Research Article Experimental Research on Passive Residual Heat Removal System of Chinese Advanced PWR
|
|
|
- Louise West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, Article ID , 8 pages Research Article Experimental Research on Passive Residual Heat Removal System of Chinese Advanced PWR Zhuo Wenbin, Huang Yanping, Xiao Zejun, Peng Chuanxin, and Lu Sansan CNNC Key Laboratory on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics Technology, Nuclear Power Institute of China, Chengdu 611, China Correspondence should be addressed to Zhuo Wenbin; npic11371@163.com Received 6 December 213; Accepted 2 February 21; Published 5 June 21 Academic Editor: Shengqiang Li Copyright 21 Zhuo Wenbin et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Passive residual heat removal system (PRHRS) for the secondary loop is one of the important features for Chinese advance pressurized water reactor (CAPWR). To prove the safety characteristics of CAPWR, serials of experiments have been done on special designed PRHRS test facility in the former stage. The test facility was built up following the scaling laws to preserve the similarity to CAPWR. A total of more than 3 tests have been performed on the test facility, including 9% steady state cases and 1% transient cases. A semiempirical model was generated for passive heat removal functions based on the experimental results of steady state cases. The dynamic capability characteristics and reliability of passive safety system for CAPWR were evidently proved by transient cases. A new simulation code, MISAP2., has been developed and calibrated by experimental results. It will be applied in future design evaluation and optimization works. 1. Introduction The passive safety feature is one important essential requirement for both integral type reactors and large scale multiloop type reactors. The steam generators (SGs) have been considered as passive safety cooling devices to provide primary loop decay heat removal capacity. There is no additional power supply needed for SGs cooling features. It is specially fit for nonloss of coolant accident applications. The steam released from SGs will be condensed in an accessory heat exchanger, which is located in a tank and submerged in low temperature coolant. To enhance the passive safety function and provide a redundant heat removal path, the secondary side passive cooling system will be necessary for advanced reactors. In order to improve the security and reliability of reactor, some evolutionary and innovative reactors, such as AP6/1, WWER6/7, APR+, SBWR, and SMART, employ passive residual heat removal systems [1]. But most of thesesystemsareprimarypassivecoolingsystems,exceptfor WWER6/7 and APR+. The passive heat removal system for the WWER6/7 reactor is located at the secondary sideofsg.incaseofnon-locasthedecayheatisremoved by coolant natural circulation to steam generator boiler water. The steam generated comes into the passive heat removal system where steam is condensed on the internal surface ofthetubesthatarecooledontheoutsidesurfacebythe water stored in the demineralized water tank outside the containment. The water inventory in this tank is sufficient for the long-term heat removal (at least 2 hours) and can be replenished if necessary from an external source [2]. The APR+ is a Generation III+ nuclear power plant being developed in Korea. The passive auxiliary feedwater system (SG secondary side passive residual heat removal system) is one of the advanced safety features being adopted in the APR+. It cools down the secondary side of the steam generator and eventually removes the decay heat from the reactor core by adopting a natural circulation mechanism, that is, condensing steam in the nearly horizontal passive condensation heat exchanger tubes submerged inside the passive condensation cooling tank [3]. The SG secondary side passive residual heat removal system (PRHRS), which removes the residual heat when station blackout occurs, is considered in Chinese advanced PWR. The passive residual heat removal system eliminates a great deal of water in the condensation tank, which is cooled by air natural circulation in the chimney. Only a small quantity of water in the emergency feedwater tank is needed for absorption of residual heat at the initial period of accident.
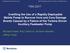
2 2 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Emergency feedwater tank VW6 VW7 F22 Chimney VS3 F23 Air cooler Safe release system SG simulator VW8 VW5 F21 Power calculation (kw) ±1% Power test data (kw) Figure 2: Power comparison between test and calculation. 3. Matrix and Startup Modes Figure 1: Schematic diagram of PRHRS test facility. In order to assess the ability of PRHRS, experimental researchhadbeendoneatadvancedpwrprhrstestfacility in Nuclear Power Institute of China; in the meantime, the computer code MISAP2. has been developed and verified. 2. Facility The test facility has been built according to two-phase natural circulation scaling methodology laws. The geometrical similarity, friction number, density ratio, Froude number, phase change number, and drift-flux number are the important similaritygroups.anditiscomposedofsteam-watercirculation loop, emergency feedwater loop, air natural circulation loop, and safe release system. The main components include steam generator, air cooler, emergency feedwater tank (EFWT), and chimney. It has a geometrical scaling ratio of 1/39 in volume, and the total height from the top of the height-adjustable chimney to the bottom of SG is about 23 m. The maximal pressure of facility is 8.6 MPa, and the core decay heat is simulated by electric heaters with a capacity of kw (DC). Figure 1 showsitsschematicdiagram. The work principle of test facility is as follows. When station blackout or other accidents occur, the isolation valves located at the outlet pipe of emergency tank are opened by a low-low water signal for the SG, so that the emergency water tank provides water to the secondary side of SG driven by gravity and maintains the water level. The water in the SG absorbs the residual heat when the water evaporates. The steam rises and passes through the air cooler where the steam is condensed into water; simultaneously, the heat is transferred into the air through the air natural circulation composed of chimney and atmosphere. Then, the condensed water returns to the SG loop driven by gravity; thereby, a continuous natural circulation flow is established. A total of 28 sets of experimental data at steady state have been obtained and the main influence factors on heat removal capability were identified. The main operation parameters are the height of chimney, the hydraulic resistance, and the initial pressure. More than 3 transient tests had been performed while the residual heat drops from 8% full power to 2% full power (Figure 2). In addition the influence factors on flow instability were identified.. Results and Analysis.1. Steady. The natural circulation is influenced by many parameters, such as the height of chimney, the hydraulic resistance, and the initial pressure. Several tests are implemented to investigate the effect of these parameters on the passive residual heat removal system. In addition a semiempirical model was generated for predicting the natural circulation behavior of Chinese advance pressurized water reactor. The equation of momentum for passive residual heat removal loop is (ρ w L w ρ s L s ρ sg L sg )g= k ww 2 2ρ w A 2 + k sw 2 W 2ρ s A 2, (1) s where the subscripts w, s,andsg are water in the down pipe, steam in the rise pipe, and SG respectively. Equation of momentum for air loop is (ρ y ρ yi )gl y = k yw 2 a 2ρ y A 2, (2) y where the subscripts y and yi are outlet and inlet of chimney, respectively. Theaircoolerheattransferequationis In steam side of the cooler, Q=KFΔT m. (3) Q=W(H s H w ). ()
3 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations 3 Height of chimney Number (m) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Table 1: Effect of the height of chimney. Temp. of condensate ( C) Power (kw) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Temp. of condensate ( C) The height between air cooler and SG is 1.5 m, the hydraulic resistance is 15, the water in SG is 5.1 m, the pressure is 6. MPa, and the temperature at the inlet is 2 C. Table 2: Effect of the hydraulic resistance. Number Hydraulic resistance (m) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Power (kw) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Power (kw) The height between air cooler and SG is 1.5 m, the height of chimney is 1.5, the water in SG is 5.1 m, the pressure is 6. MPa, and the temperature at the inlet is 2 C. Power (kw) In air side of the cooler, Q=W a (H y H yi ), (5) where K is heat transfer coefficient, F is heat transfer area, ΔT m is mean temperature difference, and W a is the air flow rate. Coupling with (1) (5), a semiempirical correlation has been built up for total PRHR system heat transfer estimation based on the test results. In this case, when system pressure, water level in SG, friction coefficient, and the height between SG and air cooler are given, the ability of heat removal can be calculated. Consider Q = 268 (.98 Lth/3).5 (.8LnH + 1.2) ( LnP) e (.5/1)K tin.2. (6) Sensitivity studies on different structure parameters have been made. The results will be described in detail as follows Effect of the Height of Chimney. The effect of the height of chimney in the passive residual heat removal system has been identified at the initial height of chimney of 9.7 m and 27.1 m. In this group of sensitive studies, the hydraulic resistance hardly keeps the same value under different condition, which is maintained at less than 1%. And the temperature of airattheinletofchimneyandpressureareunchangedvalues withonlytheheightbeingallowedtochangetofindtheeffect. Table 1 shows the experimental data and calculation of the natural circulation flow rate, power, and temperature of condensate, respectively. As the height of chimney increases, the natural circulation flow rate of air loop and power of air cooler rise. Then, the temperature of condensate decreases. When the height between air cooler and SG and hydraulic resistance is constant, the reduced density of condensate causestheincreaseofnaturalcirculationflowrate.inaddition the calculation shows good agreement with experimental data Effect of the Hydraulic Resistance. The effects of the hydraulic resistance (frictional resistance and local resistance) in the passive residual heat removal system are performed in this study (Table 2). Other parameters are kept at a constant value. The hydraulic resistance is varied from 86 to 171. We can see that the resistance increases more than 1%,butthenaturalcirculationflowrateandpowerdecrease rarely. Therefore, the hydraulic resistance has little influence on the passive residual heat removal system Effect of the Initial Pressure on the Passive Residual Heat Removal System. The initial pressure in the passive residual heat removal system changes from 3.53 MPa to 7.3 MPa, and other parameters are fixed except for the hydraulic resistance with a 1 percent deviation. As the pressure ascends, the increase of power and natural circulation flow rate is 22.3% and 25%, respectively (Table 3)..2. Transient. When the station blackout accident happens in the Chinese advance pressurized water reactor, it adopts the passive residual heat removal system to mitigate consequences of accidents. The passive residual heat removal system startup modes include warm and cold patterns when the emergency feedwater is on or off, respectively. If there is a tiny flow rate to keep a little natural circulation in both steam-water circulation loop and air natural circulation loop
