Bargaining Power & its Determinants
|
|
|
- Willa Cross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bargaining Power & its Determinants Relative versus Total Bargaining Power and Determinants of Relative and Total Bargaining Power Santanu Sarkar XLRI Jamshedpur
2 Collective Bargaining Basics Bargaining Power Environment is particularly influential through the effects it exerts on the bargaining power held by labour & management. 2 aspects of bargaining power come into play, the total & relative power of labour & management Total power concerns the total profits (or economic rents) that are available to labour & management: greater is the total power, the more profit that are available for labour & management to divide up (Size of the Pie) integrative bargaining Relative power has to do with the relative strength of labour & management ability of either side to gain a larger share of a given amount of profit (Maximizing pay off) distributive bargaining
3 CB Basics Determinants of Bargaining Power Determinants of the total bargaining power of labour & management 1. Degree of competition facing the employer: competition faced from both domestic & international competitors few competitors greater profits & thus have more resources for labour & management to divide up (long horizon / greater pie) high industry concentration & monopolistic profit model leads to easier CB 2. The state of economy affect the level of demand (sales) & profits Interest of labour & management with regard to total power are in common as both sides prefer less competition & a strong economy Determinants of the relative bargaining power of labour & management 1. Union s waiting cost / default factor cost / failure cost: abilities to withdraw their labour, usually through a strike 2. Union s ability to sustain strike, working to rule, or blue flu [large scale absenteeism] (Waiting cost) strikes once undertaken are more likely to succeed the greater the costs of the strike to the employer 3. Employer s waiting cost / default factor cost / failure cost / resistance ability: ability to withstand a strike 4. SIMPLE MEASURE: amount of STRIKE LEVERAGE each party holds (decided by what costs a strike would impose on each party & what alternative income sources there are available to each party to offset any income losses induced by a strike BATNA )
4 Microeconomic influences on total bargaining power Competitive conditions exert on a firm Greater the market power of a firm (less competition / high industry concentration CR / HHI) greater will be the profits earned by the firm Greater profits, more resources for the parties to divide based on their relative power With regard to the total bargaining power, labour & management have common interests with both sides preferring that the firm posses market power Explains why unions join with management of a firm & push for government regulations that enhance the market power of a firm (restrictive trade / import policies, restricted FDI/FII in specific sectors to limit the competitions from across the border) Eg. United Steel Workers (US) joined with a number of steel companies to lobby the U.S. federal government to restrict & impose higher tariffs on the importation of foreign steel
5 Microeconomic influences on relative bargaining power Strike Leverage & Elasticity of Demand for Labour (Wage-employment Trade off) 1. STRIKE LEVERAGE a) Management s s strike leverage more the employer is willing & able to sustain a strike, more likely the workers will be to settle a strike before attaining all the union s goals i. Effects of a strike on production 1 st indicator of workers bargaining power is the degree to which the strike has impaired production / service (availability of labour substitutes: craft workers ahead of production workers in bargaining success of craft unions in US/Europe) ii. iii. Effects of a strike on sales if the halt in production does not lead to a reduction in sales (high inventories / availability of alternative production sites [depends largely on centralized bargaining / common union in all sites & inter/intra union solidarity]) Effects of a strike on profits if the halt in production & sales does not lead essentially to a serious decline in profits (substantial savings / alternative income sources can easily absorb the cost of strike) (high ongoing capital / interest expenses will have harder time withstanding a loss of income causes by a strike) Eg. (a) construction workers, can temporarily halt costly construction projects, have so much bargaining power Eg. (b) in contrast, firms facing a strike that also shuts down all the competitors operation have an easier time withstanding strikes because their lost sales & profits may be largely postponed rather than permanently forgone
6 b) Union s s strike leverage determined by the ability & willingness of the labour to stay out on strike i. Alternative sources of worker income workers that offer ample strike benefits can better afford to stay out on strike than can those in other unions (striking workers can readily find temporary / part-time work that supplements any union strike benefits role of law) (when they have accumulated substantial savings / assets) ii. Worker solidarity attitude of union members during strike (workers feelings of solidarity with one another influence whether picket lines will be honoured, & any pent-up frustrations will influence workers willingness to stay out on strike) strike being a highly emotional undertaking 2. WAGE-EMPLOYMENT EMPLOYMENT TRADE-OFF Strike leverage determines whether workers are able to press for a higher wage settlement / other more advantageous contractual provisions Eg. higher wages often bring cuts in employment & thus union may choose not to raise wages as much as they could Eg. Unionized apparel workers received only modest wage increases in their CB agreements in recent years because they feared that any higher wage payments would cause apparel firms to more aggressively shift production offshore or to outsource production domestically to non union plants than they would otherwise
7 WAGE-EMPLOYMENT EMPLOYMENT TRADE-OFF Marshall s s 4 basic conditions: why wage increase leads to large reductions in employment in one situation & to only small reductions in employment in another is explained by Marshall s (Alfred Marshall) conditions Marshall argued that unions are most powerful when the demand for labour is highly inelastic (when increase in wages will not result in significant reductions in employment in unionized sector) 4 conditions under which the demand for union labour would be inelastic: 1. When labour cannot be easily replaced in the production process by other workers / machines 2. When the demand for the final product is price inelastic (demand is not sensitive to changes in the price of the product) 3. When the supply of non-labour factors of production is price elastic 4. When ratio of labour costs : total costs (is small)
