Instructor: Yuntian Zhu. Lecture 5
|
|
|
- Dulcie Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MSE 791: Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Office: 308 RBII Ph: Lecture 5 Grain size effect on deformation twinning and detwinning in CG and NC fcc metals. Optimal grain size Department of Materials Science and Engineering 1
2 Grain Size effect on twining in CG samples Smaller grains are harder to deform by twining Hall-Petch relationship: Dislocation slip: σ S = σ 0 +κ S d 1/2 Twinning: σ t = σ 0 +κ t d 1/2 Department of Materials Science and Engineering 2
3 Grain Size effect on twining in CG samples Smaller grains are harder to deform by twining Hall-Petch relationship: κ t κ S Dislocation slip: σ S = σ 0 +κ S d 1/2 Twinning: σ t = σ 0 +κ t d 1/2 Department of Materials Science and Engineering 3
4 Grain size effect on deformation twinning To twin or not to twin? A controversy on twinning MD simulations by Dr. Van Swygenhoven s group In nc Al, Ni and Cu, twins are rarely observed (Nature Mater. 3 (2004) 399; Adv. Eng. Mater. 7 (2005) 16) MD simulations by Dr. Wolf s group In nc Al, twins are frequently observed (Nature Mater. 1 (2002) 45; 2 (2004) 43) Experimental Observations In nc Al, Cu and Ni, twins were observed Who is right? No One is Wrong!!!
5 Grain size effect on deformation twinning Statistical grain-size effect on the formations of stacking faults and deformation twins in NC Ni. Physical Review Letters, 101 (2008)
6 Grain size effect Optimum grain size for twinning Coarse-grained fcc metal: Smaller grains are harder to twin nc fcc metal: larger grains: Smaller grains are easier to twin Normal grain size effect nc fcc metal: smaller grains Smaller grains are harder to twin Maximum grain size for stacking fault Inverse grain size effect Twinning difficulty Grain Size
7 Similar results also observed in Cu Zhang, Lu, Wang, Li, Sun, Ma, PRB, 81, (2010)
8 What s the reason for the observed inverse grain size effect and optimum grain size for twinning?
9 Theory #1: Smaller grain size favors partial activation continuously from the CG to nano grain range (Chen et al, Science, 300 (2003) 1275; Liao et al, Phil. Mag. 83 (2003) 3065/our work) The stress for activating partial dislocation is (Venables, Phil Mag. 6 (1961) 379): τ P = γ b 1 + Gb d 1 τ τ P = γ b 1 + Gb d 1 The stress for activating lattice dislocation is (Johari&Thomas, Acta Met. 2 (1964) 1152): τ L = Gb d τp increases at a slower rate with decreasing d than τl τ L = Gb d 1/dc 1/d Emission of partials = twin formation
10 Our model extends beyond the previous models Zhu et al, APL, 85 (2004) 5049.(LANL+UCD) 3 systems: Screw 60 I 60 II d τ α b1 (111) Assumption: Dislocation emission from grain boundaries Simplification: Square grain Straight dislocation line Non-relaxed dislocation line on GB Stress for emitting a 30 partial needs to overcome: 1) The lengthening of partial dislocation line on the GB 2) The increase of total stacking fault energy τ p = 1 & $ sinα % 6γ a + 2 Ga 6πd ln 2d a #! "
11 Critical Stresses vs Grain Sizes at Two angles 2 α=90 d 1 A B' τ p τ α b (111) d B B τ shrink τ twin τ L τ trail Grain Size (nm) Driving force = τ b d, Dragging force is independent of d More difficult for dislocation slip with smaller grain size
12 Our Analytical Model on Twinning Stresses vs Grain Sizes (Al) o I Screw Twin nucleation o I Screw Twin growth Grain Size d (nm) After considering all α values (stress orientations) Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5049 (2004).
13 Minimum Shear Stresses for deformation twinning: Critical stress for deformation twinning: τ m = ( ν )γ 2a Optimum grain sizes for deformation twinning: d m ln 2 d m a ( ) = 9.69 ν ( ) ν Ga 2 γ Prog. Mater. Sci. 57 (2012) 1-62.
14 Compare with Experimental Observations Critical stresses and optimum grain size range for twin nucleation Ag Al Au Cu Ni G (GPa) ν γ (mjm -2 ) A (Å) τ m (GPa) d m (nm)
15 Generalized planar fault energy effect b1 b2 Generalized Planar Fault Energy for Ni b Conventional wisdom: nc-ni should deform by full dislocation, with no stacking fault or twin Recent MD simulations: Nano-Ni should deform by partial dislocation emission from grain boundaries, creating stacking fault, but not twins (Van Swygenhoven, Nature Mater. 3 (2004) 399 ). The observed inverse grain size effect explains/reconciles the controversy
16 Detwinning is also affected by grain size Physical Review B, 84, (2011).
17 Mechanism for the grain size effect on detwinning Schematics of the grain size effect on the twinning and de-twinning tendency Physical Review B, 84, (2011).
18 Homework, due in one week Lecture 5: 2 Department of Materials Science and Engineering 18
Instructor: Yuntian Zhu. Lecture 3
 MSE 791: Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Office: 308 RBII Ph: 513-0559 ytzhu@ncsu.edu Lecture 3 Difference in
MSE 791: Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Office: 308 RBII Ph: 513-0559 ytzhu@ncsu.edu Lecture 3 Difference in
Instructor: Yuntian Zhu. Lecture 8
 MSE 791: Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Office: 308 RBII Ph: 513-0559 ytzhu@ncsu.edu Lecture 8 Deformation
MSE 791: Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Office: 308 RBII Ph: 513-0559 ytzhu@ncsu.edu Lecture 8 Deformation
3, MSE 791 Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials
 3, MSE 791 Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Lecture 1 1. What is strain (work) hardening? What is the mechanism for strain hardening?
3, MSE 791 Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Lecture 1 1. What is strain (work) hardening? What is the mechanism for strain hardening?
