CHARACTERISTICS OF FLAME STABILIZATION AND COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY IN A SUDDEN EXPANSION FLOW-BASED GAS BURNER
|
|
|
- William Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISTP-16, 2005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA CHARACTERISTICS OF FLAME STABILIZATION AND COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY IN A SUDDEN EXPANSION FLOW-BASED GAS BURNER Harinaldi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering University of Indonesia Kampus Baru, UI Depok, Jawa Barat INDONESIA Keywords: diffusion flame, flame stabilization, combustion efficiency, recirculation flow ) Abstract Present study investigates the behaviours of flame stabilization and combustion efficiency characteristics in a sudden expansion flowbased gas burner (dump combustor) which applies a backward-facing step configuration. The study focusses on parameters closely relevant to the governing condition of the mixing effectiveness, which enhance the flame stabilization and combustion efficiency including the geometry of the flow field and injection scheme. The investigations are made with experimental approach utilizing flame visualization, flow measurement and exhaust gas analysis using a gas analyzer. Some parameters of interests including the step height (h) and the distance of injection location from the step edge (L f ) are varied in order to elucidate their influence to the combustion process. Detailed discussions regarding the flame configuration types, the extinction characteristics and and combustion efficiency are given in order to elucidate the complex mechanisms affecting the relations among the amounts of burned fuel in the combustion reaction, flow geometry and the dynamical condition within the recirculation flow field where the combustion process takes place 1 Introduction In many studies of propulsion system, the most significant problems in the combustion process at high-speed environment are related to the large stagnation pressure loss and entropy rise associated with the heating of a high-speed stream and the interaction of fuel jets and the air stream. If it is seen from flame holding characteristics point of view, the fact that the flow velocities in the high-speed combustor are extremely high, imposes the requirement that the reaction between fuel and air takes place quickly, with combustion process takes place as complete as possible in a relatively short distance due to the limited geometrical size of the combustor. Among the standard flame holding techniques employed in subsonic combustion chambers, most involve the formation of recirculation zones in the flow field which assist in stabilizing the flame structures. In the past a huge number of theoretical and experimental works were published dealing with the role of flow field structure behind the step and injection and mixing of gaseous types of fuel into the flow field to the flame holding mechanism, focusing on propulsion system application. Bradshaw et al. [1] had done some investigation on the basic characteristics of recirculation flow behind the step. Later, Eaton and Johnston [2] also made a review of typical flow characteristics in the turbulent circulating flow. Haibel and Mayinger [3] conducted investigation on isothermal (Helium gas) and reactive (Hydrogen gas) mixing into high speed air streams with the existence of a step compromising normal and parallel injection by using inclined injection with injection angle θ, and made a qualitative examination with holographic interferometry technique. Their result showed that the interaction between pair of vortical structure which is common in a jet flow and the flow field condition in backward 1
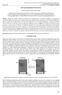
2 Harinaldi facing step which is dominated by recirculation flow induced the effect of skewed vortex generation jets from the injector. Smith [4] examined total pressure distribution, mean velocity, turbulence intensity and velocity cross correlation, gas composition, static temperature and wall static pressure distribution in a coaxialsudden expansion cylindrical combustor which formed diffusion flame of hydrogen gas. The result showed that the size and location of the recirculation zone were appreciably altered by the presence of chemical reactions. Pitz and Daily [5] made a visualization of the reacting flow of a propane/air mixture by high-speed Schlieren photography and done measurements of the mean and rms. averages of the turbulent velocity flow field at a backward facing step using laser velocimetry method. They found that the linear growth rate of the reacting mixing layer defined by mean velocity profile was unchanged by combustion. Reaction took place largely in the two-dimensional eddies which were not confined to the velocity gradient region. Considering the important role of flow field of a sudden expansion flow such in a backstep for combustion application, the present study is trying to give contribution to the continuing investigation on the flame holding mechanism using a backward facing step method. The investigation is aimed to establish a new experimental database on the flame stabilization characteristics and combustion efficiency in a sudden-expansion flow-based gas burner (dump combustor) model. Furthermore, the study investigates within practical range parameters closely relevant to the governing condition of the mixing effectiveness, which enhance the flame stabilization and combustion efficiency including the geometry of the flow field and injection scheme and fluid dynamics of injection flow. This research is expected to enrich the empirical results at fundamental level, to provide justification basis of some modeling resulted from computational works which are currently being studied by many researchers around the world, and to establish a general correlation (or correlations) of fluid dynamics and chemo-physical parameters, which could be shared to improve the effectiveness of mixing. These experimental works will lead to the development of mature criteria for combustor design. This is of scientific and industrial interests. 2 Experimental Works 2.1 Experimental Apparatus The experimental work was done in Thermodynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Indonesia. The experimental arrangement is sketched in Fig. 1. Fig. 1 Experimental Apparatus It consisted of several main sections including air flow system (electric blower, air duct, settling chamber, and nozzle), experimental model of combustion chamber (test section, injection plate and exhaust duct), and fuel flow system. The rate of air flow supply from the blower was adjusted by some bypass valves which were installed in the bypass line, and the air sequencially entered air duct, settling chamber and a converging nozzle with contraction ratio of 9.5: 1. Then the uniform air flow entered the test section. This arrangement could supply the air into the test section with maximum airflow velocity 14 m/s. At the exit of the converging nozzle, a model of combustion chamber comprises of the test section and the injection plate was attached. Test section was made from 5 mm thick brass 2
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF FLAME STABILIZATION AND COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY IN A SUDDEN EXPANSION FLOW-BASED GAS BURNER plate, with entrance cross section area 80 x 80 mm; exit cross section area is 80 x 125 mm and total length of 400 mm. The step height from the base could be varied gradually in the range of 0-45 mm by using a laboratory jack attached to the base plate. In the base of the step, a fuel injection plate with a slit opening of 70 x 1 mm spanned across the test section was installed, and by substituting the plate, the distance from step to the injection point could be varied. In the present study two distances i.e. 40 mm and 80 mm were used. Both sides of test section were covered by aluminum plate or heat proof Pyrex glass for visualization purpose. Top surface had an open-close hole with 20 mm diameter so that it was possible to insert ignition and measurement devices. At the downstream end of the test section an exhaust duct made from flexible aluminum duct with diameter of 6 inch was attached. In the exhaust duct a port for sampling probe of gas analyzer was prepared. 2.2 Measurement Apparatus In the flame stabilization experiment, the extinction limit was measured by varying the main airflow velocity. The variation could be made by adjusting the opening of a bypass valve and blower suction gate before the airflow enters the wind tunnel. The airflow velocity was measured with an orifice plate connected to a U tube water-filled manometer. Prior to the experiment, the manometer reading had been calibrated into the main airflow velocity (U 0 ) at just the entrance of test section with a hot wire anemometer (Lutron AM-4204). Gas fuel injection velocity was altered by adjusting two valves in a capillary manometer system. Prior to experiment, the manometer reading has been calibrated into the gas fuel injection velocity at the slit port with a gas meter (Wet gas meter type- Shinagawa WE 2.5 A). The dynamical behaviour of established diffusion flames and their gradual change to extinction was examined with a visualization technique. The flame image was captured by A CCD video camera (Sony Hi8-CCD-VX1) with sufficient exposure and shutter speed to grab a clear video image. In the experiment to determine the combustion efficiency, a gas analyzer (ECOM- AC 4-6 Gas Emission Analyzer) was used to analyse the flue gas composition as well as temperatures from which the combustion efficiency could be derived. The gas analyzer was a highly advanced portable emission analyzer for the direct measurement of combustion gas parameters incorporating electrochemical gas sensors and sample conditioning technology. Measured parameters included O 2, CO, NO, NO 2 and SO 2, C x H y temperature and pressure, stack draft, smoke and calculated parameters included combustion and emission factors including CO 2, combustion efficiency, losses and excess air. 2.3 Test Procedure and Conditions The measurement of flame stabilization considered fluid dynamic parameters i.e. the comparison between the fuel injection velocity and airflow velocity. In this way, the stability limit to the flame extinction condition was determined. After a stable flame was formed for a certain velocity of main airflow U 0, the velocity of gas fuel injection, V was then reduced until the flame extinct. When the flame extinction happened, the extinction limit value was defined. For a certain combination of parameter, measurement of extinction limit was done more than five times to confirm the reproducibility of the obtained data. After all necessary measurement had been taken up, all the raw data was reexamined, and in case of spurious data existed, the measurements were repeated again for those parameters condition. Meanwhile, in the investigation of combustion efficiency, it was calculated directly by the gas analyzer based on heat release principle and the result could be obtained conveniently in printed form. The parameters of experiment were the step height (h), stream wise distance from the step to the injection slot (Lf), main airflow velocity (U 0 ) and the fuel gas type. Each parameter was varied in several values. Table 1 shows the summary of the experimental condition 3