8 Marshall s s 4 basic conditions 1. Difficulty of replacing workers Unions can try to limit the ease with which management can introduce new tech. by raising the costs of substituting other factors of production for union labour (surely with dilemma since after some time such constrains on tech. change may back fire the labour with poor rate of productivity growth thereby limiting the long-run potential for wage increases) 2. Demand for product Workers face less of an employment decline from raising wages if the demand for the product produced by these workers is not sensitive to the price of the product (sensitivity elasticity of product demand) This condition is influenced by consumer preferences (willingness of consumers to substitute other products) Eg., in resistance to the foreign imports that become more attractive to domestic consumers unions do try to influence consumer actions through Buy Union campaigns stop buying Non-Union products [HUL Union s example]
9 Marshall s s 4 basic conditions 3. Supply of other inputs Responsiveness of the price of other inputs in the production process to the demand for those inputs (elasticity of supply of other factors of production) When an employer turns to alternative inputs to economize on union labour, unions will be more able to push up wages (with less fear of employment cutbacks) if the price of other inputs rises a lot as their use increases (more elasticity of the supply curve for alternative inputs, greater is union power) 4. Labor's share of total costs Union s power increases if labour costs represent only a small proportion of the total costs (importance of being unimportant) Employer is less likely to resist union pressure if a given wage increase affects only a very small proportion of the total cost of the product DO UNIONS CARE ABOUT THE WAGE-EMPLOYMENT TRADE-OFFS? Perhaps, No! Ross claims (1) political factors, & (2) orbits of coercive comparisons [making comparisons with the wages of other workers or unions to get leeway] are the factors which matter most
Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing
 Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. define marginal factor cost, marginal physical product of
Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. define marginal factor cost, marginal physical product of
Review Questions. Unions and Collective Bargaining. Choose the letter that represents the BEST response.
 192 Ehrenberg/Smith Modern Labor Economics: Theory and Public Policy, Tenth Edition Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. Unions and Collective Bargaining 1. Which of the
192 Ehrenberg/Smith Modern Labor Economics: Theory and Public Policy, Tenth Edition Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. Unions and Collective Bargaining 1. Which of the
Microeconomics. Use the graph below to answer question number 3
 More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
Microeconomics. Use the graph below to answer question number 3
 More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
Chapter 9: Labor Section 1
 Chapter 9: Labor Section 1 Key Terms labor force: all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed outsourcing: the practice of contracting with another company to do a specific job that would otherwise
Chapter 9: Labor Section 1 Key Terms labor force: all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed outsourcing: the practice of contracting with another company to do a specific job that would otherwise
OCR Economics A-level
 OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.2 Labour market issues and themes Notes The labour force and the working population The working age population is between the ages of 18 and
OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.2 Labour market issues and themes Notes The labour force and the working population The working age population is between the ages of 18 and
AP Microeconomics Review Sample Questions
 AP Microeconomics Review Sample Questions Sample Multiple-Choice Questions The following are examples of the kinds of multiple-choice questions found on the examination. The distribution of topics and
AP Microeconomics Review Sample Questions Sample Multiple-Choice Questions The following are examples of the kinds of multiple-choice questions found on the examination. The distribution of topics and
Answers To Chapter 13
 nswers To Chapter 13 Review Questions 1. nswer c. ote that bargaining often takes place simultaneously with a number of employers. The FL-CIO is largely a political action group. It is not involved directly
nswers To Chapter 13 Review Questions 1. nswer c. ote that bargaining often takes place simultaneously with a number of employers. The FL-CIO is largely a political action group. It is not involved directly
Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By
 Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By Break-even point : the point at which price equals the minimum of average total cost. Externalities : the spillover effects of production or consumption for which no
Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By Break-even point : the point at which price equals the minimum of average total cost. Externalities : the spillover effects of production or consumption for which no
Chapter 16 The Labor Market Effects of International Trade and Production Sharing
 Chapter 16 The Labor Market Effects of International Trade and Production Sharing Summary Freeing up resources so that they can be used more productively in other industries is the logic behind international
Chapter 16 The Labor Market Effects of International Trade and Production Sharing Summary Freeing up resources so that they can be used more productively in other industries is the logic behind international
ECON Chapter 5 - Labour Economics. Maggie Jones
 ECON 370 - Chapter 5 - Labour Economics Maggie Jones Demand for Labour in Competitive Labour Markets Demand for Labour in Competitive Labour Markets The principles that determine the demand for any factor
ECON 370 - Chapter 5 - Labour Economics Maggie Jones Demand for Labour in Competitive Labour Markets Demand for Labour in Competitive Labour Markets The principles that determine the demand for any factor
Chapter 21: 1/28/2014. Demand. Changes in Demand. Supply
 Demand Chapter 21: Demand and Supply Desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service Law of Demand Buy more at lower prices Buy less at higher prices Diminishing Marginal Utility satisfaction
Demand Chapter 21: Demand and Supply Desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service Law of Demand Buy more at lower prices Buy less at higher prices Diminishing Marginal Utility satisfaction
Lesson22: Trade under Monopolistic Competition
 International trade in the global economy 60 hours II Semester Luca Salvatici luca.salvatici@uniroma3.it Lesson22: Trade under Monopolistic Competition 1 Trade under Monopolistic Competition Assumptions
International trade in the global economy 60 hours II Semester Luca Salvatici luca.salvatici@uniroma3.it Lesson22: Trade under Monopolistic Competition 1 Trade under Monopolistic Competition Assumptions
Microeconomics. Use the Following Graph to Answer Question 3
