Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts
|
|
|
- Berniece McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Chapter 2 PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
2 2-2 Learning Objective 1 Identify and give examples of each of the three basic manufacturing cost categories.
3 2-3 Classifications of Manufacturing Costs Direct Materials Direct Labor The Product Manufactu ring Overhead
4 2-4 Direct Materials Raw materials that become an integral part of the product and that can be conveniently traced directly to it. Example: A radio installed in an automobile
5 2-5 Direct Labor Those labor costs that can be easily traced to individual units of product. Example: Wages paid to automobile assembly workers
6 2-6 Manufacturing Overhead Manufacturing costs that cannot be easily traced directly to specific units produced. Examples: Indirect materials and indirect labor
7 2-7 Nonmanufacturing Costs Administrative Costs All executive, organizational, and clerical costs.
8 2-8 Learning Objective 2 Distinguish between product costs and period costs and give examples of each.
9 2-9 Product Costs Versus Period Costs Product costs include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Inventory Cost of Good Sold Period costs include all selling costs and administrative costs. Expense Sale Balance Sheet Income Statement Income Statement
10 2-10 Quick Check Which of the following costs would be considered a period rather than a product cost in a manufacturing company? A. Manufacturing equipment depreciation. B. Property taxes on corporate headquarters. C. Direct materials costs. D. Electrical costs to light the production facility. E. Sales commissions.
11 2-11 Quick Check Which of the following costs would be considered a period rather than a product cost in a manufacturing company? A. Manufacturing equipment depreciation. B. Property taxes on corporate headquarters. C. Direct materials costs. D. Electrical costs to light the production facility. E. Sales commissions.
12 2-12 Classifications of Costs Manufacturing costs are often classified as follows: Direct Material Direct Labor Prime Cost Manufacturing Overhead Conversion Cost
13 2-13 Learning Objective 3 Understand cost behavior patterns including variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
14 2-14 Cost Classifications for Predicting Cost Behavior Cost behavior refers to how a cost will react to changes in the level of activity. The most common classifications are: Variable costs. Fixed costs Mixed costs.
15 2-15 Variable Cost Total Texting Bill Your total texting bill is based on how many texts you send. Number of Texts Sent
16 2-16 Variable Cost Per Unit Cost Per Text Sent The cost per text sent is constant at 5 cents per text message. Number of Texts Sent
17 2-17 The Activity Base (Cost Driver) Machine hours Units produced A measure of what causes the incurrence of a variable cost Miles driven Labor hours
18 2-18 Fixed Cost Monthly Cell Phone Contract Fee Your monthly contract fee for your cell phone is fixed for the number of monthly minutes in your contract. The monthly contract fee does not change based on the number of calls you make. Number of Minutes Used Within Monthly Plan
19 2-19 Fixed Cost Per Unit Monthly Cell Phone Contract Fee Within the monthly contract allotment, the average fixed cost per cell phone call made decreases as more calls are made. Number of Minutes Used Within Monthly Plan
20 2-20 Types of Fixed Costs Committed Discretionary Long-term, cannot be significantly reduced in the short term. May be altered in the short-term by current managerial decisions Examples Examples Depreciation on Buildings and Equipment and Real Estate Taxes Advertising and Research and Development
21 2-21 The Linearity Assumption and the Relevant Range Total Cost Economist s Curvilinear Cost Function Relevant Range A straight line closely approximates a curvilinear variable cost line within the relevant range. Accountant s Straight-Line Approximation (constant unit variable cost) Activity
22 2-22 Fixed Costs and the Relevant Range For example, assume office space is available at a rental rate of $30,000 per year in increments of 1,000 square feet. Fixed costs would increase in a step fashion at a rate of $30,000 for each additional 1,000 square feet.
23 2-23 Rent Cost in Thousands of Dollars Fixed Costs and the Relevant Range 90 Relevant 60 Range The relevant range of activity for a fixed cost is the range of activity over which the graph of the cost is flat. 1,000 2,000 3,000 Rented Area (Square Feet)
24 2-24 Cost Classifications for Predicting Cost Behavior
25 2-25 Quick Check Which of the following costs would be variable with respect to the number of cones sold at a Baskins & Robbins shop? (There may be more than one correct answer.) A. The cost of lighting the store. B. The wages of the store manager. C. The cost of ice cream. D. The cost of napkins for customers.
26 2-26 Quick Check Which of the following costs would be variable with respect to the number of cones sold at a Baskins & Robbins shop? (There may be more than one correct answer.) A. The cost of lighting the store. B. The wages of the store manager. C. The cost of ice cream. D. The cost of napkins for customers.
27 2-27 Mixed Costs (also called semivariable costs) A mixed cost contains both variable and fixed elements. Consider the example of utility cost. Total Utility Cost Y l a t o ed x i m t s o c T Variable Cost per KW Activity (Kilowatt Hours) X Fixed Monthly Utility Charge
28 2-28 Mixed Costs Total Utility Cost Y l a t o e x i m d t s o c T Variable Cost per KW Activity (Kilowatt Hours) X Fixed Monthly Utility Charge
29 2-29 Mixed Costs An Example If your fixed monthly utility charge is $40, your variable cost is $0.03 per kilowatt hour, and your monthly activity level is 2,000 kilowatt hours, what is the amount of your utility bill?
30 2-30 Analysis of Mixed Costs Account Analysis and the Engineering Approach In account analysis, each account is classified as either variable or fixed based on the analyst s knowledge of how the account behaves. The engineering approach classifies costs based upon an industrial engineer s evaluation of production methods, and material, labor, and overhead requirements.
31 2-31 Learning Objective 4 Analyze a mixed cost using a scattergraph plot and the high-low method.
32 2-32 Scattergraph Plots An Example Assume the following hours of maintenance work and the total maintenance costs for six months.
