Sonosensitizer for ROS-Mediated Eradication
|
|
|
- Shanna Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (Supporting Information for Nano Letters) Long-Circulating Au-TiO 2 Nanocomposite as a Sonosensitizer for ROS-Mediated Eradication of Cancer V. G. Deepagan,,# Dong Gil You,,,# Wooram Um,, Hyewon Ko, Seunglee Kwon, Ki Young Choi, Gi-Ra Yi, Jun Young Lee, Doo Sung Lee, Kwangmeyung Kim, Ick Chan Kwon, and Jae Hyung Park,,* School of Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 16419, Republic of Korea. Center for Theragnosis, Biomedical Research Institute, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 02792, Republic of Korea. Department of Health Sciences and Technology, SAIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul 06351, Republic of Korea. # These authors contributed equally to this work. Corresponding Author * jhpark1@skku.edu 1
2 Materials and reagents. Anatase TiO 2 NPs (25 nm in diameter), chloroauric acid, carboxymethyl dextran (CMD) sodium salt (Mw=10,000 20,000 Da), 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)- carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC HCl), N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (NHS), dopamine HCl, 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF), and sodium citrate dihydrate were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Cy5.5 was purchased from Amersham Biosciences (NJ, USA). Singlet oxygen ( 1 O 2 ) sensor green reagent was purchased from Life Technologies Korea LLC (Seoul, Korea). All other reagents were analytical grade. The deionized water (DIW) was prepared using an Aqua Max-Ultra water purification system (Younglin Co., Anyang, Korea). The SCC7 cell line was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Rockville, MD, USA). For cell culture, RPMI-1640, trypsin-edta, and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were purchased from Welgene Inc. (Daegu, Korea). All experiments involving live animals were carried out in accordance with the relevant laws and institutional guidelines of Sungkyunkwan University. The Sungkyunkwan University institutional committees approved all experimental protocols. Methods Synthesis of Au-TiO 2 nanocomposites (NCs). NCs-1, NCs-2 and NCs-3 were produced by photoreduction of Au 3+ on the surface of the TiO 2 NPs. In a typical experiment 10 mg of TiO 2 NPs was suspended in 10 ml of DIW containing 3.5 mg (0.012 mmol) of sodium citrate. To this, 10 µl of 2 N NaOH solution was added and the mixture was sonicated for 5 min using a probe type sonicator. Next, chloroauric acid (10 mm, 100 µl) was added and stirred under UV irradiation (wavelength = 256 nm, power output = 4 Watts). The size and distribution of the NPs were controlled by adjusting the irradiation time with UV light. 2
3 When the reaction was carried out for 3 min small Au NPs formed on the surface of the TiO 2 NPs (NCs-1), whereas a 10 min irradiation time resulted in the formation of large Au NPs and disappearance of some of the smaller Au NPs (NCs-2). A further increase in reaction time (up to 12 h) resulted in the complete transformation of small Au NPs into larger Au NPs (NCs-3). The morphology of the NCs was observed using TEM (JEM-2100F, JEOL, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 200 kev. The NCs were characterized using XRD (D8 ADVANCE, Bruker Corporation, USA), ICP-MS (Agilent 7500, SpectraLab Scientific Inc, Canada), and UV vis spectrophotometer (Optizen 3220UV, Mecasys Inc., Korea). Synthesis of HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs. Chemical conjugation of CMD on the surface of the nanoparticles was performed by a similar procedure to that described earlier. 1 All reactions involving TiO 2 NPs and NCs were carried out in the dark to avoid any unwanted photoreaction. First, dopamine-decorated TiO 2 NPs and NCs-2 nanocomposites were prepared with a dopamine: TiO 2 NPs ratio of 25:1 for both TiO 2 NPs and NCs-2. For this, 2 nmol dopamine was added to 5 ml of formamide solution containing 10 mg of TiO 2 NPs (anatase) under vigorous stirring. The suspension was allowed to react for 6 h at room temperature and then purified by centrifugation at 13,000 rpm. The dopamine-decorated TiO 2 NPs and NCs-2 were purified by three rounds of centrifugation at 13,000 rpm and washing with formamide. Finally, the samples were suspended in 10 ml formamide. Second, the CMD coating was generated by chemically conjugating CMD to the dopamine via EDC and NHS chemistry. In brief, 200 mg of CMD was added to 20 ml of formamide with EDC (76.7 mg, 0.4 mmol) and NHS (57.5 mg, 0.49 mmol) and stirred overnight. To this activated CMD, 2 ml of dopamine-decorated TiO 2 NPs and Au-TiO 2 NCs was added and stirred overnight to yield HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs. Finally, 100 µl of 0.1 N NaOH was added and stirred for 1 h to complete the reaction. The byproducts and the 3
4 excess polymer were removed by dialysis against sodium borate buffer (ph 8.6) at 4 C using a 50-kDa cut-off membrane for 48 h with buffer changes every 6 h. The dialysate was sonicated briefly for 10 seconds (Sonic Vibracell VCX 750, CT, USA) and filtered to remove the large aggregates. Finally, the nanosuspension was filtered through a 0.8-µm filter and lyophilized for future use. For in vivo imaging, Cy5.5-conjugated NPs were prepared by reacting NHS-activated HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs with amine-functionalized Cy5.5. The Cy5.5-labeled NPs were purified by dialysis to remove the byproducts, followed by lyophilization. The chemical structure of NPs were then confirmed using FT-IR (IFS-66/S, Bruker Corporation, USA). The hydrodynamic size of NPs were measured by dynamic light scattering using a Zetasizer (Nano ZS90, Malvern Instruments, UK) with a He-Ne laser (633 nm) at 90 collecting optics. The stability of HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs was assessed by monitoring the sizes of NPs for 6 days using the Zetasizer (Nano ZS90, Malvern Instruments, UK), in physiological saline and in the presence of 10% FBS. In vitro ROS generation of NCs, HTiO 2 NPs, and HAu-TiO 2 NCs. The in vitro ROS generation potential of all NCs and NPs was determined using DPBF. In brief, 0.5 ml of the sample (Ti 1M) suspension was added to 0.5 ml of DPBF ( M) solution. The mixture was then placed in a 3% (W/V) agarose gel mold and exposed to a pre-clinical high intensity focused ultrasound system (VIFU 2000, Alpinion Medical Systems, Seoul, Korea) equipped with a single element spherical-focused transducer (1.5MHz, 2cm x 1.5cm in size) under 10% duty cycle (power: 30 W, pulse repetition frequency: 1 Hz, X,Y interval: 2 mm) for 330 seconds. The concentration of DPBF was determined by measuring the absorbance at 413 nm as a function of time using a UV-vis spectrometer (G1103A, Agilent, USA). The rate constant for 1 O 2 generation by HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs was calculated using the following equation [ln([dpbf] t /[DPBF] 0 )= -kt]. 4