4 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Table 3: Effect of the initial pressure. Number Pressure (MPa) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Power (kw) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Power (kw) The height between air cooler and SG is 1.5 m, the height of chimney is 12.8, the water in SG is 5.1 m, the hydraulic resistance is 15, and the temperature at the inlet is 33 C. Pressure (MPa) Apr7111 warm startup mode Apr7191 cold startup mode Figure 3: The pressure of cold and warm startup mode Apr7111 warm startup mode Apr7191 cold startup mode Figure 5: The feedwater flow rate Apr7191 cold startup mode Apr7111 warm startup mode Figure : The natural circulation flow rate. before the startup of transient test, this type of startup mode is defined as warm startup. On the other hand, if the initial conditioniscold,orthereisnoflowinbothsteam-water circulation loop and air natural circulation loop, this type of startupmodeisdefinedascoldstartup. The typical results of cold and warm startup tests with emergency feedwater are shown in Figures 3 6. The pressure increases before the air natural circulation is established when the residual heat is larger than that absorbed by cold water in air cooler and EFWT. But the pressure begins to drop not only because of the residual heat decay but also Pressure (MPa) Pressure in EFWT Pressure in SG Figure 6: The pressure fluctuation when water hammer occurs. because the air flow rate reaches its maximum. As shown in Figure3, there is no remarkable difference between cold and warm startup. Figure shows the natural circulation. As the isolation valve is open, the natural circulation is established between SG and air cooler. The flow rate rises to 3 kg/h. Theflowinstabilityhappensatthebeginningofnatural circulation, which is caused by the water hammer that occurs in emergency feedwater tank. The water hammer also results in flow instability of injection from emergency feedwater tank
5 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Apr C Apr C Figure 7: Water hammer influenced by feedwater temperature Apr Apr Figure 8: Water hammer influenced by resistance of feedwater loop. as shown in Figure 5. The water hammer occurs in emergency feedwater tank when a great deal of steam, which is rushing into emergency feedwater tank through the pressure balance pipe after the feedwater valve is opened, condenses quickly. The pressure fluctuates in the emergency feedwater tank when the water hammer happens as shown in Figure 6. Some tests have been performed to avoid water hammer s appearance Effect of Temperature of Feedwater. The effect of temperature of feedwater in the passive residual heat removal system has been identified at the initial temperatures of 32 Cand 52 C and the other parameters are kept at a constant value. The results are shown in Figure 7. When the temperature of feedwater in the emergency feedwater tank is 52 C, the water hammer does not happen because the direct contact condensation is related to the temperature of fluid Effect of Resistance of Feedwater Loop. In this group of case studies, the resistance of feedwater loop is changed by +5% of the reference case, and the other parameters are the same.theresultsareshowninfigure 8. As the resistance of feedwater loop increases, the feedwater flow rate and steam flow rate decrease accordingly. As a result there is not flow instability. 5. Code Development and Verification MISAP2. code is a typical code that is used to analyze steady and transient performance of the secondary passive residual heat removal system Mathematical Model. A basic assumption is that onedimensional approach is used Single-Phase Conservative Equations. Equation of continuity is ρ τ + 1 dw =, (7) A dz where W is flow rate and ρ is density. Equation of momentum is W τ = A P Z Z (W2 ρa ) ρga U hf W2 2ρA 2, (8) where A is the cross-sectional area of the flow channel; P is pressure; U h is wetted perimeter; f is friction coefficient; g is the gravitational acceleration. Equation of energy is τ V2 V2 [ρ (u + )] + [ρ (u + 2 Z 2 )V] = qu k A + 1 A q V da (VP) ρgv, A Z where h is enthalpy; V is velocity; q V is heat generation rate of the fluid; U k is heated perimeter. The gravitational work andtheworkrelatedtothekineticenergyvariationcanbe neglected and the heat generation of the fluid is ignored; the equationcanbesimplifiedasfollows: (9) ρ h τ + W h A Z = qu h A + P t. (1) Two-Phase Mixture Conservative Equations. Equation of continuity is t [αρ g + (1 α) ρ f ]+ 1 W =, (11) A Z
6 6 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Chimney 2 SG simulator Emergency feedwater tank Air cooler Figure 9: MASAP nodalization diagram of the test facility. W SRV W 5TM W S5V (2) (23) (21) (7) (8) (6) ( 9) 5 (19) 9 (5) (1) (18) () (11) 3 (17) 1 (3) (12) 2 (16) 2 (2) (13) 1 (15) (1) (1) (22) W FW where α is void fraction; subscripts g and f stand for steam and saturated liquid, respectively. Equation of momentum is (ρv) + τ Z (ρv2 )= P Z 1 A τ f du ρg. (12) U Equation of energy is t [(1 α) ρ fh f +αρ g h g ] + 1 A Z [Wh] = qu h A Emergency Feedwater Tank. Consider + P t. (13) W tank = 2gΔH ρa ξ tank. (1) Air Loop. Momentum equation is Ly Ly Ly W a τ 1 A dz = P Z dz 1 A z (W2 a ρa )dz where Ly is the chimney height. Ly ρgdz W 2 Ly a U h A f 1 2ρA 2 dz, (15) 5.2. Numerical Model. In view of the fact that two loops closely couple with each other due to energy and momentum interactions, the two loops are solved together. Figures 9 and 1 show MASIP2. nodalization diagram of test facility and SG. After the discretization of the spatial derivative terms in Figure 1: MASAP nodalization diagram of SG. the equations, the following ordinary differential equations are obtained: d y dt = f(t, y, y ), (16) y(t )= y. Therefore, the whole system dynamic simulation can be solved as an initial value problem. For the stiff system of differential equations, Gear s algorithm is used traditionally Steady State. During the steady state calculation, several parameters, such as natural circulation flow rate, flow rate of air, temperature of condensate, and air at outlet of chimney, are calculated. And the calculations of MASIP2. are compared with the experimental data shown in Table. It shows that the error between calculation and experimental data is less than 1%. 5.. Transient State. The transient calculation results of cold startup model test are compared with experimental data in Figures 11 and 12. Figure 11 shows the pressure comparison between calculation and test. The pressure increases before the air natural circulation is established when the residual heat is larger than that absorbed by cold water in air cooler and EFWT. MISAP2. code predicts the pressure well. However, the quantitative description is poor in the initial period of the transient. The reason is that there is no direct contact condensation model in the code. Then, the calculated flow rate of feedwater is less than experimental data, as shown in Figure 12. As a result the calculation of pressure is higher than that in the tests. As for the absence of direct contact condensation model, the water hammer is not observed.
7 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations 7 Number Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) Table : Comparison between the calculation of MISAP2. and experimental data. Temp. of condensate ( C) Flow rate of air (kg/s) Temp. of air at outlet ( C) Natural circulation flow rate (kg/h) of MISAP2. Temp. of condensate ( C) Flow rate of air (kg/s) Temp. of air at outlet ( C) Pressure (MPa) Figure 11: The pressure comparison between calculation and test Figure 12: The flow rate comparison between calculation and test. 6. Conclusion The passive residual heat removal system (PRHRS) characteristics of Chinese advance pressurized water reactor (CAPWR) have been experimentally investigated. Based on the investigations, the following conclusions are drawn. (1) A total of 28 sets of tests at steady state have been implemented to investigate the effect of some parameters on the passive residual heat removal system. The result shows that the height of chimney has great influence on natural circulation flow rate. And the effect of the initial pressure and hydraulic resistance is small or negligible. (2) Based on the experiments, semiempirical model for analyzing passive residual heat removal system is established, and the calculation shows good agreement with experimental data. It can be applied to system arrangement design for PRHRS of Chinese advanced PWR. (3) In case of station blackout accident, the transient characteristics of passive residual heat removal system were studied. The natural circulation and injection of feedwater are very useful for removal of decay heat. () The increase of feedwater s initial temperature and resistance of feedwater loop is useful to avoid the water hammer. (5) A code MISAP2. has been developed, and the transient tests are used to verify the prediction of MISAP2.. The calculated parameter variation trend is reasonable. However, the flow fluctuation and water hammer cannot be simulated by MISAP2.. Now the direct contact condensation is under development for next version of MISAP. Nomenclature A: Flowarea(m 2 ) f: Friction factor g: Gravity acceleration (m/s 2 ) h: Specific enthalpy (J/kg) K: Losscoefficient H: Emergency feedwater tank water lever (m) P: Pressure (Pa) q: Heatflux(W/m 2 ) t: Time(s) U: Heated perimeter (m) U e : Wetted perimeter (m) W: Mass flow rate (kg/s) z: Special coordinate (m) α: Void fraction ρ: Density (kg/m 3 ).