 More Tutorial at www.dumblittledoctor.com Microeconomics 1. To an economist, a good is scarce when: *a. the amount of the good available is less than the amount that people want when the good's price equals
More Tutorial at www.dumblittledoctor.com Microeconomics 1. To an economist, a good is scarce when: *a. the amount of the good available is less than the amount that people want when the good's price equals
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 3: Government Microeconomic Intervention c) Labour market forces and government intervention Notes Demand for and supply of labour The labour market is a factor market. The
CIE Economics A-level Topic 3: Government Microeconomic Intervention c) Labour market forces and government intervention Notes Demand for and supply of labour The labour market is a factor market. The
Demand & Supply of Resources
 Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Mock Collective Bargaining Simulation
 Mock Collective Bargaining Simulation Mock Collective Bargaining Simulation Things are a little tense at the New Tech Plastic plant. New Tech makes plastic parts for toy makers all over the world. They
Mock Collective Bargaining Simulation Mock Collective Bargaining Simulation Things are a little tense at the New Tech Plastic plant. New Tech makes plastic parts for toy makers all over the world. They
Economics Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit Two DA
 Economics Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit Two DA If you were running a business, what would you do if you discovered that customers were suddenly willing to pay twice as much for your product? If you
Economics Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit Two DA If you were running a business, what would you do if you discovered that customers were suddenly willing to pay twice as much for your product? If you
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HW 2 - Micro - Machiorlatti MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is measured by the price elasticity of supply? 1) A) The price
HW 2 - Micro - Machiorlatti MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is measured by the price elasticity of supply? 1) A) The price
Lecture 10: THE AD-AS MODEL Reference: Chapter 8
 Lecture 10: THE AD-AS MODEL Reference: Chapter 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.What determines the shape of the aggregate demand (AD) curve and what factors shift the entire curve. 2.What determines the shape
Lecture 10: THE AD-AS MODEL Reference: Chapter 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.What determines the shape of the aggregate demand (AD) curve and what factors shift the entire curve. 2.What determines the shape
Producing Goods & Services
 Producing Goods & Services Supply is the quantities of a product or service that a firm is willing and able to make available for sale at all possible prices. The Law of Supply states that the quantity
Producing Goods & Services Supply is the quantities of a product or service that a firm is willing and able to make available for sale at all possible prices. The Law of Supply states that the quantity
UNEMPLOYMENT AND ITS NATURAL RATE
 15 UNEMPLOYMENT AND ITS NATURAL RATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: the data used to measure the amount of unemployment. how unemployment can result from minimum-wage
15 UNEMPLOYMENT AND ITS NATURAL RATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: the data used to measure the amount of unemployment. how unemployment can result from minimum-wage
Edexcel Economics AS-level
 Edexcel Economics AS-level Unit 1: Markets in Action Topic 5: Wage Determination in Labour Markets 5.1-5.2 The demand for and the supply of labour Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour
Edexcel Economics AS-level Unit 1: Markets in Action Topic 5: Wage Determination in Labour Markets 5.1-5.2 The demand for and the supply of labour Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour
The study of how people choose to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants is called
 Final Exam Review The study of how people choose to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants is called Economics The benefit gained from the use of a good or services is called The benefit gained
Final Exam Review The study of how people choose to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants is called Economics The benefit gained from the use of a good or services is called The benefit gained
Economics Unit 2. The United States Economic System
 Economics Unit 2 The United States Economic System Demand Objective 2.01: Illustrate how supply and demand affects prices. What is Demand? Demand: The desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or
Economics Unit 2 The United States Economic System Demand Objective 2.01: Illustrate how supply and demand affects prices. What is Demand? Demand: The desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or
Chapter 26 Answers to Short-Answer, Essays, and Problems
 Chapter 26 Answers to Short-Answer, Essays, and Problems 1. Why is there a need for an aggregate demand and aggregate supply model of the economy? Why can t the supply and demand model for a single product
Chapter 26 Answers to Short-Answer, Essays, and Problems 1. Why is there a need for an aggregate demand and aggregate supply model of the economy? Why can t the supply and demand model for a single product
Labor supply is the willingness and ability to work specific amounts of time at alternative wage rates in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
 Labor Unions Part I The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Labor Unions Part I The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Producing Goods & Services
 Producing Goods & Services Supply is the quantities of a product or service that a firm is willing and able to make available for sale at all possible prices. The Law of Supply states that the quantity
Producing Goods & Services Supply is the quantities of a product or service that a firm is willing and able to make available for sale at all possible prices. The Law of Supply states that the quantity
Microeconomics Exam Notes
 Microeconomics Exam Notes Opportunity Cost What you give up to get it Production Possibility Frontier Maximum attainable combination of two products (Concept of Opportunity Cost). Main Decision Makers:
Microeconomics Exam Notes Opportunity Cost What you give up to get it Production Possibility Frontier Maximum attainable combination of two products (Concept of Opportunity Cost). Main Decision Makers:
Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or on the back of the last page.
 Econ 101, Section 21, S10, Schroeter Final Exam, Special code = 2 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or on the back of the last page. 1. Which of
Econ 101, Section 21, S10, Schroeter Final Exam, Special code = 2 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or on the back of the last page. 1. Which of
Chapter 1: What is Economics? A. Economic questions arise because we face scarcity we all want more than we can get.
