Inception. Describe the vision and business case for this project. Determine if the enterprise should build or buy the necessary system.
|
|
|
- Harriet Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inception What needs to be done? Describe the vision and business case for this project. Determine if the project is feasible. Determine if the enterprise should build or buy the necessary system. Make a rough estimate of the cost of the project. Determine if we should go ahead with the project. If the answer is YES..
2 Inception Artifacts generated during Inception Artifact Vision and Business Case Use-Case Model Supplementary Spec. Glossary Prototyes and proof-ofconcepts Iteration Plan Comment Describes the high-level goals and constraints and provides an executive summary Describes the functional requirements of high-level goals, and related non-functional requirements Describes other requirements Begin keeping a dictionary of key domain terminology To clarify the vision and validate techincal ideas Describe what to do in the first Elaboration Iteration
3 Inception ATM Example: (Partial) Vision Version Date Description Author Inception Draft Sept. 1, 2004 First draft to be refined primarily during Elaboration J. TenEyck Introduction and Problem Statement We envision a banking system that provides automatic teller machines (ATMs) at which customers holding a bank card can make deposits and withdrawls to and from their accounts. The ATM machines will belong to a consortium of banks participating in this project.
4 ATM Vision (cont.) Business Opportunity ATM machines will be attractive to banking customers because they allow access to their accounts outside of regular business hours. They allow the bank to expand customer services and geographical reach without the cost of building additional branches or hiring additional tellers. Product Position Statement Here we state the outstanding or unique features of this system, who it is for and what additional potential customers it might attract, and what differentiates it from the competition. Stakeholder Descriptions Participating Banks Want to make sure that access to their customer account information is safe and secure, transaction information is accurate and reliable, and that their own account card is readily recognizable at a large number of ATMs. Bank Customers Want easy, low-cost, remote access to their accounts, but want to be assured that their accounts are secure and not accessible to hackers or other third parties.
5 ATM Vision (cont.) High-level Goal Fast, robust, and secure automated teller network. Priority -- high Problems and Concerns -- Client bank must be able to handle multiple simultaneous transactions (and possible simultaneous transactions to the same joint account). Banks owning an ATM must be able to determine the cash on hand in the ATM. The cash in the ATM must be secure. Consortium server must be able to identify the home bank of the customer card.
6 ATM Vision (cont.) User Goals Customer Make withdrawls, deposits, and balance checks to his/her account. Home Bank Provide secure access for customer to his/her account. These indicate high-level use cases to be initiated during Inception Product Overview The ATM network will consist of a large number of ATM machines distributed over a wide geographical area. The network must be able to handle a growth in ATM terminals and an expanding geographical area. It will have to be able to readily form an interface with other ATM networks in other parts of the world. The ATM network will provide services to users and collaborate with other banking networks as indicated in the diagram on the next slide.
7 ATM Vision (cont.) Customer Use services ATM Network Use services System Administrators Actors Consortium Computer System Use services <actor> Member Bank Customer Accounts Note! External agents may also be other, inplace Systems
8 ATM Vision (cont.) Summary of Benefits Supporting Feature Functionally, the system will provide teller services to bank customers Real-time transactions with member bank systems using industry standard protocols Pluggable business rules at various scenario points during transaction processing Stakeholder Benefit Automated, remote access to user accounts. Timely account updates and transaction recording Flexible business logic configuration This table relates the goals, benefits and solutions at a higher level not solely related to use cases.
9 Summary of System Features Transaction capture Transaction authorization Security of transaction information ATM Vision (cont.) Real-time transactions with other interconnected ATM networks Definition and execution of customized pluggable business rules at fixed common points in the processing scenarios Real-time interaction with member bank account processing systems Other elements of the Vision Statement include: Assumptions and Dependencies and/or Constraints Cost and Pricing of the System under construction Licensing and Installation of ATM terminals Plans for allowing expansion of the network
10 The Vision Thing The Vision Document is a useful tool for management to make determination of whether to build, buy, redefine, or abort consideration of the system. It provides sufficient nontechnical detail for evaluating the system under consideration. The Vision Document is also useful to the Technical people for beginning the process of determining and describing the requirements of the system. It indicates the important high-level and stakeholder goals that need elaboration in the use cases. Note that the class project is a system taken out of any particular context. The problem statement will serve instead of a vision document, and the remainder of the inception process will proceed from there.
11 The Glossary During Inception, the Glossary should be a simple listing of terms with brief descriptions or definitions. During Elaboration, the Glossary expands into the role of a Data Dictionary. Term Definition and Information Aliases ATM A banking terminal and required software for processing customer transactions Automatic teller machine It is important to start early in keeping a glossary of terms so that all members of the design team have the same concept of what each term means. In the example shown here, The term ATM refers to both the physical terminal and the supporting software that it contains.
12 The Glossary In subsequent elaborations the Glossary is refined to include Format (type, length, unit) Relationship to other terms (attributes, associations, methods) Range of values Validation rules
13 Use Cases During Inception some of the most important stakeholder goals should be developed as use cases. During Inception, it is not necessary, nor necessarily desirable, to generate a fully dressed use case, nor is it necessary to develop any but the most important of the stakeholder goals into use cases. Essential Use Case Statements Name Primary Actor Stakeholders and Interests Brief Narrative Preconditions Post-conditions ATM Withdrawl Valid Member Bank Account Holder Account Holder, Member Bank Useful in determining the problem domain Concepts and providing guidelines for elaboration of success scenarios, User must have a valid bank card, must indicate an amount < balance User obtains proper cash, user account correctly debited, transaction recorded at bank
14 Supplementary Specifications The difference between the component features of the supplementary specification and the Vision is that the Supplementary Specification contains information more particular to the technical specialists whereas the Vision is a broader document that is most useful for management:. Components of the Supplementary Specification Document Human Factors Reliability Performance Adaptability Business Rules Legal Issues Text vfisible from at least 1 meter. Clear, step-by-step instructions for use. The consortium computer must keep a transaction record for member banks to use for comparison Each transaction should require less than 1 minute of customer s time Projected growth rate of the ATM base and member banks. Will use an X.25 based intranet to connect ATMs and member banks Configurability with consortium computer Recommend a Linux based consortium server and java as Implementation Constraints the programming language for ATM client code. Interfaces Card reader in ATM. Touch screen monitor. Receipt printer. Fee structure charged by member banks.
