Summary & Discussion
|
|
|
- Ernest Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CPET 575 Management Of Technology Summary & Discussion Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, and Public Policy, by David J. Teece (1986) From the text book: Reading I-1, pp Robert A. Burgelman, Clayton M. Christensen, and Steven C. Wheelwright, Strategic Management of Technology and Innovation, 5th edition, McGraw-Hill, ISBN , Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor A Specialty Course for M.S. Technology Graduate Program Purdue University Fort Wayne Campus 1 Summary & Discussion Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, and Public Policy, by David J. Teece (1986) David J. Teece, Sept. 2015, 2 1
2 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy Question: Why innovating firms often fail to obtain significant economic returns from an innovation while customers, imitators, and other industry participants benefits? 3 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy Executive Summary (Abstract) Introduction The Phenomenon Profiting from Innovation: Basic Building Blocks Implications for Profitability Implications for R&D Strategy, Industry Structure, and Trade Policy 4 2
3 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy Main Questions: What is the value of technological innovation? Why innovating firms often fail to obtain significant economic returns from an innovation while customers, imitators, and other industry participants benefits? 5 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy Abstract Business strategy (integrate & collaborate) When imitation is easy, market don t work well (complementary assets => profits from innovation; IP?) ; a need to establish a prior position in these complementary assets 6 3
4 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy Abstract (continue) Innovators with new products & processes which provide values to consumers may ill positioned in the market => fail Innovating firms without the required manufacturing and related capacities may die, even though they are the best at innovation Examine Implications for trade policy and domestics economic policy 7 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy - INTRODUCTION Innovation firms 1 st to commercialize a new product or process The clear existence and persistence phenomenon: competitors/imitators profited more than the innovation Question 2 Why a fast 2 nd or even a slow 3 rd might outperform the innovator? 8 4
5 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy - INTRODUCTION Exhibit 1 Explaining the Distribution of the profits from Innovation: Customers, Imitators & followers, Suppliers, Innovator (Pie Chart) Question 3 How does a firm capture the financial returns from innovation? New product/services/improved process Commercialization Joint venture, Co-production agreements, cross distribution arrangement Technology licensing (IP) 9 Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, & Public Policy - INTRODUCTION Exhibit 1 Explaining the Distribution of the profits from Innovation: Customers, Imitators & followers, Suppliers, Innovator (Pie Chart) Question 4 What determines the share of profits captured by the innovator? 10 5
6 THE PHENOMENON Exhibit 2 Taxonomy of Outcomes from the Innovation Process Win Innovator Pilkington (Float Glass) G.D. Searle (NutraSweet) DuPont (Teflon) Follower-Imitator IBM (personal computer) Matsushita (VHS video recorders) Seiko (quartz watch) Lose RC Cola (diet cola) EMI (CAT scanner) Bowmar (pocket calculator) Xerox (Office computer) De Haviland (Comet) Kodak (instant photography) Northrup (F20) DEC (personal computer) 11 THE PHENOMENON Exhibit 2 Taxonomy of Outcomes from the Innovation Process Winners (first-to-market advantage) Pilkington (Float Glass), step.htm Pilkington Float Glass Float Process, G.D. Searle (NutraSweet), DuPont (Teflon),
7 THE PHENOMENON Exhibit 2 Taxonomy of Outcomes from the Innovation Process Winners (Follower-Imitator) IBM PC vs Apple in PC Industry, 1981 Intel 16-bit Microprocessor; DOS Personal_Computer Apple II, 1997, e_ii IBM PC Apple II 13 THE PHENOMENON Exhibit 2 Taxonomy of Outcomes from the Innovation Process Loser (Innovator) RC Cola vs Coca Cola ( )and Pepsi EMI CAT Scanner (CAT Computerized axial Tomography): 1967 introduced into the US; lost market leadership in 1973, drop out of CAT scanner business in The Scanner Story,
8 THE PHENOMENON Exhibit 2 Taxonomy of Outcomes from the Innovation Process Loser (Innovator) Bowmar (pocket calculator) vs. Texas Instrument, ml/bowmar.html Xerox (office computer) vs Apple s Macintosh Xerox Alto, lto 15 THE PHENOMENON Exhibit 2 Taxonomy of Outcomes from the Innovation Process Loser (Innovator) Bowmar (pocket calculator) vs. Texas Instrument Xerox (office computer) vs Apple s Macintosh de Haviland (Comet I jet) vs Boeing 707 MIT introduced the first personal computer (Altair),
9 THE PHENOMENON Question 5 What are the issues involved in managing technological innovation? And Why a fast second or even slow third outperform the innovator? 17 PROFITING FROM INNOVATION: Basic Building Blocks A Framework: identifies the factors which determine who wins from innovation Three fundamental building blocks The Appropriability regime The Dominant Design Paradigm Complementary Assets 18 9
10 Exhibit 3. Appropriability Regime: Key Dimensions Legal Instruments Patents Copyrights Trade secrets Nature of technology Products Process Tacit Codified 19 The Dominant Design Paradigm The Preparadigmatic Stage Trial and error in market place Fierce competition on design Dominant design begin to emerge The Paradigmatic Stage Dominant design meets the needs of majority of users Competition shifts to pricing Examples The Model T Ford IBM 360 mainframe computer Douglas DC
11 Rate of Innovation Technology Adoption Process/Product Life Cycle I n n o v a t o r s E a r l y A d o p t e r s E a r l y M a j o r i t y L a t e M a j o r i t y L a g g a r d s " T h e C h a s m " Technology Adoption Process I n t r o d u c t o r y S t a g e G r o w t h S t a g e M a t u r i t y S t a g e Decline Stage T o t a l M a r k e t S a l e s T i m e 21 Exhibit 4 Innovation over Product/Industry Life Cycle P r o d u c t I n n o v a t i o n P r o c e s s I n n o v a t i o n P r e p a r a d i g m a t i c design phase P a r a d i g m a t i c design phase 22 11
12 Complementary Assets Exhibit 5. Complementary Assets Needed to Commercialize an Innovation Core Technological Know-How in Innovation (Center) Competitive manufacturing Distribution Service Complementary Technologies Others 23 Complementary Assets Exhibit 6. Complementary Assets Dependence of the Assets on the Innovation (Vertical Axis) Dependence of Innovation on Complementary Assets Generic Specialized Unilateral dependence of assets on the innovation Unilateral dependence of innovation on the assets Co-specialized Bilateral dependence 24 12
13 IMPLICATION FOR PROFITABILITY Tight Appropriability Regimes Iron clad patent or copyright protection, or The nature of product trade secrets effectively deny imitators access to the relevant knowledge Complementary Assets Generic contractual; licensing its technology Specialized or Co-Specialized Assets Investment required Contractual Relationship (?exposed to hazards?) Integration (build or acquire?) Is this a right design, dominant design? Competitors (muted?) 25 IMPLICATION FOR PROFITABILITY Weak Appropriability Regimes Innovators must turn to business strategy to keep imitator/followers at bay Competitive process: Preparadigmatic Phase Careful let Basic Design float Design Industry Standard Examples: Microelectronic (IC) Design lock in when the circuitry is chosen; product modification: debugging and software modification New families of microprocessors define a new industry and software standard: basic design parameters less well defined, until market acceptance is apparent 26 13
