A behaviour-based system for supporting and sustaining a Just Culture. Version December 2015 Baines Simmons Limited
|
|
|
- Homer Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A behaviour-based system for supporting and sustaining a Just Culture Version December 2015 Baines Simmons Limited
2 Contents FAiR 2 System - Enhancements and Revisions...2 Just Culture Unlocking the Key to Safety Performance...3 How a Proactive Safety Culture Impacts Safety Performance...4 Using the FAiR 2 System Golden Rules of Using FAiR Application of FAiR 2 - Process Flowchart...7 STEP 1: Classify the Behaviours...8 Behaviours Analysis Flowchart...9 STEP 2: Apply the Additional Tests...10 Tests, Interventions and Accountability...11 STEP 3: Identify Effective Interventions and Accountability...12 Behaviours Linked to Interventions...14 The Proportionality Test...15 ERG Chairperson Checklist...16 Behavioural Classification Definitions...17 Baines Simmons FAiR Services...18 FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 1
3 FAiR 2 System - Enhancements and Revisions Since its conception and launch, our original FAiR System Toolkit and User Guide has been widely praised, referenced, downloaded and shared by aviation organisations (and others) worldwide seeking help with implementing a fair approach to investigating, resolving and preventing recurrence of events that had occurred within their organisations. In 2014, we invited representatives from across the aviation industry with experience of using our FAiR System to discuss how to improve it. This booklet is the result of those workshops and we would like to thank all who participated. In summary, the major changes we have made to the FAiR 2 System are: Re-working the flowcharts to reduce the emphasis on culpability and to increase emphasis on using interventions by those using the FAiR System. The FAiR 2 System is designed to minimise the likelihood of recurrence of the event being investigated, which includes identifying effective interventions and treating people fairly in terms of their accountability. Including how to intervene successfully. We have now included a few back to basics theories on how to intervene along with a basic behaviour/intervention model to assist with this. Making it clear that there are 3 Steps to using the FAiR 2 System, so the tests and interventions flowchart are now much clearer in this regard. Ensuring that people actually use the User Guide to help them in their investigations. We have introduced the 12 Golden Rules to clarify what needs to be done, by when and by whom. Widening its applicability to include the air operations field. Improving the context of FAiR - explaining its importance to achieving a performing safety culture Making clear that users of the FAiR 2 System (the Event Review Group (ERG)) need to be competent and trained to do so and to reiterate what the ERG process is tasked with achieving. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 2
4 Just Culture Unlocking the Key to Safety Performance Safety culture is the bedrock of safety performance and has at its heart a Just Culture reporting environment. A safety culture encompasses an organisation s commonly held perceptions and beliefs regarding safety and has the potential to significantly influence people s behaviour. Founded upon a Just Culture, your safety culture allows individuals to freely and openly share safety-related information in an atmosphere of trust, born from a sense of justice. How the FAiR 2 System supports and sustains a Just Culture The Baines Simmons FAiR 2 System (Flowchart Analysis of Investigation Results) is an innovative management tool designed to help organisations that are investigating events to determine the nature and causes of errors, thereby ensuring that appropriate and effective interventions are taken. Designed as a behavioural classification-based framework, the FAiR 2 System ultimately helps organisations support and sustain a Just Culture. What is Just Culture? An atmosphere of trust in which people are encouraged (even rewarded) for providing essential safety-related information, but in which they are also clear about where the line must be drawn between acceptable and unacceptable behaviour. Professor James Reason, 1997 Why have a Just Culture? A Just Culture encourages openness and proactive reporting of hazards. It enables organisations to better identify its risks and implement effective mitigations. With an enhanced risk picture and a safety-conscious workforce, it improves safety-risk management, increases operational efficiency and protects vital assets. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 3
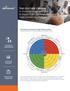
5 How a Proactive Safety Culture Impacts Safety Performance A proactive safety culture fosters an environment where people feel responsible for safety. This can be seen when they actively seek improvements, vigilantly remain aware of hazards and utilise systems and tools for continuous monitoring, analysis, and investigation. You know you have a proactive safety culture when staff feel empowered to positively challenge and change the way business is done around here, encouraging actions to be taken that minimise risk, remove inefficiency and reduce the likelihood of further incidents occurring. In terms of achieving safety performance, an organisation reaps the benefits of having a proactive safety culture when: A powerful strategic focus on safety is visible and palpable throughout the business Safety goals are actively pursued in support of an over-arching safety vision Safety is integrated into organisational structures and processes People take responsibility for managing and improving safety Responsibility for creating a proactive safety culture rests with senior management and relies on having a high degree of trust and respect between them and the workforce. The Baines Simmons SMARRT MAP assists organisations to understand, build and power-up their safety management system for organisational performance. It provides clarity, focus and direction for leaders aspiring to achieve effective safety management. Safety Performance is people/system-centric and focussed on the human in the system. It is achieved from four core management systems and five performance enablers working effectively and in harmony. Figure 1: SMARRT MAP TM Safety Management Risk Reduction Tool A key enabler to achieving safety performance is Proactive Culture. It is nurtured by a Just Culture that significantly influences people s behaviours, perceptions and beliefs, and progresses to a Reporting, Flexible, Questioning and Learning culture that exists across the organisation. Learning Culture Questioning Culture Flexible Culture Reporting Culture Just Culture Culture FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 4
6 Using the FAiR 2 System Derived from existing academic models and leading best practice, and designed with ease of use and repeatability in mind, the FAiR 2 System has been designed to enable organisations to: Identify effective interventions that help prevent or reduce events or near misses where humans and systems fail to perform in the manner expected Ensure personal accountability is balanced with the desire for learning and improvement Focus on actions and intentions rather than consequences by offering a consistent and impartial approach Practical application of the FAiR 2 System requires a degree of sensitivity and discretion but still ensures an impartial assessment of what are deemed acceptable and unacceptable actions. It is not intended to replace current disciplinary or administrative procedures but instead, to encourage a transparent and fair analysis of an individual s behaviour. Experience shows that alignment and harmonisation with an organisation s human resources department is a key component in the successful implementation of the FAiR 2 System. The FAiR 2 System - A 3-Step Approach STEP 1: Classify the Behaviours STEP 2: Apply the Additional Tests STEP 3: Identify Effective Interventions and Accountability The application of the FAiR 2 Process Flowchart on page 7 shows how to apply the system at different stages in the process. The FAiR 2 System is entirely predicated on information gathered during a Human Factors-centric investigation conducted by trained investigators. It should not be used in isolation or without an objective and comprehensive investigation being conducted first. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 5
7 12 Golden Rules of Using FAiR 2 Pre-Event Review Group (ERG) Meeting 1. Use the FAiR 2 User Guide. It is there to help and guide you and to provide consistency of results. 2. Ensure a Human Factors based investigation has been undertaken by two competent investigators (typically one a subject matter expert and one independent from the area in question) using a structured standardised taxonomy and report format. 3. Select competent Event Review Group (ERG) members (typically an odd number to allow decision-making). Where relevant, this should include a subject matter expert to help select effective interventions. Note: To minimise bias and preserve impartiality the ERG should not include the Manager from the department or area in which the event occurred. During-Event Review Group (ERG) Meeting 4. Ensure the report is complete and of a good standard. It should clearly identify the root cause and contributing factors and answer all the Why did it happen? questions. If not, clarify any points with the investigators before proceeding. 5. Classify the behaviour based solely on the facts contained within the report and not on opinion or perception. 6. Run the Substitution and Routine Tests using all available information and data (see pages 10-11). 7. Based on the results of steps 5 and 6, approve or amend the original report recommendations ensuring that all proposed interventions are achievable, realistic and sustainable to be effective. 8. Assign ownership to all agreed recommendations and track progress to implementation. 9. Reach a conclusion every time; do not spend an excessive amount of time focussing on semantics and grammar within the report. 10. If appropriate, consider the Proportionality Test (see page 15). Post-Event Review Group (ERG) Meeting 11. Ensure feedback is given to those involved in the investigation and, if appropriate, consider using the event as a lesson learned example in training and safety communication programs: - To increase awareness levels of the contributing factors within the wider organisation - To promote the value of using the FAiR 2 System in support of establishing a Just Culture as the cornerstone of Safety Culture 12. Record all ERG proceedings for any future review, analysis and assurance purposes. Table 1: 12 Golden Rules of Using FAiR FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 6
8 Application of FAiR 2 - Process Flowchart Further information required? Hazard, Near Miss or Occurrence report Immediate precautionary or containment action required? Carry out a structured Human in the System investigation using trained investigators Event Review Group (ERG) convened Investigation report reviewed, ensuring all the why questions have been answered FAiR 2 System applied Take appropriate disciplinary action (if required) Golden Rules Identification of effective and sustainable interventions from a human and system perspective Non-Judgemental Decision Judgemental Figure 2: Application of FAiR 2 - Process Flowchart INVESTIGATORS EVENT REVIEW GROUP HUMAN RESOURCES or ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 7
9 STEP 1: Classify the Behaviours To apply the FAiR 2 Behaviours Analysis Flowchart on page 9, the Event Review Group (ERG) should answer each question based upon factual information gathered during the investigation. Should these investigation results require any clarification, the ERG should verify directly with the investigation team before continuing with the analysis. In answering each of the questions, the following should be considered: Was there a conscious and substantial and unjustifiable disregard for risk? Did the individual knowingly take a significant risk whilst unjustifiably ignoring the potential for harm that could be caused? Were the consequences as intended? Did the individual deliberately set out to cause the outcome of the event? Were rules intentionally broken? Did the individual knowingly contravene rules or not follow procedures in order to undertake the task? Was a correct plan of action selected? Would the plan of action selected by the individual have ever achieved its goal? Under the circumstances were all applicable rules available and workable and intelligible and correct? In the circumstances of the event, was it possible to complete the task in line with all applicable rules or procedures? Has the investigation taken due account of local norms, for example where seemingly benign shortcuts (or workarounds) have become routine to compensate for rules and procedures that are ambiguous or difficult to apply in practice? Was the action at the time of the event beneficial to the organisation? Did the individual consider that their actions were for the good of the organisation or were they based upon self-interest Was the action at the time of the event outside of normal practice? Did the individual find themselves in a situation which differed considerably from the expected operating scenario? Having responded to each of these questions, one of the eight behavioural classifications summarised on page 14 will be reached. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 8
10 Behaviours Analysis Flowchart Start Ensure a Human in the System investigation has been completed by trained investigators and the subsequent Event Review Group (ERG) consists of trained members who use the FAiR 2 User Guide. Was there a conscious and substantial and unjustifiable disregard for risk? YES Was the consequence as intended? NO YES Sabotage NO Recklessness Were the rules intentionally broken? YES In the circumstances were all applicable rules available and workable and intelligible and correct? YES Was the action at the time beneficial to the organisation? YES Violation for organisational gain NO NO NO Was a correct plan of action selected? YES Error Violation for personal gain NO Mistake Was the action at the time outside of normal practice? YES Situational violation Figure 3: Behaviour Analysis Flowchart NO Routine violation FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 9
11 STEP 2: Apply the Additional Tests These tests and activities are designed to help the ERG confirm or modify the results of the behaviours analysis on page 9. The Substitution Test Would another person with the same levels of professional education, training and experience behave in the same way in the same circumstances? This test is used to assess whether another individual with equivalent knowledge and experience might have reasonably followed the same course of action under the circumstances. If the answer is yes, the recommended interventions primarily need to address any systemic weaknesses to prevent or reduce the likelihood of recurrence. The test could involve discussions with peers, observation and/or reference to other types of information either from the original investigation or undertaken on behalf of the Safety Manager or ERG. To prevent the introduction of pre-existing knowledge or bias at this stage in the process, subsequent evaluation of additional information by the ERG should ensure that peers: Have a similar grade, rank and/or certification capability and level of experience Must not be members of the associated investigation or ERG team, or any other associated committee The Routine Test Has this event happened before to either the individual or to the organisation? This test requires an evaluation of internal safety information and seeks to ascertain whether: The actions of the individual were in fact normative i.e. they reflected everyday working practices or a normal way of working when carrying out the task involved when the event occurred (this should align with the findings of the Substitution Test) The individual has been involved with similar events previously The organisation has experienced similar occurrences previously but remedial actions have failed to prevent recurrence. For example, replenishing an engine oil tank with incorrect fluid, or an uninitiated opening of a flight deck Direct Vision (DV) window during takeoff acceleration Test Results Evaluating the results of both the Substitution and Routine Tests (including establishing whether the behaviours are routine or whether the event has happened previously): Will have a direct influence upon determining the most appropriate interventions May diminish the level of individual accountability (See Step 3 on the Tests, Interventions and Accountability Diagram, page 11) FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 10
12 Tests, Interventions and Accountability Unintended Action Unintended Consequence Intended Action Unintended Consequence Intended Action Intended Consequence Step 1: Classify the Behaviours Error Mistake Situational violation Routine violation Violation for organisational gain the line in the sand Violation for personal gain Recklessness Sabotage Step 2: Apply the Additional Tests 1. Substitution Test: Would peers (with similar education, training and experience) behave in the same way in the same circumstances (time, goal, demands and organisational context)? 2. Routine Test: Has this event happened before to: a) the individual or b) the organisation? Step 3: Identify Effective Interventions & Accountability Manage through reducing or removing the performance influencing factors (PIFs) in the context of the person, task, situation and environment. May include coaching, consoling or training May include coaching, training and/or taking minor administrative action Increasing Accountability Manage through taking appropriate disciplinary action Figure 4: Tests, Interventions and Accountability FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 11
13 STEP 3: Identify Effective Interventions and Accountability To improve Safety Performance, one of the most important roles of the ERG is to decide on the suitability of the proposed recommendations for intervention(s) made within the Human in the System investigation report. Based on these, the results of the additional tests in Step 2, plus any supplementary information available, the ERG then has four options: Accept the original recommendation(s) Reject the original recommendation(s) Amend the original recommendation(s) Propose a new recommendation(s) The ERG should ensure that all agreed recommendations follow the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time bound) approach. Specific Measurable Achievable Note: Involving those concerned in the investigation in the identification and selection of effective interventions is highly recommended and, when appropriate, the ERG should ask Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) to help ratify the recommendations. 3.1 Determine Effective Interventions For an intervention to be successful, it needs to focus on the Human in the System and specifically relate to the performance influencing factors (PIFs) identified in the investigation as well as the type of behaviours determined by the FAiR 2 Behaviours Analysis Flowchart. Errors, mistakes and violations all have differing psychological and motivational precursors and it is essential that consideration is given to this when developing an intervention. For example, issuing a Safety Notice reminding people of their responsibilities to follow the rules, when procedures were found to be ambiguous or where the individual does not possess the skills required for the task, would be ineffective in reducing the likelihood of recurrence. Time Realistic Figure 5: SMART Recommendations Depending on the behaviour and accountability attributed, changes may be made at the individual, task, situation or environment (wider organisational systems) level to remove or reduce the PIFs. This may include coaching, training or taking appropriate administrative or disciplinary action for the individuals involved in line with existing organisational HR processes. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 12
14 STEP 3: Identify Effective Interventions and Accountability (Cont) Addressing specific types of behaviour These models can be used to develop interventions that are effective at addressing specific individual behaviour types. Errors are skill-based failures occur at the point of execution. An individual either does not possess the skills to perform a task or is undertaking a highly routine task that leaves him/her prone to slips and lapses (often caused by distractions and interruptions). Errors Skills Attitude Knowledge Mistakes Competence Mistakes are typically knowledge or rule-based and involve failures in planning or decision making. Either an individual does not possess the knowledge to undertake a task or there are issues with inadequate or ambiguous rules and procedures. Violations Figure 6: Competence Model - Behaviours Violations are motivation-based and usually involve an intentional decision by an individual to deviate from the applicable rules and procedures. Highly routine tasks Errors Mistakes Problem solving / misapplying a good rule Intervention: Increase job/task awareness, job rotation Violations Intervention: Increase job/task knowledge, improve data Intentional rule breaking Intervention: Remove the need to violate Figure 7: Interventions in relation to error types FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 13
15 STEP 3: Identify Effective Interventions and Accountability (Cont) Interventions based on types of error Once behaviour types and their precursors have been determined from factual evidence gathered following a Human in the System investigation, appropriate interventions can be developed using the table below. Behaviour Error Mistake Situational Violations Routine Violations Violations for organisational gain Violation for personal gain Recklessness Sabotage Intervention Address the human PIFs identified; this may include improving skills, a distraction policy, increased task awareness or job rotation for highly routine tasks. Encourage open reporting to highlight potential error provocative tasks and conditions. Address cognitive errors through performance management and training to improve knowledge and ensure data and information is available, workable, intelligible and correct. Encourage reporting to highlight issues with data and information. Address any systemic problems including removing the perceived need to violate. Encourage reporting from staff to uncover situations where violations may occur. Reinforce acceptable /unacceptable behaviour particularly how staff are expected to react in sub-optimal situations. For example, by encouraging a Questioning Culture enabling staff to say stop. Manage through appropriate disciplinary action. Manage through appropriate disciplinary action. Manage through disciplinary action. Civil and/or criminal prosecution. Table 2: Behaviours to Interventions FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 14
16 STEP 3: Identify Effective Interventions and Accountability (Cont) 3.2 Determine Accountability The final role of the ERG is to identify any levels of accountability for all those involved, not just focussing on personnel at the sharp end. This is done in line with an organisation s Just Culture policy and supporting procedures. A Just Culture aims to draw a notional line in the sand between acceptable and unacceptable behaviours. The Baines Simmons FAiR 2 System is designed to facilitate this aim by determining which behaviours should be managed through either administrative or disciplinary action. Behaviours that would attract an appropriate level of disciplinary action are violations (rule breaking) for personal gain, recklessness and sabotage. All other behaviours should be managed through removing or reducing PIFs and occasionally this may include taking minor administrative action. Following completion of the 3-Step FAiR 2 process, the ERG or other responsible party, may decide to apply the proportionality test. The Proportionality Test What safety value will punishment have? This test should be used to determine the appropriate extent of any administrative or disciplinary action in terms of its contribution to safety learning and improvement. In particular, it can be used to compare the benefits that may be gained by applying discipline with any potentially negative effects on Safety Culture development depending on its maturity at the time. For example, being seen to apply discipline where there is a marginal case could threaten the evolving maturity of Just and Reporting Cultures and therefore, ultimately, Safety Culture. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 15
17 Appendix 1: The Role of the Event Review Group (ERG) With the ultimate objective of improving Safety Performance, the Event Review Group (ERG) has three key functions: To ensure a Human Factors-centric investigation and report is complete, identifying the root cause, contributing factors and answering all the Why did it happen? questions To ensure effective interventions are put in place following an event To determine any potential accountability The Role of the ERG Chairperson The ERG Chairperson is responsible for ensuring that the 3-Step FAiR 2 Process has been followed according to the organisation s procedures by: Leading and facilitating the ERG and ensuring it keeps to the 3-Step agenda. Holding the ERG to account for using the FAiR 2 system appropriately and following the 12 Golden Rules. Ensuring the ERG has the appropriate composition and that everyone involved is appropriately trained with the right levels of competence. Ensuring ERG proceedings have been documented in either hardcopy or electronic format to enable the following: - Ownership and tracking of interventions - Trend analysis proof of being a Just organisation - Safety Assurance audit/review internal and external - Aiding future Routine Tests - Reviewing any decisions around levels of accountability - Safety communications/feedback on Safety Performance Typical ERG Composition SMS Manager Trained ERG members (an uneven number if possible) Subject Matter Experts (as required) Note: To minimise bias and preserve impartiality the Manager of the area in which the event has occurred should not be part of the ERG or take part in the related ERG decision(s). FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 16
18 Appendix 2: Behavioural Classification Definitions Error The plan of action may be entirely appropriate, but the action itself does not go according to plan. Skill-based errors are associated with three related aspects of human information processing: recognition, memory (an error of omission or lapse) and attention (an error of commission or slip). For example, misinterpreting information on a display or gauge; pulling an incorrect circuit breaker; forgetting to complete a step of a task because of an interruption or distraction. Mistake Situational violation An action that goes according to plan but where the plan is inadequate to achieve the desired goal. Known as cognitive errors, mistakes can be split into two categories: rule-based mistakes or knowledge-based mistakes. Mistakes often arise when dealing with a problem for the first time or during an unexpected or novel scenario. Rule-based mistakes can be divided into two categories: misapplying a good rule (assumptions) or applying a bad rule (habits). Misapplying good rules can happen in circumstances that share common features for which the rule was intended but where significant differences are overlooked. For example, using known good information based on knowledge of one aircraft type but on a new type of aircraft where it is no longer applicable. Where deliberately not following the rules was the only way to complete the task. Individuals may assert that, given the circumstances in which they found themselves, the only way to get the task done was to break the rules. For example, under time pressure, an individual uses incorrect equipment to achieve a task as the correct equipment was unserviceable at the time, or a pilot continuing with an unstable approach due to fast following traffic. Routine violation Violation for organisational gain Where deliberately not following the rules when completing a particular task was normal behaviour (accepted by peers and immediate supervisors) within the organisation in the circumstances. Deliberately not following rules with the aim of benefiting the organisation. An individual may believe that their actions are for the good of the organisation in terms of a reduction of time, cost or resource; or to achieve organisational goals such as meeting schedules or targets. For example, missing out steps in a task that are judged to be superfluous or that are unachievable within the time available to meet a deadline or schedule. Violation for personal gain Deliberately not following rules with the aim of benefiting the individual. Motivation-based, actions can be corner-cutting to complete a task more quickly or to circumvent seemingly laborious procedures. They can also be thrill-seeking as a means of alleviating boredom or as a demonstration of ability or skill. For example, not completing a task to get away from work on time; not using the correct equipment because it requires effort to obtain or taxiing at excessive speeds to meet a personal deadline. Recklessness A conscious and substantial and unjustifiable disregard of visible and significant risk. Whilst there is no intent to do harm to others, recklessness implies that an individual knowingly ignored the potential consequences of their actions. For example, coming into work under the influence of alcohol or knowingly operating a sector in an excessively fatigued state having not taken the required rest period. Sabotage Malicious or wanton damage or destruction. To determine whether an individual s actions constitute sabotage there needs to be intent for both the actions and the consequence to cause damage or disrupt operations. FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 17
19 Baines Simmons FAiR Services We are specialists in aviation regulations, compliance and safety management and partner with the world s leading civil and defence aviation organisations to improve safety performance. Baines Simmons offers a range of consulting services, competence development and training support for anyone requiring assistance in understanding the FAiR System better or wanting help with building their internal management systems to support their investigation and review processes. Copyright The FAiR System is the intellectual property of Baines Simmons Limited and is copyright protected. All rights reserved. Baines Simmons offers the FAiR System to industry free-of-charge to use and encourages organisations to adopt it into their processes and documentation. We do not levy any licensing or royalty charges for its use. However, we do request that users respect our intellectual property rights (IPR), citing Baines Simmons as the authors and intellectual owners of all aspects of the FAiR System. Baines Simmons branding and the FAiR logo must be maintained at all times. Organisations wishing to use or adapt the FAiR System to incorporate it within their own documentation should first contact Baines Simmons in writing, outlining their request in detail. Baines Simmons Limited makes every endeavour to ensure the accuracy of this document but does not accept liability for any errors or omissions. Please contact us via hello@bainessimmons.com or write to: Head of Marketing & Products, Baines Simmons Limited, Aviation Safety Centre, Fairoaks Airport, Chobham, Surrey, GU24 8HU, United Kingdom. Baines Simmons Limited FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 18
20 Notes FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 19
21 Notes FAiR 2 System : Version 2.1 : December 2015 : Baines Simmons Limited 20
22 Baines Simmons Limited Aviation Safety Centre Fairoaks Airport Chobham Surrey GU24 8HU United Kingdom Tel: +44 (0)
Just Culture for safety performance (can it work across national cultures?) Keven Baines Director 25 th March 2015 CHC Safety Summit
 (can it work across national cultures?) Keven Baines Director 25 th March 2015 CHC Safety Summit Workshop flow 1. Just Culture why? 2. What is it? 3. How to build one? 4. Does it deliver/work across national
(can it work across national cultures?) Keven Baines Director 25 th March 2015 CHC Safety Summit Workshop flow 1. Just Culture why? 2. What is it? 3. How to build one? 4. Does it deliver/work across national
Driving Your SMS Beyond Compliance to Performance
 Driving Your SMS Beyond Compliance to Performance A Baines Simmons Thought Leadership Document by Keven Baines Managing Director, Baines Simmons First published September 2011 Driving Your SMS Beyond Compliance
Driving Your SMS Beyond Compliance to Performance A Baines Simmons Thought Leadership Document by Keven Baines Managing Director, Baines Simmons First published September 2011 Driving Your SMS Beyond Compliance
JUST CULTURE : An Algorithm for Accountability Bob Henderson 13 October 2016
 JUST CULTURE : An Algorithm for Accountability Bob Henderson 13 October 2016 Human Errors Slips - an unplanned action Lapses - not completing a planned action Mistakes - doing an action incorrectly - applying
JUST CULTURE : An Algorithm for Accountability Bob Henderson 13 October 2016 Human Errors Slips - an unplanned action Lapses - not completing a planned action Mistakes - doing an action incorrectly - applying
Advisory Circular. Subject: Guidance on Acceptable and Unacceptable Behaviour Date: 1 January 2013
 Cooperative Development of Operational Safety and Continuing Airworthiness Programme COSCAP - SOUTH ASIA International Civil Aviation Organization Advisory Circular Subject: Guidance on Acceptable and
Cooperative Development of Operational Safety and Continuing Airworthiness Programme COSCAP - SOUTH ASIA International Civil Aviation Organization Advisory Circular Subject: Guidance on Acceptable and
Level 5 NVQ Diploma in Management and Leadership Complete
 Learner Achievement Portfolio Level 5 NVQ Diploma in Management and Leadership Complete Qualification Accreditation Number: 601/3550/5 Version AIQ004461 Active IQ wishes to emphasise that whilst every
Learner Achievement Portfolio Level 5 NVQ Diploma in Management and Leadership Complete Qualification Accreditation Number: 601/3550/5 Version AIQ004461 Active IQ wishes to emphasise that whilst every
Disciplinary Procedures Framework
 AIM OF THE RAAUS DISCIPLINARY PROCESS Disciplinary Procedures Framework The RAAus disciplinary procedures framework has been designed with the RAAus vision in mind Safe, Accessible, Fun and Enjoyable (SAFE
AIM OF THE RAAUS DISCIPLINARY PROCESS Disciplinary Procedures Framework The RAAus disciplinary procedures framework has been designed with the RAAus vision in mind Safe, Accessible, Fun and Enjoyable (SAFE
INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT. Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture
 INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture June 2011 Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture describes the key elements of organizational culture and business
INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture June 2011 Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture describes the key elements of organizational culture and business
Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Customer Service. Qualification Specification
 Qualification Specification ProQual 2014 Contents Page Introduction 3 The Qualifications and Credit Framework (QCF) 3 Qualification profile 4 Rules of combination 5 Credit transfer / Exemptions / Recognition
Qualification Specification ProQual 2014 Contents Page Introduction 3 The Qualifications and Credit Framework (QCF) 3 Qualification profile 4 Rules of combination 5 Credit transfer / Exemptions / Recognition
Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan. IS Business Analyst. March 2017
 Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan IS Business Analyst March 2017 1 DIGITAL INDUSTRIES APPRENTICESHIPS: ASSESSMENT PLAN FOR IS BUSINESS ANALYST General Introduction and Overview The apprenticeship
Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan IS Business Analyst March 2017 1 DIGITAL INDUSTRIES APPRENTICESHIPS: ASSESSMENT PLAN FOR IS BUSINESS ANALYST General Introduction and Overview The apprenticeship
Use of Regulatory Tools
 Page 1 of 10 Use of Regulatory Tools 1. Purpose and Scope... 2 2. Application... 2 3. Authority... 2 4. References... 2 5. The Civil Aviation Authority s regulatory tools... 3 6. Identifying appropriate
Page 1 of 10 Use of Regulatory Tools 1. Purpose and Scope... 2 2. Application... 2 3. Authority... 2 4. References... 2 5. The Civil Aviation Authority s regulatory tools... 3 6. Identifying appropriate
Behavioural Attributes Framework
 Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
The Benefit of Adopting a Management System Approach to Regulatory Compliance
 July 2018 White Paper The Benefit of Adopting a Management System Approach to Regulatory Compliance Author: Jeff Fieldhouse, Principal Consultant, Baines Simmons This paper has been developed to challenge
July 2018 White Paper The Benefit of Adopting a Management System Approach to Regulatory Compliance Author: Jeff Fieldhouse, Principal Consultant, Baines Simmons This paper has been developed to challenge
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Risk-based oversight: who has control?
 Risk-based oversight: who has control? How Operators and Regulators need to address the challenges posed by the new Air Operations regulations A Baines Simmons Thought Leadership Document by Peter Hogston
Risk-based oversight: who has control? How Operators and Regulators need to address the challenges posed by the new Air Operations regulations A Baines Simmons Thought Leadership Document by Peter Hogston
Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Customer Service. Qualification Specification
 Qualification Specification ProQual 2017 Contents Page Introduction 3 Qualification profile 3 Qualification structure 4 Centre requirements 6 Support for candidates 6 Assessment 6 Internal quality assurance
Qualification Specification ProQual 2017 Contents Page Introduction 3 Qualification profile 3 Qualification structure 4 Centre requirements 6 Support for candidates 6 Assessment 6 Internal quality assurance
Just Culture. Nick Ward NANDTB Aircraft Inspection and Maintenance Seminar October 2017
 Just Culture Nick Ward NANDTB Aircraft Inspection and Maintenance Seminar October 2017 What Just Culture isn t? Why do we need a Just Culture? Why Just Culture? Experience shows us that It s important
Just Culture Nick Ward NANDTB Aircraft Inspection and Maintenance Seminar October 2017 What Just Culture isn t? Why do we need a Just Culture? Why Just Culture? Experience shows us that It s important
Qualification Specification 601/3688/1 icq Level 3 Diploma in Management (RQF)
 Qualification Specification 601/3688/1 icq Level 3 Diploma in Management (RQF) Qualification Details Title : icq Level 3 Diploma in Management (RQF) Awarding Organisation : ican Qualifications Limited
Qualification Specification 601/3688/1 icq Level 3 Diploma in Management (RQF) Qualification Details Title : icq Level 3 Diploma in Management (RQF) Awarding Organisation : ican Qualifications Limited
Wales Millennium Centre Behavioral Competencies Framework 1
 Wales Millennium Centre Behavioural Competencies Framework Be Reflective Ensuring we understand who our customers are Taking time to listen to customers Proactively engaging with customers to find out
Wales Millennium Centre Behavioural Competencies Framework Be Reflective Ensuring we understand who our customers are Taking time to listen to customers Proactively engaging with customers to find out
3. RELATED CIVIL AVIATION SAFETY REGULATIONS. Civil Aviation Safety Regulations (CASR):
 3. RELATED CIVIL AVIATION SAFETY REGULATIONS. Civil Aviation Safety Regulations (CASR): a. Part 91, General Operating and Flight Rules; b. Part 121, Certification And Operating Requirements : Domestic,
3. RELATED CIVIL AVIATION SAFETY REGULATIONS. Civil Aviation Safety Regulations (CASR): a. Part 91, General Operating and Flight Rules; b. Part 121, Certification And Operating Requirements : Domestic,
HSE Integrated Risk Management Policy. Part 1. Managing Risk in Everyday Practice Guidance for Managers
 HSE Integrated Risk Management Policy Part 1 Managing Risk in Everyday Practice Guidance for Managers HSE Integrated Risk Management Policy Part 1 Managing Risk in Everyday Practice Guidance for Managers
HSE Integrated Risk Management Policy Part 1 Managing Risk in Everyday Practice Guidance for Managers HSE Integrated Risk Management Policy Part 1 Managing Risk in Everyday Practice Guidance for Managers
Personnel Accountability Policy (Rev 3)
 Personnel Accountability Policy (Rev 3) Purpose This policy provides guidance on the issue of personnel accountability at DCPP as it relates to Human Performance Events or Issues. The appropriate performance
Personnel Accountability Policy (Rev 3) Purpose This policy provides guidance on the issue of personnel accountability at DCPP as it relates to Human Performance Events or Issues. The appropriate performance
Our purpose, values and competencies
 Our purpose, values and competencies Last updated October 2013 The work we do and how we behave and carry out our work at The Pensions Regulator are driven by our purpose, values and competency framework.
Our purpose, values and competencies Last updated October 2013 The work we do and how we behave and carry out our work at The Pensions Regulator are driven by our purpose, values and competency framework.
City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council
 City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council 1.CM.250 Issue 3 Nov-2014 Process Owner: Organisational Development Team Authorisation: Deborah Morley Page
City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council 1.CM.250 Issue 3 Nov-2014 Process Owner: Organisational Development Team Authorisation: Deborah Morley Page
Highways England People Strategy
 Highways England People Strategy 1. Accountable Leadership 2. Capable Employees We require positive, proactive and engaging leadership to be demonstrated at all levels of the organisation, through all
Highways England People Strategy 1. Accountable Leadership 2. Capable Employees We require positive, proactive and engaging leadership to be demonstrated at all levels of the organisation, through all
Fundamentals Of Effective Supervision. Situational Leadership
 Fundamentals Of Effective Supervision Situational Leadership Situational Leadership If you want to be a successful supervisor, you need to become expert at achieving through others by means of means directing,
Fundamentals Of Effective Supervision Situational Leadership Situational Leadership If you want to be a successful supervisor, you need to become expert at achieving through others by means of means directing,
Human Failure. Overview. People are never 100% reliable. Andy Brazier. Types of human failure Slips Mistakes Violations
 Human Failure Andy Brazier Tel: (+44) 01492 879813 Mob: (+44) 07984 284642 andy@abrisk.co.uk www.abrisk.co.uk 1 Overview Types of human failure Slips Mistakes Violations Causes of human failure Things
Human Failure Andy Brazier Tel: (+44) 01492 879813 Mob: (+44) 07984 284642 andy@abrisk.co.uk www.abrisk.co.uk 1 Overview Types of human failure Slips Mistakes Violations Causes of human failure Things
Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan. Unified Communications Technician. Published in November 2016
 Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan Unified Communications Technician Published in November 2016 1 Digital Industries Apprenticeships: Assessment Plan General Introduction and Overview The
Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan Unified Communications Technician Published in November 2016 1 Digital Industries Apprenticeships: Assessment Plan General Introduction and Overview The
NS&I Consolidated Competency Framework. Setting Direction Engaging People Delivering Results. Communication. Team Working
 NS&I Consolidated Competency Framework Setting Direction Engaging People Delivering Results Leading Others Acting as a positive role model for NS&I s values and behaving with integrity by reinforcing positive
NS&I Consolidated Competency Framework Setting Direction Engaging People Delivering Results Leading Others Acting as a positive role model for NS&I s values and behaving with integrity by reinforcing positive
CORE COMPETENCIES. For all faculty and staff
 SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
Guidance Material. SMS Manual Format - Scalable. Notice to Users
 Guidance Material SMS Manual Format - Scalable Notice to Users This document is an advanced version of a draft CAA publication (proposed appendix to draft Advisory Circular AC137-1 Agricultural Aircraft
Guidance Material SMS Manual Format - Scalable Notice to Users This document is an advanced version of a draft CAA publication (proposed appendix to draft Advisory Circular AC137-1 Agricultural Aircraft
Viridor Core competencies edition
 Viridor Core competencies 2014 edition Giving the world s resources new life Challenge for change The world is changing. Once there was waste. Now there are valuable resources society must challenge itself
Viridor Core competencies 2014 edition Giving the world s resources new life Challenge for change The world is changing. Once there was waste. Now there are valuable resources society must challenge itself
The BEST Framework EDF Group s Expectations for Managing Health and Safety. The EDF Group BEST Framework
 Version 1 The BEST Framework EDF Group s Expectations for Managing Health and Safety The EDF Group BEST Framework 2 CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Leadership in Health and Safety 07 Incident Management 09 Contractor
Version 1 The BEST Framework EDF Group s Expectations for Managing Health and Safety The EDF Group BEST Framework 2 CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Leadership in Health and Safety 07 Incident Management 09 Contractor
Customer Service strategy
 Customer Service strategy and service standards Consolidating Excellence Culture change Collaboration Confident and competent workforce CUSTOMER SERVICE STRATEGY 2016/17 2018/19 Customer Insight Quality
Customer Service strategy and service standards Consolidating Excellence Culture change Collaboration Confident and competent workforce CUSTOMER SERVICE STRATEGY 2016/17 2018/19 Customer Insight Quality
Promoting a safety culture in maintenance
 Safety is of paramount importance in high risk industries, the concept of safety culture is of growing importance in these industries as a means of reducing the potential for large-scale disasters, and
Safety is of paramount importance in high risk industries, the concept of safety culture is of growing importance in these industries as a means of reducing the potential for large-scale disasters, and
Counter Fraud Strategy Social Security Scotland
 1 Background Ministers have announced their intention for a new Scottish social security agency to be administering all of the devolved benefits by the end of the Parliamentary term in May 2021. Benefit
1 Background Ministers have announced their intention for a new Scottish social security agency to be administering all of the devolved benefits by the end of the Parliamentary term in May 2021. Benefit
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA OFFICE OF THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF CIVIL AVIATION TECHNICAL CENTRE, OPPOSITE SAFDARJUNG AIRPORT, NEW DELHI
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA OFFICE OF THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF CIVIL AVIATION TECHNICAL CENTRE, OPPOSITE SAFDARJUNG AIRPORT, NEW DELHI 11 0 003 CIVIL AVIATION REQUIREMENTS SECTION 1 GENERAL SERIES 'C' PART I Issue
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA OFFICE OF THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF CIVIL AVIATION TECHNICAL CENTRE, OPPOSITE SAFDARJUNG AIRPORT, NEW DELHI 11 0 003 CIVIL AVIATION REQUIREMENTS SECTION 1 GENERAL SERIES 'C' PART I Issue
Level 3 Diploma in Management. Qualification Specification
 Qualification Specification ProQual 2017 Contents Page Introduction 3 Qualification profile 3 Qualification structure 4 Centre requirements 6 Support for candidates 6 Assessment 7 Internal quality assurance
Qualification Specification ProQual 2017 Contents Page Introduction 3 Qualification profile 3 Qualification structure 4 Centre requirements 6 Support for candidates 6 Assessment 7 Internal quality assurance
IOSH Branch event 3 rd June Making Behaviour Change Happen in Health & Safety. Jane Hopkinson, Senior Psychologist, Health and Safety Laboratory
 IOSH Branch event 3 rd June 2015 Making Behaviour Change Happen in Health & Safety Jane Hopkinson, Senior Psychologist, Health and Safety Laboratory Objectives What is behaviour and what influences it?
IOSH Branch event 3 rd June 2015 Making Behaviour Change Happen in Health & Safety Jane Hopkinson, Senior Psychologist, Health and Safety Laboratory Objectives What is behaviour and what influences it?
Practical Work Place Skills: First Steps (SCQF level 3) SDS Customised Unit H37L 04
 Practical Work Place Skills: First Steps (SCQF level 3) SDS Customised Unit H37L 04 Skills Development Scotland Practical work place skills: First Steps (SCQF level 3) This unit is designed to be delivered
Practical Work Place Skills: First Steps (SCQF level 3) SDS Customised Unit H37L 04 Skills Development Scotland Practical work place skills: First Steps (SCQF level 3) This unit is designed to be delivered
BEST PRACTICES IN Talent Management Article Title Format
 SCHOONOVER ASSOCIATES WHITE PAPER BEST PRACTICES IN Talent Management Article Title Format SCHOONOVER ASSOCIATES, LLC. 2015 Dr. Stephen C. Schoonover President, Schoonover Associates, LLC Contents Executive
SCHOONOVER ASSOCIATES WHITE PAPER BEST PRACTICES IN Talent Management Article Title Format SCHOONOVER ASSOCIATES, LLC. 2015 Dr. Stephen C. Schoonover President, Schoonover Associates, LLC Contents Executive
CORE TOPICS Core topic 3: Identifying human failures. Introduction
 CORE TOPICS Core topic 3: Identifying human failures Introduction Human failures are often recognised as being a contributor to incidents and accidents, and therefore this section has strong links to the
CORE TOPICS Core topic 3: Identifying human failures Introduction Human failures are often recognised as being a contributor to incidents and accidents, and therefore this section has strong links to the
Leadership 360. Sam Sample. Name: Date:
 Leadership 6 Name: Email: Date: Sam Sample sam.sample@example.com /Jun/8 Contents Section : Introduction Page This section offers guidance on how to read and make the most of your report. Section : Your
Leadership 6 Name: Email: Date: Sam Sample sam.sample@example.com /Jun/8 Contents Section : Introduction Page This section offers guidance on how to read and make the most of your report. Section : Your
Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan. Unified Communications Trouble Shooter. Published in November 2016
 Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan Unified Communications Trouble Shooter Published in November 2016 1 Digital Industries Apprenticeships: Assessment Plan 1. General Introduction and Overview
Digital Industries Apprenticeship: Assessment Plan Unified Communications Trouble Shooter Published in November 2016 1 Digital Industries Apprenticeships: Assessment Plan 1. General Introduction and Overview
The Quality Maturity Model: Your roadmap to a culture of quality
 The Quality Maturity Model: Your roadmap to a culture of quality F R A N K I E W I L S O N H E A D O F A S S E S S M E N T B O D L E I A N L I B R A R I E S, O X F O R D F R A N K I E. W I L S O N @ B
The Quality Maturity Model: Your roadmap to a culture of quality F R A N K I E W I L S O N H E A D O F A S S E S S M E N T B O D L E I A N L I B R A R I E S, O X F O R D F R A N K I E. W I L S O N @ B
Culpability. User Guide
 Culpability Decision Tree User Guide http://www.ppiweb.com Guidance for Using the Culpability Decision Tree This guideline provides instructions for using the Culpability Decision Tree in order to more
Culpability Decision Tree User Guide http://www.ppiweb.com Guidance for Using the Culpability Decision Tree This guideline provides instructions for using the Culpability Decision Tree in order to more
Housing Association Regulatory Assessment
 Welsh Government Housing Directorate - Regulation Housing Association Regulatory Assessment Linc-Cymru Housing Association Limited Registration number: L109 Date of publication: 21 December 2012 Welsh
Welsh Government Housing Directorate - Regulation Housing Association Regulatory Assessment Linc-Cymru Housing Association Limited Registration number: L109 Date of publication: 21 December 2012 Welsh
Culture COS April 2018
 Guidelines for Culture a Robust Safety Center for Offshore Safety Publication COS 3 044 First Edition April 2018 SPECIAL NOTES Center for Offshore Safety (COS) and American Petroleum Institute (API) publications
Guidelines for Culture a Robust Safety Center for Offshore Safety Publication COS 3 044 First Edition April 2018 SPECIAL NOTES Center for Offshore Safety (COS) and American Petroleum Institute (API) publications
Just Culture. Leading Through Shared Values and Expectations
 Just Culture Leading Through Shared Values and Expectations Objectives Understand the concepts of Just Culture Identify three predictable behaviors Understand a Just Culture investigation Describe the
Just Culture Leading Through Shared Values and Expectations Objectives Understand the concepts of Just Culture Identify three predictable behaviors Understand a Just Culture investigation Describe the
Regulatory operating model
 RAIL SAFETY Regulatory operating model NZ Transport Agency Published March 2017 Updated June 2018 (16-316) ISBN 978-1-98-851211-2 (print) ISBN 978-1-98-851212-9 (online) Copyright: March 2017 NZ Transport
RAIL SAFETY Regulatory operating model NZ Transport Agency Published March 2017 Updated June 2018 (16-316) ISBN 978-1-98-851211-2 (print) ISBN 978-1-98-851212-9 (online) Copyright: March 2017 NZ Transport
Risks, Strengths & Weaknesses Statement. November 2016
 Risks, Strengths & Weaknesses Statement November 2016 No Yorkshire Water November 2016 Risks, Strengths and Weaknesses Statement 2 Foreword In our Business Plan for 2015 2020 we made some clear promises
Risks, Strengths & Weaknesses Statement November 2016 No Yorkshire Water November 2016 Risks, Strengths and Weaknesses Statement 2 Foreword In our Business Plan for 2015 2020 we made some clear promises
DEAF DIRECT: Performance Management Policy: April Performance Management Policy
 Performance Management Policy 1 Contents Introduction Aims of the Performance Management Process Benefits of the Performance Management Process Key Principles of the Process Job Descriptions Planning Performance
Performance Management Policy 1 Contents Introduction Aims of the Performance Management Process Benefits of the Performance Management Process Key Principles of the Process Job Descriptions Planning Performance
Glasgow Caledonian University Internal Audit Annual Report for the year ended 31 July 2008
 Government and Public Sector Internal Audit Services October 2008 Internal Audit Annual Report for the year ended 31 July 2008 Contents Section Page 1. Background and Scope...1 2. Our Annual Opinion...3
Government and Public Sector Internal Audit Services October 2008 Internal Audit Annual Report for the year ended 31 July 2008 Contents Section Page 1. Background and Scope...1 2. Our Annual Opinion...3
Human Performance Blueprint UK NUCLEAR HUMAN PERFORMANCE FORUM
 UK NUCLEAR HUMAN PERFORMANCE FORUM Human Performance Blueprint This document provides a strategic approach to the implementation of a human performance programme within an organisation. Document History
UK NUCLEAR HUMAN PERFORMANCE FORUM Human Performance Blueprint This document provides a strategic approach to the implementation of a human performance programme within an organisation. Document History
COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE REGIONS
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 2.10.2013 COM(2013) 686 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 2.10.2013 COM(2013) 686 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE
ONRSR Guideline. Investigation Reports by Rail Transport Operators
 Investigation Reports by Rail Transport Operators Document control Objective Document ID: A597082 Version number: 1.0 Approved by: Chief Executive Date approved: April 2017 Office of the National Rail
Investigation Reports by Rail Transport Operators Document control Objective Document ID: A597082 Version number: 1.0 Approved by: Chief Executive Date approved: April 2017 Office of the National Rail
Leadership Competency Framework
 This competency framework is designed to develop the capabilities of leaders and managers at the Open University to improve the quality of leadership provided to staff to ensure the University successfully
This competency framework is designed to develop the capabilities of leaders and managers at the Open University to improve the quality of leadership provided to staff to ensure the University successfully
Risk Management Update ISO Overview and Implications for Managers
 Contents - ISO 31000 highlights 1 - Changes to key terms and definitions 2 - Aligning key components of the risk management framework 3 - The risk management process 4 - The principles of risk management
Contents - ISO 31000 highlights 1 - Changes to key terms and definitions 2 - Aligning key components of the risk management framework 3 - The risk management process 4 - The principles of risk management
Helicopter Association International March 2017
 Helicopter Association International March 2017 1 What is Just Culture? What is a Just Culture? Just Culture is a value-supported system of shared accountability where organizations are accountable for
Helicopter Association International March 2017 1 What is Just Culture? What is a Just Culture? Just Culture is a value-supported system of shared accountability where organizations are accountable for
Business Support Clerical Grade 5 Competencies. Introduction
 Business Support Clerical Grade 5 Competencies Introduction Competencies are the skills, knowledge, practical behaviours and attitudes which inform the way you operate in working life. Ulster s competency
Business Support Clerical Grade 5 Competencies Introduction Competencies are the skills, knowledge, practical behaviours and attitudes which inform the way you operate in working life. Ulster s competency
CONTENTS. 2 Winning hearts
 Win hearts & minds CONTENTS A little intro from Gordon...4 A Winning Hearts history lesson...6 HR plans for 2014 and beyond...7 Our vision, mission and values...8 Our values in action...10-14 The new Winning
Win hearts & minds CONTENTS A little intro from Gordon...4 A Winning Hearts history lesson...6 HR plans for 2014 and beyond...7 Our vision, mission and values...8 Our values in action...10-14 The new Winning
HDA Coaching Culture Survey Results 2011
 HDA Coaching Culture Survey Results 2011 HDA is a Human capital consultancy that has worked in the area of coaching for 17 years, developing a reputation for a highly successful, outcomes-focused approach
HDA Coaching Culture Survey Results 2011 HDA is a Human capital consultancy that has worked in the area of coaching for 17 years, developing a reputation for a highly successful, outcomes-focused approach
JOB DESCRIPTION HIAL AMSL DAL. Air Traffic Control Officer (fixed-term for 3 years) Senior Air Traffic Control Officer (SATCO)
 JOB DESCRIPTION HIAL AMSL DAL Job Title: Location: Line Manager: Air Traffic Control Officer (fixed-term for 3 years) Kirkwall Airport Senior Air Traffic Control Officer (SATCO) Purpose of the Role The
JOB DESCRIPTION HIAL AMSL DAL Job Title: Location: Line Manager: Air Traffic Control Officer (fixed-term for 3 years) Kirkwall Airport Senior Air Traffic Control Officer (SATCO) Purpose of the Role The
THE WORLD OF ORGANIZATION
 22 THE WORLD OF ORGANIZATION In today s world an individual alone can not achieve all the desired goals because any activity requires contributions from many persons. Therefore, people often get together
22 THE WORLD OF ORGANIZATION In today s world an individual alone can not achieve all the desired goals because any activity requires contributions from many persons. Therefore, people often get together
Cascading change throughout an organisation
 Cascading change throughout an organisation Author Melanie Franklin Director Agile Change Management Limited Introduction Organisations all over the world are experiencing high volumes of change as a result
Cascading change throughout an organisation Author Melanie Franklin Director Agile Change Management Limited Introduction Organisations all over the world are experiencing high volumes of change as a result
Qualification Specification 601/3690/X icq Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Management (RQF)
 Qualification Specification 601/3690/X icq Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Management (RQF) Qualification Details Title : icq Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Management (RQF) Awarding Organisation : ican Qualifications
Qualification Specification 601/3690/X icq Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Management (RQF) Qualification Details Title : icq Level 4 NVQ Diploma in Management (RQF) Awarding Organisation : ican Qualifications
Supervisor s Guide: Performance Evaluations
 Supervisor s Guide: Performance Evaluations Table of Contents Introduction... - 2 - Benefits of Productive Performance Meetings... - 3 - Performance Goals Help Employees... - 3 - Performance Goals Help
Supervisor s Guide: Performance Evaluations Table of Contents Introduction... - 2 - Benefits of Productive Performance Meetings... - 3 - Performance Goals Help Employees... - 3 - Performance Goals Help
Quality Assurance and Improvement Framework
 Quality Assurance and Improvement Framework For Modern Apprenticeships and Employability Quality Standards and Assessment Guidance April 2018 Index Page Introduction 3 Principles and purpose of the Quality
Quality Assurance and Improvement Framework For Modern Apprenticeships and Employability Quality Standards and Assessment Guidance April 2018 Index Page Introduction 3 Principles and purpose of the Quality
Food and Drink Advanced Process Operator Apprenticeship Standard Level 3. End-point Assessment Plan
 Food and Drink Advanced Process Operator Apprenticeship Standard Level 3 End-point Assessment Plan Food and Drink Advanced Process Operator Apprenticeship Standard Summary of Apprenticeship The Food and
Food and Drink Advanced Process Operator Apprenticeship Standard Level 3 End-point Assessment Plan Food and Drink Advanced Process Operator Apprenticeship Standard Summary of Apprenticeship The Food and
COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK POLICY
 COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK POLICY 1. INTRODUCTION The primary purpose of the Competency Framework is to ensure that employees are competent to carry out the tasks required of them as described in their Job Description.
COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK POLICY 1. INTRODUCTION The primary purpose of the Competency Framework is to ensure that employees are competent to carry out the tasks required of them as described in their Job Description.
Competence Development Guide for Dispatchers and Guards
 Competence Development Guide for Dispatchers and Guards ii Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background 1 1.2 Aim of this guide 1 1.3 Who should read this guide? 1 2 The Competence Development Plan
Competence Development Guide for Dispatchers and Guards ii Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background 1 1.2 Aim of this guide 1 1.3 Who should read this guide? 1 2 The Competence Development Plan
COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK Version Produced by Date 1.0 Claire Salter 15.02.2016 MESSAGE FROM THE BOARD The key to success within any organisation is how we recruit, retain and develop our staff. How each individual
COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK Version Produced by Date 1.0 Claire Salter 15.02.2016 MESSAGE FROM THE BOARD The key to success within any organisation is how we recruit, retain and develop our staff. How each individual
Employee Involvement & Teamwork
 Employee Involvement & Teamwork Purpose of this document In this document we discuss a variety of issues relating to the sponsoring of employee involvement and engagement with respect to safety, health
Employee Involvement & Teamwork Purpose of this document In this document we discuss a variety of issues relating to the sponsoring of employee involvement and engagement with respect to safety, health
A Performance Based Environment what does this mean for the aviation community?
 March 2017 White Paper A Performance Based Environment what does this mean for the aviation community? This paper has been developed to stimulate thinking around the new regulatory approach being driven
March 2017 White Paper A Performance Based Environment what does this mean for the aviation community? This paper has been developed to stimulate thinking around the new regulatory approach being driven
1.a Change Concept: Let the mission drive your actions.
 Change Concepts 1.a Let the mission drive your actions. 1.b Be the leader you would want to follow. 1.c Plant now harvest later: Nurture professional growth and foster innovation in others. 1.d Focus on
Change Concepts 1.a Let the mission drive your actions. 1.b Be the leader you would want to follow. 1.c Plant now harvest later: Nurture professional growth and foster innovation in others. 1.d Focus on
JUST CULTURE. Your Organization
 JUST CULTURE Your Organization 1 Development of JUST CULTURE No-blame culture flourished in the 1990s and still endures today. Sought to replace punitive cultures. It acknowledged that a large proportion
JUST CULTURE Your Organization 1 Development of JUST CULTURE No-blame culture flourished in the 1990s and still endures today. Sought to replace punitive cultures. It acknowledged that a large proportion
NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES. Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop HOW WE DO THINGS: OUR CORE COMPETENCIES
 NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop 1 INTRO These are behaviours that are important to achieving our goals. They describe how we work as opposed to
NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop 1 INTRO These are behaviours that are important to achieving our goals. They describe how we work as opposed to
Competency and Values Framework
 college.police.uk Competency and Values Framework Implementation guidance BetterProfessionals forbetterpolicing Limited (2017) This publication is licensed under the terms of the Non-Commercial College
college.police.uk Competency and Values Framework Implementation guidance BetterProfessionals forbetterpolicing Limited (2017) This publication is licensed under the terms of the Non-Commercial College
Sub-section Content. 1 Preliminaries - Post title: Head of Group Risk - Reports to: CRO - Division: xxx - Department: xxx - Location: xxx
 Sub-section Content 1 Preliminaries - Post title: Head of Group Risk - Reports to: CRO - Division: xxx - Department: xxx - Location: xxx 2 Job Purpose - To assist in the maintenance and development of
Sub-section Content 1 Preliminaries - Post title: Head of Group Risk - Reports to: CRO - Division: xxx - Department: xxx - Location: xxx 2 Job Purpose - To assist in the maintenance and development of
HUMAN RESOURCES STRATEGY HUMAN RESOURCES STRATEGIC PLAN
 HUMAN RESOURCES STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2020 INTRODUCTION In its Strategic Plan 2012 2015, the university has set out its vision, ambition and plans for 2020. The university has chosen a high quality research-strong
HUMAN RESOURCES STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2020 INTRODUCTION In its Strategic Plan 2012 2015, the university has set out its vision, ambition and plans for 2020. The university has chosen a high quality research-strong
ENVIRONMENTAL AUDITING GUIDE TD 16/16/E
 ENVIRONMENTAL AUDITING GUIDE MIDDLE EAST GASES ASSOCIATION (MEGA) European Business Center, Office BC 25 Dubai Investments Park, PO Box: 166 Dubai-UAE Tel: +971-4-8135525 / Fax: +971-4-8135575 / E-mail:
ENVIRONMENTAL AUDITING GUIDE MIDDLE EAST GASES ASSOCIATION (MEGA) European Business Center, Office BC 25 Dubai Investments Park, PO Box: 166 Dubai-UAE Tel: +971-4-8135525 / Fax: +971-4-8135575 / E-mail:
WORKPLACE MEDIATION. March 2013
 WORKPLACE MEDIATION March 2013 V1 Jan2010; updated May 2011 STAF'446 - Workplace Mediation Policy March 2013-1 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. POLICY AIMS 3 3. WHAT IS WORKPLACE MEDIATION? 3 4. GENERAL PRINCIPLES
WORKPLACE MEDIATION March 2013 V1 Jan2010; updated May 2011 STAF'446 - Workplace Mediation Policy March 2013-1 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. POLICY AIMS 3 3. WHAT IS WORKPLACE MEDIATION? 3 4. GENERAL PRINCIPLES
Training Needs Analysis
 OSCE OMIK Curriculum Design Course Curriculum Design Course Unit B1 Training Needs Analysis (Participant Workbook) Training Needs Analysis Aim: The Aim of this unit is to provide an understanding of the
OSCE OMIK Curriculum Design Course Curriculum Design Course Unit B1 Training Needs Analysis (Participant Workbook) Training Needs Analysis Aim: The Aim of this unit is to provide an understanding of the
COURSE CATALOG. vadoinc.net
 COURSE CATALOG 2018 vadoinc.net Welcome Welcome to the Vado 2018 Course Catalog. Vado provides any organization or learner numerous opportunities to build the skills needed to lead and manage others, as
COURSE CATALOG 2018 vadoinc.net Welcome Welcome to the Vado 2018 Course Catalog. Vado provides any organization or learner numerous opportunities to build the skills needed to lead and manage others, as
Getting Things Done Insight and Awareness Working Together Accountability Achieving goals Prioritising & Planning Learning & Change
 Competency Framework At UP Projects we have a competency-based approach to staff recruitment, performance review and development. The Framework underpins the culture of the organisation and adds to what
Competency Framework At UP Projects we have a competency-based approach to staff recruitment, performance review and development. The Framework underpins the culture of the organisation and adds to what
H7YG 04 (SCDLMCB8) Lead and Manage the Provision of Care Services that Supports the Development of Positive Behaviour
 H7YG 04 (SCDLMCB8) Lead and Manage the Provision of Care Services that Supports the Development of Positive Behaviour Overview This standard identifies the requirements associated with leading and managing
H7YG 04 (SCDLMCB8) Lead and Manage the Provision of Care Services that Supports the Development of Positive Behaviour Overview This standard identifies the requirements associated with leading and managing
Invitation to Tender RGT Evaluation Framework Agreement, 2016 to 2019
 Invitation to Tender RGT Evaluation Framework Agreement, 2016 to 2019 26th May 2016 1. Purpose of this Invitation to Tender (ITT) 1.1. This invitation to tender is for appointment to a three-year framework
Invitation to Tender RGT Evaluation Framework Agreement, 2016 to 2019 26th May 2016 1. Purpose of this Invitation to Tender (ITT) 1.1. This invitation to tender is for appointment to a three-year framework
Safety Management Introduction
 Safety Management Introduction Eduardo Chacin Regional Officer, Flight Safety ICAO NACC Regional Office Workshop St. Jonhs, Antigua and Barbuda Contents 1. Safety Management Fundamentals 2. ICAO SARPs
Safety Management Introduction Eduardo Chacin Regional Officer, Flight Safety ICAO NACC Regional Office Workshop St. Jonhs, Antigua and Barbuda Contents 1. Safety Management Fundamentals 2. ICAO SARPs
Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities
 Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities Executive (ACPO / Force Command Team) Promotes a real belief in public service, focusing on what matters to the public and will best serve their interests.
Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities Executive (ACPO / Force Command Team) Promotes a real belief in public service, focusing on what matters to the public and will best serve their interests.
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
Impact of Agile on Change Management
 Impact of Agile on Change Management Author Melanie Franklin Director Agile Change Management Limited Introduction Agile approaches and techniques are having significant impact on the volume, frequency
Impact of Agile on Change Management Author Melanie Franklin Director Agile Change Management Limited Introduction Agile approaches and techniques are having significant impact on the volume, frequency
Assessment Practice Standards. A practice development guide to understanding children s needs and family situations
 Assessment Practice Standards A practice development guide to understanding children s needs and family situations Forward Bolton can be proud of a long history of effective multi-agency working to safeguard
Assessment Practice Standards A practice development guide to understanding children s needs and family situations Forward Bolton can be proud of a long history of effective multi-agency working to safeguard
Developing Management Competence for Higher Performance
 Developing Management Competence for Higher Performance P R E S E N T E R : D R. P E T E R M E T O F E D A T E : A U G U S T 2 5 2 7, 2 0 1 4 L O C A T I O N : L O N G B E A C H, C A 9 0 8 3 1 Building
Developing Management Competence for Higher Performance P R E S E N T E R : D R. P E T E R M E T O F E D A T E : A U G U S T 2 5 2 7, 2 0 1 4 L O C A T I O N : L O N G B E A C H, C A 9 0 8 3 1 Building
The Corndel Leadership and Management Diploma: Unit 1. Leading and Managing a Team
 The Corndel Leadership and Management Diploma: Unit 1 Leading and Managing a Team 2017 Corndel Limited. All rights reserved. 2 The Corndel Leadership And Management Diploma: Unit 1 Table of contents Chapter
The Corndel Leadership and Management Diploma: Unit 1 Leading and Managing a Team 2017 Corndel Limited. All rights reserved. 2 The Corndel Leadership And Management Diploma: Unit 1 Table of contents Chapter
Level 3 NVQ Certificate in Management (QCF) Qualification Specification
 Level 3 NVQ Certificate in Management (QCF) Qualification Specification Created: January 2012 Version: 1.0 Accreditation Number: 600/4473/1 Qualification Start Date: 1 st February 2012 Qualification Last
Level 3 NVQ Certificate in Management (QCF) Qualification Specification Created: January 2012 Version: 1.0 Accreditation Number: 600/4473/1 Qualification Start Date: 1 st February 2012 Qualification Last
Our approach to regulation to support natural resource management
 Our approach to regulation to support natural resource management Working Version 1 August 2014 Contents Introduction... 3 Natural Resource Management the wider picture... 4 What is regulation in the context
Our approach to regulation to support natural resource management Working Version 1 August 2014 Contents Introduction... 3 Natural Resource Management the wider picture... 4 What is regulation in the context
LEVEL 4 CERTIFICATE IN POLICE FIRST LINE MANAGEMENT (RQF) Syllabus July 2017 Version 5
 LEVEL 4 CERTIFICATE IN POLICE FIRST LINE MANAGEMENT (RQF) Syllabus July 2017 Version 5 CONTENTS 3 Qualification Purpose 3 Titles & Reference Numbers 3 Key Dates 3 Progression 4 Entry & Recruitment Requirements
LEVEL 4 CERTIFICATE IN POLICE FIRST LINE MANAGEMENT (RQF) Syllabus July 2017 Version 5 CONTENTS 3 Qualification Purpose 3 Titles & Reference Numbers 3 Key Dates 3 Progression 4 Entry & Recruitment Requirements
Safety Management and Risk Reduction Tools Measurement and Performance
 Safety Management and Risk Reduction Tools Measurement and Performance Our SMARRT MAP model illustrates the nine essential components needed for the effective Management of Safety and represents our approach
Safety Management and Risk Reduction Tools Measurement and Performance Our SMARRT MAP model illustrates the nine essential components needed for the effective Management of Safety and represents our approach
CAAT CLIMATE ASSESSMENT AND AUDIT TOOL
 CAAT CLIMATE ASSESSMENT AND AUDIT TOOL The evolution of workplace health and safety A Guideline to Building a Strong Internal Responsibility System workplacesafetynorth.ca INTERNAL RESPONSIBILITY SYSTEM
CAAT CLIMATE ASSESSMENT AND AUDIT TOOL The evolution of workplace health and safety A Guideline to Building a Strong Internal Responsibility System workplacesafetynorth.ca INTERNAL RESPONSIBILITY SYSTEM
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK 1 Introduction to the Leadership Competency Framework The Leadership Competency Framework focuses on three levels of management: Team Leaders/Supervisors responsible for
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK 1 Introduction to the Leadership Competency Framework The Leadership Competency Framework focuses on three levels of management: Team Leaders/Supervisors responsible for
