THE DELIVERY EXPERTS
|
|
|
- Caroline Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 THE COMPANY The company Polyplus-transfection, a spin-out from the laboratory of Dr. Jean-Paul Behr at the University of Strasbourg, started to market transfection reagents in Dr. Behr is considered one of the preeminent researchers in transfection who published seminal work early 1989 on the use of polycationic lipids for transfection (1) that led to the development and commercialization of several widely used transfection reagents. The first major development in the company s business is associated with the discovery of Polyethylenimine (PEI), a cationic polymer, as an important transfection reagent in 1995 (2). PEI, and its associated proton sponge transfection mechanism, is still at the heart of many modern commercial transfection reagents. Polyplus-transfection continues this strong tradition of scientific excellence and product innovation offering some of the best performing reagents for delivery of nucleic acids and proteins commercially available. The company is founded on a broad base of technical expertise ranging from physical chemistry through advanced cell biology of transfection reagents to therapeutic aspects of delivery of nucleic acids. This core competency enables the company to constantly improve existing products as well as rapidly developing and characterizing novel compounds at the leading edge of delivery. In addition, Polyplus has developed and actively maintains a global network of academic and biotech partners as well as participates in formal collaborations to share research and to develop applications of in vivo nucleic acid delivery for therapeutic purposes. Polyplus s central mission is to act as the preferred transfection technology partner for academic research laboratories, biotechnology companies and the pharmaceutical industry. Polyplus provides high quality research tools, backed up by expert consultancy and personalized scientific support to scientists worldwide. Polyplus-transfection also offers transfection reagents manufactured to cgmp-compliant standards and has a solid expertise in the regulatory and technical requirements associated with cgmp transfection reagents in pre-clinical and all phases of clinical trials. (1) J.-P. Behr, B. Demeneix, J.-P. Loeffler, J. Perez-Mutul, "Efficient gene transfer into mammalian primary endocrine cells with lipopolyamine coated DNA", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 86, 6982, (2) O. Boussif, F. Lezoualc'h, M.A. Zanta, M.D. Mergny, D. Scherman, B. Demeneix, J.P. Behr, "A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 7297, ISO 9001 Quality Management System Certification Polyplus-transfection was awarded ISO 9001 Quality Management System Certification in This certification assures our global customers that Polyplus has established reliable and effective processes for product development, manufacturing, sales and customer support, all of which are assessed by our Quality Management System. Quality standards are also decisive factors prior to launching new reagents. At Polyplus-transfection, our permanent commitment towards maintaining high quality standards is a goal that mobilizes the entire company. The ISO 9001 Certification as well as the Quality Manual can be downloaded on the Polyplus website. 2
3 Customer Support Polyplus Customer Support is available from 9 am to 5 pm Central European Time (CET), Monday through Friday (except for public holidays) on +33 (0) and through the Polyplus website by using the contact form for: Order processing Stock availability Technical Support Our friendly, helpful technical support team of hands-on experienced scientists offers you personalized support for: Up-to-date product and application information Troubleshooting Advice to help set up your DNA, sirna and protein delivery experiments Helpful guidelines for your in vivo experiments THE COMPANY The technical support team is available from 9 am to 5 pm (CET), Monday through Friday (except for public holidays) on +33 (0) and through the Polyplus website by using the contact form. At anytime, including out-of-business hours for the Technical Support Team, you can quickly and easily find valuable product information, protocols and reference papers on the Polyplus web site at If you have published a paper or poster using Polyplus products - please let us know. We would love to hear and read about your work! In return we will send a thank you gift and recommend your publication to other scientists through our web site. Product Ordering Information Polyplus-transfection products are available through a large network of distribution partners covering most countries. Purchasing from a Polyplus distributor ensures the fastest delivery possible and allows purchases to be made in local currency supported by local language specialists. Please use the Ordering Information widget on the Polyplus website and you will be redirected to the local distributor or to Polyplus online store if your country is not covered by a distributor. See Terms and Conditions on page 54. 3
4 Gene Expression RNA Interference High Throughput Screening Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Broad Spectrum Cell Specific Labeled Reagents sirna Transfection shrna Plasmid Transfection DNA & sirna Cotransfection sirna DNA jetprime 8-9 jetpei - Hepatocyte 12 jetpei - Macrophage 13 jetpei -FluoF (green) & jetpei -FluoR (red) 15 INTERFERin Technical Note: jetprime 21 Guidelines for Successful sirna Transfection using INTERFERin 20 jetprime 21 INTERFERin -HTS Technical Note: Transfection Protocols for High Throughput Screening jetpei PULSin jetpei -HUVEC 14 FectoFly (Insect cells) Technical Note: Guidelines for Successful Plasmid Transfection using jetprime 10 Tools on Cell Transfection Database Product Citations Search for transfection conditions (over 400 cell lines and primary cells available) by cell type, transfected molecule or reagent name. 11 Search the publication database with Polyplus transfection reagents by cell type, delivered biomolecule, reagent, author or your own earch terms. 55 4
5 Bioproduction In vivo Delivery Recombinant proteins Virus Classical Media Virus Serumfree Media Insect cells Qualified Reagents 41 DNA/siRNA Delivery sirna Delivery into the Brain Ligand & Labeled Reagents Preclinical & Clinical Reagents 51 Fecturin jetprime 38 Fecturin 39 FectoFly in vivo-jetpei jetsi 10 mm 50 in vivo-jetpei -Gal (galactose) in vivo-jetpei -Man (mannose) in vivo-jetpei -FluoF (green) in vivo-jetpei -FluoR (red) 50 Technical Note: Technical Note: Guildelines to set up Nucleic Acid Delivery in Mice Published Administration Routes & Targeted Organs with DNA or sirna using Polyplus Transfection Reagents Product index: by catalog number 52 by product name 53 Ordering information Transfection Reagent Selection Guide Contact our local distributor or order online if your country is not covered by a distributor. Find the appropriate reagent for your application with a link to the corresponding product page. 5
6 GENE EXPRESSION DNA jetprime transfection reagent DNA condensation and protection Binding to anionic cell-surface residues H + H + H + Proton Sponge H + H+ H + H + H + H + H + H + H + Mechanism of in vitro DNA transfection in mammalian cells using jetprime 6
7 Cationic complexes Cytoplasm Gene delivery to mammalian cells is a fundamental technique for studying regulation of gene expression and protein function. Originally calcium phosphate was used as transfection reagent. Later, various cationic liposomal formulations were developed. Although greatly improving overall efficiency, such self-aggregating formulations are now known to be unstable, often toxic and affected by the presence of serum or antibiotics. jetprime is a proprietary transfection reagent recently developed at Polyplus that offers a powerful alternative since it is not affected by these factors. Transfection with this new generation reagent achieves highly efficient gene expression using very low amounts of reagent and DNA, hence resulting in gentle transfections and reduced costs. jetprime is the perfect reagent for dayto-day transfection experiments. Cell-specific jetpei derivatives were developed to improve gene delivery to some cell types. Fluorescently labeled jetpei -FluoF and -FluoR are designed to track the intracellular fate of jetpei /DNA complexes. GENE EXPRESSION Osmotic vacuole rupture DNA release and entry into the nucleus Gene expression Nucleus Plasmid DNA transfection of a broad range of mammalian cells: jetprime Technical Note: Guidelines for successful plasmid DNA transfection using jetprime On the website: The Cell Transfection Database Cell-specific reagents: jetpei -Hepatocyte 12 jetpei -Macrophage 13 jetpei -HUVEC 14 Labeled reagents: jetpei -FluoF and jetpei -FluoR 15 7
8 jetprime Broad spectrum: DNA &/or sirna Transfection Reagent GENE EXPRESSION Powerful Economical: low amounts of nucleic acid & reagent Gentle to cells Versatile (DNA & sirna) Convenient protocol jetprime is a new versatile and powerful DNA and sirna transfection reagent for day-to-day experiments. jetprime ensures high DNA transfection efficiency and is very gentle to cells since it requires low amounts of nucleic acid and reagent during transfection. Effective and nontoxic DNA delivery is essential for reliable scientific results. Superior DNA transfection efficiency Superior transfection efficiencies ranging between 70 and 90% are obtained when using jetprime reagent versus the top competitor reagent for several commonly used cell lines (Fig. 1). % Transfection efficiency jetprime L2K HeLa Cos-7 NIH-3T3 CHO-K1 HEK-293 Fig. 1. Transfection efficiency assessed by FACS analysis in various cell lines 24 h following transfection in 24-well plates according to the manufacturer s recommendation for competitor L2K and 0.5 µg plasmid, 1 µl reagent per well for jetprime. Many other cell lines of various origins, as well as primary cells, are transfected with unusually high percentages (Table 1). Table 1. Transfection efficiency of various cell types using jetprime. The percentage of GFP-positive cells was determined by FACS analysis 24 h after transfection. Cell types Cell lines Description Transfection efficiency B16-F10 Murine melanoma 70-80% Epithelial Fibroblast BNL-Cl2 Murine normal embryonic hepatocyte 50-60% CaCO2 Human colon carcinoma epithelial 20% CHO-K1 Chinese hamster ovary 70% HCT-116 Human colon carcinoma 70% HeLa Human cervix epitheloid carcinoma 70-90% HepG2 Human hepatocarcinoma 50-70% Huh-7 Human hepatocarcinoma 30-50% MCF-7 Human breast adenocarcinoma 50% MCF-10A Human breast adenocarcinoma 40-50% MDCK Canine kidney epithelial 20% PC-3 Human prostate carcinoma 70% Vero African green monkey kidney 50% COS-7 African green monkey kidney 60-80% HEK-293 Human embryonic kidney fibroblast 80-90% MRC-5 Human lung fibroblast 50% NIH-3T3 Murine embryonic fibroblast 50-70% Macrophage Raw Murine monocyte/macrophage 40-50% Myoblast C2C12 Murine myoblast 70-90% Neuronal SH-SY5Y Human neuroblastoma 70-80% Primary Hepatocytes Human primary hepatocyte cell 20-30% Primary Melanocytes Human primary melanocyte cell 40-50% Watch the video DNA Transfection using jetprime Reagent 8
9 Economical: less reagent and less DNA jetprime is such a powerful in vitro transfection reagent that it only requires a small amount of reagent and plasmid DNA (Table 2), making it very economical. Table 2. Amounts of reagent and DNA (jetprime and competitor) added per well of a 6-well plate for transfection according to manufacturers recommendations. Reagent Volume of reagent per well Better cell viability Amount of DNA per well Number of transfections per 1.5 ml vial jetprime 4 µl 2 µg 375 L2K 10 µl 4 µg 150 In addition to reducing costs, using less DNA also minimizes adverse cytotoxic effects triggered by transfection. Hence, jetprime is the reagent of choice for high transfection efficiency with excellent cell viability. Convenient protocol jetprime is an easy-to-use transfection reagent (Fig. 3): Fast and easy to scale up and down Compatible with serum and antibiotics Dilute DNA/siRNA in jetprime buffer Add jetprime Vortex 10 s and Incubate 10 min at RT Add transfection mix GENE EXPRESSION jetprime is extremely gentle to cells during transfection leading to increased cell viability (Fig. 2) and improved transfection results. Cells transfected with jetprime are healthy, while major cytotoxicity is observed with competitor. Incubate 24 to 72 h and measure gene or protein expression Fig. 3. jetprime convenient protocol for DNA, sirna and co-transfection of DNA and sirna. jetprime is also recommended for plasmid shrna or sirna transfection, for cotransfection of sirna and plasmid DNA (see p. 21) and for virus production in classical media (see p. 38). Fig. 2. Phase contrast microscopy of HeLa cells 24 h after transfection performed according to the manufacturer s recommendations for each reagent. Product Cat N Reagent size Buffer size jetprime ml 5 ml ml 60 ml ml 2 x 60 ml x 1.5 ml 10 x 60 ml C 5 x 1.5 ml 120 ml (5x conc.) 1.5 ml of jetprime transfection reagent is sufficient to perform ca. 375 transfections in 6-well plates. Bulk quantities are available upon request. 9
10 Technical Note Guidelines for successful DNA transfection using jetprime GENE EXPRESSION Good DNA Transfection Practices Use a reporter gene to set up and optimize transfection conditions, as those may vary depending on the cells to transfect. Various reporter systems are commercially available: Renilla/Luciferase and GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) are the most commonly used. Use high quality plasmid purification kits to obtain high grade DNA, without RNA or protein, for higher transfection efficiency and improved reproducibility. Passage cells at least twice after thawing to allow recovery before transfection, and use cells at low passage number (< 20 passages). Discard cells if they have become overconfluent. Regularly check for contaminants: yeast, bacteria and mycoplasma. Check transfection efficiency before purchasing a new batch of serum or trypsin. Store appropriately jetprime (4 C) and DNA. Prepare the plasmid DNA Measure UV absorbance at 280 nm. OD260/280 ratio should reach at least 1.8. Resuspend the plasmid in deionized water or TE buffer at a concentration of ca. 1 µg/µl. Aliquot the plasmid preparation and store it at -20 C. Check for RNA contamination by agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. Tips to increase DNA transfection efficiency Increase DNA amount up to 2 folds. Test higher DNA/jetPRIME ratios such as 1:3 or 1:4. Just after transfection, centrifuge the plates 5 min at 180 g. Tips to increase cell viability Replace medium after 4 hours. Decrease DNA amount by half or more. Analyze transfection at an earlier time point (24 h after transfection instead of 48 h for instance). Check that the target gene does not affect cell viability. DNA transfection using jetprime in 6-well plates 2 µg of DNA in 200 µl of jetprime buffer Vortex 10 s and spin down Transfection tips Add 4 µl of jetprime The day before transfection, seed the cells to obtain 60-80% confluency at the time of transfection. Prior to transfection, dilute the DNA in the provided jetprime buffer first, and then add the jetprime reagent. Vortex 10 s, spin down and incubate 10 min at RT Add 200 µl of transfection mix per well 150,000 to 250,000 cells per well seeded the day before in 2 ml of growth medium If required, replace medium 4 h after transfection Incubate 24 to 48 h and measure gene or protein expression 10
11 CELL TRANSFECTION DATABASE The Cell transfection Database on... Search for transfection conditions (over 400 cell lines and primary cells available) or click on the letter of your choice. You may search by cell type, transfected molecule or reagent name. w w w Search for transfection conditions on the Cell Transfection Database 11
12 GENE EXPRESSION jetpei -Hepatocyte Cell specific: DNA Transfection Reagent for Hepatocytes Up to 50% efficiency in hepatic cell lines and primary hepatocytes Gentle to cells Easy-to-use protocol Compatible with serum and antibiotics jetpei -Hepatocyte is a DNA transfection reagent designed to transfect hepatic cells. jetpei -Hepatocyte is recommended to transfect primary hepatocytes and cell lines such as human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 and murine hepatocytes BNL-CL.2. 50% transfection efficiency and excellent viability in primary hepatocytes Primary human hepatocytes are successfully transfected with the pcmv-egfp-luc plasmid (50% transfection efficiency). In addition, cells look healthy after transfection (Fig. 4). Easy-to-use protocol Fig. 5. BNL-CL.2 cells expressing ß-galactosidase after transfection using jetpei -Hepatocyte. β-galactosidase gene expression was visualized by X-gal staining 24 h after transfection. Fig. 6. HepG2 cells expressing GFP 72 h after transfection using jetpei -Hepatocyte. HepG2 cells (50,000 cells/well in 24-well plate) were transfected with 1 µg of pcmv- EGFP-Luc using 3.2 µl of reagent, in 1 ml of complete medium containing 10% of serum. Cells expressing GFP protein were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The jetpei -Hepatocyte protocol is very simple: Mix DNA with the reagent to form complexes and simply add the mixture to the cells. jetpei -Hepatocyte is compatible with the use of serum and antibiotics. No media changes or washes are required. Protein expression is analyzed 24 to 72 hours posttransfection. Mechanism of transfection using jetpei -Hepatocyte jetpei -Hepatocyte is a linear polyethylenimine bearing galactose residues to enhance transfection of cells expressing galactose-specific membrane lectins, such as hepatocytes expressing the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGP-R or Gal/ GalNAc receptor). Cell targeting occurs upon binding of the galactose residues to the specific cell-surface receptors, leading to internalization of the DNA complexes. Fig. 4. GFP expression in primary human hepatocytes 24 h and 48 h after transfection. Primary human hepatocytes (100,000 cells in 24-w) were transfected with 1 µg of pcmv-egfp-luc using jetpei -Hepatocyte at N/P ratio of 8, in 1 ml of complete medium containing 10% of serum. Cells were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Easy transfection of hepatic cell lines The widely-used hepatic cell lines BNL-CL.2 and HepG2 are successfully transfected using jetpei -Hepatocyte, showing approximately 50% and 30% transfection efficiency, respectively (Fig. 5 and 6). Product Cat N jetpei -Hepatocyte Reagent size Amount of NaCl sol.* N 0.1 ml 5 ml N 0.5 ml 50 ml *NaCl complex-formation solution included (adapted to proper complex-formation, as indicated in the protocol). 0.5 ml of jetpei -Hepatocyte is sufficient to perform 160 transfections in 24-well plate (1 µg of DNA per well). 12