14 IMPLICATION FOR PROFITABILITY Weak Appropriability Regimes Competitive process: Preparadigmatic Phase Examples: Steam cars/internal combustion engine De Haviland Comet I (world first commercial jet, ) Boeing 707 (1 st ) : Douglas (3 rd ) 27 IMPLICATION FOR PROFITABILITY Exhibit 7 Complementary Assets Internalized for Innovation: Hypothetical Case #1 (Innovation Integrated into All Complementary Assets) Core Technological Know-How in Innovation (center) Competitive Engineering Distribution Service Complementary Technologies Others Personal Computer Example Complementary Assets needed Prohibitively Expensive 28 14
15 IMPLICATION FOR PROFITABILITY Exhibit 8 Complementary Assets Internalized for Innovation: Hypothetical Case #2 (Innovation Subcontracted for Manufacturing and Service) Core Technological Know-How in Innovation (center) Distribution Complementary Technologies Others 29 Contractual/Integration Strategies Possible Modes acquire needed complementary assets Contractual Modes Integration Modes Mixed Modes Decisions to integrate or license Trade-offs Compromises Mixed approached 30 15
16 Contractual/Integration Strategies Contractual Modes Independent suppliers, manufacturers, or distributors No upfront capital expenditure to build or buy the assets in need Reduced risks and cash requirements Add credibility to the innovator: IBM PC + Microsoft MS-DOS (contractual/strategic partnering) Optimal strategy when Innovator s appropriability regime is tight, and Complementary assets are available in competitive supply Integration Modes Mixed Modes 31 Contractual/Integration Strategies Integration Modes If the innovation is not tightly protected and once out is easy to imitate => securing control of complementary assets (a key success factor) Integration consider: Time and the amount of investment needed to acquire needed complementary assets See Exhibit
17 How critical to success Investment required Exhibit 9 Specialized Complementary Assets and Weak Appropriability: Integration Calculus Time required to position (relative to competitors) Optimum investment for business in question Long Short Minor Major Minor OK if timing not critical Full steam ahead Internalize Critical(majority ownership) Internalize (but if cash constrained, take minority position) Major Forget it OK if cost position tolerable Not Critical Discretionary Do not internalize (contract out) 33 Integration vs. Contract Strategies: An Analytic Summary Start Exhibit 10. Flowchart for Integration versus Contract Decision 1 Innovation requires access to complementary assets for commercial success No Commercialize immediately Yes 2 Complementary assets specialized Yes 3 Appropriability regime weak Yes No No Contact for access Contact for access 4 Specialized assets critical No Contact for access Yes 5 Cash position OK No Contact for access Integarte Yes No 6 Imitators/competitors Lecture better 3positioned No Contact for access 34 17
18 Market power of innovators/imitators vs. owners of complementary assets Further Decision If Specialized Assets in Question Exhibit 11. Contract and Integration Strategies and Outcomes for Innovators: Specialized-Asset Case Key: Weak legal/technical appropriability Strategies Outcomes Strong legal/ technological appropriability Innovator excellently positioned vs. imitators with respect to commissioning complementary assets Innovator poorly positioned vs. imitators with respect to commissioning complementary assets Innovator and imitators advantageously positioned vis-à-vis independent owners of complementary assets 1 Contract 2 Contract 3 Contract Innovator and imitators disadvantageously positioned vis-à-vis independent owners of complementary assets 4 Contract if can do so on competitive terms; integrate if necessary 5 Integrate Innovator should win; may have to share profits with Innovator asset holder should win Degree of Intellectual property protection 6 Contract (to limit exposure) Innovator will probably lose to imitators and/or asset holders 35 Implications for R&D Strategy, Industry Structure, and Trade Policy (1986) Allocating R&D Resources Small-Firm vs. Large Firm Comparisons Regimes of Appropriablity and Industry Structure Industry Maturity, New Entry, and History The Importance of Manufacturing to International Competitiveness How Trade and Investment Barriers can Impact Innovators Profits 36 18
19 Implications for R&D Strategy, Industry Structure, and Trade Policy (21 st century?) Are those issues still important? Allocating R&D Resources Regimes of Appropriablity and Industry Structure Industry Maturity, New Entry, and History The Importance of Manufacturing to International Competitiveness How Trade and Investment Barriers can Impact Innovators Profits What are Implications of Internet age to innovations in 21 st century? Open Innovation model? R&D outsourcing Global Manufacturing Global distribution, services 37 SUMMARY Question: Why innovating firms often fail to obtain significant economic returns from an innovation while customers, imitators, and other industry participants benefits? The Phenomenon Lesson learned How to Profiting from Innovation: Basic Building Blocks Use the three building blocks: the appropriability regimes, the dominant design, complementary assets Implications for R&D Strategy, Industry Structure, and Trade Policy 38 19
Summary & Discussion
 CPET 575 Management Of Technology Summary & Discussion Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, and Public Policy, by David J. Teece (1986) From
CPET 575 Management Of Technology Summary & Discussion Profiting from Technological Innovation: Implications for Integration, Collaboration, Licensing, and Public Policy, by David J. Teece (1986) From
Profiting from Technological Innovation. Innovation
 Profiting from Technological Telus New Ventures BC Prof. Elicia Maine March 26, 2003 The Profitability of Profits from Value of the Innovators ability to appropriate the value of the Increased Demand Reduced
Profiting from Technological Telus New Ventures BC Prof. Elicia Maine March 26, 2003 The Profitability of Profits from Value of the Innovators ability to appropriate the value of the Increased Demand Reduced
CPET 575 Management Of Technology. PART ONE: Readings and Reviews
 CPET 575 Management Of Technology PART ONE: Design and Implementation of Technology Strategy: An Evolutional Perspective Reading I-3: The Core Competence of the Corporation, C. K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel,
CPET 575 Management Of Technology PART ONE: Design and Implementation of Technology Strategy: An Evolutional Perspective Reading I-3: The Core Competence of the Corporation, C. K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel,
Profiting from technological innovation: Implications for integration, collaboration, licensing and public policy
 by copyright This material may be protected 17 U.S. Profiting from technological innovation: Implications for integration, collaboration, licensing and public policy 285 David J. TEECE * School of Business
