Chapter 1: The Scope and Method of Economics
|
|
|
- Donald Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Week 2 Presenter: Jan 25, 2012
2 Table of Contents 1 The Study of Economics 2
3 Questions The Study of Economics what is economics?(twice 2011 Midterm I M1;2011Fin M1) What is opportunity cost?(4 times) (PEQ1 Part 1; 2012 Mid I M2; 2011 Mid I M4; 2010Mid1 M40; 2011Fin M2) What is sunk cost?(peq1 part2; 2011 Mid1 M2) What is marginal cost?(2011 Mid I M5) What is efficient market?(2012 Mid I M4) Why do you think opportunity cost is important in the economic way of thinking?
4 Economics:Definition 2011 Midterm I M1 Page 203;2011Fin M1Page 289 Economics is best defined as the study of: A financial design-making B how consumers make purchasing decision C inflation,unemployment, and economic growth D choices made by people faced with scarcity
5 Economics:Definition 2011 Midterm I M1 Page 203 Economics is best defined as the study of: A A topic in Micro B A topic in Micro C Concerns of Macro D Right Answer!
6 Trade-off The Study of Economics Figure 1: Choice between A and B
7 Opportunity Cost Figure 2: What is the opportunity cost of studying hard (playing Video Games)?
8 Opportunity Cost 2012 Midterm I M2 Page 191; 2011 Mid I M4 Page 203 Opportunity cost can be best defined as: A the value of the best alternative given up when making a choice. B the cost of making one additional unit. C the cost of finding profitable opportunities. D sunk costs E the explicit cost of an action.
9 Opportunity Cost 2012 Midterm I M2 Page 191; 2011 Mid I M4 Page 203 Opportunity cost can be best defined as: A the value of the best alternative given up when making a choice. B the cost of making one additional unit. C the cost of finding profitable opportunities. D sunk costs E the explicit cost of an action.
10 Opportunity Cost: Application PEQ 1 part 1Page 159 Q:Why would an economist argue that tuition is not the largest cost of attending a state university?
11 Opportunity Cost: Application PEQ 1 part 1Page 159 Q:Why would an economist argue that tuition is not the largest cost of attending a state university? A:The largest cost of attending a university is the opportunity cost of the student s time. This could be measured by the forgone income that could have been earned if the student worked instead of attending classes.
12 Opportunity Cost: Application 2011 Mid I M4 Page 203 Which of the following is an opportunity cost of attending college? A the income you could have earned if you didn t attend college B the cost of your apartment or dorm C the cost of the food that you consume while you are attending college D all of the above
13 Opportunity Cost: Application 2011 Mid I M4 Page 203 Which of the following is an opportunity cost of attending college? A the income you could have earned if you didn t attend college B the cost of your apartment or dorm C the cost of the food that you consume while you are attending college D all of the above
14 Opportunity Cost: Application 2011Fin M2 Page 289 You own Kil Bill on DVD. The opportunity cost of watching this DVD for the third time A is the value of the alternative use of the time you spend watching the DVD B must be the same as the opportunity cost of watching it the first time. C is one-third the cost of the DVD, as this is the third time you have watched it. D is zero,since you own it.
15 Opportunity Cost: Application 2011Fin M2 Page 289 You own Kil Bill on DVD. The opportunity cost of watching this DVD for the third time A is the value of the alternative use of the time you spend watching the DVD B must be the same as the opportunity cost of watching it the first time. C is one-third the cost of the DVD, as this is the third time you have watched it. D is zero,since you own it.
16 Sunk Cost The Study of Economics PEQ 1 part 2 Page 159 Q: Suppose that you have purchased a round trip ticket to the Bahamas for spring break. The ticket is non refundable and cannot be changed. Your best friend tells you that she is getting married during the same week in Chicago (where you live) and has asked you to be in the wedding party. Does the price you paid for your Bahamas trip matter in your decision of whether to go to the Bahamas or Chicago? Why or why not?
17 Sunk Cost The Study of Economics PEQ 1 part 2 Page 159 Q: Suppose that you have purchased a round trip ticket to the Bahamas for spring break. The ticket is non refundable and cannot be changed. Your best friend tells you that she is getting married during the same week in Chicago (where you live) and has asked you to be in the wedding party. Does the price you paid for your Bahamas trip matter in your decision of whether to go to the Bahamas or Chicago? Why or why not? A: It should not matter because the plane ticket is a sunk cost. No matter what decision you make, you will have to pay for the ticket to the Bahamas. Thus, the only thing that should factor into your decision is how much enjoyment you would gain out of the two alternatives.
18 Marginal Cost The Study of Economics 2011 Mid I M5 Page 203 If you eat at a pizza parlor that charges $5 for its all-you-can-eat buffet, then the marginal cost of your 5th slice of pizza is A $25 B zero C $1 D $5
19 Marginal Cost The Study of Economics 2011 Mid I M5 Page 203 If you eat at a pizza parlor that charges $5 for its all-you-can-eat buffet, then the marginal cost of your 5th slice of pizza is A $25 B zero C $1 D $5
20 Opportunity Cost vs Marginal Cost vs Sunk Cost Opportunity cost: the cost you think about when comparing choices Sunk cost: could not be avoided because it has been incurred Marginal Cost: additional cost of consuming or producing one more unit of goods or services
21 Efficient Market 2012 Midterm I M4 Page 191 Efficient markets are those in which A buyers and sellers do not face opportunity costs. B many people search for profit opportunities such that these opportunities are almost instantaneously eliminated. C consumers and firms consider sunk costs in their decisions to buy and produce, respectively. D buyers and sellers face difficulties in finding each other. E profit opportunities never exist.
22 Efficient Market 2012 Midterm I M4 Page 191 Efficient markets are those in which A buyers and sellers do not face opportunity costs. B many people search for profit opportunities such that these opportunities are almost instantaneously eliminated. C consumers and firms consider sunk costs in their decisions to buy and produce, respectively. D buyers and sellers face difficulties in finding each other. E profit opportunities never exist.