4 Harinaldi Table 1. Test Condition Step height (h) mm Distance from the step to the injection slot (Lf) 40 and 80 mm Main airflow velocity (U 0 ) 7,5 12 m/s Fuel gas type Propane (C 3 H 8 ) eventually the flame extinct. Hence, it is suggested that the flame extinction occurs mostly due to the weakening of chemical reactivity of the combustible mixture in the recirculation region. 3 Result and Discussion 3.1 Stable Flame Configuration Video images obtained from flame visualization provide some qualitative information about the stabilization configurations of formed diffusion flames behind the backward-facing step and the dynamical behavior of flames structure when they approach to extinction. Fig.2 shows the video image sequence describing the configuration of diffusion flame formed at recirculation zone of the backward-facing step starting from stable condition to extinction for injection of fuel at L f /h = 2 and main air velocity, U 0 = 10 m/s. Either in case of (a) h = 20 mm; L f = 40 mm or (b) h = 40 mm; L f = 80 mm, the figures show relatively similar trends. In a stable condition, the flame structures are very irregular. Close observation on the original video movies suggests that the flame highly fluctuates spatially and temporally. Sometimes the flame is broken down into flamelets. This flame appearance confirms that the combustion takes place mainly in the recirculation region so that the flame structure receives a strong influence from the recirculation flow. Furthermore, the yellow appearance that dominates the flame indicates that the combustion process tends to occur in fuel-rich environment. Therefore, it is supposed that in order to avoid flame extinction and to maintain the fuel burning, the gas fuel should be injected with excessive amount. When the fuel injection is decreased approaching the extinction limit, the flame start to extent its blue appearance although the structure becomes more vulnerable. The fuel injection can be continuously decreased until the flame appearance suggesting that combustion process occurs in a very fuel-lean condition and Fig.2 Configuration of diffusion flame formed at recirculation zone of backstep from stable condition to extinction for injection at L f /h = 2 (U 0 = 10 m/s) On the other hand, Fig. 3 shows the video image sequence describing the configuration of diffusion flame at L f /h = 4 and main air velocity, U 0 = 10 m/s. From the two series of images, either in case of (a) h = 10 mm; L f = 40 mm or (b) h = 20 mm; L f = 80 mm, the figures show relatively similar trends. In a stable condition, the flames are formed along the shear layer region starting from the step edge until the reattachment zone. The flame structure shows that the combustion reaction is distributed rather uniformly inside the shear layer region. Close observation on the original video movies suggests that the flame does not intensely fluctuate. This flame appearance confirms that the combustion takes place mainly in the shearmixing layer where the injected gas fuel mixes better with main airflow that entrains into the layer. Furthermore, the bluish appearance that dominates the flame indicates that the combustion process takes place with closer to stoichiometric mixture. When the fuel injection is decreased approaching the extinction limit, the flame start to shorten and its blue appearance become less clear. The fuel injection 4
5 CHARACTERISTICS OF FLAME STABILIZATION AND COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY IN A SUDDEN EXPANSION FLOW-BASED GAS BURNER can only be decreased continuously until certain point when flame suddenly extinct. Hence, it is suggested that the flame extinction occurs mostly due to the hydrodynamic effect. When injected from L f /h = 4 the flow field around the injection point is dominated by a high turbulence and high velocity reverse flow. Hence, it is suggested that the blowing effect to the flame anchor forces the flame to extinct. chemical reaction in the environment with higher free stream velocity. fu el in jectio n velo city, V (m / s ) 0,12 0,11 0,1 0,09 0,08 Lf/h = 2 Lf/h = 2, Lf/h = 2, Lf/h = 3,2 Lf/h = 4 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0 11,0 12,0 main air flow velocity, Uo (m/s) Fig.4 Extinction limit in case of L f = 40 mm Fig.3 Configuration of diffusion flame formed at recirculation zone of backstep from stable condition to extinction for injection at L f /h = 4 (U 0 = 10 m/s) 3.2 Flame Extinction Figure 4 shows the extinction limits of the diffusion flame in case of fuel is injected from L f = 40 mm. In each test, the step height was varied in the range of 10 to 20 mm that gave five relative position of injection location, L f /h = 2, 2.29, 2.67, 3.2, and 4. Each data series shown along with its best fitting plot represents the extinction limit for a certain L f /h. The figure indicates that generally for all condition, the extinction limit curves rise monotonically. In other word, the extinction limit shows relative similar characteristics with regard to the alteration of the main air flow velocity. If the main air flow velocity is increased the velocity of fuel injection should also be increased in order that the flame can be prevented to extinguish. This indicates that more amount of gas fuel is needed to provide a continuous On the other hand, Fig. 5 shows the extinction limits of the diffusion flame in case of fuel is injected from L f = 80 mm. In each test, the step height is varied in the range of 20 to 40 mm that gives five relative position of injection location, L f /h = 2, 2.29, 2.67, 3.2, and 4. fuel injectio n velo city, V (m / s ) 0,24 0,2 0,16 0,12 0,08 Lf/h = 2 Lf/h = 2, Lf/h = 2, Lf/h = 3,2 Lf/h = 4 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0 11,0 12,0 main airflow velocity, Uo (m/s) Fig.5 Extinction limit in case of L f = 80 mm Similar to the case of L f = 40 mm, the extinction limit curves generally rise monotonically for all conditions. In other word, the extinction limit shows relative similar characteristics with regard to the alteration of the main air flow velocity. If the main air flow velocity is increased the velocity of fuel injection should also be increased in order that the flame can be prevented to extinct. However, the variation of 5
6 Harinaldi extinction limit curves with respect to the variation of relative position of injection distance from the step edge to the step height (L f /h) for each type of injected gas show a remarkable differences to the previous case. From the data presented in the extinction limit curves, the characteristic of extinction can be further discussed with regard to the effect of geometrical parameter of injection represented by location of fuel injection (L f ), and the size of recirculation flow field determined by the step height (h). As presented in Fig. 6, the summary of the characteristics of extinction is described as the relation between the ratios of fuel injection velocity to the main airflow velocity (V/U 0 ) and the relative distance of injection to the step height (Lf/h). In each figure, the extinction characteristic is plotted for two location of injection, L f = 40 and 80 mm. V/Uo 0,025 0,020 0,015 0,010 0,005 Lf = 40 mm Lf = 80 mm 1,0 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 Lf/h Fig. 6 Extinction Characteristics From the figure, it can be figured out that the ratio V/U 0 at extinction for the case of injection at L f = 40 mm significantly lower than that for the case of L f = 80 mm. Furthermore, it is obvious that the flame extinction in case of L f = 40 mm shows relative constant value of V/U 0 for different Lf/h with very little tendency of V/U 0 to decrease when Lf/h increases. This results is indicating a weak dependent of flame extinction limit to the relative distance of injection to the step height (Lf/h). On the other hand, in case of L f = 80 mm the flame extinction limit show stronger dependent to the relative distance of injection to the step height. As seen in the figure, the value V/U 0 tend to increase when Lf/h is increased. It is considered that the different extinction characteristics for the two cases are related to the condition of the recirculation flow field formed behind the backstep. In case of injection at L f = 40 mm, the variation of step height is between 10 to 20 mm, meanwhile incase of injection at L f = 80 mm, the variation of step height is between 20 to 40 mm. The different height of the step is supposed to construct different fluid dynamical characteristics of the recirculation flow field behind the backstep where the gas fuel is injected and the flame is stablized in the rim of injection hole. Some studies [1-3,6,7] had revealed that with a low step, the size of recirculation flow field is small and the reverse flow as well as the turbulent intensity is not high. With the increasing step height the recirculation flowfield will be more complex characterized by higher reverse flow velocity and higher turbulent intensity. In some instance there exist the corner Eddy due to higher pressure differential which induced when the step height is large. We attribut the characteristics of flame extinction limit as shown Fig. 6 to this recirculation flow behavior. Uno [8] had also mentioned the different characteristics of flame stabilization due to step height difference and divide the extinction limit into low step (h < 20 mm) and high step (h > 20 mm) although there was no further discussion about the flow field condition. 3.2 Combustion Efficiency The combustion efficiency is calculated directly by the gas analyzer based on heat release principle. The exhaust gas samplings from the combustion reaction were done in three different conditions of main air flow velocity and in each condition the fuel injection velocity is set to value of 2%, 20 % and 40 % above the extinction limit. Not like the previous results in the extinction limit measurement, in general there is no remarkable different tendency of combustion efficiency between injection with L f = 40 mm and L f = 80 mm. Hence, in the following section only representative results from the case of injection at L f = 40 mm are discussed. 6