by copyright This material may be protected 17 U.S. Profiting from technological innovation: Implications for integration, collaboration, licensing and public policy 285 David J. TEECE * School of Business
CPET 575 Management Of Technology. Topics of Discussion
 CPET 575 Management Of Technology Lecture on New Product Development & Project Management References: George Gruenwald, New Product Development: Responding to Market Demand, 2nd edition, NTC Business Book,
CPET 575 Management Of Technology Lecture on New Product Development & Project Management References: George Gruenwald, New Product Development: Responding to Market Demand, 2nd edition, NTC Business Book,
CPET 575 Management Of Technology Lecture on Managing Technology-Based Project. Topics of Discussion
 CPET 575 Management Of Technology Lecture on Managing Technology-Based Project Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor http://www.etcs.ipfw.edu/~lin M.S. Technology - IT and Advanced Computer Applications Purdue University
CPET 575 Management Of Technology Lecture on Managing Technology-Based Project Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor http://www.etcs.ipfw.edu/~lin M.S. Technology - IT and Advanced Computer Applications Purdue University
B Opportunities identification
 Session 2 B Opportunities identification Patents & other IP assets role as Strategic Resources Dr. Robert Pitkethly 1 Cohen - Boyer : Key Patent on Recombinant DNA Process for Producing Biologically Functional
Session 2 B Opportunities identification Patents & other IP assets role as Strategic Resources Dr. Robert Pitkethly 1 Cohen - Boyer : Key Patent on Recombinant DNA Process for Producing Biologically Functional
CPET 575 Management Of Technology
 CPET 575 Management Of Technology Part Three Enactment of Technology Strategy Developing A Firm s Innovative Capabilities References: 1. Robert A. Burgelman, Clayton M. Christensen, and Steven C. Wheelwright,
CPET 575 Management Of Technology Part Three Enactment of Technology Strategy Developing A Firm s Innovative Capabilities References: 1. Robert A. Burgelman, Clayton M. Christensen, and Steven C. Wheelwright,
Technology & Strategy. GEST-D-484 Manuel Hensmans
 Technology & Strategy GEST-D-484 Manuel Hensmans 1 Next week Present your case in terms of relevant Sources of innovation Types and patterns of innovation Standard war dynamics Timing of entry patterns
Technology & Strategy GEST-D-484 Manuel Hensmans 1 Next week Present your case in terms of relevant Sources of innovation Types and patterns of innovation Standard war dynamics Timing of entry patterns
IT strategy and innovation. Prof. R. O Callaghan
 IT strategy and innovation Prof. R. O Callaghan Innovation as a Management Process SCANNING STRATEGY RESOURCING IMPLEMENTATION Learning and re-innovation Scanning the environment for relevant signals to
IT strategy and innovation Prof. R. O Callaghan Innovation as a Management Process SCANNING STRATEGY RESOURCING IMPLEMENTATION Learning and re-innovation Scanning the environment for relevant signals to
Strategic Management of Technology and Innovation
 INSTRUCTOR 陳家麟 (Chialin Chen) Room 410, College of Management Building 2 TEXTBOOK R.A. Burgelman, C.M. Christensen, and S.C. Wheelwright, Strategic Management of Technology and Innovation, McGraw Hill,
INSTRUCTOR 陳家麟 (Chialin Chen) Room 410, College of Management Building 2 TEXTBOOK R.A. Burgelman, C.M. Christensen, and S.C. Wheelwright, Strategic Management of Technology and Innovation, McGraw Hill,
TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology
 TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology Observation Studies Lecture note based on the Ch. 8 of the text book and supplemental materials: Cooper, D.R., & Schindler, P.S., Business Research
TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology Observation Studies Lecture note based on the Ch. 8 of the text book and supplemental materials: Cooper, D.R., & Schindler, P.S., Business Research
Capturing Value Without Appropriability in Open Source Business Models
 Capturing Value Without Appropriability in Open Source Business Models Joel West www.joelwest.org Sloan Industry Studies Conference April 25, 2007 Examples of Open Source Linux operating system Started
Capturing Value Without Appropriability in Open Source Business Models Joel West www.joelwest.org Sloan Industry Studies Conference April 25, 2007 Examples of Open Source Linux operating system Started
Terry College of Business - ECON 4950
 Terry College of Business - ECON 4950 Lecture 10: Industry Analysis Primary reference: Besanko et al, Economics of Strategy, Industry Analysis Chapter Using the Tools of Game Theory, Bargaining, Pricing,
Terry College of Business - ECON 4950 Lecture 10: Industry Analysis Primary reference: Besanko et al, Economics of Strategy, Industry Analysis Chapter Using the Tools of Game Theory, Bargaining, Pricing,
It is expected that upon completing the course, the student will be able to:
 INTERAMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO METROPOLITAN CAMPUS ECONOMICS AND ADMINISTRATIVE SCIENCES FACULTY MASER IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION FOR EXECUTIVE SYLLABUS I. GENERAL INFORMATION Course title : INTEGRATION
INTERAMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO METROPOLITAN CAMPUS ECONOMICS AND ADMINISTRATIVE SCIENCES FACULTY MASER IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION FOR EXECUTIVE SYLLABUS I. GENERAL INFORMATION Course title : INTEGRATION
New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies. Chapter 10
 New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Chapter 10 Objectives Understand how companies find and develop new-product ideas. Learn the steps in the new-product development process. Know
New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Chapter 10 Objectives Understand how companies find and develop new-product ideas. Learn the steps in the new-product development process. Know
CPET 581/499 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies
 CPET 581/499 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies Lecture 5 Project Management IT Cloud Services Project Spring 2015 A Specialty Course for Purdue University s M.S. in Technology
CPET 581/499 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies Lecture 5 Project Management IT Cloud Services Project Spring 2015 A Specialty Course for Purdue University s M.S. in Technology
CPET 581 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies
 CPET 581 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies Lecture 6 Cloud-Based IT Project Management Spring 2013 A Specialty Course for Purdue University s M.S. in Technology Graduate Program:
CPET 581 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies Lecture 6 Cloud-Based IT Project Management Spring 2013 A Specialty Course for Purdue University s M.S. in Technology Graduate Program:
Step 10 & 11 Core & Competitive Positioning MIT Global Startup Labs Peru 2018
 Peru 2018 Step 10 & 11 Core & Competitive Positioning MIT Global Startup Labs Peru 2018 Why now? You have been focusing exclusively on your customer needs Now time to focus on what about your company &
Peru 2018 Step 10 & 11 Core & Competitive Positioning MIT Global Startup Labs Peru 2018 Why now? You have been focusing exclusively on your customer needs Now time to focus on what about your company &
Innovation and the comparative efficiency of governance structures in the Dutch electricity industry: a TCE application.
