Survey of Organizational Excellence. Data Summary Report. Texas A&M International University
|
|
|
- Lawrence Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Survey of Organizational Excellence Data Summary Report Prepared Especially For Texas A&M International University ( 761 )
2 Executive Summary Survey of Organizational Excellence Table of Contents The Survey 1 Response Rates 2 Dimension Analysis 3 Construct Analysis 4 Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern 5 Organizational Change: Performance Over Time 11 Areas of Most and Least Change 12 Demographics 14 Race/Ethnic Identification 14 Age 14 Gender 14 Employee Retention 15 Promotion 15 Merit Increase 15 Special Items 16 Your Next Steps A1 Rolling the Data Back A3 Preparing the Strategic Plan A7 Preparing for the Governor's Conference A8 Follow up to the Governor's Conference A8 The University of Texas at Austin School of Social Work soe@uts.cc.utexas.edu 1925 San Jacinto Blvd Phone (512) Austin, Texas Fax (512)
3 Executive Summary Survey of Organizational Excellence Survey of Organizational Excellence The Survey Organizational improvement may generally be directed in one or more of the five Dimensions. This Summary will provide a general description of the areas of strength and areas of concern of the organization based upon the responses received from the Survey. Among the important factors to consider are how many people responded from the organization, how representative they are of the total organization as well as the information that is provided about the organization's perceived qualities. As organizations use the Survey they enhance the ability of all members to participate in thinking about how the organization functions and what can be done to improve the organization. Such a process improves both the openness and responsibility of all the members of the organization and moves it toward being a learning organization. The process of thinking about organizational properties and working jointly to improve them builds organizational capital. Organizational capital refers to those norms and patterns of interaction that develop as people have experience in an organization. Organizations that have high levels of capital are organizations where there is substantial trust among members and a strong sense of mission and shared responsibility. Through building organizational capital, people's sense of loyalty and dedication increases, as does the general ability of the organization to improve, focus upon key issues and provide needed innovation and responsiveness to the environment. Please read this Summary with a view toward looking for ways to build upon organizational strengths and detecting areas that need improvement. Survey Constructs Dimension I Work Group Dimension II Work Setting Dimension III Organizational Features Change Oriented Goal Oriented Holographic Strategic Quality Dimension IV Information Dimension V Personal Supervisor Effectiveness Fairness Team Effectiveness Diversity Fair Pay Physical Environment Benefits Employee Development Internal Availability External Job Satisfaction Time and Stress Burnout Empowerment The Survey assessment is a framework, which at its highest level, consists of five Workplace Dimensions. Taken together these five capture the total work environment. Each Workplace Dimension consists of several Survey Constructs. The Survey Constructs are designed to broadly profile organizational strengths and weaknesses so that interventions may be targeted appropriately. Survey Constructs are developed from the Primary Questions series and scores for the Constructs range from a low of 100 to a high of 500. Page 1
4 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organization Profile Surveys Distributed: 442 Organization ID: 761 Survey Responses: 149 Organization Name: Texas A&M International University Benchmark Categories: Organization Size Category: 4 Size category 4 includes organizations with 301 to 1000 employees. Mission Category: Education (Mission 3) The Education category includes Universities, Colleges, Institutes and other Agencies involved with students, teachers, administrators and families throughout many areas of learning. Response Rate High rates mean that employees have an investment in the organization, want to see the organization improve and generally have a sense of responsibility to the organization. Low response rates can mean several things. There simply may not have been enough effort in making certain employees know the importance of completing the Survey. At a more serious level, low rates of response suggest a lack of organization focus or responsiveness. It many suggest critical levels of employee alienation, anger or indifference to organizational responsibilities. As a general rule rates higher than 50 percent suggest soundness. Rates lower than 30 percent may indicate serious problems. At 34%, your response rate is considered low. Response Rate Over Time One of the values of iterations of the Survey is an opportunity to measure organizational change over time. In general, response rates should rise from the first to the second and succeeding iterations. If organizational health is sound, rates tend to plateau above the 50 percent level. Declines in participation suggest some form of general organizational problem is developing. Your response rate is lower than it was for the previous survey. On-Line Responses vs. Hard Copy Responses At the Survey of Organizational Excellence, we are moving towards serving all of our surveys on-line, instead of mailing out hard copies. On-line Surveys offer many advantages over the traditional hard copy survey. With this onpline version, we are able to administer the survey at a lower cost to your organization, as well as provide rapid results so that intervantions can be made while the issues are still current. We hope to have every organization at the 100% on-line response level in the near future. Page 2
5 Dimension Analysis Survey of Organizational Excellence In order for organizations to improve there is a need to compare performance with other organizations. This comparison process is called benchmarking. The Survey provides a number of convenient and useful comparisons. The number of employees in an organization is one important characteristic of any organization. Large organizations with different locations and where any employee will know only a few of the members are different from organizations where most interaction is face-to-face and people know each other well. A second kind of benchmark focuses upon organizations that do similar things. The nature of an organization's work can have an impact on organizational features and employee experiences. Lastly, a benchmark is provided for a comparison against all other organizations that have taken the Survey in the current time frame. The data in this table are composed of your scores for this iteration of the Survey and compared to benchmarks from the most recent past iterations of the Survey. You will receive a report at the beginning of next year that will incorporate all data gathered from the past year and a new set of benchmarks. Benchmark data for the Dimensions is shown below. The benchmark helps to illustrate how your organization is performing relative to organizations of similar size, organizations with similar missions and to the performance of all organizations that participated in this survey. The scores for your organization appear to the right. Page 3
6 Construct Analysis Survey of Organizational Excellence Constructs have been color coded to highlight the organization's areas of strength and areas of concern. The 5 highest scoring constructs are blue, the 5 lowest scoring constructs are red, and the remaining 10 constructs are yellow. Each construct is displayed below with its corresponding score. Highest scoring constructs are areas of strength for your organization while the lowest scoring constructs are areas of concern. Scores of 400 or higher indicate areas of substantial strength. Scores above 300 suggest that employees perceive the issue more positively than negatively, while scores below 300 are viewed more negatively by employees. Scores below 200 should be a significant source of concern for the organization and should receive immediate attention. Page 4
7 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern The following Constructs are relative strengths for your organization: Benefits Score: 395 General Description: This Construct provides a good indication of the role the benefit package plays in attracting and retaining employees in the organization. It reflects comparable benefits that employees feel exist with other organizations in the area. Average scores suggest that room for improvement exists and lack of attention can lead to dropping scores. Benefits are often not viewed as motivators for employees but more as hygiene factors. This means employees will become restless, upset and dissatisfied when benefits are perceived as less than needed or fair. Part of the follow up to the Survey when data are returned is to discuss the results with employees and secure more elaborate explanations of important issues. In general concerns about benefits stems from these factors: level and type of benefits available, the cost and employees being able to understand and use the benefits package. Remedying concerns about benefits requires data collection from employees and competitive organizations to determine the correct causative factors. Use the employee feedback sessions to make a more complete determination for the causes of low Benefits scores. Quality Score: 390 General Description: Focuses upon the degree to which quality principles, such as customer service and continuous improvement are a part of the organizational culture. This Construct also addresses the extent to which employees feel that they have the resources to deliver quality services. Quality comes from attention to detail, customers and overall effort. Average scores mean that there is important room for improvement. In general quality is a result of understanding the needs of customers or clients coupled with a continuous and zealous examination of products and processes for improvement. Achieving quality requires the full and thoughtful attention of all members of the organization. Essential to maintaining high levels is clear articulation of goals, careful attention to changes in the environment that might affect resources or heightened competition and vigorous participation by all members. Leadership must maintain a clear articulation of the importance of quality and the role of everyone in achieving quality. Improvement is best addressed by developing clear standards of quality at all levels, urging employee assessment and feedback, and creating measures of quality for all work. Page 5
8 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern Relative Strengths Continued: Strategic Score: 388 General Description: The Construct reflects employees' thinking about how the organization responds to external influences that should play a role in defining the organization's mission, vision, services, and products. Implied in this construct is the ability of the organization to seek out and work with relevant external entities. Average scores suggest that employees feel there is room for improvement in how the organization interprets and understands the environment. Likely there is a concern that some programs are less relevant than in the past and that some processes do not seem knit into an overall vision. In general problems with Strategic Orientation stems from these factors: employees having a limited grasp of the goals of the organization, high levels of "silos", organizational components that function in isolation from other organizational processes, and the nature of the specific work being performed. Remedying Strategic Orientation requires careful study to determine the correct causative factors but assessing environmental understandings is the starting point. Conduct and compile customer assessments and review findings with staff at all levels. Benchmark processes with similar and competitive organizations. Use the employee feedback sessions to make a more complete determination for the causes of low Strategic Orientation scores. Physical Environment Score: 382 General Description: This Construct captures employees' perceptions of the total work atmosphere and the degree to which employees believe that it is a "safe" working environment. This construct addresses the "feel" of the workplace as perceived by the employee. Average scores suggest that room for improvement exists and lack of attention can lead to dropping scores. Attention may be needed to quality and amount of office space, equipment, parking and the location of facilities. Page 6
9 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern Relative Strengths Continued: External Score: 377 General Description: This Construct looks at how information flows into the organization from external sources, and conversely, how information flows from inside the organization to external constituents. It addresses the ability of organizational members to synthesize and apply external information to work performed by the organization. Average scores suggest that immediate consideration needs to be made to improve tools and process for external communication. In general External Communication is a function of these factors: nature of the organization's services or products and those who use the products, types of technology deployed for communication and knowledge of the organization of the needs of those who use its services. Remedying External Communication requires careful study to determine the correct causative factors. Carefully examine the customer base, operating hours of the organization, location of offices and knowledge of contact personnel with customer needs. Page 7
10 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern The following Constructs are relative weaknesses for your organization: Fair Pay Score: 277 Source of Concern General Description: This Construct addresses perceptions of the overall compensation package offered by the organization. It describes how well the compensation package "holds up" when employees compare it to similar jobs in other organizations. Low scores can come from many causes and may suggest a number of remedies. Part of the follow up to the Survey when data are returned is to discuss the results with employees and secure more elaborate explanations of important issues. Failure to successfully remedy Fair Pay problems is one of the more serious mistakes that leadership can make. These scores suggest that pay is a central concern or reason for satisfaction or discontent. Problems with pay can come from two or three causes and may suggest a number of remedies. In some situations pay does not meet comparables in similar organizations. In other cases individuals may perceive that pay levels are not appropriately set to work demands, experience and ability. At some times cost of living increases may cause sharp drops in purchasing power and employees will view pay levels as unfair. Remedying Fair Pay problems requires a determination of which of the above factors are serving to create the concerns. Triangulate low scores in Fair Pay by reviewing comparable positions in other organizations and cost of living information. Use the employee feedback sessions to make a more complete determination for the causes of low Fair Pay scores. Internal Score: 323 General Description: This Construct captures the flow of communication within the organization from the top-down, bottom-up, and across divisions or departments. It addresses the extent to which communication exchanges are open and candid and move the organization toward goal achievement. Average scores suggest that room for improvement exists and lack of attention can lead to dropping scores. Employees feel that information does not arrive in a timely fashion and often it is difficult to find needed facts. In general Internal Information problems stem from these factors: an organization that has outgrown an older verbal culture based upon a few people knowing "how to work the system", lack of investment and training in modern communication technology and, perhaps, vested interests that seek to control needed information. Remedying Internal Communication requires careful study to determine the correct causative factors. Triangulate low scores in Internal Communication by reviewing existing policy and procedural manuals to determine their availability. Assess how well telephone systems are articulated and if e mail, faxing and Internet modalities are developed and in full use. Use the employee feedback sessions to make a more complete determination for the causes of low Internal Communication scores. Page 8
11 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern Relative Weaknesses Continued: Team Effectiveness Score: 334 General Description: This Construct captures employees' perceptions of the people within the organization that they work with on a daily basis to accomplish their jobs (the work group or team). This construct gathers data about how effective employees think their work group is as well as the extent to which the organizational environment supports cooperation among employees. Average scores suggest that room for improvement exists and lack of attention can lead to dropping scores. Much and often most work in organizations require regular collaboration with others, the work team. Problems with Team Effectiveness can come from many causes and may suggest a number of remedies. In general team effectiveness stems from these factors: team membership, the selection, support and training of supervisors, the maturity and experience of employees and the nature of the specific work being performed. Remedying Team Effectiveness requires careful study to determine the correct causative factors. Triangulate low scores in Team Effectiveness with Supervisory Effectiveness by reviewing how supervisors are selected and their training. Use the employee feedback sessions to make a more complete determination for the causes of low Team Effectiveness scores. Supervisor Effectiveness Score: 336 General Description: This Construct provides insight into the nature of supervisory relationships in the organization, including the quality of communication, leadership, thoroughness and fairness that employees perceive exists between supervisors and them. This Construct helps organizational leaders determine the extent to which supervisory relationships are a positive element of the organization. Average scores suggest that room for improvement exists and lack of attention can lead to dropping scores. No area in an organization is more important and often more resistant to change than the middle areas of the organization. Problems with supervision can come from many causes and may suggest a number of remedies. Part of the follow up to the Survey when data are returned is to discuss the results with employees and secure more elaborate explanations of important issues. In general supervisory effectiveness stems from these factors: the selection, support and training of supervisors, the maturity and experience of employees and the nature of the specific work being performed. A frequent problem with supervisors is that those tasks a person may be successful with are not the same tasks that are required when one is promoted to supervision. Remedying Supervisory Effectiveness requires careful study to determine the correct causative factors. Triangulate low scores in Supervisory Effectiveness by reviewing how supervisors are selected and their training. Use the employee feedback sessions to make a more complete determination for the causes of low Supervisory Effectiveness scores. Page 9
12 Survey of Organizational Excellence Organizational Typology: Areas of Strength and Areas of Concern Relative Weaknesses Continued: Change Oriented Score: 338 General Description: This Construct secures employees' perceptions of the organization's capability and readiness to change based on new information and ideas. It addresses the organization's aptitude to process information timely and act upon it effectively. This Construct also examines the organization's capacity to draw upon, develop, and utilize the strengths of all in the organization for improvement. Average scores suggest that room for improvement exists and lack of attention can lead to organizational stasis. Problems with low change orientation can come from many causes and may suggest a number of remedies. Typically the organization is isolated or maintains a culture that feels that the organization and its activities are unique. This vitiates needed comparison or benchmarking processes. Remedying Change Orientation requires opportunity for study and comparisons with other organizations. Visits to other organizations, participation in accreditation processes and developing external advisory boards can help open the organization and increase readiness to change. Page 10
13 Organizational Change: Performance Over Time Survey of Organizational Excellence One of the benefits of continuing to participate in the survey is that over time you get to see how employees' views have changed as a result of implementing efforts suggested by previous survey results. Positive changes indicate that employees perceive the issue as adequately improved since the previous survey. Negative changes indicate that the employees perceive that the issue has worsened since the previous survey. Negative changes of greater than 50 points and having 10 or more negative construct changes should be a significant source of concern for the organization and should receive immediate attention. Page 11
14 Areas of Most and Least Change Survey of Organizational Excellence Your organization has improved across many areas compared to the last survey. These constructs showed a significant improvement: Fairness measures the extent to which employees believe that equal opportunity exists for all members of the organization. Employees feel that this is one of most significant improvements compared to the last survey. Time and Stress Management looks how realistic job demands are given time and resource constraints, and also captures employees' feelings about their ability to balance home and work demands. (Standard scoring methodology is maintained; therefore, the higher the score the less likely that employees perceive time and stress management to be problematic.) Employees feel that this is one of most significant improvements compared to the last survey. Empowerment measures the degree to which employees feel that they have some control over their jobs and the outcome of their efforts. Employees feel that this is one of most significant improvements compared to the last survey. Burnout is a feeling of extreme mental exhaustion that can negatively impact employees' physical health and job performance, leading to lost resources and opportunities in the organization. (Standard scoring methodology is maintained; therefore, the higher the score the less likely that employees perceive that burnout exists in the organization.) Employees feel that this is one of most significant improvements compared to the last survey. Diversity addresses the extent to which employees feel that individual differences, including ethnicity or lifestyle, may result in alienation and/or missed opportunities for learning or advancement. Employees feel that this is one of most significant improvements compared to the last survey. Page 12
15 Areas of Most and Least Change Survey of Organizational Excellence These constructs showed the least significant improvement or a decrease in score: Fair Pay is an evaluation from the viewpoint of employees of the competitiveness of the total compensation package. It addresses how well the package 'holds up' when employees compare it to similar jobs in their own communities. Employees feel that this is one of least significant improvements compared to the last survey. Internal Communication captures the nature of communication exchanges within the organization. It addresses the extent to which employees view information exchanges as open and productive and the degree to which computerized information is efficiently exchanged across the entire organization. Employees feel that this is one of least significant improvements compared to the last survey. Adequacy of Physical Environment captures employees' perceptions of the work setting and the degree to which employees believe that a safe and pleasant working environment exists. Employees feel that this is one of least significant improvements compared to the last survey. Strategic Orientation secures employees' thinking about how the organization responds to external influence, including those which play a role in defining the mission, services and products provided by the organization. This construct includes an assessment of the organization's ability to seek out and work with relevant external entities. Employees feel that this is one of least significant improvements compared to the last survey. External Communication looks at how information flows in and out of the organization. It captures the ability of the organization to synthesize and apply external information to work performed by the organization. Employees feel that this is one of least significant improvements compared to the last survey. Page 13
16 Demographics Survey of Organizational Excellence Demography data help one to see if the Survey response rate matches the general features of all employees in the organization. It is also an important factor in being able to determine the level of consensus and shared viewpoints across the organization. It may also help to indicate the extent to which the membership of the organization is representative of the local community and those persons that use the services and products of the organization. Race/Ethnic Identification Diversity within the workplace provides resources for innovation. A diverse workforce helps insure that different ideas are understood, and that the community sees the organization as representative of the community. * There were 18 employees who chose not to respond to this item. Age Age Diversity contributes to having a wellbalanced workplace. Different age groups bring different experiences and perspectives to the organization. Large percentages of older individuals may be a cause of concern if many of your key employees are nearing retirement age. Seek ways to preserve the culture and experiences these individuals have brought to the organization. Be mindful that people have different challenges and resources at various age levels and should see that leadership incorporates these understandings. * There were 5 employees who chose not to respond to this item. Gender The ratio of males to females within an organization can vary among different organizations. However, extreme imbalances in the gender ratio should be a source of concern for the organization and may require immediate attention. Give consideration to the types of work being performed and be open to unintentional bias in job and employee selection as well as promotion consideration. * There were 9 employees who chose not to respond to this item. Page 14
17 Demographics Survey of Organizational Excellence Employee Retention The percent of employees that see themselves working for your organization in two years is a good indicator of how well your organization is doing at retaining its employees. Very low retention should be a source of concern and may require immediate attention. You have a higher than average number of employees who expect to be working for your organization in two years. * There were 10 employees who chose not to respond to this item. Promotion The percentage of employees that receive a promotion can vary among organizations. While organizational growth may increase the likelihood of promotional opportunities, organizations should not simply wait for growth. Low percentages may indicate that current employees do not compete well for promotional opportunities. This would urge study of the Employee Development Construct to gauge the level of employee interest. * There were 8 employees who chose not to respond to this item. Merit Increase The percentage of employees that receive a merit increase can vary between organizations. Low percentages may indicate that employees need to review expectations of current employees and those efforts that seek to increase performance. * There were 7 employees who chose not to respond to this item. *Charts and percentages are based on valid responses. Slight variations from the Data Aggregation Report are due so respondents who chose not to answer particular demographic items. The number of people who chose not to respond is noted for each demographic item. Page 15
18 Special Items Survey of Organizational Excellence Certain survey items should be discussed no matter how the organization scores. Low performance in any of these areas should be reason to take immediate action to resolve any issues. Statewide averages are provided to help determine how your organization compares to all other organizations. 55. I am satisfied with the opportunities I have to evaluate my supervisor's performance. Your Score: We use feedback from those we serve to improve our performance. Your Score: I believe we will use the information from this survey to improve our performance. Your Score: I have regular involvement (once a month or more) in community activities or groups. Your Score: 3.82 Page 16
19 Your Next Steps Survey of Organizational Excellence Now That I Have The Survey Data, What Do I Do? Congratulations. Now that you have the Survey Data and the Executive Summary, you are ready to take the next steps of using data to build a stronger organization. Keep in mind that the Survey is predicated upon acquiring and making data available to all members to assess strengths and weaknesses to support a continuous cycle of improvement. Survey data are used to build organizational capital, a social norm within the organization that stresses continuous improvement, pride in the organization and a vigorous attitude of acknowledging the strengths of the organizations while searching for areas of improvement. The strongest of organizations have all members committed to the pursuit of excellence. You must now make some decisions for your organization. You have made the first intervention step by taking the Survey is a. People have been asked to think about the organization, their work and make some decisions by completing the Survey. By seeking participation and engaging people on how the organization functions, you have taken a specific step in increasing organizational capital. High organizational capital means high trust among employees and a greater likelihood of improved efforts and good working relationships with clients and customers. These Survey Data now provide a unique perspective, which is the average view of all that took the Survey. It is important to examine these findings and take them back to the employees for interpretation and to select areas for priority for improvement. This also provides an opportunity for the organization to recognize and celebrate areas that members have judged to be areas of relative strength. Building a Cycle of Improvement The use of the Survey helps to create an organization focused upon awareness of effort, a thinking or learning organization. This is the Cycle: Survey Cycle Participation Intervention Preparation Interpretation Administration The Survey also has a best practices resources site that provides information on the methods used by a variety of organizations to use the data for improvement : Page A1
20 Patterns of Organization Growth and Decline In general think of your organization as falling somewhere in the following taxonomy. Targets for change are selected to move the organization to the upper part of the chart. Patterns of Organization Growth and Decline Work Group Accommodations Organization Information Personal Innovative and Self Managed Outstanding and Appealing Best of the Breed Outstanding Internal And External Communications Superb Balance of Challenge, Expectations and Creativity Advanced Teamwork High Quality Strong and Vigorous Sophisticated Outstanding Balance of Work and Human Resources Initial Teamwork Level Adequate Solid But Not Inspired Adequate Good Balance of Work Demands Compliant Marginal In A Preservation Mode Bureaucratically Controlled Challenging Environment In-Group Solidarity Inadequate Starting to Slip Impoverished Growing Problems Defensive Interactions In Teams Marginal Teamwork Highly Inadequate In Clear Decline Defensive Highly Serious Clear Signs Of Disintegration Rigid And Reactive Mechanical And Undependable Critical Maintain Effort Organizations like people do not stand still. They either improve or deteriorate. Organizational change and improvement come from making attention to quality and excellence an embedded aspect of the general culture of the organization. In time every member will be vigilant, positive and eager to improve the organization. This is the essence of high levels of organizational capital. When organizations have high levels of capital, members have pride in what they do and continually strive for improvements. Trust among all, line and leadership, is a characteristic as are high rates of quality and innovation. The Survey is a basic tool, an instrument to help keep some of the important data in front of all members to build trust and thus organizational capital. Page A2
21 Rolling the Survey Data Back to All The following steps are used to facilitate rolling the data back to everyone in the organization and developing the change strategies from the Survey Data. Now the effort is to set a direction for change and to get everyone engaged in building the organization. Here is the general flow of the work for getting the Survey Data back to all employees. 1. Establish the Overall Plan with Executive Staff 2. Designate the Organization-Wide Change Team 3. Create Groups in Each Work Unit 4. Select Top Priority Change Topic/s Rolling The Data Back Step 1 Establish the Overall Plan with Executive Staff 1. Review Survey data including the Executive Summary with executive staff. 2. Develop plans for circulating all the data sequentially and provide interpretations for all staff. Do this with 3 to 4 weekly or monthly reports or organization newsletters. Report a portion of the Constructs and Questions, providing the data along with illustrations pertinent to the given organization. 3. Designate the Change Team that will guide the effort. 4. Identify the Work Unit Groups to ensure all employees get an opportunity to see and review the data. 5. Establish Procedures for recording the deliberations of the Work Unit Group and returning those data to the Change Team so that the Team can decide upon the Top Priority Change Topic and Methods necessary for making the change. Web-based Discussion Groups are a convenient technology. 6. First change effort begins. Repeat for the next change target. Page A3
22 Survey Checklist 2 Designate the Organization's Change Team Executive Staff Member Member 2 Member 3 Member 4 Member 5 Member 6 Member 7 Member 8 Names Remember that it is best to have the Change Team composed of a diagonal slice across the organization. This provides for multiple viewpoints of the organization. Groups larger than eight persons tend to become unwieldy and fraction into subgroups. Keep the Change Team small. Page A4
23 Survey Checklist 3 Create Work Unit Groups Throughout The Organization Step One Select a time to have every employee participate in a work unit group to review the reports as they are distributed to all staff, with one group leader assigned to every group. The size of the groups should be limited to about a dozen people at a time. A time limit should be set not to exceed two hours. Step Two Build the Groups around actual organizational work units and start each meeting by reviewing strengths as indicated in the data report. Brainstorm on how to best address weaknesses. Names of Work Group Members Page A5
24 Survey Checklist 4 Select Top Priority Change Topic List the topic for Top Priority Change and describe method/s for addressing the item. Return this form from each Work Unit Group to the Change Team. Top One or Two Topics for Change Suggested Methods Page A6
25 Preparing The Strategic Plan The State of Texas requires that each state organization that seeks funding from the Texas Legislature must prepare a strategic plan. Instructions are issued from the Governor s Office of Budget and Planning and the Legislative Budget Board in years preceding a Legislative Session. The February 2000 Instructions state these as the reasons for the plan: The ultimate goal of strategic planning is to anticipate and accommodate the future by identifying issues, opportunities, and problems. Strategic planning for Texas state government serves a number of distinct, though interrelated, purposes: to establish statewide direction in key policy or functional areas to move away from crisis driven decision making; to provide a basis for aligning resources in a rational manner to address the critical issues facing the state now and in the future; to make state government more responsive to the needs of Texans by placing greater emphasis on benefits and results than on simply service efforts and workload; to bring focused issues to policymakers for review and debate; to provide a context to link the budget process and other legislative processes with priority issues, and to improve accountability for the use of state resources; to establish a means of coordinating the policy concerns of public officials with implementation efforts and to build interagency, intergovernmental, and public/private/nonprofit partnerships; and to provide a forum for communication between service providers and the constituents they serve The Survey's data provides a requisite element in the creation of the Strategic Plan and that is the internal assessment of the organization s strengths and weaknesses and the organizational plan for addressing weaknesses in the coming budget cycle. Page A7
26 Preparing For The Governor s Conference on Organizational Excellence Every two years at the start of a new State Biennium all state agencies and universities executive directors and board chairs join with the Governor and his Offices to review plans and opportunities for the new Biennium. This is the critical time for each organization to start the process of reviewing its charge from the Legislature and the Governor for the coming two years as well as examining broad changes that may be underway in the state. The Conference serves as the single opportunity for all organizations of the state to acquaint each other with their leadership and align efforts for statewide priorities. Follow-up to the Governor s Conference Based upon the charges that come out of each Conference state organizations will be asked to provide information about changes or responses that come from the charges. This website provides contemporary information on required follow-up efforts. Page A8
The University of Texas at Austin
 REPORT ID: 721 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
REPORT ID: 721 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
NMSU Administration and Finance HR Information Systems/Payroll Services
 REPORT ID: 1514 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
REPORT ID: 1514 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
Lamar State College - Orange
 Lamar State College - Orange Executive Summary 2009 ID: 787 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Organizational Profile 3 Survey Administration 3 Response Rates 4 Survey Framework and Scoring
Lamar State College - Orange Executive Summary 2009 ID: 787 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Organizational Profile 3 Survey Administration 3 Response Rates 4 Survey Framework and Scoring
NMSU Facilities and Services FS Central Utility Plant
 REPORT ID: 1504 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
REPORT ID: 1504 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
University of Texas - Pan American. Division of Academic Affairs. Executive Summary
 University of Texas - Pan American Division of Academic Affairs Executive Summary 2009 ID: 736 Category: 100 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Organizational Profile 3 Survey Administration
University of Texas - Pan American Division of Academic Affairs Executive Summary 2009 ID: 736 Category: 100 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Organizational Profile 3 Survey Administration
Our Lady of the Lake University Staff
 Our Lady of the Lake University Staff Executive Summary 2010 ID: 875 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Survey Framework & Administration 1 Organizational Category Profile 2 Synthesis Score
Our Lady of the Lake University Staff Executive Summary 2010 ID: 875 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Survey Framework & Administration 1 Organizational Category Profile 2 Synthesis Score
NMSU Facilities and Services FS Environ Health Safety Off
 REPORT ID: 1504 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
REPORT ID: 1504 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
NMSU Administration and Finance Accounts Payable
 REPORT ID: 1514 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
REPORT ID: 1514 Introduction & Survey Framework... 1 Organization Profile & Survey Administration... 2 Overall Score & Participation... 3 Construct Analysis... 4 Areas of Strength... 5 Areas of Concern...
UNT System. Executive Summary
 Univ. North Texas Health Science Ctr. Fort Worth UNT System Executive Summary 2007 ID: 763 Category: 113 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Organizational Profile 3 Survey Administration
Univ. North Texas Health Science Ctr. Fort Worth UNT System Executive Summary 2007 ID: 763 Category: 113 Executive Summary Table of Contents Introduction 1 Organizational Profile 3 Survey Administration
Finance and Administration. Data Report
 The Survey of Organizational Excellence Univ. North Texas Health Science Ctr. Fort Worth Finance and Administration Data Report 2007 ID: 763 Category: 103 Table of Contents Survey Results: Survey Respondent
The Survey of Organizational Excellence Univ. North Texas Health Science Ctr. Fort Worth Finance and Administration Data Report 2007 ID: 763 Category: 103 Table of Contents Survey Results: Survey Respondent
Survey Results: Appendix: See our Web Page: The University of Texas at Austin 2014
 REPORT ID: 721 Survey Results: Survey Respondent Information... 1 Survey Constructs... 4 Survey Climate Areas... 11 Primary Items... 13 Additional Items... 32 *Additional Items are not included if none
REPORT ID: 721 Survey Results: Survey Respondent Information... 1 Survey Constructs... 4 Survey Climate Areas... 11 Primary Items... 13 Additional Items... 32 *Additional Items are not included if none
1925 San Jacinto Blvd., D3500 Phone (512) Austin, Texas Fax (512)
 REPORT ID: 1514-265 Introduction... 1 The Survey... 2 Employee Engagement... 3 People... 4 Constructs... 5 Areas of Strength and Concern... 6 Climate... 7 Focus Forward... 8 Appendix B: Primary Items...
REPORT ID: 1514-265 Introduction... 1 The Survey... 2 Employee Engagement... 3 People... 4 Constructs... 5 Areas of Strength and Concern... 6 Climate... 7 Focus Forward... 8 Appendix B: Primary Items...
Johnson City ISD SEE: Survey of Employee Engagement 2015
 Johnson City ISD SEE: Survey of Employee Engagement 2015 INSTITUTE FOR ORGANIZATIONAL EXCELLENCE The University of Texas at Austin THANK YOU for your participation in the Survey of Employee Engagement
Johnson City ISD SEE: Survey of Employee Engagement 2015 INSTITUTE FOR ORGANIZATIONAL EXCELLENCE The University of Texas at Austin THANK YOU for your participation in the Survey of Employee Engagement
Staff Satisfaction Survey
 Staff Satisfaction Survey TTUHSC Institutional Report 2007-2008 General Information The Higher Education Excellence Survey (HEES) was administered to staff members at Texas Tech University Health Sciences
Staff Satisfaction Survey TTUHSC Institutional Report 2007-2008 General Information The Higher Education Excellence Survey (HEES) was administered to staff members at Texas Tech University Health Sciences
2016 EMPLOYEE SURVEY RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
 2016 EMPLOYEE SURVEY RESULTS AND ANALYSIS JULY 2016 Survey Administered by the Institutional Effectiveness Committee March-June 2016 Report Prepared by the Office of Institutional Advancement Data Support
2016 EMPLOYEE SURVEY RESULTS AND ANALYSIS JULY 2016 Survey Administered by the Institutional Effectiveness Committee March-June 2016 Report Prepared by the Office of Institutional Advancement Data Support
EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT. Administrative Office Circuit Court of Lake County, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey. Employee Growth & Development
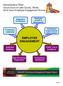 Administrative Office, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey Supportive Co-Workers Employee Growth & Development Trustworthy Leadership Continuous Organizational Improvement EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
Administrative Office, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey Supportive Co-Workers Employee Growth & Development Trustworthy Leadership Continuous Organizational Improvement EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
December 7, CFPB Annual Employee Survey
 December 7, 2012 2012 CFPB Annual Employee Survey Introduction Interpretation of results: Approximately 74 percent of CFPB employees responded to the first annual employee survey conducted by the Consumer
December 7, 2012 2012 CFPB Annual Employee Survey Introduction Interpretation of results: Approximately 74 percent of CFPB employees responded to the first annual employee survey conducted by the Consumer
Faculty/Staff Organizational Excellence Survey. Thomas J Fairchild, PhD Office of Strategy and Measurement
 Faculty/Staff Organizational Excellence Survey Thomas J Fairchild, PhD Office of Strategy and Measurement UNTHSC Five-Year Strategic Plan Recruit, develop, and retain high performing faculty UNTHSC 2011
Faculty/Staff Organizational Excellence Survey Thomas J Fairchild, PhD Office of Strategy and Measurement UNTHSC Five-Year Strategic Plan Recruit, develop, and retain high performing faculty UNTHSC 2011
DIVERSITY AND INCLUSION
 2012 Snapshot BEST PLACES TO WORK IN THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT ANALYSIS DIVERSITY AND INCLUSION U.S. demographics are shifting, with the federal government serving a more diverse population than ever before.
2012 Snapshot BEST PLACES TO WORK IN THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT ANALYSIS DIVERSITY AND INCLUSION U.S. demographics are shifting, with the federal government serving a more diverse population than ever before.
Interview Tools for Common Job Clusters for the Behavioural Competencies
 IV 72 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Supervision competency profile. It also includes the procedures
IV 72 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Supervision competency profile. It also includes the procedures
UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey. Prepared for: University of Alaska, Fairbanks Administrative Services
 UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University of Alaska, Fairbanks Administrative Services July 2009 UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University
UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University of Alaska, Fairbanks Administrative Services July 2009 UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University
2011 Smithsonian Employee Perspective Survey Dashboard of Key Metrics
 Dashboard of Key Metrics Satisfaction With Job Willing to Recommend Working at the Smithsonian 2010 Federal EVS Favorable Score, 72% 2010 SI Favorable Score, 84% 2011 SI Favorable Score, 82% 2010 Federal
Dashboard of Key Metrics Satisfaction With Job Willing to Recommend Working at the Smithsonian 2010 Federal EVS Favorable Score, 72% 2010 SI Favorable Score, 84% 2011 SI Favorable Score, 82% 2010 Federal
Section 6: Observations and Recommendations
 Section 6: Observations and Recommendations 42 Using the Survey Results To Improve Your Organization Here are some ideas to consider before reviewing the specific observations and recommendations that
Section 6: Observations and Recommendations 42 Using the Survey Results To Improve Your Organization Here are some ideas to consider before reviewing the specific observations and recommendations that
Jeffco Public Schools
 Jeffco Public Schools 2016 Employee Survey Report of Results June 2016 Prepared by: 2955 Valmont Road, Suite 300 Boulder, CO 80531 n-r-c.com 303-444-7863 Contents Executive Summary... 1 Survey Background...
Jeffco Public Schools 2016 Employee Survey Report of Results June 2016 Prepared by: 2955 Valmont Road, Suite 300 Boulder, CO 80531 n-r-c.com 303-444-7863 Contents Executive Summary... 1 Survey Background...
Creating a winning corporate culture: experience inside the Asian telecommunications industry
 Creating a winning corporate culture: experience inside the Asian telecommunications industry The author is President of Global Success, San Jose, California, USA. Keywords Corporate culture, Change management,
Creating a winning corporate culture: experience inside the Asian telecommunications industry The author is President of Global Success, San Jose, California, USA. Keywords Corporate culture, Change management,
Visionary Leadership. Systems Perspective. Student-Centered Excellence
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Executive Director Evaluation
 Executive Director Evaluation From the National Center for Nonprofit Boards Introduction By failing to adequately evaluate the chief executive, many nonprofit boards miss an opportunity to express support
Executive Director Evaluation From the National Center for Nonprofit Boards Introduction By failing to adequately evaluate the chief executive, many nonprofit boards miss an opportunity to express support
Performance Skills Leader. Individual Feedback Report
 Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
Interview Tools for Common Job Clusters for the Behavioural Competencies
 IV 54 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Senior Management competency profile. It also includes the procedures
IV 54 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Senior Management competency profile. It also includes the procedures
PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN 2019 PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Cameray s Philosophy of PQI 1 2. PQI Structure 1 Figure 1: Cameray PQI Flow Chart..2 Figure
PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN 2019 PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Cameray s Philosophy of PQI 1 2. PQI Structure 1 Figure 1: Cameray PQI Flow Chart..2 Figure
Benchmark Data Package Report Overview
 Benchmark Data Package University of Texas Pan American Prepared by: ModernThink, LLC 4519 Weldin Road Wilmington, DE 19803 Phone: 888.684.4658 Fax: 302.764.4497 www.modernthink.com Page 1 Introduction
Benchmark Data Package University of Texas Pan American Prepared by: ModernThink, LLC 4519 Weldin Road Wilmington, DE 19803 Phone: 888.684.4658 Fax: 302.764.4497 www.modernthink.com Page 1 Introduction
S & T Management Core Competency Profile
 (Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
(Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
TALENT REVIEW INSTRUCTIONS
 OFFICE OF HUMAN RESOURCES TALENT REVIEW INSTRUCTIONS SUMMARY The Talent Review process is a means to gain a better understanding of what is expected of the employee and how the employee can improve his/her
OFFICE OF HUMAN RESOURCES TALENT REVIEW INSTRUCTIONS SUMMARY The Talent Review process is a means to gain a better understanding of what is expected of the employee and how the employee can improve his/her
HRM. Human Resource Management Rapid Assessment Tool. A Guide for Strengthening HRM Systems. for Health Organizations. 2nd edition
 HRM Human Resource Management Rapid Assessment Tool for Health Organizations A Guide for Strengthening HRM Systems 2nd edition Copyright 2005, 2009 Management Sciences for Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
HRM Human Resource Management Rapid Assessment Tool for Health Organizations A Guide for Strengthening HRM Systems 2nd edition Copyright 2005, 2009 Management Sciences for Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
BOARD REPORT SELF-ASSESSMENT. Association Board SAMPLE Report December 2013
 BOARD SELF-ASSESSMENT REPORT Association Board SAMPLE December 2013 Welcome Welcome to the BoardSource Board Self-Assessment (BSA). The BSA is designed to educate and provide insights on your board's governance
BOARD SELF-ASSESSMENT REPORT Association Board SAMPLE December 2013 Welcome Welcome to the BoardSource Board Self-Assessment (BSA). The BSA is designed to educate and provide insights on your board's governance
2018 Supervisor s Guide to Performance Evaluation
 2018 Supervisor s Guide to Performance Evaluation h t t p s : / / p e d i. n n g o v. c o m Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction 3 The Objectives of the Performance Evaluation 3 Core Values 3 Core Competencies
2018 Supervisor s Guide to Performance Evaluation h t t p s : / / p e d i. n n g o v. c o m Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction 3 The Objectives of the Performance Evaluation 3 Core Values 3 Core Competencies
Core Values and Concepts
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in highperforming organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in highperforming organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Human Resources Strategic Update. Presented by Stephen Trncak October 28, 2011
 Human Resources Strategic Update Presented by Stephen Trncak October 28, 2011 Agenda Past and Future for the College The End Game (Elevating the Human and Organizational Capabilities and Capacity of the
Human Resources Strategic Update Presented by Stephen Trncak October 28, 2011 Agenda Past and Future for the College The End Game (Elevating the Human and Organizational Capabilities and Capacity of the
Chapter 7E: Nurturing Human Capital/Focus on Staff
 Chapter 7E: Nurturing Human Capital/Focus on Staff Starting Points The following points made by Jim Collins (author of the bestseller Good to Great; Why Some Companies Make the Leap And others Don t) are
Chapter 7E: Nurturing Human Capital/Focus on Staff Starting Points The following points made by Jim Collins (author of the bestseller Good to Great; Why Some Companies Make the Leap And others Don t) are
DIRECTOR TRAINING AND QUALIFICATIONS: SAMPLE SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL February 2015
 DIRECTOR TRAINING AND QUALIFICATIONS: SAMPLE SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL February 2015 DIRECTOR TRAINING AND QUALIFICATIONS SAMPLE SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL INTRODUCTION The purpose of this tool is to help determine
DIRECTOR TRAINING AND QUALIFICATIONS: SAMPLE SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL February 2015 DIRECTOR TRAINING AND QUALIFICATIONS SAMPLE SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL INTRODUCTION The purpose of this tool is to help determine
Noel-Levitz Satisfaction-Priorities Surveys Interpretive Guide
 Noel-Levitz Satisfaction-Priorities Surveys Interpretive Guide The Interpretive Guide is divided into multiple sections for your review. The General Interpretive Guide provides you with a general overview
Noel-Levitz Satisfaction-Priorities Surveys Interpretive Guide The Interpretive Guide is divided into multiple sections for your review. The General Interpretive Guide provides you with a general overview
DTR9274O1HJ/TGDTRm5Xgw33Z. Department Survey Sample Department
 DTR9274O1HJ/TGDTRm5Xgw33Z Department Survey Sample Department Feedback Report 1/9/217 About This Survey Sample Department, 1/9/217 This multi-rater survey is designed to assist your department in assessing
DTR9274O1HJ/TGDTRm5Xgw33Z Department Survey Sample Department Feedback Report 1/9/217 About This Survey Sample Department, 1/9/217 This multi-rater survey is designed to assist your department in assessing
Competency Map for the Data Science and Analytics-Enabled Graduate
 Competency Map for the Data Science and Analytics-Enabled Graduate Purpose of Competency Map The purpose of this competency map is to identify the specific skills, knowledge, abilities, and attributes
Competency Map for the Data Science and Analytics-Enabled Graduate Purpose of Competency Map The purpose of this competency map is to identify the specific skills, knowledge, abilities, and attributes
Office of the Director of National Intelligence. IC Annual Employee Climate Survey. April Summary Results
 April 2006 Summary Results 1 Background In October 2005, the Director of National Intelligence conducted the first-ever Intelligence Community (IC) Employee Climate Survey to gauge the state of the IC
April 2006 Summary Results 1 Background In October 2005, the Director of National Intelligence conducted the first-ever Intelligence Community (IC) Employee Climate Survey to gauge the state of the IC
Dartmouth College 2008 Staff Survey
 Dartmouth College 2008 Staff Survey Data Analysis Solutions Prepared for: Dartmouth College Survey Overview Revised survey allowed for new questions and comparison to results from the 2006 Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College 2008 Staff Survey Data Analysis Solutions Prepared for: Dartmouth College Survey Overview Revised survey allowed for new questions and comparison to results from the 2006 Dartmouth College
POSITION NUMBER: LOCATION: Vancouver. DATE: January 2013
 POSITION TITLE: Human Resources Consultant REGION: CLBC Headquarters CURRENT CLASSIFICATION LEVEL: Management SUPERVISOR POSITION NUMBER: POSITION NUMBER: LOCATION: Vancouver DATE: January 2013 SUPERVISOR
POSITION TITLE: Human Resources Consultant REGION: CLBC Headquarters CURRENT CLASSIFICATION LEVEL: Management SUPERVISOR POSITION NUMBER: POSITION NUMBER: LOCATION: Vancouver DATE: January 2013 SUPERVISOR
Core Values and Concepts
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
2014 Extension North Central Region Organizational Culture Assessment
 OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION 2014 Extension North Central Region Organizational Culture Assessment Summary Report of Findings Ohio State University Extension The bottom line for leaders is that if they
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION 2014 Extension North Central Region Organizational Culture Assessment Summary Report of Findings Ohio State University Extension The bottom line for leaders is that if they
Job Description: Operations Manager September 2017
 Job Description: Operations Manager September 2017 Title: Operations Manager Reporting to: Executive Director Purpose As a senior member of the Management Team, the Operations Manager is responsible for
Job Description: Operations Manager September 2017 Title: Operations Manager Reporting to: Executive Director Purpose As a senior member of the Management Team, the Operations Manager is responsible for
The shifting demographics and thriving economy of the San Francisco Bay Area have changed how we must plan for the future and created challenges in:
 2020 STRATEGIC PLAN SYNERGY SCHOOL was founded in 1973 as a teacher cooperative that would provide children of the San Francisco Bay Area a creative and diverse student-centered learning environment.
2020 STRATEGIC PLAN SYNERGY SCHOOL was founded in 1973 as a teacher cooperative that would provide children of the San Francisco Bay Area a creative and diverse student-centered learning environment.
IPMA-Canada Certification Program
 Program IPMA-CP (In Training) IPMA-CP IPMA-ACP IPMA-EX IPMA-CE International Personnel Management Association Canada 3333 333 Program IPMA-Canada is a national human resource management association whose
Program IPMA-CP (In Training) IPMA-CP IPMA-ACP IPMA-EX IPMA-CE International Personnel Management Association Canada 3333 333 Program IPMA-Canada is a national human resource management association whose
INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT. Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture
 INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture June 2011 Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture describes the key elements of organizational culture and business
INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture June 2011 Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture describes the key elements of organizational culture and business
Employee engagement is promoted by a myriad of
 SHRM Foundation Executive Briefing Employee Engagement: Your Competitive Advantage Sponsored by Randstad Employee engagement is promoted by a myriad of consultants, books and articles, but does it really
SHRM Foundation Executive Briefing Employee Engagement: Your Competitive Advantage Sponsored by Randstad Employee engagement is promoted by a myriad of consultants, books and articles, but does it really
2015 Strategic Plan. Mission and objectives designed to. ensure AFAC achieves its vision: Canada s leading force in aerospace
 2015 Strategic Plan Mission and objectives designed to ensure AFAC achieves its vision: Canada s leading force in aerospace commemoration, education and advocacy 2015 STRATEGIC PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS A.
2015 Strategic Plan Mission and objectives designed to ensure AFAC achieves its vision: Canada s leading force in aerospace commemoration, education and advocacy 2015 STRATEGIC PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS A.
DTR72KXREB7/TGDTRN24PERe. Sample Organization Sample Organization
 DTR72KXREB7/TGDTRN24PERe Sample Organization Sample Organization Feedback Report 2/27/217 About This Survey Sample Organization, 2/27/217 This multi-rater survey is designed to assist your organization
DTR72KXREB7/TGDTRN24PERe Sample Organization Sample Organization Feedback Report 2/27/217 About This Survey Sample Organization, 2/27/217 This multi-rater survey is designed to assist your organization
Volunteer Programs Manager $37,000 - $42,000 (DOE and verifiable qualifications) Competitive benefits package
 Job Title: Compensation: FLSA Status: Volunteer Programs Manager $37,000 - $42,000 (DOE and verifiable qualifications) Competitive benefits package Full-time Exempt The Humane Society for Southwest Washington
Job Title: Compensation: FLSA Status: Volunteer Programs Manager $37,000 - $42,000 (DOE and verifiable qualifications) Competitive benefits package Full-time Exempt The Humane Society for Southwest Washington
This report was obtained (via FOIA) and posted by AltGov2.
 This report was obtained (via FOIA) and posted by AltGov2 www.altgov2.org/fevs 2014 CFPB annual employee survey December 2014 Introduction Interpretation of results More than 83 percent of the CFPB employee
This report was obtained (via FOIA) and posted by AltGov2 www.altgov2.org/fevs 2014 CFPB annual employee survey December 2014 Introduction Interpretation of results More than 83 percent of the CFPB employee
Best Practices in Diversity Management
 Cornell University ILR School DigitalCommons@ILR GLADNET Collection Gladnet May 2001 Best Practices in Diversity Management Neil E. Reichenberg International Personnel Management Association Follow this
Cornell University ILR School DigitalCommons@ILR GLADNET Collection Gladnet May 2001 Best Practices in Diversity Management Neil E. Reichenberg International Personnel Management Association Follow this
2009 Smithsonian Employee Perspective Survey Office of Policy and Analysis Smithsonian Institution December 2009
 Smithsonian Employee Perspective Survey Office of Policy and Analysis Smithsonian Institution December 1. Interpretation of Results The National Defense Authorization Act of 2004 mandated that all federal
Smithsonian Employee Perspective Survey Office of Policy and Analysis Smithsonian Institution December 1. Interpretation of Results The National Defense Authorization Act of 2004 mandated that all federal
GSR Management System - A Guide for effective implementation
 GSR Management System - A Guide for effective implementation 1 Introduction Governments are facing challenges in meeting societal expectations and have an interest in Governmental Social Responsibility
GSR Management System - A Guide for effective implementation 1 Introduction Governments are facing challenges in meeting societal expectations and have an interest in Governmental Social Responsibility
INTERNSHIP STARTER HANDBOOK For Community Providers
 OFFICE OF INTERNSHIPS INTERNSHIP STARTER HANDBOOK For Community Providers Thank you for your interest in partnering with California State University San Marcos to provide internship opportunities to CSUSM
OFFICE OF INTERNSHIPS INTERNSHIP STARTER HANDBOOK For Community Providers Thank you for your interest in partnering with California State University San Marcos to provide internship opportunities to CSUSM
Board Evaluation Process
 Board Evaluation Process Brought to you by the partners at A Board should be committed to maintaining excellence in governance and, as such, should develop a practice for reviewing its own performance
Board Evaluation Process Brought to you by the partners at A Board should be committed to maintaining excellence in governance and, as such, should develop a practice for reviewing its own performance
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
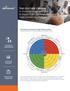 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Business Plan
 www.montanastatefund.com 2015 Business Plan July 1, 2014 through June 30, 2015 Table of Contents From the President... 1 Executive Summary... 2 Strategic Framework... 3 Key Success Measures... 4 Organizational
www.montanastatefund.com 2015 Business Plan July 1, 2014 through June 30, 2015 Table of Contents From the President... 1 Executive Summary... 2 Strategic Framework... 3 Key Success Measures... 4 Organizational
In April 2004, Executive Order RP 33 instructed the Health and Human Services Commission (HHSC) to
 2nd Quarter FY 2006 April 1, 2006 Department of Family and Protective Services Adult Protective Services Program Performance Report Executive Summary In April 2004, Executive Order RP 33 instructed the
2nd Quarter FY 2006 April 1, 2006 Department of Family and Protective Services Adult Protective Services Program Performance Report Executive Summary In April 2004, Executive Order RP 33 instructed the
SANTA MONICA COLLEGE 2017 College Employee Satisfaction Survey. Results and Findings
 SANTA MONICA COLLEGE 2017 College Employee Satisfaction Survey Results and Findings Prepared by Dr. Hannah Lawler, Dean of Institutional Research March 2018 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Santa Monica College (SMC)
SANTA MONICA COLLEGE 2017 College Employee Satisfaction Survey Results and Findings Prepared by Dr. Hannah Lawler, Dean of Institutional Research March 2018 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Santa Monica College (SMC)
Strategic Plan SFY Oklahoma Department of Human Services. Office of Intergovernmental Relations and Policy
 Strategic Plan SFY 2014-2015 Oklahoma Department of Human Services Office of Intergovernmental Relations and Policy Off Intergov Relations GROWING in a NEW DIRECTION SFY 2014-2015 Strategy Map OIRP Strategic
Strategic Plan SFY 2014-2015 Oklahoma Department of Human Services Office of Intergovernmental Relations and Policy Off Intergov Relations GROWING in a NEW DIRECTION SFY 2014-2015 Strategy Map OIRP Strategic
Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara
 Leads Innovation Leadership Styles Manages Change Models Integrity, Trust & Transparency Strategic Thinking and Planning Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara Conflict Management
Leads Innovation Leadership Styles Manages Change Models Integrity, Trust & Transparency Strategic Thinking and Planning Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara Conflict Management
POSITION NARRATIVE Director of Policy and Intergovernmental Affairs First 5 LA
 BACKGROUND POSITION NARRATIVE Director of Policy and Intergovernmental Affairs First 5 LA First 5 LA is one of 58 county commissions created by Proposition 10 in November 1998, to support children from
BACKGROUND POSITION NARRATIVE Director of Policy and Intergovernmental Affairs First 5 LA First 5 LA is one of 58 county commissions created by Proposition 10 in November 1998, to support children from
Advancement Framework Planning
 Advancement Framework Planning Monthly Progress Review Meeting March 6, 2012 Agenda Quantitative Brand Perception Analysis Progress update Qualitative Brand Dynamics & Perception Analysis Review brand
Advancement Framework Planning Monthly Progress Review Meeting March 6, 2012 Agenda Quantitative Brand Perception Analysis Progress update Qualitative Brand Dynamics & Perception Analysis Review brand
Practices for Effective Local Government Leadership
 Practices for Effective Local Government Leadership ICMA delivers the latest research in the 14 core areas critical for effective local government leadership and management. ICMA University is the premier
Practices for Effective Local Government Leadership ICMA delivers the latest research in the 14 core areas critical for effective local government leadership and management. ICMA University is the premier
COMPETENCY: Governance & Leadership. Levels 1, 2, & 3
 COMPETENCY: Governance & Leadership Levels 1, 2, & 3 Primary Themes Addressed: Effectively executes governance & leadership responsibilities Establishes and maintains collaborative, effective relationships
COMPETENCY: Governance & Leadership Levels 1, 2, & 3 Primary Themes Addressed: Effectively executes governance & leadership responsibilities Establishes and maintains collaborative, effective relationships
2016 Survey of Employee Engagement Work Group Results
 216 Survey of Employee Engagement Work Group Results 1 216 Survey of Employee Engagement - Work Group Results The Survey of Employee Engagement (SEE) is conducted every two years at Texas A&M University
216 Survey of Employee Engagement Work Group Results 1 216 Survey of Employee Engagement - Work Group Results The Survey of Employee Engagement (SEE) is conducted every two years at Texas A&M University
MODULE 1 Skill Sets and Competencies
 Handout #1 MODULE 1 Skill Sets and Competencies TOPIC: 511 FUNDAMENTALS OF CASEWORK SUPERVISION Skill Sets 511-01 Ability to create a supportive and enabling unit environment that promotes effective and
Handout #1 MODULE 1 Skill Sets and Competencies TOPIC: 511 FUNDAMENTALS OF CASEWORK SUPERVISION Skill Sets 511-01 Ability to create a supportive and enabling unit environment that promotes effective and
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
 PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Performance appraisal (PA) is the process of evaluating how well employees perform their jobs when compared to a set of standards, and then communicating that information to those
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Performance appraisal (PA) is the process of evaluating how well employees perform their jobs when compared to a set of standards, and then communicating that information to those
Indicator Unsatisfactory Needs Improvement Effective Highly Effective
 LEADERSHIP IN ASSIGNED AREA OF RESPONSIBILITY High Performing Leaders promote a positive work culture, demonstrate knowledge and apply best practices in assigned areas of responsibility, and inspire confidence,
LEADERSHIP IN ASSIGNED AREA OF RESPONSIBILITY High Performing Leaders promote a positive work culture, demonstrate knowledge and apply best practices in assigned areas of responsibility, and inspire confidence,
PAR Performance Factor Compendium Written Descriptors
 Communication, Oral Effective expression of ideas, concepts, or directions in individual or group situations, using supporting gestures, voice level, voice tone, and organization of materials. Informal
Communication, Oral Effective expression of ideas, concepts, or directions in individual or group situations, using supporting gestures, voice level, voice tone, and organization of materials. Informal
POSITION DESCRIPTION Two Rivers Supervisory Union
 POSITION DESCRIPTION Two Rivers Supervisory Union Position Title: Superintendent of Schools Reports to: Supervisory Union Board Work Year: Per Contract Position Type: Exempt Compensation: Per contract
POSITION DESCRIPTION Two Rivers Supervisory Union Position Title: Superintendent of Schools Reports to: Supervisory Union Board Work Year: Per Contract Position Type: Exempt Compensation: Per contract
Strategic Monitoring Tools and Techniques for Successful Strategic Plan Implementation
 Strategic Monitoring Tools and Techniques for Successful Strategic Plan Implementation An ECRA White Paper 2016 ECRA Group All Rights Reserved Strategic Monitoring 0 :. 1 :. Strategic Monitoring 1 :. Introduction
Strategic Monitoring Tools and Techniques for Successful Strategic Plan Implementation An ECRA White Paper 2016 ECRA Group All Rights Reserved Strategic Monitoring 0 :. 1 :. Strategic Monitoring 1 :. Introduction
Director Training and Qualifications
 4711 Yonge Street Suite 700 Toronto ON M2N 6K8 Telephone: 416-325-9444 Toll Free 1-800-268-6653 Fax: 416-325-9722 4711, rue Yonge Bureau 700 Toronto (Ontario) M2N 6K8 Téléphone : 416 325-9444 Sans frais
4711 Yonge Street Suite 700 Toronto ON M2N 6K8 Telephone: 416-325-9444 Toll Free 1-800-268-6653 Fax: 416-325-9722 4711, rue Yonge Bureau 700 Toronto (Ontario) M2N 6K8 Téléphone : 416 325-9444 Sans frais
The development of top human resources is essential in order to contribute to society as a top company that supports sustainable growth.
 Decent Work Stance on In order to create a workplace where all employees are able to work with vitality, the Calsonic Kansei Group has set the WAY (action guidelines), which defines the sense of values
Decent Work Stance on In order to create a workplace where all employees are able to work with vitality, the Calsonic Kansei Group has set the WAY (action guidelines), which defines the sense of values
Employee Satisfaction Summary. Prepared for: ABC Inc. By Insightlink Communications October 2005
 Employee Satisfaction Summary Prepared for: ABC Inc. By Insightlink Communications October 2005 Table of Contents Background and Methodology... 3 Note on the Results... 4 Executive Summary... 5 Corporate
Employee Satisfaction Summary Prepared for: ABC Inc. By Insightlink Communications October 2005 Table of Contents Background and Methodology... 3 Note on the Results... 4 Executive Summary... 5 Corporate
Watson Glaser III (US)
 Watson Glaser III (US) Development Report Candidate Name: Organization: Pearson Sample Corporation Date of Testing: (dd mm yyyy) Page 1 of 15 How to Use Your Report Success in the 21st century workplace
Watson Glaser III (US) Development Report Candidate Name: Organization: Pearson Sample Corporation Date of Testing: (dd mm yyyy) Page 1 of 15 How to Use Your Report Success in the 21st century workplace
EMPLOYEE SURVEY FALL 2003
 EMPLOYEE SURVEY FALL Barbara McNeice-Stallard Director Office of Research & Institutional Effectiveness With assistance from Pearson Reid London House, NCS Pearson February 3, 2004 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
EMPLOYEE SURVEY FALL Barbara McNeice-Stallard Director Office of Research & Institutional Effectiveness With assistance from Pearson Reid London House, NCS Pearson February 3, 2004 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
An Organizational Analysis of Leadership Effectiveness and Development Needs
 An Organizational Analysis of Leadership Effectiveness and Development Needs Prepared For ABC Company (Standard Survey) 23 June 2009 2009 Center for Creative Leadership. All Rights Reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS
An Organizational Analysis of Leadership Effectiveness and Development Needs Prepared For ABC Company (Standard Survey) 23 June 2009 2009 Center for Creative Leadership. All Rights Reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS
Gainesville Fire Rescue Diversity Initiative
 Gainesville Fire Rescue Diversity Initiative 2016 Diversity is mission-critical and relates directly to GFR s Mission Statement and Values. Gainesville Fire Rescue s Diversity Initiative began in 2012
Gainesville Fire Rescue Diversity Initiative 2016 Diversity is mission-critical and relates directly to GFR s Mission Statement and Values. Gainesville Fire Rescue s Diversity Initiative began in 2012
Generating Members, Volunteers and Leaders in Community Organizations
 COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, LEXINGTON, KY, 40546 CLD2-4 Generating Members, Volunteers and Leaders in Community Organizations Grow Your Group by Building
COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, LEXINGTON, KY, 40546 CLD2-4 Generating Members, Volunteers and Leaders in Community Organizations Grow Your Group by Building
ICMA PRACTICES FOR EFFECTIVE LOCAL GOVERNMENT LEADERSHIP Approved by the ICMA Executive Board June 2017; effective November 2017
 Reorganization The Credentialing Advisory Board proposed, and the Leadership Advisory and Executive Boards agreed, that the ICMA Practices should be organized as a narrative rather than a list. The following
Reorganization The Credentialing Advisory Board proposed, and the Leadership Advisory and Executive Boards agreed, that the ICMA Practices should be organized as a narrative rather than a list. The following
44 % 5 % 1 % 36 % 14 % Bargaining
 Talent Strategy and Transformation Our Workforce Bargaining Non-Bargaining 44 % 5 % 1 % 36 % 14 % Bargaining Temporary Craft Temporary Non-management, Professional 5% 1 % 44 % 36 % 14 % Our Approach Xcel
Talent Strategy and Transformation Our Workforce Bargaining Non-Bargaining 44 % 5 % 1 % 36 % 14 % Bargaining Temporary Craft Temporary Non-management, Professional 5% 1 % 44 % 36 % 14 % Our Approach Xcel
Quality management principles
 quality Quality management principles This document introduces seven quality management principles (QMPs). ISO 9000, ISO 9001 and related ISO quality management standards are based on these seven QMPs.
quality Quality management principles This document introduces seven quality management principles (QMPs). ISO 9000, ISO 9001 and related ISO quality management standards are based on these seven QMPs.
American Electric Power
 1 Riverside Plaza Columbus, OH 43215 Phone: (614) 716-1000 Fax: (614) 716-4800 www.aep.com Locations Columbus, OH Leadership Program Contact Michael Evarts Manager Development Solutions 1 Riverside Plaza
1 Riverside Plaza Columbus, OH 43215 Phone: (614) 716-1000 Fax: (614) 716-4800 www.aep.com Locations Columbus, OH Leadership Program Contact Michael Evarts Manager Development Solutions 1 Riverside Plaza
Iasa Engagements enhance Corporate Membership
 Iasa Engagements enhance Corporate Membership A webinar presented by Iasa Global, 19th August 2015 For more information see http://iasaglobal.org/corporate-member-engagements/ Formally known as the International
Iasa Engagements enhance Corporate Membership A webinar presented by Iasa Global, 19th August 2015 For more information see http://iasaglobal.org/corporate-member-engagements/ Formally known as the International
The High Performance Team Profile
 The High Performance Team Profile The High Performance Team Profile While there are many frameworks and methodologies that can help team effectiveness, they often fail to capture the underlying beliefs
The High Performance Team Profile The High Performance Team Profile While there are many frameworks and methodologies that can help team effectiveness, they often fail to capture the underlying beliefs
Inclusion and Diversity Initiative Benchmarking. A Monar Consulting White Paper
 Inclusion and Diversity Initiative Benchmarking A Monar Consulting White Paper Executive Summary Inclusion and diversity is no longer a business fad used to satisfy government quotas. Changing workforce
Inclusion and Diversity Initiative Benchmarking A Monar Consulting White Paper Executive Summary Inclusion and diversity is no longer a business fad used to satisfy government quotas. Changing workforce
BUREAU OF CONSUMER FINANCIAL PROTECTION DECEMBER BCFP Annual Employee Survey Results
 BUREAU OF CONSUMER FINANCIAL PROTECTION DECEMBER 2018 2018 BCFP Annual Employee Survey Results Introduction Interpretation of results More than 72 percent of the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection
BUREAU OF CONSUMER FINANCIAL PROTECTION DECEMBER 2018 2018 BCFP Annual Employee Survey Results Introduction Interpretation of results More than 72 percent of the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection
Watson-Glaser III Critical Thinking Appraisal (US)
 Watson-Glaser III Critical Thinking Appraisal (US) Development Report Candidate Name: Organization: Pearson Sample Corporation Date of Testing: 21-11-2017 (dd-mm-yyy) 21-11-2017 Page 1 of 15 How to Use
Watson-Glaser III Critical Thinking Appraisal (US) Development Report Candidate Name: Organization: Pearson Sample Corporation Date of Testing: 21-11-2017 (dd-mm-yyy) 21-11-2017 Page 1 of 15 How to Use
IC Annual Employee Climate Survey. Survey Results Office of the Intelligence Community Chief Human Capital Officer (CHCO)
 IC Annual Employee Climate Survey March 2007 Survey Results Office of the Intelligence Community Chief Human Capital Officer (CHCO) 1 Background In October 2006, the Director of National Intelligence conducted
IC Annual Employee Climate Survey March 2007 Survey Results Office of the Intelligence Community Chief Human Capital Officer (CHCO) 1 Background In October 2006, the Director of National Intelligence conducted
Communication Audit of the Academic & Career Advising Center. Table of Contents
 Helping organizations reach new heights through effective communication Communication Audit of the Academic & Career Advising Center Table of Contents Mission Statement 4 Executive Summary 5 Introduction
Helping organizations reach new heights through effective communication Communication Audit of the Academic & Career Advising Center Table of Contents Mission Statement 4 Executive Summary 5 Introduction
CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS
 CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS The Criteria are built on the following set of interrelated core values and concepts: visionary leadership customer-driven excellence organizational and personal learning valuing
CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS The Criteria are built on the following set of interrelated core values and concepts: visionary leadership customer-driven excellence organizational and personal learning valuing
Do Happy Employees Lead to Happy Customers?: Revisiting the Employee-Customer Relationship
 Do Happy Employees Lead to Happy Customers?: Revisiting the Employee-Customer Relationship AMA Web Cast October, 2008 Rick Garlick, Director of Consulting and Strategic Implementation, Maritz Research
Do Happy Employees Lead to Happy Customers?: Revisiting the Employee-Customer Relationship AMA Web Cast October, 2008 Rick Garlick, Director of Consulting and Strategic Implementation, Maritz Research