Deformation Twinning in Bulk Aluminum with Coarse Grains
 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Proceedings Alloys, of the September 12th International 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Conference Japan on 2010 Aluminum The Japan Alloys, Institute
Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Proceedings Alloys, of the September 12th International 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Conference Japan on 2010 Aluminum The Japan Alloys, Institute
M.A. Tschopp 1,2, D.L. McDowell 3,4
 1 KEYNOTE LECTURE Atomistic Simulations of Dislocation Nucleation M.A. Tschopp 1,2, D.L. McDowell 3,4 1 Center for Advanced Vehicular Systems (CAVS), Mississippi State University 2 UTC, Air Force Research
1 KEYNOTE LECTURE Atomistic Simulations of Dislocation Nucleation M.A. Tschopp 1,2, D.L. McDowell 3,4 1 Center for Advanced Vehicular Systems (CAVS), Mississippi State University 2 UTC, Air Force Research
Rate-Sensitive Deformation Characteristics of Nanostructured Materials
 Rate-Sensitive Deformation Characteristics of Nanostructured Materials Koteswararao V. Rajulapati, Sreedevi Varam and K. Bhanu Sankara Rao School of Engineering Sciences and Technology University of Hyderabad,
Rate-Sensitive Deformation Characteristics of Nanostructured Materials Koteswararao V. Rajulapati, Sreedevi Varam and K. Bhanu Sankara Rao School of Engineering Sciences and Technology University of Hyderabad,
Strengthening Mechanisms
 Strengthening Mechanisms The ability of a metal/ alloy to plastically deform depends on the ability of dislocations to move. Strengthening techniques rely on restricting dislocation motion to render a
Strengthening Mechanisms The ability of a metal/ alloy to plastically deform depends on the ability of dislocations to move. Strengthening techniques rely on restricting dislocation motion to render a
Deformation Behavior Of Hadfield Steel Single And Polycrystals Due To Twinning and Slip
 Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, Mechanics of Materials Meeting, May 5-11, 2002 Deformation Behavior Of Hadfield Steel Single And Polycrystals Due To Twinning and Slip Huseyin Sehitoglu,
Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, Mechanics of Materials Meeting, May 5-11, 2002 Deformation Behavior Of Hadfield Steel Single And Polycrystals Due To Twinning and Slip Huseyin Sehitoglu,
Atomistic Modeling of Thermally Activated Processes for Crystal Dislocations
 IPAM Workshop ELWS 2 UCLA, Oct 16-20, 2017 Atomistic Modeling of Thermally Activated Processes for Crystal Dislocations Oct 16, 2017 Wei Cai, Xiaohan Zhang, William Kuykendall* Department of Mechanical
IPAM Workshop ELWS 2 UCLA, Oct 16-20, 2017 Atomistic Modeling of Thermally Activated Processes for Crystal Dislocations Oct 16, 2017 Wei Cai, Xiaohan Zhang, William Kuykendall* Department of Mechanical
A discrete dislocation plasticity analysis of grain-size strengthening
 Materials Science and Engineering A 400 401 (2005) 186 190 A discrete dislocation plasticity analysis of grain-size strengthening D.S. Balint a,, V.S. Deshpande a, A. Needleman b, E. Van der Giessen c
Materials Science and Engineering A 400 401 (2005) 186 190 A discrete dislocation plasticity analysis of grain-size strengthening D.S. Balint a,, V.S. Deshpande a, A. Needleman b, E. Van der Giessen c
Grain-size effect on the deformation mechanisms of nanostructured copper processed by high-pressure torsion
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 96, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 2004 Grain-size effect on the deformation mechanisms of nanostructured copper processed by high-pressure torsion X. Z. Liao, Y. H. Zhao, and Y. T.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 96, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 2004 Grain-size effect on the deformation mechanisms of nanostructured copper processed by high-pressure torsion X. Z. Liao, Y. H. Zhao, and Y. T.
ENGN 2340 Final Project. Simulating the Plasticity Behavior of Nanocrystalline Cu Using ABAQUS UMAT Subroutine
 ENGN 2340 Final Project Simulating the Plasticity Behavior of Nanocrystalline Cu Using ABAQUS UMAT Subroutine By Hanxun Jin Dec 11. 2015 1. Introduction Nanocrystalline metals(nc), which have grain sizes
ENGN 2340 Final Project Simulating the Plasticity Behavior of Nanocrystalline Cu Using ABAQUS UMAT Subroutine By Hanxun Jin Dec 11. 2015 1. Introduction Nanocrystalline metals(nc), which have grain sizes
Applied stress controls the production of nano-twins in coarse-grained metals
 APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 101, 231903 (2012) Applied stress controls the production of nano-twins in coarse-grained metals Y. Cao, 1 Y. B. Wang, 1 X. Z. Liao, 1,a) M. Kawasaki, 2,3 S. P. Ringer, 1,4 T. G.
APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 101, 231903 (2012) Applied stress controls the production of nano-twins in coarse-grained metals Y. Cao, 1 Y. B. Wang, 1 X. Z. Liao, 1,a) M. Kawasaki, 2,3 S. P. Ringer, 1,4 T. G.
