as a Consultant Jill Dann FBCS CITP Presentation Summary 1. Complete the consulting skills assessment form. 2. Look at the emotional intelligence competencies involved
Facilitating Emotional Intelligence Skills in Your Fieldwork Students
 Facilitating Emotional Intelligence Skills in Your Fieldwork Students Lisa Davis MA, OTR Marilyn Rosee MS, OTR. Objectives: 1. Define emotional intelligence. 2. Identify the components of EI. 3. Identify
Facilitating Emotional Intelligence Skills in Your Fieldwork Students Lisa Davis MA, OTR Marilyn Rosee MS, OTR. Objectives: 1. Define emotional intelligence. 2. Identify the components of EI. 3. Identify
Evaluating the differences between Managerial and Executive level Personal Competencies -A critical analysis of select IT companies
 BHAVAN S INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS Vol:4, 2 (2010) 71-76 ISSN 0974-0082 Evaluating the differences between Managerial and Executive level Personal Competencies -A critical analysis of select IT
BHAVAN S INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS Vol:4, 2 (2010) 71-76 ISSN 0974-0082 Evaluating the differences between Managerial and Executive level Personal Competencies -A critical analysis of select IT
EQ 4 Law-Academy Syllabus Emotional Intelligence Training for Law Enforcement
 The ability to (a) interpret, (b) understand, and (c) manage one s own and (d) others emotions. Emotional Intelligence (E.I.) is not about becoming emotionally detached; it is about becoming emotionally
The ability to (a) interpret, (b) understand, and (c) manage one s own and (d) others emotions. Emotional Intelligence (E.I.) is not about becoming emotionally detached; it is about becoming emotionally
Replications and Refinements
 The Journal of Social Psychology, 2008, 2009, 148(2), 149(1), xxx xxx 119 124 Copyright 2008 2009 Heldref Publications Replications and Refinements Under this heading are brief reports of studies providing
The Journal of Social Psychology, 2008, 2009, 148(2), 149(1), xxx xxx 119 124 Copyright 2008 2009 Heldref Publications Replications and Refinements Under this heading are brief reports of studies providing
ASSESSING LEADERSHIP STYLE IN MULTICULTURAL TEAM
 ASSESSING LEADERSHIP STYLE IN MULTICULTURAL TEAM B. B. Biradar 1, Dr. Vishnukant. S. Chatpalli 2 1 Research Scholar, Dept of Business Administration, Rani Channamma University, Belagavi (India) 2 Professor,
ASSESSING LEADERSHIP STYLE IN MULTICULTURAL TEAM B. B. Biradar 1, Dr. Vishnukant. S. Chatpalli 2 1 Research Scholar, Dept of Business Administration, Rani Channamma University, Belagavi (India) 2 Professor,
Profile Comparison Top-Leader
 Limbic Personality GmbH Profile Comparison Top-Leader Peter Mustermann Presented by The Limbic Personality Profile Comparison for Top Leaders There are a lot of leaders in the market but only those with
Limbic Personality GmbH Profile Comparison Top-Leader Peter Mustermann Presented by The Limbic Personality Profile Comparison for Top Leaders There are a lot of leaders in the market but only those with
A Study on Employee Engagement and its importance for Employee Retention in IT industry in India
 A Study on Employee Engagement and its importance for Employee Retention in IT industry in India 1 Dr. Sanjeevani Gangwani, 2 Dr. Rajendra Singh, 3 Ms. Khushbu Dubey, 4 Dr. Pooja Dasgupta 1 Professor,
A Study on Employee Engagement and its importance for Employee Retention in IT industry in India 1 Dr. Sanjeevani Gangwani, 2 Dr. Rajendra Singh, 3 Ms. Khushbu Dubey, 4 Dr. Pooja Dasgupta 1 Professor,
Leaders are born rather than made
 Leaders are born rather than made The quotation leaders are born rather than made is a hugely debated topic around the world. There is a predominate view that a leader is born, and cannot be made through
Leaders are born rather than made The quotation leaders are born rather than made is a hugely debated topic around the world. There is a predominate view that a leader is born, and cannot be made through
From Employee Perceived HR Practices to Employee Engagement: The Influence of Psychological Empowerment and Intrinsic Motivation Jie HE 1,a
 International Conference on Management Science and Management Innovation (MSMI 2014) From Employee Perceived HR Practices to Employee Engagement: The Influence of Psychological Empowerment and Intrinsic
International Conference on Management Science and Management Innovation (MSMI 2014) From Employee Perceived HR Practices to Employee Engagement: The Influence of Psychological Empowerment and Intrinsic
MANAGEMENT. Management Certificate Major Code: C01 DEGREES AND CERTIFICATES. Management Degree Major Code: A01
 Area: Business & Computer Science Dean: Raquel Arata (Interim) Phone: (916) 484-8361 Counseling: (916) 484-8572 Degrees: A.A. - A.A. - Leadership Certificates: Conflict Leadership Introduction to Leadership
Area: Business & Computer Science Dean: Raquel Arata (Interim) Phone: (916) 484-8361 Counseling: (916) 484-8572 Degrees: A.A. - A.A. - Leadership Certificates: Conflict Leadership Introduction to Leadership
JAME Book Review. Author: Morten Huse. Cambridge University Press, pages, $45.00 Soft cover
 JAME Book Review Boards, Governance and Value Creation: The Human Side of Corporate Governance Author: Morten Huse Cambridge University Press, 2007 392 pages, $45.00 Soft cover Reviewed by: Jonas Gabrielsson,
JAME Book Review Boards, Governance and Value Creation: The Human Side of Corporate Governance Author: Morten Huse Cambridge University Press, 2007 392 pages, $45.00 Soft cover Reviewed by: Jonas Gabrielsson,
EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT. Administrative Office Circuit Court of Lake County, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey. Employee Growth & Development
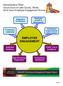 Administrative Office, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey Supportive Co-Workers Employee Growth & Development Trustworthy Leadership Continuous Organizational Improvement EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
Administrative Office, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey Supportive Co-Workers Employee Growth & Development Trustworthy Leadership Continuous Organizational Improvement EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
A STUDY ON MAPPING OF EMPLOYEES COMPETENCY
 A STUDY ON MAPPING OF EMPLOYEES COMPETENCY Krishnaveni.J BSMED, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore 641046, India. venijkrish@gmail.com Abstract This study aims to assess the competency of the employees
A STUDY ON MAPPING OF EMPLOYEES COMPETENCY Krishnaveni.J BSMED, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore 641046, India. venijkrish@gmail.com Abstract This study aims to assess the competency of the employees
Organizational Commitment. Schultz, 1
 Organizational Commitment Schultz, 1 Schultz, 2 Organizational Commitment Organizational commitment has an important place in the study of organizational behavior. This is in part due to the vast number
Organizational Commitment Schultz, 1 Schultz, 2 Organizational Commitment Organizational commitment has an important place in the study of organizational behavior. This is in part due to the vast number
Dimensions in Leadership. From Commander to Coach
 Dimensions in Leadership From Commander to Coach Take the driver s seat Engage What do I want to get out of this session? What can I contribute to this conversation? Interact What level of participation
Dimensions in Leadership From Commander to Coach Take the driver s seat Engage What do I want to get out of this session? What can I contribute to this conversation? Interact What level of participation
What do effective leaders do? What should leaders do?
 EI & Leadership What do effective leaders do? What should leaders do? Some questions to ponder Existing studies detail: What leaders are like, what they do! How they make decisions, the effects of leaders
EI & Leadership What do effective leaders do? What should leaders do? Some questions to ponder Existing studies detail: What leaders are like, what they do! How they make decisions, the effects of leaders
CASE STUDY. Incremental Validity of the Wonderlic Motivation Potential Assessment (MPA)
 Michael C. Callans, M.S.W. Daniel Nguyen, Ph.D. Brett M. Wells, Ph.D. Introduction The Wonderlic Motivation Potential Assessment (MPA) is a 30-item questionnaire that measures the extent to which employees
Michael C. Callans, M.S.W. Daniel Nguyen, Ph.D. Brett M. Wells, Ph.D. Introduction The Wonderlic Motivation Potential Assessment (MPA) is a 30-item questionnaire that measures the extent to which employees
Influences of the Organizational Citizenship Behaviors and Organizational Commitments on the Effects of Organizational Learning in Taiwan
 2010 International Conference on E-business, Management and Economics IPEDR vol.3 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Hong Kong Influences of the Organizational Citizenship Behaviors and Organizational Commitments
2010 International Conference on E-business, Management and Economics IPEDR vol.3 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Hong Kong Influences of the Organizational Citizenship Behaviors and Organizational Commitments
 I. Dealing with Other People s Negative Emotions & Reactions: The ability to effectively understand and manage other people s negative emotions and reactions in the workplace. leaders may need to exercise
I. Dealing with Other People s Negative Emotions & Reactions: The ability to effectively understand and manage other people s negative emotions and reactions in the workplace. leaders may need to exercise
Job Satisfaction among Primary School Teachers With Respect To Age, Gender and Experience
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 2, No.10, DIP: 18.01.183/20160302 ISBN: 978-1-329-99963-3 http://www.ijip.in January - March, 2016
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 2, No.10, DIP: 18.01.183/20160302 ISBN: 978-1-329-99963-3 http://www.ijip.in January - March, 2016
Perceptional Errors: Personality and Moderating Role of Age and Gender in Stock Exchanges
 IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 2278-487X, p-issn: 2319-7668. Volume 16, Issue 4. Ver. V (Apr. 2014), PP 77-81 Perceptional Errors: Personality and Moderating Role of and Gender
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 2278-487X, p-issn: 2319-7668. Volume 16, Issue 4. Ver. V (Apr. 2014), PP 77-81 Perceptional Errors: Personality and Moderating Role of and Gender
Leadership Connection to Emotional Intelligence and Stress at Workplace
 Leadership Connection to Emotional Intelligence and Stress at Workplace Nadeem Ahmad Bashir Department of Management, College of Business Administration, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia E-mail: drnab1965@hotmail.com
Leadership Connection to Emotional Intelligence and Stress at Workplace Nadeem Ahmad Bashir Department of Management, College of Business Administration, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia E-mail: drnab1965@hotmail.com
Peer reviewed. W. Lee Grubb III is an Assistant Professor of Management at East Carolina University.