23 Table of Contents 1 The Study of Economics 2
24 Questions The Study of Economics What s the difference between Positive and Normative Economics? (5 times) (2012Mid1 M1 Page 191;2011 Mid1 M3 Page 203;2010Mid1 M3 Page213;2011Fin M3 Page 289;2010Fin M36) What does Positive economics include? What is a model?2012 Midterm I M5 What is post hoc Fallacy? (PEQ1 part Midterm I M3; 2010Mid1 M4) What is fallacy of composition?
25 Method of Economics 2012 Midterm I M5 Page 191 Which statement is not true regarding the method of economics? A Positive economics includes descriptive economics and economic theory. B A model is a formal statement of a theory. C Models should contain details that are irrelevant to understand certain behavior. D An economic theory should avoid the fallacy of composition. E Empirical economics can be used to test economic theories.
26 Method of Economics 2012 Midterm I M5 Page 191 Which statement is not true regarding the method of economics? A Positive economics includes descriptive economics and economic theory. B A model is a formal statement of a theory. C Models should contain details that are irrelevant to understand certain behavior. D An economic theory should avoid the fallacy of composition. E Empirical economics can be used to test economic theories.
27 Normative vs Positive Economics 2012 Midterm I M1 Page 191 Which of the following is a normative statement? A companies earn profits from the sale of prescription drugs. B Hospital bills are greater in Canada than in the United States. C Health care costs too much. D Hospitals are under increasing pressure to cut costs. E All of these.
28 Normative vs Positive Economics 2012 Midterm I M1 Page 191 Which of the following is a normative statement? A companies earn profits from the sale of prescription drugs. B Hospital bills are greater in Canada than in the United States. C Health care costs too much. D Hospitals are under increasing pressure to cut costs. E All of these.
29 Post hoc Fallacy PEQ 1 part 3 Page 159 Q:A policymaker in a less developed nation sees that citizens of wealthy nations spend a lot of time on the Internet. He, therefore, proposes to have every household in his nation wired to the Internet to make them wealthier. How do you react to this proposal?
30 Post hoc Fallacy PEQ 1 part 3 Page 159 Q:A policymaker in a less developed nation sees that citizens of wealthy nations spend a lot of time on the Internet. He, therefore, proposes to have every household in his nation wired to the Internet to make them wealthier. How do you react to this proposal? A: This proposal suffers from the post hoc fallacy. Our nation s output did increase after and during the growth of Internet usage. Both phenomena, however, were caused by other factors such as an increase in technology.
31 Post hoc Fallacy 2012 Midterm I M3 Page 191 The Post Hoc Fallacy is defined as: A the error of mistakenly assuming that an event caused the other because it happened after. B the error of mistakenly assuming that an event caused the other because it happened before. C the error of assuming that two variables are correlated when they are not. D the error of assuming that correlation implies causation. E None of the above.
32 Post hoc Fallacy 2012 Midterm I M3 Page 191 The Post Hoc Fallacy is defined as: A the error of mistakenly assuming that an event caused the other because it happened after. B the error of mistakenly assuming that an event caused the other because it happened before. C the error of assuming that two variables are correlated when they are not. D the error of assuming that correlation implies causation. E None of the above.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Each correct answer gives you 1 pt.
 AUBG, Fall 2015, Micro 101 with P. Stankov Sample midterm ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
AUBG, Fall 2015, Micro 101 with P. Stankov Sample midterm ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
5. The English word that comes from the Greek word for "one who manages a household" is a. market b. consumer c. producer d.
 1. A worker in Equador can earn $3 per day making cotton cloth on a hand loom. A worker in the United States can earn $70 per day making cotton cloth with a mechanical loom. What accounts for the difference
1. A worker in Equador can earn $3 per day making cotton cloth on a hand loom. A worker in the United States can earn $70 per day making cotton cloth with a mechanical loom. What accounts for the difference
Name: Student ID: Use the following to answer question 3: Figure: Market for Hamburgers. Version 3 Page 1
 Name: Student ID: 1. Assume that a person is consuming the utility-maximizing quantities of pork and chicken. We can conclude that: A) the person is consuming the same amount of pork and chicken. B) the
Name: Student ID: 1. Assume that a person is consuming the utility-maximizing quantities of pork and chicken. We can conclude that: A) the person is consuming the same amount of pork and chicken. B) the
Figure: Profit Maximizing
 Name: Student ID: 1. A manufacturing company that benefits from lower costs per unit as it grows is an example of a firm experiencing: A) scale reduction. B) increasing returns to scale. C) increasing
Name: Student ID: 1. A manufacturing company that benefits from lower costs per unit as it grows is an example of a firm experiencing: A) scale reduction. B) increasing returns to scale. C) increasing
CHAPTER 1. What Is Economics? 1.1 The Economic Problem 1.2 Economic Theory 1.3 Opportunity Cost and Choice CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 1.
 CHAPTER 1 What Is Economics? 1.1 The Economic Problem 1.2 Economic Theory 1.3 Opportunity Cost and Choice 1 CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 1.1 Consider CHAPTER 1 What Is Economics? Why are characters in
CHAPTER 1 What Is Economics? 1.1 The Economic Problem 1.2 Economic Theory 1.3 Opportunity Cost and Choice 1 CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 1.1 Consider CHAPTER 1 What Is Economics? Why are characters in
Economics 1012A Introduction to Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Dr. R. E. Mueller First Midterm Examination September 28, 2006
 Economics 1012A Introduction to Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Dr. R. E. Mueller First Midterm Examination September 28, 2006 Answer all of the following questions by selecting the most appropriate answer
Economics 1012A Introduction to Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Dr. R. E. Mueller First Midterm Examination September 28, 2006 Answer all of the following questions by selecting the most appropriate answer
Econ 3144 Spring 2006 Test 1 Dr. Rupp 25 multiple choice questions (2 points each) & 5 discussion questions (10 points each)
 Econ 3144 Spring 2006 Test 1 Dr. Rupp 25 multiple choice questions (2 points each) & 5 discussion questions (10 points each) Name Sign Pledge I have neither given nor received aid on this exam Multiple
Econ 3144 Spring 2006 Test 1 Dr. Rupp 25 multiple choice questions (2 points each) & 5 discussion questions (10 points each) Name Sign Pledge I have neither given nor received aid on this exam Multiple
https://www.quia.com/servlets/quia.web.quiawebmanager?rand...