Designing martensitic steels: structure & properties Enrique Galindo-Nava and Pedro Rivera
 Designing martensitic steels: structure & properties Enrique Galindo-Nava and Pedro Rivera Feng Qian, Mark Rainforth (Sheffield); Wenwen Song (Aachen) 1 Outline Aim: Understand the factors controlling
Designing martensitic steels: structure & properties Enrique Galindo-Nava and Pedro Rivera Feng Qian, Mark Rainforth (Sheffield); Wenwen Song (Aachen) 1 Outline Aim: Understand the factors controlling
Supplementary Figure 1 Strength versus total elongation for typical steels (data with filled circles come from this study. All other data come from
 Supplementary Figure 1 Strength versus total elongation for typical steels (data with filled circles come from this study. All other data come from US Steel Co. 1 The dashed line is for guidance to show
Supplementary Figure 1 Strength versus total elongation for typical steels (data with filled circles come from this study. All other data come from US Steel Co. 1 The dashed line is for guidance to show
Size-Dependent Plasticity in Twinned Metal Nanowires
 Size-Dependent Plasticity in Twinned Metal Nanowires F. Sansoz 1 and C. Deng 1 1 School of Engineering and Materials Science Program, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405, USA 1. Introduction Face-centered
Size-Dependent Plasticity in Twinned Metal Nanowires F. Sansoz 1 and C. Deng 1 1 School of Engineering and Materials Science Program, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405, USA 1. Introduction Face-centered
The effect of twin plane spacing on the deformation of copper containing a high density of growth twins
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Birck and NCN Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center September 2008 The effect of twin plane spacing on the deformation of copper containing a high density of growth twins
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Birck and NCN Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center September 2008 The effect of twin plane spacing on the deformation of copper containing a high density of growth twins
Multiscale models of metal plasticity Part II: Crystal plasticity to subgrain microstructures
 Multiscale models of metal plasticity Part II: Crystal plasticity to subgrain microstructures M. Ortiz California Institute of Technology MULTIMAT closing meeting Bonn, Germany, September 12, 2008 Dislocation
Multiscale models of metal plasticity Part II: Crystal plasticity to subgrain microstructures M. Ortiz California Institute of Technology MULTIMAT closing meeting Bonn, Germany, September 12, 2008 Dislocation
Chapter 7: Plastic deformation, Strengthening and Recrystallisation of Metals
 Chapter 7: Plastic deformation, Strengthening and Recrystallisation of Metals What do I need to know? The Mechanism of Plastic formation in single and polycrystalline metals The slip mechanism The slip
Chapter 7: Plastic deformation, Strengthening and Recrystallisation of Metals What do I need to know? The Mechanism of Plastic formation in single and polycrystalline metals The slip mechanism The slip
The typical manners of dynamic crack propagation along the. metal/ceramics interfaces: A molecular dynamics study
 The typical manners of dynamic crack propagation along the metal/ceramics interfaces: A molecular dynamics study Yanguang Zhou 1, Zhenyu Yang 1*, Tao Wang 2, Dayong Hu 3, Xiaobing Ma 4 1 Institute of Solid
The typical manners of dynamic crack propagation along the metal/ceramics interfaces: A molecular dynamics study Yanguang Zhou 1, Zhenyu Yang 1*, Tao Wang 2, Dayong Hu 3, Xiaobing Ma 4 1 Institute of Solid
SOTERIA training school
 SOTERIA training school DOSE-DEPENDENT NANO-FEATURES AND THEIR EFFECT ON INTER-GRANULAR CRACKING SUSCEPTIBILITY (INTERNALS) OUTLINE - Previous findings, up to PERFORM60 (up to 2012) - Subsequent sub-grain
SOTERIA training school DOSE-DEPENDENT NANO-FEATURES AND THEIR EFFECT ON INTER-GRANULAR CRACKING SUSCEPTIBILITY (INTERNALS) OUTLINE - Previous findings, up to PERFORM60 (up to 2012) - Subsequent sub-grain
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 8 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 8 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 8 Nov 2016](/thumbs/72/67012024.jpg) Directional Anisotropy of Crack Propagation Along Σ3 Grain Boundary in BCC Fe G. Sainath*, B.K. Choudhary** Deformation and Damage Modeling Section, Mechanical Metallurgy Division Indira Gandhi Centre
Directional Anisotropy of Crack Propagation Along Σ3 Grain Boundary in BCC Fe G. Sainath*, B.K. Choudhary** Deformation and Damage Modeling Section, Mechanical Metallurgy Division Indira Gandhi Centre
Atomic mechanism for dislocation emission from nanosized grain boundaries
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 66, 024101 2002 Atomic mechanism for dislocation emission from nanosized grain boundaries H. Van Swygenhoven, P. M. Derlet, and A. Hasnaoui Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen, CH-5232,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 66, 024101 2002 Atomic mechanism for dislocation emission from nanosized grain boundaries H. Van Swygenhoven, P. M. Derlet, and A. Hasnaoui Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen, CH-5232,
Problems to the lecture Physical Metallurgy ( Materialkunde ) Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties
 Institut für Metallkunde und Metallphysik Direktor: Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Günter Gottstein RWTH Aachen, D-52056 Aachen Internet: http://www.imm.rwth-aachen.de E-mail: imm@imm.rwth-aachen.de Tel.: +49 241
Institut für Metallkunde und Metallphysik Direktor: Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Günter Gottstein RWTH Aachen, D-52056 Aachen Internet: http://www.imm.rwth-aachen.de E-mail: imm@imm.rwth-aachen.de Tel.: +49 241
ECE236A Semiconductor Heterostructure Materials Defects in Semiconductor Crystals Lecture 6 Oct. 19, 2017
 ECE236A Semiconductor Heterostructure Materials Defects in Semiconductor Crystals Lecture 6 Oct. 19, 2017 Stacking sequence in simple crystals. Stacking faults (intrinsic, extrinsic) Twin boundaries Dislocations
ECE236A Semiconductor Heterostructure Materials Defects in Semiconductor Crystals Lecture 6 Oct. 19, 2017 Stacking sequence in simple crystals. Stacking faults (intrinsic, extrinsic) Twin boundaries Dislocations
Alloying effect on grain-size dependent deformation twinning in nanocrystalline Cu Zn alloys
 Philosophical Magazine, 2015 Vol. 95, No. 3, 301 310, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14786435.2014.1000418 Alloying effect on grain-size dependent deformation twinning in nanocrystalline Cu Zn alloys X.L. Ma
Philosophical Magazine, 2015 Vol. 95, No. 3, 301 310, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14786435.2014.1000418 Alloying effect on grain-size dependent deformation twinning in nanocrystalline Cu Zn alloys X.L. Ma
Module-6. Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms
 Module-6 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Contents 1) Dislocations & Plastic deformation and Mechanisms of plastic deformation in metals 2) Strengthening mechanisms in metals 3) Recovery, Recrystallization
Module-6 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Contents 1) Dislocations & Plastic deformation and Mechanisms of plastic deformation in metals 2) Strengthening mechanisms in metals 3) Recovery, Recrystallization
Annealing twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals: A molecular dynamics simulation