 Innovation and the comparative efficiency of governance structures in the Dutch electricity industry: a TCE application. Eva Niesten and Albert Jolink Erasmus University Rotterdam & University of Amsterdam
Innovation and the comparative efficiency of governance structures in the Dutch electricity industry: a TCE application. Eva Niesten and Albert Jolink Erasmus University Rotterdam & University of Amsterdam
Semiconductor Marketing, Part 2. bob.bridge at zilkerlabs.com PhD, EE, UT, 1976 CEO Zilker Labs
 Semiconductor Marketing, Part 2 bob.bridge at zilkerlabs.com PhD, EE, UT, 1976 CEO Zilker Labs 1 Guide to Understanding the Material Concept is important to success in this class! Concept is important
Semiconductor Marketing, Part 2 bob.bridge at zilkerlabs.com PhD, EE, UT, 1976 CEO Zilker Labs 1 Guide to Understanding the Material Concept is important to success in this class! Concept is important
BUSA INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY: Creating Value in Global Markets
 BUSA 4800 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY: Creating Value in Global Markets The Global Economy: A Brief Overview Opportunities and risks when firms diversify abroad Trade across nations will exceed trade within
BUSA 4800 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY: Creating Value in Global Markets The Global Economy: A Brief Overview Opportunities and risks when firms diversify abroad Trade across nations will exceed trade within
CPET 581 E-Commerce & Business Technologies. Topics E-Commerce Marketing Communications
 CPET 581 E-Commerce & Business Technologies E-Commerce Marketing Communications; References: Chapter 7. E-Commerce Marketing Communications, 8 th edition, 2012, by K. C. Laudon and C. G. Traver, publisher
CPET 581 E-Commerce & Business Technologies E-Commerce Marketing Communications; References: Chapter 7. E-Commerce Marketing Communications, 8 th edition, 2012, by K. C. Laudon and C. G. Traver, publisher
CPET 575 Management of Technology. Cisco Systems, Inc.
 CPET 575 Management of Technology CASE III-6 Cisco Systems, Inc.: Implementing ERP 1997 by Mark Cotteleer From Robert A. Burgelman, Clayton M. Christensen, and Steven C. Wheelwright, Strategic Management
CPET 575 Management of Technology CASE III-6 Cisco Systems, Inc.: Implementing ERP 1997 by Mark Cotteleer From Robert A. Burgelman, Clayton M. Christensen, and Steven C. Wheelwright, Strategic Management
CPET 575 Management Of Technology. Value Chain & Supply Chain Supporting & Enabling Technologies
 CPET 575 Management Of Technology Value Chain & Supply Chain Supporting & Enabling Technologies November 4, 2010 Paul I-HaiI Lin, Professor http://www.ipfw.edu/~lin M.S. Technology - IT and Advanced Computer
CPET 575 Management Of Technology Value Chain & Supply Chain Supporting & Enabling Technologies November 4, 2010 Paul I-HaiI Lin, Professor http://www.ipfw.edu/~lin M.S. Technology - IT and Advanced Computer
American University of Beirut Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Engineering Management Program ENMG 656: Management of Technological Innovation
 American University of Beirut Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Engineering Management Program ENMG 656: Management of Technological Innovation Course Description: The course is designed for engineers
American University of Beirut Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Engineering Management Program ENMG 656: Management of Technological Innovation Course Description: The course is designed for engineers
The multinational enterprise
 CHAPTER 2 The multinational enterprise Chapter objectives 1. Describe the characteristics of multinational enterprises. 2. Explain the internationalization process. 3. Explain why firms become multinational
CHAPTER 2 The multinational enterprise Chapter objectives 1. Describe the characteristics of multinational enterprises. 2. Explain the internationalization process. 3. Explain why firms become multinational
download instant at
 CHAPTER 2 The multinational enterprise Chapter objectives 1. Describe the characteristics of multinational enterprises. 2. Explain the internationalization process. 3. Explain why firms become multinational
CHAPTER 2 The multinational enterprise Chapter objectives 1. Describe the characteristics of multinational enterprises. 2. Explain the internationalization process. 3. Explain why firms become multinational
Ch. 16 Exploring, Displaying, and Examining Data
 TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology PART IV Analysis and Presentation of Data: Data Presentation and Description; Exploring, Displaying, and Examining Data; Hypothesis Testing; Measures
TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology PART IV Analysis and Presentation of Data: Data Presentation and Description; Exploring, Displaying, and Examining Data; Hypothesis Testing; Measures
Organizing for innovation:
 Professor: Chia-Lin Chen Technology Management & Operations Strategy Session 3 : Controlling Operations Systems & Outsourcing Organizing for innovation: When is virtual virtuous? Henry W. Chesbrough &
Professor: Chia-Lin Chen Technology Management & Operations Strategy Session 3 : Controlling Operations Systems & Outsourcing Organizing for innovation: When is virtual virtuous? Henry W. Chesbrough &
Entry Strategy for International Markets Dr Gautam Dutta
 SESSION: Entry Strategy for International Markets Dr Gautam Dutta Going Global - Decisions Should I Go Abroad? Which Markets Should I Enter? How Should I Enter Them? How Should I Market My Product? Learning
SESSION: Entry Strategy for International Markets Dr Gautam Dutta Going Global - Decisions Should I Go Abroad? Which Markets Should I Enter? How Should I Enter Them? How Should I Market My Product? Learning
Competing in Standards Driven Markets
 Competing in Standards Driven Markets When can you maintain control over the use of an innovation/idea? Strong intellectual property rights First-mover advantages Customer lock-in Network effects Standards
Competing in Standards Driven Markets When can you maintain control over the use of an innovation/idea? Strong intellectual property rights First-mover advantages Customer lock-in Network effects Standards
Intellectual Assets. Why Me? Overview
 Intellectual Assets Every organization not just business need one core competence: innovation. And every organization needs a way to record and appraise its innovative performance. Peter Drucker The Information
Intellectual Assets Every organization not just business need one core competence: innovation. And every organization needs a way to record and appraise its innovative performance. Peter Drucker The Information
Strategy Formulation: Functional Strategy. and Strategic Choice. Functional Strategy. Functional Strategy. Functional Strategy. Functional Strategy
 STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT Strategy Formulation: and Strategic Choice FINANCE R&D MARKETING PRODUCTION INVENTORY /SALES PURCHASING Production Manager Product Design Models Production Run Produce to: STRATEGIC
STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT Strategy Formulation: and Strategic Choice FINANCE R&D MARKETING PRODUCTION INVENTORY /SALES PURCHASING Production Manager Product Design Models Production Run Produce to: STRATEGIC
McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 5 Timing of Entry McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 5 Timing of Entry McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Building Growth in Troubled Times
 Building Growth in Troubled Times Professor Rebecca Henderson MIT Sloan School of Management Phone: (617) 253-6618, Email: Rhenderson@mit.edu, http://www.mit.edu/people/rhenders/home.html Who am I? Eastman
Building Growth in Troubled Times Professor Rebecca Henderson MIT Sloan School of Management Phone: (617) 253-6618, Email: Rhenderson@mit.edu, http://www.mit.edu/people/rhenders/home.html Who am I? Eastman
New Product Development
 Principles of Marketing Global Edition Kotler and Armstrong Chapter 9: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 9-1 New Product Development Copyright
Principles of Marketing Global Edition Kotler and Armstrong Chapter 9: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 9-1 New Product Development Copyright
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
 1 Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software LEARNING TRACK 3: IT INFRASTRUCTURE: MANAGEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES, AND SOLUTIONS The objective of infrastructure management is to provide a
1 Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software LEARNING TRACK 3: IT INFRASTRUCTURE: MANAGEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES, AND SOLUTIONS The objective of infrastructure management is to provide a
Course Schedule. MOB game instructions and information on the course web after this lecture! Slide 1
 Course Schedule Date 14.03.2006 16.03.2006 21.03.2006 23.03.2006 28.03.2006 30.03.2006 04.04.2006 06.04.2006 11.04.2006 13.04.2006 18.04.2006 20.04.2006 25.04.2005 27.04.2006 Topic Course introduction.