 Chapter 1: What is Economics? I. Definition of Economics A. Economic questions arise because we face scarcity we all want more than we can get. 1. Because we are unable to satisfy all of our wants, we
Chapter 1: What is Economics? I. Definition of Economics A. Economic questions arise because we face scarcity we all want more than we can get. 1. Because we are unable to satisfy all of our wants, we
Economics Challenge Online State Qualification Practice Test. 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from
 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
Chapter 9: Labor Section 3
 Chapter 9: Labor Section 3 Objectives 1. Describe why American workers have formed labor unions. 2. Summarize the history of the labor movement in the United States. 3. Analyze reasons for the decline
Chapter 9: Labor Section 3 Objectives 1. Describe why American workers have formed labor unions. 2. Summarize the history of the labor movement in the United States. 3. Analyze reasons for the decline
Student Manual Principles of Economics
 Student Manual Principles of Economics Beat The Market On Line: An Interactive Microeconomics Game. GoldSimulations www.goldsimulations.com Beat The Market : Student Manual Published by GoldSimulations
Student Manual Principles of Economics Beat The Market On Line: An Interactive Microeconomics Game. GoldSimulations www.goldsimulations.com Beat The Market : Student Manual Published by GoldSimulations
Labor Unions
 Labor Unions 11.05.2010 Labor Unions Def.: A labor union is an organization of workers, which through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labor contracts
Labor Unions 11.05.2010 Labor Unions Def.: A labor union is an organization of workers, which through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labor contracts
SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4
 SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market
SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market
Summary of the Papers
 Summary of the Papers THIS ISSUE CONTAINS papers presented December 9 and 10, 1994, at the ninth meeting of the Brookings Microeconomics Panel. The papers address topics in labor economics, industrial
Summary of the Papers THIS ISSUE CONTAINS papers presented December 9 and 10, 1994, at the ninth meeting of the Brookings Microeconomics Panel. The papers address topics in labor economics, industrial
Collective Bargaining
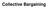 Collective Bargaining Categories for Bargaining Issues Mandatory Permissive Prohibited Direct and immediate effect on jobs or labor costs tests Do NOT require a response or bargaining by other party* Demands
Collective Bargaining Categories for Bargaining Issues Mandatory Permissive Prohibited Direct and immediate effect on jobs or labor costs tests Do NOT require a response or bargaining by other party* Demands
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even April 20, 2016 FORM 1 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number listed
YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even April 20, 2016 FORM 1 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number listed
INTRODUCTORY ECONOMICS
 4265 FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Preliminary Examination for Philosophy, Politics and Economics Preliminary Examination for Economics and Management Preliminary Examination for History and Economics INTRODUCTORY
4265 FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Preliminary Examination for Philosophy, Politics and Economics Preliminary Examination for Economics and Management Preliminary Examination for History and Economics INTRODUCTORY
Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power
 29 Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. outline the essential history of the labor union movement; 2. discuss the current
29 Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. outline the essential history of the labor union movement; 2. discuss the current
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 Name Seat Assignment ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 17, 2009 FORM 3. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
Name Seat Assignment ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 17, 2009 FORM 3. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
2. Why is a firm in a purely competitive labor market a wage taker? What would happen if it decided to pay less than the going market wage rate?
 Chapter Wage Determination QUESTIONS. Explain why the general level of wages is high in the United States and other industrially advanced countries. What is the single most important factor underlying
Chapter Wage Determination QUESTIONS. Explain why the general level of wages is high in the United States and other industrially advanced countries. What is the single most important factor underlying
International Business 9e
 International Business 9e By Charles W.L. Hill McGraw Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 13 The Strategy of International Business What Is Strategy?
International Business 9e By Charles W.L. Hill McGraw Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 13 The Strategy of International Business What Is Strategy?
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 Name Seat Assignment ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 17, 2009 FORM 4. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
Name Seat Assignment ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 17, 2009 FORM 4. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 Name Seat Assignment ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 17, 2009 FORM 1. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
Name Seat Assignment ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 17, 2009 FORM 1. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
Microeconomics. More Tutorial at
 Microeconomics 1. Suppose a firm in a perfectly competitive market produces and sells 8 units of output and has a marginal revenue of $8.00. What would be the firm s total revenue if it instead produced
Microeconomics 1. Suppose a firm in a perfectly competitive market produces and sells 8 units of output and has a marginal revenue of $8.00. What would be the firm s total revenue if it instead produced
EC1000 MICROECONOMICS ' MOCK EXAM
 EC1000 MICROECONOMICS ' MOCK EXAM Time Allowed Two Hours (2 Hours) Instructions to candidates This paper is in two sections. Students should attempt ALL the questions in both Sections The maximum mark