13 jetpei -Macrophage Cell specific: DNA Transfection Reagent for Macrophages Efficient transfection in macrophagederived cells and primary macrophages Easy-to-use protocol Compatible with serum and antibiotics jetpei -Macrophage transfects macrophages and macrophagelike cells that are considered difficult to transfect. It contains a mannose conjugated linear polyethylenimine that binds to cells expressing mannose-specific membrane receptors, such as macrophages. jetpei -Macrophage is also the reagent of choice for the transfection of cell lines such as RAW Transfection of primary human macrophages Easy-to-use protocol The jetpei -Macrophage protocol is very simple: mix the DNA with the reagent to form complexes and simply add the mixture to the cells. jetpei -Macrophage is compatible with the use of serum and antibiotics. No media changes or washes are required. Protein expression is analyzed 24 to 72 hours posttransfection. Product Cat N jetpei -Macrophage Reagent size Amount of NaCl sol.* N 0.1 ml 5 ml N 0.5 ml 50 ml *NaCl complex-formation solution included (adapted to proper complex-formation, as indicated in the protocol). 0.5 ml of jetpei -Macrophage is sufficient to perform 250 transfections in 24-well plate (1 µg of DNA per well). GENE EXPRESSION As shown in Figure 7, jetpei -Macrophage allows successful transfection of macrophages derived from monocytes maturated for 7 days in presence of GM-CSF. Search for transfection conditions on the Cell Transfection Database Fig. 7. Human macrophages expressing -Galactosidase after transfection using jetpei -Macrophage. INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY The use of polyethylenimine (PEI) or polypropylenimine (PPI) or cationic polymers similar in structure thereto for transfecting cells, as well as compositions comprising these cationic polymers and at least one nucleic acid, are the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 6,013,240, EP Patent No and foreign equivalents, for which Polyplus-transfection is the worldwide exclusive licensee. 13
14 GENE EXPRESSION jetpei -HUVEC Cell specific: DNA Transfection Reagent for HUVEC 50% transfection efficiency in HUVEC As efficient as electroporation Easy-to-use protocol Good cell viability Compatible with serum and antibiotics jetpei -HUVEC is a powerful transfection reagent optimized for the transfection of primary human endothelial cells such as HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells). Transfection efficiencies up to 50% have been obtained with this reagent. jetpei -HUVEC is recommended for the transfection of vascular endothelial cells hence well-suited for fragile primary cells. 50% Transfection efficiency in HUVEC Using the optimal conditions for jetpei -HUVEC (see next paragraph), transfection efficiencies of 50% have been obtained as observed with a fluorescent protein reporter gene (Fig 8). GFP staining Fig. 8. FACS analysis of HUVEC cells transfected with a plasmid encoding the EGFP fluorescent protein using jetpei -HUVEC. Transfection was performed in 24- well plate with 2 µg of plasmid and 4 µl of jetpei -HUVEC and in 2% serum. Complexes were incubated for 4 h with the cells. FACS analysis to quantify EGFP expression was performed 24 h after transfection. Optimization of the experimental conditions for high transfection efficiency The effect of serum concentration and incubation time on transfection efficiency was analyzed in HUVEC (Fig. 9). Transfection experiments performed in low (2%) or high (30%) concentrations of serum have shown that jetpei -HUVEC is most efficient when the cells are transfected in low serum concentrations. Gene expression is optimal after 4 h incubation with DNA/jetPEI -HUVEC complexes. jetpei -HUVEC is more efficient than other transfection reagents on HUVEC jetpei -HUVEC compares favorably to other non-viral transfection reagents whether cationic lipids or polyamine (Fig. 10). RLU/35,000 cells 3x10 6 2x10 6 RLU/35,000 cells Easy-to-use protocol jetpei -HUVEC protocol is very simple: Mix DNA with the reagent to form complexes and simply add the mixture to cells. jetpei -HUVEC is compatible with the use of serum and antibiotics. No media changes or washes are required. Protein expression is usually analyzed 24 to 72 hours post-transfection. Product Cat N jetpei -HUVEC 2% serum 30% serum Incubation time (hours) Fig. 9. Effect of low (2%) versus high (30%) serum concentrations on transfection efficiency of jetpei -HUVEC. HUVEC were transfected for 2, 4 or 24 h with 2 µg of pcmv-luc plasmid DNA and 4 µl of jetpei -HUVEC in 24-well plates. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h after transfection. 3x x10 6 2x x jetpei -HUVEC PF SF L2 Fig. 10. Comparison of transfection efficiency of jetpei -HUVEC and other commercially available reagents. Cells were transfected using optimal conditions established for each reagent. Reagent size Amount of NaCl sol.* N 0.1 ml 5 ml N 0.5 ml 50 ml *NaCl complex-formation solution included (adapted to proper complex-formation, as indicated in the protocol). 0.5 ml of jetpei -HUVEC is sufficient to perform 125 transfections in 24-well plates (2 µg of DNA per well) or 30 transfections in 60-mm dishes). 14
15 jetpei -FluoF & jetpei -FluoR Cell specific: DNA Transfection Reagent for jetpei -FluoF / jetpei -FluoR jetpei -FluoF and jetpei -FluoR are designed to investigate intracellular trafficking. Easy protocol Compatible with serum and antibiotics jetpei -FluoF is a fluorescein-conjugated linear polyethylenimine derivative (excitation at 490 nm; emission at 520 nm). It was especially designed to visualize transfected cells using confocal or normal fluorescence microscopy and FACS (Fig.11). jetpei -FluoR is a tetramethylrhodamine-conjugated linear polyethylenimine derivative (excitation at 555 nm; emission at 580 nm). This fluorescent jetpei is well-suited for double labeling and colocalization experiments with green labels: e.g. green fluorescent proteins, plasmids labeled with green fluorescent intercalating agent, fluorescein-oligonucleotide conjugates, etc (Fig.12). GENE EXPRESSION Fig 11. HeLa cells transfected for 24 h with jetpei -FluoF/DNA complexes and visualized by confocal microscopy. Fig 12. HeLa cells transfected for 24 h with jetpei -FluoR/DNA complexes and visualized by confocal microscopy. Product Cat N Reagent size Amount of NaCl sol.* jetpei -FluoF N 0.5 ml 50 ml *Complexes formation is perfectly performed with NaCl solution 0.5 ml of fluorescent jetpei -FluoF is sufficient to performed 250 transfections in 24-well plates. Product Cat N Reagent size Amount of NaCl sol.* jetpei -FluoR N 0.5 ml 50 ml *Complexes formation is perfectly performed with NaCl solution 0.5 ml of fluorescent jetpei -FluoR is sufficient to performed 250 transfections in 24-well plates. Search for publications on the database Product Citations INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY The use of polyethylenimine (PEI) or polypropylenimine (PPI) or cationic polymers similar in structure thereto for transfecting cells, as well as compositions comprising these cationic polymers and at least one nucleic acid, are the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 6,013,240, EP Patent No and foreign equivalents, for which Polyplus-transfection is the worldwide exclusive licensee. 15
16 sirna condensation and protection RNA INTERFERENCE INTERFERin transfection reagent sirna Cytoplasm Vacuole rupture Mechanism of in vitro sirna transfection in mammalian cells using INTERFERin Target mrna cleavage RISC 16
17 Cationic complexes Endocytosis RNA interference (RNAi) has revolutionized genetic studies and has become a popular field of study in itself as well as a major biological tool. The ability to activate or repress the expression of specific genes is crucial to gene function studies. Loss of function analyses have been greatly facilitated with RNAi and it is now possible to perform them rapidly and routinely. RNAi applications are very broad, ranging from studies of gene function and metabolic pathways to applied research including modeling of human diseases, drug screening, testing of gene-based therapies and loss-offunction screens. The mechanism of RNA interference naturally occurs in many species ranging from plants to humans. It is induced by double-stranded RNA molecules which after cleavage lead to silencing of gene expression, either by inducing sequence-specific degradation of complementary mrna or by inhibiting translation. This pathway uses two types of small RNA molecules, sirna (small interfering RNA) or mirna (micro RNA) to direct sequence-specific downregulation of target genes. Several strategies have been designed to trigger the RNAi pathway; however, the most common approaches to perform silencing studies are based on introducing synthetic sirna or mature mirna duplexes into cells, or on transfecting plasmid DNA vectors expressing short hairpins RNAs (shrnas) or micrornas (mirnas). At Polyplus-transfection, we offer two reagents suitable for most RNAi studies and other gene regulation pathways. INTERFERin is a last-generation sirna delivery reagent that achieves high transfection efficiency and hence efficient gene silencing with very low sirna concentration, thereby reducing off-target effects. INTERFERin is also recommended for the delivery of mature mirna duplexes (or mimic mirnas). jetprime is the reagent of choice for plasmid-based approaches such as shrna and mirna expression vectors. jetprime is also recommended for cotransfection of plasmid DNA and synthetic sirna or mirna duplexes. RNA INTERFERENCE sirna pool Nucleus sirna transfection: INTERFERin Guidelines for successful sirna transfection using INTERFERin 20 shrna transfection: jetprime 21 Gene silencing Co-transfection of plasmid DNA and sirna: jetprime 21 17
18 INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent RNA INTERFERENCE Great silencing at 1 nm sirna and LESS for reliable results and cost saving Over 90% gene silencing in a wide range of cell types Excellent cell viability Extremely simple protocol, compatible with serum and antibiotics Recommended for mirna duplex transfection INTERFERin is a new generation sirna transfection reagent which provides more than 90% silencing efficiency at 1 nm sirna in a large variety of cells. Less is more: with INTERFERin you ll get more valuable data using less sirna INTERFERin achieves a remarkable 90% silencing with only 1 nm sirna in the presence of serum (Fig. 13). Using subnanomolar sirna concentrations avoids unwanted toxic and off-target effects usually associated with reagents requiring higher sirna concentrations 1, 2, well plates Efficient in many cell types: Over 90% gene silencing in a wide variety of cells For adherent cell lines and primary cells, 1 nm sirna concentration is sufficient to obtain over 90% gene silencing for all genes tested. For difficult-to-transfect suspension cells, 80% silencing can still be reached with INTERFERin using 5 nm sirna (Table 3). Table 3. Successfully transfected cell lines and silencing efficiencies obtained with INTERFERin. Adherent cell lines (1nM sirna) A549 Luciferase HeLa GAPDH / Lamin A/C CaSki GAPDH / Lamin A/C MCF7 GAPDH / Lamin A/C > 90% NIH-3T3 Vimentin RAW Eg5 SiHa GAPDH / Lamin A/C HepG2 GAPDH 60-70% Primary cells (1 nm sirna) Murine embryonic fibroblasts Primary human fibroblasts Primary human hepatocytes Suspension cell lines (5 nm sirna) K562 THP-1 GAPDH GAPDH / Lamin A/C GAPDH GAPDH GAPDH > 90% > 80% As an example, transfection of 1 nm sirna duplexes targeting endogenous lamin A/C with INTERFERin reduces endogenous lamin gene expression to barely detectable levels (Fig. 14) % inhibition nm 100 pm 10 pm sirna concentration Fig. 13. INTERFERin -mediated sirna transfection inhibits luciferase expression in A549-GL3Luc cells. Cells were transfected in 24-well plates in the presence of serum with decreasing concentrations of Luciferase sirna (GL3Luc) duplexes using INTERFERin. Luciferase expression was measured after 48 h. No inhibition was observed with control sirna duplexes (mismatch GL2Luc, data not shown). Fig. 14. Endogenous Lamin A/C silencing using INTERFERin. CaSki cells were transfected with 1 nm of 21-mer sirna duplexes matching the lamin A/C sequence using INTERFERin. After 48 h, lamin A/C silencing efficiency was determined by immunofluorescence microscopy. 18
19 Extremely simple protocol INTERFERin solution is ready-to-use and the protocol is straightforward. 1 nm sirna is recommended as starting concentration for silencing of most genes and cell types (Fig. 15). INTERFERin is compatible with the use of serum and antibiotics. Forget time consuming medium changes and washes. INTERFERin can be left on the cells with no effect. 1nM sirna in serum-free medium Add INTERFERin Vortex ans incubate 10 min Add to cells in complete medium Less toxicity INTERFERin was compared to another well-known reagent. Cells transfected with INTERFERin appeared healthy under the microscope, while toxicity was evident when using reagent S (Fig. 16). Fig. 16. Comparison of cell morphology 48 h after sirna delivery using INTERFERin or competitor reagent. A549-GL3Luc cells were transfected in the presence of serum with 1 nm of GL3Luc sirna duplexes using INTERFERin or competitor S according to the manufacturer s protocol. Product Cat N Reagent size INTERFERin ml ml x 1 ml RNA INTERFERENCE 1 ml of INTERFERin is sufficient to perform transfections in 24-well plates. Incubate at 37 C and measure gene expression Fig. 15. INTERFERin standard protocol for 24-well plates. 1. Semizarov D. et al. (2003) Specificity of short interfering RNA determined through gene expression signatures. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100: Persengiev S.P. et al. (2004) Nonspecific, concentration-dependent stimulation and repression of mammalian gene expression by small interfering RNAs. RNA 10: Birmingham A. et al. (2006) 3 UTR seed matches, but not overall identity, are associated with RNAi off-targets, Nat Methods. Mar;3(3):
20 Technical Note Guideline for successful sirna transfection using INTERFERin reagent RNA INTERFERENCE Good sirna Transfection Practices Use a sirna against a housekeeping gene (GAPDH, cyclophylin B) as a positive control. Use a commercially available negative control (mismatch, non-targeting). Avoid fluorescent sirna controls when working at low sirna concentration since high sirna concentration is required for detection (20-50 nm). Use high quality desalted sirna and verify sirna concentration and annealing. Passage cells at least twice after thawing to allow recovery before transfection, and use cells at low passage number (< 20 passages). Discard cells if they have become overconfluent. Regularly check for contaminants: yeast, bacteria and mycoplasma. Check transfection efficiency before purchasing a new batch of serum or trypsin. Store appropriately INTERFERin (4 C, do not freeze) and the sirna. Know the target gene Design the sirna sequence as efficiently as possible by using several algorithms. The better the sirna, the lower the concentration needed for high silencing. Check the half-lives of the protein and of the mrna of interest to determine the best time point of analysis, or analyze at 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours after transfection. Analyze gene silencing at both the mrna and the protein level. Transfection tips The day before transfection, seed the cells to obtain 30-50% confluency at the time of transfection. Perform transfection in regular growth medium containing serum and antibiotics. Prior to transfection, dilute the sirna in Opti-MEM first, and then add the INTERFERin reagent. When using low sirna concentrations, adapt the concentration of the sirna stock solution allowing you to pipet accurate volumes. Proceed the same way for small volumes of INTERFERin : dilute 1 to 5 in sterile water. Do not incubate the sirna with INTERFERin for more than 30 minutes. Tips to increase sirna silencing Use higher sirna concentration (10, 20 or even 50 nm) and higher volume of INTERFERin. Perform transfection in half as much growth medium. Centrifuge the plate at 180 g for 5 min and replace medium after 4 hours. Tips to increase cell viability Replace medium after 4 to 6 hours. Reduce the volume of INTERFERin. Decrease sirna concentration. Transfection protocol in 24-well plates (per well and for 1 nm sirna final) 8.4 ng (0.6 pmoles) sirna into 100 µl Opti-MEM Vortex 10 s and spin down 15,000 to 35,000 cells seeded per well the day before in 1 ml growth medium Incubate at 37 C and measure gene expression Add 2 µl INTERFERin Vortex 10 s Incubate 10 min at RT Remove growth medium and replace with 0.5 ml fresh growth medium Add transfection mix to cells Opti-MEM is a trademark of Invitrogen Corporation. 20
21 jetprime sirna & shrna plasmid transfection - cotransfection of DNA + sirna Powerful and versatile Efficient gene silencing for: > sirna at 10 nm concentration > shrna plasmid transfection > cotransfection of plasmid DNA and sirna Economical: low amounts of nucleic acid & reagent Gentle to cells Convenient protocol jetprime is a new, versatile and powerful transfection reagent for day-to-day experiments. jetprime is very gentle to cells since it requires low amounts of nucleic acid and reagent during transfection. Effective and nontoxic nucleic acid delivery is essential for reliable scientific results. jetprime ensures high DNA transfection efficiency and excellent gene silencing in a variety of adherent cells. jetprime is ideal for DNA/siRNA co-transfection. Excellent gene silencing jetprime leads to over 90% knock-down of endogenous gene expression in a variety of cell lines. For example, jetprime -mediated transfection of 10 nm sirna duplexes targeting endogenous lamin A/C in HeLa cells drastically reduces gene expression to barely detectable level (Fig. 17). shrna Plasmid Transfection with jetprime RNA interference can be achieved by means other than delivery of synthetic sirna,. e.g. using plasmid-based methods. For transfection of plasmids expressing small hairpin RNA (shrna), the standard transfection method using jetprime (see page 8-9) is applicable and ensures reliable transfection efficiency. Cotransfection of DNA & sirna with jetprime jetprime is the best reagent for gene (see page 8-9) and sirna co-transfection experiments. It shows highly efficient gene silencing in a variety of cell lines with very low toxicity. Over 90% silencing is achieved in adherent cells, using 10 nm sirna (Fig. 18). luciferase gene silencing (%) well plates HeLa PC-3 HEK-293 Fig. 18. Exogenous luciferase gene silencing in several cell lines after DNA & sirna cotransfection using jetprime performed with 400 ng pcmv-luc and 10 nm of sirna anti-luc per well in 6-well plates. Product Cat N Reagent size Buffer size ml 5 ml ml 60 ml jetprime ml 2 x 60 ml x 1.5 ml 10 x 60 ml C 5 x 1.5 ml 120 ml (5x) RNA INTERFERENCE 1.5 ml of jetprime transfection reagent is sufficient to perform ca. 375 transfections in 6-well plates. Bulk quantities are available upon request. Fig. 17. Endogenous lamin A/C silencing using jetprime. HeLa cells were transfected with 10 nm of 21-mer sirna duplexes matching the lamin A/C sequence. After 48 h, lamin A/C silencing efficiency was determined by immunofluorescence microscopy using an antibody against lamin A/C. 21
22 HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING 22
23 Conducting high throughput transfections enables to screen sirna, shrna or plasmid DNA libraries, among others for pathway analysis or drug discovery. This method requires the use of robust reagents that offer specific features such as reducing global time to results with the use of a reverse transfection protocol. Moreover, HTS transfection reagents must show high efficiency and reproducible results. To this goal, Polyplus recently developed INTERFERin -HTS, a reagent that is fully dedicated to sirna HTS transfection. jetpei is recommended for DNA HTS transfection, owing to its robustness and remarkable reproducibility. HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING sirna HTS Transfection: INTERFERin -HTS DNA HTS Transfection: jetpei Technical Note: Transfection protocols for High Throughput Screening
24 INTERFERin -HTS sirna Transfection Reagent for HTS Applications HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING Great silencing at low sirna concentration Designed for automated procedures Reproducible at all levels Small volume of reagent per well Cost effective INTERFERin -HTS is a new generation sirna transfection reagent especially developed for high throughput screening (HTS) applications providing great silencing efficiency, excellent reproducibility and high cell viability with very low amounts of reagent. INTERFERin -HTS is cost-effective, easy to handle, compatible with the use of serum and antibiotics, and comes with reverse and forward protocols for 96- and 384-well plates. Efficient gene silencing with low cytotoxicity using a standard phenotypic assay INTERFERin -HTS leads to over 90% cell death in a standard phenotypic cell death assay, using 10 nm of a cell deathinducing PLK1 sirna (Fig. 19). The assay is significant, as INTERFERin -HTS shows minimal cytotoxicity (89% ± 7% cell viability) with non-targeting sirna. Relative cell viability (%) Untransfected Negative Cell death inducing- cells control sirna sirna (PLK1) The highest efficiency Transfection of a sirna targeting endogenous lamin A/C using INTERFERin -HTS leads to higher silencing efficiency than the same experiment performed with three other popular transfection reagents (Fig. 20). Silencing / negative control (%) Reagent L Reagent D Reagent H Fig. 20. sirna transfection with INTERFERin -HTS gives higher silencing efficiency than competitor reagents. HeLa cells were transfected in 96-well plates with 10 nm sirna duplexes targeting lamin A/C following a reverse transfection protocol according to the manufacturer s recommendations. Lamin A/C expression was measured 24 hours after transfection by branched DNA assay and normalized to GAPDH expression. Especially designed for automated procedures INTERFERin-HTS Easy to use: the reagent is an aqueous solution stored at 4 C with a shelf-life of one year, compatible with the use of both serum and antibiotics. Working solution of INTERFERin -HTS diluted in ddh 2 O is stable for more than a week. sirna/interferin -HTS complexes are stable up to 8 hours at room temperature. sirna/reagent complexes can be frozen and stored at -80 C in plates. Reverse and forward protocols are provided for 96- and 384-well plates. Fig. 19. Highly efficient sirna-induced cell death in HeLa cells in 384-well plates using INTERFERin -HTS. HeLa cells were transfected with sirna inducing cell death (PLK1) and negative control (non-targeting sirna) following a reverse transfection protocol (10 nm sirna; 0.05 µl INTERFERin -HTS per well). Cell viability was measured by automated fluorescent microscopy after DAPI staining 72 hours after transfection (Data kindly provided by the Transfected Cell Arrays Platform IGBMC-CERBM, Illkirch, France). 24
25 Robust - Reproducible INTERFERin -HTS gives highly reproducible results at all levels: Well to well The data presented in Figure 19 were done in triplicate yielding a very small standard deviation and highly significant comparisons. One experiment to the next Three independent transfection experiments using the same batch of INTERFERin -HTS show identical silencing efficiencies (Fig. 21). Batch to batch Transfection using three different batches of INTERFERin -HTS shows highly consistent results (Fig. 22). With INTERFERin -HTS, your results are reliable. Silencing / negative control (%) Silencing / negative control (%) Experiment #1 Experiment #2 Experiment #3 Fig. 21. Experiment to experiment reproducibility in 96-well plates. A549 cells stably expressing the luciferase gene were transfected with 10 nm GL3Luc sirna and negative control duplexes using 0.05 µl of INTERFERin -HTS in 3 independent experiments. Luciferase expression was measured 48 hours after transfection Batch PN04208 Batch PN04127 Batch FSIV284 Fig. 22. Batch to batch reproducibility in 96-well plates. A549 cells stably expressing the luciferase gene were transfected with 10 nm GL3Luc sirna duplexes and negative control using 0.05 µl of INTERFERin -HTS from 3 different batches. Luciferase expression was measured 48 hours after transfection. Lower reagent volume per well More transfections per vial Higher inhibition of gene expression is obtained with INTERFERin -HTS using lower amounts of reagent than competitors; at least twice as many plates can be transfected with the same vial size (Table 4). Table 4. Volume of reagent (INTERFERin -HTS and competitors) required per well in 96-well plates and number of transfected plates with 1.5 ml reagent size, according to the manufacturer s recommendations for sirna reverse transfection. 1.5 ml reagent size Volume of reagent per well (µl) in 96-well plates Number of transfected 96-well plates INTERFERin -HTS Reagent L Reagent H Reagent D Product Cat N Reagent size INTERFERin ml -HTS x 1.5 ml 1.5 ml of INTERFERin -HTS transfection reagent is sufficient to transfect plates (96-well). HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING 25
26 jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS Applications HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING Fast and efficient methods to transfect cells for HTS Exceptionally reproducible results Well-suited for automated approaches Compatible with serum and antibiotics Reverse, batch & forward protocols available jetpei transfection reagent forms robust transfection complexes with DNA, providing highly effective and reproducible plasmid delivery for several hours. jetpei transfection reagent is therefore particularly well suited for automated or manual HTS (High Throughput Screening) with three protocols available: reverse, batch and forward. Three protocols to suit your application The Reverse protocol is the most appropriate when transfecting a pool of genes, such as a DNA library (Fig. 23). In this protocol, the jetpei /DNA complexes are prepared or deposited in the wells prior to addition of the cells. Complexes are stable for up to 4 hours (Fig. 24). The Batch protocol was developed to prepare a homogeneous pool of transfected cells. For this purpose, the cells are transfected just after trypsinization, while still in suspension. This protocol is preferred for drug screening applications and allows rapid processing, one day faster than the forward protocol. Following the Forward protocol, cells are split the day before transfection and the jetpei /DNA complexes are added to the adherent cells. DAY 1 Prepare the cells Transfect and Plate DAY 2 Assay Add jetpei /DNA complexes to the plate Prepare jetpei /DNA complexes Incubate 24 to 72 h at 37 C Measure gene or protein expression Robust transfection complexes Complexes formed with the water-soluble polymer jetpei and DNA allow efficient transfection for up to 4 hours, in contrast to lipid-based reagents and calcium phosphate. Thus they allow plenty of time to dispense the complexes into the plates (Fig. 24). Transfection efficiency (RLU/well) Fig. 23. jetpei reverse protocol for HTS applications Cells alone 0 15 min q Trypsinize cells Add cells to the plate containing complexes Efficient jetpei/dna complexes 30 min 1h 2h 3h 4h Incubation time for complex formation Fig. 24. Effect of complex formation incubation time on transfection efficiency with jetpei. HEK 293 cells were transfected in 96-well plates in the presence of 10% serum with pcmv-luc following the reverse transfection protocol. Luciferase assays were performed 24 h after transfection. 26
27 Batch to batch reproducibility HTS DNA transfection using jetpei gives highly consistent transfection efficiency from batch-to-batch (Fig. 25). Transfection efficiency (RLU/mg prot) Fig. 25. Batch to batch reproducibility using jetpei. For each lot, HeLa cells were transfected in triplicate in the presence of 10% serum using the standard protocol. Efficient in a wide range of cell types jetpei successfully delivers plasmid DNA to various cell lines, as well as primary cells (Table 5). Over 400 publications using jetpei can be found in the Product Citation Database on the Polyplus website. In addition, a Cell Transfection Database gives specific transfection conditions for over 400 cell lines and primary cells. Table 5. Some common cell lines and primary cells successfully transfected using jetpei. 3T3-21 A549 B BHK Lot # COS-1 COS-7 CV-1 HeLa NIH-3T3 PC12 RAW SiHa Primary hepatocytes Primary human fibroblasts Primary keratinocytes Primary pre-adipocytes Superior transfection results jetpei was compared to several other popular transfection reagents (Fig. 26). jetpei was found to offer the best performance: high efficiency and low variability (small standard deviation). Transfection efficiency (RLU/mg prot) jetpei L1 P1 L2 L3 L4 P2 L5 L6 L7 Fig. 26. Transfection efficiency of a series of commercial reagents. HeLa cells were transfected with pcmv-luc in the presence of 10% serum according to the manufacturers protocols. Luciferase assays were performed 24 h after transfection. Product Cat N Reagent size Amount of NaCl sol.* N* 0.1 ml 5 ml ml N* 1 ml 50 ml jetpei x 1 ml N* 4 x 1 ml 4 x 50 ml 101B ml - 101B-010N* 10 ml 2 x 250 ml 1 ml of jetpei is sufficient to perform 1200 to 1600 transfections in 96-well plates. Bulk quantities available upon request. *When included, the NaCl complex-formation solution is adapted to proper complex formation, as indicated in the protocol. HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING BNL CL.2 HEK293 SK-N-MC C2C12 HepG-2 SKOV3 CaCo2 CHO MCF-7 MRC-5 VERO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY The use of polyethylenimine (PEI) or polypropylenimine (PPI) or cationic polymers similar in structure thereto for transfecting cells, as well as compositions comprising these cationic polymers and at least one nucleic acid, are the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 6,013,240, EP Patent No and foreign equivalents, for which Polyplus-transfection is the worldwide exclusive licensee. 27
28 Technical Note Transfection protocols for high throughput screening (HTS) HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING For sirna transfection: INTERFERin -HTS (see page 24-25) For DNA transfection: jetpei (see page 26-27) Fast and efficient methods to transfect cells for HTS Reproducible: guaranteed quality from batch to batch No medium changes required, since both jetpei and INTERFERin -HTS are compatible with serum and antibiotics Transfection in the presence of antibiotics decreases the risk of contamination in HTS How to choose the best protocol Our HTS dedicated transfection reagents can be used efficiently with three different protocols depending on the experiment: Reverse protocol: The most appropriate when transfecting a DNA or a sirna library. In this protocol, the transfection complexes are prepared or deposited in the wells prior to addition of the cells. Transfection complexes formed with jetpei or INTERFERin -HTS are stable for up to 4 hours. The reverse protocol is the most commonly used for HTS applications. Batch protocol: Developed to prepare a homogeneous pool of transfected cells. For this purpose, the cells are transfected just after trypsinization, while still in suspension. This protocol is prefered for drug screening applications and allows rapid processing, one day faster than the forward protocol. Forward protocol: Cells are split the day before transfection and the transfection complexes are added to the adherent cells. Reverse HTS Protocol Well-suited for plasmid or sirna library screening approaches and automated cell distribution Transfection complexes are deposited or prepared in the wells prior to cell distribution Adaptable to any plate size (from 96- up to well plates) Easy and straightforward 2-step protocol DAY 1 Transfect DAY 2-4 Assay Add transfection complexes to the plate Measure gene or protein expression Prepare transfection complexes Incubate 24 to 72 h at 37 C q Trypsinize cells Add cells to the plate containing complexes 28
29 Batch HTS Protocol Well-suited for drug screening requiring one cell line transfected with the same plasmid or sirna Cell plating and transfection are performed on the same day Ideal to ensure homogenous and reproducible transfection Easy and straightforward 2-step protocol DAY 1 Transfect DAY 2-4 Assay Add transfection complexes q Trypsinize cells Cells in suspension Vortex gently Measure gene or protein expression Distribute cells and transfection complexes to plate Incubate 24 to 72 h at 37 C Forward HTS Protocol Cells are plated the day before transfection and transfection complexes are added to the cells the next day Very gentle to cells, recommended for all type of cell lines, including sensitive cells 3-step reproducible and straightforward protocol DAY 1 Prepare the cells DAY 2 Transfect DAY 3-5 Assay Measure gene or protein expression Plate cells 24 h prior to transfection q Add transfection complexes to plate Incubate 24 to 72 h at 37 C HIGH THROUGHPUT SCREENING 29
30 PROTEIN, ANTIBODY & PEPTIDE DELIVERY Mechanism of protein, antibody and peptide delivery using PULSin Proteins Complex formation Cellular uptake PULSin delivery reagent Endosome formation 30
31 Cytoplasm Protein diffusion Specific cellular localization Nucleus Protein delivery is emerging as an interesting technique that complements gene transfection and RNA interference for studying protein function and cellular pathways. Moreover, delivery of antibodies allows staining in live, non-fixed cells or silencing at the protein level (similar to intrabodies). Unlike nucleic acids, proteins display a large variety of structures and electric charges, which make a general delivery solution problematic. Protein delivery reagents function by one of two mechanisms: chemical reactions of the protein with a polycation or complex formation with amphiphilic peptides or lipids; the goal being to convert the protein into a polycation for subsequent cell binding and entry via anionic adhesion molecules. Since cell binding and entry are not limiting steps for polycationic delivery, we concentrated our efforts on the last step, i.e., intracytoplasmic release, using our previous experience with amphiphilic endosomereleasing agents. PULSin delivery reagent contains a cationic amphiphile and is efficient with proteins that are able to associate with it through electrostatic and/or lipophilic forces, as is the case for anionic proteins (i.e. proteins having an isoelectric point <7), and thus includes antibodies. Yet delivery is not restricted to anions, as most proteins have a lipophilic core. PULSin PROTEIN, ANTIBODY & PEPTIDE DELIVERY 31
32 PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent PROTEIN, ANTIBODY & PEPTIDE DELIVERY Delivery of functional protein, antibody & peptide into the cell Delivery to a wide variety of cells including primary cells Highly efficient transfer Easy-to-use The delivery of protein 1-2, antibody 3-6 and peptide 7-8 using PULSin represents a powerful approach for functional studies. For example, PULSin enables the study of lethal proteins by controlling the level and time course of protein delivery into the cells. Similarly, delivery of blocking antibodies may provide additional information to traditional RNA interference experiments. With PULSin, it is possible to target intracellular proteins with antibodies in living cells without fixation. Efficient delivery of proteins and antibodies to the cytoplasm PROTEINS PULSin was shown to deliver R-phycoerythrin, a fluorescent protein (240 kd) to the cytoplasm of up to 98% cells. As shown in Figure 27, the protein is evenly distributed in the cytoplasm and excluded from the nucleus due to its large size. Fig. 27. PULSin -mediated intracellular delivery of R-phycoerythrin to NIH-3T3 cells. R-phycoerythrin (1 µg) was complexed with 4 µl of PULSin for 15 min and added to NIH-3T3 cells in a 24-well plate. Live cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy after 16 h. ANTIBODIES Antibodies were also successfully delivered to a variety of cells and able to recognize their target protein inside the cytoplasm. For example, anti-giantin Alexa Fluor 488 was delivered using PULSin to the cytoplasm of 98% of live HeLa cells, labeling the Golgi apparatus (Fig. 28). Similarly, PULSin permits the delivery of bloking antibodies into human cancer cell lines 3 and primary mouse Sertoli cells 4. Antibody delivery may also be used for localization studies 5. PEPTIDES Peptides are biomolecules acting with high specificity at low concentrations. The delivery of substrate, inhibitor, modulator, or blocking peptides into cells allows protein function studies as well as development of therapeutic approaches. PULSin was shown to successfully deliver anionic peptides such as Streptococcus TPE B epitope into HeLa cells (Fig. 29) as well as functional peptides into neurones Weill C. 0. et al. (2008). A practical approach for intracellular protein delivery, Cytotechnology 56: Spagnolo J.F. et al. (2010). Enzymatic and nonenzymatic functions of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases within oligomeric arrays, RNA 16(2): Cassinelli G. et al. (2006). Inhibition of c-met and prevention of spontaneous metastatic spreading by the 2-indolinone RPI-1, Mol Cancer Ther 5(9): Ying M. et al. (2007). Nuclear import of human sexual regulator DMRT1 is mediated by importin-beta, Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(6): Cortes C. et al. (2007). Chlamydia pneumoniae inclusion membrane protein Cpn0585 interacts with multiple Rab GTPases, Infect Immun 75(12): Okamoto T. et al. (2011). Connexin32 protects against vascular inflammation by modulating inflammatory cytokine expression by endothelial cells, Exp Cell Res 317(3): Leshchyns ka I. et al. (2006). The adhesion molecule CHL1 regulates uncoating of clathrin-coated synaptic vesicles, Neuron 52(6): Weiss A. et al. (2011). Intracellular peptide delivery using amphiphilic lipid-based formulations, Biotechnol Bioeng, Fig. 28. Golgi labeling (green) of HeLa cells 24 h after delivery of 1 µg Alexa Fluor 488 anti-giantin using PULSin. Plasma membrane was stained with ConA-rhodamine. Cells were observed by confocal microscopy. Fig. 29. Delivery of Pep-A (Streptococcus TPE B epitope, 16 aa), into HeLa cells. Complexes were formed with Pep-A (1 µg, lissamine-rhodamine derivative, Sigma) and PULSin (4 µl). Observation was carried out 16 h post-delivery. 32
33 Delivery to a wide variety of cells PULSin was shown to deliver proteins and antibodies and peptides to a large variety of cell lines and primary cells (Table 6, Fig ). Table 6. Efficiency of R -phycoerythrin delivery using PULSin in selected cells. Adherent cell lines 3T3 L % HepaRG 60-70% A549 80% HepG2 20% BHK % MCF % CaSki 80-90% MLE % CHO 80-90% NIH-3T % CV-1 50% RAW % HEK % SiHa 60-70% HeLa 80-90% Suspension cell lines HEK % K % Jurkat 70% THP-1 10% Adherent primary cells Human fibroblasts 60-70% Human hepatocytes 50-40% Human keratinocytes 55-70% Human visceral preadipocytes 60-75% Primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) 80% PULSin is easy to use and fast PULSin will save you time and effort compared to other techniques using viral transduction or chemical conjugation (Fig. 30). Protein (1 µg) in 100 µl Hepeses Incubate 15 min at RT Add to well containing cells Incubate 4 h Add PULSin (4 µl) Fig. 30. PULSin delivery protocol for 24-well plates (per well). PULSin reagent is ready-to-use and provided with a dilution buffer and a fluorescent control protein (R-phycoerythrin). Simply add the reagent to the protein, incubate and add to the cells. Cells can be analyzed starting 4 hours post-delivery. Highly efficient transfer The comparison of PULSin with two other protein delivery reagents shows a higher efficiency of protein delivery (Fig. 31). Moreover, the amount of protein delivered per cell is higher with PULSin as measured for R-phycoerythrin protein (Fig. 32). PULSin % of gated cells x Mean fluorescence intensity (AU) Fig. 31. Comparison of PULSin efficiency with two other protein delivery reagents. R-phycoerythrin (1 µg) was complexed with each reagent according to the manufacturer s protocol. Complexes were added to HeLa cells and observed by fluorescence microscopy over 24 hours. 1 µg R-phycoerythrin Autofluorescent cells Positive cells Control cells PULSin Reagent B Reagent C Fig. 32. FACS analysis of HeLa cells after delivery of R -phycoerythrin with PULSin or with competitor reagents B and C. Data are presented as histograms of the mean intensity of fluorescence for each cell population (AU= Arbitrary Units). Product Cat N Reagent Nb. of reactions in 6-well plates * 0.1 ml 6 PULSin * 0.4 ml ** 4 x 0.4 ml 96 * This kit contains 20 µg of R-Phycoerythrin (positive control) and 20 ml of Hepes dilution buffer. ** This kit contains 20 µg of R-Phycoerythrin (positive control) and 4 x 20 ml of Hepes dilution buffer. PROTEIN, ANTIBODY & PEPTIDE DELIVERY 33
34 BIOPRODUCTION 34
35 Transfection of mammalian and insect cells is a widely used means of producing biomolecules such as recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, viral vectors and vaccines. With increasing regulatory demands for the production of human therapeutics, high quality grade reagents are required for both cell culture media and transfection reagents. Polyplus-transfection offers a range of transfection reagents to suit your needs for recombinant protein and virus production at small, medium and large scale: Fecturin is especially designed for highly efficient transfection in serum-free synthetic media, for recombinant protein or virus production in mammalian cells. jetprime is the reagent of choice when using classical cell culture media. Finally, FectoFly is dedicated to baculovirus or protein production in insect cells. BIOPRODUCTION As high quality grade products are required for the production of human therapeutics, Polyplus-transfection supplies upon request qualified transfection reagents with the required appropriate documentation. Recombinant Protein Production: Fecturin Virus production in Classical Media: jetprime 38 Virus production in Serum-free Media: Fecturin 39 Protein Production in Insect Cells: FectoFly Qualified Reagents 41 35
36 Fecturin DNA Transfection Reagent for Recombinant Protein Production BIOPRODUCTION High yields of recombinant protein in HEK-293, CHO, and derivatives (HEK EBNA, CHO DG44 ) Specifically designed for cells grown in suspension in synthetic media Guaranteed free of animal-origin material Easy process upscale Fecturin is a transfection reagent specifically designed for high yield recombinant protein production in mammalian cells grown in suspension in serum-free synthetic media. Fecturin is perfectly suited to achieve high yield protein production with HEK-293 and CHO cell lines (fig. 33) as well as derivatives such as HEK EBNA and CHO DG44. Fecturin is chemically defined and does not contain any component of animal-origin. Luciferase production (ng luciferase/10 6 cells/ml/day) LP1 Fecturin Fig. 34. Comparison of protein expression levels after transfection of HEK-293 cells with Fecturin and LP1 reagent. Suspension cells were seeded at 1 million per ml in FS medium and incubated at 37 C, 8% CO 2 with constant shaking. Cells were transfected with Fecturin or LP1 following the manufacturer s recommendations. Luciferase protein content is quantified 24 h post-transfection. High yields of protein production in CHO cells in suspension Fecturin results in high yields of protein production in CHO suspension culture when compared to a well-known lipid, LP2, in two different commercially available synthetic media (Fig. 35). Up to 9 µg of luciferase 10 6 cells/ml/day was produced using Fecturin in C-CHO medium. HEK-293 cells CHO cells Fig. 33. Transfection of HEK-293 and CHO using Fecturin. Cells were seeded at 1 million per ml in either FS or C-CHO media, two commercially available synthetic media. HEK-293 or CHO cells were transfected with pcmv-egfp plasmid following the standard Fecturin protocol. Cells were visualized by fluorescent microscopy 24 h post-transfection. Highly efficient for HEK-293 cells in suspension High yields of secreted VEGF were obtained following transfection with Fecturin in FS commercial synthetic medium (400 ng VEGF /10 6 cells/day). Moreover, Fecturin compares favourably to the commercially available reagent LP1 for the transfection of HEK-293 cells in suspension in FS synthetic medium (Fig. 34). Luciferase production (RLU/10 6 cells/ml/day) LP2 Fecturin LP2 Fecturin I-CHO C-CHO Fig. 35. Comparison of protein expression levels after transfection of suspension CHO cells with Fecturin and LP2 in two commercially available synthetic media. Cells were seeded at 1 million per ml in either I-CHO or C-CHO synthetic media and incubated at 37 C, 8% CO 2 with constant shaking. Cells were transfected with Fecturin or LP2 following the manufacturer s recommendations. Luciferase expression (RLU) was assayed 24 h after transfection. 36
37 Stable protein production over several days Upon transfection of CHO cells with Fecturin, the daily expression of secreted VEGF increases over four days (Fig. 36). VEGF production (ng VEGF/10 6 cells/ml) days after transfection Easy scale-up of protein production Protein production in suspension culture of CHO cells can be easily scaled-up with Fecturin. Fecturin -mediated transfection leads to 10 µg of VEGF/10 6 cells /ml /day (Fig. 38) in 500 ml suspension culture of CHO. The yield in protein production per ml increases significantly as the cell culture volume is scaled up. VEGF production (µg VEGF/10 6 cells/ml) volume of culture (ml) BIOPRODUCTION Fig. 36. Daily VEGF production in suspension CHO cells. Cells were seeded at 1 million per ml in C-CHO synthetic medium and incubated at 37 C, 8% CO 2 with constant shaking. Cells were transfected with a VEGF expressing plasmid according to the standard protocol. Culture medium was replaced every day. VEGF protein production was quantified by ELISA. Fig. 38. VEGF production in increasing volumes of culture. CHO cells were seeded at 1 million per ml in increasing volumes of C-CHO synthetic medium and incubated at 37 C, 8% CO 2 with constant shaking. Cells were transfected with a VEGF expressing plasmid according to the standard protocol. VEGF protein production was quantified by ELISA, 2 days after transfection. The cumulative VEGF production also increases steadily over 9 days (Fig. 37). VEGF production (ng of VEGF/10 6 cells/ml) days after transfection Fig. 37. Cumulative VEGF production in CHO cells in suspension. Cells were seeded at 1 million per ml in C-CHO synthetic medium and incubated at 37 C, 8% CO 2 with constant shaking. Cells were transfected with a VEGF expressing plasmid according to the standard protocol. VEGF protein production was quantified by ELISA. Product Cat N Unit Amount of transfected DNA Fecturin ml 0.3 to 1 mg Bulk quantities available upon request. 37
38 jetprime Transfection Reagent for Virus Production in Classical Media BIOPRODUCTION High transfection efficiency in adherent cells High viral titers Suitable for multiple plasmid cotransfections Requires small amounts of DNA Compatible with both serum and antibiotics jetprime transfection reagent is highly effective for routine virus production in adherent cells grown in classical media such as DMEM in the presence of serum. High transfection efficiency Transfection efficiency using jetprime reaches up to 90% in cells commonly used for virus production, such as HEK 293 and derivatives, CHO, VERO and BHK cells. Hence, jetprime is the reagent of choice for viral expression vectors transfection, leading to high viral titers. Suitable for multiple plasmid cotransfection Virus production often requires the simultaneous transfection of multiple plasmids to form viral particles. With its ability to efficiently compact several DNA molecules into positively charged transfection complexes, jetprime is perfectly suited for multiple plasmid cotransfection. Requires small amounts of DNA As shown on page 8-9, jetprime is highly efficient and only requires small amounts of DNA for high transfection efficiency in adherent cells commonly used for virus production. Easy to use jetprime comes with an easy and straightforward protocol. It is compatible with the use of both serum and antibiotics, avoiding the need for media changes and facilitating the manipulation of a large number of vessels. High viral titers jetprime gives high viral titers for both AAV and lentivirus production using small amounts of DNA. Product Cat N Reagent size Buffer size jetprime ml 5 ml ml 60 ml ml 2 x 60 ml x 1.5 ml 10 x 60 ml C 5 x 1.5 ml 120 ml (5x) 1.5 ml of jetprime transfection reagent is sufficient to perform ca. 375 transfections in 6-well plates. Bulk quantities are available upon request. 38
39 Fecturin DNA Transfection Reagent for Virus Production in Serum-free Synthetic Media Superior viral titers Specifically designed for cells grown in serum-free synthetic media Guaranteed free of animal-origin material Batch to batch reproducibility Suitable for multiple plasmid cotransfections Fecturin transfection reagent is well-suited for virus production in serum-free synthetic media. It performs high transfection of the most commonly used virus producing and packaging cell lines grown in synthetic media. Fecturin is chemically defined and thus does not contain any component of animal-origin. Superior viral titers in serum-free synthetic media Fecturin condenses multiple plasmid DNA into cationic complexes ensuring high DNA transfection efficiency (above 70%) as well as high viral titers. Due to its high DNA transfection efficiency combined with a low toxicity, high viral production can be kept over several days. Most commonly cells used for virus production including HEK- 293, HEK EBNA, HEK-293T, NIH-3T3, CHO, VERO, MCDK and BHK-21 cells are successfully transfected with Fecturin. Batch to batch reproducibility Our ISO 9001 certification ensures high quality grade as well as batch to batch reproducibility. Fecturin is thoroughly tested and validated according to stringent procedures. With Fecturin, reproducibility of virus production in routine and large scale is guaranteed. Easy to implement in your lab Fecturin is ideal for all type of cell culture flasks and containers including tissue culture flasks, cell factories and multitrays, bags, spinner flasks, shaker flasks and bioreactors. The protocol is straightforward and easily scalable (Fig. 39). Simple protocol: 2 µg of total DNA + 2 µl of Fecturin per ml of culture Plasmids in medium q q q Add to cells Add Fecturin in medium Vortex and centrifuge Incubate min at RT Collect supernatant and perform virus titration Expected virus titration > TU per L of culture for AAV Fig. 39. Virus production protocol using Fecturin. Perfectly suited for biomanufacturing processes In addition to its exceptional batch to batch reproducibility, Fecturin also presents the advantage of limiting DNA carryover thanks to its high transfection efficiency, leaving little DNA on the outer layer of the cell surface. As a result, the downstream purification step is facilitated, saving time and money. Fecturin is chemically defined and does not contain any component of animal-origin, hence suitable for virus bioproduction for therapeutic purposes. BIOPRODUCTION Fecturin transfection reagent is specifically designed for serum-free and chemically defined synthetic media. In addition, Fecturin is compatible with antibiotics, thus reducing time consuming media changes required with other transfection reagents. Product Cat N Unit Amount of transfected DNA Fecturin ml 0.3 to 1 mg Bulk quantities available upon request. 39
40 FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells BIOPRODUCTION Global transfection solution for insect cells High protein expression and baculovirus production High transfection efficiency in both adherent and suspension insect cells Guaranteed free of animal-origin material FectoFly is a DNA transfection reagent dedicated to insect cells for high level transgene expression leading to high yield production of baculovirus and recombinant proteins. Adapted to a range of insect cells FectoFly provides high transfection efficiency in most commonly used insect cells (Fig. 41) allowing efficient protein production. Luciferase production (ng luciferase/mg prot) Protein production levels Sf9 Sf21 S2 Tn5 Cell lines Fig. 41. Comparison of FectoFly in various adherent cell lines. Sf9, Sf21, S2 or Tn5 adherent cells were transfected with pcmv-egfp-luc plasmid using FectoFly. Luciferase assays were performed 72 h after transfection. Suitable for both adherent and suspension cells Robust protein production By simple and rapid transient transfection method, FectoFly provides high transfection efficiency in insect cells and robust protein production over several days (Fig. 40). FectoFly allows successful transfection of adherent and suspension insect cell cultures both in the latest generation of synthetic serum-free media (Fig.40, 42 - Sf21 and Sf9) and in the presence of serum (Fig.42 - S2). Transfection efficiency ranges routinely from 30% to 50% and cell viability is above 80%. 6 Luciferase production (ng luciferase/ml of culture) days after transfection Fig. 40. Protein production in S2 cells over 5 days using FectoFly transfection reagent. Cells were seeded at 10 6 cells/ml in Insect-XPRESS medium (Lonza) and transfected with pcmv-egfp-luc using FectoFly. Luciferase assays were performed 1 to 5 days after transfection. Fig. 42. GFP expression in Sf21, Sf9 cells grown in suspension and in S2 cells grown in the presence of serum, 72 h after transfection of pcmv-egfp-luc plasmid using FectoFly. 40
41 Superior protein production levels FectoFly was compared to other commercially available reagents dedicated to the transfection of insect cells (Fig. 43). As shown for Sf9 cells, the highest protein expression levels were obtained with FectoFly. Luciferase production (ng luciferase/well) Extremely simple protocol Protein production in Sf9 cells F T C FectoFly Transfection Reagents Fig. 43. Comparison of FectoFly with other insect cell-specific transfection reagents. Sf9 adherent cells were transfected with pcmv-egfp-luc plasmid using insect cell transfection reagents according to the supplier s recommendations. Luciferase assays were performed 72 h after transfection. q Transfection of insect cells with FectoFly is straightforward (Fig. 44). Fast: 3-step protocol Simple: 1 µl of FectoFly per µg of DNA, 1:1 ratio Versatile: efficient in serum-free synthetic media and in the presence of serum DNA + cell culture medium or 150 mm NaCl q q Vortex and centrifuge FectoFly + cell culture medium or 150 mm NaCl Qualified Reagents for Bioproduction For Biomanufacturing use, whether in-process development or cgmp production of recombinant protein, antibody or virus, Polyplus-transfection is able to supply qualified transfection reagents with the required quality and relevant documentation. These qualified reagents will guarantee reliable, safe and reproducible production from batch to batch. Custom packaging and formulation to suit your needs Detailed documentation supplied with your product: Certificate of Analysis including inprocess and final product quality control tests, Certificate of Origin, or other documentation requested Fully synthetic reagents: free of animal origin components Qualified reagents are provided with the following additional quality control tests: BIOPRODUCTION Incubate 30 min at RT q Bacterial Endotoxin assay (LAL) (Ph. Eur ) (USP <85>) Mycoplasma detection test Sterility test (Ph. Eur ) (USP<71>) Incubate 72 h and measure recombinant protein expression Fig. 44. FectoFly standard protocol. Product Cat N Reagent size 150 mm NaCl Sol. FectoFly N 1 ml 50 ml N 0.1 ml 5 ml N 4 x 1 ml 4 x 50 ml 1.5 ml of FectoFly is sufficient to perform transfections in 6-well plates. Bulk quantities are available upon request. If required, Polyplus supplies cgmp custom transfection reagents (see page 51). For more information and pricing, contact us through the website using the contact form. Insect-XPRESS is a registered trademark of Lonza. 41
42 IN VIVO DELIVERY 42
43 The delivery of nucleic acid to living organisms, especially to animals and humans, has become a key technology for gene therapy and genetic immunization as well as for fundamental research including gene, RNA interference and protein function studies. The use of recombinant viruses as carriers has greatly improved the efficiency of delivery and the stability of gene expression in vivo. However, viral approaches have shown limitations mainly due to safety considerations. As a result, non-viral reagents offer safe alternatives to viruses. Polyplus-transfection has worked on non-viral carriers with a focus on polyethylenimine (PEI), a linear cationic polymer widely used in vivo over the last few years. A specific formulation called in vivo-jetpei has been developed and is extensively used for in vivo applications. It has been selected as the most efficient amongst a range of linear and branched derivatives. in vivo-jetpei has been used for local and topical applications, as well as for systemic injection routes on a wide range of animal models. Furthermore, in vivo-jetpei is available as preclinical and cgmp grade with appropriate quality certificates. It is currently used in several phase I and II clinical trials. Ligand conjugated in vivo-jetpei derivatives are designed to enhance binding to cell surface receptors thereby facilitating internalization of the DNA complexes. Labeled in vivo-jetpei derivatives are designed for biodistribution studies using fluorescent labeling. IN VIVO DELIVERY Xenopus brain transfected with a RFP (red fluorescent protein) gene using in vivo-jetpei Courtesy L. Cohen, MNHN, Paris DNA/siRNA in vivo Delivery: in vivo-jetpei Technical note: Guidelines to set up Nucleic Acid Delivery Experiments in Mice Technical Note: Published Administration Routes using DNA and/or sirna with Polyplus-transfection Reagents Technical Note: Published Targeted Organs using DNA and/or sirna with Polyplustransfection Reagents sirna Delivery into the brain: jetsi 10 mm 50 Ligand and labeled in vivo-jetpei 50 Preclinical and Clinical Reagents 51 43
44 in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna in vivo Delivery Reagent IN VIVO DELIVERY Successful in vivo delivery of DNA, sirna and oligonucleotides Multiple modes of administration in many species Delivery to various organs No detectable inflammatory response in vivo-jetpei reagent provides versatile, reproducible and reliable nucleic acid delivery in animals. This linear polyethylenimine reagent is used for: gene therapy 1,2 RNA Interference 3,4,5 genetic vaccination 6 in vivo-jetpei is currently used in several phase I and II human clinical trials as a delivery vector, for example for cancer gene therapy 1. Successful in vivo delivery of DNA, sirna and oligonucleotides in vivo-jetpei is able to deliver DNA and to mediate gene expression in various tissues. For example, the highest level of luciferase expression is detected in the lung following intravenous injection in mice (Fig. 45). Depending on the route of administration, in vivo-jetpei mediated gene expression is also observed in the brain, liver, pancreas, spleen, kidney, heart, bladder, skin and artery (see page 46-47, Technical Note: Guidelines to set up your nucleic acid delivery experiments in mice). Specific inhibition of gene expression can be achieved by delivering small oligonucleotides such as sirna, antisense or mimic mirna with in vivo-jetpei in animal models (Fig. 46). sirna complexed with in vivo-jetpei are protected from degradation and can be efficiently delivered to various organs using various administration routes (pages 48-49). Fig. 46. RNA interference in the lung with in vivojetpei. pcmv-luc (40 µg) was co-transfected with 10 µg of specific anti-luc sirna (upper) or with a control sirna (lower). The complexes were injected into the tail vein of nude mice. Luciferase gene expression was monitored in living mice 24 h later by bioluminescence imaging using a cooled CCD camera. Multiple modes of administration in many species Numerous delivery routes of administration have been tested using in vivo-jetpei. Selected literature references are listed per administration routes, organs and nucleic acids pages and extensive information is available on the Polyplus website (Product Citation Database). in vivo-jetpei was successfully used to deliver different types of nucleic acids in many species including mouse, rat, guinea pig, duck, rabbit, monkey, goat, sheep, chicken, quail, hamster cow, tadpole, shrimp and fish. Fig. 45. Systemic delivery using in vivo-jetpei. Bioluminescent imaging of luciferase expression in living Balb/C mouse using a cooled camera 24 h after gene delivery. pcmv-luc (50 µg) was complexed with in vivo-jetpei in 400 µl of 5% glucose solution and injected into the tail vein. Courtesy J.L. Coll. No detectable inflammatory response Linear PEI does not induce any pro-inflammatory response after systemic injection 7, especially when compared to highly immunogenic compounds such as lipid transfection reagents or branched PEI 8. Additionally, linear PEI does not generate neutralizing antibodies, permitting repeated administrations 6. 44
45 Unique properties of in vivo-jetpei in vivo-jetpei condenses nucleic acids into approximately 50 nm nanoparticles 9 that are stable for several hours. As a result of this unique protection mechanism, aggregation of blood cells following injection is reduced compared to other reagents 10, thereby preventing restricted diffusion within a tissue, erythrocyte aggregation and microembolia. These nanoparticles are sufficiently small to diffuse into the tissues and enter the cells by endocytosis. in vivo-jetpei favors nucleic acids release from the endosome and transfer across the nuclear membrane. Reproducible results Gene delivery using in vivo-jetpei is reliable and provides reproducible data experiment after experiment (Fig. 47), without any noticeable toxic side effects observed using other methods. Luciferase expression (RLU/mg of protein) Lung STICKY SIRNA The STICKY SIRNA (ssirnas) are a new class of small interfering RNAs designed to improve in vivo sirna delivery. The technology involves extending the opposite ends of sirnas with short complementary A(5-8)/T(5-8) 3 sequences able to form concatemers in the presence of a cationic polymer such as in vivo-jetpei, thereby mimicking the DNA structure*. These STICKY SIRNAs form more stable complexes with in vivo-jetpei than standard sirna, and are released more efficiently in the cytoplasm, increasing subsequent silencing efficiency. This innovation is applicable to therapeutic sirnas for a wide variety of pathologies. Please contact us through the website for more information. *Bolcato-Bellemin et al. (2007). PNAS 104: IN VIVO DELIVERY Fig. 47. Systemic delivery using in vivo-jetpei. pcmv-luc (50 µg) was complexed with in vivo-jetpei in 5% glucose and injected retro-orbitally. After 24 h, luciferase gene expression was assessed in the lung (n=8). Viability of mice was 100%. Reagent Cat. N Size 10% Glucose solution in vivo-jetpei G 0.1 ml 10 ml G 0.5 ml 2 x 10 ml 0.1ml of in vivo-jetpei is sufficient to perform up to 20 intravenous injections in mouse (50 µg of DNA per injection). Bulk quantities are available upon request. QC reports and cgmp-in vivo-jetpei are available upon request for clinical trials (see page 51). 1. Ohana et al. (2004). Gene Ther Mol Bio 8: Vernejoul et al. (2002). Cancer Research 62: Busser et al. (2010). Mol Ther 18, Batassa et al. (2010). Neurosci Lett 471, Poeck (2008). Nature Med 14, Garzon et al. (2005). Vacine 23: Bonnet et al. (2008). Pharma Res 25: Kawakani et al. (2006). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317: Goula et al. (1998). Gene Therapy 5: Kircheis et al. (2001). Gene Therapy 8:28. INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY The use of polyethylenimine (PEI) or polypropylenimine (PPI) or cationic polymers similar in structure thereto for transfecting cells, as well as compositions comprising these cationic polymers and at least one nucleic acid, are the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 6,013,240, EP Patent No and foreign equivalents, for which Polyplus-transfection is the worldwide exclusive licensee. 45
46 Technical Note Guidelines to set up Nucleic Acid Delivery Experiments in Mice IN VIVO DELIVERY General considerations High-quality preparations of nucleic acid are required. Resuspend nucleic acid in water or low salt buffer at high concentration (3-7 µg/µl for DNA and 5-10 µg/µl for sirna). Form in vivo-jetpei /nucleic acid complexes in 5% glucose (final concentration). The volumes of the in vivo-jetpei solution and of the nucleic acid solution should be similar to ensure homogenous complex formation upon mixing. The concentration of nucleic acid in the final injection volume should not exceed 0.5 µg/µl. The volume of in vivo-jetpei is determined by the N/P ratio which is a measure of the ionic balance of the complexes, referring to the number of nitrogen residues of in vivo-jetpei per phosphate in the nucleic acid. Animal experiments must be approved by the local ethics committee and carried out humanly. At Polyplus, mice are anaesthetized by inhalation using anaesthetic metoxyflurane or by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital or Ketamine/xylasine. Tail vein injection Nucleic acid: 50 µg in vivo-jetpei : 5-8 µl N/P ratio: 5-8 Injection volume: µl, 5% glucose Method: The mouse is placed in a restainer and 70% ethanol is applied on the tail in order to slightly swell the vein. Complexes in solution are injected into the tail vein over 10 sec, using a ½ inch 26 gauge needle and a 1 ml syringe. Intestinee Pancreas Ovary Brain Spleen Kidney Heart Tissue distribution of luciferase transgene Liver expression 24 h following tail vein Lung injection Relative gene transfer efficiency Reagent Cat. N Size 10% Glucose solution ml G 0.1 ml 10 ml ml G 0.2 ml 10 ml ml G 0.5 ml 2 x 10 ml Bulk quantities are available upon request. in vivo-jetpei The use of polyethylenimine (PEI) or polypropylenimine (PPI) or cationic polymers similar in structure thereto for transfecting cells, as well as compositions comprising these cationic polymers and at least one nucleic acid, are the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 6,013,240, EP Patent No and foreign equivalents, for which Polyplus-transfection is the worldwide exclusive licensee. Nucleic acid: 100 µg in vivo-jetpei : µl N/P ratio: 6-8 Injection volume: 400 µl to 1 ml, 5% glucose Method: Complexes in solution are injected into the peritoneal cavity over 10 sec, using a ½ inch 26 gauge needle and a 1 ml syringe. Tissue distribution of luciferase transgene expression 24 h following i.p. injection. Intraperitoneal injection Diaphragm Uterus Salivary gland Intestine Muscle Stomach Ovary Pancreas Brain Spleen Kidney Liver Lung Relative gene transfer efficiency 46
47 sirna: 0.1 µg/µl using jetsi 10 mm (see page 50) Injection volume: 1-4 µl Method: Single injection into either lateral ventricle or stereotaxical injection. DNA: 1 µg (for 8-12 week-old mice) in vivo-jetpei : 0.12 µl N/P ratio: 6 Injection volume: 5 µl, 5% glucose Method: Single injection (5 µl) into either lateral ventricle (0.2 mm posterior to the bregma line, 1.1 mm lateral, and 2.2 mm deep from the pial surface) to pentobarbital anesthetized mice (65 mg/kg). Retro-orbital injection Nucleic acid: 40 µg in vivo-jetpei : 6.4 µl N/P ratio: 8 Injection volume: µl, 5% glucose Method: The tip of a 27 g hypodermic needle is introduced carefully in front of the eye. Follow the edge of the orbit down until feeling the needle tip at the base beneath the eye. Inject complexes in solution within 2 sec. If performed carefully, there will be little or no bleeding. The capillary nexus will take up the injected solution rapidly. Brain Salivary gland d Spleen n Kidney y Example of transfected cells expressing the ß-galactosidase and found in the anterior subventricular zone (1 week after intraventricular injection of pcmv-lacz). Courtesy B. Demeneix Heartt Liverr Lung g Relative gene transfer efficiency 106 Tissue distribution of luciferase transgene expression 24 h following retro-orbital injection. IN VIVO DELIVERY Intracerebral injection (stereotaxic injection) Nasal instillation for trachea and lung delivery Nucleic acid: 20 µg in vivo-jetpei : µl N/P ratio: 6-8 Injection volume: µl, 5% glucose Method: Mice are held supine at an angle of 45 with pressure applied to the lower mandibule to immobilize the tongue and prevent swallowing. Complexes in solution are then introduced to the nasal planum using a micropipet. Intratumoral injection Subcutaneous injection Nucleic acid: µg in vivo-jetpei : µl N/P ratio: 6-8 Injection volume: µl, 5% glucose Method: For implanted subcutaneous tumors (size> 5 mm³), perform multiple injections of µl complexes at different sites of the tumor to avoid reflux. Nucleic acid: 3-5 µg in vivo-jetpei : µl N/P ratio: 5-7 Injection volume: 10 µl, 5% glucose Method: Mice are restained and complexes are injected subcutaneously in the region of interest. For other delivery routes or animal models, please contact our Delivery Experts through the contact form on the Polyplus website. They will be pleased to assist you. 47
48 IN VIVO DELIVERY Technical Note Publications on in vivo delivery of nucleic acid with Polyplus reagents using the most common administration routes Reagent used: in vivo-jetpei, unless specified Delivery mode DNA, oligonucleotides and plasmid-based shrna sirna, STICKY SIRNA, RNA DNA Bhang et al., (2011) Nat Med 17, 123 Lin et al., (2011) Biomaterials 32, 1978 Wang et al., (2011) Arch Biochem Biophys 508, 93 Wong et al., (2011) Gene Ther 18, 82 Rodrigo-Garzon et al., (2010) Cancer Gene Ther 17, 20 Klucar et al., (2009) Vaccine 27, 1816 Nishikawa et al., (2008) Hum Gene Ther 19, 1009 Bonnet et al., (2008) Pharma Res 25, 2972 sirna Kim et al., (2010) Cardiovasc Res 87, 119 Chalmin et al., (2010) J Clin Invest 120, 457 Miyamoto et al., (2010) Arthritis Res Ther 12, R87 Besch et al., (2009) J. Clin. Invest 119, 2399 Filippi et al., (2009) J Clin Invest 119, 1515 Poeck et al., (2008) Nature Med Bonnet et al., (2008) Pharma Res 25, 2972 Yang et al., (2008), Nature 455, 1210 Systemic injection (IV) Robbins et al., (2008) Hum Gene Ther 19, 991 Lively et al., (2008) J Allergy Clin immunol 121, 88 Liu et al., (2006) Mol Ther 13, 1006 Ito et al., (2008), Cancer Res 68, 3214 Ge et al., (2004) PNAS 101, 8676 Dallabrida et al., (2008) Faseb J 22, 3010 Liu et al., (2006) Faseb J 20, 2384 Wang et al.,(2008) Hypertension 52, 484 Song et al., (2007) Circulation 116, 1585 Choi et al., (2008) J Biol Chem 283, Intraperitoneal injection (IP) Intratumoral injection DNA delivery Kitamura et al., (2011) BBRC 404, 599 Smitha et al., (2010) J Helminthol 84, 149 Serba et al., (2008) Gut 57, 344 Buckley et al., (2008) Hum Gene Ther 19, 1050 Louis et al., (2006) Cancer Gene Ther 13, 367 Caldas (2006) Mol Cancer Ther 5, 693 ODN (Oligodeoxynucleotides) delivery Nickerson and Colledge (2004) Gene Ther 11, 1351 Tormo et al., (2009) Cancer Cell 16, 103 DNA delivery Kang et al., (2009) BMC Cancer 9, 126 Stone et al., (2009) PLoS One 4, e7334 Garg et al., (2009) Cancer Gene Therapy 17, 155 Prados et al., (2009) Exp Dermatol 19, 363 Kang et al., (2009) BMC Cancer 9, 126 Ortiz et al., (2009) J Mol Med 87, 899 Jeudy et al., (2008) Cancer Gene Ther 15, 742 Chumakova et al., (2008) Cancer Lett 261, 215 Hua et al., (2007) Cancer Gene Ther 14, 815 Lavergne et al., (2004) J Immunol 173, 3755 Ohlfest et al., (2004) Mol Ther 10, 260 Lavergne et al., (2003) Cancer Res 63, 7468 STICKY SIRNA Bonnet et al., (2008) Pharma Res 25, 2972 Bolcato-Bellemin et al., (2007) PNAS 104, mrna Ranjan et al., (2010) Virol J 7, 102 sirna delivery Busser et al., (2010) Mol Ther 18, 528 Cubillos-Ruiz et al., (2009) J. Clin. Invest 119, 2231 Storci et al., (2008) J Pathol 214, 25 sirna delivery Zhang et al., (2010) Ann Surg Oncol 16, 2617 Intratracheal delivery Intranasal Sub-cutaneous (SC) and subepidermal (SE) Topical application Intrathecal delivery Intracerebral Small DNA oligonucleotides (Dbait) delivery Quanz et al., (2009) Clin Cancer Res 15, 308 shrna delivery Zhang et al., (2009) Ann Surg Onc 16, 2617 Niola et al., (2006) Cancer Biol Ther 5, 174 Hua et al., (2007) Cancer Gene Ther 14, 815 DNA delivery Hu et al., (2010) J Gene Med 12, 276 Gregory et al., (2009) Vaccine 27, 5299 Tian et al., (2008) J Asthma 45, 715 Liu et al., (2006) Faseb J 20, 2384 Liu et al., (2006) Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173, 566 DNA delivery Buckley et al., (2008) Hum Gene Ther 19, 1050 DNA delivery Subcutaneous injection Cid-Arregui et al., (2003) J Virol 77, 4928 Topical DNA delivery to the skin Angelos et al., (2011). Arch Facial Plast Surg Doi:archfacial [pii] McKnight et al., (2008), Ortolaryn Head Neck Surg 139, 2459 Lisziewicz et al., (2005) J Invest Dermatol. 124, 160 using vivo-jetpei -Man Lisziewicz et al., (2005) Aids 19, 35 using vivo-jetpei -Man Lisziewicz et al., (2006) Curr Drug Delivery 3, 83 using vivo-jetpei -Man DNA delivery Schaffer et al., (2010) Brain Res 1362, 32 Uchida et al., (2010) J Neurosci 30, Wiesner et al., (2009) Cancer Res 69, 431 Jouvert et al., (2004) J Neurosci. 24, Wu et al., (2004) Brain Res. 1008, 284 shrna delivery Hassani et al., (2007) Nucl Acid Res 35, e65 ODN (oligodeoxynucleotides) delivery Zhang et al., (2009), J Neurosci 29, sirna- Subepidermal injection Murase et al., (2009) J Biol Chem 284, 4343 Topical sirna delivery to blood vessels Kudo et al., (2007) Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27, 1562 sirna delivery Lan et al., (2010). Mol Pain 6, 2 sirna delivery Badaut et al., (2011) J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31, 819 using INTERFERin Batassa et al., (2010) Neurosci Lett 471, 188 using in vivo-jetpei Cakir et al., (2009) PLoS One 4, e8322 using jetsi 10 mm Dominska et al., (20101) J Cell Sci 123, 1183 using jetsi 10 mm Cheret et al., (2008) J Neurosci 28, using jetsi 10 mm Froidevaux et al., (2006) EMBO Rep. 7, 1035 using jetsi 10 mm Guissouma et al., (2006) Neurosci Lett, 406, 240 using jetsi 10 mm Kumar et al., (2006) PLoS Med 3, e using jetsi 10 mm Hassani et al, (2005). J Gene Med 7, 198 using jetsi 10 mm 48
49 Technical Note Publications on in vivo delivery of nucleic acid with Polyplus reagents by target organs/tissue Reagent used: in vivo-jetpei, unless specified Target organ DNA, oligonucleotides and shrna (Plasmid) sirna and dsrna sirna delivery Hlawaty et al., (2009). J Gene Med 11, 92 using jetsi -ENDO Blood vessel Choi et al., (2008) J Biol Chem 283, Wang et al., (2008) Hypertension 52, 484 Kudo et al., (2007) Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27, 1562 Song et al., (2007) Circulation 116, 1585 DNA delivery by bladder instillation Bladder Ohana et al., (2004) Gene Ther Mol Bio 8, 182 Sidi et al., (2008) J Urology Supplement 179 DNA delivery sirna delivery Schaffer et al., (2010) Brain Res 1362, 32-9 Badaut et al., (2011) J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31, 819 using INTERFERin Uchida et al., (2010) J Neurosci 30, Batassa et al., (2010) Neurosci Lett 471, 185 using in vivo-jetpei Wiesner et al., (2009) Cancer Res 69, 431 Cakir et al., (2009) PLoS One 4, e8322 using jetsi 10 mm Jouvert et al., (2004) J Neurosci 24, Dominska et al., (20101) J Cell Sci 123, 1183 using jetsi 10 mm Brain Wu et al., (2004) Brain Res 1008, 284 Cheret et al., (2008) J Neurosci 28, using jetsi 10 mm shrna delivery Froidevaux et al., (2006) EMBO Rep. 7, 1035 using jetsi 10 mm Hassani et al., (2007) Nucl Acid Res 35, e65 Guissouma et al., (2006) Neuroscience Letters, 406, 240 using jetsi 10 mm ODN (oligodeoxynucleotides) delivery Kumar et al., (2006) PLoS Med 3, e using jetsi 10 mm Zhang et al., (2009), J Neurosci 29, Hassani et al, (2005). J Gene Med 7, 198 using jetsi 10 mm Brain slices (ex vivo approach) Eye Heart Immune system Joints and articulations Kidney Liver Lung Nerve/Spinal chord Skin Tumors Intravitreal shrna delivery Liao and Yau (2007) Biotechniques 42, 285 DNA delivery Dallabrida et al., (2008) Faseb J 22, 3010 DNA delivery Serba et al., (2008) Gut 57, 344 Robbins et al., (2008) Hum Gene Ther 19, 991 Lisziewicz et al., (2006) Curr Drug Deliv 3, 83 Cid-Arregui et al., (2003) J Virol 77, 4928 Intracortical DNA delivery Yamada et al., (2005) PNAS 102, 7736 Intracortical AS-ODN (anti-sense oligodeoxynucleotides) delivery Yamada et al., (2005) PNAS 102, 7736 Renal infusion of shrna Liu et al., (2008) Physiological genomics 36, 52 ODN (oligodeoxynucleotides) delivery via the renal vein Hernandez-Vargas et al., (2005) J Am Soc Nephrol 16, 1673 Intramedullar DNA delivery Wang et al, (2010) Hypertension 55, 1129 DNA delivery via the mesenteric vein Nishikawa et al., (2008) Hum Gene Ther 19, 1009 shrna delivery via the mesenteric vein George and Tsutsumi (2007) Gene Ther 14, 890 shrna delivery via IP injection Paranjpe et al., (2007) Hepatology, 45, 1471 DNA delivery Ranjan et al., (2010) Virol J, 7, 102 Lin et al., (2011) Biomaterials 32, 1978 Wang et al., (2011) Arch Biochem Biophys 508, 93 Hu et al., (2010) J Gene Med 12, 276 Gregory et al., (2009) Vaccine 27, 5299 Poeck et al., (2008) Nature Med 14, 1256 Liu et al., (2006) Mol Ther. 13, 1006 Liu et al., (2006) Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173, 566 Liu et al., (2006) Faseb J 20, 2384 Ge et al., (2004) PNAS. 101, 8676 Topical DNA delivery Angelos et al., (2011). Arch Facial Plast Surg. 13, 185 McKnight et al., (2008), Ortolaryngol Head Neck Surg 139, 2459 Topical DNA delivery to target Dendritic cells Lisziewicz et al., (2005) J Invest Dermatol. 124, 160 using in vivo-jetpei -Man Lisziewicz et al., (2005) Aids. 19, 35 using in vivo-jetpei -Man Lisziewicz et al., (2006) Curr Drug Deliv 3, 83 using in vivo-jetpei -Man DNA delivery Kang et al., (2009) BMC Cancer 9, 126 Stone et al., (2009) PLoS One 4, e7334 Garg et al., (2009) Cancer Gene Therapy 17, 155 Prados et al., (2009) Exp Dermatol 19, 363 Kang et al., (2009) BMC Cancer 9, 126 Ortiz et al., (2009) J Mol Med 87, 899 Jeudy et al., (2008) Cancer Gene Ther 15, 742 Chumakova et al., (2008) Cancer Lett 261, 215 Hua et al., (2007) Cancer Gene Ther 14, 815 Paranjpe et al., (2007) Hepatology, 45, 1471 Caldas et al., (2006) Mol Cancer Ther 5, 693 Lavergne et al., (2004) J Immunol 173, 3755 Ohlfest et al., (2004) Mol Ther 10, 260 Lavergne et al., (2003) Cancer Res 63, 7468 PolyIC Tormo et al., (2009) Cancer Cell 16, 103 Small DNA oligonucleotides (Dbait) delivery Quanz et al., (2009) Clin Cancer Res 15, 308 shrna delivery Zhang et al., (2009) Ann Surg Onc 16, 2617 Niola et al., (2006) Cancer Biol Ther 5, 174 Hua et al., (2007) Cancer Gene Ther 14, 815 sirna Delivery using INTERFERin Tam et al., (2011) Neuroscience, 172, 562 Badaut et al, (2011) J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31, 819 sirna delivery Kim et al., (2010) Cardiovasc Res 87, 119 sirna delivery Besch et al., (2009) J Clin Invest 119, 2399 Poeck et al., (2008) Nature Med 14, 1256 Cubillos-Ruiz et al., (2009) J Clin Invest 119, 2231 dsrna Magnusson et al., (2006) Arthritis Rheum 54, 148 Zare et al.,(2006) J Leukoc Biol 79, 482 sirna delivery Lively et al., (2008) J Allergy Clin immunol 121, 88 Liu et al., (2006) Faseb J 20, 2384 Liu et al., (2006) Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173, 566 sirna delivery by perineural injection Kiguchi et al., (2010). Pain 149, 305 sirna delivery by paravertebral injection (peri DG) Patte-Mensah et al., (2010) Pain 150, 522 sirna delivery by intrathecal injection Lan et al., (2010) Molecular Pain 6, 2 Subepidermal injection of sirna Murase et al., (2009) J Biol Chem 284, 4343 sirna delivery Busser et al., (2010) Mol Ther 18, 528 Zhang et al., (2010) Ann Surg Oncol 16, 2617 Besch et al., (2009) J Clin Invest 119, 2399 Storci et al., (2008) J Pathol 214, 25 Poeck et al., (2008) Nature Med 14, 1256 IN VIVO DELIVERY 49
50 IN VIVO DELIVERY sirna Delivery into the brain: jetsi 10 mm Polyplus-transfection has developed jetsi 10 mm for sirna delivery to the brain. The choice of the most effective sirna carrier may depend on the in vivo context. Indeed, while in vivo-jetpei was superior to cationic liposomes for plasmid DNA delivery in the mouse brain, jetsi 10 mm was found to be the carrier of choice for sirna delivery to this organ (Froidevaux et al. (2006), EMBO Rep 7:1035; Guissouma et al. (2006), Neurosci Lett 406: 240; Kumar et al. (2006), PLOS Med. 3: 0505; Hassani et al. (2005), J Gene Med 7:198). When using plasmid based approaches (shrna) in the brain, we recommend in vivo-jetpei. Reagent Cat. N Amount of reagent jetsi 10 mm ml Please note that neither glucose solution nor DOPE is included Ligand & Labeled in vivo-jetpei in vivo-jetpei ligand-conjugated derivatives are designed to enhance delivery to cell expressing specific receptors: in vivo-jetpei -Gal: A galactose-conjugated in vivo-jetpei designed to enhance delivery to cells expressing galactose-specific membrane lectins, such as the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGP-R or Gal/GalNAc receptor). in vivo-jetpei -Man: A mannose-conjugated in vivo-jetpei designed to enhance delivery to cells expressing mannose-specific membrane receptors. Labeled in vivo-jetpei transfection reagents are designed for biodistribution studies using fluorescent labeling: in vivo-jetpei -FluoF: A fluorescein-conjugated linear polyethylenimine derivative (green label, excitation at 490 nm; emission at 520 nm). in vivo-jetpei -FluoR (Fig. 48): A tetramethylrhodamine-conjugated linear polyethylenimine derivative (red label, excitation at 555 nm; emission at 580 nm). Fig. 48. Biodistribution ib ti of fluorescent complexes in the lungs after intravenous administration. in vivo-jetpei -FluoR/DNA complexes were injected in the tail vein of C57Bl6 mice.mice were sacrified 6 h after injection and the lungs were collected. Cryosections of the lungs were visualized by fluorescence microscopy (Courtesy J-L Coll). INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY The use of polyethylenimine (PEI) or polypropylenimine (PPI) or cationic polymers similar in structure thereto for transfecting cells, as well as compositions comprising these cationic polymers and at least one nucleic acid, are the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 6,013,240, EP Patent No and foreign equivalents, for which Polyplus-transfection is the worldwide exclusive licensee. Reagent Cat. N Size Amount of Glucose solution in vivo-jetpei -Gal G 0.1 ml 10 ml in vivo-jetpei -Man G 0.1 ml 10 ml in vivo-jetpei -FluoF G 0.1 ml 10 ml in vivo-jetpei -FluoR G 0.1 ml 10 ml 50
51 Preclinical and Clinical Transfection Reagents For pre-clinical use, toxicological studies in animal and human clinical trials, in vivo-jetpei and its derivatives are available from Polyplus-transfection supported by the appropriate manufacturing quality controls, full documentation and certification. Pre-clinical Materials Polyplus-transfection is able to supply batches of in vivojetpei for all preclinical studies including GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) toxicology support. Preclinical batches are available in volumes from 50 ml to multiple liters. Custom packaging and formulation are available to suit all your needs including filling in sealed glass vials. Each GLP batch meets stringent release specifications and is supplied with a complete Certificate of Analysis including in-process and final product quality controls. Additional quality controls or assays are available upon request. Polyplus is able to assist in the design and performance of stability programs to support preclinical studies. GMP batches are available for clinical studies phase I to III inclusive. In-process and release quality controls are in place in combination with full specifications for the drug substance/product. Polyplus manages the Aseptic Fill and Finish step (formulation, sterilization, aseptic filling, etc) for the preparation of the Final Drug Product according to your specific needs. Fill and Finish is performed by a qualified and audited subcontractor. Custom filling volumes and packaging are available on request. Long-term and short-term stability testing data at intended and accelerated storage temperatures as per ICH (International Conference on Harmonization) guidelines can be designed and managed by Polyplus. A type II Drug Master File (DMF) entitled in vivo-jetpei, Non-sterile Bulk Drug Substance is on file with the FDA and can be cross-referenced when submitting IND s to the US FDA. With GMP batches, Polyplus provides all the information related to the manufacturing procedures and controls for finished dosage forms (Final Drug Product) to customers to be included in the IND or clinical applications. IN VIVO DELIVERY Clinical Drug Substance and Drug Product To support the development of your Investigational New Drug (IND) or an Investigational Medicinal Product (IMP) containing in vivo-jetpei or its derivatives, Polyplus is able to supply batches of drug substance and drug product manufactured in compliance with applicable European Commission (EC) guide to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and FDA requirements. Polyplus supplies either the bulk Active Drug Substance (non-formulated bulk product) or the Final Drug Product (sterile liquid formulated product). With several clinical trials using Polyplus-transfection s in vivo delivery reagents, the company has acquired a widely acknowledged expertise in the regulatory and technical issues in this domain. Clinical trials are currently being carried out for cancer therapy in Israel and the USA (P. Ohana et al., Gene Ther Mol Biol, 8, 181, 2004; Sidi et al., J Urol., 180, 2008) and for HIV immune therapy in Germany and Sweden (J. Lisziewicz et al., J Invest Dermatol 124, 160, 2005). For more information, please contact us through the website using the contact form. 51
52 PRODUCT INDEX by catalog number Product Number Product Name Content Page N jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 0.1 ml + NaCl sol jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 1 ml N jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 1 ml + NaCl sol jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 4 x 1 ml N jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 4 x 1 ml + NaCl sol B-010 jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 10 ml B-010N jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 10 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -Hepatocyte DNA Transfection Reagent 0.1 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -Hepatocyte DNA Transfection Reagent 0.5 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -Macrophage DNA Transfection Reagent 0.1 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -Macrophage DNA Transfection Reagent 0.5 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -FluoF DNA Transfection Reagent 0.5 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -FluoR DNA Transfection Reagent 0.5 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -HUVEC DNA Transfection Reagent 0.1 ml + NaCl sol N jetpei -HUVEC DNA Transfection Reagent 0.5 ml + NaCl sol Fecturin for Protein and Virus Production in Synthetic Media 1 ml 36-37, N FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells 0.1 ml + NaCl sol N FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells 1 ml + NaCl sol N FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells 4 x 1 ml + NaCl sol jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent 0.1 ml + buffer 8-9, 21, jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent 0.75 ml + buffer 8-9, 21, jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent 1.5 ml + buffer 8-9, 21, jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent 5 x 1.5 ml + buffer 8-9, 21, C jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent 5 x 1.5 ml + (5 x conc.) buffer 8-9, 21, G in vivo-jetpei Delivery Reagent 0.1 ml + Glucose sol G in vivo-jetpei Delivery Reagent 0.5 ml + Glucose sol G in vivo-jetpei -Gal Delivery Reagent 0.1 ml + Glucose sol G in vivo-jetpei -Man Delivery Reagent 0.1 ml + Glucose sol G in vivo-jetpei -FluoF Delivery Reagent 0.1 ml + Glucose sol G in vivo-jetpei -FluoR Delivery Reagent 0.1 ml + Glucose sol jetsi 10 mm for sirna Delivery into the Brain 0.5 ml INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent 0.1 ml INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent 1 ml INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent 5 x 1 ml INTERFERin -HTS sirna Transfection Reagent 1.5 ml INTERFERin -HTS sirna Transfection Reagent 4 x 1.5 ml PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent 0.1 ml + RPE + Hepes PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent 0.4 ml + RPE + Hepes PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent 4 x 0.4 ml + RPE + Hepes
53 by product name Product Name Product Number Content Page FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells N 0.1 ml + NaCl sol FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells N 1 ml + NaCl sol FectoFly DNA Transfection Reagent for Insect Cells N 4 x 1 ml + NaCl sol Fecturin for Protein and Virus Production in Synthetic Media ml 36-37, 39 INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent ml INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent ml INTERFERin sirna Transfection Reagent x 1 ml INTERFERin -HTS sirna Transfection Reagent ml INTERFERin -HTS sirna Transfection Reagent x 1.5 ml in vivo-jetpei Delivery Reagent G 0.1 ml + Glucose sol in vivo-jetpei Delivery Reagent G 0.5 ml + Glucose sol in vivo-jetpei -FluoF Delivery Reagent G 0.1 ml + Glucose sol. 50 in vivo-jetpei -FluoR Delivery Reagent G 0.1 ml + Glucose sol. 50 in vivo-jetpei -Gal Delivery Reagent G 0.1 ml + Glucose sol. 50 in vivo-jetpei -Man Delivery Reagent G 0.1 ml + Glucose sol. 50 jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS N 0.1 ml + NaCl sol jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS ml jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS N 1 ml + NaCl sol jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS x 1 ml jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS N 4 x 1 ml + NaCl sol jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 101B ml jetpei DNA Transfection Reagent for HTS 101B-010N 10 ml + NaCl sol jetpei -FluoF DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.5 ml + NaCl sol. 15 jetpei -FluoR DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.5 ml + NaCl sol. 15 jetpei -HUVEC DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.1 ml + NaCl sol. 14 jetpei -HUVEC DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.5 ml + NaCl sol. 14 jetpei -Hepatocyte DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.1 ml + NaCl sol. 12 jetpei -Hepatocyte DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.5 ml + NaCl sol. 12 jetpei -Macrophage DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.1 ml + NaCl sol. 13 jetpei -Macrophage DNA Transfection Reagent N 0.5 ml + NaCl sol. 13 jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent ml + buffer 8-9, 21, 38 jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent ml + buffer 8-9, 21, 38 jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent ml + buffer 8-9, 21, 38 jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent x 1.5 ml + buffer 8-9, 21, 38 jetprime DNA and/or sirna Transfection Reagent C 5 x 1.5 ml + (5 x conc.) buffer 8-9, 21, 38 jetsi 10 mm for sirna Delivery into the Brain ml 50 PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent ml + RPE + Hepes PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent ml + RPE + Hepes PULSin Protein, Antibody & Peptide Delivery Reagent x 0.4 ml + RPE + Hepes PRODUCT INDEX 53
54 Are you a transfection expert? Find out by taking the DNA transfection challenge on Facebook. Watch the DNA Transfection video. Share pictures with us. Join us on Facebook! Polyplus-transfection Follow us on Twitter! Polyplus Transfection Terms & conditions PRODUCT USE LIMITATION All Polyplus-transfection reagents have been developed, designed and sold exclusively for research purposes in vitro and nonhuman in vivo laboratory applications. They have not been tested for drug development, nor are they suitable for administration to humans. ORDER All sales are subject to and expressly conditioned upon the terms contained herein, and the purchaser s agreement. Any variation of these terms and conditions has to be written and signed by the purchaser and Polyplus-transfection s representative. When placing an order, purchaser must provide the following information: customer account number (attributed on the first invoice), name and department, invoice address and phone number, delivery address and phone number, catalog number and description of product, quantity and size of product, purchase order number. From Monday through Wednesday, orders received before 12:00 pm, local time, are shipped the same day. On Thursday and Friday, orders are shipped the following Monday morning. Orders are delivered by FedEx or other express delivery couriers according to the destination country. Orders may be placed via our web site ( by fax +33 (0) , phone +33 (0) and in writing to Polyplus-transfection, BP90018, ILLKIRCH CEDEX FRANCE. Written confirmation of a telephone order should be clearly marked «CONFIRMATION». PRICES Prices are net and quoted in EURO and do not include value added taxes or cost of delivery. Prices are subject to change without notice. DELIVERY/TRANSFER OF OWNERSHIP AND OF RISK Unless otherwise specified, products are shipped EXW origin Polyplus-transfection, Bioparc, Boulevard Sebastien Brant Illkirch - France - ICC 2010 via express delivery. A minimum of fifty Euros (shipping and handling charges) are prepaid and added to the invoice for Room Temperature delivery, regarding the destination country. The purchaser cannot derive any right from delay, nor cancel the order. Polyplus-transfection reserves the ownership of all delivered products upon itself until all amounts owed by the purchaser in respect to concerned invoice or former invoices are fully paid. Polyplus-transfection shall not be liable for any loss, damage or penalty as a result of any delay in or failure to manufacture or to deliver due to a «force majeure» cause. «force majeure» shall be understood as any circumstance beyond the control of Polyplus-transfection, such as war or danger of war, civil war, riot, strike, or natural disaster such as fire and flood. Risks for goods sold shall pass to the purchaser upon delivery to the carrier even though freight costs are prepaid by Polyplustransfection. If a shipment is damaged, the purchaser must claim for damage to the carrier. If a shipment is incomplete or different from the order, the purchaser must notify Polyplus-transfection within 8 days to have it replaced free of charge. PAYMENT Payment terms are net thirty days of the invoice date in EURO. Any purchaser who has not effected payment by the due date shall by operation of law be deemed to be in default and without any exhortation being required shall owe interest on the outstanding amount from the final due date. The applicable rate shall be three times the legal interest rate. Any purchaser who fails to pay the amount owed by the due date shall be obliged to reimburse Polyplus-transfection for any expenses, including extra judicial collection charges and the cost of legal aid incurred to collect the claim in a legal procedure. WARRANTY/LIABILITY Products are not taken in part exchange. Polyplus-transfection warrants that all products will perform according to the stated specifications up to the product limit use and for laboratory research purposes only. No warranty is applicable unless the products are stored in accordance with Polyplus-transfection s instructions. This warranty limits Polyplus-transfection liability to the replacement of the product free of charge or the refunding of the product s purchase price. No other warranties of any kind, express or implied, including without limitation, imply warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, are provided by Polyplus-transfection. Polyplus-transfection shall have no liability for any direct, indirect, consequential or incidental damages arising out of the use, the results of use or the inability to use any product. APPLICABLE LAW As concerns by any disputes, which may arise between the purchaser and Polyplus-transfection from the conclusion, interpretation or implementation of the agreement concluded by them, the Strasbourg s Courts shall be exclusively competent. The French Law shall be the only applicable. 54
55 w PRODUCT CITATION DATABASE The Online Product Citation Database on... A helpful tool for your literature searches Under the Technical Support Heading, you will find a powerful tool enabling you to search published citations featuring Polyplus-transfection reagents. w 1 Search page Tick the application you are interested in (in vitro transfection or in vivo delivery), and if required, add the cell type, the delivered biomolecule, the reagent, the author and/or the keyword of your choice. w 2 Results page View the matching citations featuring highlights of the product used in the paper as well as the cell types and the method when applicable. Search for publications on the database Product Citations 3 Abstract page View the abstract Downloading of the references is fast and easy: if you click on the reference, you will be automatically redirected to PubMed, saving you time and effort. TRADEMARKS Polyplus-transfection, jetpei, jetprime, jetsi, FectoFly, Fecturin, PULSin and INTERFERin are registered trademarks of Polyplus-transfection SA. 55
56 Polyplus-transfection BP Illkirch Cedex France Phone: +33 (0) Fax: +33 (0) Polyplus-transfection 1251 Ave of the Americas 34th fl. New York NY USA design: sacha nikolic
jetpei -FluoF in vitro DNA Transfection Protocol
 jetpei -FluoF in vitro DNA Transfection Protocol Company Information... 2 Product Information... 3 Contact our Technical Assistance and Scientific Advice Service... 4 1.Transfection protocol... 5 1. 1.
jetpei -FluoF in vitro DNA Transfection Protocol Company Information... 2 Product Information... 3 Contact our Technical Assistance and Scientific Advice Service... 4 1.Transfection protocol... 5 1. 1.
Convoy TM Transfection Reagent
 Convoy TM Transfection Reagent Catalog No.11103 0.25ml (40-80 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11105 0.5 ml (80-165 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11110 1.0 ml (165-330 transfections
Convoy TM Transfection Reagent Catalog No.11103 0.25ml (40-80 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11105 0.5 ml (80-165 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11110 1.0 ml (165-330 transfections
THE DELIVERY EXPERTS PROTOCOL
 THE DELIVERY EXPERTS jetprime in vitro DNA & sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetprime is a novel powerful molecule based on a polymer formulation manufactured at Polyplustransfection. jetprime
THE DELIVERY EXPERTS jetprime in vitro DNA & sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetprime is a novel powerful molecule based on a polymer formulation manufactured at Polyplustransfection. jetprime
jetpei In vitro Transfection Protocol
 jetpei Cationic polymer transfection reagent In vitro Transfection Protocol 101-05 0.5 ml (250 transfections in 24-well plates) 101-05N 0.5 ml 50ml of 150 mm NaCl (250 transfections in 24-well plates)
jetpei Cationic polymer transfection reagent In vitro Transfection Protocol 101-05 0.5 ml (250 transfections in 24-well plates) 101-05N 0.5 ml 50ml of 150 mm NaCl (250 transfections in 24-well plates)
jetpei Cationic polymer transfection reagent
 jetpei Cationic polymer transfection reagent Cat# GDSP10105 (0.5 ml) Cat# GDSP10110 (1.0 ml) Cat# GDSP10140 (4 x 1.0 ml) developed by PolyPlus-transfection Product Description jetpei is a powerful transfection
jetpei Cationic polymer transfection reagent Cat# GDSP10105 (0.5 ml) Cat# GDSP10110 (1.0 ml) Cat# GDSP10140 (4 x 1.0 ml) developed by PolyPlus-transfection Product Description jetpei is a powerful transfection
jetprime in vitro DNA & sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL
 jetprime in vitro DNA & sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetprime is a novel powerful transfection reagent based on a polymer formulation manufactured at Polyplus-transfection. jetprime
jetprime in vitro DNA & sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetprime is a novel powerful transfection reagent based on a polymer formulation manufactured at Polyplus-transfection. jetprime
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL
 INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
Sunma Biotech Co., Ltd. Sofast transfection reagent
 Sunma Sofast Transfection Reagent Catalog No.11103 0.3ml (50-100 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11105 0.5 ml (80-165 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11110 1.0 ml (165-330 transfections
Sunma Sofast Transfection Reagent Catalog No.11103 0.3ml (50-100 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11105 0.5 ml (80-165 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11110 1.0 ml (165-330 transfections
THE DELIVERY EXPERTS. INTERFERin in vitro sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL
 THE DELIVERY EXPERTS INTERFERin in vitro sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection
THE DELIVERY EXPERTS INTERFERin in vitro sirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection
INTERFERin sirna transfection reagent
 INTERFERin in vitro sirna Transfection Protocol Company Information... 2 Product Information... 3 1. Standard sirna transfection of adherent cells... 4 (forward transfection)... 4 1.1 Cell seeding... 5
INTERFERin in vitro sirna Transfection Protocol Company Information... 2 Product Information... 3 1. Standard sirna transfection of adherent cells... 4 (forward transfection)... 4 1.1 Cell seeding... 5
in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna delivery reagent
 in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna Delivery Protocol Company Information... 2 Product Information... 3 In vivo Delivery Protocol... 5 1. Reagents required... 5 2. Recommended amount of nucleic acid and injection
in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna Delivery Protocol Company Information... 2 Product Information... 3 In vivo Delivery Protocol... 5 1. Reagents required... 5 2. Recommended amount of nucleic acid and injection
jetpei -Macrophage in vitro DNA transfection reagent PROTOCOL
 jetpei - in vitro DNA transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetpei - allows DNA transfection of macrophages and macrophage-like cells. It contains a mannose-conjugated linear polyethylenimine that
jetpei - in vitro DNA transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetpei - allows DNA transfection of macrophages and macrophage-like cells. It contains a mannose-conjugated linear polyethylenimine that
Avalanche -Everyday Transfection Reagent
 The Transfection & Gene Expression Experts Avalanche -Everyday Transfection Reagent Cat. No. EZT-EVDY-1 Description Size: 0.75 ml 1.5 ml Store at 4 C As the simplified version of our most popular and powerful
The Transfection & Gene Expression Experts Avalanche -Everyday Transfection Reagent Cat. No. EZT-EVDY-1 Description Size: 0.75 ml 1.5 ml Store at 4 C As the simplified version of our most popular and powerful
Comparison of Commercial Transfection Reagents: Cell line optimized transfection kits for in vitro cancer research.
 Comparison of Commercial Transfection Reagents: Cell line optimized transfection kits for in vitro cancer research. by Altogen Labs, 11200 Manchaca Road, Suite 203 Austin TX 78748 USA Tel. (512) 433-6177
Comparison of Commercial Transfection Reagents: Cell line optimized transfection kits for in vitro cancer research. by Altogen Labs, 11200 Manchaca Road, Suite 203 Austin TX 78748 USA Tel. (512) 433-6177
M X 500 µl. M X 1000 µl
 GeneGlide TM sirna Transfection Reagent (Catalog # M1081-300, -500, -1000; Store at 4 C) I. Introduction: BioVision s GeneGlide TM sirna Transfection reagent is a cationic proprietary polymer/lipid formulation,
GeneGlide TM sirna Transfection Reagent (Catalog # M1081-300, -500, -1000; Store at 4 C) I. Introduction: BioVision s GeneGlide TM sirna Transfection reagent is a cationic proprietary polymer/lipid formulation,
Avalanche -Omni Transfection Reagent
 The Transfection & Gene Expression Experts Avalanche -Omni Transfection Reagent Cat. No. EZT-OMNI-1 Description Size: 0.75 ml 1.5 ml Store at 4 C Avalanche -Omni Transfection Reagent is a proprietary lipid-polymer
The Transfection & Gene Expression Experts Avalanche -Omni Transfection Reagent Cat. No. EZT-OMNI-1 Description Size: 0.75 ml 1.5 ml Store at 4 C Avalanche -Omni Transfection Reagent is a proprietary lipid-polymer
jetcrispr RNP transfection reagent PROTOCOL
 jetcrispr RNP transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetcrispr is a RiboNucleoProtein (RNP) transfection reagent designed to perform CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in mammalian cells. This reagent has been
jetcrispr RNP transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetcrispr is a RiboNucleoProtein (RNP) transfection reagent designed to perform CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in mammalian cells. This reagent has been
Nucleic Acid Transfection. Genomics. TransIT Transfection Tools. Technical tip D.103
 The nucleic acids delivery specialists design our transfection reagents. Our formulations provide superior transfection efficiency and cell viability. This complete range includes TransIT reagents, based
The nucleic acids delivery specialists design our transfection reagents. Our formulations provide superior transfection efficiency and cell viability. This complete range includes TransIT reagents, based
THE DELIVERY EXPERTS. in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna Delivery Protocol PROTOCOL
 THE DELIVERY EXPERTS in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna Delivery Protocol PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION in vivo-jetpei is a linear polyethylenimine, which mediates efficient nucleic acid (DNA, shrna, sirna, oligonucelotides,
THE DELIVERY EXPERTS in vivo-jetpei DNA & sirna Delivery Protocol PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION in vivo-jetpei is a linear polyethylenimine, which mediates efficient nucleic acid (DNA, shrna, sirna, oligonucelotides,
TransIT-TKO Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2150 INTRODUCTION TransIT-TKO is a broad spectrum sirna transfection reagent that enables high efficiency sirna delivery
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2150 INTRODUCTION TransIT-TKO is a broad spectrum sirna transfection reagent that enables high efficiency sirna delivery
Thermo Scientific DharmaFECT Transfection Reagents sirna Transfection Protocol
 Protocol Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents sirna Transfection Protocol The following is a general protocol for use of Thermo Scientific transfection reagents to deliver sirna into cultured mammalian
Protocol Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents sirna Transfection Protocol The following is a general protocol for use of Thermo Scientific transfection reagents to deliver sirna into cultured mammalian
Product: Arrest-In TM Transfection Reagent for RNAi
 Product: Arrest-In TM Transfection Reagent for RNAi Catalog #: ATR1740, ATR1741, ATR1742, ATR1743 Product Description Arrest-In transfection reagent is a proprietary polymeric formulation, developed and
Product: Arrest-In TM Transfection Reagent for RNAi Catalog #: ATR1740, ATR1741, ATR1742, ATR1743 Product Description Arrest-In transfection reagent is a proprietary polymeric formulation, developed and
TurboFect in vitro Transfection Reagent. Description. Storage. Reagents to be Supplied by the User. #R ml ( for in vitro transfections)
 TurboFect in vitro Transfection Reagent #R0531 1 ml ( for 300-500 in vitro transfections) Description TurboFect in vitro Transfection Reagent* is a sterile solution of a cationic polymer in water. The
TurboFect in vitro Transfection Reagent #R0531 1 ml ( for 300-500 in vitro transfections) Description TurboFect in vitro Transfection Reagent* is a sterile solution of a cationic polymer in water. The
Transfection Reagents That Really Work
 Transfection Reagents That Really Work non-toxic, biodegradable, highly efficient, serum-compatible Available for DNA,, protein, stem cells www.clontech.com/xf P L A S M I D T R A N S F E C T I O N R E
Transfection Reagents That Really Work non-toxic, biodegradable, highly efficient, serum-compatible Available for DNA,, protein, stem cells www.clontech.com/xf P L A S M I D T R A N S F E C T I O N R E
CHOgro Expression System
 SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/6260 INTRODUCTION The CHOgro Expression System is an optimized platform for transient, high titer protein production in suspension CHO derived
SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/6260 INTRODUCTION The CHOgro Expression System is an optimized platform for transient, high titer protein production in suspension CHO derived
TransIT -mrna Transfection Kit
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -mrna Transfection Kit is designed to transfect RNA into a broad range of cell types with minimal cellular toxicity. RNA delivery avoids transcriptional regulation effects by directly
INTRODUCTION TransIT -mrna Transfection Kit is designed to transfect RNA into a broad range of cell types with minimal cellular toxicity. RNA delivery avoids transcriptional regulation effects by directly
TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2300 INTRODUCTION TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent is a broad spectrum reagent that provides high efficiency plasmid
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2300 INTRODUCTION TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent is a broad spectrum reagent that provides high efficiency plasmid
ExGen 500 in vitro Transfection Reagent
 ExGen 500 in vitro Transfection Reagent Catalog No: 53087 Lot No: XXXXX Supplied as: liquid Stability: store at +4 C Background ExGen 500, polyethylenimine, belongs to an efficient new class of non-viral,
ExGen 500 in vitro Transfection Reagent Catalog No: 53087 Lot No: XXXXX Supplied as: liquid Stability: store at +4 C Background ExGen 500, polyethylenimine, belongs to an efficient new class of non-viral,
TransIT -mrna Transfection Kit
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2225 INTRODUCTION TransIT -mrna Transfection Kit is designed to transfect RNA into a broad range of cell types with
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2225 INTRODUCTION TransIT -mrna Transfection Kit is designed to transfect RNA into a broad range of cell types with
GeneCellin TM Transfection Reagent Protocol
 GeneCellin TM Transfection Reagent Protocol Table of content Description......3 Content......3 Storage......3 Certificate of quality......4 Parameters influencing transfection efficiency......4 Nucleic
GeneCellin TM Transfection Reagent Protocol Table of content Description......3 Content......3 Storage......3 Certificate of quality......4 Parameters influencing transfection efficiency......4 Nucleic
Lipodin Pro Protein Transfection Reagent
 From Biology to Discovery Lipodin Pro Protein Transfection Reagent Cat. No 500100 Cat. No 500110 (version 01 08) ABBIOTEC 7955 Dunbrook Road, Suite B San Diego, California 92126, USA Toll Free: 1 800 854
From Biology to Discovery Lipodin Pro Protein Transfection Reagent Cat. No 500100 Cat. No 500110 (version 01 08) ABBIOTEC 7955 Dunbrook Road, Suite B San Diego, California 92126, USA Toll Free: 1 800 854
TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent is a broad spectrum reagent that provides high efficiency plasmid DNA delivery in many mammalian cell types including primary cells. TransIT-LT1 is a low
INTRODUCTION TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent is a broad spectrum reagent that provides high efficiency plasmid DNA delivery in many mammalian cell types including primary cells. TransIT-LT1 is a low
TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent
 TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2700 INTRODUCTION TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide
TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2700 INTRODUCTION TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide
Ingenio Electroporation Kits and Solution
 Protocol for MIR 08, 09, 01, 0111, 0112, 0113, 0114, 011, 0116, 0117, 0118, 0119 Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/0111 INTRODUCTION Ingenio Electroporation
Protocol for MIR 08, 09, 01, 0111, 0112, 0113, 0114, 011, 0116, 0117, 0118, 0119 Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/0111 INTRODUCTION Ingenio Electroporation
Instructions. Fuse-It-siRNA. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview
 SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview Pathway-Focused sirna-based RNA Interference Topics to be Covered Who is SuperArray? Brief Introduction to RNA Interference Challenges Facing RNA Interference
SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview Pathway-Focused sirna-based RNA Interference Topics to be Covered Who is SuperArray? Brief Introduction to RNA Interference Challenges Facing RNA Interference
DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kits
 DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kits User Manual P/N 10586 Rev. C 06.09.16 DRAFT September 16, 2006 3:54 pm DeliverXTtile.fm Panomics, Inc. DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kit
DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kits User Manual P/N 10586 Rev. C 06.09.16 DRAFT September 16, 2006 3:54 pm DeliverXTtile.fm Panomics, Inc. DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kit
TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in HEK 293 and cell types of associated lineage. TransIT-293 provides
INTRODUCTION TransIT -293 Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in HEK 293 and cell types of associated lineage. TransIT-293 provides
TransIT Transfection Reagent
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 is a broad spectrum transfection reagent that provides superior transfection of plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. TransIT-2020 is suitable for both transient and stable transfection
INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 is a broad spectrum transfection reagent that provides superior transfection of plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. TransIT-2020 is suitable for both transient and stable transfection
ingenio electroporation kits & solution
 ingenio electroporation kits & solution Electroporation x DEFINITION and OPTIMIZATION What is ELECTROPORATION? Electroporation is a physical method of nucleic acid transfer wherein the cells and nucleic
ingenio electroporation kits & solution Electroporation x DEFINITION and OPTIMIZATION What is ELECTROPORATION? Electroporation is a physical method of nucleic acid transfer wherein the cells and nucleic
Silencer Select Pre-designed sirna Silencer Select Validated sirna Silencer Select Custom Designed sirna Custom Select sirna
 Catalog #: Various Silencer Select Pre-designed sirna Silencer Select Validated sirna Silencer Select Custom Designed sirna Custom Select sirna General Product Details and User Information Refer to page
Catalog #: Various Silencer Select Pre-designed sirna Silencer Select Validated sirna Silencer Select Custom Designed sirna Custom Select sirna General Product Details and User Information Refer to page
TransIT -BrCa Transfection Reagent
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -BrCa Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in breast cancer and related cell types including: MCF-7, MDA-MB-231
INTRODUCTION TransIT -BrCa Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in breast cancer and related cell types including: MCF-7, MDA-MB-231
DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kits
 DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kits User Manual P/N 10586.060504 Rev. A DRAFT May 4, 2006 4:41 pm DeliverXTtile.fm Panomics, Inc. DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kit User Manual
DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kits User Manual P/N 10586.060504 Rev. A DRAFT May 4, 2006 4:41 pm DeliverXTtile.fm Panomics, Inc. DeliverX and DeliverX Plus sirna Transfection Kit User Manual
sirna Overview and Technical Tips
 1 sirna Overview and Technical Tips 2 CONTENTS 3 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 14 18 19 20 21 Introduction Applications How Does It Work? Handy Tips Troubleshooting Conclusions Further References Contact Us 3 INTRODUCTION
1 sirna Overview and Technical Tips 2 CONTENTS 3 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 14 18 19 20 21 Introduction Applications How Does It Work? Handy Tips Troubleshooting Conclusions Further References Contact Us 3 INTRODUCTION
ViaFect Transfection Reagent
 TECHNICAL MANUAL ViaFect Transfection Reagent Instructions for Use of Products E4981, E4982 and E4983 Revised 7/17 TM409 ViaFect Transfection Reagent All technical literature is available at: www.promega.com/protocols/
TECHNICAL MANUAL ViaFect Transfection Reagent Instructions for Use of Products E4981, E4982 and E4983 Revised 7/17 TM409 ViaFect Transfection Reagent All technical literature is available at: www.promega.com/protocols/
ExGen 500 in vitro Transfection Reagent (#R0511, 1ml (for in vitro transfections))
 1 ExGen 500 in vitro Transfection Reagent (#R0511, 1ml (for 100-200 in vitro transfections)) Cationic polymer transfection reagent Concentration 5.47mM in nitrogen residues or 10µM in PEI. Reagent no Supplied
1 ExGen 500 in vitro Transfection Reagent (#R0511, 1ml (for 100-200 in vitro transfections)) Cationic polymer transfection reagent Concentration 5.47mM in nitrogen residues or 10µM in PEI. Reagent no Supplied
Transfection Reagent INTRODUCTION SPECIFICATIONS MATERIALS. For Research Use Only. Materials Supplied. Materials required, but not supplied
 TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent INTRODUCTION TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in various neural cell types.
TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent INTRODUCTION TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in various neural cell types.
TransIT Transfection Reagent
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent that provides exceptional transfection of plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. TransIT-2020
INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent that provides exceptional transfection of plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. TransIT-2020
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon SMARTvector 2.0 Lentiviral shrna Particles
 Thermo Scientific Dharmacon SMARTvector 2.0 Lentiviral shrna Particles Long-term gene silencing shrna-specific design algorithm High titer, purified particles Thermo Scientific Dharmacon SMARTvector shrna
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon SMARTvector 2.0 Lentiviral shrna Particles Long-term gene silencing shrna-specific design algorithm High titer, purified particles Thermo Scientific Dharmacon SMARTvector shrna
sirna Transfection Reagent
 Description RiboJuice 0.3 ml 71115-3 1.0 ml 71115-4 Description RiboJuice efficiently delivers small interfering RNA (sirna) into a wide range of mammalian cell lines for targeted gene suppression (1).
Description RiboJuice 0.3 ml 71115-3 1.0 ml 71115-4 Description RiboJuice efficiently delivers small interfering RNA (sirna) into a wide range of mammalian cell lines for targeted gene suppression (1).
TransIT -Prostate Transfection Kit
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -Prostate Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in Prostate cell types. Generally, prostate cell types have been
INTRODUCTION TransIT -Prostate Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in Prostate cell types. Generally, prostate cell types have been
FectoPRO DNA transfection kit for Bioproduction PROTOCOL
 DNA transfection kit for Bioproduction PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION transfection kit is specifically designed for enhanced Transient Gene Expression using low DNA amounts, in suspension CHO and HEK-293 cells as
DNA transfection kit for Bioproduction PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION transfection kit is specifically designed for enhanced Transient Gene Expression using low DNA amounts, in suspension CHO and HEK-293 cells as
Transfection Kit Protocol for MIR 2900, 2904, 2905, 2906
 TransIT-HeLaMONSTER Transfection Kit INTRODUCTION TransIT-HeLaMONSTER Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in HeLa cells and cell types
TransIT-HeLaMONSTER Transfection Kit INTRODUCTION TransIT-HeLaMONSTER Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in HeLa cells and cell types
User s Guide MegaTran 1.0 Transfection Reagent
 User s Guide MegaTran 1.0 Transfection Reagent Package Contents and Storage Conditions... 2 Related products... 2 Introduction... 2 Production and Quality Assurance:... 3 Experimental Procedures... 3 Transfection
User s Guide MegaTran 1.0 Transfection Reagent Package Contents and Storage Conditions... 2 Related products... 2 Introduction... 2 Production and Quality Assurance:... 3 Experimental Procedures... 3 Transfection
TransIT -BrCa Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5500 INTRODUCTION TransIT -BrCa Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5500 INTRODUCTION TransIT -BrCa Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency
TransIT -LT1 Transfection Reagent
 Protocol for Product Nos. MIR 2300, 2304, 2305, 2306 i n t r o d u c t i o n The easy to use TransIT-LT1 (Low Toxicity) Transfection Reagent provides superior transfection efficiency, cell viability, and
Protocol for Product Nos. MIR 2300, 2304, 2305, 2306 i n t r o d u c t i o n The easy to use TransIT-LT1 (Low Toxicity) Transfection Reagent provides superior transfection efficiency, cell viability, and
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in CHO cells and cell types of associated lineage. TransIT-CHO Transfection
INTRODUCTION TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in CHO cells and cell types of associated lineage. TransIT-CHO Transfection
TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit
 INTRODUCTION TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in CHO cells and cell types of associated lineage. TransIT-CHO Transfection
INTRODUCTION TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in CHO cells and cell types of associated lineage. TransIT-CHO Transfection
Transfection. How do you study and control gene expression? How do you detect mycoplasma contamination?
 PROTEIN FUNCTION & ANALYSIS Transfection How do you study and control gene expression? How do you detect mycoplasma contamination? How do you ensure the success of your RNA or protein transfection? TRANSFECTION
PROTEIN FUNCTION & ANALYSIS Transfection How do you study and control gene expression? How do you detect mycoplasma contamination? How do you ensure the success of your RNA or protein transfection? TRANSFECTION
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA
 sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
TransIT-PRO Transfection Reagent Protocol for MIR 5740 and 5750
 Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5740 INTRODUCTION TransIT-PRO Transfection Reagent was developed by empirically testing proprietary lipid and polymer
Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5740 INTRODUCTION TransIT-PRO Transfection Reagent was developed by empirically testing proprietary lipid and polymer
TransIT -Keratinocyte Transfection Reagent
 TransIT -Keratinocyte Transfection Reagent Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2800 INTRODUCTION TransIT -Keratinocyte Transfection Reagent is specifically
TransIT -Keratinocyte Transfection Reagent Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2800 INTRODUCTION TransIT -Keratinocyte Transfection Reagent is specifically
TransIT -Lenti Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/6600 INTRODUCTION Lentivirus is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus from the Retroviridae family capable of infecting
Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/6600 INTRODUCTION Lentivirus is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus from the Retroviridae family capable of infecting
TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2170 INTRODUCTION TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/2170 INTRODUCTION TransIT -CHO Transfection Kit is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency
pdsipher and pdsipher -GFP shrna Vector User s Guide
 pdsipher and pdsipher -GFP shrna Vector User s Guide NOTE: PLEASE READ THE ENTIRE PROTOCOL CAREFULLY BEFORE USE Page 1. Introduction... 1 2. Vector Overview... 1 3. Vector Maps 2 4. Materials Provided...
pdsipher and pdsipher -GFP shrna Vector User s Guide NOTE: PLEASE READ THE ENTIRE PROTOCOL CAREFULLY BEFORE USE Page 1. Introduction... 1 2. Vector Overview... 1 3. Vector Maps 2 4. Materials Provided...
In vitro Transfection Protocol
 BIOMOL GmbH Waidmannstr. 35 22769 Hamburg info@biomol.de www.biomol.de Phone:+49-40-8532600 or 0800-2466651 (D) Fax: +49-40-85326022 or 0800-2466652 (D) In vitro Transfection Protocol Technical Assistance...
BIOMOL GmbH Waidmannstr. 35 22769 Hamburg info@biomol.de www.biomol.de Phone:+49-40-8532600 or 0800-2466651 (D) Fax: +49-40-85326022 or 0800-2466652 (D) In vitro Transfection Protocol Technical Assistance...
TRANSFEX - SUPERIOR GENE EXPRESSION FOR HARD-TO-TRANSFECT CELL TYPES. Kevin Grady Product Line Business Manager ASCB Vendor Showcase Dec.
 TRANSFEX - SUPERIOR GENE EXPRESSION FOR HARD-TO-TRANSFECT CELL TYPES Kevin Grady Product Line Business Manager ASCB Vendor Showcase Dec. 15, 2013 Outline Overview of transfection TransfeX Primary/hTERT
TRANSFEX - SUPERIOR GENE EXPRESSION FOR HARD-TO-TRANSFECT CELL TYPES Kevin Grady Product Line Business Manager ASCB Vendor Showcase Dec. 15, 2013 Outline Overview of transfection TransfeX Primary/hTERT
PRODUCT INFORMATION...
 VIROMER GREEN In vitro sirna/microrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 BLUE OR GREEN?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
VIROMER GREEN In vitro sirna/microrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 BLUE OR GREEN?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
LabBOOK VIROMER BLUE VIROMER GREEN. sirna /mirna transfection
 LabBOOK VIROMER BLUE VIROMER GREEN sirna /mirna transfection Contact General information Bettina Weber (Biologist) +49 345 55 59 625 bettina.weber@lipocalyx.de Dr. Sandra Lagauzère (Biologist) +49 345
LabBOOK VIROMER BLUE VIROMER GREEN sirna /mirna transfection Contact General information Bettina Weber (Biologist) +49 345 55 59 625 bettina.weber@lipocalyx.de Dr. Sandra Lagauzère (Biologist) +49 345
RmesFect Stem Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Li StarFish S.r.l. Via Cavour, 35-20063 Cernusco S/N (MI), Italy Tel. +39-02-92150794 - Fax. +39-02-92157285 info@listarfish.it -www.listarfish.it RmesFect Stem Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Li StarFish S.r.l. Via Cavour, 35-20063 Cernusco S/N (MI), Italy Tel. +39-02-92150794 - Fax. +39-02-92157285 info@listarfish.it -www.listarfish.it RmesFect Stem Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Viromer RED and YELLOW
 Viromer RED and YELLOW in vitro plasmid DNA Transfection Protocol Product Information 2 Before You Start 4 Standard Transfection Protocol 5 Alternative Protocol: the direct complexation 6 Troubleshooting
Viromer RED and YELLOW in vitro plasmid DNA Transfection Protocol Product Information 2 Before You Start 4 Standard Transfection Protocol 5 Alternative Protocol: the direct complexation 6 Troubleshooting
Certified. TransIT Broad Spectrum Transfection Reagents. TransIT-X2. TransIT -LT1. TransIT TransIT -mrna
 Broad Spectrum Reagents For more than two decades Mirus Bio has been dedicated to developing reagents that feature high efficiency, low toxicity transfections. The products included in this piece are our
Broad Spectrum Reagents For more than two decades Mirus Bio has been dedicated to developing reagents that feature high efficiency, low toxicity transfections. The products included in this piece are our
XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual
 XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual An RNA-guided recombinant endonuclease for efficient targeted DNA cleavage Catalog Numbers CE1000-50K, CE1000-50, CE1000-250, CE1001-250, CE1001-1000 Table of
XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual An RNA-guided recombinant endonuclease for efficient targeted DNA cleavage Catalog Numbers CE1000-50K, CE1000-50, CE1000-250, CE1001-250, CE1001-1000 Table of
Transfection of neural stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent in StemPro medium
 TRANSFECTION PROTOCOL Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent Transfection of neural stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent in StemPro medium NSC media, passaging reagents, and complexation
TRANSFECTION PROTOCOL Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent Transfection of neural stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent in StemPro medium NSC media, passaging reagents, and complexation
SuperPrep Cell Lysis & RT Kit for qpcr
 SuperPrep Cell Lysis & RT Kit for qpcr 1402 F1267K SuperPrep Cell Lysis & RT Kit for qpcr SCQ-101 100 reactions Store at -20 C SuperPrep Cell Lysis Kit for qpcr SCQ-201 100 preparations Store at -20 C
SuperPrep Cell Lysis & RT Kit for qpcr 1402 F1267K SuperPrep Cell Lysis & RT Kit for qpcr SCQ-101 100 reactions Store at -20 C SuperPrep Cell Lysis Kit for qpcr SCQ-201 100 preparations Store at -20 C
Cell Culture, Transfection and Microscopy in one Slide
 www.biontex.com www.ibidi.com µ Transfection Kit VI Cell Culture, Transfection and Microscopy in one Slide The µ Transfection Kit VI combines the efficient transfection of METAFECTENE µ (Biontex Laboratories
www.biontex.com www.ibidi.com µ Transfection Kit VI Cell Culture, Transfection and Microscopy in one Slide The µ Transfection Kit VI combines the efficient transfection of METAFECTENE µ (Biontex Laboratories
DreamFect INSTRUCTION MANUAL. OZ Biosciences / Protocol DreamFect /
 DreamFect INSTRUCTION MANUAL www.ozbiosciences.com OZ Biosciences / Protocol DreamFect / www.ozbiosciences.com - 0 - www.ozbiosciences.com DreamFect Instruction Manual DreamFect The next generation of
DreamFect INSTRUCTION MANUAL www.ozbiosciences.com OZ Biosciences / Protocol DreamFect / www.ozbiosciences.com - 0 - www.ozbiosciences.com DreamFect Instruction Manual DreamFect The next generation of
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX
 Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
3D Transfection System
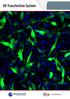 3D Transfection System Why 3D Technology? Introduction to Three Dimensional (3D) Cell Culture The goal of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture is to eliminate the stress and artificial responses cells experience
3D Transfection System Why 3D Technology? Introduction to Three Dimensional (3D) Cell Culture The goal of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture is to eliminate the stress and artificial responses cells experience
ScreenFect mrna Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 l ScreenFect mrna Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL S-5001 Cat. No. S-5001-2 S-5001-3 Contents 1. Overview: How to use ScreenFect mrna 2 2. Advantages of mrna Transfection and ScreenFect mrna 3 3.
l ScreenFect mrna Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL S-5001 Cat. No. S-5001-2 S-5001-3 Contents 1. Overview: How to use ScreenFect mrna 2 2. Advantages of mrna Transfection and ScreenFect mrna 3 3.
TransIT -Lenti Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/6600 INTRODUCTION Lentivirus is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus from the Retroviridae family capable of infecting
Quick Reference Protocol, SDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/6600 INTRODUCTION Lentivirus is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus from the Retroviridae family capable of infecting
Cignal Reporter Assay Handbook
 January 2011 Cignal Reporter Assay Handbook For cell-based pathway activity assays Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the leading provider of innovative sample and
January 2011 Cignal Reporter Assay Handbook For cell-based pathway activity assays Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the leading provider of innovative sample and
VIROMER RED and YELLOW
 VIROMER RED and YELLOW In vitro plasmid DNA Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 INITIAL
VIROMER RED and YELLOW In vitro plasmid DNA Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 INITIAL
Calcium Assay Kit. Technical Data Sheet. Product Information. Description. Storage. Materials not included
 BD Technical Data Sheet Calcium Assay Kit Product Information Catalog Number: 640176 Size Reagents for 10 plates Components: Calcium Indicator, 1 vial, lyophilized 10X Signal Enhancer, 10 ml 1X Calcium
BD Technical Data Sheet Calcium Assay Kit Product Information Catalog Number: 640176 Size Reagents for 10 plates Components: Calcium Indicator, 1 vial, lyophilized 10X Signal Enhancer, 10 ml 1X Calcium
amaxa Peptide Transfection Control 2-3 Product specifications 2 Storage and stability 3 Product use limitations 3 Intended use 3
 Contents amaxa Peptide Transfection Control 2-3 Product specifications 2 Storage and stability 3 Product use limitations 3 Intended use 3 Background Information 4 Cell culture 4 Supporting Data 5-8 Equipment
Contents amaxa Peptide Transfection Control 2-3 Product specifications 2 Storage and stability 3 Product use limitations 3 Intended use 3 Background Information 4 Cell culture 4 Supporting Data 5-8 Equipment
The RNAi Consortium (TRC) Broad Institute
 TRC Laboratory Protocols Protocol Title: Lentivirus production of shrna, CRISPR, or ORF-pLX clones in 10 cm dishes or 6- well plates Current Revision Date: 6/3/2015 RNAi Platform,, trc_info@broadinstitute.org
TRC Laboratory Protocols Protocol Title: Lentivirus production of shrna, CRISPR, or ORF-pLX clones in 10 cm dishes or 6- well plates Current Revision Date: 6/3/2015 RNAi Platform,, trc_info@broadinstitute.org
In-Cell Western Kits I and II
 Odyssey and Aerius Infrared Imaging Systems In-Cell Western Assay Kits I and II Published November, 2006. The most recent version of this protocol is posted at http://biosupport.licor.com/protocols.jsp
Odyssey and Aerius Infrared Imaging Systems In-Cell Western Assay Kits I and II Published November, 2006. The most recent version of this protocol is posted at http://biosupport.licor.com/protocols.jsp
Stem cell transfection guide
 APPLICATION NOTE Stem cell transfection guide Gene delivery solutions Introduction Stem cells continue to show immense promise for the future of regenerative medicine and personalized therapeutic treatments.
APPLICATION NOTE Stem cell transfection guide Gene delivery solutions Introduction Stem cells continue to show immense promise for the future of regenerative medicine and personalized therapeutic treatments.
Luc-Pair Duo-Luciferase Assay Kit 2.0
 G e n e C o p o eia TM Expressway to Discovery Luc-Pair Duo-Luciferase Assay Kit 2.0 For luciferase assays Cat. No. LF001 (Old Cat. No. LPFR-P010, 100 reactions) Cat. No. LF002 (Old Cat. No. LPFR-P030,
G e n e C o p o eia TM Expressway to Discovery Luc-Pair Duo-Luciferase Assay Kit 2.0 For luciferase assays Cat. No. LF001 (Old Cat. No. LPFR-P010, 100 reactions) Cat. No. LF002 (Old Cat. No. LPFR-P030,
Data Sheet. Hippo Pathway TEAD Reporter MCF7 Cell Line Catalog #: 60618
 Data Sheet Hippo Pathway TEAD Reporter MCF7 Cell Line Catalog #: 6618 Background The Hippo pathway regulates cell proliferation and cell death. It is activated by high cell density and cell stress to stop
Data Sheet Hippo Pathway TEAD Reporter MCF7 Cell Line Catalog #: 6618 Background The Hippo pathway regulates cell proliferation and cell death. It is activated by high cell density and cell stress to stop
Functional Analysis. LNA longrna GapmeR
 Functional Analysis LNA longrna GapmeR Instruction manual v2.0 August 2013 Table of contents Product Summary............................................................ Content...................................................................
Functional Analysis LNA longrna GapmeR Instruction manual v2.0 August 2013 Table of contents Product Summary............................................................ Content...................................................................
Protocol. High-throughput Transfection Protocol for GoClone Reporter Assays. Tech support: Luciferase Assay System
 Luciferase Assay System Protocol High-throughput Transfection Protocol for GoClone Reporter Assays LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow promoter luciferase Step 1: Simultaneously
Luciferase Assay System Protocol High-throughput Transfection Protocol for GoClone Reporter Assays LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow promoter luciferase Step 1: Simultaneously
COSFect Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL. OZ Biosciences / Protocol RmesFect/
 COSFect Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL www.ozbiosciences.com OZ Biosciences / Protocol RmesFect/ www.ozbiosciences.com / -0- COSFect Instruction Manual COSFect is the ideal transfection reagent
COSFect Transfection Reagent INSTRUCTION MANUAL www.ozbiosciences.com OZ Biosciences / Protocol RmesFect/ www.ozbiosciences.com / -0- COSFect Instruction Manual COSFect is the ideal transfection reagent
EpiQuik General Protein-DNA Binding Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 EpiQuik General Protein-DNA Binding Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik General Protein-DNA Binding Assay Kit (Fluorometric) is suitable for
EpiQuik General Protein-DNA Binding Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik General Protein-DNA Binding Assay Kit (Fluorometric) is suitable for
CRE/CREB Reporter Assay Kit camp/pka Cell Signaling Pathway Catalog #: 60611
 Data Sheet CRE/CREB Reporter Assay Kit camp/pka Cell Signaling Pathway Catalog #: 60611 Background The main role of the camp response element, or CRE, is mediating the effects of Protein Kinase A (PKA)
Data Sheet CRE/CREB Reporter Assay Kit camp/pka Cell Signaling Pathway Catalog #: 60611 Background The main role of the camp response element, or CRE, is mediating the effects of Protein Kinase A (PKA)
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay. Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung *
 In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung * Clinical Oncology Department, The Univerisity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR *For
In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung * Clinical Oncology Department, The Univerisity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR *For
Application Note sirna dependent gene silencing in HeLa cells cultivated on various cell culture surfaces
 Application Note sirna dependent gene silencing in HeLa cells cultivated on various cell culture surfaces 1 Introduction 1.1 RNA interference (RNAi) One of the most important advances in biology in the
Application Note sirna dependent gene silencing in HeLa cells cultivated on various cell culture surfaces 1 Introduction 1.1 RNA interference (RNAi) One of the most important advances in biology in the
Automated Optimization of Cell Transfection
 Automated Optimization of Cell Transfection Abstract Cell transfection is an essential technique for interrogating cellular pathways. Determining the optimal conditions for introducing nucleic acids into
Automated Optimization of Cell Transfection Abstract Cell transfection is an essential technique for interrogating cellular pathways. Determining the optimal conditions for introducing nucleic acids into
