VBCDHD Just-in-Time Training Checklist for Distribution Node Operations. A. Basic DN Principles Refer to Attachment J of the VBCDHD DSNS Plan.
|
|
|
- Betty Moore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VBCDHD Just-in-Time Training Checklist for Distribution Node Operations Purpose: provide supervisors with the necessary information to train DN staff. Supervisors: 1. Distribute the job action sheets to your staff. 2. Review the following information with your staff and check each item as completed. A. Basic DN Principles Refer to Attachment J of the VBCDHD DSNS Plan. B. DN Functions/Operations Describe how the DN s purpose is to facilitate SNS assets to PODs. Review the DN floor plan and warehouse flow chart. o Describe the activities that take place within the assigned section. For example, in the operations section briefly explain the processes for receiving, repackaging, picking, etc. o Stress that no one should talk to the media. If they are approached by the media they should politely refer the media representative to their supervisor. If the media are unescorted, attempt to escort them to your supervisor. If they will not cooperate, contact your supervisor. C. General housekeeping items: Explain the process for receiving prophylaxis. Describe the location of the following: Restroom Supplies First-aid Break areas for RTP staff Describe protocol for breaks, food, drinks, and communicating with family members. D. Job Action Sheet Review the job action sheet and explain the duties in more detail. Go over the length of the shift. o Ensure training is received on the equipment necessary to perform the job. Review forms applicable to the job. Provide instructions for personal protective equipment, if applicable. Explain the checkout process. E. Answer additional questions about the job action sheets or any other DN aspect.
2 Node Job Duties NODE MANAGER DUTIES The Node Manager is provided by State/Local officials and should not have any other collateral duties during an event/exercise. The manager has responsibility for receiving, storing, order picking, shipping of product, Node safety and Node personnel administration. The manager may also be responsible for requesting additional supplies from SNS, distributing local stockpiles, coordinating the prophylaxis of Node personnel and their families and coordinating Node security. Establish Receiving, Storage, and Dispensing plans. o Locate Nodes to be utilized in time of emergency. Each regional hub needs at least one primary and one alternate Node that can be used in an emergency. Ensure the Nodes selected meet the SNS Node checklist standards. Prepare a Memorandum of Understanding or contract with the building owner. o Layout the Node for receipt of SNS assets. Identify areas for the Push Package, Secure Storage Area, Receiving, Shipping Staging, Re-packaging. Provide office space for Node Manager, Inventory Control and TARU. Label areas with signs. o Determine Dispensing Plan Receive/validate orders for product from supported sites or receive patient counts from sites and determine needs based on treatment regimen. Apportion available product to sites if there is not enough product to fill all orders. Set order fill priorities (the order that picks will be completed). Prepare a Memorandum of Understanding or contract with trucking companies and/or government agencies with vehicles. Determine shipping routes to dispensing sites and treatment centers. If more than 1 delivery is loaded on a truck, determine delivery order. Open the Node or coordinate with tenants about your arrival and requirements. Personnel Administration o Determine work schedule/shifts. o Determine Node positions and prepare work instructions and Node safety and administrative rules. o Recall Node personnel. o Provide briefing to Node personnel on the situation. o Assign personnel to Node positions. o Ensure personnel have all the proper tools and supplies they need to perform their job. o Ensure personnel s personal needs are addressed. Provide Node status to the EOC. o Provide Situation Report to Public Health Operations Center (PHOC), as required.
3 o Alert PHOC of any problems or needs that require their action. Provide necessary equipment and supplies to Node. o Pallet jacks, forklifts, dock plates, and wheel chocks. o Pallets, pallet wrap, forms (SNS Inventory form, receiving reports), pens, markers and paper. Request additional supplies to fill needs. o Local sources for administrative and Node supplies (pallets, wrap). o SNS for most medical supplies. Recover any unused assets from Dispensing Sites and Treatment Centers. o Coordinate and provide transportation to pick up assets. o Inspect asset conditions. o Coordinate the return of assets to SNS and local stockpiles.
4 NODE INVENTORY CONTROL DUTIES Record all receipts and issues in Inventory Management files Load all receipt data into accounting records. o If you have an inventory database, follow the instructions to upload the pipedelineated file of the Push Package contents. You will get this from the Stockpile TARU Logistics Lead. o If you do not have an inventory database, open the file in excel. Go to File/Open, then select A: drive and look for text files. When you open the file, the text import wizard will appear. Step 1 Choose Delimited under the Original data type and click next. Step 2 Click on Other in the delimiters (unclick any others) and enter (the button just below the backspace). Then click Next. Step 3 Click on Finish. Click Ctrl-A to select all. Go to Format, Columns, and select Autofit Selection. (This will allow you to read all the information in each column.) Go to Data, and select Sort. Sort by column A. (This will eliminate all the extra spaces.) Insert a new row on the top line and title the columns Column Title A Container # B Seal # C Locator (this column can be deleted) D Item # E Description F Qty G Unit of Measure H No longer used (Delete column) I Case pack (qty per case) J Lot # K Expiration date L Item type o All other receipts will have to be added manually. Subtract quantities of product that have been shipped. Provide current status of all products. Select items to spot inventory, as time permits, to validate inventory records.
5 NODE STORAGE AND PICKING UNIT LEAD DUTIES Obtain product requirements for dispensing sites from Node manager. (VBCDHD designated POD's) Push Kit Pick Lists) Determine apportionment of available supplies, as needed. Create pick lists and assign them to pickers. Assist pickers NODE PICKER DUTIES Teams of three people; Picker, Recorder and Stacker. These positions should be rotated among the three. Obtain Hospital and LHD Push Kit Pick List from picking lead Go to the location indicated on the pick list. o If you are sent to an unopened container, break the seals with a quick snap or with scissors/knife. o Pull the locking bars toward the center of the container. Use the strap to lift up and out from the bottom. o Remove the packing list and container layout from the front pocket and place them in the container. o Slide the container door to the lean on the right side of the container. Select the required product. o Picker The pick list will provide you with the item number and description of the product. If you don t see the product immediately, refer to the container layout to find where it is located. Check each carton to ensure you pick the right item (many look alike) and to see the lot number. Tell the recorder the lots and expiration dates of the product selected. o Recorder Tell the person picking the product needed and the quantity. Annotate the lot number and expiration date for every product selected on the pick sheet. When all pallets are picked for the order, label each pallet with its destination and assign a pallet number, (1 of 1, 1 of 3, 2 of 3 ). Verify that everything on the pick list is on a pallet for the order. Leave the pick sheet with the order and let quality assurance know that the order is complete. o Stacker Stack the pallet with the largest/heaviest cases on the base and work up. Restack, as needed. Do not let product hang over the edge of the pallet and do not stack more than 4 high. If the pallet is full and more picks are required, move the pallet to the appropriate staging area and start again with another pallet. Label multiple pallets for one order like; 1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 of 3.
6 NODE QUALITY CONTROL DUTIES Ensure that all pallets are validated for each order. o The packing list is with the pallet(s). o Correct Quantity o Cases are in good condition and properly stacked. o Pallet labeling is correct (pallet numbers for multiple pallet orders). Correct any discrepancies on the pick list, if needed. o If the pallet is short, check with the pickers and inventory control to see if they want to fill the shortage, or ship as-is. Sign the pick list as being inspected by quality assurance. Wrap the cases to the pallet with stretch film, tight enough to avoid shifting during movement on the truck. Make a copy of the pick list and attach it to the lead pallet (pallet 1) of the order and let shipping know that it is complete. Provide the original pick list to inventory control.
7 NODE RECEIVING UNIT LEADER DUTIES Ensure trailer is chocked (trailer wheel blocked from rolling) prior to entry of any personnel. Ensure all incoming stock is inspected for quality and quantity. Determine storage locations of received product. Ensure that Inventory Control is informed of all received stock and its condition. Sign SNS Inventory Form from delivery trucks. Annotate discrepancies, as required. Assist in unloading, inspecting, and storage of stock. NODE RECEIVING CLERK DUTIES Offload trailers with forklift (if qualified and approved by supervisor) or pallet jack into the receiving area. Inspect material for quality and quantity after the entire trailer has been offloaded. o If a carton looks damaged, open the carton to see if material is damaged. o Fill out receiving report and identify any discrepancies in quantity and quality. o Validate your counts with the shipping manifest and Bill of Lading (BOL). The driver has the BOL and may have the manifest. Otherwise, the manifest should be located on the lead container. Move product to the designated storage area. o Identify the location where the product was placed on the receiving report. o If bulk storage is being used, mark the pallet with a pallet ID and write this on the receiving report. o Push Package containers do not require a detailed receiving report. Simply write each container number received, per trailer, on the report. Sign the receiving report and turn it in to Inventory Control. Assume the role of shipping lead when the assigned lead is not present. Assist other areas, as needed.
8 NODE SHIPPING DUTIES Ensure trailer is chocked (trailer wheels blocked) prior to entry of any personnel. Notify carriers of transportation requirements. Fill out SNS Inventory Form for all shipments. o Write in the shipping address and point of contact, with a telephone number. o Write in total number of pallets. o In the comments section, write that you want a call from the POC upon receipt. When notified that an order is ready to ship, and the carrier for that shipment has arrived, move the product to the truck. o Verify that all of the pallets for the order are accounted for. o Reverse load multiple shipments on the truck so that the 1 st one to be delivered in the last loaded. o Balance the load on the truck to keep the pallets from shifting during transport. Get an estimated time of delivery from the driver and have the driver sign the Transfer of Custody Form after the truck is loaded. Provide the driver with the original SNS Inventory Form (packing slip) and keep a copy of the Inventory Form for your records. Place this Inventory Form in a pending delivery file. Call the delivery point after the estimated time of delivery has passed to confirm receipt of the order. Once receipt is confirmed, annotate the Inventory Form as complete and file it in the completed file. Assist in other areas, as needed.
9 Shift Supervisor Duties Take attendance and fill vacancies, as needed. Ensure employees understand their work instructions. Ensure employees have the necessary tools to complete their work. Coordinate efforts to receive, store and ship required supplies to customers. Assume Node Manager s duties in her/his absence. Ensure employee welfare is cared for. Resolve employee problems. Node Safety and Administrative Rules No Smoking in building. No eating in storage area. Only approved licensed drivers will operate forklifts. Do not leave without informing your supervisor.