EC1000 MICROECONOMICS ' MOCK EXAM Time Allowed Two Hours (2 Hours) Instructions to candidates This paper is in two sections. Students should attempt ALL the questions in both Sections The maximum mark
OCR Economics A-level
 OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.1 Wage determination Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour markets The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour
OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.1 Wage determination Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour markets The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour
Learning Objectives. The Labor Relations Framework. The Labor Relations Framework. Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage
 Handout 6-1 Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage Chapter 14 Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe
Handout 6-1 Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage Chapter 14 Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe
Chapter 13 Unions and the Labor Market
 Chapter 13 nions and the Labor Market ummary Chapter 12 introduced an objective framework for analyzing the earnings differences that accompany gender, race, and ethnicity. This framework was then used
Chapter 13 nions and the Labor Market ummary Chapter 12 introduced an objective framework for analyzing the earnings differences that accompany gender, race, and ethnicity. This framework was then used
Chapter 5: Supply Section 1
 Chapter 5: Supply Section 1 Key Terms supply: the amount of goods available law of supply: producers offer more of a good as its price increases and less as its price falls quantity supplied: the amount
Chapter 5: Supply Section 1 Key Terms supply: the amount of goods available law of supply: producers offer more of a good as its price increases and less as its price falls quantity supplied: the amount
DOWNLOAD PDF JOB SEARCH IN A DYNAMIC ECONOMY
 Chapter 1 : Job Search General Dynamics JOB SEARCH IN A DYNAMIC ECONOMY The random variable N, the number of offers until R is exceeded, has a geometric distribution with parameter p = 1 - F(R) and expected
Chapter 1 : Job Search General Dynamics JOB SEARCH IN A DYNAMIC ECONOMY The random variable N, the number of offers until R is exceeded, has a geometric distribution with parameter p = 1 - F(R) and expected
Topic 3.1b Long-Run Labour Demand. Professor H.J. Schuetze Economics 370
 Topic 3.1b Long-Run Labour Demand Professor H.J. Schuetze Economics 370 Long-Run Labour Demand In the long-run the firm can now vary both inputs and. Typically the firms production and employment decisions
Topic 3.1b Long-Run Labour Demand Professor H.J. Schuetze Economics 370 Long-Run Labour Demand In the long-run the firm can now vary both inputs and. Typically the firms production and employment decisions
causing MARGINAL PRODUCT OF LABOR to fall beyond some point. iv. PRODUCT PRICE : Because this is a competitive market, the PRODUCT PRICE = MARKET
 WAGE DETERMINATION I. A FOCUS ON LABOR a. The basic principles for labor also apply to other factors of production b. About 70% of all income in the U.S. flows to households in the form of wages and salaries.
WAGE DETERMINATION I. A FOCUS ON LABOR a. The basic principles for labor also apply to other factors of production b. About 70% of all income in the U.S. flows to households in the form of wages and salaries.
Homework 2 Answer Key
 Econ 226 Principles of Microeconomics Fall, 24 Dr. Kathryn Wilson Due Date: Tuesday, September 28 th Homework 2 Answer Key 1. When the of movie admissions increases from $7 to $8, the demanded falls from
Econ 226 Principles of Microeconomics Fall, 24 Dr. Kathryn Wilson Due Date: Tuesday, September 28 th Homework 2 Answer Key 1. When the of movie admissions increases from $7 to $8, the demanded falls from
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ECONOMICS 9708/22 Paper 2 Data Response and Essay MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ECONOMICS 9708/22 Paper 2 Data Response and Essay MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 2281 ECONOMICS
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 2281 ECONOMICS 2281/23 Paper 2 (Structured Questions), maximum raw mark 90 This mark scheme
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 2281 ECONOMICS 2281/23 Paper 2 (Structured Questions), maximum raw mark 90 This mark scheme
At the end of chapter 6, you will be able to:
 1 How to Study for Chapter 6 Supply and Equilibrium Chapter 6 introduces the factors that will affect the supply of a product, the price elasticity of supply, and the concept of equilibrium price and equilibrium
1 How to Study for Chapter 6 Supply and Equilibrium Chapter 6 introduces the factors that will affect the supply of a product, the price elasticity of supply, and the concept of equilibrium price and equilibrium
COMMON LABOR TERMS. Arbitration A way of settling disputes by calling in an impartial third party whose decision is final and binding on both parties.
 COMMON LABOR TERMS Agency Shop A union security clause providing that an employee in the bargaining unit refusing to join the union must pay a service fee to the union equal to union dues. Arbitration
COMMON LABOR TERMS Agency Shop A union security clause providing that an employee in the bargaining unit refusing to join the union must pay a service fee to the union equal to union dues. Arbitration
UNDERSTANDING OUR CONTRACT
 UNDERSTANDING OUR CONTRACT Total Time 1 hour Learning Goals l Learn more about what s in our contract. l Practice finding specific language in our contract. l Discuss collective bargaining and the factors
UNDERSTANDING OUR CONTRACT Total Time 1 hour Learning Goals l Learn more about what s in our contract. l Practice finding specific language in our contract. l Discuss collective bargaining and the factors
Labor Unions: Membership, Wages, Competition, and Performance in the Private and Public Sectors
 Labor Unions: Membership, Wages, Competition, and Performance in the Private and Public Sectors Barry Hirsch Economics 8220 Human Resources & Labor Markets April 2013 0 1. The labor demand curve D L as
Labor Unions: Membership, Wages, Competition, and Performance in the Private and Public Sectors Barry Hirsch Economics 8220 Human Resources & Labor Markets April 2013 0 1. The labor demand curve D L as
To produce more beach balls, you must give up ever increasing quantities of ice cream cones.