7 CHARACTERISTICS OF FLAME STABILIZATION AND COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY IN A SUDDEN EXPANSION FLOW-BASED GAS BURNER The combustion efficiency of propane is shown in Fig. 7 (a)-(c). Combustion Eff., hc (%) Combustion Eff., hc (%) Combustion Eff., hc (%) Lf/h Uo=7,55 m/s Uo=9,1m/s (a) V = 2% above extinction Uo=10,6 m/s Lf/h Uo=7,55 m/s Uo=9,1m/s Uo=10,6 m/s (b) V = 20% above extinction Lf/h Uo=7,55 m/s Uo=9,1m/s Uo=10,6 m/s (c) V = 40% above extinction Fig. 7 Combustion Efficiency (Propane) Comparison of all the plots also suggest that the combustion takes place more efficiently if the fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber with the velocity near to the flame extinction limits. Increasing the injection velocity above the extinction limits will decrease the combustion efficiency. In each condition of fuel injection velocity it is observed that the curves of combustion efficiency do not decrease monotonically with an increase of L f /h. Instead, the curves exhibit a plateau for L f /h in the range of between around 2 and 3.5 and then decreases substantially for L f /h = 4. Meanwhile, although not too obvious, for injection with a certain L f /h the combustion efficiency will increase if the main air flow velocity is increased. The above results indicates that the mechanisms governing combustion efficiency characteristics suggest a complex relations among the amount of burned fuel, the amount of heat releases in the combustion reaction and the fluid dynamical condition within the recirculation flow field where the combustion process takes place. As shown in the figures of combustion efficiency characteristics some peculiarities such as the plateau appearance in the combustion efficiency curves seem to be better explained if attributed to the mixing effectiveness of the injected fuel and the entrained air flow. Some flow field measurement behind the backstep [2, 3, 6] has shown that the middle region of recirculation flow has relatively constant flow structure dominated by moderate reverse flow velocity as well as turbulent intensity. This proposed to provide a rather uniform mixing that result a rather constant efficiency if the fuel is injected and undergo combustion reaction in that region 3 Concluding Remarks The present work has studied comprehensively the behaviours of flame stabilization and combustion efficiency characteristics in a sudden expansion flow-based gas burner (dump combustor) applying a backward-facing flow step configuration. The investigations were made with experimental approach utilizing flame visualization, flow measurement and exhaust gas analysis using a gas analyzer. Some important aspects can be concluded as follows: 1. Stable flame configuration can be divided into two different types, the one stabilized within the recirculation region and another 7
8 Harinaldi one stabilized in the shear layer region. The former configuration highly fluctuates spatially and temporally indicates that the combustion process tends to occur in fuelrich environment. Meanwhile the later shows that the combustion reaction is distributed rather uniformly inside the shear layer region. The flame does not intensely fluctuate and indicates that combustion process takes place with closer to stoichiometric mixture. 2. The extinction characteristics are related to the condition of the recirculation flow field formed behind the backstep yielding two different cases. With lower step height (h less than 20 mm) the flame shows relative constant value of V/U 0 for different Lf/h indicating a weak dependent of flame extinction limit to the relative distance of injection to the step height (Lf/h). With higher step height (h more than 20 mm) the flame extinction limit shows that value of V/U 0 remarkably depend on the relative distance of injection to the step height (Lf/h) 3. The combustion efficiency characteristics suggest complex mechanisms governing relations among the amounts of burned fuel, the amount of heat releases in the combustion reaction and the fluid dynamical condition within the recirculation flow field where the combustion process takes place. The competition between the penetration capabilities of injected gas having higher momentum when injected with higher velocity with the capability of recirculation flow to engulf the supplied fuel in the recirculation region determined the fuel consumption as well as the combustion efficiency. References [1] P. Bradshaw and F.Y.F. Wong, The Reattachment and Relaxation of Turbulent Shear Layer, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 52, pp , [2] Eaton, J.K., Johnston, J.P., A Review of Research on Subsonic Turbulent Flow Reattachment, AIAA Journal, Vol. 19, No. 9, pp , [3] Haibel, M., Mayinger, F., The Effect of Turbulence Structures on the Development of Mixing and Combustion Processes in sub-and supersonic H 2 flames, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol.37, Suppl. 1, pp , [4] Smith, G.D., Measurement of Reactive Recirculating Jet Mixing in a Combustor, AIAA Journal, Vol. 21, No. 2, pp ,1983. [5] Pitz, R.W., Daily, J.W., Combustion in a Turbulent Mixing Layer Formed at a Rearward Facing Step, AIAA Journal, Vol. 21, No. 11, pp ,1983. [6] Harinaldi, Ueda, T., Mizomoto, M., Effect of Slot Gas Injection to the Flow Field and Coherent Structure Characteristics of a Backstep Flow, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 44(14, pp ), [7] Coats, C.M, Richardson, A.P. and Wang, S., Nonpremixed combustion in turbulent mixing layers part 2: recirculation, mixing and flame stabilization, Combustion and Flame, 122, , [8] Uno, T. Mechanism of Diffusion Flame Stabilization in a Backward Facing Step, The 32 nd Japanese Symposium on Combustion, Tokyo, pp , Acknowledgements The author gratefully acknowledges the Osaka Gas Foundation of International Cultural Exchange for providing financial support to the accomplishment of this study. Special thank to Mr. Yuwono P, Mr. Aditya N.S and Mr. Maymuhar for their support during the experimentations. 8
A STUDY ON FLOW BEHAVIOR INSIDE A SIMPLE MODEL OF EJECTOR
 A STUDY ON FLOW BEHAVIOR INSIDE A SIMPLE MODEL OF EJECTOR Taketoshi Koita 1 and Junjiro Iwamoto ABSTRACT This paper is concerned with the experimental results on the internal flow of the ejector. To improve
A STUDY ON FLOW BEHAVIOR INSIDE A SIMPLE MODEL OF EJECTOR Taketoshi Koita 1 and Junjiro Iwamoto ABSTRACT This paper is concerned with the experimental results on the internal flow of the ejector. To improve
Experimental Analysis of Flow through Rotating Swirler with Effect of Guide Vane
 Experimental Analysis of Flow through Rotating Swirler with Effect of Guide Vane Mansha kumari 1, Shah Jagruti 2, Arvind.S.Mohite 3 M.E. (JPGTP)Student, Department of mechanical engineering, Faculty of
Experimental Analysis of Flow through Rotating Swirler with Effect of Guide Vane Mansha kumari 1, Shah Jagruti 2, Arvind.S.Mohite 3 M.E. (JPGTP)Student, Department of mechanical engineering, Faculty of
Experimental Analysis Of Flow Through Rotating Swirler In Combustion Chamber
 Experimental Analysis Of Flow Through Rotating Swirler In Combustion Chamber Mansha kumari 1, Shah Jagruti 2 M.E. (JPGTP)Student,Department of mechanical engineering, Faculty of technology & engineering,
Experimental Analysis Of Flow Through Rotating Swirler In Combustion Chamber Mansha kumari 1, Shah Jagruti 2 M.E. (JPGTP)Student,Department of mechanical engineering, Faculty of technology & engineering,
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Study of combustion process in all combustion systems is one of the most important and complex problems. Generally, the main objective is to achieve a stable combustion proves that
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Study of combustion process in all combustion systems is one of the most important and complex problems. Generally, the main objective is to achieve a stable combustion proves that
Study of flow through combustion swirler with the effect of diffuser on the recirculation zone
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 6 (September 2012), PP. 68-73 Study of flow through combustion swirler
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 3, Issue 6 (September 2012), PP. 68-73 Study of flow through combustion swirler
Experimental Analysis Of Flow Through Rotating Combustion Swirler With Zero Degree Inlet and Outlet Angle Of Guide Vane
 Experimental Analysis Of Flow Through Rotating Combustion Swirler With Zero Degree Inlet and Outlet Angle Of Guide Vane MANSHA KUMARI Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Technology & Engineering,
Experimental Analysis Of Flow Through Rotating Combustion Swirler With Zero Degree Inlet and Outlet Angle Of Guide Vane MANSHA KUMARI Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Technology & Engineering,