33 2-33 The Scattergraph Method Plot the data points on a graph (Total Cost Y vs. Activity X). Total Maintenance Cost Y X Hours of Maintenance
34 2-34 The High-Low Method An Example The variable cost per hour of maintenance is equal to the change in cost divided by the change in hours. $2,400 = $6.00/hour 400
35 2-35 The High-Low Method An Example Total Fixed Cost = Total Cost Total Variable Cost Total Fixed Cost = $9,800 ($6/hour 850 hours) Total Fixed Cost = $9,800 $5,100 Total Fixed Cost = $4,700
36 2-36 The High-Low Method An Example The Cost Equation for Maintenance Y = $4,700 + $6.00X
37 2-37 Quick Check Sales salaries and commissions are $10,000 when 80,000 units are sold, and $14,000 when 120,000 units are sold. Using the high-low method, what is the variable portion of sales salaries and commission? a. $0.08 per unit b. $0.10 per unit c. $0.12 per unit d. $0.125 per unit
38 2-38 Quick Check Sales salaries and commissions are $10,000 when 80,000 units are sold, and $14,000 when 120,000 units are sold. Using the high-low method, what is the variable portion of sales salaries and commission? a. $0.08 per unit b. $0.10 per unit c. $0.12 per unit d. $0.125 per unit
39 2-39 Quick Check Sales salaries and commissions are $10,000 when 80,000 units are sold, and $14,000 when 120,000 units are sold. Using the high-low method, what is the fixed portion of sales salaries and commissions? a. $ 2,000 b. $ 4,000 c. $10,000 d. $12,000
40 2-40 Quick Check Sales salaries and commissions are $10,000 when 80,000 units are sold, and $14,000 when 120,000 units are sold. Using the high-low method, what is the fixed portion of sales salaries and commissions? a. $ 2,000 b. $ 4,000 c. $10,000 d. $12,000
41 2-41 Least-Squares Regression Method A method used to analyze mixed costs if a scattergraph plot reveals an approximately linear relationship between the X and Y variables. This method uses all of the data points to estimate the fixed and variable cost components of a mixed cost. The goal of this method is to fit a straight line to the data that minimizes the sum of the squared errors.
42 2-42 Least-Squares Regression Method Software can be used to fit a regression line through the data points. The cost analysis objective is the same: Y = a + bx Least-squares regression also provides a statistic, called the R2, which is a measure of the goodness of fit of the regression line to the data points.
43 2-43 Comparing Results From the Two Methods The two methods just discussed provide different estimates of the fixed and variable cost components of a mixed cost. This is to be expected because each method uses differing amounts of the data points to provide estimates. Least-squares regression provides the most accurate estimate because it uses all the data points.
44 2-44 Learning Objective 5 Prepare income statements for a merchandising company using the traditional and contribution formats.
45 2-45 The Traditional and Contribution Formats Used primarily for external reporting.
46 2-46 Uses of the Contribution Format The contribution income statement format is used as an internal planning and decision-making tool. We will use this approach for: 1.Cost-volume-profit analysis (Chapter 5). 2.Budgeting (Chapter 8). 3.Segmented reporting of profit data (Chapter 6). 4.Special decisions such as pricing and make-or-buy analysis (Chapter 12).
47 2-47 Learning Objective 6 Understand the differences between direct and indirect costs.
48 2-48 Assigning Costs to Cost Objects Direct costs Indirect costs Costs that can be easily and conveniently traced to a unit of product or other cost object. Examples: direct material and direct labor Costs that cannot be easily and conveniently traced to a unit of product or other cost object. Example: manufacturing overhead
49 2-49 Learning Objective 7 Understand cost classifications used in making decisions: differential costs, opportunity costs, and sunk costs.
50 2-50 Cost Classifications for Decision Making Every decision involves a choice between at least two alternatives. Only those costs and benefits that differ between alternatives are relevant in a decision. All other costs and benefits can and should be ignored as irrelevant.
51 2-51 Differential Cost and Revenue Costs and revenues that differ among alternatives. Example: You have a job paying $1,500 per month in your hometown. You have a job offer in a neighboring city that pays $2,000 per month. The commuting cost to the city is $300 per month. Differential revenue is: $2,000 $1,500 = $500 Differential cost is: $300
52 2-52 Opportunity Cost The potential benefit that is given up when one alternative is selected over another. Example: If you were not attending college, you could be earning $15,000 per year. Your opportunity cost of attending college for one year is $15,000.
53 2-53 Sunk Costs Sunk costs have already been incurred and cannot be changed now or in the future. These costs should be ignored when making decisions. Example: Suppose you had purchased gold for $400 an ounce, but now it is selling for $250 an ounce. Should you wait for the gold to reach $400 an ounce before selling it? You may say, Yes even though the $400 purchase is a sunk costs.
54 2-54 Quick Check Suppose you are trying to decide whether to drive or take the train to Portland to attend a concert. You have ample cash to do either, but you don t want to waste money needlessly. Is the cost of the train ticket relevant in this decision? In other words, should the cost of the train ticket affect the decision of whether you drive or take the train to Portland? A. Yes, the cost of the train ticket is relevant. B. No, the cost of the train ticket is not relevant.
55 2-55 Quick Check Suppose you are trying to decide whether to drive or take the train to Portland to attend a concert. You have ample cash to do either, but you don t want to waste money needlessly. Is the cost of the train ticket relevant in this decision? In other words, should the cost of the train ticket affect the decision of whether you drive or take the train to Portland? A. Yes, the cost of the train ticket is relevant. B. No, the cost of the train ticket is not relevant.
56 2-56 Quick Check Suppose you are trying to decide whether to drive or take the train to Portland to attend a concert. You have ample cash to do either, but you don t want to waste money needlessly. Is the annual cost of licensing your car relevant in this decision? A. Yes, the licensing cost is relevant. B. No, the licensing cost is not relevant.
57 2-57 Quick Check Suppose you are trying to decide whether to drive or take the train to Portland to attend a concert. You have ample cash to do either, but you don t want to waste money needlessly. Is the annual cost of licensing your car relevant in this decision? A. Yes, the licensing cost is relevant. B. No, the licensing cost is not relevant.
58 2-58 Quick Check Suppose that your car could be sold now for $5,000. Is this a sunk cost? A. Yes, it is a sunk cost. B. No, it is not a sunk cost.
59 2-59 Quick Check Suppose that your car could be sold now for $5,000. Is this a sunk cost? A. Yes, it is a sunk cost. B. No, it is not a sunk cost.
60 2-60 Summary of the Types of Cost Classifications Financial Reporting Predicting Cost Behavior Assigning Costs to Cost Objects Making Business Decisions
61 Least-Squares Regression Computations Appendix 2A PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
62 2-62 Learning Objective 8 Analyze a mixed cost using a scattergraph plot and the least-squares regression method.
63 2-63 Simple Regression Analysis Matrix, Inc. wants to know its average fixed cost and variable cost per meals served. Using the data to the right, let s see how to do a regression using Microsoft Excel.
64 2-64 Simple Regression Using Excel You will need three pieces of information from your regression analysis: 1. Estimated Variable Cost Per Unit (line slope) 2. Estimated Fixed Costs (line intercept) 3. Goodness of fit, or R2 To get these three pieces information we will need to use three Excel functions. SLOPE, INTERCEPT, and RSQ
65 2-65 Simple Regression Using Excel Place your cursor in cell F4 and press the = key. Click on the pull down menu and scroll down to More Functions...
66 2-66 Simple Regression Using Excel Scroll down to the Statistical functions. Now scroll down the statistical functions until you highlight SLOPE
67 2-67 Simple Regression Using Excel 1. In the Known_y s box, enter C4:C19 for the range. 2. In the Known_x s box, enter D4:D19 for the range.