 Unit 01: Basic Concepts (Macro/Micro) Scarcity The Economic Problem: Unlimited wants, limited economic resources Factors of Production: -Land -Labor -Capital -Entrepreneurship Big 3 Questions: -What to
Unit 01: Basic Concepts (Macro/Micro) Scarcity The Economic Problem: Unlimited wants, limited economic resources Factors of Production: -Land -Labor -Capital -Entrepreneurship Big 3 Questions: -What to
1.3. Levels and Rates of Change Levels: example, wages and income versus Rates: example, inflation and growth Example: Box 1.3
 1 Chapter 1 1.1. Scarcity, Choice, Opportunity Cost Definition of Economics: Resources versus Wants Wants: more and better unlimited Versus Needs: essential limited Versus Demand: ability to pay + want
1 Chapter 1 1.1. Scarcity, Choice, Opportunity Cost Definition of Economics: Resources versus Wants Wants: more and better unlimited Versus Needs: essential limited Versus Demand: ability to pay + want
3.5.3 Wage determination in competitive and non-competitive markets
 3.5.3 Wage determination in competitive and non-competitive markets Labour market equilibrium: The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour is determined by those who want to be employed
3.5.3 Wage determination in competitive and non-competitive markets Labour market equilibrium: The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour is determined by those who want to be employed
5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market
 Summary - Chapter 5 Labour Markets and Unemployment 5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market 5.2.1 Labour Supply and the Consumption Leisure Trade-off - The consumption leisure trade-off is the fundamental
Summary - Chapter 5 Labour Markets and Unemployment 5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market 5.2.1 Labour Supply and the Consumption Leisure Trade-off - The consumption leisure trade-off is the fundamental
Professor Christina Romer SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO PROBLEM SET 4
 Economics 2 Spring 2018 rofessor Christina Romer rofessor David Romer SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO ROBLEM SET 4 1.a. If the government increases the number of H-1B visas, this will increase the number of highskilled
Economics 2 Spring 2018 rofessor Christina Romer rofessor David Romer SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO ROBLEM SET 4 1.a. If the government increases the number of H-1B visas, this will increase the number of highskilled
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 YOUR NAME (please print) ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 6, 2007 FORM 3. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
YOUR NAME (please print) ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION November 6, 2007 FORM 3. Directions 1. FILL IN YOUR SCANTRON WITH YOUR UNIQUE ID AND THE FORM NUMBER LISTED ON THIS
Name: Class: Date: 2. Patents, quotas, tariffs, and government licensing can all create barriers to entry into oligopoly industries. a.
 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Import tariffs in the United States are likely to reduce U.S. exports, both because of the resulting decrease in foreign earnings of dollars from exports
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Import tariffs in the United States are likely to reduce U.S. exports, both because of the resulting decrease in foreign earnings of dollars from exports
Microeconomics: MIE1102
 TEXT CHAPTERS TOPICS 1, 2 ECONOMICS, ECONOMIC SYSTEMS, MARKET ECONOMY 3 DEMAND AND SUPPLY. MARKET EQUILIBRIUM 4 ELASTICITY OF DEMAND AND SUPPLY 5 DEMAND & CONSUMER BEHAVIOR 6 PRODUCTION FUNCTION 7 COSTS
TEXT CHAPTERS TOPICS 1, 2 ECONOMICS, ECONOMIC SYSTEMS, MARKET ECONOMY 3 DEMAND AND SUPPLY. MARKET EQUILIBRIUM 4 ELASTICITY OF DEMAND AND SUPPLY 5 DEMAND & CONSUMER BEHAVIOR 6 PRODUCTION FUNCTION 7 COSTS
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
 INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA EXAMINATIONS 2 nd November 2015 Subject CT7 Business Economics Time allowed: Three Hours (10.30 to 13.30 Hrs.) Total Marks: 100 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES 1. Please
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA EXAMINATIONS 2 nd November 2015 Subject CT7 Business Economics Time allowed: Three Hours (10.30 to 13.30 Hrs.) Total Marks: 100 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES 1. Please
Midterm Exam Solution Sketch
 University of California, Santa Cruz Economics 1 Winter 2002 Professor Kletzer The exam has a total of 63 points. Midterm Exam Solution Sketch Part I. True/False/Uncertain and Explain. 5 points each. (Your
University of California, Santa Cruz Economics 1 Winter 2002 Professor Kletzer The exam has a total of 63 points. Midterm Exam Solution Sketch Part I. True/False/Uncertain and Explain. 5 points each. (Your
2007 NATIONAL ECONOMICS CHALLENGE NCEE/Goldman Sachs Foundation
 2007 NATIONAL ECONOMICS CHALLENGE NCEE/Goldman Sachs Foundation National Round I: Microeconomics David Ricardo Division 1. If your income tax liability is $15,000 and your income is $60,000, your A. average
2007 NATIONAL ECONOMICS CHALLENGE NCEE/Goldman Sachs Foundation National Round I: Microeconomics David Ricardo Division 1. If your income tax liability is $15,000 and your income is $60,000, your A. average
2.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 2.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand (AD): the total spending on all goods and services in an economy at a given price level over a period of time. The macroeconomic concept of aggregate
2.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand (AD): the total spending on all goods and services in an economy at a given price level over a period of time. The macroeconomic concept of aggregate
Competitive markets. Microéconomie, chapter 9. Solvay Business School Université Libre de Bruxelles
 Competitive markets Microéconomie, chapter 9 Solvay Business School Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 List of subjects Evaluation of public policies Efficiency of competitive markets Minimum prices Support
Competitive markets Microéconomie, chapter 9 Solvay Business School Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 List of subjects Evaluation of public policies Efficiency of competitive markets Minimum prices Support
ORGANIZING PRODUCTION
 ORGANIZING PRODUCTION M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1 Objectives After studying this lecture, you will able to Explain what a firm is and describe the economic problems that all firms face Distinguish
ORGANIZING PRODUCTION M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1 Objectives After studying this lecture, you will able to Explain what a firm is and describe the economic problems that all firms face Distinguish
Lecture 5. Unemployment and its natural rate Prof. Samuel Moon Jung 1
 Lecture 5. Unemployment and its natural rate Prof. Samuel Moon Jung 1 Main concepts: Identifying unemployment, job search, minimum-wage laws, unions and collective bargaining, the theory of efficiency
Lecture 5. Unemployment and its natural rate Prof. Samuel Moon Jung 1 Main concepts: Identifying unemployment, job search, minimum-wage laws, unions and collective bargaining, the theory of efficiency
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA BUSINESS FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 181: INTRODUCTORY ECONOMICS FINAL EXAMINATION: AUGUST 2003 SESSION
 ECO 181 (F) / Page 1 of 15 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA BUSINESS FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 181: INTRODUCTORY ECONOMICS FINAL EXAMINATION: AUGUST 2003 SESSION SECTION A There are SIXTY questions on this paper.