CFD Analysis of recirculating flows induced by Axial Swirler
 CFD Analysis of recirculating flows induced by Axial Swirler P.Muthukumar 1, S.R.Balakrishnan 2 PG scholar 1, Director/H.O.D 2 1, 2, Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Nehru institute of engineering
CFD Analysis of recirculating flows induced by Axial Swirler P.Muthukumar 1, S.R.Balakrishnan 2 PG scholar 1, Director/H.O.D 2 1, 2, Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Nehru institute of engineering
FLAMEHOLDING IN NON-PREMIXED SUPERSONIC FLOWS
 FLAMEHOLDING IN NON-PREMIXED SUPERSONIC FLOWS C. Segal 1 Introduction University of Florida, Gainesville, Fl, 32611, US A balance between the flame propagation speed and the fluid velocity must be maintained
FLAMEHOLDING IN NON-PREMIXED SUPERSONIC FLOWS C. Segal 1 Introduction University of Florida, Gainesville, Fl, 32611, US A balance between the flame propagation speed and the fluid velocity must be maintained
EFFECT OF MIXTURE CONSTITUENTS ON THE LAMINAR BURNING VELOCITY OF LPG-CO2-AIR MIXTURES
 EFFECT OF MIXTURE CONSTITUENTS ON THE LAMINAR BURNING VELOCITY OF LPG-CO2-AIR MIXTURES Ajay Tripathi 1, H. Chandra 2 and M. Agrawal 3 1 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, U. P., India 2 Bhilai
EFFECT OF MIXTURE CONSTITUENTS ON THE LAMINAR BURNING VELOCITY OF LPG-CO2-AIR MIXTURES Ajay Tripathi 1, H. Chandra 2 and M. Agrawal 3 1 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, U. P., India 2 Bhilai
Self-Aspirating Radiant Tube Burner
 Self-Aspirating Radiant Tube Burner Chanon Chuenchit and Sumrerng Jugjai * Combustion and Engine Research Laboratory (CERL), Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s
Self-Aspirating Radiant Tube Burner Chanon Chuenchit and Sumrerng Jugjai * Combustion and Engine Research Laboratory (CERL), Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut s
Investigation of Non-Premixed Opposed Flow H 2 /Air Laminar Flames using Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering (CARS)
 8 th US National Technical Meeting of the Combustion Institute Hosted by University of Utah, Park City, Utah May 19-22, 2013 Investigation of Non-Premixed Opposed Flow H 2 /Air Laminar Flames using Coherent
8 th US National Technical Meeting of the Combustion Institute Hosted by University of Utah, Park City, Utah May 19-22, 2013 Investigation of Non-Premixed Opposed Flow H 2 /Air Laminar Flames using Coherent
THE EFFECT OF CO2 FRACTION ON THE FLAME STABILITY OF BIOGAS PREMIXED FLAME
 THE EFFECT OF C FRACTION ON THE FLAME STABILITY OF BIOGAS PREMIXED FLAME Mega Nur Sasongko and Widya Wijayanti Mechanical Engineering, University of Brawijaya Jalan Mayjend Haryono Malang, East Java, Indonesia
THE EFFECT OF C FRACTION ON THE FLAME STABILITY OF BIOGAS PREMIXED FLAME Mega Nur Sasongko and Widya Wijayanti Mechanical Engineering, University of Brawijaya Jalan Mayjend Haryono Malang, East Java, Indonesia
COMBUSTION DYNAMICS AT BIOMASS THERMOCHEMICAL CONVERSION DOWNSTREAM OF INTEGRATED GASIFIER AND COMBUSTOR
 ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 3.-4.5.3. COMBUSTION DYNAMICS AT BIOMASS THERMOCHEMICAL CONVERSION DOWNSTREAM OF INTEGRATED GASIFIER AND COMBUSTOR Monika Abricka, Inesa Barmina, Vera Suzdalenko,
ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 3.-4.5.3. COMBUSTION DYNAMICS AT BIOMASS THERMOCHEMICAL CONVERSION DOWNSTREAM OF INTEGRATED GASIFIER AND COMBUSTOR Monika Abricka, Inesa Barmina, Vera Suzdalenko,
FUEL- OXYDANT FLEXIBLE COMBUSTION
 FUEL- OXYDANT FLEXIBLE COMBUSTION WITH FLAMELESS OXIDATION A. Milani, J.G. Wünning WS GmbH Recent and expected measures for reducing CO 2 released from combustion equipment affect the composition of both
FUEL- OXYDANT FLEXIBLE COMBUSTION WITH FLAMELESS OXIDATION A. Milani, J.G. Wünning WS GmbH Recent and expected measures for reducing CO 2 released from combustion equipment affect the composition of both
EFEECT OF HYDROGEN ADDITION ON METHANE COMBUSTION IN A CAN TYPE COMBUSTOR
 EFEECT OF HYDROGEN ADDITION ON METHANE COMBUSTION IN A CAN TYPE COMBUSTOR Ramesh E (Roll No. 10105144) Abstract The effects of hydrogen addition on lean methane combustion was numerically investigated
EFEECT OF HYDROGEN ADDITION ON METHANE COMBUSTION IN A CAN TYPE COMBUSTOR Ramesh E (Roll No. 10105144) Abstract The effects of hydrogen addition on lean methane combustion was numerically investigated
Data File. May Contacts Details:
 Adelaide Jet Flame 3 Data File May 2016 Adelaide Jet Flame 3 C2H4-H2-N2-D80-15K Contacts Details: Prof Bassam Dally School of Mechanical Engineering The University of Adelaide South Australia, 5005, SA
Adelaide Jet Flame 3 Data File May 2016 Adelaide Jet Flame 3 C2H4-H2-N2-D80-15K Contacts Details: Prof Bassam Dally School of Mechanical Engineering The University of Adelaide South Australia, 5005, SA
Laminar Burning Velocity under Quenching Conditions for Propane-Air and Ethylene-Air Flames
 archivum combustionis Vol. 26 (2006) No.3-4 Laminar Burning Velocity under Quenching Conditions for Propane-Air and Ethylene-Air Flames Department of Heat Technology and Refrigeration, Technical University
archivum combustionis Vol. 26 (2006) No.3-4 Laminar Burning Velocity under Quenching Conditions for Propane-Air and Ethylene-Air Flames Department of Heat Technology and Refrigeration, Technical University
Data File. May Contacts Details:
 Adelaide Jet Flame 2 Data File May 2016 Adelaide Jet Flame 2 C2H4-H2-N2-D58-15K Contacts Details: Prof Bassam Dally School of Mechanical Engineering The University of Adelaide South Australia, 5005, SA
Adelaide Jet Flame 2 Data File May 2016 Adelaide Jet Flame 2 C2H4-H2-N2-D58-15K Contacts Details: Prof Bassam Dally School of Mechanical Engineering The University of Adelaide South Australia, 5005, SA
Changes in combustion properties of Natural gas when mixed with Hydrogen
 Changes in combustion properties of Natural gas when mixed with Hydrogen PARISA SAYAD, ALESSANDRO SCHÖNBORN AND JENS KLINGMANN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY SCIENCES, LUND UNIVERSITY PARISA.SAYAD@ENERGY.LTH.SE
Changes in combustion properties of Natural gas when mixed with Hydrogen PARISA SAYAD, ALESSANDRO SCHÖNBORN AND JENS KLINGMANN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY SCIENCES, LUND UNIVERSITY PARISA.SAYAD@ENERGY.LTH.SE
Problems with Pitots. Issues with flow measurement in stacks.
 CEM-2004 Problems with Pitots. Issues with flow measurement in stacks. R A Robinson 1, D Butterfield 1, D Curtis 2, T Thompson 3 1 National Physical Laboratory Queens Road Teddington Middlesex TW11 0AX
CEM-2004 Problems with Pitots. Issues with flow measurement in stacks. R A Robinson 1, D Butterfield 1, D Curtis 2, T Thompson 3 1 National Physical Laboratory Queens Road Teddington Middlesex TW11 0AX
The Stability of Turbulent Hydrogen Diffusion Jet Flames
 The Stability of Turbulent Hydrogen Diffusion Jet Flames Wu, Y. 1, Al-Rahbi, I. S. 1 and Kalghatgi, G. T. 2 1 Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S1 3JD,
The Stability of Turbulent Hydrogen Diffusion Jet Flames Wu, Y. 1, Al-Rahbi, I. S. 1 and Kalghatgi, G. T. 2 1 Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S1 3JD,
Comparison Between PIV Measurements and CFD Simulation on a Model of GT Annular Burner
 Comparison Between PIV Measurements and CFD Simulation on a Model of GT Annular Burner D. Giordano, S. Giammartini, M. Rufoloni, G. Calchetti, F. Manfredi, E. Giacomazzi ENEA - C. R. Casaccia Sec. ENE-IMP
Comparison Between PIV Measurements and CFD Simulation on a Model of GT Annular Burner D. Giordano, S. Giammartini, M. Rufoloni, G. Calchetti, F. Manfredi, E. Giacomazzi ENEA - C. R. Casaccia Sec. ENE-IMP
Computational Analyses of Combustive Vortex Flows in Liquid Rocket Engines
 McNair Scholars Research Journal Volume 2 Article 2 2015 Computational Analyses of Combustive Vortex Flows in Liquid Rocket Engines Nadia M. Numa numan@my.erau.edu Follow this and additional works at:
McNair Scholars Research Journal Volume 2 Article 2 2015 Computational Analyses of Combustive Vortex Flows in Liquid Rocket Engines Nadia M. Numa numan@my.erau.edu Follow this and additional works at:
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF A TRAPPED-VORTEX COMBUSTION CHAMBER FOR GAS TURBINE FED BY SYNGAS
 DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF A TRAPPED-VORTEX COMBUSTION CHAMBER FOR GAS TURBINE FED BY SYNGAS A. Di Nardo, G. Calchetti, C. Mongiello antonio.dinardo@enea.it via Anguillarese 301-00123 Roma Abstract The trapped
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF A TRAPPED-VORTEX COMBUSTION CHAMBER FOR GAS TURBINE FED BY SYNGAS A. Di Nardo, G. Calchetti, C. Mongiello antonio.dinardo@enea.it via Anguillarese 301-00123 Roma Abstract The trapped
An experimental study of a film cooling with swirling flow on the endwall of a high loaded 1st nozzle
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XII 85 An experimental study of a film cooling with swirling flow on the endwall of a high loaded 1st nozzle K. Takeishi, Y. Oda & S. Kondo
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XII 85 An experimental study of a film cooling with swirling flow on the endwall of a high loaded 1st nozzle K. Takeishi, Y. Oda & S. Kondo
Theory Comparison between Propane and Methane Combustion inside the Furnace
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Theory
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Theory
Chapter 2: Introduction of Low-Speed Wind Tunnel
 Chapter 2: Introduction of Low-Speed Wind Tunnel Low speed is referred to the air flow speed lower than 100 m/s, for which the incompressible flow condition is satisfied. Wind tunnel is referred to a facility
Chapter 2: Introduction of Low-Speed Wind Tunnel Low speed is referred to the air flow speed lower than 100 m/s, for which the incompressible flow condition is satisfied. Wind tunnel is referred to a facility
The Influence of Chemical Inhibitor Addition on Reverse-Jet Flame Stabilization
 68 -GT-39 The Society shall not be responsible for statements or opinions advanced in papers or in discussion at meetings of the Society or of its Divisions or Sections, or printed in its publications.