8 8 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. References [1] Passive safety systems and natural circulation in water cooled nuclear power plants, IAEA-TECDOC-162, IAEA, Vienna, Austria, 29. [2] Status of advanced light water reactor designs 2, IAEA- TECDOC-1391, IAEA, Vienna, Austria, 2. [3] S. Kim, B. Byoung-Uhn, C. Yun-Je, P. Yu-Sun, K. Kyoung-Ho, and Y. Byong-Jo, An experimental study on the validation of cooling capability for the passive auxiliary feedwater system (PAFS) condensation heat exchanger, Nuclear Engineering and Design,vol.26,pp.5 63,213.
9 Energy International Rotating Machinery Wind Energy The Scientific World Journal Structures Industrial Engineering Petroleum Engineering Solar Energy Submit your manuscripts at Fuels Engineering Advances in Power Electronics International High Energy Physics Photoenergy International Advances in Combustion Nuclear Energy Renewable Energy International Advances in Science and Technology of Tribology Nuclear Installations Aerospace Engineering
Research Article Investigation of TASS/SMR Capability to Predict a Natural Circulation in the Test Facility for an Integral Reactor
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, Article ID 18182, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/18182 Research Article Investigation of TASS/SMR Capability to Predict a Natural Circulation in the
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, Article ID 18182, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/18182 Research Article Investigation of TASS/SMR Capability to Predict a Natural Circulation in the
EVALUATION OF RELAP5/MOD3.2 FOR AP1000 PASSIVE RESIDUAL HEAT REMOVAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF RELAP5/MOD3.2 FOR AP1000 PASSIVE RESIDUAL HEAT REMOVAL SYSTEM Houjun Gong, Zhao Xi, Wenbin Zhuo, Yanping Huang* CNNC Key Laboratory on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics Technology, Chengdu,
EVALUATION OF RELAP5/MOD3.2 FOR AP1000 PASSIVE RESIDUAL HEAT REMOVAL SYSTEM Houjun Gong, Zhao Xi, Wenbin Zhuo, Yanping Huang* CNNC Key Laboratory on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics Technology, Chengdu,
Station Blackout Analysis for a 3-Loop Westinghouse PWR Reactor Using TRACE
 The Egyptian Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications Society of Nuclear Vol 50, 3, (229-239) 2017 Sciences and Applications ISSN 1110-0451 Web site: esnsa-eg.com (ESNSA) Station Blackout Analysis
The Egyptian Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications Society of Nuclear Vol 50, 3, (229-239) 2017 Sciences and Applications ISSN 1110-0451 Web site: esnsa-eg.com (ESNSA) Station Blackout Analysis
Nuclear Power Plants Authority, 4 El-Nasr Avenue, Nasr City, P.O. Box 8191, Nasr City 11371, Cairo, Egypt
 International Nuclear Energy, Article ID 569658, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/569658 Research Article A Parametric Study of the Impact of the Cooling Water Site Specific Conditions on the Efficiency
International Nuclear Energy, Article ID 569658, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/569658 Research Article A Parametric Study of the Impact of the Cooling Water Site Specific Conditions on the Efficiency
Investigation on Core Downward Flow by a Passive Residual Heat Removal System of Research Reactor
 Investigation on Core Downward Flow by a Passive Residual Heat Removal System of Research Reactor W.K. Lee 1, S.J. Kim 1, D.Y. Lee 1, W.K. Hwang 1, K.Y. Lee 1 1) Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering,
Investigation on Core Downward Flow by a Passive Residual Heat Removal System of Research Reactor W.K. Lee 1, S.J. Kim 1, D.Y. Lee 1, W.K. Hwang 1, K.Y. Lee 1 1) Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering,
Experimental Research on Non-Condensable Gases Effects in Passive Decay Heat Removal System
 Experimental Research on Non-Condensable Gases Effects in Passive Decay Heat Removal System LIU Yang, JIA Hai-jun Institute of Nuclear and New Energy Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Experimental Research on Non-Condensable Gases Effects in Passive Decay Heat Removal System LIU Yang, JIA Hai-jun Institute of Nuclear and New Energy Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Research Article Research and Evaluation for Passive Safety System in Low Pressure Reactor
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 2015, Article ID 179235, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/179235 Research Article Research and Evaluation for Passive Safety System in Low Pressure
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 2015, Article ID 179235, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/179235 Research Article Research and Evaluation for Passive Safety System in Low Pressure
TOPIC: KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [2.5/2.5]
![TOPIC: KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [2.5/2.5] TOPIC: KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [2.5/2.5]](/thumbs/96/127964750.jpg) KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [2.5/2.5] P283 The transfer of heat from the reactor fuel pellets to the fuel cladding during normal plant operation is primarily accomplished via heat transfer. A. conduction B. convection
KNOWLEDGE: K1.01 [2.5/2.5] P283 The transfer of heat from the reactor fuel pellets to the fuel cladding during normal plant operation is primarily accomplished via heat transfer. A. conduction B. convection
AP1000 European 15. Accident Analysis Design Control Document
 15.2 Decrease in Heat Removal by the Secondary System A number of transients and accidents that could result in a reduction of the capacity of the secondary system to remove heat generated in the reactor
15.2 Decrease in Heat Removal by the Secondary System A number of transients and accidents that could result in a reduction of the capacity of the secondary system to remove heat generated in the reactor
SMR/1848-T21b. Course on Natural Circulation Phenomena and Modelling in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors June 2007
 SMR/1848-T21b Course on Natural Circulation Phenomena and Modelling in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors 25-29 June 2007 T21b - Selected Examples of Natural Circulation for Small Break LOCA and Som Severe
SMR/1848-T21b Course on Natural Circulation Phenomena and Modelling in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors 25-29 June 2007 T21b - Selected Examples of Natural Circulation for Small Break LOCA and Som Severe
EXPERIMENTS ON THE PERFORMANCE SENSITIVITY OF THE PASSIVE RESIDUAL HEAT REMOVAL SYSTEM OF AN ADVANCED INTEGRAL TYPE REACTOR
 EXPERIMENTS ON THE PERFORMANCE SENSITIVITY OF THE PASSIVE RESIDUAL HEAT REMOVAL SYSTEM OF AN ADVANCED INTEGRAL TYPE REACTOR HYUN-SIK PARK *, KI-YONG CHOI, SEOK CHO, SUNG-JAE YI, CHOON-KYUNG PARK and MOON-KI
EXPERIMENTS ON THE PERFORMANCE SENSITIVITY OF THE PASSIVE RESIDUAL HEAT REMOVAL SYSTEM OF AN ADVANCED INTEGRAL TYPE REACTOR HYUN-SIK PARK *, KI-YONG CHOI, SEOK CHO, SUNG-JAE YI, CHOON-KYUNG PARK and MOON-KI
INTEGRAL EFFECT NON-LOCA TEST RESULTS FOR THE INTEGRAL TYPE REACTOR SMPART-P USING THE VISTA FACILITY
 HEFAT7 5 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 1- July 7, Sun City, South Africa CK INTEGRAL EFFECT NON-LOCA TEST RESULTS FOR THE INTEGRAL TYPE REACTOR SMPART-P
HEFAT7 5 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 1- July 7, Sun City, South Africa CK INTEGRAL EFFECT NON-LOCA TEST RESULTS FOR THE INTEGRAL TYPE REACTOR SMPART-P
Research Article The Investigation of Nonavailability of Passive Safety Systems Effects on Small Break LOCA Sequence in AP1000 Using RELAP5 MOD 4.