Course Schedule Date 14.03.2006 16.03.2006 21.03.2006 23.03.2006 28.03.2006 30.03.2006 04.04.2006 06.04.2006 11.04.2006 13.04.2006 18.04.2006 20.04.2006 25.04.2005 27.04.2006 Topic Course introduction.
Technology Strategy Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.912 Technology Strategy Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Strategic Management of Platforms
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.912 Technology Strategy Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Strategic Management of Platforms
Chapter Seven. New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies
 Chapter Seven New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Topic Outline New-Product Development Strategy New-Product Development
Chapter Seven New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Topic Outline New-Product Development Strategy New-Product Development
BSM906 Economic Environment of Business
 BSM906 Economic Environment of Business Lecture 5 Transactions cost Dr Sumon Bhaumik http://www.sumonbhaumik.net Problems with contracts What have we learnt so far? Property rights Are property rights
BSM906 Economic Environment of Business Lecture 5 Transactions cost Dr Sumon Bhaumik http://www.sumonbhaumik.net Problems with contracts What have we learnt so far? Property rights Are property rights
McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 7 Choosing Innovation Projects McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 7 Choosing Innovation Projects McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights
Managing Technological Innovation
 Articles Managing Technological Innovation Technological Innovation Definition: The process of developing new, marketed products and/or new production and delivery systems. Burgelman et al. 1A. Tinkering/
Articles Managing Technological Innovation Technological Innovation Definition: The process of developing new, marketed products and/or new production and delivery systems. Burgelman et al. 1A. Tinkering/
Thomas H. Byers Stanford University. Richard C. Dorf University of California, Davis. Andrew J. Nelson University of Oregon
 ' - ' ' " - Technology Ventures From Idea to Enterprise Thomas H. Byers Stanford University Richard C. Dorf University of California, Davis Andrew J. Nelson University of Oregon ^Connect Me I \ Learn 1
' - ' ' " - Technology Ventures From Idea to Enterprise Thomas H. Byers Stanford University Richard C. Dorf University of California, Davis Andrew J. Nelson University of Oregon ^Connect Me I \ Learn 1
The innovator s dilemma (Christensen) Sustaining innovation Disruptive innovation
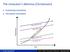 The innovator s dilemma (Christensen) Sustaining innovation Disruptive innovation 1 Change Management Peter G. Klein University of Missouri September 2009 Some recent trends Increased role of information
The innovator s dilemma (Christensen) Sustaining innovation Disruptive innovation 1 Change Management Peter G. Klein University of Missouri September 2009 Some recent trends Increased role of information
Competitive and Corporate Strategy
 Competitive and Corporate Strategy What is Strategy? Professor Nicolaj Siggelkow Different Types of Strategies Seven (7) different types of strategies as described by Henry Mintzberg (Strategy Safari)
Competitive and Corporate Strategy What is Strategy? Professor Nicolaj Siggelkow Different Types of Strategies Seven (7) different types of strategies as described by Henry Mintzberg (Strategy Safari)
Participants Guide Sustaining Competitive Advantage
 Participants Guide Sustaining Competitive Advantage 2011 RAN ONE Americas Basically there are three main ways in which you can compete in the marketplace: On Price By serving a niche market better than
Participants Guide Sustaining Competitive Advantage 2011 RAN ONE Americas Basically there are three main ways in which you can compete in the marketplace: On Price By serving a niche market better than
Profiting from Innovation
 Profiting from Innovation David J. Teece Thomas W. Tusher Professor in Global Business Director, Center for Global Strategy and Governance Faculty Director, Institute for Business Innovation UC Berkeley,
Profiting from Innovation David J. Teece Thomas W. Tusher Professor in Global Business Director, Center for Global Strategy and Governance Faculty Director, Institute for Business Innovation UC Berkeley,
Eco380: Managerial Economics I. Competitive Strategy
 Eco380: Managerial Economics I Competitive Strategy Simon Board Monday 1 3, Spring 2005 Eco380, Competitive Strategy 1 Competitive Strategy: Week 1 Introduction and Industry Analysis Simon Board Eco380,
Eco380: Managerial Economics I Competitive Strategy Simon Board Monday 1 3, Spring 2005 Eco380, Competitive Strategy 1 Competitive Strategy: Week 1 Introduction and Industry Analysis Simon Board Eco380,
Topic 2 Revision Notes
 Topic 2 Revision Notes The Environment: The industrial organisations (I/O) Paradigm: Is a theory based around the belief that organisations either succeed or fail depending upon their fit with their industry
Topic 2 Revision Notes The Environment: The industrial organisations (I/O) Paradigm: Is a theory based around the belief that organisations either succeed or fail depending upon their fit with their industry
Chapter 9 6/2/10. Global Strategy. Framework for Global Competition. Labor Pooling. Why Do Regions Matter? Technological Spillovers
 Chapter 9 Global Strategy Framework for Global Competition The economic logic of global competition depends on the costs and benefits of geographical location Regional advantages National advantages Global
Chapter 9 Global Strategy Framework for Global Competition The economic logic of global competition depends on the costs and benefits of geographical location Regional advantages National advantages Global
McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Collaboration Strategies McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Collaboration Strategies McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights
1980s. 1970s. 1990s 15/09/2015. Global Marketing Management: Planning and Organization. Learning Objectives. Global Marketing Management.