68 -GT-39 The Society shall not be responsible for statements or opinions advanced in papers or in discussion at meetings of the Society or of its Divisions or Sections, or printed in its publications.
Research Paper MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLAME QUENCHING PHENOMENA IN A CATALYTIC COATED FOUR STROKE SI ENGINE
 Research Paper MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLAME QUENCHING PHENOMENA IN A CATALYTIC COATED FOUR STROKE SI ENGINE 1 Dr. P. Ponnusamy, 2 Dr. N. Nedunchezhian, 3 W.Edwin Santhkumar Address for Correspondence
Research Paper MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLAME QUENCHING PHENOMENA IN A CATALYTIC COATED FOUR STROKE SI ENGINE 1 Dr. P. Ponnusamy, 2 Dr. N. Nedunchezhian, 3 W.Edwin Santhkumar Address for Correspondence
Reforming and burning of ammonia in micro hydrogen and power generation systems
 8 th Annual Ammonia Fuel Conference Portland, OR, USA, 18-21 September 2011 Reforming and burning of ammonia in micro hydrogen and power generation systems O.C. Kwon *, J.M. Joo, S.I. Lee and D.H. Um School
8 th Annual Ammonia Fuel Conference Portland, OR, USA, 18-21 September 2011 Reforming and burning of ammonia in micro hydrogen and power generation systems O.C. Kwon *, J.M. Joo, S.I. Lee and D.H. Um School
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF SUPERSONIC INLET FOR SUPPRESSION OF BUZZ IN SUBCRITICAL OPERATION
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES SUPPRESSION OF BUZZ IN SUBCRITICAL OPERATION Yasushi Watanabe*, Shou Hattori**, Masaharu Kameda** *Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, **Tokyo
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES SUPPRESSION OF BUZZ IN SUBCRITICAL OPERATION Yasushi Watanabe*, Shou Hattori**, Masaharu Kameda** *Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, **Tokyo
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF SWIRL AND AIR DILUTION ON BIOGAS NON-PREMIXED FLAME STABILITY
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2161-2169 2161 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF SWIRL AND AIR DILUTION ON BIOGAS NON-PREMIXED FLAME STABILITY by Amir ROWHANI * and Sadegh TABEJAMAAT
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2161-2169 2161 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF SWIRL AND AIR DILUTION ON BIOGAS NON-PREMIXED FLAME STABILITY by Amir ROWHANI * and Sadegh TABEJAMAAT
Flow Visualization of Secondary Flow near Blade/Endwall Region in a Linear Turbine Cascade
 การประช มว ชาการเคร อข ายว ศวกรรมเคร องกลแห งประเทศไทยคร งท 17 15-17 ต ลาคม 2546 จ งหว ดปราจ นบ ร Flow Visualization of Secondary Flow near /Endwall Region in a Linear Turbine Cascade Surachai Sanitjai*
การประช มว ชาการเคร อข ายว ศวกรรมเคร องกลแห งประเทศไทยคร งท 17 15-17 ต ลาคม 2546 จ งหว ดปราจ นบ ร Flow Visualization of Secondary Flow near /Endwall Region in a Linear Turbine Cascade Surachai Sanitjai*
Numerical Prediction of Turbulent Combustion Flows for 1700 C Class Gas Turbine Combustor
 Chapter 3 Epoch Making Simulation Numerical Prediction of Turbulent Combustion Flows for 1700 C Class Gas Turbine Combustor Project Representative Nobuyuki Oshima Author Nobuyuki Oshima Division of Mechanical
Chapter 3 Epoch Making Simulation Numerical Prediction of Turbulent Combustion Flows for 1700 C Class Gas Turbine Combustor Project Representative Nobuyuki Oshima Author Nobuyuki Oshima Division of Mechanical
Detached Eddy Simulation of High Turbulent Swirling Reacting Flow in a Premixed Model Burner
 25 th ICDERS August 2 7, 2015 Leeds, UK Detached Eddy Simulation of High Turbulent Swirling Reacting Flow in a Premixed Model Burner 1,2 Mansouri Zakaria, 1 Aouissi Mokhtar, 2 Abdallah Elorf, 2 Boushaki
25 th ICDERS August 2 7, 2015 Leeds, UK Detached Eddy Simulation of High Turbulent Swirling Reacting Flow in a Premixed Model Burner 1,2 Mansouri Zakaria, 1 Aouissi Mokhtar, 2 Abdallah Elorf, 2 Boushaki
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION ON PITCH DISTANCE, COMPOUND ANGLE AND TURBULENCE INTENSITY OFDOUBLE CYLINDRICAL FILM COOLING HOLE GEOMETRY
 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION ON PITCH DISTANCE, COMPOUND ANGLE AND TURBULENCE INTENSITY OFDOUBLE CYLINDRICAL FILM COOLING HOLE GEOMETRY Hazim Fadli Aminnuddin and Kamil Abdullah Center for Energy and Industrial
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION ON PITCH DISTANCE, COMPOUND ANGLE AND TURBULENCE INTENSITY OFDOUBLE CYLINDRICAL FILM COOLING HOLE GEOMETRY Hazim Fadli Aminnuddin and Kamil Abdullah Center for Energy and Industrial
Prediction of Pollutant Emissions from Industrial Furnaces Using Large Eddy Simulation
 Paper # B03 Topic: Turbulent Flames 5 th US Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and Hosted by the University of California at San Diego March 25-28, 2007.
Paper # B03 Topic: Turbulent Flames 5 th US Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and Hosted by the University of California at San Diego March 25-28, 2007.
Further Development of Low Pressure Drop Duct Burners
 Further Development of Low Pressure Drop Duct Burners Prepared by: Christopher Bolin UTSR Fellow, FlexEnergy, Inc Graduate Assistant, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Michigan State University Prepared
Further Development of Low Pressure Drop Duct Burners Prepared by: Christopher Bolin UTSR Fellow, FlexEnergy, Inc Graduate Assistant, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Michigan State University Prepared
Mechanical Engineering Journal
 Bulletin of the JSME Mechanical Engineering Journal Vol.3, No.6, 2016 Experimental study on the behavior of the two phase flow shock waves occurring in the ejector refrigeration cycle Haruyuki NISHIJIMA*,
Bulletin of the JSME Mechanical Engineering Journal Vol.3, No.6, 2016 Experimental study on the behavior of the two phase flow shock waves occurring in the ejector refrigeration cycle Haruyuki NISHIJIMA*,
NUTC R203. Safety Risks of Hydrogen Fuel for Applications in Transportation Vehicles. Shravan K. Vudumu
 Safety Risks of Hydrogen Fuel for Applications in Transportation Vehicles by Shravan K. Vudumu NUTC R203 A National University Transportation Center at Missouri University of Science and Technology Disclaimer
Safety Risks of Hydrogen Fuel for Applications in Transportation Vehicles by Shravan K. Vudumu NUTC R203 A National University Transportation Center at Missouri University of Science and Technology Disclaimer
Numerical study on the thermodynamic characteristics. in a Twin Swirl pulverized coal Combustor
 ICCM2015, 14-17 th July, Auckland, NZ Abstract Numerical study on the thermodynamic characteristics in a Twin Swirl pulverized coal Combustor Yinli LIU, * Hao TANG, Yongfen WANG College of Energy and Power
ICCM2015, 14-17 th July, Auckland, NZ Abstract Numerical study on the thermodynamic characteristics in a Twin Swirl pulverized coal Combustor Yinli LIU, * Hao TANG, Yongfen WANG College of Energy and Power
IFRF Combustion Journal Article Number , June 2000 ISSN X
 IFRF Combustion Journal Article Number 200005, June 2000 ISSN 1562-479X SCALING OF LOW NO X FLAMES OF NATURAL GAS S. Orsino and R. Weber Corresponding Author: Stefano Orsino IFRF Research Station B.V.
IFRF Combustion Journal Article Number 200005, June 2000 ISSN 1562-479X SCALING OF LOW NO X FLAMES OF NATURAL GAS S. Orsino and R. Weber Corresponding Author: Stefano Orsino IFRF Research Station B.V.