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 1, Article ID 79151, 11 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/1/79151 Research Article The Investigation of Nonavailability of Passive Safety Systems Effects
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 1, Article ID 79151, 11 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/1/79151 Research Article The Investigation of Nonavailability of Passive Safety Systems Effects
Passive Cooldown Performance of Integral Pressurized Water Reactor
 Energy and Power Engineering, 2013, 5, 505-509 doi:10.4236/epe.2013.54b097 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe) Passive Cooldown Performance of Integral Pressurized Water Reactor
Energy and Power Engineering, 2013, 5, 505-509 doi:10.4236/epe.2013.54b097 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe) Passive Cooldown Performance of Integral Pressurized Water Reactor
Research Article Evaluation of Heat Removal from RBMK-1500 Core Using Control Rods Cooling Circuit
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 8, Article ID 378, 8 pages doi:1155/8/378 Research Article Evaluation of Heat Removal from RBMK-15 Core Using Control Rods Cooling Circuit A Kaliatka,
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 8, Article ID 378, 8 pages doi:1155/8/378 Research Article Evaluation of Heat Removal from RBMK-15 Core Using Control Rods Cooling Circuit A Kaliatka,
Simulation of thermal hydraulics accidental transients: evaluation of MAAP5.02 versus CATHAREv2.5
 1/12 Simulation of thermal hydraulics accidental transients: evaluation of MAAP5.02 versus CATHAREv2.5 J. Bittan¹ 1) EDF R&D, Clamart (F) Summary MAAP is a deterministic code developed by EPRI that can
1/12 Simulation of thermal hydraulics accidental transients: evaluation of MAAP5.02 versus CATHAREv2.5 J. Bittan¹ 1) EDF R&D, Clamart (F) Summary MAAP is a deterministic code developed by EPRI that can
Evaluation of Two Phase Natural Circulation Flow in the Reactor Cavity under IVR-ERVC for Different Thermal Power Reactors
 Evaluation of Two Phase Natural Circulation Flow in the Reactor Cavity under IVR-ERVC for Different Thermal Power Reactors Rae-Joon Park, Kwang-Soon Ha, Hwan-Yeol Kim Severe Accident & PHWR Safety Research
Evaluation of Two Phase Natural Circulation Flow in the Reactor Cavity under IVR-ERVC for Different Thermal Power Reactors Rae-Joon Park, Kwang-Soon Ha, Hwan-Yeol Kim Severe Accident & PHWR Safety Research
Research Article Assessment of Severe Accident Depressurization Valve Activation Strategy for Chinese Improved 1000 MWe PWR
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 3, Article ID 79437, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/79437 Research Article Assessment of Severe Accident Depressurization Valve Activation Strategy
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 3, Article ID 79437, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/79437 Research Article Assessment of Severe Accident Depressurization Valve Activation Strategy
Chapter 8. Vapor Power Systems
 Chapter 8 Vapor Power Systems Introducing Power Generation To meet our national power needs there are challenges related to Declining economically recoverable supplies of nonrenewable energy resources.
Chapter 8 Vapor Power Systems Introducing Power Generation To meet our national power needs there are challenges related to Declining economically recoverable supplies of nonrenewable energy resources.
Application of COMSOL Pipe Flow Module to Develop a High Flux Isotope Reactor System Loop Model
 Application of COMSOL Pipe Flow Module to Develop a High Flux Isotope Reactor System Loop Model D. Wang *1, P. K. Jain 1, and J. D. Freels 1 1 Oak Ridge National Laboratory *1 Bethel Valley RD, Oak Ridge,
Application of COMSOL Pipe Flow Module to Develop a High Flux Isotope Reactor System Loop Model D. Wang *1, P. K. Jain 1, and J. D. Freels 1 1 Oak Ridge National Laboratory *1 Bethel Valley RD, Oak Ridge,
COMPARATIVE ANALYSES OF TWO IMPROVED CO 2 COMBINED COOLING, HEATING, AND POWER SYSTEMS DRIVEN BY SOLAR ENERGY
 S93 Introduction COMPARATIVE ANALYSES OF TWO IMPROVED CO 2 COMBINED COOLING, HEATING, AND POWER SYSTEMS DRIVEN BY SOLAR ENERGY by Wanjin BAI a* and Xiaoxiao XU b a School of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering,
S93 Introduction COMPARATIVE ANALYSES OF TWO IMPROVED CO 2 COMBINED COOLING, HEATING, AND POWER SYSTEMS DRIVEN BY SOLAR ENERGY by Wanjin BAI a* and Xiaoxiao XU b a School of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR NATURAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL RADIATION IN PASSIVE CONTAINMENT COOLING SYSTEM
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR NATURAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL RADIATION IN PASSIVE CONTAINMENT COOLING SYSTEM Weizhong Zhang and Qian Lin Advanced Nuclear Power Technology R&D Center, Shanghai Nuclear Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR NATURAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL RADIATION IN PASSIVE CONTAINMENT COOLING SYSTEM Weizhong Zhang and Qian Lin Advanced Nuclear Power Technology R&D Center, Shanghai Nuclear Engineering
Application of averaging bidirectional flow tube for measurement of single-phase flow rate in a piping system
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 758~767 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-009-0208-8 Application of averaging
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 758~767 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-009-0208-8 Application of averaging
Research Article Natural Circulation Characteristics of a Symmetric Loop under Inclined Conditions
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, Article ID 925760, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/925760 Research Article Natural Circulation Characteristics of a Symmetric Loop under Inclined
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, Article ID 925760, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/925760 Research Article Natural Circulation Characteristics of a Symmetric Loop under Inclined
SMR/1848-T03. Course on Natural Circulation Phenomena and Modelling in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors June 2007
 SMR/1848-T03 Course on Natural Circulation Phenomena and Modelling in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors 25-29 June 2007 Applications of Natural Circulation Systems N. Aksan Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI), Villingen,
SMR/1848-T03 Course on Natural Circulation Phenomena and Modelling in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors 25-29 June 2007 Applications of Natural Circulation Systems N. Aksan Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI), Villingen,
Estimation of natural circulation flow based on temperature in the FASSIP-02 large-scale test loop facility
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Estimation of natural circulation flow based on temperature in the FASSIP-0 large-scale test loop facility To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Estimation of natural circulation flow based on temperature in the FASSIP-0 large-scale test loop facility To cite this article:
Development Projects of Supercritical-water Cooled Power Reactor (SCPR) in JAPAN
 Development Projects of Supercritical-water Cooled Power Reactor (SCPR) in JAPAN Information Exchange Meeting on SCWR Development 1 November 19, 2002 The University of Tokyo Toshiba Corp. Hitachi, Ltd.
Development Projects of Supercritical-water Cooled Power Reactor (SCPR) in JAPAN Information Exchange Meeting on SCWR Development 1 November 19, 2002 The University of Tokyo Toshiba Corp. Hitachi, Ltd.