5 Cell culture. SCC7 cells (mouse squamous carcinoma cell line) were cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin at 37 C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO 2 atmosphere. In vitro cytotoxicity assay. The biocompatibility of HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs was tested using SCC7 cells. In a typical experiment cells/well were seeded in 96-well flat-bottomed plates and incubated for 24 h. The cells were then washed twice with PBS and replenished with media containing various concentrations of the test samples. After treatment the cells were washed once with PBS and replenished with 100 µl of basal media containing 10% MTT solution (5 mg/ml). After incubation for 3 h the spent medium was removed and the MTT crystals were dissolved in DMSO. The absorbance of each well was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader (VERSA max, Molecular Devices Corp., USA). For the apoptosis assay, SCC7 cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of cells/well and incubated until they formed a monolayer. The cells were washed twice with PBS and replenished with media containing 100 µg/ml of the test sample. After incubation, the cells were harvested and incubated with FITC-labeled annexin V antibody and propidium iodide for 30 min. The level of apoptosis was measured using flow cytometry (Guava easycyte, Merck Millipore, USA). In vivo biodistribution. To observe the in vivo biodistribution of nanoparticles, a SCC7 flank tumor model was prepared by subcutaneous injection of 80 µl of cell suspension containing cells in PBS into athymic mice. After 10 days, Cy5.5-labeled NPs were injected into the tail vein of the mice at a dose of 3 mg/kg. To observe the biodistribution of the NPs at predetermined time points, the animals were imaged using the Explore Optix system (Optix MX3, Advanced Research Technologies Inc., Canada) with the 670 nm 5
6 excitation pulsed laser set to an output power of 10 µw for 0.3 seconds/point. The tumortargeting characteristics of NPs were evaluated by measuring the NIR fluorescence intensity at the tumor site (28 mm 2 ). All data were calculated using the region of interest function of Analysis Workstation software (Optix MX3, Advanced Research Technologies Inc., Canada). The distribution of nanoparticles in tumor tissue was analyzed using a small-animal imaging system (OV-100, Olympus, Center Valley, PA) with the green fluorescent protein (GFP) channel (λ ex = nm, λ em = nm) and Cy5.5 channel (λ ex = nm, λ em = nm). The skin over the tumor of the mice was scraped off 12 h after intravenous injection of Cy5.5-labeled NPs (3 mg/kg) and the NIR fluorescence images of the tumor were recorded. To visualize the tumor blood vessels, FITC-labeled dextran (10 mg/kg) was administered intravenously to the mice immediately before measurement. In vivo ROS imaging. To determine in vivo ROS generation SCC7 tumor-bearing mice were prepared as described earlier. The mice were divided into six groups: (a) saline, (b) saline + US, (c) HTiO 2 NPs (Ti 3 mg/kg), (d) HTiO 2 NPs (Ti 3 mg/kg) + US, (e) HAu- TiO 2 NCs (Ti 3 mg/kg), and (f) HAu-TiO 2 NCs (Ti 3 mg/kg) + US. Each sample was administered intravenously. At 12 h post injection, 100 µl of 1 O 2 sensor green reagent (50 µm) was injected directly into the tumor mass, which was immediately treated with US (power: 30 W, frequency: 1.5 MHz, duty cycle: 10%, pulse repetition frequency: 1 Hz, interval: 2 mm, time: 30 s). The same ultrasound system and transducer as we used for in vitro ROS generation were employed. After US exposure, a portion of tumor tissue was collected and cryosectioned at 10-µm thickness. Fluorescence images of tumor sections were obtained by fluorescence microscopy (IX81-ZDC, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) using a GFP filter. 6
7 Antitumor efficacy of SDT with HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs. The antitumor efficacy of nanoparticles was determined by measuring the tumor volume once every 2 days for 32 days. Tumor-bearing mice were prepared by subcutaneous injection of 80 µl of SCC7 cell suspension containing approximately cells into the flank region of C3H/HeN mice. When the tumors reached a volume of 250 mm 3, the mice were divided into six groups: (a) saline, (b) saline + US, (c) HTiO 2 NPs (Ti 3 mg/kg), (d) HTiO 2 NPs (Ti 3 mg/kg) + US, (e) HAu-TiO 2 NCs (Ti 3 mg/kg), and (f) HAu-TiO 2 NCs (Ti 3 mg/kg) + US. Each sample was injected intravenously into mice. US (power: 30 W, frequency: 1.5 MHz, duty cycle: 10%, pulse repetition frequency: 1 Hz, interval: 2 mm, time: 30 s) was administered 12 h post injection. For SDT, the experimental set-up for ultrasound exposure was exactly same as the one we used for in vivo ROS imaging. This treatment was given once every 4 days with the pre-set conditions. The mice were ethically sacrificed when the tumor volume exceeded 5000 mm 3. Tumor volumes were calculated as a b , where a represents the largest and b the smallest diameter. Histology. For the histopathologic study the major organs including liver, heart, kidneys, and spleen were excised from mice 24 h post injection. Organs were fixed in 3.7% neutral buffered formalin, processed into paraffin, sectioned into approximately 4-µm slices, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Samples were chosen at random and examined by bright-field microscopy (BX51, Olympus, Japan). 7
8 Figure S1. Physicochemical characterization. (a) XRD patterns of bare TiO 2 NPs and NCs, (b) Representative EDS spectrum of NCs, (c) XRD spectra and (d) UV-vis spectra of bare TiO 2 NPs and NCs. 8
9 500 Size (nm) HTiO 2 NPs HAu-TiO 2 NCs Time (days) Figure S2. Stability of HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs in the presence of serum. The error bar represents standard deviation (n=3). 9