 Version A Name Date Unit 4 Practice all at once 1. Refer to the following table about the production function for Terry's Widget Shoppe to answer questions 1-4. Assume labor is the only variable input
Version A Name Date Unit 4 Practice all at once 1. Refer to the following table about the production function for Terry's Widget Shoppe to answer questions 1-4. Assume labor is the only variable input
The Principles and Practice of Economics
 Chapter 1 The Principles and Practice of Economics Questions 1. Why do we have to pay a price for most of the goods we consume? The inputs we use to produce most goods and services (for example, capital
Chapter 1 The Principles and Practice of Economics Questions 1. Why do we have to pay a price for most of the goods we consume? The inputs we use to produce most goods and services (for example, capital
ECONOMICS 103. Dr. Emma Hutchinson, Fall 2018
 ECONOMICS 103 Dr. Emma Hutchinson, Fall 2018 http://web.uvic.ca/~ehutchin/teach/103/103f18.html Reminder: familiarize yourself with all course policies by reading the course outline and all posted info.
ECONOMICS 103 Dr. Emma Hutchinson, Fall 2018 http://web.uvic.ca/~ehutchin/teach/103/103f18.html Reminder: familiarize yourself with all course policies by reading the course outline and all posted info.
Benefits, Costs, and Maximization
 11 Benefits, Costs, and Maximization CHAPTER OBJECTIVES To explain the basic process of balancing costs and benefits in economic decision making. To introduce marginal analysis, and to define marginal
11 Benefits, Costs, and Maximization CHAPTER OBJECTIVES To explain the basic process of balancing costs and benefits in economic decision making. To introduce marginal analysis, and to define marginal
ECONOMICS 103. Dr. Emma Hutchinson, Fall 2017
 ECONOMICS 103 Dr. Emma Hutchinson, Fall 2017 http://web.uvic.ca/~ehutchin/teach/103/103f17.html Reminder: familiarize yourself with all course policies by reading the course outline and all posted info.
ECONOMICS 103 Dr. Emma Hutchinson, Fall 2017 http://web.uvic.ca/~ehutchin/teach/103/103f17.html Reminder: familiarize yourself with all course policies by reading the course outline and all posted info.
Competitive Markets. Jeffrey Ely. January 13, This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License.
 January 13, 2010 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Profit Maximizing Auctions Last time we saw that a profit maximizing seller will choose
January 13, 2010 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Profit Maximizing Auctions Last time we saw that a profit maximizing seller will choose
The Economist as a Scientist
 Mind Map of Economics Lecture 2 Thinking Like an Economist Dr. Eva Jílková Moravian University College Olomouc, Kosmonautů 1288/1, 779 00 Olomouc eva.jilkova@mvso.cz, veronika.rihova@mvso.cz Thinking Like
Mind Map of Economics Lecture 2 Thinking Like an Economist Dr. Eva Jílková Moravian University College Olomouc, Kosmonautů 1288/1, 779 00 Olomouc eva.jilkova@mvso.cz, veronika.rihova@mvso.cz Thinking Like
File: Chapter 001 Thinking Like an Economist. Multiple Choice Questions
 Principles of Macroeconomics Brief Edition 3rd Edition Frank Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/principles-of-macroeconomics-brief-edition-3rd-edition-frank-test-bank/ File: Chapter
Principles of Macroeconomics Brief Edition 3rd Edition Frank Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/principles-of-macroeconomics-brief-edition-3rd-edition-frank-test-bank/ File: Chapter
Problem Set 1 Suggested Answers
 Problem Set 1 Suggested Answers Problem 1. Think what is the cost of one can of Coca-cola. First try to figure out what is the accounting cost, i.e. the monetary cost. Next think what would be a total
Problem Set 1 Suggested Answers Problem 1. Think what is the cost of one can of Coca-cola. First try to figure out what is the accounting cost, i.e. the monetary cost. Next think what would be a total
ECON 120 SAMPLE QUESTIONS
 ECON 120 SAMPLE QUESTIONS 1) The price of cotton clothing falls. As a result, 1) A) the demand for cotton clothing decreases. B) the quantity demanded of cotton clothing increases. C) the demand for cotton
ECON 120 SAMPLE QUESTIONS 1) The price of cotton clothing falls. As a result, 1) A) the demand for cotton clothing decreases. B) the quantity demanded of cotton clothing increases. C) the demand for cotton
Iowa State University Economics 101 Microeconomics Principles Prof. Kilkenny Spring First Exam February 25, 2005
 Iowa State University Economics 101 Microeconomics Principles Prof. Kilkenny Spring 2005 First Exam February 25, 2005 General Instructions: 1. Write your name here: 2. USE a #2 PENCIL: Write your name,
Iowa State University Economics 101 Microeconomics Principles Prof. Kilkenny Spring 2005 First Exam February 25, 2005 General Instructions: 1. Write your name here: 2. USE a #2 PENCIL: Write your name,
Economics Lecture notes- Semester 1:
 Economics Lecture notes- Semester 1: Lecture 1: What is economics? The word economy comes from the Greek word meaning one who manages a household. Households and economies have much in common; both face
Economics Lecture notes- Semester 1: Lecture 1: What is economics? The word economy comes from the Greek word meaning one who manages a household. Households and economies have much in common; both face
FIRST INTRODUCTION TO. Dr. Mohammed A. Alwosabi. ECON140: Microeconomics Ch.1 Dr. Mohammed Alwosabi. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 FIRST INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Dr. Mohammed A. Alwosabi 1 The Fundamental Problem of Economics: Scarcity and Choice It is a fact of life that we cannot get everything we want. We all want more
Chapter 1 FIRST INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Dr. Mohammed A. Alwosabi 1 The Fundamental Problem of Economics: Scarcity and Choice It is a fact of life that we cannot get everything we want. We all want more
Microeconomics PART A. More Tutorial at
 Microeconomics PART A 1. For Italy, the opportunity cost incurred when 6 cheeses are produced is 8 watches. For Switzerland, the opportunity cost incurred when 10 cheeses are produced is 50 watches. Which
Microeconomics PART A 1. For Italy, the opportunity cost incurred when 6 cheeses are produced is 8 watches. For Switzerland, the opportunity cost incurred when 10 cheeses are produced is 50 watches. Which