10 Just-In-Time (JIT) Training Protocol & Briefing Topics Chain of Custody Protocol The VO and escorting security personnel will sign the SNS Order Form in accordance with established chain of custody procedures. One (1) copy of the SNS Order Form with the Transfer Form, and 1 copy of the Transfer Form only will be sent with the shipment. The Inventory Control Unit will print two copies of the Picking List and provide one copy to the Transportation Branch Director. This copy will be provided to the VO/AVO to take on the mission to provide a brief inventory list for the receiving site to verify the order. Transfer Forms. A Transfer Form (TAB A) will be completed when supplies are off-loaded at the DN/TC. The VO/AVO will ensure this form is returned to the RSS upon mission completion. Controlled Substance Transfer Forms. The Push Packages contain Schedule II (morphine) and IV (diazepam and midazolam) substances. Schedule II substances must be stored in a safe or vault and Schedule IV substances in a locked drug cabinet. Certain Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) requirements exist for transferring Schedule II materials to appropriate registrants at each location where such materials are to be delivered. The request to transfer such material is to be recorded on the DEA Form-222 (See TAB B). Although DEA has agreed to allow transfer of controlled substances without completion of this form during a public health emergency, even if a DEA registrant is unavailable to accept and sign a Form-222 for Schedule II transfers, the registrants eventually must provide the signed forms for each transfer. Given this, planning should be conducted to identify sufficient DEA registrants so that there will be a high likelihood that the Form-222 will be completed at the time of transfer and not days or weeks later. Should a DEA registrant not be available, Vehicle Operators and Assistant Vehicle Operators (AVO) will be skilled in ensuring the following occurs at the time of delivery: - Registrant Information. They will obtain the name and DEA number of the person who will eventually sign the Form Signatory Certifications. They will require the person who received the material to show a government issued ID (e.g., drivers license) and sign copies of the manifest that itemizes the controlled substances being transferred. - Completion of DEA Form-222. The individuals receiving the substance are made fully aware that the registrant is required to sign a DEA Form-222 for the transfer of the Schedule II items as soon as practical.
11 Routing Information The following information is provided regarding road networks throughout the State: Mattawan All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: Paw Paw All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: Lawrence All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: Hartford All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: Decatur/Dowagiac All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: Cassopolis All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: South Haven All networks open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS: Other Airport /Routes Open Minor Traffic Congestion Significant Traffic Congestion Road Closures Entry Points Unusable REMARKS:
12 Security / Communications Procedures Security of the SNS materials must be maintained at all times. One security element will accompany each mission. Communications procedures will be in accordance with the COI provided during briefing. Radio Communications Checks will be performed prior to departing the Node. Temperature of the SNS materials must stay between 58 degrees and 86 degrees Fahrenheit. If the temperature falls outside of this acceptable range, this will be reported via SITREP. The vehicle should not make unscheduled stops unless absolutely necessary (e.g., refueling operations.) The VO / AVO and one member of the Security Escort will remain with the vehicle when supplies are on board. Reports: VO/AVO will submit the following type reports while performing distribution operations. Mission Updates. Verbal reports are provided to the Dispatcher when a delivery vehicle arrives at and departs from a scheduled POD. Situation Reports (SITREPS). A verbal SITREP is submitted to the Communications Branch when any situation is encountered that may significantly slow, hamper or otherwise jeopardize the successful accomplishment of the distribution mission. These reports may be submitted by the VO/AVO/Security Escort at any time and the reports will be used to advise the PHOC and POD management, as appropriate. (See Michigan s SNS Plan). Should a SITREP be made regarding questions related to temperature control in the vehicle, this question will be relayed to the Pharmacy & Dispensing Branch Director and/or CDC TARU staff. Mission Completion Report. When distribution vehicles notify the Communications Branch that they have returned to the Node from their mission, a Mission Completion Report will be prepared by the Dispatch Unit, Transportation Branch. This informal report will be derived from the Mission Status Board maintained by the Dispatch Section (discussed below) and simply annotates the Mission Number, the times of arrival and departure of each mission at each DN/TC, time of return to the RSS, and any remarks of problems or circumstances negatively affecting the mission. This information will be used during the After Action Report process to gauge the effectiveness of the planned distribution runs. Mission numbers are assigned by the Dispatcher and will be used when making reports. While on the move, should the 800 MHz radio and cell phone become non-operational; the VO/AVO will endeavor to relay urgent information through the security escort. Non-urgent information will be reported via landline at the next DN/TC stop.
13 Appropriate Use of MHE Only those VO/AVO and individuals at DN and TC who have been trained on the use of pallet jacks and/or fork lifts, as appropriate, will operate such equipment. VO/AVO will strictly follow safety requirements when operating such equipment (See TAB C Pallet Jacks (i.e., Operational & Safety Instructions) & TAB D Powered Industrial Trucks (i.e., Fork Lift Operational Safety & Use). VO/AVO will wear work gloves and safety glasses when operating fork lifts and pallet jacks. Fork lifts must be in the to 5000-pound capacity. Fork lifts greater 6000 pounds are not efficient. Loading & Off-Loading Materials Loading of materials at the RSS will be under the supervision of the Receiving and Shipping Unit which will ensure the pallets are loaded in the proper sequence (i.e., last delivery is loaded first). The Inventory Processing Branch Director will coordinate with the Transportation Branch for VO and AVO to assist the Inventory Team with uploading SNS materials into their vehicles, as appropriate. Off loading of materials at each DN/TC is the responsibility of the receiving agency. However, in some instances, it may be appropriate for VO/AVO to render assistance, providing certification for use of MHE (as specified above.) To expedite distribution operations, pallets will not be returned to the RSS. Safety Notice Because of their extensive knowledge of the facility to house the RSS operation, the MDCH/OPHP has entered into a MOA with (deleted for security purposes). Accordingly, key members of this agency are to be available to serve in the capacity of Safety Officers during use of their facility. The Safety Officers will attend each of the various RSS Manager and Branch Managers initial briefings to their staffs and volunteers to ensure all safety issues are addressed.
14 TAB A TAB B
15
16 7 Step Checklist 1. Name of supplier, address, city and state are correct. 2. Form is dated. 3. Number of packages, size of package, and strength desired is correct. 4. The NO. OF LINES COMPLETED block is filled in. 5. Authorized individual has signed the form. 6. Form contains no erasures or alterations. 7. Remove the purchaser s copy (blue copy) and place in your records.
17 TAB C TAB D
18 MIOSHA-STD-1119 /06) 12 Pages Fork Lift Operational & Safety of Use DEPARTMENT OF LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH DIRECTOR'S OFFICE GENERAL INDUSTRY SAFETY STANDARDS Filed with the Secretary of State on December 28, 1970 (as amended October 25, 1972) (as amended November 1, 1974) (as amended October 28, 1976) (as amended April 2, 1979) (as amended November 7, 1980) (as amended March 2, 1983) (as amended April 11, 2000) These rules take effect 15 days after filing with the Secretary of State (By authority conferred on the director of the department of consumer and industry services by sections 16 and 21 of PA 154 of the Public Acts of 1974 as amended, and Executive Reorganization Order Number , being '' , , and of the Michigan Compiled Laws) R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R , and R , of the Michigan Administrative Code are amended and R , R , R , and R of the Michigan Administrative Code are rescinded as follows: PART 21. POWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS TABLE OF CONTENTS R Scope...1 R Definitions; A to C...1 R Rescinded...2 R Definitions; D to F...2 R Definitions; H to I...2 R Definitions; L...2 R Definitions; M and N...2 R Definitions; O, P...3 R Definitions; R to U...3 R Adoption of standards...3 R Rescinded...3 R Approved labels...3 R Rescinded...3 R Warning devices and lights...4 R Modifications...4 R Parking brakes; tires...4 R Rescinded...4 R Operator platforms...4 R Steering control...4 R Load handling controls, general...4 R Load handling controls; direction of motion and guards...4 R Overhead guard on high-lift truck...5 R Operator selection...5 R Training...6 R Testing...6 R Permits...6 R Restriction of use...7 R Mechanical condition and maintenance...7 R Blocks and safety stands for maintenance...7 R Fuel. R Electric trucks...8 R Dockboards and plates...8 R Order picker trucks, high-lift-platforms...8 R Fork lift truck platforms...9 R Load backrest extensions...9 R Spinner knobs...9 R Daily checks...9 R General operating rules...9
19 R Position of arms and legs...9 R Parking...9 R Towing and pushing...9 R Loading trucks, trailers, and railcars...9 R Surveying path of travel...9 R Operations in hazardous areas...10 R Reporting accidents...10 R Clear access...10 R Making repairs...10 R Flammables...10 R Operation...10 R Slow down at crossings and obstructions..10 R Clear view...10 R Ascending and descending grades...10 R Traveling...10 R Starts, stops and turns...10 R Horseplay...10 R Wet floors, dockboards, and bridgeplates..10 R Entering elevators...10 R Running over loose objects...10 R Operators' loading rules...10 GENERAL PROVISIONS R Scope. Rule The purpose of this part is to provide, in or about places of employment, minimum safety rules for the care and use of powered industrial trucks and to provide for operator safety and specifications of equipment. R Definitions; A to C. Rule (1) Attachment means a device, other than conventional forks or load backrest extension, mounted permanently or removed on the elevating mechanism of a truck for handling the load. Popular attachments are fork extensions, clamps, rotating devices, side shifters, load stabilizers, rams and booms. (2) Cantilever truck means a self-loading counter-balanced or noncounterbalanced truck equipped with cantilever load engaging means. (Appendix A, Fig. 1). (3) Capacity when referring to trucks, means: (a) The capacity of a truck equipped with a load carriage and forks, or with attachments, is the maximum weight in pounds, at a specified load center which the truck, based on the strength of its various components and applicable stability, can lift to the maximum elevation of the load engaging means. Alternate capacities may be established at the same specified load center and at less than maximum elevation of the load engaging means. (b) The capacity of a truck equipped with a platform is the maximum weight in pounds, at a specified load center which the truck, based on the strength of its various components, can lift to the maximum elevation of the load engaging means. (4) Carriage means a support structure for forks or attachment, generally roller mounted, traveling vertically within the mast of a cantilever truck. (5) Center-control truck means a truck in which the operator's control position is located near the longitudinal center of the truck. (6) Counterbalanced truck means a truck equipped with load engaging means wherein all the load during normal transporting is external to the polygon formed by the wheel contacts. (Appendix A, Fig. 1). R Rescinded. R Definitions; D to F. Rule (1) Drift means to move without control. (2) Electric truck means a truck in which the principal energy is transmitted to motors in the form of electricity from a power source such as, but not limited to, a battery or motor generator. (3) End-control truck means a truck in which the operator's position is located at the end opposite the load. (4) Fixed platform truck means a truck equipped with a load platform which is non-elevating. (5) "Forks" means horizontal tine-like projections, normally suspended from the carriage, for engaging and supporting loads. (6) Fork height means the vertical distance from the floor to the load carrying surface adjacent to the heel of the forks with mast vertical, and in the case of a reach truck, with the forks extended. (7) Fork-lift truck means a light-lift self-loading truck equipped with load carriage and forks for transporting and tiering loads. (8) Free play means an uncontrolled movement.