 Annealing twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals: A molecular dynamics simulation Diana Farkas, 1 Eduardo Bringa, 2 and Alfredo Caro 2 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg,
Annealing twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals: A molecular dynamics simulation Diana Farkas, 1 Eduardo Bringa, 2 and Alfredo Caro 2 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg,
VERIFICATION OF HALL-PETCH EQUATION OF NANOCRYSTALLINE COPPER. Katarína Sülleiová a Michal Besterci a Tibor Kvačkaj b
 VERIFICATION OF HALL-PETCH EQUATION OF NANOCRYSTALLINE COPPER Katarína Sülleiová a Michal Besterci a Tibor Kvačkaj b a Institute of Materials Research of SAS, Watsonova 47, 040 01 Košice, SR, E-mail address:mbesterci@imr.saske.sk,
VERIFICATION OF HALL-PETCH EQUATION OF NANOCRYSTALLINE COPPER Katarína Sülleiová a Michal Besterci a Tibor Kvačkaj b a Institute of Materials Research of SAS, Watsonova 47, 040 01 Košice, SR, E-mail address:mbesterci@imr.saske.sk,
Reaction pathway analysis for dislocation nucleation from a Ni surface step. Abstract
 APS/123-QED Reaction pathway analysis for dislocation nucleation from a Ni surface step Shotaro Hara, Satoshi Izumi, and Shinsuke Sakai Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo
APS/123-QED Reaction pathway analysis for dislocation nucleation from a Ni surface step Shotaro Hara, Satoshi Izumi, and Shinsuke Sakai Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo
STRENGTHENING MECHANISM IN METALS
 Background Knowledge Yield Strength STRENGTHENING MECHANISM IN METALS Metals yield when dislocations start to move (slip). Yield means permanently change shape. Slip Systems Slip plane: the plane on which
Background Knowledge Yield Strength STRENGTHENING MECHANISM IN METALS Metals yield when dislocations start to move (slip). Yield means permanently change shape. Slip Systems Slip plane: the plane on which
Creep behavior study of join of nano crystalline Stainless steel and nanocrystalline Nickel using molecular dynamics simulation
 Creep behavior study of join of nano crystalline Stainless steel and nanocrystalline Nickel using molecular dynamics simulation Md. Meraj and S. Pal * Computational Material Engineering Group, Department
Creep behavior study of join of nano crystalline Stainless steel and nanocrystalline Nickel using molecular dynamics simulation Md. Meraj and S. Pal * Computational Material Engineering Group, Department
A Continuum Formulation of Stress Correlations of Dislocations in Two Dimensions
 TECHNISCHE MECHANIK, 34, 3-4, (2014), 205 212 submitted: October 15, 2013 A Continuum Formulation of Stress Correlations of Dislocations in Two Dimensions D. E. Dickel, K. Schulz, S. Schmitt, P. Gumbsch
TECHNISCHE MECHANIK, 34, 3-4, (2014), 205 212 submitted: October 15, 2013 A Continuum Formulation of Stress Correlations of Dislocations in Two Dimensions D. E. Dickel, K. Schulz, S. Schmitt, P. Gumbsch
Formation of single and multiple deformation twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Acta Materialia 57 (2009) 3763 3770 www.elsevier.com/locate/actamat Formation of single and multiple deformation twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals Y.T. Zhu a,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Acta Materialia 57 (2009) 3763 3770 www.elsevier.com/locate/actamat Formation of single and multiple deformation twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals Y.T. Zhu a,
Microstructural parameters from Multiple Whole Profile (MWP) or Convolutional Multiple Whole Profile (CMWP) computer programs
 Microstructural parameters from Multiple Whole Profile (MWP) or Convolutional Multiple Whole Profile (CMWP) computer programs Iuliana Dragomir-Cernatescu School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia
Microstructural parameters from Multiple Whole Profile (MWP) or Convolutional Multiple Whole Profile (CMWP) computer programs Iuliana Dragomir-Cernatescu School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia
Effects of Grain Boundary Disorder on Yield Strength
 Effects of Grain Boundary Disorder on Yield Strength Valery Borovikov 1, Mikhail I. Mendelev 1 and Alexander H. King 1,2 1 Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering, Ames Laboratory, Ames, IA 50011
Effects of Grain Boundary Disorder on Yield Strength Valery Borovikov 1, Mikhail I. Mendelev 1 and Alexander H. King 1,2 1 Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering, Ames Laboratory, Ames, IA 50011
Macroscopic Twinning Strain in Nanocrystalline Cu. F. Wu, Y.T. Zhu and J. Narayan
 Vol. 2, No. 2, 63 69, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2013.862874 www.tandfonline.com/toc/tmrl20/current Macroscopic Twinning Strain in Nanocrystalline Cu F. Wu, Y.T. Zhu and J. Narayan Department of
Vol. 2, No. 2, 63 69, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2013.862874 www.tandfonline.com/toc/tmrl20/current Macroscopic Twinning Strain in Nanocrystalline Cu F. Wu, Y.T. Zhu and J. Narayan Department of
First-Principles Study of the Bonding and Mechanical Properties of Metallic Grain Boundaries
 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1405-1412 1405 First-Principles Study of the Bonding
Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1405-1412 1405 First-Principles Study of the Bonding
Molecular dynamics study on the grain boundary dislocation source in nanocrystalline copper under tensile loading
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2015 Molecular dynamics study on the grain boundary
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2015 Molecular dynamics study on the grain boundary
Chapter 8 Strain Hardening and Annealing
 Chapter 8 Strain Hardening and Annealing This is a further application of our knowledge of plastic deformation and is an introduction to heat treatment. Part of this lecture is covered by Chapter 4 of
Chapter 8 Strain Hardening and Annealing This is a further application of our knowledge of plastic deformation and is an introduction to heat treatment. Part of this lecture is covered by Chapter 4 of
Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Evolution of Recrystallization Textures in Drawn Wires and Rolled Sheets
 Materials Science Forum Vols. 495-497 (2005) pp. 1243-1248 online at http://www.scientific.net 2005 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland 194 Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Evolution of Recrystallization
Materials Science Forum Vols. 495-497 (2005) pp. 1243-1248 online at http://www.scientific.net 2005 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland 194 Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Evolution of Recrystallization
Influence of alloying additions on grain boundary cohesion in tungsten: First-principles predictions. Xuebang Wu and C.S. Liu
 2016 Joint ICTP/CAS/IAEA School and Workshop on PMI in Fusion Device Influence of alloying additions on grain boundary cohesion in tungsten: First-principles predictions Xuebang Wu and C.S. Liu Institute
2016 Joint ICTP/CAS/IAEA School and Workshop on PMI in Fusion Device Influence of alloying additions on grain boundary cohesion in tungsten: First-principles predictions Xuebang Wu and C.S. Liu Institute
Hall-Petch Analysis from a Combined Mechanics and Materials Viewpoint
 Hall-Petch Analysis from a Combined Mechanics and Materials Viewpoint TOPICS CHARTS 1. Outline and historical introduction 4 2. Hall-Petch and TASRA model descriptions 2 3. Experimental measurements 3.1.
Hall-Petch Analysis from a Combined Mechanics and Materials Viewpoint TOPICS CHARTS 1. Outline and historical introduction 4 2. Hall-Petch and TASRA model descriptions 2 3. Experimental measurements 3.1.