10 Figure S3. UV-vis spectra of DPBF with increasing exposure time (a) HTiO 2 NPs and (b) HAu-TiO 2 NCs. 10
11 Figure S4. Toxicity of HTiO 2 NPs. (a) In vitro cytotoxicity of HTiO 2 NPs and HAu-TiO 2 NCs, measured by the MTT assay. Apoptosis assay for (b) HTiO 2 NPs and (c) HAu-TiO 2 NCs by flow cytometry. 11
12 Figure S5. H&E staining of major organs after SDT (Scale bar, 250 µm). 12
13 REFERENCES 1. You, D. G.; Deepagan, V. G.; Um, W.; Jeon, S.; Son, S.; Chang, H.; Yoon, H. I.; Cho, Y. W.; Swierczewska, M.; Lee, S.; Pomper, M. G.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, K.; Park, J. H. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6,
Electronic Supplementary Information. MMP2-targeting and redox-responsive PEGylated chlorin e6
 Electronic Supplementary Information MMP2-targeting and redox-responsive PEGylated chlorin e6 nanoparticles for cancer near-infrared imaging and photodynamic therapy Wenxiu Hou 1,2, Fangfang Xia 1, Carla
Electronic Supplementary Information MMP2-targeting and redox-responsive PEGylated chlorin e6 nanoparticles for cancer near-infrared imaging and photodynamic therapy Wenxiu Hou 1,2, Fangfang Xia 1, Carla
Smart Nanocarrier Based on PEGylated Hyaluronic Acid for Cancer Therapy
 (Supporting information for ACS Nano) Smart Nanocarrier Based on PEGylated Hyaluronic Acid for Cancer Therapy Ki Young Choi,, Hong Yeol Yoon,, Jong-Ho Kim, Sang Mun Bae, Rang-Woon Park, Young Mo Kang,
(Supporting information for ACS Nano) Smart Nanocarrier Based on PEGylated Hyaluronic Acid for Cancer Therapy Ki Young Choi,, Hong Yeol Yoon,, Jong-Ho Kim, Sang Mun Bae, Rang-Woon Park, Young Mo Kang,
Supplementary Information Temperature-responsive Gene Silencing by a Smart Polymer
 Supplementary Information Temperature-responsive Gene Silencing by a Smart Polymer Mingming Wang, Yiyun Cheng * Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal
Supplementary Information Temperature-responsive Gene Silencing by a Smart Polymer Mingming Wang, Yiyun Cheng * Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Photosensitizer-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles for redox-responsive fluorescence imaging and photodynamic therapy Hyunjin Kim, a Saehun Mun b and Yongdoo Choi* a a Molecular
Supporting Information Photosensitizer-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles for redox-responsive fluorescence imaging and photodynamic therapy Hyunjin Kim, a Saehun Mun b and Yongdoo Choi* a a Molecular
A histone H1-binding-aptide based apoptosis-imaging probe for monitoring
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information A histone H1-binding-aptide based apoptosis-imaging probe for monitoring
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information A histone H1-binding-aptide based apoptosis-imaging probe for monitoring
<Supplementary Information> Gold-Installed Biostable Nanocomplexes for Tumor-Targeted. sirna Delivery In Vivo
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Gold-Installed Biostable Nanocomplexes for Tumor-Targeted sirna Delivery
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Gold-Installed Biostable Nanocomplexes for Tumor-Targeted sirna Delivery
Reverse Microemulsion-Mediated Synthesis of Bi 2 S 3 2 -PEG for Dual Modal CT/ Fluorescence Imaging in vitro and in vivo
 Supporting Information Reverse Microemulsion-Mediated Synthesis of Bi 2 S 3 -QD@SiO 2 -PEG for Dual Modal CT/ Fluorescence Imaging in vitro and in vivo Jun Chen +, Xiao-Quan Yang +, Yuan-Zheng Meng, Meng-Yao
Supporting Information Reverse Microemulsion-Mediated Synthesis of Bi 2 S 3 -QD@SiO 2 -PEG for Dual Modal CT/ Fluorescence Imaging in vitro and in vivo Jun Chen +, Xiao-Quan Yang +, Yuan-Zheng Meng, Meng-Yao
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Near Infrared Light-responsive and Injectable Supramolecular Hydrogels for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Near Infrared Light-responsive and Injectable Supramolecular Hydrogels for
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nuclear-Targeted Photothermal Therapy Prevents Cancer Recurrence with Near-Infrared Triggered Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles Na Li, Qiaoqiao Sun, Zhengze Yu, Xiaonan Gao, Wei Pan,
Supporting Information Nuclear-Targeted Photothermal Therapy Prevents Cancer Recurrence with Near-Infrared Triggered Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles Na Li, Qiaoqiao Sun, Zhengze Yu, Xiaonan Gao, Wei Pan,
1 Electronic Supplementary information. 2 Co-assembling FRET nanomedicine with self-indicating drug
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 1 Electronic Supplementary information 2 Co-assembling FRET nanomedicine with self-indicating drug
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 1 Electronic Supplementary information 2 Co-assembling FRET nanomedicine with self-indicating drug
Supporting information. Magnetic nanoscale metal organic frameworks for potential targeted anticancer drug delivery, imaging and MRI contrast agent
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Magnetic nanoscale metal organic frameworks for potential targeted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Magnetic nanoscale metal organic frameworks for potential targeted
Nuclear-Targeting Gold Nanorods for Extremely Low NIR Activated Photothermal Therapy
 Supporting Information Nuclear-Targeting Gold Nanorods for Extremely Low NIR Activated Photothermal Therapy Limin Pan, Jianan Liu, and Jianlin Shi* State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and
Supporting Information Nuclear-Targeting Gold Nanorods for Extremely Low NIR Activated Photothermal Therapy Limin Pan, Jianan Liu, and Jianlin Shi* State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots coupled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots coupled
Supplementary Information. Trojan Horse Nanotheranostics with Dual Transformability and Multifunctionality. for Highly Effective Cancer Treatment
 Supplementary Information Trojan Horse Nanotheranostics with Dual Transformability and Multifunctionality for Highly Effective Cancer Treatment Xue et. al. Supplementary Figure 1. Synthetic route of PhD
Supplementary Information Trojan Horse Nanotheranostics with Dual Transformability and Multifunctionality for Highly Effective Cancer Treatment Xue et. al. Supplementary Figure 1. Synthetic route of PhD
Silica/Porphyrin Hybrid Nanotubes for In Vivo Cell Tracking