20 R Definitions; H to I. Rule (1) High-lift truck means a self-loading truck equipped with an elevating mechanism designed to permit tiering. Popular types are high-lift fork trucks, high-lift ram trucks, high-lift boom trucks, high-lift clamp trucks and high-lift platform trucks. (Appendix A, Fig. 1). (2) High-lift platform truck means a self-loading truck equipped with a load platform, intended platforms. (Appendix A, Fig. 2). (3) Industrial crane truck means a truck intended primarily for pick and carry use in warehousing, yarding, or industrial plant operation over improved or hard surfaced roads and yards, including maintenance within these areas. (4) Industrial tractor means a truck designed primarily to draw 1 or more nonpowered trucks, trailers or other mobile loads. (Appendix A, Fig. 5). (5) Internal combustion engine truck means a truck in which the power source is a gas, LP gas, gasoline or diesel type engine. (6) Issuing authority means an employer or his designated representative who instructed and trained the operator. R Definitions; L. Rule (1) Liquefied petroleum gas (LP gas) means a fuel which is composed predominantly of any of the following hydrocarbons, or mixtures of them: propane, propylene, butanes (normal butane or iso-butane) and butylenes. (2) Load-axle means the truck axle nearest the load. (3) Load backrest extension means a device extending vertically from the fork carriage frame. (4) Load center means the horizontal longitudinal distance from the intersection of the horizontal load-carrying surfaces and vertical load-engaging faces of the forks, or equivalent load positioning structure, to the center of gravity of the load. (5) Load engaging means a load handling device attached to a powered industrial truck for the purpose of handling a load. (6) Low-lift truck means a self-loading truck equipped with an elevating mechanism designed to raise the load sufficiently to permit horizontal movement. Popular types are low-lift platform trucks and pallet trucks. (Appendix A, Fig. 3). (7) Low-lift platform truck means a self-loading truck equipped with a load platform intended primarily for transporting loaded skid platforms. (Appendix A, Fig. 3). R Definitions; M and N. Rule (1) Mast means a support member providing the guideways permitting vertical movement of the carriage. It is usually constructed in the form of channels or similar sections providing the supporting pathway for the carriage rollers. (2) Motorized hand truck means a truck designed to be controlled by a walking operator and used to lift, tow, carry, stock and tier materials. (Appendix A, Fig. 4). (3) Motorized hand or rider truck means a dual purpose truck designed to be controlled by a walking operator or by a riding operator. (Appendix A, Fig. 6). (4) Narrow aisle truck means a self-loading truck primarily intended for right angle stacking in aisles narrower than those normally required by counterbalanced trucks of the same capacity. (Appendix A, Fig. 10). (5) Non-elevating truck means a noncounterbalanced truck designed primarily for burden-carrying and not capable of self-loading. R Definitions; O, P. Rule (1) Operator means an employee who has been trained, tested, and authorized by the present employer to operate a powered industrial truck. (2) Order picker truck, high-lift means a high-lift truck controlled by the operator stationed on a platform movable with the load engaging means and intended for manual stock selection. The truck may be capable of self-loading or tiering or both. (Appendix A, Fig. 9). (3) Overhead guard means a framework fitted to a truck over the head of a riding operator. (4) Overall lowered mast height means the maximum vertical dimension from the ground or floor to the extreme top point of the mast with the fork carriage in the fully lowered position and unloaded. (5) Pallet truck means a self-loading low-lift truck equipped with wheeled forks of dimensions to go under a single faced pallet or between the top and bottom boards of a double faced pallet and having wheels capable of lowering into spaces between the bottom boards so as to raise the pallet off the floor for transportation. (Appendix A, Fig. 4). (6) Parking brake means a device to prevent the movement of a stationary truck. (7) Powered industrial truck or truck means a mobile, power driven vehicle used to carry, push, pull, lift, stack, or tier material. R Definitions; R to U. Rule (1) Reach truck means a self-loading truck, generally high-lift, having load engaging means mounted so the means can be extended forwardly under control to permit a load to be picked up and deposited in the extended position and transported in the retracted position. (Appendix A, Fig. 7).
21 (2) Rough terrain forklift truck means a wheeled-type truck which is designed primarily as a fork truck that has a vertical mast or pivoted boom, or both, which has variable fixed length reach and which may be equipped with attachments and that is intended for operation on unimproved natural terrain as well as the disturbed terrain of construction sites. A machine that is designed primarily for earth-moving, such as a loader or dozer, even though its buckets and blades are replaced with forks or a machine that is designed primarily as an over-the-road truck that has a lifting device, is not a rough terrain forklift truck. (3) Self-loading means the capability of a truck to pick up, carry, set down and, in the case of high-lift types to stack or tier its load without the aid of external means. (4) Service brake means a device designed to bring a moving truck to a halt. (5) Side loader means a self-loading truck, generally high-lift, having load engaging means mounted in such a manner that the means can be extended laterally under control to permit a load to be picked up and deposited in the extended position and transported in the retracted position. (Appendix A, Fig. 8). (6) Straddle truck means a general class of cantilever truck with horizontal structural wheel supported members extending forward from the main body of the truck, generally high-lift, for picking up and hauling loads between its outrigger arms. (Appendix A, Fig. 10). (7) Tire means a tire which may be standard solid, cushion solid, pneumatic or solid pneumatic style. (8) Tiering means a process of placing a load on or above another load. (9) Unattended truck means 1 which is beyond the vision or more than 25 feet from the operator, whichever is less. R Adoption of standards. Rule (1) A powered industrial truck manufactured after January 15, 1971, but before 1993, shall be certified by the manufacturer that the truck covered by this part has been produced according to the mandatory requirements of section 3 and 4, except subsection 421 of section 4, of the ANSI standard B Safety Standards For Powered Industrial Trucks. (2) A low lift or high lift truck manufactured after the effective date of this part shall be in compliance with the requirements of the ANSI standard B Safety Standard For Low Lift And High Lift Trucks, except as noted in subrule (1) of this rule. (3) A rough terrain fork lift truck manufactured after the effective date of this part shall be in compliance with the requirements of ANSI standard B Rough Terrain Fork Lift Trucks. (4) A industrial crane truck manufactured after the effective date of this part shall be in compliance with ANSI standard B Safety Standard For Industrial Crane Trucks. (5) A tow tractor manufactured after the effective date of this part shall be in compliance with ANSI standard B Operator Controlled Industrial Tow Tractors. (6) A manually propelled high lift industrial truck manufactured after the effective date of this part shall be in compliance with ANSI standard B Manually Propelled High Lift Industrial Trucks. (7) The standards specified in this rule are adopted by reference. These standards may be purchased from Global Engineering Documents, 15 Inverness Way East, Englewood, Colorado, 80112, USA, telephone number: and web-site global@ihs.com. at a cost of respectively, $97.00, $77.00, $56.00, $56.00, and $70.00, as of the time of the adoption of these rules, or from the Michigan Department of Consumer and Industry Services, Standards Division, 7150 Harris Drive, Box 30643, Lansing, Michigan, R Rescinded. NAMEPLATES AND MARKINGS EQUIPMENT R Warning devices and lights. Rule (1) A truck, except a motorized hand truck, shall be equipped with an audible device to warn of approach. (2) A truck used in areas where general lighting is less than 2 foot-candles shall be equipped with auxiliary lights that illuminate work in process. R Modifications. Rule (1) The employer shall not install an additional counterweight without written assurance from the manufacturer of the truck that the truck will meet the stability requirements of ANSI standard B Safety Standard For Low Lift And High Lift Trucks. (2) An employer shall not make other modifications affecting capacity or safety without written approval of the manufacturer or an engineer knowledgeable on the subject. Capacity, operation, and maintenance instruction plates, tags, or decals shall be changed accordingly. (3) If the truck is equipped with front end attachments, the name plate shall be marked to show all of the following: (a) Identification of the attachments. (b) The approximate weight of the truck and attachment. (c) The load capacity of the truck and attachment combination at maximum elevation of the load engaging means with load laterally centered.
22 R Parking brakes; tires. Rule (1) The parking brake on a sitdown rider truck shall be capable of holding the truck on the maximum grade which the truck can negotiate with rated load, or on a 15% grade, whichever is lesser. The parking brake shall be manually or automatically applied and shall remain applied until released by the operator. (2) Tires shall be used as recommended by the truck manufacturer. R Rescinded. R Operator platforms. Rule (1) An end control, reach, narrow aisle, order picker high-lift, order picking and stacking, and motorized hand rider truck shall be equipped with a platform extended beyond the operator's position, and shall withstand a compression load equal to the weight of the loaded vehicle applied along the longitudinal axis of the truck with the outermost projection of the platform against a flat vertical surface. The back protective guard where provided shall permit rapid and unobstructed ingress or egress from the platform. R Approved labels. Rule (1) A powered industrial truck which has been accepted by an approved testing laboratory shall bear a label or marking indicating such acceptance. (2) A nameplate, label or tag provided on such a truck shall be maintained in place and in legible condition. R Rescinded. (2) On a double end control baggage type truck or a truck which may be transported on short elevators, means should be provided to prevent accidental folding of the operator's folding platform. (3) All of the following apply to an order picker truck, high-lift: (a) A removable operator platform shall be provided with a device that attaches the platform to the lifting means. (b) The operator platform shall be equipped with side guard rails. (c) When the platform is elevated, the horizontal travel speed of the truck shall be automatically reduced to a degree necessary to maintain stability under maximum braking load and turning. (d) Paragraphs (a) and (c) pertain only to a truck manufactured after the effective date of this part. (Note: The effective date was January 15, 1971.) R Steering control. Rule (1) An employer shall assure that, except on a motorized hand and motorized hand or rider truck, the steering control of a powered industrial truck is contained within the outlines of the planes of the truck, or guarded to prevent injury to the operator during movement of the controls when passing an obstacle such as a wall, post, equipment, box, or other truck. (2) An employer shall assure that on a motorized hand and motorized hand or rider truck, the steering handle is provided with a guard or device to protect the operator's hands from injury when passing an obstacle such as a wall, post, equipment, box, or another truck. R Load handling controls, general. Rule (1) All of the following apply to a load handling control on a truck: (a) Is preferably located for right hand operation. (b) Is a single lever used to perform more than one function. Push button or pre-selected controls shall be properly identified. (c) Is clearly and durably identified to indicate function and direction of motion of load or equipment. (d) Is self-centering. R Load handling controls; direction of motion and guards. Rule (1) A lever or handle type control, including a toggle switch, shall be in accordance with the following table:
23