Common Sense Economics: What Everyone Should Know About Wealth and Prosperity (Gwartney, Stroup, Lee, and Ferrarini - St. Martin s Press, 2010)
 1 Common Sense Economics: What Everyone Should Know About Wealth and Prosperity (Gwartney, Stroup, Lee, and Ferrarini - St. Martin s Press, 2010) Reading Guide Part I. Twelve Key Elements of Economics
1 Common Sense Economics: What Everyone Should Know About Wealth and Prosperity (Gwartney, Stroup, Lee, and Ferrarini - St. Martin s Press, 2010) Reading Guide Part I. Twelve Key Elements of Economics
Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Business and Economics Department of Economics Spring Semester
 Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Business and Economics Department of Economics 2015 16 Spring Semester ECON101 Introduction to Economics I First Midterm Exam Duration: 90 minutes Answer Key
Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Business and Economics Department of Economics 2015 16 Spring Semester ECON101 Introduction to Economics I First Midterm Exam Duration: 90 minutes Answer Key
Ten Principles of Economics
 C H A P T E R 1 Ten Principles of Economics Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
C H A P T E R 1 Ten Principles of Economics Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
Principles of Macroeconomics, 11e - TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice
 Principles of Macroeconomics, 11e - TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice 2.1 Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Cost 1) The process by which resources are transformed
Principles of Macroeconomics, 11e - TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice 2.1 Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Cost 1) The process by which resources are transformed
Economics for Business Decision Making
 Week 1: Explain that: People are rational Consumers and firms use as much of the available information as they can to achieve their goals rational individuals weigh the benefits and costs of each action,
Week 1: Explain that: People are rational Consumers and firms use as much of the available information as they can to achieve their goals rational individuals weigh the benefits and costs of each action,
ECO402 Microeconomics Mid Term Examination Spring 2006 Time Allowed: 90 Minutes
 INSTRUCTIONS: ECO402 Microeconomics Mid Term Examination Spring 2006 Time Allowed: 90 Minutes Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting any question: All questions are compulsory.
INSTRUCTIONS: ECO402 Microeconomics Mid Term Examination Spring 2006 Time Allowed: 90 Minutes Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting any question: All questions are compulsory.
Microeconomics. Ten Principles of Economics. Principles of. N. Gregory Mankiw. Sixth Edition. Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich
 N. Gregory Mankiw Microeconomics Principles of Sixth Edition 1 Ten Principles of Economics Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: What kinds
N. Gregory Mankiw Microeconomics Principles of Sixth Edition 1 Ten Principles of Economics Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: What kinds
Econ Midterm One Practice Questions
 Econ 101-008 Midterm One Practice Questions The following questions will help students prepare for the first midterm examination in Econ 101-008. Each question has one correct answer. However, Professor
Econ 101-008 Midterm One Practice Questions The following questions will help students prepare for the first midterm examination in Econ 101-008. Each question has one correct answer. However, Professor
Principles of Microeconomics, 11e -TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice
 Principles of Microeconomics, 11e -TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice 2.1 Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Cost 1) The process by which resources are transformed
Principles of Microeconomics, 11e -TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice 2.1 Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Cost 1) The process by which resources are transformed
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 185 : BASIC ECONOMICS 1 RESIT EXAMINATION : APRIL 2003 SESSION
 ECO 185 (R) / Page 1 of 10 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 185 : BASIC ECONOMICS 1 RESIT EXAMINATION : APRIL 2003 SESSION Answer ALL questions in SECTION A in the OMR sheet provided
ECO 185 (R) / Page 1 of 10 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 185 : BASIC ECONOMICS 1 RESIT EXAMINATION : APRIL 2003 SESSION Answer ALL questions in SECTION A in the OMR sheet provided
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. FIGURE 1-2
 Questions of this SAMPLE exam were randomly chosen and may NOT be representative of the difficulty or focus of the actual examination. The professor did NOT review these questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose
Questions of this SAMPLE exam were randomly chosen and may NOT be representative of the difficulty or focus of the actual examination. The professor did NOT review these questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose
Answers to Text Questions and Problems, Chapter 1
 1 of 9 1/3/2010 2:31 PM Answers to Text Questions and Problems, Chapter 1 Answers to Review Questions 1. Your friend probably means that your tennis game will improve faster if you take solo private lessons
1 of 9 1/3/2010 2:31 PM Answers to Text Questions and Problems, Chapter 1 Answers to Review Questions 1. Your friend probably means that your tennis game will improve faster if you take solo private lessons
full file at
 Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A business owner makes 1000 items a day. Each day he or she contributes 8 hours to produce those items. If hired, elsewhere he/she could have earned $250 an hour.
Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A business owner makes 1000 items a day. Each day he or she contributes 8 hours to produce those items. If hired, elsewhere he/she could have earned $250 an hour.
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics. Midterm Exam #1. Professor: David Aadland. Spring Semester February 14, 2017.
 ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Midterm Exam #1 Professor: David Aadland Spring Semester 2017 February 14, 2017 Your Name Section 1: Multiple Choice and T/F (60 pts). Circle the correct answer;
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Midterm Exam #1 Professor: David Aadland Spring Semester 2017 February 14, 2017 Your Name Section 1: Multiple Choice and T/F (60 pts). Circle the correct answer;
1. The rate at which buyers exchange money for a good or service is known as the price.
 Chapter 02 Demand and Supply True / False Questions 1. The rate at which buyers exchange money for a good or service is known as the price. Explanation: The rate at which the buyer and seller exchange
Chapter 02 Demand and Supply True / False Questions 1. The rate at which buyers exchange money for a good or service is known as the price. Explanation: The rate at which the buyer and seller exchange
Ten Principles of Economics
 Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Economics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER 1 Ten Principles of Economics In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What kinds of questions
Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Economics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER 1 Ten Principles of Economics In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What kinds of questions
 Name Framingham State College Department of Economics and Business Principles of Microeconomics Section D Practice Final Exam Spring 2006 - VERSION 2 WITH ANSWERS This exam provides questions that are
Name Framingham State College Department of Economics and Business Principles of Microeconomics Section D Practice Final Exam Spring 2006 - VERSION 2 WITH ANSWERS This exam provides questions that are
Ten Principles of Economics
 Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw The principles of HOW PEOPLE MAKE DECISIONS CHAPTER 1 Ten Principles of Economics lithian/shutterstock.com In
Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw The principles of HOW PEOPLE MAKE DECISIONS CHAPTER 1 Ten Principles of Economics lithian/shutterstock.com In
EconS 301 Intermediate Microeconomics Review Session #9 Chapter 12: Capturing Surplus
 EconS 30 Intermediate Microeconomics Review Session #9 Chapter : Capturing Surplus. With second-degree price discrimination a) The firm tries to price each unit at the consumer s reservation price. b)
EconS 30 Intermediate Microeconomics Review Session #9 Chapter : Capturing Surplus. With second-degree price discrimination a) The firm tries to price each unit at the consumer s reservation price. b)
CHAPTER 1 ECONOMICS: THE STUDY OF OPPORTUNITY COST
 CHAPTER 1 ECONOMICS: THE STUDY OF OPPORTUNITY COST DEFINITION OF ECONOMICS According to Guell: Economics: the study of the allocation and use of scarce resources to satisfy unlimited human wants Opportunity
CHAPTER 1 ECONOMICS: THE STUDY OF OPPORTUNITY COST DEFINITION OF ECONOMICS According to Guell: Economics: the study of the allocation and use of scarce resources to satisfy unlimited human wants Opportunity
Do not remove any pages or add any pages. No additional paper is supplied
 ECON 001 Spring 2018 Midterm 1 February 13, 2018 Time Limit: 60 Minutes Name (Print): Recitation Section: Name of TA: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 11 questions. Check to see
ECON 001 Spring 2018 Midterm 1 February 13, 2018 Time Limit: 60 Minutes Name (Print): Recitation Section: Name of TA: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 11 questions. Check to see
Microeconomics. More Tutorial at
 Microeconomics 1. Economists assume that the goal of the firm is to maximize A. total revenue B. total profit C. total costs D. total satisfaction 2. If a perfectly competitive firm produces 100 units
Microeconomics 1. Economists assume that the goal of the firm is to maximize A. total revenue B. total profit C. total costs D. total satisfaction 2. If a perfectly competitive firm produces 100 units
Economics. Econ, Econ. Econ
 Economics Econ, Econ Econ Introduction to Economics I WON THE LOTTERY! I ll give you anything you want other than money. What do you want? Would your list ever end? Why not? Scarcity!!! What is Economics?
Economics Econ, Econ Econ Introduction to Economics I WON THE LOTTERY! I ll give you anything you want other than money. What do you want? Would your list ever end? Why not? Scarcity!!! What is Economics?
+ What is Economics? societies use scarce resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people
 ECONOMICS The word economy comes from a Greek word oikonomia for one who manages a household. is the study of how society manages its scarce resources. Traditionally land, labor, and capital resources
ECONOMICS The word economy comes from a Greek word oikonomia for one who manages a household. is the study of how society manages its scarce resources. Traditionally land, labor, and capital resources
Key Topics demand law of demand change in quantity demanded change in demand determinants of demand
 54 Chapter 5 DEMAND Key Topics demand law of demand change in quantity demanded change in demand determinants of demand Goals know the definition of demand understand that demand slopes downward to the
54 Chapter 5 DEMAND Key Topics demand law of demand change in quantity demanded change in demand determinants of demand Goals know the definition of demand understand that demand slopes downward to the
The University of Zambia School of Humanities and Social Sciences The Department of Economics
 The University of Zambia School of Humanities and Social Sciences The Department of Economics ECN 1115 INTRODUCTION TO MICRO ECONOMICS- ASSIGNMENT 1 Attempt ALL Questions and briefly explain why your answer
The University of Zambia School of Humanities and Social Sciences The Department of Economics ECN 1115 INTRODUCTION TO MICRO ECONOMICS- ASSIGNMENT 1 Attempt ALL Questions and briefly explain why your answer
Economics 103 Midterm #1: Spring 2019 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME:
 Economics 103 Midterm #1: Spring 2019 Instructions: 1. Fill in the information below. LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: 2. On your answer sheet, (i) write your name, (ii) write and bubble in your
Economics 103 Midterm #1: Spring 2019 Instructions: 1. Fill in the information below. LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: 2. On your answer sheet, (i) write your name, (ii) write and bubble in your
Exercise questions. ECON 102. Answer all questions. Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best answer.