 Electronic Supplementary Information Silica/Porphyrin Hybrid Nanotubes for In Vivo Cell Tracking by Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Koichiro Hayashi,* Michihiro Nakamura and Kazunori Ishimura Department
Electronic Supplementary Information Silica/Porphyrin Hybrid Nanotubes for In Vivo Cell Tracking by Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Koichiro Hayashi,* Michihiro Nakamura and Kazunori Ishimura Department
Low Background D-A-D Type Fluorescent Probe for Imaging of Biothiols
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Low Background D-A-D Type Fluorescent
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Low Background D-A-D Type Fluorescent
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Carrier-Free Nano-Integrated Strategy for Synergetic Cancer Anti-angiogenic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Carrier-Free Nano-Integrated Strategy for Synergetic Cancer Anti-angiogenic
Aryl-thioether substituted nitrobenzothiadiazole probe for selective detection of cysteine and homocysteine
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal
Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Robust and Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Robust and Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles Hongje Jang, Young-Kwan Kim, Soo-Ryoon Ryoo, Mi-Hee Kim, Dal-Hee Min* Department of Chemistry, Institute for the BioCentury,
Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Robust and Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles Hongje Jang, Young-Kwan Kim, Soo-Ryoon Ryoo, Mi-Hee Kim, Dal-Hee Min* Department of Chemistry, Institute for the BioCentury,
Self-assembled, Redox-sensitive, H-shaped Pegylated Methotrexate Conjugates with. High Drug-carrying Capability for Intracellular Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Self-assembled, Redox-sensitive, H-shaped Pegylated Methotrexate Conjugates with High Drug-carrying Capability for Intracellular Drug Delivery Haiqing Dong, Chunyan Dong, Wenjuan
Supporting Information Self-assembled, Redox-sensitive, H-shaped Pegylated Methotrexate Conjugates with High Drug-carrying Capability for Intracellular Drug Delivery Haiqing Dong, Chunyan Dong, Wenjuan
Enzyme-mediated preparation of hydrogels composed of poly(ethylene glycol) and gelatin as cell culture platforms
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Enzyme-mediated preparation of hydrogels composed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Enzyme-mediated preparation of hydrogels composed
A Supramolecular Approach to Improve the Gene Transfection Efficacy of Dendrimers
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Supramolecular Approach to Improve the Gene Transfection Efficacy of Dendrimers Naimin Shao,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Supramolecular Approach to Improve the Gene Transfection Efficacy of Dendrimers Naimin Shao,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Cascade Promoted Photo-Chemotherapy against Resistant Cancers by Enzyme-Responsive Polyprodrug Nanoplatforms Wenhui Wang,, Guohai Liang,, Wenjia Zhang,, Da Xing,*,, and Xianglong
Supplementary Information Cascade Promoted Photo-Chemotherapy against Resistant Cancers by Enzyme-Responsive Polyprodrug Nanoplatforms Wenhui Wang,, Guohai Liang,, Wenjia Zhang,, Da Xing,*,, and Xianglong
Qi Peng, Fujie Chen, Zhenlin Zhong,* Renxi Zhuo
 Electronic Supplementary Information Enhanced Gene Transfection Capability of Polyethylenimine by Incorporating Boronic Acid Groups Qi Peng, Fujie Chen, Zhenlin Zhong,* Renxi Zhuo Key Laboratory of Biomedical
Electronic Supplementary Information Enhanced Gene Transfection Capability of Polyethylenimine by Incorporating Boronic Acid Groups Qi Peng, Fujie Chen, Zhenlin Zhong,* Renxi Zhuo Key Laboratory of Biomedical
Real-Time Monitoring of Arsenic Trioxide Release and Delivery
 Real-Time Monitoring of Arsenic Trioxide Release and Delivery by Activatable T 1 Imaging Zhenghuan Zhao, Xiaomin Wang, Zongjun Zhang, Hui Zhang, Hanyu Liu, Xianglong Zhu, Hui Li, Xiaoqin Chi, Zhenyu Yin,
Real-Time Monitoring of Arsenic Trioxide Release and Delivery by Activatable T 1 Imaging Zhenghuan Zhao, Xiaomin Wang, Zongjun Zhang, Hui Zhang, Hanyu Liu, Xianglong Zhu, Hui Li, Xiaoqin Chi, Zhenyu Yin,
Relaxivity Control of Magnetic Nanoclusters for Efficient Magnetic. Relaxation Switching Assay
 Supplementary Information Relaxivity Control of Magnetic Nanoclusters for Efficient Magnetic Relaxation Switching Assay Jinmyung Cha, a Yong-Su Kwon, b Tae-Jong Yoon *b and Jin-Kyu Lee *a a Department
Supplementary Information Relaxivity Control of Magnetic Nanoclusters for Efficient Magnetic Relaxation Switching Assay Jinmyung Cha, a Yong-Su Kwon, b Tae-Jong Yoon *b and Jin-Kyu Lee *a a Department
Transcutaneous Patches for Glucose-Mediated
 Supporting Information H 2 2 -Responsive Vesicles Integrated with Transcutaneous Patches for Glucose-Mediated Insulin Delivery Xiuli Hu,, Jicheng Yu, Chenggen Qian, Yue Lu, Anna R. Kahkoska, Zhigang Xie,
Supporting Information H 2 2 -Responsive Vesicles Integrated with Transcutaneous Patches for Glucose-Mediated Insulin Delivery Xiuli Hu,, Jicheng Yu, Chenggen Qian, Yue Lu, Anna R. Kahkoska, Zhigang Xie,
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells
 Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Graphene Oxide/Photosensitizer Complex as an Enzyme-Activatable Theranostic Youngnam Cho, Hyunjin Kim, and Yongdoo Choi* Molecular Imaging & Therapy Branch, National Cancer Center,
Supporting Information A Graphene Oxide/Photosensitizer Complex as an Enzyme-Activatable Theranostic Youngnam Cho, Hyunjin Kim, and Yongdoo Choi* Molecular Imaging & Therapy Branch, National Cancer Center,
Supporting Information. A Real-Time Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Study of Plasmonic Photothermal Cell Death Using Targeted Gold Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information A Real-Time Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Study of Plasmonic Photothermal Cell Death Using Targeted Gold Nanoparticles Mena Aioub and Mostafa A. El-Sayed* Laser Dynamics Laboratory,
Supporting Information A Real-Time Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Study of Plasmonic Photothermal Cell Death Using Targeted Gold Nanoparticles Mena Aioub and Mostafa A. El-Sayed* Laser Dynamics Laboratory,
Supporting info. Size Effect of Gold on Ag-coated Au nanoparticlesembedded