68 2-68 Simple Regression Using Excel Here is the estimate of the slope of the line. 1. In the Known_y s box, enter C4:C19 for the range. 2. In the Known_x s box, enter D4:D19 for the range.
69 2-69 Simple Regression Using Excel With your cursor in cell F5, press the = key and go to the pull down menu for Special Functions. Select Statistical and scroll down to highlight the INTERCEPT function.
70 2-70 Simple Regression Using Excel Here is the estimate of the fixed costs. 1. In the Known_y s box, enter C4:C19 for the range. 2. In the Known_x s box, enter D4:D19 for the range.
71 2-71 Simple Regression Using Excel Finally, we will determine the goodness of fit, or R2, by using the RSQ function.
72 2-72 Simple Regression Using Excel Here is the estimate of R2. 1. In the Known_y s box, enter C4:C19 for the range. 2. In the Known_x s box, enter D4:D19 for the range.
MBP1133 Managerial Accounting Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar
 MBP1133 Managerial Accounting Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L2 Managerial Accounting and Costs Concepts www.notes638.wordpress.com 1 Summary of the Types of Cost Classifications Financial Reporting Predicting
MBP1133 Managerial Accounting Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L2 Managerial Accounting and Costs Concepts www.notes638.wordpress.com 1 Summary of the Types of Cost Classifications Financial Reporting Predicting
CHAPTER. Activity Cost Behavior
 3-1 CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior 3-2 Objectives 1. Define cost behavior After for fixed, variable, and studying this mixed costs. chapter, you should 2. Explain the role of be the resource usage model
3-1 CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior 3-2 Objectives 1. Define cost behavior After for fixed, variable, and studying this mixed costs. chapter, you should 2. Explain the role of be the resource usage model
Differential Analysis: The Key to Decision Making
 Differential Analysis: The Key to Decision Making Chapter 10 Learning Objective 1 Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA
Differential Analysis: The Key to Decision Making Chapter 10 Learning Objective 1 Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA
TM 2-1 MANUFACTURING COST CLASSIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL REPORTING
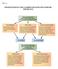 TM 2-1 MANUFACTURING COST CLASSIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL REPORTING TM 2-2 COST CLASSIFICATIONS TO PREDICT COST BEHAVIOR To predict how costs react to changes in activity, costs are often classified as variable
TM 2-1 MANUFACTURING COST CLASSIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL REPORTING TM 2-2 COST CLASSIFICATIONS TO PREDICT COST BEHAVIOR To predict how costs react to changes in activity, costs are often classified as variable
PROCESS COST ACCOUNTING
 Chapter 20 PROCESS COST ACCOUNTING PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright 2015 by
Chapter 20 PROCESS COST ACCOUNTING PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright 2015 by
DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS
 DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS ** CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS IN THIS MODULE APPEAR IN VARIOUS CHAPTERS ** Key Terms and Concepts to Know Major Management Activities Planning - formulating long and short-term plans
DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS ** CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS IN THIS MODULE APPEAR IN VARIOUS CHAPTERS ** Key Terms and Concepts to Know Major Management Activities Planning - formulating long and short-term plans
ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING OPERATIONS
 Chapter 05 ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING OPERATIONS PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Chapter 05 ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING OPERATIONS PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA McGraw-Hill/Irwin
CHAPTER ONE: OVEVIEW OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING
 CHAPTER ONE: OVEVIEW OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING The Basic Objectives of Accounting Basic objective of accounting is to provide stakeholders with useful information about a business enterprise in order to
CHAPTER ONE: OVEVIEW OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING The Basic Objectives of Accounting Basic objective of accounting is to provide stakeholders with useful information about a business enterprise in order to
TYPES OF COST CLASSIFICATIONS CLASSIFICATION BY BEHAVIOR
 18-11 C 2 Cost TYPES OF COST CLASSIFICATIONS CLASSIFICATION BY BEHAVIOR Cost Activity Activity Cost Cost behavior refers to how a cost will react to changes in the level of business activity. Total fixed
18-11 C 2 Cost TYPES OF COST CLASSIFICATIONS CLASSIFICATION BY BEHAVIOR Cost Activity Activity Cost Cost behavior refers to how a cost will react to changes in the level of business activity. Total fixed
HUM 211: Financial & Managerial Accounting
 Chapter 20 HUM 211: Financial & Managerial Accounting Lecture 08: Managerial Accounting (Concepts & Principles) Masud Jahan Department of Science and Humanities Military Institute of Science and Technology
Chapter 20 HUM 211: Financial & Managerial Accounting Lecture 08: Managerial Accounting (Concepts & Principles) Masud Jahan Department of Science and Humanities Military Institute of Science and Technology
10-1. Learning Objective. Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision.