Molecular dynamics simulations of stress-induced phase transformations and grain nucleation at crack tips in Fe
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING MODELLING AND SIMULATION IN MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 11 (2003) 745 753 PII: S0965-0393(03)64097-0 Molecular dynamics simulations
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING MODELLING AND SIMULATION IN MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 11 (2003) 745 753 PII: S0965-0393(03)64097-0 Molecular dynamics simulations
Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms. Introduction
 Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms What is happening in material during plastic deformation? Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Motion of dislocations in response to stress Slip
Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms What is happening in material during plastic deformation? Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Motion of dislocations in response to stress Slip
Plastic deformation mechanisms in nanocrystalline columnar grain structures
 Plastic deformation mechanisms in nanocrystalline columnar grain structures Diana Farkas a and William A. Curtin b a Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061,
Plastic deformation mechanisms in nanocrystalline columnar grain structures Diana Farkas a and William A. Curtin b a Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061,
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms. Strengthening by grain size reduction
 Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Mechanisms of strengthening in metals Strengthening by grain size reduction Solid-solution strengthening Strain hardening Recovery, recrystallization,
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Mechanisms of strengthening in metals Strengthening by grain size reduction Solid-solution strengthening Strain hardening Recovery, recrystallization,
Role of SFE on deformation texture evolution in non-equiatomic fcc CrFeMnCoNi high-entropy alloys
 Role of SFE on deformation texture evolution in non-equiatomic fcc CrFeMnCoNi high-entropy alloys 1 Dan Sathiaraj G, 2 Rajib Kalsar, 2 Satyam Suwas, 1 Werner Skrotzki 1 Institute of Solid State and Materials
Role of SFE on deformation texture evolution in non-equiatomic fcc CrFeMnCoNi high-entropy alloys 1 Dan Sathiaraj G, 2 Rajib Kalsar, 2 Satyam Suwas, 1 Werner Skrotzki 1 Institute of Solid State and Materials
Elastic, Plastic, Cracking Aspects of Material Behaviors in Indentation Hardness Tests
 Elastic, Plastic, Cracking Aspects of Material Behaviors in Indentation Hardness Tests Ron Armstrong Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 31 March 2011 Hardness Aspects of Elastic, Plastic, Cracking
Elastic, Plastic, Cracking Aspects of Material Behaviors in Indentation Hardness Tests Ron Armstrong Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 31 March 2011 Hardness Aspects of Elastic, Plastic, Cracking
Microstructure, Slip Systems and Yield Stress Anisotropy in Plastic Deformation
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 13, 218 Microstructure, Slip Systems and Yield Stress Anisotropy in Plastic Deformation Winther, Grethe; You, Ze Sheng; Lu, Lei Publication date: 212 Link back to DTU
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 13, 218 Microstructure, Slip Systems and Yield Stress Anisotropy in Plastic Deformation Winther, Grethe; You, Ze Sheng; Lu, Lei Publication date: 212 Link back to DTU
Effects of Grain Boundary Disorder on Yield Strength
 Materials Science and Engineering Publications Materials Science and Engineering 2018 Effects of Grain Boundary Disorder on Yield Strength Valery Borovikov Iowa State University and Ames Laboratory, valery@ameslab.gov
Materials Science and Engineering Publications Materials Science and Engineering 2018 Effects of Grain Boundary Disorder on Yield Strength Valery Borovikov Iowa State University and Ames Laboratory, valery@ameslab.gov
Twin boundary migration creating zero shear strain: In-situ TEM observations and atomistic simulations
 Magnesium Technology 2013 Edited by: Norbert Hort, SuveenN. Mathaudhu, Ne ale R. Neelameggham, andmartyn Alderman TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2013 Twin boundary migration creating zero
Magnesium Technology 2013 Edited by: Norbert Hort, SuveenN. Mathaudhu, Ne ale R. Neelameggham, andmartyn Alderman TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2013 Twin boundary migration creating zero
Molecular dynamics based modelling of the dislocation motion in bulk nanostructuring of a FCC material
 Molecular dynamics based modelling of the dislocation motion in bulk nanostructuring of a FCC material ALICE BURUIANA, MIHAELA BANU, ALEXANDRU EPUREANU, FELICIA STAN Manufacturing Science and Engineering
Molecular dynamics based modelling of the dislocation motion in bulk nanostructuring of a FCC material ALICE BURUIANA, MIHAELA BANU, ALEXANDRU EPUREANU, FELICIA STAN Manufacturing Science and Engineering
Formation of deformation twin boundaries in a coarse-grained aluminum
 Formation of deformation twin boundaries in a coarse-grained aluminum Shenbao Jin 1, Kai Zhang 1, Ruben Bjørge 2, Nairong Tao 3, Knut Marthinsen 1, Ke Lu 3 and Yanjun Li 1,* 1. Department of Materials
Formation of deformation twin boundaries in a coarse-grained aluminum Shenbao Jin 1, Kai Zhang 1, Ruben Bjørge 2, Nairong Tao 3, Knut Marthinsen 1, Ke Lu 3 and Yanjun Li 1,* 1. Department of Materials
Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Mechanism of Plastic Deformation in Nanotwinned FCC Metals
 Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Mechanism of Plastic Deformation in Nanotwinned FCC Metals Valery Borovikov 1, Mikhail I. Mendelev 1, Alexander H. King 1,2 and Richard LeSar 1,2 1 Division of Materials
Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Mechanism of Plastic Deformation in Nanotwinned FCC Metals Valery Borovikov 1, Mikhail I. Mendelev 1, Alexander H. King 1,2 and Richard LeSar 1,2 1 Division of Materials
Interactions between dislocations and threedimensional annealing twins in face centered cubic metals
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Mechanical & Materials Engineering Faculty Publications Mechanical & Materials Engineering, Department of 3-209 Interactions
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Mechanical & Materials Engineering Faculty Publications Mechanical & Materials Engineering, Department of 3-209 Interactions
Nanostructured surface layer on metallic materials induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment
 Materials Science and Engineering A 375 377 (2004) 38 45 Nanostructured surface layer on metallic materials induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment K. Lu a,,j.lu b a Institute of Metal Research,