15 Iteration Plan Time frame for the iteration: Start date: Sept. 15, 2004 End Date: Oct. 6, 2004 Deliverable Artifacts Use cases: Access Account Deposit Withdraw Identify concepts within the ATM network to help develop an initial concept model diagram Balance Statement Use Case Diagrams Identify boundary between system and identified actors Domain Model (Concept Model Diagram) State Diagram Software prototype Test Plan Identify states and state transitions for each user initiated button event A simulation demonstrating the user interaction with an ATM terminal Develop and Execute a Plan to ensure that the various user events do not cause the system to enter an error state or to hangup.
16 Iteration Plan (cont.) Preliminary User Manual Developed Describe the appearance of the screen and the sequence of actions that the user must perform
Comp435 Object-Oriented Design. Requirements and Use Cases. Requirements Analysis. Outline. Requirements Analysis. Requirements change
 Comp435 Object-Oriented Design Requirements and Use Cases Week 2 Computer Science PSU HBG 1 3 Outline Requirements Analysis Types of Requirements Requirements in Iterative Development Requirements Artifacts
Comp435 Object-Oriented Design Requirements and Use Cases Week 2 Computer Science PSU HBG 1 3 Outline Requirements Analysis Types of Requirements Requirements in Iterative Development Requirements Artifacts
Requirements Analysis
 Requirements Analysis Analysis and Design? Analysis emphasizes an investigation of the problem and requirements, rather than a solution. Analysis = requirements analysis + object analysis. Requirement
Requirements Analysis Analysis and Design? Analysis emphasizes an investigation of the problem and requirements, rather than a solution. Analysis = requirements analysis + object analysis. Requirement
Requirements Analysis. Requirements Analysis is Hard
 Requirements Analysis Classify categories of requirements Define the principles of iterative requirements analysis Learn about use cases and their elements Focusing on the WHAT not the HOW 1 Requirements
Requirements Analysis Classify categories of requirements Define the principles of iterative requirements analysis Learn about use cases and their elements Focusing on the WHAT not the HOW 1 Requirements
Requirements Analysis. Overview
 Requirements Analysis Overview What is requirement? Classification of requirements Iterative and evolutionary requirements analysis Use Cases Domain models N. Meng, B. Ryder 2 1 Requirements Definition
Requirements Analysis Overview What is requirement? Classification of requirements Iterative and evolutionary requirements analysis Use Cases Domain models N. Meng, B. Ryder 2 1 Requirements Definition
Requirements Analysis
 Objectives Classify categories of requirements Requirements Analysis Define the principles of iterative requirements analysis Learn about use cases and their elements Define system sequence diagrams for
Objectives Classify categories of requirements Requirements Analysis Define the principles of iterative requirements analysis Learn about use cases and their elements Define system sequence diagrams for
Essentials of IBM Rational Requirements Composer, v3. Module 4: Creating a use-case model
 Essentials of IBM Rational Requirements Composer, v3 Module 4: Creating a use-case model Copyright IBM Corporation 2010, 2011 Module overview After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain
Essentials of IBM Rational Requirements Composer, v3 Module 4: Creating a use-case model Copyright IBM Corporation 2010, 2011 Module overview After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain
COMPONENT DIAGRAMS CASE STUDIES
 COMPONENT DIAGRAMS CASE STUDIES UML Component Diagram Component diagram represents the components in which the particular application needs to be installed or implemented on. It also shows the type of
COMPONENT DIAGRAMS CASE STUDIES UML Component Diagram Component diagram represents the components in which the particular application needs to be installed or implemented on. It also shows the type of
Automatic Demand Draft Generation using the Automated Teller Machine
 Automatic Demand Draft Generation using the Automated Teller Machine Shraddha V MTech in CSE, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, AMC Engineering College Bangalore, Jayashubha J Associate Prof,
Automatic Demand Draft Generation using the Automated Teller Machine Shraddha V MTech in CSE, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, AMC Engineering College Bangalore, Jayashubha J Associate Prof,
Description: The customer logs into an ATM machine and withdraws a desired amount of cash.