 Peer reviewed W. Lee Grubb III (grubbw@mail.ecu.edu) is an Assistant Professor of Management at East Carolina University. Abstract As organizations continue to strive to hire the most productive employees,
Peer reviewed W. Lee Grubb III (grubbw@mail.ecu.edu) is an Assistant Professor of Management at East Carolina University. Abstract As organizations continue to strive to hire the most productive employees,
Global Adjustment Challenges Facing Female Business Expatriates
 Strategic Management Quarterly March 2014, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 01 10 ISSN: 2372-4951 (Print), 2372-496X (Online) Copyright The Author(s). 2014. All Rights Reserved. American Research Institute for Policy
Strategic Management Quarterly March 2014, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 01 10 ISSN: 2372-4951 (Print), 2372-496X (Online) Copyright The Author(s). 2014. All Rights Reserved. American Research Institute for Policy
THE EFFECT OF UNEQUAL SALARY SCALE ON HUMAN RESOURCES TURNOVER
 THE EFFECT OF UNEQUAL SALARY SCALE ON HUMAN RESOURCES TURNOVER Dr. Ziad Alzubi Department of Accounting, Al-Zaytoonah University of Jordan Amman-Jordan Abstract Unequal salary scale is considered one of
THE EFFECT OF UNEQUAL SALARY SCALE ON HUMAN RESOURCES TURNOVER Dr. Ziad Alzubi Department of Accounting, Al-Zaytoonah University of Jordan Amman-Jordan Abstract Unequal salary scale is considered one of
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit VI
 UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Motivation and Leadership Reading Assignment Chapter 13: Motivation and Performance Chapter 14: Leadership Suggested Reading See information below. Learning Activities (Non-Graded)
UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Motivation and Leadership Reading Assignment Chapter 13: Motivation and Performance Chapter 14: Leadership Suggested Reading See information below. Learning Activities (Non-Graded)
SUPERVISORY COMMUNICATION AND ITS EFFECT ON EMPLOYEE SATISFACTION AT THE CUT, WELKOM CAMPUS
 SUPERVISORY COMMUNICATION AND ITS EFFECT ON EMPLOYEE SATISFACTION AT THE CUT, WELKOM CAMPUS Abstract M. MOLEFE AND M. VAN DEVENTER Many large organisations tend to focus on their external communication
SUPERVISORY COMMUNICATION AND ITS EFFECT ON EMPLOYEE SATISFACTION AT THE CUT, WELKOM CAMPUS Abstract M. MOLEFE AND M. VAN DEVENTER Many large organisations tend to focus on their external communication
Antecedents and Outcomes of Employee Benefit Satisfaction: An Updated Model
 Antecedents and Outcomes of Employee Benefit Satisfaction: An Updated Model Mel E. Schnake Valdosta State University Previous research on the antecedents and outcomes of employee benefit satisfaction is
Antecedents and Outcomes of Employee Benefit Satisfaction: An Updated Model Mel E. Schnake Valdosta State University Previous research on the antecedents and outcomes of employee benefit satisfaction is
Exploring the Relative Relevance of Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Emotional Intelligence
 87 Journal of the Indian Academy of Applied Psychology, January 2009, Vol. 35, No.1, 87-97. Exploring the Relative Relevance of Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Emotional Intelligence Ajay K Jain
87 Journal of the Indian Academy of Applied Psychology, January 2009, Vol. 35, No.1, 87-97. Exploring the Relative Relevance of Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Emotional Intelligence Ajay K Jain
Thomas Kilman Conflict Resolution Grid. Compromise
 Thomas Kilman Conflict Resolution Grid Compete Collaborate (Achievement of Own Interests) (Need for Justice) (Value of Issue) Compromise Avoid Accommodate (Value of Relationship) (Importance Placed on
Thomas Kilman Conflict Resolution Grid Compete Collaborate (Achievement of Own Interests) (Need for Justice) (Value of Issue) Compromise Avoid Accommodate (Value of Relationship) (Importance Placed on
A Study of Employer Branding on Employee Attitude
 A Study of Employer Branding on Employee Attitude Seema Wadhawan 1 and Smrita Sinha 2 1 Research Scholar -Amity Business School, Amity University, Noida 2 Assistant Professor, Head of the Dept., Business
A Study of Employer Branding on Employee Attitude Seema Wadhawan 1 and Smrita Sinha 2 1 Research Scholar -Amity Business School, Amity University, Noida 2 Assistant Professor, Head of the Dept., Business
