Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
|
|
|
- Marybeth Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District January 2014 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation, plans and resource management objectives. For example, federal and provincial acts and regulations, Land Use and Forest Stewardship plans, and protected areas and reserves collectively contribute to achieving balanced environmental, social and economic objectives. Sustainable forest management is key to achieving this balance and a central component of forest management certification programs. The purpose of the Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) report is to provide resource professionals and decision makers with information about the environmental component of this balance so that they can assess the consistency of actual outcomes with their expectations. The Forest and Range Practices Act (FRPA) lists 11 resource values essential to sustainable forest management in the province; biodiversity, cultural heritage, fish/riparian and watershed, forage and associated plant communities, recreation, resource features, soils, timber, visual quality, water, and wildlife. The MRVA report is a summary of the available field-based assessments of the conditions of these values. Field assessments are generally conducted on or near recently harvested cut blocks and therefore are only evaluating the impact of industrial activity and not the condition of the value overall (e.g. they don t take into account protected areas and reserves). Most of the information is focused on the ecological state of the values and provides useful information to resource managers and professionals on the outcomes of their plans and practices. This information is also valuable for communicating resource management outcomes to stakeholders, First Nations and the public, and as a foundation for refining government s expectations for sustainable resource management in specific areas of the province. I encourage readers to review the full report and direct any questions or comments to the appropriate district office. Tom Ethier Assistant Deputy Minister Resource Stewardship Division Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations 1
2 MULTIPLE RESOURCE VALUE ASSESSENTS IN BRIEF Multiple resource value assessments show the results of stand and landscape-level monitoring carried out under the Forest and Range Evaluation Program (FREP). This report summarizes results for riparian, biodiversity, water quality (sediment), visual quality and timber (stand development) monitoring conducted in the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District from 2006 to 2012, and includes a district manager commentary of key strengths and weaknesses. Through MRVA reports, decision makers communicate expectations for sustainable resource management of public resources and identify opportunities for continued improvement. Figure 1: Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District site-level stewardship impact rating by resource value with trend (Riparian, stand-level biodiversity and visual quality trend by harvest year/era. Water quality trends by evaluation year. Timber samples are all post-free growing.) 100% FRPA 90% 80% 70% % of Samples 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% n = 27 n = 38 Riparian n = 123 n = 107 Water Quality n = 37 n = 35 Stand-level Biodiversity n = 20 Visual Quality n = 14 Timber Important Context for Understanding this Assessment The extraction and development of natural resources, along with natural factors (e.g., insects, wind, floods), influence and impact ecological condition. The goal of effectiveness evaluations is to assess these impacts on the state of public natural resource values (status, trends, and causal factors); such evaluations do not assess compliance with legal requirements. These evaluations help resource managers: assess whether the impacts of resource development result in sustainable resource management; provide transparency and accountability for the management of public resources; support the decision-making balance between environmental, social, and economic factors inform the ongoing improvement of resource management practices, policies, and legislation. The resource development impact ratings contained in this report are based on assessments conducted within the areas where resource development takes place and do not reflect the ecological contributions of parks, protected areas, or other conservancy areas. Although this report focuses on forestry-related activities, FREP monitoring protocols have also been applied to other resource sector activities, including mining (roads) and linear developments (hydro and pipelines). Procedures are being adapted to expand monitoring into these resource sectors over time. 2
3 INTRODUCTION The development of the Forest and Range Practices Act (FRPA) had several key objectives, including: simplifying the forest management legal framework reducing operational costs to both industry and government allowing freedom to manage maintaining the high environmental standards of the Forest Practices Code of British Columbia Act (FPC). As part of the results-based FRPA framework, the provincial government committed to conducting effectiveness evaluations and publically reporting the monitoring results. The science-based information provided by these evaluations will be used to determine whether FRPA is achieving the government s objectives of maintaining high environmental standards and ensuring sustainable management of public resources. If those objectives are not being met the monitoring results will be used to help inform the necessary adjustments to practices, policies, and legislation. Government is delivering its effectiveness evaluation commitment through the Forest and Range Evaluation Program (FREP; for details, see The 11 FRPA resource values monitored under FREP include: biodiversity, cultural heritage, fish/ riparian & watershed, forage and associated plant communities, recreation, resource features, soils, timber, visual quality, water and wildlife. Multiple Resource Value Assessments (MRVAs) reflect the results of stand- and landscape-level monitoring carried out under FREP. The program s stand-level monitoring is generally conducted on forestry cutblocks, resource roads, or other areas of industrial activity. As such, these evaluations provide a stewardship assessment of resource development practices. Landscape-level monitoring of biodiversity, visual quality, and wildlife resource values is more broadly an assessment of the overall landscape. Reports on MRVAs are designed to inform decision making related to on-the-ground management practices, statutory decision maker approvals, and data for the assessment of cumulative effects. This report summarizes FREP monitoring results for the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District. MRVA reports clarify resource stewardship expectations, and promote the open and transparent discussion needed to achieve short- and long-term sustainable resource management in British Columbia. MRVA reports are intended for those interested in the status and trends of resource values at the timber supply area (TSA) or natural resource district scale, such as natural resource managers and professionals, government decision makers, and First Nations. These reports are also useful in communicating resource management outcomes to the public. Government managers and decision makers are encouraged to consider this information when: discussing district or TSA-level resource stewardship with staff, licenced stakeholders, tenure holders and First Nations clarifying expectations for sustainable resource management of public land integrating social and economic considerations into balanced decision making reviewing and approving forest stewardship plans developing silviculture strategies for TSAs assessing Timber Supply Reviews and their supporting rationale informing decision making at multiple scales. 3
4 Natural resource professionals are encouraged to consider this information, along with other FREP information such as reports, extension notes, protocols, and monitoring data to: maintain current knowledge of the resources they manage inform professional recommendations and decisions, particularly when balancing environmental, social, and economic values enhance resource management, consultation, and treaty rights discussions between First Nations, government, and licensees. Published FREP reports and extension notes contain detailed findings for each resource value. These documents are available on the FREP website at: Licensees can request data collected on their operating areas. FREP staff will assist licensees with the analysis of their data and the preparation of licenseespecific MRVA reports. Although this MRVA report documents monitoring results at the district or TSA level, the MRVA concept is scalable. Reports for individual licensees, treaty settlement areas, or landscape units can be produced when sufficient monitoring data is available. Reports can also be prepared at the regional or provincial levels. This report provides site-level resource value assessments and trends through comparisons of cutblocks harvested before 2005 with those harvested in 2005 or later (where data is sufficient). FREP s site assessment monitoring results on each resource value are categorized by impact (very low, low, medium, or high). This classification reflects how well site-level practices achieve government s overall goal of sustainable resource management. Site-level practices that result in very low or low impact are consistent with sustainable management objectives. Practices resulting in high impact are seen as inconsistent with government s sustainability objectives. For a description of the MRVA methodology used in this report, see Appendix 1. 4
5 SUNSHINE COAST NATURAL RESOURCE DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL AND STEWARDSHIP CONTEXT This report covers the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District encompassing the Sunshine Coast TSA, and portions of the Pacific TSA and Tree Farm Licenses 43 and 39 (figure 2). This district extends from Howe Sound in the south to the head of Bute Inlet in the north. The district covers approximately 1.9 million hectares. The mountainous topography and associated high rainfall in the Sunshine Coast District produce a diverse climate and ecology. The landscape ranges from rocky shorelines and coastal plains to rugged ice-capped mountains. The Coast Mountains dominate the District, with nutrient-rich, moist floodplains in valley bottoms and alpine meadows at higher elevations. Several significant coastal fjords, most notably Bute, Toba and Jervis inlets occur in the District. The forests and landscapes of the Sunshine Coast District are home to a wide variety of wildlife species, including grizzly and black bear, black-tailed deer, Roosevelt elk, mountain goat, cougar and wolf, as well as isolated populations of moose. Currently, eight species identified as at risk may be found in the Sunshine Coast TSA, including the Northern goshawk, marbled murrelet and Keen s long-eared myotis. Fourteen First Nations have asserted traditional territory in the Sunshine Coast TSA. They are the Shíshálh Nation, Sliammon First Nation, Xwémalhkwu First Nation, Klahoose First Nation Squamish Nation, We Wai Kai First Nation, Wei Wai Kum First Nation, Kwiakah First Nation, the Snaw-Naw-As First Nation, K omoks First Nation, Qualicum First Nation, Líl wat First Nation, Tsleil-Waututh First Nation, and the Ulkatcho First Nation. Within the land base currently considered available for timber harvesting, Douglas-fir, hemlock western redcedar and balsam are the major tree species, while, yellow cedar, spruce, pine, red alder, cottonwood and maple also occur. The district has a long history of harvesting activity, resulting in younger forests on better quality, more accessible growing sites, and older forests on the poorer and less accessible areas. As a result of this harvesting the majority of forest stands are younger than 150 years. Historically, forest health issues in the district have included bear damage, Douglas-fir bark beetle, mountain pine beetle, root diseases, spruce beetle and western hemlock looper. Currently the agents of most concern are Phellinus weirii root disease, Armillaria root disease and Douglas fir bark beetle. By far the most significant losses are from Phellinus in the CDF and CWHxm subzones The district has a diverse array of forest tenures including 12 Woodlot Licenses, 5 Community Forest Agreements, several Forest Licenses, portions of 2 Tree Farm Licenses and a vibrant BCTS program. The forests of the Sunshine Coast District provide a wide range of forest land resources, including forest products (timber and non-timber, such as wild mushrooms), recreation and tourism amenities, and a variety of fishery and wildlife habitats. There are currently 26 community watersheds within the Sunshine Coast District. Residents and visitors make extensive use of the forests of the district for recreational activities. Parks, recreation sites and trails, and roaded and non-roaded areas in the district provide opportunities for numerous outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, skiing, mountain biking,, mountaineering, angling, hunting, canoeing and kayaking, as well as more passive activities such as wildlife or forest viewing. 5
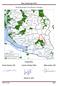
6 Figure 2: Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District, showing FREP sample locations and results (see for a high-resolution version of this map). 6
7 KEY RESULTS BY RESOURCE VALUE AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR CONTINUED IMPROVEMENT Table 1 shows the resource values assessed for the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District, and includes a summary of key findings, causal factors, trends, and opportunities for continued improvement. Data are presented for FPC-era samples at sites harvested before 2005 and FRPA-era samples at sites harvested in 2005 or later. This approximates the Forest and Range Practices Act (FRPA) era, and allows for a comparison between earlier and later stewardship practices. The impact rating indicates the effect of resource development on the resource value, from very low to high impact. Table 1: Resource development impact rating, key findings, and opportunities for improvement by resource value for the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District. Riparian: Resource Development Impacts on Stream Function (n = 38) (n = 27) 16% 21% 26% 37% 15% 22% 30% 33% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% % of Samples Impact Rating High Medium Low Very Low Summary: Of the 65 streams monitored (combined FPC and FRPAeras), 63% were rated as very low or low harvestrelated impacts: 35% of streams are Properly Functioning ( very low impact), 28% are Properly Functioning with limited impact ( low impact), 22% are Properly Functioning with impact ( medium impact) and 15% are Not Properly Functioning ( high impact). Causal Factors: Factors that contributed to high or medium impact ratings included: insufficient vegetation near stream banks for adequate root network and large woody debris; impacted riparian vegetation in first 10 m; low moss levels indicative of unstable systems, and excessive amounts of in-stream slash. Number of Samples by Stream Class and Impact Rating: Class High Medium Low Very low Total S S S S S Total Overall Stewardship Trend: Neutral Overall there is no change in impact rating. For individual riparian questions however, there are variations between the eras. Opportunities For Continued Improvement: Use full 10 m windfirm treed buffer where possible, particularly on high-priority S6 streams that flow into fish streams or community watersheds. Where the full buffers are not possible, maintain vegetation (e.g., understory, shrubs, non-merchantable trees) to the fullest extent possible within the first 5 m of the channel bank to keep an adequate root network and large woody debris supply. Minimize sediment source from roads. 7
8 Water Quality (fine sediment): Resource Development Impacts on Water Quality (n = 107) 20% 50% 31% (n = 123) 17% 42% 39% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% % of Samples Impact Rating High Medium Low Very Low Summary: Of the 230 road segments assessed from 2008 to 2012, 81% were rated as very low or low road-related impact. Site assessments show the range for potential sediment generation as 35% very low (same as very low impact on water quality), 46% low ( low impact) 18% moderate ( medium impact), 1% high ( high impact). Causal Factors: See opportunities for improvement for high or medium impacted road segments. Overall Stewardship Trend: Neutral Trending for water quality is based on survey years, to capture impact of road traffic and maintenance. There is little change between samples in the two time frames. Opportunities For Improvement: The most frequent suggested maintenance issues are: armour seed and protect bare soil; use cross ditches and kickouts; and use better quality materials for road building. Visual Quality: Resource Development Impacts on Achievement of Visual Quality Objectives (VQO) Visual Quality (FRPA) 20% 15% 40% 25% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Summary: Of the 20 landforms assessed (all originating from openings harvest under FRPA), 65% were rated with very low or low harvest-related impacts on achieving the VQO. VQOs were well met ( very low impact to achieving objective) on 25% of landforms, met ( low impact) on 40%, borderline ( medium impact) on 15%, not met on 5% and clearly not met ( high impact includes two categories) on 15%. Causal Factors: 5% of the openings contained visually effective levels of tree retention (>22% by volume or stem count) and 20% of landforms sampled had good visual quality design (cutblock shaping). % of Samples (n = 20) Impact Rating High Medium Low Very Low Number of Samples by VQO and Impact Rating: VQO 1 High Medium Low Very Low Total M PR R 1 1 Total M = modification, PR = partial retention, R = retention Overall Stewardship Trend: Insufficient data No data for FPC cutblocks to allow for trending. Future trend analysis will use year of harvest. Opportunities For Improvement: Use existing visual design techniques to create more natural-looking openings and better achieve VQOs. Use partial cutting to retain higher levels of volume/stems. Reduce opening size in retention and partial retention VQO areas. 8
9 Stand-level Biodiversity: Resource Development Impacts on Stand-Level Biodiversity (n = 35) 9% 66% 23% (n = 37) 19% 19% 46% 16% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% % of Samples Impact Rating High Medium Low Very Low Summary: Of 72 cutblocks (combined FPC and FRPA-eras), 68% of sites were rated as very low or low harvest-related impact. Considering total retention, retention quality, and coarse woody debris quantity and quality, 17% of sites are rated as very low impact on biodiversity, 51% as low, 21% as medium, and 11% as high impact. Another 14 blocks were sampled and assessed for some indicators but could not be ranked since there was no patch plot data for 10 blocks where patches existed (likely due to safety issues) and no baseline was available on four in biogeoclimatic ecosystem classification subzones with insufficient baseline. Causal Factors: Large snag retention density in both eras is less than expected from baseline. Big tree density ( 70 cm dbh) has increased and is at an average density in FRPA-era similar to expected from baseline. Tree species numbers also improved and is similar to expected. Range of coarse woody debris volume over many blocks is skewed to higher amounts compared to baseline (that found in retention patches). Coarse woody debris quality (volume from 30 cm pieces and pieces/ha of 20 cm and 10 m) has improved. Overall Stewardship Trend: Improving Retention increased from an average 13.6% in the FPC to 16.5% in the FRPA-era. 91% of all blocks had more than 3.5% treed retention, increasing to 96% considering only the FRPAera blocks. Opportunities For Continued Improvement: Continue trend to leave at least low levels of retention on every cutblock with a larger range of retention (e.g., 3 to 30%) over many blocks. Improve retention quality by leaving higher densities of large dead trees. 9
10 Timber Resource Value: Resource development impacts on the overall health and productivity of managed year stands Timber 7% 7% 86% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% % of Samples (n = 14) Summary: Of the 14 polygons sampled in 2011 and 2012 the weighted average well-spaced density over the 3 biogeoclimatic ecosystem classification (BEC) zones achieved 93% of target stocking standard (TSS). Percent of target stocking standard by BEC BEC CDF CWH MH Average WS/TSS 84% 94% 100% 93% 93% of the polygons were rated very low or low impact to health and stocking and 7% high. 91% of all trees sampled (all BEC s) were acceptable, with no serious stand damage. The top stand damaging agents for all BEC s are: tree competition (29/120); unknown (28/120); snow press (21/120); and armillaria (9/120). Impact Rating High Medium Low Very Low Causal Factors: From only 14 polygons sampled to-date it appears that the stands in the Sunshine Coast TSA are very healthy and productive. The majority of stand damage is due to abiotic tree competition and snow press. Overall Stewardship Trend: Insufficient data Opportunities For Improvement: Spacing of young productive stands would decrease the inter-tree competition and snow press. Soils: Resource Development Impacts on Soil Productivity and Hydrologic Function There are currently only five soils samples in the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District. Analysis will be completed in subsequent years when more samples are available. Landscape-level Biodiversity: Is the forested matrix at the landscape-level providing the range of habitat understood as necessary for maintaining ecosystem function and old and mature forest dependant species? In development. The three primary landscape-level biodiversity indicators are: (1) site index by leading species (ecosystem representativeness); (2) percent of TSA by age class (young, mid-, mature, and old forest); and (3) percent interior habitat of old forest. Each indicator is categorized by percent in noncommercial land base, timber harvesting land base, and protected areas. Data for these indicators is derived from Hectares BC and other spatial databases. 10
11 RESOURCE VALUE STEWARDSHIP RESULTS COMPARISON Table 2 provides ratings of stewardship effectiveness at varying scales. Effectiveness is determined by the percentage of samples with a very low or low resource development impact rating. Appendix 2 shows results by resource value for the North, South and Coast Areas and the province as a whole. Table 2: Stewardship effectiveness within the South Coast Region as determined by resource development impact rating (ID = Insufficient Data; sample sizes in brackets). Effectiveness of Practices in Achieving Resource Stewardship Objectives: % Very low + low resource development impact rating South Coast Region Comparison Resource Value Riparian all data FRPA-era data FPC-era data Sunshine Coast District Chilliwack District Sea to Sky District 63% (65) 63% (38) 63% (27) 59% (66) 69% (26) 53% (40) 59% (66) 69% (26) 53% (40) South Coast Region 1 62% (186) 69% (80) 58% (106) Water quality all data samples samples 81% (230) 83% (157) 77% (73) 55% (212) 55% (133) 54% (79) 55% (212) 55% (133) 54% (79) 66% (578) 70% (351) 60% (227) Stand-level biodiversity all data FRPA-era data FPC-era data 75% (72) 89% (35) 62% (37) 81% (58) 86% (22) 78% (36) 81% (58) 86% (22) 78% (36) 82% (182) 91% (74) 77% (108) Visual Quality FRPA FPC 65% (20) ID 2 (0) 100% (20) 73% (22) 1 Sunshine Coast, Squamish and Chilliwack Natural Resource Districts 2 No FPC sampling 100% (20) 73% (22) 86% (52) 73% (40) 11
12 DISTRICT MANAGER COMMENTARY 1 The evaluation criteria in this report are based upon stewardship objectives (e.g., sustainable resource management practices) which do not always correspond with the minimum standards set in legislation. A high resource development impact rating does not necessarily mean that a practice has not met legislation or the results and strategies contained within a licensee s forest stewardship plan. It is expected and accepted that development of natural resources will result in some level of environmental impact. However these impacts are expected to be within the parameters set down in legislation and forest stewardship plans. FREP resource value assessments help determine whether these impacts are consistent with expected outcomes and/or achieve sustainable levels of resource stewardship. Generally, assessments indicate there has been no significant change in the results under the FRPA from the Forest Practices Code era. However, one exception is stand-level biodiversity assessment results which indicate an improvement under the FRPA over the FPC-era. This is definitely a positive trend. I am pleased to see that forest stewardship values have generally been well met in the Sunshine Coast District. The results of the water quality assessments are particularly encouraging with 81% of the samples rated as very low or low for sediment generation potential. This is significantly better than coastal or provincial averages. Initial stand development monitoring assessment results indicate stewardship quality is well met. While only 14 of the proposed 30 polygons have been sampled to date; 86% of these polygons were rated as very low or low impact to achieving overall health and stand productivity. These results are very encouraging and indicate our year old stands are progressing well. Riparian assessments indicate that stewardship quality has generally been well met. However, there appears to be room for improvement with respect to S6 streams as 8 of the 38 S6 streams sampled were classified as highly impacted. Areas within the Sunshine Coast District are important for destination tourism e.g., Desolation Sound/ Discovery Islands. Licensees are encouraged to use existing visual design techniques to improve the overall conformance with the Visual Quality Objectives throughout the district. Updates are being completed on Visual inventories to confirm VQO s. I encourage forest professionals to consider the resource value results and opportunities for improvement identified in this document, along with other FREP monitoring results, when preparing, reviewing, and implementing forest stewardship plans and operational plans. 1 Commentary supplied by Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District Manager, Mark Anderson. 12
13 APPENDIX 1. SUMMARY DESCRIPTION OF RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT IMPACT RATING CRITERIA Table A1.1 shows the criteria used to determine the resource development impact ratings for each resource value. Detailed rating criteria, methodology, and definition of terms used are described in the companion document FREP Technical Note #6: Methodologies for Converting FREP Monitoring Results to Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Resource Development Impact Ratings ( The ratings of very low, low, medium, and high are technical ratings based on best available science. Table A1.1: Criteria for determining resource development impact rating outcomes for each resource value. Resource Value FREP Evaluation Question Indicators Resource Development Impact Rating Criteria Very low Low Medium High Riparian Stand-level Biodiversity Water Quality (sediment) Soils Cultural Heritage Timber: Stand Development Monitoring Landscape-level Biodiversity Visual Quality Are riparian forestry and range practices effective in maintaining the proper functioning of riparian areas? Is stand-level retention providing the range of habitat and attributes understood as necessary for maintaining species dependant on wildlife trees and coarse woody debris? Fifteen key questions (e.g., intact channel banks, fine sediments, riparian vegetation) Percent retention, retention quality from nine key attributes (e.g., big patches, density of large diameter trees), coarse woody debris volume, coarse woody debris quality from two key attributes (e.g., density of pieces 10 m and 20 cm, and volume of large diameter pieces Are forest practices effective in Fine sediment potential protecting water quality? Are forest practices preventing site Amount of access, restoration of natural disturbance that is detrimental to soil drainage patterns, road side work area soil productivity and hydrologic function? disturbance, amount of mature forest and coarse woody debris and restoration of natural drainage patterns Are cultural heritage resources being conserved and where necessary protected for First Nations cultural and traditional activities? What is the overall health and productivity of managed year stands? Evidence and extent of damage to features, operational limitations, management strategies and type and extent of features Impacts of forest health factors on stand stocking (ratio of total and well spaced) Is the forested matrix at the Ecosystem representativeness, age class landscape-level providing the range and interior old of habitat understood as necessary for maintaining ecosystem function and old and mature forest dependant species? How are we managing views in scenic areas and achieving visual quality objectives? Visual evaluation of block, design of block, percent of landform altered, impact of roads, tree retention and view point importance Number of no answers on assessment questions of channel and riparian conditions > 6 Cumulative score. A 60/40 weighting is used for tree retention versus coarse woody debris, recognizing the longer-term ecological value of standing retention. > 70% 55 70% 40 55% < 40% Fine sediment (m 3 ) due to expected surface erosion or past mass wasting < 0.1 < > 5 Overall assessment of practices on cutblock to maintain soil productivity and hydrologic function Well Moderately Poor Combined overall cutblock assessment results with consideration of individual feature assessment results Forest health damaging agent (% level of incidence) and level of stocking (well spaced stems per hectare) Overall ranking: within protected and nonprotected areas Basic visual quality class (determined using the VQC definitions) is compared with the Adjusted VQC (derived using percent alteration measurements and adjustment factors) to determine if VQO is achieved. 13 See methodology report VQO achieved, and % alteration low or mid-range Ranking under development VQO achieved, but % alteration for one or both close to alteration limit Only one method indicates VQO achieved Both methods indicate VQO not achieved
14 APPENDIX 2. COMPARATIVE FREP RESULTS BY RESOURCE VALUE FOR OTHER AREAS Table 2 in the main body of the report describes overall ratings for the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District as compared to adjacent TSAs or districts. The table below describes the same results but by the North, South and Coast areas and the province as a whole. The three operational areas represent combined natural resource regions. Table A2.1: FREP monitoring results by resource value for the North, South, and Coast Areas and the province as a whole compared to the Sunshine Coast Natural Resource District. Effectiveness of Practices in Achieving Resource Stewardship Objectives: % Very low + low resource development impact rating (sample size in brackets) Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations Areas Resource Value Sunshine Coast District North South Coast Province Riparian all data FRPA-era data FPC-era data 63% (65) 63% (38) 63% (27) 71% (654) 71% (257) 71% (394) 69% (678) 68% (277) 70% (401) 58% (451) 62% (198) 55% (253) 67% (1783) 67% (732) 67% (1048) Water quality all data samples samples 81% (230) 83% (157) 77% (73) 66% (992) 67% (505) 64% (487) 70% (1515) 70% (823) 70% (692) 76% (1526) 79% (1021) 70% (505) 71% (4033) 73%(2349) 68% (1684) Stand-level biodiversity all data FRPA-era data FPC-era data 75% (72) 89% (35) 62% (37) 42% (655) 49% (270) 38% (385) 54% (780) 61% (347) 49% (433) 77% (455) 84% (201) 72% (254) 56% (1890) 63% (818) 50% (1072) Visual Quality FRPA FPC 65% (20) ID (0) 73% (122) 56% (96) 54% (136) 65% (85) 78% (153) 62% (68) 69% (411) 61% (249) 14
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Chilliwack Natural Resource District November 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation, plans and resource
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Chilliwack Natural Resource District November 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation, plans and resource
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Fort St. James Natural Resource District Prince George Timber Supply Area December 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Fort St. James Natural Resource District Prince George Timber Supply Area December 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy
Forest and Range Evaluation Program Multiple Resource Value Assessment Report
 Forest and Range Evaluation Program Multiple Resource Value Assessment Report Campbell River District November 2015 1 CONTEXT FOR UNDERSTANDING THIS REPORT All natural resource development will have an
Forest and Range Evaluation Program Multiple Resource Value Assessment Report Campbell River District November 2015 1 CONTEXT FOR UNDERSTANDING THIS REPORT All natural resource development will have an
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Bulkley Timber Supply Area Skeena Stikine Natural Resource District December 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Bulkley Timber Supply Area Skeena Stikine Natural Resource District December 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Ecosystem Based Management (EBM) Area Within the North Island-Central Coast Natural Resource District February 2014 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Ecosystem Based Management (EBM) Area Within the North Island-Central Coast Natural Resource District February 2014 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia
Multiple Resource Value Assessments (MRVA)
 % of Samples MRVA in Brief Multiple Resource Value Assessments (MRVA) Lakes Timber Supply Area - Nadina Resource District July 26, 2013 This document reports monitoring results for riparian, biodiversity
% of Samples MRVA in Brief Multiple Resource Value Assessments (MRVA) Lakes Timber Supply Area - Nadina Resource District July 26, 2013 This document reports monitoring results for riparian, biodiversity
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Vanderhoof Natural Resource District Prince George Timber Supply Area January 2014 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Vanderhoof Natural Resource District Prince George Timber Supply Area January 2014 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Haida Gwaii Natural Resource District December 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation, plans and resource
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Haida Gwaii Natural Resource District December 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation, plans and resource
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA)
 Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Merritt Timber Supply Area Cascades Natural Resource District November 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation,
Multiple Resource Value Assessment (MRVA) Merritt Timber Supply Area Cascades Natural Resource District November 2013 FOREWORD Forest management in British Columbia is governed by a hierarchy of legislation,
FREP/MRVA & WQEE. by: Dave Maloney and Brian Carson
 FREP/MRVA & WQEE by: Dave Maloney and Brian Carson Outline What is FREP/MRVA, how and why they got started Values monitored What happens to the information we collect Is the information reported back to
FREP/MRVA & WQEE by: Dave Maloney and Brian Carson Outline What is FREP/MRVA, how and why they got started Values monitored What happens to the information we collect Is the information reported back to
This Notice applies to the Squamish Forest District. Schedule 1. 1) Marbled Murrelet (Brachyramphus marmoratus) Amount:
 December 30, 2004 NOTICE INDICATORS OF THE AMOUNT, DISTRIBUTION AND ATTRIBUTES OF WILDLIFE HABITAT REQUIRED FOR THE SURVIVAL OF SPECIES AT RISK IN THE SQUAMISH FOREST DISTRICT This Notice is given under
December 30, 2004 NOTICE INDICATORS OF THE AMOUNT, DISTRIBUTION AND ATTRIBUTES OF WILDLIFE HABITAT REQUIRED FOR THE SURVIVAL OF SPECIES AT RISK IN THE SQUAMISH FOREST DISTRICT This Notice is given under
Baseline Datasets for Evaluating Wildlife Tree Patches
 FRPA Resource Evaluation Program Scientifically Valid Evaluations of Forest Practices under the Forest and Range Practices Act Baseline Datasets for Evaluating Wildlife Tree Patches Introduction In November
FRPA Resource Evaluation Program Scientifically Valid Evaluations of Forest Practices under the Forest and Range Practices Act Baseline Datasets for Evaluating Wildlife Tree Patches Introduction In November
Vancouver Island Land Use Plan Higher Level Plan Order
 Order Establishing Resource Management Zones and Resource Management Zone Objectives within the area covered by the Vancouver Island Land Use Plan, pursuant to sections 3(1) and 3(2), as well as section
Order Establishing Resource Management Zones and Resource Management Zone Objectives within the area covered by the Vancouver Island Land Use Plan, pursuant to sections 3(1) and 3(2), as well as section
Vancouver Island Land Use Plan Higher Level Plan Order
 Order Establishing Resource Management Zones and Resource Management Zone Objectives within the area covered by the Vancouver Island Land Use Plan, pursuant to sections 3(1) and 3(2), as well as section
Order Establishing Resource Management Zones and Resource Management Zone Objectives within the area covered by the Vancouver Island Land Use Plan, pursuant to sections 3(1) and 3(2), as well as section
Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area
 Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area Vegetation Resources Inventory Photo Interpretation Project Implementation Plan PREPARED BY: GERRY SOMMERS & WARREN NIMCHUK ISSUED: AUGUST 2005 REVISED: MARCH 2006 1.
Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area Vegetation Resources Inventory Photo Interpretation Project Implementation Plan PREPARED BY: GERRY SOMMERS & WARREN NIMCHUK ISSUED: AUGUST 2005 REVISED: MARCH 2006 1.
An Example of Long-Form Audit Reporting
 An Example of Long-Form Audit Reporting Special Report www.fpb.gov.bc.ca FPB/SR/15 May 2003 Introduction The Forest Practices Board is changing its approach to compliance audits of certified forest licensees.
An Example of Long-Form Audit Reporting Special Report www.fpb.gov.bc.ca FPB/SR/15 May 2003 Introduction The Forest Practices Board is changing its approach to compliance audits of certified forest licensees.
Forest Stewardship Plan Tree Farm License 58
 2017 2022 Tree Farm License 58 A&A Trading (Haida Gwaii) Ltd. 1210-1111 Melville Street Vancouver, British Columbia, V6E 3V6 Authorized Licensee Signature: Name: Marty Locker, R.P.F. Operations Manager
2017 2022 Tree Farm License 58 A&A Trading (Haida Gwaii) Ltd. 1210-1111 Melville Street Vancouver, British Columbia, V6E 3V6 Authorized Licensee Signature: Name: Marty Locker, R.P.F. Operations Manager
Haida Gwaii Land Use Objectives Order. Consolidated Version 1 For Communication Only. Background
 Haida Gwaii Land Use Objectives Order Consolidated Version 1 For Communication Only Background A community-based, strategic-level land use planning process led by the Council of the Haida Nation and the
Haida Gwaii Land Use Objectives Order Consolidated Version 1 For Communication Only Background A community-based, strategic-level land use planning process led by the Council of the Haida Nation and the
Forest & Range Evaluation Program
 Forest & Range Evaluation Program Riparian Management Effectiveness & the Fish Value Post-Harvest Assessments of Riparian, Stream, & Fish Habitat Conditions Peter J. Tschaplinski Ministry of Environment
Forest & Range Evaluation Program Riparian Management Effectiveness & the Fish Value Post-Harvest Assessments of Riparian, Stream, & Fish Habitat Conditions Peter J. Tschaplinski Ministry of Environment
Implementation of Biodiversity Measures under the Forest Practices Code
 Implementation of Biodiversity Measures under the Forest Practices Code Implications for the Transition to the Forest and Range Practices Act Special Report www.fpb.gov.bc.ca FPB/SR/17 March 2004 Executive
Implementation of Biodiversity Measures under the Forest Practices Code Implications for the Transition to the Forest and Range Practices Act Special Report www.fpb.gov.bc.ca FPB/SR/17 March 2004 Executive
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN 2016
 FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN 2016 Forest Operations of A&A Trading Ltd. and Klahoose Forestry Limited Partnership Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Areas Forest License A19229, A80590 & A84120 Version 1.1 November
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN 2016 Forest Operations of A&A Trading Ltd. and Klahoose Forestry Limited Partnership Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Areas Forest License A19229, A80590 & A84120 Version 1.1 November
Interwest Timber Ltd FSP Back Ground Document
 Interwest Timber Ltd FSP Back Ground Document Response to the District Manager s Expectations Letter First Nations Interwest has built a strong relationship with First Nations communities and tribal associations
Interwest Timber Ltd FSP Back Ground Document Response to the District Manager s Expectations Letter First Nations Interwest has built a strong relationship with First Nations communities and tribal associations
A Framework for Monitoring & Evaluating Wildlife Resource Values
 A Framework for Monitoring & Evaluating Wildlife Resource Values RESOURCE VALUE FRAMEWORK September 2009 Prepared by Kathy Paige, Ministry of Environment Laura Darling, Ministry of Forests and Range Introduction
A Framework for Monitoring & Evaluating Wildlife Resource Values RESOURCE VALUE FRAMEWORK September 2009 Prepared by Kathy Paige, Ministry of Environment Laura Darling, Ministry of Forests and Range Introduction
2.0 APPLICATION, TERM AND COMMENCEMENT OF TERM OF THIS FSP...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 1 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN... 3 2.0 APPLICATION, TERM AND COMMENCEMENT OF TERM OF THIS FSP... 5 2.1 APPLICATION OF THIS FSP (FRPA SECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 1 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN... 3 2.0 APPLICATION, TERM AND COMMENCEMENT OF TERM OF THIS FSP... 5 2.1 APPLICATION OF THIS FSP (FRPA SECTION
WOODLOT LICENCE W1900 WOODLOT LICENCE PLAN TERM 10 YEARS. August, 2007 to August, 2017
 WOODLOT LICENCE W1900 WOODLOT LICENCE PLAN TERM 10 YEARS August, 2007 to August, 2017 Campbell River Indian Band 1400 Weiwaikum Road Campbell River, B.C. V9W 5W8 Phone: (250) 286-6949 Fax: (250) 286-8838
WOODLOT LICENCE W1900 WOODLOT LICENCE PLAN TERM 10 YEARS August, 2007 to August, 2017 Campbell River Indian Band 1400 Weiwaikum Road Campbell River, B.C. V9W 5W8 Phone: (250) 286-6949 Fax: (250) 286-8838
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN #601
 BC Timber Sales Kootenay Business Area FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN #601 2017 to 2022 This Forest Stewardship Plan is applicable to BC Timber Sales planning, operations, licences and permits within: Rocky Mountain
BC Timber Sales Kootenay Business Area FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN #601 2017 to 2022 This Forest Stewardship Plan is applicable to BC Timber Sales planning, operations, licences and permits within: Rocky Mountain
Great Bear Rainforest Order
 Great Bear Rainforest Order January 2016 Great Bear Rainforest Order 1 Great Bear Rainforest Order Preamble It is the goal of the Province, through land use objectives and other measures, to implement
Great Bear Rainforest Order January 2016 Great Bear Rainforest Order 1 Great Bear Rainforest Order Preamble It is the goal of the Province, through land use objectives and other measures, to implement
Timber Harvesting and Fishing Lodge Interests near Morrison Arm
 Timber Harvesting and Fishing Lodge Interests near Morrison Arm Complaint Investigation 000284 FPB/IRC/59 January 2002 Table of Contents The Investigation... 1 Background... 1 Relevant Legislation... 2
Timber Harvesting and Fishing Lodge Interests near Morrison Arm Complaint Investigation 000284 FPB/IRC/59 January 2002 Table of Contents The Investigation... 1 Background... 1 Relevant Legislation... 2
South Island District Woodlots Woodlot Licences W0011, W0020, W1479, W1526, W1713, W1902, W1903, W1906 FPB/ARC/158
 Audit of Forest Planning and Practices South Island District Woodlots Woodlot Licences W0011, W0020, W1479, W1526, W1713, W1902, W1903, W1906 FPB/ARC/158 December 2013 Table of Contents Audit Results...1
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices South Island District Woodlots Woodlot Licences W0011, W0020, W1479, W1526, W1713, W1902, W1903, W1906 FPB/ARC/158 December 2013 Table of Contents Audit Results...1
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices
 Audit of Forest Planning and Practices TimberWest Forest Corporation Tree Farm Licence 47 FPB/ARC/174 February 2015 Table of Contents Audit Results...1 Background...1 Audit Approach and Scope...2 Planning
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices TimberWest Forest Corporation Tree Farm Licence 47 FPB/ARC/174 February 2015 Table of Contents Audit Results...1 Background...1 Audit Approach and Scope...2 Planning
Covering. Of Western Forest Products Inc. July 14, 2006 Version III (Submission)
 FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN s Covering Queen Charlotte Islands, Mid Island, Stillwater, Port Alberni and Portions of Port McNeill, Mainland Coast, Nootka Sound and Zeballos Forest Operations Of Western Forest
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN s Covering Queen Charlotte Islands, Mid Island, Stillwater, Port Alberni and Portions of Port McNeill, Mainland Coast, Nootka Sound and Zeballos Forest Operations Of Western Forest
Why more woodlots on Gambier?
 On July 9, 2013 the Gambier Island Conservancy and staff from Forestry, Lands and Natural Resources Operations Sunshine Coast District office met for an information gathering session regarding the proposed
On July 9, 2013 the Gambier Island Conservancy and staff from Forestry, Lands and Natural Resources Operations Sunshine Coast District office met for an information gathering session regarding the proposed
5. How does the designation of these woodlots fit into FLNRO s Principles for locating new forest tenures of Nov 2011?
 1 QUESTIONS FROM THE GAMBIER ISLAND CONSERVANCY AND ANSWERED BY BRIAN KUKULIES, FLNRO, ABOUT THE PROPOSED NEW GAMBIER WOODLOTS (JULY 2013) Part 1 Planning and background questions Why more woodlots on
1 QUESTIONS FROM THE GAMBIER ISLAND CONSERVANCY AND ANSWERED BY BRIAN KUKULIES, FLNRO, ABOUT THE PROPOSED NEW GAMBIER WOODLOTS (JULY 2013) Part 1 Planning and background questions Why more woodlots on
Facts and Figures. Greater Victoria Water Supply Area. May 2015
 Facts and Figures Greater Victoria Water Supply Area May 2015 Greater Victoria Water Supply Area The Greater Victoria Water Supply Area is made up of 20,549 hectares of land in the Sooke, Goldstream, Council,
Facts and Figures Greater Victoria Water Supply Area May 2015 Greater Victoria Water Supply Area The Greater Victoria Water Supply Area is made up of 20,549 hectares of land in the Sooke, Goldstream, Council,
Lillooet Forest District. Inventory Plan
 Lillooet Forest District Inventory Plan MINISTRY OF FORESTS RESOURCES INVENTORY BRANCH JUNE 1998 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 1.1 Background...1 1.2 Objectives...2 2. BUSINESS CONSIDERATIONS...3
Lillooet Forest District Inventory Plan MINISTRY OF FORESTS RESOURCES INVENTORY BRANCH JUNE 1998 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 1.1 Background...1 1.2 Objectives...2 2. BUSINESS CONSIDERATIONS...3
Timber Salvage Harvesting and Fisher Management in the Nazko Area. Complaint Investigation #16037
 Timber Salvage Harvesting and Fisher Management in the Nazko Area Complaint Investigation #16037 FPB/IRC/217 October 2018 Table of Contents Board Commentary... i Executive Summary... ii Introduction...
Timber Salvage Harvesting and Fisher Management in the Nazko Area Complaint Investigation #16037 FPB/IRC/217 October 2018 Table of Contents Board Commentary... i Executive Summary... ii Introduction...
Outdoor Recreation and the Forests & Range Practices Act.
 Outdoor Recreation and the Forests & Range Practices Act. Forest Practices Branch Range and Integrated Resources Section March 2005 Outdoor Recreation and the Forest and Range Practices Act - March 17,
Outdoor Recreation and the Forests & Range Practices Act. Forest Practices Branch Range and Integrated Resources Section March 2005 Outdoor Recreation and the Forest and Range Practices Act - March 17,
Forest Stewardship Plan Amendment
 Forest Stewardship Plan Amendment January 16, 2009 Cowichan Lake Community Forest Co-Operative Ltd Table of Contents 1 Interpretation 1-1 11 Definitions 1-1 12 Definitions from Legislation 1-1 13 Relevant
Forest Stewardship Plan Amendment January 16, 2009 Cowichan Lake Community Forest Co-Operative Ltd Table of Contents 1 Interpretation 1-1 11 Definitions 1-1 12 Definitions from Legislation 1-1 13 Relevant
Mid Coast Timber Supply Area
 Timber Mid Coast Timber Area Information Report April 1998 Ministry of Forests Introduction The British Columbia Forest Service is required by law to formally review the timber supply* in all timber supply
Timber Mid Coast Timber Area Information Report April 1998 Ministry of Forests Introduction The British Columbia Forest Service is required by law to formally review the timber supply* in all timber supply
West Coast Forest Stewardship Plan
 SOUTH ISLAND RESOURCE DISTRICT West Coast Forest Stewardship Plan B.C. Timber Sales, Strait of Georgia Business Area Consolidated to 2013 Major Amendment Original Approved July 17, 2006; Amended September
SOUTH ISLAND RESOURCE DISTRICT West Coast Forest Stewardship Plan B.C. Timber Sales, Strait of Georgia Business Area Consolidated to 2013 Major Amendment Original Approved July 17, 2006; Amended September
Tree Farm Licence 37
 BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF FORESTS, LANDS, NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT Tree Farm Licence 37 held by Western Forest Products Inc. Rationale for Allowable Annual Cut (AAC) Determination
BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF FORESTS, LANDS, NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT Tree Farm Licence 37 held by Western Forest Products Inc. Rationale for Allowable Annual Cut (AAC) Determination
Bulkley Land and Resource Management Plan - Higher Level Plan Order
 Bulkley Land and Resource Management Plan - Higher Level Plan Order Order Establishing Resource Management Zones and Resource Management Zone Objectives within the area covered by the Bulkley Land and
Bulkley Land and Resource Management Plan - Higher Level Plan Order Order Establishing Resource Management Zones and Resource Management Zone Objectives within the area covered by the Bulkley Land and
Q&A: Omineca spruce beetle outbreak May 4, 2018
 Q&A: Omineca spruce beetle outbreak May 4, 2018 Q. How big is this outbreak? What kind of impact has it had so far? The most recent provincial aerial overview survey was completed in fall 2017 and found
Q&A: Omineca spruce beetle outbreak May 4, 2018 Q. How big is this outbreak? What kind of impact has it had so far? The most recent provincial aerial overview survey was completed in fall 2017 and found
The following expectations are not legally binding; however they do constitute policy guidance under the FRPA non legal realm.
 Ref: 18046-00/2016, 18045-00/2016 November 30, 2016 By email Re:, District Manager Letter of Expectation Regarding Forest Stewardship Plan replacement Dear Forest Licensees and Forest Professionals: The
Ref: 18046-00/2016, 18045-00/2016 November 30, 2016 By email Re:, District Manager Letter of Expectation Regarding Forest Stewardship Plan replacement Dear Forest Licensees and Forest Professionals: The
Preamble. Objectives October 20, 2004 page 1 of 13
 Preamble This order establishes landscape biodiversity objectives, across the Prince George Timber Supply Area, for: A. old forest retention; B. old interior forest; and, C. young forest patch size distribution.
Preamble This order establishes landscape biodiversity objectives, across the Prince George Timber Supply Area, for: A. old forest retention; B. old interior forest; and, C. young forest patch size distribution.
Forest Stewardship Plan Tree Farm License 58, Forest License A16870 and Timber License T0184
 A & A TRADING LTD Forest Stewardship Plan 2018-2023 Tree Farm License 58, Forest License A16870 and Timber License T0184 Consolidated version for communication purposes only 1 1210-1111 Melville Street
A & A TRADING LTD Forest Stewardship Plan 2018-2023 Tree Farm License 58, Forest License A16870 and Timber License T0184 Consolidated version for communication purposes only 1 1210-1111 Melville Street
Forest Health Program
 Forest Health Program June 2007 www.for.gov.bc.ca/ hfp/health/ Library and Archives Canada Cataloguing in Publication Data British Columbia. Forest Health Program. Forest Health Program ISBN 978-0-7726-5814-2
Forest Health Program June 2007 www.for.gov.bc.ca/ hfp/health/ Library and Archives Canada Cataloguing in Publication Data British Columbia. Forest Health Program. Forest Health Program ISBN 978-0-7726-5814-2
E8 Forest Management Plan
 E8 Forest Management Plan Alberta Sustainable Resource Development in cooperation with Foothills Forest Products Forestry Division Foothills Forest Area Hinton, Alberta 1 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction...11
E8 Forest Management Plan Alberta Sustainable Resource Development in cooperation with Foothills Forest Products Forestry Division Foothills Forest Area Hinton, Alberta 1 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction...11
Complaint Investigation
 Wood Waste in Bigmouth Creek Complaint Investigation 090915 FPB/IRC/172 November 2010 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 The Complaint... 1 Background... 1 Discussion... 2 Timber Left On The Block Does
Wood Waste in Bigmouth Creek Complaint Investigation 090915 FPB/IRC/172 November 2010 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 The Complaint... 1 Background... 1 Discussion... 2 Timber Left On The Block Does
CCLUP Land Use Order
 MINISTRY OF FORESTS, LANDS AND NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS CCLUP Land Use Order Implementation Direction June 21, 2011 1. Introduction The purpose of this document is to assist with implementation of the
MINISTRY OF FORESTS, LANDS AND NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS CCLUP Land Use Order Implementation Direction June 21, 2011 1. Introduction The purpose of this document is to assist with implementation of the
Preamble. Objectives October 20, 2004 page 1 of 13
 Preamble This order establishes landscape biodiversity objectives, across the Prince George Timber Supply Area, for: A. old forest retention; B. old interior forest; and, C. young forest patch size distribution.
Preamble This order establishes landscape biodiversity objectives, across the Prince George Timber Supply Area, for: A. old forest retention; B. old interior forest; and, C. young forest patch size distribution.
B.9.6 Ungulate Winter Range
 B.9.6 Ungulate Winter Range Suitability, capability and availability of winter range habitat are the principle limiting factors regulating ungulate carrying capacity and, accordingly, are significant with
B.9.6 Ungulate Winter Range Suitability, capability and availability of winter range habitat are the principle limiting factors regulating ungulate carrying capacity and, accordingly, are significant with
TIMBERWEST FOREST CORP BONANZA FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN
 TIMBERWEST FOREST CORP BONANZA FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN Replacing the FSP approved April 12, 2007 and extended to April 11, 2017 Submitted TBA, 2017 This page is intentionally blank. Authorized Licensee
TIMBERWEST FOREST CORP BONANZA FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN Replacing the FSP approved April 12, 2007 and extended to April 11, 2017 Submitted TBA, 2017 This page is intentionally blank. Authorized Licensee
Provincial Wildlife Tree Policy and Management Recommendations
 Provincial Wildlife Tree Policy and Management Recommendations This document was compiled by Forest Practices Branch of the Ministry of Forests and Habitat Branch of the Ministry of Environment, Lands
Provincial Wildlife Tree Policy and Management Recommendations This document was compiled by Forest Practices Branch of the Ministry of Forests and Habitat Branch of the Ministry of Environment, Lands
KOOTENAY-BOUNDARY HIGHER LEVEL PLAN ORDER
 KOOTENAY-BOUNDARY HIGHER LEVEL PLAN ORDER ORDER ESTABLISHING RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ZONES AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ZONE OBJECTIVES WITHIN THE AREA COVERED BY THE KOOTENAY-BOUNDARY LAND USE PLAN AS A HIGHER
KOOTENAY-BOUNDARY HIGHER LEVEL PLAN ORDER ORDER ESTABLISHING RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ZONES AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ZONE OBJECTIVES WITHIN THE AREA COVERED BY THE KOOTENAY-BOUNDARY LAND USE PLAN AS A HIGHER
Sea to Sky Floodplain Management Plan
 Sea to Sky Floodplain Management Plan June 2010 Sea-to-Sky Floodplain Management Plan The Sea-to-Sky Floodplain Management Plan was developed through consultation with the following organizations and was
Sea to Sky Floodplain Management Plan June 2010 Sea-to-Sky Floodplain Management Plan The Sea-to-Sky Floodplain Management Plan was developed through consultation with the following organizations and was
Skeena Sawmills Ltd SFI Certification Audit
 Skeena Sawmills Ltd. 2017 SFI Certification Audit From September 27-29 an audit team from KPMG Performance Registrar Inc. (KPMG PRI) carried out an SFI registration audit of Skeena Sawmills Ltd. woodlands
Skeena Sawmills Ltd. 2017 SFI Certification Audit From September 27-29 an audit team from KPMG Performance Registrar Inc. (KPMG PRI) carried out an SFI registration audit of Skeena Sawmills Ltd. woodlands
Forest Stewardship Action Plan for Climate Change Adaptation
 Forest Stewardship Action Plan for Climate Change Adaptation 2012-2017 February 27, 2012 Forest Stewardship Action Plan for Climate Change Adaptation 2012 2017 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1
Forest Stewardship Action Plan for Climate Change Adaptation 2012-2017 February 27, 2012 Forest Stewardship Action Plan for Climate Change Adaptation 2012 2017 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1
Effects of Future Forest Harvest on Wildlife Habitat in southeast British Columbia
 Effects of Future Forest Harvest on Wildlife Habitat in southeast British Columbia 14 September, 2016 Tyler Muhly, Ph.D., R.P.Bio. Ministry of Forest, Lands and Natural Resource Operations Tony Button,
Effects of Future Forest Harvest on Wildlife Habitat in southeast British Columbia 14 September, 2016 Tyler Muhly, Ph.D., R.P.Bio. Ministry of Forest, Lands and Natural Resource Operations Tony Button,
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices
 Audit of Forest Planning and Practices BC Timber Sales and Timber Sale Licence Holders Chilliwack Natural Resource District portion of the Chinook Business Area FPB/ARC/178 April 2015 Table of Contents
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices BC Timber Sales and Timber Sale Licence Holders Chilliwack Natural Resource District portion of the Chinook Business Area FPB/ARC/178 April 2015 Table of Contents
Instructions for Printing the Final Copy of the WLP without Hidden Text. HIDDEN TEXT FORMATTING 1 View or Hide Hidden Text viewed on the screen only.
 Woodlot Licence Plan Template November 15 2007 Version Instructions: (Delete this page before submitting the WLP) This Woodlot Licence Plan (WLP) template has been prepared in Word / XP. Blue italicized
Woodlot Licence Plan Template November 15 2007 Version Instructions: (Delete this page before submitting the WLP) This Woodlot Licence Plan (WLP) template has been prepared in Word / XP. Blue italicized
Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area Timber Supply Review. Data Package. July 2010
 Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area Timber Supply Review Data Package July 2010 Table of Contents Overview of the Sunshine Coast TSA Timber Supply Review (TSR)... 1 1. Introduction... 2 1.1 Overview of the
Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area Timber Supply Review Data Package July 2010 Table of Contents Overview of the Sunshine Coast TSA Timber Supply Review (TSR)... 1 1. Introduction... 2 1.1 Overview of the
Managing Natural Range. Forests and Range Practices Act
 Managing Natural Range Barriers under the Forests and Range Practices Act Managing Natural Range Barriers (NRBs) under FRPA: Introduction What is a Natural Range Barrier? Managing Cumulative Effects of
Managing Natural Range Barriers under the Forests and Range Practices Act Managing Natural Range Barriers (NRBs) under FRPA: Introduction What is a Natural Range Barrier? Managing Cumulative Effects of
Golden Timber Supply Area
 BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF FORESTS AND RANGE Golden Timber Supply Area Rationale for Allowable Annual Cut (AAC) Determination Effective June 3, 2010 Jim Snetsinger, RPF Chief Forester Table of Contents
BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF FORESTS AND RANGE Golden Timber Supply Area Rationale for Allowable Annual Cut (AAC) Determination Effective June 3, 2010 Jim Snetsinger, RPF Chief Forester Table of Contents
Sunshine Coast Forest District Landscape Unit Planning Homathko Landscape Unit Plan
 Sunshine Coast Forest District Landscape Unit Planning Homathko Landscape Unit Plan September 27, 2001 Prepared by the Sunshine Coast Landscape Unit Planning Team: Steve Gordon, R.P.Bio. Forest Ecosystem
Sunshine Coast Forest District Landscape Unit Planning Homathko Landscape Unit Plan September 27, 2001 Prepared by the Sunshine Coast Landscape Unit Planning Team: Steve Gordon, R.P.Bio. Forest Ecosystem
Timber Removal in Mountain Caribou Habitat
 Timber Removal in Mountain Caribou Habitat Special Investigation FPB/SIR/45 December 2015 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Scope... 5 Approach... 5 Legal Framework...
Timber Removal in Mountain Caribou Habitat Special Investigation FPB/SIR/45 December 2015 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Scope... 5 Approach... 5 Legal Framework...
GREAT BEAR RAINFOREST EBM BULLETIN
 GREAT BEAR RAINFOREST EBM BULLETIN Bulletin Number: EBM-2016-05 Subject: 2016 Great Bear Rainforest Land Use Order and the Great Bear Rainforest Forest Management Act Content Highlights: Given the unique
GREAT BEAR RAINFOREST EBM BULLETIN Bulletin Number: EBM-2016-05 Subject: 2016 Great Bear Rainforest Land Use Order and the Great Bear Rainforest Forest Management Act Content Highlights: Given the unique
Ndazkhot en Forest Management Ltd. Forest Licences A65926 and A81934 FPB/ARC/159
 Audit of Forest Planning and Practices Ndazkhot en Forest Management Ltd. Forest Licences A65926 and A81934 FPB/ARC/159 December 2013 Table of Contents Audit Results...1 Background...1 Audit Approach and
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices Ndazkhot en Forest Management Ltd. Forest Licences A65926 and A81934 FPB/ARC/159 December 2013 Table of Contents Audit Results...1 Background...1 Audit Approach and
GREAT BEAR RAINFOREST UPDATE MAY 2010 Key milestones achieved March 2009 and Five-Year Plan
 Andrew Wright photo GREAT BEAR RAINFOREST UPDATE MAY 2010 Key milestones achieved March 2009 and Five-Year Plan 2009 2014 A global treasure and conservation model Canada is home to the Great Bear Rainforest
Andrew Wright photo GREAT BEAR RAINFOREST UPDATE MAY 2010 Key milestones achieved March 2009 and Five-Year Plan 2009 2014 A global treasure and conservation model Canada is home to the Great Bear Rainforest
Tree Farm Licence 46
 BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF FORESTS, LANDS AND NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS Tree Farm Licence 46 held by Teal Cedar Products Ltd. Rationale for Allowable Annual Cut (AAC) Determination Effective May 24,
BRITISH COLUMBIA MINISTRY OF FORESTS, LANDS AND NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS Tree Farm Licence 46 held by Teal Cedar Products Ltd. Rationale for Allowable Annual Cut (AAC) Determination Effective May 24,
Chief Forester Order Respecting the AAC Determination for the Nass Timber Supply Area
 Chief Forester Order Respecting the AAC Determination for the Nass Timber Supply Area Section 8 (3.1) of the Forest Act stipulates in part that: If the chief forester considers that the allowable annual
Chief Forester Order Respecting the AAC Determination for the Nass Timber Supply Area Section 8 (3.1) of the Forest Act stipulates in part that: If the chief forester considers that the allowable annual
Policy and Administration
 Timber Pricing Branch 1 July 15, 2011 Amendment No. 19 1-1 Provincial Logging Residue & Waste Measurement Procedures Manual FLNRO 1.1 Waste Assessment Policy Figure 1-1 Waste Assessment Policy. 1-2 Amendment
Timber Pricing Branch 1 July 15, 2011 Amendment No. 19 1-1 Provincial Logging Residue & Waste Measurement Procedures Manual FLNRO 1.1 Waste Assessment Policy Figure 1-1 Waste Assessment Policy. 1-2 Amendment
ORDER UNGULATE WINTER RANGE U GOLDEN TSA
 ORDER UNGULATE WINTER RANGE U-4-007 - GOLDEN TSA The following order applies to the area identified within the attached Schedule A and takes effect on the day of, 2006. This order is given under the authority
ORDER UNGULATE WINTER RANGE U-4-007 - GOLDEN TSA The following order applies to the area identified within the attached Schedule A and takes effect on the day of, 2006. This order is given under the authority
FOREST AND RANGE PRACTICES ACT
 DELEGATION OF MINISTER OF FORESTS, LANDS, NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT POWERS AND DUTIES UNDER THE FOREST AND RANGE PRACTICES ACT AND REGULATIONS, January 2019 A = CF = DCEB = DDCEB
DELEGATION OF MINISTER OF FORESTS, LANDS, NATURAL RESOURCE OPERATIONS AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT POWERS AND DUTIES UNDER THE FOREST AND RANGE PRACTICES ACT AND REGULATIONS, January 2019 A = CF = DCEB = DDCEB
Fort St. John Timber Supply Area
 Timber Supply Review Fort St. John Timber Supply Area P u b l i c D i s c u s s i o n P a p e r June 2002 Ministry of Forests Introduction Welcome to the timber supply review in the Fort St. John Timber
Timber Supply Review Fort St. John Timber Supply Area P u b l i c D i s c u s s i o n P a p e r June 2002 Ministry of Forests Introduction Welcome to the timber supply review in the Fort St. John Timber
Fraser TSA Timber Supply Analysis Discussion Paper Ministry of Forests, Lands, and Natural Resource Operations 727 Fisgard Street Victoria, B.C.
 Fraser TSA Timber Supply Analysis Discussion Paper Ministry of Forests, Lands, and Natural Resource Operations 727 Fisgard Street Victoria, B.C. V8W 1R8 March 2015 Jim Brown - Analyst Cover photograph
Fraser TSA Timber Supply Analysis Discussion Paper Ministry of Forests, Lands, and Natural Resource Operations 727 Fisgard Street Victoria, B.C. V8W 1R8 March 2015 Jim Brown - Analyst Cover photograph
Whistler Landscape Unit Plan
 Whistler Landscape Unit Plan for Old-Growth Management Areas Sea to Sky Natural Resource District South Coast Region Executive Summary This landscape unit plan (LUP) is a companion document to the Ministerial
Whistler Landscape Unit Plan for Old-Growth Management Areas Sea to Sky Natural Resource District South Coast Region Executive Summary This landscape unit plan (LUP) is a companion document to the Ministerial
Sunshine Coast Timber Supply Area Timber Supply Review. Summary of Public Input
 Timber Supply Review Summary of Public Input B.C. Ministry of Forests Sunshine Coast Forest District 7077 Duncan Street Powell River, B.C. V8A 1W1 This is a summary of the public input that has been received
Timber Supply Review Summary of Public Input B.C. Ministry of Forests Sunshine Coast Forest District 7077 Duncan Street Powell River, B.C. V8A 1W1 This is a summary of the public input that has been received
Appendix B: Timber Supply Analysis
 Appendix B: Timber Supply Analysis TFL 6 Management Plan #10 Page 156 Executive Summary This analysis examines timber supply projections for Tree Farm Licence 6 located on northern Vancouver Island.
Appendix B: Timber Supply Analysis TFL 6 Management Plan #10 Page 156 Executive Summary This analysis examines timber supply projections for Tree Farm Licence 6 located on northern Vancouver Island.
South Island District Woodlot Woodlot Licence W1632 FPB/ARC/162
 Audit of Forest Planning and Practices South Island District Woodlot Woodlot Licence W1632 FPB/ARC/162 February 2014 Table of Contents Board Commentary...1 Audit Results...3 Background...3 Audit Approach
Audit of Forest Planning and Practices South Island District Woodlot Woodlot Licence W1632 FPB/ARC/162 February 2014 Table of Contents Board Commentary...1 Audit Results...3 Background...3 Audit Approach
Small Stream Riparian Zones: Why are they important and how can we manage them?
 Small Stream Riparian Zones: Why are they important and how can we manage them? Southern Interior Silviculture Committee Annual Meeting Kamloops, BC February 1, 2017 John Rex, Ph.D., P.Ag. Research Hydrologist
Small Stream Riparian Zones: Why are they important and how can we manage them? Southern Interior Silviculture Committee Annual Meeting Kamloops, BC February 1, 2017 John Rex, Ph.D., P.Ag. Research Hydrologist
TABLE OF CONTENTS 5.0 FOREST MANAGEMENT PLANNING...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 5.0 FOREST MANAGEMENT PLANNING... 1 5.1 Planning Framework... 1 5.1.1 Sustainable Forest Management Planning... 1 5.1.2 Five-Year Operating Plan... 1 5.1.3 Annual Operating Plans... 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS 5.0 FOREST MANAGEMENT PLANNING... 1 5.1 Planning Framework... 1 5.1.1 Sustainable Forest Management Planning... 1 5.1.2 Five-Year Operating Plan... 1 5.1.3 Annual Operating Plans... 3
Disposition of Crown Timber on Grazing Leases Effective: May 1, 2015
 Thompson Rivers District Policy Disposition of Crown Timber on Grazing Leases Effective: May 1, 2015 Purpose The purpose of this policy is to guide the disposition of Crown timber on grazing leases in
Thompson Rivers District Policy Disposition of Crown Timber on Grazing Leases Effective: May 1, 2015 Purpose The purpose of this policy is to guide the disposition of Crown timber on grazing leases in
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN for Community Forest License K3G
 Powell River Community Forest Ltd. FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN for Community Forest License K3G Approved December 19, 2008 Consolidated to Amendment # 1 and 5 year Extension effective, 2013 Sunshine Coast
Powell River Community Forest Ltd. FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN for Community Forest License K3G Approved December 19, 2008 Consolidated to Amendment # 1 and 5 year Extension effective, 2013 Sunshine Coast
Prince George Forest District
 Prince George Forest District Vegetation Resources Inventory Strategic Inventory Plan PREPARED BY: MINISTRY OF FORESTS RESOURCES INVENTORY BRANCH 3 JANUARY 2000 VSIP: Prince George Forest District Page
Prince George Forest District Vegetation Resources Inventory Strategic Inventory Plan PREPARED BY: MINISTRY OF FORESTS RESOURCES INVENTORY BRANCH 3 JANUARY 2000 VSIP: Prince George Forest District Page
LITTLE PRAIRIE COMMUNITY FOREST: B2B October 12, 2016 Presented by Jeff Beale, RPF
 LITTLE PRAIRIE COMMUNITY FOREST: B2B October 12, 2016 Presented by Jeff Beale, RPF Little Prairie Community Forest 2016 Map ~ 13,500 hectares total gross area ~ 3,500 hectares in an old growth management
LITTLE PRAIRIE COMMUNITY FOREST: B2B October 12, 2016 Presented by Jeff Beale, RPF Little Prairie Community Forest 2016 Map ~ 13,500 hectares total gross area ~ 3,500 hectares in an old growth management
14. Sustainable Forestry Principals
 14. Sustainable Forestry Principals Fish River Lakes Concept Plan Addendum Materials April 2018 14. SUSTAINABLE FORESTRY PRINCIPLES In response to our discussion with LUPC Staff and others on the topic
14. Sustainable Forestry Principals Fish River Lakes Concept Plan Addendum Materials April 2018 14. SUSTAINABLE FORESTRY PRINCIPLES In response to our discussion with LUPC Staff and others on the topic
Logging and Conservation of Endangered Plant Communities on Vancouver Island. Complaint Investigation
 Logging and Conservation of Endangered Plant Communities on Vancouver Island Complaint Investigation 040555 FPB/IRC/112 August 2005 Key Concepts and Terms Plant community A natural plant community is a
Logging and Conservation of Endangered Plant Communities on Vancouver Island Complaint Investigation 040555 FPB/IRC/112 August 2005 Key Concepts and Terms Plant community A natural plant community is a
Trends in Silviculture in B.C. ( )
 Forests Trends in Silviculture in B.C. (1970-2012) Silviculture is the practice of growing and cultivating trees in forests to meet certain objectives, such as timber production, biodiversity, wildlife
Forests Trends in Silviculture in B.C. (1970-2012) Silviculture is the practice of growing and cultivating trees in forests to meet certain objectives, such as timber production, biodiversity, wildlife
kpmg TimberWest Forest Corporation 2018 SFI Forest Management Surveillance Audit
 TimberWest Forest Corporation 2018 SFI Forest Management Surveillance Audit In April/May 2018 an audit team from KPMG Performance Registrar Inc. (KPMG PRI) carried out a surveillance audit of TimberWest
TimberWest Forest Corporation 2018 SFI Forest Management Surveillance Audit In April/May 2018 an audit team from KPMG Performance Registrar Inc. (KPMG PRI) carried out a surveillance audit of TimberWest
Overview of Forest Stewardship Plan. Public Workshop January 11, 2015
 Overview of Forest Stewardship Plan Public Workshop January 11, 2015 What is a Community Forest? In British Columbia, a community forest can be described as any forestry operation managed by a local government,
Overview of Forest Stewardship Plan Public Workshop January 11, 2015 What is a Community Forest? In British Columbia, a community forest can be described as any forestry operation managed by a local government,
1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PACIFIC MARITIME FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN. 4
 Page 2 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PACIFIC MARITIME FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN. 4 1.1 APPLICATION OF THE FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN (FRPA S. 3(4))... 4 1.2 DEFINITIONS... 4 1.3 RELEVANT DATE FOR
Page 2 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PACIFIC MARITIME FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN. 4 1.1 APPLICATION OF THE FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN (FRPA S. 3(4))... 4 1.2 DEFINITIONS... 4 1.3 RELEVANT DATE FOR
Sim Landscape Unit. Draft Strategic-Level Reserve Design. Prepared by: Darrin Finnerty, RPF Warren Warttig, RPBio Mike Landers, RPF.
 Draft Strategic-Level Reserve Design Prepared by: Darrin Finnerty, RPF Warren Warttig, RPBio Mike Landers, RPF March 31, 2011 March 31, 2011 Page 1 Table of Contents 1. PREFACE... 3 2. LANDSCAPE UNIT DESCRIPTION...
Draft Strategic-Level Reserve Design Prepared by: Darrin Finnerty, RPF Warren Warttig, RPBio Mike Landers, RPF March 31, 2011 March 31, 2011 Page 1 Table of Contents 1. PREFACE... 3 2. LANDSCAPE UNIT DESCRIPTION...
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN December 22, Sechelt Community Projects Incorporated. Sechelt Community Forest
 FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN December 22, 2006 Sechelt Community Projects Incorporated Sechelt Community Forest 1 Table of Contents 1 Forest Stewardship Plan... 3 1.1 Abbreviations used in this plan... 3 1.1
FOREST STEWARDSHIP PLAN December 22, 2006 Sechelt Community Projects Incorporated Sechelt Community Forest 1 Table of Contents 1 Forest Stewardship Plan... 3 1.1 Abbreviations used in this plan... 3 1.1
Appendix 1: Forest Carbon Emission Offset Project Development Guidance
 The Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations (FLNRO) supports the use of forest carbon management options that satisfy the diverse values that British Columbians seek from their forests.
The Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations (FLNRO) supports the use of forest carbon management options that satisfy the diverse values that British Columbians seek from their forests.
Why is Red Alder Important?
 9 Extension Note JUNE 1997 Effects of Red Alder on Stand Dynamics and Nitrogen Availability FRBC Project HQ964-RE (MOF EP 1121.1) Phil Comeau George Harper Balvinder Biring Peter Fielder Bill Reid B.C.
9 Extension Note JUNE 1997 Effects of Red Alder on Stand Dynamics and Nitrogen Availability FRBC Project HQ964-RE (MOF EP 1121.1) Phil Comeau George Harper Balvinder Biring Peter Fielder Bill Reid B.C.
As of 2000, 51% of Basin forests were between 21 and 140 years old, 37% older than 140 years, and 12% younger than 20 years. 1
 2006 STATE OF THE FRASER BASIN REPORT SUSTAINABILITY SNAPSHOT 3 - Inspiring Action Forests & Forestry SUSTAINABILITY HIGHLIGHTS Forest covers more than 17 million hectares (75%) of the Fraser Basin, providing
2006 STATE OF THE FRASER BASIN REPORT SUSTAINABILITY SNAPSHOT 3 - Inspiring Action Forests & Forestry SUSTAINABILITY HIGHLIGHTS Forest covers more than 17 million hectares (75%) of the Fraser Basin, providing