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. Supporting info Size Effect of Gold on Ag-coated Au nanoparticlesembedded silica nanospheres Seongbo Shim, a+ Xuan-Hung Pham, a+ Myeong Geun Cha,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. Supporting info Size Effect of Gold on Ag-coated Au nanoparticlesembedded silica nanospheres Seongbo Shim, a+ Xuan-Hung Pham, a+ Myeong Geun Cha,
Supporting Information. Quantum Dot NanoLuc Bioluminescence. Resonance Energy Transfer Enables Tumor Imaging
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Quantum Dot NanoLuc Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer Enables Tumor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Quantum Dot NanoLuc Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer Enables Tumor
PRODUCT DATA SHEET. Carboxylated Fluorescent Gold Nanoparticles. Description. Characteristics
 PRODUCT DATA SHEET Carboxylated Fluorescent Gold Nanoparticles Description Cytodiagnostics carboxylated fluorescent gold nanoparticles is a unique product that combines our Cyto fluorescent dyes and gold
PRODUCT DATA SHEET Carboxylated Fluorescent Gold Nanoparticles Description Cytodiagnostics carboxylated fluorescent gold nanoparticles is a unique product that combines our Cyto fluorescent dyes and gold
Dual Responsive Supramolecular Nanogels for Intracellular Drug
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Dual Responsive Supramolecular Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Dual Responsive Supramolecular Nanogels for Intracellular Drug Delivery
Supporting Information. Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
 Supporting Information Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide and Graphene in Human Erythrocytes and Skin Fibroblasts Ken-Hsuan Liao,, Yu-Shen Lin,, Christopher W. Macosko,, * and Christy L. Haynes,, * Department
Supporting Information Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide and Graphene in Human Erythrocytes and Skin Fibroblasts Ken-Hsuan Liao,, Yu-Shen Lin,, Christopher W. Macosko,, * and Christy L. Haynes,, * Department
Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine, Shanghai , People s Republic of China.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Phase and Morphological Control of MoO 3-x Nanostructures for Efficient Cancer Theragnosis Therapy
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Phase and Morphological Control of MoO 3-x Nanostructures for Efficient Cancer Theragnosis Therapy
A comparative study of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon
 A comparative study of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotube, graphene oxide, and nanodiamond Xiaoyong Zhang,* a,b Wenbing Hu, a Jing Li, a Lei tao, b and Yen wei b Preparation
A comparative study of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotube, graphene oxide, and nanodiamond Xiaoyong Zhang,* a,b Wenbing Hu, a Jing Li, a Lei tao, b and Yen wei b Preparation
Supplementary Information. A narrow-bandgap benzobisthiadiazole derivative with high nearinfrared. photothermal conversion efficiency and robust
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information A narrow-bandgap benzobisthiadiazole derivative with high nearinfrared
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information A narrow-bandgap benzobisthiadiazole derivative with high nearinfrared
Cathepsin B-sensitive nanoprobe for in vivo tumor diagnosis
 Supplementary Information Cathepsin B-sensitive nanoprobe for in vivo tumor diagnosis Ju Hee Ryu, Sun Ah Kim, Heebeom Koo, Ji Young Yhee, Aeju Lee, Jin Hee Na,, Kuiwon Choi, Ick Chan Kwon, Byung-Soo Kim
Supplementary Information Cathepsin B-sensitive nanoprobe for in vivo tumor diagnosis Ju Hee Ryu, Sun Ah Kim, Heebeom Koo, Ji Young Yhee, Aeju Lee, Jin Hee Na,, Kuiwon Choi, Ick Chan Kwon, Byung-Soo Kim
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Biomimetic nanoflowers by self-assembly of nanozymes to induce intracellular oxidative damage against hypoxic tumors Wang et al. Supplementary Figure 1. The effect of Pt/Co ratio
Supplementary Information Biomimetic nanoflowers by self-assembly of nanozymes to induce intracellular oxidative damage against hypoxic tumors Wang et al. Supplementary Figure 1. The effect of Pt/Co ratio
Hyaluronic acid-polypyrrole nanoparticles as ph-responsive theranostics
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Hyaluronic acid-polypyrrole nanoparticles as ph-responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Hyaluronic acid-polypyrrole nanoparticles as ph-responsive
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ultra-robust Biochips with Metal-Organic Framework Coating for Point-of-Care Diagnosis Congzhou Wang, Lu Wang, Sirimuvva Tadepalli, Jeremiah J. Morrissey, Evan D. Kharasch, Rajesh
Supporting Information Ultra-robust Biochips with Metal-Organic Framework Coating for Point-of-Care Diagnosis Congzhou Wang, Lu Wang, Sirimuvva Tadepalli, Jeremiah J. Morrissey, Evan D. Kharasch, Rajesh
PRODUCT DATA SHEET. Carboxylated Gold Nanoparticles. Description. Features. Storage. Applications. Handling. Characteristics
 PRODUCT DATA SHEET Carboxylated Gold Nanoparticles Description Cytodiagnostics carboxylated gold nanoparticles are available with two different lengths of PEG surface spacers, i.e. 3000Da and 5000Da offering
PRODUCT DATA SHEET Carboxylated Gold Nanoparticles Description Cytodiagnostics carboxylated gold nanoparticles are available with two different lengths of PEG surface spacers, i.e. 3000Da and 5000Da offering
Oligonucleotide Loading Determines Cellular Uptake of DNA- Modified Gold Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information for: Oligonucleotide Loading Determines Cellular Uptake of DNA- Modified Gold Nanoparticles David A. Giljohann, Dwight S. Seferos, Pinal C. Patel, Jill E. Millstone, Nathaniel L.
Supporting Information for: Oligonucleotide Loading Determines Cellular Uptake of DNA- Modified Gold Nanoparticles David A. Giljohann, Dwight S. Seferos, Pinal C. Patel, Jill E. Millstone, Nathaniel L.
Dynamic light scattering (DLS)-based immunoassay for. ultrasensitive detection of tumor marker protein
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Dynamic light scattering (DLS)-based immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Dynamic light scattering (DLS)-based immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011.