A Study of the Employee Engagement Practices in the Indian Manufacturing Sector
 A Study of the Employee Engagement Practices in the Indian Manufacturing Sector 1 Dr Shilpa Varma, 2 Ms PriyaVij, 3 Dr R Gopal 1 Associate Professor DY Patil University School of Management 2 Assistant
A Study of the Employee Engagement Practices in the Indian Manufacturing Sector 1 Dr Shilpa Varma, 2 Ms PriyaVij, 3 Dr R Gopal 1 Associate Professor DY Patil University School of Management 2 Assistant
Original Article The Moderating Role of Power Distance on the Relationship between Employee Participation and Outcome Variables
 International Journal of Health Policy and Management, 2013, 1(1), 79-83 International Journal of Health Policy and Management Kerman University of Medical Sciences Journal homepage: http://ijhpm.com Original
International Journal of Health Policy and Management, 2013, 1(1), 79-83 International Journal of Health Policy and Management Kerman University of Medical Sciences Journal homepage: http://ijhpm.com Original
City of Madison. Women s Leadership Series LEADERSHIP ASSESSMENTS. DAY 5: June 28, 2016
 City of Madison Women s Leadership Series DAY 5: June 28, 2016 LEADERSHIP ASSESSMENTS Presented by: Krista R. Morrissey ASSESSMENTS AS A TOOL Assessments are a tool to highlight areas of strength and
City of Madison Women s Leadership Series DAY 5: June 28, 2016 LEADERSHIP ASSESSMENTS Presented by: Krista R. Morrissey ASSESSMENTS AS A TOOL Assessments are a tool to highlight areas of strength and
Dr. Renu Sharma. Associate Professor, Department of Management, Institute of Innovation in Technology & Management New Delhi.
 The Impact of various of on the Motivation level of employees A comparative study of selected Indian Public and Private sector Banks Dr. Renu Sharma Associate Professor, Department of Management, Institute
The Impact of various of on the Motivation level of employees A comparative study of selected Indian Public and Private sector Banks Dr. Renu Sharma Associate Professor, Department of Management, Institute
Assessments and Tools in Coaching. Assessments
 Assessments and Tools in Coaching by Brian Nichol and Lou Raye Nichol Business coaches draw on many assessment instruments and training tools in their work with clients. It s important that a coach becomes
Assessments and Tools in Coaching by Brian Nichol and Lou Raye Nichol Business coaches draw on many assessment instruments and training tools in their work with clients. It s important that a coach becomes
The Emotional Competence Framework
 The Emotional Competence Self-Awareness Personal Competence Emotional awareness: Recognising one s emotions and their effects. Know which emotions they are feeling and why Realise the links between their
The Emotional Competence Self-Awareness Personal Competence Emotional awareness: Recognising one s emotions and their effects. Know which emotions they are feeling and why Realise the links between their
Job Satisfaction And Gender Factor Of Administrative Staff In South West Nigeria Universities E. O. Olorunsola, University Of Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria
 Job Satisfaction And Gender Factor Of Administrative Staff In South West Nigeria Universities E. O. Olorunsola, University Of Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria ABSTRACT The study investigated the level of job satisfaction
Job Satisfaction And Gender Factor Of Administrative Staff In South West Nigeria Universities E. O. Olorunsola, University Of Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria ABSTRACT The study investigated the level of job satisfaction
Explaining Organizational Responsiveness to Work-Life Balance Issues: The Role of Business Strategy and High Performance Work System
 Explaining Organizational Responsiveness to Work-Life Balance Issues: The Role of Business Strategy and High Performance Work System Jing Wang1 Anil Verma 2 1 Sobey School of Business, Saint Mary's University,
Explaining Organizational Responsiveness to Work-Life Balance Issues: The Role of Business Strategy and High Performance Work System Jing Wang1 Anil Verma 2 1 Sobey School of Business, Saint Mary's University,