 10-1 Learning Objective Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 10-2 Relevant Costs and Benefits A relevant cost is a cost that differs between alternatives. A relevant benefit
10-1 Learning Objective Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 10-2 Relevant Costs and Benefits A relevant cost is a cost that differs between alternatives. A relevant benefit
Relevant Costs for Decision Making
 11-1 Management Accounting Lecture 17 (Chapter 11) Relevant Costs for Decision Making Today s Agenda Relevant Costs vs. Irrelevant Costs Differential Approach vs. Total Cost Approach Product Transfer Decision
11-1 Management Accounting Lecture 17 (Chapter 11) Relevant Costs for Decision Making Today s Agenda Relevant Costs vs. Irrelevant Costs Differential Approach vs. Total Cost Approach Product Transfer Decision
Relevant Costs for Decision Making
 Relevant Costs for Decision Making Chapter Thirteen 13-2 Learning Objective 1 Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 13-3 Cost Concepts for Decision Making A relevant cost is
Relevant Costs for Decision Making Chapter Thirteen 13-2 Learning Objective 1 Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 13-3 Cost Concepts for Decision Making A relevant cost is
An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes
 CHAPTER 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Overview This chapter introduces the basic terminology of cost accounting. Communication among managers and management accountants is greatly facilitated
CHAPTER 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Overview This chapter introduces the basic terminology of cost accounting. Communication among managers and management accountants is greatly facilitated
Full file at https://fratstock.eu
 Chapter 02 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts True / False Questions 1. Selling costs can be either direct or indirect costs. True False 2. A direct cost is a cost that cannot be easily traced to
Chapter 02 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts True / False Questions 1. Selling costs can be either direct or indirect costs. True False 2. A direct cost is a cost that cannot be easily traced to
Managerial Accounting Chapter 5
 Managerial Accounting Chapter 5 It s really Economics Except we analyze entries to do the calculations Cost Behavior Analysis The study of how specific costs respond to changes in the level of business
Managerial Accounting Chapter 5 It s really Economics Except we analyze entries to do the calculations Cost Behavior Analysis The study of how specific costs respond to changes in the level of business
Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use
 Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use least three cost behavior patterns variable, fixed, and mixed are found in most organizations.of course, many other types of cost behavior patterns exist, but these three
Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use least three cost behavior patterns variable, fixed, and mixed are found in most organizations.of course, many other types of cost behavior patterns exist, but these three
Full file at Chapter 02 - Basic Cost Management Concepts
 CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS Learning Objectives 1. Explain what is meant by the word cost. 2. Distinguish among product costs, period costs, and expenses. 3. Describe the role of costs in
CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS Learning Objectives 1. Explain what is meant by the word cost. 2. Distinguish among product costs, period costs, and expenses. 3. Describe the role of costs in
Introduction to Managerial Accounting 7th Edition Brewer Garrison Noreen Test Bank. Download:
 Introduction to Managerial Accounting 7th Edition Brewer Garrison Noreen Test Bank. Download: https://testbankarea.com/download/introduction-managerial-accounting- 7th-edition-brewer-garrison-noreen-test-bank/
Introduction to Managerial Accounting 7th Edition Brewer Garrison Noreen Test Bank. Download: https://testbankarea.com/download/introduction-managerial-accounting- 7th-edition-brewer-garrison-noreen-test-bank/
Introduction to Managerial Accounting 7th Edition Brewer Garrison Noreen Test Bank. Download:
 Introduction to Managerial Accounting 7th Edition Brewer Garrison Noreen Test Bank. Download: https://testbankarea.com/download/introduction-managerial-accounting- 7th-edition-brewer-garrison-noreen-test-bank/
Introduction to Managerial Accounting 7th Edition Brewer Garrison Noreen Test Bank. Download: https://testbankarea.com/download/introduction-managerial-accounting- 7th-edition-brewer-garrison-noreen-test-bank/
3. Which is not an inventory account manufacturing companies have: a) Raw Materials b) Manufacturing Overhead c) Work in Process d) Finished Goods
 Chapter 1 Question Review 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of managerial accounting: a) Emphasizes decisions affecting the future b) Mandatory for external reports c) Need not follow GAAP
Chapter 1 Question Review 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of managerial accounting: a) Emphasizes decisions affecting the future b) Mandatory for external reports c) Need not follow GAAP
Chapter 2 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts
 Chapter 2 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Solutions to Questions 2-1 The three major elements of product costs in a manufacturing company are direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Chapter 2 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Solutions to Questions 2-1 The three major elements of product costs in a manufacturing company are direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Managerial Accounting: An Overview
 Managerial Accounting: An Overview Chapter 1 PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright
Managerial Accounting: An Overview Chapter 1 PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright
INVENTORIES AND COST OF SALES
 Chapter 06 INVENTORIES AND COST OF SALES PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Chapter 06 INVENTORIES AND COST OF SALES PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Fill-in-the-Blank Equations. Exercises
 Chapter 15 (1) Introduction to Managerial Accounting Study Guide Solutions 1. Merchandise available for sale 2. Cost of merchandise sold Fill-in-the-Blank Equations 3. Cost of goods manufactured during
Chapter 15 (1) Introduction to Managerial Accounting Study Guide Solutions 1. Merchandise available for sale 2. Cost of merchandise sold Fill-in-the-Blank Equations 3. Cost of goods manufactured during
Chapter 02 Cost Terminology and Cost Behaviors. Lecture Outline. LO.1 Why are costs associated with a cost object? A. Introduction
 Solution Manual for Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions 8th Edition by Kinney and Raiborn Link full download of Solution Manual: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/solution-manual-for-costaccounting-foundations-and-evolutions-8th-edition-by-kinney-and-raiborn/
Solution Manual for Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions 8th Edition by Kinney and Raiborn Link full download of Solution Manual: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/solution-manual-for-costaccounting-foundations-and-evolutions-8th-edition-by-kinney-and-raiborn/
1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice of resources made to acquire it. 2. An expense is a cost charged against revenue in an accounting period.
 Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior True / False Questions 1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice of resources made to acquire it. True False 2. An expense is a cost charged against revenue in an accounting
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior True / False Questions 1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice of resources made to acquire it. True False 2. An expense is a cost charged against revenue in an accounting
Chapter 2 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts
 Chapter 2 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Solutions to Questions 2-1 The three major elements of product costs in a manufacturing company are direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Chapter 2 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Solutions to Questions 2-1 The three major elements of product costs in a manufacturing company are direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
AP Microeconomics Chapter 8 Outline
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students should learn: A. Why economic costs include both explicit (revealed and expressed) costs and implicit (present but not obvious) costs. B. How the law of
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students should learn: A. Why economic costs include both explicit (revealed and expressed) costs and implicit (present but not obvious) costs. B. How the law of
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior rue/false Questions F 1. he cost of an item is the sacrifice made to acquire it. Answer: rue Difficulty: Simple Learning Objective: 1 F 2. A cost can either be an asset
Chapter 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior rue/false Questions F 1. he cost of an item is the sacrifice made to acquire it. Answer: rue Difficulty: Simple Learning Objective: 1 F 2. A cost can either be an asset
Chapter #2: Cost Concepts and Design Economics
 ENGINEERING ECONOMY Chapter #2: Cost Concepts and Design Economics By: Eng. Ahmed Y Manama Outline Fixed, Variable, and Incremental Cost Recurring and Nonrecurring Costs Direct, Indirect and Overhead Costs
ENGINEERING ECONOMY Chapter #2: Cost Concepts and Design Economics By: Eng. Ahmed Y Manama Outline Fixed, Variable, and Incremental Cost Recurring and Nonrecurring Costs Direct, Indirect and Overhead Costs
Full file at
 Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior True / False Questions 1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice made to acquire it. True False 2. An expense is an expired cost matched with revenues in a specific
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior True / False Questions 1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice made to acquire it. True False 2. An expense is an expired cost matched with revenues in a specific
BAB. PERILAKU BIAYA : Analisis dan Penggunaan
 BAB 3 PERILAKU BIAYA : Analisis dan Penggunaan Types of Cost Behavior Patterns Recall the summary of our cost behavior discussion from Chapter 2. Summary of Variable and Fixed Cost Behavior Cost In Total
BAB 3 PERILAKU BIAYA : Analisis dan Penggunaan Types of Cost Behavior Patterns Recall the summary of our cost behavior discussion from Chapter 2. Summary of Variable and Fixed Cost Behavior Cost In Total
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING SPRING 2014 MIDTERM EXAM. PROBLEM 1 Kennedy Company reports the following costs and expenses in May.