ECO 181 (F) / Page 1 of 15 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA BUSINESS FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 181: INTRODUCTORY ECONOMICS FINAL EXAMINATION: AUGUST 2003 SESSION SECTION A There are SIXTY questions on this paper.
ECON 1101 Microeconomics Notes. Table of Contents
 ECON 1101 Microeconomics Notes Table of Contents Comparative Advantage and the Reason for Trade... 2 Perfectly Competitive Markets... 3 Demand... 6 Special Lecture... Error! Bookmark not defined. Demand
ECON 1101 Microeconomics Notes Table of Contents Comparative Advantage and the Reason for Trade... 2 Perfectly Competitive Markets... 3 Demand... 6 Special Lecture... Error! Bookmark not defined. Demand
NAME: INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMIC THEORY FALL 2006 ECONOMICS 300/012 Final Exam December 8, 2006
 NAME: INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMIC THEORY FALL 2006 ECONOMICS 300/012 Section I: Multiple Choice (4 points each) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The slope
NAME: INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMIC THEORY FALL 2006 ECONOMICS 300/012 Section I: Multiple Choice (4 points each) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The slope
Principles of Marketing Seventeenth Edition
 Principles of Marketing Seventeenth Edition Chapter 10 Pricing: Understanding and Capturing Customer Value Learning Objectives 10-1 Answer the question What is a price? and discuss the importance of pricing
Principles of Marketing Seventeenth Edition Chapter 10 Pricing: Understanding and Capturing Customer Value Learning Objectives 10-1 Answer the question What is a price? and discuss the importance of pricing
Crafting your business model
 Cambridge Judge Business School Crafting your business model Simon Stockley Senior Teaching Faculty in Entrepreneurship What is a Business Model? A business model explains how an organisation creates,
Cambridge Judge Business School Crafting your business model Simon Stockley Senior Teaching Faculty in Entrepreneurship What is a Business Model? A business model explains how an organisation creates,
BA5101 ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR BUSINESS MBA/IYear/ I Semester 2 Marks Questions & Answers
 BA5101 ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR BUSINESS MBA/IYear/ I Semester 2 Marks Questions & Answers 1. Define consumer behavior Consumer behavior is the study of when, why, how, and where people do or do not buy a
BA5101 ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR BUSINESS MBA/IYear/ I Semester 2 Marks Questions & Answers 1. Define consumer behavior Consumer behavior is the study of when, why, how, and where people do or do not buy a
1. The Heckscher Olin model emphasizes as the source of comparative advantage.
 Study Questions for Week 3 1. The Heckscher Olin model emphasizes as the source of comparative advantage. 2. Examine table 3.2. According to the data in this table, who would have a comparative advantage
Study Questions for Week 3 1. The Heckscher Olin model emphasizes as the source of comparative advantage. 2. Examine table 3.2. According to the data in this table, who would have a comparative advantage
UNEMPLOYMENT WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: LEARNING OBJECTIVES: CONTEXT AND PURPOSE:
 28 UNEMPLOYMENT WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: The Bureau of Labor Statistics definitions of employed, unemployed, and not in the labor force have been clarified. There is a new FYI box on Who Earns
28 UNEMPLOYMENT WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: The Bureau of Labor Statistics definitions of employed, unemployed, and not in the labor force have been clarified. There is a new FYI box on Who Earns
Taxation by another name
 Government Intervention as Implicit Taxation Taxation by another name 7-4 Control Government intervention in the form of price controls can be viewed as a combination tax and subsidy. A price ceiling is
Government Intervention as Implicit Taxation Taxation by another name 7-4 Control Government intervention in the form of price controls can be viewed as a combination tax and subsidy. A price ceiling is
CONTENTS. Introduction to the Series. 1 Introduction to Economics 5 2 Competitive Markets, Demand and Supply Elasticities 37
 CONTENTS Introduction to the Series iv 1 Introduction to Economics 5 2 Competitive Markets, Demand and Supply 17 3 Elasticities 37 4 Government Intervention in Markets 44 5 Market Failure 53 6 Costs of
CONTENTS Introduction to the Series iv 1 Introduction to Economics 5 2 Competitive Markets, Demand and Supply 17 3 Elasticities 37 4 Government Intervention in Markets 44 5 Market Failure 53 6 Costs of
Employer/employee Relations Trade Unions and ACAS
 W J E C B U S I N E S S S T U D I E S A L E V E L R E S O U R C E S. 2009 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2012 Page 1 Employer/employee Relations Trade Unions and ACAS Specification requirement Changing working practices
W J E C B U S I N E S S S T U D I E S A L E V E L R E S O U R C E S. 2009 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2012 Page 1 Employer/employee Relations Trade Unions and ACAS Specification requirement Changing working practices