 Global Marketing Management: Planning and Organization Chapter 12 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives LO1 LO2 LO3 LO4 How global
Global Marketing Management: Planning and Organization Chapter 12 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives LO1 LO2 LO3 LO4 How global
I N T R O D U C T I O N. Business Models. Tom O Donnell 03/01/ Prof. Tom O Donnell
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Business Models Tom O Donnell 03/01/2018 20016 Prof. Tom O Donnell Business Model: A Definition busi ness mod el Noun noun: business model;; plural noun: business models a design
I N T R O D U C T I O N Business Models Tom O Donnell 03/01/2018 20016 Prof. Tom O Donnell Business Model: A Definition busi ness mod el Noun noun: business model;; plural noun: business models a design
I N T R O D U C T I O N. Business Models. Tom O Donnell 02/27/ Prof. Tom O Donnell
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Business Models Tom O Donnell 02/27/2017 20016 Prof. Tom O Donnell Business Model: A Definition busi ness mod el Noun noun: business model;; plural noun: business models a design
I N T R O D U C T I O N Business Models Tom O Donnell 02/27/2017 20016 Prof. Tom O Donnell Business Model: A Definition busi ness mod el Noun noun: business model;; plural noun: business models a design
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e
 Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part II: Strategic Actions: Strategy Formulation Chapter 9: Cooperative Strategy 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated,
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part II: Strategic Actions: Strategy Formulation Chapter 9: Cooperative Strategy 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated,
Ch. 15 Data Preparation and Description
 TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology PART IV Analysis and Presentation of Data: Data Presentation and Description; Exploring, Displaying, and Examining Data; Hypothesis Testing; Measures
TECH 646 Analysis of Research in Industry and Technology PART IV Analysis and Presentation of Data: Data Presentation and Description; Exploring, Displaying, and Examining Data; Hypothesis Testing; Measures
4800/4810. INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY: Creating Value in Global Markets 4/3/2014. The Global Economy: A Brief Overview
 4800/4810 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY: Creating Value in Global Markets The Global Economy: A Brief Overview Opportunities and risks when firms diversify abroad Trade across nations will exceed trade within
4800/4810 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY: Creating Value in Global Markets The Global Economy: A Brief Overview Opportunities and risks when firms diversify abroad Trade across nations will exceed trade within
I N T R O D U C T I O N. Business Models. Tom O Donnell 02/23/ Prof. Tom O Donnell
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Business Models Tom O Donnell 02/23/2016 20016 Prof. Tom O Donnell Business Model: A Definition busi ness mod el Noun noun: business model;; plural noun: business models a design
I N T R O D U C T I O N Business Models Tom O Donnell 02/23/2016 20016 Prof. Tom O Donnell Business Model: A Definition busi ness mod el Noun noun: business model;; plural noun: business models a design
Managing Innovation and Entrepreneurship Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.351 Managing Innovation and Entrepreneurship Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 15.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.351 Managing Innovation and Entrepreneurship Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 15.
Competition and Strategies (Courcoubetis&Weber: Chapter 6.4)
 Competition and Strategies (Courcoubetis&Weber: Chapter 6.4) Slide 1 Generic Business Strategies Michael Porter (1980) suggested three generic strategies in positioning products or services. Cost leadership
Competition and Strategies (Courcoubetis&Weber: Chapter 6.4) Slide 1 Generic Business Strategies Michael Porter (1980) suggested three generic strategies in positioning products or services. Cost leadership
Chapter 1 THE INFORMATION AGE IN WHICH YOU LIVE Changing the Face of Business
 Chapter 1 THE INFORMATION AGE IN WHICH YOU LIVE Changing the Face of Business McGraw-Hill 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reser STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Describe MIS and the 3 important
Chapter 1 THE INFORMATION AGE IN WHICH YOU LIVE Changing the Face of Business McGraw-Hill 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reser STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Describe MIS and the 3 important
INTRODUCTION TO SERVICE STRATEGY
 LECTURE - 1 INTRODUCTION TO SERVICE STRATEGY Learning objectives To introduce the competitive environment of services and formulate competitive strategies 2.1 Strategy 2.1.1. What is strategy? Determination
LECTURE - 1 INTRODUCTION TO SERVICE STRATEGY Learning objectives To introduce the competitive environment of services and formulate competitive strategies 2.1 Strategy 2.1.1. What is strategy? Determination
ABUSE OF DOMINANCE. John Pheasant Lecture to National Law University, Jodhpur 24 January 2014
 ABUSE OF DOMINANCE Lecture to National Law University, Jodhpur 24 January 2014 2 The Competition Laws Cartels Abuse of dominance Control of mergers 3 Competition Policy Goals The Protection of: Competitive
ABUSE OF DOMINANCE Lecture to National Law University, Jodhpur 24 January 2014 2 The Competition Laws Cartels Abuse of dominance Control of mergers 3 Competition Policy Goals The Protection of: Competitive
Lecture 7 Production Cost and Theory of the Firm
 Lecture 7 Production Cost and Theory of the Firm Business 5017 Managerial Economics Kam Yu Fall 2013 Outline 1 Cost Structure of a Firm Production Costs Marginal Cost in the Short Run 2 Supply Function
Lecture 7 Production Cost and Theory of the Firm Business 5017 Managerial Economics Kam Yu Fall 2013 Outline 1 Cost Structure of a Firm Production Costs Marginal Cost in the Short Run 2 Supply Function
BUSA 4800 Lecture Porter model 1/17/2008
 Forces Driving Industry Competition POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS SUPPLIERS BUYERS Rivalry Among Existing Firms Bargaining power of buyers
Forces Driving Industry Competition POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS SUPPLIERS BUYERS Rivalry Among Existing Firms Bargaining power of buyers
Econ Microeconomics Notes
 Econ 120 - Microeconomics Notes Daniel Bramucci December 1, 2016 1 Section 1 - Thinking like an economist 1.1 Definitions Cost-Benefit Principle An action should be taken only when its benefit exceeds
Econ 120 - Microeconomics Notes Daniel Bramucci December 1, 2016 1 Section 1 - Thinking like an economist 1.1 Definitions Cost-Benefit Principle An action should be taken only when its benefit exceeds
Chinese Economy and International Exposure
 Chinese Economy and International Exposure Lecture 4 International Operations of Chinese multinationals Prof. Dr. Ping Lv( 吕萍 ) School of Economics and Management University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Economy and International Exposure Lecture 4 International Operations of Chinese multinationals Prof. Dr. Ping Lv( 吕萍 ) School of Economics and Management University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
D Dr T. W.. Liu 25 July 2014
 Dr. TW T.W. Liu 25 July 2014 IP RIGHTS DO NOT ASSURE QUALITY HAVE A PATENT ON MILK PRODUCT HAVE COPYRIGHT IN A BOOK HAVE TRADEMARK FOR A WATCH HAVE INDUSTRIAL DESIGN FOR A PHONE 2 What items have patents?