 PROBLEM 1 Kennedy Company reports the following costs and expenses in May. Factory utilities $ 13,500 Direct labor $79,100 Depreciation on factory Sales salaries 48,400 equipment 12,650 Property taxes
PROBLEM 1 Kennedy Company reports the following costs and expenses in May. Factory utilities $ 13,500 Direct labor $79,100 Depreciation on factory Sales salaries 48,400 equipment 12,650 Property taxes
Identifying Relevant Costs. Identifying Relevant Costs. Identifying Relevant Costs. A relevant cost is a cost that differs between alternatives.
 Identifying Relevant Costs Relevant tcosts for Decision Making Cynthia, a Boston student, is considering visiting her friend in New York. She can drive or take the train. By car, it is 230 miles to her
Identifying Relevant Costs Relevant tcosts for Decision Making Cynthia, a Boston student, is considering visiting her friend in New York. She can drive or take the train. By car, it is 230 miles to her
Cost Accounting. Multiple Choice Questions:
 Multiple Choice Questions: 1- The Value Chain a- Involves external companies as well as internal activities. b- Is the sequence of business functions in which customer usefulness is added to products or
Multiple Choice Questions: 1- The Value Chain a- Involves external companies as well as internal activities. b- Is the sequence of business functions in which customer usefulness is added to products or
COST C O S T COST 1/12/2011
 Chapter 3 COST CONCEPT AND DESIGN ECONOMICS C O S T Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka COST Cost is not a simple concept. It is important
Chapter 3 COST CONCEPT AND DESIGN ECONOMICS C O S T Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka COST Cost is not a simple concept. It is important
Management s Accountability to Stakeholders Stakeholders Provide Management is accountable for: Owners Operating activities Government Creditors
 Chapter 15 Distinguish management accounting from financial accounting Management Management s Accountability to Stakeholders Stakeholders Owners Government Provide Management is accountable for: Operating
Chapter 15 Distinguish management accounting from financial accounting Management Management s Accountability to Stakeholders Stakeholders Owners Government Provide Management is accountable for: Operating
Activity-Based Costing
 Activity-Based Costing Total Class Costing Designing ABC System Traditional System vs. Activity-Based Cost System Traditional System Activity-Based Cost System Activity-Based Costing Shifts Analysis from
Activity-Based Costing Total Class Costing Designing ABC System Traditional System vs. Activity-Based Cost System Traditional System Activity-Based Cost System Activity-Based Costing Shifts Analysis from
Chapter 2 Cost Terms, Concepts, and Classifications
 Multiple Choice Questions 16. Indirect labor is a part of: A) Prime cost. B) Conversion cost. C) Period cost. D) Nonmanufacturing cost. Answer: B Level: Medium LO: 1,2 Source: CPA, adapted 17. The cost
Multiple Choice Questions 16. Indirect labor is a part of: A) Prime cost. B) Conversion cost. C) Period cost. D) Nonmanufacturing cost. Answer: B Level: Medium LO: 1,2 Source: CPA, adapted 17. The cost
COST COST OBJECT. Cost centre. Profit centre. Investment centre
 COST The amount of money or property paid for a good or service. Cost is an expense for both personal and business assets. If a cost is for a business expense, it may be tax deductible. A cost may be paid
COST The amount of money or property paid for a good or service. Cost is an expense for both personal and business assets. If a cost is for a business expense, it may be tax deductible. A cost may be paid
Introduction to Management Accounting
 Smeal College of Business Managerial Accounting: ACCTG 404 Pennsylvania State University Professor Huddart 1. What is Management Accounting? Purpose is to provide information to allow users to make better
Smeal College of Business Managerial Accounting: ACCTG 404 Pennsylvania State University Professor Huddart 1. What is Management Accounting? Purpose is to provide information to allow users to make better
Cost concepts, Cost Classification and Estimation
 Cost concepts, Cost Classification and Estimation BY G H A N E N DR A F A G O Cost Concepts Cost refers the amount of expenses spent to generate product or services. Cost refers expenditure that may be
Cost concepts, Cost Classification and Estimation BY G H A N E N DR A F A G O Cost Concepts Cost refers the amount of expenses spent to generate product or services. Cost refers expenditure that may be
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation
 Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation
 Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Activity-Based Costing Systems
 4 Activity-Based Costing Systems 4-2 Learning Objective 1 4-3 Traditional Costing Systems Traditional cost systems were created when manufacturing processes were labor intensive. A single company-wide
4 Activity-Based Costing Systems 4-2 Learning Objective 1 4-3 Traditional Costing Systems Traditional cost systems were created when manufacturing processes were labor intensive. A single company-wide
How Can Entrepreneurs Control Costs? Council for Economic Education, New York, NY Entrepreneurship in the U.S. Economy, Lesson 20
 How Can Entrepreneurs Control Costs? Council for Economic Education, New York, NY Entrepreneurship in the U.S. Economy, Lesson 20 Lesson Description DESCRIPTION In this lesson students will learn that
How Can Entrepreneurs Control Costs? Council for Economic Education, New York, NY Entrepreneurship in the U.S. Economy, Lesson 20 Lesson Description DESCRIPTION In this lesson students will learn that
Test Bank For Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis Fifth Canadian 5th Edition By Horngren Foster Datar And Gowing
 Test Bank For Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis Fifth Canadian 5th Edition By Horngren Foster Datar And Gowing Link full download: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-cost-accounting-amanagerial-emphasis-fifth-canadian-5th-edition-by-horngren-foster-datar-andgowing/
Test Bank For Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis Fifth Canadian 5th Edition By Horngren Foster Datar And Gowing Link full download: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-cost-accounting-amanagerial-emphasis-fifth-canadian-5th-edition-by-horngren-foster-datar-andgowing/
BIAYA: Konsep, Klasifikasi dan Perilaku
 BAB BIAYA: Konsep, 2 Klasifikasi dan Perilaku Manufacturing Cost Concepts Financial Accounting Cost is a measure of resources used or given up to achieve a stated purpose. Managerial Accounting Product
BAB BIAYA: Konsep, 2 Klasifikasi dan Perilaku Manufacturing Cost Concepts Financial Accounting Cost is a measure of resources used or given up to achieve a stated purpose. Managerial Accounting Product
Part 3 : 11/11/10 07:42:55. MultiFrame Company has the following revenue and cost budgets for the two products it sells.