 Exercise questions. ECON 102 Answer all questions. Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best answer. 1.On Saturday morning, you rank your choices for activities in the following order: go to the library,
Exercise questions. ECON 102 Answer all questions. Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best answer. 1.On Saturday morning, you rank your choices for activities in the following order: go to the library,
The principles of HOW PEOPLE MAKE DECISIONS
 1 Ten Principles of Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F MICROECONOMICS FOURTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2007 update 2008 Thomson South-Western, all rights reserved
1 Ten Principles of Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F MICROECONOMICS FOURTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2007 update 2008 Thomson South-Western, all rights reserved
Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives
 CHAPTER 11 Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 11.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets (pages 369 371) Explain what a perfectly competitive market is and why a perfect
CHAPTER 11 Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 11.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets (pages 369 371) Explain what a perfectly competitive market is and why a perfect
Econ351 Lecture 2. Review of Main Economic Concepts
 Econ351 Lecture 2. Review of Main Economic Concepts Lecture outline Rationality Consumer surplus Costs (opportunity costs, social vs. private costs, sunk costs) Efficiency (productive and allocative) Compensated
Econ351 Lecture 2. Review of Main Economic Concepts Lecture outline Rationality Consumer surplus Costs (opportunity costs, social vs. private costs, sunk costs) Efficiency (productive and allocative) Compensated
7chapter. Making Decisions. 1. a. Hiro s accounting profit is:
 Making Decisions 1. a. Hiro s accounting profit is: $1, (total revenue) $55, (travel, other expenses, and supplies) $2, (depreciation) $43, (accounting profit) b. Hiro s economic profit is: $1, (total
Making Decisions 1. a. Hiro s accounting profit is: $1, (total revenue) $55, (travel, other expenses, and supplies) $2, (depreciation) $43, (accounting profit) b. Hiro s economic profit is: $1, (total
Relevant Costs for Decision Making
 11-1 Management Accounting Lecture 17 (Chapter 11) Relevant Costs for Decision Making Today s Agenda Relevant Costs vs. Irrelevant Costs Differential Approach vs. Total Cost Approach Product Transfer Decision
11-1 Management Accounting Lecture 17 (Chapter 11) Relevant Costs for Decision Making Today s Agenda Relevant Costs vs. Irrelevant Costs Differential Approach vs. Total Cost Approach Product Transfer Decision
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND. Mr. Cline Economics Marshall High School Unit Two CA
 ELASTICITY OF DEMAND Mr. Cline Economics Marshall High School Unit Two CA The Correct Response Is.. Economists describe the ways in which consumers respond to price changes as Elasticity of Demand. Are
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND Mr. Cline Economics Marshall High School Unit Two CA The Correct Response Is.. Economists describe the ways in which consumers respond to price changes as Elasticity of Demand. Are
Economics : Principles of Microeconomics Spring 2014 Instructor: Robert Munk April 24, Final Exam
 Economics 001.01: Principles of Microeconomics Spring 01 Instructor: Robert Munk April, 01 Final Exam Exam Guidelines: The exam consists of 5 multiple choice questions. The exam is closed book and closed
Economics 001.01: Principles of Microeconomics Spring 01 Instructor: Robert Munk April, 01 Final Exam Exam Guidelines: The exam consists of 5 multiple choice questions. The exam is closed book and closed
Micro chapter 1 study guide questions
 Micro chapter 1 study guide questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is true? a. Scarcity and poverty are basically
Micro chapter 1 study guide questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is true? a. Scarcity and poverty are basically
Macroeconomics, 4e (Hubbard/O'Brien) Chapter 1 Economics: Foundations and Models. 1.3 Economic Models
 Macroeconomics, 4e (Hubbard/O'Brien) Chapter 1 Economics: Foundations and Models 1.3 Economic Models 1) Economic models do all of the following except A) answer economic questions. B) portray reality in
Macroeconomics, 4e (Hubbard/O'Brien) Chapter 1 Economics: Foundations and Models 1.3 Economic Models 1) Economic models do all of the following except A) answer economic questions. B) portray reality in
Got stuff? I. The Economic Problem. Chapter 1: The Economic Way of Thinking
 Chapter 1: The Economic Way of Thinking The Economic Problem Production Possibilities Economic Analysis Got stuff? Who made it? How was it made? How did you get it? I. The Economic Problem the basic economic
Chapter 1: The Economic Way of Thinking The Economic Problem Production Possibilities Economic Analysis Got stuff? Who made it? How was it made? How did you get it? I. The Economic Problem the basic economic
Do not remove any pages or add any pages. No additional paper is supplied
 ECON 001 Spring 2018 Midterm 1 February 13, 2018 Time Limit: 60 Minutes Name (Print): Recitation Section: Name of TA: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 11 questions. Check to see
ECON 001 Spring 2018 Midterm 1 February 13, 2018 Time Limit: 60 Minutes Name (Print): Recitation Section: Name of TA: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 11 questions. Check to see
Chapter 2--Observing and Explaining the Economy
 Chapter 2--Observing and Explaining the Economy Student: 1. All of the following are what economists commonly do except A. describing economic events. B. explaining why economic events occur. C. making
Chapter 2--Observing and Explaining the Economy Student: 1. All of the following are what economists commonly do except A. describing economic events. B. explaining why economic events occur. C. making
Chapter 1 Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 Limits, Alternatives, and Choices This chapter begins with a discussion of the meaning and importance of economics. In this first chapter, however, we will not plunge into problems
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 Limits, Alternatives, and Choices This chapter begins with a discussion of the meaning and importance of economics. In this first chapter, however, we will not plunge into problems
Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 6: Elasticity Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions 1. ANSWER: d. ceiling. 2. ANSWER: a. a shortage, which cannot be eliminated through market adjustment. 3. ANSWER: b. the equilibrium price is below
Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions 1. ANSWER: d. ceiling. 2. ANSWER: a. a shortage, which cannot be eliminated through market adjustment. 3. ANSWER: b. the equilibrium price is below
What Economics Is. Chapter 1: Economics and Economic Reasoning. What Economics Is. What Economics Is. What Economics Is.
 Chapter 1: Economics and Economic Reasoning Prepared by: Kevin Richter, Douglas College Charlene Richter, British Columbia Institute of Technology Economics is the study of how individuals, firms, and
Chapter 1: Economics and Economic Reasoning Prepared by: Kevin Richter, Douglas College Charlene Richter, British Columbia Institute of Technology Economics is the study of how individuals, firms, and
TM 2-1 MANUFACTURING COST CLASSIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL REPORTING
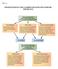 TM 2-1 MANUFACTURING COST CLASSIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL REPORTING TM 2-2 COST CLASSIFICATIONS TO PREDICT COST BEHAVIOR To predict how costs react to changes in activity, costs are often classified as variable
TM 2-1 MANUFACTURING COST CLASSIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL REPORTING TM 2-2 COST CLASSIFICATIONS TO PREDICT COST BEHAVIOR To predict how costs react to changes in activity, costs are often classified as variable
Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages.