 UC1: Withdraw Cash Description: The customer logs into an ATM machine and withdraws a desired amount of cash. Primary Actor: Customer Stakeholders and Interests: - Customer: Wants quick, accurate withdrawal
UC1: Withdraw Cash Description: The customer logs into an ATM machine and withdraws a desired amount of cash. Primary Actor: Customer Stakeholders and Interests: - Customer: Wants quick, accurate withdrawal
Chapter 3 Prescriptive Process Models
 Chapter 3 Prescriptive Process Models - Generic process framework (revisited) - Traditional process models - Specialized process models - The unified process Generic Process Framework Communication Involves
Chapter 3 Prescriptive Process Models - Generic process framework (revisited) - Traditional process models - Specialized process models - The unified process Generic Process Framework Communication Involves
Software Development Methodologies. CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1
 Software Development Methodologies CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1 Topics 1. The Waterfall Model 2. Agile Software Development 3. The Unified Process 4. Object-Oriented Analysis and Design 5. The
Software Development Methodologies CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1 Topics 1. The Waterfall Model 2. Agile Software Development 3. The Unified Process 4. Object-Oriented Analysis and Design 5. The
IBM Software Group. Mastering Requirements Management with Use Cases Module 4: Analyze the Problem
 IBM Software Group Mastering Requirements Management with Use Cases Module 4: Analyze the Problem 1 Objectives Define problem analysis and its goal. Describe activities for problem analysis. Identify the
IBM Software Group Mastering Requirements Management with Use Cases Module 4: Analyze the Problem 1 Objectives Define problem analysis and its goal. Describe activities for problem analysis. Identify the
Communication Model for Cooperative Robotics Simulator. Project Plan. Version 1.0
 Communication Model for Cooperative Robotics Simulator Project Plan Version 1.0 1 Introduction This document provides an overview of project plan for Communication Model for Cooperative Robotics Simulator
Communication Model for Cooperative Robotics Simulator Project Plan Version 1.0 1 Introduction This document provides an overview of project plan for Communication Model for Cooperative Robotics Simulator
Oracle FLEXCUBE ATM User Manual Release Part No E
 Oracle FLEXCUBE ATM User Manual Release 4.3.1.0.0 Part No E52075-01 ATM User Manual Table of Contents (index) 1. ATM... 3 1.1. ATM01 - ATM Bank Params Maintenance... 4 1.2. ATM02 - ATM Acquirer POS Id
Oracle FLEXCUBE ATM User Manual Release 4.3.1.0.0 Part No E52075-01 ATM User Manual Table of Contents (index) 1. ATM... 3 1.1. ATM01 - ATM Bank Params Maintenance... 4 1.2. ATM02 - ATM Acquirer POS Id
Oracle FLEXCUBE Core Banking
 Oracle FLEXCUBE Core Banking Automated Teller Machine User Manual Release 5.2.0.0.0 Part No. E71602-01 March 2016 ATM User Manual March 2016 Oracle Financial Services Software Limited Oracle Park Off Western
Oracle FLEXCUBE Core Banking Automated Teller Machine User Manual Release 5.2.0.0.0 Part No. E71602-01 March 2016 ATM User Manual March 2016 Oracle Financial Services Software Limited Oracle Park Off Western
Requirements Engineering
 Requirements Engineering Software Engineering Andreas Zeller Saarland University Requirements Engineering The Real World Requirements Engineering A description of what the system should do (but not how)
Requirements Engineering Software Engineering Andreas Zeller Saarland University Requirements Engineering The Real World Requirements Engineering A description of what the system should do (but not how)
Power grids & Actors
 EH2750 Computer Applications in Power Systems, Advanced Course. Lecture 2 31 August 2011 Professor Lars Nordström Dept of Industrial Information & Control systems, KTH larsn@ics.kth.se Power grids & Actors
EH2750 Computer Applications in Power Systems, Advanced Course. Lecture 2 31 August 2011 Professor Lars Nordström Dept of Industrial Information & Control systems, KTH larsn@ics.kth.se Power grids & Actors
Requirements elicitation: Finding the Voice of the Customer
 Requirements elicitation: Finding the Voice of the Customer Establishing customer requirements for a software system Identify sources of user requirements on your project Identify different classes of
Requirements elicitation: Finding the Voice of the Customer Establishing customer requirements for a software system Identify sources of user requirements on your project Identify different classes of
Use cases. Version 2.6 November 2015
 Use cases Version 2.6 November 2015 Maurizio Morisio, Marco Torchiano, 2014 Requirements Document 1. Purpose and scope 2. The terms used / Glossary 3. The use cases 4. The technology to be used 5. Other
Use cases Version 2.6 November 2015 Maurizio Morisio, Marco Torchiano, 2014 Requirements Document 1. Purpose and scope 2. The terms used / Glossary 3. The use cases 4. The technology to be used 5. Other
2009 Spring. Software Modeling & Analysis. Introduction to OSP. Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO
 2009 Spring Software Modeling & Analysis Introduction to OSP OSP Stage 1000 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is OSP? OSP (Object Space Process) A software process based on RUP Tailored to
2009 Spring Software Modeling & Analysis Introduction to OSP OSP Stage 1000 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is OSP? OSP (Object Space Process) A software process based on RUP Tailored to
PART II Inception. Chapter 4 Inception is Not the Requirements Phase. development cycle. phase. iteration. inc. elaboration construction transition
 PART II Inception development cycle iteration phase inc. elaboration construction transition 1 Chapter 4 Inception is Not the Requirements Phase 1 What is Inception? 1 Inception is the initial short step
PART II Inception development cycle iteration phase inc. elaboration construction transition 1 Chapter 4 Inception is Not the Requirements Phase 1 What is Inception? 1 Inception is the initial short step
Arcade Game Maker Product Line Concept of Operations
 Arcade Game Maker Product Line Concept of Operations ArcadeGame Team July 2003 Table of Contents 1 Overview 1 1.1 Identification 2 1.2 Document Map 2 1.3 Concepts 3 1.4 Readership 3 2 Approach 4 3 Background
Arcade Game Maker Product Line Concept of Operations ArcadeGame Team July 2003 Table of Contents 1 Overview 1 1.1 Identification 2 1.2 Document Map 2 1.3 Concepts 3 1.4 Readership 3 2 Approach 4 3 Background
<Project Name> Development Case
 Version [Note: The following template is provided for use with the Rational Unified Process. Text enclosed in square brackets and displayed in blue italics (style=infoblue) is included
Version [Note: The following template is provided for use with the Rational Unified Process. Text enclosed in square brackets and displayed in blue italics (style=infoblue) is included
Introduction of RUP - The Rational Unified Process
 Introduction of RUP - The Rational Unified Process Jong-Hoon Lee Dependable Software Laboratory Konkuk University References Textbook: The Rational Unified Process Made Easy A Practitioner s Guide to the
Introduction of RUP - The Rational Unified Process Jong-Hoon Lee Dependable Software Laboratory Konkuk University References Textbook: The Rational Unified Process Made Easy A Practitioner s Guide to the
MSO Lecture 2. Wouter Swierstra (adapted by HP) September 14, 2017