Materials Science and Engineering A 375 377 (2004) 38 45 Nanostructured surface layer on metallic materials induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment K. Lu a,,j.lu b a Institute of Metal Research,
Engineering materials
 1 Engineering materials Lecture 2 Imperfections and defects Response of materials to stress 2 Crystalline Imperfections (4.4) No crystal is perfect. Imperfections affect mechanical properties, chemical
1 Engineering materials Lecture 2 Imperfections and defects Response of materials to stress 2 Crystalline Imperfections (4.4) No crystal is perfect. Imperfections affect mechanical properties, chemical
Point coordinates. x z
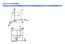 Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
PLASTIC DEFORMATION AND FRACTURE PROCESSES IN METALLIC AND CERAMIC NANOMATERIALS WITH BIMODAL STRUCTURES
 Plastic Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. deformation 16(2007) and fracture 1-9processes in metallic and ceramic nanomaterials... 1 PLASTIC DEFORMATION AND FRACTURE PROCESSES IN METALLIC AND CERAMIC NANOMATERIALS WITH
Plastic Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. deformation 16(2007) and fracture 1-9processes in metallic and ceramic nanomaterials... 1 PLASTIC DEFORMATION AND FRACTURE PROCESSES IN METALLIC AND CERAMIC NANOMATERIALS WITH
PLANAR DEFECTS ON {121} PLANE IN 2H STRUCTURE
 PLANAR DEFECTS ON {121} PLANE IN 2H STRUCTURE Authors: Andriy OSTAPOVETS 1,2*, Vaclav PAIDAR 1 Workplace: 1 Institute of Physics of the ASCR, Prague, Czech Republic 2 Institute of Chemical Technology,
PLANAR DEFECTS ON {121} PLANE IN 2H STRUCTURE Authors: Andriy OSTAPOVETS 1,2*, Vaclav PAIDAR 1 Workplace: 1 Institute of Physics of the ASCR, Prague, Czech Republic 2 Institute of Chemical Technology,
Lecture # 11 References:
 Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC Dr.Haydar Al-Ethari
Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC Dr.Haydar Al-Ethari
sensitivity in a Mg-Al-Zn alloy at moderate temperatures
 Influence of the grain size on the strain rate sensitivity in a Mg-Al-Zn alloy at moderate temperatures J. A. del Valle and O. A. Ruano Dept. of Physical Metallurgy, Centro Nacional de Investigaciones
Influence of the grain size on the strain rate sensitivity in a Mg-Al-Zn alloy at moderate temperatures J. A. del Valle and O. A. Ruano Dept. of Physical Metallurgy, Centro Nacional de Investigaciones
Solute effect on twinning deformation in Mg alloys
 Solute effect on twinning deformation in Mg alloys A. Luque1, M. Ghazisaeidi2, W.A. Curtin1 1 Institute of Mechanical Engineering, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland 2 Department of
Solute effect on twinning deformation in Mg alloys A. Luque1, M. Ghazisaeidi2, W.A. Curtin1 1 Institute of Mechanical Engineering, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland 2 Department of
Formation of incoherent deformation twin boundaries in a coarse-grained Al-7Mg alloy
 Formation of incoherent deformation twin boundaries in a coarse-grained Al-7Mg alloy S. B. Jin, K. Zhang, R. Bjørge, N. R. Tao, K. Marthinsen, K. Lu, and Y. J. Li Citation: Applied Physics Letters 107,
Formation of incoherent deformation twin boundaries in a coarse-grained Al-7Mg alloy S. B. Jin, K. Zhang, R. Bjørge, N. R. Tao, K. Marthinsen, K. Lu, and Y. J. Li Citation: Applied Physics Letters 107,
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number:
 Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
MSE 6020: Defects and Microstructure in Materials Spring 2015, Tuesday and Thursday, 3:30-4:45 pm, Rice Hall 032
 MSE 6020: Defects and Microstructure in Materials Spring 2015, Tuesday and Thursday, 3:30-4:45 pm, Rice Hall 032 Contact Information: Instructor: Leonid Zhigilei Office: Wilsdorf Hall 303D Office Hours:
MSE 6020: Defects and Microstructure in Materials Spring 2015, Tuesday and Thursday, 3:30-4:45 pm, Rice Hall 032 Contact Information: Instructor: Leonid Zhigilei Office: Wilsdorf Hall 303D Office Hours:
Structural change during cold rolling of electrodeposited copper
 Materials Science Forum Vols. 539-543 (2007) pp. 5013-5018 online at http://www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural change during cold rolling of electrodeposited copper
Materials Science Forum Vols. 539-543 (2007) pp. 5013-5018 online at http://www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural change during cold rolling of electrodeposited copper
Torsional properties of bamboo-like structured Cu nanowires. Haifei Zhan and Yuantong Gu *
 Torsional properties of bamboo-like structured Cu nanowires Haifei Zhan and Yuantong Gu * School of Chemistry, Physics and Mechanical Engineering, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, QLD, 4001,
Torsional properties of bamboo-like structured Cu nanowires Haifei Zhan and Yuantong Gu * School of Chemistry, Physics and Mechanical Engineering, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, QLD, 4001,
Models for the Yield Strength of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys
 Models for the Yield Strength of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys Marco Starink, Xiaomei Li, Shuncai Wang School of Engineering Sciences University of Southampton Presented at ASM Materials Solutions Conf. 2003, 1st
Models for the Yield Strength of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys Marco Starink, Xiaomei Li, Shuncai Wang School of Engineering Sciences University of Southampton Presented at ASM Materials Solutions Conf. 2003, 1st
The Effect of Size on the Deformation Twinning Behavior in Hexagonal Close-Packed Ti and Mg
 JOM, Vol. 64, No. 10, 2012 DOI: 10.1007/s11837-012-0437-7 Ó 2012 TMS (outside the U.S.) The Effect of Size on the Deformation Twinning Behavior in Hexagonal Close-Packed Ti and Mg QIAN YU, 1,2 RAJA K.
JOM, Vol. 64, No. 10, 2012 DOI: 10.1007/s11837-012-0437-7 Ó 2012 TMS (outside the U.S.) The Effect of Size on the Deformation Twinning Behavior in Hexagonal Close-Packed Ti and Mg QIAN YU, 1,2 RAJA K.
A Phase Field Model for Grain Growth and Thermal Grooving in Thin Films with Orientation Dependent Surface Energy
 Solid State Phenomena Vol. 129 (2007) pp. 89-94 online at http://www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A Phase Field Model for Grain Growth and Thermal Grooving in Thin Films with
Solid State Phenomena Vol. 129 (2007) pp. 89-94 online at http://www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A Phase Field Model for Grain Growth and Thermal Grooving in Thin Films with
Dislocation Dynamics in Metals at Atomic-scale: Interactions between Dislocations and Obstacles with Dislocation Character. David Bacon.