SIMULATION OF CCFL EXPERIMENTS IN A PWR HOT LEG GEOMETRY WITH RELAP5/MOD3.3
 007 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 007 Santos, SP, Brazil, September 0 to October 5, 007 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-994-0- SIMULATION OF CCFL EXPERIMENTS
007 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 007 Santos, SP, Brazil, September 0 to October 5, 007 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-994-0- SIMULATION OF CCFL EXPERIMENTS
ANALYSIS ON NON-UNIFORM FLOW IN STEAM GENERATOR DURING STEADY STATE NATURAL CIRCULATION COOLING
 ANALYSIS ON NON-UNIFORM FLOW IN STEAM GENERATOR DURING STEADY STATE NATURAL CIRCULATION COOLING Susyadi 1 and T. Yonomoto 2 1 Center for Reactor Technology and Nuclear Safety - BATAN Puspiptek, Tangerang
ANALYSIS ON NON-UNIFORM FLOW IN STEAM GENERATOR DURING STEADY STATE NATURAL CIRCULATION COOLING Susyadi 1 and T. Yonomoto 2 1 Center for Reactor Technology and Nuclear Safety - BATAN Puspiptek, Tangerang
Boiler Efficiency Testing. To understand the operation of a fire tube boiler To determine the operating efficiency of the boiler
 Boiler Efficiency Testing Objectives: To understand the operation of a fire tube boiler To determine the operating efficiency of the boiler Theory Most industrial processes require heating. This is usually
Boiler Efficiency Testing Objectives: To understand the operation of a fire tube boiler To determine the operating efficiency of the boiler Theory Most industrial processes require heating. This is usually
NSSS Design (Ex: PWR) Reactor Coolant System (RCS)
 NSSS Design (Ex: PWR) Reactor Coolant System (RCS) Purpose: Remove energy from core Transport energy to S/G to convert to steam of desired pressure (and temperature if superheated) and moisture content
NSSS Design (Ex: PWR) Reactor Coolant System (RCS) Purpose: Remove energy from core Transport energy to S/G to convert to steam of desired pressure (and temperature if superheated) and moisture content
System Analysis of Pb-Bi Cooled Fast Reactor PEACER
 OE-INES-1 International Symposium on Innovative Nuclear Energy Systems for Sustainable Development of the World Tokyo, Japan, October 31 - November 4, 2004 System Analysis of Pb-Bi ooled Fast Reactor PEAER
OE-INES-1 International Symposium on Innovative Nuclear Energy Systems for Sustainable Development of the World Tokyo, Japan, October 31 - November 4, 2004 System Analysis of Pb-Bi ooled Fast Reactor PEAER
OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 STEADY FLOW PLANT
 UNIT 47: Engineering Plant Technology Unit code: F/601/1433 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 STEADY FLOW PLANT 2 Be able to apply the steady flow energy equation (SFEE) to plant and equipment
UNIT 47: Engineering Plant Technology Unit code: F/601/1433 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 STEADY FLOW PLANT 2 Be able to apply the steady flow energy equation (SFEE) to plant and equipment
ME ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT III QUESTION BANK SVCET
 1. A vessel of volume 0.04m 3 contains a mixture of saturated water and steam at a temperature of 250 0 C. The mass of the liquid present is 9 kg. Find the pressure, mass, specific volume, enthalpy, entropy
1. A vessel of volume 0.04m 3 contains a mixture of saturated water and steam at a temperature of 250 0 C. The mass of the liquid present is 9 kg. Find the pressure, mass, specific volume, enthalpy, entropy
Profile LFR-48 SIRIO ITALY. Pressurized Water. ENEA - Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development, Italy
 Profile LFR-48 SIRIO ITALY GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE LOCATION (address): Sistema di rimozione della potenza di decadimento per reattori nucleari innovativi Decay heat removal
Profile LFR-48 SIRIO ITALY GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE LOCATION (address): Sistema di rimozione della potenza di decadimento per reattori nucleari innovativi Decay heat removal
A. Kaliatka, S. Rimkevicius, E. Uspuras Lithuanian Energy Institute (LEI) Safety Assessment of Shutdown Reactors at the Ignalina NPP
 A. Kaliatka, S. Rimkevicius, E. Uspuras Lithuanian Energy Institute (LEI) Safety Assessment of Shutdown Reactors at the Ignalina NPP Outline Introduction Specific of heat removal from shutdown RBMK-type
A. Kaliatka, S. Rimkevicius, E. Uspuras Lithuanian Energy Institute (LEI) Safety Assessment of Shutdown Reactors at the Ignalina NPP Outline Introduction Specific of heat removal from shutdown RBMK-type
Secondary Systems: Steam System
 Secondary Systems: Steam System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 10 Table of Contents 1 SECONDARY SYSTEM
Secondary Systems: Steam System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 10 Table of Contents 1 SECONDARY SYSTEM
Research Article Effect of Heating Method on Hydrogen Production by Biomass Gasification in Supercritical Water
 Advances in Condensed Matter hysics, Article ID 519389, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2014/519389 Research Article Effect of Heating Method on Hydrogen roduction by Biomass Gasification in Supercritical
Advances in Condensed Matter hysics, Article ID 519389, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2014/519389 Research Article Effect of Heating Method on Hydrogen roduction by Biomass Gasification in Supercritical
The Comparison and Analysis of the System Utilizing the General Boiler Flue Gas Waste Heat
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-05-23 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 926-930, pp 829-832 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.926-930.829 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland The Comparison and Analysis
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-05-23 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 926-930, pp 829-832 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.926-930.829 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland The Comparison and Analysis
CONTROL VOLUME ANALYSIS USING ENERGY. By Ertanto Vetra
 CONTROL VOLUME ANALYSIS USING ENERGY 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Mass Balance Energy Balance Steady State and Transient Analysis Applications 2 Conservation of mass Conservation of mass is one of the most
CONTROL VOLUME ANALYSIS USING ENERGY 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Mass Balance Energy Balance Steady State and Transient Analysis Applications 2 Conservation of mass Conservation of mass is one of the most
Supersonic Nozzle Flow in the Two-Phase Ejector as Water Refrigeration System by Using Waste Heat
 HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta Supersonic Nozzle Flow in the Two-Phase Ejector as Water Refrigeration System by Using
HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta Supersonic Nozzle Flow in the Two-Phase Ejector as Water Refrigeration System by Using
Research Article Experimental Study of Thermal Performance of One-Ended Evacuated Tubes for Producing Hot Air
 Solar Energy Volume 213, Article ID 524715, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/524715 Research Article Experimental Study of Thermal Performance of One-Ended Evacuated Tubes for Producing Hot Air Ashish
Solar Energy Volume 213, Article ID 524715, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/524715 Research Article Experimental Study of Thermal Performance of One-Ended Evacuated Tubes for Producing Hot Air Ashish
DETAILED ANALYSIS OF GEOMETRY EFFECT ON TWO PHASE NATURAL CIRCULATION FLOW UNDER IVR-ERVC
 DETAILED ANALYSIS OF GEOMETRY EFFECT ON TWO PHASE NATURAL CIRCULATION FLOW UNDER IVR-ERVC R. J. Park 1, K. S. Ha 1, and H. Y. Kim 1 Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute 989-111 Daedeok-daero,Yuseong-Gu,
DETAILED ANALYSIS OF GEOMETRY EFFECT ON TWO PHASE NATURAL CIRCULATION FLOW UNDER IVR-ERVC R. J. Park 1, K. S. Ha 1, and H. Y. Kim 1 Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute 989-111 Daedeok-daero,Yuseong-Gu,
THE ROLE OF PASSIVE SYSTEMS IN ENHANCING SAFETY AND PREVENTING ACCIDENTS IN ADVANCED REACTORS
 THE ROLE OF PASSIVE SYSTEMS IN ENHANCING SAFETY AND PREVENTING ACCIDENTS IN ADVANCED REACTORS M. Aziz Nuclear and radiological regulatory authority Cairo, Egypt moustafaaaai@yahoo.com Abstract Most of
THE ROLE OF PASSIVE SYSTEMS IN ENHANCING SAFETY AND PREVENTING ACCIDENTS IN ADVANCED REACTORS M. Aziz Nuclear and radiological regulatory authority Cairo, Egypt moustafaaaai@yahoo.com Abstract Most of
Research Article The Effect of PCM Capsule Material on the Thermal Energy Storage System Performance
 ISRN Renewable Energy, Article ID 52928, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/214/52928 Research Article The Effect of PCM Capsule Material on the Thermal Energy Storage System Performance R. Meenakshi Reddy,
ISRN Renewable Energy, Article ID 52928, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/214/52928 Research Article The Effect of PCM Capsule Material on the Thermal Energy Storage System Performance R. Meenakshi Reddy,
Design Verification Program of SMART
 GENES4/ANP2003, Sep. 15-19, 2003, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 1047 Design Verification Program of SMART Si-Hwan Kim, Keung Koo Kim,* Ji Won Yeo, Moon Hee Chang and Sung Quun Zee Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute
GENES4/ANP2003, Sep. 15-19, 2003, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 1047 Design Verification Program of SMART Si-Hwan Kim, Keung Koo Kim,* Ji Won Yeo, Moon Hee Chang and Sung Quun Zee Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute
Profile LFR-56 HELIOS. KOREA Republic of. Molten lead-bismuth eutectic
 Profile LFR-56 HELIOS KOREA Republic of GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE FACILITY ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE FACILITY LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone,
Profile LFR-56 HELIOS KOREA Republic of GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE FACILITY ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE FACILITY LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone,
PSA Michael Powell, Roy Linthicum, Richard Haessler, Jeffrey Taylor
 PSA-2017 Crediting the Use of a Rapidly Deployable Mobile to Recover from and Core Damage Events Caused by a Failure of the Turbine Driven Auxiliary Feedwater Michael Powell, Roy Linthicum, Richard Haessler,
PSA-2017 Crediting the Use of a Rapidly Deployable Mobile to Recover from and Core Damage Events Caused by a Failure of the Turbine Driven Auxiliary Feedwater Michael Powell, Roy Linthicum, Richard Haessler,
Enhancement of CO2 Refrigeration Cycle Using an Ejector: 1D Analysis
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Enhancement of CO2 Refrigeration Cycle Using an Ejector: 1D Analysis Elias
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Enhancement of CO2 Refrigeration Cycle Using an Ejector: 1D Analysis Elias
NPP Simulators Workshop for Education - Passive PWR NPP & Simulator Overview
 NPP Simulators Workshop for Education - Passive PWR NPP & Simulator Overview Wilson Lam (wilson@cti-simulation.com) CTI Simulation International Corp. www.cti-simulation.com Sponsored by IAEA Modified
NPP Simulators Workshop for Education - Passive PWR NPP & Simulator Overview Wilson Lam (wilson@cti-simulation.com) CTI Simulation International Corp. www.cti-simulation.com Sponsored by IAEA Modified
Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector
 Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector 1 OBJECTIVE: Performance Study of Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector Operation with Variation in Mass Flow Rate and Level of Radiation INTRODUCTION: Solar water heater
Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector 1 OBJECTIVE: Performance Study of Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector Operation with Variation in Mass Flow Rate and Level of Radiation INTRODUCTION: Solar water heater
4.2 DEVELOPMENT OF FUEL TEST LOOP IN HANARO
 4.2 DEVELOPMENT OF FUEL TEST LOOP IN HANARO Sungho Ahn a, Jongmin Lee a, Suki Park a, Daeyoung Chi a, Bongsik Sim a, Chungyoung Lee a, Youngki Kim a and Kyehong Lee b a Research Reactor Engineering Division,
4.2 DEVELOPMENT OF FUEL TEST LOOP IN HANARO Sungho Ahn a, Jongmin Lee a, Suki Park a, Daeyoung Chi a, Bongsik Sim a, Chungyoung Lee a, Youngki Kim a and Kyehong Lee b a Research Reactor Engineering Division,
Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy
 SECTION 1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy Ed Haack Duke Energy 1-1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy By Ed Haack, Duke Power Company The PEPSE model for the Catawba Units have been
SECTION 1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy Ed Haack Duke Energy 1-1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy By Ed Haack, Duke Power Company The PEPSE model for the Catawba Units have been
Thermal Performances of U Shape Molten Salt Steam Generator
 Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Thermal Sciences 17, 1st ACTS March 26-, 17, Jeju Island, Korea Thermal Performances of U Shape Molten Salt Steam Generator Canming He, Jianfeng Lu*, Jing Ding *,
Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Thermal Sciences 17, 1st ACTS March 26-, 17, Jeju Island, Korea Thermal Performances of U Shape Molten Salt Steam Generator Canming He, Jianfeng Lu*, Jing Ding *,
Application of Passive Autocatalytic Recombiner (PAR) for BWR Plants in Japan
 FR02002 Application of Passive Autocatalytic Recombiner (PAR) for BWR Plants in Japan K. Kobayashi, Tokyo Electric Power Company -3 Uchisaiwai-cho -Chôme Chiyoda-ku Tokyo 00-00 Japan E-mail: T03035@Pmail.tepco.co.jp
FR02002 Application of Passive Autocatalytic Recombiner (PAR) for BWR Plants in Japan K. Kobayashi, Tokyo Electric Power Company -3 Uchisaiwai-cho -Chôme Chiyoda-ku Tokyo 00-00 Japan E-mail: T03035@Pmail.tepco.co.jp
The ESBWR an advanced Passive LWR
 1 IAEA PC-Based Simulators Workshop Politecnico di Milano, 3-14 October 2011 The ES an advanced Passive LWR Prof. George Yadigaroglu, em. ETH-Zurich and ASCOMP yadi@ethz.ch 2 Removal of decay heat from
1 IAEA PC-Based Simulators Workshop Politecnico di Milano, 3-14 October 2011 The ES an advanced Passive LWR Prof. George Yadigaroglu, em. ETH-Zurich and ASCOMP yadi@ethz.ch 2 Removal of decay heat from
Thermal and Stability Analyses on Supercritical Water-cooled Fast Reactor during Power-Raising Phase of Plant Startup
 Thermal and Stability Analyses on Supercritical Water-cooled Fast Reactor during Power-Raising Phase of Plant Startup Jiejin Cai, Yuki Ishiwatari, Satoshi Ikejiri and Yoshiaki Oka The University of Tokyo
Thermal and Stability Analyses on Supercritical Water-cooled Fast Reactor during Power-Raising Phase of Plant Startup Jiejin Cai, Yuki Ishiwatari, Satoshi Ikejiri and Yoshiaki Oka The University of Tokyo
Critical Issues Concerned with the Assessment of Passive System Reliability
 IAEA Technical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment for New Nuclear Power Plants Design Vienna, October 1-5 2012 Critical Issues Concerned with the Assessment of Passive System Reliability Luciano
IAEA Technical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment for New Nuclear Power Plants Design Vienna, October 1-5 2012 Critical Issues Concerned with the Assessment of Passive System Reliability Luciano
Analysis of the Presence of Vapor in Residual Heat Removal System in Modes 3/4 Loss-of-Coolant Accident Conditions using RELAP5
 4 th European Nuclear Young Generation Forum Prague, 17-22 May 2011 Analysis of the Presence of Vapor in Residual Heat Removal System in Modes 3/4 Loss-of-Coolant Accident Conditions using RELAP5 Kerim
4 th European Nuclear Young Generation Forum Prague, 17-22 May 2011 Analysis of the Presence of Vapor in Residual Heat Removal System in Modes 3/4 Loss-of-Coolant Accident Conditions using RELAP5 Kerim
Conceptual Design of Nuclear CCHP Using Absorption Cycle
 Conceptual Design of Nuclear CCHP Using Absorption Cycle International Conference on Opportunities and Challenges for Water Cooled Reactors in the 21 st Century Vienna, Austria, October 27-30, 2009 Gyunyoung
Conceptual Design of Nuclear CCHP Using Absorption Cycle International Conference on Opportunities and Challenges for Water Cooled Reactors in the 21 st Century Vienna, Austria, October 27-30, 2009 Gyunyoung
COOLING TOWER DESIGN FOR CENTRAL GENERATORS OF CUET, BANGLADESH. Mohammad Sharif Khan, Golam Mainuddin, Abu Sadat Mohammad Sayem, Nadeem Nafis
 Proceedings of the 4 th BSME-ASME International Conference on Thermal Engineering 7-9 December, 008, Dhaka, Bangladesh COOLING TOWER DESIGN FOR CENTRAL GENERATORS OF CUET, BANGLADESH. Mohammad Sharif Khan,
Proceedings of the 4 th BSME-ASME International Conference on Thermal Engineering 7-9 December, 008, Dhaka, Bangladesh COOLING TOWER DESIGN FOR CENTRAL GENERATORS OF CUET, BANGLADESH. Mohammad Sharif Khan,
Conceptual system design of non-nuclear grade IS process to be coupled with the HTTR
 Conceptual system design of non-nuclear grade IS process to be coupled with the HTTR N. Sakaba, H. Sato, H. Ohashi, T. Nishihara, K. Kunitomi Monday, 16 April 2007 IAEA-CN-152, Oarai, Japan Japan Atomic
Conceptual system design of non-nuclear grade IS process to be coupled with the HTTR N. Sakaba, H. Sato, H. Ohashi, T. Nishihara, K. Kunitomi Monday, 16 April 2007 IAEA-CN-152, Oarai, Japan Japan Atomic
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF A SCALED REACTOR CAVITY COOLING SYSTEM WITH AIR FOR THE VHTR
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF A SCALED REACTOR CAVITY COOLING SYSTEM WITH AIR FOR THE VHTR M. A. Muci 1, D. D. Lisowski 2, M. H. Anderson 3, and M. L. Corradini 3 1 : Duke Energy, 139 East 4 th Street
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF A SCALED REACTOR CAVITY COOLING SYSTEM WITH AIR FOR THE VHTR M. A. Muci 1, D. D. Lisowski 2, M. H. Anderson 3, and M. L. Corradini 3 1 : Duke Energy, 139 East 4 th Street
RELAP 5 ANALYSIS OF PACTEL PRIMARY-TO-SECONDARY LEAKAGE EXPERIMENT PSL-07
 Fifth International Seminar on Horizontal Steam Generators 22 March 21, Lappeenranta, Finland. 5 ANALYSIS OF PACTEL PRIMARY-TO-SECONDARY LEAKAGE EXPERIMENT PSL-7 József Bánáti Lappeenranta University of
Fifth International Seminar on Horizontal Steam Generators 22 March 21, Lappeenranta, Finland. 5 ANALYSIS OF PACTEL PRIMARY-TO-SECONDARY LEAKAGE EXPERIMENT PSL-7 József Bánáti Lappeenranta University of
Elena Dinca CNCAN Daniel Dupleac - UPB Ilie Prisecaru UPB. Politehnica University of Bucharest, Romania (UPB)