 1 MSO Lecture 2 Wouter Swierstra (adapted by HP) September 14, 2017 2 LABS No lab partner? Speed dating in front of the blackboard during the break. 3 LAST LECTURE Overview of course: object oriented analysis
1 MSO Lecture 2 Wouter Swierstra (adapted by HP) September 14, 2017 2 LABS No lab partner? Speed dating in front of the blackboard during the break. 3 LAST LECTURE Overview of course: object oriented analysis
Software Modeling & Analysis
 Software Modeling & Analysis OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is OOPT? OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) A software process based on RUP Revision
Software Modeling & Analysis OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is OOPT? OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) A software process based on RUP Revision
Test Workflow. Michael Fourman Cs2 Software Engineering
 Test Workflow Michael Fourman Introduction Verify the result from implementation by testing each build Plan the tests in each iteration Integration tests for every build within the iteration System tests
Test Workflow Michael Fourman Introduction Verify the result from implementation by testing each build Plan the tests in each iteration Integration tests for every build within the iteration System tests
The Use Case Technique: An Overview
 The Use Case Technique: An Overview Sponsored by: Karl Wiegers Principal Consultant, Process Impact www.processimpact.com Sponsor: CEG Save 20% on training* with promo code: MAWEB14 Free BA online training
The Use Case Technique: An Overview Sponsored by: Karl Wiegers Principal Consultant, Process Impact www.processimpact.com Sponsor: CEG Save 20% on training* with promo code: MAWEB14 Free BA online training
Object-Oriented Analysis/Design and Use Cases Object Oriented Analysis and Design
 Object-Oriented Analysis/Design and Use Cases Object Oriented Analysis and Design Aron Trauring T++ Technical Skills Training Program CUNY Institute for Software Design & Development (CISDD) New York Software
Object-Oriented Analysis/Design and Use Cases Object Oriented Analysis and Design Aron Trauring T++ Technical Skills Training Program CUNY Institute for Software Design & Development (CISDD) New York Software
System Analysis and Design Week 1 Introduction
 System Analysis and Design Week 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction This is a short session to familiarize understanding some of System Analysis concepts. Here we are going to focus on the following: 1.2 System
System Analysis and Design Week 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction This is a short session to familiarize understanding some of System Analysis concepts. Here we are going to focus on the following: 1.2 System
Sistemi ICT per il Business Networking
 Corso di Laurea Specialistica Ingegneria Gestionale Sistemi ICT per il Business Networking Requirements Engineering Docente: Vito Morreale (vito.morreale@eng.it) 17 October 2006 1 UP Phases 1. Inception
Corso di Laurea Specialistica Ingegneria Gestionale Sistemi ICT per il Business Networking Requirements Engineering Docente: Vito Morreale (vito.morreale@eng.it) 17 October 2006 1 UP Phases 1. Inception
Product Requirements Documentation: Use Cases
 Product Documentation: Use Cases Software Engineering and Databases Group Department of Computer Languages and Systems University of Seville November 2013 Learning objectives Know the use cases technique.
Product Documentation: Use Cases Software Engineering and Databases Group Department of Computer Languages and Systems University of Seville November 2013 Learning objectives Know the use cases technique.
An Introduction to Use-Case Modeling
 An Introduction to Use-Case Modeling The process of modeling a system s functions in terms of business events who initiated the events how the system responds to those events An approach that facilitates
An Introduction to Use-Case Modeling The process of modeling a system s functions in terms of business events who initiated the events how the system responds to those events An approach that facilitates
Use cases. Version October 2013
 Use cases Version 2.3 20 October 2013 Maurizio Morisio, Marco Torchiano, 2012 Requirements Document 1. Purpose and scope 2. The terms used / Glossary 3. The use cases 4. The technology to be used 5. Other
Use cases Version 2.3 20 October 2013 Maurizio Morisio, Marco Torchiano, 2012 Requirements Document 1. Purpose and scope 2. The terms used / Glossary 3. The use cases 4. The technology to be used 5. Other
Software Processes. Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1
 Software Processes Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be
Software Processes Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be
Babu Madhav Institute of Information Technology, UTU 2017
 Five Years Integrated M.Sc. (IT) Semester 3 Question Bank 060010312 CC9 Software Engineering Unit 1 Introduction to Software Engineering and Object-Oriented Concepts 1. What is software? 2. Which documents
Five Years Integrated M.Sc. (IT) Semester 3 Question Bank 060010312 CC9 Software Engineering Unit 1 Introduction to Software Engineering and Object-Oriented Concepts 1. What is software? 2. Which documents
version NDIA CMMI Conf 3.5 SE Tutorial RE - 1
 Requirements Engineering SE Tutorial RE - 1 What Are Requirements? Customer s needs, expectations, and measures of effectiveness Items that are necessary, needed, or demanded Implicit or explicit criteria
Requirements Engineering SE Tutorial RE - 1 What Are Requirements? Customer s needs, expectations, and measures of effectiveness Items that are necessary, needed, or demanded Implicit or explicit criteria
Work Product Dependency Diagram
 Work Product Dependency Diagram Project Definition System Context Subject Area Model Architectural Decisions Requirements Matrix Use Case Model Service Model Non Functional Requirements Component Model
Work Product Dependency Diagram Project Definition System Context Subject Area Model Architectural Decisions Requirements Matrix Use Case Model Service Model Non Functional Requirements Component Model
Development Process and Analysis. LTOOD/OOAD - Verified Software Systems 1
 Development Process and Analysis LTOOD/OOAD - Verified Software Systems 1 Software Crisis Declared in the late 60 s Expressed by delays and failures of major software projects (unreached goals, unpredictable
Development Process and Analysis LTOOD/OOAD - Verified Software Systems 1 Software Crisis Declared in the late 60 s Expressed by delays and failures of major software projects (unreached goals, unpredictable
Example1: Courseware System Description
 Use Case Examples Example1: Courseware System Description The organization offers courses. Each course is made up of a set of topics. Tutors in the organization are assigned courses to teach according
Use Case Examples Example1: Courseware System Description The organization offers courses. Each course is made up of a set of topics. Tutors in the organization are assigned courses to teach according
Passit4Sure.OG Questions. TOGAF 9 Combined Part 1 and Part 2
 Passit4Sure.OG0-093.221Questions Number: OG0-093 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.1 TOGAF 9 Combined Part 1 and Part 2 One of the great thing about pass4sure is that is saves our
Passit4Sure.OG0-093.221Questions Number: OG0-093 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.1 TOGAF 9 Combined Part 1 and Part 2 One of the great thing about pass4sure is that is saves our
1 Descriptions of Function
 1 Descriptions of Function Consumer Portal Scenario P4 Account Move All prior work (intellectual property of the company or individual) or proprietary (non-publicly available) work should be so noted.