Combustion of Polymers in a Fluidised Bed Reactor
 Archivum Combustionis Vol. 30 (2010) no. 4 Combustion of Polymers in a Fluidised Bed Reactor J. Połomska *, W. Żukowski **, J. Zabagło ** * Faculty of Environmental Engineering, **Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Archivum Combustionis Vol. 30 (2010) no. 4 Combustion of Polymers in a Fluidised Bed Reactor J. Połomska *, W. Żukowski **, J. Zabagło ** * Faculty of Environmental Engineering, **Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Experimental Study of Pre-mixed Flames on a Multi-Hole Matrix Burner
 International Journal of Integrated Engineering, Vol. 4 No. 1 (2012) p. 1-5 Experimental Study of Pre-mixed Flames on a Multi-Hole Matrix Burner Arvind Jatoliya 1, B. Pandian 1 and Vasudevan Raghavan 1,*
International Journal of Integrated Engineering, Vol. 4 No. 1 (2012) p. 1-5 Experimental Study of Pre-mixed Flames on a Multi-Hole Matrix Burner Arvind Jatoliya 1, B. Pandian 1 and Vasudevan Raghavan 1,*
The Effect of Radial Swirl Generator on Reducing Emissions from Bio-Fuel Burner System
 The Effect of Radial Swirl Generator on Reducing Emissions from Bio-Fuel Burner System Mohamad Shaiful Ashrul Ishak School of Manufacturing Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Perlis PO Box 77, Pejabat Pos
The Effect of Radial Swirl Generator on Reducing Emissions from Bio-Fuel Burner System Mohamad Shaiful Ashrul Ishak School of Manufacturing Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Perlis PO Box 77, Pejabat Pos
Experimental Investigation of Plasma Assisted Reforming of Propane
 PSFC/JA-05-15 Experimental Investigation of Plasma Assisted Reforming of Propane L. Bromberg K. Hadidi D.R. Cohn August 25, 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Plasma Science and Fusion Center Supported
PSFC/JA-05-15 Experimental Investigation of Plasma Assisted Reforming of Propane L. Bromberg K. Hadidi D.R. Cohn August 25, 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Plasma Science and Fusion Center Supported
Stefan Elbel Pega Hrnjak University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Experimental Validation of a CO 2 Prototype Ejector with Integrated High-Side Pressure Control Stefan Elbel (elbel@uiuc.edu), Pega Hrnjak (pega@uiuc.edu) University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Saalfelden,
Experimental Validation of a CO 2 Prototype Ejector with Integrated High-Side Pressure Control Stefan Elbel (elbel@uiuc.edu), Pega Hrnjak (pega@uiuc.edu) University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Saalfelden,
CFD analysis of double-chambered crematories using biomass producer gas as a fuel source
 CFD analysis of double-chambered crematories using biomass producer gas as a fuel source Yaowateera Achawangkul 1, Naoki Maruyama 1, Chatchawan Chaichana 2 Masafumi Hirota 1, Akira Nishimura 1, Pimpawat
CFD analysis of double-chambered crematories using biomass producer gas as a fuel source Yaowateera Achawangkul 1, Naoki Maruyama 1, Chatchawan Chaichana 2 Masafumi Hirota 1, Akira Nishimura 1, Pimpawat
How iron ore pelletizing has recently gained new kiln efficiencies
 How iron ore pelletizing has recently gained new kiln efficiencies More stable kilns, improved productivity and enhanced process control are delivering more for the industry than ever before. Extract from
How iron ore pelletizing has recently gained new kiln efficiencies More stable kilns, improved productivity and enhanced process control are delivering more for the industry than ever before. Extract from
CFD Analysis of a Mixture Flow in a Producer Gas Carburetor for optimizing the design configuration
 CFD Analysis of a Mixture Flow in a Producer Gas Carburetor for optimizing the design configuration T.R.Ani1 l, S.D.Ravi 2, M.Shashikanth 2, P.G.Tewari 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l Research student, and Assistant
CFD Analysis of a Mixture Flow in a Producer Gas Carburetor for optimizing the design configuration T.R.Ani1 l, S.D.Ravi 2, M.Shashikanth 2, P.G.Tewari 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l Research student, and Assistant
Sulfur Tail Gas Thermal Oxidizer Systems By Peter Pickard
 Sulfur Tail Gas Thermal Oxidizer Systems By Peter Pickard Introduction SRU s (Sulfur Recovery Units) are critical pieces of equipment in refineries and gas plants. SRUs remove sulfur compounds from certain
Sulfur Tail Gas Thermal Oxidizer Systems By Peter Pickard Introduction SRU s (Sulfur Recovery Units) are critical pieces of equipment in refineries and gas plants. SRUs remove sulfur compounds from certain
AFOSR FINAL REPORT FRACTAL IMAGE COMPRESSION OF RAYLEIGH, RAMAN, LIF AND LDV DATA IN TURBULENT REACTING FLOWS
 AFOSR FINAL REPORT FRACTAL IMAGE COMPRESSION OF RAYLEIGH, RAMAN, LIF AND LDV DATA IN TURBULENT REACTING FLOWS Co-Principal Investigators Warren C. Strahle Jechiel I. Jagoda Prepared for AIR FORCE OFFICE
AFOSR FINAL REPORT FRACTAL IMAGE COMPRESSION OF RAYLEIGH, RAMAN, LIF AND LDV DATA IN TURBULENT REACTING FLOWS Co-Principal Investigators Warren C. Strahle Jechiel I. Jagoda Prepared for AIR FORCE OFFICE
PREDICTION OF THE FLOW INSIDE A MICRO GAS TURBINE COMBUSTOR
 PREDICTION OF THE FLOW INSIDE A MICRO GAS TURBINE COMBUSTOR Johann Jeffrie Bin Muhamad Ridzwan Mohammad Nazri Mohd Jaafar Department of Aeronautics and Automotive Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti
PREDICTION OF THE FLOW INSIDE A MICRO GAS TURBINE COMBUSTOR Johann Jeffrie Bin Muhamad Ridzwan Mohammad Nazri Mohd Jaafar Department of Aeronautics and Automotive Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF DOWNSTREAM FLOW FIELD IN A LINEAR TURBINE CASCADE: EFFECTS OF RELATIVE WALL MOTION
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF DOWNSTREAM FLOW FIELD IN A LINEAR TURBINE CASCADE: EFFECTS OF RELATIVE WALL MOTION V. Uma Maheshwar, Associate Professor, Dept of Mechanical Engineering, University College
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF DOWNSTREAM FLOW FIELD IN A LINEAR TURBINE CASCADE: EFFECTS OF RELATIVE WALL MOTION V. Uma Maheshwar, Associate Professor, Dept of Mechanical Engineering, University College
FLAME AERODYNAMICS COMBUSTION AND FUELS
 FLAME AERODYNAMICS IMPORTANCE OF AERODYNAMICS IN COMBUSTION Fuel Heat Combustion chamber, furnace Flue gas Air Heat Flow reactor Oxidizer: Fuel: Flue gas: MEDIA - air: primary, secondary sometimes tetriary
FLAME AERODYNAMICS IMPORTANCE OF AERODYNAMICS IN COMBUSTION Fuel Heat Combustion chamber, furnace Flue gas Air Heat Flow reactor Oxidizer: Fuel: Flue gas: MEDIA - air: primary, secondary sometimes tetriary
Estimation of the Air-Demand, Flame Height, and Radiation Load from Low-Profile Flare using ISIS-3D
 Estimation of the Air-Demand, Flame Height, and Radiation Load from Low-Profile Flare using ISIS-3D J.D. Smith, Ph.D. and A. Suo-Ahttila, Ph.D., Alion Science and Technology, Owasso, Oklahoma, USA and
Estimation of the Air-Demand, Flame Height, and Radiation Load from Low-Profile Flare using ISIS-3D J.D. Smith, Ph.D. and A. Suo-Ahttila, Ph.D., Alion Science and Technology, Owasso, Oklahoma, USA and
Analysis of Uniformity and Energy Consumption in. Supermarket installed DurkeeSox Air Dispersion System. with PE Air Dispersion Model
 Analysis of Uniformity and Energy Consumption in Supermarket installed DurkeeSox Air Dispersion System with PE Air Dispersion Model Summary: Taking partial area of a large supermarket for example, to simulate
Analysis of Uniformity and Energy Consumption in Supermarket installed DurkeeSox Air Dispersion System with PE Air Dispersion Model Summary: Taking partial area of a large supermarket for example, to simulate
UTSR Fellowship Project: Further Development of Low Pressure Drop Duct Burners
 UTSR Fellowship Project: Further Development of Low Pressure Drop Duct Burners Christopher Bolin 1 Purpose Improve startup and operation of FP250 system Develop duct burners for new fuels and lower emissions
UTSR Fellowship Project: Further Development of Low Pressure Drop Duct Burners Christopher Bolin 1 Purpose Improve startup and operation of FP250 system Develop duct burners for new fuels and lower emissions
Combustion and Turbulence Research Laboratory, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran b
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 217, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 1453-1462 1453 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF SWIRLING OXIDIZER FLOW AND DIAMETER OF FUEL NOZZLE ON BEHAVIOUR AND LIGHT EMITTANCE OF PROPANE-OXYGEN
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 217, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 1453-1462 1453 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF SWIRLING OXIDIZER FLOW AND DIAMETER OF FUEL NOZZLE ON BEHAVIOUR AND LIGHT EMITTANCE OF PROPANE-OXYGEN
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM VI(ME-61,62,63 & 64)] QUIZ TEST-1 Q-1). A jet strikes a smooth curved vane moving in the same direction as the jet and the jet get reversed in the direction. Show that the maximum efficiency
B.Tech. [SEM VI(ME-61,62,63 & 64)] QUIZ TEST-1 Q-1). A jet strikes a smooth curved vane moving in the same direction as the jet and the jet get reversed in the direction. Show that the maximum efficiency
Experimental Campaign on a Hydrogen Fuelled Combustor for a 10 MW Class Gas Turbine with Reduced NOx Emissions
 Experimental Campaign on a Hydrogen Fuelled Combustor for a 10 MW Class Gas Turbine with Reduced NOx Emissions S. Cocchi 1, M. Provenzale 1, S. Sigali 2, L. Carrai 2 1. GE Oil&Gas NUOVO PIGNONE SpA, Firenze
Experimental Campaign on a Hydrogen Fuelled Combustor for a 10 MW Class Gas Turbine with Reduced NOx Emissions S. Cocchi 1, M. Provenzale 1, S. Sigali 2, L. Carrai 2 1. GE Oil&Gas NUOVO PIGNONE SpA, Firenze
Application of Particle Image Velocimetry in Hydraulic Engineering Research. Michael Horst, Ph.D., P.E., ASCE 1
 Application of Particle Image Velocimetry in Hydraulic Engineering Research Michael Horst, Ph.D., P.E., ASCE 1 Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a non-intrusive method used for ascertaining hydraulic
Application of Particle Image Velocimetry in Hydraulic Engineering Research Michael Horst, Ph.D., P.E., ASCE 1 Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a non-intrusive method used for ascertaining hydraulic
Flameless Combustion and its Applications
 Flameless Combustion and its Applications Joachim G. Wünning WS, 2004 Noordwijkerhout, May 2004 Driving Forces for New Technology Energy Prices Carbon Tax Pollution Limits (NO x ) Productivity Quality.