24 (3) An overhead guard may be omitted from a high-lift truck if the truck is never used to lift or raise material or objects more than 72 inches measured from the floor to the forks and if all of the following are complied with: (a) The load is limited to a single rack or pallet. (b) The truck is not operated in an area where material or objects are stacked above the operator's head. (c) A sign with lettering not less than 1/2 inch high is securely attached and the area of the operator's controls stating, This truck shall not be used to lift materials above the operator's head or in an area where materials are stacked above the operator's head. (4) A low-lift rider truck which is used to lift material stacked higher than the head of the operator, and which would likely vibrate and fall back onto the operator, shall be provided with an overhead guard. (5) The overhead guard shall be capable of withstanding the impact of a 100-pound solid hardwood cube, or equivalent, dropped a distance of 5 feet 10 times, without failure or without permanent deflection exceeding 3/4 inch. (6) The overhead guard shall be constructed in a manner that does not interfere with visibility. Openings in the top shall not exceed 6 inches in 1 of the 2 dimensions, width or length. The guard shall be large enough to extend over the operator under all normal circumstances of truck operation, including forward tilt. (7) A fork truck equipped with a single-tilt cylinder shall be made to avoid injury to the operator by the overhead guard resulting from failure of this cylinder or associated parts. (8) On a truck where the operator is seated, a vertical clearance of not less than 39 inches should be maintained from the point of maximum depression of the seat under the operator to the underside of the section of the overhead guard under which the operator's head moves during normal operation. (9) On a powered industrial truck where the operator stands on a platform, a vertical clearance of not less than 74 inches should be maintained from the platform to the underside of the section of the overhead guard under which the operator s head moves during normal operation. (10) Where head room conditions limit the overall lowered height of the truck, a normal overhead guard height may be reduced. (11) An overhead guard is intended to offer protection from the impact of small packages, boxes, and bagged material representative of the job application, but not to withstand the impact of a falling capacity load. EMPLOYER RESPONSIBILITIES R Operator selection. Rule (1) An employer shall assure that an employee assigned to operate a powered industrial truck shall meet the following minimum requirements, except as noted in subrule (3) of this rule: (a) Have corrected vision that meets the same requirements as those for a valid Michigan driver's license. Evidence of meeting this requirement shall be a Michigan driver's license or a doctor's certificate. (b) Have effective use of all 4 limbs, unless the powered industrial truck has been modified, as prescribed in R , to permit operation with fewer than 4 limbs. A prosthetic device is to effectively operate the controls. (c) Be of a height sufficient to operate the controls and have an unobstructed view over the controls and dashboard. (d) Have coordination between eyes, hands, and feet. (e) Have freedom from known convulsive disorders and episodes of unconsciousness for a period of 1 year before obtaining a powered industrial truck operator's permit or a lesser time with the assurance from a neurologist that the disorders or episodes are under control. (f) Have the ability to understand signs, labels, and instructions. (2) An employer shall assure that an employee assigned to operate a powered industrial truck shall meet the minimum requirements stated in this rule and shall be retested not less than every 3 years. (3) Requirements listed in subdivisions (b) and (c) of subrule (1) of this rule and of subrule (2) of this rule are optional for operators of a motorized hand low lift truck. (4) An employee who was operating a powered industrial truck before November 9, 1972, but does not meet the requirements of subdivisions (a), (b), (c), and (d) of subrule (1) of this rule and of subrule (2) of this rule, may be continued as an operator if the handicap or inability does not prove detrimental to the assigned task. R Training. Rule (1) An employer shall provide training to the employee before the employee's assignment as an operator of a powered industrial truck. Instruction shall include all of the following: (a) Capacities of the equipment and attachments. (b) Purpose, use, and limitations of controls. (c) How to make daily checks. (d) Practice and operating assigned vehicles through the mechanical functions necessary to perform the required job. (e) State safety standard rules 2171 to 2193 of Part 21 Powered Industrial Trucks, being R to R of the Michigan Administrative Code. (f) Hazards associated with exhaust gases produced by fossil fuel powered industrial trucks (e.g. carbon monoxide, components of diesel exhaust), and hazards associated with the handling of electrolyte
25 chemicals used for battery operated trucks (e.g. sulphuric acid), shall be provided in accordance with the Michigan Right To Know Law, Hazard Communications standards 29 C.F.R. ' as adopted by R and R (2) Training shall consist of a combination of formal instruction (e.g. lecture, discussion, interactive computer learning, videotape, written material), practical training, and testing of the operator=s performance in the workplace as required in R (3) Refresher training in relevant topics shall be provided to an operator under any of the following conditions: (a) An operator has been observed to operate the vehicle in an unsafe manner. (b) An operator has been involved in an accident or a near-miss incident. (c) An operator has received an evaluation that reveals that the operator is not operating the truck safely. (d) An operator is assigned to a different type of truck. (e) A condition in the workplace changes that could affect safe operation of the truck. (4) An evaluation of each operator=s performance shall be conducted before renewal of a truck operator permit. An individual who is authorized by the employer and who has the knowledge, training, and experience to train and evaluate the competence of the operator shall provide training and evaluation. R Testing. Rule (1) An employer shall test an employee before authorizing the employee to operate a powered industrial truck, except a motorized hand truck. The test shall check the employees: (a) Operating ability. (b) Knowledge of the equipment. (c) Knowledge of state safety standard rules 2171 to 2193 of Part 21. Powered Industrial Trucks, being R to R of the Michigan Administrative Code. (d) Knowledge of daily checks. (2) A performance test shall be given to determine whether the employee can operate the assigned powered industrial truck through the functions necessary to perform the required work. (3) An employee who has a valid permit to operate a powered industrial truck issued by another employer may be tested as prescribed in this rule without meeting the training requirements of R R Permits. Rule (1) An employer shall provide the employee with a permit to operate a powered industrial truck only after meeting the requirements prescribed in R , R , and R A permit is optional for operators of motorized hand low lift trucks. (2) An employee being trained is exempt from the permit requirement for a period of not more than 30 days, provided the employee is under the supervision of an individual who is authorized by the employer and who has the knowledge, training, and experience to train operators and to evaluate their competence, and that the training period does not endanger the trainee or other employees. (3) A permit shall be carried by the operator or be available upon request by a department representative at all times during working hours. (4) A permit shall indicate the type of truck an operator has been trained on and is qualified to operate. (5) A permit to operate a powered industrial truck shall be valid only with the employer who issued the permit, and the permit shall be issued for a period of not more than 3 years and shall be consistent with subrule (2) of R An employee who is exempt under subrule (4) of R may continue to operate a powered industrial truck if the employee=s handicaps or inabilities do not prove detrimental to his or her task. (6) A permit shall contain the following information (see sample permit): (a) Firm name. (b) Operator's name. (c) Operator I.D. number, if any. (d) Name of issuing authority. (e) Type of truck authorized to operate. (f) Operator restrictions, if any. The permit shall state the nature of the restriction. (g) Date issued. (h) Date expiring. (7) A sample permit is set forth as follows:
26 SAMPLE PERMIT INDUSTRIAL TRUCK OPERATOR PERMIT (firm name) OPERATOR'S NAME: OPERATOR'S NUMBER: IS AUTHORIZED TO OPERATE: (insert type of truck(s) authorized) RESTRICTIONS:(explanation of restrictions) DATE ISSUED: (month - day- year) DATE EXPIRING: (month - day- year) BY ISSUING AUTHORITY: TITLE loaded or unloaded in excess of 5 inches in 5 minutes. (d) A tilt cylinder of a mast allows a forward drift of the mast in excess of 2 degrees in 5 minutes with the mast in a vertical position and a capacity load on the fork or load engaging means. (e) The steering mechanism allows free play of the steering wheel of more than 1/4 turn on trucks capable of speeds up to 8 miles per hour and more than 1/8 turn on trucks capable of speeds over 8 miles per hour. (f) A hydraulic system leaks and creates a hazard for an employee and equipment in the area. (2) Repairs to a fuel and ignition system which involve a fire hazard shall be made only in a designated location. Repairs shall not be made in a location made hazardous by: (a) Flammable gases or vapors. (b) Combustible dusts. (c) Ignitable fibers. (3) Repairs to the truck electrical system shall be made only after the battery has been disconnected. (4) A replacement part shall have not less than the equivalent safety of the original part. (5) A water muffler shall have the water maintained at not less than 75% of capacity. A water muffler equipped with a screen shall have the screen maintained to accomplish its intended purpose. When an exhaust system of this type emits sparks or flames, the truck shall be removed from service and repaired. (6) A truck running in excess of normal operating temperature which creates a hazardous condition shall be removed from service and repaired. (7) A truck shall be maintained in a condition, reasonably free of lint, excess oil and grease. Solvent with a flash point of less than 100 degrees Fahrenheit shall not be used to clean the truck. Precautions regarding ventilation, fire and toxicity shall be observed when using a cleaning agent. (8) A truck approved for use of 1 type of fuel may be converted to another type of fuel if the conversion qualifies the truck to its new designation, such as GS, LP, or LPS. Only approved parts shall be used. The conversion shall be as prescribed in subrule (2) of rule (9) All repairs shall be made by authorized personnel. R Blocks and safety stands for maintenance. Rule (1) An employer shall provide the following: (a) Chock blocks, support blocks, or jack stands for the maintenance department's use when repairing powered industrial trucks or their components. (b) Blocks or safety stands as a means of support for powered industrial trucks elevated from the floor by a hoist or chain fall. (2) When repairing a powered industrial truck, an employee shall use chock blocks, support blocks, or jack stands if there is a hazard from movement. (3) An employee shall not place his or her body under a powered industrial truck unless the powered industrial truck is supported by properly arranged blocks or jack stands capable, in total, of supporting a minimum of 1 1/2 times the weight of the component of the truck to be repaired. R Fuel. Rule (1) An employer shall provide safety fuel cans where trucks are refueled with gasoline at other than a gas pump area. (2) An employer shall provide a special area for refueling that is not less than 25 feet from a source of open flame or spark and the area shall be posted to this effect. (3) Use and storage of LP gas shall be as specified by 29 C.F.R. ' , Storage And Handling Of Liquefied Petroleum Gases, which was adopted by reference in General Industry Safety Standard Part 56 Storage And Handling Of Liquefied Petroleum Gases, being R et seq. This standard is available from the
FORKLIFT AND INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS SAFETY PROGRAM
 TRUCKS SAFETY 1. PURPOSE Establish requirements and procedures for the safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks. 2. SCOPE To all D&D TECH SYSTEMS, INC. employees who operate a Powered Industrial
TRUCKS SAFETY 1. PURPOSE Establish requirements and procedures for the safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks. 2. SCOPE To all D&D TECH SYSTEMS, INC. employees who operate a Powered Industrial
HEALTH AND SAFETY MANUAL
 1 Purpose/Scope: HEALTH AND SAFETY MANUAL Title: Powered Industrial Trucks, (Forklifts) Approved by: Greg Savoy Rev. 4/1/08 The purpose of this program is to establish requirements for the safe operation
1 Purpose/Scope: HEALTH AND SAFETY MANUAL Title: Powered Industrial Trucks, (Forklifts) Approved by: Greg Savoy Rev. 4/1/08 The purpose of this program is to establish requirements for the safe operation
240- POWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS
 240.1 PURPOSE A. To establish safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks (PIT s). 240.2 SCOPE A. This program applies to all Central New Mexico Community College (CNM) employees who operate a
240.1 PURPOSE A. To establish safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks (PIT s). 240.2 SCOPE A. This program applies to all Central New Mexico Community College (CNM) employees who operate a
COMPANY HEALTH & SAFETY PROGRAM. Title: Forklift Operation Section No: 17
 Page 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this section is to address the safe operation of powered industrial trucks (forklifts) in the PPP Plymouth, MI facilities, including: 1. Provide a safe working environment;
Page 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this section is to address the safe operation of powered industrial trucks (forklifts) in the PPP Plymouth, MI facilities, including: 1. Provide a safe working environment;
Process Name Powered Industrial Trucks Program. Purpose: To establish safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks (PIT s).