 Question 1 - CMA 1290 4-4 - Decision Making MultiFrame Company has the following revenue and cost budgets for the two products it sells. Plastic Frames Glass Frames Budgeted unit sales 100,000 300,000
Question 1 - CMA 1290 4-4 - Decision Making MultiFrame Company has the following revenue and cost budgets for the two products it sells. Plastic Frames Glass Frames Budgeted unit sales 100,000 300,000
Cost Behavior. Material Cost: Direct material: 1. seen in the final product 2. economic/visible to trace Indirect Material:
 1 Chapter 2 Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Cost A cost is the value of economic resources (e.g., money) sacrificed or used up to achieve a particular objective (e.g., produce a product or perform
1 Chapter 2 Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Cost A cost is the value of economic resources (e.g., money) sacrificed or used up to achieve a particular objective (e.g., produce a product or perform
2 Cost Concepts and Behavior
 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An expense is
2 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An expense is
Managerial Accounting: Making Decisions and Motivating Performance (Datar/Rajan) Chapter 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes
 Managerial Accounting: Making Decisions and Motivating Performance (Datar/Rajan) Chapter 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Learning Objective 2-1 1) The cost incurred is: A) actual costs. B)
Managerial Accounting: Making Decisions and Motivating Performance (Datar/Rajan) Chapter 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Learning Objective 2-1 1) The cost incurred is: A) actual costs. B)
Basic Cost Management Concepts. M. En C. Eduardo Bustos as
 Basic Cost Management Concepts M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías as 1 Objectives 1. Explain what is meant by the word "cost." 2. Distinguish among product costs, period costs,, and expenses. 3. Describe the
Basic Cost Management Concepts M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías as 1 Objectives 1. Explain what is meant by the word "cost." 2. Distinguish among product costs, period costs,, and expenses. 3. Describe the
Chapter 2--Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, Cost Terminology, and Cost Flows
 Chapter 2--Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, Cost Terminology, and Cost Flows Student: 1. Which of the following types of organizations is most likely to have a raw materials inventory account?
Chapter 2--Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, Cost Terminology, and Cost Flows Student: 1. Which of the following types of organizations is most likely to have a raw materials inventory account?
Chapter 2 Cost Classification & Cost Behaviour. Ibrahim Sameer (MBA - Specialized in Finance, B.Com Specialized in Accounting & Marketing)
 Chapter 2 Cost Classification & Cost Behaviour Ibrahim Sameer (MBA - Specialized in Finance, B.Com Specialized in Accounting & Marketing) Total Cost / Service Costs The total cost of making a product or
Chapter 2 Cost Classification & Cost Behaviour Ibrahim Sameer (MBA - Specialized in Finance, B.Com Specialized in Accounting & Marketing) Total Cost / Service Costs The total cost of making a product or
COST CONCEPTS Introduction: Cost: Types of cost: Direct cost or explicit cost:
 COST CONCEPTS Introduction: A firm carries out business to earn maximum profits. Profits are the revenues collected by a business firm after production and sale of their goods and services. But to gain
COST CONCEPTS Introduction: A firm carries out business to earn maximum profits. Profits are the revenues collected by a business firm after production and sale of their goods and services. But to gain
Part 1 Study Unit 4. Cost Management Concepts Patricia Burnett, CMA Ronald Schmidt, CMA, CFM
 Part 1 Study Unit 4 Cost Management Concepts Patricia Burnett, CMA Ronald Schmidt, CMA, CFM 1 Remember most common reasons for missing questions! 1. Misreading the requirement (stem) Read the question
Part 1 Study Unit 4 Cost Management Concepts Patricia Burnett, CMA Ronald Schmidt, CMA, CFM 1 Remember most common reasons for missing questions! 1. Misreading the requirement (stem) Read the question
Chapter 3--Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, Cost Terminology, and Cost Flows
 Chapter 3--Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, Cost Terminology, and Cost Flows Student: 1. Which of the following types of organizations is most likely to have a raw materials inventory account?
Chapter 3--Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, Cost Terminology, and Cost Flows Student: 1. Which of the following types of organizations is most likely to have a raw materials inventory account?
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior
 Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An
Managerial Accounting Prof. Dr. Varadraj Bapat School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Managerial Accounting Prof. Dr. Varadraj Bapat School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 9 Lecture - 20 Accounting for Costs Dear students, in our last session we have started
Managerial Accounting Prof. Dr. Varadraj Bapat School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 9 Lecture - 20 Accounting for Costs Dear students, in our last session we have started
Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs
 Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs Cost Object: anything for which a separate measurement of costs is required, e.g. products, services, customers, projects, processes, segments of the value chain, divisions/departments,
Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs Cost Object: anything for which a separate measurement of costs is required, e.g. products, services, customers, projects, processes, segments of the value chain, divisions/departments,
UNIT 8 COST CONCEPTS AND ANALYSIS I
 UNIT 8 COST CONCEPTS AND ANALYSIS I Objectives After going through this unit, you should be able to: understand some of the cost concepts that are frequently used in the managerial decision making process;
UNIT 8 COST CONCEPTS AND ANALYSIS I Objectives After going through this unit, you should be able to: understand some of the cost concepts that are frequently used in the managerial decision making process;
Commuter Benefits Overview. Why Commuter Benefits? How Does the Program Work? Let s get started! Registration is Simple
 Commuter Benefits Overview Commuting to work each day can be expensive. The commuter benefit program offered by your employer will help you save money on your commuting costs along with the convenience
Commuter Benefits Overview Commuting to work each day can be expensive. The commuter benefit program offered by your employer will help you save money on your commuting costs along with the convenience
Student Name: Student No.: Seat No
 Hashemite University Faculty of Economic and Administrative Sciences Department of Accounting- Dr Husam Al-Khadash Course: Managerial Accounting, Course No: 0202311 - mid-term exam Student Name: Student
Hashemite University Faculty of Economic and Administrative Sciences Department of Accounting- Dr Husam Al-Khadash Course: Managerial Accounting, Course No: 0202311 - mid-term exam Student Name: Student
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 Cost, Revenue, and Profit Maximization ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do companies determine the most profitable way to operate? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary generates produces or brings into
Lesson 3 Cost, Revenue, and Profit Maximization ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do companies determine the most profitable way to operate? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary generates produces or brings into
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING. 2 nd topic COST CLASSIFICATION
 MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 2 nd topic COST CLASSIFICATION Structureofthelecture2 2.1 Definition of cost and related terms 2.2 Types of cost classification 2.3 Identification of cost classification 2.4 Reporting
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 2 nd topic COST CLASSIFICATION Structureofthelecture2 2.1 Definition of cost and related terms 2.2 Types of cost classification 2.3 Identification of cost classification 2.4 Reporting
Full file at https://fratstock.eu. Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting
 Chapter 2 Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting Quick Check Questions Answers: QC2-1. b QC2-3. a QC2-5. c QC2-7. b QC2-9. b QC2-2. b QC2-4. b QC2-6. b QC2-8. d QC2-10. c Chapter 2 Building Blocks of
Chapter 2 Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting Quick Check Questions Answers: QC2-1. b QC2-3. a QC2-5. c QC2-7. b QC2-9. b QC2-2. b QC2-4. b QC2-6. b QC2-8. d QC2-10. c Chapter 2 Building Blocks of
Hilton Chapter14 Adobe Connect CHAPTER 14: DECISION MAKING, RELEVANT COSTS & BENEFITS. The decision process consists of the six steps that follow.