Flameless Combustion and its Applications Joachim G. Wünning WS, 2004 Noordwijkerhout, May 2004 Driving Forces for New Technology Energy Prices Carbon Tax Pollution Limits (NO x ) Productivity Quality.
Lab #3 Conservation Equations and the Hydraulic Jump CEE 331 Fall 2004
 CEE 33 Lab 3 Page of 8 Lab #3 Conservation Equations and the Hydraulic Jump CEE 33 Fall 004 Safety The major safety hazard in this laboratory is a shock hazard. Given that you will be working with water
CEE 33 Lab 3 Page of 8 Lab #3 Conservation Equations and the Hydraulic Jump CEE 33 Fall 004 Safety The major safety hazard in this laboratory is a shock hazard. Given that you will be working with water
NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE
 S643 NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE by Yong-Hui XIE *, Dong-Ting YE, and Zhong-Yang SHEN School of Energy
S643 NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE by Yong-Hui XIE *, Dong-Ting YE, and Zhong-Yang SHEN School of Energy
Ammonia Injection and Mixing Systems 101
 Ammonia Injection and Mixing Systems 101 Kanthan Rajendran, P.E. Airflow Sciences Corporation 2018 NOx-Combustion-CCR Round Table February 19, 2018 St Louis, MO Agenda Intro Coal Fired SCR Gas Turbine
Ammonia Injection and Mixing Systems 101 Kanthan Rajendran, P.E. Airflow Sciences Corporation 2018 NOx-Combustion-CCR Round Table February 19, 2018 St Louis, MO Agenda Intro Coal Fired SCR Gas Turbine
Investigation of the Discharge Flow of a Reciprocating Compressor Using PIV
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Investigation of the Discharge Flow of a Reciprocating Compressor Using PIV H. J. Myung
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Investigation of the Discharge Flow of a Reciprocating Compressor Using PIV H. J. Myung
Effects of non axisymmetric endwall contouring and film cooling on the passage flowfield in a linear turbine cascade
 Exp Fluids (2016) 57:1 DOI 10.1007/s00348-015-2093-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of non axisymmetric endwall contouring and film cooling on the passage flowfield in a linear turbine cascade Amy E. Mensch
Exp Fluids (2016) 57:1 DOI 10.1007/s00348-015-2093-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of non axisymmetric endwall contouring and film cooling on the passage flowfield in a linear turbine cascade Amy E. Mensch
Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor
 Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor S.S.Vinay l, S.D.Ravi 2, G PremaKumar 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l M.E Student, Bangalore University, Bangalore. 2 Project Assistant, CGPL, Dept
Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor S.S.Vinay l, S.D.Ravi 2, G PremaKumar 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l M.E Student, Bangalore University, Bangalore. 2 Project Assistant, CGPL, Dept
Combustion Characteristics of Inverse Diffusion Flames with Elliptic Swirlers
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 04 (April. 2016), V3 PP 27-44 www.iosrjen.org Combustion Characteristics of Inverse Diffusion Flames with Elliptic
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 04 (April. 2016), V3 PP 27-44 www.iosrjen.org Combustion Characteristics of Inverse Diffusion Flames with Elliptic
The Study of Interference Effect for Cascaded Diffuser Augmented Wind Turbines
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-2, 29, Taipei, Taiwan The Study of Interference Effect for Cascaded Diffuser Augmented Wind Turbines ABSTRACT Sheng-Huan Wang and Shih-Hsiung
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, November 8-2, 29, Taipei, Taiwan The Study of Interference Effect for Cascaded Diffuser Augmented Wind Turbines ABSTRACT Sheng-Huan Wang and Shih-Hsiung
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland
 Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0252 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 The effect of spray cooling in long and narrow space for two jet sources with intensive turbulence at
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0252 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 The effect of spray cooling in long and narrow space for two jet sources with intensive turbulence at
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 ) 529 536 6th BSME International Conference on Thermal Engineering (ICTE 2014) Effects of baffles on flow distribution
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 ) 529 536 6th BSME International Conference on Thermal Engineering (ICTE 2014) Effects of baffles on flow distribution
EFFECTS OF LoD AND PoD IN COMBINED-HOLE FILM COOLING
 EFFECTS OF LoD AND PoD IN COMBINED-HOLE FILM COOLING Haswira Hassan and Kamil Abdullah Center for Energy and Industrial Environmental Studies, Faculty of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Universiti
EFFECTS OF LoD AND PoD IN COMBINED-HOLE FILM COOLING Haswira Hassan and Kamil Abdullah Center for Energy and Industrial Environmental Studies, Faculty of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Universiti
Performance and Diagnostic by PIV of LPG Cooking Burners in Thailand
 The 20th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 18-20 October 2006, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand Performance and Diagnostic by PIV of LPG Cooking Burners in Thailand Usa Makmool 1, Suvit
The 20th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 18-20 October 2006, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand Performance and Diagnostic by PIV of LPG Cooking Burners in Thailand Usa Makmool 1, Suvit
Evaluation of new combustion technologies for CO 2 and NO x reduction in steel industries
 Evaluation of new combustion technologies for CO 2 and NO x reduction in steel industries W. Blasiak, K. Narayanan & W. Yang Division of Energy and Furnace Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH),
Evaluation of new combustion technologies for CO 2 and NO x reduction in steel industries W. Blasiak, K. Narayanan & W. Yang Division of Energy and Furnace Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH),
Simulation of Flameless Combustion of Natural Gas in a Laboratory Scale Furnace
 Turkish J. Eng. Env. Sci. 30 (2006), 135 143. c TÜBİTAK Simulation of Flameless Combustion of Natural Gas in a Laboratory Scale Furnace Sébastien MURER, Barbara PESENTI and Paul LYBAERT Thermal Engineering
Turkish J. Eng. Env. Sci. 30 (2006), 135 143. c TÜBİTAK Simulation of Flameless Combustion of Natural Gas in a Laboratory Scale Furnace Sébastien MURER, Barbara PESENTI and Paul LYBAERT Thermal Engineering
FLOW VISUALIZATION IN A SWIRLING FLUIDIZED BED Sulastri Sabudin 1*, Shahzada Khan Nawab Khan 1 and Mohd Faizal Mohideen Batcha 1
 International Conference on Mechanical Engineering Research (ICMER2013), 1-3 July 2013 Bukit Gambang Resort City, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia Organized by Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Malaysia
International Conference on Mechanical Engineering Research (ICMER2013), 1-3 July 2013 Bukit Gambang Resort City, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia Organized by Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Malaysia
PIV Applications to Thermal Performance of LPG Cooking Burners
 PIV Applications to Thermal Performance of LPG Cooking Burners Usa Makmool 1, Sumrerng Jugjai 2,*, Suvit Tia 3, Pumyos Vallikul 4 and Bundit Fungtammasan 1 1 The Joint Graduate School of Energy and Environment,
PIV Applications to Thermal Performance of LPG Cooking Burners Usa Makmool 1, Sumrerng Jugjai 2,*, Suvit Tia 3, Pumyos Vallikul 4 and Bundit Fungtammasan 1 1 The Joint Graduate School of Energy and Environment,
Heat transfer modelling of slot jet impinging on an inclined plate
 Heat transfer modelling of slot jet impinging on an inclined plate A. Ramezanpour 1, H. Shirvani 1 & I. Mirzaee 2 1 School of Design and Communication Systems, APU University, UK 2 CFD Research Centre,
Heat transfer modelling of slot jet impinging on an inclined plate A. Ramezanpour 1, H. Shirvani 1 & I. Mirzaee 2 1 School of Design and Communication Systems, APU University, UK 2 CFD Research Centre,
Simulation and Visualisation of Wire-Arc Additive Manufacture. Ioannis Bitharas Jialuo Ding Andrew Moore Stuart Williams
 Simulation and Visualisation of Wire-Arc Additive Manufacture Ioannis Bitharas Jialuo Ding Andrew Moore Stuart Williams Overview Background previous work, WAAM process MHD flow modelling Plasma arc welding
Simulation and Visualisation of Wire-Arc Additive Manufacture Ioannis Bitharas Jialuo Ding Andrew Moore Stuart Williams Overview Background previous work, WAAM process MHD flow modelling Plasma arc welding
Study on the design of high thermal efficiency gas stove based on waste heat recovery
 2nd Annual International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Information Science (EEEIS 2016) Study on the design of high thermal efficiency gas stove based on waste heat recovery Jian-Feng
2nd Annual International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Information Science (EEEIS 2016) Study on the design of high thermal efficiency gas stove based on waste heat recovery Jian-Feng
Impact of Selective Oxygen Injection on NO, LOI, and Flame Luminosity in a Fine Particle, Swirl-Stabilized Wood Flame
 Paper # 7CO-63 Topic: Coal and Biomass Combustion and Gasification 8 th U. S. National Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and hosted by the University
Paper # 7CO-63 Topic: Coal and Biomass Combustion and Gasification 8 th U. S. National Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and hosted by the University
Investigation of Vitiated Species on the Effect of Scramjet Combustion Using Fuel of Hydrogen or Ethylene
 Investigation of Vitiated Species on the Effect of Scramjet Combustion Using Fuel of Hydrogen or Ethylene Weiqiang Li 1, Wenyan Song 1 & Jianping Li 1 1 School of Power and Energy, Northwestern Polytechnical
Investigation of Vitiated Species on the Effect of Scramjet Combustion Using Fuel of Hydrogen or Ethylene Weiqiang Li 1, Wenyan Song 1 & Jianping Li 1 1 School of Power and Energy, Northwestern Polytechnical
Supersonic Nozzle Flow in the Two-Phase Ejector as Water Refrigeration System by Using Waste Heat
 HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta Supersonic Nozzle Flow in the Two-Phase Ejector as Water Refrigeration System by Using
HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta Supersonic Nozzle Flow in the Two-Phase Ejector as Water Refrigeration System by Using
THE EFFECT OF LARGE-SCALE TURBULENT STRUCTURES ON A SIMPLE 2-D CANYON-TYPE FLOW. Guildford GU2 5XH, United Kingdom.