 Experimental: MTT assay: To determine cell viability the colorimetric MTT metabolic activity assay was used. Hela cells (1 10 4 cells/well) were cultured in a 96-well plate at 37 C, and exposed to varying
Experimental: MTT assay: To determine cell viability the colorimetric MTT metabolic activity assay was used. Hela cells (1 10 4 cells/well) were cultured in a 96-well plate at 37 C, and exposed to varying
Exploration of Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Effect of. Quantitative Photothermal Immunoassay
 Analytical Chemistry Supporting Information Exploration of Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Effect of TMB-H 2 O 2 Colorimetric System and Its Application in a Visual Quantitative Photothermal Immunoassay
Analytical Chemistry Supporting Information Exploration of Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Effect of TMB-H 2 O 2 Colorimetric System and Its Application in a Visual Quantitative Photothermal Immunoassay
Indocyanine Green Encapsulated Nanogels for Hyaluronidase Activatable and Selective Near Infrared Imaging of Tumors and Lymph Nodes
 Supporting Information Indocyanine Green Encapsulated Nanogels for Hyaluronidase Activatable and Selective Near Infrared Imaging of Tumors and Lymph Nodes Hyejung Mok a,b, Hyunkyung Jeong a, Sun-Jung Kim
Supporting Information Indocyanine Green Encapsulated Nanogels for Hyaluronidase Activatable and Selective Near Infrared Imaging of Tumors and Lymph Nodes Hyejung Mok a,b, Hyunkyung Jeong a, Sun-Jung Kim
Experimental supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental supporting information Preparation of peptide derivatives: The peptide derivative
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental supporting information Preparation of peptide derivatives: The peptide derivative
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Multifunctional PEI-entrapped gold nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Multifunctional PEI-entrapped gold nanoparticles
ph-responsive gold nanoparticles-in-liposome hybrid nanostructures for
 Electronic Supplementary Information ph-responsive gold nanoparticles-in-liposome hybrid nanostructures for enhanced systemic tumor delivery Jutaek Nam, a Yeong Su Ha, b Sekyu Hwang, a Woonghee Lee, b
Electronic Supplementary Information ph-responsive gold nanoparticles-in-liposome hybrid nanostructures for enhanced systemic tumor delivery Jutaek Nam, a Yeong Su Ha, b Sekyu Hwang, a Woonghee Lee, b
Obtaining More Accurate Signals: Spatiotemporal Imaging of Cancer Sites Enabled by a Photoactivatable Aptamer-Based Strategy
 Supporting Information Obtaining More Accurate Signals: Spatiotemporal Imaging of Cancer Sites Enabled by a Photoactivatable Aptamer-Based Strategy Heng Xiao,,, Yuqi Chen,, Erfeng Yuan,, Wei Li, Zhuoran
Supporting Information Obtaining More Accurate Signals: Spatiotemporal Imaging of Cancer Sites Enabled by a Photoactivatable Aptamer-Based Strategy Heng Xiao,,, Yuqi Chen,, Erfeng Yuan,, Wei Li, Zhuoran
Supporting Information. A Fluorogenic Resveratrol-Confined Graphene Oxide For Economic and Rapid. Detection Of Alzheimer's Disease
 Supporting Information A Fluorogenic Resveratrol-Confined Graphene Oxide For Economic and Rapid Detection Of Alzheimer's Disease Xiao-Peng He, 1 Qiong Deng, 1 Liang Cai, 1 Chang-Zheng Wang, 1,2 Yi Zang,*,2
Supporting Information A Fluorogenic Resveratrol-Confined Graphene Oxide For Economic and Rapid Detection Of Alzheimer's Disease Xiao-Peng He, 1 Qiong Deng, 1 Liang Cai, 1 Chang-Zheng Wang, 1,2 Yi Zang,*,2
Compact Plasmonic Blackbody for Cancer Theranosis in Near-Infrared II Window
 Supporting Information for Compact Plasmonic Blackbody for Cancer Theranosis in Near-Infrared II Window Jiajing Zhou,, Yuyan Jiang,, Shuai Hou, Paul Kumar Upputuri, Di Wu,, Jingchao Li, Peng Wang, Xu Zhen,
Supporting Information for Compact Plasmonic Blackbody for Cancer Theranosis in Near-Infrared II Window Jiajing Zhou,, Yuyan Jiang,, Shuai Hou, Paul Kumar Upputuri, Di Wu,, Jingchao Li, Peng Wang, Xu Zhen,
<Supplementary Information> Self-assembled dextran sulphate nanoparticles for targeting rheumatoid arthritis
 Self-assembled dextran sulphate nanoparticles for targeting rheumatoid arthritis Seol-Hee Kim, a Jong-Ho Kim, b Dong Gil You, c Gurusamy Saravanakumar, a Hong Yeol Yoon, c Ki
Self-assembled dextran sulphate nanoparticles for targeting rheumatoid arthritis Seol-Hee Kim, a Jong-Ho Kim, b Dong Gil You, c Gurusamy Saravanakumar, a Hong Yeol Yoon, c Ki
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Redox-Hypersensitive Organic Nanoparticles for Selective Treatment of Cancer Cells Wei Zhang,, Wenhai Lin,, Qing Pei,, Xiuli Hu, Zhigang Xie, *, and Xiabin Jing State Key Laboratory
Supplementary Information Redox-Hypersensitive Organic Nanoparticles for Selective Treatment of Cancer Cells Wei Zhang,, Wenhai Lin,, Qing Pei,, Xiuli Hu, Zhigang Xie, *, and Xiabin Jing State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information. Controlled cutting and hydroxyl functionalization of carbon nanotubes. through autoclaving and sonication in hydrogen peroxide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Controlled cutting and hydroxyl functionalization of carbon nanotubes through
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Controlled cutting and hydroxyl functionalization of carbon nanotubes through
Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Western Blotting Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using T-PER tissue protein extraction buffer. Protein concentrations were determined
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Western Blotting Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using T-PER tissue protein extraction buffer. Protein concentrations were determined
Physicochemical Properties and Cellular Toxicity of Nanocrystal Quantum
 Physicochemical Properties and Cellular Toxicity of Nanocrystal Quantum Dots Depend on their Surface Modification. Akiyoshi Hoshino 1,2,3, Kouki Fujioka 1,3, Taisuke Oku 1, Masakazu Suga 1, Yu F. Sasaki
Physicochemical Properties and Cellular Toxicity of Nanocrystal Quantum Dots Depend on their Surface Modification. Akiyoshi Hoshino 1,2,3, Kouki Fujioka 1,3, Taisuke Oku 1, Masakazu Suga 1, Yu F. Sasaki
A protein-polymer hybrid gene carrier based on thermophilic histone. and polyethylenimine
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2015 A protein-polymer hybrid gene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2015 A protein-polymer hybrid gene
Colorimetric detection of influenza A (H1N1) virus based on peptide functionalized polydiacetylene (PEP-PDA) nanosensor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supporting Information Colorimetric detection of influenza A (H1N1) virus based
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supporting Information Colorimetric detection of influenza A (H1N1) virus based
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Enzyme-Responsive Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles for Combined Photoacoustic Imaging, Tumor-Selective Chemotherapy and Photothermal Therapy Zhengbao Zha, b Shuhai Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Enzyme-Responsive Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles for Combined Photoacoustic Imaging, Tumor-Selective Chemotherapy and Photothermal Therapy Zhengbao Zha, b Shuhai Zhang,
A TEMPO-Conjugated Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Mitochondrial
 Supporting Information for A TEMPO-Conjugated Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Mitochondrial Redox Reactions Shota Hirosawa, a Satoshi Arai b and Shinji Takeoka* a a Department of Life Science and Medical
Supporting Information for A TEMPO-Conjugated Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Mitochondrial Redox Reactions Shota Hirosawa, a Satoshi Arai b and Shinji Takeoka* a a Department of Life Science and Medical
Janus Iron Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticle Tracer for
 Supporting Information Janus Iron Oxides @ Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticle Tracer for Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging Guosheng Song, Min Chen, Yanrong Zhang, Liyang Cui, Haibo Qu, Xianchuang
Supporting Information Janus Iron Oxides @ Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticle Tracer for Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging Guosheng Song, Min Chen, Yanrong Zhang, Liyang Cui, Haibo Qu, Xianchuang
Star poly(β-amino esters) obtained from the combination of linear poly(β-amino esters) and polyethyleneimine
 Supporting information Star poly(β-amino esters) obtained from the combination of linear poly(β-amino esters) and polyethyleneimine Xiaobei Huang,, Dezhong Zhou,,* Ming Zeng, Fatma Alshehri, Xiaolin Li,
Supporting information Star poly(β-amino esters) obtained from the combination of linear poly(β-amino esters) and polyethyleneimine Xiaobei Huang,, Dezhong Zhou,,* Ming Zeng, Fatma Alshehri, Xiaolin Li,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information RGD-QD-MoS 2 nanosheets for targeted fluorescent imaging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information RGD-QD-MoS 2 nanosheets for targeted fluorescent imaging
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Biosynthesis of Luminescent Quantum Dots in an Earthworm S.R. Stürzenbaum, a# M. Hoeckner, a# A. Panneerselvam, b J. Levitt, b J.-S. Bouillard, b S. Taniguchi, b L.-A. Dailey, d R. Ahmad Khanbeigi, d E.