1 Descriptions of Function Consumer Portal Scenario P4 Account Move All prior work (intellectual property of the company or individual) or proprietary (non-publicly available) work should be so noted.
CHAPTER 2: IMPLEMENTATION PHASES AND OFFERINGS
 CHAPTER 2: IMPLEMENTATION PHASES AND OFFERINGS Objectives Introduction The objectives are: Describe the purpose of the phase planning activity, preconditions, and deliverables in the implementation methodology.
CHAPTER 2: IMPLEMENTATION PHASES AND OFFERINGS Objectives Introduction The objectives are: Describe the purpose of the phase planning activity, preconditions, and deliverables in the implementation methodology.
Software Processes. Objectives. Topics covered. The software process. Waterfall model. Generic software process models
 Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Electronic Banking (E-Banking)
 Electronic Banking (E-Banking) E-banking is defined as the automated delivery of new and traditional banking products and services directly to customers through electronic, interactive communication channels.
Electronic Banking (E-Banking) E-banking is defined as the automated delivery of new and traditional banking products and services directly to customers through electronic, interactive communication channels.
Questions which state 'This question does NOT use the case study' do not use the case study, and may be answered without reference to it.
 ITIL Qualification: MANAGING ACROSS THE LIFECYCLE (MALC) CERTIFICATE Case Study 1, version 1.1 CASE STUDY BOOKLET This booklet contains the case study upon which at least 8 of the 10 examination questions
ITIL Qualification: MANAGING ACROSS THE LIFECYCLE (MALC) CERTIFICATE Case Study 1, version 1.1 CASE STUDY BOOKLET This booklet contains the case study upon which at least 8 of the 10 examination questions
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Software Engineering Third Year CSE( Sem:I) 2 marks Questions and Answers
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Software Engineering Third Year CSE( Sem:I) 2 marks Questions and Answers UNIT 1 1. What are software myths Answer: Management myths: We already have a book
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Software Engineering Third Year CSE( Sem:I) 2 marks Questions and Answers UNIT 1 1. What are software myths Answer: Management myths: We already have a book
How do you develop software? 12/01/2012. Great, You? Resources. OO Design and Programming. Congratulations New Job. what next?
 M.Sc Computer Science Object Oriented Design and Programming Session 1 Oded Lachish Room: (FT session) Malet 404 13:30 17:00, (PT Session) Malet 407 18:00 21:00 Visiting Hours: Tuesday 17:00 to 19:00 Email:
M.Sc Computer Science Object Oriented Design and Programming Session 1 Oded Lachish Room: (FT session) Malet 404 13:30 17:00, (PT Session) Malet 407 18:00 21:00 Visiting Hours: Tuesday 17:00 to 19:00 Email:
Question 2: Requirements Engineering. Part a. Answer: Requirements Engineering Process
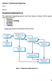 Question 2: Requirements Engineering Part a. Answer: Requirements Engineering Process The requirements engineering process varies from domain to domain. But the general activities involved are: Elicitation
Question 2: Requirements Engineering Part a. Answer: Requirements Engineering Process The requirements engineering process varies from domain to domain. But the general activities involved are: Elicitation
Requirements Engineering with Use Cases
 Requirements Engineering with Use Cases Csaba Veres Outline What are use cases? What do they tell us? How can you write them (properly)? What is a use case? A use case specifies the behavior of a system
Requirements Engineering with Use Cases Csaba Veres Outline What are use cases? What do they tell us? How can you write them (properly)? What is a use case? A use case specifies the behavior of a system
VISION MANAGEMENT SOLUTION
 VISION MANAGEMENT SOLUTION THE MOST ADVANCED MANAGEMENT SOLUTION ON THE MARKET TODAY, FUTURE-PROOFED TO SUPPORT CONTINUOUS GROWTH AND EVOLUTION IN THE RETAIL BANKING ENVIRONMENT. An NCR Buyer s Guide TAKE
VISION MANAGEMENT SOLUTION THE MOST ADVANCED MANAGEMENT SOLUTION ON THE MARKET TODAY, FUTURE-PROOFED TO SUPPORT CONTINUOUS GROWTH AND EVOLUTION IN THE RETAIL BANKING ENVIRONMENT. An NCR Buyer s Guide TAKE
8 Steps to Effective Use Cases
 8 Steps to Effective Use Cases Linda Westfall lwestfall@westfallteam.com www.westfallteam.com Sponsored by Linda Westfall 3000 Custer Road Suite 270, PMB 101 Plano, TX 75075-4499 phone: (972) 867-1172
8 Steps to Effective Use Cases Linda Westfall lwestfall@westfallteam.com www.westfallteam.com Sponsored by Linda Westfall 3000 Custer Road Suite 270, PMB 101 Plano, TX 75075-4499 phone: (972) 867-1172
NCR APTRA PASSPORT An enterprise hub for remote deposit capture
 NCR APTRA PASSPORT An enterprise hub for remote deposit capture A better way for your customers to deposit checks Banks and financial institutions continue to face the challenges of managing new and evolving
NCR APTRA PASSPORT An enterprise hub for remote deposit capture A better way for your customers to deposit checks Banks and financial institutions continue to face the challenges of managing new and evolving
(Sample) Use-Case Model Survey. For an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) Handout 1. Introduction
 Use-Case-Model Survey (ATM) Handout 1 Page 1 of 6 (Sample) Use-Case Model Survey For an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) Handout 1 Introduction This set of suggested solutions on the classical ATM problem
Use-Case-Model Survey (ATM) Handout 1 Page 1 of 6 (Sample) Use-Case Model Survey For an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) Handout 1 Introduction This set of suggested solutions on the classical ATM problem
The Business Process Environment
 The Business Process Environment Flexible, Sensible Process Empowerment EMCONEX TECHNICAL BRIEF Richer Systems Group, Inc. February 2012 IDE Script Writer Alert System Audit Tracking Content Manager TABLE
The Business Process Environment Flexible, Sensible Process Empowerment EMCONEX TECHNICAL BRIEF Richer Systems Group, Inc. February 2012 IDE Script Writer Alert System Audit Tracking Content Manager TABLE
The Enterprise Systems Engineering Center Requirements Management Guide - Analysis
 The Enterprise Systems Engineering Center Requirements Management Guide - The Enterprise Requirements Management Guide - Introduction Innumerable studies have concluded that requirements problems are the
The Enterprise Systems Engineering Center Requirements Management Guide - The Enterprise Requirements Management Guide - Introduction Innumerable studies have concluded that requirements problems are the
1 Descriptions of Function