 RELAP/SCDAP Sensitivity Study on the Efficiency in Severe Core Degradation Prevention of Depressurization and Water Injection into Steam Generators following SBO at a CANDU-6 NPP National Commission for
RELAP/SCDAP Sensitivity Study on the Efficiency in Severe Core Degradation Prevention of Depressurization and Water Injection into Steam Generators following SBO at a CANDU-6 NPP National Commission for
Network Analysis of Turbine and Feedwater Systems of the Fugen Nuclear Power Plant
 Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology ISSN: 00-33 (Print) 88-48 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnst Network Analysis of Turbine and Feedwater Systems of the Fugen Nuclear
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology ISSN: 00-33 (Print) 88-48 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnst Network Analysis of Turbine and Feedwater Systems of the Fugen Nuclear
IAEA-TECDOC-1361 Assessment and management of ageing of major nuclear power plant components important to safety
 IAEA-TECDOC-1361 Assessment and management of ageing of major nuclear power plant components important to safety Primary piping in PWRs July 2003 The originating Section of this publication in the IAEA
IAEA-TECDOC-1361 Assessment and management of ageing of major nuclear power plant components important to safety Primary piping in PWRs July 2003 The originating Section of this publication in the IAEA
ACR Safety Systems Safety Support Systems Safety Assessment
 ACR Safety Systems Safety Support Systems Safety Assessment By Massimo Bonechi, Safety & Licensing Manager ACR Development Project Presented to US Nuclear Regulatory Commission Office of Nuclear Reactor
ACR Safety Systems Safety Support Systems Safety Assessment By Massimo Bonechi, Safety & Licensing Manager ACR Development Project Presented to US Nuclear Regulatory Commission Office of Nuclear Reactor
Technologies of HTR-PM Plant and its economic potential
 IAEA Technical Meeting on the Economic Analysis of HTGRs and SMRs 25-28 August 2015, Vienna, Austria Technologies of HTR-PM Plant and its economic potential Prof. Dr. Yujie Dong INET/Tsinghua University
IAEA Technical Meeting on the Economic Analysis of HTGRs and SMRs 25-28 August 2015, Vienna, Austria Technologies of HTR-PM Plant and its economic potential Prof. Dr. Yujie Dong INET/Tsinghua University
Scenarios of Heavy Beyond-Design-Basis Accidents in HTGRs N.G. Kodochigov, Yu.P. Sukharev
 Scenarios of Heavy Beyond-Design-Basis Accidents in HTGRs N.G. Kodochigov, Yu.P. Sukharev IAEA Technical Meeting on the Safety of High Temperature Gas Cooled Reactors in the Light of the Fukushima Daiichi
Scenarios of Heavy Beyond-Design-Basis Accidents in HTGRs N.G. Kodochigov, Yu.P. Sukharev IAEA Technical Meeting on the Safety of High Temperature Gas Cooled Reactors in the Light of the Fukushima Daiichi
RELAP5/MOD3.2 INVESTIGATION OF A VVER-440 STEAM GENERATOR HEADER COVER LIFTING
 Science and Technology Journal of BgNS, Vol. 8, 1, September 2003, ISSN 1310-8727 RELAP5/MOD3.2 INVESTIGATION OF A VVER-440 STEAM GENERATOR HEADER COVER LIFTING Pavlin P. Groudev, Rositsa V. Gencheva,
Science and Technology Journal of BgNS, Vol. 8, 1, September 2003, ISSN 1310-8727 RELAP5/MOD3.2 INVESTIGATION OF A VVER-440 STEAM GENERATOR HEADER COVER LIFTING Pavlin P. Groudev, Rositsa V. Gencheva,
Numerical Simulation of the Flue Gas Desulfurization in the Sieve Tray Tower
 52 China Steel Technical Report, No. Numerical 28, pp.52-57, Simulation (2015) of the Flue Gas Desulfurization in the Sieve Tray Tower Numerical Simulation of the Flue Gas Desulfurization in the Sieve
52 China Steel Technical Report, No. Numerical 28, pp.52-57, Simulation (2015) of the Flue Gas Desulfurization in the Sieve Tray Tower Numerical Simulation of the Flue Gas Desulfurization in the Sieve
Preliminary Lessons Learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Accident for Advanced Nuclear Power Plant Technology Development
 Preliminary Lessons Learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Accident for Advanced Nuclear Power Plant Technology Development A. Introduction The IAEA Report on Reactor and Spent Fuel Safety in the Light of
Preliminary Lessons Learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Accident for Advanced Nuclear Power Plant Technology Development A. Introduction The IAEA Report on Reactor and Spent Fuel Safety in the Light of
Westinghouse AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant
 Westinghouse Non-Proprietary Class 3 April 2011 Westinghouse AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant Coping with Station Blackout Westinghouse Non-Proprietary Class 3 April 2011 Westinghouse AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant
Westinghouse Non-Proprietary Class 3 April 2011 Westinghouse AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant Coping with Station Blackout Westinghouse Non-Proprietary Class 3 April 2011 Westinghouse AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant
Draft proposals for Test methods for close-coupled solar water heating systems - Reliability and safety
 IEA/SHC Task 57, Subtask B Draft proposals for new test procedures B4: Final Draft Draft proposals for Test methods for close-coupled solar water heating systems - Reliability and safety HE Zinian Beijing
IEA/SHC Task 57, Subtask B Draft proposals for new test procedures B4: Final Draft Draft proposals for Test methods for close-coupled solar water heating systems - Reliability and safety HE Zinian Beijing
Evaluation of Safety Improvement by Hybrid Heat Pipe/Control Rod using Level 1 PSA. Seok Bin Seo, In Cheol Bang*
 Evaluation of Safety Improvement by Hybrid Heat Pipe/Control Rod using Level 1 PSA Seok Bin Seo, In Cheol Bang* Department of Nuclear Engineering Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST)
Evaluation of Safety Improvement by Hybrid Heat Pipe/Control Rod using Level 1 PSA Seok Bin Seo, In Cheol Bang* Department of Nuclear Engineering Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST)
NATURAL CONVECTION IN SECONDARY SODIUM CIRCUIT OF FAST BREEDER TEST REACTOR
 International Journal on Design and Manufacturing Technologies, Vol. 5, No.1, January 2011 1 NATURAL CONVECTION IN SECONDARY SODIUM CIRCUIT OF FAST BREEDER TEST REACTOR Abstract Vaidyanathan G. 1, Kasinathan
International Journal on Design and Manufacturing Technologies, Vol. 5, No.1, January 2011 1 NATURAL CONVECTION IN SECONDARY SODIUM CIRCUIT OF FAST BREEDER TEST REACTOR Abstract Vaidyanathan G. 1, Kasinathan
Research Article Modelling of the Radiological Contamination of the RBMK-1500 Reactor Water Purification and Cooling System
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 14, Article ID 293158, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/293158 Research Article Modelling of the Radiological Contamination of the RBMK-15 Reactor
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 14, Article ID 293158, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/293158 Research Article Modelling of the Radiological Contamination of the RBMK-15 Reactor
START UP ANALYSIS OF A H2-O2 FIRED GAS TURBINE CYCLE
 START UP ANALYSIS OF A HO FIRED GAS TURBINE CYCLE T. Funatsu Toshiba Corporation Heavy Apparatus Engineering Laboratory, Suehirochou, Tsurumiku, Yokohama, Japan M. Fukuda, Y. Dohzono Toshiba Corporation
START UP ANALYSIS OF A HO FIRED GAS TURBINE CYCLE T. Funatsu Toshiba Corporation Heavy Apparatus Engineering Laboratory, Suehirochou, Tsurumiku, Yokohama, Japan M. Fukuda, Y. Dohzono Toshiba Corporation
Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics
 Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics 9-82 Air is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Brayton cycle that has a pressure ratio of 12, a compressor inlet temperature of 300 K, and a turbine inlet
Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics 9-82 Air is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Brayton cycle that has a pressure ratio of 12, a compressor inlet temperature of 300 K, and a turbine inlet
GAS COOLING HEAT TRANSFER AND PRESSURE DROP CHARATERICTICS OF CO 2 /OIL MIXTURE IN A MICROCHANNEL ABSTRACT
 GAS COOLING HEAT TRANSFER AND PRESSURE DROP CHARATERICTICS OF CO /OIL MIXTURE IN A MICROCHANNEL R. YUN, Y. HWANG*, AND R. RADERMACHER Center for Environmental Energy Engineering, Department of Mechanical
GAS COOLING HEAT TRANSFER AND PRESSURE DROP CHARATERICTICS OF CO /OIL MIXTURE IN A MICROCHANNEL R. YUN, Y. HWANG*, AND R. RADERMACHER Center for Environmental Energy Engineering, Department of Mechanical
LOCA analysis of high temperature reactor cooled and moderated by supercritical light water
 GENES4/ANP23, Sep. 15-19, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 116 LOCA analysis of high temperature reactor cooled and moderated by supercritical light water Yuki Ishiwatari 1*, Yoshiaki Oka 1 and Seiichi Koshizuka 1 1
GENES4/ANP23, Sep. 15-19, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 116 LOCA analysis of high temperature reactor cooled and moderated by supercritical light water Yuki Ishiwatari 1*, Yoshiaki Oka 1 and Seiichi Koshizuka 1 1
Secondary side Passive Residual Heat Removal System R&D and Engineering Applications. Liang Ren Nov. 2017
 Secondary side Passive Residual Heat Removal System R&D and Engineering Applications Liang Ren Nov. 2017 00.CGN? 01.What is SPRHR? 02. Why we need it? 03. How to achieve it? 04. What have we achieved?