Biosynthesis of Luminescent Quantum Dots in an Earthworm S.R. Stürzenbaum, a# M. Hoeckner, a# A. Panneerselvam, b J. Levitt, b J.-S. Bouillard, b S. Taniguchi, b L.-A. Dailey, d R. Ahmad Khanbeigi, d E.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A Sensitive and Reliable Detection of Thrombin via Enzyme-Precipitate- Coating-Linked Aptamer Assay Hye-Jin Lee a, Byoung Chan Kim b, Min-Kyu Oh a,*, Jungbae Kim a,* a Department
Supplementary Information A Sensitive and Reliable Detection of Thrombin via Enzyme-Precipitate- Coating-Linked Aptamer Assay Hye-Jin Lee a, Byoung Chan Kim b, Min-Kyu Oh a,*, Jungbae Kim a,* a Department
Local ph Tracking in Living Cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Local ph Tracking in Living Cells Chieh-Jui Tsou, a Chih-Hao Hsia, b Jia-Yin Chu, a Yann Hung,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Local ph Tracking in Living Cells Chieh-Jui Tsou, a Chih-Hao Hsia, b Jia-Yin Chu, a Yann Hung,
Smart nanoprobes for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity during osteoblast differentiation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supporting Information Smart nanoprobes for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supporting Information Smart nanoprobes for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information FRET-based probing to gain direct information on sirna sustainability in live cells: Asymmetric degradation of sirna strands Seonmi Shin, a Hyun-Mi Kwon, b Kyung-Sik
Electronic Supplementary Information FRET-based probing to gain direct information on sirna sustainability in live cells: Asymmetric degradation of sirna strands Seonmi Shin, a Hyun-Mi Kwon, b Kyung-Sik
phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes
 TECHNICAL MANUAL phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes Instructions for Use of Products G9831, G9835, G9841 and G9845 4/15 TM451 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes All technical literature is available at:
TECHNICAL MANUAL phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes Instructions for Use of Products G9831, G9835, G9841 and G9845 4/15 TM451 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes All technical literature is available at:
Electronic Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information Synthesis of novel luminescent copper nanoclusters
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information Synthesis of novel luminescent copper nanoclusters
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Ball-in-ball ZrO 2 Nanostructure for Simultaneous CT Imaging and Highly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Ball-in-ball ZrO 2 Nanostructure for Simultaneous CT Imaging and Highly
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Jingwen Xu, Di Wu, Yuzhen Li, Jing Xu, Zhida Gao, Yan-Yan Song* Department of Chemistry, Northeastern University, Shenyang 114, China E-mail: yysong@mail.neu.edu.cn S 1 Materials
Supporting Information Jingwen Xu, Di Wu, Yuzhen Li, Jing Xu, Zhida Gao, Yan-Yan Song* Department of Chemistry, Northeastern University, Shenyang 114, China E-mail: yysong@mail.neu.edu.cn S 1 Materials
phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes
 TECHNICAL MANUAL phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes Instructions for Use of Products G9831, G9835, G9841 and G9845 Revised 12/17 TM451 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes All technical literature is available
TECHNICAL MANUAL phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes Instructions for Use of Products G9831, G9835, G9841 and G9845 Revised 12/17 TM451 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes All technical literature is available
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany Quantitative Analysis of the Fate of Gold Nanocages In Vitro and In Vivo after Uptake by U87-MG Tumor Cells** Eun Chul Cho, Yu Zhang, Xin Cai,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany Quantitative Analysis of the Fate of Gold Nanocages In Vitro and In Vivo after Uptake by U87-MG Tumor Cells** Eun Chul Cho, Yu Zhang, Xin Cai,
Supporting Information. Ultrasensitive Tyrosinase-Activated Turn-On Near-Infrared. Fluorescent Probe with a Rationally Designed Urea Bond for
 Supporting Information Ultrasensitive Tyrosinase-Activated Turn-On Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe with a Rationally Designed Urea Bond for Selective Imaging and Photodamage to Melanoma Cells Zhipeng Li,,
Supporting Information Ultrasensitive Tyrosinase-Activated Turn-On Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe with a Rationally Designed Urea Bond for Selective Imaging and Photodamage to Melanoma Cells Zhipeng Li,,
B. ADM: C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% Figure.S1,Li et al. number. invaded cells. HuH7 BxPC-3 DLD-1.
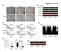 A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
ab JC1 - Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit
 ab113850 JC1 - Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential by fluorescence plate reader This product is for research use only
ab113850 JC1 - Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential by fluorescence plate reader This product is for research use only
AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72053 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate 5-FAM SE (5-carboxyfluorescein) to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72053 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate 5-FAM SE (5-carboxyfluorescein) to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72049 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 647 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72049 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 647 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
Page 1 of 5. Product Name Label Quantity Product No. Cy 3 10 µg (~0.75 nmol) MIR Cy µg (~7.5 nmol) MIR 7901
 Page 1 of 5 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Product Name Label Quantity Product No. Cy 3 10 µg (~0.75 nmol) MIR 7900 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Cy 3 100 µg (~7.5 nmol) MIR 7901 Fluorescein 10 µg (~0.75
Page 1 of 5 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Product Name Label Quantity Product No. Cy 3 10 µg (~0.75 nmol) MIR 7900 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Cy 3 100 µg (~7.5 nmol) MIR 7901 Fluorescein 10 µg (~0.75
Selective growth of Au nanograins on specific positions (tips, edges. heterostructures.
 Selective growth of Au nanograins on specific positions (tips, edges and facets) of Cu 2 O octahedrons to form Cu 2 O-Au hierarchical heterostructures. Han Zhu b, MingLiang Du* a,b, DongLiang Yu b, Yin
Selective growth of Au nanograins on specific positions (tips, edges and facets) of Cu 2 O octahedrons to form Cu 2 O-Au hierarchical heterostructures. Han Zhu b, MingLiang Du* a,b, DongLiang Yu b, Yin
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Fluorogenic sensing of H 2 S in blood and living cells based on reduction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Fluorogenic sensing of H 2 S in blood and living cells based on reduction
Supporting information
 Supporting information Large Hollow Cavity Luminous Nanoparticles with Near-Infrared Persistent Luminescence and Tunable Sizes for Tumor Afterglow Imaging and Chemo/Photodynamic Therapies Jun Wang, Jinlei
Supporting information Large Hollow Cavity Luminous Nanoparticles with Near-Infrared Persistent Luminescence and Tunable Sizes for Tumor Afterglow Imaging and Chemo/Photodynamic Therapies Jun Wang, Jinlei
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Injectable Shear-Thinning Hydrogel with Enhanced Strength and Temperature
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Injectable Shear-Thinning Hydrogel with Enhanced Strength and Temperature
Supporting Information. Low temperature synthesis of silicon carbide nanomaterials using
 Supporting Information Low temperature synthesis of silicon carbide nanomaterials using solid-state method Mita Dasog, Larissa F. Smith, Tapas K. Purkait and Jonathan G. C. Veinot * Department of Chemistry,
Supporting Information Low temperature synthesis of silicon carbide nanomaterials using solid-state method Mita Dasog, Larissa F. Smith, Tapas K. Purkait and Jonathan G. C. Veinot * Department of Chemistry,
Department of Chemistry, Capital Normal University, Beijing , People s
 Supporting Information Polydopamine-encapsulated Fe 3 O 4 with an adsorbed HSP70 inhibitor for improved photothermal inactivation of bacteria Dongdong Liu, Liyi Ma, Lidong Liu, Lu Wang, Yuxin Liu, Qi Jia,
Supporting Information Polydopamine-encapsulated Fe 3 O 4 with an adsorbed HSP70 inhibitor for improved photothermal inactivation of bacteria Dongdong Liu, Liyi Ma, Lidong Liu, Lu Wang, Yuxin Liu, Qi Jia,
Supporting information
 Supporting information Bioengineered Boronic Esters Modified Dextran Polymer Nanoparticles as Reactive Oxygen Species Responsive Nanocarrier for Ischemic Stroke Treatment Wei Lv 1, 3#, Jianpei Xu 1#, Xiaoqi
Supporting information Bioengineered Boronic Esters Modified Dextran Polymer Nanoparticles as Reactive Oxygen Species Responsive Nanocarrier for Ischemic Stroke Treatment Wei Lv 1, 3#, Jianpei Xu 1#, Xiaoqi
Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with high stability and reusability
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Microfluidic Electroporation-Facilitated Synthesis of Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy Lang Rao, Bo Cai, Lin-Lin Bu,
Supporting Information Microfluidic Electroporation-Facilitated Synthesis of Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy Lang Rao, Bo Cai, Lin-Lin Bu,
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2015. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201501942 Rational Design and Synthesis of γfe 2 O 3 @Au Magnetic Gold
Copyright WILEY VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2015. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201501942 Rational Design and Synthesis of γfe 2 O 3 @Au Magnetic Gold
Supplementary information. Simple and rapid detection of L-Dopa decarboxylase activity using gold nanoparticles
 Supplementary information Simple and rapid detection of L-Dopa decarboxylase activity using gold nanoparticles So Young Park, a,b Dohyoung Kwon, a Hyejung Mok a,c and Bong Hyun Chung *a,b a BioNanotechnology
Supplementary information Simple and rapid detection of L-Dopa decarboxylase activity using gold nanoparticles So Young Park, a,b Dohyoung Kwon, a Hyejung Mok a,c and Bong Hyun Chung *a,b a BioNanotechnology
Electronic Supplementary information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary information for Targeted Cancer Imaging and Photothermal Therapy via Monosaccharide-Imprinted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary information for Targeted Cancer Imaging and Photothermal Therapy via Monosaccharide-Imprinted
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Black Phosphorus Nanosheets-Based sirna Delivery System for Synergistic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Black Phosphorus Nanosheets-Based sirna Delivery System for Synergistic
A Cell-Surface-Anchored Ratiometric I-Motif Sensor for. Extracellular ph Detection
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) A Cell-Surface-Anchored Ratiometric I-Motif Sensor for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) A Cell-Surface-Anchored Ratiometric I-Motif Sensor for
Y 2 O 3 Nanoparticles Caused Bone Tissue Damage by Breaking the Intracellular Phosphate Balance in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells
 Supporting Information Y 2 O 3 Nanoparticles Caused Bone Tissue Damage by Breaking the Intracellular Phosphate Balance in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Chunyue Gao, Yi Jin*,, Guang Jia, Xiaomin Suo, Huifang
Supporting Information Y 2 O 3 Nanoparticles Caused Bone Tissue Damage by Breaking the Intracellular Phosphate Balance in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Chunyue Gao, Yi Jin*,, Guang Jia, Xiaomin Suo, Huifang
Microbubble Sonosensitiser Conjugates as Therapeutics in Sonodynamic Therapy
 Microbubble Sonosensitiser Conjugates as Therapeutics in Sonodynamic Therapy SUPPORTING INFORMATION Nikolitsa Nomikou 1, Colin Fowley 2, Niall M. Byrne 2, Bridgeen McCaughan 2, Anthony P. McHale* 2 and
Microbubble Sonosensitiser Conjugates as Therapeutics in Sonodynamic Therapy SUPPORTING INFORMATION Nikolitsa Nomikou 1, Colin Fowley 2, Niall M. Byrne 2, Bridgeen McCaughan 2, Anthony P. McHale* 2 and
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Highly Selective Mitochondria-Targeting Fluorescent K + Sensor Xiangxing Kong, Fengyu Su, Liqiang Zhang, Jordan Yaron, Fred Lee, Zhengwei Shi, Yanqing Tian,* and Deirdre R. Meldrum*
Supporting Information A Highly Selective Mitochondria-Targeting Fluorescent K + Sensor Xiangxing Kong, Fengyu Su, Liqiang Zhang, Jordan Yaron, Fred Lee, Zhengwei Shi, Yanqing Tian,* and Deirdre R. Meldrum*