 Econ 101, Sections 3 and 4, S11, Schroeter Exam #1, Special code = 0002 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages. 1. When a society
Econ 101, Sections 3 and 4, S11, Schroeter Exam #1, Special code = 0002 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages. 1. When a society
Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages.
 Econ 101, Sections 3 and 4, S11, Schroeter Exam #1, Special code = 0001 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages. 1. When a society
Econ 101, Sections 3 and 4, S11, Schroeter Exam #1, Special code = 0001 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages. 1. When a society
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HW 1 - Micro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When Fresh Express Salads decides to mechanically pick all of its lettuce, it directly
HW 1 - Micro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When Fresh Express Salads decides to mechanically pick all of its lettuce, it directly
Econ Final Exam Review Study Guide Chapter 1 Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use the scarce resources that nature
 Econ Final Exam Review Study Guide Chapter 1 Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use the scarce resources that nature and previous generations have provided. Why study economics?
Econ Final Exam Review Study Guide Chapter 1 Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use the scarce resources that nature and previous generations have provided. Why study economics?
Consumer Choice and Behavioral Economics. Can Jay-Z Get You to Drink Cherry Coke? Learning Objectives. Chapter 9. Utility and Consumer Decision Making
 Chapter 9 Consumer Choice and Behavioral Economics Prepared by: Fernando & Yvonn Quijano 008 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O Brien, e. Can Jay-Z Get You
Chapter 9 Consumer Choice and Behavioral Economics Prepared by: Fernando & Yvonn Quijano 008 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O Brien, e. Can Jay-Z Get You
Ch. 1 LECTURE NOTES Learning objectives II. Definition of Economics III. The Economic Perspective CONSIDER THIS Free for All?
 Ch. 1 LECTURE NOTES I. Learning objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. The definitions of economics and the features of the economic perspective. B. The role of economic theory in economics.
Ch. 1 LECTURE NOTES I. Learning objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. The definitions of economics and the features of the economic perspective. B. The role of economic theory in economics.
Econ Basics. You should copy some information directly into your notebooks (Look for the Dollar Sign) LARGE = Grab as much (all) from the slide
 Econ Basics You should copy some information directly into your notebooks (Look for the Dollar Sign) LARGE = Grab as much (all) from the slide small = bookend key phrases or ideas What is Economics? Economics
Econ Basics You should copy some information directly into your notebooks (Look for the Dollar Sign) LARGE = Grab as much (all) from the slide small = bookend key phrases or ideas What is Economics? Economics
AIU Exam Markets & Decision Making
 AIU Exam Markets & Decision Making School: Business & Economics Major: Economics Course title: Markets & Decision Making Credits for course: 3 credits Description of course: The effects of taxes on supply
AIU Exam Markets & Decision Making School: Business & Economics Major: Economics Course title: Markets & Decision Making Credits for course: 3 credits Description of course: The effects of taxes on supply
ECO 100Y INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Midterm Test # 1
 Department of Economics Prof. Gustavo Indart University of Toronto October 17, 2008 ECO 100Y INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Midterm Test # 1 LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The total time
Department of Economics Prof. Gustavo Indart University of Toronto October 17, 2008 ECO 100Y INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Midterm Test # 1 LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The total time
Lecture 5: Work, Wellbeing, and Scarcity
 Lecture 5: Work, Wellbeing, and Scarcity UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION UNIT 4: BASIC CONCEPTS Three important concepts in economic modelling: 1. Ceteris paribus 2. Incentives
Lecture 5: Work, Wellbeing, and Scarcity UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION UNIT 4: BASIC CONCEPTS Three important concepts in economic modelling: 1. Ceteris paribus 2. Incentives
University of Nevada-Reno College of Business-Department of Economics Ec 103: Principles of Macroeconomics; Fall 2003 Professor Federico Guerrero
 University of Nevada-Reno College of Business-Department of Economics Ec 103: Principles of Macroeconomics; Fall 2003 Professor Federico Guerrero 1 st MIDTERM EXAM-Tuesday, September 30 th, 2003 There
University of Nevada-Reno College of Business-Department of Economics Ec 103: Principles of Macroeconomics; Fall 2003 Professor Federico Guerrero 1 st MIDTERM EXAM-Tuesday, September 30 th, 2003 There
Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity, and Choice Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair, 8e
 Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity, and Choice Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair, 8e 2.1 Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Cost Multiple Choice 1) The process by which resources are transformed
Chapter 2 The Economic Problem: Scarcity, and Choice Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair, 8e 2.1 Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Cost Multiple Choice 1) The process by which resources are transformed
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even Novermber 12, 2014 FORM 1 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number
YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even Novermber 12, 2014 FORM 1 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even Novermber 12, 2014 FORM 3 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number
YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even Novermber 12, 2014 FORM 3 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number
Multiple Choice questions /60 Problem 1 /20 Problem 2 /12 Problem 3 /8
 Econ 200 Midterm 1 Spring 2011 March 29 2011 Instructions : 1-) The exam is 65 minutes 2-) You have to provide detailed solution to each problem 3-) Any form of cheating (Peeking to other s exam, use your
Econ 200 Midterm 1 Spring 2011 March 29 2011 Instructions : 1-) The exam is 65 minutes 2-) You have to provide detailed solution to each problem 3-) Any form of cheating (Peeking to other s exam, use your
9/5/2017. Introduction & Chapter 1
 Introduction & Chapter 1 Economics is the study of the allocation of scarce resources How do people make choices under scarcity and what are the results of these choices for society? While microeconomics
Introduction & Chapter 1 Economics is the study of the allocation of scarce resources How do people make choices under scarcity and what are the results of these choices for society? While microeconomics
Economics is the social science concerned with how individuals, institutions, and society make optimal (best) choices under conditions of scarcity.