Secondary side Passive Residual Heat Removal System R&D and Engineering Applications Liang Ren Nov. 2017 00.CGN? 01.What is SPRHR? 02. Why we need it? 03. How to achieve it? 04. What have we achieved?
Application of Technologies in CANDU Reactors to Prevent/Mitigate the Consequences of a Severe Accidents
 Application of Technologies in CANDU Reactors to Prevent/Mitigate the Consequences of a Severe Accidents Lovell Gilbert Section Manager/Technical Advisor, Reactor Safety Engineering Bruce Power IAEA International
Application of Technologies in CANDU Reactors to Prevent/Mitigate the Consequences of a Severe Accidents Lovell Gilbert Section Manager/Technical Advisor, Reactor Safety Engineering Bruce Power IAEA International
RESEARCH ON INTEGRATION OF VAPOR CYCLE/LIQUID-COOLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR HELICOPTERS
 RESEARCH ON INTEGRATION OF VAPOR CYCLE/LIQUID-COOLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR HELICOPTERS Hu Liang ECS Department, Nanjing Engineering Institute of Aircraft Systems, AVIC/ Aviation Key Laboratory of Science
RESEARCH ON INTEGRATION OF VAPOR CYCLE/LIQUID-COOLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR HELICOPTERS Hu Liang ECS Department, Nanjing Engineering Institute of Aircraft Systems, AVIC/ Aviation Key Laboratory of Science
Profile SFR-52 SWAT JAPAN. Japan Atomic Energy Agency, 4002 Narita, Oarai-machi, Ibaraki, Japan.
 Profile SFR-52 SWAT JAPAN GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE FACILITY ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE FACILITY LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone, email):
Profile SFR-52 SWAT JAPAN GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE FACILITY ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE FACILITY LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone, email):
CHAPTER 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION
 58 CHAPTER 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION 3.1 NEED FOR SIMULATION Simulation is the use of modeling to represent (but not replicate ) a system or process at an appropriate level of detail, and thereby help
58 CHAPTER 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION 3.1 NEED FOR SIMULATION Simulation is the use of modeling to represent (but not replicate ) a system or process at an appropriate level of detail, and thereby help
Small Modular Nuclear Reactor (SMR) Research and Development (R&D) and Deployment in China
 Small Modular Nuclear Reactor (SMR) Research and Development (R&D) and Deployment in China Danrong Song, Biao Quan Nuclear Power Institute of China, Chengdu, China songdr@gmail.com Abstract Developing
Small Modular Nuclear Reactor (SMR) Research and Development (R&D) and Deployment in China Danrong Song, Biao Quan Nuclear Power Institute of China, Chengdu, China songdr@gmail.com Abstract Developing
Fatigue Monitoring for Demonstrating
 Fatigue Monitoring for Demonstrating Fatigue Design Basis Compliance Timothy J. Griesbach Structural Integrity Associates IAEA 2 nd International Symposium on Nuclear Power Plant Life Mgmt. 15-18 October,
Fatigue Monitoring for Demonstrating Fatigue Design Basis Compliance Timothy J. Griesbach Structural Integrity Associates IAEA 2 nd International Symposium on Nuclear Power Plant Life Mgmt. 15-18 October,
CHAPTER 3 HEURISTIC APPROACH TO MODELING THE BOILER FURNACE
 CHAPTER 3 HEURISTIC APPROACH TO MODELING THE BOILER FURNACE 3.1 INTRODUCTION Modeling and simulation of boiler systems has been an interesting subject of investigation for many years. Mathematical modeling
CHAPTER 3 HEURISTIC APPROACH TO MODELING THE BOILER FURNACE 3.1 INTRODUCTION Modeling and simulation of boiler systems has been an interesting subject of investigation for many years. Mathematical modeling
Research and Development Program on HTTR Hydrogen Production System
 GENES4/ANP2003, Sep. 15-19, 2003, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 1062 Research and Development Program on HTTR Hydrogen Production System Yoshiyuki INAGAKI, Tetsuo NISHIHARA, Tetsuaki TAKEDA, Koji HAYASHI, Yoshitomo
GENES4/ANP2003, Sep. 15-19, 2003, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 1062 Research and Development Program on HTTR Hydrogen Production System Yoshiyuki INAGAKI, Tetsuo NISHIHARA, Tetsuaki TAKEDA, Koji HAYASHI, Yoshitomo
Numerical Analysis of Two-phase Flow and Heat Transfer in External Cyclic Purification Hot-dip Galvanizing Bath
 2nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2016) Numerical Analysis of Two-phase Flow and Heat Transfer in External Cyclic Purification Hot-dip Galvanizing Bath Hui SUN1,
2nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2016) Numerical Analysis of Two-phase Flow and Heat Transfer in External Cyclic Purification Hot-dip Galvanizing Bath Hui SUN1,
Chapters 5, 6, and 7. Use T 0 = 20 C and p 0 = 100 kpa and constant specific heats unless otherwise noted. Note also that 1 bar = 100 kpa.
 Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Use T 0 = 20 C and p 0 = 100 kpa and constant specific heats unless otherwise noted. Note also that 1 bar = 100 kpa. 5-1. Steam enters a steady-flow device at 16 MPa and 560 C with
Chapters 5, 6, and 7 Use T 0 = 20 C and p 0 = 100 kpa and constant specific heats unless otherwise noted. Note also that 1 bar = 100 kpa. 5-1. Steam enters a steady-flow device at 16 MPa and 560 C with
AP1000 European 16. Technical Specifications Design Control Document
 16.3 Investment Protection 16.3.1 Investment Protection Short-term Availability Controls The importance of nonsafety-related systems, structures and components in the AP1000 has been evaluated. The evaluation
16.3 Investment Protection 16.3.1 Investment Protection Short-term Availability Controls The importance of nonsafety-related systems, structures and components in the AP1000 has been evaluated. The evaluation
Numerical Simulation on Effects of Electromagnetic Force on the Centrifugal Casting Process of High Speed Steel Roll
 Modeling and Numerical Simulation of Material Science, 2014, 4, 20-24 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/mnsms) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/mnsms.2014.41004 Numerical Simulation
Modeling and Numerical Simulation of Material Science, 2014, 4, 20-24 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/mnsms) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/mnsms.2014.41004 Numerical Simulation
Fatigue Strength Evaluation of Pressurizer Wall Structure in Pressurized Water Reactor
 International Conference on Nuclear Energy Technologies and Sciences (2015), Volume 2016 Conference Paper Fatigue Strength Evaluation of Pressurizer Wall Structure in Pressurized Water Reactor Roziq Himawan
International Conference on Nuclear Energy Technologies and Sciences (2015), Volume 2016 Conference Paper Fatigue Strength Evaluation of Pressurizer Wall Structure in Pressurized Water Reactor Roziq Himawan
PAPER-I (Conventional)
 1. a. PAPER-I (Conventional) 10 kg of pure ice at 10 ºC is separated from 6 kg of pure water at +10 O C in an adiabatic chamber using a thin adiabatic membrane. Upon rupture of the membrane, ice and water
1. a. PAPER-I (Conventional) 10 kg of pure ice at 10 ºC is separated from 6 kg of pure water at +10 O C in an adiabatic chamber using a thin adiabatic membrane. Upon rupture of the membrane, ice and water
AREN 2110: Thermodynamics Spring 2010 Homework 7: Due Friday, March 12, 6 PM
 AREN 2110: Thermodynamics Spring 2010 Homework 7: Due Friday, March 12, 6 PM 1. Answer the following by circling the BEST answer. 1) The boundary work associated with a constant volume process is always
AREN 2110: Thermodynamics Spring 2010 Homework 7: Due Friday, March 12, 6 PM 1. Answer the following by circling the BEST answer. 1) The boundary work associated with a constant volume process is always
Experimental Analyses on Parabolic Solar Collector at Various Operating Conditions
 Universal Journal of Mechanical Engineering 5(2): 25-34, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujme.2017.050201 http://www.hrpub.org Experimental Analyses on Parabolic Solar Collector at Various Operating Conditions Rajat
Universal Journal of Mechanical Engineering 5(2): 25-34, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujme.2017.050201 http://www.hrpub.org Experimental Analyses on Parabolic Solar Collector at Various Operating Conditions Rajat
Improvement of the Performance for an Absorption Refrigerating System with. Lithium bromide-water as Refrigerant by Increasing Absorption Pressure 1
 Improvement of the Performance for an Absorption Refrigerating System with Lithium bromide-water as Refrigerant by Increasing Absorption Pressure 1 Guozhen Xie Guogang Sheng Guang Li Shuyuan Pan Professor
Improvement of the Performance for an Absorption Refrigerating System with Lithium bromide-water as Refrigerant by Increasing Absorption Pressure 1 Guozhen Xie Guogang Sheng Guang Li Shuyuan Pan Professor