 Dislocation Dynamics in Metals at Atomic-scale: Interactions between Dislocations and Obstacles with Dislocation Character David Bacon The University of Liverpool, UK Yuri Osetsky Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Dislocation Dynamics in Metals at Atomic-scale: Interactions between Dislocations and Obstacles with Dislocation Character David Bacon The University of Liverpool, UK Yuri Osetsky Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Lecture # 11. Line defects (1D) / Dislocations
 Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC References: 1-
Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC References: 1-
Design of High Strength Wrought Magnesium Alloys!
 Design of High Strength Wrought Magnesium Alloys! Joseph Robson! School of Materials! University of Manchester UK! joseph.robson@manchester.ac.uk! ! Strengthening of Mg! Mg has low density (2/3 Al, 1/4
Design of High Strength Wrought Magnesium Alloys! Joseph Robson! School of Materials! University of Manchester UK! joseph.robson@manchester.ac.uk! ! Strengthening of Mg! Mg has low density (2/3 Al, 1/4
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT. Sub-topics. Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface
 IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
Stress and strain gradient in the deformed metallic surface
 Stress and strain gradient in the deformed metallic surface Xiaodan Zhang Section for Materials Science and Advanced Characterization, Department of Wind Energy, DTU Risø Campus, Roskilde, Denmark Vintermødet
Stress and strain gradient in the deformed metallic surface Xiaodan Zhang Section for Materials Science and Advanced Characterization, Department of Wind Energy, DTU Risø Campus, Roskilde, Denmark Vintermødet
A Comparison of Strain Deformation Mechanism of Al, Mo, MgO & CaO in Harper-Dorn Creep
 Pak. j. eng. technol. sci. Volume 2, No 1, 2012, 27-38 ISSN: 2222-9930 print ISSN: 2224-2333 online A Comparison of Strain Deformation Mechanism of Al, Mo, MgO & CaO in Harper-Dorn Creep Mukhtar Ahmed
Pak. j. eng. technol. sci. Volume 2, No 1, 2012, 27-38 ISSN: 2222-9930 print ISSN: 2224-2333 online A Comparison of Strain Deformation Mechanism of Al, Mo, MgO & CaO in Harper-Dorn Creep Mukhtar Ahmed
Point coordinates. Point coordinates for unit cell center are. Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111
 Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Size dependence of rate-controlling deformation mechanisms in nanotwinned copper
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Scripta Materialia 60 (2009) 1062 1066 www.elsevier.com/locate/scriptamat Viewpoint Paper Size dependence of rate-controlling deformation mechanisms in nanotwinned
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Scripta Materialia 60 (2009) 1062 1066 www.elsevier.com/locate/scriptamat Viewpoint Paper Size dependence of rate-controlling deformation mechanisms in nanotwinned
Hexagonal close-packed magnesium alloys are only 30% The Nanostructured Origin of Deformation Twinning
 pubs.acs.org/nanolett The Nanostructured Origin of Deformation Twinning Qian Yu,,, Liang Qi,,, Kai Chen, Raja K. Mishra, Ju Li,,, and Andrew M. Minor*,, Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
pubs.acs.org/nanolett The Nanostructured Origin of Deformation Twinning Qian Yu,,, Liang Qi,,, Kai Chen, Raja K. Mishra, Ju Li,,, and Andrew M. Minor*,, Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
LASER SHOCK COMPRESSION OF COPPER MONOCRYSTALS: MECHANISMS FOR DISLOCATION AND VOID GENERATION
 LASER SHOCK COMPRESSION OF COPPER MONOCRYSTALS: MECHANISMS FOR DISLOCATION AND VOID GENERATION M. A. MEYERS, M. S. SCHNEIDER, B. K KAD, V. A. LUBARDA, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, California
LASER SHOCK COMPRESSION OF COPPER MONOCRYSTALS: MECHANISMS FOR DISLOCATION AND VOID GENERATION M. A. MEYERS, M. S. SCHNEIDER, B. K KAD, V. A. LUBARDA, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, California
Experiments and Simulations in Plasticity- From Atoms to Continuum
 Experiments and Simulations in Plasticity- From toms to ontinuum Huseyin Sehitoglu Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-hampaign Symposium in Honor of David
Experiments and Simulations in Plasticity- From toms to ontinuum Huseyin Sehitoglu Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-hampaign Symposium in Honor of David
A COMPUTATIONAL APPROACH FOR DESIGNING TRIP STEELs STUDYING
 A COMPUTATIONAL APPROACH FOR DESIGNING TRIP STEELs STUDYING Shengyen Li Shengyen.li@nist.gov June 2, 2014 1 Alloy Design 2 True stress, MPa Eperimental Results - Fe-0.32C-1.42Mn-1.56Si 1200 800 400 0 0.00
A COMPUTATIONAL APPROACH FOR DESIGNING TRIP STEELs STUDYING Shengyen Li Shengyen.li@nist.gov June 2, 2014 1 Alloy Design 2 True stress, MPa Eperimental Results - Fe-0.32C-1.42Mn-1.56Si 1200 800 400 0 0.00
The effects of annealing treatment on mechanical properties of nanocrystalline α-iron: an atomistic study. Xuhang Tong
 The effects of annealing treatment on mechanical properties of nanocrystalline α-iron: an atomistic study by Xuhang Tong A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
The effects of annealing treatment on mechanical properties of nanocrystalline α-iron: an atomistic study by Xuhang Tong A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
ATOMISTIC STUDIES OF DISLOCATION GLIDE IN γγγ-tial
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 753 2003 Materials Research Society BB4.3. ATOMISTIC STUDIES OF DISLOCATION GLIDE IN γγγ-tial R. Porizek*, S. Znam*, D. Nguyen-Manh**, V. Vitek* and D. G. Pettifor** *Department
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 753 2003 Materials Research Society BB4.3. ATOMISTIC STUDIES OF DISLOCATION GLIDE IN γγγ-tial R. Porizek*, S. Znam*, D. Nguyen-Manh**, V. Vitek* and D. G. Pettifor** *Department
DISLOCATION DENSITIES AND CHARACTER EVOLUTION IN COPPER DEFORMED BY ROLLING UNDER LIQUID NITROGEN FROM X-RAY PEAK PROFILE ANALYSIS
 Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 2005, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 48. 67 DISLOCATION DENSITIES AND CHARACTER EVOLUTION IN COPPER DEFORMED BY ROLLING UNDER LIQUID NITROGEN
Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 2005, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 48. 67 DISLOCATION DENSITIES AND CHARACTER EVOLUTION IN COPPER DEFORMED BY ROLLING UNDER LIQUID NITROGEN