ECON 101 MIDTERM 1 REVIEW SESSION SOLUTIONS (WINTER 2015) BY BENJI HUANG
 ECON 101 MIDTERM 1 REVIEW SESSION SOLUTIONS (WINTER 2015) BY BENJI HUANG TABLE OF CONTENT I. CHAPTER 1: WHAT IS ECONOMICS II. CHAPTER 2: THE ECONOMIC PROBLEM III. CHAPTER 3: DEMAND AND SUPPLY IV. CHAPTER
ECON 101 MIDTERM 1 REVIEW SESSION SOLUTIONS (WINTER 2015) BY BENJI HUANG TABLE OF CONTENT I. CHAPTER 1: WHAT IS ECONOMICS II. CHAPTER 2: THE ECONOMIC PROBLEM III. CHAPTER 3: DEMAND AND SUPPLY IV. CHAPTER
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY
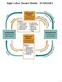 Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Monopoly. The single seller or firm referred to as a monopolist or monopolistic firm. Characteristics of a monopolistic industry
 Monopoly Monopoly: a market structure in which there is only one seller of a good or service that has no close substitutes and entry to the market is completely blocked. The single seller or firm referred
Monopoly Monopoly: a market structure in which there is only one seller of a good or service that has no close substitutes and entry to the market is completely blocked. The single seller or firm referred
Chapter 17: Labor Markets
 Chapter 17: Labor Markets Econ 102: Introduction to Microeconomics 1 1.1 Goals of this class Goals of this class Learn how employment and wages are determined in equilibrium. Learn what can shift labor
Chapter 17: Labor Markets Econ 102: Introduction to Microeconomics 1 1.1 Goals of this class Goals of this class Learn how employment and wages are determined in equilibrium. Learn what can shift labor
 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 01:24:42 PM ) Total Marks: 1 A person with a diminishing marginal utility of income: Will be risk averse. Will be risk neutral. Will be risk loving. Cannot decide without
Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 01:24:42 PM ) Total Marks: 1 A person with a diminishing marginal utility of income: Will be risk averse. Will be risk neutral. Will be risk loving. Cannot decide without
Chapter 1- Introduction
 Chapter 1- Introduction A SIMPLE ECONOMY Central PROBLEMS OF AN ECONOMY: scarcity of resources problem of choice Every society has to decide on how to use its scarce resources. Production, exchange and
Chapter 1- Introduction A SIMPLE ECONOMY Central PROBLEMS OF AN ECONOMY: scarcity of resources problem of choice Every society has to decide on how to use its scarce resources. Production, exchange and
Homework 4 Economics
 Homework 4 Economics 501.01 Manisha Goel Due: Tuesday, March 1, 011 (beginning of class). Draw and label all graphs clearly. Show all work. Explain. Question 1. Governments often regulate the price of
Homework 4 Economics 501.01 Manisha Goel Due: Tuesday, March 1, 011 (beginning of class). Draw and label all graphs clearly. Show all work. Explain. Question 1. Governments often regulate the price of
Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 6: Elasticity Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions 1. ANSWER: d. ceiling. 2. ANSWER: a. a shortage, which cannot be eliminated through market adjustment. 3. ANSWER: b. the equilibrium price is below
Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions 1. ANSWER: d. ceiling. 2. ANSWER: a. a shortage, which cannot be eliminated through market adjustment. 3. ANSWER: b. the equilibrium price is below
Week One What is economics? Chapter 1
 Week One What is economics? Chapter 1 Economics: is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments, and entire societies make as they cope with scarcity and the incentives
Week One What is economics? Chapter 1 Economics: is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments, and entire societies make as they cope with scarcity and the incentives
CHAPTER 15 MANAGING INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS
 CHAPTER 15 MANAGING INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Identify the elements that are important to consider when formulating production strategies. 2. Identify key considerations when acquiring
CHAPTER 15 MANAGING INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Identify the elements that are important to consider when formulating production strategies. 2. Identify key considerations when acquiring
Unit 4 Labor and Careers
 Unit 4 Labor and Careers - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1. Describe our Labor force 2. Learning Effect 3. Equilibrium wage 4. Labor pool 5. White Collar 6. Blue Collar 7. Skilled
Unit 4 Labor and Careers - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1. Describe our Labor force 2. Learning Effect 3. Equilibrium wage 4. Labor pool 5. White Collar 6. Blue Collar 7. Skilled
What Is Covered. Econ 2 Final Exam. The Big Concepts. An Outline of Topics Covered In Econ 2
 What Is Covered Econ 2 Final Exam Where: Price Center Theatre Date: Friday March 24 Time: 8:00-11:00 a.m. Final is cumulative Heavier emphasis on chapters (14&15) not covered on earlier midterms Format:
What Is Covered Econ 2 Final Exam Where: Price Center Theatre Date: Friday March 24 Time: 8:00-11:00 a.m. Final is cumulative Heavier emphasis on chapters (14&15) not covered on earlier midterms Format:
