Hydrogel and Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined Treatment to Accelerate Wound Healing in a Nude Mouse Model
|
|
|
- Florence Sims
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hydrogel and Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined Treatment to Accelerate Wound Healing in a Nude Mouse Model Original Article Yu Gil Park 1, In Ho Lee 2, Eun Soo Park 1, Jin Young Kim 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon; 2 Onjin-gun Public Health Center, Inchoen, Korea Background Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) contains high concentrations of growth factors involved in wound healing. Hydrogel is a 3-dimensional, hydrophilic, high-molecular, reticular substance generally used as a dressing formulation to accelerate wound healing, and also used as a bio-applicable scaffold or vehicle. This study aimed to investigate the effects of PRP and hydrogel on wound healing, in combination and separately, in an animal wound model. Methods A total of 64 wounds, with 2 wounds on the back of each nude mouse, were classified into 4 groups: a control group, a hydrogel-only group, a PRP-only group, and a combined-treatment group. All mice were assessed for changes in wound size and photographed on scheduled dates. The number of blood vessels was measured in all specimens. Immunohistochemical staining was used for the analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. Results Differences in the decrease and change in wound size in the combined-treatment group were more significant than those in the single-treatment groups on days 3, 5, 7, and 10. Analysis of the number of blood vessels through histological examination showed a pattern of increase over time that occurred in all groups, but the combined-treatment group exhibited the greatest increase on days 7 and 14. Immunohistochemical staining showed that VEGF expression in the combined-treatment group exhibited its highest value on day 7. Conclusions This experiment demonstrated improved wound healing using a PRP hydrogel combined treatment compared to either treatment individually, resulting in a decrease in wound size and a shortening of the healing period. Correspondence: Eun Soo Park Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, 170 Jomaru-ro, Wonmi-gu, Bucheon 14584, Korea Tel: Fax: peunsoo@schmc.ac.kr This work is supported by Soonchunhyang University Research Fund. Keywords Platelet-rich plasma / Hydrogel / Tissue scaffold / Wound healing No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. Received: 12 Nov 2016 Revised: 26 Apr 2017 Accepted: 28 Apr 2017 pissn: eissn: Arch Plast Surg 2017;44: INTRODUCTION The components of blood platelets include glycoproteins, α-granules, and δ-granules. Among these, α-granules contain at least 7 growth factors, and these growth factors help accelerate the normal wound healing process [1]. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a plasma from which blood cells are removed by centrifugation of the whole blood of normal persons. The platelets are thus sequestered and contain high concentrations of selfgrowth factors [2,3]. Previous studies have reported that the ap- Copyright 2017 The Korean Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited
2 Vol. 44 / No. 3 / May 2017 plication of PRP can promote the healing process of a wound, a fracture surface, or a bone defect. As a result, there have been attempts to apply PRP clinically to accelerate the healing of diabetic foot ulcers or engraftment during bone grafting. However, the efficacy of PRP is still controversial [1,2,4]. Recently, studies have attempted to produce and apply single recombinant growth factors to wound healing, but such studies are limited by cost and a short half-life [5,6]. Hydrogel generally refers to a 3-dimensional, hydrophilic, high-molecular, reticular substance that easily expands on account of its considerable degree of moisture. Hydrogel has been used as a dressing formulation. Due to its high water content, hydrogel provides a humid environment for a wound, promotes cell migration and epithelialization, and accelerates wound healing by dead-tissue removal. Additionally, it is characterized as having superior biocompatibility and adequate mechanical traits, its biodegradation can be controlled, and it shows cell adhesion. In particular, due to its high biocompatibility, it can be used as a soft-form bio-applicable scaffold or vehicle [7]. On this basis, an experiment was carried out using an animal model under the assumption that in a combined treatment of hydrogel and PRP, hydrogel would act as an effective scaffold for growth factors and help in their maintenance and expression, thereby accelerating wound healing. METHODS Creation of the animal experimental model For this experiment, 32 9-week-old female BALB/c nude mice with a weight of g (26 g on average) and without a thymus gland (Orientbio Inc., Sungnam, South Korea) were used. They underwent a 1-week adaptation period while being bred, fed, and given water at the laboratory. For anesthesia, 40 mg/kg of tiletamine and zolazepam (Zoletil50, Virbac, France) and 5 Fig. 1. Skin defects in the nude mouse model Circular full-thickness (8-mm-diameter) skin defects were made on the back of a nude mouse. mg/kg of xylazine (Rompun, Bayer, Germany) were injected into the peritoneal cavity. After the removal of the hair in the dorsum of each mouse using an epilator, the dorsum was disinfected with chlorhexidine, and circular wounds were drawn in the head and tail sides at a 10-mm distance from one another, using a sterilized punch biopsy tool with an 8-mm diameter in the center. With a no. 15 blade and fine scissors, a full-thickness skin defect wound reaching the panniculus carnosus was made (Fig. 1). To inhibit the building up of the wound and to accurately measure epithelialization, a 0.5-mm-thick donut-shaped silicone sheet 1 mm larger than the diameter of the wound was placed and fixed using no. 5 nylon (Ethicon, Cornelia, GA, USA). The 32 mice were divided into 2 groups: a group of 16 mice to which PRP was applied, and a group of 16 mice to which PRP was not applied. In all mice, hydrogel was applied to the wound on the tail side, while hydrogel was not applied to the wound on the head side. Therefore, a total of 64 wounds (n = 16 per group) were created. They were divided into 4 treatment method groups: the control group, to which neither PRP nor hydrogel was applied, the hydrogel-only group, the PRP-only group, and the combined-treatment group, to which both hydrogel and PRP treatment were applied. For each wound, occlusive film dressing was applied using Opsite (Smith & Nephew, London, UK) and Surgifix (Panamedic, Seoul, Korea). The dressing was replaced daily, and the wounds were photographed on days 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 to assess their size. Production of PRP The production of PRP required the collection of 54 ml of blood from the vein of a donor, a 30-year-old adult male. The collected blood was mixed with 6 ml of anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution. Using the double-spin method, centrifugation was performed for 10 minutes at 3,000 rpm at room temperature, and after the removal of the underlying blood cell layer, the rest of the blood was divided into 2 test tubes. Centrifugation was repeated on the 2 test tubes for 5 minutes at 5,000 rpm. The precipitated PRP layer was carefully separated with a micropipette, and 6.5 ml of PRP was produced (Fig. 2). An automated hematology system (XE-2100, Sysmex, Kobe, Japan) was used to measure the average platelet count of the normal Fig. 2. Preparation of platelet-rich plasma Platelet-rich plasma was prepared with an injectable syringe. 195
3 Park YG et al. Platelet-rich plasma loaded hydrogel scaffold blood of the donors (as /L), and the average platelet count of the manufactured PRP as /L, indicating that the process resulted in an approximately fold higher platelet concentration. PRP application and treatment Purified bovine thrombin (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany) was diluted at 100 units per ml in 10% calcium chloride and was then coagulated and activated by mixing with PRP. The hydrogel that was used in this experiment was Purilon gel (Coloplast, Humlebæk, Denmark), which has an amorphous property. For the hydrogel-only group, a 0.1-mL saline solution was injected into the base of each wound with a 1-mL syringe and a 27-gauge needle in place of PRP. In the PRP-only and combined-treatment groups, 0.1 ml of activated PRP was injected into the base of each wound using a 1-mL syringe and a 27-gauge needle. For the wound on the tail side, about 1 ml of hydrogel was applied locally. Each wound was dressed using Opsite (Smith & Nephew, London, UK), and the dressing was fixed with Surgifix (Panamedic). Each mouse was placed in a separate cage and observed for 2 weeks. Visual examination and measurement of wound size After the creation of the wound, the dressing was replaced daily, and photos of the wound were taken on days 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 at the same resolution and distance using a digital single-lens reflex camera (Nikon D90, macro-lens 50 mm, Tokyo, Japan), to reduce errors. The photos were taken with a ruler placed next to the wound to show the wound size. The quantitative assessment of the wound size was based on the edge of the epithelialized portion. The area was measured at the pixel level using the ImageJ software program (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). Measurement of the average number of blood vessels On days 7 and 14, 16 mice were sacrificed, respectively, and 8 specimens were collected from each group. The samples, including about 1 mm of normal skin from the edge of the wound (including the epithelialized portion), were resected with a no. 15 blade. After resection of the center of the wound, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was applied to 1 fragment and immunohistochemical analysis was applied to another. The collected samples were stored by freezing them at 70 C and fixed in 10% formalin for 1 day in order to produce histopathology slides. Thereafter, paraffin embedding was performed, the specimens were sliced into 4-μm-thick parts, and H&E staining was applied to produce tissue sample slides. To determine the number of blood vessels, structures with the shape of the inner diameter of a blood vessel were observed with a microscope in each of the different fields of 3 sites for each slide, at 100 magnification. Analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor expression Immunohistochemistry was performed to analyze vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. The VEGF signal protein (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) was used as a mouse monoclonal antibody, with beta-actin (1:1,000, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) used as a reference value antibody. After dissolving the tissue samples in a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample and buffer solution, they were passed through 10% polyacrylamide gel. Thereafter, they were passed through a nitrocellulose membrane, and the first and second antibodies were reacted. Immune protein analysis was performed through chemical fluorescence analysis of the X-ray film, and the size of the expressed band was determined by measuring the area using the software program ImageJ. The values compared to the reference value of beta-actin expression were used for relative comparison of the groups, Statistical analysis To compare the wound sizes, change rates, and numbers of blood vessels at the different time points per group, 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted. To determine if the difference between the groups at each time point was significant, ANOVA tests were performed at each time point, and post hoc tests were conducted using the Tukey honest significant difference test. All statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS ver. 14.0KO (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria), and the significance level was set at P < RESULTS Quantitative analysis of wound size The initial wound sizes were similar across all groups. The wounds of the mice in the combined-treatment group on day 3 were smaller than those of the mice in the PRP-only, hydrogelonly, and control groups. On days 3, 5, and 10, the same results were obtained, and on day 14, wound healing was complete in the combined-treatment group, while the wounds of the mice in the other groups remained (Fig. 3). In the quantitative analysis, the differences in wound size between the combined-treatment group and the 3 other groups on days 3, 5, 7, and 10 were all significant (P < 0.05). The differences in the changes in the wound size were also significant (P < 0.05) (Table 1). For the PRP- and hydrogel-only groups, the differences and changes in the wound 196
4 Vol. 44 / No. 3 / May 2017 Fig. 3. Gross appearance of the wounds Time course of the gross appearance of the wounds: control, hydrogel-only, PRP-only, and combined-treatment groups. PRP, platelet-rich plasma. Day 3 Control Hydrogel only PRP only Combined Day 5 Day 4 Day 10 Day 14 Table 1. Comparison of wound sizes in all groups with time progression Category Measurement At baseline Day 3 Day 5 Day 7 Day 10 Day 14 Wound size (pixel) Control 129± ±1.3 a,b,c) 89 ± 1.7 a,b,c) 70.1 ± 3.2 a,b,c) 46.9 ± 6.0 a) 24.6 ± 3.2 a) Hydrogel-only 127.5± ±2.0 a) 75.2 ± 1.9 a) 55.1 ± 3.4 a) 38 ± 4.5 a) 15.9 ± 2.6 a) PRP-only 128.4± ±1.5 a) 68.1 ± 1.7 a) 45.9 ± 2.0 a) 31.5 ± 3.0 a) 16.1 ± 2.4 a) Combined ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.5 These results were derived through 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation. PRP, platelet-rich plasma; SE, standard error; ANOVA, analysis of variance; HSD, honest significant differences. At each time point, a post-hoc comparison was made using the Tukey HSD test. a) Significant difference with the combined treatment; b) Significant difference with PRP-only; c) Significant difference with hydrogel-only. Comparison (P-value) Group, < Time, <0.001 Interaction, < size and were significant on days 3, 5, and 7 compared to the control group, but they were not significant after day 10. Measurement of the average number of blood vessels The number of blood vessels was determined using an optical microscope, and the changes were analyzed (Figs. 4, 5). After 197
5 Park YG et al. Platelet-rich plasma loaded hydrogel scaffold treatment, the differences in the average number of blood vessels in the 4 groups were found to be significant (P < 0.05), and the increase in the number of blood vessels over time was found to be significant in all groups (P < 0.05) (Table 2). The increase patterns were the same with regard to the number of blood vessels in the 4 groups, but there was no difference due to the inter- Fig. 4. Histologic findings on day 7 H&E, 100. (A) Control group. (B) Hydrogel-only group. (C) PRP-only group. (D) Combined-treatment group. PRP, platelet-rich plasma. The black arrows indicate the staining of the blood vessels. A B A B C D Fig. 5. Histologic findings on day 14 H&E, 100. (A) Control group. (B) Hydrogel-only group. (C) PRP-only group. (D) Combined-treatment group. PRP, platelet-rich plasma. The black arrows indicate the staining of the blood vessels. A B A B C D 198
6 Vol. 44 / No. 3 / May 2017 action effect (P = 0.747). In a comparison of the average numbers of blood vessels per area, the combined-treatment group showed significant differences on days 7 and 14 compared to the hydrogel-only and control groups, but showed no significant difference compared to the PRP-only group. Compared to the hydrogel-only and control groups, the PRP-only group showed a significant difference on day 7, but only showed a significant difference on day 14 compared to the control group. Analysis of VEGF expression The VEGF expression values were compared by measuring the size of the band expressed through the projection of an X-ray film using ImageJ. On day 7, the combined-treatment group showed the highest value, which represented a 1.79-fold increase compared to that of the control group. On day 14, a Table 2. Comparison of the average numbers of blood vessels per unit area Category Measurement Day 7 Day 14 No. of blood vessels Control 4.7±0.2 a,b) 5.2±0.1 a,b) Hydrogel-only 5.1±0.1 a,b) 5.6±0.2 a) PRP-only 5.6± ±0.2 Combined 5.9± ±0.2 Comparison (P-value) Group, < Time, < Interaction, = These results were derived through 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA. At each time point, a post-hoc comparison was made using the Tukey HSD test. Values are presented as mean ± standard error. PRP, platelet-rich plasma; ANOVA, analysis of variance; HSD, honest significant differences. a) Significant difference with the combined treatment; b) Significant difference with PRP-only. fold increase was also observed. The PRP-only group showed a 1.46-fold increase on day 7 compared to the control group. On day 14, a 1.93-fold increase was also observed, which did not differ significantly from that of the combined-treatment group (Fig. 6). DISCUSSION The α-granules of PRP contain 7 major growth factors, including 3 isomers of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-αα, PDGF-αβ, and PDGF-ββ), 2 isomers of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1 and TGF-β2), VEGF, and epithelial growth factor (EGF) [2]. They are secreted by activated platelets in the process of wound healing, and each serves to promote wound healing as a growth factor or cytokine [8]. PRP can be injected into the base of the wound or applied directly to the wound. It can promote activation of the physiological functions by supplying a greater than normal amount of growth factors to the damaged site, and can reduce the chance of infection, as well as pain and blood loss [9]. Some clinical trials have reported that PRP is effective for wound healing, but no evidence of its efficacy has been clearly established [10]. A study reported that due to its short half-life, the effect of PRP is weak, and it should be used within a certain period of time after its production [11]. However, another study reported that PRP has a sufficient effect if it is repeatedly applied [12]. In such cases, repeated application of PRP imposes an inconvenience, and there is a disadvantage in that the quality of PRP (i.e., the concentration) may not be consistent. To overcome this limitation, a study was conducted on increasing the Fig. 6. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression Vascular endothelial growth factor expression was measured using a computer planimetry software program. The 4 graphs on the left pertain to day 7, while the 4 graphs on the right pertain to day 14. VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; PRP, platelet-rich plasma VEGF expression Fold intensity Control Hydrogel only PRP only Combined Control Hydrogel only PRP only Combined Day 7 Day
7 Park YG et al. Platelet-rich plasma loaded hydrogel scaffold action time and effect by utilizing a scaffold or vehicle along with a bioactive substance such as PRP [13]; in particular, this study aimed to investigate the effect by using hydrogel as a scaffold. Hydrogel generally refers to a 3-dimensional, hydrophilic, high-molecular, reticular substance that can easily expand on account of its considerable degree of moisture. Hydrogel has received much attention and has been extensively discussed in the literature as a dressing formulation. It is in current use in clinics. It comes in various types, including amorphous hydrogel, hydrogel-impregnated gauze dressing, and sheet hydrogel. Hydrogel dressing acts as a humectant, prevents the formation of a scab by maintaining the water content of the wound, and promotes wound healing in the center. Hydrogel has a 3-dimensional structure, absorbs secretions and foreign materials, and secures a space by dilating the polymer chain cross-linking structure. Additionally, hydrogel does not strongly adhere to the wound surface and does not cause irritation. It can also be easily removed, without pain. The biodegradation and cell adhesion of hydrogel can be controlled, with superior biocompatibility, and it is mechanically adequate for use as a soft-form bio-applicable scaffold. One study has reported on its use as a combination treatment with biological materials [14]. Since hydrogel has dual properties as a scaffold or vehicle due to its 3-dimensional structure, previous studies have noted its use for promoting the healing of soft tissue and bone defects by the addition of other bioactive substances. The added substances have varied and include traditional antibiotic substances such as povidone-iodine, collagen or antibiotics, PRP, polydeoxyribonucleotide, and stem cells [14]. The hydrogel that was used in this experiment was Purilon gel (Coloplast), an amorphous gel consisting of natural materials with high biocompatibility, such as purified water, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and calcium alginate; it is applicable to any type of wound. The increased size and number of blood vessels are among the factors important for wound healing, because blood vessels supply oxygen and nutrients to the tissues undergoing regeneration. Various factors are known to induce angiogenesis [15], and among them, VEGF is the most powerful angiogenic cytokine secreted from platelets, macrophages, and fibroblasts. It diffuses the vascular endothelial cells and increases vascular permeability [16]. Thus, the abundant supply and maintenance of these factors can be helpful for wound healing, and a study has reported that VEGF concentration alone induced accelerated in wound healing [17]. This study showed that wound healing was significantly accelerated in the combined-treatment (PRP and hydrogel) group compared to the PRP- and hydrogel-only groups. The degree of wound healing acceleration in the PRP-only group was significant compared to the control group, but there was no significant difference between the PRP- and hydrogel-only groups in this regard. Additionally, in the analysis of the number of blood vessels per unit area, the differences and changes in the number of blood vessels were significant in the combined-treatment group compared to the control and hydrogel-only groups on days 7 and 14. In the PRP-only group, significant differences were observed on days 7 and 14 compared to the control group, and on day 7 compared to the hydrogel-only group. Therefore, it can be said that the application of PRP accelerated angiogenesis. Moreover, while there was no significant difference in the hydrogelonly group compared to the control group, an increase in the overall number of blood vessels was observed. Thus, it is thought that angiogenesis was promoted by the cell migration due to the humid environment of the hydrogel. The effective results in the combined-treatment group are thought to have been due to the fact that hydrogel served as a scaffold to increase maintenance and expression, promoted angiogenesis, and further accelerated wound healing. In addition, in the analysis of the VEGF expression on the wound surface using immunohistochemistry, the most greatly increased values were observed on days 7 and 14 in the combined-treatment group. Since hydrogel acts as a scaffold for PRP, it increased the expression of growth factors and helped in the maintenance and acceleration of wound healing. There are limitations to this study. Since the wounds were located in 2 different areas (in the head and tail of each mouse, respectively) the wound locations did not exactly match for each experimental group. This introduces a potential bias due to the fact that differences in the movement of the head and tail at different wound locations can affect the healing of the wound. However, the distance between these 2 areas was within 10 mm, with wounds largely located in the dorsum and central portions, and we believe this limitation is unlikely to have significantly affected the results. Further work including quantitative analysis and measurement is required to accurately assess the effects of VEGF expression. Although H&E staining was used in our study, another important way of identifying the number of blood vessels generated would be through the use of CD31 staining, which would provide a potential area for further research. In this study, the application of PRP hydrogel combination therapy resulted in more effective wound healing acceleration. It is thought that hydrogel acted as a scaffold for the growth factor, which led to an increase of the expression of growth factors and angiogenesis. 200
8 Vol. 44 / No. 3 / May 2017 REFERENCES 1. Man D, Plosker H, Winland-Brown JE. The use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (platelet gel) and autologous platelet-poor plasma (fibrin glue) in cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 2001;107: Marx RE. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2004;62: Bhanot S, Alex JC. Current applications of platelet gels in facial plastic surgery. Facial Plast Surg 2002;18: Abegao KG, Bracale BN, Delfim IG, et al. Effects of heterologous platelet-rich plasma gel on standardized dermal wound healing in rabbits. Acta Cir Bras 2015;30: Ito R, Morimoto N, Pham LH, et al. Efficacy of the controlled release of concentrated platelet lysate from a collagen/gelatin scaffold for dermis-like tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A 2013;19: Morimoto N, Yoshimura K, Niimi M, et al. Novel collagen/ gelatin scaffold with sustained release of basic fibroblast growth factor: clinical trial for chronic skin ulcers. Tissue Eng Part A 2013;19: Montoya TI, Acevedo JF, Smith B, et al. Myogenic stem cellladen hydrogel scaffold in wound healing of the disrupted external anal sphincter. Int Urogynecol J 2015;26: Eppley BL, Pietrzak WS, Blanton M. Platelet-rich plasma: a review of biology and applications in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006;118:147e-159e. 9. Hahn HM, Jeon YR, Rha DK, et al. Acceleration of wound healing using adipose-derived stem cell therapy with platelet concentrates: platelet-rich plasma (PRP) vs. Platelet-rich Fibrin (PRF). J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg 2011;38: Martinez-Zapata MJ, Marti-Carvajal AJ, Sola I, et al. Autologous platelet-rich plasma for treating chronic wounds. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;10:CD Sugimori E, Shintani S, Ishikawa K, et al. Effects of apatite foam combined with platelet-rich plasma on regeneration of bone defects. Dent Mater J 2006;25: Serra R, Buffone G, Dominijanni A, et al. Application of platelet-rich gel to enhance healing of transmetatarsal amputations in diabetic dysvascular patients. Int Wound J 2013; 10: Miyoshi M, Kawazoe T, Igawa HH, et al. Effects of bfgf incorporated into a gelatin sheet on wound healing. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 2005;16: Wang C, Varshney RR, Wang DA. Therapeutic cell delivery and fate control in hydrogels and hydrogel hybrids. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2010;62: Schilling JA, Favata BV, Radakovich M. Studies of fibroplasia in wound healing. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1953;96: Banks RE, Forbes MA, Kinsey SE, et al. Release of the angiogenic cytokine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from platelets: significance for VEGF measurements and cancer biology. Br J Cancer 1998;77: Birkenhauer E, Neethirajan S. A double-edged sword: the role of VEGF in wound repair and chemoattraction of opportunist pathogens. Int J Mol Sci 2015;16:
Discover TruPRP. PRP the way you want it.
 Discover TruPRP PRP the way you want it. Discover TruPRP Discover the quality of Magellan TruPRP. The Magellan technology provides an automated dual spin processing system that can deliver (PRP) Platelet
Discover TruPRP PRP the way you want it. Discover TruPRP Discover the quality of Magellan TruPRP. The Magellan technology provides an automated dual spin processing system that can deliver (PRP) Platelet
Discover TruPRP. PRP the way you want it.
 Discover TruPRP PRP the way you want it. Discover TruPRP Discover the quality of Magellan TruPRP. The Magellan technology provides an automated dual spin processing system that can deliver (PRP) Platelet
Discover TruPRP PRP the way you want it. Discover TruPRP Discover the quality of Magellan TruPRP. The Magellan technology provides an automated dual spin processing system that can deliver (PRP) Platelet
BUILT TO CONCENTRATE. Magellan is an autologous concentration system that delivers concentrated platelets and cells at the point of care.
 BUILT TO CONCENTRATE Magellan is an autologous concentration system that delivers concentrated platelets and cells at the point of care. DELIVER PERSONALIZED MEDICINE Every patient has a unique biology
BUILT TO CONCENTRATE Magellan is an autologous concentration system that delivers concentrated platelets and cells at the point of care. DELIVER PERSONALIZED MEDICINE Every patient has a unique biology
ARTHREX ACP. Features and Benefits: Introduction
 ARTHREX ACP Introduction Autologous blood products have created a growing interest for use in a number of orthopaedic therapies. The healing effects of plasma are supported by growth factors released by
ARTHREX ACP Introduction Autologous blood products have created a growing interest for use in a number of orthopaedic therapies. The healing effects of plasma are supported by growth factors released by
RegenACR. autologous cellular regeneration. RegenACR A-PRP treatment. collagen fibers. 1,2 texture and elasticity. 3 volume & strength.
 RegenACR autologous cellular regeneration RegenACR A-PRP treatment collagen fibers. 1,2 texture and elasticity. 3 volume & strength. 4,5 WHAT IS A-PRP Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Plasma contains many
RegenACR autologous cellular regeneration RegenACR A-PRP treatment collagen fibers. 1,2 texture and elasticity. 3 volume & strength. 4,5 WHAT IS A-PRP Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Plasma contains many
PRP Preparation. Simplicity for Success
 PRP Preparation Simplicity for Success Features and Benefits of the Tropocells System Effectiveness Enables high platelet concentration by reducing the volume of plasma. Rapid and simple one step process
PRP Preparation Simplicity for Success Features and Benefits of the Tropocells System Effectiveness Enables high platelet concentration by reducing the volume of plasma. Rapid and simple one step process
THE SCIENCE OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA
 THE SCIENCE OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA Cheri A. Ong, MD FACS ONG INSTITUTE FOR PLASTIC SURGERY & HEALTH WHAT IS PRP BLOOD PLASMA 55% of the body s today body volume 45% blood cells:- Red blood cells, White
THE SCIENCE OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA Cheri A. Ong, MD FACS ONG INSTITUTE FOR PLASTIC SURGERY & HEALTH WHAT IS PRP BLOOD PLASMA 55% of the body s today body volume 45% blood cells:- Red blood cells, White
Platelet-Rich Plasma: Quantitative Assessment of Growth Factor Levels and Comparative Analysis of Activated and Inactivated Groups
 Original Article Platelet-Rich Plasma: Quantitative Assessment of Growth Factor Levels and Comparative Analysis of Activated and Inactivated Groups Jeong Woo Lee 1, O Hyun Kwon 1, Taek Kyun Kim 1, Young
Original Article Platelet-Rich Plasma: Quantitative Assessment of Growth Factor Levels and Comparative Analysis of Activated and Inactivated Groups Jeong Woo Lee 1, O Hyun Kwon 1, Taek Kyun Kim 1, Young
Double Syringe System Autologous Conditioned Plasma
 TM Double Syringe System Autologous Conditioned Plasma Autologous Conditioned Plasma Introduction Autologous blood products have created a growing interest for use in a number of orthopaedic therapies.
TM Double Syringe System Autologous Conditioned Plasma Autologous Conditioned Plasma Introduction Autologous blood products have created a growing interest for use in a number of orthopaedic therapies.
A.P.A.G. Activated Plasma Albumin Gel
 A.P.A.G. Activated Plasma Albumin Gel How Does This Work In a new wound, platelets are the first cells which arrive. They aggregate to stop the bleeding and then release substances (growth factors, cytokines,
A.P.A.G. Activated Plasma Albumin Gel How Does This Work In a new wound, platelets are the first cells which arrive. They aggregate to stop the bleeding and then release substances (growth factors, cytokines,
Methods Western blot analysis of plg Quantification of plasminogen accumulation by ELISA Immunohistochemical analysis
 Methods Western blot analysis of plg Wild-type mice first received a standardized burn wound and then were intravenously administered 2 mg of human plg (Omnio AB, Umeå, Sweden). 24 hours after wounding
Methods Western blot analysis of plg Wild-type mice first received a standardized burn wound and then were intravenously administered 2 mg of human plg (Omnio AB, Umeå, Sweden). 24 hours after wounding
"Release of growth factors in PRP activated with thrombin."
 "Release of growth factors in PRP activated with thrombin." Carrasco, Joaquin phd Dp. Surgery Universitat de València. Presenter Bonete, Daniel MD Hospital La Fe de València Gomar, Francisco MD Hospital
"Release of growth factors in PRP activated with thrombin." Carrasco, Joaquin phd Dp. Surgery Universitat de València. Presenter Bonete, Daniel MD Hospital La Fe de València Gomar, Francisco MD Hospital
SmartPReP 2: The Gold Standard
 The Optimal Platelet Rich Plasma Composition SmartPReP 2: The Gold Standard Harvest Technologies is the leader in developing point-of-care cellular platforms to isolate and concentrate autologous growth
The Optimal Platelet Rich Plasma Composition SmartPReP 2: The Gold Standard Harvest Technologies is the leader in developing point-of-care cellular platforms to isolate and concentrate autologous growth
The Power in You. TM
 RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The Power in You. TM Biologics Concentrated on Healing RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The RegenKit THT is designed to be used
RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The Power in You. TM Biologics Concentrated on Healing RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The RegenKit THT is designed to be used
Get the most out of Pure PRP
 Get the most out of Pure PRP The Basic Science of PRP Platelets are small non-nucleated bodies in peripheral blood known for role in hemostasis Platelets contain proteins, cytokines & other bioactive factors
Get the most out of Pure PRP The Basic Science of PRP Platelets are small non-nucleated bodies in peripheral blood known for role in hemostasis Platelets contain proteins, cytokines & other bioactive factors
Life Science Products Collagen and Gelatin. Product Guide
 Life Science Products Collagen and Gelatin Product Guide Collagen for Cell Culture Collagen for Three-dimensional Culture / Collagen for Coating Collagen solution at ph 3 with a concentration of 3 mg/ml
Life Science Products Collagen and Gelatin Product Guide Collagen for Cell Culture Collagen for Three-dimensional Culture / Collagen for Coating Collagen solution at ph 3 with a concentration of 3 mg/ml
TROPOCELLS TM PLUS. PRP Preparation Simplicity for Success
 TROPOCELLS TM PLUS PRP Preparation Simplicity for Success TROPOCELLS TM Features and Benefits of the Tropocells System Effectiveness Enables high platelet concentration by reducing the volume of plasma.
TROPOCELLS TM PLUS PRP Preparation Simplicity for Success TROPOCELLS TM Features and Benefits of the Tropocells System Effectiveness Enables high platelet concentration by reducing the volume of plasma.
ALL THE ESSENTIALS OF HEALING, NATURALLY
 ALL THE ESSENTIALS OF HEALING, NATURALLY Harvest Technologies Developing Cellular platforms that may help optimize conditions for healing orthopedic sites Unlocking the Biologic Potential What is the Optimal
ALL THE ESSENTIALS OF HEALING, NATURALLY Harvest Technologies Developing Cellular platforms that may help optimize conditions for healing orthopedic sites Unlocking the Biologic Potential What is the Optimal
VIII. Validation Evaluation Comparative Chart Application Fields of PRP Advantages of MiroPRP for skin treatments MicroPRP and Mico-Mesotherapy
 The New Technology for Safe Platelet Activation INDEX I. Blood Composition II. What is PRP Therapy? III. Growth Factors Present in PRP IV. Why is PRP concentration significant? V. How are Platelets Activated?
The New Technology for Safe Platelet Activation INDEX I. Blood Composition II. What is PRP Therapy? III. Growth Factors Present in PRP IV. Why is PRP concentration significant? V. How are Platelets Activated?
Autohemotherapy. Dermoelectroporation. a new science in skin care. The Effectiveness of Biological Therapy with maximum Comfort in total Safety
 a new science in skin care Dermoelectroporation Autohemotherapy The Effectiveness of Biological Therapy with maximum Comfort in total Safety A partnership: & Autohemotherapy Autohemotherapy can be considered
a new science in skin care Dermoelectroporation Autohemotherapy The Effectiveness of Biological Therapy with maximum Comfort in total Safety A partnership: & Autohemotherapy Autohemotherapy can be considered
All THE E SSEn TIAl S OF H EAl I ng, natu RAlly. P RIvATE PRACTICE
 All THE E SSEn TIAl S OF H EAl I ng, natu RAlly P RIvATE PRACTICE Harvest Technologies Developing Cellular platforms that may help optimize conditions for healing orthopedic sites Unlocking the Biologic
All THE E SSEn TIAl S OF H EAl I ng, natu RAlly P RIvATE PRACTICE Harvest Technologies Developing Cellular platforms that may help optimize conditions for healing orthopedic sites Unlocking the Biologic
A review of Dr. Dinakar Golla s clinical research with AdMatrix surgical grafts for soft tissue repair
 TEAMeffort: Using aggressive surgical techniques in combination with AdMatrix (Lattice Biologics acellular dermal scaffold product) to heal difficult and persistent wounds A review of Dr. Dinakar Golla
TEAMeffort: Using aggressive surgical techniques in combination with AdMatrix (Lattice Biologics acellular dermal scaffold product) to heal difficult and persistent wounds A review of Dr. Dinakar Golla
Dressing Material Moisture facilitate
 Wound Healing Concept Dressing Material นพ.ส ทธ ส ทธ ส ณห ส ณห จ นทร ขจร ศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง โรงพยาบาลพระมงก ฎเกล า Moisture facilitate - Epidermal migration - Angiogenesis - Connective tissue synthesis -
Wound Healing Concept Dressing Material นพ.ส ทธ ส ทธ ส ณห ส ณห จ นทร ขจร ศ ลยศาสตร ตกแต ง โรงพยาบาลพระมงก ฎเกล า Moisture facilitate - Epidermal migration - Angiogenesis - Connective tissue synthesis -
Lyset BOOST YOUR CELL CULTURE TODAY FOR THE EXPERIMENTS OF TOMORROW
 Lyset BOOST YOUR CELL CULTURE TODAY FOR THE EXPERIMENTS OF TOMORROW Lyset, the human platelet derived supplement for cell culture Among the different alternatives to animal serum, platelet derived preparations
Lyset BOOST YOUR CELL CULTURE TODAY FOR THE EXPERIMENTS OF TOMORROW Lyset, the human platelet derived supplement for cell culture Among the different alternatives to animal serum, platelet derived preparations
CHAPTER 4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
 CHAPTER 4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES Wound infections are the major challenges in the wound care management. Infection can be either due to microbial attack or due to some diseases. This infection
CHAPTER 4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES Wound infections are the major challenges in the wound care management. Infection can be either due to microbial attack or due to some diseases. This infection
Research Study Comparison of. Angel Whole Blood Separation System and EmCyte PurePRP
 Research Study Comparison of Angel Whole Blood Separation and EmCyte PurePRP Prepared by Robert Mandle, PhD Biosciences Research Associates Cambridge, MA Study Date March 6, 2014 Contents 1. Introduction
Research Study Comparison of Angel Whole Blood Separation and EmCyte PurePRP Prepared by Robert Mandle, PhD Biosciences Research Associates Cambridge, MA Study Date March 6, 2014 Contents 1. Introduction
B i o m a t e r i a l s E n g i n e e r i n g
 B i o m a t e r i a l s E n g i n e e r i n g Collagen, a key factor for clinical success INTRODUCTION A REVOLUTIONARY INNOVATION Tecnoss exclusive manufacturing process is able to neutralize the antigenic
B i o m a t e r i a l s E n g i n e e r i n g Collagen, a key factor for clinical success INTRODUCTION A REVOLUTIONARY INNOVATION Tecnoss exclusive manufacturing process is able to neutralize the antigenic
Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: a comparison of seven commercial separation systems
 DOI 10.1007/s10047-014-0761-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Others Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: a comparison of seven commercial separation s Satoshi Kushida Natsuko
DOI 10.1007/s10047-014-0761-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Others Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: a comparison of seven commercial separation s Satoshi Kushida Natsuko
The Use of Amnion-Derived Cellular Cytokine Solution (ACCS) in Accelerating Closure of Interstices in Explanted Meshed Human Skin Grafts
 The Use of Amnion-Derived Cellular Cytokine Solution (ACCS) in Accelerating Closure of Interstices in Explanted Meshed Human Skin Grafts M. Georgina Uberti, MD, a Francis Ko, BS, a Yvonne N. Pierpont,
The Use of Amnion-Derived Cellular Cytokine Solution (ACCS) in Accelerating Closure of Interstices in Explanted Meshed Human Skin Grafts M. Georgina Uberti, MD, a Francis Ko, BS, a Yvonne N. Pierpont,
Arthrex Angel TM System. Indication-specific PRP and PRF gel preparations
 Arthrex Angel TM System Indication-specific PRP and PRF gel preparations Arthrex Angel TM System The Arthrex Angel TM System is a revolutionary production system for platelet-rich plasma (PRP) formulations
Arthrex Angel TM System Indication-specific PRP and PRF gel preparations Arthrex Angel TM System The Arthrex Angel TM System is a revolutionary production system for platelet-rich plasma (PRP) formulations
Research Study. Comparison of EmCyte GS30-PurePRP II, EmCyte GS60-PurePRP II, Arteriocyte MAGELLAN, Stryker REGENKIT THT, and ECLIPSE PRP
 Research Study Comparison of EmCyte GS30-PurePRP II, EmCyte GS60-PurePRP II, Arteriocyte MAGELLAN, Stryker REGENKIT THT, and ECLIPSE PRP Principle Investigator Robert Mandle, PhD Biosciences Research Associates
Research Study Comparison of EmCyte GS30-PurePRP II, EmCyte GS60-PurePRP II, Arteriocyte MAGELLAN, Stryker REGENKIT THT, and ECLIPSE PRP Principle Investigator Robert Mandle, PhD Biosciences Research Associates
Description. Used materials. Warnings and precautions
 USER MANUAL Description The GPS II System separates the blood components, present in blood, on the basis of density, through application of the GPS -Thermo International Equipment Company (IEC)-Centrifuge.
USER MANUAL Description The GPS II System separates the blood components, present in blood, on the basis of density, through application of the GPS -Thermo International Equipment Company (IEC)-Centrifuge.
PCCS Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation Final Assignment. Igneris Rosado-Erazo. Panama College of Cell Science
 Running Head: Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation PCCS Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation Final Assignment Igneris Rosado-Erazo Panama College of Cell Science In partial fulfillment of
Running Head: Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation PCCS Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation Final Assignment Igneris Rosado-Erazo Panama College of Cell Science In partial fulfillment of
Growth factor delivery
 Growth factor delivery S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative of IITs
Growth factor delivery S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative of IITs
Wound Repair and Regeneration
 Wound Repair and Regeneration Mark A. Carlson, MD Department of Surgery University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha VA Medical Center Omaha, Nebraska USA UNMC Dept Surgery Research Conference, 3/24/10
Wound Repair and Regeneration Mark A. Carlson, MD Department of Surgery University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha VA Medical Center Omaha, Nebraska USA UNMC Dept Surgery Research Conference, 3/24/10
A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING
 A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING Umadevi Kandalam, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry College of Dental Medicine Nova Southeastern University Fort Lauderdale, Florida
A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING Umadevi Kandalam, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry College of Dental Medicine Nova Southeastern University Fort Lauderdale, Florida
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
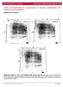 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
YOUR OWN LIFE
 YOUR OWN LIFE Stromal Tissue (ST), a Regenerative Source There is a worldwide consensus that the isolation and collection of regenerative Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC s) from differentiated body tissues
YOUR OWN LIFE Stromal Tissue (ST), a Regenerative Source There is a worldwide consensus that the isolation and collection of regenerative Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC s) from differentiated body tissues
In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay. Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung *
 In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung * Clinical Oncology Department, The Univerisity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR *For
In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung * Clinical Oncology Department, The Univerisity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR *For
Cellular Matrix HYDRATION & REGENERATION. Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma combined with Hyaluronic Acid for Skin Regeneration
 Cellular Matrix HYDRATION & REGENERATION Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma combined with Hyaluronic Acid for Skin Regeneration A-PRP & HA Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Hyaluronic Acid Cellular Matrix is
Cellular Matrix HYDRATION & REGENERATION Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma combined with Hyaluronic Acid for Skin Regeneration A-PRP & HA Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Hyaluronic Acid Cellular Matrix is
Home Study Program. Intraoperative use of autologous platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma for orthopedic surgery patients T
 Home Study Program OCTOBER 2004, VOL 80, NO 4 Home Study Program Intraoperative use of autologous platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma for orthopedic surgery patients T he article Intraoperative use
Home Study Program OCTOBER 2004, VOL 80, NO 4 Home Study Program Intraoperative use of autologous platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma for orthopedic surgery patients T he article Intraoperative use
Electron microscopy technology of reticulocytes after sorting with
 Electron microscopy technology of reticulocytes after sorting with magnetic beads The Cell Analysis Center Scientific Bulletin Part 2 For efficient analysis of cells, sorting of the target cells is crucial.
Electron microscopy technology of reticulocytes after sorting with magnetic beads The Cell Analysis Center Scientific Bulletin Part 2 For efficient analysis of cells, sorting of the target cells is crucial.
Adipose rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the chronic scar tissue of the vocal cords
 Adipose rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the chronic scar tissue of the vocal cords Dr. Vasiliki E Kalodimou, Head of Flow Cytometry-Research and Regenerative Medicine Department, IASO-Maternity
Adipose rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the chronic scar tissue of the vocal cords Dr. Vasiliki E Kalodimou, Head of Flow Cytometry-Research and Regenerative Medicine Department, IASO-Maternity
RECOMBINANT AND AUTOLOGOUS PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTORS AS A TREATMENT OF WOUND HEALING AND OTHER NON-ORTHOPEDIC CONDITIONS
 CONDITIONS Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
CONDITIONS Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
Platelet Concentrate in Total Knees BIOLOGICS. This brochure is for International use only. It is not for distribution in the United States.
 Platelet Concentrate in Total Knees BIOLOGICS This brochure is for International use only. It is not for distribution in the United States. Platelet Concentrate in Total Knees Total Knee Arthroplasty Total
Platelet Concentrate in Total Knees BIOLOGICS This brochure is for International use only. It is not for distribution in the United States. Platelet Concentrate in Total Knees Total Knee Arthroplasty Total
APPLICATION OF AUTOLOGOUS PLATELET RICH PLASMA (APRP) AS AN ADJUVANT THERAPY IN PLASTIC SURGERY
 Plastic Surgery Original Article International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 4, Issue 6, Nov-Dec 2016. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. APPLICATION OF AUTOLOGOUS
Plastic Surgery Original Article International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 4, Issue 6, Nov-Dec 2016. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. APPLICATION OF AUTOLOGOUS
Median Sternotomy Closure Utilizing Platelet Concentrate BIOLOGICS
 Median Sternotomy Closure Utilizing Platelet Concentrate BIOLOGICS This brochure is for International use only. It is not for distribution in the United States. The Surgical Procedure: Median Sternotomy
Median Sternotomy Closure Utilizing Platelet Concentrate BIOLOGICS This brochure is for International use only. It is not for distribution in the United States. The Surgical Procedure: Median Sternotomy
DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. Comparative testing.
 DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. Comparative testing. Natural, like native tissue Minimally processed Strong and flexible DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. Human dermal collagen matrix. Unique process DermaMatrix
DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. Comparative testing. Natural, like native tissue Minimally processed Strong and flexible DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. Human dermal collagen matrix. Unique process DermaMatrix
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cheng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1207354109 SI Materials and Methods Generation of Stim1 Stim2 Double-KO Mice and Assessment of Saliva Secretion. T-cell specific deletion of Stim1 and Stim2
Supporting Information Cheng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1207354109 SI Materials and Methods Generation of Stim1 Stim2 Double-KO Mice and Assessment of Saliva Secretion. T-cell specific deletion of Stim1 and Stim2
Thirupathi Kumara Raja. S, 1 Thiruselvi. T, 1 Asit Baran Mandal, 1 Gnanamani. A, 1* Adyar, Chennai Tamil Nadu, India
 Supplementary File ph and redox sensitive albumin hydrogel : A self-derived biomaterial Thirupathi Kumara Raja. S, 1 Thiruselvi. T, 1 Asit Baran Mandal, 1 Gnanamani. A, 1* 1 CSIR-CLRI Adyar, Chennai Tamil
Supplementary File ph and redox sensitive albumin hydrogel : A self-derived biomaterial Thirupathi Kumara Raja. S, 1 Thiruselvi. T, 1 Asit Baran Mandal, 1 Gnanamani. A, 1* 1 CSIR-CLRI Adyar, Chennai Tamil
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information
 Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Surgical Adhesives in Facial Plastic Surgery
 Surgical Adhesives in Facial Plastic Surgery Dean M. Toriumi, Victor K. Chung, Quintin M. Cappelle University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL Supplement to Toriumi DM, Chung VK, Cappelle QM. Surgical
Surgical Adhesives in Facial Plastic Surgery Dean M. Toriumi, Victor K. Chung, Quintin M. Cappelle University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL Supplement to Toriumi DM, Chung VK, Cappelle QM. Surgical
Therapeutic angiogenesis via solar cell facilitated electrical
 Supporting information Therapeutic angiogenesis via solar cell facilitated electrical stimulation Gun-Jae Jeong 1,, Jin Young Oh 2,, Yeon-Ju Kim 3,, Suk Ho Bhang 4, Hyeon-Ki Jang 5, Jin Han 1, Jeong-Kee
Supporting information Therapeutic angiogenesis via solar cell facilitated electrical stimulation Gun-Jae Jeong 1,, Jin Young Oh 2,, Yeon-Ju Kim 3,, Suk Ho Bhang 4, Hyeon-Ki Jang 5, Jin Han 1, Jeong-Kee
Evaluation of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) polymer-coated dressing on surgical wounds
 J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 115 121 Original Article Evaluation of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) polymer-coated dressing on surgical wounds Osamu Katakura 1,3, Nobuyuki Morimoto 2,3, Yasuhiko
J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 115 121 Original Article Evaluation of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) polymer-coated dressing on surgical wounds Osamu Katakura 1,3, Nobuyuki Morimoto 2,3, Yasuhiko
Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis
 Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis Yan Liu 1,*, Zhipeng Han 1,*, Yingying Jing 1,*, Xue Yang 1, Shanshan Zhang 1, Chen
Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis Yan Liu 1,*, Zhipeng Han 1,*, Yingying Jing 1,*, Xue Yang 1, Shanshan Zhang 1, Chen
Mouse VEGF ELISA. Cat. No: KB2155 Ver3.0 RUO. ELISA for Accurate Quantitation from Cell Culture Supernatant, Serum, Plasma, or Other Bodily Fluids
 Mouse VEGF ELISA Cat. No: KB2155 Ver3.0 RUO ELISA for Accurate Quantitation from Cell Culture Supernatant, Serum, Plasma, or Other Bodily Fluids RUO For Research Use Only REF Catalog Number Store At Manufactured
Mouse VEGF ELISA Cat. No: KB2155 Ver3.0 RUO ELISA for Accurate Quantitation from Cell Culture Supernatant, Serum, Plasma, or Other Bodily Fluids RUO For Research Use Only REF Catalog Number Store At Manufactured
Lipopolysaccharide inhibits Th2 lung inflammation induced by house dust mite allergens in
 Online data supplement Lipopolysaccharide inhibits Th2 lung inflammation induced by house dust mite allergens in mice J. Daan de Boer, Joris J.T.H. Roelofs, Alex F. de Vos, Regina de Beer, Marcel Schouten,
Online data supplement Lipopolysaccharide inhibits Th2 lung inflammation induced by house dust mite allergens in mice J. Daan de Boer, Joris J.T.H. Roelofs, Alex F. de Vos, Regina de Beer, Marcel Schouten,
Regenerative Medicine. Speaker Disclosures. What is regenerative medicine? 6/22/2016
 Regenerative Medicine Halland Chen, MD Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am not a consultant or have any financial interests. 2 What is regenerative medicine? Regeneration of human cells, tissues,
Regenerative Medicine Halland Chen, MD Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am not a consultant or have any financial interests. 2 What is regenerative medicine? Regeneration of human cells, tissues,
بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم
 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Definition Multiple myeloma is a neoplastic plasma cell dyscrasia (PCD) that generally produced a monoclonal immunoglobulin protein, characterized by a clinical pentad: (a) anemia;
بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Definition Multiple myeloma is a neoplastic plasma cell dyscrasia (PCD) that generally produced a monoclonal immunoglobulin protein, characterized by a clinical pentad: (a) anemia;
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Montfoort, M. L. (2014). Factor XI
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Montfoort, M. L. (2014). Factor XI
Anika Therapeutics, Inc.
 Anika Therapeutics, Inc. Jefferies Global Healthcare Conference June 4, 2015 Safe Harbor Statement The statements made in this presentation that are not statements of historical fact are forward looking
Anika Therapeutics, Inc. Jefferies Global Healthcare Conference June 4, 2015 Safe Harbor Statement The statements made in this presentation that are not statements of historical fact are forward looking
Swelling Behavior Study of γ-irradiated Gelatin Hydrogels Prepared in Organic/Aqueous Mixtures
 J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 6, (2007) 997-1001 Swelling Behavior Study of γ-irradiated Gelatin Hydrogels Prepared in Organic/Aqueous Mixtures Junhwa Shin, Youn Mook Lim, Joon-Pyo Jeun, and Young Chang
J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 6, (2007) 997-1001 Swelling Behavior Study of γ-irradiated Gelatin Hydrogels Prepared in Organic/Aqueous Mixtures Junhwa Shin, Youn Mook Lim, Joon-Pyo Jeun, and Young Chang
Prof. Oded Shoseyov The Hebrew University of Jerusalem NANO BIO MIMETICS: MATERIALS FOR THE FUTURE.
 Prof. Oded Shoseyov The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Shoseyov@agri.huji.ac.il NANO BIO MIMETICS: MATERIALS FOR THE FUTURE Oded Shoseyov Our current materials, structures and machines Our current materials
Prof. Oded Shoseyov The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Shoseyov@agri.huji.ac.il NANO BIO MIMETICS: MATERIALS FOR THE FUTURE Oded Shoseyov Our current materials, structures and machines Our current materials
European Regenerative Medicine Firms & Their Strategic Approaches. Michael Morrison University of York
 European Regenerative Medicine Firms & Their Strategic Approaches Michael Morrison University of York OVERVIEW Creating the European RM Universe of firms Characterizing the European RM Universe Strategic
European Regenerative Medicine Firms & Their Strategic Approaches Michael Morrison University of York OVERVIEW Creating the European RM Universe of firms Characterizing the European RM Universe Strategic
Monitoring Pig Body Temperature Using Infrared Sensors
 Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 40(4):368-372. (2015. 12) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2015.40.4.368 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Monitoring Pig Body Temperature
Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 40(4):368-372. (2015. 12) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2015.40.4.368 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Monitoring Pig Body Temperature
RegenKit THT. Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) Reference Guide. Biologics. Concentrated on Healing
 RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) Reference Guide Biologics Concentrated on Healing Step I: Collect Whole Blood RegenKit THT Simple 4-Step Process e single use RegenKit THT is designed
RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) Reference Guide Biologics Concentrated on Healing Step I: Collect Whole Blood RegenKit THT Simple 4-Step Process e single use RegenKit THT is designed
Certified Skin & Wound Specialist Examination
 Certified Skin & Wound Specialist Examination INSTRUCTIONS Please submit the following documents to the American Board of Wound Healing: 1. Signed Attestation Statement (See attached PDF) Confirming the
Certified Skin & Wound Specialist Examination INSTRUCTIONS Please submit the following documents to the American Board of Wound Healing: 1. Signed Attestation Statement (See attached PDF) Confirming the
CHARACTERIZATION AND APPLICATION OF COLLAGEN-POLYMER BASED COMPOSITE AS WOUND HEALING MATERIAL
 th ICAMS 2012 4 International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems CHARACTERIZATION AND APPLICATION OF COLLAGEN-POLYMER BASED COMPOSITE AS WOUND HEALING MATERIAL DENİZ GÜRLER, EYLEM KILIÇ Uşak
th ICAMS 2012 4 International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems CHARACTERIZATION AND APPLICATION OF COLLAGEN-POLYMER BASED COMPOSITE AS WOUND HEALING MATERIAL DENİZ GÜRLER, EYLEM KILIÇ Uşak
Supplementary Information. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells
 Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With chronic wounds
 Autologous Platelet-Derived Growth Factors for Wound Healing (20116) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/15 Next Review Date: 07/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 05/13, 05/14,
Autologous Platelet-Derived Growth Factors for Wound Healing (20116) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/15 Next Review Date: 07/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 05/13, 05/14,
Figure legend. The expression of BAFF and its receptors in macrophages was detected at lesion areas of atherosclerosis and arthritis.
 Data supplement #1 Figure legend. The expression of BAFF and its receptors in macrophages was detected at lesion areas of atherosclerosis and arthritis. A. Consecutive sections of an atherosclerotic plaque
Data supplement #1 Figure legend. The expression of BAFF and its receptors in macrophages was detected at lesion areas of atherosclerosis and arthritis. A. Consecutive sections of an atherosclerotic plaque
York University School of Medicine, NY. Bhagavathi A. Narayanan, PhD 1, Caroline Cunnigham 1 and Amitabha Mazumder, MD 2. Title
 Title Suppression of Human Multiple Myeloma Cell Growth by TBL-12 in Combination with low doses of Velcade: Insight in to the modulation of IL-6/STAT-3 mechanisms Bhagavathi A. Narayanan, PhD 1, Caroline
Title Suppression of Human Multiple Myeloma Cell Growth by TBL-12 in Combination with low doses of Velcade: Insight in to the modulation of IL-6/STAT-3 mechanisms Bhagavathi A. Narayanan, PhD 1, Caroline
Tissue Engineered Vascular Grafts
 Tissue Engineered Vascular Grafts Jeffrey H. Lawson, M.D., Ph.D. Chief Medical Officer Humacyte Incorporated Professor of Surgery and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Disclosure Information Financial
Tissue Engineered Vascular Grafts Jeffrey H. Lawson, M.D., Ph.D. Chief Medical Officer Humacyte Incorporated Professor of Surgery and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Disclosure Information Financial
The Healing Of Tibial And Calvarial Defect Using Runx2-transfected Adipose Stem Cells
 The Healing Of Tibial And Calvarial Defect Using Runx2-transfected Adipose Stem Cells Jong-Min Lee, Ph.D. 1, Eun-Ah Kim, MS 2, Gun-Il Im, MD 2. 1 Dongguk University, Goyang, Korea, Republic of, 2 Dongguk
The Healing Of Tibial And Calvarial Defect Using Runx2-transfected Adipose Stem Cells Jong-Min Lee, Ph.D. 1, Eun-Ah Kim, MS 2, Gun-Il Im, MD 2. 1 Dongguk University, Goyang, Korea, Republic of, 2 Dongguk
Mice TRAMP mice were maintained in a C57BL/6J background. Syngeneic UBI-GFP/BL6 mice were used for bone marrow engraftment. 2
 Antibodies Chicken IgY polyclonal α-gfp antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA) and were detected using α-chicken IgY-FITC or α-chicken-hrp (also purchased from Abcam). The CD31-PE, CD11b-PE,
Antibodies Chicken IgY polyclonal α-gfp antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA) and were detected using α-chicken IgY-FITC or α-chicken-hrp (also purchased from Abcam). The CD31-PE, CD11b-PE,
Background. Background. Background. Background. Background 3/4/2013
 3/4/213 Human Very Small Embryonic-like Stem Cells (s) Capacity to Regenerate Bone Tissue: A Potential Cell-based Therapy for Autogenous Bone Grafting Aaron M. Havens, DMD Need to discover an improved
3/4/213 Human Very Small Embryonic-like Stem Cells (s) Capacity to Regenerate Bone Tissue: A Potential Cell-based Therapy for Autogenous Bone Grafting Aaron M. Havens, DMD Need to discover an improved
GSI Equine VEGF ELISA Kit-DataSheet
 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF) or vasculotropin, is a homodimeric 34-42 kda, heparin-binding glycoprotein with potent angiogenic, mitogenic
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF) or vasculotropin, is a homodimeric 34-42 kda, heparin-binding glycoprotein with potent angiogenic, mitogenic
MAXIMAL PRP BANK. Utility Model Patent Registered Apply for PCT.
 MAXIMAL PRP BANK Utility Model Patent Registered Apply for PCT www.ycellbio.de 0120 What is PRP? Platelet Rich Plasma (abbreviated PRP) is a concentration of platelet cells taken from your blood, and these
MAXIMAL PRP BANK Utility Model Patent Registered Apply for PCT www.ycellbio.de 0120 What is PRP? Platelet Rich Plasma (abbreviated PRP) is a concentration of platelet cells taken from your blood, and these
Artist Proof: Clotalyst. Autologous Serum Collection System
 Artist Proof: 01-15-10 Clotalyst Autologous Serum Collection System Clotalyst Autologous Serum The kit is designed for the preparation of autologous serum that is to be mixed with PRP and autograft or
Artist Proof: 01-15-10 Clotalyst Autologous Serum Collection System Clotalyst Autologous Serum The kit is designed for the preparation of autologous serum that is to be mixed with PRP and autograft or
How You Can Use Stem Cells
 How You Can Use Stem Cells Dr. Ralph T Bright Macquarie Cosmetic Medicine 21B Bathurst Street Liverpool NSW 2170 www.cosmeticmedicine.com.au (02) 9824 3044 Stem Cell Transfer Many of the people in this
How You Can Use Stem Cells Dr. Ralph T Bright Macquarie Cosmetic Medicine 21B Bathurst Street Liverpool NSW 2170 www.cosmeticmedicine.com.au (02) 9824 3044 Stem Cell Transfer Many of the people in this
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 The Cardiovascular System: Blood The Functions of Blood General Overview Provides a system for rapid transport within the body Nutrients Hormones Waste products Respiratory gases Cells & Blood Components
The Cardiovascular System: Blood The Functions of Blood General Overview Provides a system for rapid transport within the body Nutrients Hormones Waste products Respiratory gases Cells & Blood Components
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENT SCIENCE WEEK. St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC
 HIGH SCHOOL STUDENT SCIENCE WEEK St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC Sponsors 2 AGENDA Location: UBC James Hogg Research Centre (JHRC), St. Paul s Hospital, Room 166 Burrard Building, 1081 Burrard Street,
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENT SCIENCE WEEK St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC Sponsors 2 AGENDA Location: UBC James Hogg Research Centre (JHRC), St. Paul s Hospital, Room 166 Burrard Building, 1081 Burrard Street,
The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Survival of the Composite Graft and the Proper Time of Injection in a Rabbit Ear Composite Graft Model
 The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Survival of the Composite Graft and the Proper Time of Injection in a Rabbit Ear Composite Graft Model Hyun Nam Choi 1, Yea Sik Han 1, Sin Rak Kim 1, Han Kyeol Kim
The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Survival of the Composite Graft and the Proper Time of Injection in a Rabbit Ear Composite Graft Model Hyun Nam Choi 1, Yea Sik Han 1, Sin Rak Kim 1, Han Kyeol Kim
Human CXCL4/PF4 PicoKine ELISA Kit
 BOSTER BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY 3942 B Valley Ave, Pleasanton, CA 94566 Phone: 888-466-3604 Fax: 925-215-2184 Email: boster@bosterbio.com Web: www.bosterbio.com Human CXCL4/PF4 PicoKine ELISA Kit Catalog
BOSTER BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY 3942 B Valley Ave, Pleasanton, CA 94566 Phone: 888-466-3604 Fax: 925-215-2184 Email: boster@bosterbio.com Web: www.bosterbio.com Human CXCL4/PF4 PicoKine ELISA Kit Catalog
Database Review of Possible Factors Influencing Point-of-Care Platelet Gel Manufacture
 The Journal of The American Society of Extra-Corporeal Technology Database Review of Possible Factors Influencing Point-of-Care Platelet Gel Manufacture Jonathan H. Waters, MD;* K.C. Roberts, MS, CP, CCA
The Journal of The American Society of Extra-Corporeal Technology Database Review of Possible Factors Influencing Point-of-Care Platelet Gel Manufacture Jonathan H. Waters, MD;* K.C. Roberts, MS, CP, CCA
Catalog: DEIABL218. For the qualitative determination of antibodies to pegfilgrastim in human serum or plasma. For Research Use Only
 Pegfilgrastim ADA ELISA Kit Catalog: DEIABL218 For the qualitative determination of antibodies to pegfilgrastim in human serum or plasma. For Research Use Only 1 INTRODUCTION Filgrastim is a granulocyte
Pegfilgrastim ADA ELISA Kit Catalog: DEIABL218 For the qualitative determination of antibodies to pegfilgrastim in human serum or plasma. For Research Use Only 1 INTRODUCTION Filgrastim is a granulocyte
Anika Therapeutics, Inc.
 Anika Therapeutics, Inc. Canaccord Genuity 34th Annual Growth Conference August 14 th, 2014 Safe Harbor Statement The statements made in this presentation, which are not statements of historical fact,
Anika Therapeutics, Inc. Canaccord Genuity 34th Annual Growth Conference August 14 th, 2014 Safe Harbor Statement The statements made in this presentation, which are not statements of historical fact,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information PDGFRα plays a crucial role in connective tissue remodeling Shinjiro Horikawa 1,2, Yoko Ishii 1, Takeru Hamashima 1, Seiji Yamamoto 1,*, Hisashi Mori 3, Toshihiko Fujimori 4,
Supplementary Information PDGFRα plays a crucial role in connective tissue remodeling Shinjiro Horikawa 1,2, Yoko Ishii 1, Takeru Hamashima 1, Seiji Yamamoto 1,*, Hisashi Mori 3, Toshihiko Fujimori 4,
Importance of inflammation reaction of scaffold for the application of regenerative medicine
 Review ArticleInflammation reaction of scaffold for regenerative medicine 178 Review Article Importance of inflammation reaction of scaffold for the application of regenerative medicine Gilson Khang Department
Review ArticleInflammation reaction of scaffold for regenerative medicine 178 Review Article Importance of inflammation reaction of scaffold for the application of regenerative medicine Gilson Khang Department
Processed from Donated Human Tissue by LifeCell Corporation for KCI USA, Inc.
 for wounds instructions for use Processed from Donated Human Tissue by LifeCell Corporation for KCI USA, Inc. marketed by KCI USA, Inc. San Antonio, TX 78219 USA 800.275.4524 www.kci1.com www.graftjacketbykci.com
for wounds instructions for use Processed from Donated Human Tissue by LifeCell Corporation for KCI USA, Inc. marketed by KCI USA, Inc. San Antonio, TX 78219 USA 800.275.4524 www.kci1.com www.graftjacketbykci.com
Cat. # For Research Use. TaKaRa DEXPAT. Product Manual. v201209da_201803
 Cat. # 9091 For Research Use TaKaRa DEXPAT Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Equipment required... 2 IV. Storage... 2 V. Note... 2 VI. Protocol... 3 VII.
Cat. # 9091 For Research Use TaKaRa DEXPAT Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Equipment required... 2 IV. Storage... 2 V. Note... 2 VI. Protocol... 3 VII.
Lecture 6: Programmed/Pulsed Drug Delivery and Drug Delivery in Tissue Engineering
 Lecture 6: Programmed/Pulsed Drug Delivery and Drug Delivery in Tissue Engineering Last time: principles of controlled release from solid polymers Today: Reading: Pulsatile/regulated/multifactor controlled
Lecture 6: Programmed/Pulsed Drug Delivery and Drug Delivery in Tissue Engineering Last time: principles of controlled release from solid polymers Today: Reading: Pulsatile/regulated/multifactor controlled
SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS AND ENDORSEMENT OF NITTA CASINGS COLLAGEN GEL
 SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS AND ENDORSEMENT OF NITTA CASINGS COLLAGEN GEL 12/26/2017 For Nitta Casings TABLE OF CONTENTS About Dr. Silvia Minardi 2 Background on Collagen.. 3 Analysis of NITTA GEL. 3 Endorsement
SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS AND ENDORSEMENT OF NITTA CASINGS COLLAGEN GEL 12/26/2017 For Nitta Casings TABLE OF CONTENTS About Dr. Silvia Minardi 2 Background on Collagen.. 3 Analysis of NITTA GEL. 3 Endorsement
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental Methods:
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Skin Grafting. Biomaterials. Denis Suljendic Christian van der Pol
 Skin Grafting Biomaterials Denis Suljendic Christian van der Pol Overview Structure and function of skin History Reasons for a skin graft Traditional methods Modern solutions Future advancements 2 Structure
Skin Grafting Biomaterials Denis Suljendic Christian van der Pol Overview Structure and function of skin History Reasons for a skin graft Traditional methods Modern solutions Future advancements 2 Structure
Raw Materials: Sourcing and Qualification Testing
 Raw Materials: Sourcing and Qualification Testing Scott R. Burger, MD Advanced Cell & Gene Therapy Technical Applications Track 2 ISCT 2009 Sourcing Raw Materials Raw materials for cell/gene therapy manufacturing
Raw Materials: Sourcing and Qualification Testing Scott R. Burger, MD Advanced Cell & Gene Therapy Technical Applications Track 2 ISCT 2009 Sourcing Raw Materials Raw materials for cell/gene therapy manufacturing
Cell culture and drug treatment. Lineage - Sca-1+ CD31+ EPCs were cultured on
 Supplemental Material Detailed Methods Cell culture and drug treatment. Lineage - Sca-1+ CD31+ EPCs were cultured on 5µg/mL human fibronectin coated plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and penicillin/streptomycin
Supplemental Material Detailed Methods Cell culture and drug treatment. Lineage - Sca-1+ CD31+ EPCs were cultured on 5µg/mL human fibronectin coated plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and penicillin/streptomycin
In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit
 In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1323 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1323 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 29 July 2004 CPMP/BPWG/1089/00 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF PLASMA
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 29 July 2004 CPMP/BPWG/1089/00 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF PLASMA