 THE EFFECT OF LARGE-SCALE TURBULENT STRUCTURES ON A SIMPLE 2-D CANYON-TYPE FLOW SAVORY E. 1 and ABDELQARI A. 2 1 Fluid Mechanics Research Group, School of Engineering in the Environment, University of
THE EFFECT OF LARGE-SCALE TURBULENT STRUCTURES ON A SIMPLE 2-D CANYON-TYPE FLOW SAVORY E. 1 and ABDELQARI A. 2 1 Fluid Mechanics Research Group, School of Engineering in the Environment, University of
MECHANISMS OF EDDY FORMATION IN SWIRLING FLOWS
 MECHANISMS OF EDDY FORMATION IN SWIRLING FLOWS Vladimir Shtern 1 and Guy Marin 2 1 Shtern Research and Consulting, Houston, USA vshtern40@gmail.com 2 Ghent University, LCT, Belgium Guy.Marin@ugent.be 1
MECHANISMS OF EDDY FORMATION IN SWIRLING FLOWS Vladimir Shtern 1 and Guy Marin 2 1 Shtern Research and Consulting, Houston, USA vshtern40@gmail.com 2 Ghent University, LCT, Belgium Guy.Marin@ugent.be 1
Laminar Impinging Jet Heat Transfer for Curved Plates
 Laminar Impinging Jet Heat Transfer for Curved Plates A. M. Tahsini, and S. Tadayon Mousavi Digital Open Science Index, Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering waset.org/publication/2230 Abstract The purpose
Laminar Impinging Jet Heat Transfer for Curved Plates A. M. Tahsini, and S. Tadayon Mousavi Digital Open Science Index, Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering waset.org/publication/2230 Abstract The purpose
Simulation of Engine Flow with Swirl Using Re-Stress Turbulence Model in KIVA Code
 Simulation of Engine Flow with Swirl Using Re-Stress Turbulence Model in KIVA Code S. L. Yang, * Y. K. Siow, and B. D. Peschke Michigan Technological University and R. R. Tacina NASA John H. Glenn Research
Simulation of Engine Flow with Swirl Using Re-Stress Turbulence Model in KIVA Code S. L. Yang, * Y. K. Siow, and B. D. Peschke Michigan Technological University and R. R. Tacina NASA John H. Glenn Research
Numerical Simulation Of A New LNG Vaporizer Using Flue Gas To Impact Umbrella Rotor
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 6 Issue 8 Ver. II ǁ 2018 ǁ PP. 54-59 Numerical Simulation Of A New LNG Vaporizer
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 6 Issue 8 Ver. II ǁ 2018 ǁ PP. 54-59 Numerical Simulation Of A New LNG Vaporizer
Quenching steels with gas jet arrays
 Quenching steels with gas jet arrays PAUL F STRATTON ANDREW P RICHARDSON BOC Rother Valley Way, Holbrook, Sheffield UNITED KINGDOM Paul.stratton@boc.com http://www.catweb.boc.com Abstract: - Single components
Quenching steels with gas jet arrays PAUL F STRATTON ANDREW P RICHARDSON BOC Rother Valley Way, Holbrook, Sheffield UNITED KINGDOM Paul.stratton@boc.com http://www.catweb.boc.com Abstract: - Single components
National Center for Hypersonic Combined Cycle Propulsion
 National Center for Hypersonic Combined Cycle Propulsion Professor Jim McDaniel Principal Investigator University of Virginia AFOSR-NASA Hypersonics Research Review Williamsburg, VA June 16, 2011 Review
National Center for Hypersonic Combined Cycle Propulsion Professor Jim McDaniel Principal Investigator University of Virginia AFOSR-NASA Hypersonics Research Review Williamsburg, VA June 16, 2011 Review
Figure 2. Corrugated nozzle family with equivalent area of the output cross section
 Publishable summary In the domain of civilian aeronautics, the increasing noise restrictions around airports are a challenging problem for aircraft and engine manufacturers. By 2020, the ACARE agenda has
Publishable summary In the domain of civilian aeronautics, the increasing noise restrictions around airports are a challenging problem for aircraft and engine manufacturers. By 2020, the ACARE agenda has
Experimental Analysis of Heat Transfer Enhancement Using Fins in Pin Fin Apparatus
 Experimental Analysis of Heat Transfer Enhancement Using Fins in Pin Fin Apparatus Allan Harry Richard.T.L Dept of Mechanical Engineering Kings College Of Engineering Thanjavur, India allhelan@gmail.com
Experimental Analysis of Heat Transfer Enhancement Using Fins in Pin Fin Apparatus Allan Harry Richard.T.L Dept of Mechanical Engineering Kings College Of Engineering Thanjavur, India allhelan@gmail.com
Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software To cite this article: D Zahariea 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software To cite this article: D Zahariea 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Compound Cooling Holes for Film Cooling of Combustor Simulator: A Review
 Compound Cooling Holes for Film Cooling of Combustor Simulator: A Review S. Salimi *,1,a, E. Kianpour 2,b and A. Fazeli 1,c 1 =Department of Thermo-Fluids, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universtiti
Compound Cooling Holes for Film Cooling of Combustor Simulator: A Review S. Salimi *,1,a, E. Kianpour 2,b and A. Fazeli 1,c 1 =Department of Thermo-Fluids, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universtiti
Aerodynamic Investigation of Upstream Misalignment over the Nozzle Guide Vane in a Transonic Cascade
 Aerodynamic Investigation of Upstream Misalignment over the Nozzle Guide Vane in a Transonic Cascade Yeongjin Lee Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Aerodynamic Investigation of Upstream Misalignment over the Nozzle Guide Vane in a Transonic Cascade Yeongjin Lee Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Lab #3 Conservation Equations and the Hydraulic Jump CEE 331 Fall 2003
 CEE 33 Lab 3 Page of 8 Lab #3 Conservation Equations and the Hydraulic Jump CEE 33 Fall 003 Safety The major safety hazard in this laboratory is a shock hazard. Given that you will be working with water
CEE 33 Lab 3 Page of 8 Lab #3 Conservation Equations and the Hydraulic Jump CEE 33 Fall 003 Safety The major safety hazard in this laboratory is a shock hazard. Given that you will be working with water
Literature Review on CFD Study of Producer Gas Carburetor
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 05, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Literature Review on CFD Study of Producer Gas Carburetor Shirish L. Konde 1 Dr.R. B.
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 05, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Literature Review on CFD Study of Producer Gas Carburetor Shirish L. Konde 1 Dr.R. B.
Flameless Oxidation Technology
 Flameless Oxidation Technology A.Milani, J.G.Wünning WS Wärmeprozesstechnik Dornierstr 14 71272 Germany WS Abstract Flameless combustion is the most significant recent advancement in high temperature combustion
Flameless Oxidation Technology A.Milani, J.G.Wünning WS Wärmeprozesstechnik Dornierstr 14 71272 Germany WS Abstract Flameless combustion is the most significant recent advancement in high temperature combustion