 1 Descriptions of Function Customer Communications Portal Management System Issues Issues confronting an Energy Company s Management Systems responsible for management of Telecommunications and Access
1 Descriptions of Function Customer Communications Portal Management System Issues Issues confronting an Energy Company s Management Systems responsible for management of Telecommunications and Access
Software Engineering Modern Approaches
 Software Engineering Modern Approaches Chapter : Software Process Eric Braude and Michael Bernstein Maintenance Testing The Software Development Lifecycle Implementation Design Phase most relevant to this
Software Engineering Modern Approaches Chapter : Software Process Eric Braude and Michael Bernstein Maintenance Testing The Software Development Lifecycle Implementation Design Phase most relevant to this
System Sequence Diagrams. CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1
 System Sequence Diagrams CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1 Topics 1. Objectives 2. What is a SSD? 3. Notation 4. SSDs and Use Cases CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #2 What is a SSD? A quick and
System Sequence Diagrams CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1 Topics 1. Objectives 2. What is a SSD? 3. Notation 4. SSDs and Use Cases CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #2 What is a SSD? A quick and
Arcade Game Maker Product Line - Concep of Operations
 Arcade Game Maker Product Line - Concep of Operations ArcadeGame Team July 2003 Table of Contents 1 Overview 1 1.1 Identification 1 1.2 Document Map 1 1.3 Concepts 2 1.4 Readership 2 2 Approach 3 3 Background
Arcade Game Maker Product Line - Concep of Operations ArcadeGame Team July 2003 Table of Contents 1 Overview 1 1.1 Identification 1 1.2 Document Map 1 1.3 Concepts 2 1.4 Readership 2 2 Approach 3 3 Background
Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description
 Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description Requirements Engineering Project Description The project is student-driven. There will be external sponsors, users, and others that
Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description Requirements Engineering Project Description The project is student-driven. There will be external sponsors, users, and others that
Product. LynxGate Build Member Relationships With a Powerful, Secure, Real-Time Transaction Solution
 Product LynxGate Build Member Relationships With a Powerful, Secure, Real-Time Transaction Solution Product Today s consumers live in the now. They ve become accustomed to a world that provides immediate
Product LynxGate Build Member Relationships With a Powerful, Secure, Real-Time Transaction Solution Product Today s consumers live in the now. They ve become accustomed to a world that provides immediate
Electronic Banking Bonanza
 Total Points Earned 24 Total Points Possible Percentage Electronic Banking Bonanza 2.7.1.L1 Note Taking Guide Name Date Class Directions: Complete the following note taking guide during the PowerPoint
Total Points Earned 24 Total Points Possible Percentage Electronic Banking Bonanza 2.7.1.L1 Note Taking Guide Name Date Class Directions: Complete the following note taking guide during the PowerPoint
CHAPTER 3 Use Cases. 3. Use Cases
 CHAPTER 3 Use Cases Introduction When, Why, Where, What Iteratively Developing Use Cases Inception + Scope Definition + Risk Identification + Actors & Use cases + Project Plan Elaboration + Primary & Secondary
CHAPTER 3 Use Cases Introduction When, Why, Where, What Iteratively Developing Use Cases Inception + Scope Definition + Risk Identification + Actors & Use cases + Project Plan Elaboration + Primary & Secondary
CHAPTER 3 Use Cases. 3. Use Cases
 CHAPTER 3 Use Cases Introduction When, Why, Where, What Iteratively Developing Use Cases Inception + Scope Definition + Risk Identification + Actors & Use cases + Project Plan Elaboration + Primary & Secondary
CHAPTER 3 Use Cases Introduction When, Why, Where, What Iteratively Developing Use Cases Inception + Scope Definition + Risk Identification + Actors & Use cases + Project Plan Elaboration + Primary & Secondary
1 Smart Grid function description
 NIST SG function description and use case template DGH ver.2 (Building-centric view of Smart Grid) 1 Smart Grid function description 1.1 SG function name Load management with dynamic tariffs, predictable
NIST SG function description and use case template DGH ver.2 (Building-centric view of Smart Grid) 1 Smart Grid function description 1.1 SG function name Load management with dynamic tariffs, predictable
Chapter 1. What is Software Engineering. Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee. 4 th Edition
 Chapter 1 What is Software Engineering Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee 4 th Edition Contents 1.1 What is Software Engineering? 1.2 How Successful Have We Been? 1.3 What Is Good Software? 1.4 Who Does
Chapter 1 What is Software Engineering Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee 4 th Edition Contents 1.1 What is Software Engineering? 1.2 How Successful Have We Been? 1.3 What Is Good Software? 1.4 Who Does
Use case methodology (IEC 62559) International Electrotechnical Commission
 Use case methodology (IEC 62559) International Electrotechnical Commission From lagging to leading standardization In the past standardization took place only after successful market introduction of a
Use case methodology (IEC 62559) International Electrotechnical Commission From lagging to leading standardization In the past standardization took place only after successful market introduction of a
Software Modeling & Analysis. - Fundamentals of Software Engineering - Software Process Model. Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO
 Software Modeling & Analysis - Fundamentals of Software Engineering - Software Process Model Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is Software Engineering? [ IEEE Standard 610.12-1990 ] Software
Software Modeling & Analysis - Fundamentals of Software Engineering - Software Process Model Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is Software Engineering? [ IEEE Standard 610.12-1990 ] Software
Channels Methodology: Feasibility Study Internal Analysis
 Channels Methodology: Feasibility Study Internal Analysis Use this document as a guiding tool to facilitate assessment of internal capacity Commercial in Confidence Accion International Overview of Internal
Channels Methodology: Feasibility Study Internal Analysis Use this document as a guiding tool to facilitate assessment of internal capacity Commercial in Confidence Accion International Overview of Internal
Electronic Banking. Describe electronic transactions you can make. Discuss your rights and responsibilities in electronic transactions
 Electronic Banking Describe electronic transactions you can make Discuss your rights and responsibilities in electronic transactions Electronic Funds Transfer Banks move money from one account to another
Electronic Banking Describe electronic transactions you can make Discuss your rights and responsibilities in electronic transactions Electronic Funds Transfer Banks move money from one account to another
Software Architecture and Engineering Requirements Elicitation Peter Müller
 Software Architecture and Engineering Requirements Elicitation Peter Müller Chair of Programming Methodology Spring Semester 2018 2. Requirements Elicitation Main Activities of Software Development 2 Requirements
Software Architecture and Engineering Requirements Elicitation Peter Müller Chair of Programming Methodology Spring Semester 2018 2. Requirements Elicitation Main Activities of Software Development 2 Requirements
7. Model based software architecture
 UNIT - III Model based software architectures: A Management perspective and technical perspective. Work Flows of the process: Software process workflows, Iteration workflows. Check Points of The process
UNIT - III Model based software architectures: A Management perspective and technical perspective. Work Flows of the process: Software process workflows, Iteration workflows. Check Points of The process
Object-Oriented Analysis and Design PART1: ANALYSIS
 Object-Oriented Analysis and Design PART: ANALYSIS Textbook Text: Applying UML and Patterns: An Introduction to Object-Oriented Analysis and Design and Iterative Development, Craig Larman, ISBN: 03 48
Object-Oriented Analysis and Design PART: ANALYSIS Textbook Text: Applying UML and Patterns: An Introduction to Object-Oriented Analysis and Design and Iterative Development, Craig Larman, ISBN: 03 48
Requirements Engineering. Andreas Zeller Saarland University
 Requirements Engineering Software Engineering Andreas Zeller Saarland University Communication project initiation requirements gathering Planning estimating scheduling tracking Waterfall Model (1968) Modeling
Requirements Engineering Software Engineering Andreas Zeller Saarland University Communication project initiation requirements gathering Planning estimating scheduling tracking Waterfall Model (1968) Modeling
Topics covered. Software process models Process iteration Process activities The Rational Unified Process Computer-aided software engineering
 Software Processes Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Software Processes Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Nigel Beacham Department of Computing Science L4 REQUIREMENTS DURING INCEPTION (CS5037 SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN)
 Nigel Beacham Department of Computing Science L4 REQUIREMENTS DURING INCEPTION (CS5037 SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN) WHERE ARE WE NOW? Software development paradigms The Unified Process (UP) paradigm UP
Nigel Beacham Department of Computing Science L4 REQUIREMENTS DURING INCEPTION (CS5037 SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN) WHERE ARE WE NOW? Software development paradigms The Unified Process (UP) paradigm UP
Objectives. The software process. Topics covered. Waterfall model. Generic software process models. Software Processes
 Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Chapter 1. Contents. What is Software Engineering 9/9/13. Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee. 4 th Edition
 Chapter 1 What is Software Engineering Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee 4 th Edition Contents 1.1 What is Software Engineering? 1.2 How Successful Have We Been? 1.3 What Is Good Software? 1.4 Who Does
Chapter 1 What is Software Engineering Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee 4 th Edition Contents 1.1 What is Software Engineering? 1.2 How Successful Have We Been? 1.3 What Is Good Software? 1.4 Who Does
Program Lifecycle Methodology Version 1.7
 Version 1.7 March 30, 2011 REVISION HISTORY VERSION NO. DATE DESCRIPTION AUTHOR 1.0 Initial Draft Hkelley 1.2 10/22/08 Updated with feedback Hkelley 1.3 1/7/2009 Copy edited Kevans 1.4 4/22/2010 Updated
Version 1.7 March 30, 2011 REVISION HISTORY VERSION NO. DATE DESCRIPTION AUTHOR 1.0 Initial Draft Hkelley 1.2 10/22/08 Updated with feedback Hkelley 1.3 1/7/2009 Copy edited Kevans 1.4 4/22/2010 Updated
Software Architecture and Engineering Requirements Elicitation Peter Müller
 Software Architecture and Engineering Requirements Elicitation Peter Müller Chair of Programming Methodology Spring Semester 2017 2. Requirements Elicitation Main Activities of Software Development 2 Requirements
Software Architecture and Engineering Requirements Elicitation Peter Müller Chair of Programming Methodology Spring Semester 2017 2. Requirements Elicitation Main Activities of Software Development 2 Requirements
1 Descriptions of Function
 1 Descriptions of Function Equipment Control within Smart House by All prior work (intellectual property of the company or individual) or proprietary (non-publicly available) work should be so noted. 1.1
1 Descriptions of Function Equipment Control within Smart House by All prior work (intellectual property of the company or individual) or proprietary (non-publicly available) work should be so noted. 1.1
NCR APTRA Vision The business intelligence you need to make smarter decisions today, so you can achieve your goals tomorrow. An NCR Buyer s Guide
 NCR APTRA Vision The business intelligence you need to make smarter decisions today, so you can achieve your goals tomorrow An NCR Buyer s Guide Take out the guesswork on performance measurement With the
NCR APTRA Vision The business intelligence you need to make smarter decisions today, so you can achieve your goals tomorrow An NCR Buyer s Guide Take out the guesswork on performance measurement With the
Getting Started. Chapter 1
 schneider01.fm Page 1 Friday, February 16, 2001 5:14 PM Chapter 1 Getting Started Use cases are used to describe the outwardly visible requirements of a system. They are used in the requirements analysis
schneider01.fm Page 1 Friday, February 16, 2001 5:14 PM Chapter 1 Getting Started Use cases are used to describe the outwardly visible requirements of a system. They are used in the requirements analysis
1 Descriptions of Function
 Customer Communications Portal Management Telecommunications Issues 1 Descriptions of Function Issues confronting an Energy Company s Management Systems responsible for management of Telecommunications
Customer Communications Portal Management Telecommunications Issues 1 Descriptions of Function Issues confronting an Energy Company s Management Systems responsible for management of Telecommunications
Analysing client requirements
 Analysing client requirements Before you can start to analyse the information you have gathered you should think about what you are trying to achieve . The client has presented you with a business problem.
Analysing client requirements Before you can start to analyse the information you have gathered you should think about what you are trying to achieve . The client has presented you with a business problem.
Chapter 2 Analyzing the Business Case
 Chapter 2 Analyzing the Business Case Explain the concept of a business case and how a business case affects an IT project Describe the strategic planning process and why it is important to the IT team
Chapter 2 Analyzing the Business Case Explain the concept of a business case and how a business case affects an IT project Describe the strategic planning process and why it is important to the IT team
Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description
 Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description Requirements Engineering Project Description This project is student-driven. There will be external sponsors, users, and others that
Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description Requirements Engineering Project Description This project is student-driven. There will be external sponsors, users, and others that
Software Engineering
 Software Engineering Lecture 02: Processes Peter Thiemann University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2013 Peter Thiemann (Univ. Freiburg) Software Engineering SWT 1 / 41 Terms Software Component SW System Organized
Software Engineering Lecture 02: Processes Peter Thiemann University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2013 Peter Thiemann (Univ. Freiburg) Software Engineering SWT 1 / 41 Terms Software Component SW System Organized
Object-Oriented & Classical Soft Engineering
 Object-Oriented & Classical Soft Engineering Seventh Edition Stephen R. Schach Vanderbilt University Higher Education Boston Burr Ridge, IL Dubuque, IA New York San Francisco St. Louis Bangkok Bogota Caracas
Object-Oriented & Classical Soft Engineering Seventh Edition Stephen R. Schach Vanderbilt University Higher Education Boston Burr Ridge, IL Dubuque, IA New York San Francisco St. Louis Bangkok Bogota Caracas
Service Virtualization
 Service Virtualization A faster, more efficient and less costly way to develop and test enterprise-class applications As cloud and mobile computing gain rapid acceptance, IT departments are expected to
Service Virtualization A faster, more efficient and less costly way to develop and test enterprise-class applications As cloud and mobile computing gain rapid acceptance, IT departments are expected to
Identification Selection Definition Execution. Schedule.
 SCHEDULE DEVELOPMENT Schedule development is the identification, definition and sequencing of activities that are required to be performed for successful completion of the project scope. Identification
SCHEDULE DEVELOPMENT Schedule development is the identification, definition and sequencing of activities that are required to be performed for successful completion of the project scope. Identification
Functional requirements and acceptance testing
 Functional requirements and acceptance testing Lecture 3 Software Engineering TDDC88/TDDC93 autumn 2007 Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Message from the course
Functional requirements and acceptance testing Lecture 3 Software Engineering TDDC88/TDDC93 autumn 2007 Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Message from the course
Interoperable Payment Systems: Requirements Driven Architecture for Ethiopian Banking Sector
 Interoperable Payment Systems: Requirements Driven Architecture for Ethiopian Banking Sector Abebe Girmay Dashen Bank S. Co., Addis Ababa, Ethiopia abebegirmay@yahoo.com Fantahun Abera PhD Candidate, Addis
Interoperable Payment Systems: Requirements Driven Architecture for Ethiopian Banking Sector Abebe Girmay Dashen Bank S. Co., Addis Ababa, Ethiopia abebegirmay@yahoo.com Fantahun Abera PhD Candidate, Addis
making money from customer use of kiosk attracting more customers to the store saving money if the kiosk replaces manual operations
 Business Requirements Business requirements collected from multiple sources might conflict. For example, consider a kiosk product with embedded software that will be sold to retail stores and used by the
Business Requirements Business requirements collected from multiple sources might conflict. For example, consider a kiosk product with embedded software that will be sold to retail stores and used by the
Requirements Elicitation
 Requirements Elicitation Software Engineering I Lecture 4 14. November 2006 Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen 1 Outline Motivation Requirements elicitation challenges
Requirements Elicitation Software Engineering I Lecture 4 14. November 2006 Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen 1 Outline Motivation Requirements elicitation challenges
City of Tacoma Department of Public Utilities - Tacoma Power
 City of Tacoma Department of Public Utilities - Tacoma Power Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) Integration Infrastructure Implementation RFP Specification No. PS15-0233F QUESTIONS and ANSWERS All interested
City of Tacoma Department of Public Utilities - Tacoma Power Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) Integration Infrastructure Implementation RFP Specification No. PS15-0233F QUESTIONS and ANSWERS All interested
Project Management CSC 310 Spring 2018 Howard Rosenthal
 Project Management CSC 310 Spring 2018 Howard Rosenthal 1 Notice This course is based on and includes material from the text: A User s Manual To the PMBOK Guide Authors: Cynthia Stackpole Snyder Publisher:
Project Management CSC 310 Spring 2018 Howard Rosenthal 1 Notice This course is based on and includes material from the text: A User s Manual To the PMBOK Guide Authors: Cynthia Stackpole Snyder Publisher:
TOKENIZATION OF A PHYSICAL DEBIT OR CREDIT CARD FOR PAYMENT
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series January 31, 2016 TOKENIZATION OF A PHYSICAL DEBIT OR CREDIT CARD FOR PAYMENT Ritcha Ranjan Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series January 31, 2016 TOKENIZATION OF A PHYSICAL DEBIT OR CREDIT CARD FOR PAYMENT Ritcha Ranjan Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Lecture 1: Processes, Requirements, and Use Cases
 Lecture 1: Processes, Requirements, and Use Cases 1 Development Processes Early Days: evolve a system Build and fix Leads to chaos Need for intelligent design Waterfall Model Requirements, Design, Code,
Lecture 1: Processes, Requirements, and Use Cases 1 Development Processes Early Days: evolve a system Build and fix Leads to chaos Need for intelligent design Waterfall Model Requirements, Design, Code,