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Powered Industrial Trucks Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Power Industrial Trucks Program Purpose: To establish safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Powered Industrial Trucks Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Power Industrial Trucks Program Purpose: To establish safe operation and use of Powered Industrial Trucks
Forklift Operator Safety Program
 Forklift Operator Safety Program Program originated: 9/2009 Last updated: 1/2015 Wendel Reece University Safety Manager FORWARD The University of Northern Iowa Forklift Operator Safety Program is a guide
Forklift Operator Safety Program Program originated: 9/2009 Last updated: 1/2015 Wendel Reece University Safety Manager FORWARD The University of Northern Iowa Forklift Operator Safety Program is a guide
Powered Industrial Trucks Safety Checklist
 Powered Industrial Trucks Safety Checklist This safety checklist will help employees and supervisors follow minimal safety practices. This list is not meant to be comprehensive nor is it meant to form
Powered Industrial Trucks Safety Checklist This safety checklist will help employees and supervisors follow minimal safety practices. This list is not meant to be comprehensive nor is it meant to form
Forklift Operator Training
 Forklift Operator Training the tireless workhorse of the lumber industry Before you start, keep this in mind Forklifts are the backbone of 84 Lumber and 84 Components Without them, we cannot receive material
Forklift Operator Training the tireless workhorse of the lumber industry Before you start, keep this in mind Forklifts are the backbone of 84 Lumber and 84 Components Without them, we cannot receive material
OWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS (FORKLIFTS) A Berea College Employee Workplace Safety Program
 OWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS (FORKLIFTS) A Berea College Employee Workplace Safety Program PURPOSE This program is designed to meet the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.178, regarding protection from hazards of
OWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS (FORKLIFTS) A Berea College Employee Workplace Safety Program PURPOSE This program is designed to meet the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.178, regarding protection from hazards of
FORKLIFT OPERATOR SAFETY
 Table of Contents SECTION 1. TRAINING PROGRAM INTRODUCTION..................3 Training Objectives...........................................3 Rationale for Training.........................................3
Table of Contents SECTION 1. TRAINING PROGRAM INTRODUCTION..................3 Training Objectives...........................................3 Rationale for Training.........................................3
DEPARTMENT OF FACILITIES MANAGEMENT
 DEPARTMENT OF FACILITIES MANAGEMENT SUBJECT: Forklift Policy ISSUED DATE: 01-15-00 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this policy is to provide safe practices for the operation, maintenance, and inspection of
DEPARTMENT OF FACILITIES MANAGEMENT SUBJECT: Forklift Policy ISSUED DATE: 01-15-00 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this policy is to provide safe practices for the operation, maintenance, and inspection of
Material Handling. Chapter 5
 Material Handling Chapter 5 Designing material handling systems Overview of material handling equipment Unit load design Material handling equipment selection Material Handling Definitions Material handling
Material Handling Chapter 5 Designing material handling systems Overview of material handling equipment Unit load design Material handling equipment selection Material Handling Definitions Material handling
Powered Industrial Truck/Forklift Operations Standards and Procedures. Disaster Cycle Services Standards & Procedures DCS SP DMWT
 Powered Industrial Truck/Forklift Operations Standards and Procedures Disaster Cycle Services Standards & Procedures DCS SP DMWT April 2015 Change Log Date Page(s) Section Change Author: Deploy Materials,
Powered Industrial Truck/Forklift Operations Standards and Procedures Disaster Cycle Services Standards & Procedures DCS SP DMWT April 2015 Change Log Date Page(s) Section Change Author: Deploy Materials,
Forklift Operator Safety Safe Operation and Pre-Use Inspection
 EXERCISE #1 Target Audience: Forklift operators Exercise Objective: Evaluate understanding of safe forklift operation and pre-use inspection criteria Instructions: Answer the questions below. Review your
EXERCISE #1 Target Audience: Forklift operators Exercise Objective: Evaluate understanding of safe forklift operation and pre-use inspection criteria Instructions: Answer the questions below. Review your
Warehouse Safety Checklist
 s Good Housekeeping Are all areas kept clean and neat, with everything in its proper place? Is lighting in all parts of the warehouse adequate, and are bulbs replaced on a schedule before they burn out?
s Good Housekeeping Are all areas kept clean and neat, with everything in its proper place? Is lighting in all parts of the warehouse adequate, and are bulbs replaced on a schedule before they burn out?
Instructions for the use of the Link 4 Pallet Rack Lifter (PRL) model 5000
 Instructions for the use of the Link 4 Pallet Rack Lifter (PRL) model 5000 (How to move your pallet racking using the Link 4 Pallet Rack Lifter) This process is for a typical rack move and reset. Each
Instructions for the use of the Link 4 Pallet Rack Lifter (PRL) model 5000 (How to move your pallet racking using the Link 4 Pallet Rack Lifter) This process is for a typical rack move and reset. Each
POWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS Forklift Safety Plan
 South Central College Faribault Campus 1225 Third St. SW Faribault, MN 55021-5782 North Mankato/Mankato Campus 1920 Lee Boulevard N. Mankato, MN 56002-1920 Adoption Date: 07-08-15 Revision Date: 01-04-17
South Central College Faribault Campus 1225 Third St. SW Faribault, MN 55021-5782 North Mankato/Mankato Campus 1920 Lee Boulevard N. Mankato, MN 56002-1920 Adoption Date: 07-08-15 Revision Date: 01-04-17
1 IMHOFF CUSTOM SERVICES INC. AERIAL LIFT POLICY
 1 IMHOFF CUSTOM SERVICES INC. AERIAL LIFT POLICY Purpose and Applicability The purpose of this Program is to ensure that Imhoff Custom Services Inc. employees who operate aerial or scissor lifts have the
1 IMHOFF CUSTOM SERVICES INC. AERIAL LIFT POLICY Purpose and Applicability The purpose of this Program is to ensure that Imhoff Custom Services Inc. employees who operate aerial or scissor lifts have the
Craven Community College Forklift Safety Program
 Craven Community College Forklift Safety Program Check Your Understanding. Do you need a Forklift Safety Program? If you use forklifts in your organization the answer is YES. Department of Labor statistics
Craven Community College Forklift Safety Program Check Your Understanding. Do you need a Forklift Safety Program? If you use forklifts in your organization the answer is YES. Department of Labor statistics
Part III MATERIAL HANDLING AND IDENTIFICATION TECHNOLOGIES
 Part III MATERIAL HANDLING AND IDENTIFICATION TECHNOLOGIES Chapters: 10.Material Transport Systems 11.Storage Systems 12.Automatic Identification and Data Capture Material Handling Technologies in the
Part III MATERIAL HANDLING AND IDENTIFICATION TECHNOLOGIES Chapters: 10.Material Transport Systems 11.Storage Systems 12.Automatic Identification and Data Capture Material Handling Technologies in the
OSHA Update - Powered Pallet Trucks
 Thompson & Johnson Equipment Co., Inc. June 2006 OSHA Update - Powered Pallet Trucks You have to train your forklift operators in a formal classroom setting and hands-on training courses using each style
Thompson & Johnson Equipment Co., Inc. June 2006 OSHA Update - Powered Pallet Trucks You have to train your forklift operators in a formal classroom setting and hands-on training courses using each style
FACILITIES MANAGEMENT OFFICE OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY AERIAL WORK PLATFORM POLICY 09/06/17 Last Revision
 FACILITIES MANAGEMENT OFFICE OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY AERIAL WORK PLATFORM POLICY 09/06/17 Last Revision 1. Intent This program has been developed to reduce the risk of physical injury or property
FACILITIES MANAGEMENT OFFICE OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY AERIAL WORK PLATFORM POLICY 09/06/17 Last Revision 1. Intent This program has been developed to reduce the risk of physical injury or property
Warehouse & Forklift Safety Manual
 INTRODUCTION/OVERVIEW On the job accident prevention is the responsibility of all the district s employees. It is the further responsibility of each employee to correct or report any unsafe condition or
INTRODUCTION/OVERVIEW On the job accident prevention is the responsibility of all the district s employees. It is the further responsibility of each employee to correct or report any unsafe condition or
C 3858 Forklifts: Handle With Care
 C 3858 Forklifts: Handle With Care Leader s Guide HANDLE WITH CARE: Forklift Safety Training This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are:
C 3858 Forklifts: Handle With Care Leader s Guide HANDLE WITH CARE: Forklift Safety Training This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are:
EASTERN MICHIGAN U N I V E R S I T Y AERIAL WORK PLATFORMS PROGRAM
 EASTERN MICHIGAN U N I V E R S I T Y AERIAL WORK PLATFORMS PROGRAM Department of Public Safety Health and Safety Office 1200 Oakwood Ypsilanti, Ml 48197 734.487.0794 January 2007 EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY
EASTERN MICHIGAN U N I V E R S I T Y AERIAL WORK PLATFORMS PROGRAM Department of Public Safety Health and Safety Office 1200 Oakwood Ypsilanti, Ml 48197 734.487.0794 January 2007 EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY
Using this Template. Provided By Truck Writers, Inc.
 Using this Template The following template can be used to help your organization develop a written Forklift Safety Program. This template cannot be used as is you must customize the template to meet the
Using this Template The following template can be used to help your organization develop a written Forklift Safety Program. This template cannot be used as is you must customize the template to meet the
Safety Instructions For Overhead Crane Operators
 Safety Instructions For Overhead Crane Operators Contents Forward -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 Qualifications --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
Safety Instructions For Overhead Crane Operators Contents Forward -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 Qualifications --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
Questions for Written Evaluation
 Questions for Written Evaluation Name: Date: 1 When must the operator complete the pre-shift safety checklist? a. At the end of the operators shift b. At the beginning of the operators shift and/or before
Questions for Written Evaluation Name: Date: 1 When must the operator complete the pre-shift safety checklist? a. At the end of the operators shift b. At the beginning of the operators shift and/or before
Forklift Course Pre-Reading Information. Version 2.0. March 2011
 Forklift Course Pre-Reading Information Version 2.0 March 2011 Reading through this manual prior to sitting your forklift course will assist you in preparing for your in-class theory session and written
Forklift Course Pre-Reading Information Version 2.0 March 2011 Reading through this manual prior to sitting your forklift course will assist you in preparing for your in-class theory session and written
Effective Date: 10-January Table of Contents
 Version: 3 Page: 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 2 1.1 Purpose... 2 1.2 Scope... 2 1.3 Definitions... 2 1.4 Responsibilities... 2 Environmental Health and Safety Office (EHSO) and Emory Healthcare
Version: 3 Page: 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 2 1.1 Purpose... 2 1.2 Scope... 2 1.3 Definitions... 2 1.4 Responsibilities... 2 Environmental Health and Safety Office (EHSO) and Emory Healthcare
Materials Handling Guideline OHS709
 Materials Handling Guideline OHS709 Policy Hierarchy link OHS Act 2000, OHS Regulation 2001 UNSW OHS Policy Responsible Officer David Ward, Director Human Resources Contact Officer Adam Janssen, Manager,
Materials Handling Guideline OHS709 Policy Hierarchy link OHS Act 2000, OHS Regulation 2001 UNSW OHS Policy Responsible Officer David Ward, Director Human Resources Contact Officer Adam Janssen, Manager,
Multi-Fab sells to registered dealers only; however, we can assist in finding you a dealer.
 ATTACHMENTS This term refers to implements that can be added to a fork truck for handling a load. Attachments such as clamps, slip sheet forks and carpet poles can have an effect on capacity and should
ATTACHMENTS This term refers to implements that can be added to a fork truck for handling a load. Attachments such as clamps, slip sheet forks and carpet poles can have an effect on capacity and should
HS709 Materials Handling Guideline
 HS709 Materials Handling Guideline Policy Hierarchy link Responsible Officer Contact Officer Superseded Documents File Number 2016/00370 Work Health and Safety Act 2011 Work Health and Safety Regulation
HS709 Materials Handling Guideline Policy Hierarchy link Responsible Officer Contact Officer Superseded Documents File Number 2016/00370 Work Health and Safety Act 2011 Work Health and Safety Regulation
Safety Services Policy and Procedure
 Title: Industrial Powered Equipment: Truck/Forklift Powered Platforms Aerial Lifts Electric Pallet Jack Policy Number: 10.15 Regulation: Reference: OSHA 1910.178, 1926.602 and NFPA 505 OSHA 1910.66 OSHA
Title: Industrial Powered Equipment: Truck/Forklift Powered Platforms Aerial Lifts Electric Pallet Jack Policy Number: 10.15 Regulation: Reference: OSHA 1910.178, 1926.602 and NFPA 505 OSHA 1910.66 OSHA
The following is Queen's Printer for Ontario, Occupational Health and Safety Act - R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 851
 Ontario Lift Truck - Chariot de levage industriel This material has been extracted from the Acts and Regulations of the Province to help students understand the subject. It is not an official source of
Ontario Lift Truck - Chariot de levage industriel This material has been extracted from the Acts and Regulations of the Province to help students understand the subject. It is not an official source of
Operator Training Program. PROSTAK Storage Management Systems
 Operator Training Program PROSTAK Storage Management Systems Operator Training Index 1. PROSTAK System Nomenclature Slide 3 2. Safe Operating Guidelines Slides 4 and 5 3. Types of PROSTAK Stackers Slide
Operator Training Program PROSTAK Storage Management Systems Operator Training Index 1. PROSTAK System Nomenclature Slide 3 2. Safe Operating Guidelines Slides 4 and 5 3. Types of PROSTAK Stackers Slide
TLILIC2001 Licence to Operate a Forklift Truck
 TLILIC2001 Licence to Operate a Forklift Truck Multiple Choice Questions PARTICIPANT NAME : Forklift Multiple Choice Questions V080217 Page 1 of 13 LF Forklift Work Sheet Trainee to circle the correct
TLILIC2001 Licence to Operate a Forklift Truck Multiple Choice Questions PARTICIPANT NAME : Forklift Multiple Choice Questions V080217 Page 1 of 13 LF Forklift Work Sheet Trainee to circle the correct
Powered Industrial Trucks (Forklift) Program. Elizabeth City State University Office of Environmental Health & Safety
 Powered Industrial Trucks (Forklift) Program Elizabeth City State University Office of Environmental Health & Safety I. Purpose In accordance to the provisions of the NC OSHA Powered Industrial Truck Standard
Powered Industrial Trucks (Forklift) Program Elizabeth City State University Office of Environmental Health & Safety I. Purpose In accordance to the provisions of the NC OSHA Powered Industrial Truck Standard
Standards of Practice Powered Industrial Truck/Forklift
 Standards of Practice Powered Industrial Truck/Forklift Document Authority: EH&S Director Document Custodian: EH&S Director Effective Date: 2/1/2018 Issuing Dept: College of Agriculture EH&S Office Next
Standards of Practice Powered Industrial Truck/Forklift Document Authority: EH&S Director Document Custodian: EH&S Director Effective Date: 2/1/2018 Issuing Dept: College of Agriculture EH&S Office Next
NILESH PANCHOLI B.E. (Mech.), M.E. (CAD/CAM) Indus Institute of Technology & Engineering Ahmedabad
 NILESH PANCHOLI B.E. (Mech.), M.E. (CAD/CAM) Indus Institute of Technology & Engineering Ahmedabad 1 Introduction and Concept 2 Material handling is the function of moving the right material to the right
NILESH PANCHOLI B.E. (Mech.), M.E. (CAD/CAM) Indus Institute of Technology & Engineering Ahmedabad 1 Introduction and Concept 2 Material handling is the function of moving the right material to the right
Reva Golden & Tony McCrimmon
 FORKLIFT SAFETY Best Management Practice for the Management of Powered Industrial Trucks Presented By Reva Golden & Tony McCrimmon Safety Subcommittee Agenda Background OSHA and Regulatory Compliance Training
FORKLIFT SAFETY Best Management Practice for the Management of Powered Industrial Trucks Presented By Reva Golden & Tony McCrimmon Safety Subcommittee Agenda Background OSHA and Regulatory Compliance Training
WARNING ELECTRIC PALLET TRUCK EPT Revised A company dedicated to solving ergonomic and material handling problems since 1955.
 VESTIL MANUFACTURING CORPORATION 2999 North Wayne Street, P.O. Box 507 Angola, Indiana 46703 USA Phone (260) 665-7586 Fax (260) 665-1339 sales@vestil.com www.vestil.com SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS & OPERATING
VESTIL MANUFACTURING CORPORATION 2999 North Wayne Street, P.O. Box 507 Angola, Indiana 46703 USA Phone (260) 665-7586 Fax (260) 665-1339 sales@vestil.com www.vestil.com SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS & OPERATING
AERIAL LIFT MANUAL. Environmental Health & Safety. Oklahoma State University
 Environmental Health & Safety Oklahoma State University AERIAL LIFT MANUAL Environmental Health and Safety University Health Services Suite 002 Stillwater, OK 74078 (405) 744-7241 www.ehs.okstate.edu Reviewed
Environmental Health & Safety Oklahoma State University AERIAL LIFT MANUAL Environmental Health and Safety University Health Services Suite 002 Stillwater, OK 74078 (405) 744-7241 www.ehs.okstate.edu Reviewed
PALLET LIFTER OPERATOR SAFETY MANUAL
 PALLET LIFTER OPERATOR SAFETY MANUAL Page 1 INTRODUCTION Pallet lifters are a versatile tool for loading, unloading and transporting materials that are placed on pallets or dunnage to allow for fork entrance.
PALLET LIFTER OPERATOR SAFETY MANUAL Page 1 INTRODUCTION Pallet lifters are a versatile tool for loading, unloading and transporting materials that are placed on pallets or dunnage to allow for fork entrance.
WAREHOUSE SUPERVISOR
 PERSONNEL COMMISSION Class Code: 0300 Salary Range: 29 (S1) WAREHOUSE SUPERVISOR JOB SUMMARY Under general direction, plan, organize, oversee and participate in the operations and activities of the District
PERSONNEL COMMISSION Class Code: 0300 Salary Range: 29 (S1) WAREHOUSE SUPERVISOR JOB SUMMARY Under general direction, plan, organize, oversee and participate in the operations and activities of the District
Light Duty Ramps. Loadingdocksupply.com PHONE:
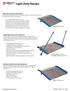 Light Duty Ramps Light Duty Aluminum Dockplates Designed for use by pallet trucks, carts, and foot traffic the A & B model Aluminum Dockplate is lightweight and portable. Accomodates differentials up to
Light Duty Ramps Light Duty Aluminum Dockplates Designed for use by pallet trucks, carts, and foot traffic the A & B model Aluminum Dockplate is lightweight and portable. Accomodates differentials up to
DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATORY AFFAIRS DIRECTOR'S OFFICE CONSTRUCTION SAFETY STANDARDS PART 20. DEMOLITION
 DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATORY AFFAIRS DIRECTOR'S OFFICE CONSTRUCTION SAFETY STANDARDS (By authority conferred on the director of the department of licensing and regulatory affairs by sections
DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATORY AFFAIRS DIRECTOR'S OFFICE CONSTRUCTION SAFETY STANDARDS (By authority conferred on the director of the department of licensing and regulatory affairs by sections
POWERED MOBILE EQUIPMENT PROGRAM
 POWERED MOBILE EQUIPMENT PROGRAM INTRODUCTION/OVERVIEW The safe operation of material handling and/or personnel lifting equipment on and around the jobsite is essential. To help prevent injury to fellow
POWERED MOBILE EQUIPMENT PROGRAM INTRODUCTION/OVERVIEW The safe operation of material handling and/or personnel lifting equipment on and around the jobsite is essential. To help prevent injury to fellow
Legal Summary SHE-037 Handbook of Business Operation in Thailand s Industrial Estate Version 2
 Ministerial Regulations Specification of administration standard and the process of safety, industrial hygiene and environment at workplace in respect of machine, crane and boiler BE 2552 (2009) 1. Publication
Ministerial Regulations Specification of administration standard and the process of safety, industrial hygiene and environment at workplace in respect of machine, crane and boiler BE 2552 (2009) 1. Publication
BOOM-SUPPORTED ELEVATING WORK PLATFORM PROGRAM
 Page: 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE and APPLICABILITY 1.1 It is the policy of the University of Pennsylvania in coordination with the Office of Environmental Health and Radiation Safety to provide the University
Page: 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE and APPLICABILITY 1.1 It is the policy of the University of Pennsylvania in coordination with the Office of Environmental Health and Radiation Safety to provide the University
OPERATOR S MANUAL. LINKIT Series LKS300/LKS450 Portable Conveyor. InterQuip USA LLC interquip.net DISTRIBUTED BY: OPERATOR S MANUAL
 OPERATOR S MANUAL LINKIT Series LKS300/LKS450 Portable Conveyor DISTRIBUTED BY: InterQuip USA LLC 203.322.2600 interquip.net 1 IMPORTANT Read, understand and obey these safety rules and operating instructions
OPERATOR S MANUAL LINKIT Series LKS300/LKS450 Portable Conveyor DISTRIBUTED BY: InterQuip USA LLC 203.322.2600 interquip.net 1 IMPORTANT Read, understand and obey these safety rules and operating instructions
Transport bulk gases by road
 Page 1 of 9 Transport bulk gases by road Level 4 Credits 15 Purpose This unit standard is for drivers of road tank wagons who load, transport and unload bulk gases under pressure, including hazardous and
Page 1 of 9 Transport bulk gases by road Level 4 Credits 15 Purpose This unit standard is for drivers of road tank wagons who load, transport and unload bulk gases under pressure, including hazardous and
Logistics Community of Interest 5704 Forklift Operating Series Competency-Based Learning Map and Training Strategy. Page 1
 Page 1 Forklift Operating Competency-Based Learning Map Overview The United States Marine Corps (USMC) Logistics Community of Interest (COI) developed this competency-based learning map to support 5704
Page 1 Forklift Operating Competency-Based Learning Map Overview The United States Marine Corps (USMC) Logistics Community of Interest (COI) developed this competency-based learning map to support 5704
GENERAL GUIDE FOR WORKPLACE TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT
 1 This General Guide provides information on how to manage traffic risks at a workplace. It is supported by specific guidance material on traffic management for shopping centres, construction workplaces,
1 This General Guide provides information on how to manage traffic risks at a workplace. It is supported by specific guidance material on traffic management for shopping centres, construction workplaces,
General Guidelines. Instructions for Part # WP Safety. It is the user s responsibility to read and follow all instructions.
 General Guidelines It is the user s responsibility to read and follow all instructions. Instructions for Part # WP-48-1000 Keep these instructions with the product at all times and review before each use.
General Guidelines It is the user s responsibility to read and follow all instructions. Instructions for Part # WP-48-1000 Keep these instructions with the product at all times and review before each use.
Document Revision Change Table Revision Number
 Beaumont Site Procedure No.: BMEHS-002.025 Reviewed: 01/17 Page: 1 of 7 Document Revision Change Table Revision Number Revision Description Revised By Revision Date Rev. 03 Considered as starting document
Beaumont Site Procedure No.: BMEHS-002.025 Reviewed: 01/17 Page: 1 of 7 Document Revision Change Table Revision Number Revision Description Revised By Revision Date Rev. 03 Considered as starting document
2200-Lb. Semi-Electric Stacker OWNER S MANUAL
 2200-Lb. Semi-Electric Stacker OWNER S MANUAL WARNING: Read carefully and understand all ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS before operating. Failure to follow the safety rules and other basic safety
2200-Lb. Semi-Electric Stacker OWNER S MANUAL WARNING: Read carefully and understand all ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS before operating. Failure to follow the safety rules and other basic safety
POWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCK SAFETY PROGRAM
 Quality. Integrity. Experience. Electrical Engineers and Contractors Since 1918 Specializing in Design/Build POWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCK SAFETY PROGRAM Operator Training Certification Accident Investigation
Quality. Integrity. Experience. Electrical Engineers and Contractors Since 1918 Specializing in Design/Build POWERED INDUSTRIAL TRUCK SAFETY PROGRAM Operator Training Certification Accident Investigation
Move It Safely: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials. Leader Guide
 4398 Move It Safely: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials Leader Guide MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful
4398 Move It Safely: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials Leader Guide MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful
Operating a forklift is a big responsibility, and it s one that requires you to pay attention to safety at all times. Forklifts are very useful for
 Operating a forklift is a big responsibility, and it s one that requires you to pay attention to safety at all times. Forklifts are very useful for handling heavy materials, but remember that they are
Operating a forklift is a big responsibility, and it s one that requires you to pay attention to safety at all times. Forklifts are very useful for handling heavy materials, but remember that they are
ERI Safety Videos DVDs, Digital Media & Custom Production MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials. Leader s Guide.
 ERI Safety Videos DVDs, Digital Media & Custom Production 1309 MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials
ERI Safety Videos DVDs, Digital Media & Custom Production 1309 MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos MOVE IT SAFELY: Avoiding Injury While Moving Materials
MATERIAL HANDLING OPTIONS IN THE BEVERAGE INDUSTRY: Choosing Right and Staying Efficient
 MATERIAL HANDLING OPTIONS IN THE BEVERAGE INDUSTRY: Choosing Right and Staying Efficient MATERIAL HANDLING OPTIONS IN THE BEVERAGE INDUSTRY: Choosing Right and Staying Efficient In recent years, the beverage
MATERIAL HANDLING OPTIONS IN THE BEVERAGE INDUSTRY: Choosing Right and Staying Efficient MATERIAL HANDLING OPTIONS IN THE BEVERAGE INDUSTRY: Choosing Right and Staying Efficient In recent years, the beverage
Operator s Manual for Morse Heavy-Duty Kontrol-Karrier with 3-Piece Drum Holder
 CONTENTS Page Receiving Procedures.................... 1 Warranty............................. 1 Safety Information..................... 1-2 Machine Description................... 3 Operating Instructions....................
CONTENTS Page Receiving Procedures.................... 1 Warranty............................. 1 Safety Information..................... 1-2 Machine Description................... 3 Operating Instructions....................
2200-Lb. Stacker. Fixed Straddle Leg OWNER S MANUAL
 2200-Lb. Stacker Fixed Straddle Leg OWNER S MANUAL WARNING: Read carefully and understand all ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS before operating. Failure to follow the safety rules and other basic safety
2200-Lb. Stacker Fixed Straddle Leg OWNER S MANUAL WARNING: Read carefully and understand all ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS before operating. Failure to follow the safety rules and other basic safety
Rocky Top Materials, Inc.
 Rocky Top Materials, Inc. 2707 John Deere Dr. Knoxville, TN 37917 (865) 522-0060 1806 Middlecreek Rd. Pigeon Forge, TN 37863 (865) 453-3723 Disclaimer: This document contains brief descriptions of Rocky
Rocky Top Materials, Inc. 2707 John Deere Dr. Knoxville, TN 37917 (865) 522-0060 1806 Middlecreek Rd. Pigeon Forge, TN 37863 (865) 453-3723 Disclaimer: This document contains brief descriptions of Rocky
PREVENTING COMMON WAREHOUSE HAZARDS
 DEXTERS GUIDE TO PREVENTING COMMON WAREHOUSE HAZARDS NEW ZEALAND IN REVIEW ACCIDENT STATISTICS 233,000 claims in 2016 30,700 for serious claims in 2016 Someone in New Zealand is injured every 20 seconds
DEXTERS GUIDE TO PREVENTING COMMON WAREHOUSE HAZARDS NEW ZEALAND IN REVIEW ACCIDENT STATISTICS 233,000 claims in 2016 30,700 for serious claims in 2016 Someone in New Zealand is injured every 20 seconds
Work Instruction Pontiac LOC Version 1.0 WI-B404 Bulk Hi-Lo Picker April, 07
 This section describes the process a Hi-Lo Operator / Picker will go through on a "typical" cycle for Bulk. Equipment: 1. Hi-Lo 2. Pen 3. Marker 4. Clipboard General Guidelines: 1) Seat belts will be used
This section describes the process a Hi-Lo Operator / Picker will go through on a "typical" cycle for Bulk. Equipment: 1. Hi-Lo 2. Pen 3. Marker 4. Clipboard General Guidelines: 1) Seat belts will be used
Load Handling (Hoisting) Policy
 1.0 PURPOSE This policy is to promote safe load handling (hoisting) practices and reduce the frequency and severity of incidents. The purpose is to protect personnel from injury, the environment from harm,
1.0 PURPOSE This policy is to promote safe load handling (hoisting) practices and reduce the frequency and severity of incidents. The purpose is to protect personnel from injury, the environment from harm,
Forklift Safety for Supervisors
 Forklift Safety for Supervisors Supervisor s responsibilities > Ensure new employees understand the requirement for specific equipment training. Forklifts (we use 5 classes (or OSHA classifications) of
Forklift Safety for Supervisors Supervisor s responsibilities > Ensure new employees understand the requirement for specific equipment training. Forklifts (we use 5 classes (or OSHA classifications) of
CR-3000 Car Rotator Capacity 3,000 lbs Installation Manual 2016 Mar
 Car Rotator Capacity 3,000 lbs Installation Manual 2016 Mar INDEX 1. OWNER / USER RESPONSIBILITIES---------------------------------------- PAGE 3 2. SAFETY PROCEDURES---------------------------------------------------------
Car Rotator Capacity 3,000 lbs Installation Manual 2016 Mar INDEX 1. OWNER / USER RESPONSIBILITIES---------------------------------------- PAGE 3 2. SAFETY PROCEDURES---------------------------------------------------------
STANDARD PRACTICE INSTRUCTION
 STANDARD PRACTICE INSTRUCTION DATE: March 1, 2001 SUBJECT: Scaffolding Safety Program. REGULATORY STANDARDS: 29 CFR 1910.28 Safety Requirements For Scaffolding. 29 CFR 1910.29 Manually Propelled Mobile
STANDARD PRACTICE INSTRUCTION DATE: March 1, 2001 SUBJECT: Scaffolding Safety Program. REGULATORY STANDARDS: 29 CFR 1910.28 Safety Requirements For Scaffolding. 29 CFR 1910.29 Manually Propelled Mobile
MMM MASONRY, INC. Employee Safety Guidelines
 MMM MASONRY, INC. Employee Safety Guidelines This manual represents common hazards associated with masonry construction and is no way intended to replace the OSHA 29CFR 1926 Safety Standards. It is the
MMM MASONRY, INC. Employee Safety Guidelines This manual represents common hazards associated with masonry construction and is no way intended to replace the OSHA 29CFR 1926 Safety Standards. It is the
PENTALIFT VEHICLE RESTRAINTS
 PRODUCT INFORMATION PENTALIFT VEHICLE RESTRAINTS 2946 Larimer St. Denver, CO 80205 303-295-1100 / 800-373-7693 FAX 303-295-2464 Email info@snyderequipment.com www.snyderequipment.com Why the Pentahook?
PRODUCT INFORMATION PENTALIFT VEHICLE RESTRAINTS 2946 Larimer St. Denver, CO 80205 303-295-1100 / 800-373-7693 FAX 303-295-2464 Email info@snyderequipment.com www.snyderequipment.com Why the Pentahook?
(4) Production inspection is the inspection that must initially be conducted on each newly manufactured IBC.
 Subpart O Testing of IBCs 178.800 Purpose and scope. This subpart prescribes certain testing requirements for IBCs identified in subpart N of this part. [Amdt. 178 103, 59 FR 38074, July 26, 1994, as amended
Subpart O Testing of IBCs 178.800 Purpose and scope. This subpart prescribes certain testing requirements for IBCs identified in subpart N of this part. [Amdt. 178 103, 59 FR 38074, July 26, 1994, as amended
Universal-Fit LIFT HOOK - Model 1371B
 4101 GARLAND DR, FORT WORTH, TX 76117 Ph 817-485-6073 Fax 817-428-6008 www.starindustries.com Bulletin LH- OM0510B Universal-Fit LIFT HOOK - Model 1371B Installation, Use & Safety Precautions SPECIFICATIONS:
4101 GARLAND DR, FORT WORTH, TX 76117 Ph 817-485-6073 Fax 817-428-6008 www.starindustries.com Bulletin LH- OM0510B Universal-Fit LIFT HOOK - Model 1371B Installation, Use & Safety Precautions SPECIFICATIONS:
Main Page The Company The Technology Safety Locks Electric Lifts. Air Lifts
 Incorporated date: 1985 Location: Walled Lake, Michigan Lot size: Approximately 3 acres Building: Approximately 33,000 square feet Military Application Employees: 40 Strengths: ISO certified Long Term
Incorporated date: 1985 Location: Walled Lake, Michigan Lot size: Approximately 3 acres Building: Approximately 33,000 square feet Military Application Employees: 40 Strengths: ISO certified Long Term
PAGE 1 OF 10 HEALTH, SAFETY & ENVIRONMENTAL MANUAL PROCEDURE: S370 Mobile Cranes Procedure REV /14/2012
 PAGE 1 OF 10 PURPOSE: MOBILE CRANES PROCEDURE To establish a procedure that provides guidelines that constitute safe operation of mobile cranes. It is not all encompassing or intended to replace common
PAGE 1 OF 10 PURPOSE: MOBILE CRANES PROCEDURE To establish a procedure that provides guidelines that constitute safe operation of mobile cranes. It is not all encompassing or intended to replace common
FORKLIFT TRAINING MANUAL. Safety & Risk Services Unit Human Resources Service Group UPD Building, Third Floor Phone:
 FORKLIFT TRAINING MANUAL Safety & Risk Services Unit Human Resources Service Group UPD Building, Third Floor Phone: 408-924-2150 Revised: 10/2005 Notes OSHA REQUIREMENTS: FORKLIFT OPERATOR TRAINING The
FORKLIFT TRAINING MANUAL Safety & Risk Services Unit Human Resources Service Group UPD Building, Third Floor Phone: 408-924-2150 Revised: 10/2005 Notes OSHA REQUIREMENTS: FORKLIFT OPERATOR TRAINING The
k e e p t h e i r l o a d i n g d o c k s s a f e. T h a t s w h y w e v e d e v e l o p e d a
 V E H I C L E RESTR AINTS EVE R Y DAY, THOUSANDS OF PEOPLE COUNT ON KELLEY t o k e e p t h e i r l o a d i n g d o c k s s a f e. T h a t s w h y w e v e d e v e l o p e d a c o m p r e h e n s i v e l
V E H I C L E RESTR AINTS EVE R Y DAY, THOUSANDS OF PEOPLE COUNT ON KELLEY t o k e e p t h e i r l o a d i n g d o c k s s a f e. T h a t s w h y w e v e d e v e l o p e d a c o m p r e h e n s i v e l
BBL-4 FORK-MOUNTED BULK BAG LIFTER USE AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
 VESTIL MANUFACTURING CORP. 2999 North Wayne Street, P.O. Box 507, Angola, IN 46703 Telephone: (260) 665-7586 -or- Toll Free (800) 348-0868 Fax: (260) 665-1339 www.vestilmfg.com e-mail: sales@vestil.com
VESTIL MANUFACTURING CORP. 2999 North Wayne Street, P.O. Box 507, Angola, IN 46703 Telephone: (260) 665-7586 -or- Toll Free (800) 348-0868 Fax: (260) 665-1339 www.vestilmfg.com e-mail: sales@vestil.com
MODEL 185R Kontrol-Karrier Operator s Manual for Morse Kontrol-Karrier
 Contents Page Receiving Procedures.................... 1 Warranty............................. 1 Safety Information..................... 1-2 Machine Description................... 3 Operating Instructions....................
Contents Page Receiving Procedures.................... 1 Warranty............................. 1 Safety Information..................... 1-2 Machine Description................... 3 Operating Instructions....................
WELCOME TO RAMPMASTER
 WELCOME TO RAMPMASTER Thor-Weld Industries was incorporated in 1972. In the early years our core business was steel and aluminum fabrication. After fifteen years of business an industrial caster company
WELCOME TO RAMPMASTER Thor-Weld Industries was incorporated in 1972. In the early years our core business was steel and aluminum fabrication. After fifteen years of business an industrial caster company
EKX k. Man-Up Turret Truck (2,750-3,300 lbs.) Versatile design with modular construction and intelligent truck management system
 Versatile design with modular construction and intelligent truck management system 80 Volt 3-phase advanced AC technology providing powerful torque and high productivity Low cost of operation through two-fold
Versatile design with modular construction and intelligent truck management system 80 Volt 3-phase advanced AC technology providing powerful torque and high productivity Low cost of operation through two-fold
40/50/55/60/70 IC-CUSHION LPG. 8,000 / 10,000 / 12,000 / 13,500 / 15,500 lbs. / 5000 / 5500 / 6000 /7000 kg)
 CGC (4000 40/50/55/60/70 IC-CUSHION 8,000 / 10,000 / 12,000 / 13,500 / 15,500 lbs. / 5000 / 5500 / 6000 /7000 kg) 7 metric tons With a capacity of up to 15,500 lbs. the CLARK CGC 40/50/55/60/70 gets the
CGC (4000 40/50/55/60/70 IC-CUSHION 8,000 / 10,000 / 12,000 / 13,500 / 15,500 lbs. / 5000 / 5500 / 6000 /7000 kg) 7 metric tons With a capacity of up to 15,500 lbs. the CLARK CGC 40/50/55/60/70 gets the
Forklift Operator Safety
 Title: Forklift Safety Effective Date: 4/1/2014 Control Number: THG_0021 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/13/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 CONTENTS Forklift Operator Safety I. OBJECTIVE II. ASSIGNMENT
Title: Forklift Safety Effective Date: 4/1/2014 Control Number: THG_0021 Revision Number: 1 Date: 10/13/2015 Annual Review Completed: 5/13/2015 CONTENTS Forklift Operator Safety I. OBJECTIVE II. ASSIGNMENT
Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation Project
 )$&(,19(67,*$7,215(3257 Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation Project FACE #96-NJ-062-01 Warehouse Checker Crushed Under a 4,000 Pound Crate Falling From a Forklift Truck New Jersey Department of
)$&(,19(67,*$7,215(3257 Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation Project FACE #96-NJ-062-01 Warehouse Checker Crushed Under a 4,000 Pound Crate Falling From a Forklift Truck New Jersey Department of
MATERIAL-STORAGE INJURIES
 MATERIAL-STORAGE INJURIES A SAFETY TALK FOR DISCUSSION LEADERS This safety talk is designed for discussion leaders to use in preparing safety meetings. Set a specific time and date for your safety meeting.
MATERIAL-STORAGE INJURIES A SAFETY TALK FOR DISCUSSION LEADERS This safety talk is designed for discussion leaders to use in preparing safety meetings. Set a specific time and date for your safety meeting.
Safety Information for The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
 Job Safety Analysis Safety Information for The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS TOPIC: Energy Services CoGeneration Facility- Operating a Forklift; Mechanical Maintenance
Job Safety Analysis Safety Information for The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS TOPIC: Energy Services CoGeneration Facility- Operating a Forklift; Mechanical Maintenance
Guidance Notes FSR 2014
 Definition (page 13) TERM DEFINITION GUIDANCE/ AMENDMENT BACKED UP To make a copy of a data file which is stored securely in a separate location and can be used as a security copy. To make a copy of a
Definition (page 13) TERM DEFINITION GUIDANCE/ AMENDMENT BACKED UP To make a copy of a data file which is stored securely in a separate location and can be used as a security copy. To make a copy of a
Forklift Safety. University of Tennessee Safety Guide GS-130. Purpose. Scope and Applicability. Abbreviations and Definitions.
 Forklift Safety University of Tennessee Safety Guide GS-130 Document Contact: EHS-General Safety Date effective: August 1, 2009 Revision Date: April 24, 2018 Purpose The purpose of this guide is to inform
Forklift Safety University of Tennessee Safety Guide GS-130 Document Contact: EHS-General Safety Date effective: August 1, 2009 Revision Date: April 24, 2018 Purpose The purpose of this guide is to inform
TENTS, CANOPIES AND OTHER MEMBRANE STRUCTURES
 CHAPTER 24 TENTS, CANOPIES AND OTHER MEMBRANE STRUCTURES SECTION 2401 GENERAL 2401.1 Scope. Tents, canopies and membrane structures shall comply with this chapter. The provisions of Section 2403 are applicable
CHAPTER 24 TENTS, CANOPIES AND OTHER MEMBRANE STRUCTURES SECTION 2401 GENERAL 2401.1 Scope. Tents, canopies and membrane structures shall comply with this chapter. The provisions of Section 2403 are applicable
CARTONFLO Live Storage of Cartons For Rapid, Efficient Order Filling
 CARTONFLO Live Storage of Cartons For Rapid, Efficient Order Filling Saves Space Speeds Picking Reduces Error Protects Product Improves Inventory Control KORYNYLAK CORPORATION 400 Heaton St., Hamilton,
CARTONFLO Live Storage of Cartons For Rapid, Efficient Order Filling Saves Space Speeds Picking Reduces Error Protects Product Improves Inventory Control KORYNYLAK CORPORATION 400 Heaton St., Hamilton,
Understanding Materials Handling Applications, Solutions for the Paper Industry
 Solutions for the Paper Industry This white paper explores some of the environmental impacts and operating conditions typically found in the paper products industry. Also included is an overview of some
Solutions for the Paper Industry This white paper explores some of the environmental impacts and operating conditions typically found in the paper products industry. Also included is an overview of some
Forklift operation guidelines
 Description Forklift operation guidelines introduction As a *** Forklift Operator you have certain occupational health and safety responsibilities, these responsibilities are: - To work safely. - To suggest
Description Forklift operation guidelines introduction As a *** Forklift Operator you have certain occupational health and safety responsibilities, these responsibilities are: - To work safely. - To suggest
PalletPal Low Profile Disc Turntable
 OWNER S MANUAL PalletPal Low Profile Disc Turntable Model # Serial # Date placed in Service SOUTHWORTH PRODUCTS CORP P.O. Box 1380 Portland, ME 04104-1380 Telephone: (207) 878-0700 or (800) 743-1000 Fax:
OWNER S MANUAL PalletPal Low Profile Disc Turntable Model # Serial # Date placed in Service SOUTHWORTH PRODUCTS CORP P.O. Box 1380 Portland, ME 04104-1380 Telephone: (207) 878-0700 or (800) 743-1000 Fax:
MATERIALS HANDLING EQUIPMENT OBSERVATION ASSESSMENTS
 MATERIALS HANDLING EQUIPMENT OBSERVATION ASSESSMENTS This guidance provides details of a methodology that can be adopted by organisations to carry out observation assessments of their operatives using
MATERIALS HANDLING EQUIPMENT OBSERVATION ASSESSMENTS This guidance provides details of a methodology that can be adopted by organisations to carry out observation assessments of their operatives using
Depot Dry Receiving Guidelines. Standard Operating Procedure TABLE OF CONTENTS
 I s s u e d a t e D o c u m e n t N o. Costco AUS SOP-209 P a g e 1 of 13 Depot Dry Receiving Guidelines Standard Operating Procedure TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE 1. INTRODUCTION 2 1.1 Key Information 1.1.1
I s s u e d a t e D o c u m e n t N o. Costco AUS SOP-209 P a g e 1 of 13 Depot Dry Receiving Guidelines Standard Operating Procedure TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE 1. INTRODUCTION 2 1.1 Key Information 1.1.1
Chapter 9 Storage & Warehouse Systems
 FACILITIES PLANNING & DESIGN Alberto Garcia-Diaz J. MacGregor Smith Chapter 9 Storage & Warehouse Systems 1. Warehouse Layout Model 2. Storage Equipment 3. Automated Storage & Retrieval System 1 Dedicated
FACILITIES PLANNING & DESIGN Alberto Garcia-Diaz J. MacGregor Smith Chapter 9 Storage & Warehouse Systems 1. Warehouse Layout Model 2. Storage Equipment 3. Automated Storage & Retrieval System 1 Dedicated
ELEVATORS & SERVICE LIFTS FREIGHT HOIST MAST LIFTS FREIGHT HOIST SCISSOR LIFTS ELEVATING DOCK SCISSOR LIFTS DOCK LEVELLERS
 ELEVATORS & SERVICE LIFTS FREIGHT HOIST MAST LIFTS FREIGHT HOIST SCISSOR LIFTS ELEVATING DOCK SCISSOR LIFTS DOCK LEVELLERS McGrath Industries Ltd. 2017. All rights reserved. Ed04, CJM. ELEVATORS SERVICE
ELEVATORS & SERVICE LIFTS FREIGHT HOIST MAST LIFTS FREIGHT HOIST SCISSOR LIFTS ELEVATING DOCK SCISSOR LIFTS DOCK LEVELLERS McGrath Industries Ltd. 2017. All rights reserved. Ed04, CJM. ELEVATORS SERVICE
Driver Learning Record
 TRAINING TOOL Driver Learning Record DRIVING THE FUTURE 2 Driver Learning Record TRAINING TOOL Driver Learning Record The Driver Learning Record is a tool that can be used to monitor and document the on-the-job
TRAINING TOOL Driver Learning Record DRIVING THE FUTURE 2 Driver Learning Record TRAINING TOOL Driver Learning Record The Driver Learning Record is a tool that can be used to monitor and document the on-the-job