Leveraging Employee Engagement Surveys Using the Turnover Stimulator Approach: A Case Study of Automotive Enterprises in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Management; Vol. 8, No. 6; 2013 ISSN 1833-3850 E-ISSN 1833-8119 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Leveraging Employee Engagement Surveys Using
International Journal of Business and Management; Vol. 8, No. 6; 2013 ISSN 1833-3850 E-ISSN 1833-8119 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Leveraging Employee Engagement Surveys Using
Cognitive Factors and its Impact on Job Satisfaction- A Study on Selected Information Technology Enabled Service Companies in Bengaluru
 DOI:10.18311/sdmimd/2017/15724 Cognitive Factors and its Impact on Job Satisfaction- A Study on Selected Information Technology Enabled Service Companies in Bengaluru Anthony Samson 1 * and K. Nagendra
DOI:10.18311/sdmimd/2017/15724 Cognitive Factors and its Impact on Job Satisfaction- A Study on Selected Information Technology Enabled Service Companies in Bengaluru Anthony Samson 1 * and K. Nagendra
TEAM EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE SURVEY REPORT
 TEAM EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE SURVEY REPORT April 15, 2013 For further information about Team Emotional Intelligence: www.geipartners.com GEI Partners 2013 This report is the property of GEI Partners (Professor
TEAM EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE SURVEY REPORT April 15, 2013 For further information about Team Emotional Intelligence: www.geipartners.com GEI Partners 2013 This report is the property of GEI Partners (Professor
A STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN JOB SATISFACTION AND EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
 A STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN JOB SATISFACTION AND EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT Shweta Malhotra Assistant Professor, Geetaratan Institute of Business Studies Affiliated to GGSIP University, Delhi 1 A STUDY OF
A STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN JOB SATISFACTION AND EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT Shweta Malhotra Assistant Professor, Geetaratan Institute of Business Studies Affiliated to GGSIP University, Delhi 1 A STUDY OF
INDEPENDENT JOURNAL OF MANAGEMENT & PRODUCTION (IJM&P)
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND ORGANIZATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS: MANAGEMENT MODEL APPROACH John N. N. Ugoani College of Management and Social Sciences, Rhema University, Nigeria E-mail: drjohnugoani@yahoo.com
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND ORGANIZATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS: MANAGEMENT MODEL APPROACH John N. N. Ugoani College of Management and Social Sciences, Rhema University, Nigeria E-mail: drjohnugoani@yahoo.com
I experience conflict in the health-care setting
 Denise A. Kish Christian Health Care Center Director, Organizational Development and Service Excellence October 2011 I experience conflict in the health-care setting 1. Never 2. Sometimes 3. Frequently
Denise A. Kish Christian Health Care Center Director, Organizational Development and Service Excellence October 2011 I experience conflict in the health-care setting 1. Never 2. Sometimes 3. Frequently
U S I N G T H E T K I A S S E S S M E N T W I T H T H E V O I C E S I N S T R U M E N T / P A G E 1. Using the TKI Assessment with the Voices
 U S I N G T H E T K I A S S E S S M E N T W I T H T H E V O I C E S I N S T R U M E N T / P A G E 1 Using the TKI Assessment with the Voices Instrument The Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode Instrument (TKI)
U S I N G T H E T K I A S S E S S M E N T W I T H T H E V O I C E S I N S T R U M E N T / P A G E 1 Using the TKI Assessment with the Voices Instrument The Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode Instrument (TKI)
The Leadership Style Preference among Sabah Ethnicities
 The Leadership Style Preference among Sabah Ethnicities Dg Kamisah A.B (Corresponding author) Faculty of Business Management P.O.Box 71, 88997 Kota Kinabalu, Sabah Universiti Teknologi MARA E-mail: dkamisah@yahoo.com
The Leadership Style Preference among Sabah Ethnicities Dg Kamisah A.B (Corresponding author) Faculty of Business Management P.O.Box 71, 88997 Kota Kinabalu, Sabah Universiti Teknologi MARA E-mail: dkamisah@yahoo.com