 1 Hilton Chapter14 Adobe Connect CHAPTER 14: DECISION MAKING, RELEVANT COSTS & BENEFITS Chapter 14 concerns decision making. In one sense, the entire book leads to this chapter. THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
1 Hilton Chapter14 Adobe Connect CHAPTER 14: DECISION MAKING, RELEVANT COSTS & BENEFITS Chapter 14 concerns decision making. In one sense, the entire book leads to this chapter. THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior
 Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An
Full file at
 02 Student: 1. All costs incurred in a merchandising firm are considered to be period costs. True False 2. Amortization is always considered a product cost for external financial reporting purposes in
02 Student: 1. All costs incurred in a merchandising firm are considered to be period costs. True False 2. Amortization is always considered a product cost for external financial reporting purposes in
Chapter 2 The Cost Function SOLUTIONS Eldenburg & Wolcott 2e August 2010
 Chapter 2 The Cost Function SOLUTIONS Eldenburg & Wolcott 2e August 2010 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Chapter 2 addresses the following questions: Q1 What are different ways to describe cost behavior? Q2 What process
Chapter 2 The Cost Function SOLUTIONS Eldenburg & Wolcott 2e August 2010 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Chapter 2 addresses the following questions: Q1 What are different ways to describe cost behavior? Q2 What process
AGENDA: JOB-ORDER COSTING
 TM 3-1 AGENDA: JOB-ORDER COSTING A. The documents in a job-order costing system. 1. Materials requisition form. 2. Direct labor time ticket. 3. Job cost sheet. B. Applying overhead using a predetermined
TM 3-1 AGENDA: JOB-ORDER COSTING A. The documents in a job-order costing system. 1. Materials requisition form. 2. Direct labor time ticket. 3. Job cost sheet. B. Applying overhead using a predetermined
Cost Concepts and Behavior
 2 Chapter Two Cost Concepts and Behavior LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: L.O.1 L.O.2 L.O.3 L.O.4 L.O.5 L.O.6 L.O.7 Explain the basic concept of cost. Explain how
2 Chapter Two Cost Concepts and Behavior LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: L.O.1 L.O.2 L.O.3 L.O.4 L.O.5 L.O.6 L.O.7 Explain the basic concept of cost. Explain how
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, 4e (Nobles) Chapter 16 Introduction to Managerial Accounting. Learning Objective 16-1
 Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, 4e (Nobles) Chapter 16 Introduction to Managerial Accounting Learning Objective 16-1 1) Managerial accounting focuses on providing information for internal
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, 4e (Nobles) Chapter 16 Introduction to Managerial Accounting Learning Objective 16-1 1) Managerial accounting focuses on providing information for internal
An accounting perspective: Business insight
 An accounting perspective: Business insight Engineers for automobile companies in the United States believe that Japanese manufacturers can build cars for considerably less than their US counterparts.
An accounting perspective: Business insight Engineers for automobile companies in the United States believe that Japanese manufacturers can build cars for considerably less than their US counterparts.
Chapter 2 - Basic Managerial Accounting Concepts
 1. It is beneficial to assign indirect costs to cost objects. True 2. Price must be greater than cost in order for the firm to generate revenue. False 3. Accumulating costs is the way that costs are measured
1. It is beneficial to assign indirect costs to cost objects. True 2. Price must be greater than cost in order for the firm to generate revenue. False 3. Accumulating costs is the way that costs are measured
Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis, 16e, Global Edition (Horngren) Chapter 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes
 Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis, 16e, Global Edition (Horngren) Chapter 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes 2.1 Objective 2.1 1) Which of the following would be considered an actual cost
Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis, 16e, Global Edition (Horngren) Chapter 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes 2.1 Objective 2.1 1) Which of the following would be considered an actual cost
 THE APPRENTICE As we ve seen in The Apprentice, it all comes down to cost.. How much have we spent and how much did we make in return? THE EQUATION IS SIMPLE PROFIT What we make What we spend OR LOSS If
THE APPRENTICE As we ve seen in The Apprentice, it all comes down to cost.. How much have we spent and how much did we make in return? THE EQUATION IS SIMPLE PROFIT What we make What we spend OR LOSS If
The Structure of Costs in the
 The Structure of s in the Short Run The Structure of s in the Short Run By: OpenStaxCollege The cost of producing a firm s output depends on how much labor and physical capital the firm uses. A list of
The Structure of s in the Short Run The Structure of s in the Short Run By: OpenStaxCollege The cost of producing a firm s output depends on how much labor and physical capital the firm uses. A list of
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Behavior Solution manual for Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th by Lanen Anderson Maher
 Solution manual for Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th by Lanen Anderson Maher Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/solution-manual-for-fundamentals-of-costaccounting-4th-by-lanen-anderson-maher/
Solution manual for Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th by Lanen Anderson Maher Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/solution-manual-for-fundamentals-of-costaccounting-4th-by-lanen-anderson-maher/
COMM 294 MIDTERM REVIEW SESSION QUESTIONS BY LINH VO
 COMM 294 MIDTERM REVIEW SESSION QUESTIONS BY LINH VO TABLE OF CONTENT I. Introduction II. Cost terms, concepts, classification and Cost Behaviour (Chap. 2, 3) III. Job-order Costing (Chap. 5) --------------BREAK--------------
COMM 294 MIDTERM REVIEW SESSION QUESTIONS BY LINH VO TABLE OF CONTENT I. Introduction II. Cost terms, concepts, classification and Cost Behaviour (Chap. 2, 3) III. Job-order Costing (Chap. 5) --------------BREAK--------------
MANAGEMENT 9 ACCOUNTING
 9-1 9-2 Chapter MANAGEMENT 9 ACCOUNTING A BUSINESS PARTNER To explain the three principles guiding the design of management accounting systems. LO1 Management Accounting: Basic Framework 9-3 Management
9-1 9-2 Chapter MANAGEMENT 9 ACCOUNTING A BUSINESS PARTNER To explain the three principles guiding the design of management accounting systems. LO1 Management Accounting: Basic Framework 9-3 Management
Gatsby s Accounting System and Policies Designed by Regina Rexrode Copyright - Armond Dalton
 Gatsby s Accounting System and Policies a Images used on the front cover and throughout this book were obtained under license from Shutterstock.com 2017, by Armond Dalton Publishers, Inc. All rights reserved.