Dr. TW T.W. Liu 25 July 2014 IP RIGHTS DO NOT ASSURE QUALITY HAVE A PATENT ON MILK PRODUCT HAVE COPYRIGHT IN A BOOK HAVE TRADEMARK FOR A WATCH HAVE INDUSTRIAL DESIGN FOR A PHONE 2 What items have patents?
Marketing COURSE NUMBER: 22:630:609 COURSE TITLE: Marketing Strategy
 Marketing COURSE NUMBER: 22:630:609 COURSE TITLE: Marketing Strategy COURSE DESCRIPTION This is a hands-on course that emphasizes decision-making. Throughout the course, the focus is on helping you to
Marketing COURSE NUMBER: 22:630:609 COURSE TITLE: Marketing Strategy COURSE DESCRIPTION This is a hands-on course that emphasizes decision-making. Throughout the course, the focus is on helping you to
Masters Degree in Business Administration & Diploma in Management Studies. Vasiliki Kazantzi, PhD
 Technological Education Institute of Larissa Department of Project Management School of Business Administration Staffordshire University, Business School Masters Degree in Business Administration & Diploma
Technological Education Institute of Larissa Department of Project Management School of Business Administration Staffordshire University, Business School Masters Degree in Business Administration & Diploma
RESOURCES AND CAPABILITIES ANALYSIS
 INTRODUCTION RESOURCES AND CAPABILITIES ANALYSIS Differences between organisations and companies need to be taken into account Problematic : the strategic importance of organisation s resources and capabilities
INTRODUCTION RESOURCES AND CAPABILITIES ANALYSIS Differences between organisations and companies need to be taken into account Problematic : the strategic importance of organisation s resources and capabilities
Defining your own sustainable future
 University of Copenhagen From the SelectedWorks of Jacob Johnsen, MSc September 28, 2015 Defining your own sustainable future Jacob Johnsen Available at: http://works.bepress.com/jacob_johnsen/20/ DEFINING
University of Copenhagen From the SelectedWorks of Jacob Johnsen, MSc September 28, 2015 Defining your own sustainable future Jacob Johnsen Available at: http://works.bepress.com/jacob_johnsen/20/ DEFINING
THE AMA HANDBOOK OF DUE DILIGENCE
 This is a complete list of the nearly-400 ready-to-use forms you ll find in The AMA Handbook of Due Diligence, the most exhaustive guide available on how to properly perform a due dilgence investigation
This is a complete list of the nearly-400 ready-to-use forms you ll find in The AMA Handbook of Due Diligence, the most exhaustive guide available on how to properly perform a due dilgence investigation
THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY IN THE PROCESS OF PLANNING THE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR A PROJECT
 THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY IN THE PROCESS OF PLANNING THE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR A PROJECT PhD. Student Mircea NEGRUŢĂ, Professor PhD. Ion NĂFTĂNĂILĂ, The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies ABSTRACT The
THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY IN THE PROCESS OF PLANNING THE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR A PROJECT PhD. Student Mircea NEGRUŢĂ, Professor PhD. Ion NĂFTĂNĂILĂ, The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies ABSTRACT The
Introduction to Strategic Management
 Introduction to Strategic Management Session 4 Business strategy, strategic capabilities and competitive advantage Jens Schmidt I. Why are some companies more successful than others? Operating profit per
Introduction to Strategic Management Session 4 Business strategy, strategic capabilities and competitive advantage Jens Schmidt I. Why are some companies more successful than others? Operating profit per
Business Level Strategy and Competitive Positioning
 Business Level Strategy and Competitive Positioning Chapter 5 5 1 By now teams should have gone to the course materials webpage and signed up for their Oral Presentation and evaluation 5 2 All men can
Business Level Strategy and Competitive Positioning Chapter 5 5 1 By now teams should have gone to the course materials webpage and signed up for their Oral Presentation and evaluation 5 2 All men can
Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic Competition Chapter 8 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic Competition Chapter 8 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1. Distinguish among three types
Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic Competition Chapter 8 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1. Distinguish among three types
Porter 5 forces, Generic, Value Chain 1/21/2010
 FORCES DRIVING INDUSTRY COMPETITION PORTER S FIVE FORCE ANALYSIS POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS SUPPLIERS BUYERS Threat of substitute products
FORCES DRIVING INDUSTRY COMPETITION PORTER S FIVE FORCE ANALYSIS POTENTIAL ENTRANTS Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers INDUSTRY COMPETITORS SUPPLIERS BUYERS Threat of substitute products
Henry: Understanding Strategic Management, 3 rd edition Chapter 3: Industry Analysis
 Tools and Techniques: How to undertake an analysis of Porter s five forces The five forces framework is undertaken from the perspective of an incumbent organization, i.e. an organization already operating
Tools and Techniques: How to undertake an analysis of Porter s five forces The five forces framework is undertaken from the perspective of an incumbent organization, i.e. an organization already operating
How do we begin? Strategic Management and Strategic Competitiveness. The Strategic Management Process. Defining Entrepreneurship
 Chapters 1 & 13 Strategic Management and Strategic Competitiveness How do we begin? 1 The Strategic Management Process Involves the full set of: Commitments Decisions Actions which are required for firms
Chapters 1 & 13 Strategic Management and Strategic Competitiveness How do we begin? 1 The Strategic Management Process Involves the full set of: Commitments Decisions Actions which are required for firms
CPET 581 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies
 CPET 581 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies Lecture 6-1 Cloud-Based IT Project System Requirements and Specifications Spring 2013 A Specialty Course for Purdue University s M.S.
CPET 581 Cloud Computing: Technologies and Enterprise IT Strategies Lecture 6-1 Cloud-Based IT Project System Requirements and Specifications Spring 2013 A Specialty Course for Purdue University s M.S.