 Chapter 1: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices Learning objectives: List the ten key concepts to retain for a lifetime. Define economics and the features of the economic way of thinking. Describe the role
Chapter 1: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices Learning objectives: List the ten key concepts to retain for a lifetime. Define economics and the features of the economic way of thinking. Describe the role
Introduction to Economics
 Introduction to Economics The foundation for economics as a discipline of systematic study was laid in 1776, when Adam Smith (1723-1790) published An Inquiry Into the Natures and Causes of the Wealth of
Introduction to Economics The foundation for economics as a discipline of systematic study was laid in 1776, when Adam Smith (1723-1790) published An Inquiry Into the Natures and Causes of the Wealth of
Mechanism through which buyers (demanders) and sellers (suppliers) communicate to trade goods and services.
 By the end of this learning plan, you will be able to: Use marginal (Cost-Benefit) analysis in decision-making Apply supply and demand analysis to price determination Assess the role price plays in a market
By the end of this learning plan, you will be able to: Use marginal (Cost-Benefit) analysis in decision-making Apply supply and demand analysis to price determination Assess the role price plays in a market
University of Toronto October 17, ECO 100Y INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Midterm Test # 1
 Department of Economics Prof. Gustavo Indart University of Toronto October 17, 2008 SOLUTIONS ECO 100Y INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Midterm Test # 1 LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The
Department of Economics Prof. Gustavo Indart University of Toronto October 17, 2008 SOLUTIONS ECO 100Y INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Midterm Test # 1 LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The
Extra Credit. Student:
 Extra Credit Student: 1. A glass company making windows for houses also makes windows for other things (cars, boats, planes, etc.). We would expect its supply curve for house windows to be: A. Dependent
Extra Credit Student: 1. A glass company making windows for houses also makes windows for other things (cars, boats, planes, etc.). We would expect its supply curve for house windows to be: A. Dependent
Microeconomics (Spring 2015) Final Exam Study Guide
 Microeconomics (Spring 2015) Final Exam Study Guide 1 Note: Below is a list of study questions for the upcoming Part 1 of the final exam, June 10 (Ch. 13, 14, 15, and 17). Please answer them (all of them
Microeconomics (Spring 2015) Final Exam Study Guide 1 Note: Below is a list of study questions for the upcoming Part 1 of the final exam, June 10 (Ch. 13, 14, 15, and 17). Please answer them (all of them
File: ch01, Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems. Multiple Choice
 File: ch01, Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems Multiple Choice 1. The analytical tools underlying nearly all microeconomic studies are: a) Unconstrained optimization and comparative b) Comparative
File: ch01, Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems Multiple Choice 1. The analytical tools underlying nearly all microeconomic studies are: a) Unconstrained optimization and comparative b) Comparative
ECON 1000 Contemporary Economic Issues (Summer 2018) Foundations of Economics
 ECON 1000 Contemporary Economic Issues (Summer 2018) Foundations of Economics Relevant Readings from the Required Textbook: Chapter 1, Foundations of Economics Definitions and Concepts: economics the social
ECON 1000 Contemporary Economic Issues (Summer 2018) Foundations of Economics Relevant Readings from the Required Textbook: Chapter 1, Foundations of Economics Definitions and Concepts: economics the social
6) The mailing must be postmarked by June 15. 7) If you have any questions please me at
 Examination Instructions: 1) Answer the examination only after you have read the honesty pledge below. 2) The multiple choice section will be taken in WebCT and a tutorial for using WebCT is to be found
Examination Instructions: 1) Answer the examination only after you have read the honesty pledge below. 2) The multiple choice section will be taken in WebCT and a tutorial for using WebCT is to be found
Chapter 1 Ten Principles of Economics
 Chapter 1 Ten Principles of Economics TRUE/FALSE 1. Scarcity means that there is less of a good or resource available than people wish to have. ANS: T TOP: Scarcity 2. Economics is the study of how evenly
Chapter 1 Ten Principles of Economics TRUE/FALSE 1. Scarcity means that there is less of a good or resource available than people wish to have. ANS: T TOP: Scarcity 2. Economics is the study of how evenly
Goldwasser AP Microeconomics
 Goldwasser AP Microeconomics Name Unit 4 Problem Set 1. Hiro owns and operates a small business that provides economic consulting services. During the year he spends $55,000 on travel to clients and other
Goldwasser AP Microeconomics Name Unit 4 Problem Set 1. Hiro owns and operates a small business that provides economic consulting services. During the year he spends $55,000 on travel to clients and other
Week 1 (Part 1) Introduction Econ 101
 Week 1 (art 1) Introduction Econ 101 reliminary Concepts (Chapter 2 g 38-41 & 47-50) Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use scarce resources that nature and previous generations
Week 1 (art 1) Introduction Econ 101 reliminary Concepts (Chapter 2 g 38-41 & 47-50) Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use scarce resources that nature and previous generations
ECON 1000 (Fall 2017 Section 07) Exam #1A
 ECON 1000 (Fall 2017 Section 07) Exam #1A Multiple Choice Questions: (3 points each) 1. I am taking of the exam. A. Version A 2. The present economic system of the United Kingdom would be most accurately
ECON 1000 (Fall 2017 Section 07) Exam #1A Multiple Choice Questions: (3 points each) 1. I am taking of the exam. A. Version A 2. The present economic system of the United Kingdom would be most accurately
Econ Principles of Microeconomics - Assignment 1
 Econ 2302 - Principles of Microeconomics - Assignment 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A likely effect of government policies that redistribute
Econ 2302 - Principles of Microeconomics - Assignment 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A likely effect of government policies that redistribute
Macro Chapter 2 study guide questions
 Macro Chapter 2 study guide questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The opportunity cost to the United States of placing a man on the
Macro Chapter 2 study guide questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The opportunity cost to the United States of placing a man on the