Gatsby s Accounting System and Policies a Images used on the front cover and throughout this book were obtained under license from Shutterstock.com 2017, by Armond Dalton Publishers, Inc. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCTION TO COST BEHAVIOR AND COST-VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS
 CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCTION TO COST BEHAVIOR AND COST-VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain how cost drivers affect cost behavior. 2. Show how changes in cost-driver activity levels affect variable
CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCTION TO COST BEHAVIOR AND COST-VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain how cost drivers affect cost behavior. 2. Show how changes in cost-driver activity levels affect variable
Full file at
 CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCTION TO COST BEHAVIOR AND COST-VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain how cost drivers affect cost behavior. 2. Show how changes in cost-driver activity levels affect variable
CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCTION TO COST BEHAVIOR AND COST-VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain how cost drivers affect cost behavior. 2. Show how changes in cost-driver activity levels affect variable
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING (135) Post-secondary
 Page 1 of 10 Contestant Number: Time: Rank: MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING (135) Post-secondary REGIONAL 2016 Multiple Choice & Short Answer Section: Multiple Choice (20 @ 2 points each) Matching (50 @ 1 point
Page 1 of 10 Contestant Number: Time: Rank: MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING (135) Post-secondary REGIONAL 2016 Multiple Choice & Short Answer Section: Multiple Choice (20 @ 2 points each) Matching (50 @ 1 point
- 1 - Direct Material (Rs.) Material Cost Per Unit Units Produced
 - 1 - COST BEHAVIOR THE NATURE OF COSTS: Before one can begin to understand how a business is going to perform over time and with shifts in volume, it is imperative to first consider the cost structure
- 1 - COST BEHAVIOR THE NATURE OF COSTS: Before one can begin to understand how a business is going to perform over time and with shifts in volume, it is imperative to first consider the cost structure
1. F; I 2. V ; D 3. V ; D 4. F; I 5. F; I 6. F; I 7. V ; D 8. F; I 9. F; I 10. V ; D 11. F; I 12. F; I 13. F; I 14. F; I
 SOLUTIONS TO EERCISES EERCISE 2-1 (15 minutes) 1. F; I 2. V ; D 3. V ; D 4. F; I 5. F; I 6. F; I 7. V ; D 8. F; I 9. F; I 10. V ; D 11. F; I 12. F; I 13. F; I 14. F; I EERCISE 2-2 (15 minutes) 1. Product
SOLUTIONS TO EERCISES EERCISE 2-1 (15 minutes) 1. F; I 2. V ; D 3. V ; D 4. F; I 5. F; I 6. F; I 7. V ; D 8. F; I 9. F; I 10. V ; D 11. F; I 12. F; I 13. F; I 14. F; I EERCISE 2-2 (15 minutes) 1. Product
17(2) Job Order Costing. chapter OPENING COMMENTS
 ing chapter 17(2) OPENING COMMENTS Chapter 17(2) introduces students to managerial job order cost systems. Students will be exposed to the terminology used to describe costs related to manufacturing. The
ing chapter 17(2) OPENING COMMENTS Chapter 17(2) introduces students to managerial job order cost systems. Students will be exposed to the terminology used to describe costs related to manufacturing. The
2 Cost Concepts and Behavior
 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An expense is
2 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An expense is
Moore Accounting Notes
 Moore Accounting Notes These notes were prepared specifically for my accounting students as a part of my teaching and preparation for the CXC CAPE [A level] Examinations in Accounting. RM ACCOUNTS ED COST
Moore Accounting Notes These notes were prepared specifically for my accounting students as a part of my teaching and preparation for the CXC CAPE [A level] Examinations in Accounting. RM ACCOUNTS ED COST
Test Bank Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting The Managerial Chapters 5th Edition Miller-Nobles
 Test Bank Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting The Managerial Chapters 5th Edition Miller-Nobles TEST BANK for Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting The Managerial Chapters 5th Edition by
Test Bank Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting The Managerial Chapters 5th Edition Miller-Nobles TEST BANK for Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting The Managerial Chapters 5th Edition by
Managerial Accounting, 2e Braun/Tietz/Harrison Test Item File Chapter 2: Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting
 Managerial Accounting, 2e Braun/Tietz/Harrison Test Item File Chapter 2: Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting 2.1-1 Retailers sell their products to other wholesalers. Answer: False LO: 2-1 EOC: E
Managerial Accounting, 2e Braun/Tietz/Harrison Test Item File Chapter 2: Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting 2.1-1 Retailers sell their products to other wholesalers. Answer: False LO: 2-1 EOC: E
Breaking Down Break-Even
 Xxxxx Xxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxx Xxx xx xxxxxxxiness stay in business? One way is by preparing and Did you using ever run a well-thought-out a lemonade stand budget. in your neighborhood when Believe you it were
Xxxxx Xxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxx Xxx xx xxxxxxxiness stay in business? One way is by preparing and Did you using ever run a well-thought-out a lemonade stand budget. in your neighborhood when Believe you it were
Supply. Understanding Economics, Chapter 5
 Supply Understanding Economics, Chapter 5 What is Supply? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 What is Supply?! Supply the amount of a product a producer or seller would be willing to offer for sale at all possible prices
Supply Understanding Economics, Chapter 5 What is Supply? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 What is Supply?! Supply the amount of a product a producer or seller would be willing to offer for sale at all possible prices
Topic 2: Accounting Information for Decision Making and Control
 Learning Objectives BUS 211 Fall 2014 Topic 1: Introduction Not applicable Topic 2: Accounting Information for Decision Making and Control State and describe each of the 4 items in the planning and control
Learning Objectives BUS 211 Fall 2014 Topic 1: Introduction Not applicable Topic 2: Accounting Information for Decision Making and Control State and describe each of the 4 items in the planning and control
Link full download Test bank:
 Solution manual for Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th by William N. Lanen, Shannon Anderson, Michael W Maher Link full download Solutions: http://testbankcollection.com/download/solutionmanual-for-fundamentals-of-cost-accounting-4th-bylanen-anderson-maher/
Solution manual for Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th by William N. Lanen, Shannon Anderson, Michael W Maher Link full download Solutions: http://testbankcollection.com/download/solutionmanual-for-fundamentals-of-cost-accounting-4th-bylanen-anderson-maher/
1. III. COST BEHAVIOR
 Chapter 3 Cost Behavior Page 1 1. III. COST BEHAVIOR In this chapter we discuss the manner in which costs behave. We will discuss fixed and variable costs. As part of this discussion, we will discuss learning
Chapter 3 Cost Behavior Page 1 1. III. COST BEHAVIOR In this chapter we discuss the manner in which costs behave. We will discuss fixed and variable costs. As part of this discussion, we will discuss learning
Decision making and Relevant Information
 Decision making and Relevant Information 1 Introduction This chapter explores the decision-making process. It focuses on specific decisions such as accepting or rejecting a one-time-only special order,
Decision making and Relevant Information 1 Introduction This chapter explores the decision-making process. It focuses on specific decisions such as accepting or rejecting a one-time-only special order,