Technology Strategy. Professor Rebecca Henderson MIT Sloan School of Management
 Technology Strategy Professor Rebecca Henderson MIT Sloan School of Management Effective strategies address three key problems: How will we Create value? How will we Deliver value? How will we Capture
Technology Strategy Professor Rebecca Henderson MIT Sloan School of Management Effective strategies address three key problems: How will we Create value? How will we Deliver value? How will we Capture
Knowledge Assets Management
 Theme 11 Knowledge Assets Management Spring, 2014 Sang W. KIM, Ph.D Professor, Chungbuk National University sierra@cbnu.ac.kr 0 contents 목차 1. Four Types of Knowledge Assets 1 2 1. Four Types of Knowledge
Theme 11 Knowledge Assets Management Spring, 2014 Sang W. KIM, Ph.D Professor, Chungbuk National University sierra@cbnu.ac.kr 0 contents 목차 1. Four Types of Knowledge Assets 1 2 1. Four Types of Knowledge
Chapter Nine. New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies. Chapter 9- slide 1
 Chapter Nine New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 9- slide 1 New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle
Chapter Nine New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 9- slide 1 New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle
Volume Title: The Rate and Direction of Inventive Activity Revisited. Volume Author/Editor: Josh Lerner and Scott Stern, editors
 This PDF is a selection from a published volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: The Rate and Direction of Inventive Activity Revisited Volume Author/Editor: Josh Lerner and
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: The Rate and Direction of Inventive Activity Revisited Volume Author/Editor: Josh Lerner and
STRATEGIES FOR MATURE AND DECLINING MARKETS
 STRATEGIES FOR MATURE AND DECLINING MARKETS MKTG902 Summer 10 Harmancioglu 1 Transition From Market Growth to Maturity to Decline The Transition or Shake out Stage of the Generalized PLC Product categ
STRATEGIES FOR MATURE AND DECLINING MARKETS MKTG902 Summer 10 Harmancioglu 1 Transition From Market Growth to Maturity to Decline The Transition or Shake out Stage of the Generalized PLC Product categ
Strategic Management. Gregory G. Dess University of Texas at Dallas. G. T. Lumpkin Syracuse University. Alan B. Eisner Pace University.
 Gregory G. Dess University of Texas at Dallas G. T. Lumpkin Syracuse University Alan B. Eisner Pace University Strategic Management text and cases fifth edition I McGraw-Hill Irwin Contents port l Strategic
Gregory G. Dess University of Texas at Dallas G. T. Lumpkin Syracuse University Alan B. Eisner Pace University Strategic Management text and cases fifth edition I McGraw-Hill Irwin Contents port l Strategic
Lecture 4 The Vertical Boundaries of the Firm: Make vs. Buy
 Lecture 4 The Vertical Boundaries of the Firm: Make vs. Buy 1 Overview Make vs. Buy Upstream, downstream Defining boundaries Some make-or-buy fallacies Reasons to buy Reasons to make Summarizing make or
Lecture 4 The Vertical Boundaries of the Firm: Make vs. Buy 1 Overview Make vs. Buy Upstream, downstream Defining boundaries Some make-or-buy fallacies Reasons to buy Reasons to make Summarizing make or
IP Leaders Forum, Taipei - Best Practices in Building a Defensive Patent Strategy
 IP Leaders Forum, Taipei - Best Practices in Building a Defensive Patent Strategy Jason Resnick July 2012 Fact: Patent litigation is now a highly successful and reproducible business model, starting to
IP Leaders Forum, Taipei - Best Practices in Building a Defensive Patent Strategy Jason Resnick July 2012 Fact: Patent litigation is now a highly successful and reproducible business model, starting to
Strategic Management
 CHAPTER NINE Strategic Management DETAILED LECTURE OUTLINE I. Importance of strategic management A. Strategic management consists of the analysis and decisions necessary to formulate and implement strategy
CHAPTER NINE Strategic Management DETAILED LECTURE OUTLINE I. Importance of strategic management A. Strategic management consists of the analysis and decisions necessary to formulate and implement strategy
MGMT 7160 Global Strategic Management
 Global Strategic Management Strategy Formulation: Corporate Strategy Levels of Strategy Functional Strategy How do we coordinate? Business Level Strategy How do we compete? Corporate Level Strategy Where
Global Strategic Management Strategy Formulation: Corporate Strategy Levels of Strategy Functional Strategy How do we coordinate? Business Level Strategy How do we compete? Corporate Level Strategy Where
The 16th Annual The Nuts and Bolts of Business Plans MIT Course January 2005
 Background Image by MIT OCW. The 16th Annual The MIT Course 15.975 January 2005 Joost Bonsen MIT Sloan Graduate Student Former Lead Organizer, MIT $50K Competition Joe Hadzima (MIT S.B., M.S. in Management;
Background Image by MIT OCW. The 16th Annual The MIT Course 15.975 January 2005 Joost Bonsen MIT Sloan Graduate Student Former Lead Organizer, MIT $50K Competition Joe Hadzima (MIT S.B., M.S. in Management;
The mystery surrounding data rights stems from the fact that intellectual
 The Myth of Data Rights Peter A. Czech The mystery surrounding data rights stems from the fact that intellectual property (IP) and data rights are among the more complex issues in acquisition management.
The Myth of Data Rights Peter A. Czech The mystery surrounding data rights stems from the fact that intellectual property (IP) and data rights are among the more complex issues in acquisition management.
Queens College GLOBAL ECONOMICS. Professor: Queens College Faculty
 . Queens College GLOBAL ECONOMICS Professor: Queens College Faculty Texts: Global Business Today, 4 th edition, by Charles W. L. Hill, McGraw-Hill, 2006 Additional Reading Materials: The Company, by John
. Queens College GLOBAL ECONOMICS Professor: Queens College Faculty Texts: Global Business Today, 4 th edition, by Charles W. L. Hill, McGraw-Hill, 2006 Additional Reading Materials: The Company, by John
35C04000 Global Logistics and Distribution Networks (6 cr) Responsible teacher: Markku Tinnilä Status of the Course: Bachelor s programme,
 Contents 35C04000 Global Logistics and Distribution Networks (6 cr)... 2 35E03000 Sustainable Supply Chains (6 cr)... 3 35E02000 Procurement and Strategic Sourcing (6 cr)... 4 35E00400 Coordination of
Contents 35C04000 Global Logistics and Distribution Networks (6 cr)... 2 35E03000 Sustainable Supply Chains (6 cr)... 3 35E02000 Procurement and Strategic Sourcing (6 cr)... 4 35E00400 Coordination of
MBA Essentials for Lawyers. Module 3
 MBA Essentials for Lawyers Module 3 Introduction Course Objective: To provide you with an understanding of the core strategic tools, skills, models and concepts that lie at the heart of all MBA courses
MBA Essentials for Lawyers Module 3 Introduction Course Objective: To provide you with an understanding of the core strategic tools, skills, models and concepts that lie at the heart of all MBA courses
Constructing the Price of the Technology in IP Licensing Negotiations
 Constructing the Price of the Technology in IP Licensing Negotiations Topics What is Valuation Value and Price Key Terms of a Licensing Agreement Constructing the Price IP Valuation Valuation The process
Constructing the Price of the Technology in IP Licensing Negotiations Topics What is Valuation Value and Price Key Terms of a Licensing Agreement Constructing the Price IP Valuation Valuation The process
CPET 581 E-Commerce & Business Technologies
 CPET 581 E-Commerce & Business Technologies Technologies for E-Commerce Marketing References: Chapter 6. E-Commerce Marketing Concepts: Social, Mobile, Local, from the text book: e-commerce: Business,
CPET 581 E-Commerce & Business Technologies Technologies for E-Commerce Marketing References: Chapter 6. E-Commerce Marketing Concepts: Social, Mobile, Local, from the text book: e-commerce: Business,
