Notes on Introduction to Contract Theory
|
|
|
- Darrell Cole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Notes on Introduction to Contract Theory John Morgan Haas School of Business and Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley 1 Overview of the Course This is a readings course. The lectures are designed to distill the central ideas of the readings into models capturing the main insights leaving many of the technical details to be explained in the readings themselves. The hope is that the combination of being exposed to the motivating problems for many of these excursions in contract theory combined with the modeling exercise of distilling things down to the fundamental economic ideas will enable students wishing to pursue contract theory either in its own right or as a front-end to experimental or empirical work will have the tools and skills required to use these ideas as part of a thesis. All materials pertaining to the course are located on the course website: To summarize, in this course you will: Learn the basic tools/main ideas of contract theory Touch on the relationship between the main theoretical insights to come out of this literature and empirical/experimental work. Learn how the main ideas of contract theory can be usefully applied in a variety of economics settings including areas of nance, industrial organization, labor, and public economics. 2 Major Families of Models The course is organized along the lines of the major families of models in contract theory. The models mainly consist of interaction between a single principal and a single agent where the principal is assumed to have all the bargaining power. That is, the principal can propose a take it or leave it contract which the agent can either accept or not. The major families are organized along two axes : The rst axis concerns whether the primary concern of the principal is hidden information or 1
2 hidden action. When the problem is hidden information, the agent knows something economically relevant to the principal. When the problem is one of hidden action, the agent must undertake some e ort to produce economic value to the principal but this e ort cannot be monitored directly. The second axis concerns the timing of moves. Either the principal moves rst and e ectively speci es the contract (or, more generally, the game form) or the agent moves rst. In the latter case, the modeler essentially determines the extensive form of the game played between principal and agent. The following table summarizes the two axes. Each of the main families of models is listed in bold and is detailed below. Hidden: Information Action P moves: First Adverse Selection Moral Hazard Second Signaling Adverse Selection In adverse selection models, the agent possesses economically relevant information that the principal would like to know. The archetypal example occurs with a price discriminating monopoly. The agent knows her willingness to pay for the item. Since, by assumption, the principal has all the bargaining power, if it knew this information, it could structure a contract to extract all of the surplus from the agent. Since it doesn t know this information, the contract proposed must be structured to induce the agent to reveal it truthfully. The key point is that, to obtain truthful reporting on the part of the agent, the principal has to pay an information rent to induce agents with di erent willingnesses to pay to report truthfully. It is worth noting that the space of contracts the principal might employ to achieve its ends is quite large. As we shall see later, this problem is dramatically simpli ed by the key tool in this section the revelation principle. We ll return to this in more detail later. Key question: How to structure contracts to maximize surplus extraction Key tool: Revelation principle. Signaling In signaling models, the central problem is that the agent wants to credibly convey his hidden information to the principal. The problem is that many types of agent all want to be perceived to be the best type. The archetypal example of this type of situation occurs with used durable goods of heterogeneous quality. All sellers want to be perceived as selling high quality goods and the question turns on how to credibly convey this information. In this setting, the use of money back guarantees re ects a sort of signaling solution. Key distinction: We will distinguish between costly signaling, where the key economic force is that sending a given signal is di erentially costly for di erent types and costless signaling, where credibility of a signal depends on di erences in the economic outcome obtained by sending di ering signals (more detail on this later in the course). 2
3 Key tool: Equilibrium re nements. Moral Hazard In moral hazard models, the central concern of the principal is to set incentives in such a way as to obtain the desired level of e ort at lowest cost. Incentive contracts in industry are the archetypal example of this type of contract. The main result in this area is that, if the agent is risk-averse, then there is a trade-o between o ering highpowered incentives, which motivate e ort but entail substantial risk to the agent, and o ering insurance. Thus, risk-aversion blunts the high-poweredness of incentives. Key questions: How do incentives change with multiple agents? Multiple tasks? Key tool: First-order approach After covering the main families of models, we ll talk about some extensions along three lines: 1. Long-term contracting 2. Imperfect commitment 3. Incomplete contracting We now turn to the revelation principle: 3 Direct and Indirect Mechanisms What is a contract? On a general level, a contract is a game designed by the principal and played by the agent or agents. There may be various institutional restrictions placed on the set of feasible game forms the principal may choose from. Thus, a contract can be thought of as a game that designates the strategies available to the agents as well as the payo s from the realizations of the strategies. We call such a contract an indirect mechanism. Suppose agent i s type is i and her equilibrium strategy in game chosen by all of the agents given their type. So we have is i ( i ) : Let () denote the vector of strategies & v i ( ()) () The mechanism is indirect since ultimately the vector of types determines the payo s to each of the agents; however this information is transmitted indirectly through the strategy (). In contrast, the principal might elect to use a direct mechanism. In a direct mechanism: Agents report their types to an neutral intermediary 3
4 The intermediary then implements the strategy i () on behalf of the agent And the agent earns v i ( ()) : Thus, the direct mechanism looks like:. v ( ()) () Indirect Mechanisms in Practice Now we will have you participate in an indirect mechanism. I ll play the role of principal and you will be the agents. As principal, my objective is to maximize the amount of money I get from you. As agents, you care about your surplus. Now there are a huge number of game forms I might select from. I ll choose this one: I m going to auction the following object using an auction mechanism used to sell art and wines as Sotheby s. This mechanism is sometimes called an English or open outcry auction. Notice how this is an indirect mechanism. Your type (your WTP for the candy bar) is transmitted only indirectly through your bidding behavior. Direct Mechanisms in Practice Now consider the auction format on ebay. With ebay, you submit your type to a bidder elf who bids on your behalf up to the value you told it. Thus, ebay is a kind of direct mechanism version of the Sotheby s auction. Let s try this mechanism. The Revelation Principle Suppose we use the solution concept of Bayes Nash equilibrium then it must be the case that for agent i of type i ; v i i ( i ) ; i ( i ) v 0 i i; i ( i ) for all 0 i in the indirect mechanism. That is, no agent should have a pro table deviation. We might also require that the agent have an incentive to participate in the game in the rst place. That is v i ( ()) v for some outside option v: The point of the direct mechanism is that, through the revelation principle, it allows us to ignore analyzing all of the indirect mechanisms and focus only on the direct mechanism. Speci cally, Theorem 1 (Revelation Principle, Myerson, 1981) Suppose that was a Baye- Nash equilibrium of the indirect mechanism : Then there exists a direct mechanism that is payo -equivalent and where truthful revelation is an equilibrium. 4
5 Sketch Proof. By construction, if agents tell the truth in the direct mechanism, it is payo equivalent to playing the equilibrium strategies in the indirect mechanism : To see that truth-telling is an equilibrium, notice that if player i with type i deviates and reports his type as 0 i then she earns v i i ( 0 i) ; i ( i ) = v 0 i i; i ( i ) for some 0 i and, from above, we know v i i ( i ) ; i ( i ) v 0 i i; i ( i ) Therefore, this is not pro table. QED Mechanism Design So far, all we have done is showed that the principal could limit him or herself to ebay style auctions without any giving up anything in terms of revenues. The principal has other tools available on ebay. In particular, P could set a reserve price and an opening bid level for the auction. We ll try that now. Notice that people with WTP below the reserve level are excluded from the auction. Many of these mechanisms are strategically equivalent. Speci cally, Proposition 1 Any two ebay auctions that exclude the set of types are strategically equivalent. Further, in these auctions, the seller earns the same expected revenues. The proof is obvious from the revelation principle. How does this implication of the revelation principle fare in practice? The results of Hossain and Morgan (2003) shed some light. [Explain ebay eld experiments here.] Main Lessons The revelation principle should be used with care. Psychological factors can play a key role. 5
Information Design: Murat Sertel Lecture
 nformation Design: Murat Sertel Lecture stanbul Bilgi University: Conference on Economic Design Stephen Morris July 2015 Mechanism Design and nformation Design Mechanism Design: Fix an economic environment
nformation Design: Murat Sertel Lecture stanbul Bilgi University: Conference on Economic Design Stephen Morris July 2015 Mechanism Design and nformation Design Mechanism Design: Fix an economic environment
TOPIC 4. ADVERSE SELECTION, SIGNALING, AND SCREENING
 TOPIC 4. ADVERSE SELECTION, SIGNALING, AND SCREENING In many economic situations, there exists asymmetric information between the di erent agents. Examples are abundant: A seller has better information
TOPIC 4. ADVERSE SELECTION, SIGNALING, AND SCREENING In many economic situations, there exists asymmetric information between the di erent agents. Examples are abundant: A seller has better information
Auction Theory An Intrroduction into Mechanism Design. Dirk Bergemann
 Auction Theory An Intrroduction into Mechanism Design Dirk Bergemann Mechanism Design game theory: take the rules as given, analyze outcomes mechanism design: what kind of rules should be employed abstract
Auction Theory An Intrroduction into Mechanism Design Dirk Bergemann Mechanism Design game theory: take the rules as given, analyze outcomes mechanism design: what kind of rules should be employed abstract
Do not open this exam until told to do so. Solution
 Do not open this exam until told to do so. Department of Economics College of Social and Applied Human Sciences K. Annen, Fall 003 Final (Version): Intermediate Microeconomics (ECON30) Solution Final (Version
Do not open this exam until told to do so. Department of Economics College of Social and Applied Human Sciences K. Annen, Fall 003 Final (Version): Intermediate Microeconomics (ECON30) Solution Final (Version
Efficiency and Robustness of Binary Online Feedback Mechanisms in Trading Environments with Moral Hazard
 Efficiency and Robustness of Binary Online Feedback Mechanisms in Trading Environments with Moral Hazard Chris Dellarocas MIT Sloan School of Management dell@mit.edu Introduction and Motivation Outline
Efficiency and Robustness of Binary Online Feedback Mechanisms in Trading Environments with Moral Hazard Chris Dellarocas MIT Sloan School of Management dell@mit.edu Introduction and Motivation Outline
A Note on Revenue Sharing in Sports Leagues
 A Note on Revenue Sharing in Sports Leagues Matthias Kräkel, University of Bonn Abstract We discuss the optimal sharing of broadcasting revenues given a central marketing system. The league s sports association
A Note on Revenue Sharing in Sports Leagues Matthias Kräkel, University of Bonn Abstract We discuss the optimal sharing of broadcasting revenues given a central marketing system. The league s sports association
Counterfeiting as Private Money in Mechanism Design
 Counterfeiting as Private Money in Mechanism Design Ricardo Cavalcanti Getulio Vargas Foundation Ed Nosal Cleveland Fed November 006 Preliminary and Incomplete Abstract We describe counterfeiting activity
Counterfeiting as Private Money in Mechanism Design Ricardo Cavalcanti Getulio Vargas Foundation Ed Nosal Cleveland Fed November 006 Preliminary and Incomplete Abstract We describe counterfeiting activity
Price of anarchy in auctions & the smoothness framework. Faidra Monachou Algorithmic Game Theory 2016 CoReLab, NTUA
 Price of anarchy in auctions & the smoothness framework Faidra Monachou Algorithmic Game Theory 2016 CoReLab, NTUA Introduction: The price of anarchy in auctions COMPLETE INFORMATION GAMES Example: Chicken
Price of anarchy in auctions & the smoothness framework Faidra Monachou Algorithmic Game Theory 2016 CoReLab, NTUA Introduction: The price of anarchy in auctions COMPLETE INFORMATION GAMES Example: Chicken
Module 11: A Simple Model of Reputation - Moral Hazard and Product Quality
 Module 11: A Simple Model of Reputation - Moral Hazard and Product Quality Information Economics (Ec 515) George Georgiadis Consider a firm that sells an experience good. Experience good: product or service
Module 11: A Simple Model of Reputation - Moral Hazard and Product Quality Information Economics (Ec 515) George Georgiadis Consider a firm that sells an experience good. Experience good: product or service
Strategic Ignorance in the Second-Price Auction
 Strategic Ignorance in the Second-Price Auction David McAdams September 23, 20 Abstract Suppose bidders may publicly choose not to learn their values prior to a second-price auction with costly bidding.
Strategic Ignorance in the Second-Price Auction David McAdams September 23, 20 Abstract Suppose bidders may publicly choose not to learn their values prior to a second-price auction with costly bidding.
Market Design: Theory and Applications
 Market Design: Theory and Applications ebay and Amazon Instructor: Itay Fainmesser Fall 2010 1 Timing of transactions and their impact on markets I We ve discussed unraveling. And we noticed that transactions
Market Design: Theory and Applications ebay and Amazon Instructor: Itay Fainmesser Fall 2010 1 Timing of transactions and their impact on markets I We ve discussed unraveling. And we noticed that transactions
Competitive Markets. Jeffrey Ely. January 13, This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License.
 January 13, 2010 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Profit Maximizing Auctions Last time we saw that a profit maximizing seller will choose
January 13, 2010 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Profit Maximizing Auctions Last time we saw that a profit maximizing seller will choose
Search and Categorization
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Search and Categorization Chaim Fershtman and Arthur Fishman and Jidong Zhou Tel Aviv University, Bar-Ilan University, NYU Stern December 03 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/5366/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Search and Categorization Chaim Fershtman and Arthur Fishman and Jidong Zhou Tel Aviv University, Bar-Ilan University, NYU Stern December 03 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/5366/
Exam #2 (100 Points Total) Answer Key
 Exam #2 (100 Points Total) Answer Key 1. A Pareto efficient outcome may not be good, but a Pareto inefficient outcome is in some meaningful sense bad. (a) (5 points) Give an example or otherwise explain,
Exam #2 (100 Points Total) Answer Key 1. A Pareto efficient outcome may not be good, but a Pareto inefficient outcome is in some meaningful sense bad. (a) (5 points) Give an example or otherwise explain,
14.01 Principles of Microeconomics, Fall 2007 Chia-Hui Chen November 7, Lecture 22
 Monopoly. Principles of Microeconomics, Fall Chia-Hui Chen November, Lecture Monopoly Outline. Chap : Monopoly. Chap : Shift in Demand and Effect of Tax Monopoly The monopolist is the single supply-side
Monopoly. Principles of Microeconomics, Fall Chia-Hui Chen November, Lecture Monopoly Outline. Chap : Monopoly. Chap : Shift in Demand and Effect of Tax Monopoly The monopolist is the single supply-side
Econ 001 Levinson -- Fall 2009
 Page 1 of 9 Print this page. Econ 001 Levinson -- Fall 2009 Homework 8 An industry contains 5 firms, with the following sales: Firm 1 $80 million Firm 2 $50 million Firm 3 $40 million Firm 4 $10 million
Page 1 of 9 Print this page. Econ 001 Levinson -- Fall 2009 Homework 8 An industry contains 5 firms, with the following sales: Firm 1 $80 million Firm 2 $50 million Firm 3 $40 million Firm 4 $10 million
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION
 MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION William F. Samuelson Boston University Stephen G. Marks Boston University WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Economic Decision Making 1
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION William F. Samuelson Boston University Stephen G. Marks Boston University WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Economic Decision Making 1
Resale and Bundling in Multi-Object Auctions
 Resale and Bundling in Multi-Object Auctions Marco Pagnozzi Università di Napoli Federico II and CSEF Allowing resale after an auction helps to achieve an e cient allocation Spectrum trading should be
Resale and Bundling in Multi-Object Auctions Marco Pagnozzi Università di Napoli Federico II and CSEF Allowing resale after an auction helps to achieve an e cient allocation Spectrum trading should be
Labor Economics, Lectures 9 and 10: Investments in General and Speci c Skills
 Labor Economics, 14.661. Lectures 9 and 10: Investments in General and Speci c Skills Daron Acemoglu MIT Nov. 29 and Dec. 1, 2011. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) General and Speci c Skills Nov. 29 and Dec. 1, 2011.
Labor Economics, 14.661. Lectures 9 and 10: Investments in General and Speci c Skills Daron Acemoglu MIT Nov. 29 and Dec. 1, 2011. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) General and Speci c Skills Nov. 29 and Dec. 1, 2011.
Silvia Rossi. Auctions. Lezione n. Corso di Laurea: Informatica. Insegnamento: Sistemi multi-agente. A.A.
 Silvia Rossi Auctions Lezione n. 16 Corso di Laurea: Informatica Insegnamento: Sistemi multi-agente Email: silrossi@unina.it A.A. 2014-2015 Reaching Agreements - Auctions (W: 7.2, 9.2.1 MAS: 11.1) 2 Any
Silvia Rossi Auctions Lezione n. 16 Corso di Laurea: Informatica Insegnamento: Sistemi multi-agente Email: silrossi@unina.it A.A. 2014-2015 Reaching Agreements - Auctions (W: 7.2, 9.2.1 MAS: 11.1) 2 Any
Empirical Approaches to Regulation Theory Philippe Gagnepain
 Empirical Approaches to Regulation Theory Philippe Gagnepain Paris School of Economics-Université Paris 1 and CEPR 1 Introduction A regulator (public authority) delegates a task to a firm (monopoly). Telecommunications,
Empirical Approaches to Regulation Theory Philippe Gagnepain Paris School of Economics-Université Paris 1 and CEPR 1 Introduction A regulator (public authority) delegates a task to a firm (monopoly). Telecommunications,
Note on webpage about sequential ascending auctions
 Econ 805 Advanced Micro Theory I Dan Quint Fall 2007 Lecture 20 Nov 13 2007 Second problem set due next Tuesday SCHEDULING STUDENT PRESENTATIONS Note on webpage about sequential ascending auctions Everything
Econ 805 Advanced Micro Theory I Dan Quint Fall 2007 Lecture 20 Nov 13 2007 Second problem set due next Tuesday SCHEDULING STUDENT PRESENTATIONS Note on webpage about sequential ascending auctions Everything
The Impact of Bargaining on Markets with Price Takers: Too Many Bargainers Spoil The Broth
 The Impact of Bargaining on Markets with Price Takers: Too Many Bargainers Spoil The Broth David Gill Division of Economics University of Southampton John Thanassoulis Dept. of Economics & Christ Church
The Impact of Bargaining on Markets with Price Takers: Too Many Bargainers Spoil The Broth David Gill Division of Economics University of Southampton John Thanassoulis Dept. of Economics & Christ Church
UC Berkeley Recent Work
 UC Berkeley Recent Work Title How much is a Dollar Worth? Tipping versus Equilibrium Coexistence on Competing Online Auction Sites Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3c21w91h Authors Brown, Jennifer
UC Berkeley Recent Work Title How much is a Dollar Worth? Tipping versus Equilibrium Coexistence on Competing Online Auction Sites Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3c21w91h Authors Brown, Jennifer
Microeconomics LESSON 6 ACTIVITY 40
 Microeconomics LESSON 6 ACTIVITY 40 Monopolistic Competition Figure 40.1 Monopolistically Competitive Firm in the Short Run MC COSTS/REVENUE (DOLLARS) E D C B A F H K G ATC D 0 MR L M QUANTITY 1. Use Figure
Microeconomics LESSON 6 ACTIVITY 40 Monopolistic Competition Figure 40.1 Monopolistically Competitive Firm in the Short Run MC COSTS/REVENUE (DOLLARS) E D C B A F H K G ATC D 0 MR L M QUANTITY 1. Use Figure
Cooperative Search Advertising
 MIT Sloan School of Management MIT Sloan School Working Paper 5176-16 Cooperative Search Advertising Xinyu Cao and T. Tony Ke This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial License
MIT Sloan School of Management MIT Sloan School Working Paper 5176-16 Cooperative Search Advertising Xinyu Cao and T. Tony Ke This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial License
INNOVATION, RENT EXTRACTION, AND INTEGRATION IN SYSTEMS MARKETS*
 THE JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS 0022-1821 Volume XLVIII December 2000 No. 4 INNOVATION, RENT EXTRACTION, AND INTEGRATION IN SYSTEMS MARKETS* Joseph Farrell{ and Michael L. Katz{ We consider innovation
THE JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS 0022-1821 Volume XLVIII December 2000 No. 4 INNOVATION, RENT EXTRACTION, AND INTEGRATION IN SYSTEMS MARKETS* Joseph Farrell{ and Michael L. Katz{ We consider innovation
Product Improvement and Technological Tying in a Winner-Take-All Market. Richard J. Gilbert University of California
 Product Improvement and Technological Tying in a Winner-Take-All Market Richard J. Gilbert University of California Michael H. Riordan Columbia University CPDP-17-E October 2005 This article is written
Product Improvement and Technological Tying in a Winner-Take-All Market Richard J. Gilbert University of California Michael H. Riordan Columbia University CPDP-17-E October 2005 This article is written
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS THEORY, APPLICATIONS, AND CASES EIGHTH EDITION. W.Bruce Allen The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania
 MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS THEORY, APPLICATIONS, AND CASES EIGHTH EDITION W.Bruce Allen The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania Neil A. Doherty The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania Keith Weigelt
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS THEORY, APPLICATIONS, AND CASES EIGHTH EDITION W.Bruce Allen The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania Neil A. Doherty The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania Keith Weigelt
Nonlinear pricing of a congestible network good. Abstract
 Nonlinear pricing of a congestible network good haïreddine Jebsi LEGI, Ecole Polytechnique, La Marsa and Faculté de Droit et des Sciences Economiques et Politiques de Sousse, Tunisia Lionel Thomas CRESE,
Nonlinear pricing of a congestible network good haïreddine Jebsi LEGI, Ecole Polytechnique, La Marsa and Faculté de Droit et des Sciences Economiques et Politiques de Sousse, Tunisia Lionel Thomas CRESE,
THE CENTER FOR THE STUDY
 THE CENTER FOR THE STUDY OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATION AT NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY Working Paper #0078 An Empirical Perspective on Auctions By Ken Hendricks University of Texas and Robert H. Porter * Northwestern
THE CENTER FOR THE STUDY OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATION AT NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY Working Paper #0078 An Empirical Perspective on Auctions By Ken Hendricks University of Texas and Robert H. Porter * Northwestern
Using Last-Minute Sales for Vertical Differentiation on the Internet
 Abstract Number 011-0050 Using Last-Minute Sales for Vertical Differentiation on the Internet Ori Marom RSM Erasmus University Burgmeester Oudlaan 50 3062 PA Rotterdam, The Netherlands omarom@rsm.nl Abraham
Abstract Number 011-0050 Using Last-Minute Sales for Vertical Differentiation on the Internet Ori Marom RSM Erasmus University Burgmeester Oudlaan 50 3062 PA Rotterdam, The Netherlands omarom@rsm.nl Abraham
Umbrella Branding Can Leverage Reputation, but only with Market Power. May 19, Eric B. Rasmusen
 Umbrella Branding Can Leverage Reputation, but only with Market Power May 19, 2012 Eric B. Rasmusen Dan R. and Catherine M. Dalton Professor, Department of Business Economics and Public Policy, Kelley
Umbrella Branding Can Leverage Reputation, but only with Market Power May 19, 2012 Eric B. Rasmusen Dan R. and Catherine M. Dalton Professor, Department of Business Economics and Public Policy, Kelley
Ph.D. thesis. An empirical analysis of a discriminat. i i tory, closed, BY TOR HUGO HAUGE INSTITUTT FOR SAMFUNNSØKONOMI DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS
 INSTITUTT FOR SAMFUNNSØKONOMI Ph.D. thesis DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS No. 2010/01 An empirical analysis of a discriminat i i tory, closed, simultaneous, multi-object auction BY TOR HUGO HAUGE To my parents
INSTITUTT FOR SAMFUNNSØKONOMI Ph.D. thesis DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS No. 2010/01 An empirical analysis of a discriminat i i tory, closed, simultaneous, multi-object auction BY TOR HUGO HAUGE To my parents
Valuation Uncertainty and Imperfect Introspection in Second-Price Auctions
 Valuation Uncertainty and Imperfect Introspection in Second-Price Auctions Abstract In auction theory, agents are typically presumed to have perfect knowledge of their valuations. In practice, though,
Valuation Uncertainty and Imperfect Introspection in Second-Price Auctions Abstract In auction theory, agents are typically presumed to have perfect knowledge of their valuations. In practice, though,
Buy-It-Now or Snipe on ebay?
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ICIS 2003 Proceedings International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) December 2003 Buy-It-Now or Snipe on ebay? Ilke Onur Kerem
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ICIS 2003 Proceedings International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) December 2003 Buy-It-Now or Snipe on ebay? Ilke Onur Kerem
Modeling of competition in revenue management Petr Fiala 1
 Modeling of competition in revenue management Petr Fiala 1 Abstract. Revenue management (RM) is the art and science of predicting consumer behavior and optimizing price and product availability to maximize
Modeling of competition in revenue management Petr Fiala 1 Abstract. Revenue management (RM) is the art and science of predicting consumer behavior and optimizing price and product availability to maximize
Government Regulation of Industry Spring 2002 Page 1 of 5 FINAL EXAMINATION SKETCH OF SOLUTIONS 2002
 Government Regulation of Industry Spring 2002 Page 1 of 5 FINAL EXAMINATION SKETCH OF SOLUTIONS 2002 Instructions: You have three hours to complete this exam. This exam is closed-book: no books or notes
Government Regulation of Industry Spring 2002 Page 1 of 5 FINAL EXAMINATION SKETCH OF SOLUTIONS 2002 Instructions: You have three hours to complete this exam. This exam is closed-book: no books or notes
Advanced Topics in Computer Science 2. Networks, Crowds and Markets. Fall,
 Advanced Topics in Computer Science 2 Networks, Crowds and Markets Fall, 2012-2013 Prof. Klara Kedem klara@cs.bgu.ac.il Office 110/37 Office hours by email appointment The textbook Chapters from the book
Advanced Topics in Computer Science 2 Networks, Crowds and Markets Fall, 2012-2013 Prof. Klara Kedem klara@cs.bgu.ac.il Office 110/37 Office hours by email appointment The textbook Chapters from the book
Competitive Analysis of Incentive Compatible On-line Auctions
 Competitive Analysis of Incentive Compatible On-line Auctions Ron Lavi and Noam Nisan Theoretical Computer Science, 310 (2004) 159-180 Presented by Xi LI Apr 2006 COMP670O HKUST Outline The On-line Auction
Competitive Analysis of Incentive Compatible On-line Auctions Ron Lavi and Noam Nisan Theoretical Computer Science, 310 (2004) 159-180 Presented by Xi LI Apr 2006 COMP670O HKUST Outline The On-line Auction
MOT Seminar. John Musacchio 4/16/09
 Game Theory MOT Seminar John Musacchio johnm@soe.ucsc.edu 4/16/09 1 Who am I? John Musacchio Assistant Professor in ISTM Joined January 2005 PhD from Berkeley in Electrical l Engineering i Research Interests
Game Theory MOT Seminar John Musacchio johnm@soe.ucsc.edu 4/16/09 1 Who am I? John Musacchio Assistant Professor in ISTM Joined January 2005 PhD from Berkeley in Electrical l Engineering i Research Interests
Solution. Solution. Consumer and Producer Surplus
 Consumer and Producer Surplus chapter: 4 1. Determine the amount of consumer surplus generated in each of the following situations. a. Leon goes to the clothing store to buy a new T-shirt, for which he
Consumer and Producer Surplus chapter: 4 1. Determine the amount of consumer surplus generated in each of the following situations. a. Leon goes to the clothing store to buy a new T-shirt, for which he
UC Berkeley Recent Work
 UC Berkeley Recent Work Title Product Improvement and Technological Tying in a Winner-Take-All Market Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3v04b2rx Authors Gilbert, Richard J Riordan, Michael H Publication
UC Berkeley Recent Work Title Product Improvement and Technological Tying in a Winner-Take-All Market Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3v04b2rx Authors Gilbert, Richard J Riordan, Michael H Publication
Monitoring and Collusion with Soft Information
 434 JLEO, V15 N2 Monitoring and Collusion with Soft Information Sandeep Baliga Northwestern University In the standard principal-supervisor-agent model with collusion, Tirole (1986) shows that employing
434 JLEO, V15 N2 Monitoring and Collusion with Soft Information Sandeep Baliga Northwestern University In the standard principal-supervisor-agent model with collusion, Tirole (1986) shows that employing
Lecture 19: Imperfect Competition and Monopoly
 Lecture 19: Imperfect Competition and Monopoly No Lectures Next Week (No Lecture Tuesday, Nov 21) No discussion sections next week! Rent-Seeking p 1 A royalty charge for fish p 2 Perfect and Imperfect
Lecture 19: Imperfect Competition and Monopoly No Lectures Next Week (No Lecture Tuesday, Nov 21) No discussion sections next week! Rent-Seeking p 1 A royalty charge for fish p 2 Perfect and Imperfect
Loss Leading as an Exploitative Practice
 Loss Leading as an Exploitative Practice Patrick Rey Toulouse School of Economics based on joint work with Zhijun Chen (University of Auckland and Ecole Polytechnique) Bergen, September 2011 atrick Rey
Loss Leading as an Exploitative Practice Patrick Rey Toulouse School of Economics based on joint work with Zhijun Chen (University of Auckland and Ecole Polytechnique) Bergen, September 2011 atrick Rey
Robust Multi-unit Auction Protocol against False-name Bids
 17th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-2001) Robust Multi-unit Auction Protocol against False-name Bids Makoto Yokoo, Yuko Sakurai, and Shigeo Matsubara NTT Communication
17th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-2001) Robust Multi-unit Auction Protocol against False-name Bids Makoto Yokoo, Yuko Sakurai, and Shigeo Matsubara NTT Communication
VALUE OF SHARING DATA
 VALUE OF SHARING DATA PATRICK HUMMEL* FEBRUARY 12, 2018 Abstract. This paper analyzes whether advertisers would be better off using data that would enable them to target users more accurately if the only
VALUE OF SHARING DATA PATRICK HUMMEL* FEBRUARY 12, 2018 Abstract. This paper analyzes whether advertisers would be better off using data that would enable them to target users more accurately if the only
An Evaluation of the Proposed Procurement Auction for the Purchase of Medicare Equipment: Experimental Tests of the Auction Architecture 1
 An Evaluation of the Proposed Procurement Auction for the Purchase of Medicare Equipment: Experimental Tests of the Auction Architecture 1 Caroline Kim, Brian Merlob, Kathryn Peters, Charles R. Plott,
An Evaluation of the Proposed Procurement Auction for the Purchase of Medicare Equipment: Experimental Tests of the Auction Architecture 1 Caroline Kim, Brian Merlob, Kathryn Peters, Charles R. Plott,
Managing Innovation in Vertical Relationships
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Discussion Papers Department of Economics 2010 Managing Innovation in Vertical Relationships Chifeng Dai Southern Illinois University Carbondale Dongsoo
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Discussion Papers Department of Economics 2010 Managing Innovation in Vertical Relationships Chifeng Dai Southern Illinois University Carbondale Dongsoo
After studying this chapter you will be able to
 3 Demand and Supply After studying this chapter you will be able to Describe a competitive market and think about a price as an opportunity cost Explain the influences on demand Explain the influences
3 Demand and Supply After studying this chapter you will be able to Describe a competitive market and think about a price as an opportunity cost Explain the influences on demand Explain the influences
1. Fill in the missing blanks ( XXXXXXXXXXX means that there is nothing to fill in this spot):
 1. Fill in the missing blanks ( XXXXXXXXXXX means that there is nothing to fill in this spot): Quantity Total utility Marginal utility 0 0 XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX 200 0 = 200 1 200 XXXXXXXXXXX
1. Fill in the missing blanks ( XXXXXXXXXXX means that there is nothing to fill in this spot): Quantity Total utility Marginal utility 0 0 XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX 200 0 = 200 1 200 XXXXXXXXXXX
Assortative Matching > 0. (2)
 Assortative Matching In a marriage market the competition for spouse leads to sorting of mates by characteristics such as wealth, education, and other characteristics. Positive assortative matching refers
Assortative Matching In a marriage market the competition for spouse leads to sorting of mates by characteristics such as wealth, education, and other characteristics. Positive assortative matching refers
Education, Institutions, Migration, Trade, and The Development of Talent
 Education, Institutions, Migration, Trade, and The Development of Talent Dhimitri Qirjo Florida International University This Version: March 2010 Abstract This paper proposes a theory of free movement
Education, Institutions, Migration, Trade, and The Development of Talent Dhimitri Qirjo Florida International University This Version: March 2010 Abstract This paper proposes a theory of free movement
2, 1 EE CONOMIC SYSTEMS
 2, 1 For use with textbook pages 31 38 EE CONOMIC SYSTEMS KEY TERMS economic system The way in which a nation uses its resources to satisfy its people s needs and wants (page 31) traditional economy A
2, 1 For use with textbook pages 31 38 EE CONOMIC SYSTEMS KEY TERMS economic system The way in which a nation uses its resources to satisfy its people s needs and wants (page 31) traditional economy A
Chapter 15 Oligopoly
 Goldwasser AP Microeconomics Chapter 15 Oligopoly BEFORE YOU READ THE CHAPTER Summary This chapter explores oligopoly, a market structure characterized by a few firms producing a product that mayor may
Goldwasser AP Microeconomics Chapter 15 Oligopoly BEFORE YOU READ THE CHAPTER Summary This chapter explores oligopoly, a market structure characterized by a few firms producing a product that mayor may
BUYER POWER AND EXCLUSION IN VERTICALLY RELATED MARKETS.
 WORKING PAPERS IN ECONOMICS No.01/12 TOMMY STAAHL GABRIELSEN AND BJØRN OLAV JOHANSEN BUYER POWER AND EXCLUSION IN VERTICALLY RELATED MARKETS. Department of Economics U N I V E R S I T Y OF B E R G EN Buyer
WORKING PAPERS IN ECONOMICS No.01/12 TOMMY STAAHL GABRIELSEN AND BJØRN OLAV JOHANSEN BUYER POWER AND EXCLUSION IN VERTICALLY RELATED MARKETS. Department of Economics U N I V E R S I T Y OF B E R G EN Buyer
Bidding for Sponsored Link Advertisements at Internet
 Bidding for Sponsored Link Advertisements at Internet Search Engines Benjamin Edelman Portions with Michael Ostrovsky and Michael Schwarz Industrial Organization Student Seminar September 2006 Project
Bidding for Sponsored Link Advertisements at Internet Search Engines Benjamin Edelman Portions with Michael Ostrovsky and Michael Schwarz Industrial Organization Student Seminar September 2006 Project
Perfectly competitive markets: Efficiency and distribution
 Perfectly competitive markets: Efficiency and distribution By Fernando del Río Assistant Professor, University of Santiago de Compostela Introduction Free markets have been the main mechanism used to allocate
Perfectly competitive markets: Efficiency and distribution By Fernando del Río Assistant Professor, University of Santiago de Compostela Introduction Free markets have been the main mechanism used to allocate
Chapter 5: Variable pay or straight salary
 Chapter 5: Variable pay or straight salary University Professors get a straight salary which is not even based on age (may be considered high or low, depending on your point of view). Should we introduce
Chapter 5: Variable pay or straight salary University Professors get a straight salary which is not even based on age (may be considered high or low, depending on your point of view). Should we introduce
Competition in Two-Sided Markets
 Competition in Two-Sided Markets Mark Armstrong Department of Economics University College London August 2002: revised May 2005 Abstract There are many examples of markets involving two groups of agents
Competition in Two-Sided Markets Mark Armstrong Department of Economics University College London August 2002: revised May 2005 Abstract There are many examples of markets involving two groups of agents
Benefits, Costs, and Maximization
 11 Benefits, Costs, and Maximization CHAPTER OBJECTIVES To explain the basic process of balancing costs and benefits in economic decision making. To introduce marginal analysis, and to define marginal
11 Benefits, Costs, and Maximization CHAPTER OBJECTIVES To explain the basic process of balancing costs and benefits in economic decision making. To introduce marginal analysis, and to define marginal
Lecture 22. Oligopoly & Monopolistic Competition
 Lecture 22. Oligopoly & Monopolistic Competition Course Evaluations on Thursday: Be sure to bring laptop, smartphone, or tablet with browser, so that you can complete your evaluation in class. Oligopoly
Lecture 22. Oligopoly & Monopolistic Competition Course Evaluations on Thursday: Be sure to bring laptop, smartphone, or tablet with browser, so that you can complete your evaluation in class. Oligopoly
Economics : Principles of Microeconomics Spring 2014 Instructor: Robert Munk April 24, Final Exam
 Economics 001.01: Principles of Microeconomics Spring 01 Instructor: Robert Munk April, 01 Final Exam Exam Guidelines: The exam consists of 5 multiple choice questions. The exam is closed book and closed
Economics 001.01: Principles of Microeconomics Spring 01 Instructor: Robert Munk April, 01 Final Exam Exam Guidelines: The exam consists of 5 multiple choice questions. The exam is closed book and closed
Advance Selling, Competition, and Brand Substitutability
 Advance Selling, Competition, and Brand Substitutability Oksana Loginova October 27, 2016 Abstract This paper studies the impact of competition on the benefits of advance selling. I construct a two-period
Advance Selling, Competition, and Brand Substitutability Oksana Loginova October 27, 2016 Abstract This paper studies the impact of competition on the benefits of advance selling. I construct a two-period
Multilateral negotiations with private side deals: a multiplicity example. Abstract
 Multilateral negotiations with private side deals: a multiplicity example Sandeep Baliga Northwestern University and Institute for Advanced Study Roberto Serrano Brown University Abstract We study a multilateral
Multilateral negotiations with private side deals: a multiplicity example Sandeep Baliga Northwestern University and Institute for Advanced Study Roberto Serrano Brown University Abstract We study a multilateral
EconS Bundling and Tying
 EconS 425 - Bundling and Tying Eric Dunaway Washington State University eric.dunaway@wsu.edu Industrial Organization Eric Dunaway (WSU) EconS 425 Industrial Organization 1 / 39 Introduction Let s talk
EconS 425 - Bundling and Tying Eric Dunaway Washington State University eric.dunaway@wsu.edu Industrial Organization Eric Dunaway (WSU) EconS 425 Industrial Organization 1 / 39 Introduction Let s talk
Incentive-Compatible Escrow Mechanisms
 Incentive-Compatible Escrow Mechanisms Jens Witkowski Department of Computer Sence Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg, Germany witkowsk@informatik.uni-freiburg.de Sven Seuken School of Eng. & Applied
Incentive-Compatible Escrow Mechanisms Jens Witkowski Department of Computer Sence Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg, Germany witkowsk@informatik.uni-freiburg.de Sven Seuken School of Eng. & Applied
Competition and Fraud in Online Advertising Markets
 Competition and Fraud in Online Advertising Markets Bob Mungamuru 1 and Stephen Weis 2 1 Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA 94305 2 Google Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA 94043 Abstract. An economic model
Competition and Fraud in Online Advertising Markets Bob Mungamuru 1 and Stephen Weis 2 1 Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA 94305 2 Google Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA 94043 Abstract. An economic model
Networks: Spring 2010 Homework 3 David Easley and Jon Kleinberg Due February 26, 2010
 Networks: Spring 2010 Homework 3 David Easley and Jon Kleinberg Due February 26, 2010 As noted on the course home page, homework solutions must be submitted by upload to the CMS site, at https://cms.csuglab.cornell.edu/.
Networks: Spring 2010 Homework 3 David Easley and Jon Kleinberg Due February 26, 2010 As noted on the course home page, homework solutions must be submitted by upload to the CMS site, at https://cms.csuglab.cornell.edu/.
ECMC02H Intermediate Microeconomics - Topics in Price Theory
 1 ECMC02H Intermediate Microeconomics - Topics in Price Theory Answers to the Term Test June 23, 2010 Version A of the test Your name (Print clearly and underline your last name) Your student number 1.
1 ECMC02H Intermediate Microeconomics - Topics in Price Theory Answers to the Term Test June 23, 2010 Version A of the test Your name (Print clearly and underline your last name) Your student number 1.
TriNet and Venture Capital Firms: Three Case Studies
 TriNet and Venture Capital Firms: Three Case Studies Venture capital firms, like many other small companies, often try to handle HR internally until they make a costly mistake or realize the administrative
TriNet and Venture Capital Firms: Three Case Studies Venture capital firms, like many other small companies, often try to handle HR internally until they make a costly mistake or realize the administrative
Rapport 1/2018. Prosjektet har mottatt midler fra det alminnelige prisreguleringsfondet.
 Rapport 1/2018 Prosjektet har mottatt midler fra det alminnelige prisreguleringsfondet. When Should Retailers Accept Slotting Allowances Tommy Staahl Gabrielsen University of Bergen Bjørn Olav Johansen
Rapport 1/2018 Prosjektet har mottatt midler fra det alminnelige prisreguleringsfondet. When Should Retailers Accept Slotting Allowances Tommy Staahl Gabrielsen University of Bergen Bjørn Olav Johansen
Matching: The Theory. Muriel Niederle Stanford and NBER. October 5, 2011
 Matching: The Theory Muriel Niederle Stanford and NBER October 5, 2011 NRMP match variations: Couples: Submit rank oders over pairs of programs, and must be matched to two positions Applicants who match
Matching: The Theory Muriel Niederle Stanford and NBER October 5, 2011 NRMP match variations: Couples: Submit rank oders over pairs of programs, and must be matched to two positions Applicants who match
Fishing for Fools. June Abstract
 Fishing for Fools Ulrike Malmendier UC Berkeley and NBER Adam Szeidl UC Berkeley June 2008 Abstract How big is the e ect of a few fools on market outcomes? We argue that in auctions, even a small share
Fishing for Fools Ulrike Malmendier UC Berkeley and NBER Adam Szeidl UC Berkeley June 2008 Abstract How big is the e ect of a few fools on market outcomes? We argue that in auctions, even a small share
UC Berkeley Recent Work
 UC Berkeley Recent Work Title Brand and Price Advertising in Online Markets Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9760k3hz Authors Baye, Michael Morgan, John Publication Date 2004-10-01 escholarship.org
UC Berkeley Recent Work Title Brand and Price Advertising in Online Markets Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9760k3hz Authors Baye, Michael Morgan, John Publication Date 2004-10-01 escholarship.org
sample test 3 - spring 2013
 sample test 3 - spring 2013 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A natural monopoly occurs when a. the product is sold in its
sample test 3 - spring 2013 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A natural monopoly occurs when a. the product is sold in its
Ph.D. MICROECONOMICS CORE EXAM August IMPORTANT. You are expected to adhere to the following guidelines in completing the exam:
 Ph.D. MICROECONOMICS CORE EXAM August 2009 This exam is designed to test your broad knowledge of microeconomics. There are three sections: one required and two choice sections. You must complete all three
Ph.D. MICROECONOMICS CORE EXAM August 2009 This exam is designed to test your broad knowledge of microeconomics. There are three sections: one required and two choice sections. You must complete all three
Part III: Big Applications
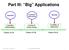 Part III: Big Applications Repetition Asymmetric Information Signaling Long-Run Relationships Auctions & Market Design Credibility & Reputation Classes 12-14 Classes 15-18 Classes 19-21 MIT Sloan 15.025
Part III: Big Applications Repetition Asymmetric Information Signaling Long-Run Relationships Auctions & Market Design Credibility & Reputation Classes 12-14 Classes 15-18 Classes 19-21 MIT Sloan 15.025
Multi-player and Multi-round Auctions with Severely Bounded Communication
 Multi-player and Multi-round Auctions with Severely Bounded Communication Liad Blumrosen 1, Noam Nisan 1, and Ilya Segal 1 School of Engineering and Computer Science. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
Multi-player and Multi-round Auctions with Severely Bounded Communication Liad Blumrosen 1, Noam Nisan 1, and Ilya Segal 1 School of Engineering and Computer Science. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
S11Microeconomics, Exam 3 Answer Key. Instruction:
 S11Microeconomics, Exam 3 Answer Key Instruction: Exam 3 Student Name: Microeconomics, several versions Early May, 2011 Instructions: I) On your Scantron card you must print three things: 1) Full name
S11Microeconomics, Exam 3 Answer Key Instruction: Exam 3 Student Name: Microeconomics, several versions Early May, 2011 Instructions: I) On your Scantron card you must print three things: 1) Full name
Coalitions and Networks in Industrial Organization
 Coalitions and Networks in Industrial Organization Francis Bloch May 28, 2001 1 Introduction Recent years have witnessed a surge of interest in the formation of coalitions and networks in Industrial Organization.
Coalitions and Networks in Industrial Organization Francis Bloch May 28, 2001 1 Introduction Recent years have witnessed a surge of interest in the formation of coalitions and networks in Industrial Organization.
Econ Microeconomic Analysis and Policy
 ECON 500 Microeconomic Theory Econ 500 - Microeconomic Analysis and Policy Monopoly Monopoly A monopoly is a single firm that serves an entire market and faces the market demand curve for its output. Unlike
ECON 500 Microeconomic Theory Econ 500 - Microeconomic Analysis and Policy Monopoly Monopoly A monopoly is a single firm that serves an entire market and faces the market demand curve for its output. Unlike
Discussion Paper No. 16. Platform Ownership. Volker Nocke* Martin Peitz** Konrad Stahl*** July 2004
 Discussion Paper No. 16 Platform Ownership Volker Nocke* Martin Peitz** Konrad Stahl*** July 2004 *Volker Nocke, Department of Economics, University of Pennsylvania, 3718 Locust Walk, Philadelphia, PA
Discussion Paper No. 16 Platform Ownership Volker Nocke* Martin Peitz** Konrad Stahl*** July 2004 *Volker Nocke, Department of Economics, University of Pennsylvania, 3718 Locust Walk, Philadelphia, PA
Countervailing Power and Product Diversity
 Countervailing Power and Product Diversity by Zhiqi Chen Carleton University Work in Progress December 6, 2003 Abstract To analyse the effects of countervailing power on product variety, I construct a
Countervailing Power and Product Diversity by Zhiqi Chen Carleton University Work in Progress December 6, 2003 Abstract To analyse the effects of countervailing power on product variety, I construct a
Principles of Economics Final Exam. Name: Student ID:
 Principles of Economics Final Exam Name: Student ID: 1. In the absence of externalities, the "invisible hand" leads a competitive market to maximize (a) producer profit from that market. (b) total benefit
Principles of Economics Final Exam Name: Student ID: 1. In the absence of externalities, the "invisible hand" leads a competitive market to maximize (a) producer profit from that market. (b) total benefit
JANUARY EXAMINATIONS 2008
 No. of Pages: (A) 9 No. of Questions: 38 EC1000A micro 2008 JANUARY EXAMINATIONS 2008 Subject Title of Paper ECONOMICS EC1000 MICROECONOMICS Time Allowed Two Hours (2 Hours) Instructions to candidates
No. of Pages: (A) 9 No. of Questions: 38 EC1000A micro 2008 JANUARY EXAMINATIONS 2008 Subject Title of Paper ECONOMICS EC1000 MICROECONOMICS Time Allowed Two Hours (2 Hours) Instructions to candidates
Behavioural Industrial Organization. Response by Vernon Smith. Introductory example: the first market experiment 3/16/2010. Sotiris Georganas.
 price Behavioural Industrial Organization Supply Sotiris Georganas p* Demand Introductory example: the first market experiment Chamberlin (JPE, 1948)conducted bilateral trading experiments with his graduate
price Behavioural Industrial Organization Supply Sotiris Georganas p* Demand Introductory example: the first market experiment Chamberlin (JPE, 1948)conducted bilateral trading experiments with his graduate
Applied Welfare Economics
 Economics Monika Köppl - Turyna Department of Economics ISCTE-IUL Summer 2014/2015 Introduction We will have lectures and problem solving sessions (usually one per two lectures) Attendance is generally
Economics Monika Köppl - Turyna Department of Economics ISCTE-IUL Summer 2014/2015 Introduction We will have lectures and problem solving sessions (usually one per two lectures) Attendance is generally
Analytic Preliminaries for Social Acceptability of Legal Norms &
 Analytic Preliminaries for Social Acceptability of John Asker February 7, 2013 Yale Law School Roadmap Build on case studies of environments where extra-legal norms are at least as important as formal
Analytic Preliminaries for Social Acceptability of John Asker February 7, 2013 Yale Law School Roadmap Build on case studies of environments where extra-legal norms are at least as important as formal
Tradable Pollution Permits
 Tradable Pollution Permits More Realistic Interventions to Solve Externality Problem Efficient Tax requires a lot of knowledge that government needs to have. Assigning property rights is not enough when
Tradable Pollution Permits More Realistic Interventions to Solve Externality Problem Efficient Tax requires a lot of knowledge that government needs to have. Assigning property rights is not enough when
Buyer Power and Functional Competition for Innovation
 Buyer Power and Functional Competition for Innovation Roman Inderst y Zlata Jakubovic z Dragan Jovanovic x November 2013 Abstract Our analysis starts from the observation that with progressive consolidation
Buyer Power and Functional Competition for Innovation Roman Inderst y Zlata Jakubovic z Dragan Jovanovic x November 2013 Abstract Our analysis starts from the observation that with progressive consolidation
Econ 001: Midterm 2 (Dr. Stein) Answer Key Nov 13, 2007
 Instructions: Econ 001: Midterm 2 (Dr. Stein) Answer Key Nov 13, 2007 This is a 60-minute examination. Write all answers in the blue books provided. Show all work. Use diagrams where appropriate and label
Instructions: Econ 001: Midterm 2 (Dr. Stein) Answer Key Nov 13, 2007 This is a 60-minute examination. Write all answers in the blue books provided. Show all work. Use diagrams where appropriate and label
ECON 230-D2-002 Version 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ECON 230-D2-002 Version 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The two largest auto manufacturers, Toyota and GM, have experimented
ECON 230-D2-002 Version 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The two largest auto manufacturers, Toyota and GM, have experimented
Comparative Price Signaling by a Multiproduct Firm
 Comparative Price Signaling by a Multiproduct Firm Michael R. Baye and Rick Harbaugh May, 013 Abstract Existing work on price signaling finds that, in the absence of reputational or other effects, a firm
Comparative Price Signaling by a Multiproduct Firm Michael R. Baye and Rick Harbaugh May, 013 Abstract Existing work on price signaling finds that, in the absence of reputational or other effects, a firm
MICROECONOMICS. London School of Economics. University of Western Ontario. Prentice Hall FINANCIAL TIMES
 .&*,- *>"> MICROECONOMICS Saul Estrin London School of Economics David Laidler University of Western Ontario Michael Dietrich University of Sheffield Prentice Hall FINANCIAL TIMES An imprint of Pearson
.&*,- *>"> MICROECONOMICS Saul Estrin London School of Economics David Laidler University of Western Ontario Michael Dietrich University of Sheffield Prentice Hall FINANCIAL TIMES An imprint of Pearson
School of Economic Sciences
 School of Economic Sciences Working Paper Series WP 2016-10 Promoting Residential Recycling: An Alternative Policy Based on a Recycling Reward System Tongzhe Li Ana Espinola-Arredondo Jill McCluskey June,
School of Economic Sciences Working Paper Series WP 2016-10 Promoting Residential Recycling: An Alternative Policy Based on a Recycling Reward System Tongzhe Li Ana Espinola-Arredondo Jill McCluskey June,
Anytime Adviser New Car Buying Coach
 Anytime Adviser New Car Buying Coach Welcome. This interactive guide offers you strategies for getting the best deal on a new car. Let's begin. Interested in a little guidance to negotiate your best deal
Anytime Adviser New Car Buying Coach Welcome. This interactive guide offers you strategies for getting the best deal on a new car. Let's begin. Interested in a little guidance to negotiate your best deal
A FREE ENTRY AND EXIT EXPERIMENT*
 A FREE ENTRY AND EXIT EXPERIMENT* Rod Garratt Department of Economics University of California Santa Barbara, CA 93106 * I thank Ken Ardon, Ken Danger and Mark Walker for helpful comments. In competitive
A FREE ENTRY AND EXIT EXPERIMENT* Rod Garratt Department of Economics University of California Santa Barbara, CA 93106 * I thank Ken Ardon, Ken Danger and Mark Walker for helpful comments. In competitive
ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even Novermber 12, 2014 FORM 1 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number
YOUR NAME Row Number ECO201: PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Prof. Bill Even Novermber 12, 2014 FORM 1 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique-id and the form number