3D EBSD analysis of mechanical size effects during indentation: EBSD tomography and crystal plasticity FEM
 3D EBSD analysis of mechanical size effects during indentation: EBSD tomography and crystal plasticity FEM E. Demir, N. Zaafarani, F. Weber, D. Ma, S. Zaefferer, F. Roters, D. Raabe Department of Microstructure
3D EBSD analysis of mechanical size effects during indentation: EBSD tomography and crystal plasticity FEM E. Demir, N. Zaafarani, F. Weber, D. Ma, S. Zaefferer, F. Roters, D. Raabe Department of Microstructure
ME254: Materials Engineering Second Midterm Exam 1 st semester December 10, 2015 Time: 2 hrs
 ME254: Materials Engineering Second Midterm Exam 1 st semester 1436-1437 December 10, 2015 Time: 2 hrs Problem 1: (24 points) A o = π/4*d o 2 = π/4*17 2 = 227 mm 2 L o = 32 mm a) Determine the following
ME254: Materials Engineering Second Midterm Exam 1 st semester 1436-1437 December 10, 2015 Time: 2 hrs Problem 1: (24 points) A o = π/4*d o 2 = π/4*17 2 = 227 mm 2 L o = 32 mm a) Determine the following
Nano-indentation of Nanocrystalline Tungsten A Molecular Dynamic Simulation
 Nano-indentation of Nanocrystalline Tungsten A Molecular Dynamic Simulation A.Tahiri*, M. Idiri, S. El joumani, B.Boubeker Laboratoire d'ingénierie et Matériaux (LIMAT), Faculté des Sciences Ben M Sik
Nano-indentation of Nanocrystalline Tungsten A Molecular Dynamic Simulation A.Tahiri*, M. Idiri, S. El joumani, B.Boubeker Laboratoire d'ingénierie et Matériaux (LIMAT), Faculté des Sciences Ben M Sik
I t has long been recognized that grain boundaries (GBs) are important microstructure features and can
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES Received 19 March 2014 Accepted 14 July 2014 Published 1 August 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES Received 19 March 2014 Accepted 14 July 2014 Published 1 August 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms
 Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Introduction Basic concepts Characteristics of dislocations Slip systems Slip in single crystals Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials Plastically
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Introduction Basic concepts Characteristics of dislocations Slip systems Slip in single crystals Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials Plastically
Mechanical Properties
 Mechanical Properties Elastic deformation Plastic deformation Fracture II. Stable Plastic Deformation S s y For a typical ductile metal: I. Elastic deformation II. Stable plastic deformation III. Unstable
Mechanical Properties Elastic deformation Plastic deformation Fracture II. Stable Plastic Deformation S s y For a typical ductile metal: I. Elastic deformation II. Stable plastic deformation III. Unstable
Analytical and numerical determination of the elastic interaction energy between glissile dislocations and stacking fault tetrahedra in FCC metals
 Materials Science and Engineering A09 0 200 78 8 Analytical and numerical determination of the elastic interaction energy between glissile dislocations and stacking fault tetrahedra in FCC metals L.Z.
Materials Science and Engineering A09 0 200 78 8 Analytical and numerical determination of the elastic interaction energy between glissile dislocations and stacking fault tetrahedra in FCC metals L.Z.
Lectures on: Introduction to and fundamentals of discrete dislocations and dislocation dynamics. Theoretical concepts and computational methods
 Lectures on: Introduction to and fundamentals of discrete dislocations and dislocation dynamics. Theoretical concepts and computational methods Hussein M. Zbib School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering
Lectures on: Introduction to and fundamentals of discrete dislocations and dislocation dynamics. Theoretical concepts and computational methods Hussein M. Zbib School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering
Creep Characteristics of Ag-4 wt% Cu Alloy at High Stresses
 Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 79 Creep Characteristics of Ag-4 wt% Cu Alloy at High Stresses A. Fawzy, M.T. Mostafa and F. Abd El-Salam Department of Physics, Faculty of Education, Ain Shams
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 79 Creep Characteristics of Ag-4 wt% Cu Alloy at High Stresses A. Fawzy, M.T. Mostafa and F. Abd El-Salam Department of Physics, Faculty of Education, Ain Shams
factured pillars, even though the strength is significantly higher than in the bulk. These yield stress values, y
 Abstract The size effect in body-centered cubic (bcc) metals was comprehensively investigated through microcompression tests performed on focused ion beam machined tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo) and niobium
Abstract The size effect in body-centered cubic (bcc) metals was comprehensively investigated through microcompression tests performed on focused ion beam machined tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo) and niobium
In-situ nano-mechanical tests in the light of μlaue diffraction
 Engineering Conferences International ECI Digital Archives Nanomechanical Testing in Materials Research and Development V Proceedings Fall 10-8-2015 In-situ nano-mechanical tests in the light of μlaue
Engineering Conferences International ECI Digital Archives Nanomechanical Testing in Materials Research and Development V Proceedings Fall 10-8-2015 In-situ nano-mechanical tests in the light of μlaue
Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews. Cindy Smith
 Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews Cindy Smith Motivation Review: Outline Crystal lattices (fcc, bcc, hcp) Fcc vs. hcp stacking sequences Cubic {hkl} naming Hcp {hkil} naming Twinning
Twins & Dislocations in HCP Textbook & Paper Reviews Cindy Smith Motivation Review: Outline Crystal lattices (fcc, bcc, hcp) Fcc vs. hcp stacking sequences Cubic {hkl} naming Hcp {hkil} naming Twinning
Length scale and strain rate dependent shear banding deformation in nanoscale Cu/W multilayers
 Length scale and strain rate dependent shear banding deformation in nanoscale Cu/W multilayers Yuan Li 1), *Fei Wang 2), Ping Huang 3) and Ke-Wei Xu 4) 1), 3), 4) State-key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior
Length scale and strain rate dependent shear banding deformation in nanoscale Cu/W multilayers Yuan Li 1), *Fei Wang 2), Ping Huang 3) and Ke-Wei Xu 4) 1), 3), 4) State-key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior
